Patents
Literature
62 results about "Epiphysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The epiphysis is the rounded end of a long bone, at its joint with adjacent bone(s). Between the epiphysis and diaphysis (the long midsection of the long bone) lies the metaphysis, including the epiphyseal plate (growth plate). At the joint, the epiphysis is covered with articular cartilage; below that covering is a zone similar to the epiphyseal plate, known as subchondral bone.
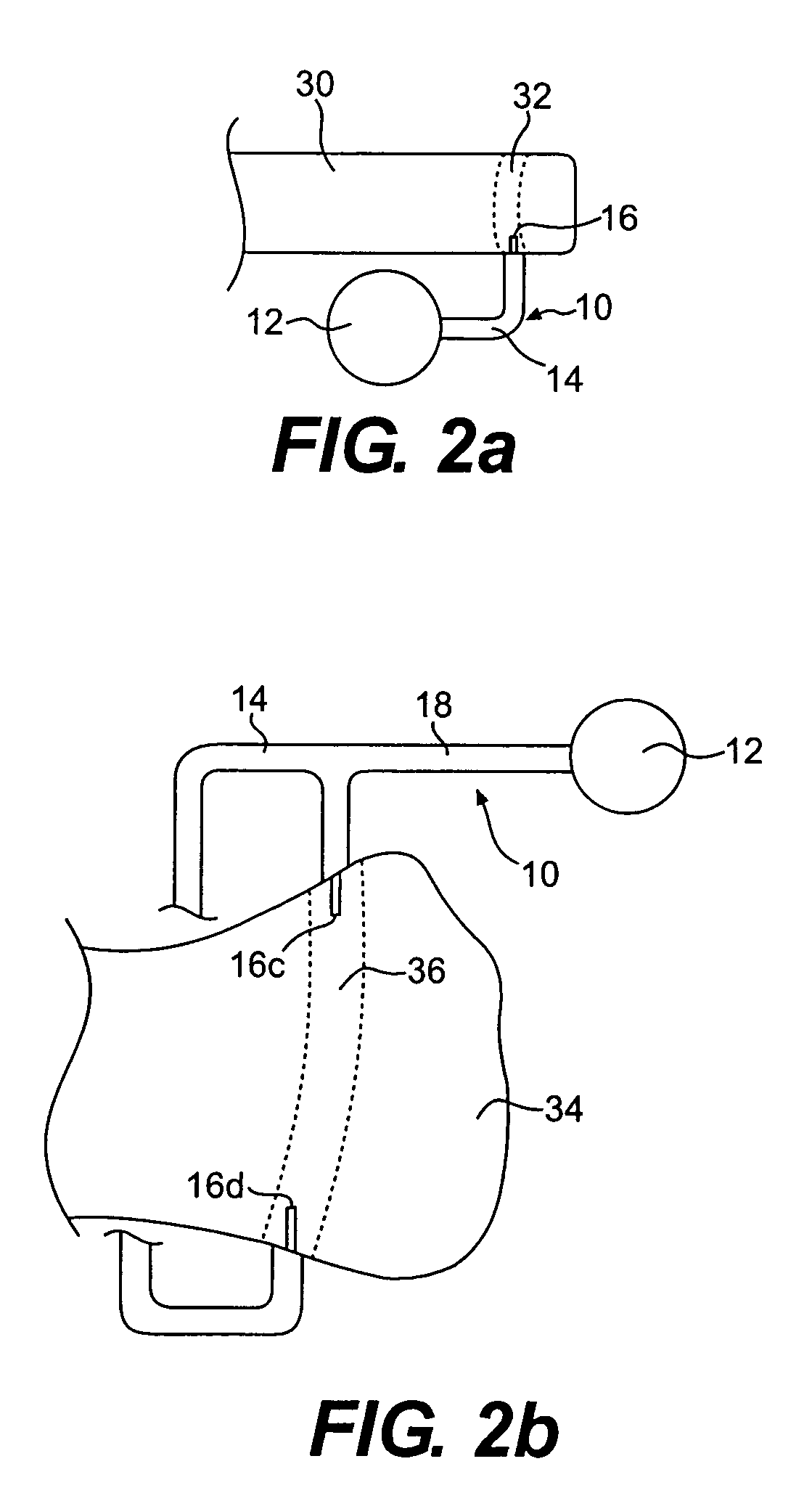
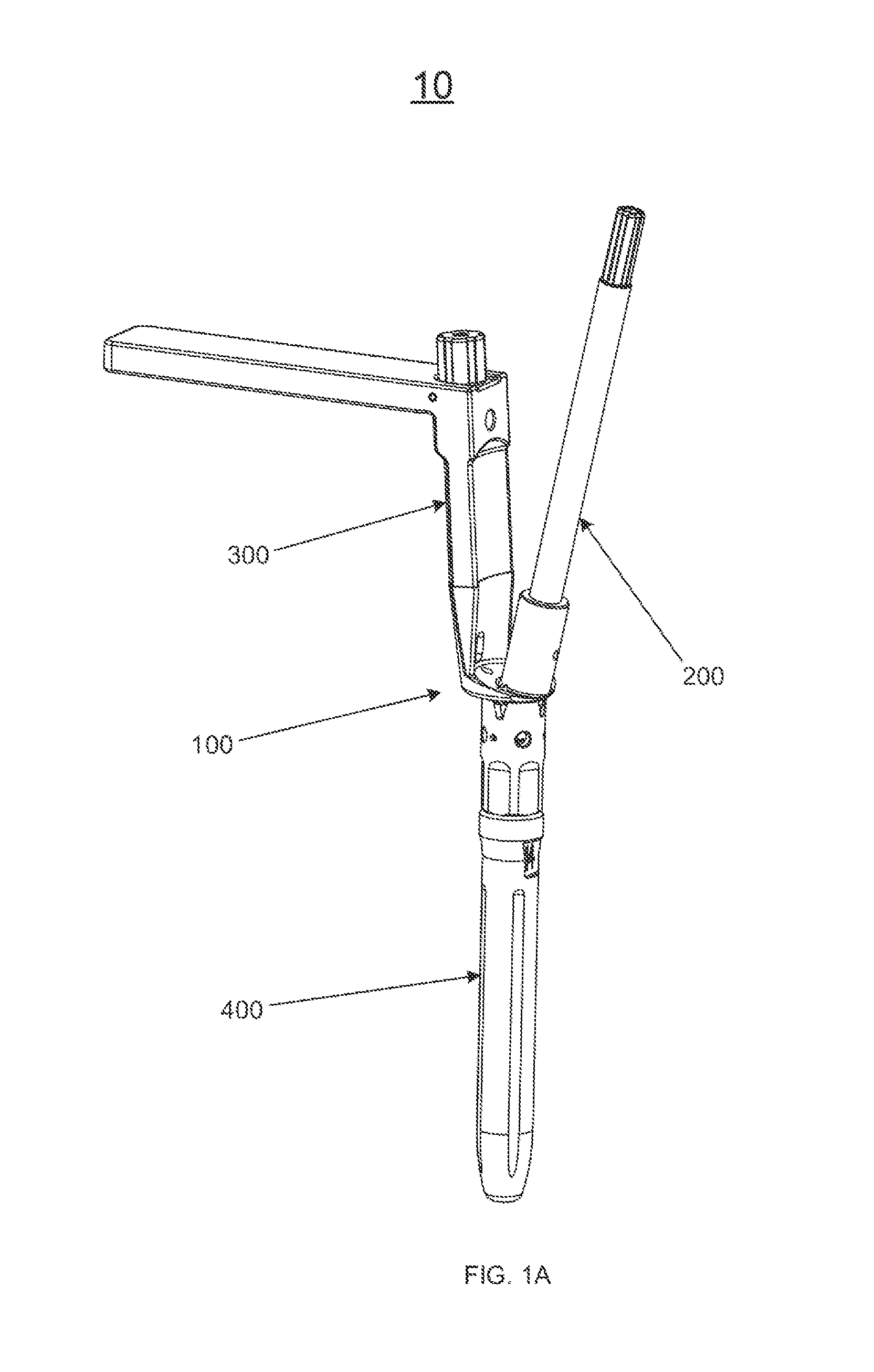
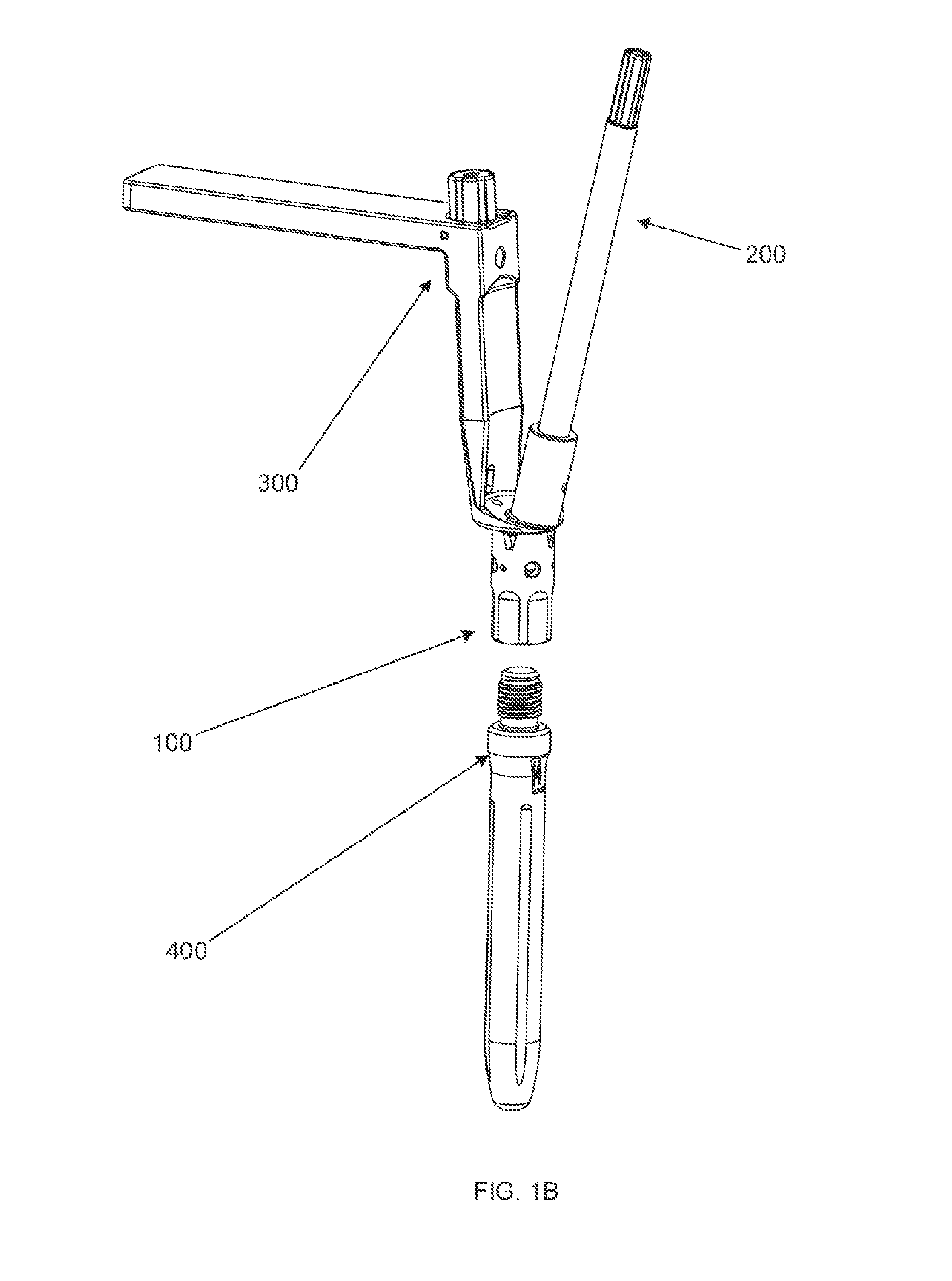
Method and apparatus for use of a non-invasive expandable implant
The present invention relates to a non-invasive expandable implant utilizing energy from an epiphyseal growth plate of a human long bone to expand the implant. A bone replacement section includes a housing, an expansion shaft, a connection system, and an implant member. An anchoring member is secured to the second bone portion and spaced from the implant member. The expansion shaft is configured to translate a first distance between the housing and the first bone member. Growth of the bone causes an increase of a second distance between an implant portion and the anchoring member. The increase of the second distance causes the anchoring member to exert a force on a connection system causing an increase of the first distance, thus expanding the implant.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Systems and methods for preparing bone voids to receive a prosthesis
Systems and methods for shaping and filling offset bone voids during revision procedures of total knee replacements are disclosed. The systems disclosed herein generally include an intramedullary reamer, an offset driver, a cylindrical reaming tool, an offset reaming guide, and a conical reamer. An alternate embodiment of the system may also generally include an IM reamer, an offset driver, an offset broaching tool, and a second stage broaching tool. Yet another embodiment may generally include an elongate IM reamer, a cone reamer, a reamer guide shaft, a cone trial, a sizing template, a template guide, an offset lobe reamer, and offset lobe reamer retainer. Metaphyseal reconstruction devices and void filling cones can be used to fill the bone voids in conjunction with the systems and methods disclosed herein.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
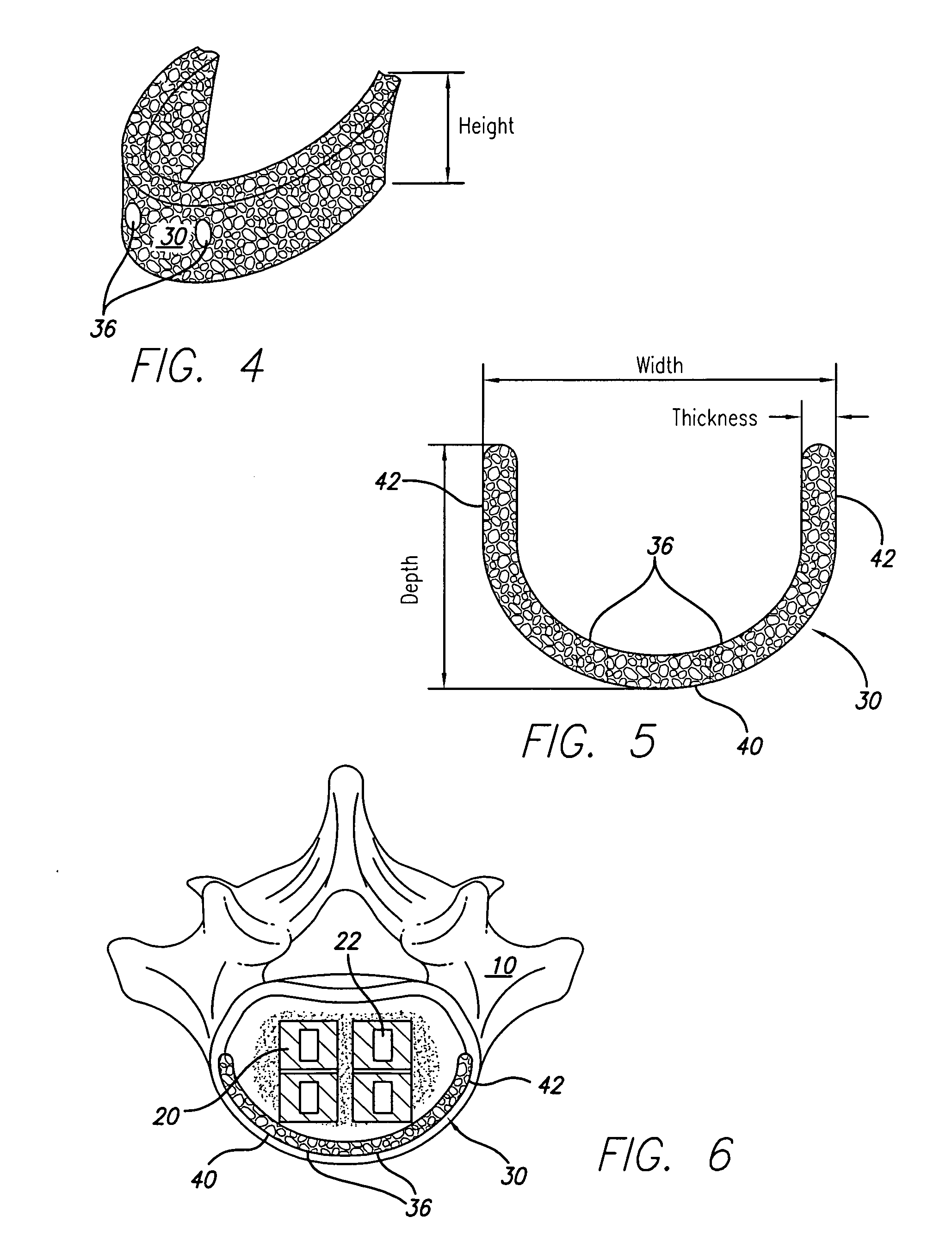
Support device for vertebral fusion
InactiveUS20060173543A1Improve fusion rateAvoid problemsBone implantJoint implantsEpiphysisALIF - Anterior lumbar interbody fusion
A support for vertebral fusion prevents subsidence and eliminates the need for posterior surgery and instrumentation. The support is constructed of an implantable man-made material. One embodiment is generally a U-shaped metal support that rests on the apophyseal ring of a patient's vertebrae, with the open portion of the U facing the patient's posterior. The metal support is connected to a previously placed threaded cage or bone dowel such as that used in anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF). The U-shaped support is preferably comprised of a trabecular metal such as tantalum.
