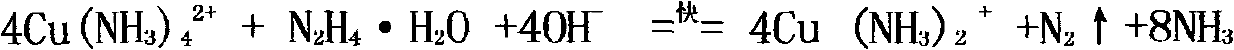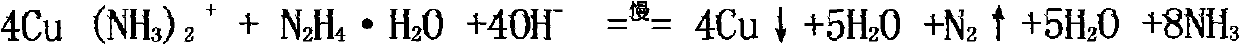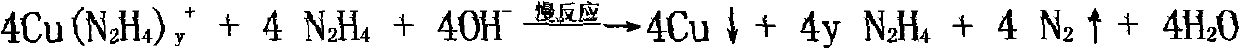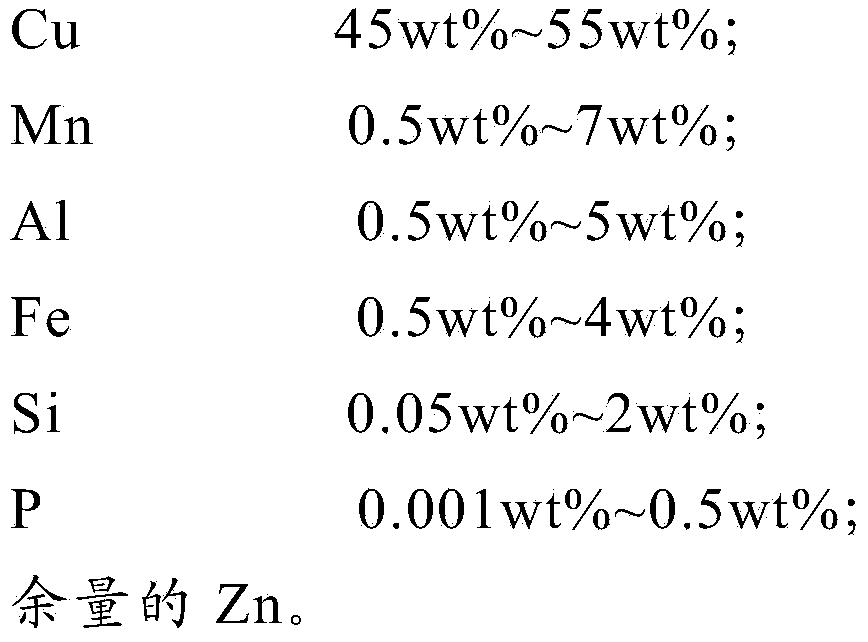Patents
Literature
181results about How to "Reduce copper content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lead-free environmental silicon brass alloy bar or alloy ingot and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a lead-free environmental silicon brass alloy bar or alloy ingot and the alloy material comprises the following chemical elements by weight percent: 60%-70% of copper, 0.7%-3.0% of silicon, 0.15% or less of aluminium, 0.25% or less of lead, 0.5% or less of iron, 0.3% or less of tin, 0.1% or less of phosphorus, 0.2% or less of nickel, 0.25% or less of antimony and the balance zinc and unavoidable impurities. The lead content of the silicon brass alloy material of the invention is greatly reduced, which corresponds to the demand of environmental protection and health; the alloy material has good casting property and is applicable to casting, in particular to large-scale gravity casting so as to have broad application prospect in health fittings industry.
Owner:浙江天申铜业有限公司
Lead-free solder with low copper dissolution
InactiveUS20070172381A1Minimize formation of oxideAdvantageously producedWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaDissolutionImpurity
Lead-free solder compositions suitable for joining electronic devices to printed wiring boards, which comprises by weight 0.2 to 0.9% copper, 0.006 to 0.07% nickel, 0.03 to 0.08% bismuth, less than 0.5% silver, less than 0.010% phosphorus, and a balance of tin and inevitable impurities. A solder composition embodying this invention finds particular application in automated wave-soldering machines where conventional lead-free solders dissolve excessive copper from printed wiring circuitry and component terminations.
Owner:KESTER
Method for Bulk Sorting Shredded Scrap Metal
InactiveUS20090236268A1Increase valueReduce copper contentSeparation devicesSortingChemical compositionBulk material analyzer
A stream of shredded scrap metal is divided into increments. A bulk material analyzer is employed to determine the bulk chemical composition of each increment. The increments are then sorted on the basis of the bulk chemical composition of each increment.
Owner:SHULMAN ALVIN D
