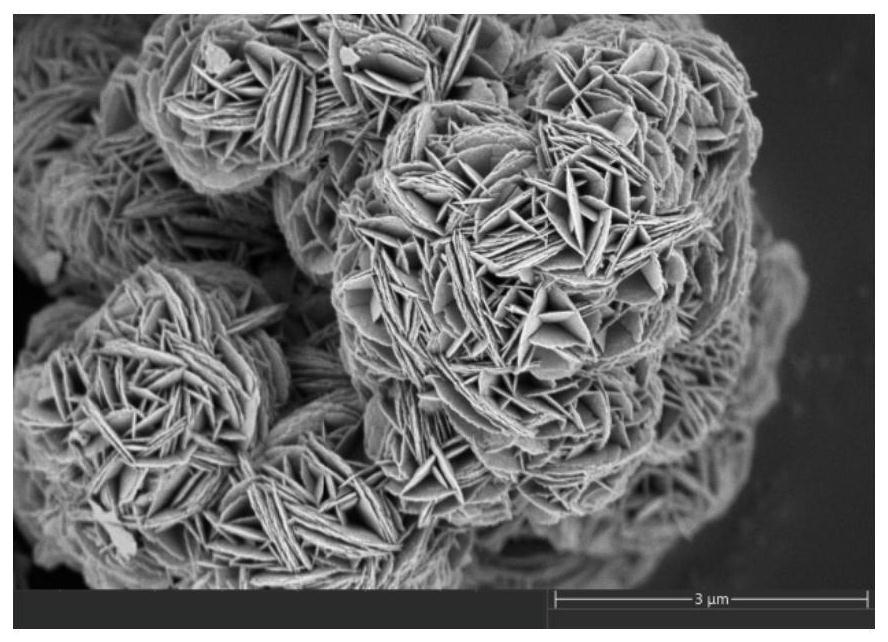
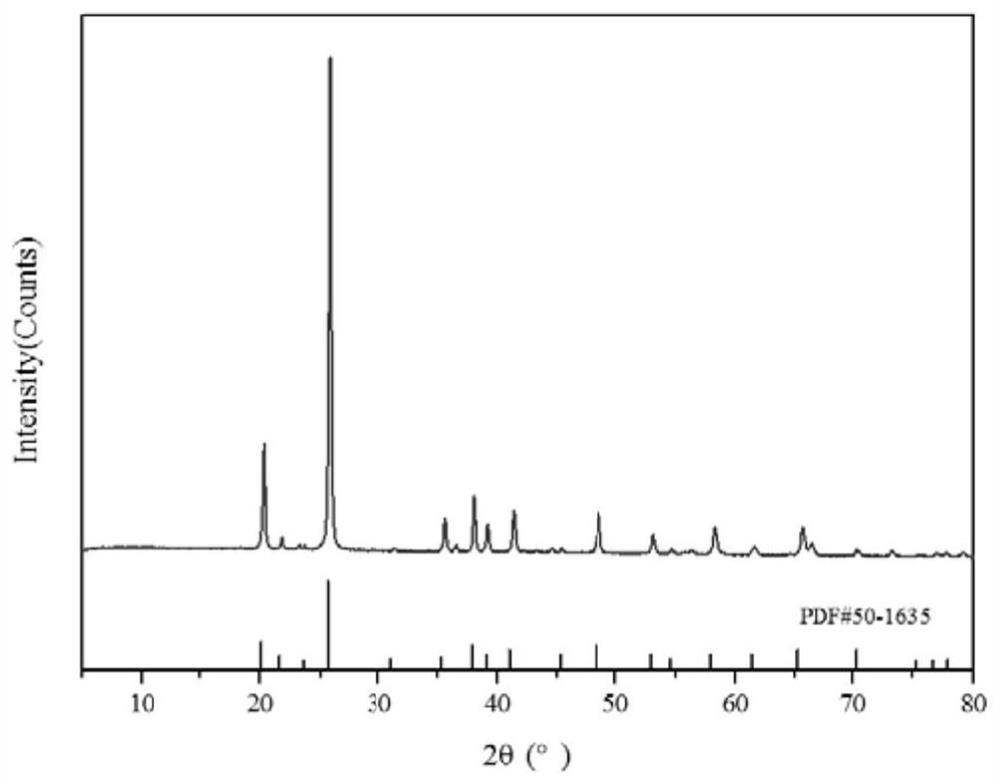
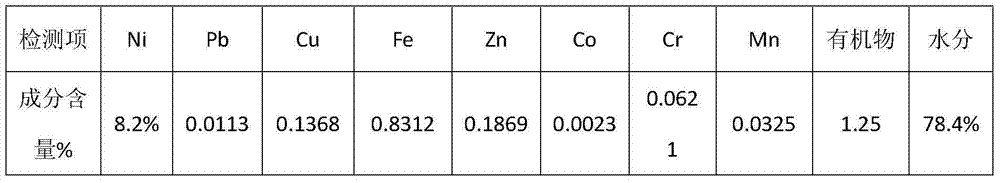
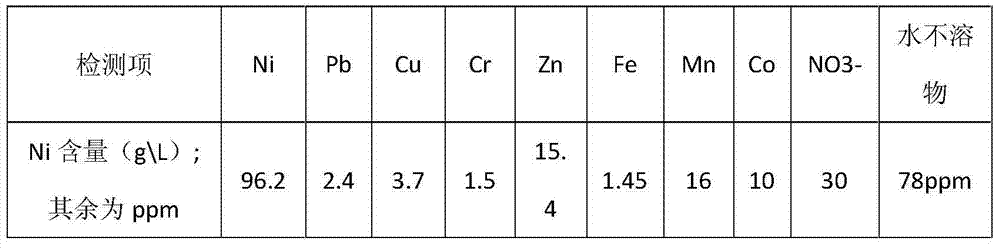
Patents
Literature
360results about "Nickel sulfates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
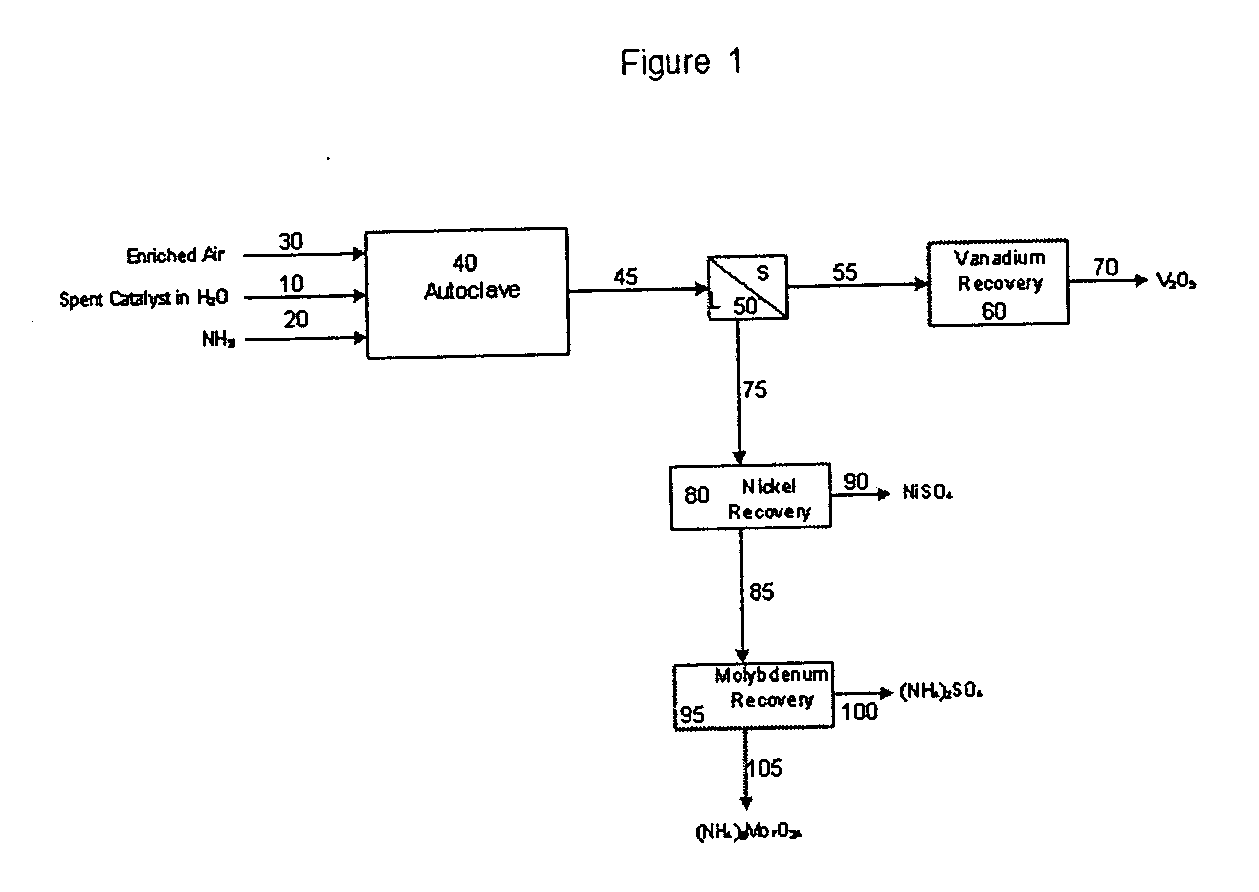
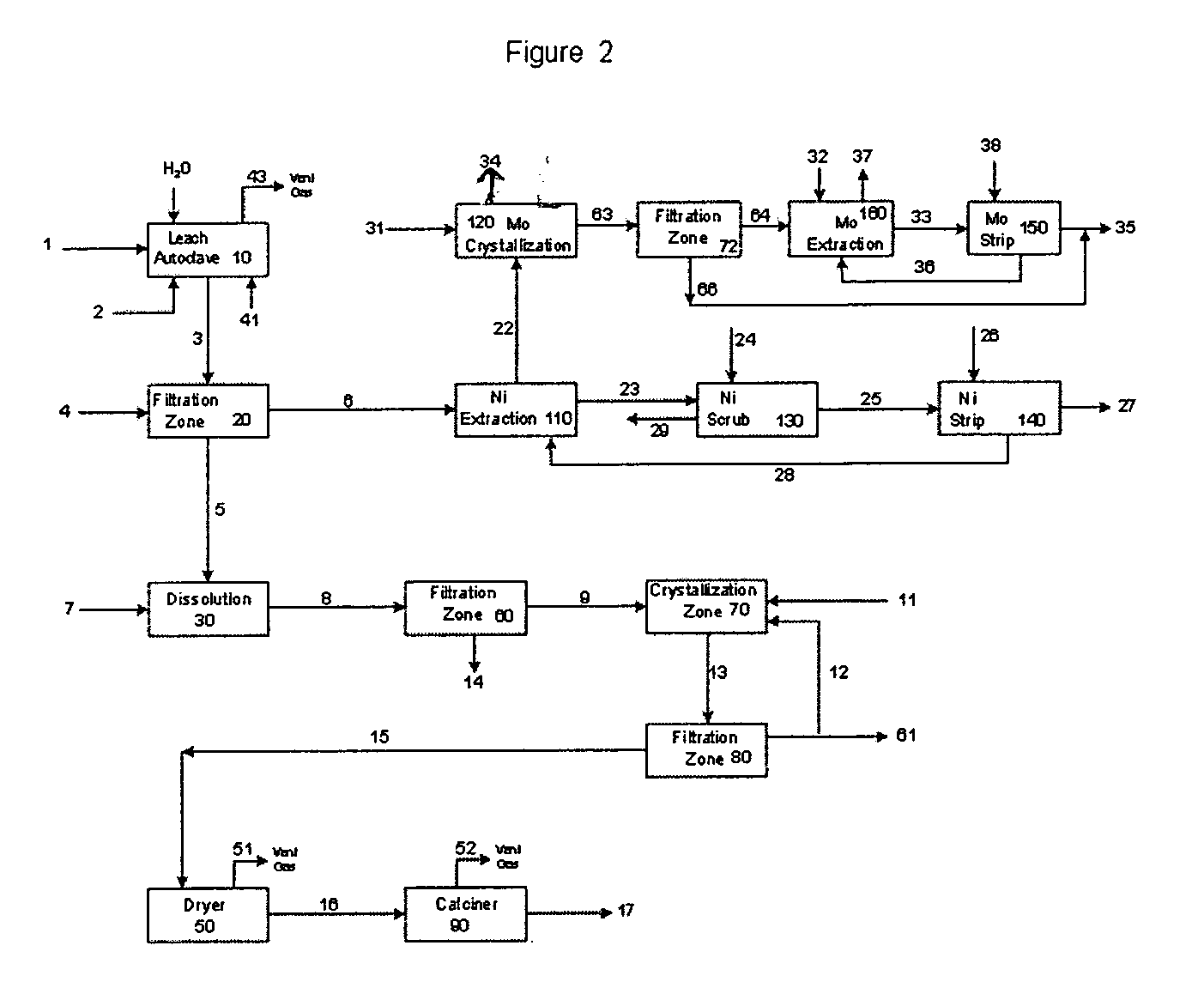
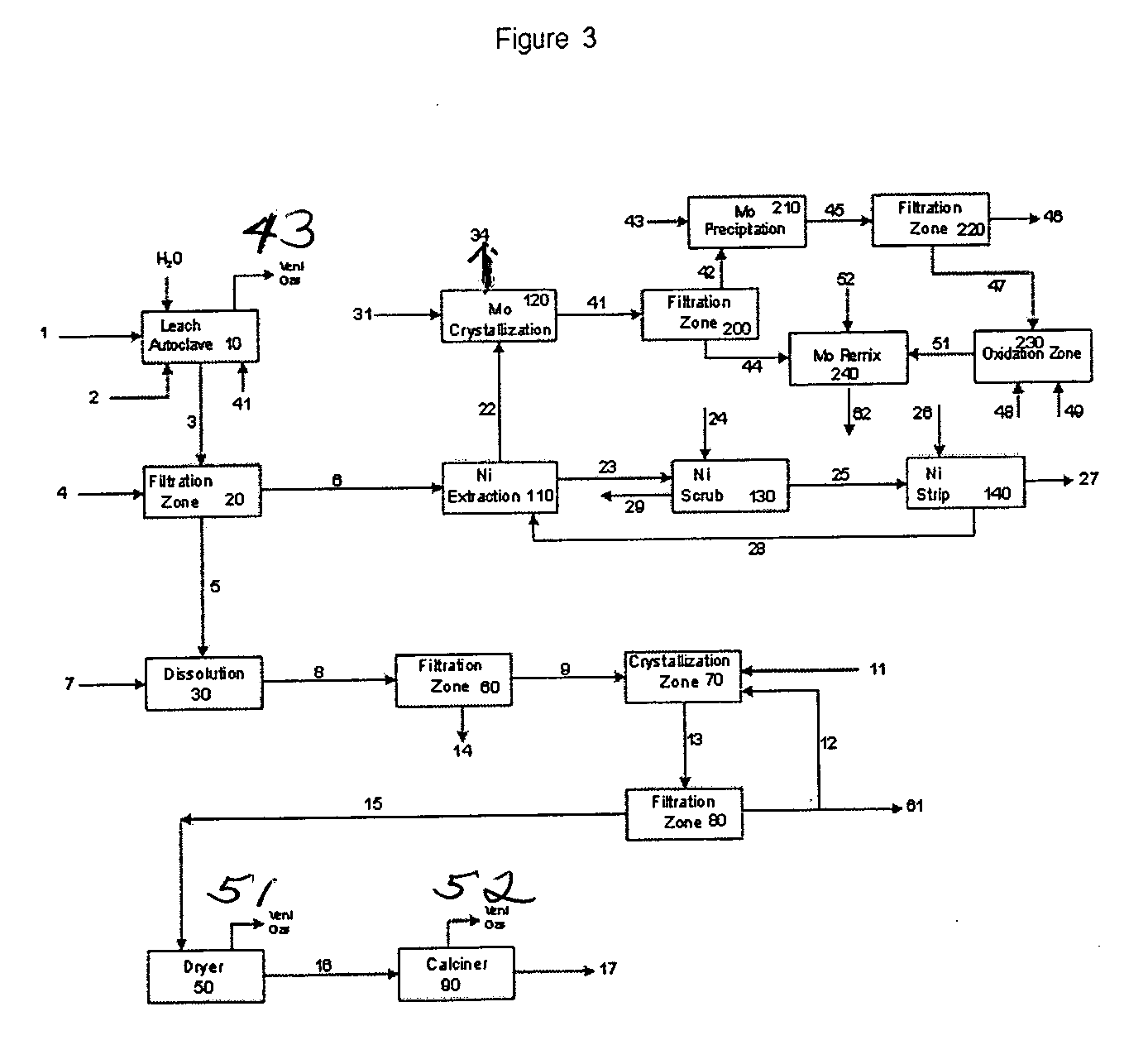
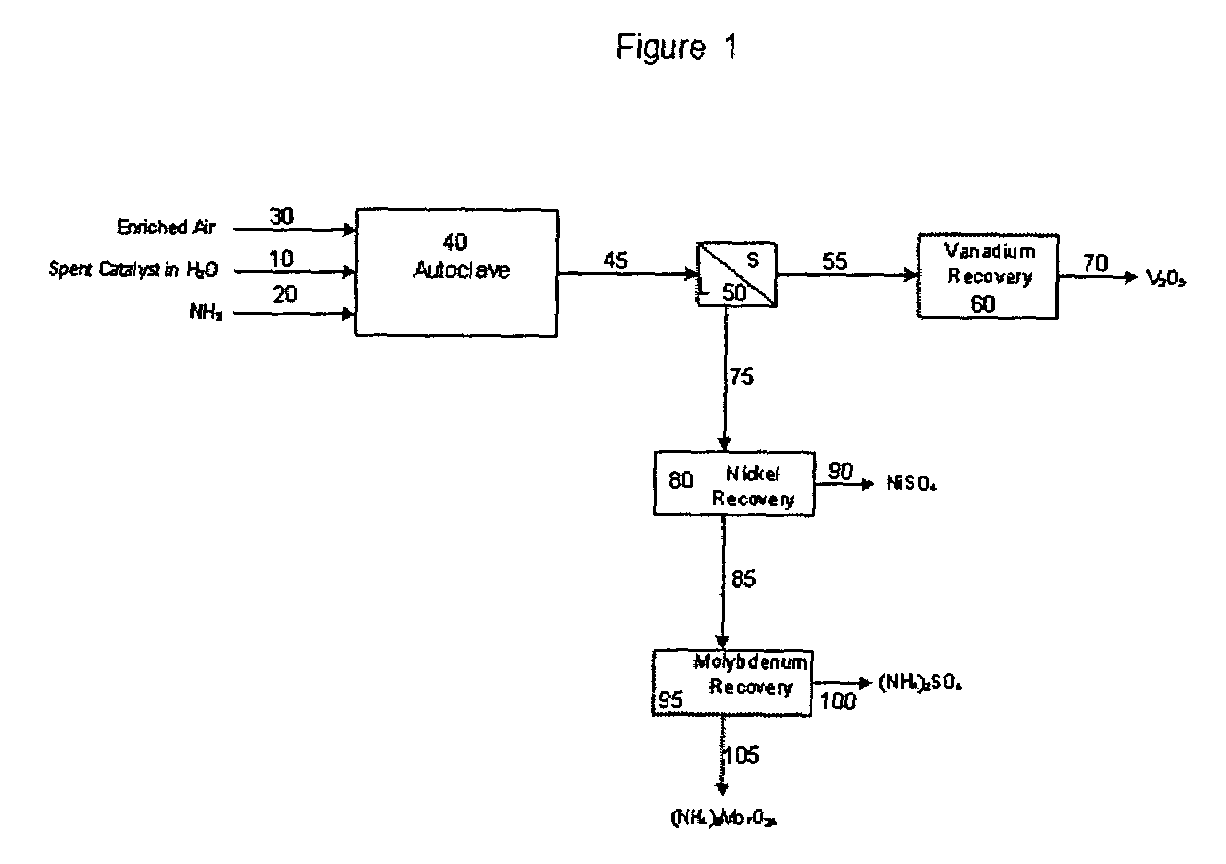
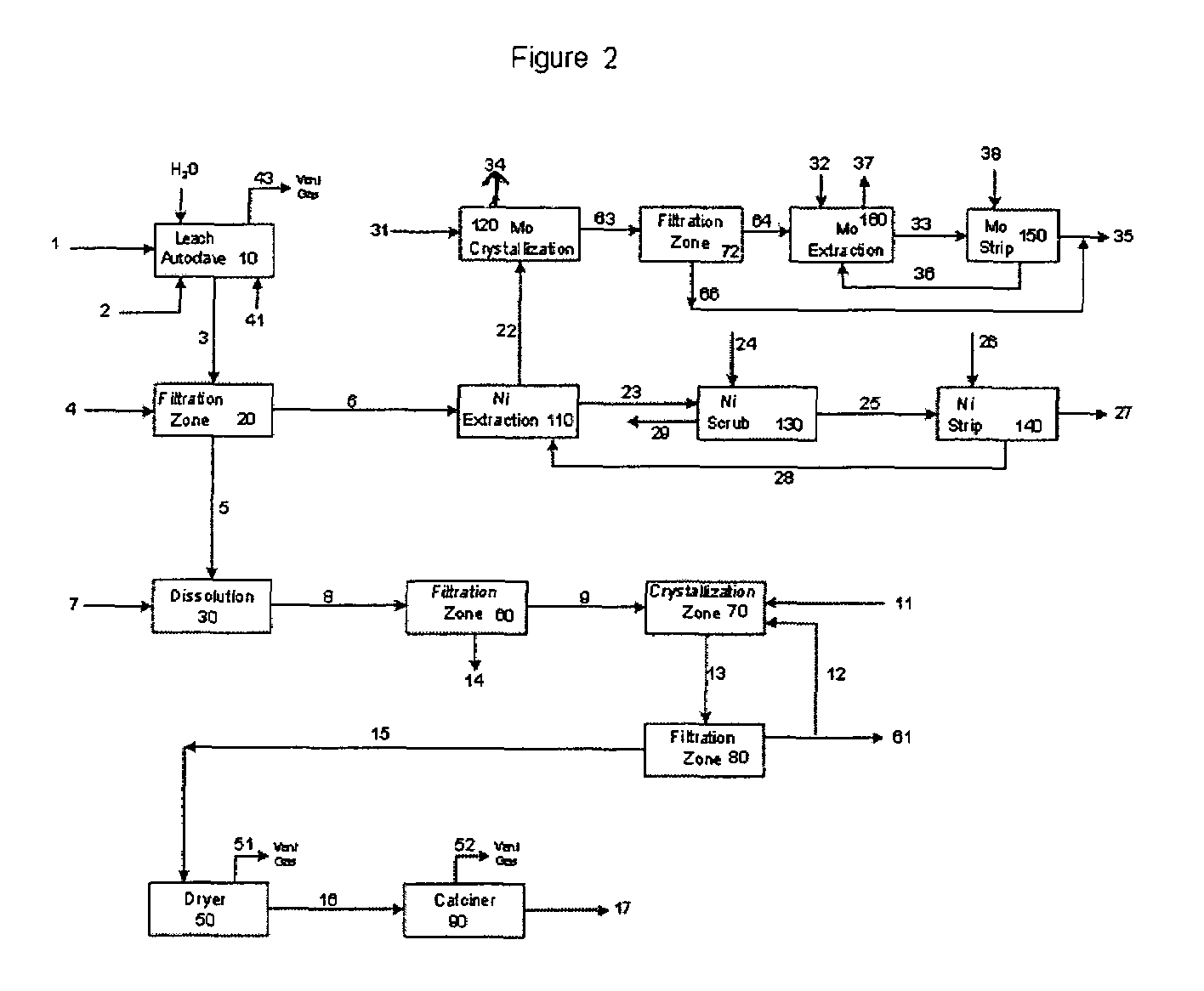
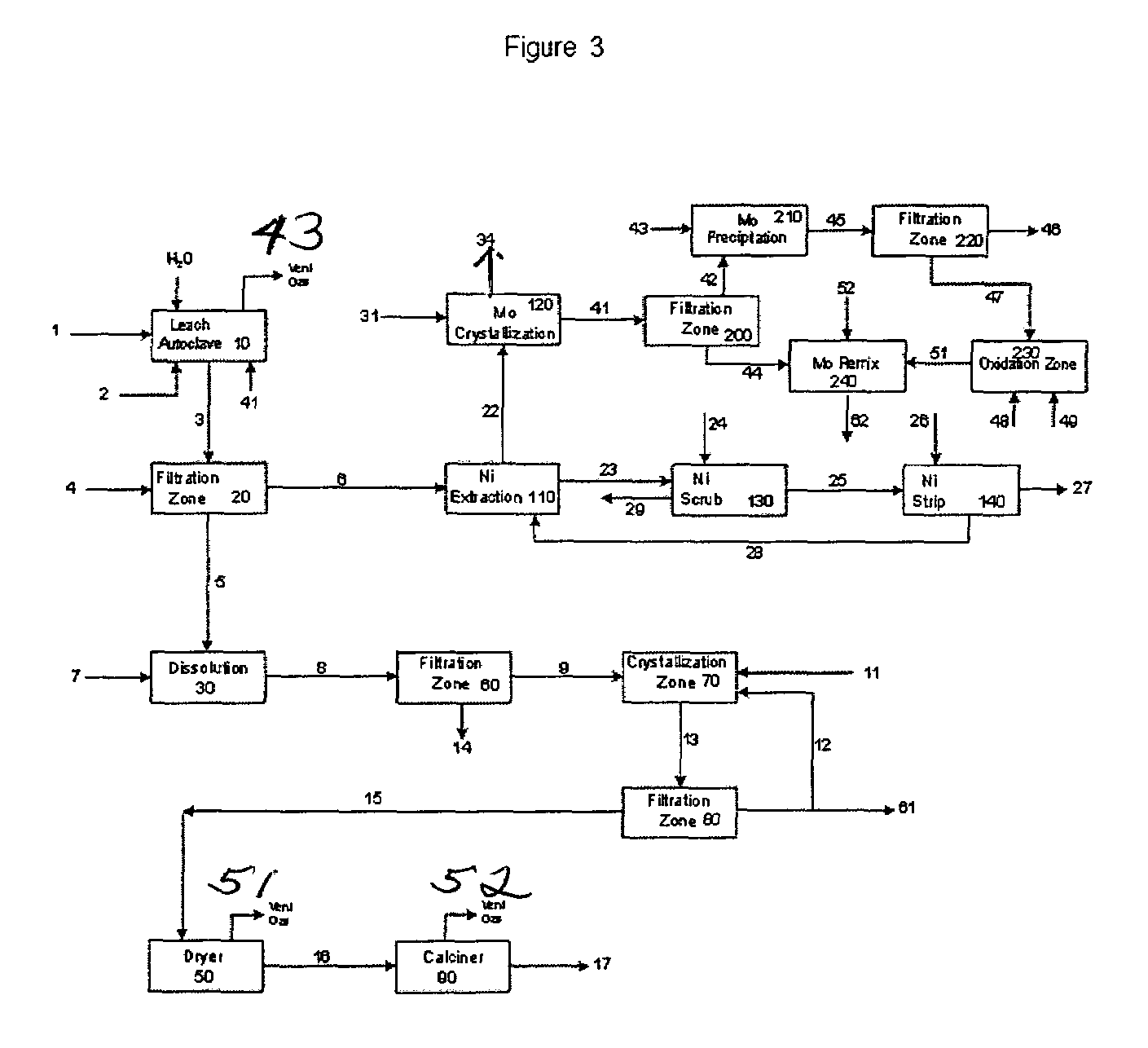
Process for metals recovery from spent catalyst
The process of this invention is directed to the removal of metals from an unsupported spent catalyst. The catalyst is subjected to leaching reactions. Vanadium is removed as a precipitate, while a solution comprising molybdenum and nickel is subjected to further extraction steps for the removal of these metals. Molybdenum may alternately be removed through precipitation.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
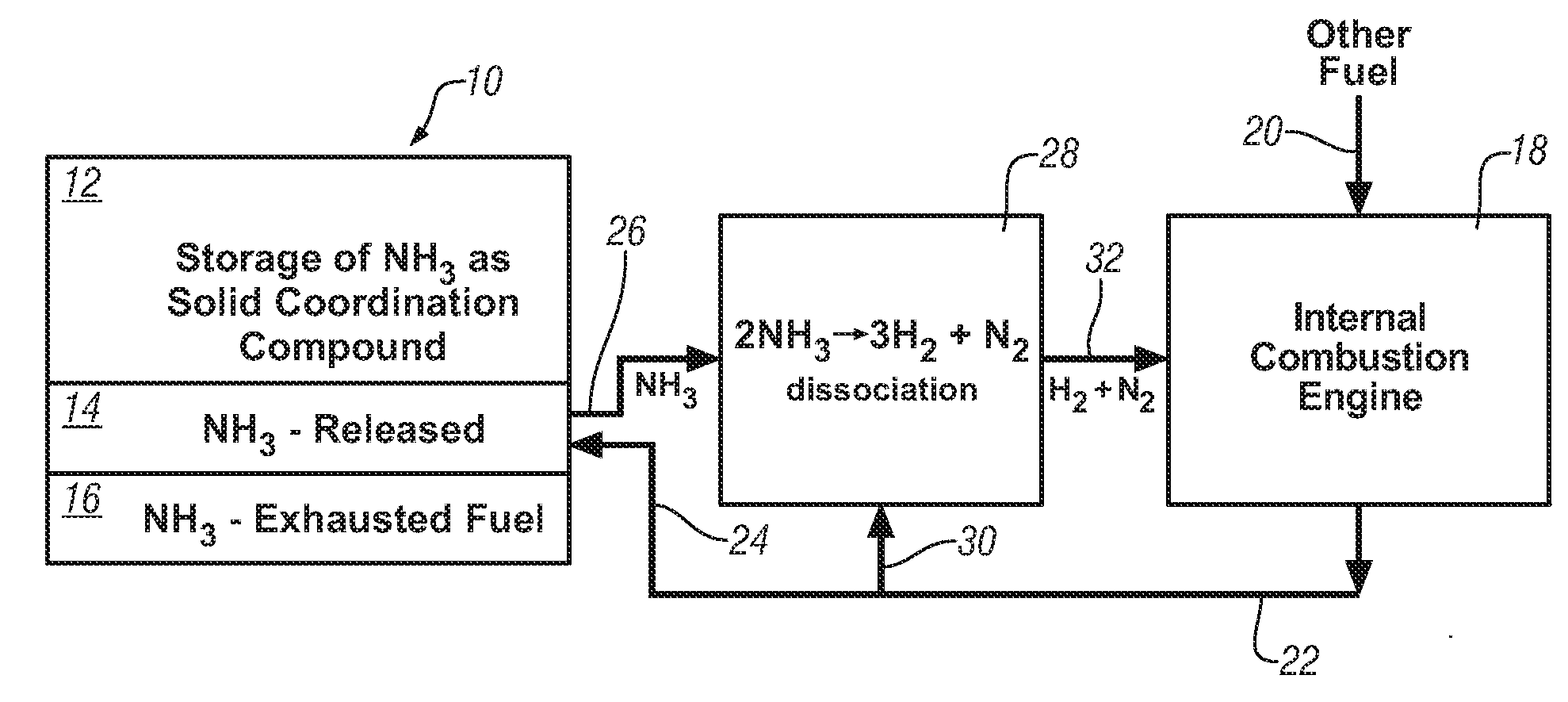
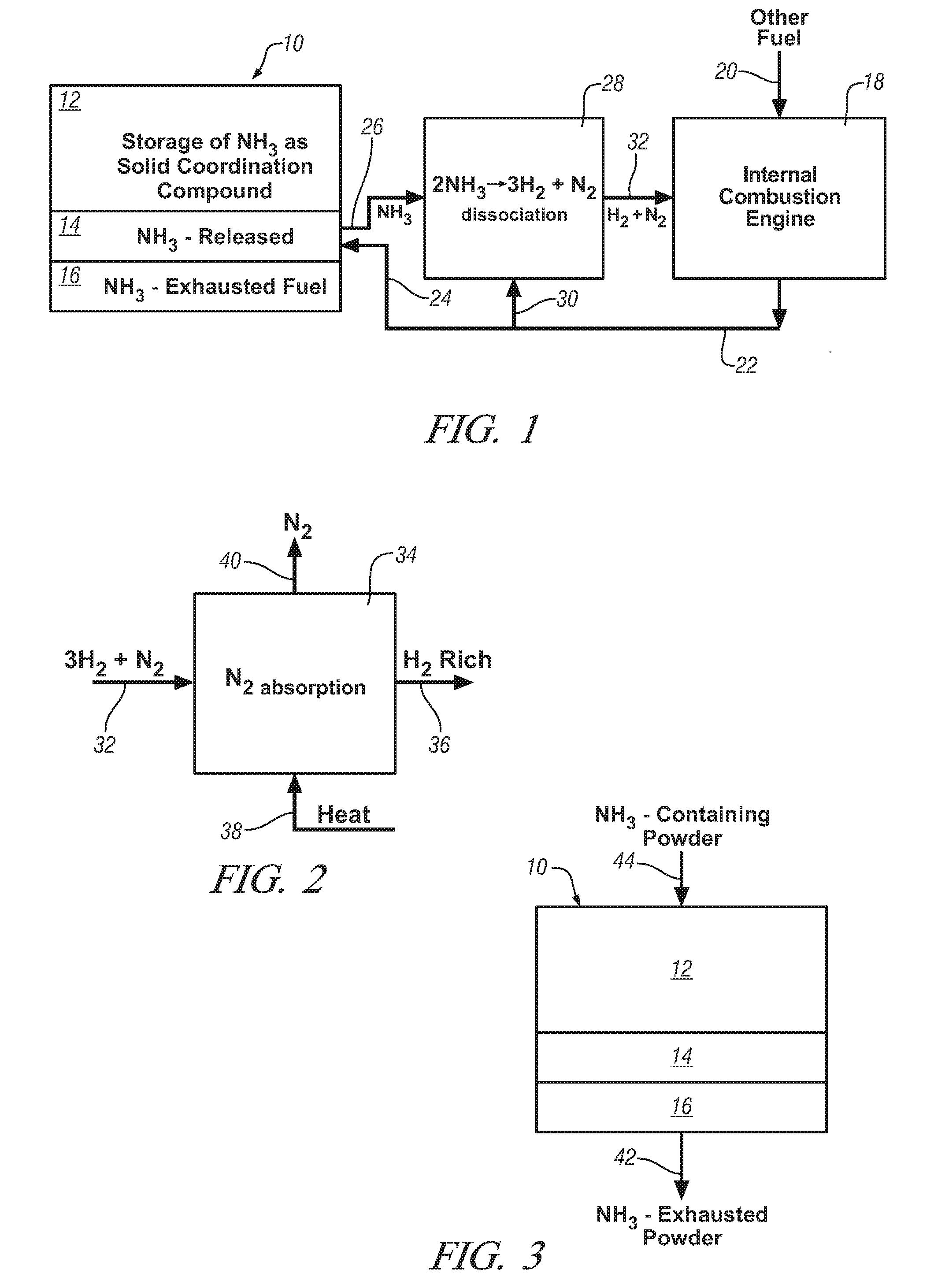
Ammonia storage for on-vehicle engine
InactiveUS20080241033A1Efficient and reversible processCobalt ammonia complexesCyanogen compoundsAmmonia storageExternal combustion engine
Ammonia is used as precursor source of hydrogen fuel in an on-vehicle internal combustion engine. Ammonia is stored as, for example, a ligand in an on-vehicle transition metal composition. Upon demand for hydrogen by the vehicle's engine control system, ammonia is