Owner:BRAU SALVADOR A +1
Bone Implant
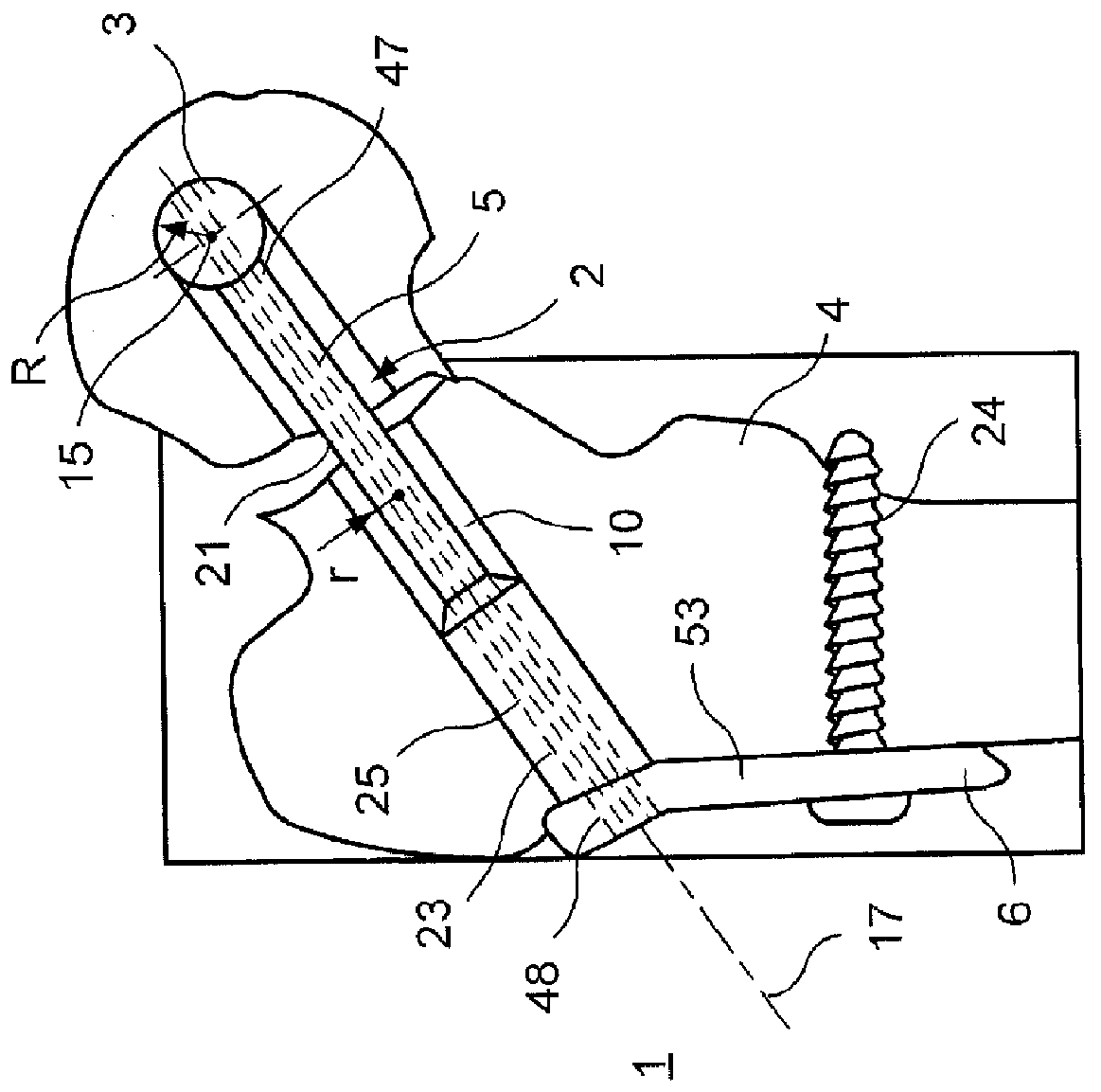
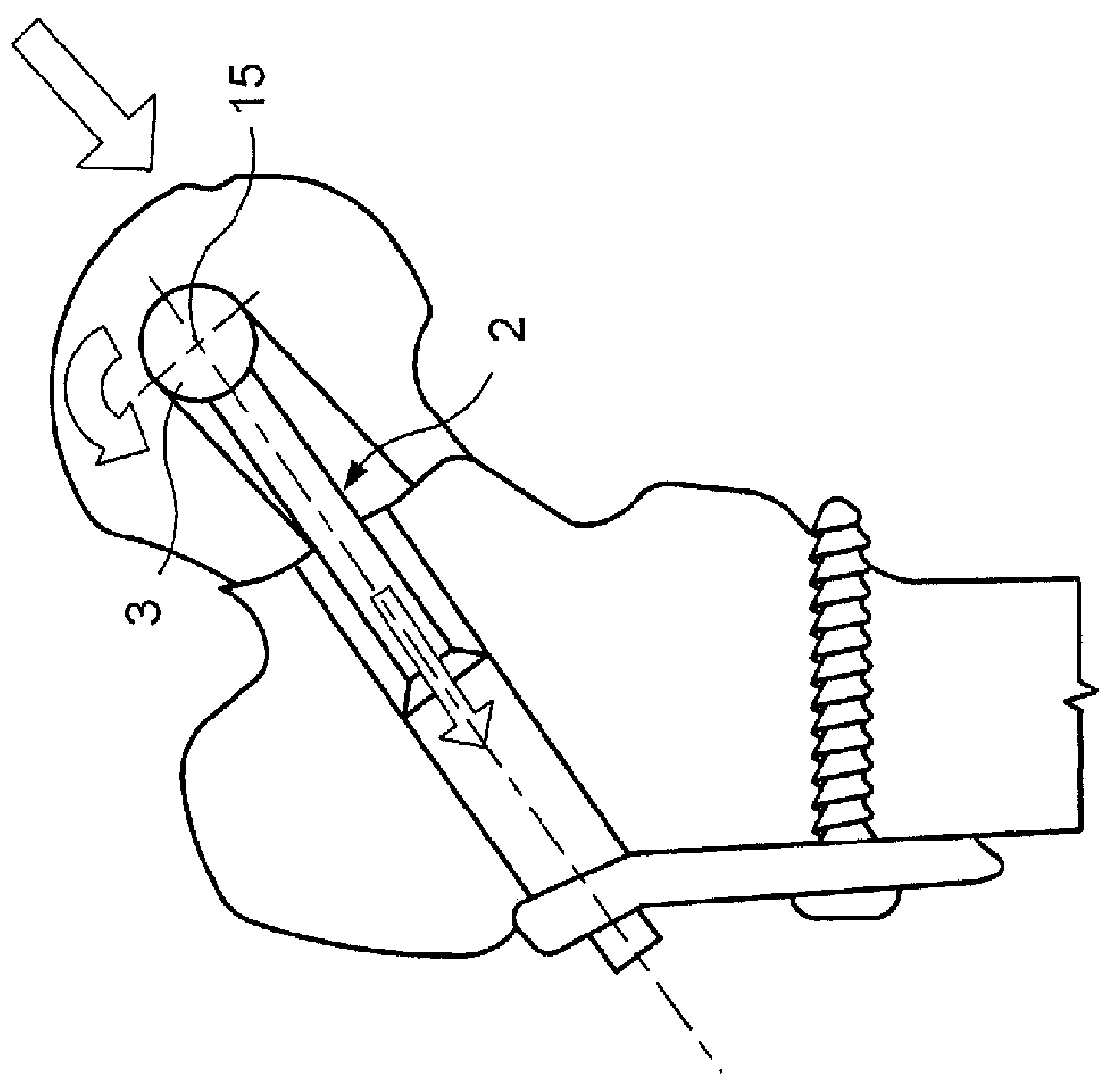
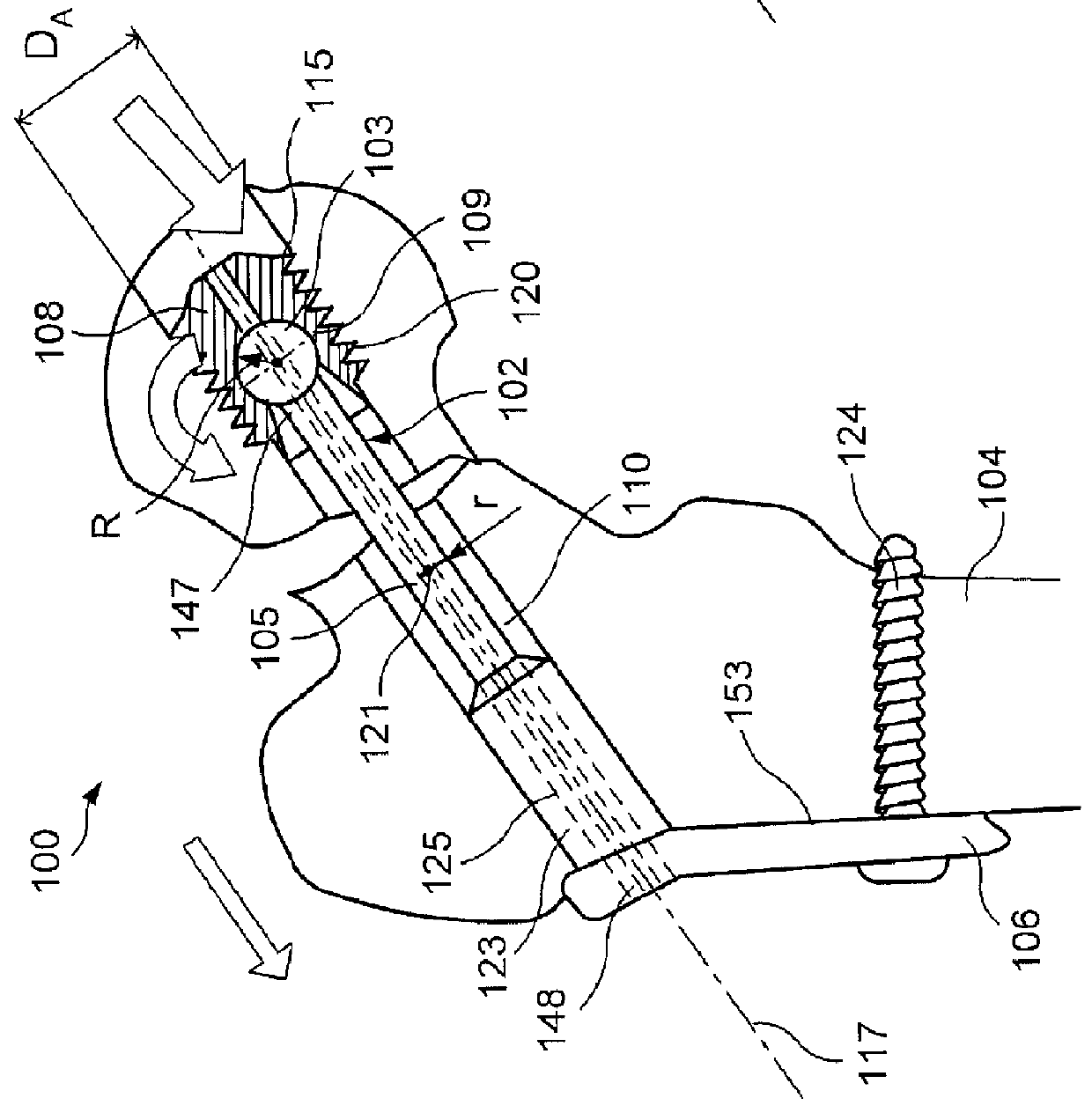
ActiveUS20120109128A1Fracture stability is improvedImprove stabilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEpiphysisBone implant
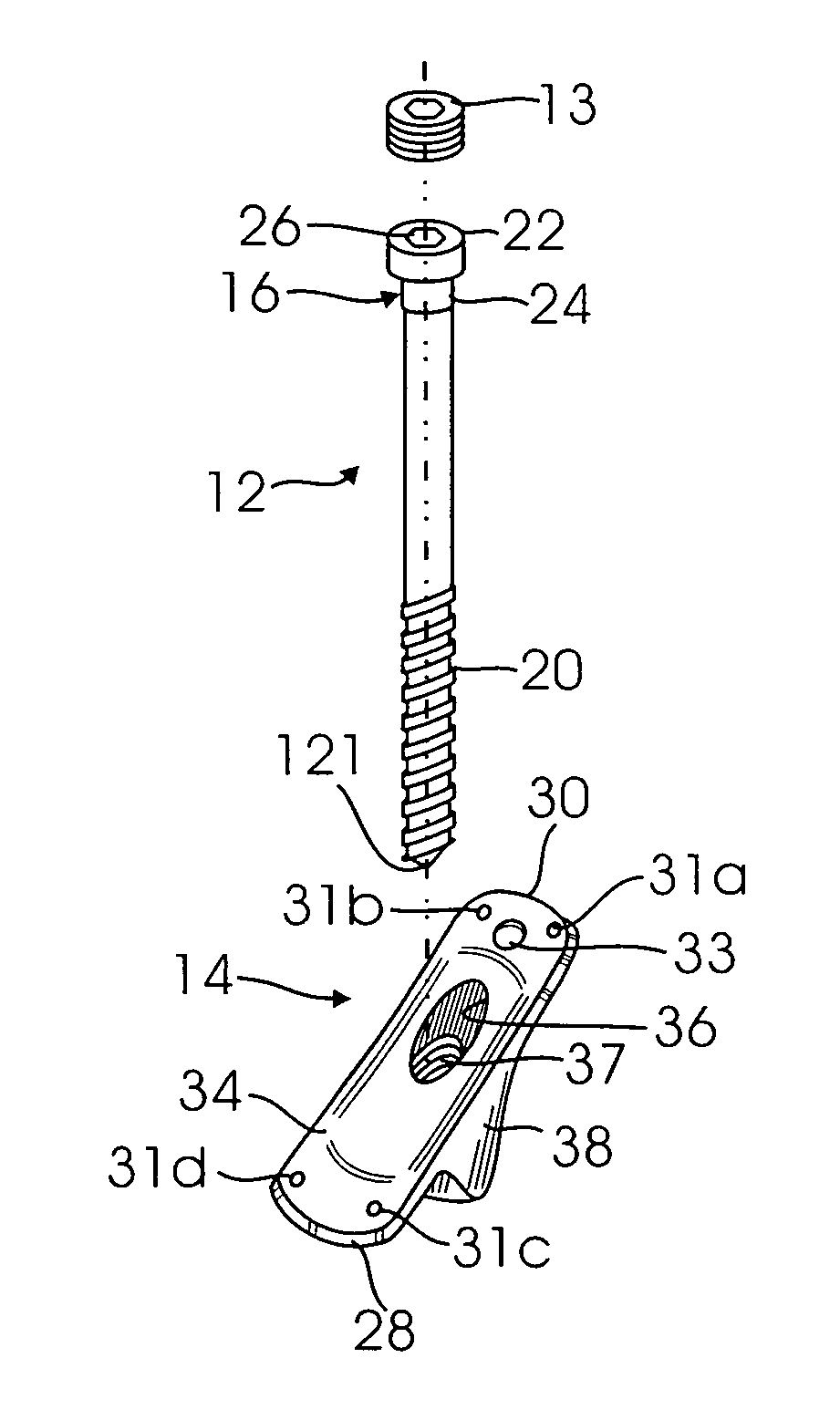
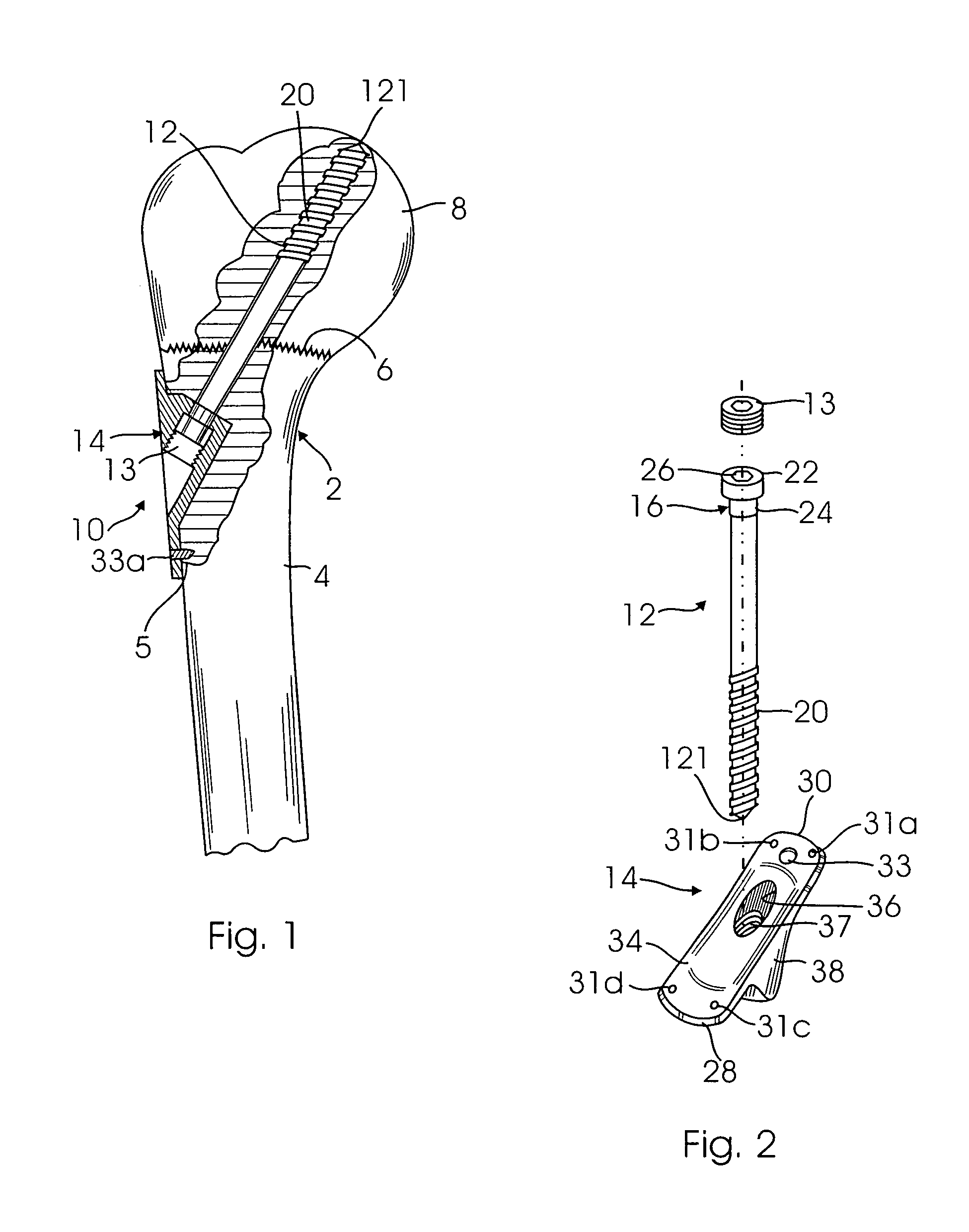
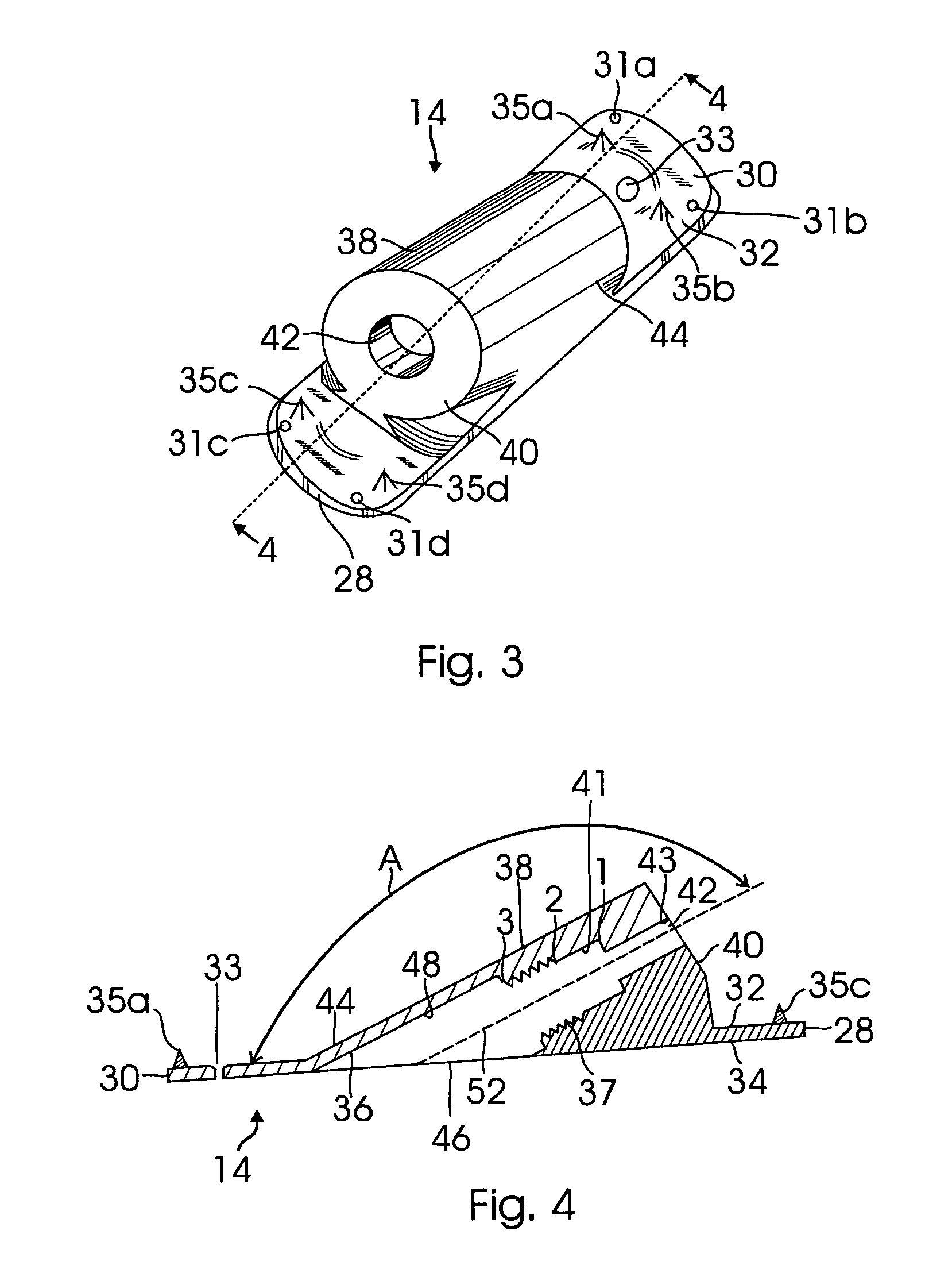
A fixation device for treating an epiphyseal fracture, comprises a shaft extending longitudinally along a central axis from a first end to a second end configured to slidably engage a bone implant opening and a having a maximum radius r and a spherical head element attached to the first end of the shaft and having a radius R>r, the spherical head element configured to be inserted into a fragmented portion of bone such that the fragmented portion rotates about the spherical head element relative to the central axis of the shaft.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Odd angle internal bone fixation device for use in a transverse fracture of a humerus
InactiveUS8187276B1Reliable lockingInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsInternal bone fixationGun barrel
The present invention is an improved unique odd angle internal fixation device for both a transverse and longitudinal fracture located at the junction of the metaphysis and diaphysis of a long bone such as the proximal humerus. The improved odd angle internal fixation device includes an elongated lag screw and a rectangular shaped guide plate having multiple holes throughout the plate to host pins and screws and four tips on the front side of the plate. A lag screw with a cylindric head having a hexagonal cavity introduced through the diaphyseal segment of the fracture at three angles, 90, and 150 and 160 degrees, cross fixing the respective bone longitudinal and transverse fracture line and settling in the depth of the epiphysis. An additional locking screw is introduced on the top of the lag screw head to securely lock the lag screw after being settled into the epiphysis. The guide plate serves as a guide for the lag screw and allows the engagement of the head of the lag screw to the inner wall of its short barrel portion. The engagement would cause the guide plate which is attached to the barrel, to be compressed against the diaphyseal cortex as the lag screw advances deeper into the epiphysis at said three angles.