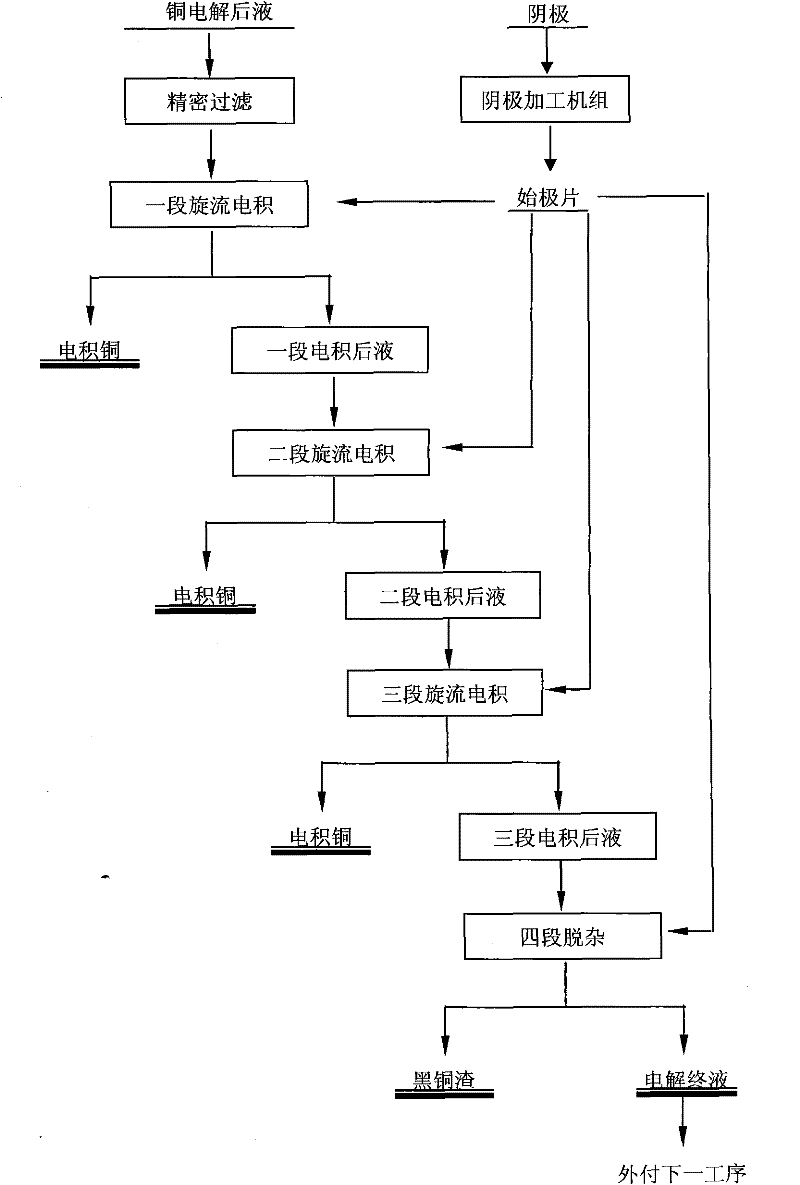
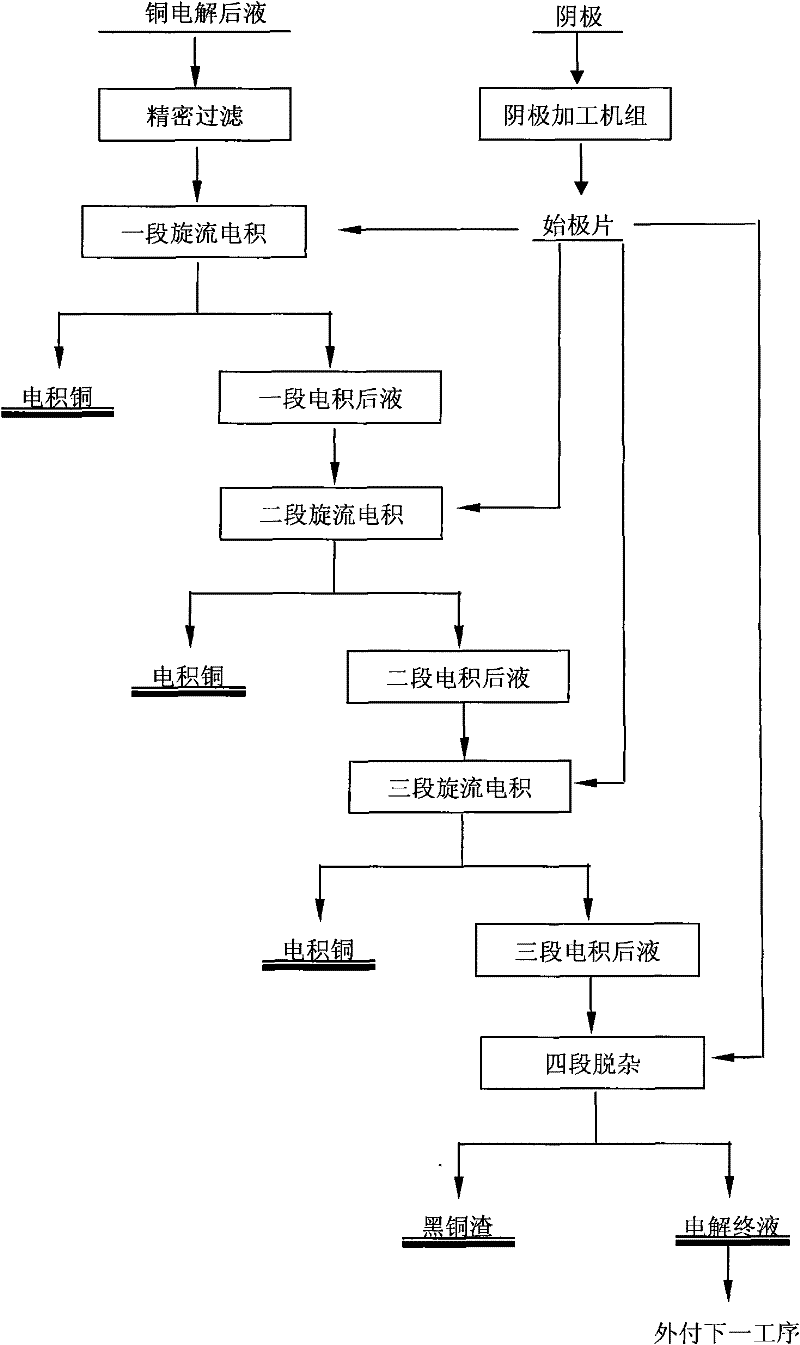
Technology for treating and purifying copper electrolyte by vortex electrolysis
InactiveCN102453931AIncrease current densityImprove current efficiencyPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisBismuth
A technology for treating and purifying copper electrolyte by vortex electrolysis relates to the technical field of copper electrolyte purification. The treatment process comprises the steps of: 1. carrying out secondary filter on copper electrolyte to be purified and treated; 2. sending into a vortex electrolysis system to produce standard cathode copper; 3. after three segments of vortex electrolysis, sending the solution with a copper content of 2-4g / L to a vortex electrolysis powder impurity removal stage; 4. removing impurities of arsenic, antimony and bismuth in a powder vortex electrolytic tank; and 5. forming a small amount of black copper ash with a low copper content in a filter cake after press filtration and sending a filtrate into a next operation. The technology of the invention can substitute a traditional induction copper and impurity removal method for purifying and treating copper electrolysis waste liquid, so as to provide an electrolysis technical scheme, which is efficient and reliable, and has simple process flow, simple operation and low cost, for purifying copper electrolysis waste liquid.
Owner:浙江科菲科技股份有限公司
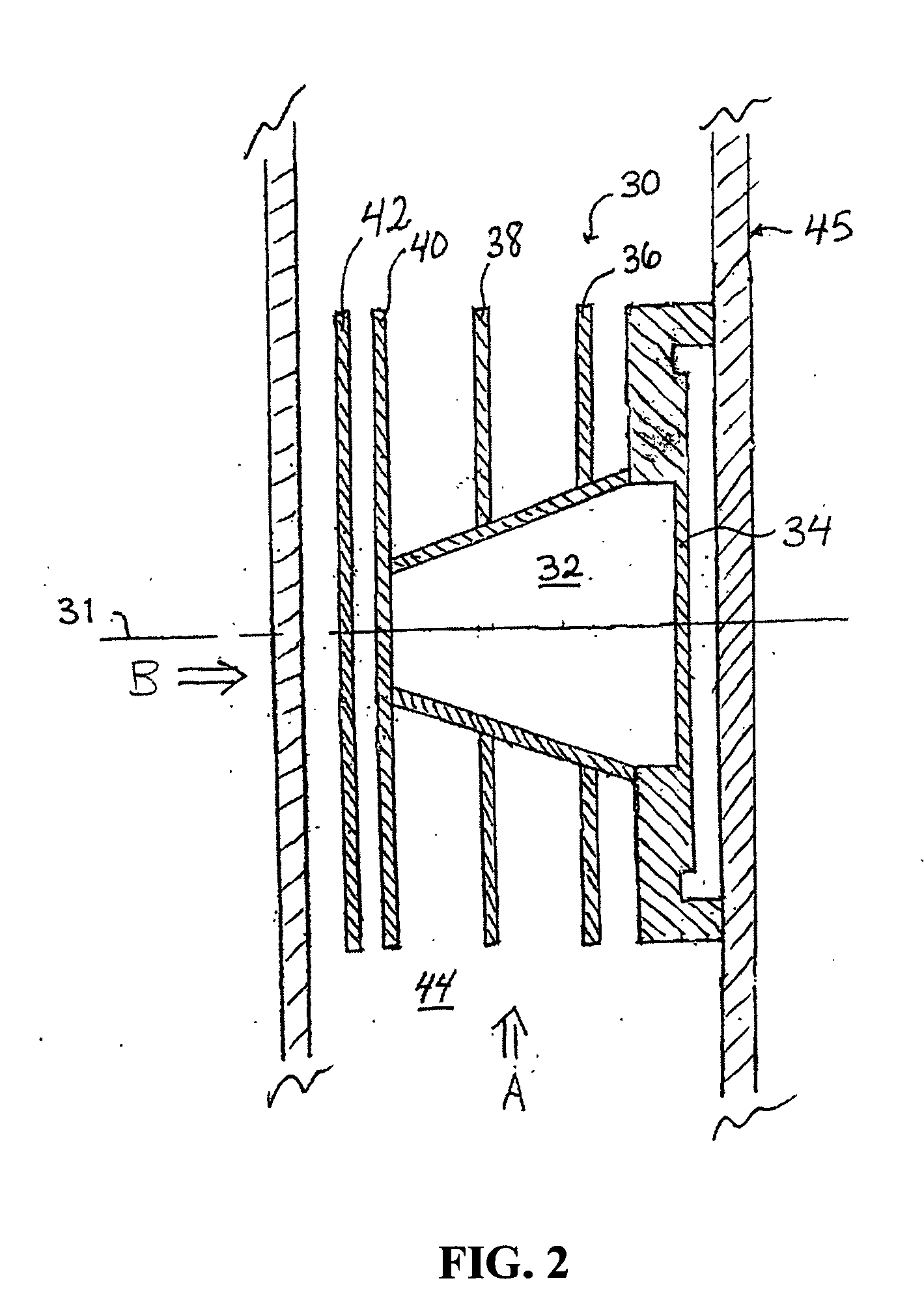
Methods for making and processing metal targets for producing Cu-67 radioisotope for medical applications
ActiveUS20100028234A1Improve productivitySimple methodBacterial antigen ingredientsTransuranic element compoundsHigh energyCompound (substance)
The present invention provides a method for producing Cu67 radioisotope suitable for use in medical applications. The method comprises irradiating a metallic zinc-68 (Zn68) target with a high energy gamma ray beam. After irradiation, the Cu67 is isolated from the Zn68 by any suitable method (e.g., chemical and / or physical separation). In a preferred embodiment, the Cu67 is isolated by sublimation of the zinc (e.g., at about 500-700° C. under reduced pressure) to afford a copper residue containing Cu67. The Cu67 can be further purified by chemical means (i.e., dissolution in acid, followed by ion exchange).
