Self-adaptive sum-difference angle measurement method for plane phased array
An adaptive, planar phase technology, applied in measuring devices, radio wave measurement systems, radio wave reflection/re-radiation, etc., can solve the problems of target signal attenuation, inability to estimate target angle, increase target angle error, etc., to achieve The effects of enhancing the target signal, improving the performance of anti-mainlobe interference, and improving the accuracy of angle measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
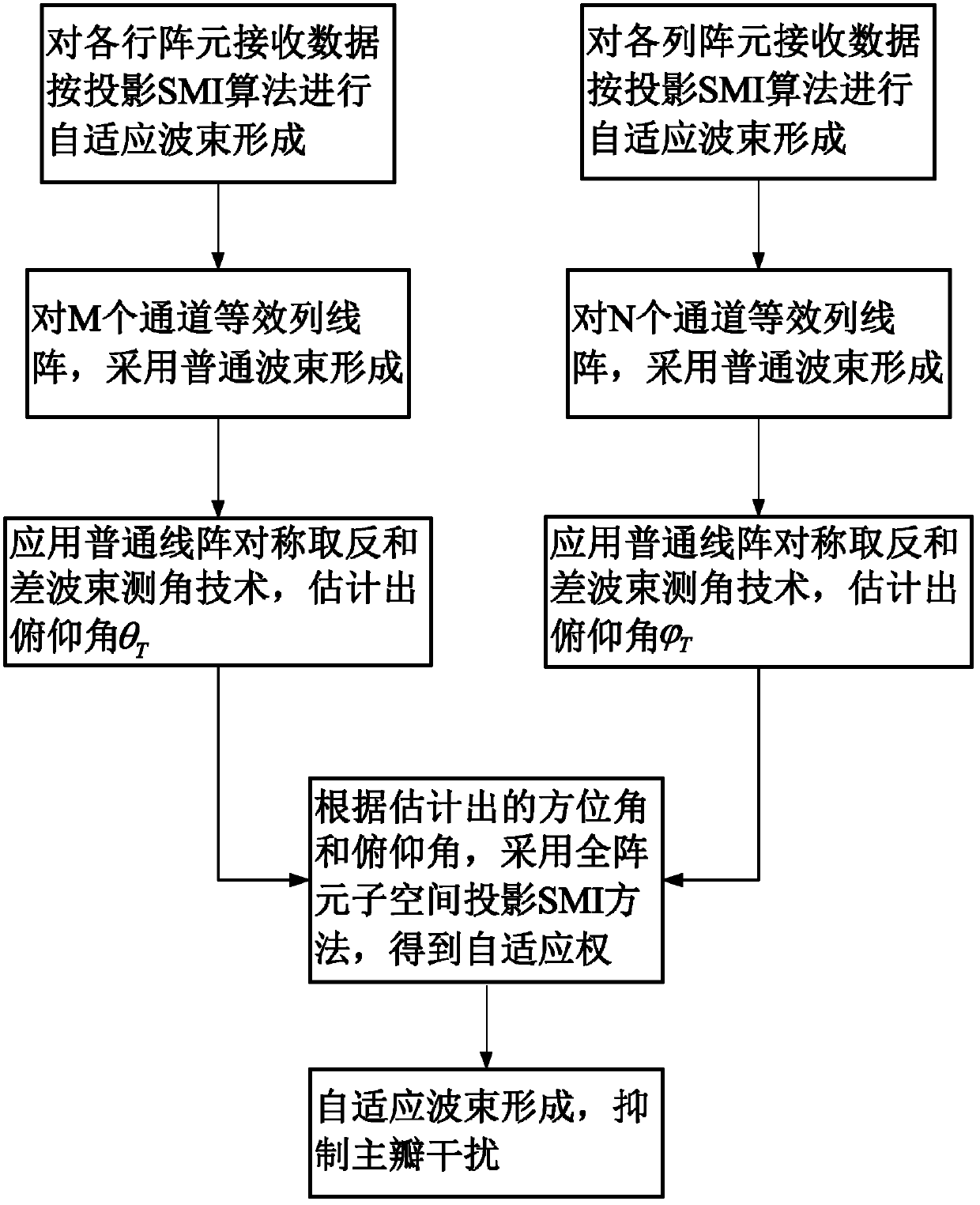
[0024] refer to figure 1 , realize the steps of the present invention as follows:
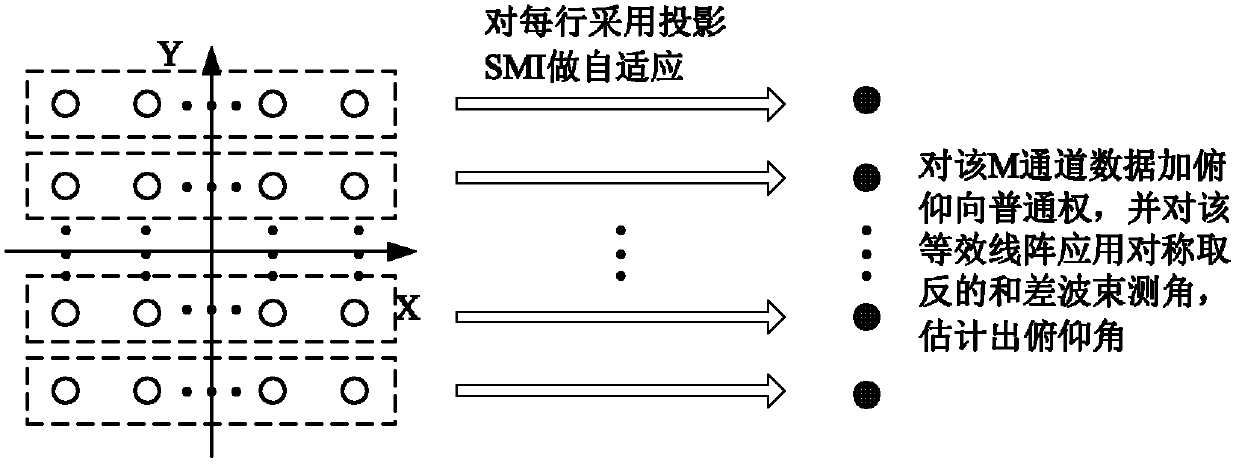
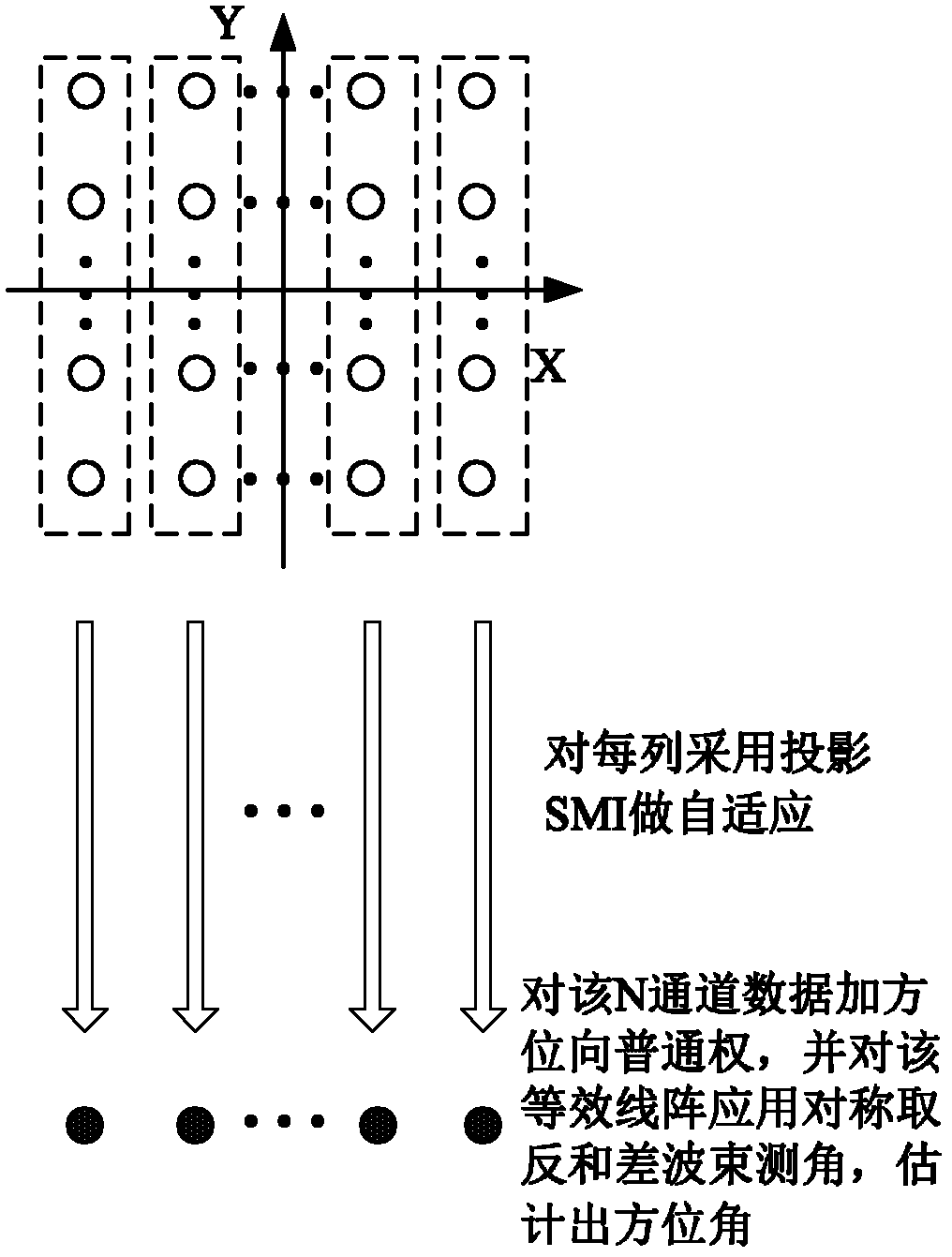
[0025] Step 1 performs adaptive beamforming on the received data of each row of array elements, and its output forms an equivalent linear array in the Y direction.
[0026] refer to figure 2 , this step is specifically implemented as follows:
[0027] (1a) Denote the received data of each row of array elements in the planar array as x r_k (t), where k=1, 2, ... M, first fix k=1, means to process the received data of the first row, and then use the sampling values of 128 times at different times to estimate the received data x of the row array element r_k The covariance matrix of (t): in,(·) H Indicates matrix conjugate transpose, K=128, x r_k (t i ), i=1, 2, ..., K represents the sampling value of each row of array elements at different times;
[0028] (1b) Covariance matrix of row array elements Carry out eigendecomposition, decompose it into the multiplication and accumulation f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com