expelled as a gas from some of the composition and the ammonia gas is dissociated into a mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen and delivered as a fuel-containing mixture to the engine. In a preferred embodiment, the hydrogen is used as a supplement to gasoline as a fuel for engine operation.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
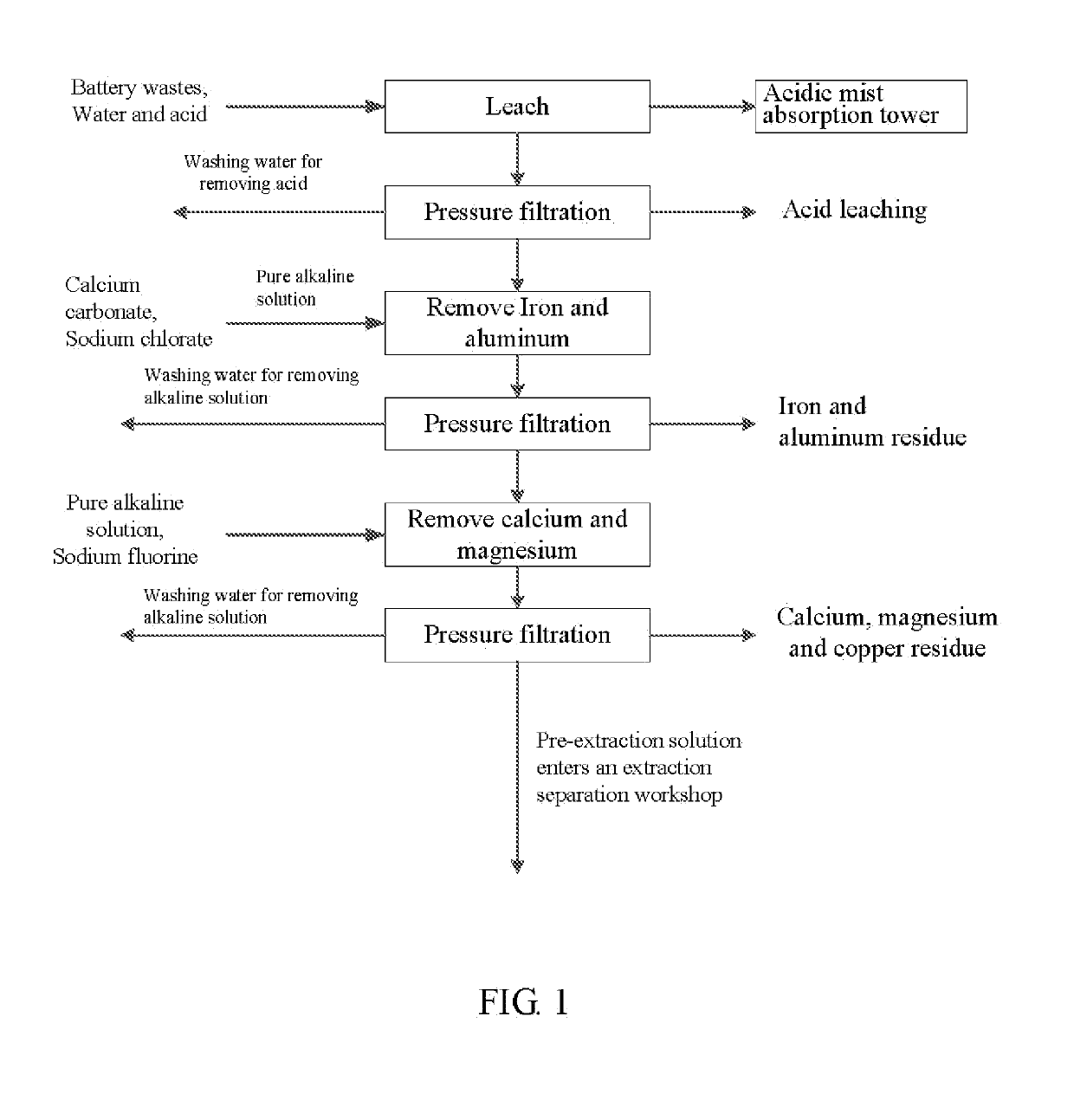
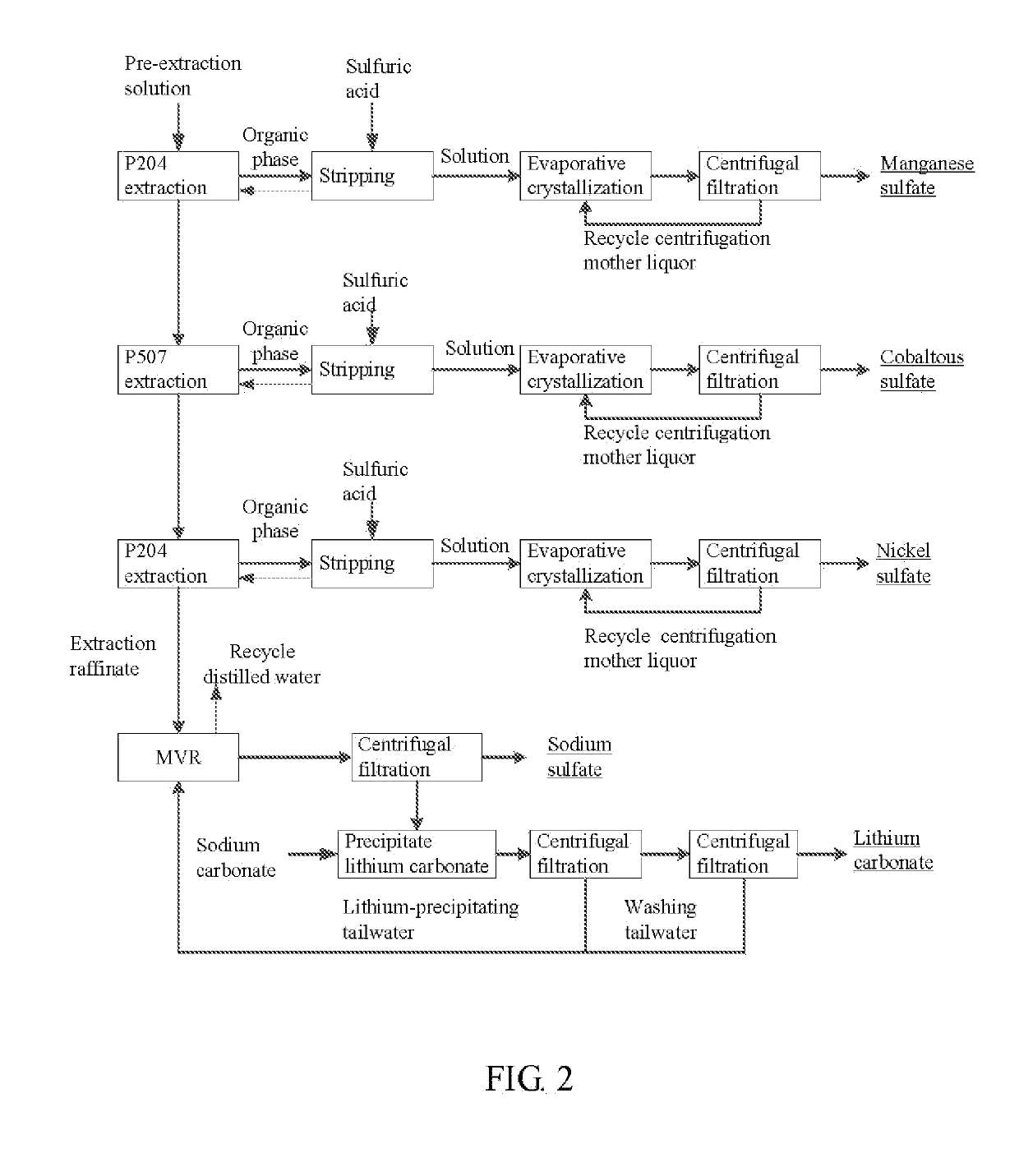
Method for preparing nickel/manganese/lithium/cobalt sulfate and tricobalt tetraoxide from battery wastes
ActiveUS20190152797A1Reduce productionHigh puritySolvent extractionCobalt sulfatesManganeseCobalt Sulfate
A method for preparing nickel / manganese / lithium / cobalt sulfate and tricobalt tetraoxide from battery wastes adopts the following process: dissolving battery wastes with acid, removing iron and aluminum, removing calcium, magnesium and copper, carrying extraction separation, and carrying out evaporative crystallization to prepare nickel sulfate, manganese sulfate, lithium sulfate, cobalt sulfate or / and tricobalt tetraoxide. By using the method, multiple metal elements, such as nickel, manganese, lithium and cobalt, can be simultaneously recovered from the battery wastes, the recovered products are high in purity and can reach battery grade, battery-grade tricobalt tetraoxide can also be directly produced. The method is simple in process, low in, energy consumption and free in exhaust gas pollution, and can realize zero release of wastewater.