Owner:ZAHIRI CHRISTOPHER A +1
Surgical reaming instrument for shaping a bone cavity
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for shaping bone voids during revision procedures of total knee replacements. The systems disclosed herein generally include a cannulated reamer assembly, a reaming guide assembly, a guide tube assembly, a trial stem assembly, and an optional insertion / removal tool. Metaphyseal reconstruction devices can be used to fill the bone voids in conjunction with the systems and methods disclosed herein.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Orthopedic device for an articular joint
ActiveUS8118875B2Ensure mechanical stabilityUndesirable unscrewing of the fixing screw may be avoidedSuture equipmentsJoint implantsArticular surfacesArticular surface
An orthopedic device for ball and socket joint reconstruction. The anchor stem is adapted to be anchored in a medullary canal. A proximal portion of the anchor stem includes a threaded hole oriented along a longitudinal axis thereof. Metaphyseal portion includes a proximal end with recess and a longitudinal bore in fluid communication with the recess, and a distal end adapted to interface with the proximal portion of the anchor stem. An anti-rotation structure is preferably located at an interface of the anchoring stem to the metaphyseal portion to prevent rotation of the anchor stem relative to the metaphyseal portion around the longitudinal axis. A fastener is provided to extend through the longitudinal bore and to engage with the threaded hole on the anchor stem to fix the metaphyseal portion to the anchoring stem. The locking assembly is located in the recess and mechanically couples the head of the fastener to the metaphyseal portion to limit rotation of the fastener relative to the metaphyseal portion. An insert with an articular surface is provided that engages with the proximal end of the metaphysical portion and extends over the recess in the metaphyseal portion.
Owner:TORNIER SA SAINT ISMIER
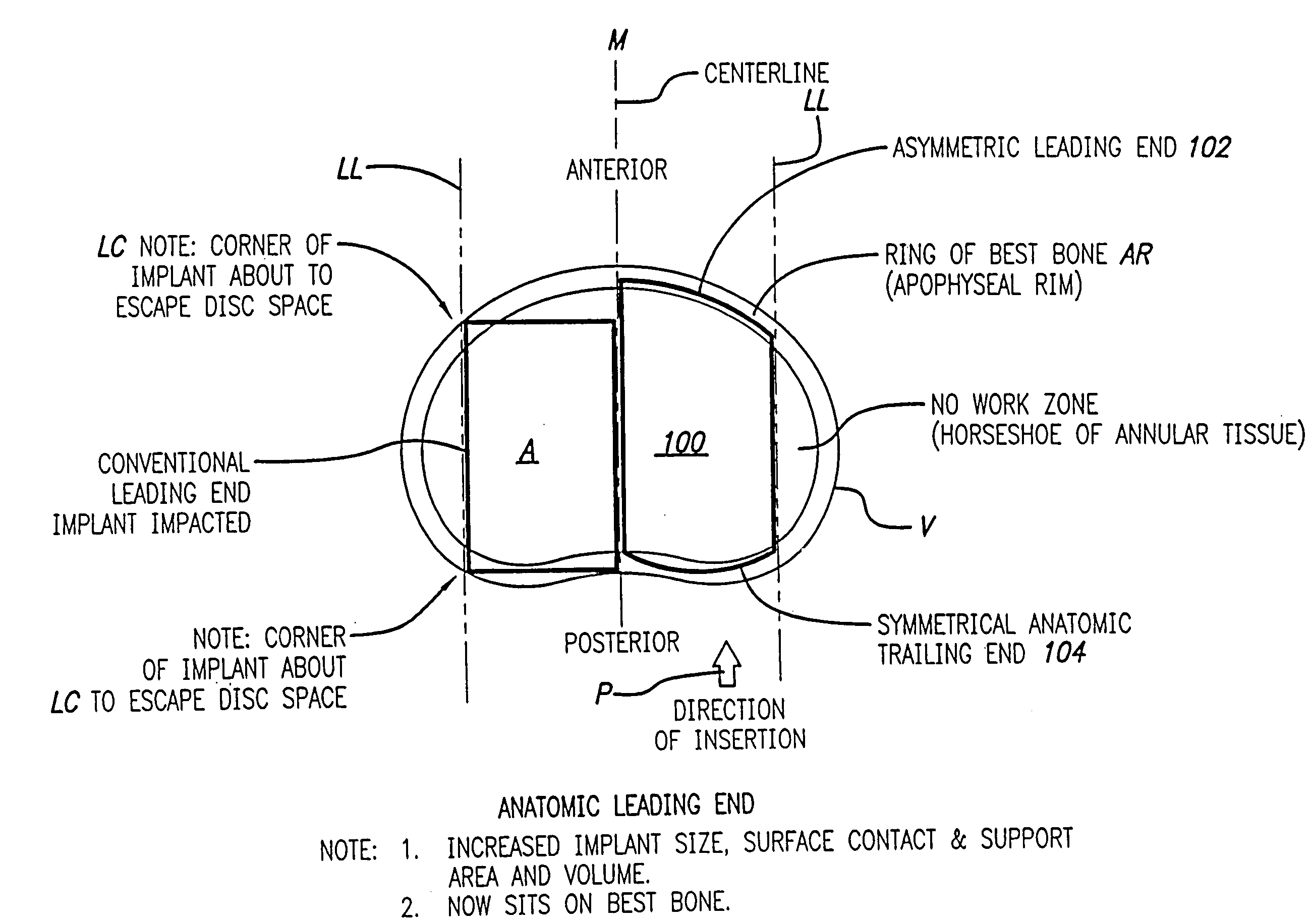
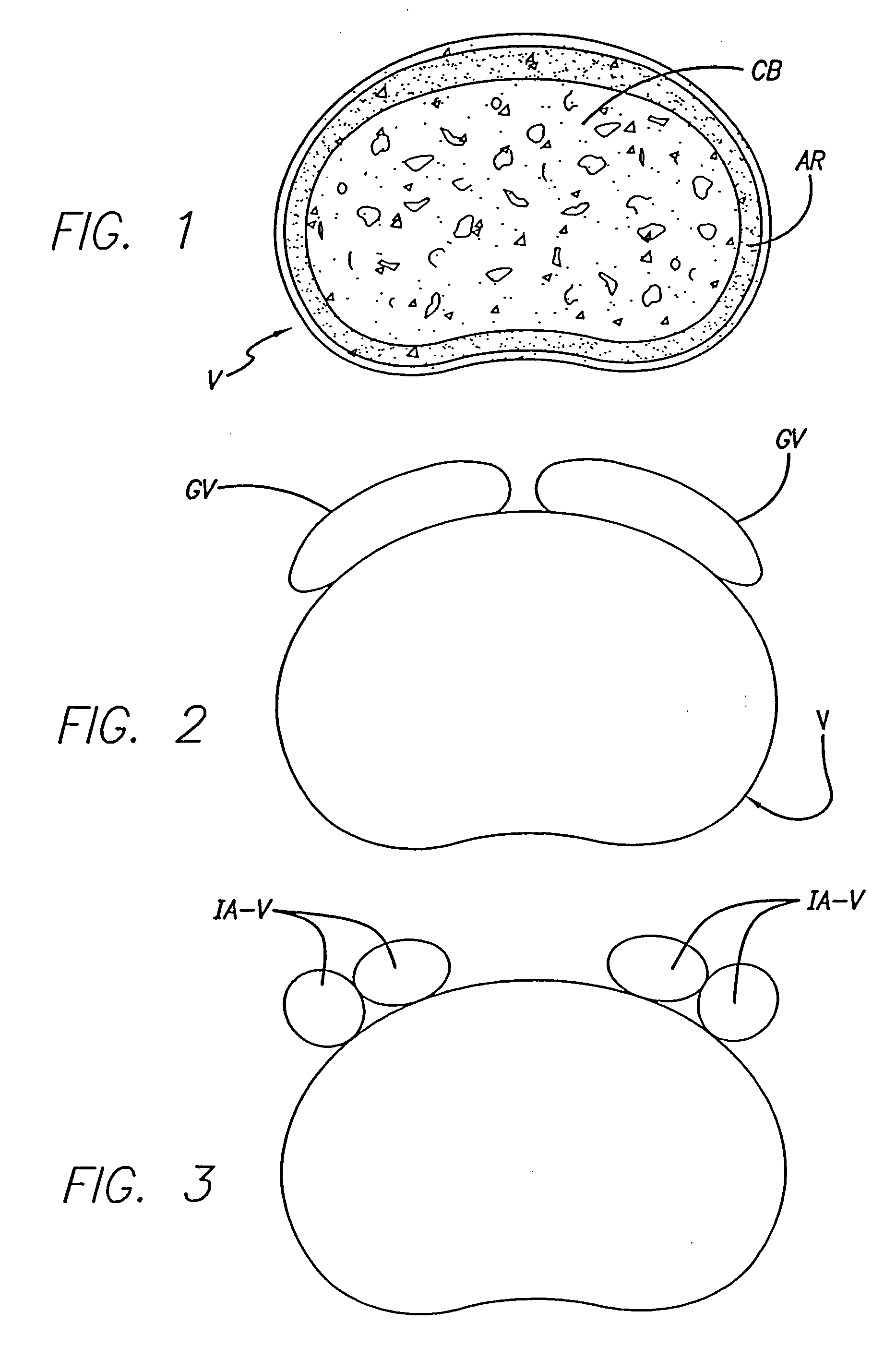
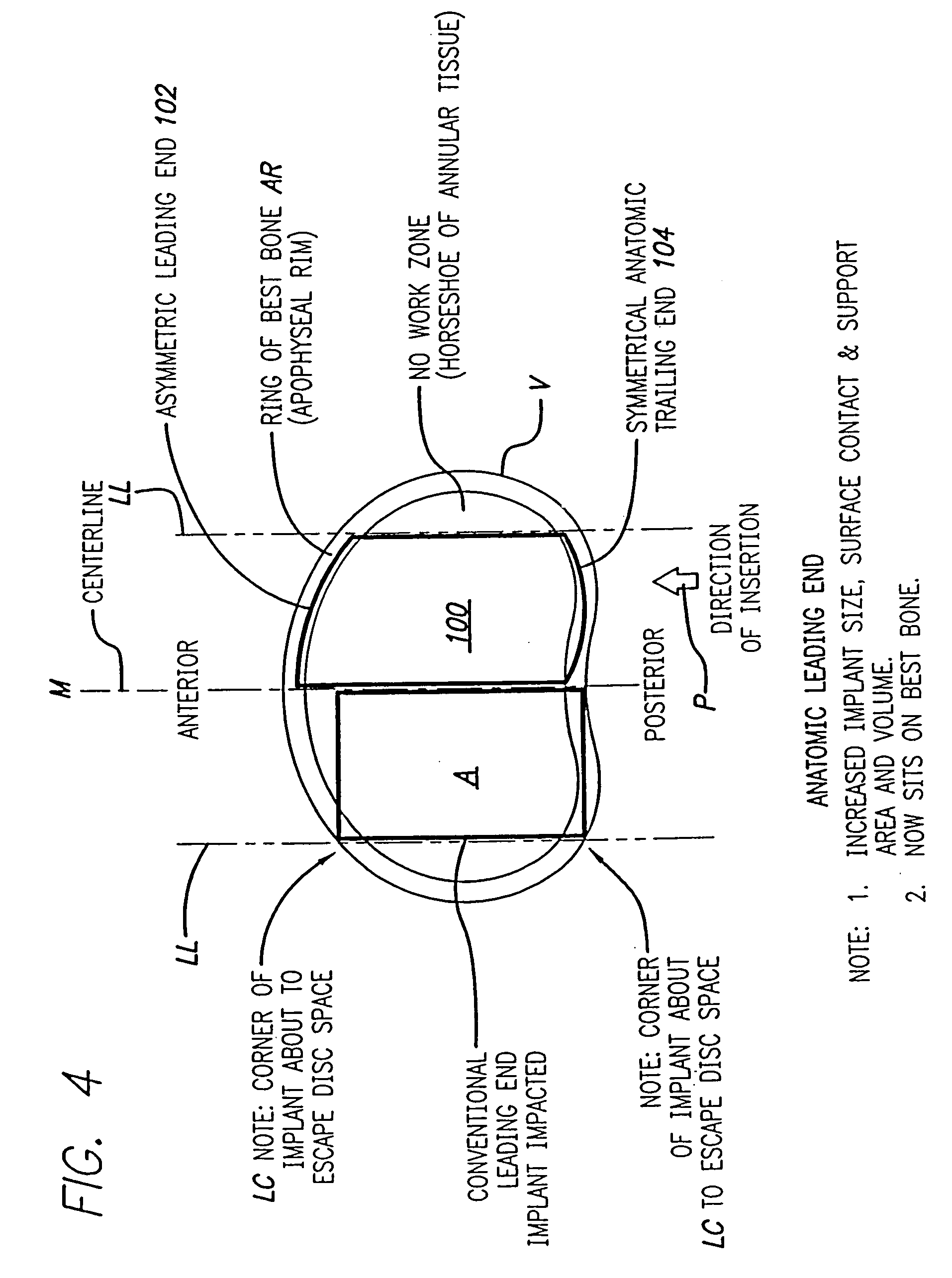
Bone hemi-lumbar arcuate interbody spinal fusion implant having an asymmetrical leading end
InactiveUS20060235519A1Maximize contact areaIncrease the lengthBone implantJoint implantsSpinal columnIntervertebral space
