Patents
Literature
42 results about "Conductive atomic force microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
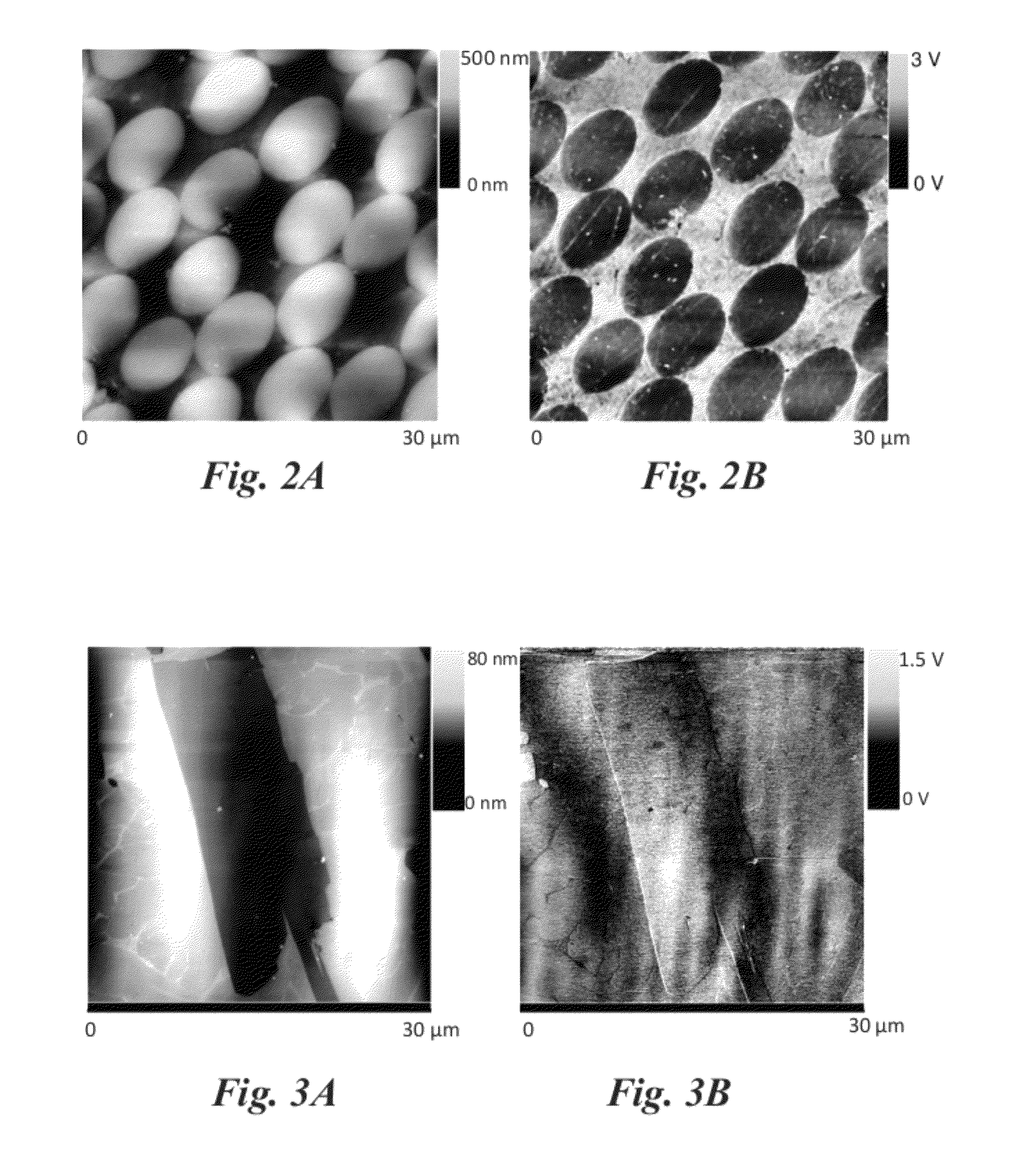
Conductive atomic force microscopy (C-AFM) or current sensing atomic force microscopy (CS-AFM) is a mode in atomic force microscopy (AFM) that simultaneously measures the topography of a material and the electric current flow at the contact point of the tip with the surface of the sample. The topography is measured by detecting the deflection of the cantilever using an optical system (laser + photodiode), while the current is detected using a current-to-voltage preamplifier. The fact that the CAFM uses two different detection systems (optical for the topography and preamplifier for the current) is a strong advantage compared to scanning tunneling microscopy (STM). Basically, in STM the topography picture is constructed based on the current flowing between the tip and the sample (the distance can be calculated depending on the current). Therefore, when a portion of a sample is scanned with an STM, it is not possible to discern if the current fluctutations are related to a change in the topography (due to surface roughness) or to a change in the sample conductivity (due to intrinsic inhomogeneities).
Probe of conducting atomic force microscope and measuring methods employing probe
ActiveCN102353817AImprove conductivityLow carrier injection potentialElectrical testingScanning probe microscopyMagnetic force microscopeConductive atomic force microscopy
The invention relates to a probe of a conducting atomic force microscope. The probe comprises: a substrate of a cantilever probe; a needle tip; and a conductive film, which is arranged at a surface of the needle tip. Besides, the material of the conductive film is graphene. Moreover, the invention provides a method that employs the probe to measure local conductivity of a semiconductor and a needle tip-free near-field optical detection method that employs the probe to measure a terahertz wave band. According to the invention, graphene is utilized, wherein the grapheme has the following characteristics that: the graphene is composed of carbon atoms and is thin to a monatomic layer; and the graphene is a semimetal two-dimensional thin material that has a zero gap; besides, the probe has advantages of good conductivity and high electron mobility; moreover, a Fermi surface can carry out self-adjustment with charging and discharging motions and a carrier injection potential is low. In addition, an electronic plasmon oscillating frequency of the graphene is just at a terahertz wave band; and the graphene has soft materials and strong stability on thermodynamics. The above-mentioned statements are physical bases on which the graphene is utilized to replace a traditional metal material as a plated film of a surface of an atomic force microscope probe, so that the above-mentioned limitations are broken through.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Preparation method of graphene complex based humidity sensor
ActiveCN101793856ASimple methodRealize fixed-point positioning measurementMaterial resistanceConductive atomic force microscopyMetal electrodes
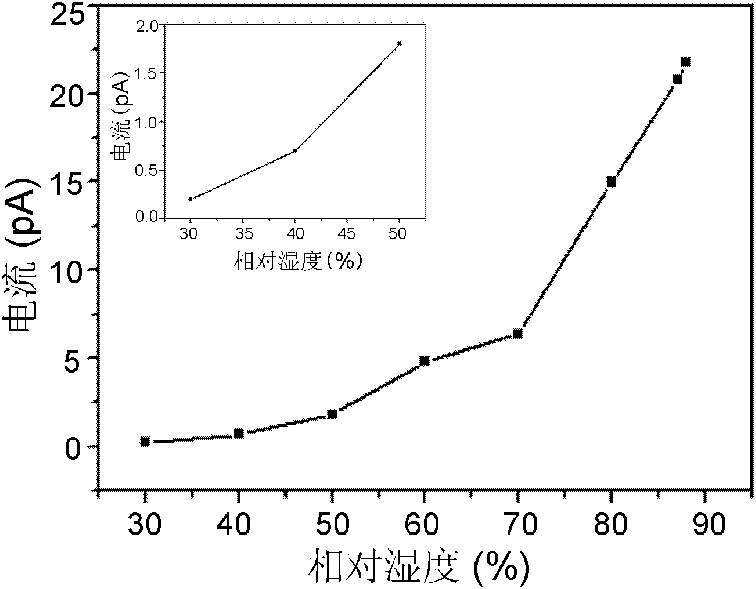
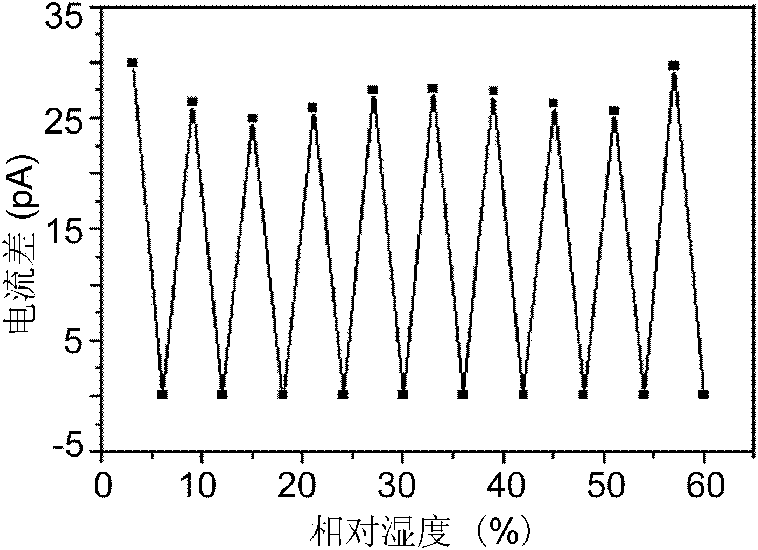
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene complex based humidity sensor in the technical field of nano materials. The humidity sensor is prepared through the following steps of: diluting a polyvinylpyrrolidone-graphene complex, coating on the surface of a substrate by spinning in the form of a single-layer film, electroplating a layer of metal electrodes on the single-layer film, and finally drying under vacuum. In the invention, by adopting the favorable hygroscopicity and the conductivity of the polyvinylpyrrolidone-graphene, a single-layer film of a humidity sensitive complex is formed on the surface of the substrate by using a spin coating method, and the sensitivity of the complex to the humidity is detected through an I-V curve measured by a conducting atomic force microscope at different humidities.
Owner:上海碳源汇谷新材料科技有限公司
Vacuum atomic force microscope and using method thereof
InactiveCN101625303ASolving Design DifficultiesRealize continuous measurementSurface/boundary effectInstrumental componentsMagnetic force microscopeConductive atomic force microscopy
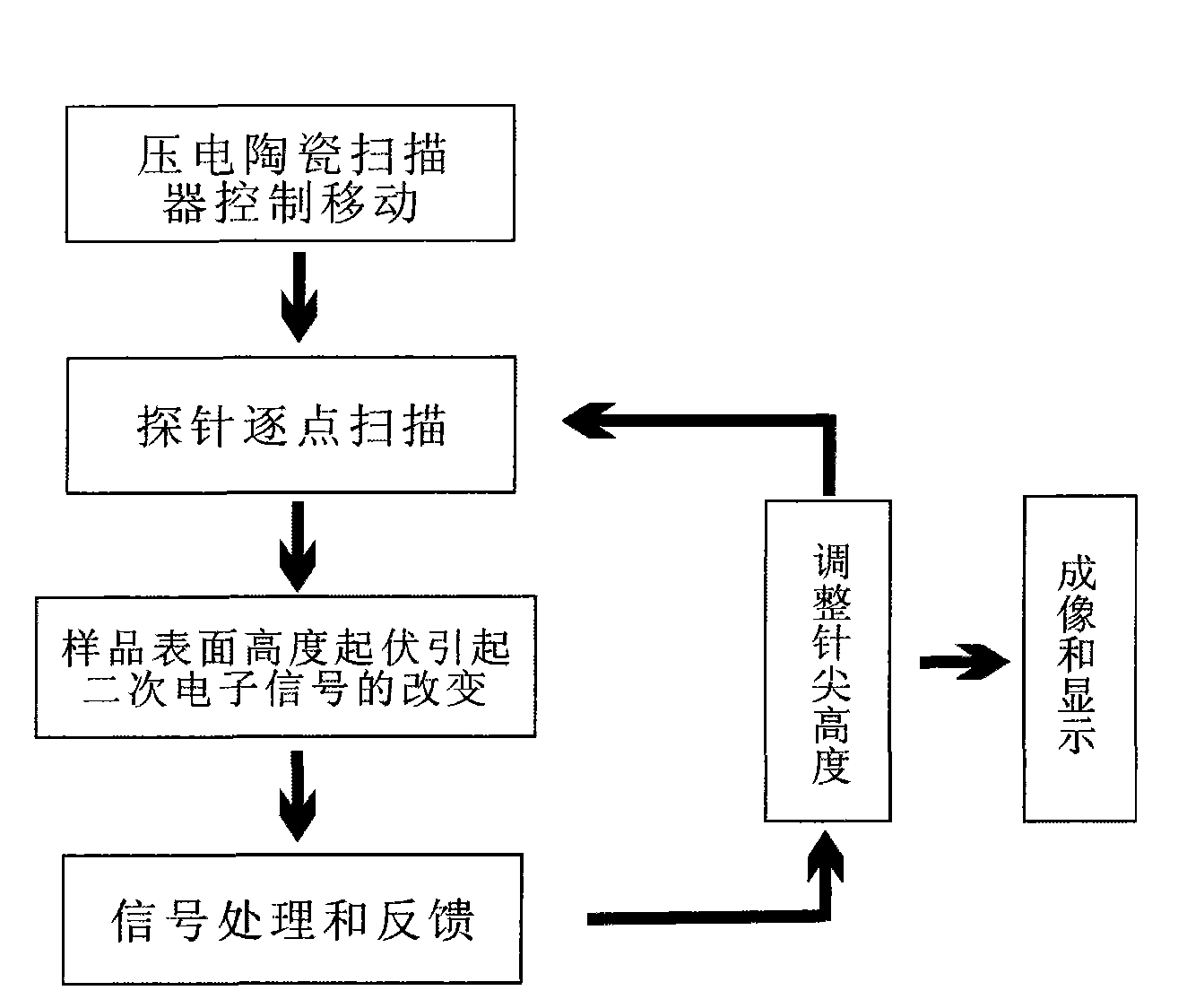
The invention discloses a vacuum atomic force microscope and a using method thereof, belonging to the field of micro-topography detecting equipment; the microscope comprises an electron beam launching device, a secondary electron detector, a probe with a cantilever, a piezoelectric ceramics scanner and a feedback controller. When in work, electron beams are irradiated to the cantilever of the probe; as the acting force between the probe and sample atoms causes the cantilever to become deformed; a secondary electron signal changes; the acting force between a pinpoint and the sample is controlled to be constant by the signal feedback; the pinpoint scans the surface of the sample point by point and can image surface topography of the sample. The currently common optical lever does not need to be drawn into the invention; the invention overcomes design difficulty brought about by the conventional atomic force microscope applied in vacuum environment, synthesizes two nanophase material characterization methods which are the advantages of the atomic force microscope and an electronic microscope, and can realize the continuous measuring on the material from millimeter size to the sub-nanometer size.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Preparation of silver nanometer electrodes
InactiveCN1681095AAtomic level flatteningImprove hydrophilicityNanostructure manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive atomic force microscopyOrganic solvent