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Method for recovering copper from alkaline etching waste liquid and recycling alkaline etching liquid
The invention discloses a method for recovering copper from alkaline etching waste liquid and recycling the alkaline etching liquid, comprising the step of adding a hydrazine hydrate reducing agent and a catalyst into the alkaline etching waste liquid to recover copper powder, wherein the alkaline etching waste liquid can be recycled after the copper powder is recovered. The invention has the optimum conditions of: placing the alkaline etching waste liquid into a reactor; adding hydrazine hydrate with mass percent concentration of 40 percent according to added quantity of 160-200mL / L; adding a solution of various salts of ruthenium, palladium, nickel and cobalt as the catalyst with added quantity of 0.01-0.2g / L (metered by the masses of the ruthenium, the palladium, the nickel and the cobalt), reacting for 30-35 minutes at temperature between 70DEG C and 100DEG C; and separating to obtain the copper powder. The invention has the beneficial effect that after the copper is recovered from the alkaline etching waste liquid, the alkaline etching waste liquid can be regenerated and recycled, therefore, various resources in the alkaline etching waste liquid can be used fully, and the etching cost of a printing plate and the discharge of pollutants can be reduced.
Owner:FUQING BRANCH OF FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for bulk sorting shredded scrap metal
InactiveUS7886915B2Reduce copper contentIncrease valueSeparation devicesGrain treatmentsChemical compositionBulk material analyzer
Owner:SHULMAN ALVIN D
Point-of-use removal of lead and copper in drinking water using hydroxylapatite and carbonate minerals
InactiveUS6106725AReduce copper contentGreat tasteWater contaminantsSolid sorbent liquid separationEnvironmental chemistrySolubility
A process for removing lead and copper from drinking water discharged from a drinking water outlet while suppressing the concentration of phosphate ions comprising directing the water through a matrix comprising phosphate mineral with a very low phosphate solubility, and a solid carbonate mineral which is slightly soluble in water. The matrix is sized such that there is sufficient contacting between the water and the matrix to form a lead phosphate precipitate, reduce the lead concentration in the water to below 15 parts per billion, and suppress the phosphate ion concentration to 5 mg / L, preferably 3 mg / L, or below.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
Electrothermal copper-smelting slag depleted furnace
ActiveCN101839631ADowngradeHigh recovery rateRotary drum furnacesProcess efficiency improvementSiphonElectricity
The invention discloses an electrothermal copper-smelting slag depleted furnace, which comprises a furnace body, supports, an oxygen lance and electrodes; the furnace body comprises a furnace shell defining a furnace chamber and a refractory material layer arranged on the inner wall of the furnace shell, the furnace body is provided with a feed inlet for feeding copper-smelting slag and vulcanizing agent into the furnace chamber, a siphon inlet for discharging copper matte, a waste slag-discharging outlet, electrode plugholes, a smoke outlet and an oxygen lance plughole, wherein the oxygen lance plughole is formed at the bottom of the furnace shell; the furnace body is supported by the supports; the oxygen lance is plugged into the oxygen lance plughole; and the electrodes are plugged into the furnace body via the electrode plugholes. When the electrothermal copper-smelting slag depleted furnace is used for bottom-blowing electrothermal copper-smelting slag depletion, the copper content in waste slag can be reduced, and electricity consumption can be decreased.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
Dilution treatment method for copper smelting slag
InactiveCN105671325AImprove dynamic conditionsReduce copper contentProcess efficiency improvementSlagAfter treatment
The invention provides a dilution treatment method for copper smelting slag. The dilution treatment method includes the technological steps that firstly, a mechanical stirring device is introduced into a dilution furnace, the high-temperature molten state copper smelting slag at the temperature ranging from 1150 DEG C to 1350 DEG C is guided into the dilution furnace, a stirring paddle is adjusted to stretch to the part from the 1 / 3 position of the liquid level of the copper smelting slag to the 1 / 2 position of the liquid level of the copper smelting slag, heating and stirring are started, the temperature of the copper smelting slag is controlled to range from 1200 DEG C to 1350 DEG C, the stirring speed ranges from 50 r / min to 200 r / min, and a vortex with the diameter height ratio ranging from 0.5 to 3 is formed; secondly, a vulcanizing agent is carried through carrier gas and injected to the position, close to the center of the vortex, of the surface of a copper smelting slag pool through a nozzle above the liquid level of the high-temperature molten state copper smelting slag, the adding amount of the vulcanizing agent is 0.3-8% of the mass of the copper smelting slag, and heat-preservation stirring is conducted for 10-60 min; and thirdly, standing layering is conducted, and copper matte on the lower layer and diluted slag on the upper layer are collected. The copper content of the diluted slag obtained after treatment is below 0.3%.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Process for making finished or semi-finished articles of silver alloy
Owner:ARGENTIUM INT
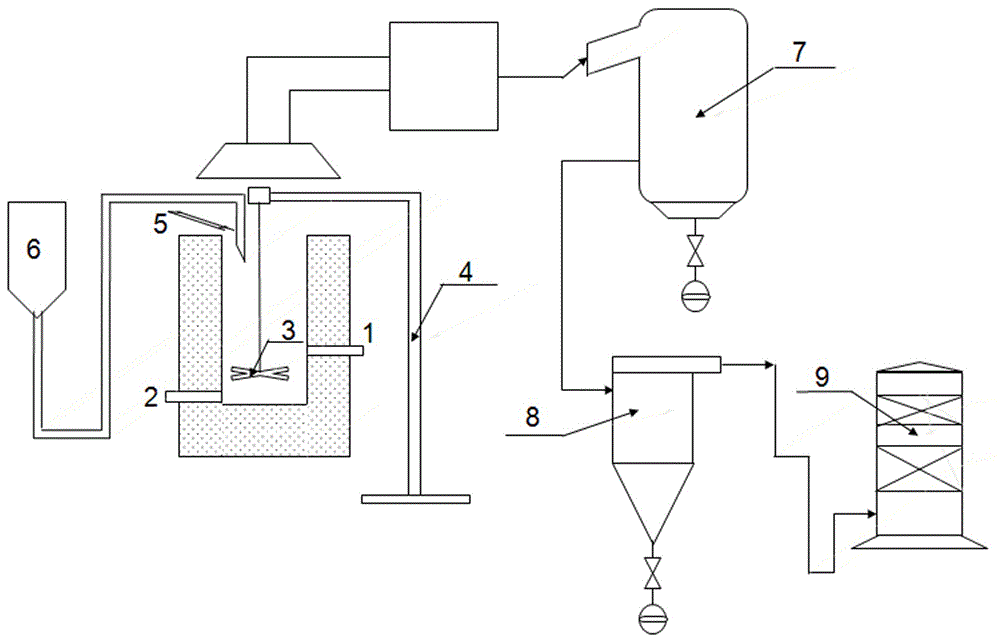
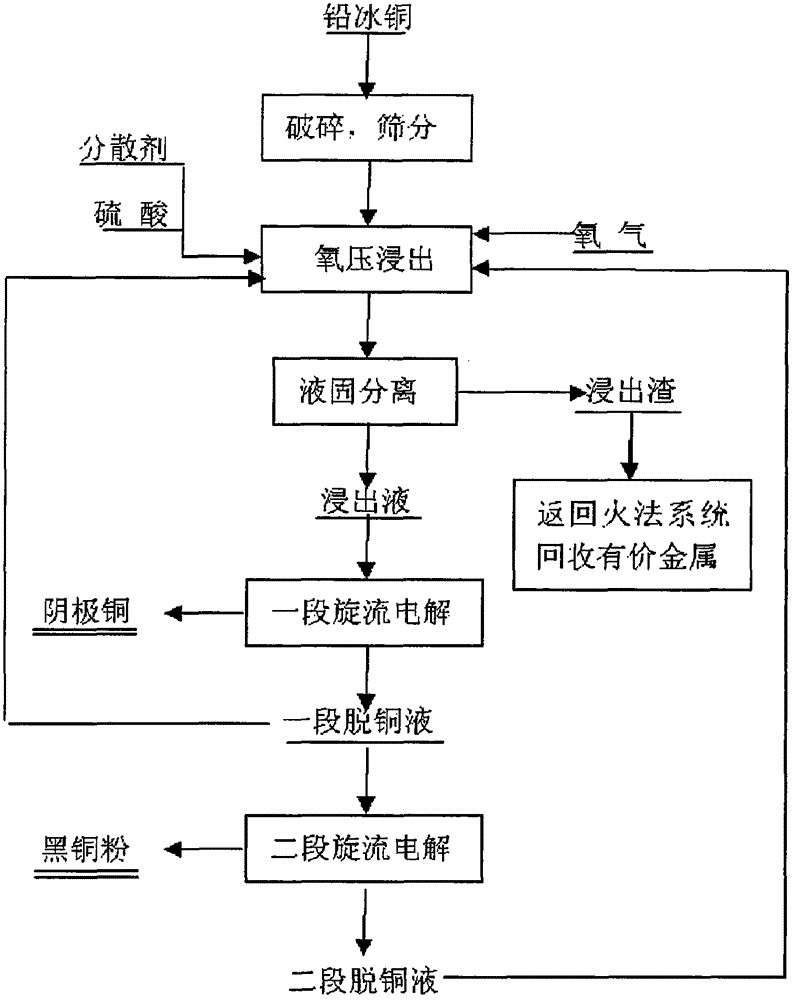
Process of efficiently recovering copper from lead matte according to oxygen pressure acid leaching and vortex electrolysis techniques