An interbody spinal implant is formed of cortical bone adapted for placement across an intervertebral space formed across the height of a disc space between two adjacent vertebral bodies. An asymmetrical leading end on the implant is adapted to sit upon the peripheral areas, such as the apophyseal rim and the apophyseal rim area, of the vertebral end plate region of the vertebral bodies without protruding therefrom. The asymmetrical leading end allows for the safe use of an implant of maximum length for the implantation space into which it is installed. The implant can also include an asymmetric trailing end adapted to sit upon the more peripheral areas of the vertebral end plate region of the vertebral bodies.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
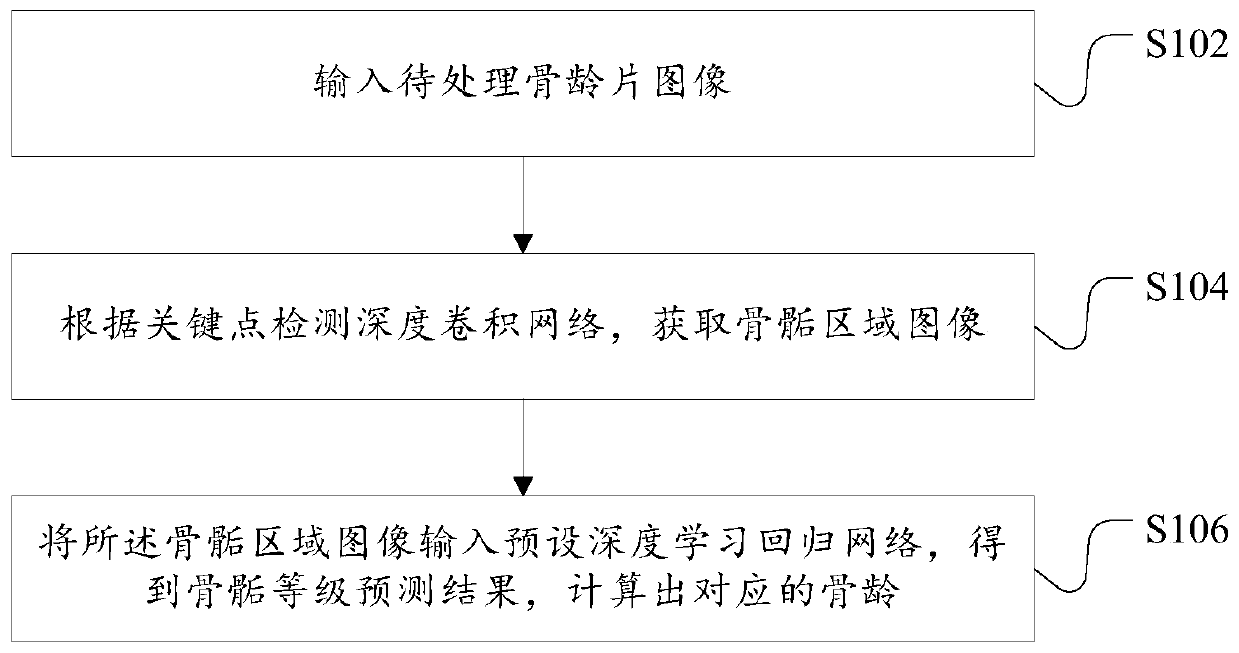
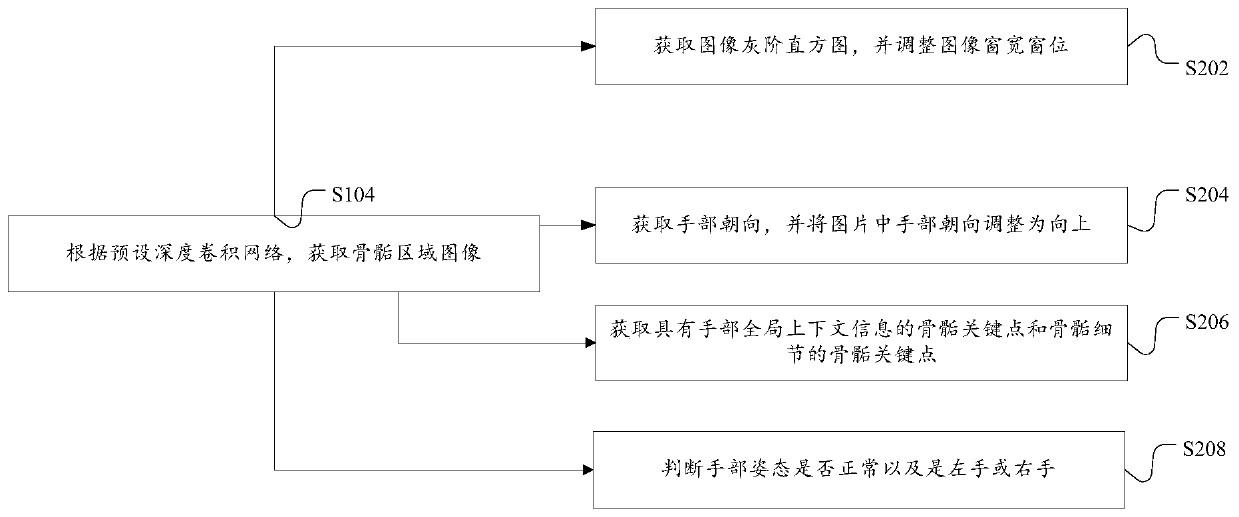
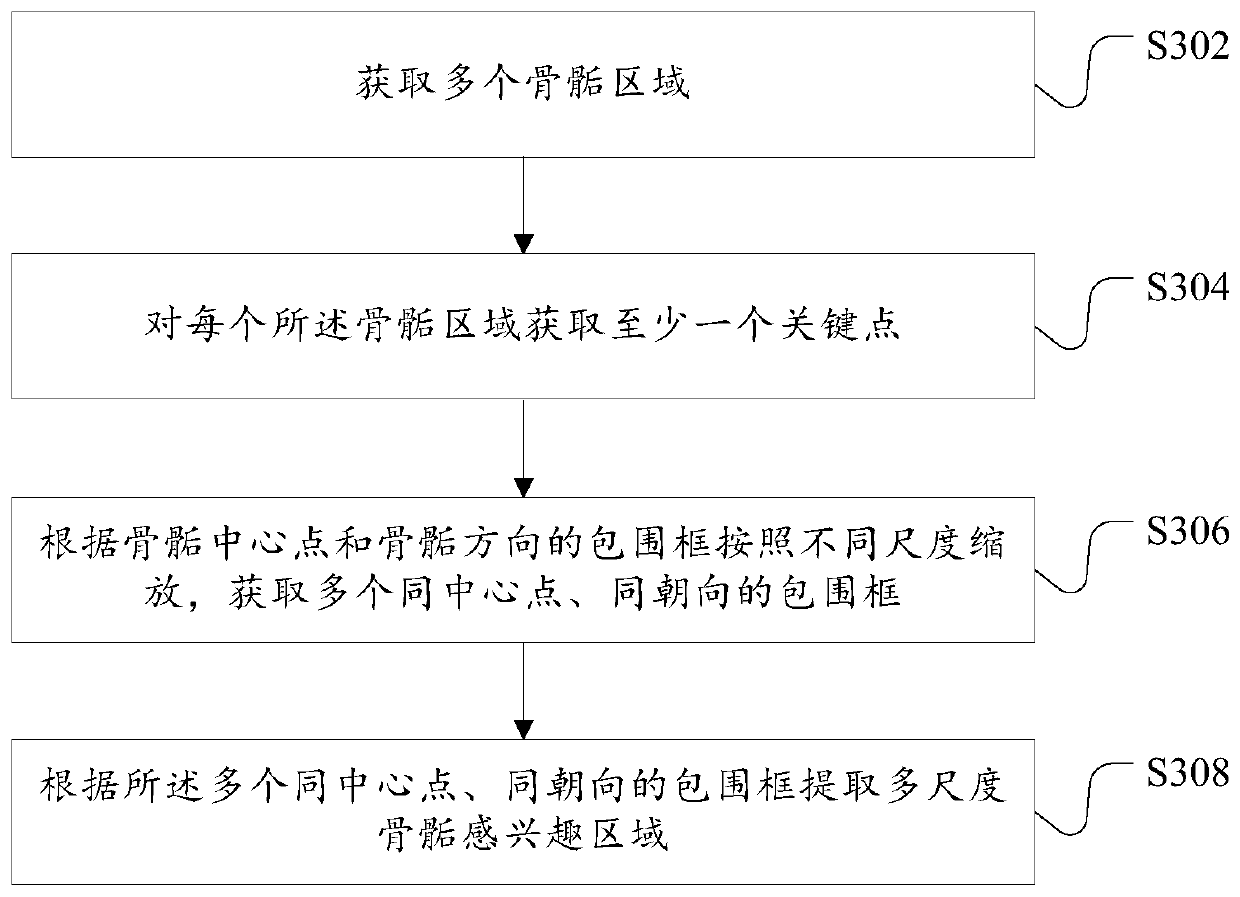
A bone age prediction method and device based on a deep regression network
ActiveCN109741309AAvoid influenceTroubleshoot technical issues with poor performanceImage analysisNeural architecturesEpiphysisBone age
The invention discloses a bone age prediction method and device based on a deep regression network. The method comprises the following steps: inputting a to-be-processed bone age slice image; according to the multi-level key point detection deep convolutional network, obtaining a epiphyseal area image; and inputting the epiphysis region image into a preset deep learning regression network to obtain an epiphysis grade prediction result, and calculating the corresponding bone age. The technical problem that a bone age prediction method is poor in effect is solved. According to the method and thedevice, the epiphysis grade prediction result can be directly output without linking the epiphysis grade labeling database, and the bone age can be accurately predicted. According to the method, theepiphysis area obtained based on multi-level key point detection serves as input, the epiphysis level prediction result is output through the multi-branch deep regression network after the epiphysis area passes through the convolutional network, and the obtained prediction effect is good.
Owner:HANGZHOU SHENRUI BOLIAN TECH CO LTD +1
Systems and methods for preparing bone voids to receive a prosthesis