The method includes following steps: (1) preparation of self-assembly substrate, offering a P type Si(100) substrate that is treated by ultrasonic in organic solvent; after treated by placing into Piranha solution, and it is dried by blowing non-oxidizability gas, and then is treated by OTS solution and is cleaned up by using organic solvent; (2) nano-line etching, the nano-line is etched on self assembly substrate by using current of conduct atomic force microscope, the radius of curvature of pinpoint is less than 50 nm; (3) nanometer generating, the etched substrate is placed in the silver acetate for dipping, and then is taken out to place in ethanol in short time, and then is placed in sodium borohydride aqueous solution for dipping, washing, and then is dried by blowing non-oxidizbility gas, finally the silver enhancement solution is inputted for heighten the electrode line.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Periodic stripe domain structure of ferroelectric thin film and method for characterizing same
ActiveCN110634871ALarge polarization valueImprove ferroelectric propertiesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesMicro nanoConductive atomic force microscopy
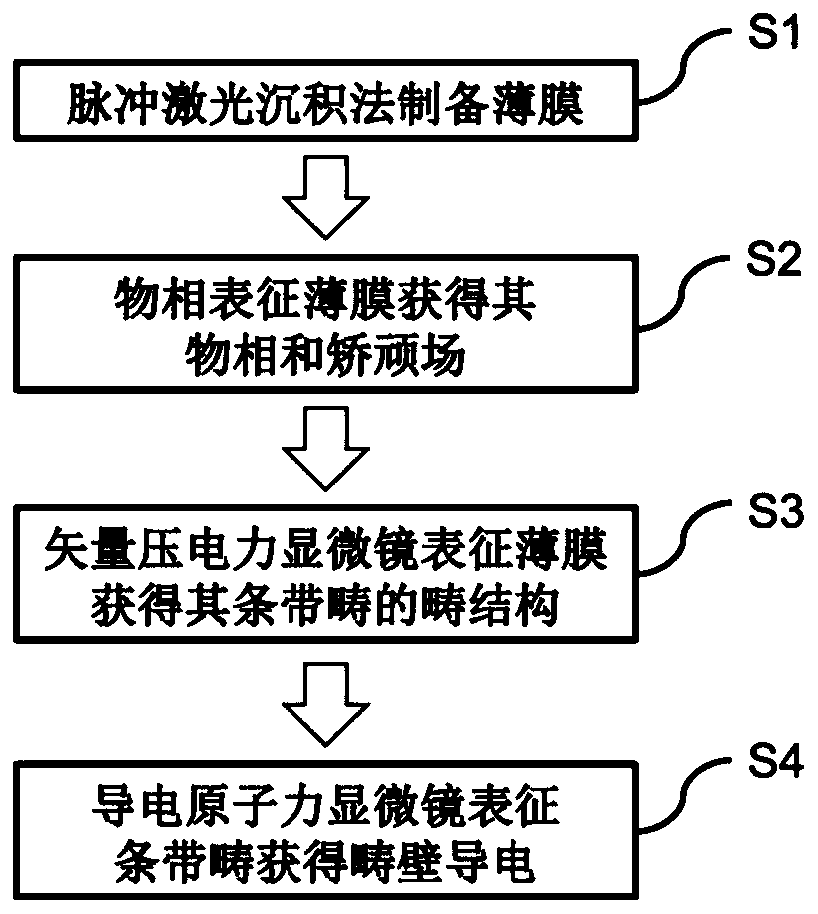
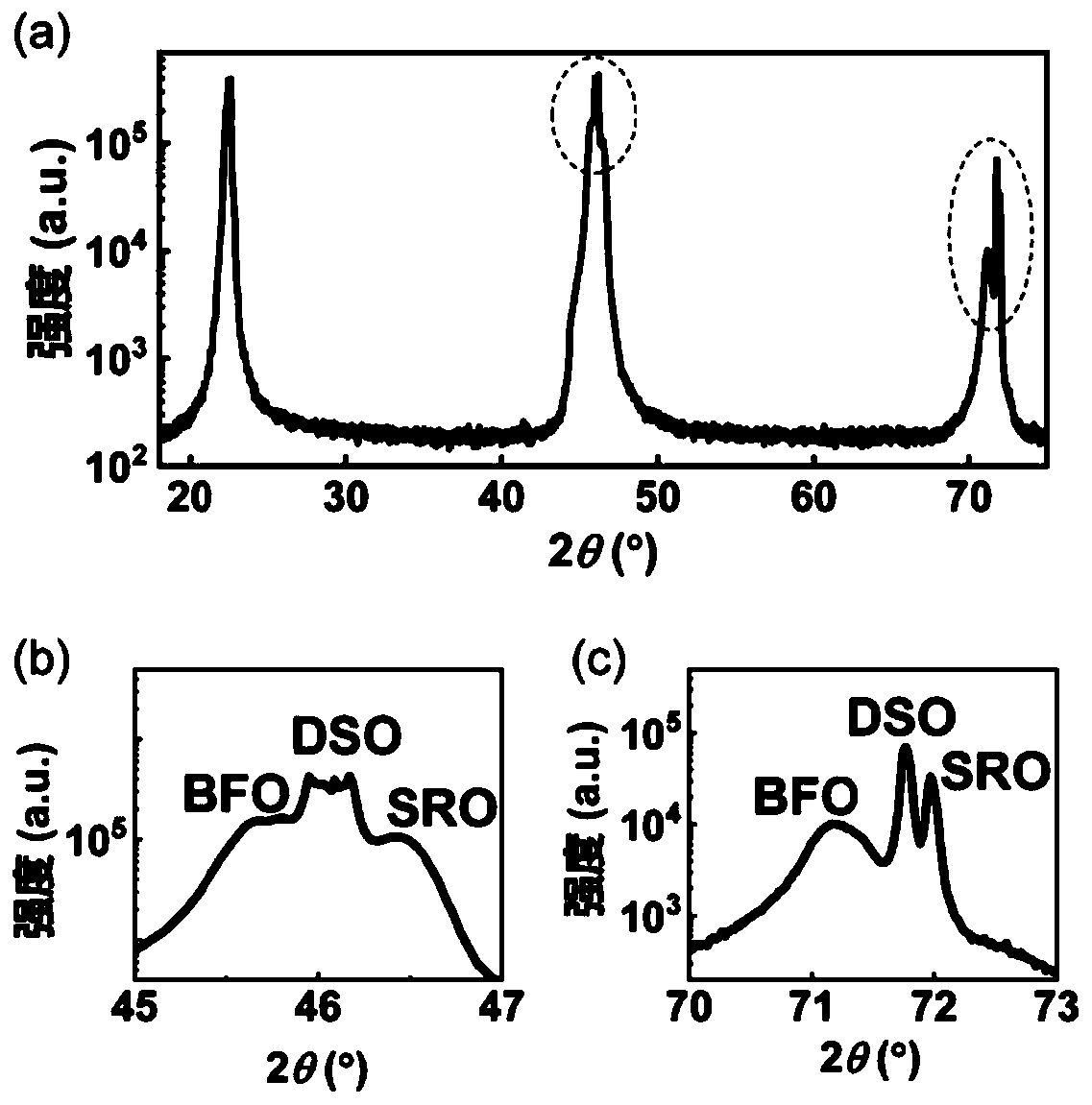
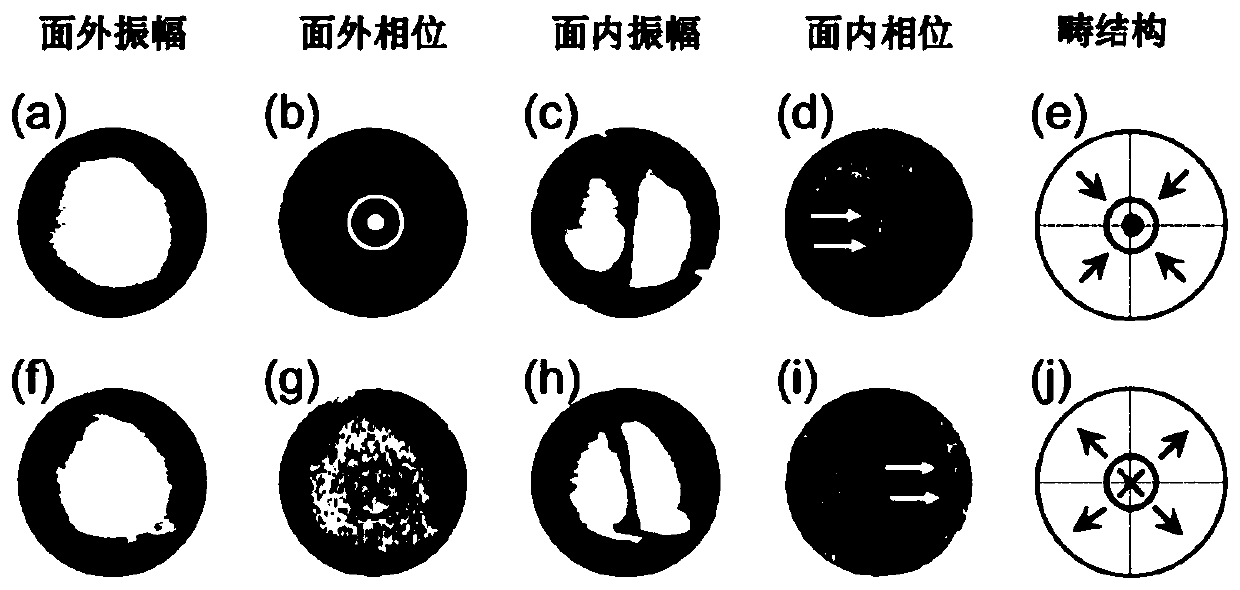
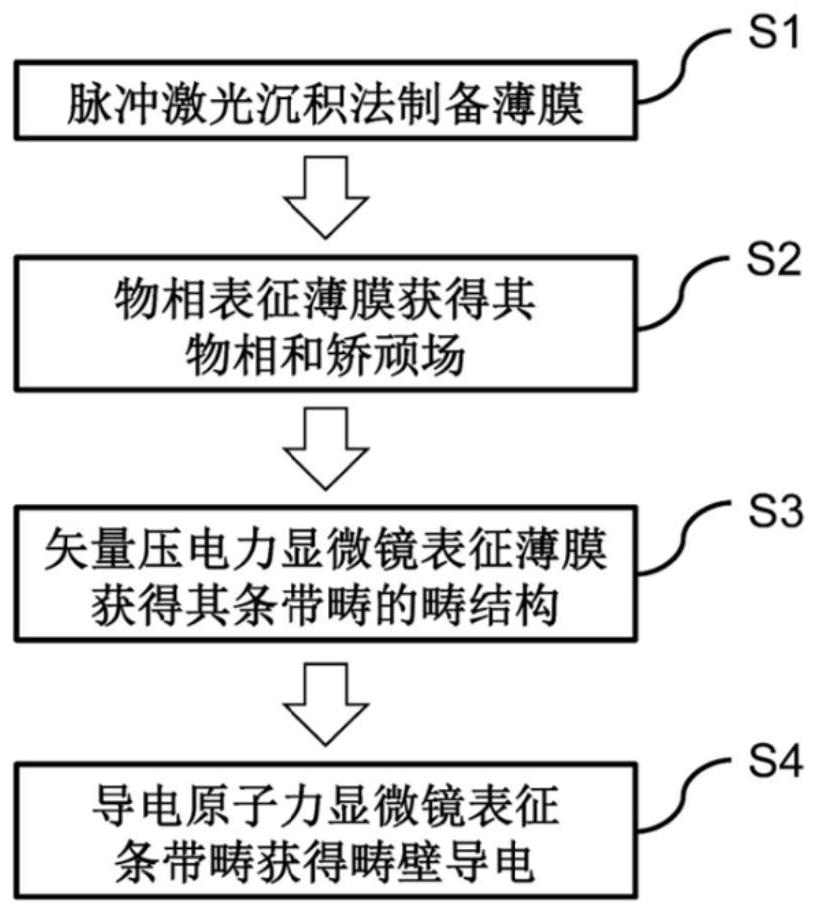
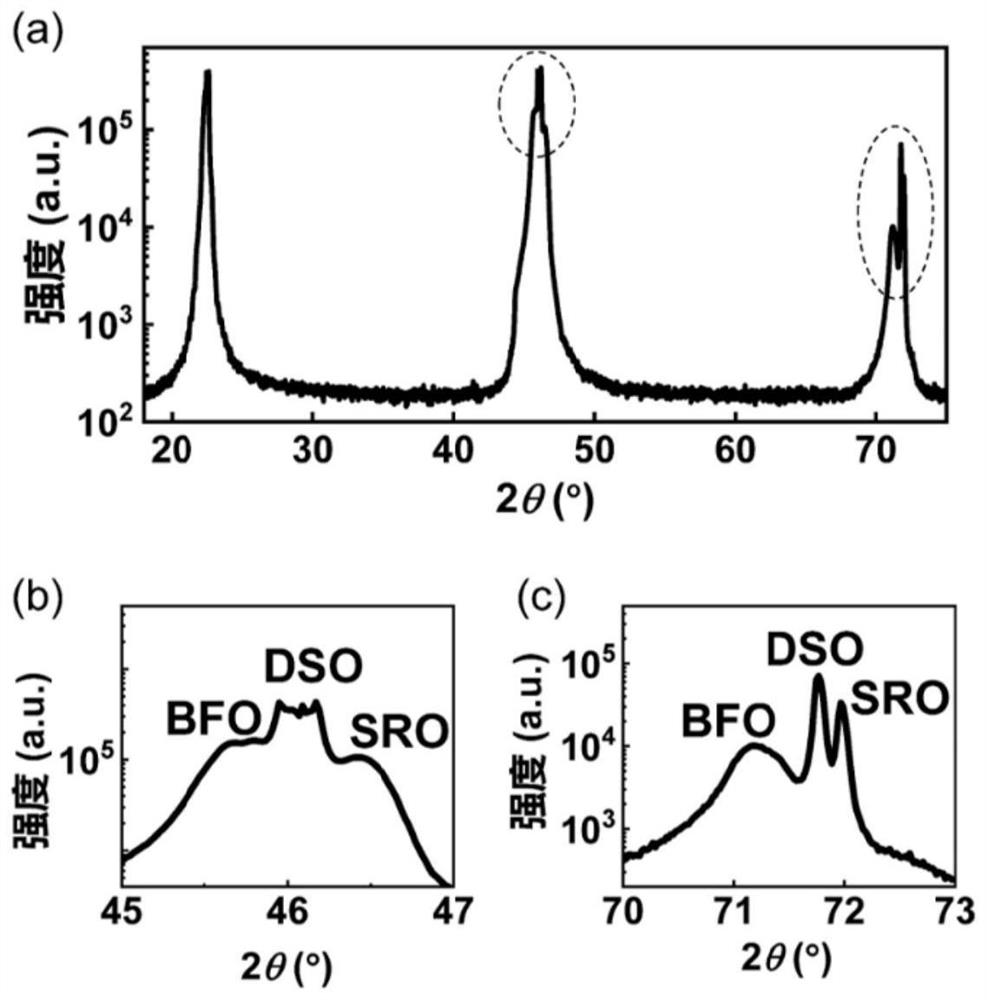
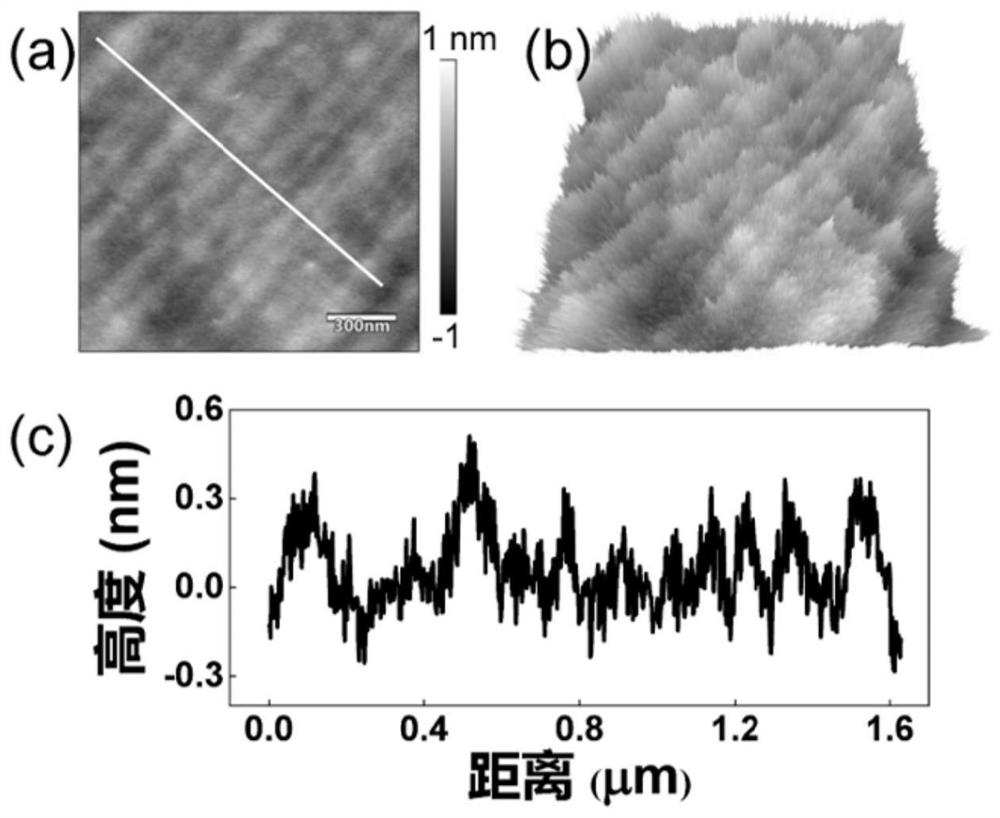
The invention discloses a periodic stripe domain structure of a ferroelectric thin film and a method for characterizing the same and belongs to the technical field of micro-nano characterization. Themethod includes the following steps: preparing a bismuth ferrite thin film by pulsed laser deposition; characterizing the lattice constant of the bismuth ferrite thin film by an X-ray diffraction instrument, determining the bismuth ferrite thin film to be a rhombus phase structure, confirming good ferroelectricity and coercive voltage of the bismuth ferrite thin film by a piezoelectric butterfly curve, and characterizing the shape of the bismuth ferrite thin film by atomic force microscopy; characterizing the periodic stripe domain in the nano-ferroelectric thin film by vector piezoresponse force microscopy, and determining the three-dimensional structure of the ferroelectric thin film by a fine vector piezoelectric microscopy analytical method; and observing the conduction of the domain wall of the stripe domain by using conductive atomic force microscopy. The method for preparing the ferroelectric thin film provided by the present invention can be used for a nonvolatile and high-density ferroelectric random access memory. Further, the provided characterization method can accurately provide the three-dimensional domain structure and the domain wall conduction of the periodic stripe domain, and provides a solution for the development of high-density ferroelectric memory devices and characterization detection.
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Electrically-induced reduction method for degraded graphene oxide
The invention belongs to the technical field of manufacturing for carbon-based integrated circuit, and particularly relates to a reduction method for degraded graphene oxide. The reduction method for degraded graphene oxide disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: performing controllable reduction on a graphene oxide on a conductive substrate by a contact probe electrically-induced reduction method; and controlling the ingredients of the reduced graphene oxide by controlling the voltage applied by the probe of a conductive atomic force microscopy, thereby controlling the resistivity of the reduced graphene oxide. The method for reducing a graphene oxide by a conductive contact probe is a novel method for reducing a graphene oxide, and the method can be directly applied to preparation for planar device with nanoscale, thereby greatly simplifying the complexity of preparation for the device. Additionally, the method can also be used as basic machining process for grapheme-based electronic device.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for measuring mobility of graphene microcell with semiconductor as substrate
ActiveCN107037284AAccurate evaluationElectrical testingConductive atomic force microscopyWork function
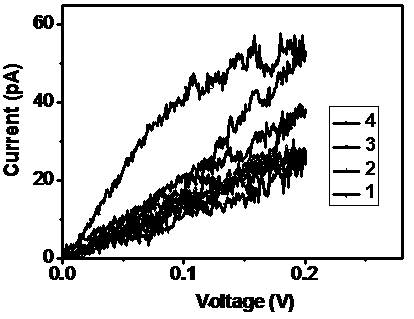
The invention provides a method for measuring the mobility of a graphene microcell with a semiconductor as a substrate. The method comprises steps of coating the surface of the semiconductor substrate with graphene to form a graphene microcell and disposing a conductive probe in contact with the graphene microcell; connecting the conductive probe with a scanning Kelvin probe force microscope to measure the actual work function of the graphene microcell to obtain a barrier height [Phi]Bn0 between the graphene microcell and the semiconductor substrate; connecting the conductive probe with a conductive atomic force microscope to collect a current-voltage curve of the graphene microcell; analyzing and fitting the current-voltage curve according to the barrier height [Phi]Bn0 between the graphene microcell and the semiconductor substrate and a hot electron emission model to obtain the effective contact radius of the conductive probe and the graphene microcell; and calculating the value of the graphene microcell mobility [mu] based on the effective contact radius of the conductive probe and the graphene microcell and the actual contact radius. The method can measure the mobility of the graphene microcell with any semiconductor as the substrate.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Electrical atomic force microscope probe adopting conductive nanowires
InactiveCN107782919ASolve bottlenecksIncrease horizontal resolutionScanning probe microscopyNanowireConductive atomic force microscopy
The invention discloses an electrical and conductive atomic force microscope probe using conductive nanowires and a preparation method thereof, which solves the bottleneck problem of the current electrical and conductive atomic force microscope probe, and greatly improves the service life and resolution of the atomic force microscope probe. The conductive nanowire probe can be prepared by direct bonding method and chemical vapor deposition growth method. Fully utilizing the ultra-high resolution and ultra-long service life of the conductive one-dimensional nanomaterial probe, it solves the long-term problems of short life and easy wear of the electrical and conductive atomic force microscope probes, improves the consistency of the test, and meets It meets the needs of different application fields such as scientific research, production and teaching.
