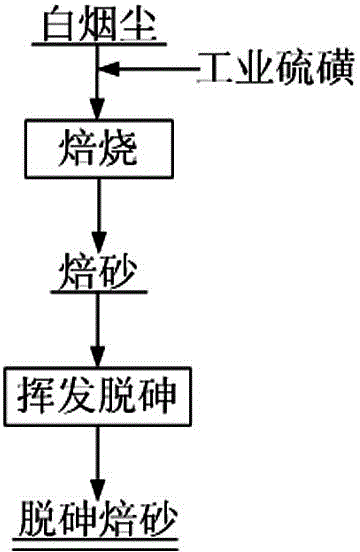
Method for removing arsenic from white smoke
A technology for white smoke and arsenic removal, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problem of low direct yield, etc., and achieve the effects of short process flow, high calcining rate, and complete removal of arsenic.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0011] Example 1: The raw material composition of white soot is: arsenic: 15.32%, zinc: 12.52%, lead: 17.46%, bismuth: 4.36%, indium: 0.125%, copper: 3.12%, silver: 137.3g / t.
[0012] Mix white soot: industrial sulfur at a ratio of 1:0.3 (weight ratio), that is, add 250 grams of white soot (75 grams of industrial sulfur) into the muffle furnace, react at 350 ° C for 2 hours, and obtain the calcined sand. Volatilize and remove arsenic at 610°C±10°C for 2 hours.
[0013] The obtained calcine contains: arsenic: 2.0%, zinc: 17.9%, lead: 23.41%, bismuth: 6.5%, indium: 0.174%, copper: 4.87%, silver: 212g / t.
[0014] The removal rate of arsenic in this test is 91.39%, and the rates of valuable metals into the calcine are: lead: 90%, zinc: 91.98%, bismuth: 95.92%, indium: 95.95%, copper: 95.49%, silver: 99.56% %.
Embodiment 2
[0015] Example 2: The raw material composition of white soot is: arsenic: 13.5%, zinc: 12.15%, lead: 19.38%, bismuth: 4.12%, indium: 0.125%, copper: 3.68%, silver: 138.4g / t.
[0016] Mix white soot: industrial sulfur at a ratio of 1:0.4 (weight ratio), add 250 grams of white soot (100 grams of industrial sulfur) into the muffle furnace, and react at 335°C for 3 hours. Volatilize and remove arsenic at ±10°C for 2.5 hours.
[0017] The obtained calcine contains: arsenic: 0.67%, zinc: 18.39%, lead: 24.84%, bismuth: 6.66%, indium: 0.181%, copper: 4.82%, silver: 229.4g / t.
[0018] The removal rate of arsenic in this test is 97.39%, and the rates of valuable metals entering the calcine are: lead: 85%, zinc: 95.0%, bismuth: 91.07%, indium: 88.71%, copper: 92.09%, silver: 95.70% %.
Embodiment 3
[0019] Example 3: The raw material composition of white soot is: arsenic: 16.48%, zinc: 12.85%, lead: 16.42%, bismuth: 4.17%, indium: 0.132%, copper: 3.24%, silver: 136.8g / t.
[0020] Mix white soot: industrial sulfur at 1:0.5 (weight ratio), that is, add 250 grams of white soot (125 grams of industrial sulfur) into the muffle furnace, and react at 365 ° C for 1.5 hours to obtain calcined sand. Volatilize and remove arsenic at 630°C±10°C for 2 hours.
[0021] The obtained calcine contains: arsenic: 1.2%, zinc: 18.34%, lead: 24.51%, bismuth: 6.41%, indium: 0.176%, copper: 4.74%, silver: 208g / t.
[0022] The removal rate of arsenic in this test is 96.42%, and the rates of valuable metals entering the calcine are: lead: 87%, zinc: 92.43%, bismuth: 95.64%, indium: 96.17%, copper: 95.22%, silver: 99.38 %.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com