InactiveCN104831064AAdaptableImprove leaching ratePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisHydrometallurgy
The invention belongs to the field of nonferrous metal hydrometallurgy and discloses a process of efficiently recovering copper from lead matte according to oxygen pressure acid leaching and vortex electrolysis techniques. The method includes: taking lead matte as a raw material, crushing and grinding the lead matte, screening through a 100-mesh sieve, adding into a high-pressure autoclave along with sulfuric acid and a dispersing agent, feeding oxygen for leaching, carrying out liquid-solid separation to obtain solution containing copper sulfate, subjecting the solution containing copper sulfate to vortex electrolytic decopperation to obtain cathode copper, and returning after-electrodeposition liquid to the leaching procedure to replace sulfuric acid serving as the leaching agent. High efficiency in copper recycling can be realized, electrodeposition of copper can be selectively carried out according to the vortex electrolysis techniques, and high current level and current efficiency, low reagent consumption, reduction of production cost and improvement of enterprise benefits are realized. In addition, due to closed cycle of solution, harmful gas emission is avoided, and current concepts of circular economy and environment protection are met.
Owner:XIANGNAN UNIV +1
Method for depleting refining slag of copper
The invention discloses a method for depleting refining slag of copper. The method comprises the following steps of: adding recovered waste copper into a reverberatory furnace, heating and melting, inserting a blast pipe into molten copper to blow air, and stirring for oxidization with blasting to ensure that impurities are oxidized and partial copper is oxidized into cuprous oxide; taking a molten copper sample for observation, and adding quartz sand in an amount which is 1.2 to 1.4 percent of the weight of the total charging material for slagging when the section is brick red so as to ensure that the oxidized impurities in the molten copper such as Fe, Pb, Sn and the like and quartz react to form silicate slag; covering a carbonaceous reducing agent in an amount which is 0.13 to 0.17 percent of the total amount of the charged waste copper on the slag, inserting the blast pipe into the molten copper to blow the air, and stirring for 5 to 10 minutes, wherein a considerable amount of copper which enters a slag phase is reduced and enters a molten copper phase because copper is reduced more easily than other impurity elements. About 35 percent of copper content in the slag is reduced, and the method is favorable for recycling reclaimed copper resources. The production process is easy to operate, and the conventional production equipment can be directly utilized.
Owner:NINGBO JINTIAN SMELTING +1
Brass alloy
The invention provides a brass alloy. The brass alloy comprises 45wt%-55wt% of Cu, 0.5wt-7wt% of Mn, 0.5wt%-5wt% of Al, 0.5wt%-4wt% of Fe, 0.05wt%-2wt% of Si, 0.001wt%-0.5wt% of P, and the balance of Zn According to the application of the invention, Cu and Zn are used as main addition elements, and the elements of Mn, Al, Fe, Si and P , which have strengthening effects, are added, so that the brass alloy uses a beta phase as a matrix, and the brass alloy has higher plasticity and higher strength; under the circumstance of ensuring that the brass alloy has higher strength and higher plasticity, the content of the copper is reduced, so that the cost of the brass alloy is reduced.
Owner:NINGBO POWERWAY ALLOY MATERIAL
Mine selecting and copper extracting process
InactiveCN103157557AReduce copper contentPrevent "overgrinding" phenomenonFlotationMaterials scienceCopper slag
The invention relates to the technical field of copper smelting and provides a mine selecting and copper extracting process. The mine selecting and copper extracting process comprises the following steps: a) primary grinding of copper slag is conducted; b) primary select flotation of slag obtained in the step a) is conducted, and primary slag concentrate and primary select flotation of tailings are obtained; c) secondary grinding of the primary select flotation of tailings is conducted; d) slag obtained in the step c) is activated, and secondary select flotation of activated slag is conducted. Copper in smelting slag is extracted repeatedly in a staged mode, so that copper content in the slag is reduced, and waste slag standard is reached. An experimental result shows that the copper content of slag tailings obtained is 0.30wt%-0.35wt% after select flotation and activating, and the waste slag standard is reached.
Owner:YANGGU XIANGGUANG COPPER
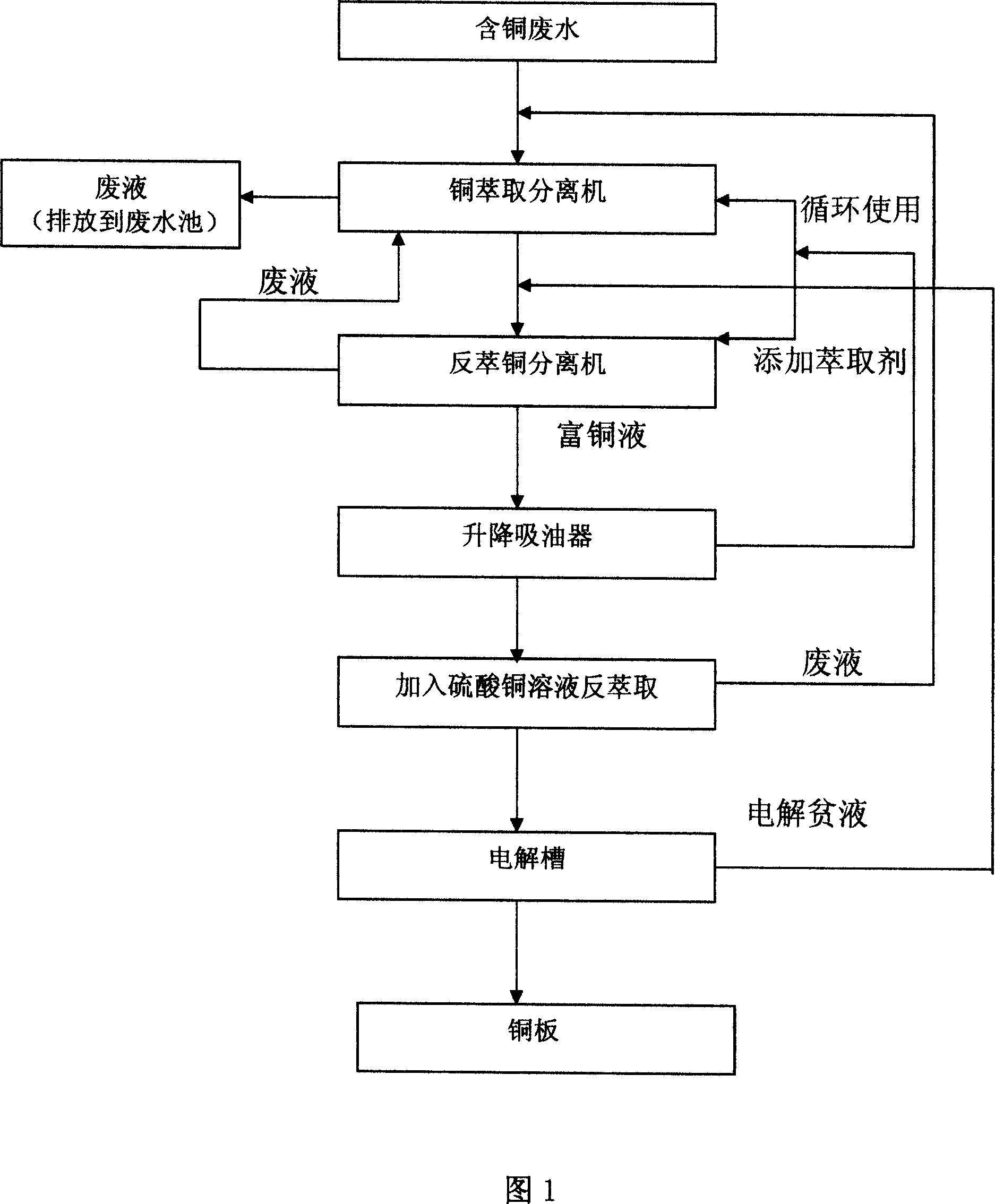
System and method for treating wastewater of containing copper from microetching printed circuit board
InactiveCN101003396ASimplified processingEasy to controlWater/sewage treatment by extractionOil separationEtching
This invention discloses a system for treating copper-containing wastewater from micro etching of printed circuit board. The system comprises a copper separation system, an electrolysis system, a wastewater pre-treatment system and a wastewater post-treatment system. The copper separation system comprises a copper extractor and a copper back extractor. The electrolysis system comprises an electrolysis tank and a NaClO electrolysis membrane. The wastewater pre-treatment system comprises a copper-containing wastewater pool and an automatic pH detector. The wastewater post-treatment system comprises an oil-separation tank, a stirrer and a lift oil-absorber. The treatment method combines stirring, clarification and back extraction, and recovers solutes from aqueous solution by using extraction technique. The copper-removing rate is up to 90%, and the copper content in the wastewater is reduced by at least 80%. The wastewater can meet discharge standards.