Owner:苏州泰岩新材料有限公司
Method for detecting photoelectric current signal of photoelectric conversion material via conductive atomic force microscope
ActiveCN106546771ASuppress unwanted noiseImprove detection signal-to-noise ratioScanning probe microscopyConductive atomic force microscopyPower flow
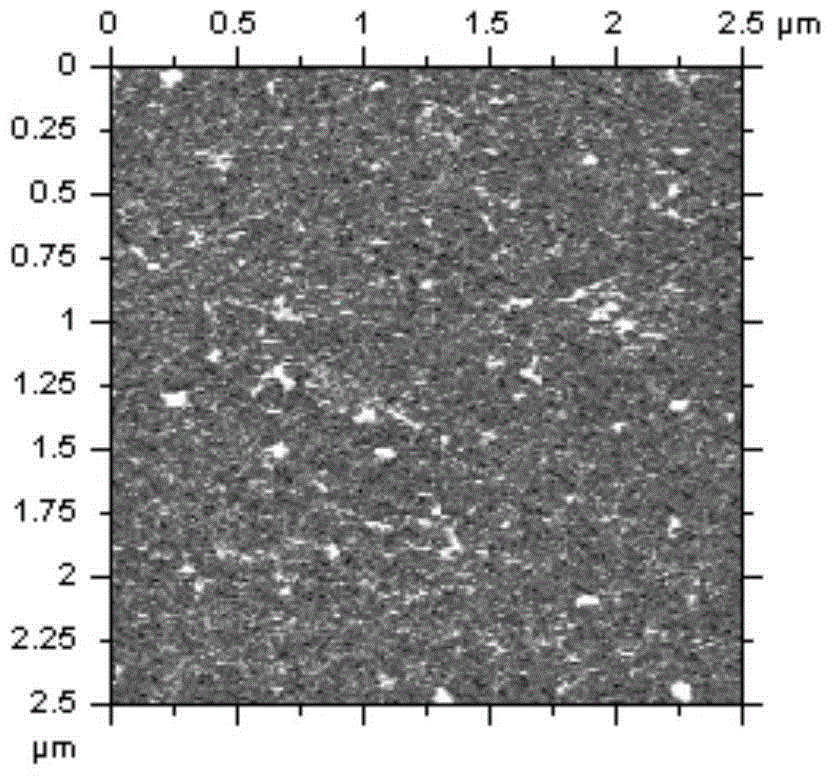
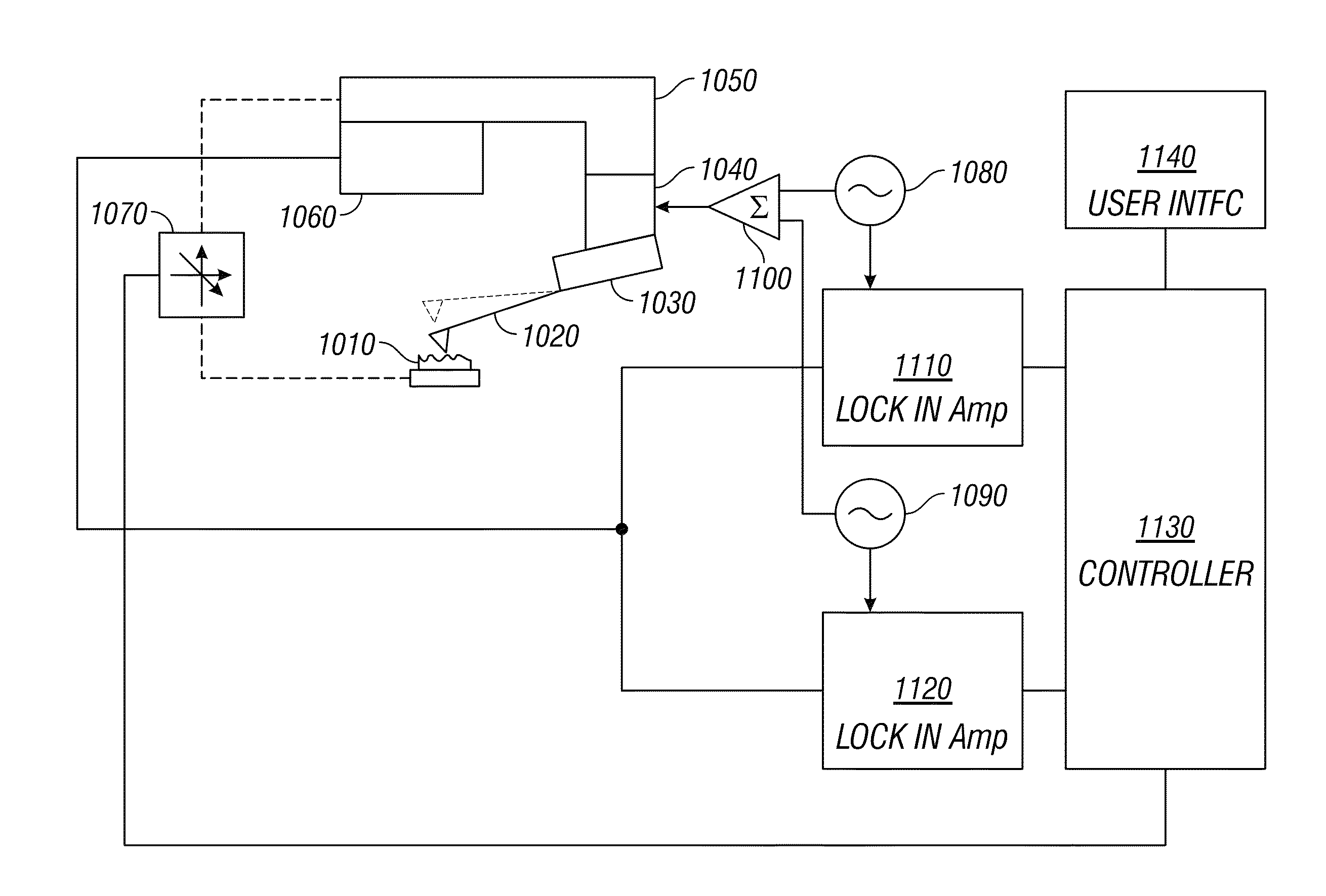
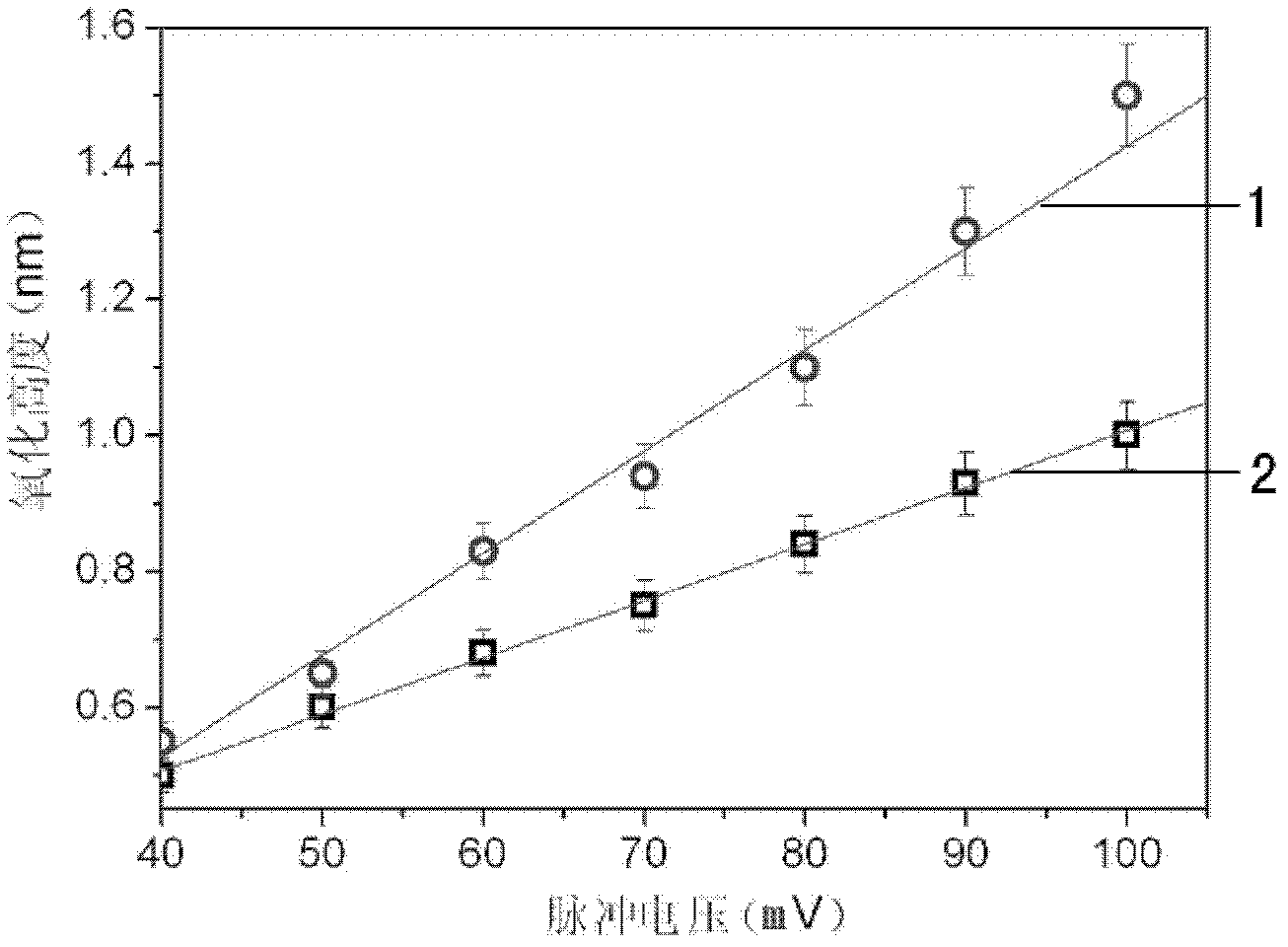
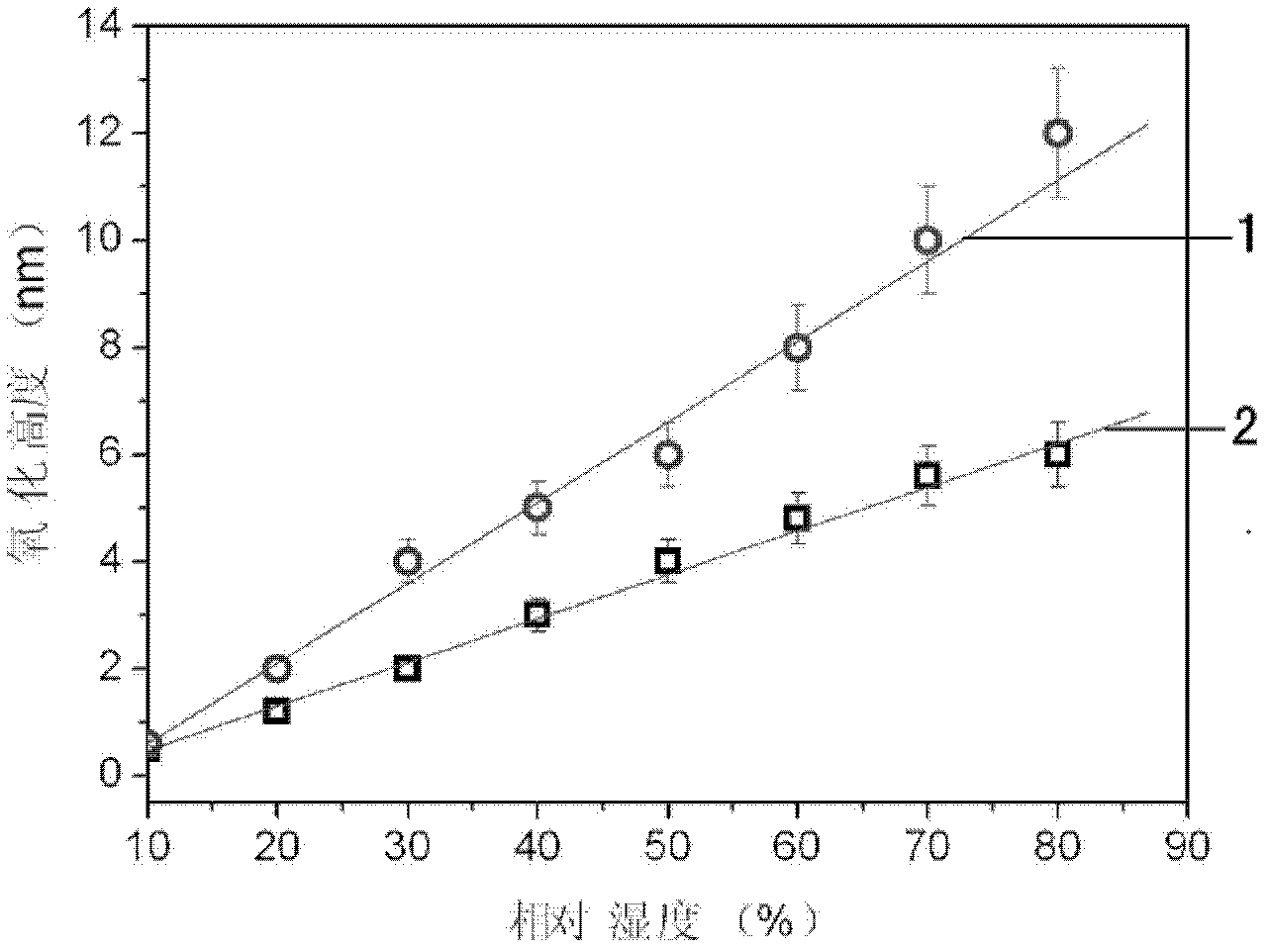
The invention provides a method for detecting a photoelectric current signal of a photoelectric conversion material via a conductive atomic force microscope. A lock-in amplifier is used, the lock-in amplifier provides an alternating driving voltage so that a light source is driven to emit light to irradiate a material sample, the sample generates an optical current due to a photoelectric conversion effect, a conductive probe makes contact with the sample to detect the photoelectric current signal and transmits the photoelectric current signal to a current amplifier to obtain a current amplification signal, and the current amplification signal is then input to the lock-in amplifier. Thus, the frequency of a reference signal of lock-in amplification is the same with that of the driving voltage, lock-in amplification of the photoelectric current signal is realized, and the sensitivity and signal to noise ratio of photoelectric current detection are improved.
Owner:宁波新材料测试评价中心有限公司
Thermal measurements using multiple frequency atomic force microscopy
ActiveUS8677809B2NanotechnologyMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsElectricityConductive atomic force microscopy
Apparatus and techniques for extracting information carried in higher eigenmodes or harmonics of an oscillating cantilever or other oscillating sensors in atomic force microscopy and related MEMs work are described. Similar apparatus and techniques for extracting information from piezoelectric, polymer and other materials using contact resonance with multiple excitation signals are also described.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR ASYLUM RES INC
Solid barrier needle point contact type scanning tunnel microscope
ActiveCN106226560AHigh hardnessChange widthScanning probe microscopyConductive atomic force microscopyScanning tunneling microscope
The invention discloses a solid barrier needle point contact type scanning tunnel microscope. A conductive probe is formed by a conductive probe body and a conductive needle point arranged on the free end of the conductive probe body, wherein at least one layer of solid dielectric film is covered on the conductive needle point to form a solid barrier needle point. During an imaging process, the height of a sample bench or / and a probe bench is adjusted to allow the solid barrier needle point to scan in a way of contacting a sample, and the obtained tunneling current passing through the solid barrier needle point is input to a scanning tunnel microscope testing system and / or the current amplification circuit of a conductive atomic force microscope testing system. Obtained output and corresponding coordinate information of the tunneling current are input to the scanning tunnel microscope testing system and / or a data processing and imaging module of the conductive atomic force microscope testing system, and the electronic state density distribution information of a sample surface is obtained. The novel working mode of the scanning tunnel microscope is created, the anti-vibration capability and success rate are high, the cost is low and the resolution is high.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
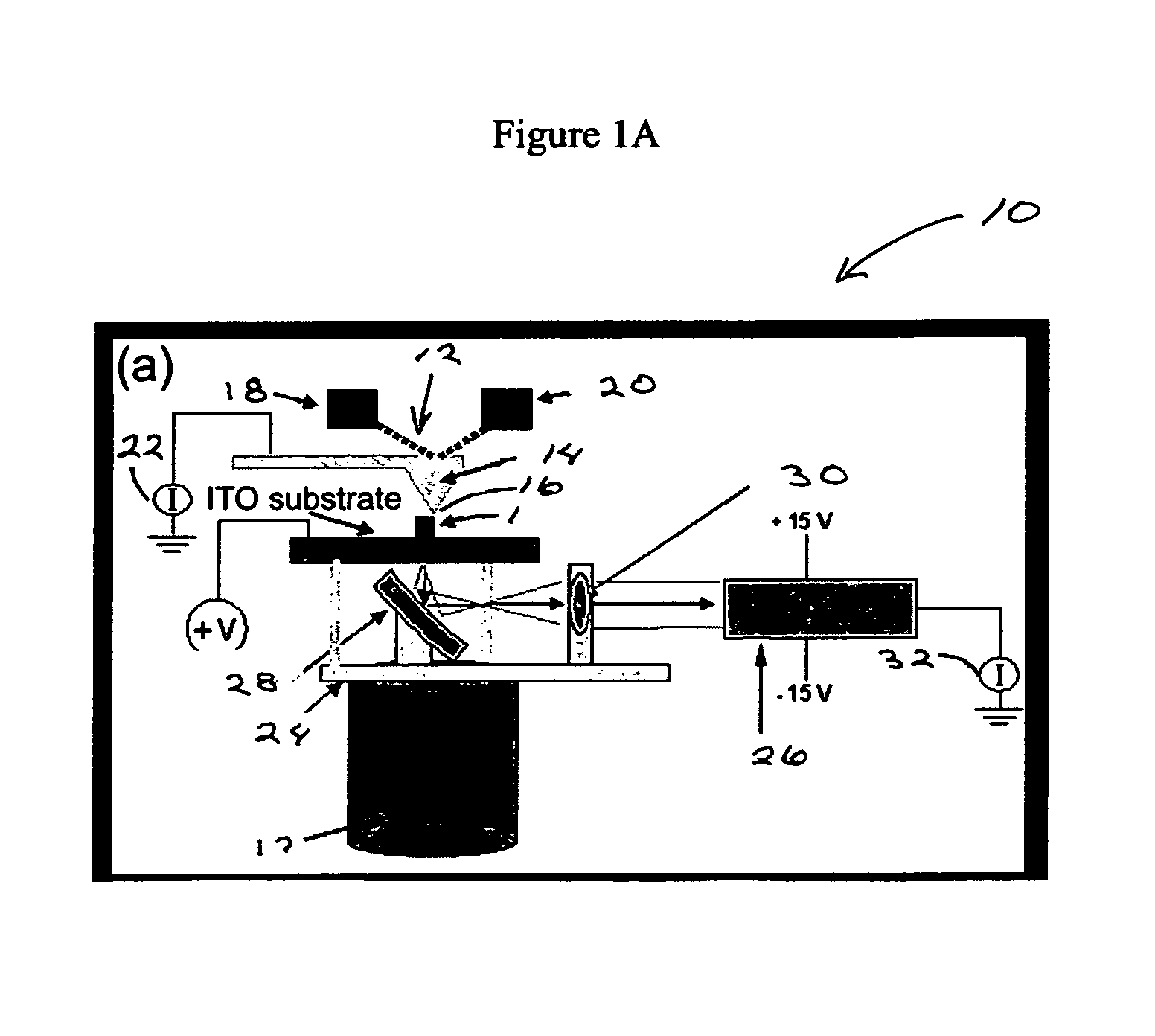
Methods and apparatus of spatially resolved electroluminescence of operating organic light-emitting diodes using conductive atomic force microscopy
InactiveUS7358490B1Effective characterizationNanotechMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSpatially resolvedElectricity
A conductive atomic force microscopy (cAFM) technique which can concurrently monitor topography, charge transport, and electroluminescence with nanometer spatial resolution. This cAFM approach is particularly well suited for probing the electroluminescent response characteristics of operating organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) over short length scales.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
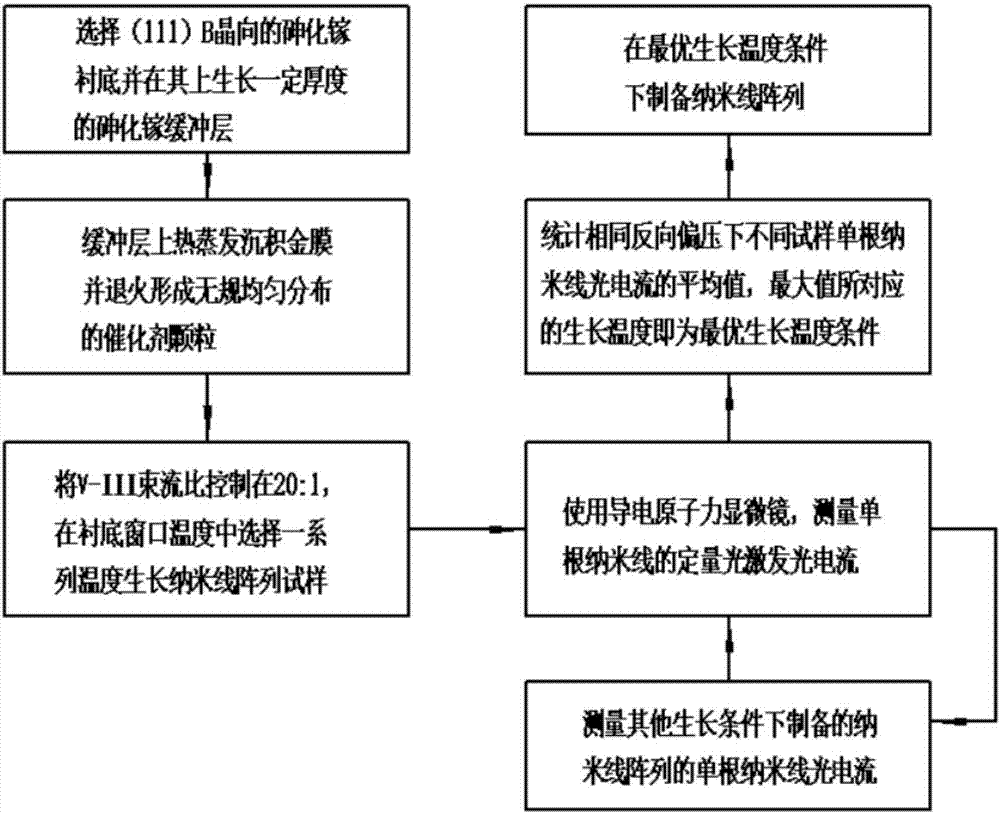
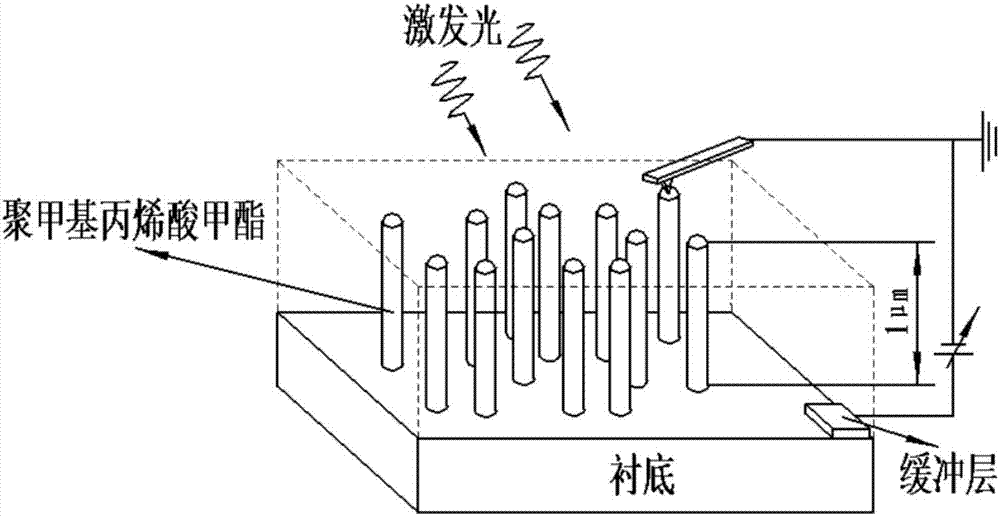
Preparation method of semiconductor nanowire array with optimal photoelectric efficiency
InactiveCN107248537AEasy to prepareStrong controllabilityMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive atomic force microscopyEvaporation
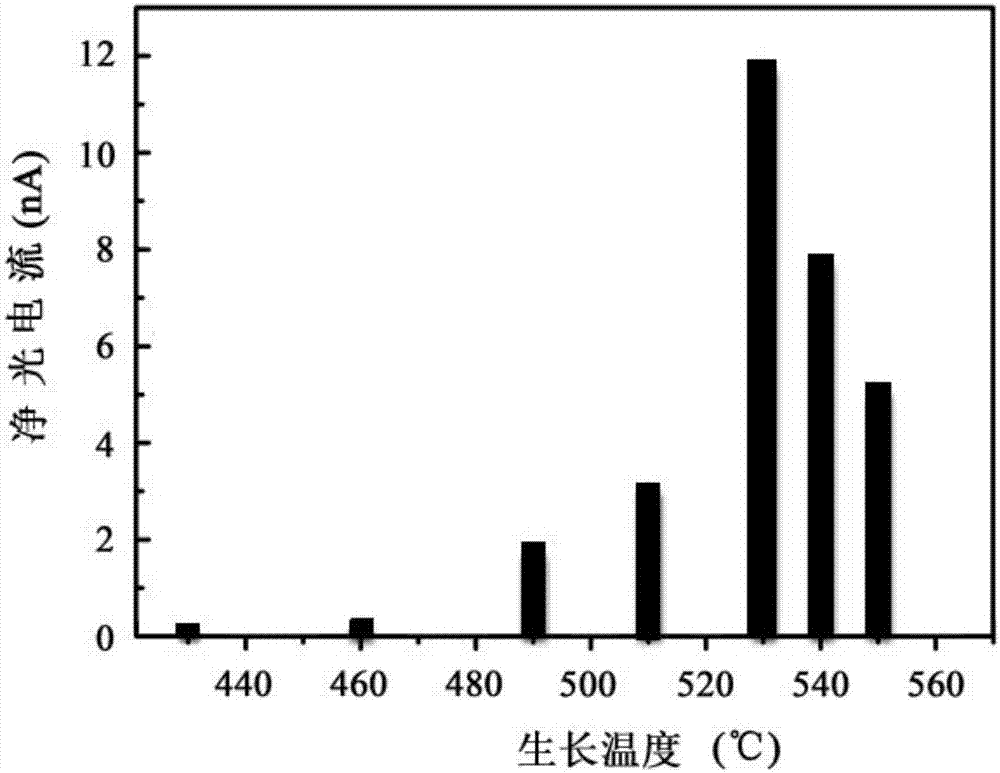