Owner:HUNAN JINYUAN NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Iron-nickel alloy resource recycling method and application
ActiveCN113044821ALow impurity contentAchieving RecoveryProcess efficiency improvementPhosphorus compoundsPregnant leach solutionLithium iron phosphate
The invention belongs to the field of iron-nickel alloy hydrometallurgy, and discloses an iron-nickel alloy resource recycling method and application. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out ball milling, crushing and sieving on iron-nickel alloy to obtain iron-nickel alloy powder; (2) leaching the iron-nickel alloy powder with an acid solution, heating and stirring, and filtering to obtain a leaching solution and leaching residues; (3) adding a phosphorus source into the leaching solution, mixing, stirring, heating, and filtering to obtain iron phosphate and a post-precipitation solution; and (4) adding a neutralizer into the post-precipitation solution, heating and stirring, and filtering to obtain a nickel-containing solution. According to the method, after a nickel-iron alloy is dissolved by using an acid solution, iron phosphate is prepared under the action of a phosphorus source or a phosphorus source added oxidant and a precipitation auxiliary agent, the iron phosphate can be further used as a precursor of lithium iron phosphate to prepare a lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material, and the nickel-containing solution with relatively low impurity content can be obtained after the solution after precipitation is subjected to impurity removal.
Owner:HUNAN BRUNP RECYCLING TECH +2
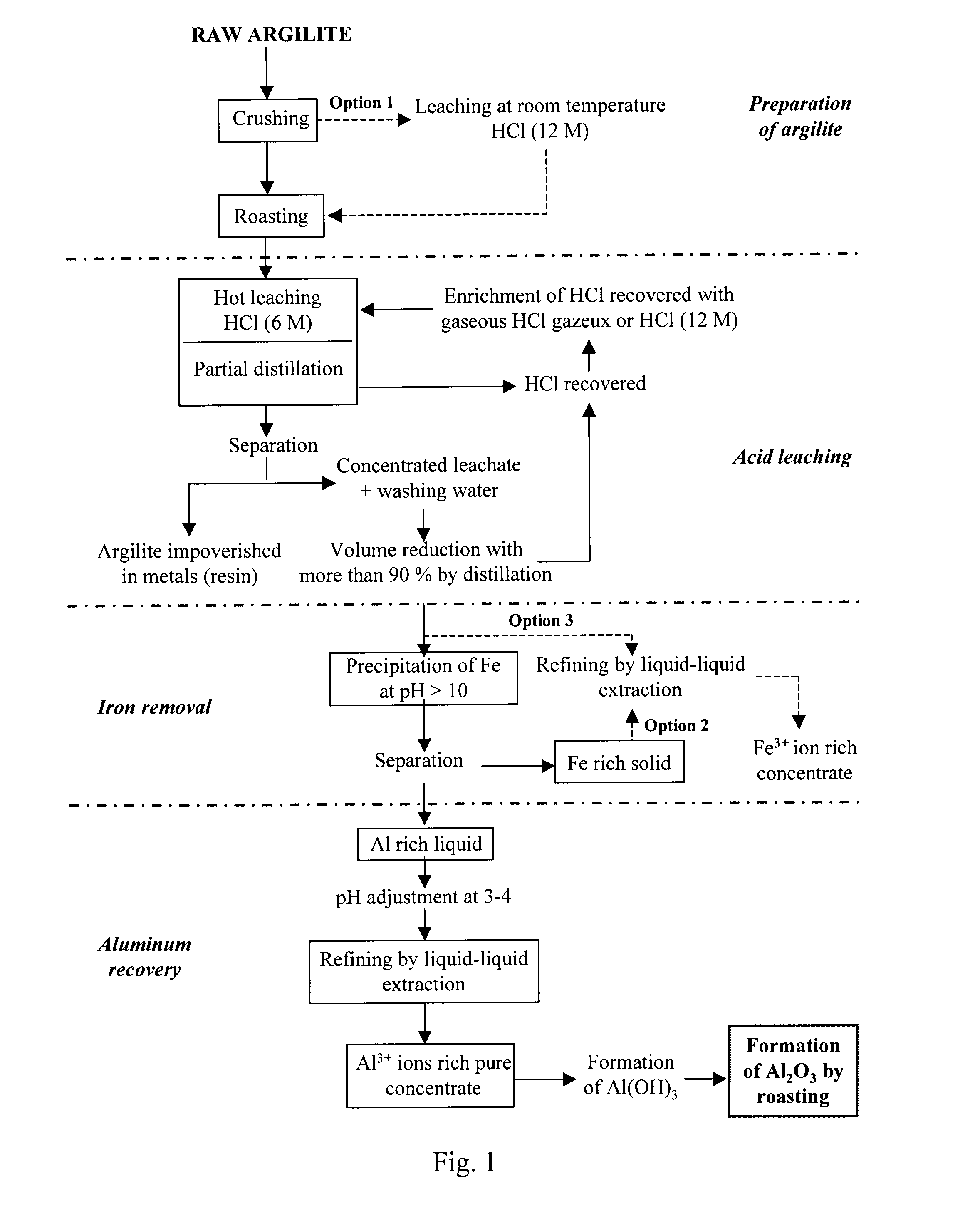
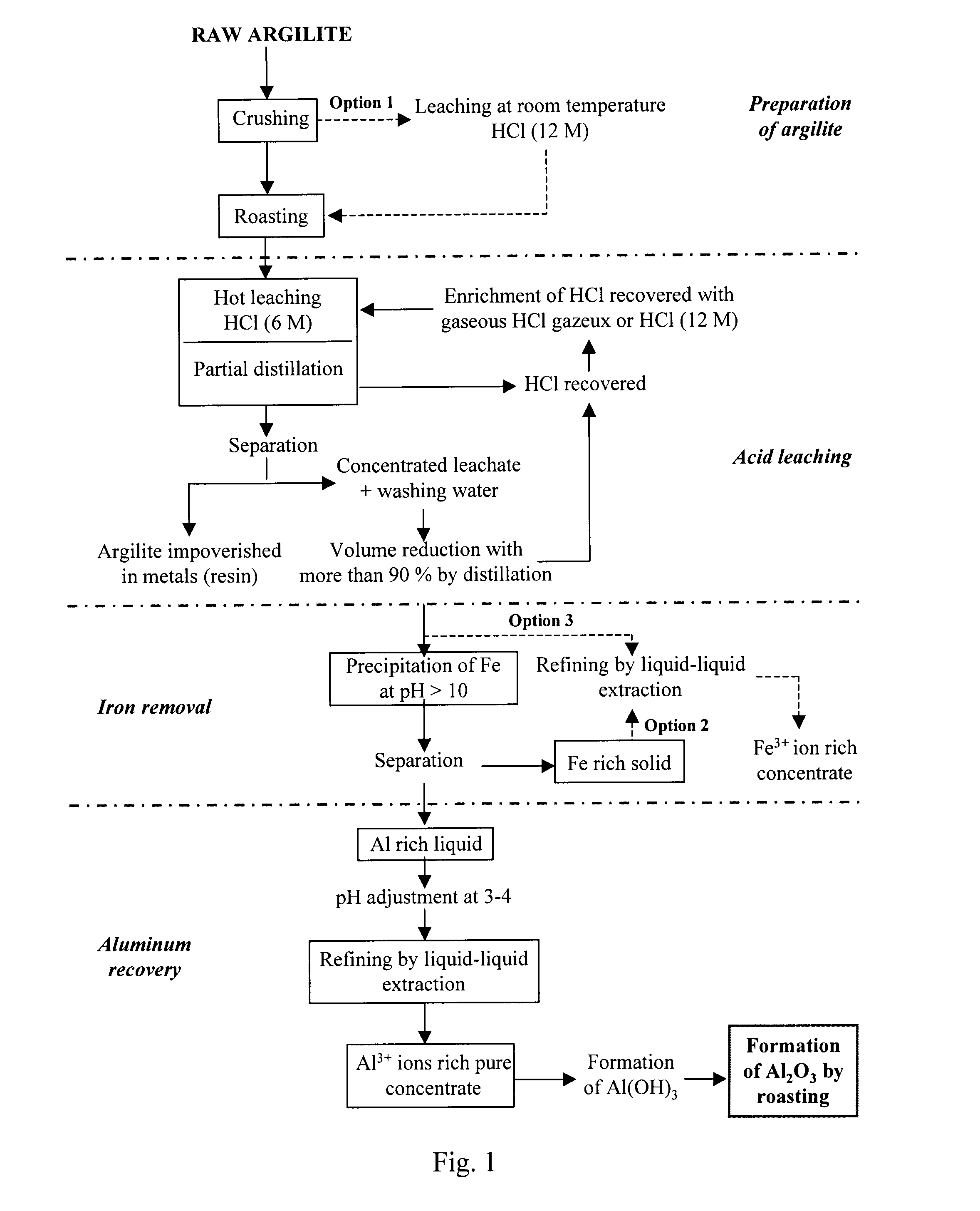
Processes for extracting aluminum and iron from aluminous ores
Owner:ORBITE ALUMINAE INC
Processes for extracting aluminum and iron from aluminous ores
Owner:ORBITE ALUMINAE INC
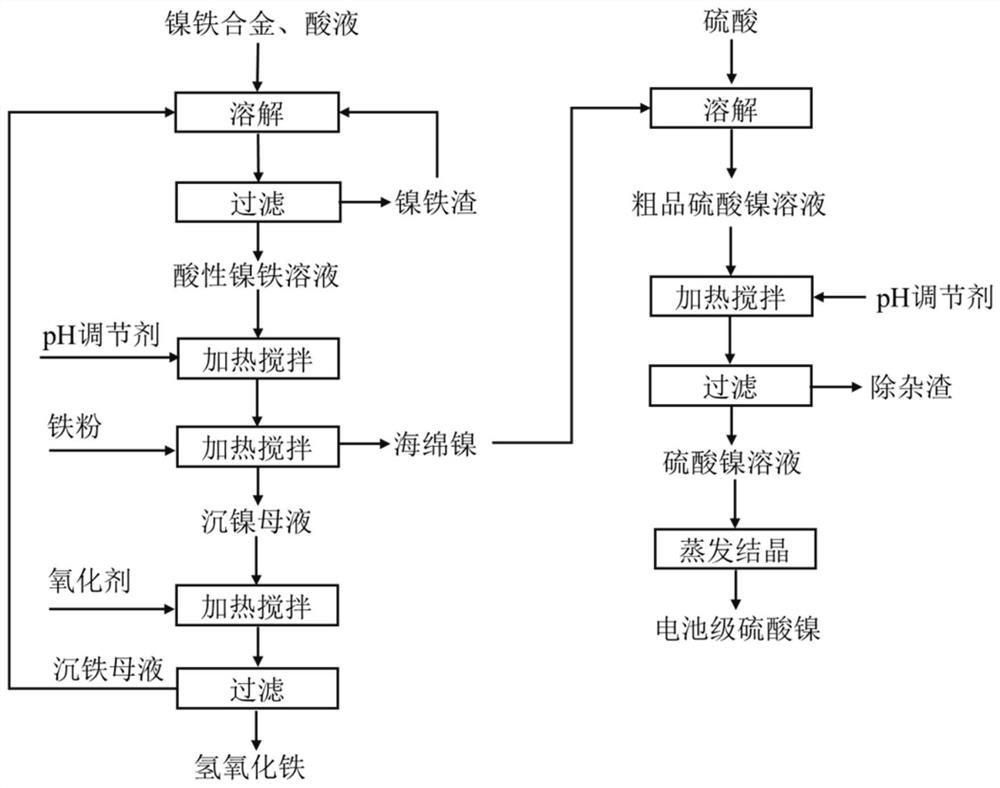
Method for separating nickel and iron from nickel-iron alloy and application
ActiveCN112941314AAchieve separationHas economic valueIron oxides/hydroxidesNickel sulfatesFerric hydroxideIron powder
The invention belongs to the field of hydrometallurgy, and discloses a method for separating nickel and iron from a nickel-iron alloy and application. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving the nickel-iron alloy in an acid solution, filtering, and taking filtrate to obtain an acidic nickel-iron solution; adjusting the pH value of the acidic nickel-iron solution, heating, stirring, adding iron powder, and continuously heating and stirring to obtain sponge nickel and nickel precipitation mother liquor; enabling the nickel precipitation mother liquor to be subjected to oxidation iron precipitation to obtain ferric hydroxide slag and iron precipitation mother liquor; and dissolving sponge nickel into sulfuric acid, filtering, collecting filtrate, heating, and adjusting the pH value to obtain a nickel sulfate solution; According to the method, after the nickel-iron alloy is dissolved by using the acid liquor, nickel in the solution is replaced by iron powder to obtain sponge nickel, the nickel precipitation mother liquor is oxidized to generate ferric hydroxide, the nickel content is lower than 0.4%, the iron precipitation mother liquor can be returned to a leaching section, and the sponge nickel is subjected to acid dissolution, impurity removal and evaporative crystallization to obtain a battery-grade nickel sulfate product.
Owner:HUNAN BRUNP RECYCLING TECH +2
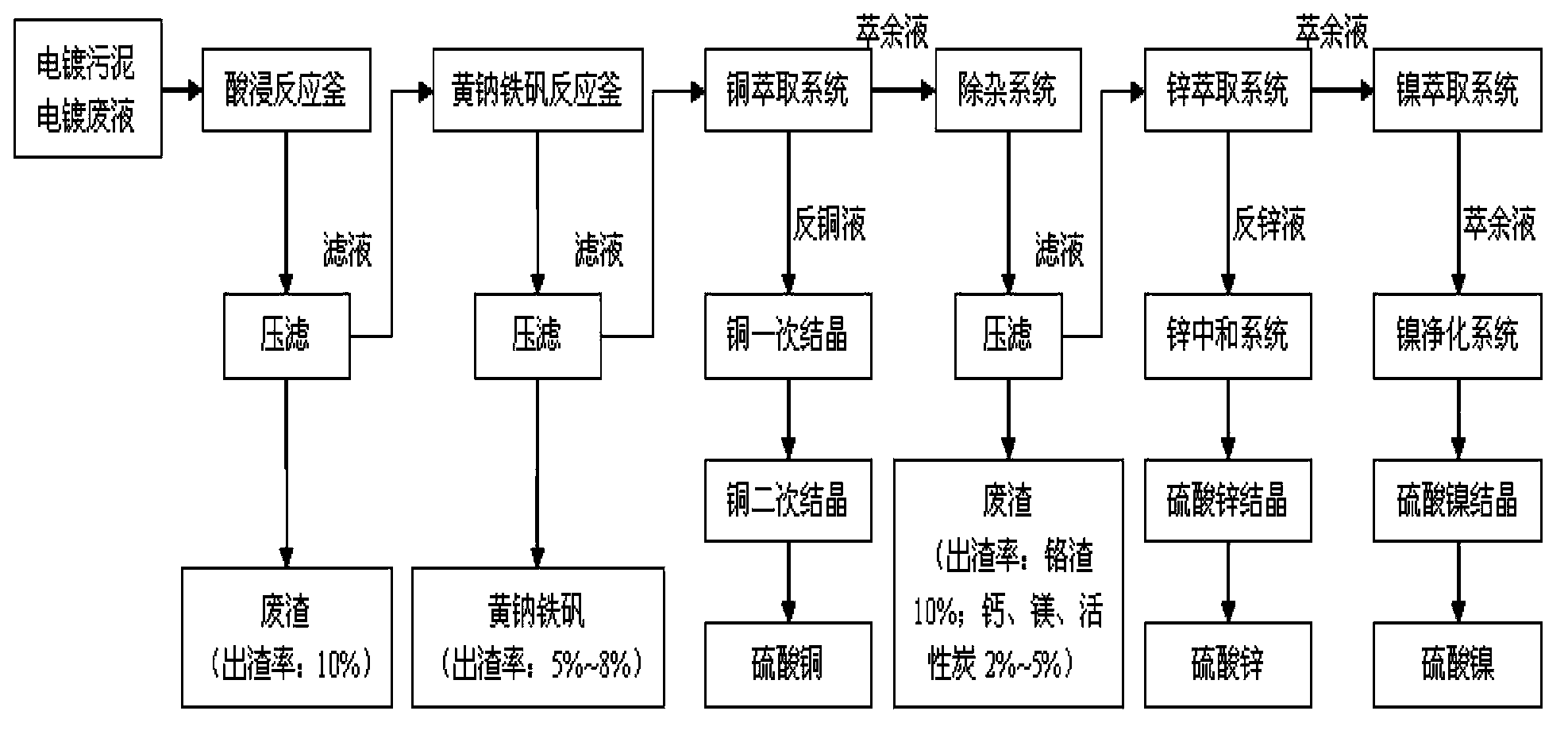
Electroplating sludge recycling technology
InactiveCN104099474AReduce dosageGuaranteed leaching rateZinc sulatesSludge treatmentLiquid wasteSludge
The invention discloses an electroplating sludge recycling technology. The technology comprises the steps of acid dipping, iron removal, copper extraction, impurity removal, zinc extraction, nickel extraction, low acid leaching and high acid leaching, tailings are washed with water, the iron removal step is carried out through a sodium jarosite process, copper extraction adopts two stage extraction, two stage water washing, four stage back extraction, and second stage extraction is carried out after first stage extraction, precipitation, washing and acid dissolution. The technology has the advantages of technological period shortening, guarantee of the product purity through multiple stage extraction, effective use of the waste resource, and reduction of the emission of a waste liquid.