Owner:陈尚林 +1
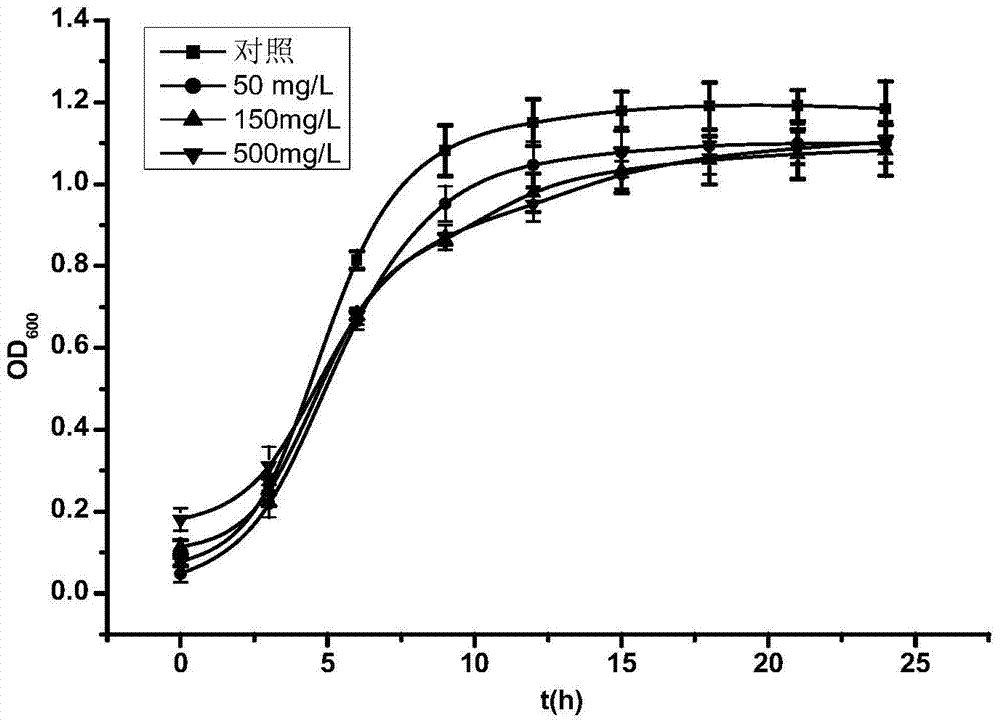
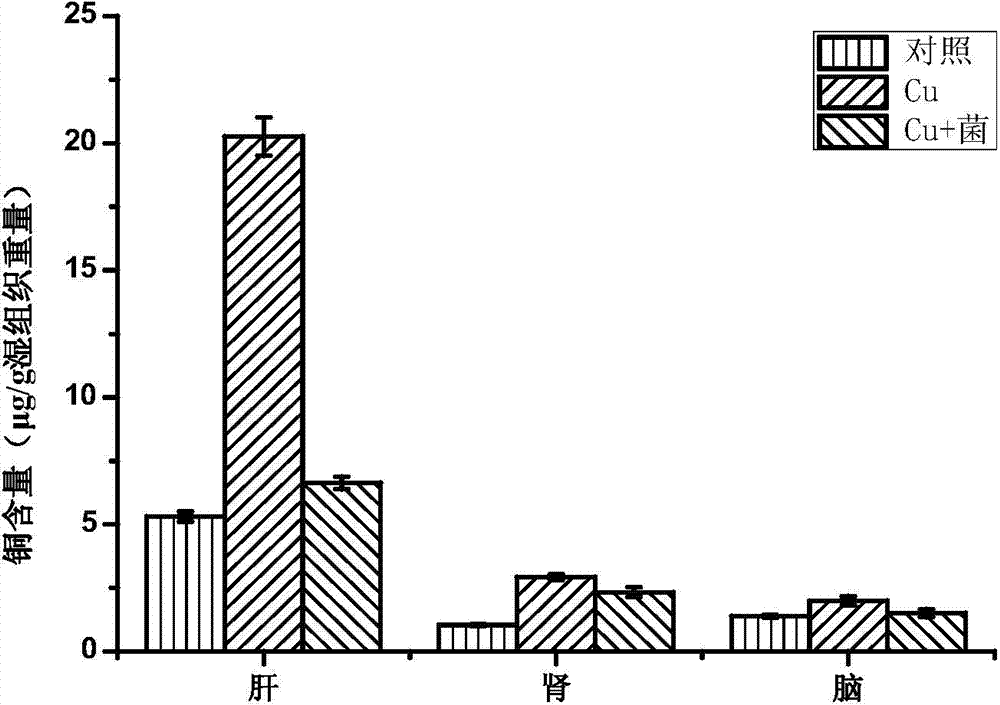
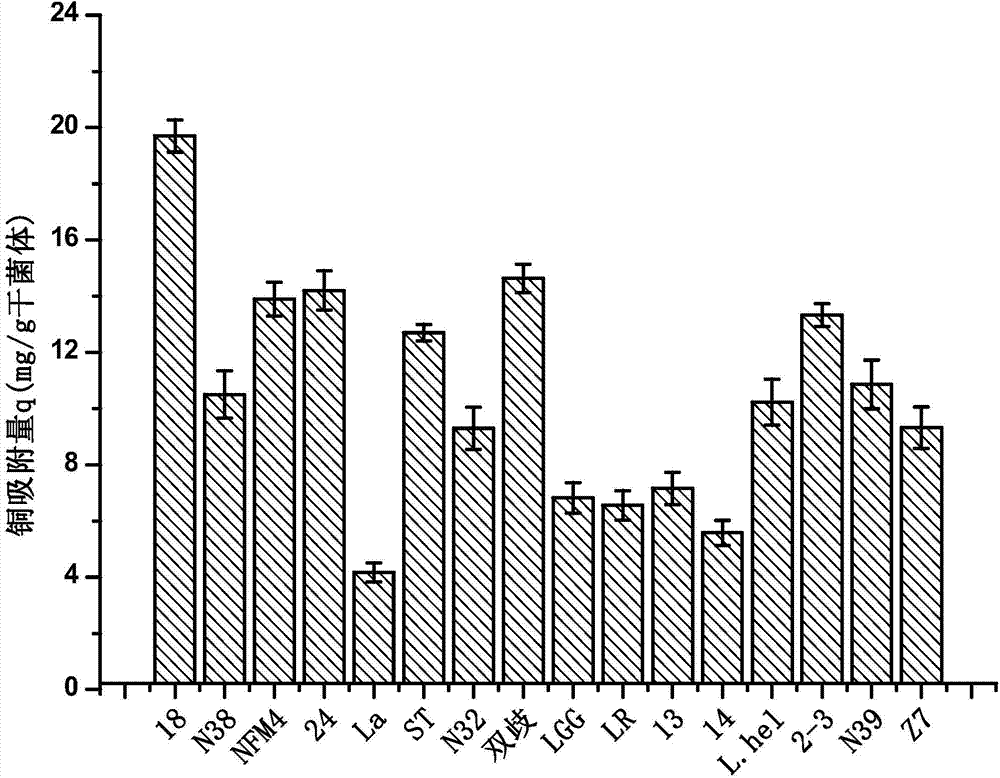
Lactobacillus plantarum capable of alleviating copper toxicity and purpose thereof
The invention discloses a Lactobacillus plantarum, which is preserved on September 23, 2013 in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center belonging to China?Committee?for?Culture?Collection?of?Microorganisms, and has a preservation number of CGMCC NO.8246; and the preservation address is Institute of microbiology of Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, Yard No.1, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. The Lactobacillus plantarum provided by the invention has acid resistance, good in vitro tolerance to copper ions, can tolerate copper ion solution with initial concentration of 50 mg / L, has strong adsorption of copper ions, and can reduce the copper content in liver, kidney and brain of copper-exposed mice, mitigate the pathological symptoms of copper-exposed mice, alleviate liver injury and lower AST and ALT contents in serum of mice. The Lactobacillus plantarum is used for the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions and fermented food to alleviate the toxicity of copper, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Submerged arc welding wire for superstrength pipeline steel and production method thereof
InactiveCN102069320AHigh strengthIncrease contentArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsSubmerged arc weldingCopper plating
The invention relates to a submerged arc welding wire for superstrength pipeline steel and a production method thereof. The technical scheme is that: the submerged arc welding wire comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.04 to 0.06 percent of C, 1.40 to 2.00 percent of Mn, 0.70 to 1.10 percent of Mo, 2.00 to 2.60 percent of Ni, 0.80 to 1.20 percent of Cr, 0.10 to 0.30 percent of Cu, less than or equal to 0.0005 percent of B, less than or equal to 0.01 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.01 percent of P and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The production method comprises the following steps of: adding 0.01 to 0.5 weight percent of composite additive when the components are smelted, forming a square billet in a pouring way, hot-rolling the square billet to form a steel wire rod with the diameter of Phi 5.5 to Phi 7.5mm, removing oxide skin from a surface, drawing the steel wire rod to form the welding wire with the diameter of Phi 3.2 to Phi 4.0mm and performing copper plating, wherein the composite additive is added in form of cored wire. The welding wire produced by the method is welded together with an SJ105 welding flux so as to achieve the tensile strength sigmab of more than or equal to 910MPa and the impact toughness Akv at -30 DEG C of more than or equal to 84J of a weld metal, and is suitable for the submerged arc welding of X120 pipeline steel with superstrength.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Brass alloy coverage slag removal agent and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a brass alloy coverage slag removal agent and a preparation method thereof. The brass alloy coverage slag removal agent is characterized by comprising following components in percent by mass: 10-20% of a chloride, 20-30% of a fluoride, 10-15% of charcoal dust and the balance of a carbonate. The preparation method of the brass alloy coverage slag removal agent comprises the following steps: burdening by means of putting the components from a large ratio to a small ratio; mixing and uniformly stirring; secondly, drying a mixture and controlling a water content within a range of 0.5%; finally, grinding the dried materials in a powder manner, and controlling the particle size of the powder within a range of 80 meshes. The brass alloy coverage slag removal agent provided by the invention has the advantages of good spreading property, coverage property, separation property and purification property and good