The invention discloses a method for preparing a semiconductor nanowire array with optimal photoelectric performance. The method first deposits a gold film by thermal evaporation and anneals to form random and uniformly distributed catalyst particles, and then according to the prepared III-V nanowire material system, select the optimal V / III beam current ratio, grow a series of nanowire array samples at different substrate temperatures, and then use a conductive atomic force microscope to perform statistical evaluation of the vertical photoelectric properties of a single nanowire, and finally The optimal preparation conditions were determined according to the average optoelectronic properties of single nanowires. This method is suitable for catalytic molecular beam epitaxy to grow III-V nanowire arrays such as gallium arsenide, and uses a direct, fast and simple method to evaluate and determine the optimal growth conditions of nanowire arrays through metal catalysis, and then prepares a arrays of semiconducting nanowires with optimal optoelectronic efficiency, and thus, the method is of great interest for the fabrication of high-efficiency solar cells and ultrasensitive photodetectors.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Detection system and method for detecting thin film memristive characteristics by utilizing conductive atomic force microscope device
InactiveCN108362959AAdd current limiting functionDetection uniformityElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingConductive atomic force microscopyCurrent limiting
The invention relates to the technical field of microelectronics, and more particularly relates to a detection system and a detection method for detecting thin film memristive characteristics by utilizing a conductive atomic force microscope device. The detection system is characterized in that the structure of a test sample only comprises a conductive substrate and a variable-resistance dielectric layer. Since the radius of a probe of a conductive atomic force microscope is usually about 20 nm, the detection system can be used for detecting device characteristics under nano-sized microelectrodes, can detect the memristive characteristics under different limited currents through improving the current limiting function of the conductive atomic force microscope, and can detect uniformity ofthin film variable-resistance characteristics by further utilizing the scanning function of the conductive atomic force microscope. The detection method provides a convenient thin film variable-resistance characteristic detection method.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Processing method of binary transition metal oxide film nanometer patterns
The invention discloses a processing method of binary transition metal oxide film nanometer patterns. According to the processing method, a conducting atomic force microscopy (C-AFM) probe needle point is applied with a certain direct current bias, so that ionic electrochemical reaction at the contact interface of a binary transition metal oxide film and the probe is realized, the amplitude value,applying times, needle point effect zone, and scanning times are controlled, so that processing of binary transition metal oxide film nanometer patterns of different shapes is realized. The processing method possesses following advantages: nanometer grade processing precision is achieved, processing process is simple and convenient, energy consumption is super low, no pollution is caused, and nomask is needed. The processing method is capable of reducing physical damage on probe needle point.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Characterization method for conductivity regulation in ferroelectric nano dot array
PendingCN110514872ALarge polarization valueAdvanced technologyMaterial nanotechnologyScanning probe microscopyMicro nanoNanodot
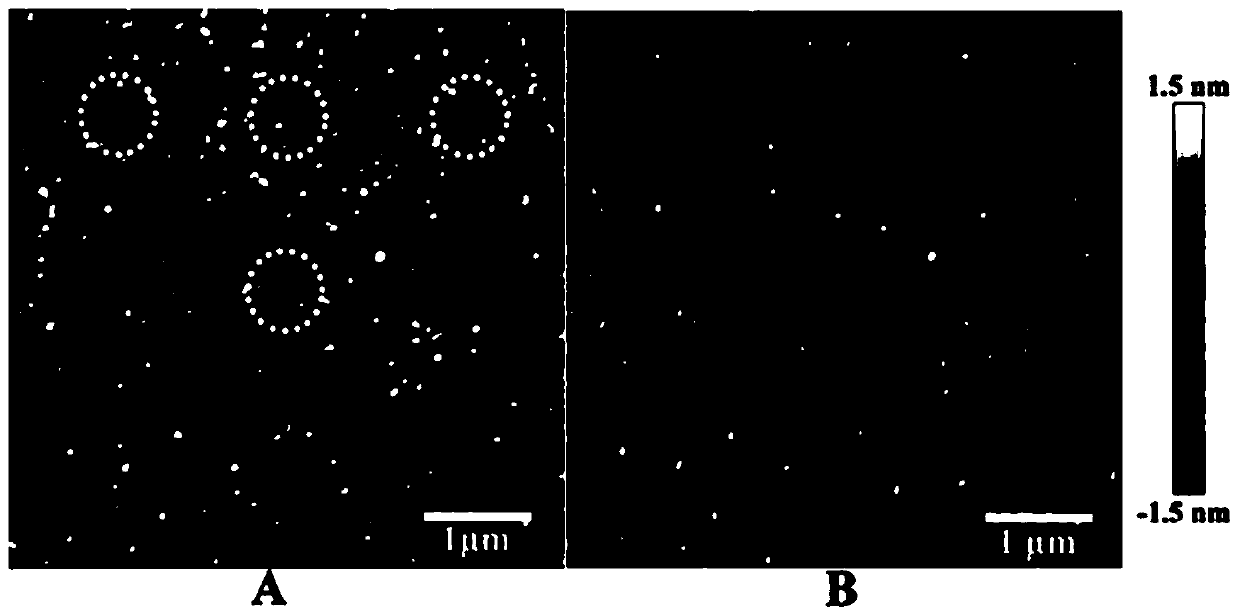
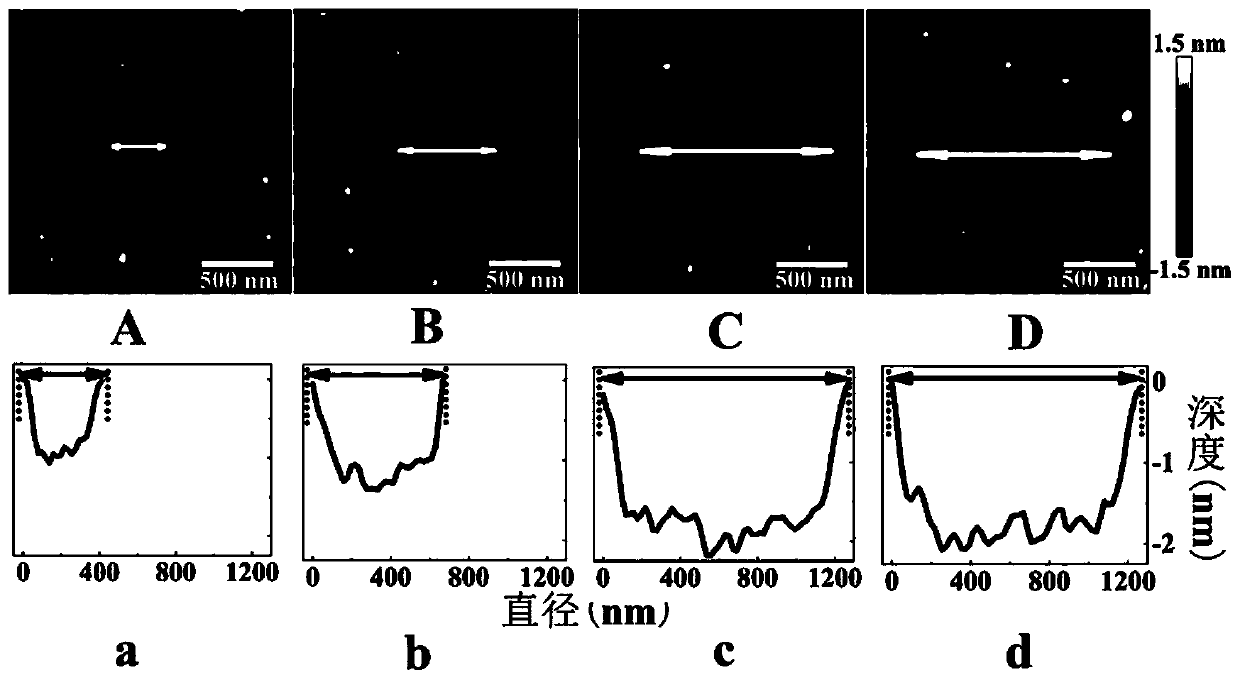
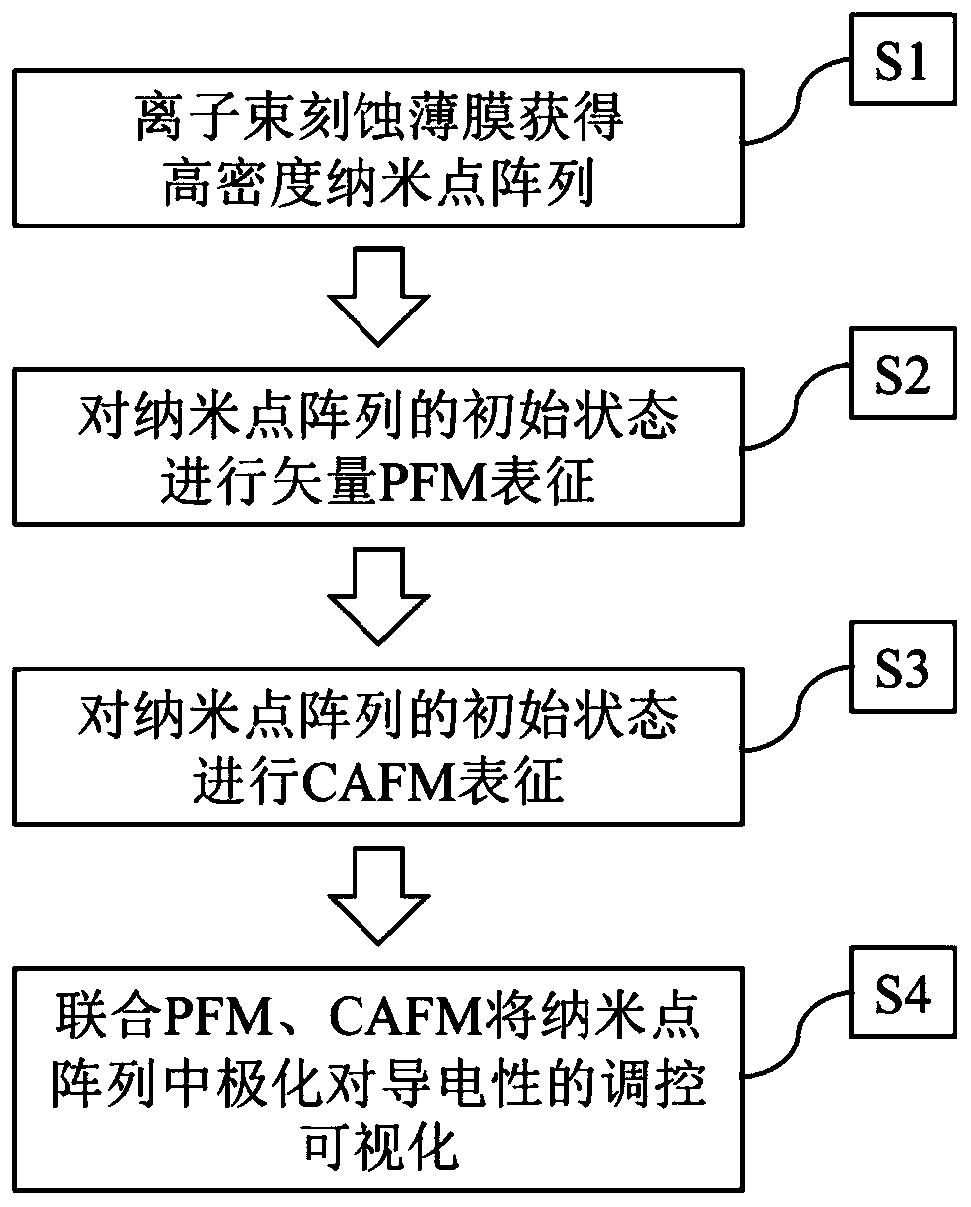
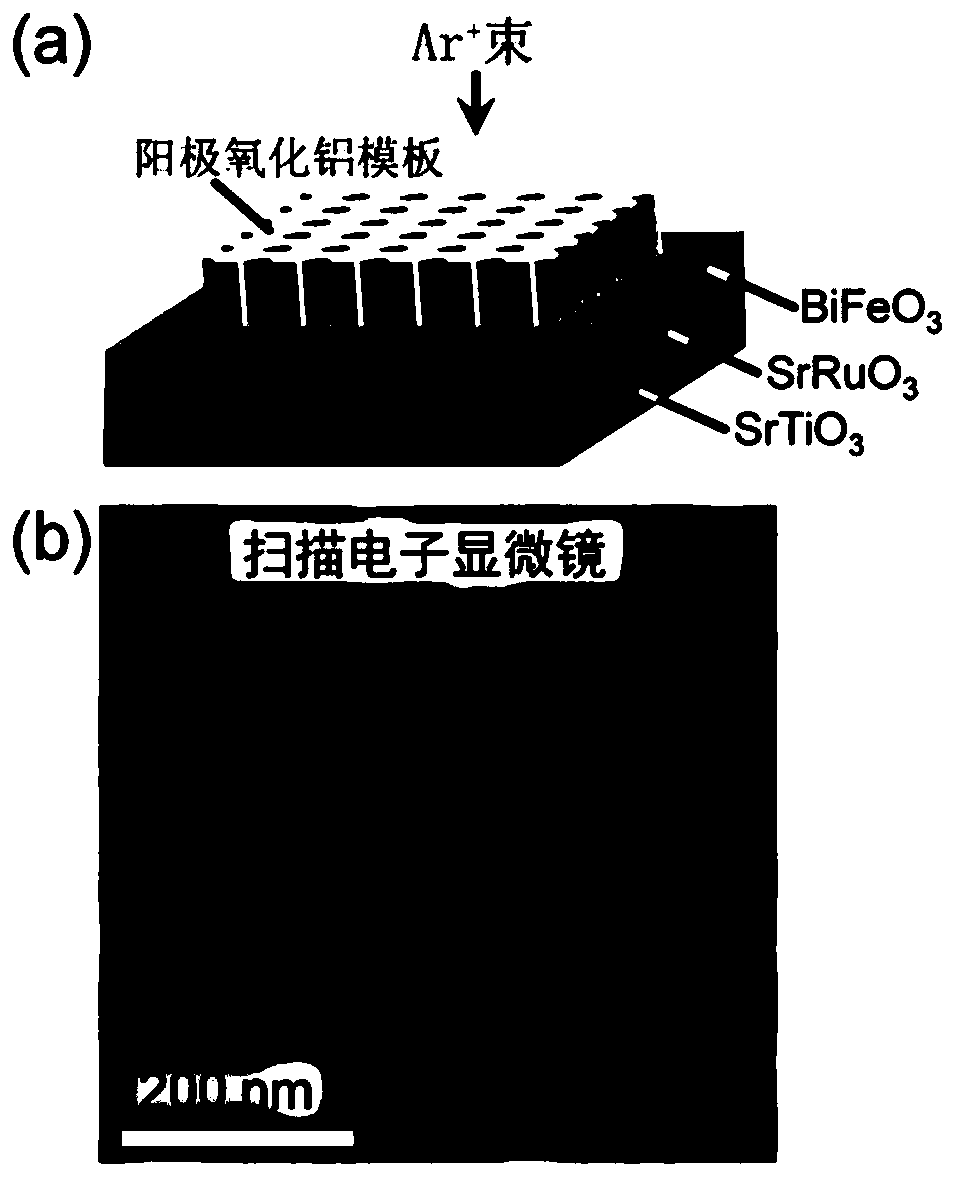
The invention discloses a characterization method for conductivity regulation in a ferroelectric nano dot array, and belongs to the technical field of nano ferroelectric material preparation and micro-nano characterization. A ferroelectric film is etched by an ion beam to obtain a high-density nano dot array; a domain structure of a ferroelectric topological domain is obtained by means of vector piezoelectric power microscopy characterization; a conductive atomic force microscope is used for observing conductive channels in the nanodots, that the conductive area in a single nanodot is dozens of nanometers according to a two-dimensional current image, and the conductive channels have the characteristic similar to metal conductivity; and a piezoelectric force microscope and a conductive atomic force microscope are combined to obtain regulation of polarization on conductivity. The method can be used for developing a nonvolatile and high-density ferroelectric random access memory; the central domain structure of the nanodot provides a scheme for researching the ferroelectric topological domain and a topological material; and the conductivity of the nanodots can be regulated through polarization inversion, regulation control can be visualized through the provided characterization method, and the visibility and reliability of data are improved.
