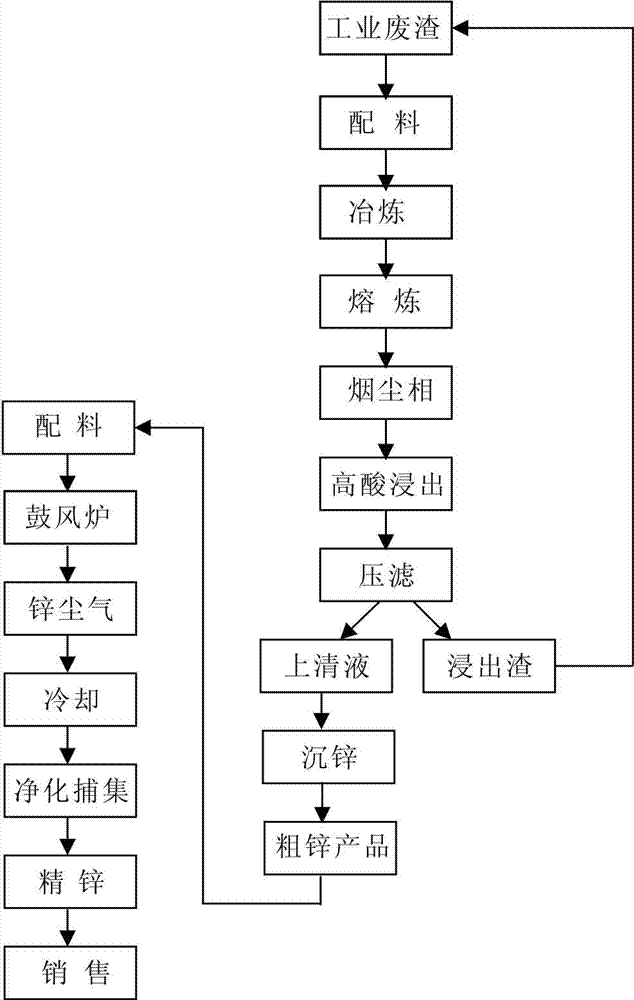
Method for extracting zinc from non-ferrous metal waste residue
A non-ferrous metal and waste slag technology, applied in the field of zinc extraction, can solve the problems of high impurity content and low recovery rate, and achieve the effect of good taste, high recovery rate and simple principle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] a. Take 300kg of non-ferrous metal waste slag (main content: 20-30% lead, 6-8% zinc) from an electrolytic zinc enterprise in Hanyuan County, mix it with coal powder at a mass ratio of 1:0.05, and add it to the rotary kiln. Smelt at 500°C for 5 hours, and then collect the soot phase secondary zinc oxide through a bag filter; the main chemical composition of secondary zinc oxide is: zinc 30%, lead 10%;
[0018] b. Under normal temperature and pressure, mix and stir secondary zinc oxide and water according to the solid-to-liquid mass ratio of 1:3.5, react for 10 minutes, add concentrated sulfuric acid with a mass fraction of 98%, carry out acid leaching, then wash and press filter , to obtain leaching slag and leaching solution; the leaching slag is returned to the precious metal smelting system; wherein, the process parameters of the acid leaching step are: initial acid concentration 170g / L, final acid concentration 5g / L, leaching temperature is 70°C, and reaction time is ...
Embodiment 2
[0022] a. Take 100kg of non-ferrous metal waste slag (main content: 20-30% lead, 6-8% zinc) from an electrolytic zinc enterprise in Shimian County, mix it with coal powder at a mass ratio of 1:0.1, and add it to the rotary kiln. Smelt at 600°C for 6 hours, then collect the soot phase secondary zinc oxide through a bag filter; the main chemical composition of secondary zinc oxide is: zinc 40%, lead 20%;
[0023] b. Under normal temperature and pressure, mix and stir secondary zinc oxide and water according to the solid-to-liquid mass ratio of 1:3.5, react for 10 minutes, add concentrated sulfuric acid with a mass fraction of 98%, carry out acid leaching, then wash and press filter , to obtain leaching slag and leaching solution; the leaching slag is returned to the precious metal smelting system; wherein, the process parameters of the acid leaching step are: initial acid concentration 180g / L, final acid concentration 8g / L, leaching temperature 80°C, reaction time 3.5 Hour;
[...
Embodiment 3
[0027] a. Take 200kg of non-ferrous metal waste slag (main content: lead 20-30%, zinc 6-8%) from an electrolytic zinc enterprise in Hanyuan County, mix it with coal powder at a mass ratio of 1:0.15, and add it to the rotary kiln. Smelt at 550°C for 5.5 hours, and then collect the soot phase secondary zinc oxide through a bag filter; among them, the main chemical composition of secondary zinc oxide is: zinc 35%, lead 30%;
[0028] b. Under normal temperature and pressure, mix and stir secondary zinc oxide and water according to the solid-to-liquid mass ratio of 1:3.5, react for 10 minutes, add concentrated sulfuric acid with a mass fraction of 98%, carry out acid leaching, then wash and press filter , to obtain leaching slag and leaching solution; the leaching slag is returned to the precious metal smelting system; wherein, the process parameters of the acid leaching step are: initial acid concentration 175g / L, final acid concentration 10g / L, leaching temperature is 75°C, and th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com