Lead-free brass alloy
A lead-free brass and brass alloy technology, applied in the field of brass alloys, can solve the problems of material embrittlement, brass tube perforation, poor machinability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0036] A copper gravity casting machine is used to cast castings, and copper alloys with different additives are tested to verify the improvement efficiency of the ratio of added elements. For each test process, fixed casting shapes, sand core particles and hardness, resin gas generation, resin and curing agent materials are used. First add the proportions of each component to the induction furnace. After the brass alloy reaches a certain molten state (hereinafter referred to as molten copper), the composition is checked by a spectrometer. When the composition of the test is met, the temperature of the molten metal is increased and maintained at 1030 Between 1050°C and 150°C to 170°C mold temperature, melting begins.
[0037] Use a metal gravity casting machine with a sand core and a gravity casting mold for casting. The feeding amount for each casting is 1 to 2 kg, the casting time is controlled within 3 to 5 seconds, and the cooling time in the fixed mold is controlled. Afte...
Embodiment 1
[0045] According to the composition ratio shown in Table 1, the lead-free brass alloy sample 1 of the present invention was obtained according to the above steps, and the quality inspection and analysis results and the total production pass rate are recorded in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0048] Repeat the steps of Example 1, adjust the alloy composition as shown in Table 1, increase the proportion of iron in the alloy to 0.613% by weight, and match the manganese composition of 0.158% by weight to obtain the lead-free brass alloy sample 2 of the present invention. The results of quality inspection and analysis and the total pass rate of production are recorded in Table 1.
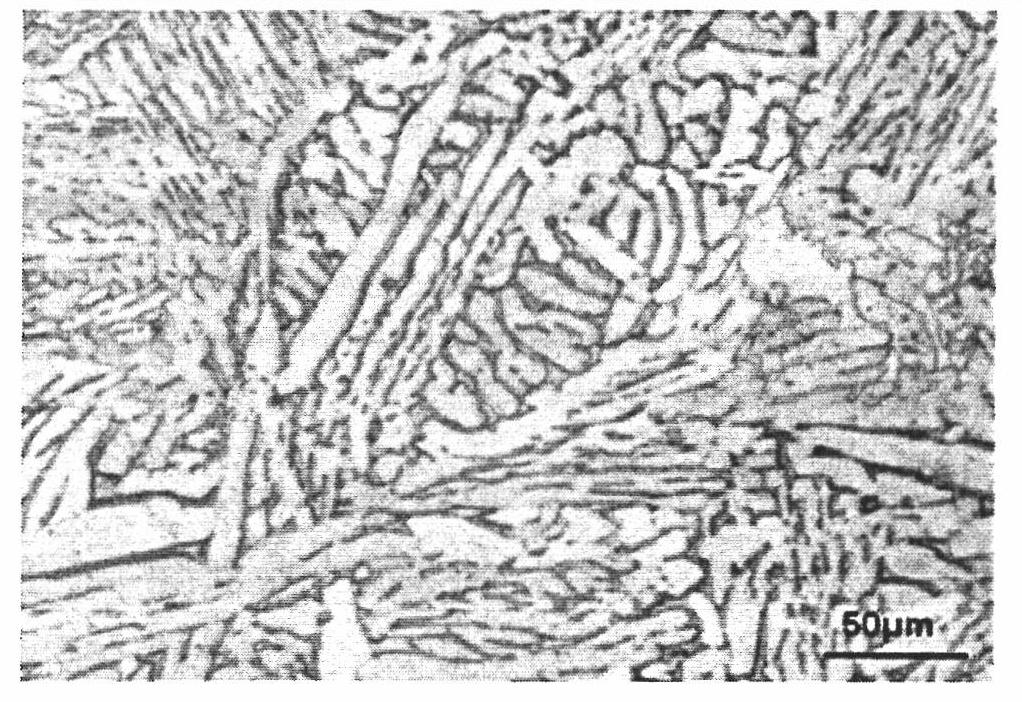
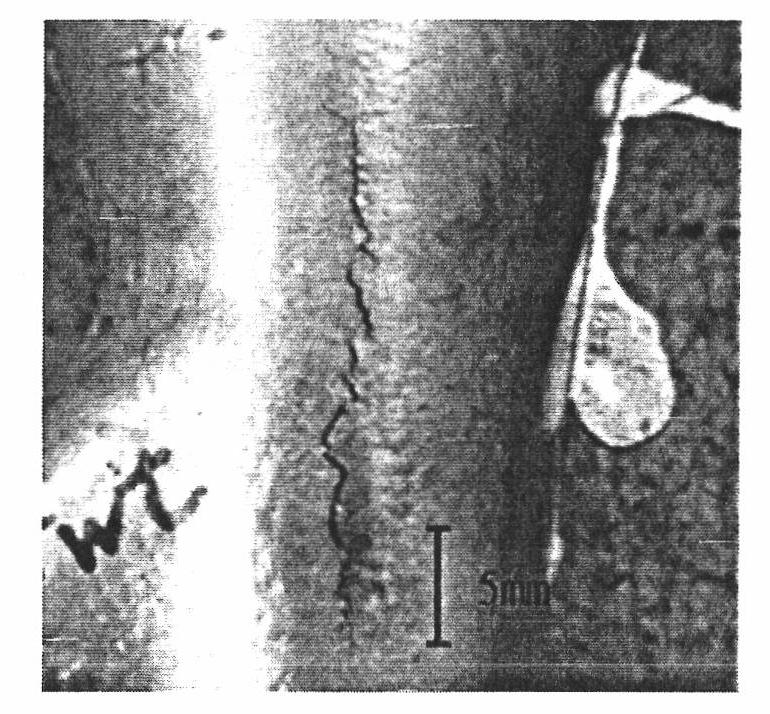
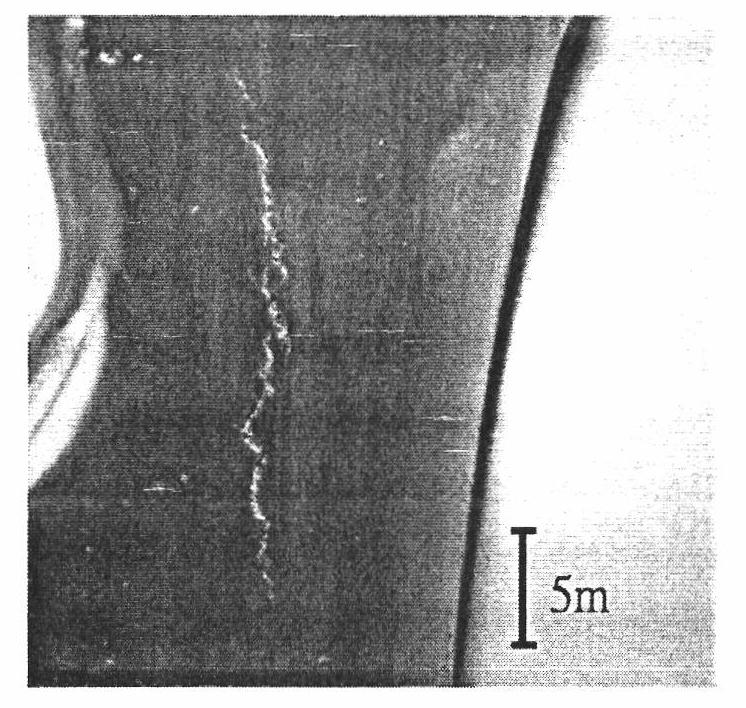
[0049] The metallographic structure distribution of lead-free brass alloy sample 2 of the present invention is as follows Figure 3A As shown, compared with sample 1, the crystal grains of sample 2 are thinner and shorter, the grain size of the crystal grains is about 35 to 40 microns, and it has better material toughness. Such as Figure 3B As shown, there is no obvious crack defect on the surface of the casting embryo. After the finished product is polished, almost no cracks can be observed on the surface, such as Figure 3C shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com