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
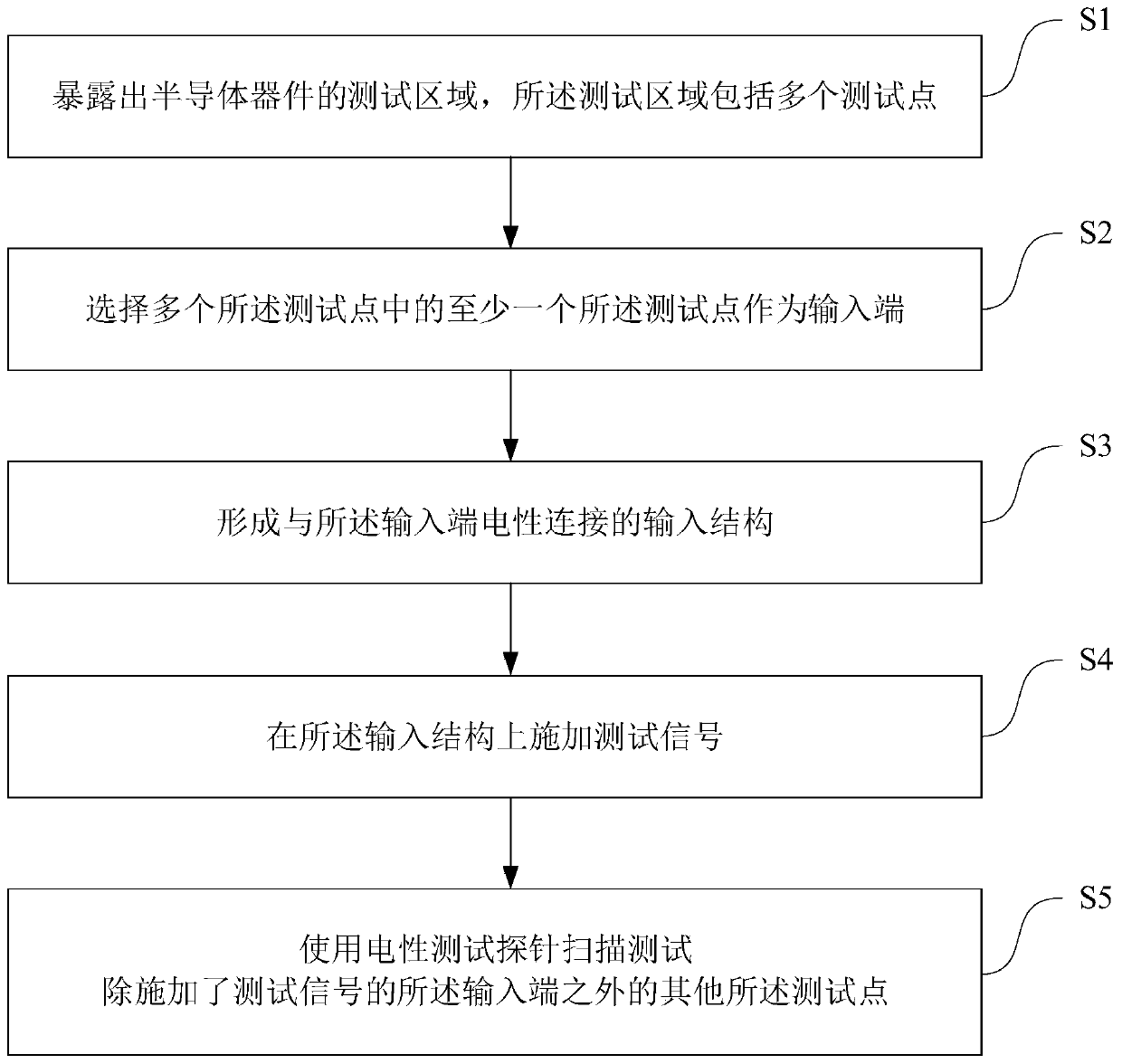
Semiconductor device failure analysis method
InactiveCN110261753AReduce labor costsAvoid time costScanning probe microscopyIndividual semiconductor device testingConductive atomic force microscopyTime cost
The invention provides a semiconductor device failure analysis method. The method comprises the following steps of exposing a test area of a semiconductor device, wherein the test area includes a plurality of test points; selecting at least one of the plurality of test points as an input end; forming an input structure electrically connected to the input end; applying a test signal to the input structure; and using an electrical test probe to scan and test the test points except for the input end to which the test signal is applied. Through introducing the new semiconductor device failure analysis method, when a semiconductor device is tested and analyzed by using an electrical probe test method such as a conductive atomic force microscope and the like, input structures electrically connected to the test points are formed. A bias voltage is applied to the test points through the input structures and labor and time cost required for failure analysis can be effectively reduced through the multiple input structures.
Owner:YANGTZE MEMORY TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing nano texture through local anodic oxidation
InactiveCN102530842AGood anti-adhesionPrevent large contactDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingElectricityMicro nano
The invention discloses a method for preparing nano texture through local anodic oxidation. In the method, the nano texture is prepared by adopting a local anodic oxidation method based on a conductive atomic force microscopy, and the height (0.5-12nm) of the nano texture can be controlled through selecting different pulse voltages, pulse widths and surface humidity values. With the application of the nano texture, the large-area contact with the surface of a micro-nano optical mechanical and electrical system device can be effectively blocked, and the surface adhesive force of the micro-nano optical mechanical and electrical system device can be remarkably reduced. Therefore, the surface nano texture prepared by the method has good anti-adhesion performance.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Atomic force microscopy system and method for nanoscale measurement
ActiveUS8726410B2NanotechnologyScanning probe microscopyConductive atomic force microscopyNanoscopic scale
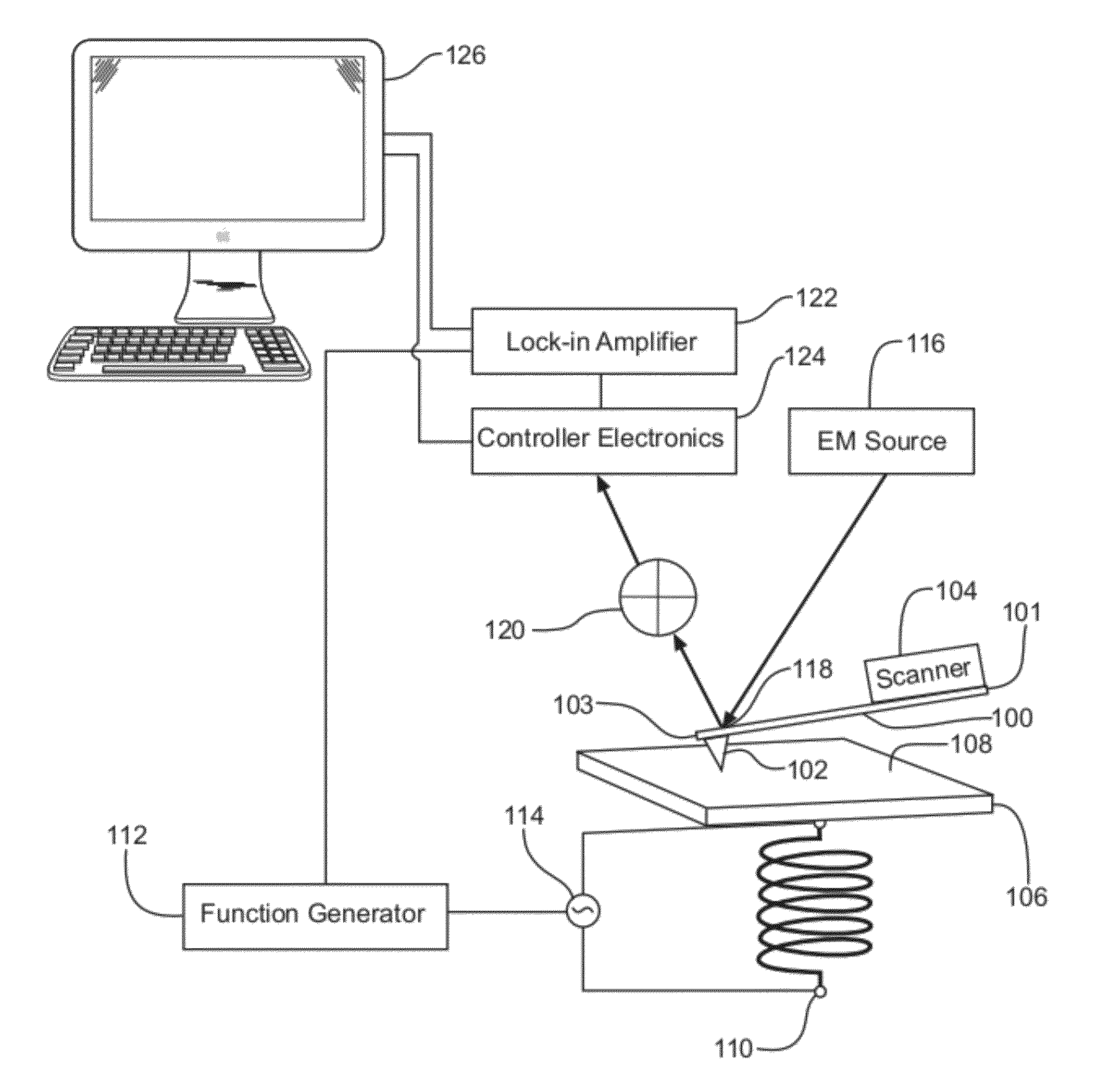
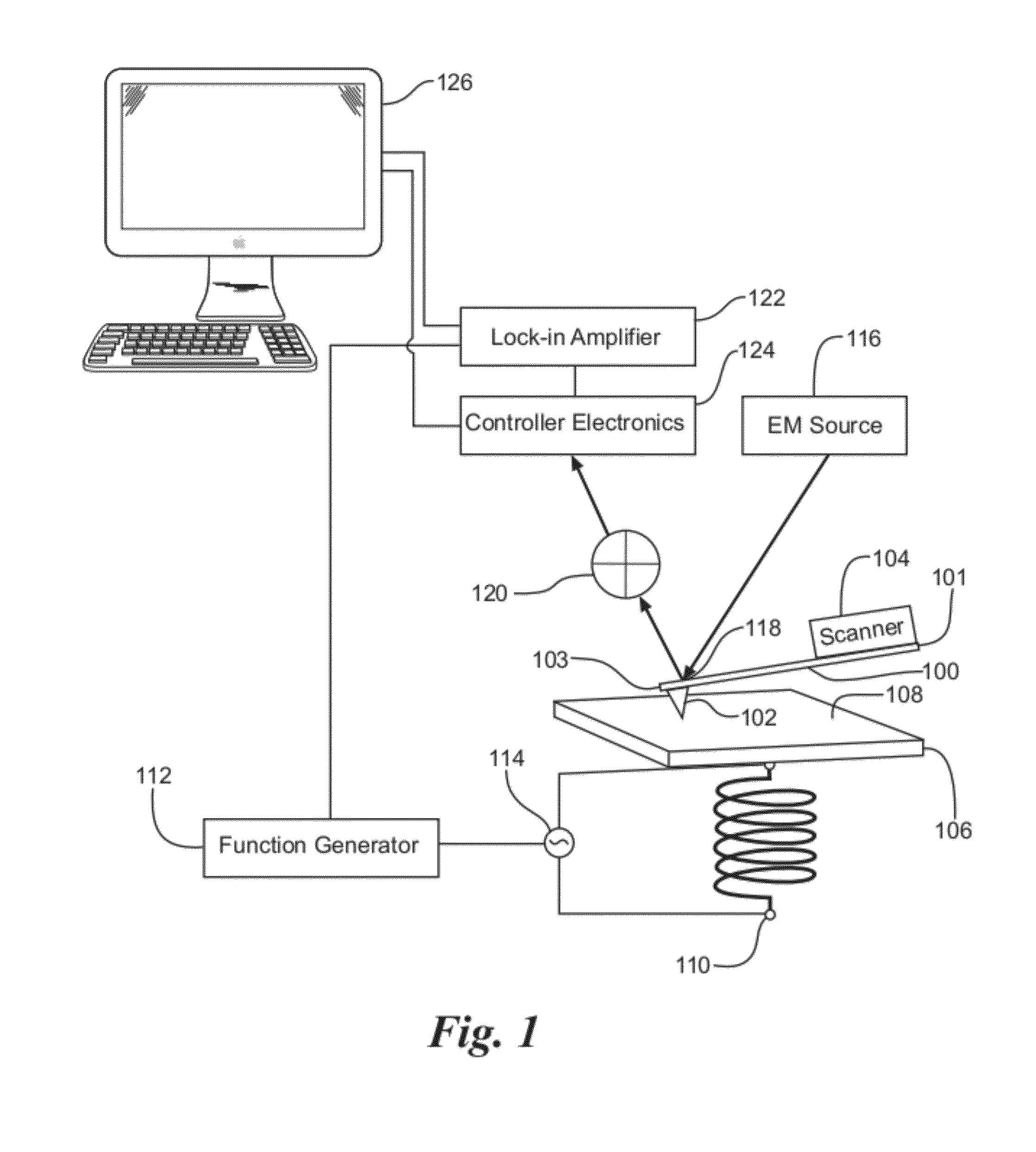
An atomic force microscope (AFM) system capable of imaging multiple physical properties of a sample material at the nanoscale level. The system provides an apparatus and method for imaging physical properties using an electromagnetic coil placed under the sample. Excitation of the coil creates currents in the sample, which may be used to image a topography of the sample, a physical property of the sample, or both.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
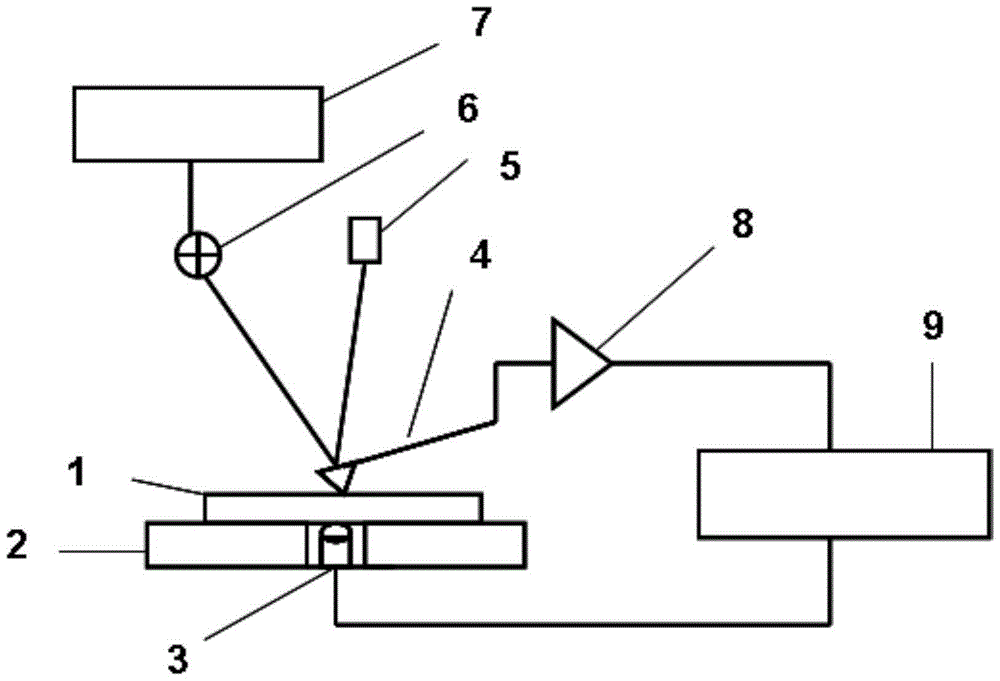
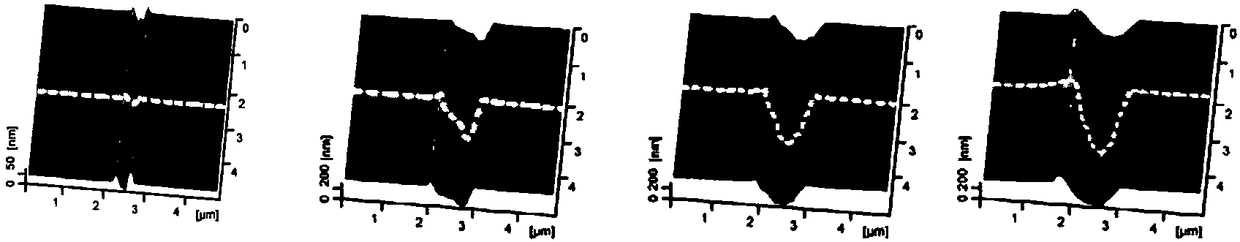
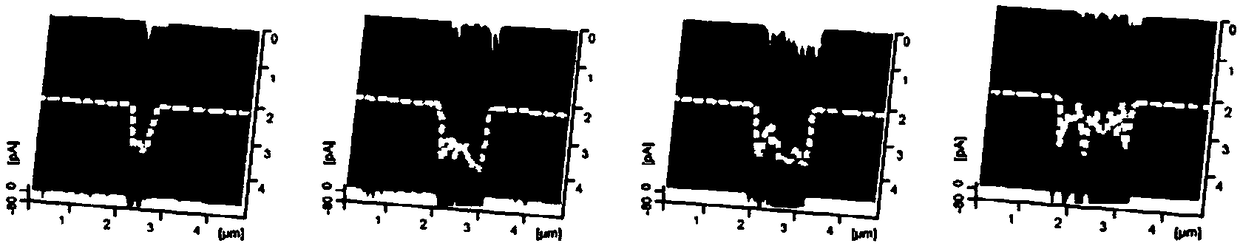
Single-crystal-silicon surface mechanical damage detecting method based on conductivity variation
InactiveCN108333390ADamage will notSimple methodScanning probe microscopyContact pressureConductive atomic force microscopy
The invention discloses a single-crystal-silicon surface mechanical damage detecting method based on conductivity variation. The method includes the following steps of placing a clean and dry to-be-detected single-crystal-silicon wafer into a conductive atomic power microscope sample cavity, scanning a to-be-detected damage area to obtain a surface topography and a current distribution diagram, comparing and analyzing a scanning result, and finding the position of the single-crystal-silicon surface mechanical damage to obtain the detection result. In the method, scanning and detecting are conducted by means of a micro tip of an atomic power microscope, the contact pressure is far smaller than the clinical contact pressure of single crystal silicon during yielding, and a sample can not be damaged. The method is suitable for detecting the mechanical damage generated in the cutting, grinding, polishing and other machining processes of single-crystal-silicon surfaces.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
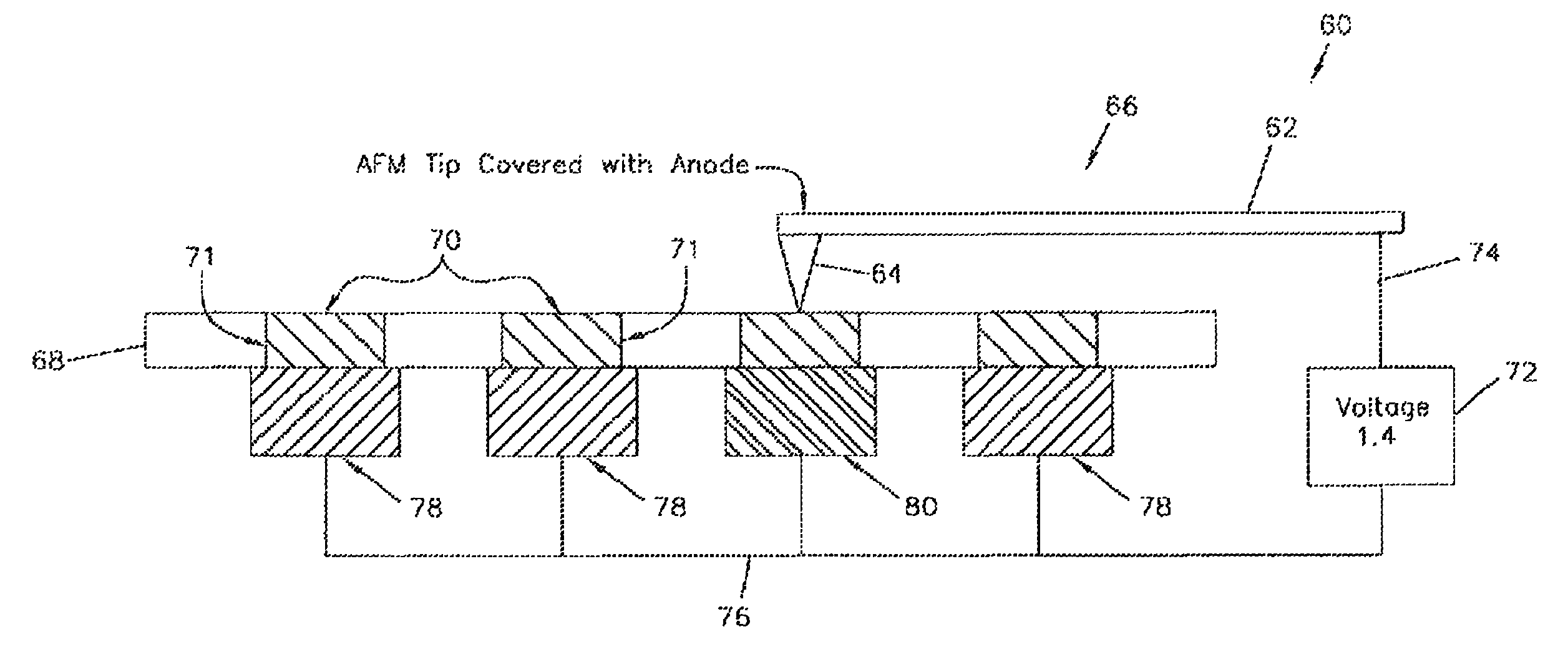
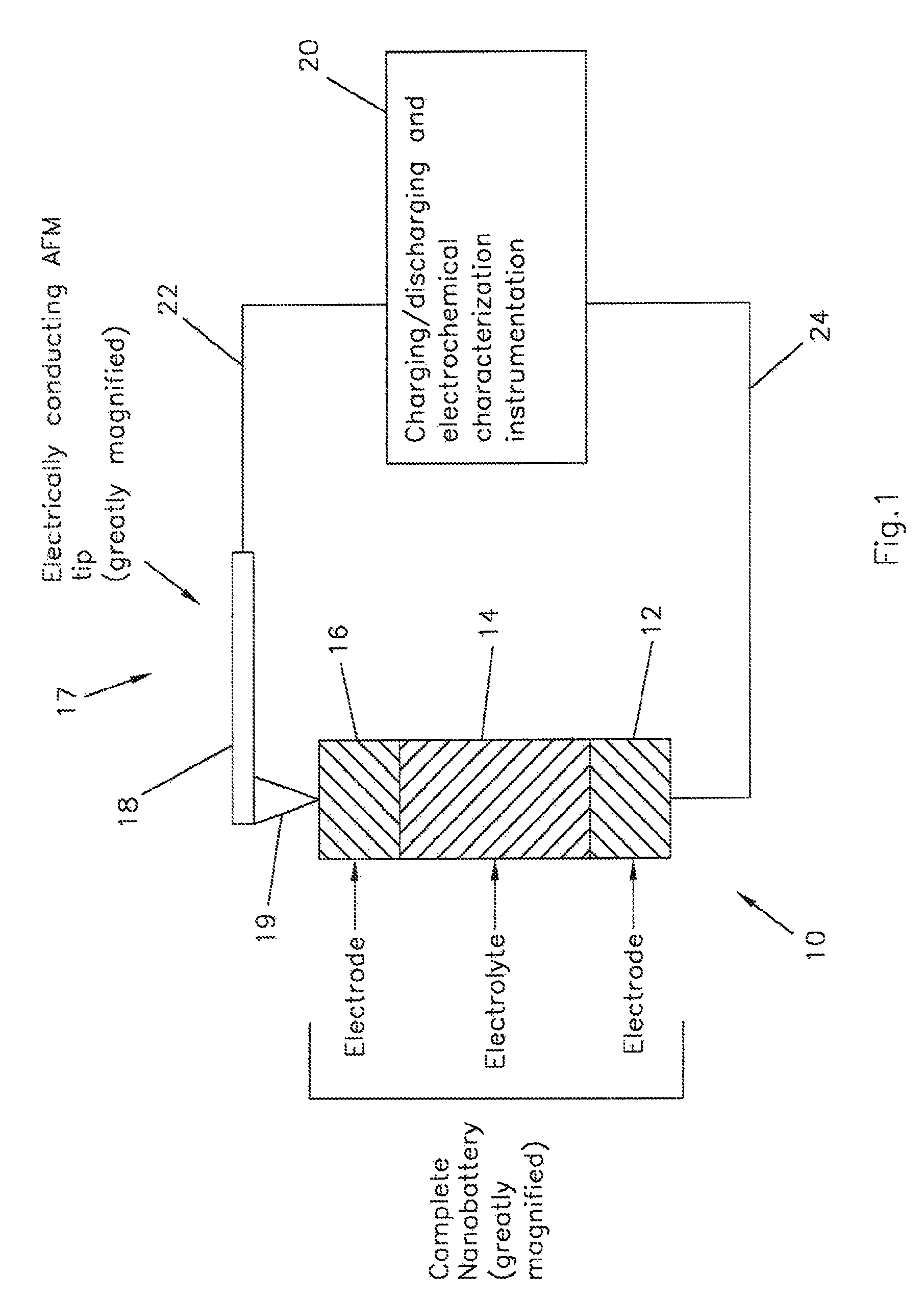
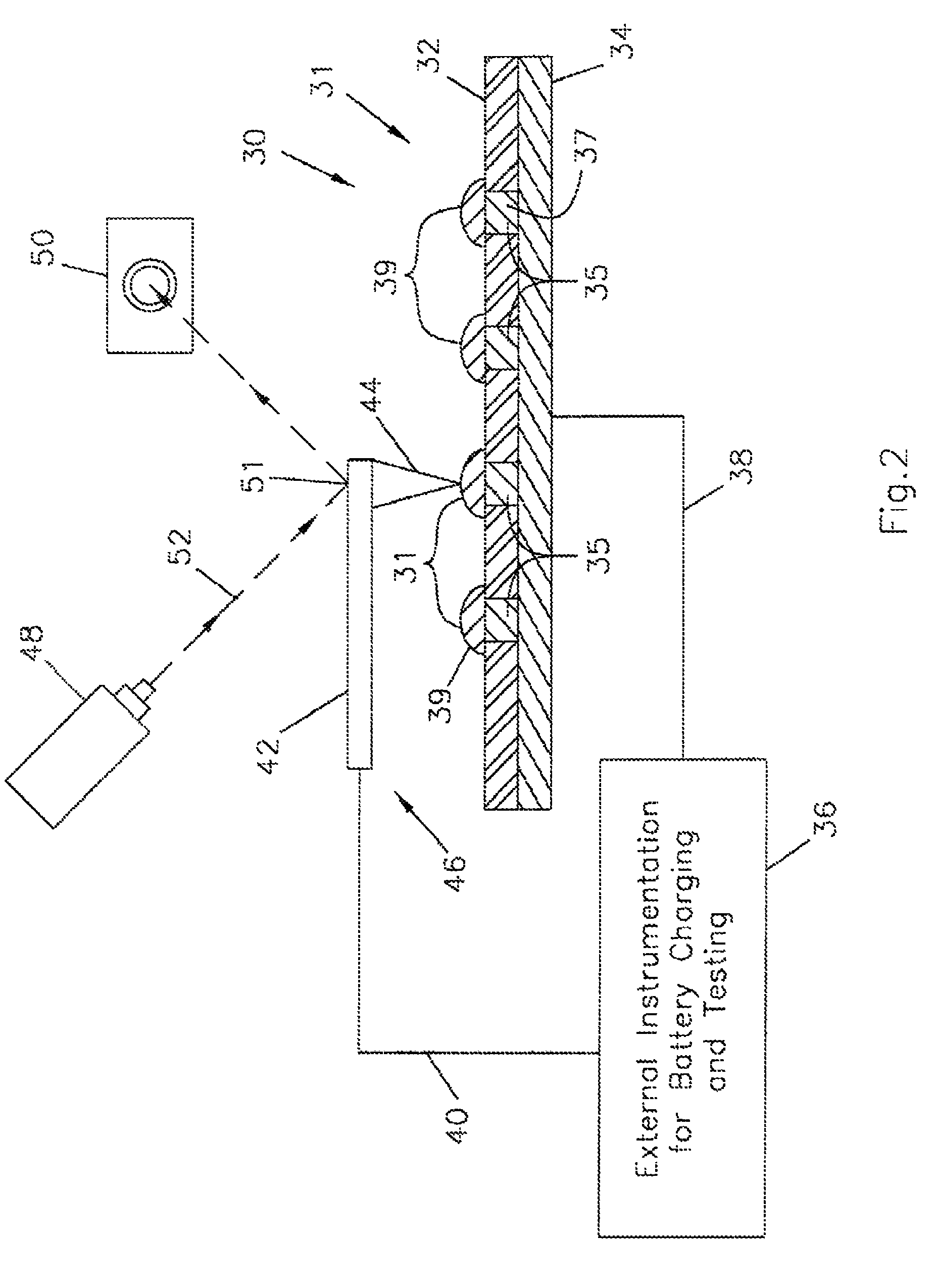
Charged arrays of micro and nanoscale electrochemical cells and batteries for computer and nanodevice memory and power supply
ActiveUS7862920B1Shorten the timePrimary cell to battery groupingElectrostatic charge injection carrier recordingConductive atomic force microscopyInformation density
A sequence or array of electrochemical cells storing both digital and analog data. Both binary code and codes having a higher base may be stored in the memory device to increase information density. Such battery arrays could also provide power for the micro or nanodevice. Devices are microscale and nanoscale in size and utilize electrically conductive atomic force microscopy tips to record and read data stored in the device.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TULSA