Systems and methods for shaping and filling offset bone voids during revision procedures of total knee replacements are disclosed. The systems disclosed herein generally include an intramedullary reamer, an offset driver, a cylindrical reaming tool, an offset reaming guide, and a conical reamer. An alternate embodiment of the system may also generally include an IM reamer, an offset driver, an offset broaching tool, and a second stage broaching tool. Yet another embodiment may generally include an elongate IM reamer, a cone reamer, a reamer guide shaft, a cone trial, a sizing template, a template guide, an offset lobe reamer, and offset lobe reamer retainer. Metaphyseal reconstruction devices and void filling cones can be used to fill the bone voids in conjunction with the systems and methods disclosed herein.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Electrical current induced inhibition of bone growth
Owner:THE NEMOURS FOUND
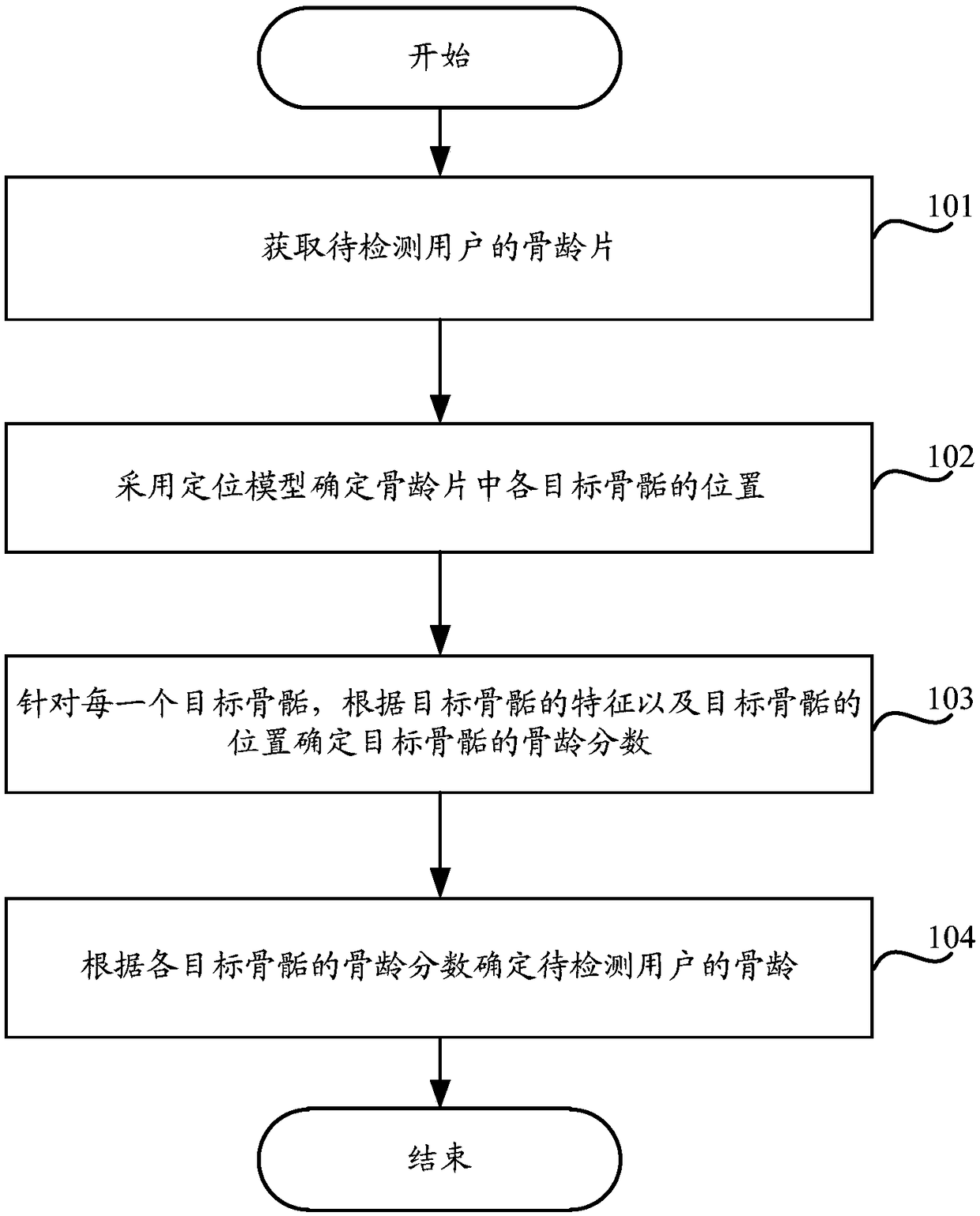
Method and device for detecting bone age
ActiveCN109377484AHigh precisionImprove the efficiency of detecting bone ageImage enhancementImage analysisEpiphysisBone age
Embodiments of the present application provide a method and a device for detecting bone age, which relate to the technical field of machine learning. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a bone age sheet of a user to be detected; and determining the position of each target epiphysis in the bone age sheet by using a positioning model. For each target epiphysis, the bone age score ofthe target epiphysis is determined according to the characteristics of the target epiphysis and the position of the target epiphysis, and finally, the bone age of the user to be detected is determinedaccording to the bone age score of each target epiphysis. Because the different forms of epiphysis represent different stages of bone age, there are also some differences in the shape of the epiphyses at different locations, as such, embodiment of that present application employ a positioning model to automatically determine the position of the target epiphysis, then, the bone age score is determined based on the characteristics of target epiphysis and the position of target epiphysis, and the bone age of the user to be detected is determined based on the bone age score, without artificial subjective judgment of bone age according to bone age slices, so that on the one hand, the precision of detecting bone age is improved, and on the other hand, the efficiency of detecting bone age is improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU YITU MEDIAL TECH CO LTD