effect of slag removal. Not only can slag of a furnace wall and a furnace bottom be removed in a furnace cleaning process by using a manual sprinkling and stirring method, but also the brass alloy coverage slag removal agent can be directly and uniformly sprinkled to the surface of a brass alloy molten body. Compared with the traditional slag removal agent, the additive amount of the slag removal agent provided by the invention is only 0.3-0.5% of a processing amount of brass, so that the copper content in the furnace slag can be effectively reduced, and the gas removal and coverage effects can be realized.
Owner:JINTIAN COPPER GROUP CORP NINGBO
Smelting furnace for continuously smelting blister copper through copper sulfide concentrate and smelting method of smelting furnace
ActiveCN105087956ATake advantage ofImprove energy savingRotary drum furnacesCrucible furnacesSlagCupric sulfide
The invention provides a smelting furnace for continuously smelting blister copper through copper sulfide concentrate and a smelting method of the smelting furnace. The smelting furnace is an integrated metallurgical furnace with the front-end top-blown smelting function, the middle electric furnace setting function and the tail-end matte continuous converting function and comprises a front-end top-blown smelting furnace, a middle setting electric furnace and a tail-end matte continuous converting furnace with the bottoms communicated sequentially. According to the smelting method, the procedures that the copper sulfide concentrate is continuously smelted into mixed melt of matte and slag through the converting furnace, settling separation of the matte and the slag is performed continuously, and the matte is continuously blown into blister copper are not needed. The three metallurgical processes that the copper sulfide concentrate is smelted into the mixed melt of the matte and the slag, settling separation of the matte and the slag is performed, and the matte is continuously blown into the blister copper can be continuously finished, the equipment structure and the operation process are simple, energy consumption is low, and environmental friendliness and safety are achieved.
Owner:YUNNAN TIN
Powder metallurgy Fe-Cu-Sn oil-retaining bearing and manufacturing technique thereof
The invention relates to a powder metallurgy Fe-Cu-Sn oil-retained bearing and the production process for the bearing. The bearing essentially comprises the following raw materials by weight: -100 mesh reduction Fe powder 96.5 swung dash 98%, -325 mesh Cu-Sn powder 2 swung dash 3.5%, lithium stearate 0.6 swung dash 1.0%. Wherein, in Cu-Sn alloy, Cu:Sn=7:2.5 swung dash 3.5 by weight. The production process is: weighing -100 mesh reduction Fe powder, -325 mesh Cu-Sn powder and lithium stearate by proper proportions; mixing them in a double-conic mixer at 19 swung dash 21r / min for 30-35 min; pressing the mixture under 300MPa swung dash 450MPa into blanks for oil-retained bearing; sintering the pressed blanks for 20-30 min under 880 swung dash 900 Celsius system, so sintered blanks are obtained; finishing and soaking by lubricating oil. The invention is of high strength, high oil content, low friction coefficient, low copper content, low material cost and process cost.
Owner:包敢锋
Aluminum alloy material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an aluminum alloy material which is characterized in that the material consists of the following components by weight percent: 0.6-1.3% of copper, 0.9-1.6% of magnesium, 5.3-6.7% of zinc, 0.03-0.2% of chromium, 0.03-0.2% of titanium, not more than 0.5% of iron, not more than 0.5% of silicon, not more than 0.3% of manganese and the balance of aluminum. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the aluminum alloy material. The aluminum alloy disclosed by the invention has the advantages of good oxidation performance, low copper content, low production cost, good extrusion performance, good corrosion resistance, difficult generation of cracking and good overall mechanical properties.