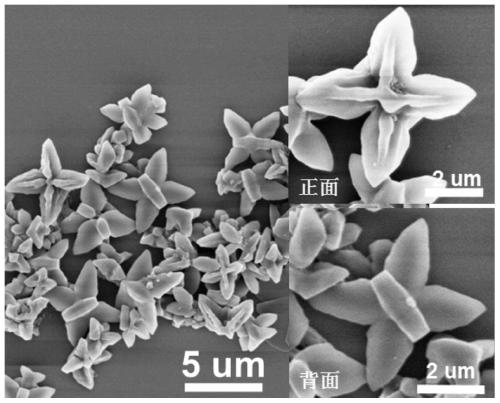
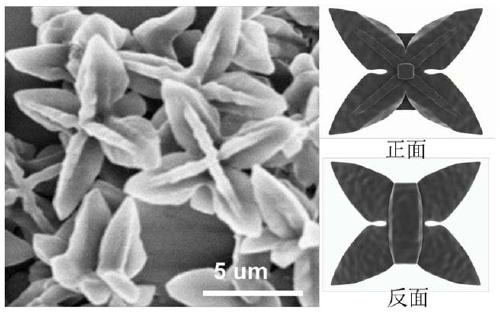
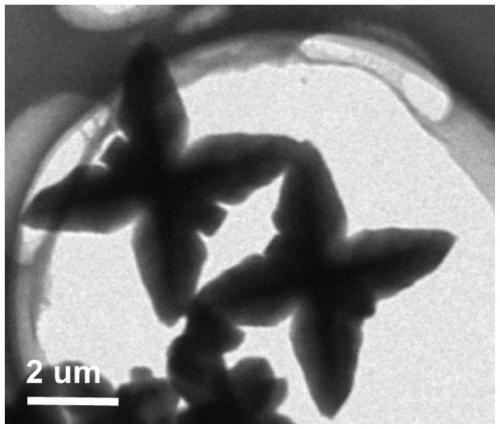
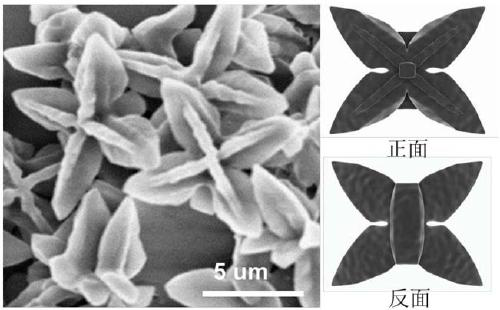
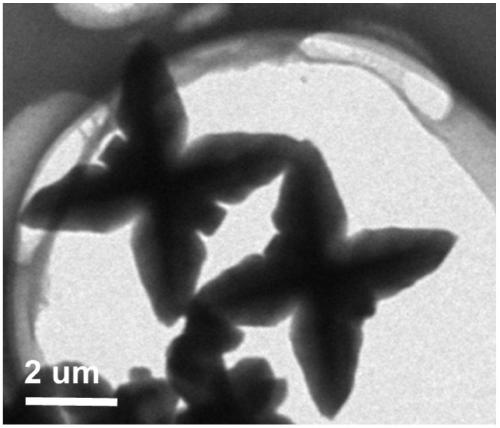
Azafluorene-based small molecule butterfly-shaped organic nanocrystal material and its preparation method and application
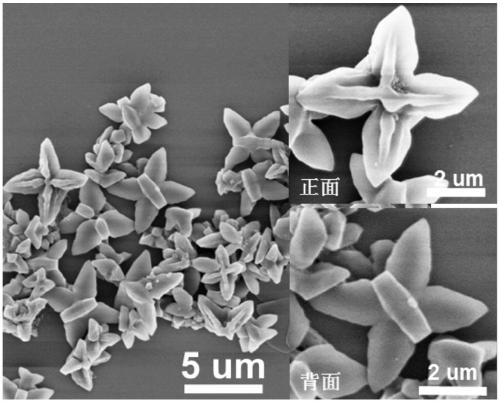
ActiveCN109678893BEasy to operateLow costOrganic chemistry methodsSolid-state devicesConductive atomic force microscopyOrganic semiconductor
The invention discloses an azafluorene-based small molecule butterfly-shaped organic nanocrystal material and its preparation method and application. The azafluorene-based small-molecule butterfly-shaped organic nanocrystal material has an asymmetric double-sided butterfly-shaped multi-dimensional micron structure , one side is plum-shaped and the other is butterfly-shaped. The invention realizes the controllable preparation of pure organic small molecule nanometer material in the field of multi-dimensional structure. Through the corresponding dynamic growth process and single crystal analysis and other characterization methods, the growth mechanism of this organic nanomaterial and the deep relationship between the morphology and molecular structure were confirmed. In addition, the excellent wire performance of the structure was verified based on the conductive atomic force microscopy platform. The application potential of such organic semiconductor materials in future optoelectronic devices is demonstrated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Probe of conducting atomic force microscope and measuring methods employing probe
ActiveCN102353817BImprove conductivityLow carrier injection potentialElectrical testingScanning probe microscopyMagnetic force microscopeConductive atomic force microscopy
The invention relates to a probe of a conducting atomic force microscope. The probe comprises: a substrate of a cantilever probe; a needle tip; and a conductive film, which is arranged at a surface of the needle tip. Besides, the material of the conductive film is graphene. Moreover, the invention provides a method that employs the probe to measure local conductivity of a semiconductor and a needle tip-free near-field optical detection method that employs the probe to measure a terahertz wave band. According to the invention, graphene is utilized, wherein the grapheme has the following characteristics that: the graphene is composed of carbon atoms and is thin to a monatomic layer; and the graphene is a semimetal two-dimensional thin material that has a zero gap; besides, the probe has advantages of good conductivity and high electron mobility; moreover, a Fermi surface can carry out self-adjustment with charging and discharging motions and a carrier injection potential is low. In addition, an electronic plasmon oscillating frequency of the graphene is just at a terahertz wave band; and the graphene has soft materials and strong stability on thermodynamics. The above-mentioned statements are physical bases on which the graphene is utilized to replace a traditional metal material as a plated film of a surface of an atomic force microscope probe, so that the above-mentioned limitations are broken through.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
A Characterization Method of Periodic Stripe Domain Structure of Ferroelectric Thin Films
ActiveCN110634871BLarge polarization valueImprove ferroelectric propertiesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPiezoelectric force microscopyConductive atomic force microscopy
The invention discloses a periodic striped domain structure of a ferroelectric thin film and a characterization method thereof, belonging to the technical field of micro-nano characterization, and the method comprises the following steps: preparing a bismuth ferrite thin film by pulse laser deposition; characterizing it by an X-ray diffractometer The lattice constant is determined to be a rhomboid phase structure, the piezoelectric butterfly curve is used to confirm its ferroelectricity and coercive voltage, and its morphology is characterized by atomic force microscopy; the periodic stripes in nanoferroelectric thin films are characterized by vector piezoelectric force microscopy Banded domains, the three-dimensional domain structure was determined by fine vector piezoelectric force microscopy analysis method; the domain walls of the striped domains were observed to conduct electricity by using conductive atomic force microscopy. The ferroelectric thin film preparation method provided by the present invention can be used in non-volatile, high-density ferroelectric random access memory; at the same time, the provided characterization method can accurately provide the three-dimensional domain structure and domain wall of the periodic strip domain Conduction; provide solutions for the development and characterization of high-density ferroelectric memory devices.
