Fast treating method for copper mine waste water
A treatment method and technology for copper mine wastewater, applied in mining wastewater treatment, multi-stage water treatment, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as waste of water resources, pollution of surrounding water environment, etc., achieve reduction of copper content, cheap raw materials, Practical effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
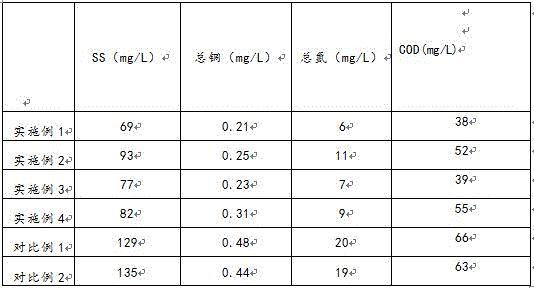
[0021] 1) Add alkaline white mud to the waste water, stir and react at 35°C for 20 minutes, filter after standing for precipitation, and then add a purifying agent in an amount of 35 mg / L. The purifying agent is composed of: 25 parts of polyaluminum chloride, 20 parts of potassium ferrate, 20 parts of dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride, 15 parts of potassium feldspar, 10 parts of bis-succinimide, 10 parts of quartz sand, 8 parts of polyacrylamide, diethylenetriaminepenta 5 parts of methylene phosphonic acid, 5 parts of urea, 2 parts of citric acid and 20 parts of activated sludge were stirred for 30 minutes at a speed of 15 rpm, left to stand for 3 hours, and the waste water was stratified into supernatant and solid precipitation;
[0022] 2) Send the supernatant to the deep oxidation tower, adjust the pH of the supernatant to 2, aerate evenly, add oxidants, carry out deep oxidation, and measure the water quality indicators in real time. When the concentration of heavy metals i...
Embodiment 2
[0029] 1) Add alkaline white mud to the waste water, stir and react at 55°C for 35 minutes, filter after standing for precipitation, and then add a purifying agent in an amount of 35 mg / L. The purifying agent consists of: 30 parts of polyaluminum chloride, 25 parts of potassium ferrate, 25 parts of dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride, 20 parts of potassium feldspar, 15 parts of bis-succinimide, 13 parts of quartz sand, 10 parts of polyacrylamide, diethylenetriaminepenta 7 parts of methylene phosphonic acid, 8 parts of urea, 4 parts of citric acid, and 25 parts of activated sludge were stirred for 40 minutes at a speed of 25 rpm, left to stand for 3.5 hours, and the waste water was stratified into supernatant and solid precipitation;
[0030] 2) Send the supernatant to the deep oxidation tower, adjust the pH of the supernatant to 2.5, aerate evenly, add oxidants, carry out deep oxidation, and measure the water quality indicators in real time. When the concentration of heavy metal...
Embodiment 3
[0037] 1) Add alkaline white mud to the waste water, stir and react at 70°C for 50 minutes, let it sit for precipitation and then filter, then add a purifying agent in an amount of 35 mg / L. The purifying agent consists of: 35 parts of polyaluminum chloride, 30 parts of potassium ferrate, 30 parts of dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride, 25 parts of potassium feldspar, 20 parts of bis-succinimide, 15 parts of quartz sand, 12 parts of polyacrylamide, diethylenetriaminepenta 10 parts of methylene phosphonic acid, 10 parts of urea, 5 parts of citric acid, and 30 parts of activated sludge were stirred for 50 minutes at a speed of 30 rpm, left to stand for 4 hours, and the waste water was stratified into supernatant and solid precipitation;
[0038] 2) Send the supernatant to the deep oxidation tower, adjust the pH of the supernatant to 3, aerate evenly, add oxidants, carry out deep oxidation, and measure the water quality indicators in real time. When the concentration of heavy metals...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com