Owner:宁波环球输变电设备有限公司
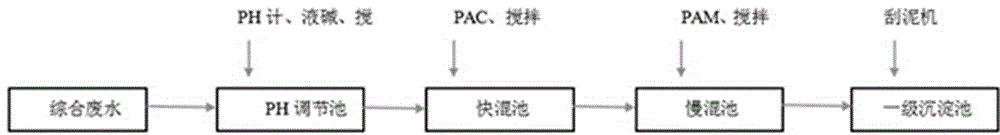
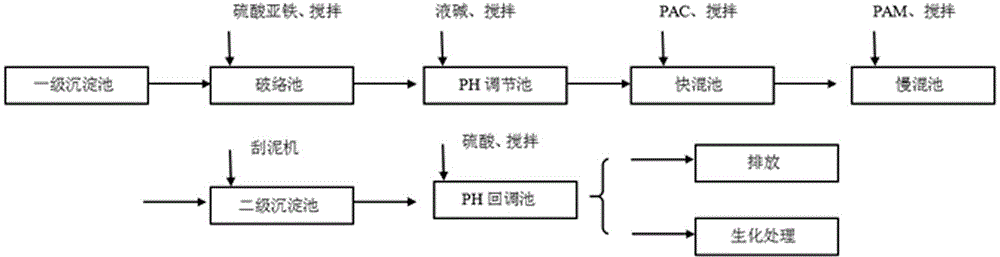
Two-level copper removing technology for treating low-concentration comprehensive wastewater in PCB electroplating
InactiveCN104944698AReduce dosageLow costWaste water treatment from metallurgical processMultistage water/sewage treatmentSludgeResource utilization
The invention discloses a two-level copper removing technology for treating low-concentration comprehensive wastewater in PCB electroplating. The two-level copper removing technology comprises a two-level copper removing process: hydrated copper ions in wastewater are removed in a primary cooper removing process; complex cooper irons are removed in a secondary cooper removing process. The two-level copper removing technology specifically comprises the following steps: after being lifted, the wastewater enters a pH adjustment tank; through pumping, an alkaline chemical agent is added to control the pH value of the wastewater to be 8.5-9; the adjusted wastewater I enters a quick mixing tank and a slow mixing tank in sequence; clear water obtained through primary precipitation is lifted through pumping and enters a complex breaking tank; a proper amount of ferrous sulfate is added for complex breaking; the pH value of the primarily treated wastewater is adjusted to be 8-9; the adjusted wastewater II enters the quick mixing tank and the slow mixing tank in sequence; the wastewater subjected to secondary precipitation enters a pH call-back tank for biochemical treatment; the standard wastewater is discharged. The two-level copper removing technology has the advantages that the chemical agent treatment cost is reduced, the discharged water quality is stabilized, the sludge minimization and the recovery value resource utilization are facilitated, and a high popularization value is achieved for wastewater treatment in the conventional PCB industry.
Owner:湖南景翌湘台环保高新技术开发有限公司
Lead-free brass alloy
The invention relates to a lead-free brass alloy containing the following components in percentage by weight: 0.3%-0.8% of aluminum, 0.01%-0.4% of bismuth, 0.05%-0.15% of ferrum and more than 96% of copper and zinc, wherein the copper content of the lead-free brass alloy is 58%-75%. The brass not only accords with the standard of the lead-free alloy environmental protection laws and regulations that the lead content is less than 0.25%, but also contains 0.05%-1.5% of ferrum and less than 0.4% of bismuth, so that the production cost can be reduced, the defects of cracks, slag inclusion and the like existing in castings can also be reduced, and therefore, the yield and the qualified rate of the product are effectively improved.
Owner:MODERN ISLANDS
Method for preparing polytriazole through catalysis of recyclable supported cuprous catalyst and prepared polytriazole
InactiveCN103408756AIncrease contact areaIncrease the rate of polymerizationChemical recyclingPolymer dissolutionSolubility
The invention discloses a method for preparing polytriazole through catalysis of a recyclable supported cuprous catalyst and prepared polytriazole. The method comprises the following steps: under the catalysis of a supported click polymerization catalyst, a nitrine monomer and an alkyne monomer are subjected to click polymerization reaction in an organic solvent so as to form polytriazole. The method realizes the click polymerization reaction through catalysis of the supported cuprous catalyst, and has the advantages that the activity is high, the condition is gentle, the stereoselectivity is high, and the solubility of polymer is excellent, and the copper content of the polymer prepared by utilizing the reaction is low. In addition, after the supported cuprous catalyst used by the reaction is recycled for 4 times, the reaction activity of the supported cuprous catalyst is not subjected to obvious change.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
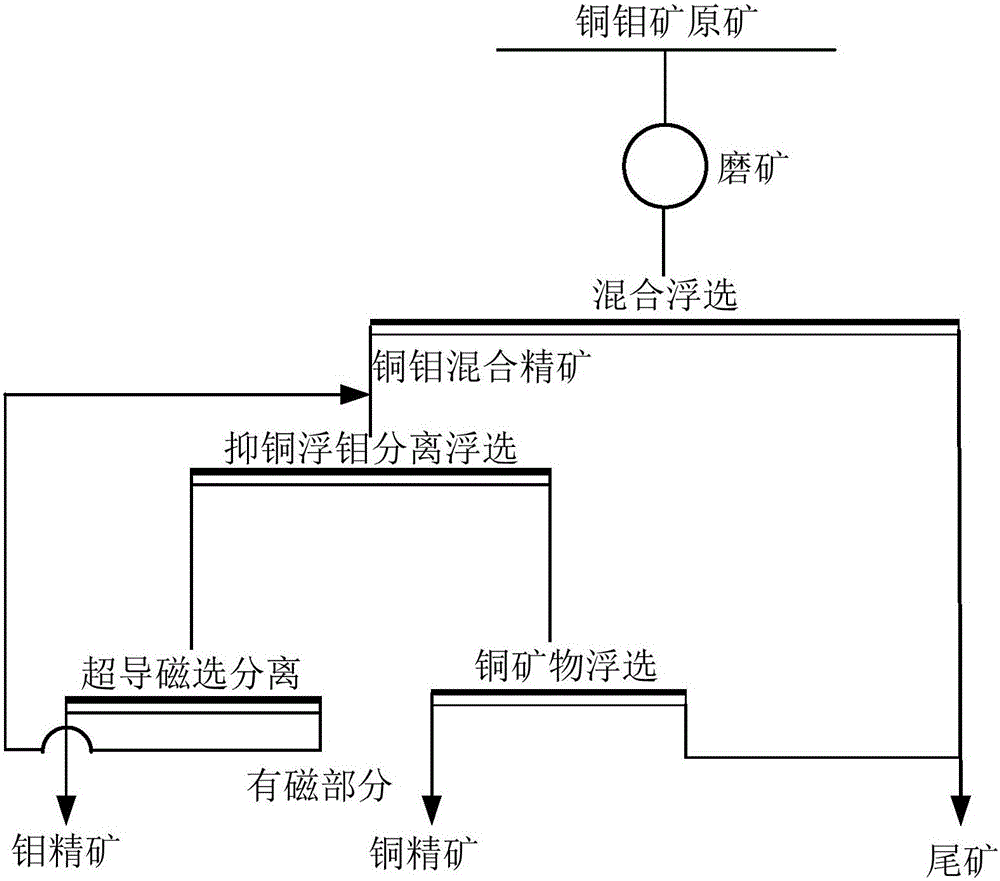
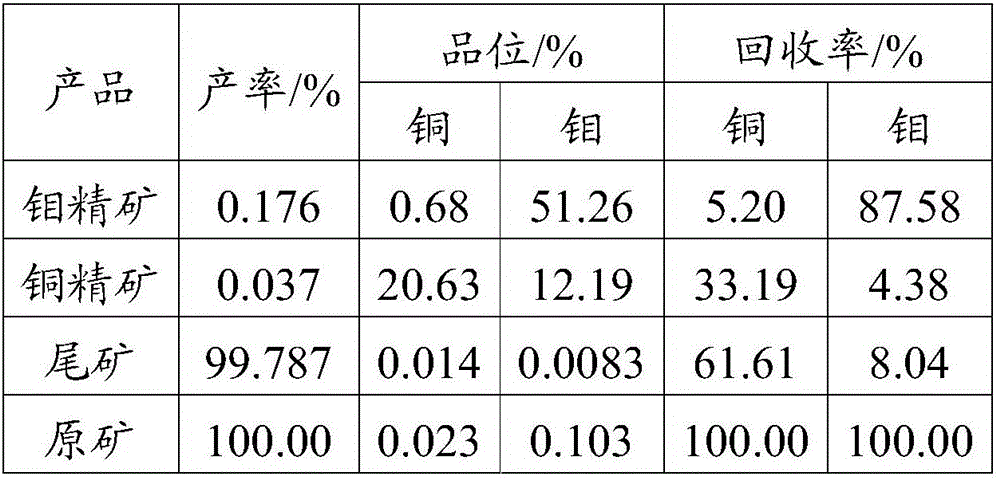
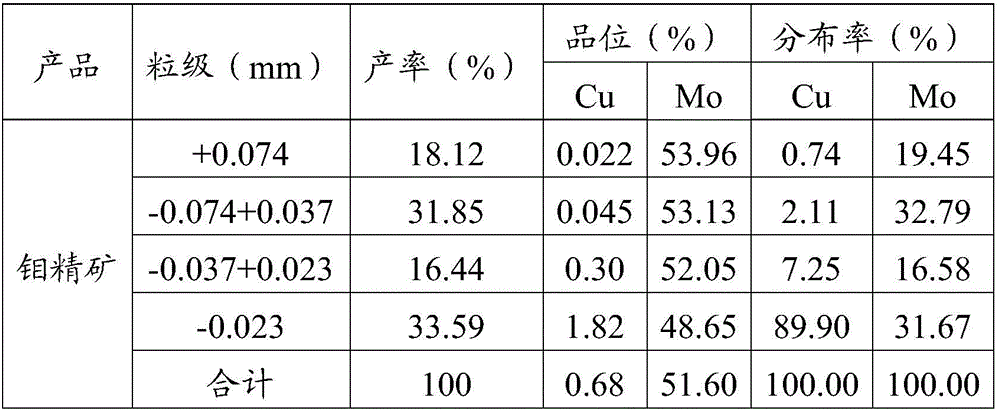
Floating magnetic combined copper-molybdenum sorting-separation method
ActiveCN106583026AReduce lossesGuaranteed RecoveryFlotationMagnetic separationMagnetic separatorNon magnetic
The invention discloses a floating magnetic combined copper-molybdenum sorting-separation method. Copper-molybdenum bulk concentrate is adopted as fed ore, copper-inhibiting molybdenum-floating flotation separation is carried out, and a foam product generated after copper-inhibiting molybdenum-floating flotation separation is subjected to copper-molybdenum re-separation with a superconductive magnetic separator with the background magnetic field strength being 3,200 kA / m to 4,800 kA / ml; an obtained non-magnetic part is a molybdenum concentrate product, and an obtained magnetic part serves as middling and is returned to be subjected to copper-inhibiting molybdenum-floating flotation separation roughing work; and an underflow product obtained after copper-inhibiting molybdenum-floating flotation separation is subjected to copper ore flotation, and copper concentrate is obtained. Collection of the copper ore is reinforced in a superconductive magnetic separation manner, the separation effect of copper and molybdenum is further improved, the copper content in later molybdenum concentrate is reduced, and then the recovery rate of molybdenum and copper is increased.