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Azafluorene micromolecule based butterfly organic nanocrystal material, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109678893AEasy to operateLow costOrganic chemistry methodsSolid-state devicesConductive atomic force microscopySingle crystal
The invention discloses an azafluorene micromolecule based butterfly organic nanocrystal material and a preparation method and an application of the material. The azafluorene micromolecule based butterfly organic nanocrystal material has an asymmetric double-faced butterfly multidimensional micron structure, wherein one side is quincuncial, and the other side is butterfly-shaped. Controllable preparation of a pure organic micromolecule nanomaterial in the field of a multidimensional structure is achieved. A deep relationship between a growth mechanism and a morphology of the organic nanomaterial and a molecular structure is confirmed by corresponding characterization means such as dynamic growth process and monocrystal analysis. In addition, excellent lead performance of the structure is verified based on a conductive atomic force microscope platform. An application potential of the organic semiconductor material in future photoelectronic devices is shown.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
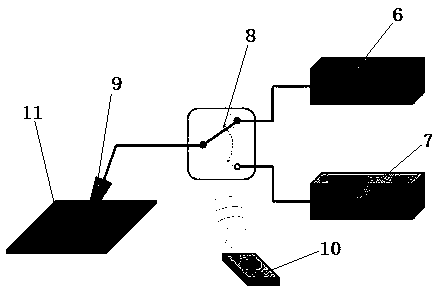
Method for optimizing combination of conductive atomic force microscope and digital source meter
PendingCN111122912AEasy to operateEfficient experimental operation processScanning probe microscopyConductive atomic force microscopyTest sample
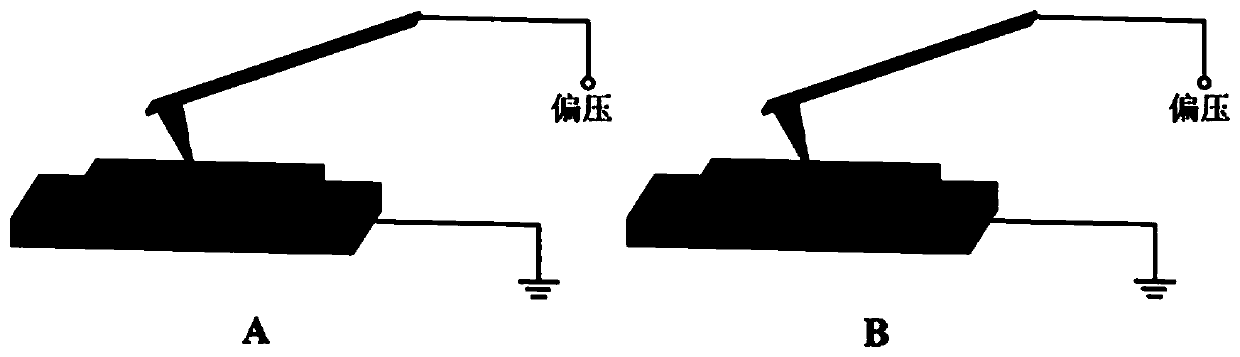
The invention relates to a method for optimizing combination of a conduction atomic force microscope (CAFM) and a digital source meter. A conductive module (CAFM Mode) and a digital source meter of aconductive atomic force microscope are connected with a conductive atomic force microscope through a single-pole double-throw radio frequency switch, so that a probe is selectively connected with theconductive module of the conductive atomic force microscope or the digital source meter. According to the method for combining a conductive atomic force microscope and a digital source meter, a novelsystem accessory is created and applied to the conductive atomic force microscope. The conductive atomic force microscope can be freely switched to different modes (CAFM mode or source meter), the position of the needle tip is not changed in the switching process, and the same area of the test sample can be represented at the same time, so that the original defects of the AFM instrument in use aregreatly overcome, technicians in the field are simpler, more convenient and more efficient in the experimental operation process, and the time cost of the scientific research personnel can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for measuring distance between graphite and metal surface
InactiveCN105699702ASimple processEasy to implementAnalysis by electrical excitationScanning probe microscopyConductive atomic force microscopyGraphite
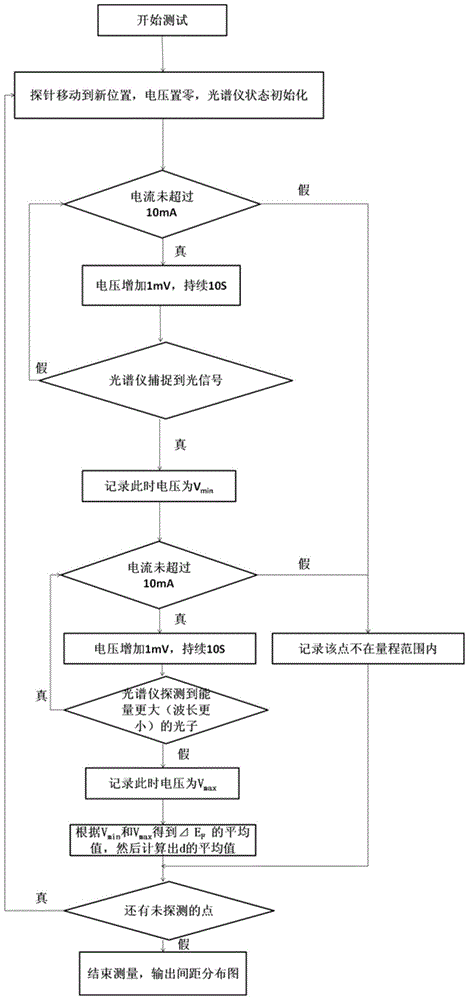
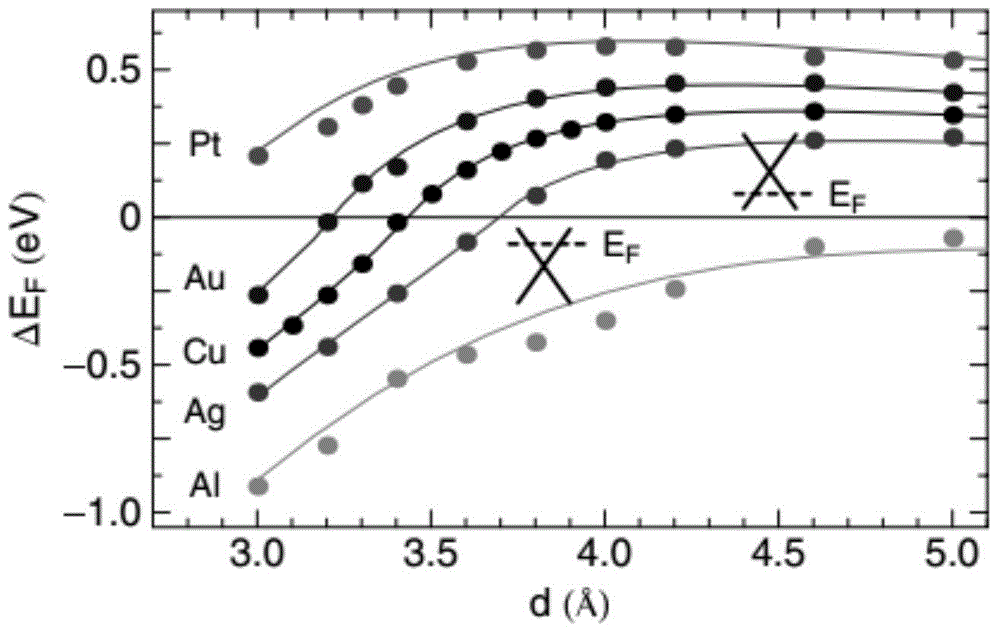
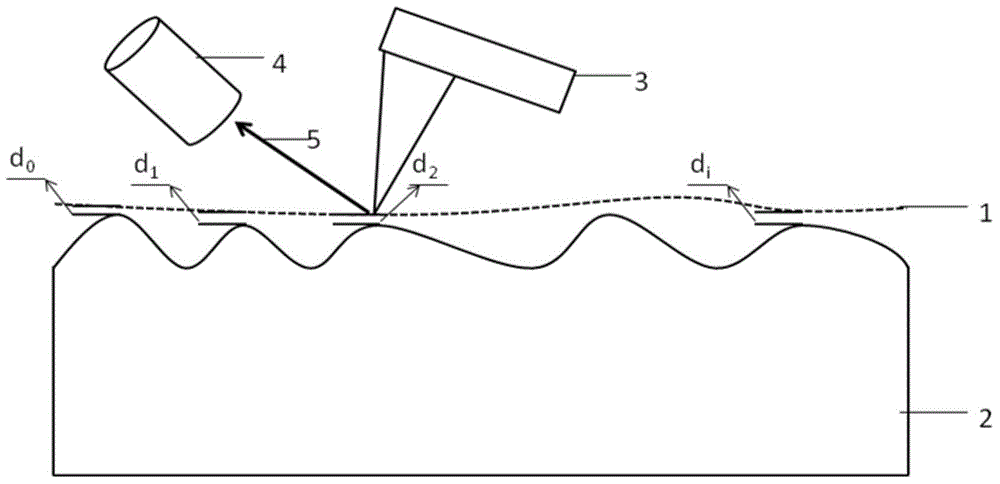