Owner:ZHENJIANG HUAKE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Process for metals recovery from spent catalyst
The process of this invention is directed to the removal of metals from an unsupported spent catalyst. The catalyst is subjected to leaching reactions. Vanadium is removed as a precipitate, while a solution comprising molybdenum and nickel is subjected to further extraction steps for the removal of these metals. Molybdenum may alternately be removed through precipitation.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Method for preparing nickel sulfate solution and battery grade ferric phosphate from nickel-containing pig iron
ActiveCN106829907AImprove use valueReduce processing costsNickel compounds preparationNickel sulfatesSulfatePhosphate
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nickel sulfate solution and battery grade ferric phosphate from nickel-containing pig iron. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out raw materials pretreatment, acid leaching treatment, sedimentation treatment, ferric phosphate drying treatment, nickel-containing filtrate extraction treatment and reverse extraction to obtain the nickel sulfate solution. The method for preparing the nickel sulfate solution and the battery grade ferric phosphate from the nickel-containing pig iron has the characteristics of simpleness in technology, high recovery rate of the nickel-containing pig iron, low cost and good performance of a product.
Owner:GUANGDONG JIANA ENERGY TECH CO LTD +1
Method for producing battery-level refined nickel sulfate with electrolyte
The invention discloses a method for producing battery-level refined nickel sulfate with electrolyte. The method comprises the following steps: (1) concentrating and crystallizing: putting the nickel-containing electrolyte in which the copper is removed (nickel content is greater than or equal to 1 g / L) into a reaction kettle, steam-heating, concentrating and separating to obtain coarse nickel sulfate; (2) oxidizing to remove iron: dissolving the coarse nickel sulfate in water, and adding hydrogen peroxide; (3) vulcanizing to remove copper, lead and zinc: vulcanizing to remove copper, lead and zinc through the reaction of sodium sulfide and sulfuric acid; (4) concentrating to remove calcium and magnesium: removing calcium and magnesium by evaporation and concentration; (5) removing calcium and magnesium with sodium fluoride: under the action of mechanical stirring, adding second-grade sodium fluoride, and controlling the pH value with alkali liquid so that calcium and magnesium become fluoride precipitates to be removed; and (6) concentrating and crystallizing: concentrating the purified solution, and crystallizing to obtain the battery-level refined nickel sulfate. The product produced by the invention is an emerald granular crystal which is a square crystal, and the crystal grain diameter is greater than 2 mm and conforms to the HG / T2824-1997 standard.
Owner:中科铜都粉体新材料股份有限公司
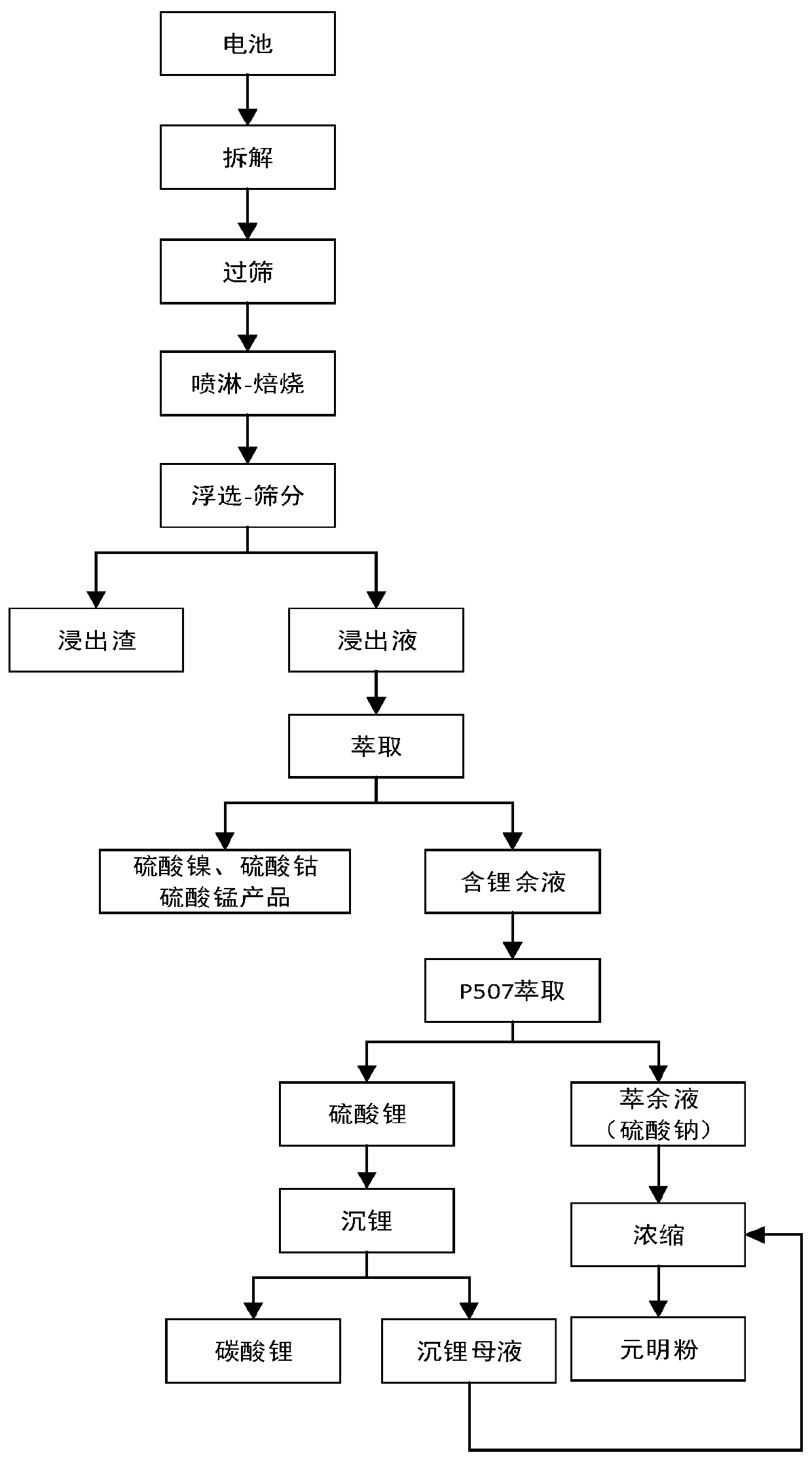
Power lithium ion battery all metal recycling and cyclic utilizing method
ActiveCN110616331AAchieve recyclingShort processCobalt sulfatesWaste accumulators reclaimingElectrical batteryLithium carbonate
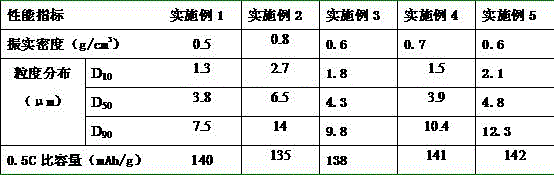
The invention discloses a power lithium ion battery all metal recycling and cyclic utilizing method. Waste lithium ion batteries serve as raw materials, the disassembling-screening and roasting procedures are adopted for separating battery pole powder from other parts in the batteries, then, acid leaching is conducted, and leaching liquid containing cobalt, nickel, manganese and lithium is obtained; through extraction, separation and purification of cobalt, nickel, manganese and lithium are achieved, battery-level cobaltous sulfate, nickel sulfate and manganese sulfate are obtained, then, lithium-sodium separation is conducted, and lithium carbonate and sodium sulfate products are obtained through lithium deposition and concentration. The power lithium ion battery all metal recycling and cyclic utilizing method is green and efficient, danger waste generation is avoided, and large-scale production can be achieved. Various valuable metals are systematically recycled from the waste powerlithium batteries, according to the recycling rates, Co is larger than 95%, Ni is larger than 95%, Mn is larger than 98%, Li is larger than or equal to 94%, and the water cyclic utilization rate is larger than 95%. Nickel sulfate liquid, cobaltous sulfate liquid, manganese sulfate liquid and lithium carbonate obtained through the power lithium ion battery all metal recycling and cyclic utilizing method meet the battery level product standard.
Owner:衢州华友资源再生科技有限公司
Laterite nickel ore treatment method
ActiveCN109234526AReduce the amount of saline wastewaterReduce foulingCobalt sulfatesNickel sulfatesLateriteEnergy conservation
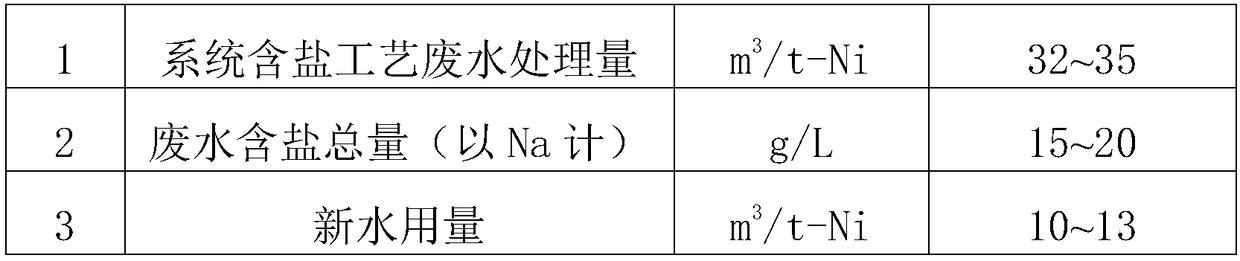
The invention provides a laterite nickel ore treatment method, which comprises the following steps: sulfuric acid is adopted to carry out pressure leaching treatment on laterite nickel ore pulp, so that laterite nickel ore leachate is obtained; first neutralizer is added into the laterite nickel ore leachate to precipitate iron and aluminum, so that a nickel-and-cobalt-contained solution is obtained; second neutralizer is added into the nickel-and-cobalt-contained solution to precipitate nickel and cobalt, so that a crude product is obtained, and the crude product is gypseous nickel cobalt hydroxide; sulfuric acid is adopted to carry out releaching treatment on the crude product, so that a nickel cobalt sulfate solution and gypsum ore pulp are obtained; after the nickel cobalt sulfate solution is extracted, purified and evaporatively crystallized, nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate are respectively obtained; the first neutralizer is limestone ore pulp or calcium hydroxide pulp, and thesecond neutralizer is calcium hydroxide pulp. When the treatment method disclosed by the invention is adopted, the amount of wastewater in a production system can be remarkably reduced, energy is saved and energy consumption is reduced, so that the treatment cost is reduced, and moreover, the production efficiency can also be increased.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