Owner:江苏旌凯中科超导高技术有限公司
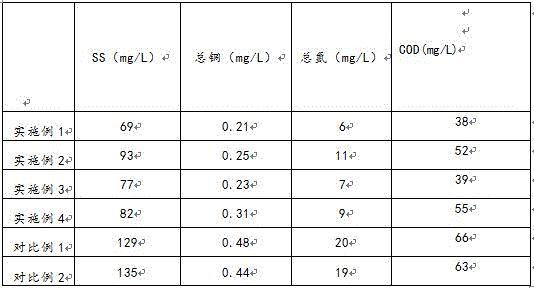
Fast treating method for copper mine waste water
InactiveCN106430754AReduce copper contentReduce organic contentWaste water treatment from quariesWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsActivated sludgeAluminium chloride
The invention discloses a fast treating method for copper mine waste water. A mixture composed of poly aluminium chloride, potassium ferrate, dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride, potassium feldspar, bissuccinimide, quartz sand, polyacrylamide, diethylenetriaminepenta acid, urea, citric acid and activated sludge is adopted as a cleaning agent, matched with a flocculating agent with polyferric sulfate, bentonite, zeolite powder, ethoxylated lauryl alcohol sulfate and alum as constituents, and assisted with technologies of deep oxidation, flocculation, ultrasound, resin adsorption, filtration, sterilization, membrane separation and the like, therefore, the copper content and the COD value in the copper mine waste water are effectively reduced, industrial requirements can be met, and the method has a good application prospect.
Owner:吴小慧
Micro-copper-formulated ceramic brake pad
InactiveCN103821859ALight weightUniform surface distributionOther chemical processesFriction liningSulfideBoron nitride
A micro-copper-formulated ceramic brake pad is made with aramid pulp, carbon fiber, magnesium hydroxide, copper fiber, brown fused alumina, antimony sulfide, ceramic fiber, superfine iron oxide powder, calcium sulfate whisker, potassium titanate, barite, crystalline flake graphite, calcined petroleum coke, nano hollow float beads, flake aluminum powder, nitrile butadiene rubber powder, cashew nut shell oil modified phenolic resin, zirconite, boron nitride, zinc oxide, and benzoxazine resin. The components are reasonably matched, and advantages of the materials can be given to full play in abrasive materials. The novel fiber materials are reasonably composited, performance defects of the materials can be mutually complemented, and high performance is achieved through mutual connective action. The micro-copper-formulated ceramic brake pad has low content of heavy metals and smaller than 0.5% of copper content and therefore, is very environment friendly.
Owner:RUIYANG AUTOMOTIVE MATERIALS XIANTAO
Wear resistant cast iron
InactiveCN101440454AImprove hardness and wear resistanceImprove metallographic structureWear resistantCast iron
The invention discloses a cast iron material with higher hardness, corrosion resistance, high-temperature oxidation resistance and abrasion endurance of an abrasive material with larger impact load. The cast iron material consists of the following compositions by weight percentage: 2.8 percent of C, 0.2 to 1.0 percent of Si, 0.5 to 1.0 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.06 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.1 percent of P, 21 to 23 percent of Cr, 0 to 1.5 percent of Ni, 1.0 to 1.5 percent of Mo, and the balance being Fe and unavoidable impurities. The cast iron material has the advantages of improving hardness and other comprehensive performances of the material, and being helpful for prolonging the service life of a finished product manufactured by the cast iron material.
Owner:蔡柏林
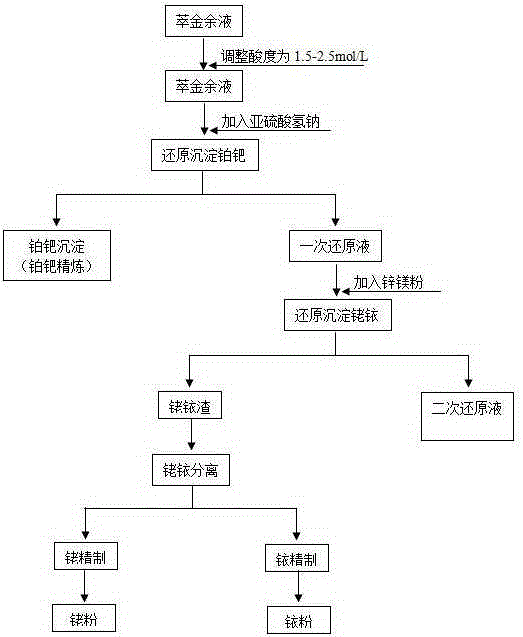
Method for reducing gold extraction residual liquid
The invention discloses a method for reducing gold extraction residual liquid, and relates to a process for separating platinum palladium and other metals from the gold extraction residual liquid by using sodium hydrogen sulfite and settling zinc magnesium powder to separate rhodium iridium and base metals; after the acidity of the gold extraction residual liquid is adjusted, the sodium hydrogen sulfite is reduced; the zinc magnetism powder is settled through once reducing liquid; and rhodium refining and iridium refining are respectively performed for produced rhodium iridium slag after the separation of rhodium and iridium to generate rhodium powder and iridium powder accordant with the national standards. The method is simple in process flow, convenient for operation and reasonable in procedure joint. The method can enable the copper content in the subsequently produce once reducing liquid to largely reduce; the platinum and palladium settling rates are both higher than 99%; the once reducing liquid is prepared to secondary reducing liquid by the replacement of zinc magnesium powder; the settling rates of noble metals in the secondary reducing process are higher than 99.95%; the rhodium iridium slag weight generated by secondary reduction is reduced by above 65% compared with a traditional process; the method can shorten the process flow of rhodium and iridium refining; and the product pass percent is largely increased.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com