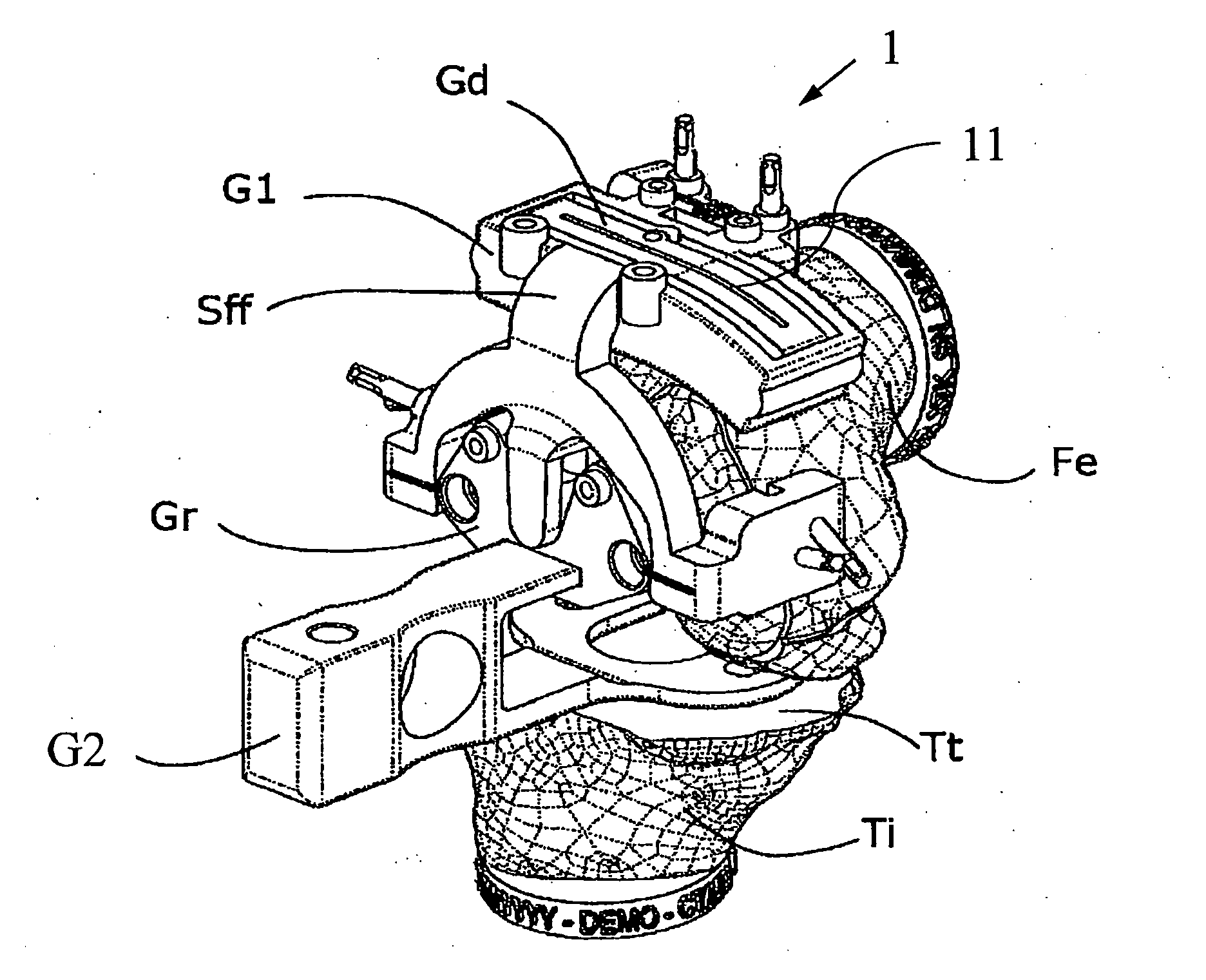
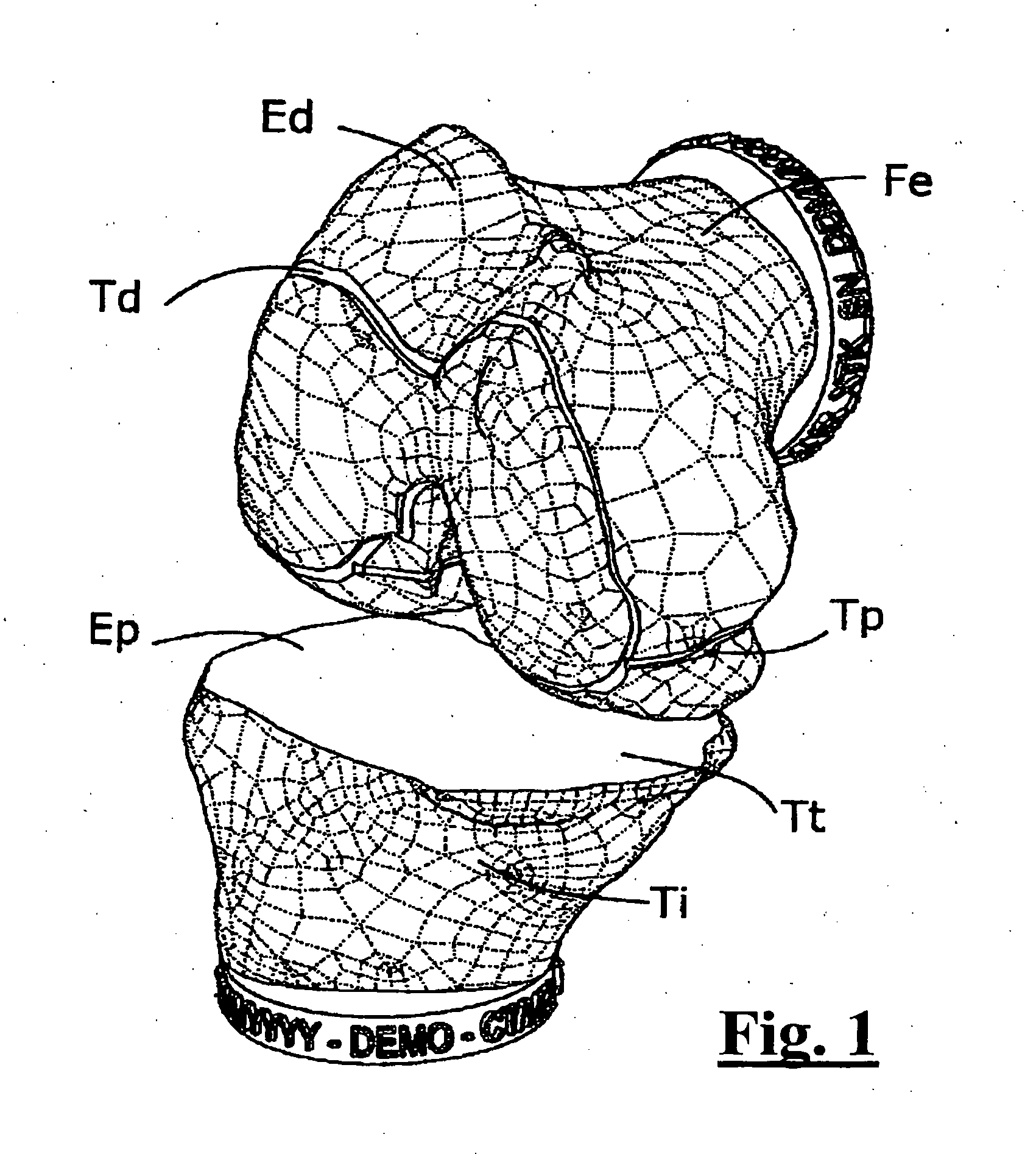
Surgical guide for implanting a knee prosthesis
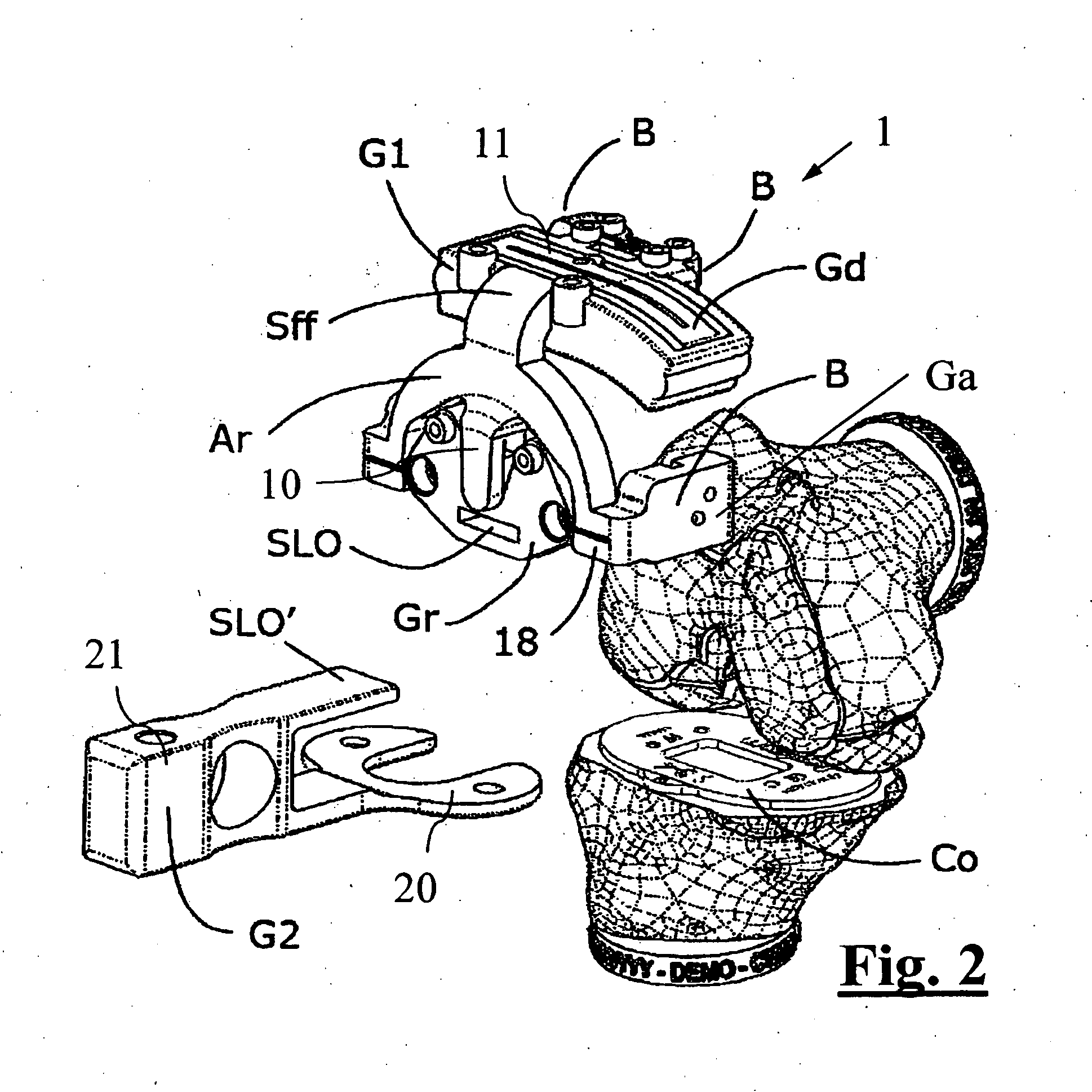
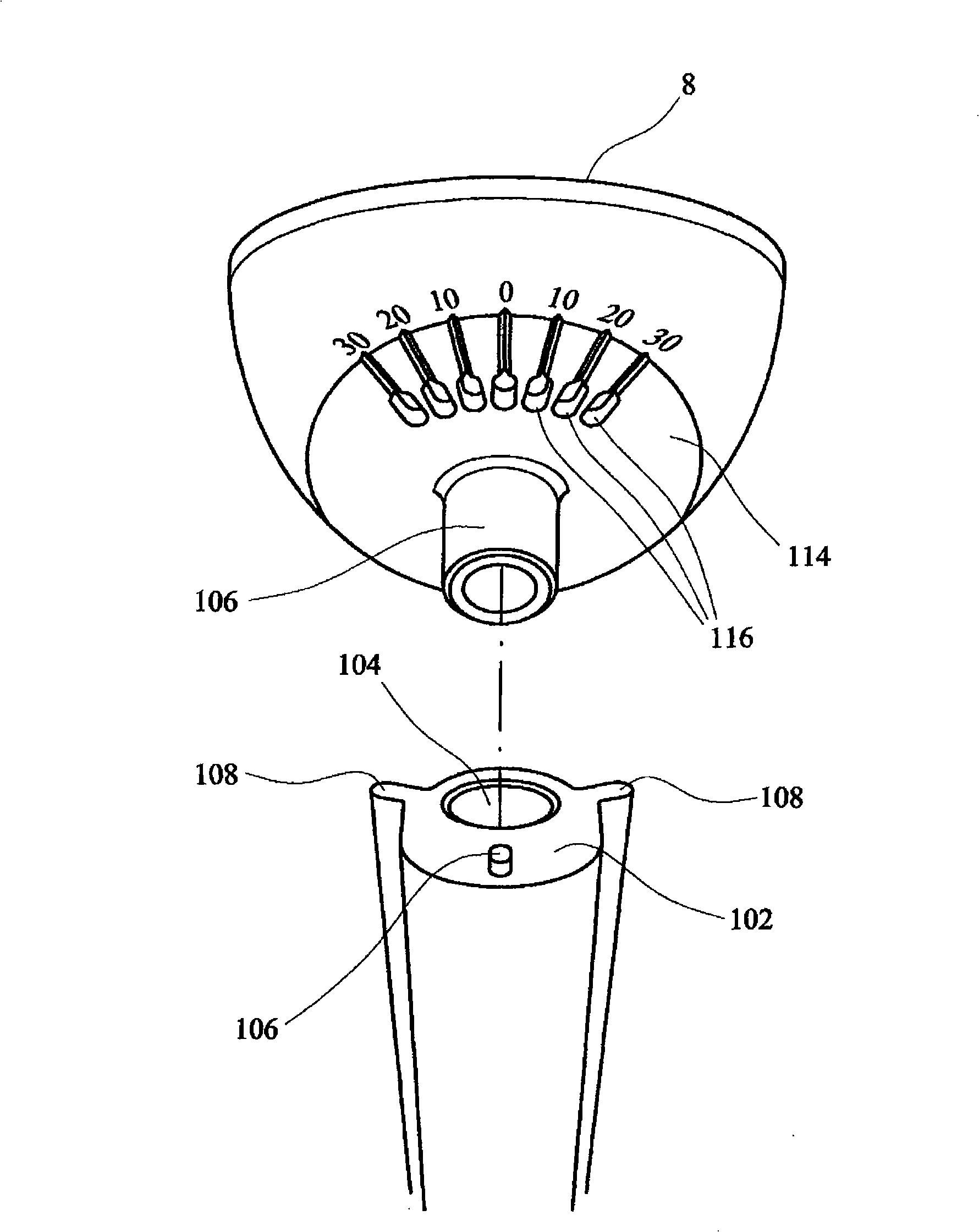
The invention relates to a surgical guide (1, 1′) for implanting a knee prosthesis, advantageously capable of allowing the intraoperative balancing of the knee ligaments, comprising: a first component (G1, G1′) intended for uniquely coupling with the distal epiphyseal end (Ed) of a femur (Fe); a template (Gr, Gr′) rotatably mounted with respect to said first component (G1, G1′) and intended for guiding a marking operation of said distal epiphyseal end (Ed) aimed to determine the position of a knee prosthesis to be implanted; and a second component (G2) intended for solidly coupling said template (Gr, Gr′) with a proximal epiphyseal end (Ep) of a tibia (Ti) corresponding to said femur (Fe).
Owner:MEDACTA INT SA
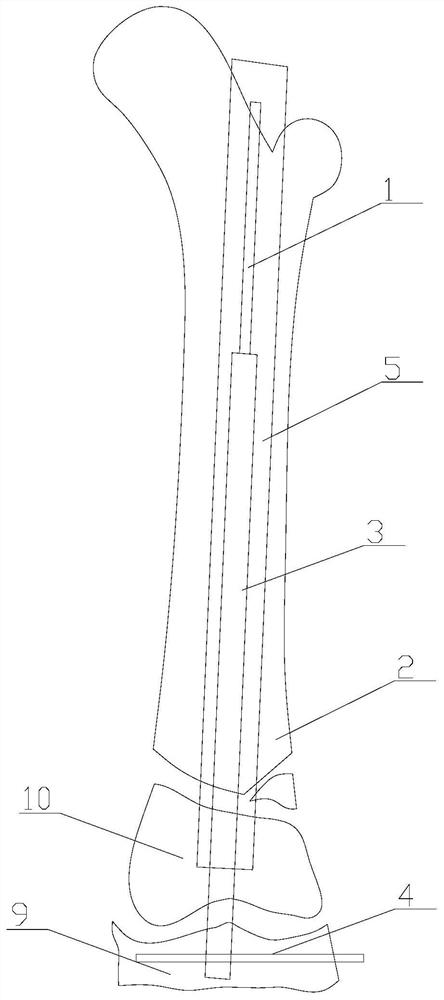
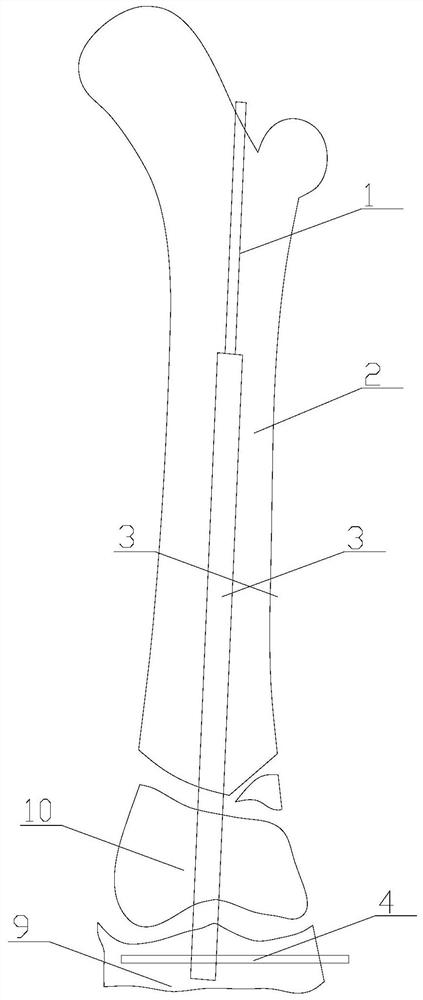
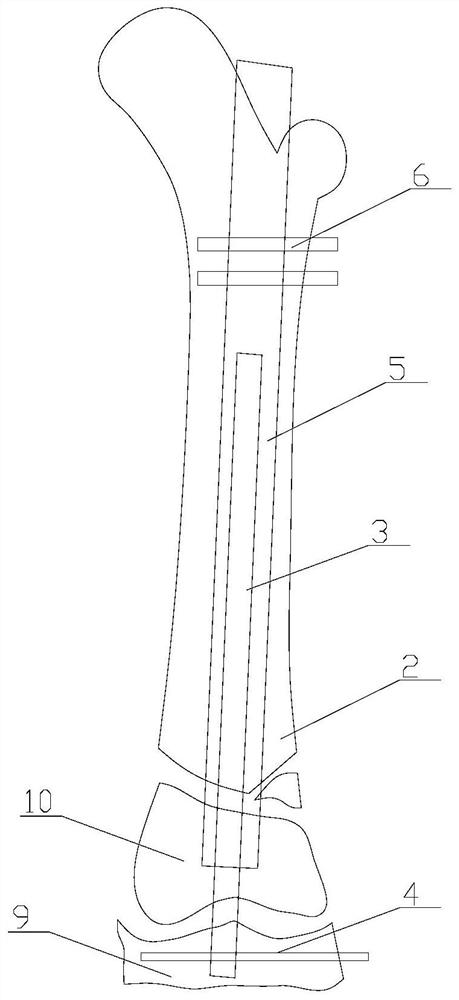
Ratcheting epiphysiodesis plate
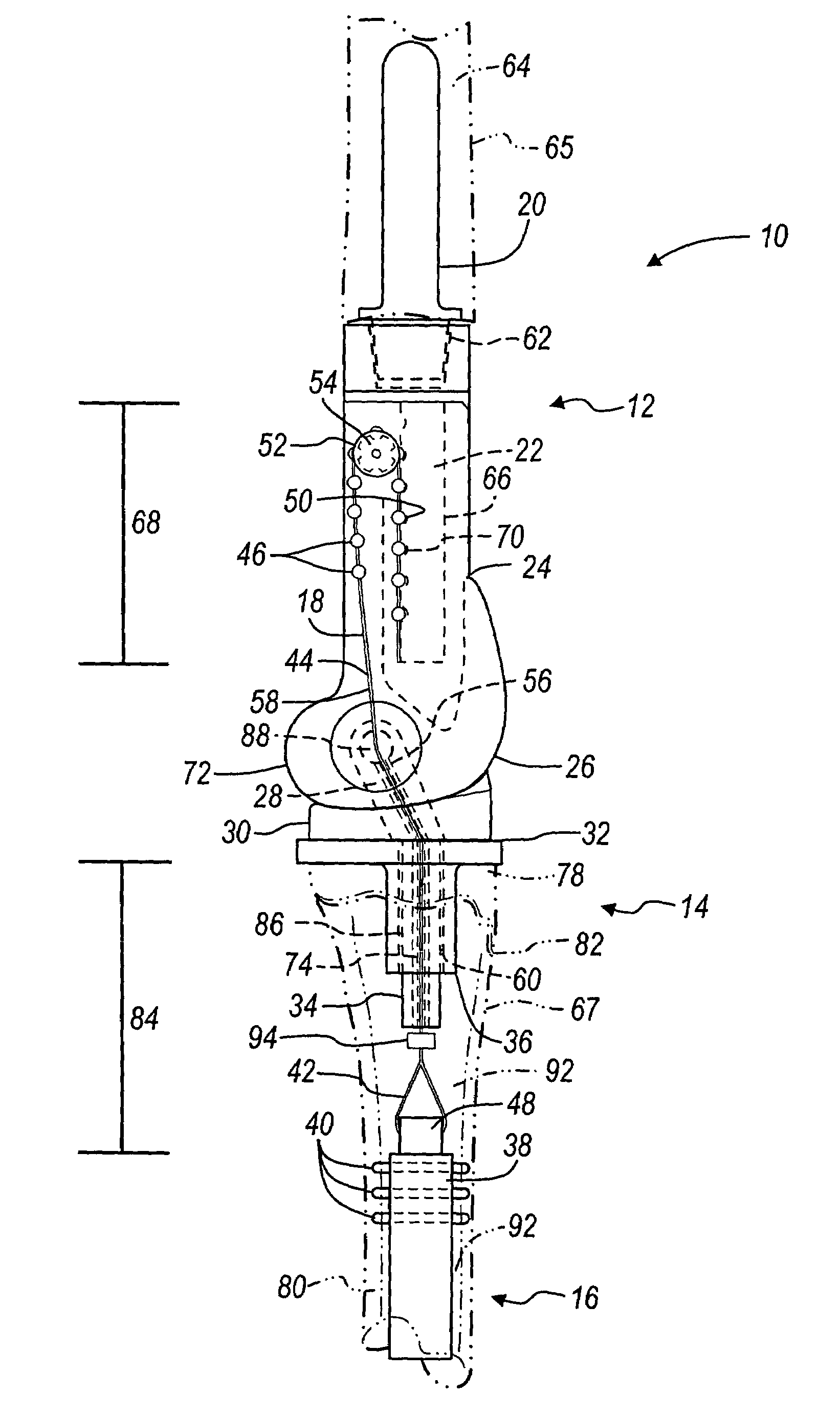
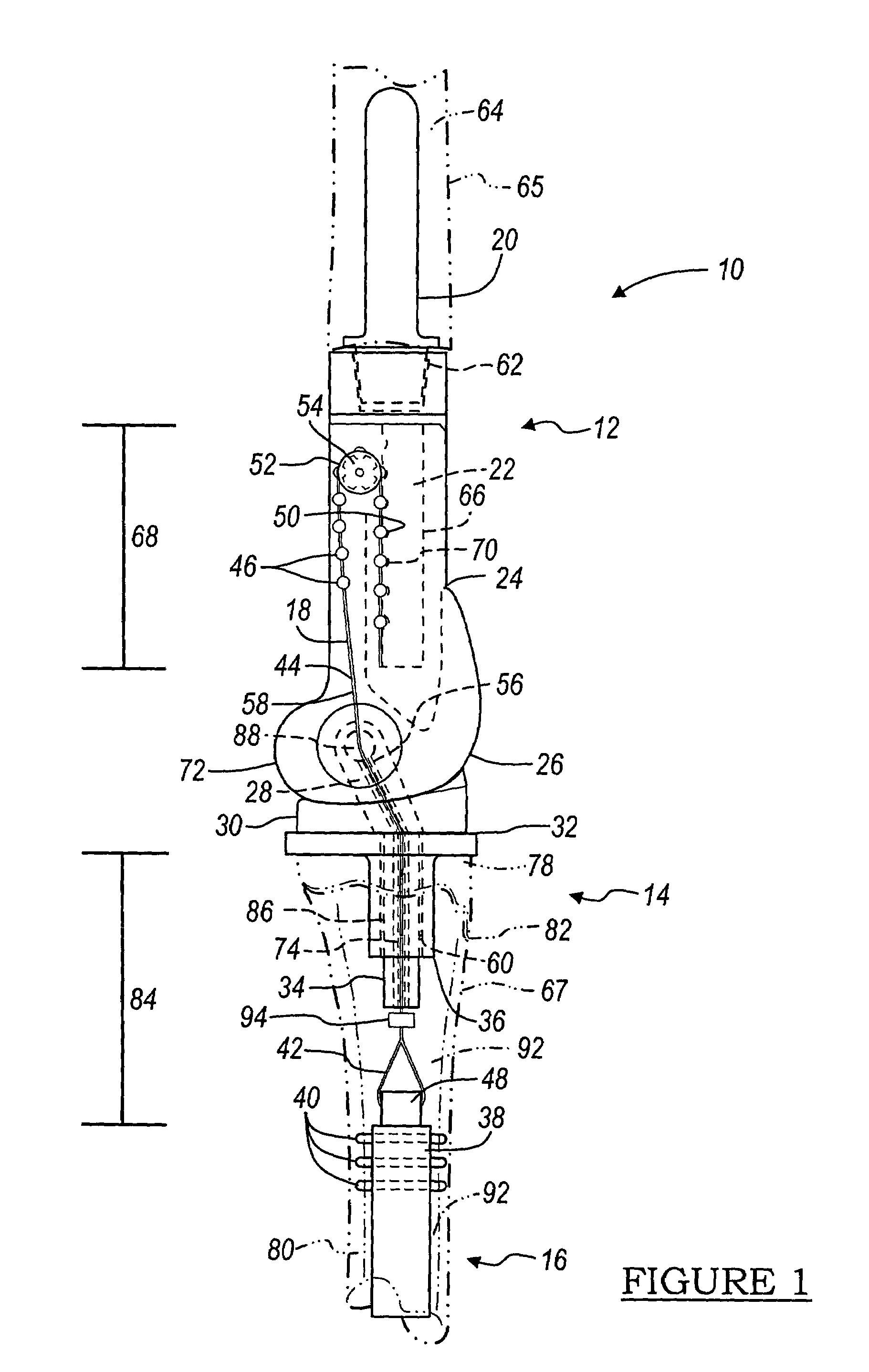
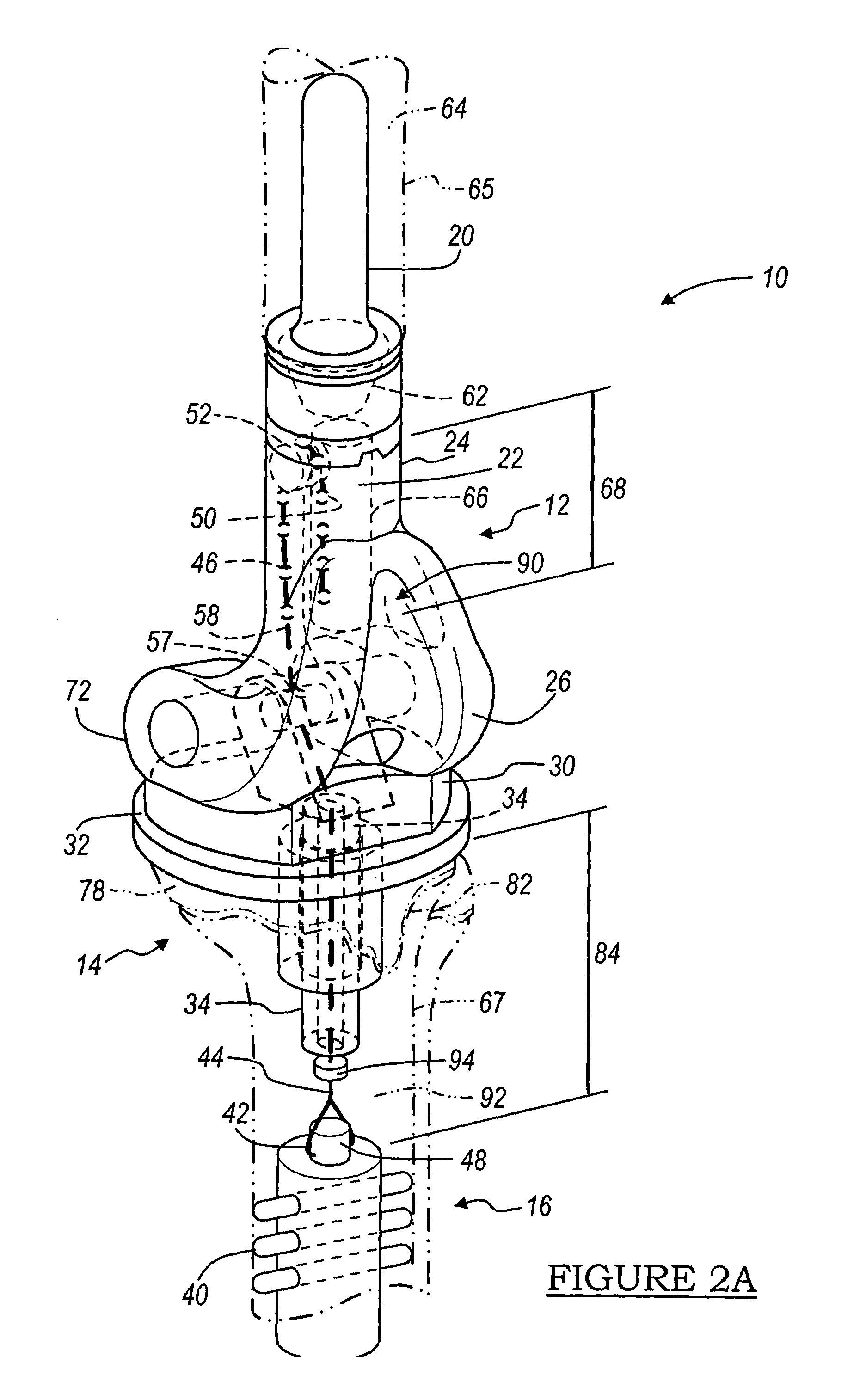
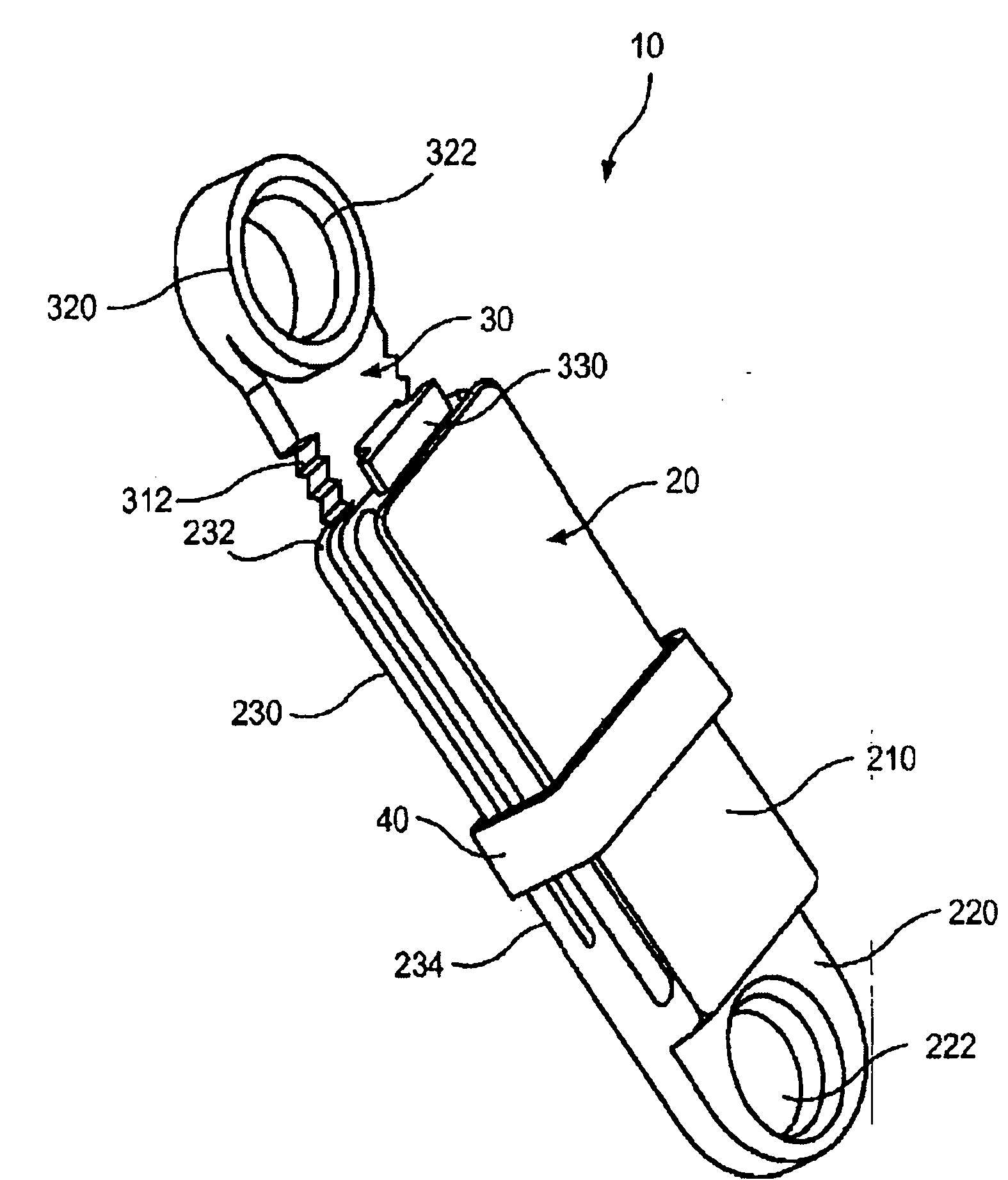
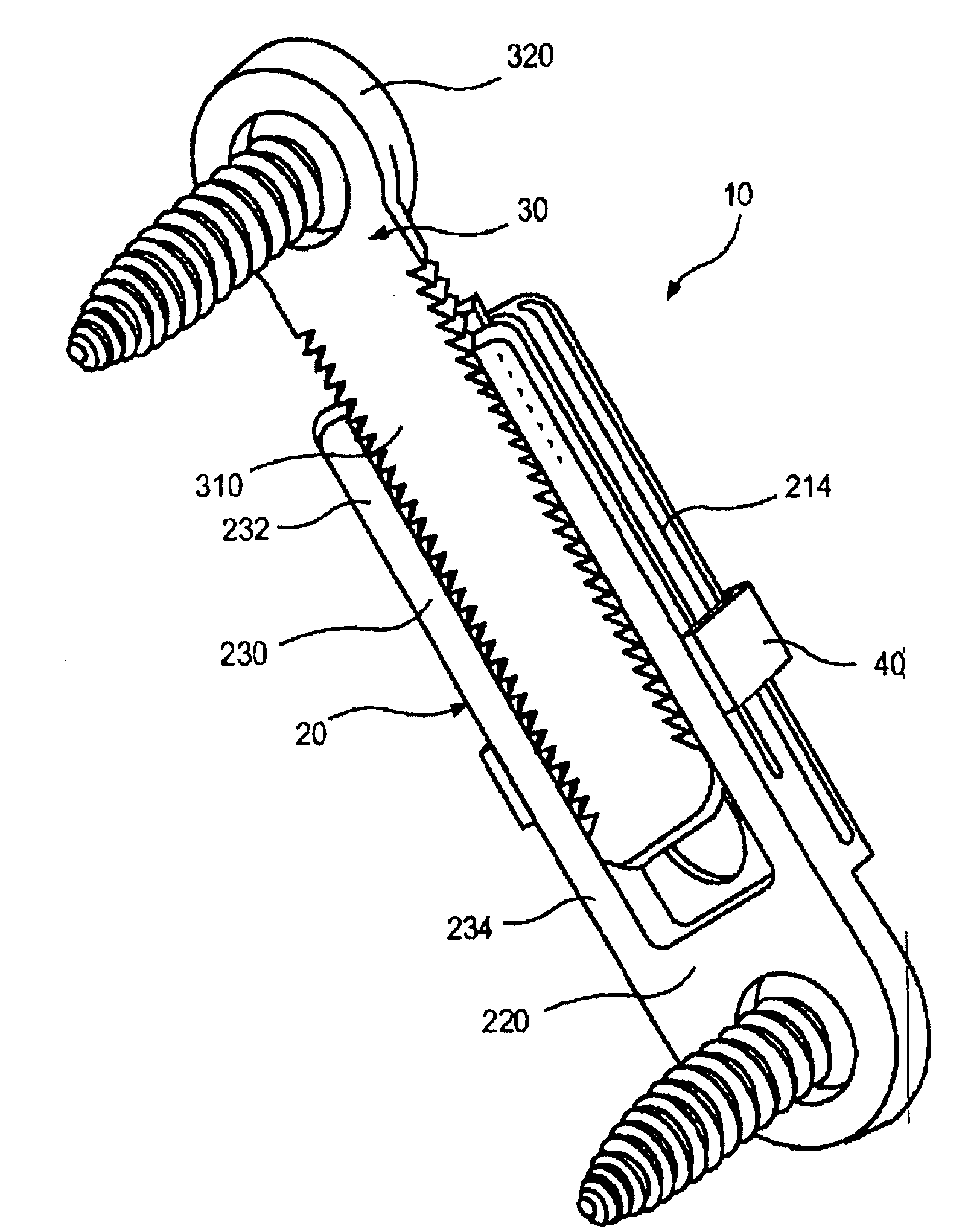
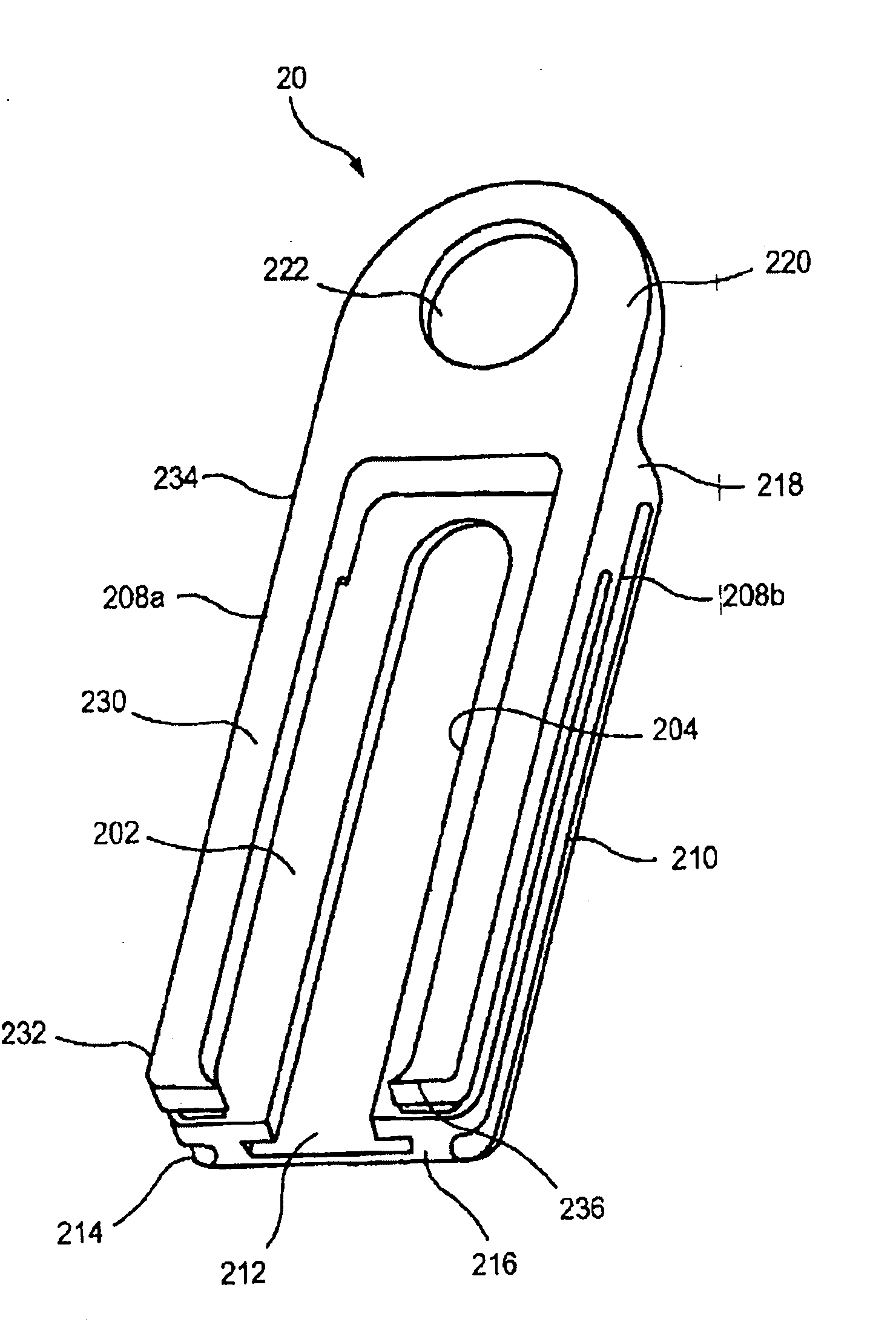
A ratcheting epiphysiodesis plate comprises a female base half (20) having a ratchet arm (230) and a male sliding half (30) having a series of ratchet teeth (312), the male sliding half being slidably connected to the female base half with the ratchet arm engaging the ratchet teeth, one of the female and male sliding halves including a first fixation element receiving hole (222), (322) for receiving therethrough a fixation element for binding the plate to a bone. The plate may further comprise a slider band (40) slidably connected to the female base half over the ratchet arm, or a plurality of female base halves with ratchet arms of different lengths, in order to adjust the preset load required to release the ratchet arms from the ratchet teeth.