The present invention discloses a method for measuring a distance between a graphite and a metal surface based on a spectrometer and a conductive atomic force microscope. By using a phenomenon that a graphene-metal junction can emit light in an atmosphere environment at a particular voltage, with the cooperation of the spectrometer and the conductive atomic force microscope, the control of probe movement is realized, corresponding voltage is measured, the average value of Delta EF is extracted, according to the corresponding relation between the Delta EF and d, the distance d between the graphite at a light emitting point and the metal surface is obtained, and finally the distance distribution map of samples is obtained.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
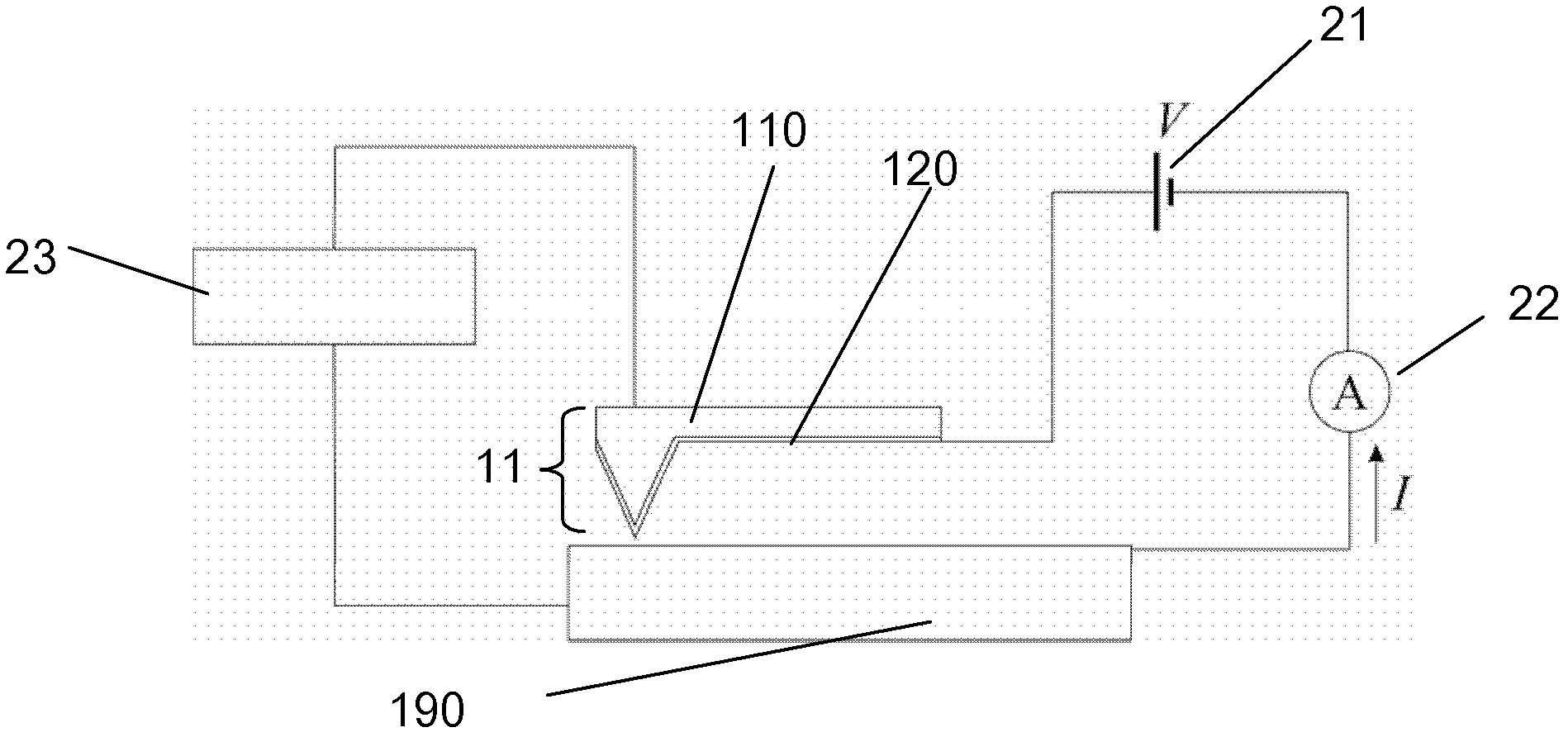
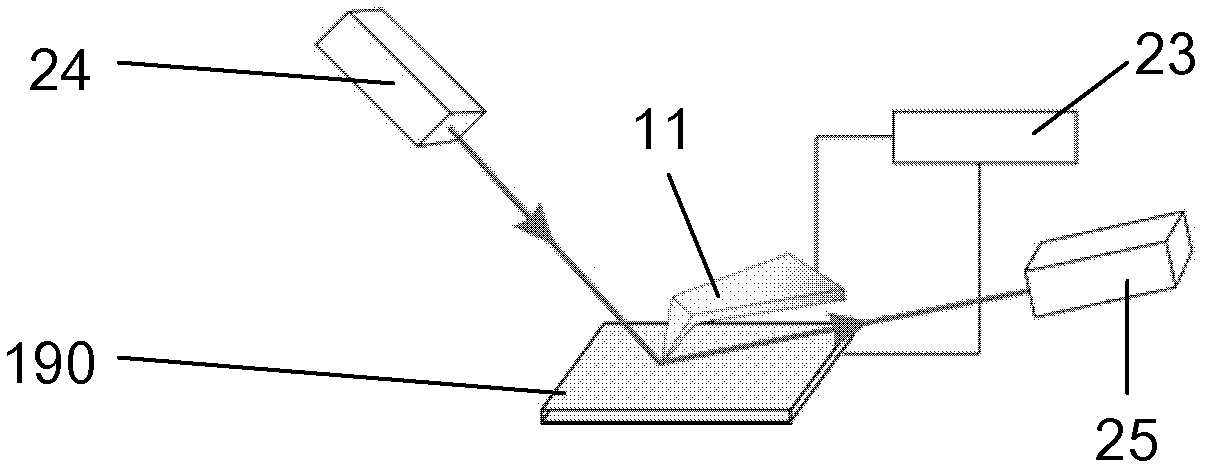
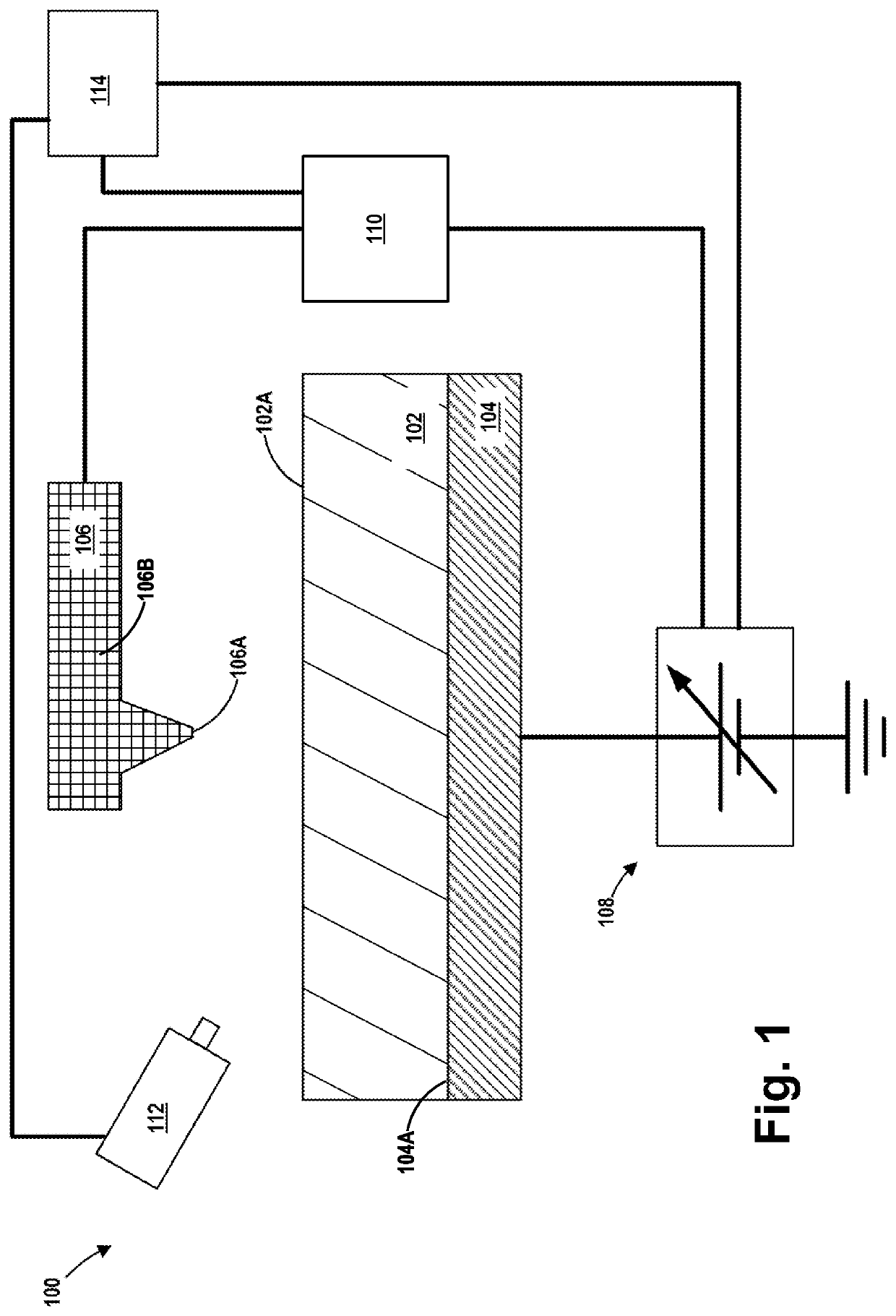
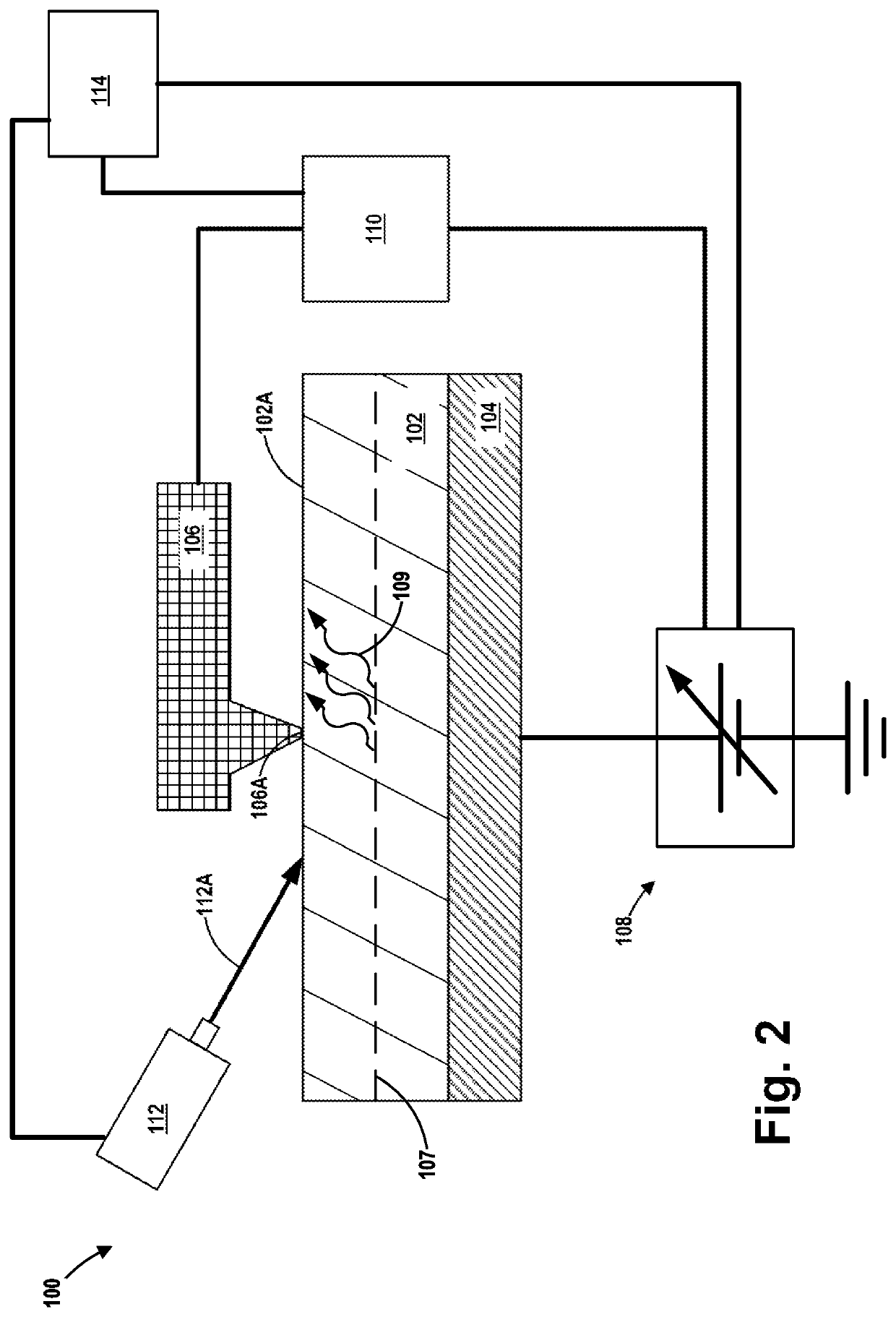
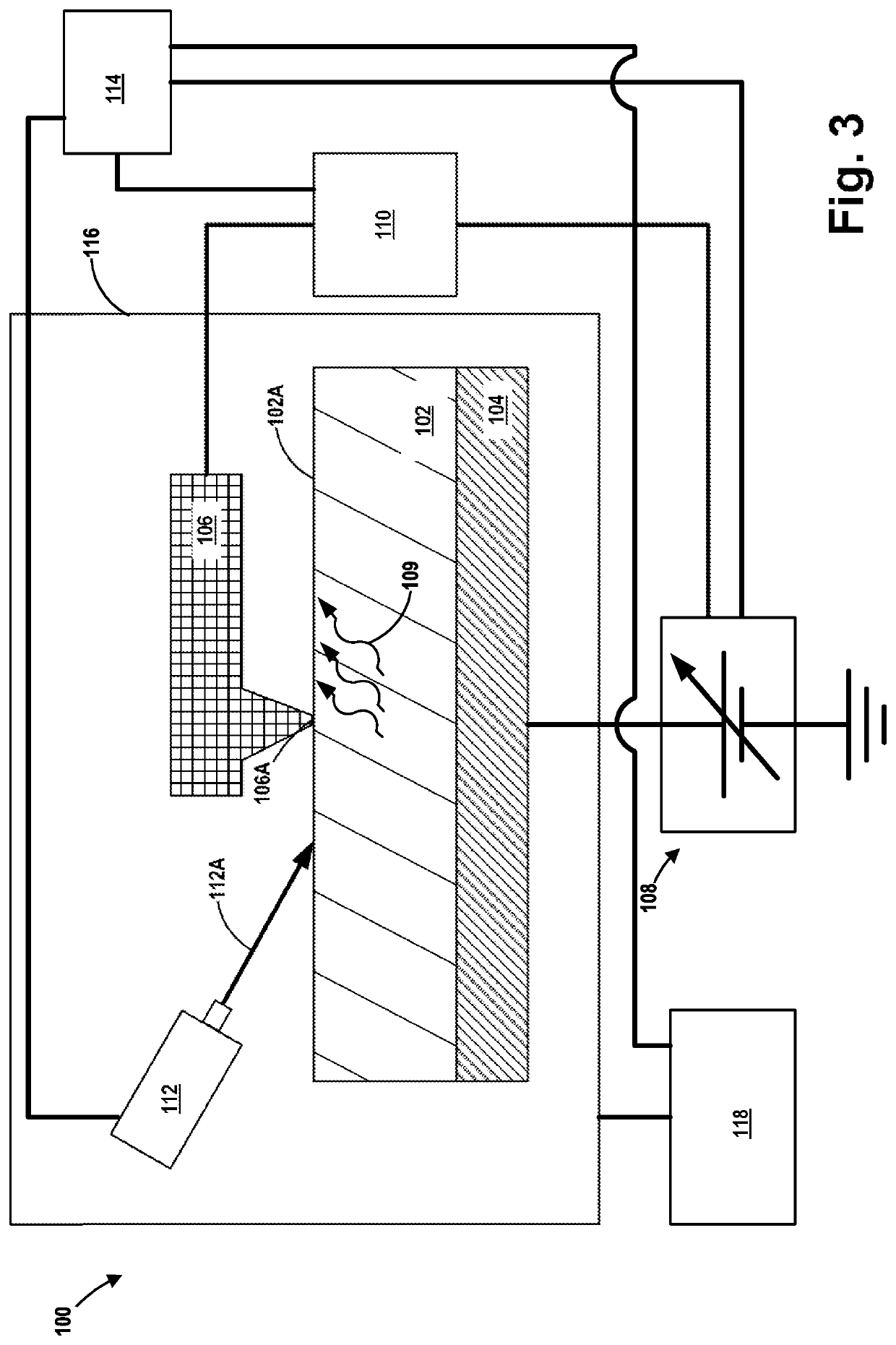
Conductive atomic force microscopy system with enhanced sensitivity and methods of using such a system
An illustrative method disclosed herein includes measuring at least one electrical-related parameter of a doped semiconductor material by simultaneously irradiating at least a portion of an upper surface of the doped semiconductor material, urging a conductive tip of a cantilever beam probe into conductive contact with the upper surface of the irradiated portion of the doped semiconductor material, and generating an electrical current that flows through the doped semiconductor material, through a measurement device that is operatively coupled to the cantilever beam probe and through the cantilever beam probe, wherein the measurement device measures the at least one electrical-related parameter of the doped semiconductor material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Nanoscale electrode processing method based on AFM (atomic force microscopy)
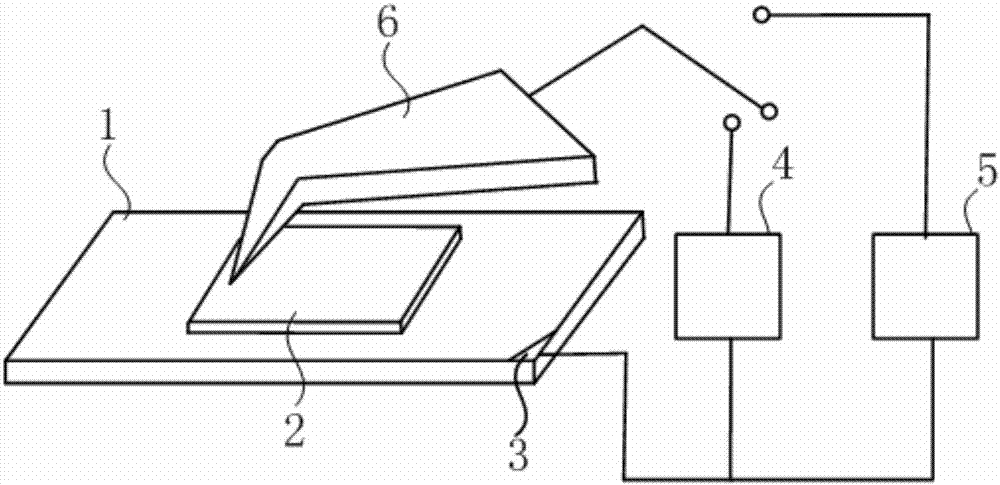
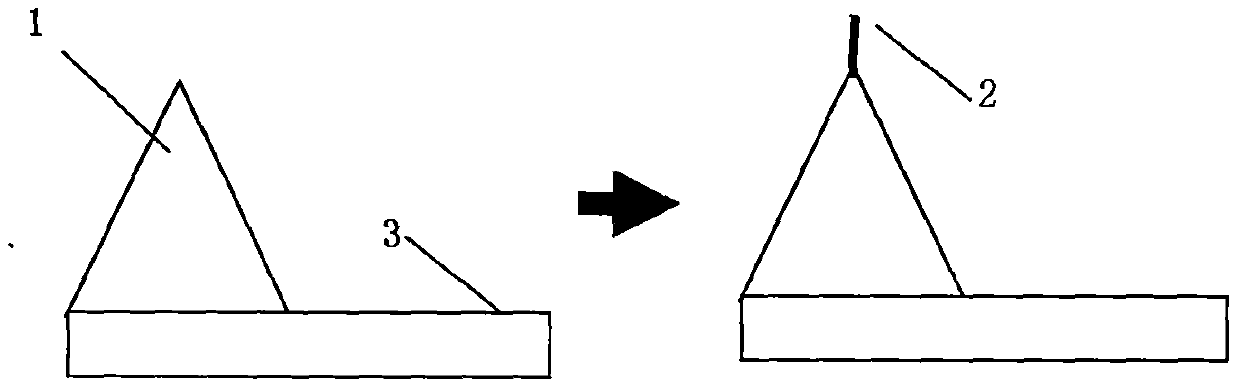
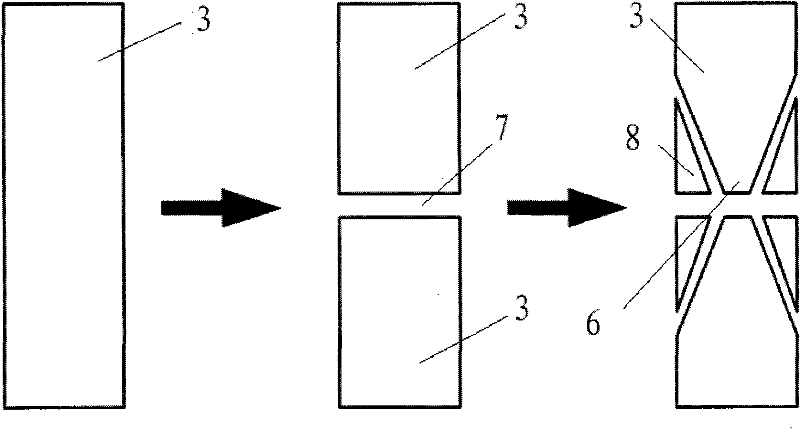
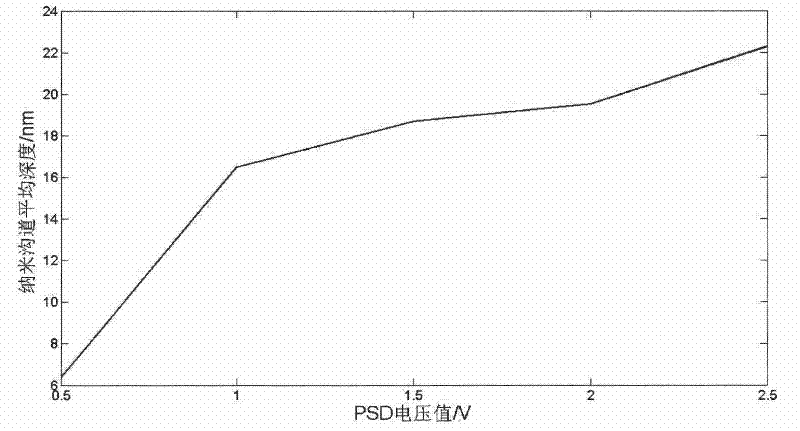
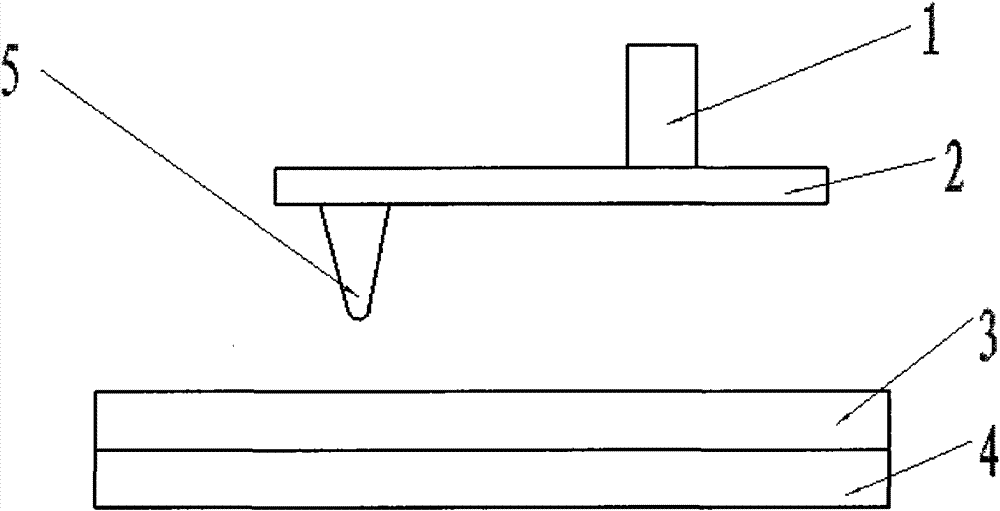
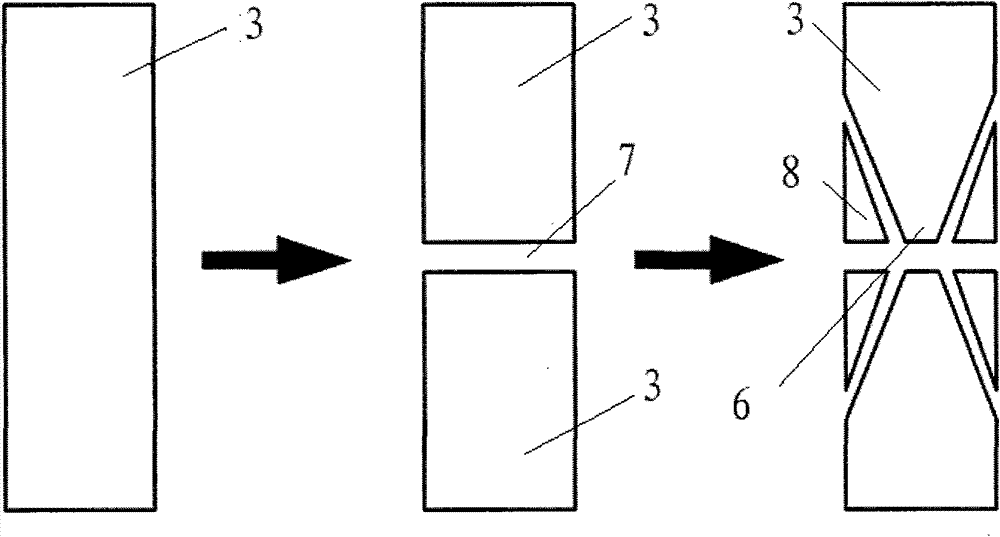
InactiveCN102211755AFlexible processing methodSimple processing methodNanostructure manufactureConductive atomic force microscopyMicrometer
The invention discloses a nanoscale electrode processing method based on an AFM (atomic force microscopy). According to the method, a micrometer level electrode is cut and processed through the controlling on the action force of an AFM probe on a sample and the movement path and speed of the probe, thus the processing of the nanoscale electrode of which a front end has width within100 nanometers is realized, and the detection accuracy and flexibility in a nano fluidic test are increased. The nanoscale electrode processing method provided by the invention can be applied to high-flexibility detection and analysis of the fluid characteristics of fluid in a nano channel in the nano fluidic chip and biology monomolecules.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nanoscale electrode processing method based on AFM (atomic force microscopy)
InactiveCN102211755BFlexible processing methodSimple processing methodSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive atomic force microscopyMicrometer
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com