Method for preparing nickel salt through direct leaching of nickel oxide at normal pressure
InactiveCN107935063AImprove qualityEasy to produceNickel halidesNickel sulfatesSulfateDistilled water
The invention discloses a method for preparing nickel sulfate or nickel chloride through normal-pressure leaching of a nickel oxide. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a dilute sulfuricacid solution with a nickel oxide, and carrying out a stirring reaction at 50 to 100 DEG C for 1 to 5 h so as to gradually produce a yellow-green solid; carrying out solid-liquid separation, washing the yellow-green solid with distilled water until the solid is weakly acid and then dissolving the solid with distilled water or with an aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution with a concentration of 1 to5% so as to produce a corresponding nickel sulfate solution; and mixing a hydrochloric acid solution with the nickel oxide and carrying out a stirring reaction at 50 to 100 DEG C for 1 to 3 h so as togradually produce a green nickel chloride solution. A nickel salt solution prepared by using the method has nickel content of 110 g / L or above. According to the method, direct leaching reaction at normal pressure is carried out so as to obtain nickel sulfate and nickel chloride, so production flow of nickel sulfate and nickel chloride is effectively simplified, and cost is lowered; and impurity introduction is reduced from the source, so the quality of nickel sulfate is effectively improved.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for recycling high-purity nickel sulfate from nickel-bearing waste batteries
InactiveCN107162067AReduce distractionsAchieve separationMagnesium carbonatesNickel compounds preparationSulfateChelating resin
The invention relates to the field of recycling of solid waste and particularly discloses a method for recycling high-purity nickel sulfate from nickel-bearing waste batteries; the method comprises the steps of disassembling the nickel-bearing waste batteries into battery powder; dissolving the battery powder with an acid to obtain dissolved solution, and adding alkali metal sulfate; removing iron by an oxidative precipitation process, and removing impurities from the dissolved solution with iron removed via an extraction process to obtain magnesium-bearing nickel liquid; passing the magnesium-bearing nickel liquid through chelate resin exchange columns, with nickel ions adsorbed by chelate resin, and magnesium-rich solution flowing out for treatment; desorbing the nickel ions to obtain nickel sulfate solution; evaporating the nickel sulfate solution, cooling, crystallizing, filtering, and drying to obtain finished nickel sulfate. By using the method, it is effectively guaranteed that the recycled finished nickel sulfate is a high-purity product having a content up to 99.5% and above, the impurity Mg content is less than 0.005% and below, and the product fully meets the standard for nickel sulfate products in HG / T2824-1997.
Owner:中矿(赣州)国际钴业有限公司
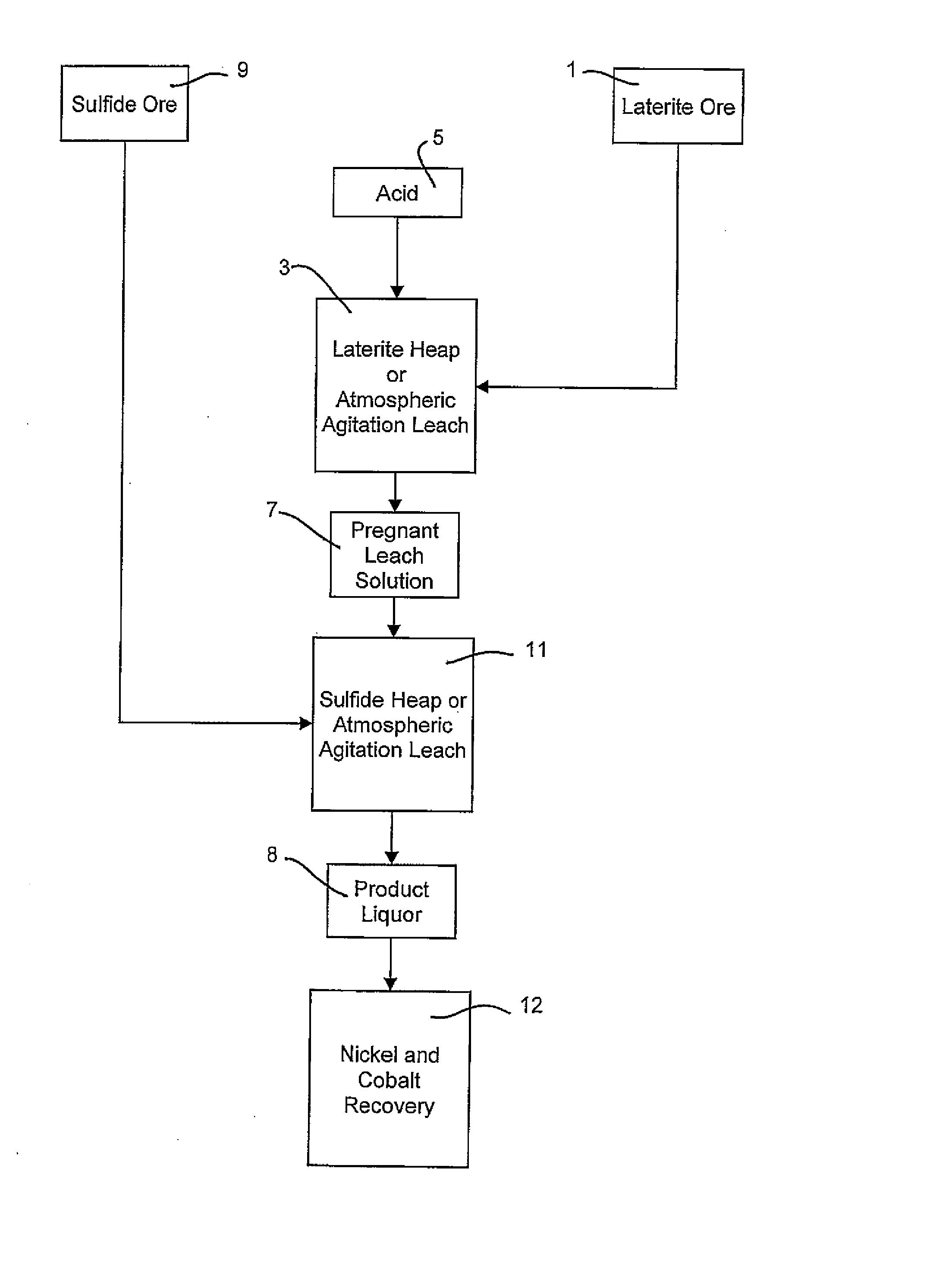
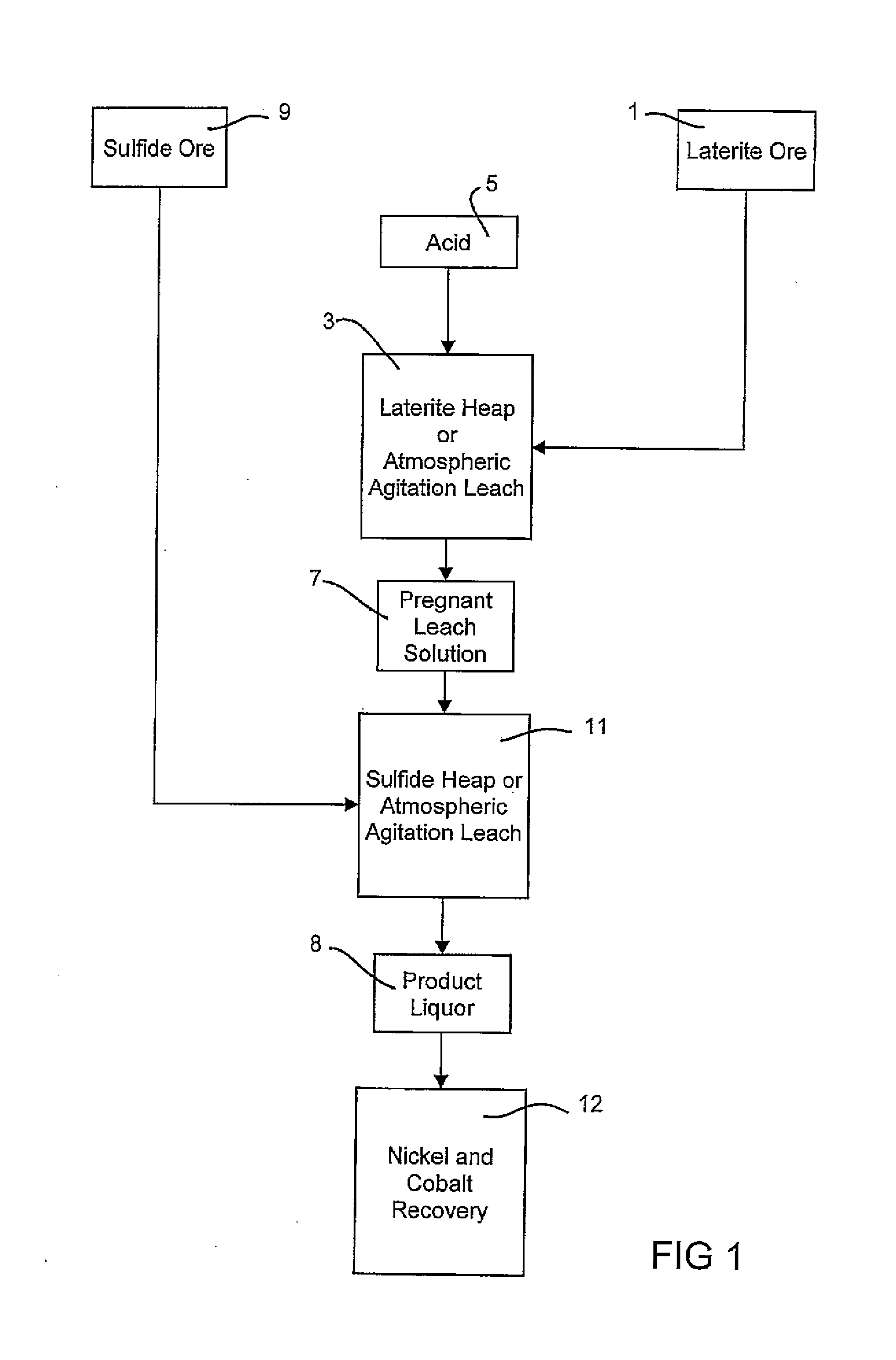
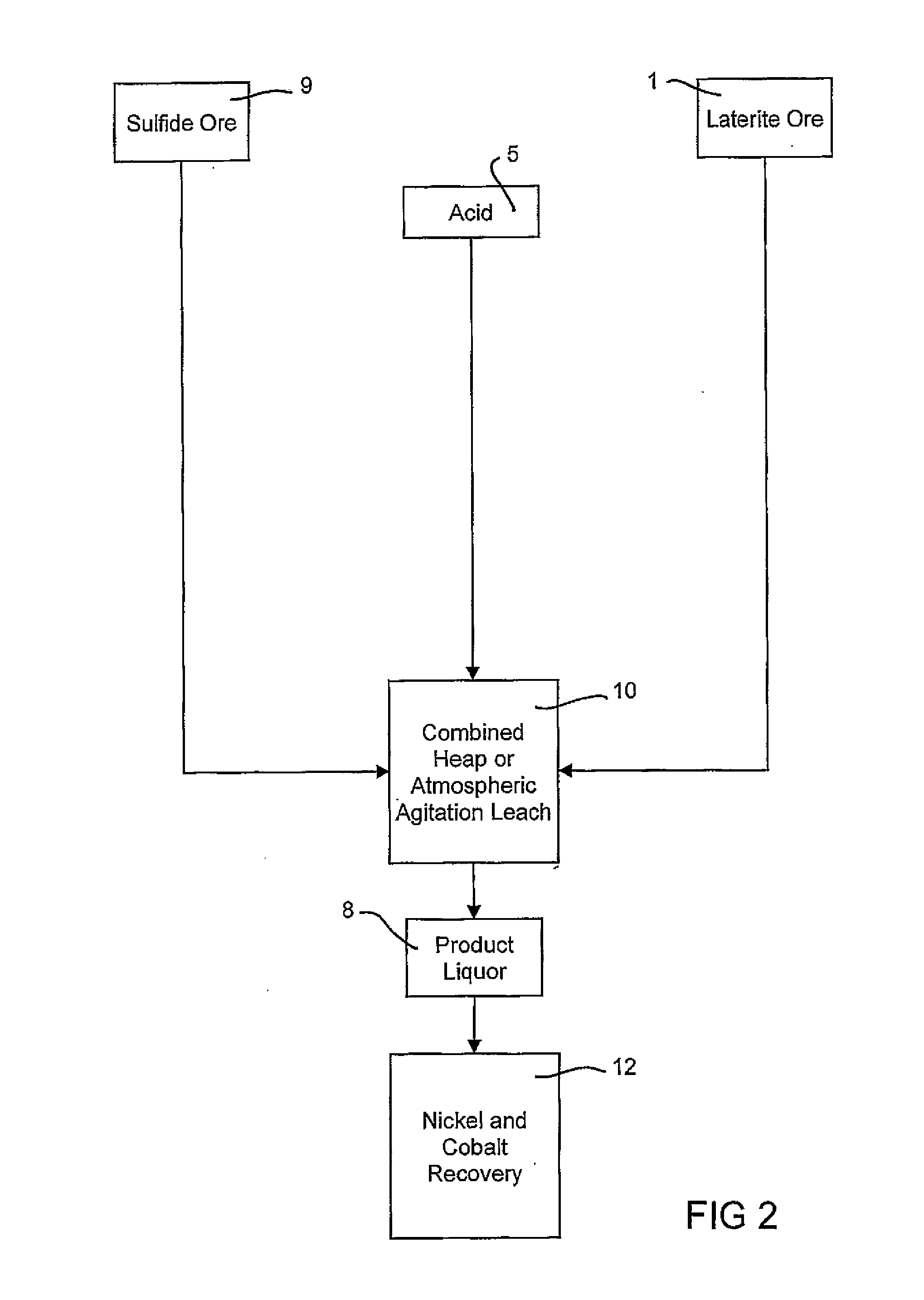
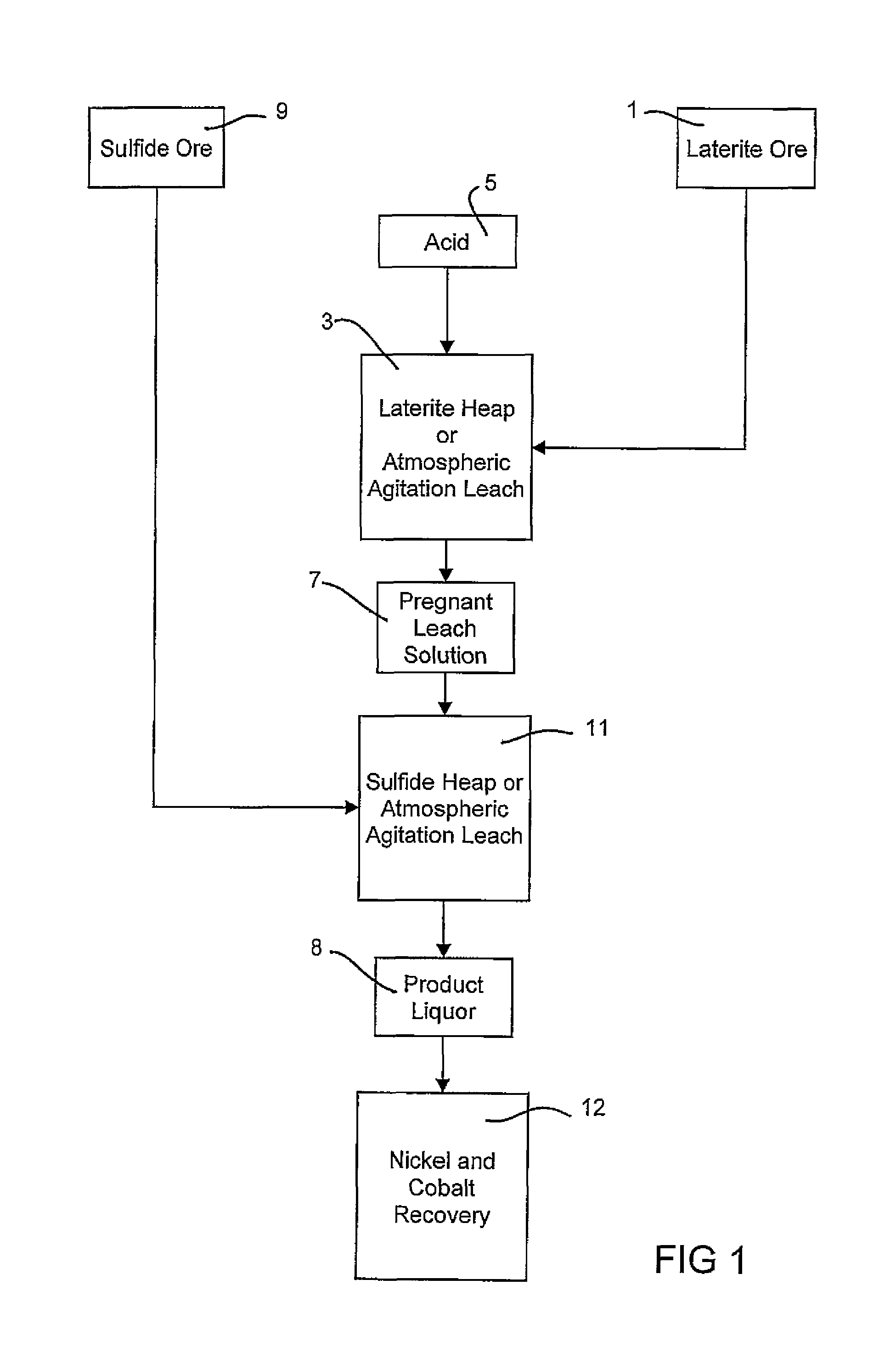
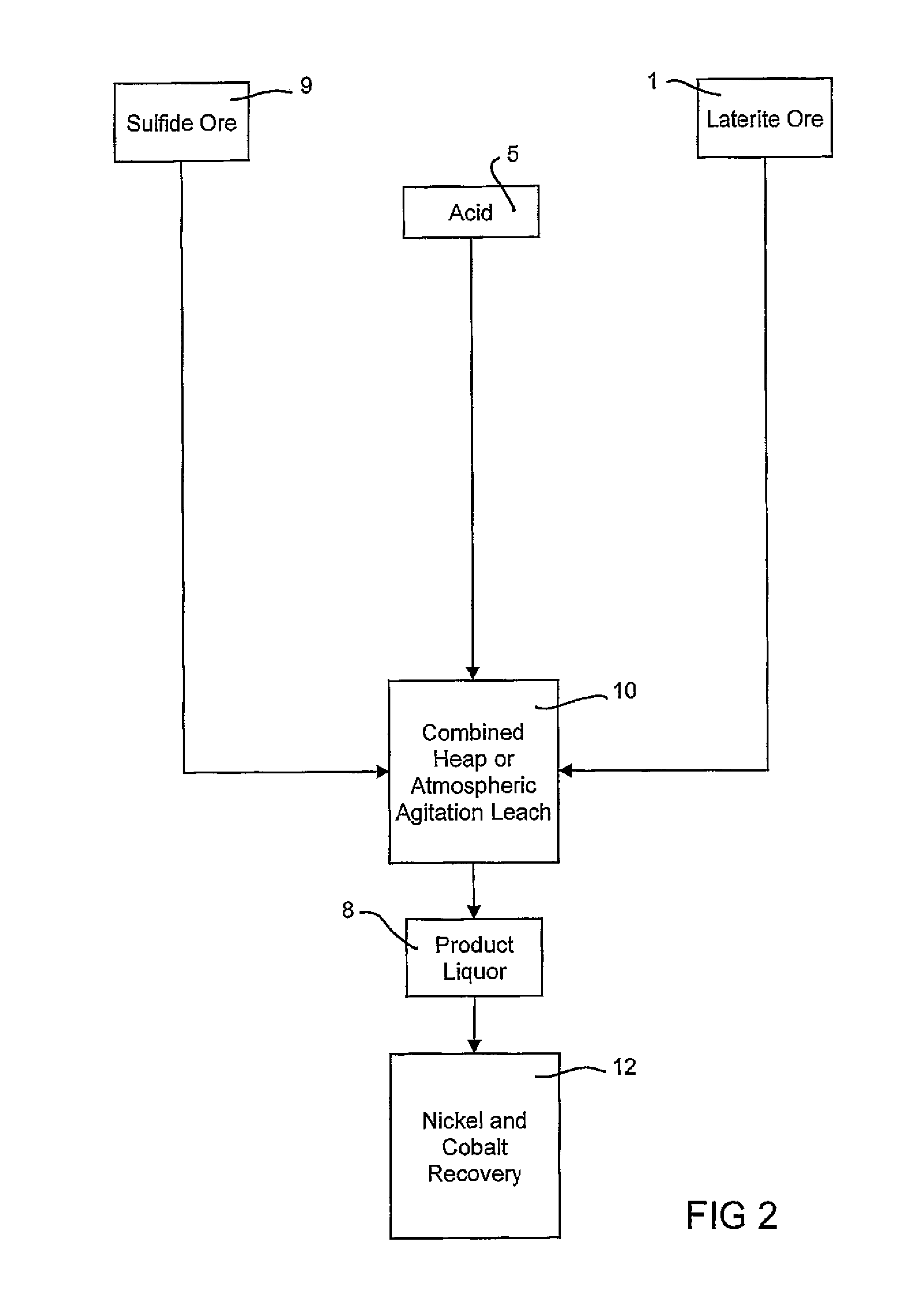
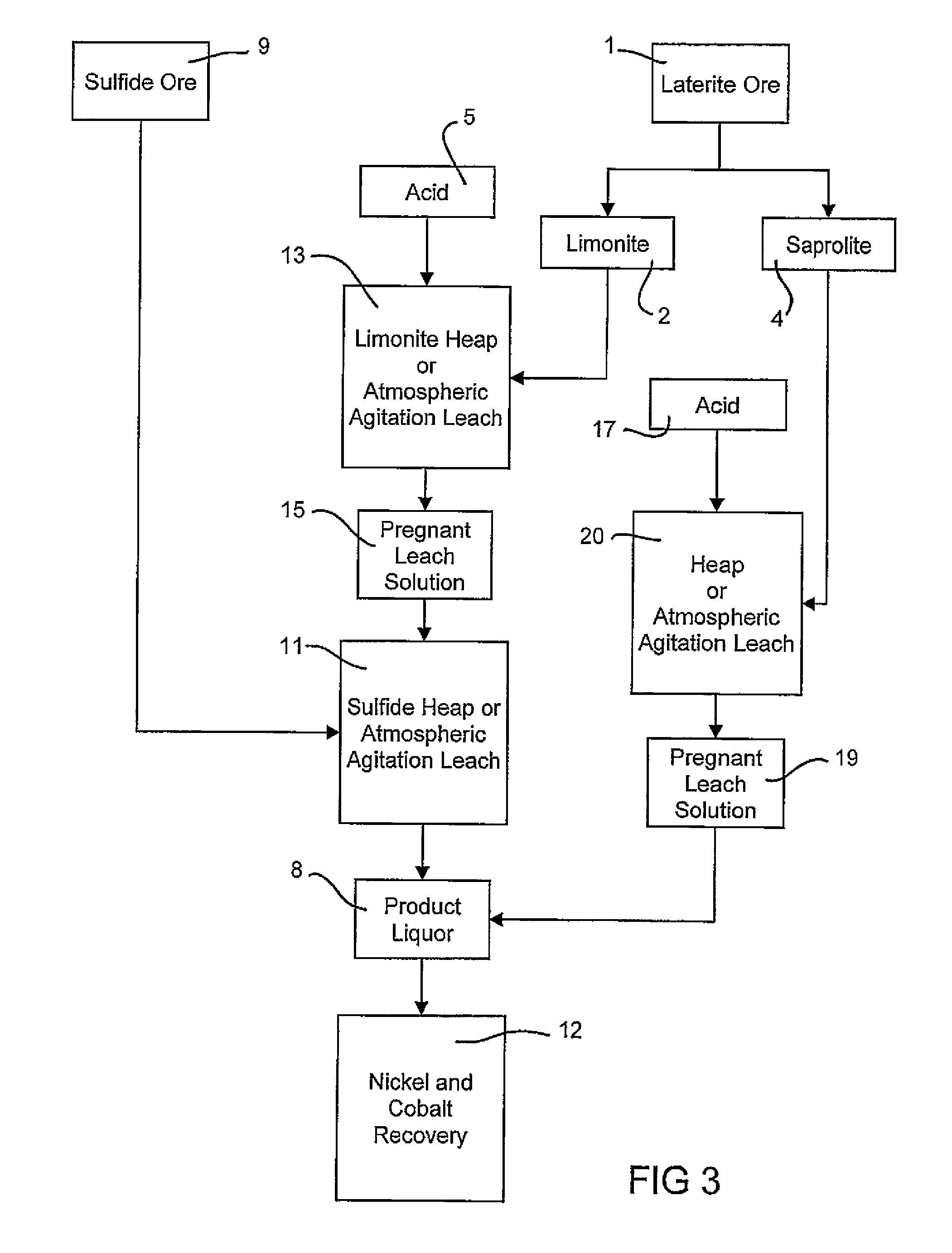
Consecutive or Simultaneous Leaching of Nickel and Cobalt Containing Ores
InactiveUS20080050294A1Minimize equipment sizeIncrease consumptionCobalt ammonia complexesIron oxides/hydroxidesPregnant leach solutionSulfide
A process for the recovery of nickel and cobalt from nickel and cobalt containing ores, including the steps of first leaching a laterite ore and / or a partially oxidised sulfide ore with an acid solution to produce a pregnant leach solution containing at least dissolved nickel, cobalt and ferric ions, and subsequently leaching a sulfide ore or concentrate with the pregnant leach solution to produce a product liquor. Alternatively, the laterite ore and / or partially oxidised sulfide ore can be leached in a combined leach with the sulfide ore or concentrate. The ferric ion content in the pregnant leach solution or in the combined leach is sufficient to maintain the oxidation and reduction potential in the sulfide leach high enough to assist in leaching nickel from the sulfide ore or concentrate.
Owner:BHP BILLITON SSM TECH PTY LTD
Method for preparing lithium-ion sieve from waste lithium-ion batteries
InactiveCN109761250ASimple processReduce manufacturing costCobalt sulfatesNickel sulfatesSlagManganese
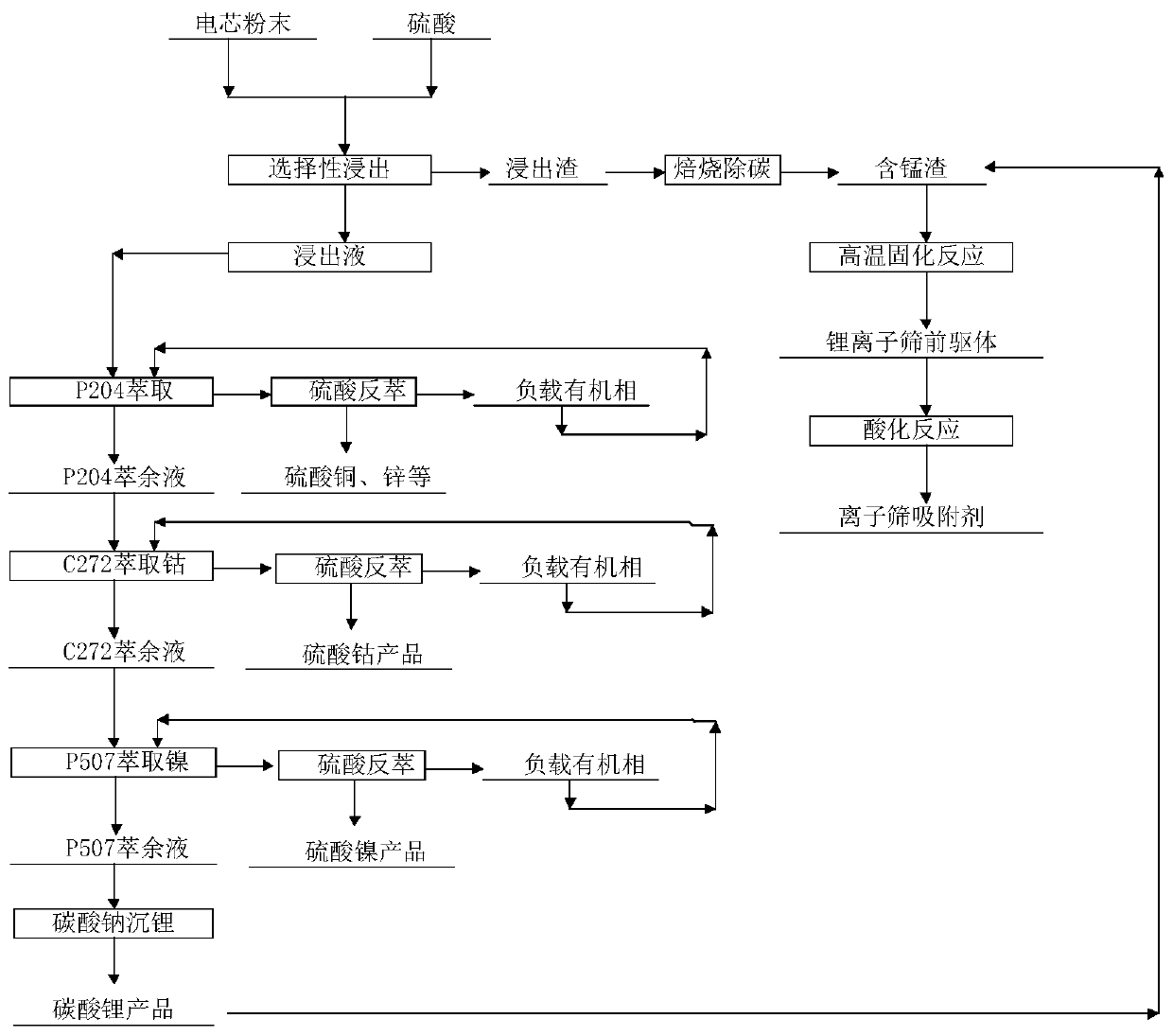
The invention discloses a method for preparing a lithium-ion sieve from waste lithium-ion batteries. The method is characterized by comprising the steps: sulfuric acid and a manganese-containing wastelithium-ion battery cathode material react at 40-100 DEG C to obtain leaching slag and leachate; the pH of the leachate is adjusted, and the leachate is subjected to extraction for impurity removingthrough P204; the pH of P204 raffinate is adjusted, and cobalt is extracted from the P204 raffinate through C272; the C272 after extracting is subjected to reextraction, and evaporative crystallization is conducted to obtain a cobalt sulfate product; the pH of C272 raffinate is adjusted, and nickel is extracted from the C272 raffinate through P507; the P507 after extracting is subjected to reextraction, and evaporative crystallization is conducted to obtain a nickel sulfate product; P507 raffinate is subjected to a sodium carbonate lithium sinking process to obtain a lithium carbonate product;the leaching slag and the lithium carbonate product are mixed to be roasted, and a lithium-ion sieve precursor is obtained; and the lithium-ion sieve precursor is subjected to acidic conversion through hydrochloric acid, and the lithium-ion sieve is obtained. The technological process is simple, and battery-grade cobalt sulfate, nickel sulfate, lithium carbonate and lithium-ion sieve with high added value can be obtained.