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
Dynamic intervertebral spacer implant
ActiveUS10299938B1Eases end plate preparationReduces expulsionJoint implantsSpinal implantsEpiphysisNative state
Intervertebral spacer implants with dynamic load spreading features responsive to external loads and having attachment mechanisms. The dynamic load spreading features having a native state and a loaded state, which complements vertebral end plate geometry and disperses load to the epiphyseal rim.
Owner:ADDITIVE IMPLANTS INC
Instruments and methods for shaping a bone cavity
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for shaping bone voids during revision procedures of total knee replacements. The systems disclosed herein generally include a cannulated reamer assembly, a reaming guide assembly, a guide tube assembly, a trial stem assembly, and an optional insertion / removal tool. Metaphyseal reconstruction devices can be used to fill the bone voids in conjunction with the systems and methods disclosed herein.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
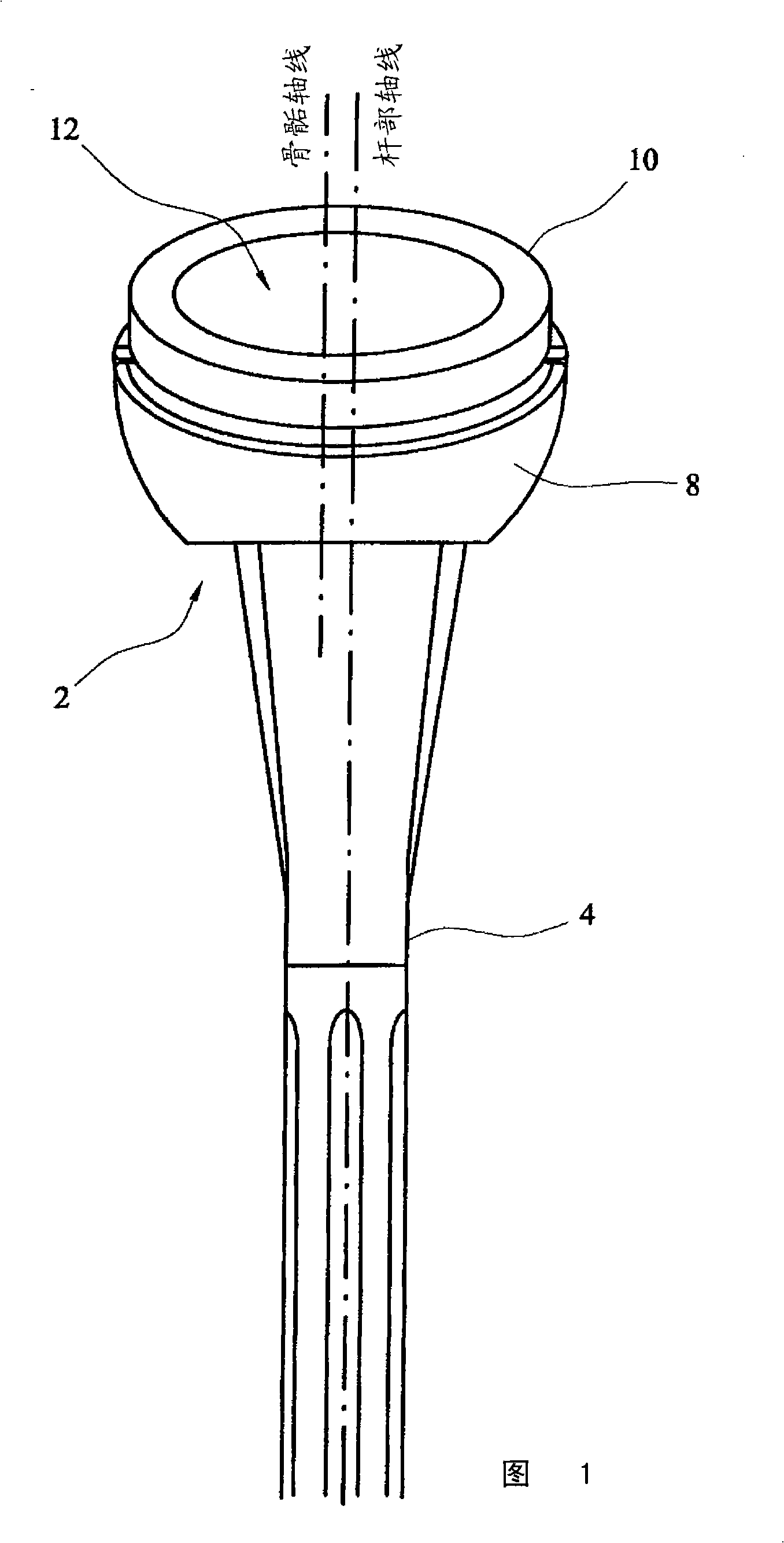
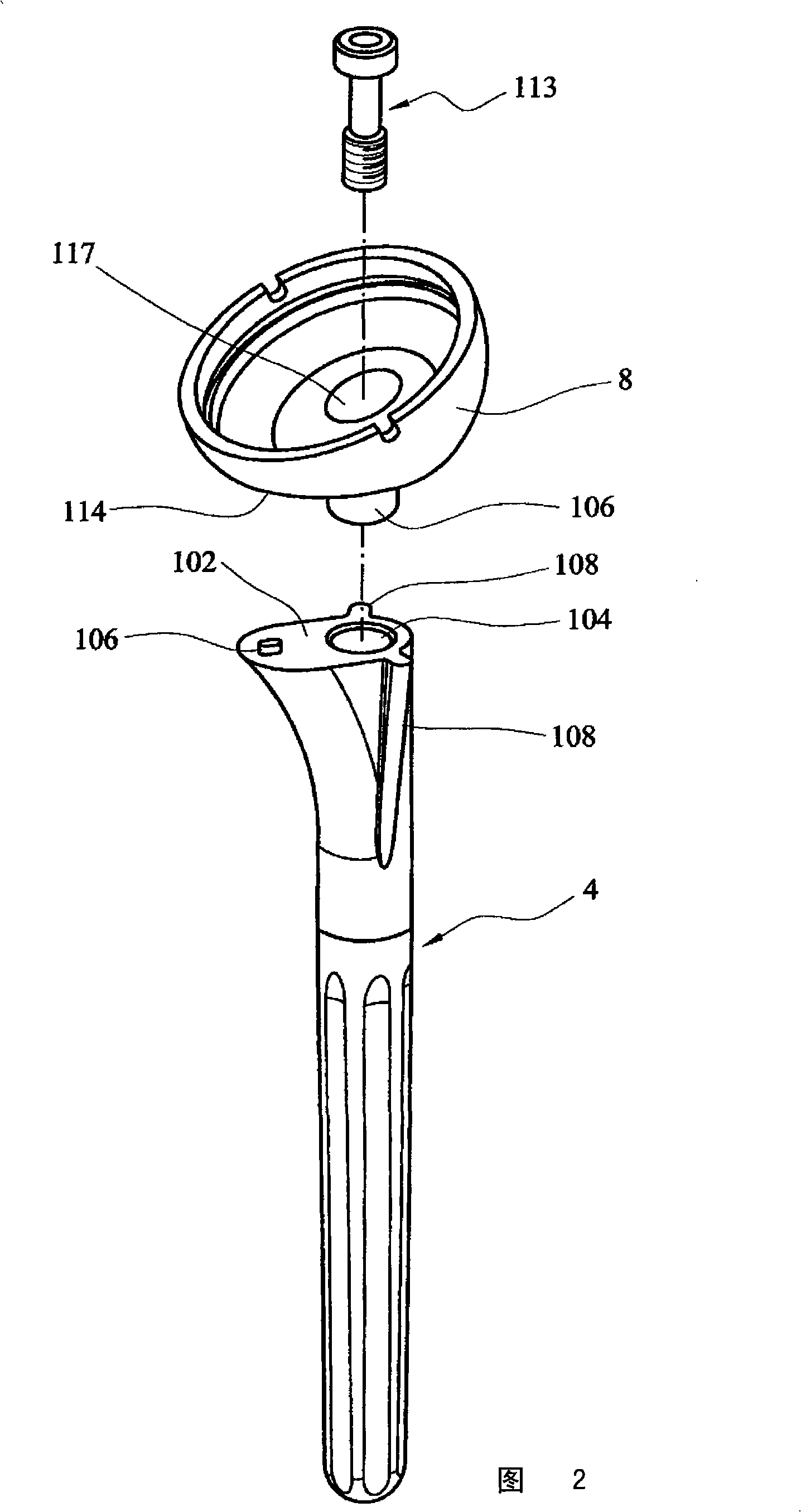
Humeral component of a shoulder joint prosthesis
ActiveCN101321507AReduce the risk of impactJoint implantsShoulder jointsEpiphysisShoulder joint prosthesis
A humeral component of a reverse shoulder prosthesis (2) comprises an elongate stem part (4) for location within the intramedullary cavity of the humerus, and an epiphyseal part having a concave bearing surface (12) for articulation with the convex bearing surface (12) of a glenoid component (8). The elongate stem part (4) defines a stem axis and the concave bearing surface of the epiphyseal part defines an epiphyseal axis. The epiphyseal axis is offset posteriorly relative to the stem axis.
Owner:大卫·科林斯 +1
Dendritic cell separating and extracting method
InactiveCN107129970AA large amountHigh purityBlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsDendritic cellEpiphysis
The invention discloses a method for isolating dendritic cells, which comprises the following steps: (1) preparation of bone marrow mononuclear cell suspension: taking bone, cutting the epiphysis, washing the middle bone to obtain bone marrow fluid, and cutting the epiphysis until it becomes viscous mixed with the aforementioned bone marrow fluid, placed on a strainer, washed 3 to 4 times to obtain a cell suspension, centrifuged, collected the precipitate, added red blood cell lysate, left standing, centrifuged, washed, and obtained bone marrow mononuclear cells; (2) imDC Cell culture: the bone marrow mononuclear cells obtained in step (1) were resuspended in medium 1, inoculated and cultured, centrifuged, cultured in medium 2 added with growth factors, and cultured continuously for 7 days to obtain imDC cells; (3) mDC Cell culture: Add cell culture medium 3 containing maturation-promoting factors to imDC cells to continue induction culture. The method for isolating dendritic cells of the present invention can effectively separate dendritic cells from mouse bone marrow, and has excellent clinical application prospects.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Bone age evaluation method and system based on graph convolutional neural network, terminal and storage medium
PendingCN111882517AAchieve precisionEfficient deliveryImage enhancementImage analysisWrist boneEpiphysis
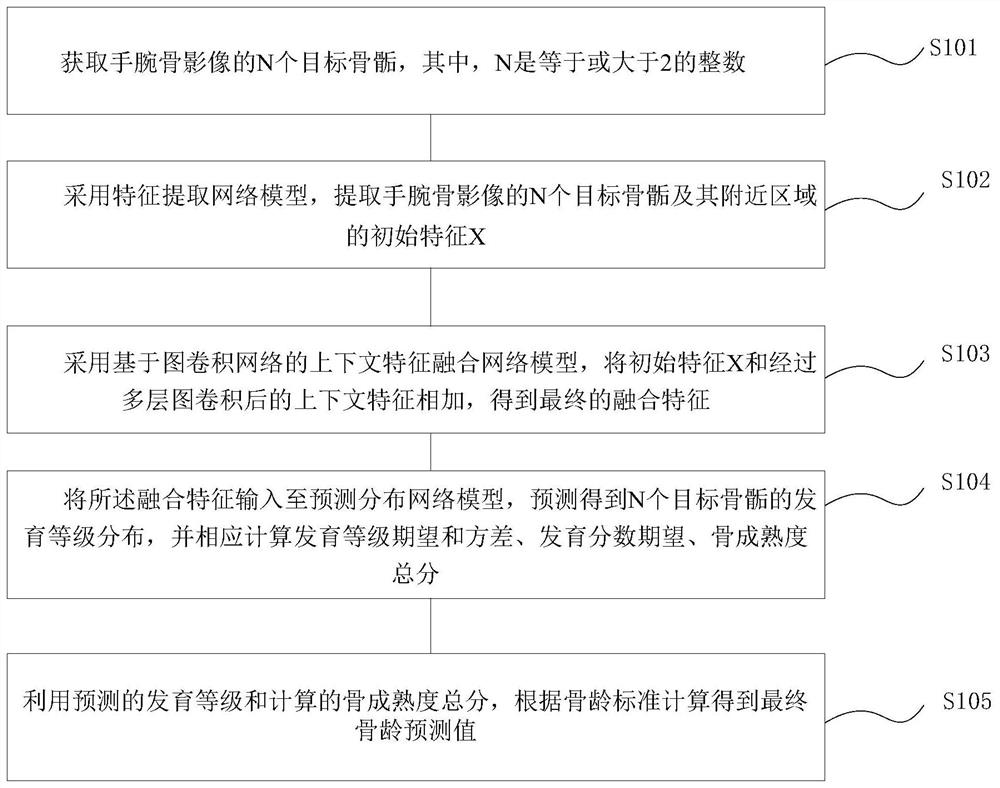
The invention provides a bone age evaluation method and system based on a graph convolutional neural network, a terminal and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps: obtaining N target epiphysis of a wrist bone image; adopting a feature extraction network model to extract initial features X of N target epiphysis and nearby areas of the wrist bone image; adopting a context feature fusion network model based on a graph convolution network, adding the initial feature X and the context feature subjected to multilayer graph convolution to obtain a final fusion feature, inputting the fusionfeature into a prediction distribution network model, and predicting to obtain development level distribution of N target epiphysis, correspondingly calculating development grade expectation and variance, development score expectation and bone maturity total score; and performing calculating to obtain a final bone age prediction value according to a bone age standard by utilizing the predicted development grade and the calculated bone maturity total score. Context feature fusion is realized through the graph convolution network to promote information communication among different local bone regions, accumulated bone age errors are avoided through a bone maturity total score loss function, and bone age evaluation accuracy and robustness are realized.
