Method for recovery of palladium from waste palladium-carbon catalyst
A technology of palladium-carbon catalyst and waste catalyst, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of unsuitable industrial production, environmental pollution, and expensive extraction agent, and achieve the effects of less equipment investment, environmental friendliness, and high palladium recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
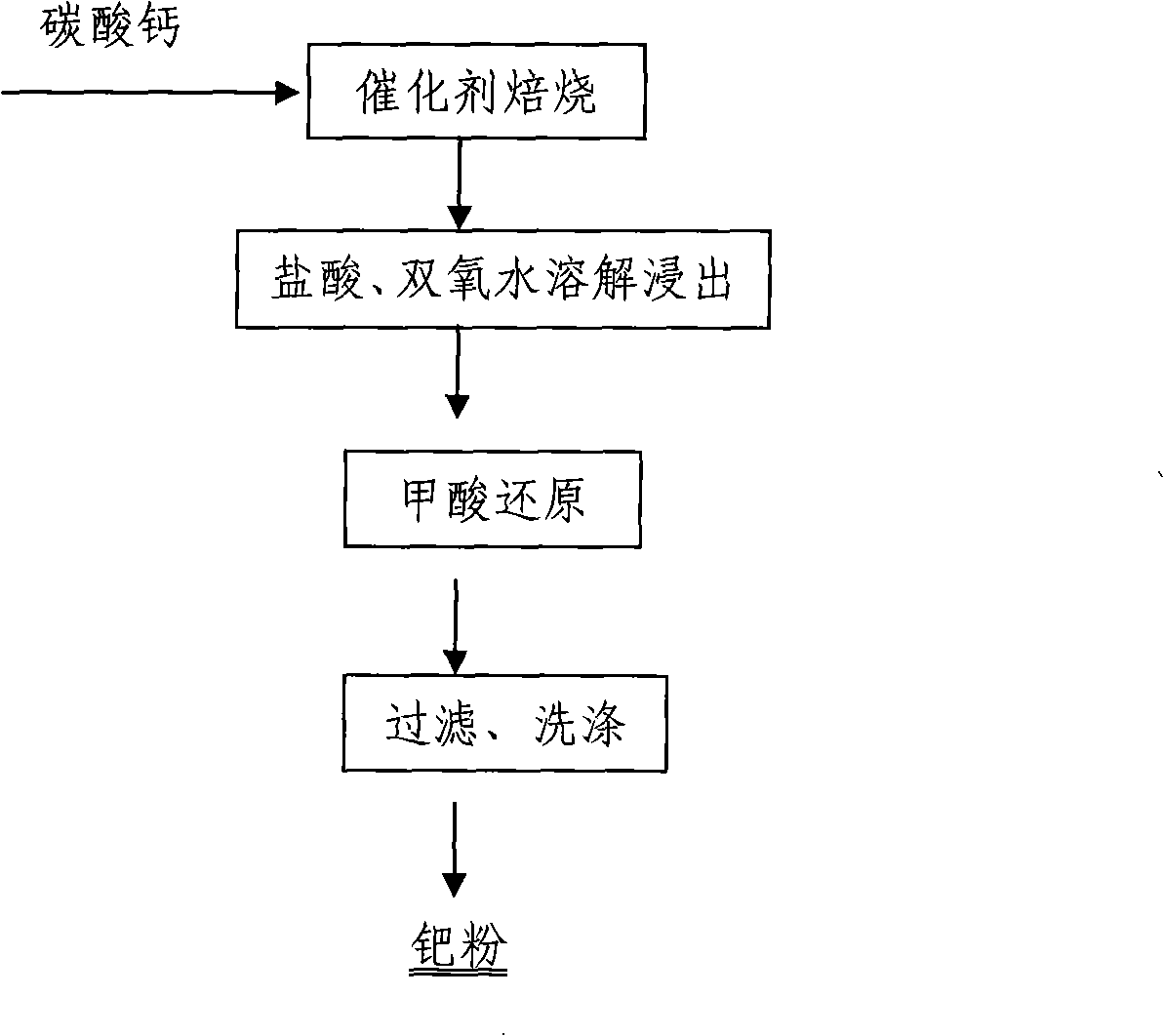
[0030] After the waste palladium carbon catalyst is mixed with the ashing agent calcium carbonate and slurried evenly, the ratio of the waste catalyst to calcium carbonate is 1-3:1; the liquid-solid ratio of the slurry is 20:1, and it is roasted at a temperature of 600°C After 2 hours, cook the roasted residue with hydrochloric acid at 100°C for 1 hour, then add hydrogen peroxide and cook at 90°C for 2 hours, then filter, then wash the filter residue, and combine the filtrate and washing liquid to adjust the pH value to 6.5- 7.5, at a temperature of 110°C, use formic acid reduction to obtain coarse palladium powder.
Embodiment 2
[0032] After the waste palladium carbon catalyst and the ashing agent calcium carbonate are mixed and slurried uniformly, the ratio of the spent catalyst to calcium carbonate is 1: 1; the liquid-solid ratio of the slurry is 6: 1, and roasting at 400° C. for 7 hours, Then the roasting residue was cooked with hydrochloric acid at 70°C for 4 hours, then added hydrogen peroxide and cooked at 75°C for 6 hours, then filtered, and then the filter residue was washed, and the filtrate and washing liquid were combined to adjust the pH value to 6.5-7.5. At a temperature of 80° C., the recovery rate of the crude palladium powder obtained by reduction with formic acid is 99.99%.
[0033] Example 2
[0034] After the spent palladium carbon catalyst and the ashing agent calcium carbonate are mixed and slurried uniformly, the ratio of the spent catalyst to calcium carbonate is 3: 1; the liquid-solid ratio of the slurry is 20: 1, and roasted at 500° C. for 2 hours, Then cook the roasted resid...
Embodiment 3
[0036]After the spent palladium charcoal catalyst is mixed and slurried evenly with the ashing agent calcium carbonate, the ratio of the spent catalyst to calcium carbonate is 2: 1; the liquid-solid ratio of the slurry is 10: 1, and roasted at 450° C. for 6 hours, Then cook the roasted residue with hydrochloric acid at 900°C for 3 hours, then add hydrogen peroxide and cook at 85°C for 5 hours, then filter, then wash the filter residue, combine the filtrate and washing liquid to adjust the pH value to 7.5, and then add it at 90°C At low temperature, the recovery rate of crude palladium powder obtained by reduction with formic acid is 99.99%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com