Owner:天齐锂业资源循环技术研发(江苏)有限公司
Material utilization method for electroplating sludge
ActiveCN105923658AGood gelling and curing propertiesImprove water resistanceFerric oxidesIron sulfatesSludgePre treatment
The invention provides a material utilization method for electroplating sludge. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreatment; (2) preparation of a gypsum material; (3) preparation of a clinker; and (4) preparation of an ultrafine gypsum filling material or anhydrite gelling material. According to the invention, a sulfuric acid leaching method and a biological leaching method belonging to mature wet processes are employed for pretreatment and separation of heavy metals in electroplating sludge, and lime or limestone is used for neutralization, so most valuable metals or heavy metals can be recovered at low cost for preparation of corresponding metal or metal salt materials, high-purity metal or metal salt materials or raw materials can be easily obtained, and waste sludge residues with dihydrate gypsum as a main mineral, i.e., a usable gypsum-based resource, can be easily obtained; and waste residues of electroplating sludge are not discharged, so environmental pollution and hidden troubles caused by the waste residues are thoroughly eliminated and environmental protection is benefited.
Owner:湖南省小尹无忌环境能源科技开发有限公司 +1
Method for extracting nickel from nickel-containing iron powder and preparing iron phosphate and application
ActiveCN113025822AImplement extractionEfficient separationNickel sulfatesProcess efficiency improvementO-Phosphoric AcidSulfate
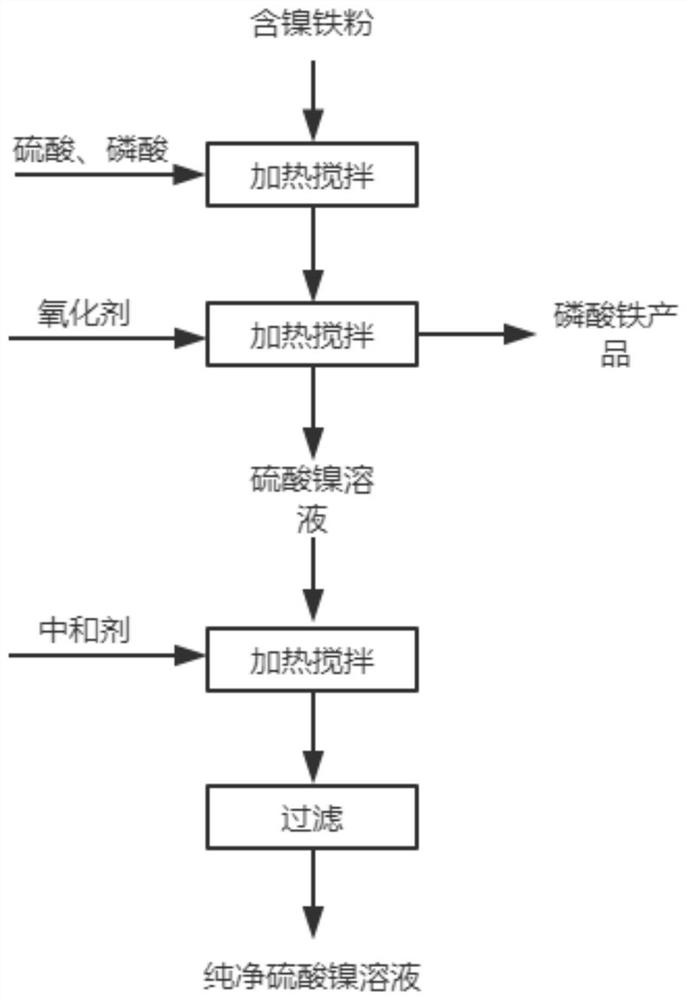
The invention discloses a method for extracting nickel from nickel-containing iron powder and preparing iron phosphate and application. The method comprises the following steps of (1) adding sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid into the nickel-containing iron powder, and carrying out heating and stirring so as to obtain mixed slurry; (2) adding an oxidizing agent into the mixed slurry, carrying out heating and stirring, and carrying out filtering so as to obtain an iron phosphate and nickel sulfate solution; (3) washing, filtering and drying the iron phosphate so as to obtain an iron phosphate product; and (4) adding a neutralizer into the nickel sulfate solution, carrying out heating and stirring, and carrying out filtering so as to obtain the nickel sulfate solution subjected to impurity removal. According to the method and the application, the nickel-containing iron powder is subjected to acid leaching by using mixed acid, the mixed acid is added by proportioning the content of iron and nickel in the raw materials, the nickel can enter the solution in the form of ions, the iron exists in a solid phase in the form of the iron phosphate, so that the nickel and the iron in the solid phase can be effectively separated, the process is simple, energy consumption is low, the cost is low, meanwhile, large economic benefits are achieved, and the method is suitable for industrial production and application.
Owner:HUNAN BRUNP RECYCLING TECH +2
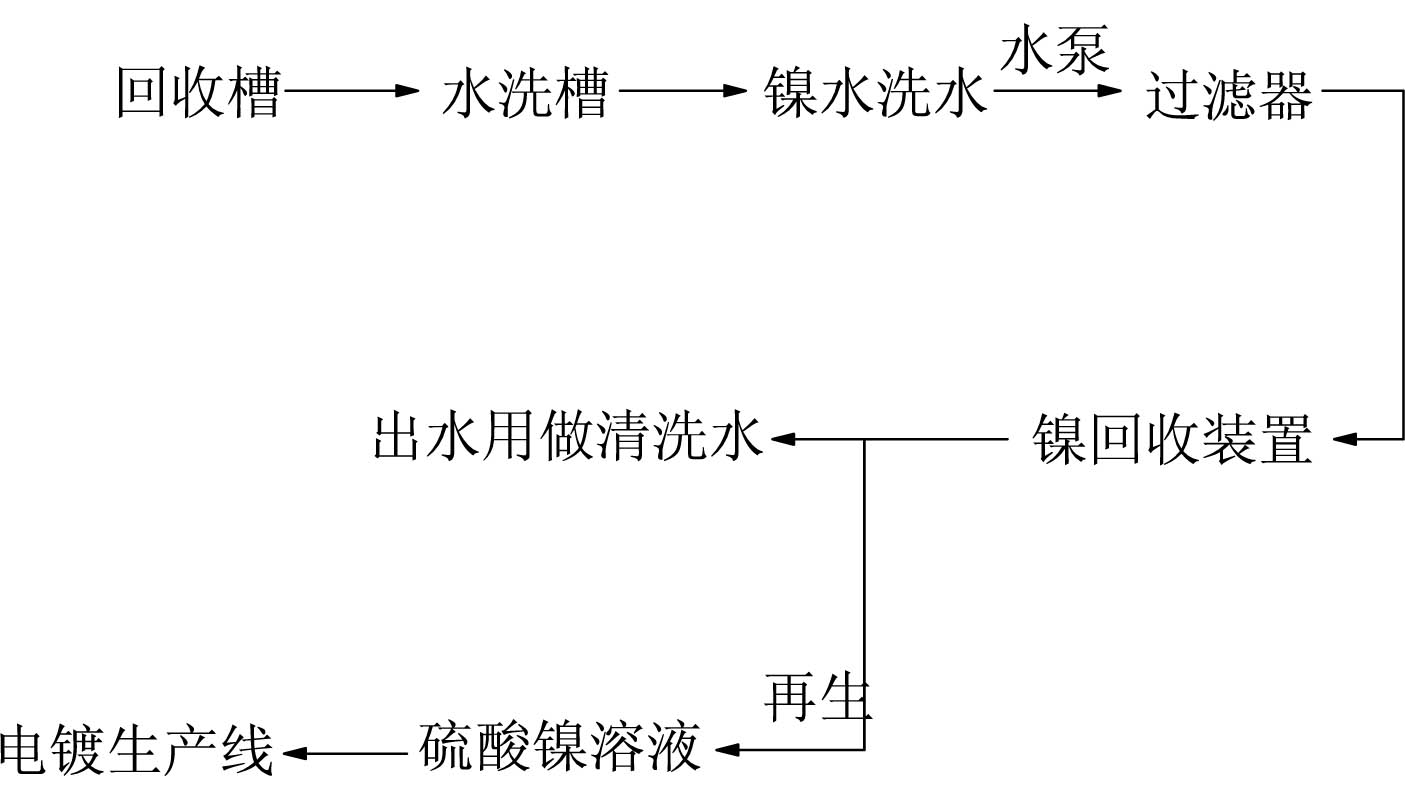
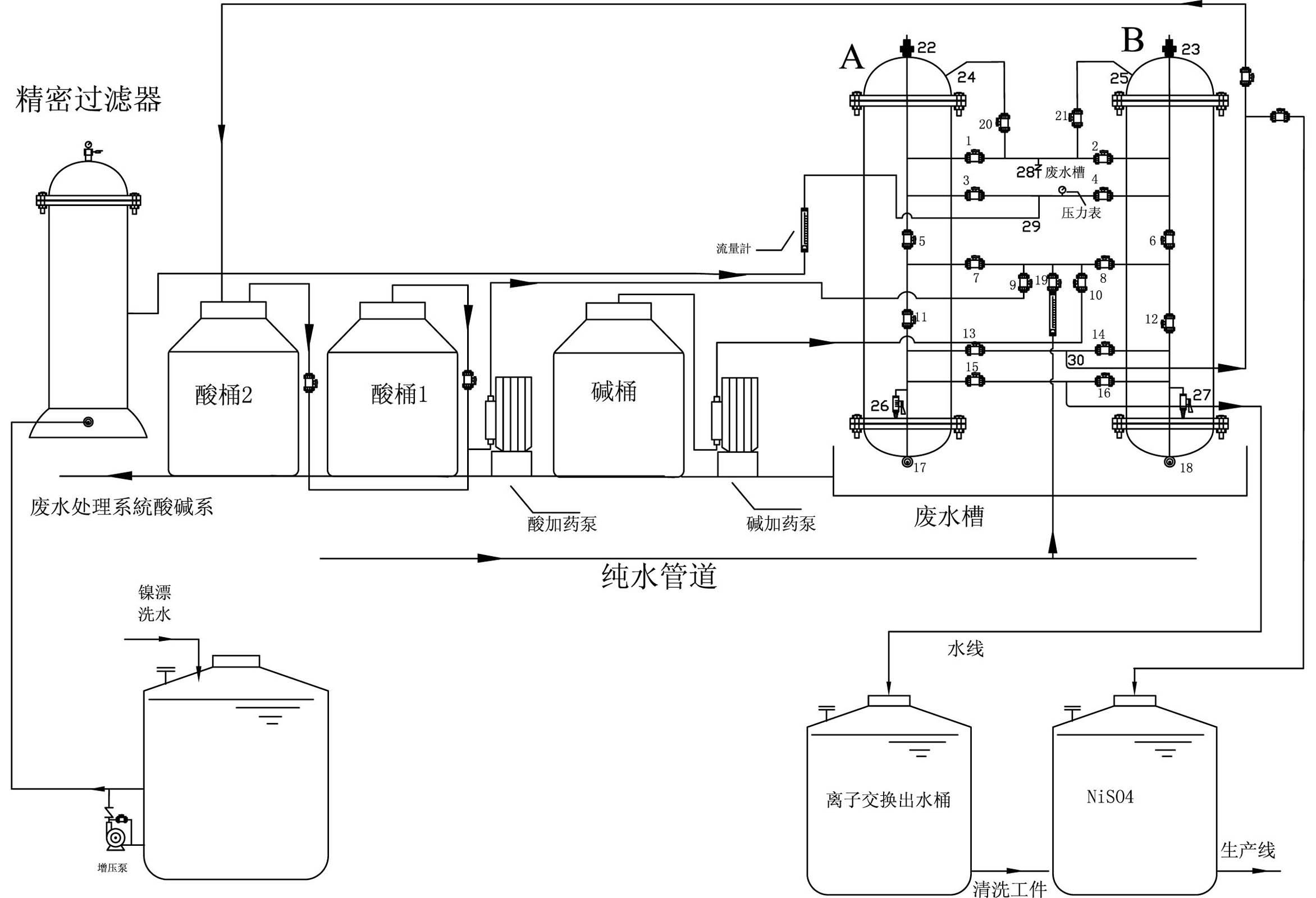
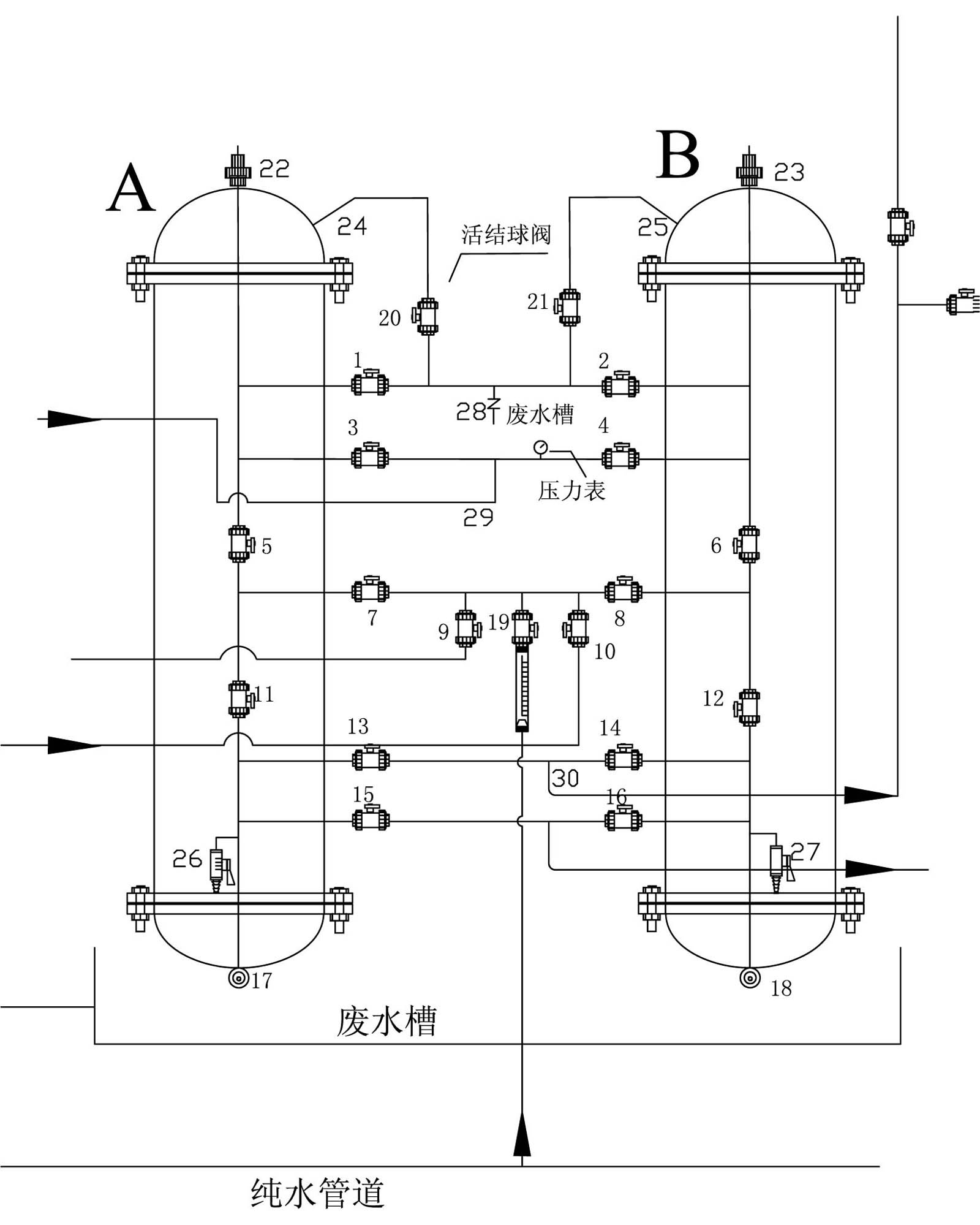
Method and device for recovering nickel resource and water resource in nickel plating wastewater
ActiveCN101885520AReasonable process designReduce energy consumptionWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeWaste water treatment from metallurgical processIon exchangeWater resources
The invention relates to a method and a device for recovering nickel resource and water resource in nickel plating rinsing wastewater. The method is characterized by ensuring that nickel ions and nickel highly selective resin generate ion exchange by using the nickel highly selective resin in a process of recovering the nickel plating rinsing wastewater resource, the nickel resource is absorbed on the nickel highly selective resin; under the condition of wasting the nickel resource by using a reclaiming agent, the invention has reasonable process design, low energy consumption and high recovered nickel resource purity, and can meet the requirements on the nickel resource for on-line use; in addition, water obtained by exchange can be directly used in productions of nickel plating, alloy, base copper, acid copper, thermal desorption, ultrasonic wave, deplating cleaning and the like without being treated by active carbon, thereby further lightening the load of environment protection treatment.
Owner:江门市瑞期精细化学工程有限公司
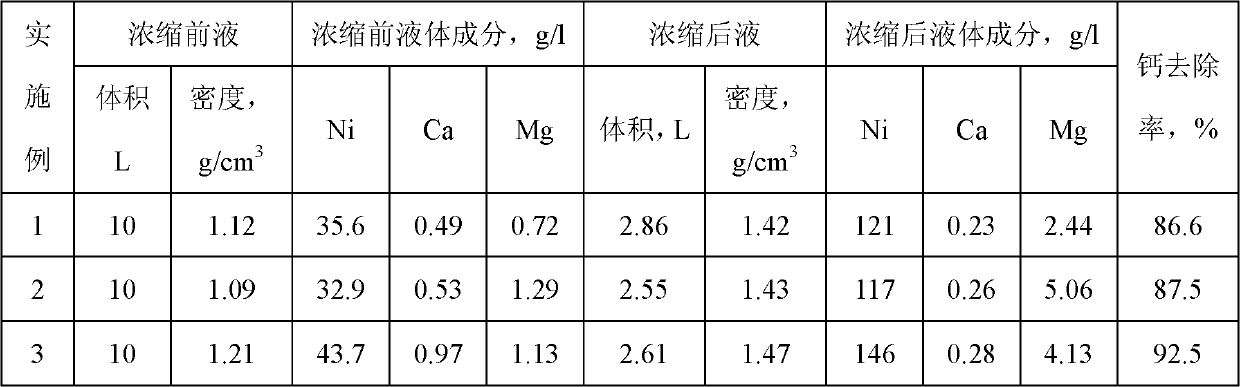
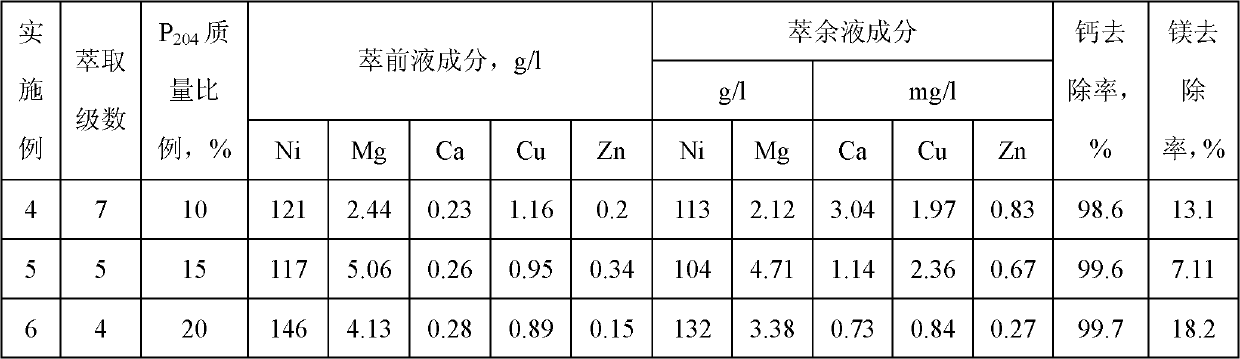
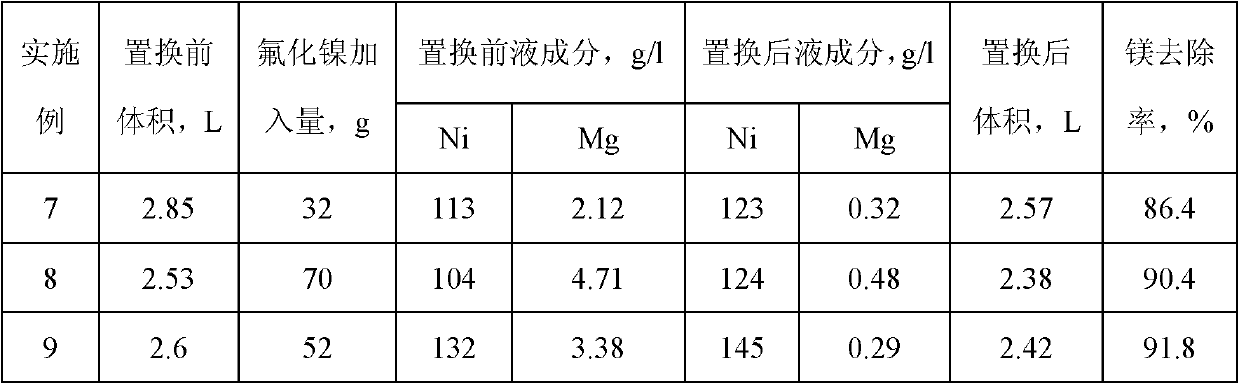
Method for removing calcium-magnesium impurities from nickel sulfate solution
The invention discloses a method for removing calcium-magnesium impurities from a nickel sulfate solution. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) heating a nickel sulfate raw material solution, concentrating, cooling and removing a precipitated solid; (2) extracting a filtrate obtained in the step (1) with a phosphorus-containing extracting agent; and adding nickel fluoride into a raffinate obtained in the step (2), heating to 60-90 DEG C for reacting, cooling and filtering to obtain a needed nickel sulfate solution. Due to the adoption of the method, the using amount of a fluorine salt and the discharge of fluorine-containing waste water are greatly reduced, and new impurity irons are not introduced, the nickel yield is high; and the method is particularly suitable for sulfate systems with high calcium content and low magnesium content.
Owner:SHANGHAI LIGHT IND RES INST
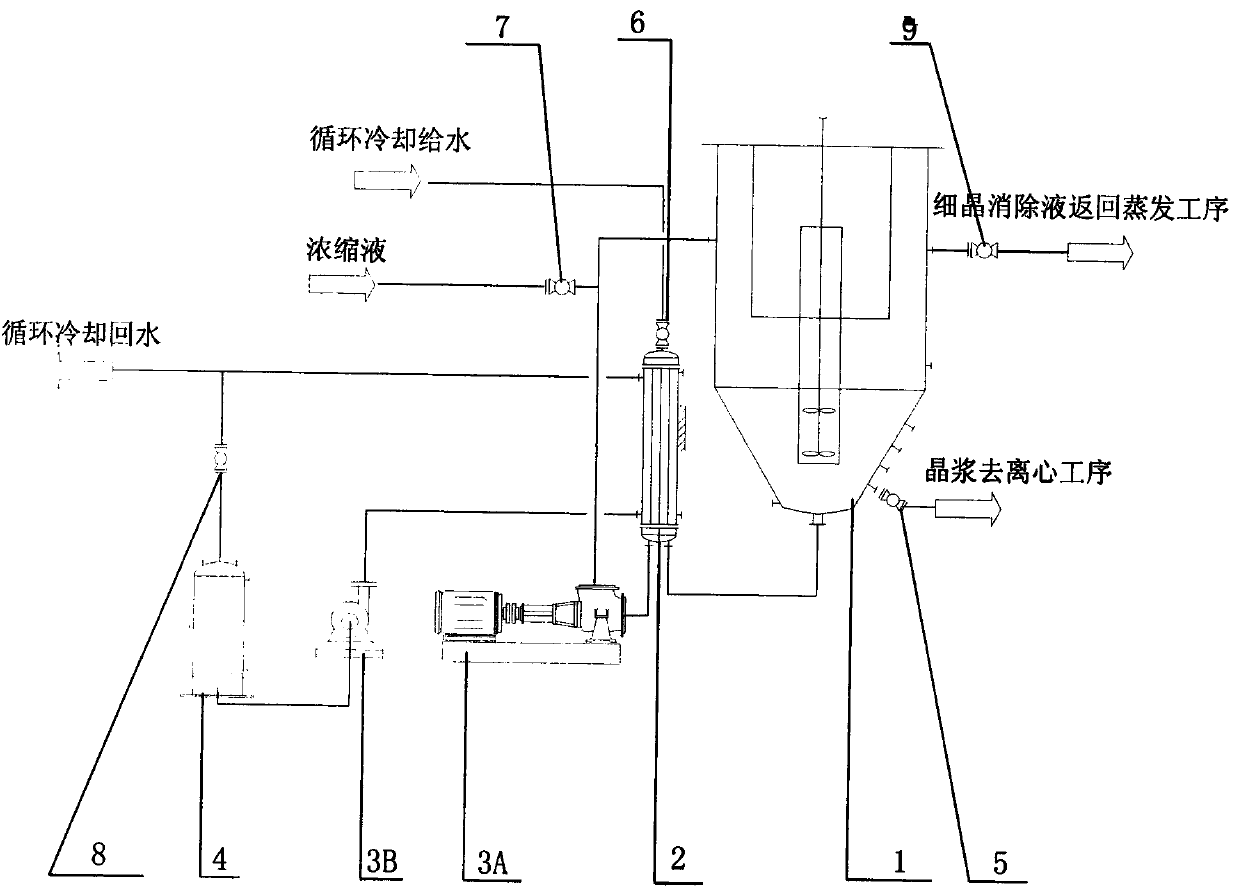
Nickel-cobalt sulfate continuous-crystallizing process
ActiveCN104192917AImprove energy savingRealize continuous productionNickel sulfatesEvaporationSlurry
The invention discloses a nickel sulfate hexahydrate crystal and cobalt sulfate heptahydrate crystal continuous-crystallizing process which comprises the following steps: firstly carrying out MVR evaporation concentration on a high-purity solution produced through an extraction procedure to 30%-39%, and secondly continuously cooling and crystallizing through an improved cooling type internal-circulating continuous crystallizer; continuously discharging crystal slurry from the bottom of the crystallizer for centrifugal solid-liquid separation; and continuously drying a crystal product at low temperature to produce product crystals with large granularity and uniform size distribution, and recovering a mother solution to an evaporation process. Compared with the traditional periodic crystallization process, the nickel sulfate hexahydrate crystal and cobalt sulfate heptahydrate crystal continuous-crystallizing process disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low evaporation energy consumption, fewer crystallization control process parameters, stability in operation, high automation degree, high production efficiency and the like and is easy to control, and operators are reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAYOU COBALT
Method and means for using microwave energy to oxidize sulfidic copper ore into a prescribed oxide-sulfate product
InactiveUS20080118421A1Highly solubleLow costOxide/hydroxide preparationCobalt sulfatesMicrowaveChalcopyrite
The present invention is directed to the microwave treatment of a class of selected metal ores and concentrates, particularly those known as chalcopyrite, in a fluidized bed reactor. The end product is commonly a mixture of copper oxide and copper sulfate, both of which are liquid soluble and directly recoverable by known techniques. The ratio of the oxide-sulfate mixture end product may be controlled by suitable control of microwave parameters.
Owner:HW PROCESS TECH
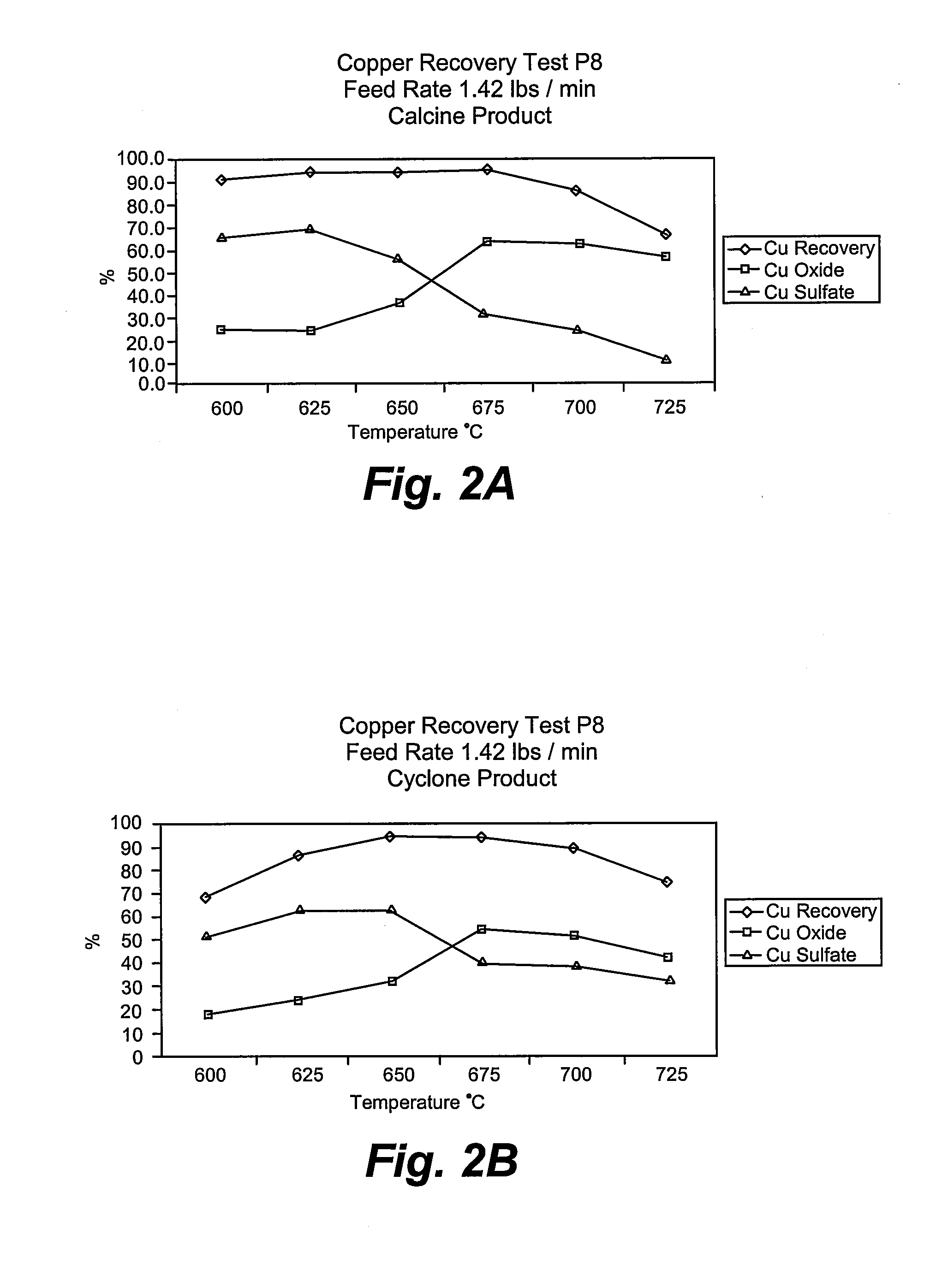
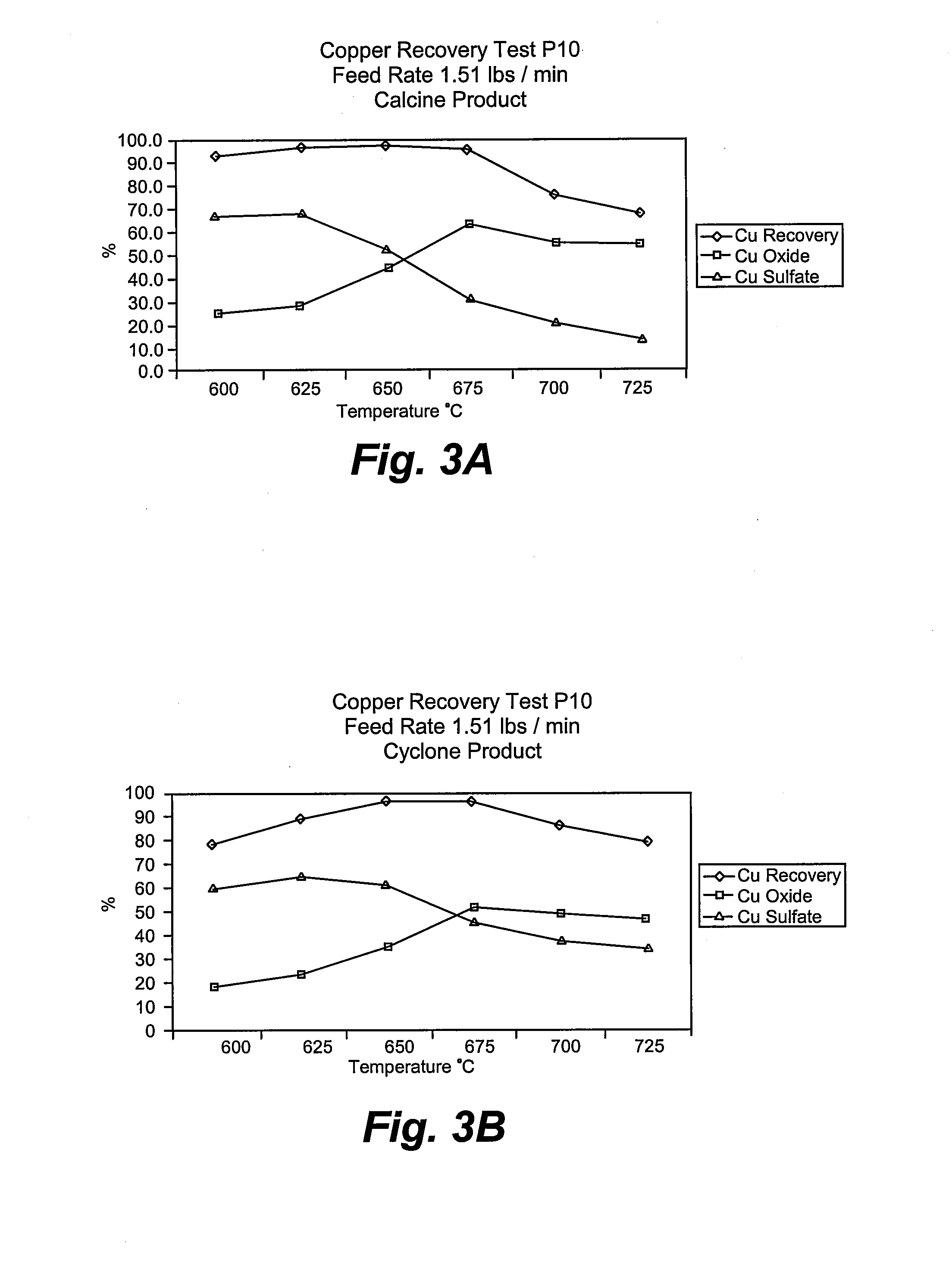
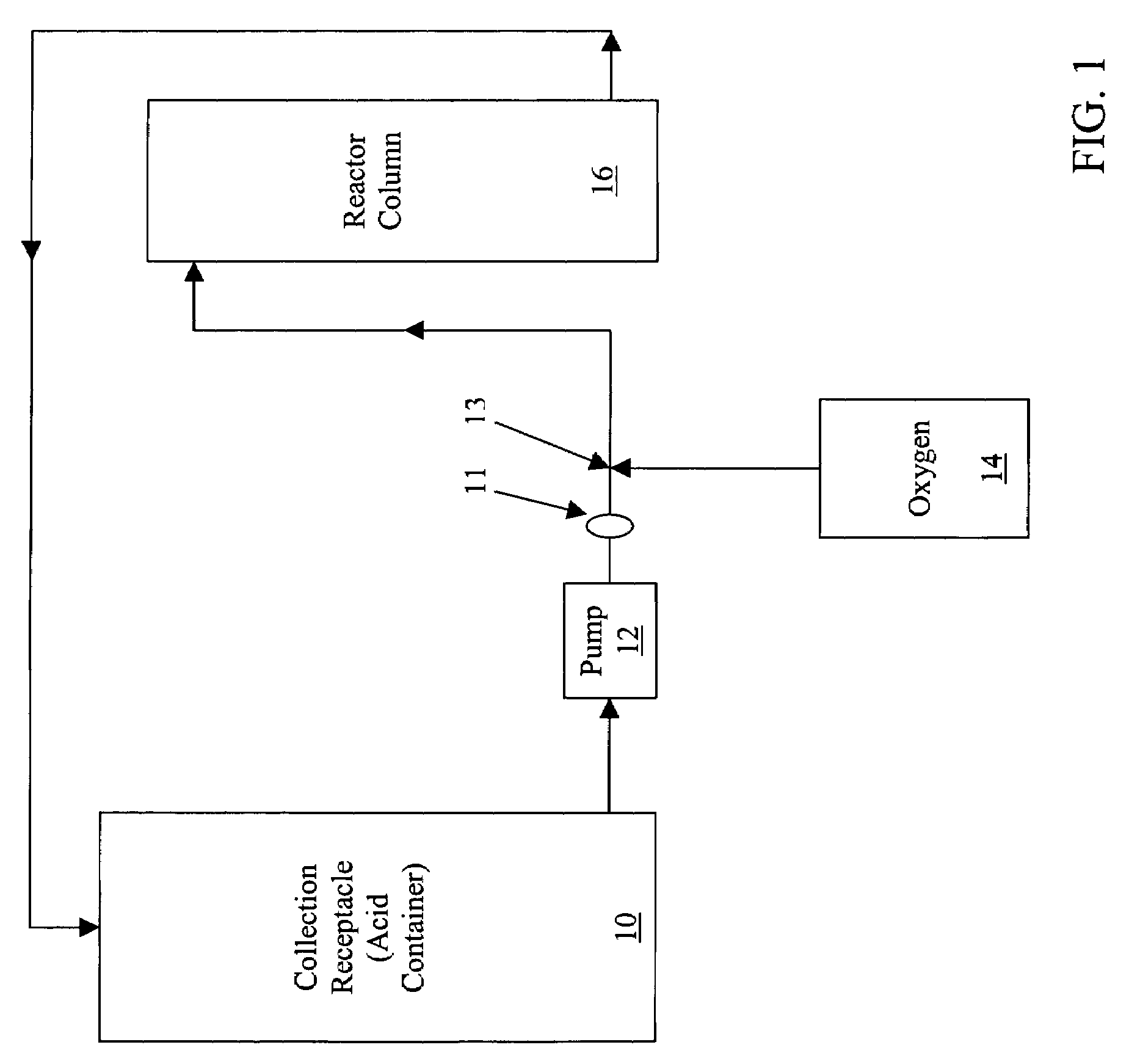
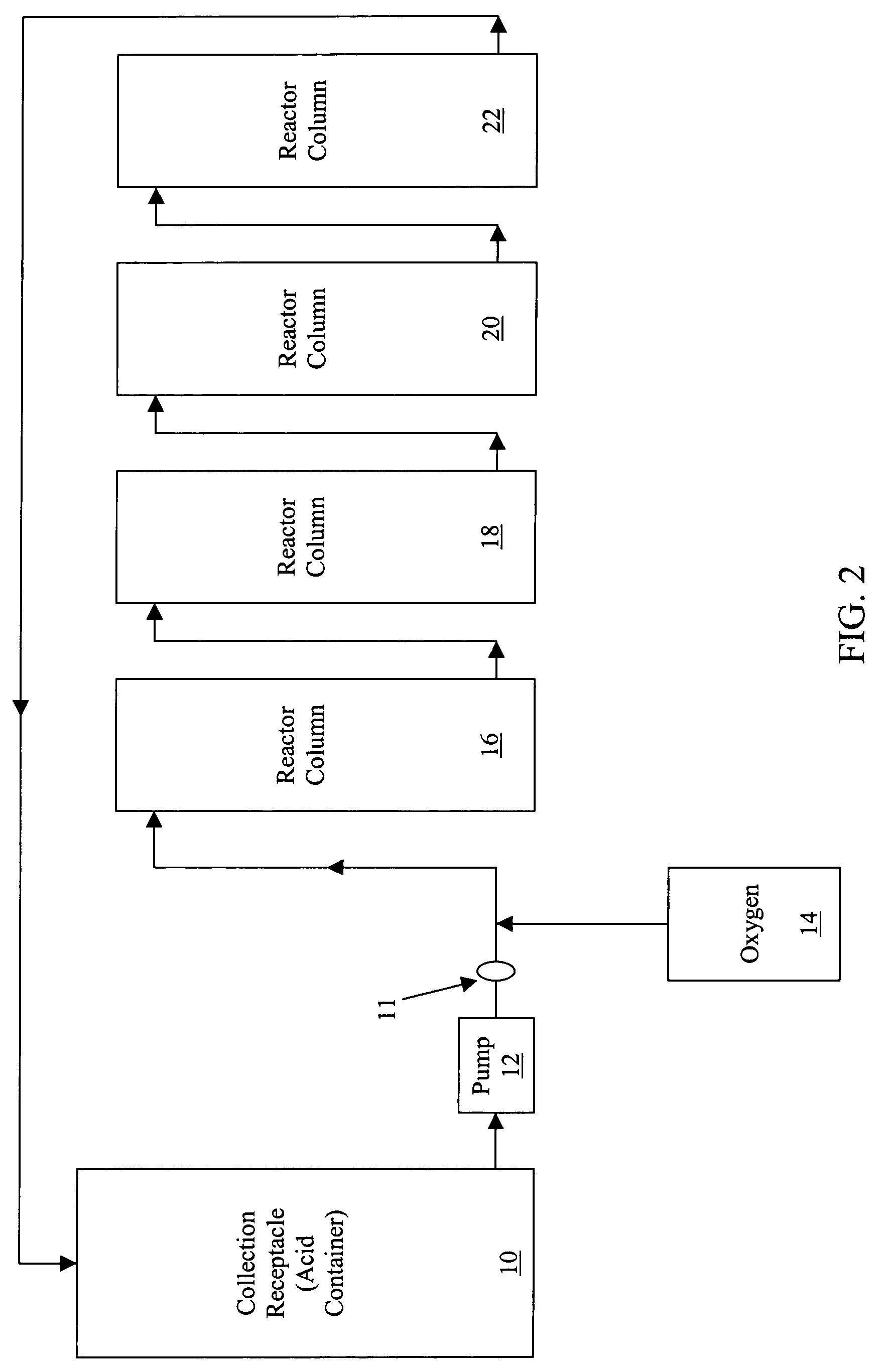
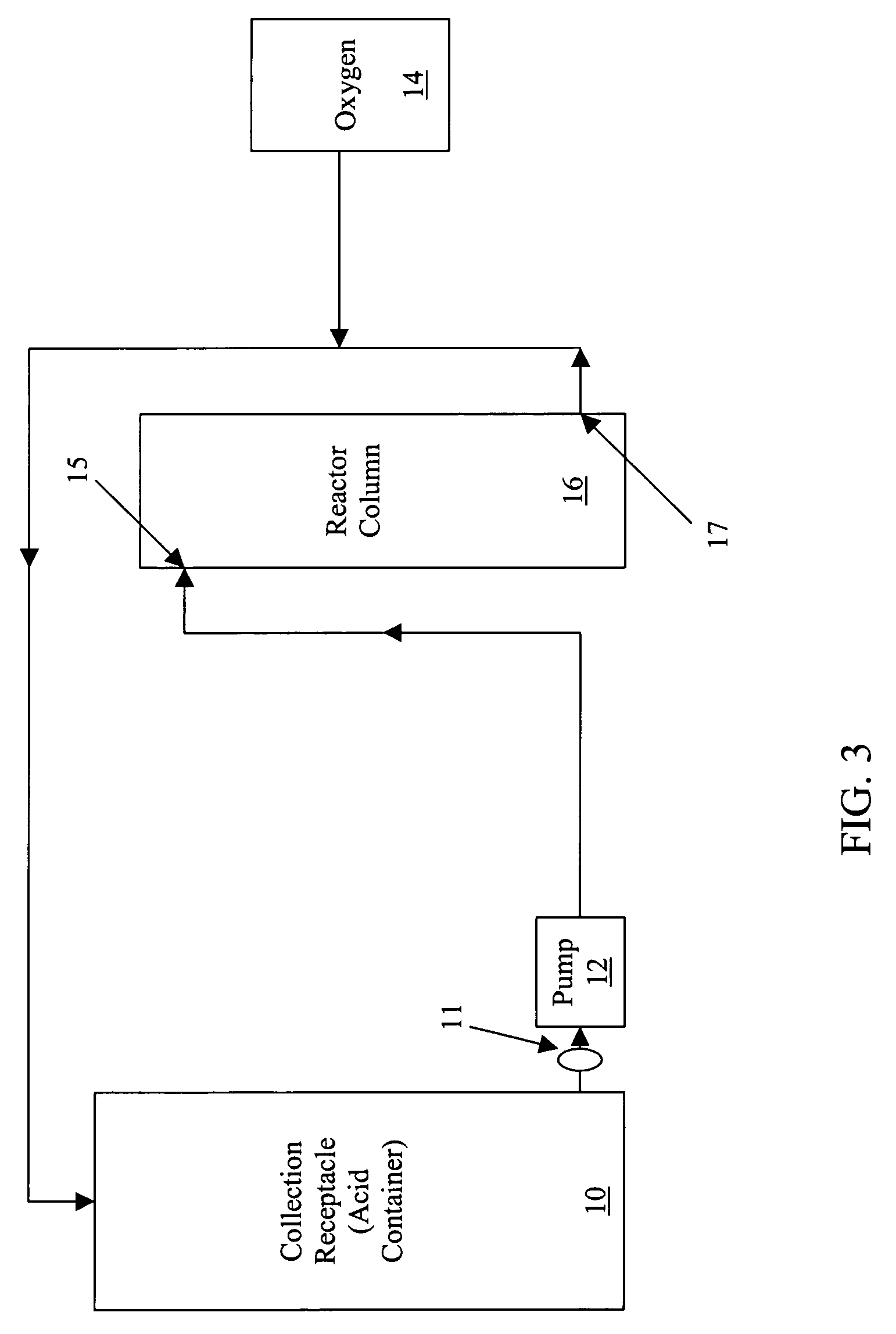
Process for converting nickel to nickel sulfate
A preferred embodiment of the present invention provides a process for making nickel sulfate by converting nickel metal into nickel sulfate, which may be converted to nickel hydroxide. Nickel metal is dissolved in sulfuric acid and oxygen containing gas is introduced to produce a nickel sulfate solution having nickel sulfate and water as illustrated in the following chemical equation.Ni+H2SO4+½O2→NiSO4+H2OThe nickel sulfate is filtered and sulfuric acid is continually added to maintain stoichiometry within a reactor until the nickel metal is dissolved. The sulfuric acid, oxygen containing gas and nickel metal may be heated to facilitate the desired reaction. Then, the nickel sulfate may be utilized to produce nickel hydroxide.
Owner:CHEVRON TECH VENTURES +1
Method for producing battery grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate by waste nickel cobalt alloy
ActiveCN108622943AMild responseReduce pollutionCobalt sulfatesNickel compounds preparationNew energyEvaporation
The invention discloses a method for producing battery grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate by waste nickel cobalt alloy. The method comprises the following steps of performing pretreatment on nickel cobalt alloy waste materials; then, performing electrochemical dissolution; removing impurities such as iron, chromium and aluminum from the obtained solution step by step by a chemical method andan extraction method; firstly extracting cobalt from the solution subjected to impurity removal; then extracting nickel; thus respectively obtaining extraction liquid containing cobalt and nickel; after the reverse extraction, obtaining nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate solution; then, respectively performing evaporation, cooling crystallization, and centrifugal dewatering on the solution to obtain a product of the battery grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate. The problems of low nickel and cobalt leaching efficiency, low dissolution speed and the like in the waste nickel and cobalt alloy recovery process by a conventional wet process can be effectively solved; the battery grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate conforming to the product quality standard requirement can be produced, andcan be used as a new energy source battery raw material to be applied to the field of new energy source battery manufacturing. The process is simple; the environment pollution is low; the metal recovery rate is high; good practical values and economic values are realized.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
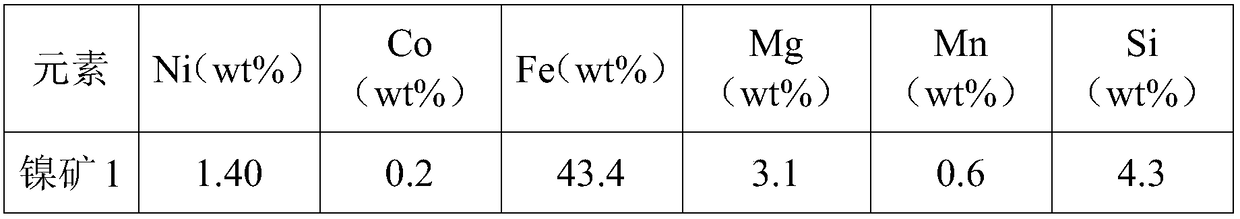
Wet treatment process of ferronickel material
ActiveCN111498918AReduce consumptionAvoid security issuesTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusSulfatePhysical chemistry
The invention provides a wet treatment process of a ferronickel material. The wet treatment process comprises the following steps: carrying out oxygen leaching treatment on ferronickel powder to obtain a nickel sulphate solution and a solid containing ferric oxide, wherein the oxygen leaching treatment comprises the steps that sulfuric acid and ferronickel powder are mixed to form a to-be-leachedsystem, an oxidizing agent and an enhancer are added into the to-be-leached system for oxidation leaching, ore pulp containing nickel sulfate and ferric oxide is obtained, and the enhancer is a compound containing SO2 groups. The oxidizing agent and the enhancer are added in the oxygen leaching treatment process, iron in the ferronickel powder is oxidized into ferric oxide by the oxidizing agent,then the ferric oxide is separated from a solution in a precipitation form, and nickel and sulfuric acid react to form nickel sulfate under the action of the enhancer. According to the wet treatment process, the consumption of sulfuric acid is low, no obvious bubbles are generated in the reaction process, it is indicated that no hydrogen is generated in the process, and the safety problem is effectively solved. Meanwhile, iron is precipitated in the form of iron oxide so as to be separated from nickel, and the iron oxide can be directly used as an iron oxide red product.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
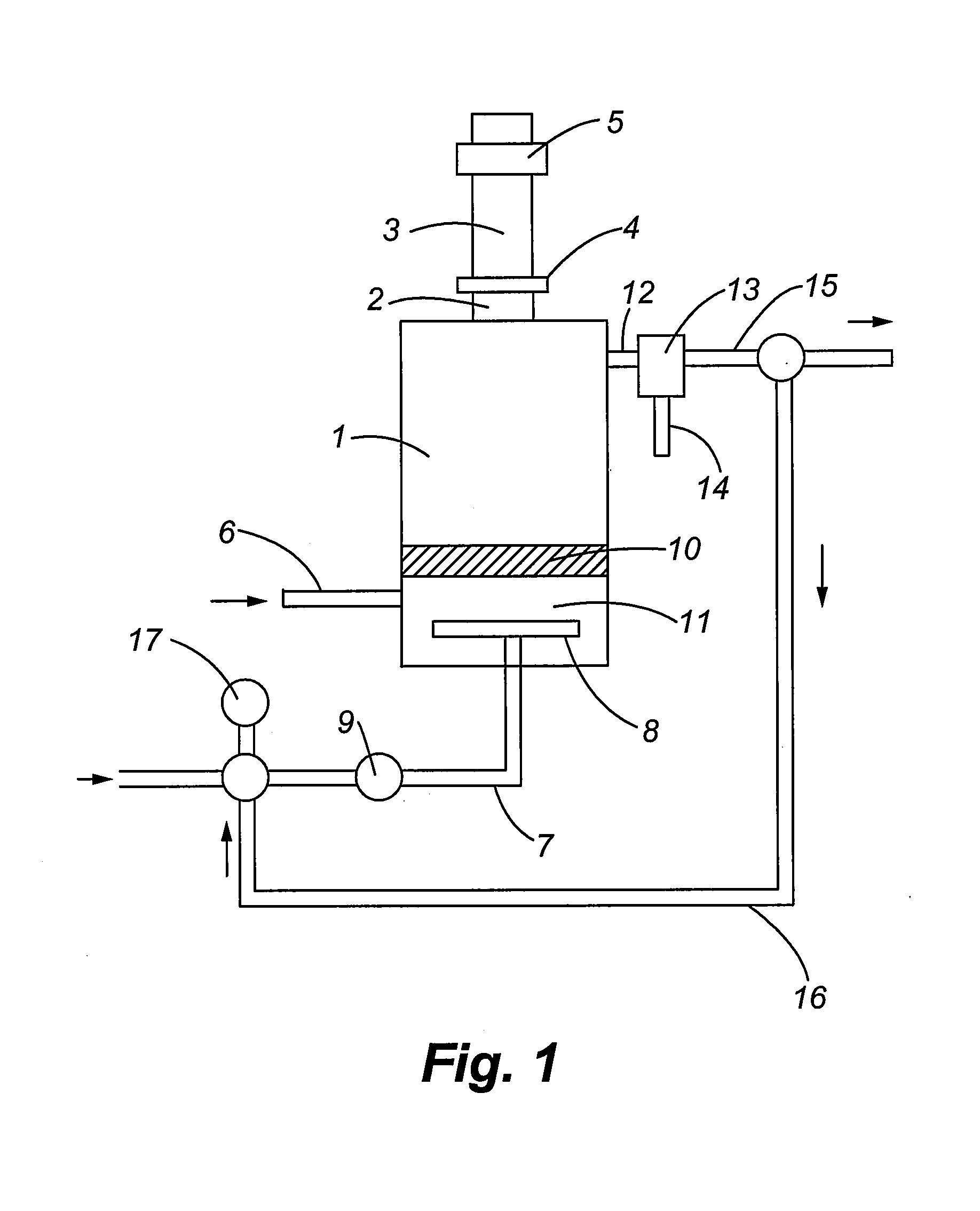
Easy-to-clean extraction device for extracting nickel sulfate from used batteries
InactiveCN106730993AEasy maintenance and repairEasy to operateHollow article cleaningLiquid solutions solvent extractionSulfateLiquid storage tank
The invention relates to an extraction device, and in particular relates to an easy-to-clean extraction device for extracting nickel sulfate from used batteries. The invention aims at providing an easy-to-clean extraction device for extracting nickel sulfate from used batteries. To achieve the aim, the invention provides the easy-to-clean extraction device for extracting nickel sulfate from used batteries that comprises a left liquid storage tank, a left liquid inlet pipe, a left valve, an extraction tank, a left liquid sprayer, a stirrer, a cleaner, a right liquid sprayer, a right liquid inlet pipe, a right valve, etc. The left liquid inlet pipe is connected to the left liquid storage tank. The left valve is arranged on the left liquid inlet pipe. The extraction tank is arranged on the right side of the left liquid inlet pipe. A hole is provided in a left sidewall of the extraction tank. The easy-to-clean extraction device for extracting nickel sulfate from used batteries provided in the invention has the stirrer and the cleaner that match to achieve thorough cleaning.
Owner:南昌浩牛科技有限公司
Consecutive or simultaneous leaching of nickel and cobalt containing ores
InactiveUS7871584B2Minimize equipment sizeIncrease consumptionCobalt ammonia complexesIron oxides/hydroxidesPregnant leach solutionSulfide
A process for the recovery of nickel and cobalt from nickel and cobalt containing ores, including the steps of first leaching a laterite ore and / or a partially oxidized sulfide ore with an acid solution to produce a pregnant leach solution containing at least dissolved nickel, cobalt and ferric ions, and subsequently leaching a sulfide ore or concentrate with the pregnant leach solution to produce a product liquor. Alternatively, the laterite ore and / or partially oxidized sulfide ore can be leached in a combined leach with the sulfide ore or concentrate. The ferric ion content in the pregnant leach solution or in the combined leach is sufficient to maintain the oxidation and reduction potential in the sulfide leach high enough to assist in leaching nickel from the sulfide ore or concentrate.
Owner:BHP BILLITON SSM TECH PTY LTD
Technology for recycling nickel sulfate from nickel slag
InactiveCN106756051AReduce generationSolution to consuming large amounts of acidNickel sulfatesProcess efficiency improvementSlagOxygen
The invention belongs to the technical field of resource recycling, and particularly relates to a technology for recycling nickel sulfate from nickel slag. The nickel slag is crushed into powder through a crusher; the powder is dissolved by adding a sulfuric acid solution, and filter liquor A is obtained through filtering after stirring; the obtained filter liquor A is cooled and crystallized, crude nickel sulfate crystals and mother liquor A are obtained, then pure water is used for dissolving the crude nickel sulfate crystals, and a solution B is obtained; hydrogen peroxide is added in the solution B or the solution B is inflated with oxygen, a sodium hydroxide solution is added for pH adjustment, sediments are removed through filtering, and a pure nickel sulfate solution is obtained; and the pure nickel sulfate solution is recrystallized, and nickel sulfate crystals and mother liquor B are obtained. The technology solves the problem of the reaction of excessive sulfuric acid and alkali, a large number of resources are saved, economic benefits are obvious, and environment pollution is effectively reduced.
Owner:山东飞源科技有限公司
Method and equipment for preparing electroplating-grade nickel sulfate from nickel-containing wastewater produced in surface treatment process
ActiveCN104229906AReduce carryoverReduce volumeMultistage water/sewage treatmentNickel sulfatesFiltrationSulfate
The invention discloses a method and equipment for preparing electroplating-grade nickel sulfate from nickel-containing wastewater produced in a surface treatment process, and belongs to the technical field of nickel-containing wastewater treatment process. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) collecting nickel-containing wastewater; (2) performing sedimentation and press filtration on nickel in the nickel-containing wastewater, and smashing nickel mud to obtain nickel slurry; (3) dissolving the nickel slurry into acid; (4) filtering a nickel sulfate solution; (5) removing impurities from the nickel sulfate solution for purification, and performing secondary filtration; (6) performing vacuum evaporative concentration, crystallization, filtration and centrifugal drying on the nickel sulfate solution to obtain nickel sulfate crystals. The invention aims to provide the method and the equipment which can reduce the waste of nickel resources, reduce potential hazard of nickel to the natural environment and realize recycling of the nickel resources and are used for preparing the electroplating-grade nickel sulfate from the nickel-containing wastewater produced in the surface treatment process. The method and the equipment are used for treating the nickel-containing wastewater.
Owner:MEIZHOU ENVIRONMENTAL EQUIP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com