Owner:HANGZHOU SHENRUI BOLIAN TECH CO LTD +1
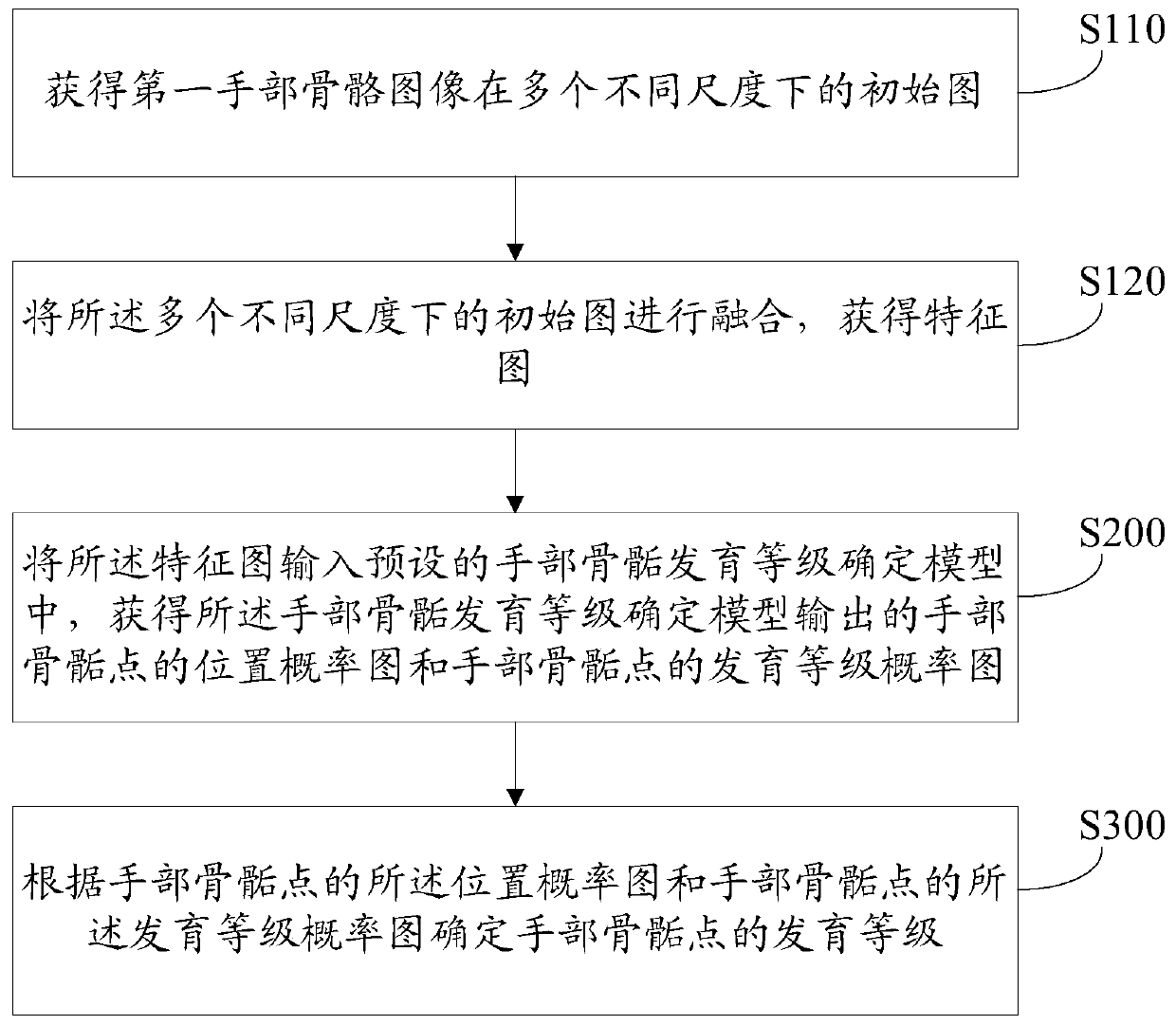
Hand epiphysis development grade determination method and related equipment
ActiveCN110853003AOvercoming technical issues with low credibilityAchieve the technical effect of scientifically determining the bone ageImage enhancementImage analysisEpiphysisBone age
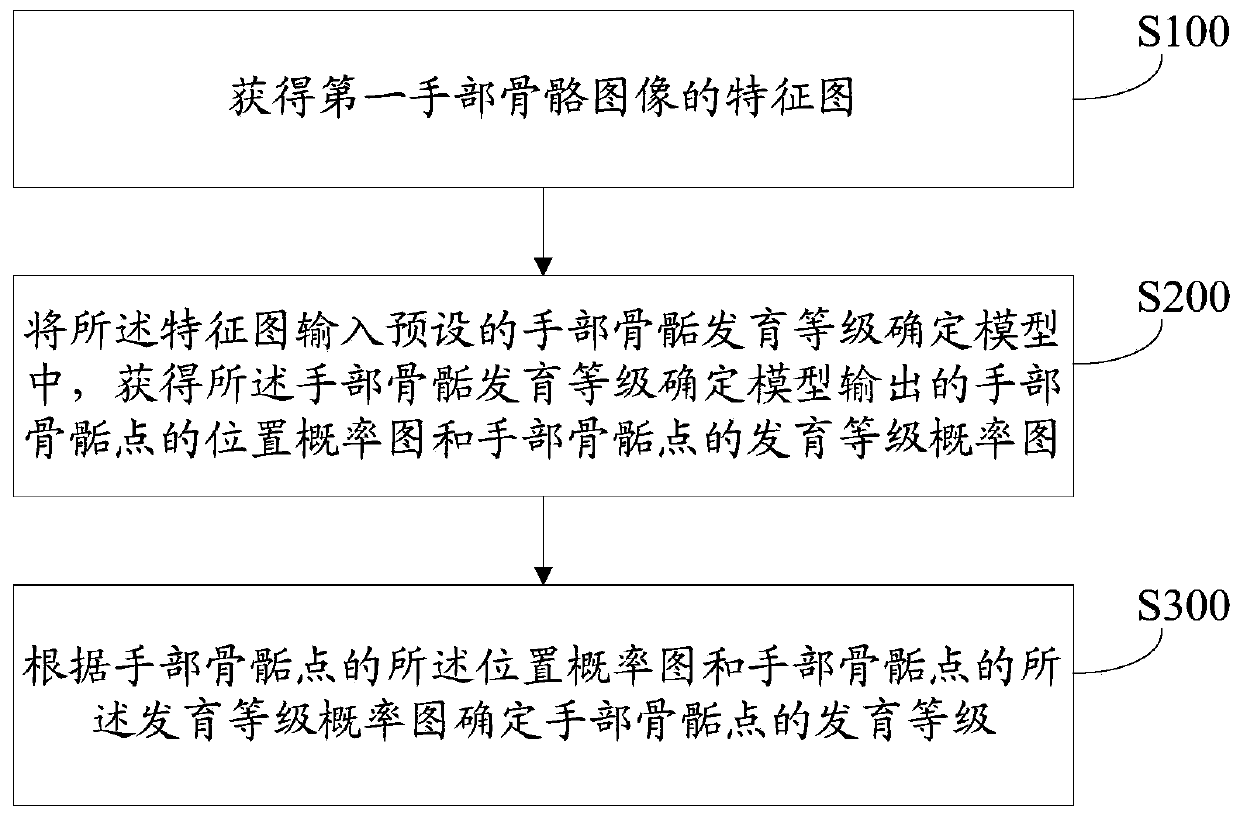
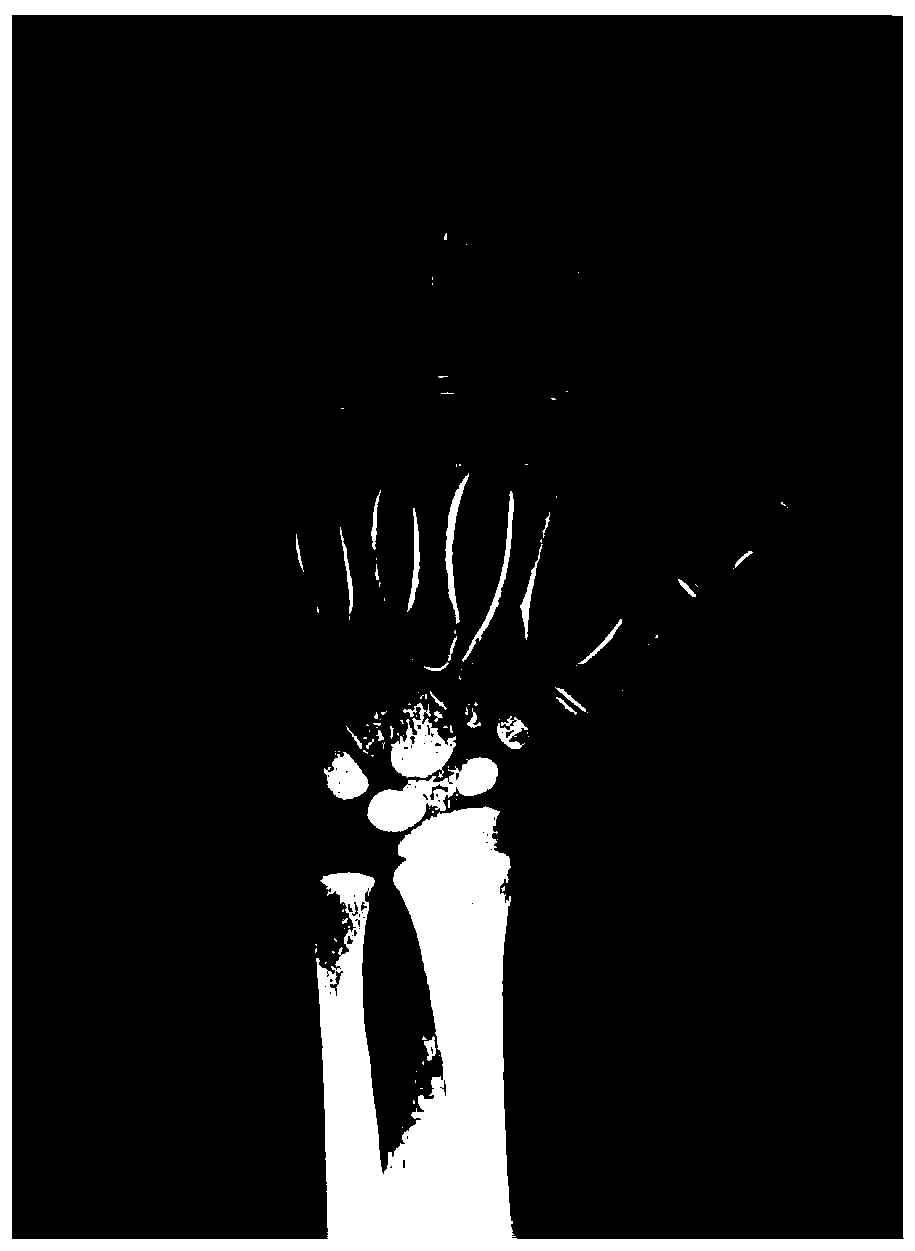
The invention discloses a hand epiphysis development grade determination method and related equipment. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a feature map of a first hand skeleton image; inputting the feature map into a preset hand epiphysis development grade determination model to obtain a position probability map of hand epiphysis points and a development grade probability map of the handepiphysis points output by the hand epiphysis development grade determination model; and determining the development level of the hand epiphysis point according to the position probability graph of the hand epiphysis point and the development level probability graph of the hand epiphysis point. According to the invention, the probability that each position in the hand bone image is an epiphysis point position and the probability that the development level of each position is determined are determined through the hand epiphysis development level determination model, and the development level ofeach hand epiphysis point in the hand skeleton image is determined; according to the technical means, the technical problem that an existing bone age prediction method is low in reliability is solved, and then the technical effect of scientifically determining the bone age is achieved.
Owner:INFERVISION MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Magnetism driving epiphysis traction and pressurization device
PendingCN111759431APromote healingIncrease the lengthInternal osteosythesisEpiphysisBone marrow cavity
The invention relates to a magnetism driving epiphysis traction and pressurization device. The magnetism driving epiphysis traction and pressurization device comprises a near end fixing sleeve, a permanent magnet, a linear screw rod, and a far end moving sleeve, wherein the near end of the near end fixing sleeve is used for being fixed in the medullary cavity of the near end bone, and the far endof the near end fixing sleeve is used for forming an opening end; the permanent magnet is rotatably arranged in the near end fixing sleeve, and can rotate forwards or backwards around the axis of thenear end fixing sleeve; the linear screw rod is rotatably supported in the near end fixing sleeve along the axial direction of the near end fixing sleeve; the near end of the linear screw rod is connected with the permanent magnet and can synchronously rotate along with the permanent magnet; the near end of the far end moving sleeve is arranged in the near end fixing sleeve through the opening endof the near end fixing sleeve in a sliding manner; internal threads which cooperate with external threads of the linear screw rod are formed in the near end of the far end moving sleeve; the far endmoving sleeve is in threaded rotating cooperation to the linear screw rod; and the far end of the far end moving sleeve is used for being fixed in a medullary cavity of the far end bone. Through the adoption of the magnetism driving epiphysis traction and pressurization device disclosed by the invention, periosteum at an osteotomy location can be subjected to traction in a noninvasive and uniform-speed manner to induce ossification of the periosteum, so that the length of skeletal is extended, and continuous pressurizing effect can also be provided for the fracture end through abbreviation topromote healing of the fracture end.
Owner:姬涛
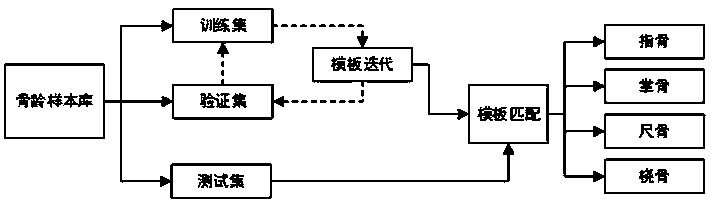
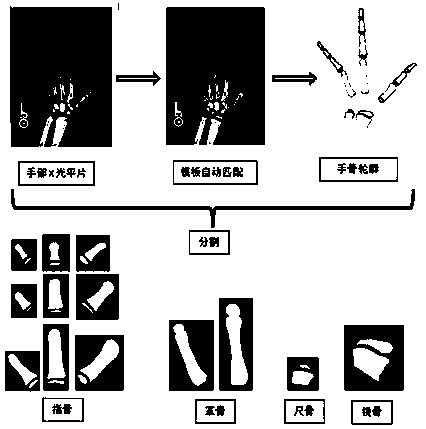
An automatic hand bone segmentation method based on template
InactiveCN109242867ASolve the Segmentation DilemmaEnrich bone development informationImage enhancementImage analysisManual annotationEpiphysis
The invention discloses an automatic hand bone segmentation method based on a template. At first, a bone age sample database is established. Then samples are trained and templates is created, in thesame period of time, templates are createdfor all segments of the bone respectively. Finally, hand bone segmentation is performed based on template. The method extracts intact bone shape features including epiphysis, and more bone development information is contained. At the same time, the method avoids falling into endless tuning parameters; And through the training set update method, the workload of manual annotation is effectively reduced. The invention solves the problem of hand bone segmentation and provides a powerful tool for subsequent bone age assessment.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Separation and culture of mouse mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN110387350AHigh purityHigh activityCell culture supports/coatingSkeletal/connective tissue cellsTibiaElisa method
The invention provides a separation and culture method of mouse mesenchymal stem cells. The separation and culture method comprises the following steps: (1) an ICR mouse is anesthetized and killed; (2) thighbones and tibiae are taken and placed in ethyl alcohol of 75% to be soaked and disinfected; (3) washing is conducted for three times through PBS, and the epiphysis ends of the thighbones and the tibiae are cut off; (4) a culture medium containing double resistants is sucked through a needle tube of 10 ml to rush out bone marrow; (5) a percoll separating medium is used for centrifuging through a density gradient method, and a middle white layer is taken; (6) washing is conducted for two times through the PBS; (7) the cell activity is detected; (8) the cells are counted; (9) the cell morphology is identified; (10) detecting is conducted through an ELISA method; and (11) RT-PCR detection is conducted. The separation and culture method of the mouse mesenchymal stem cells is easy to operate, large in number of the obtained cells, high in survival rate and ideal, and provides the reliable cell resource for experiments.
Owner:JIANGYIN CHI SCI
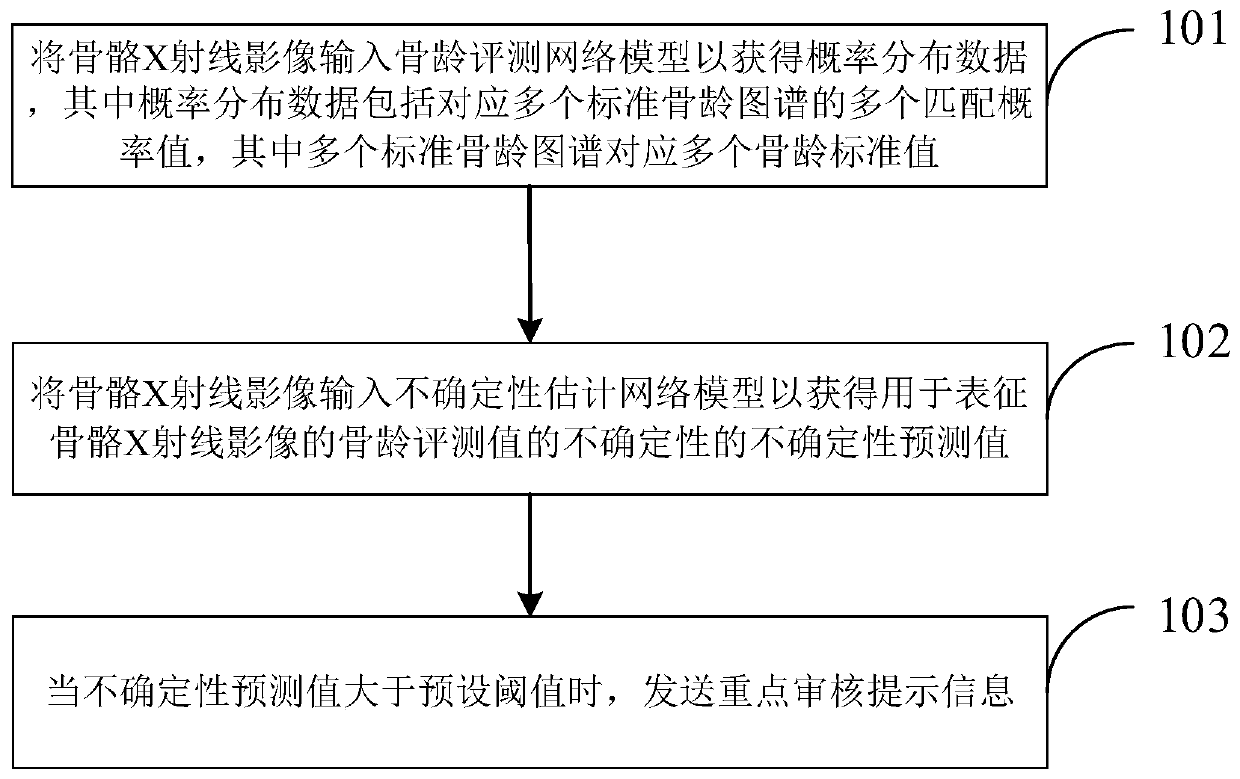
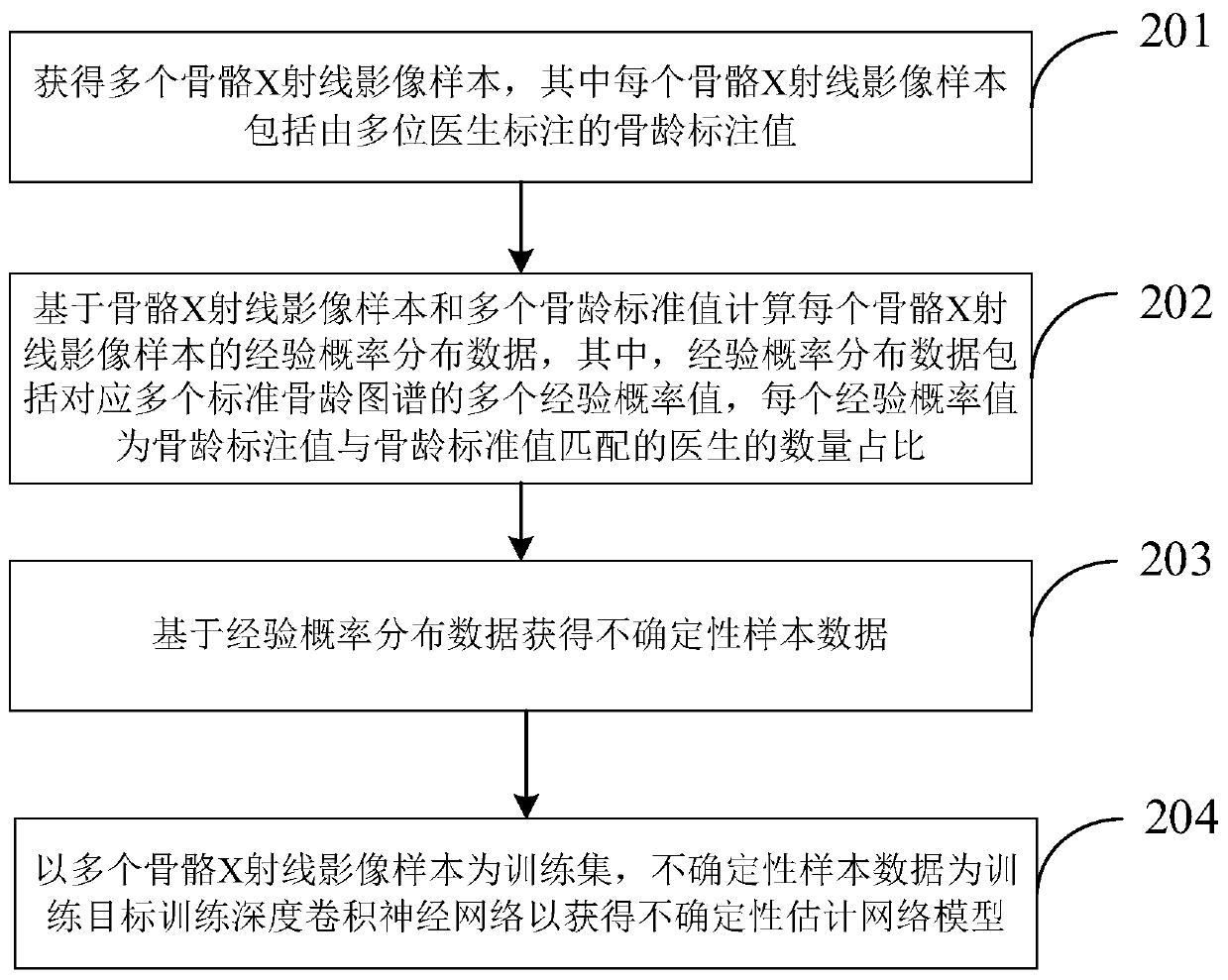
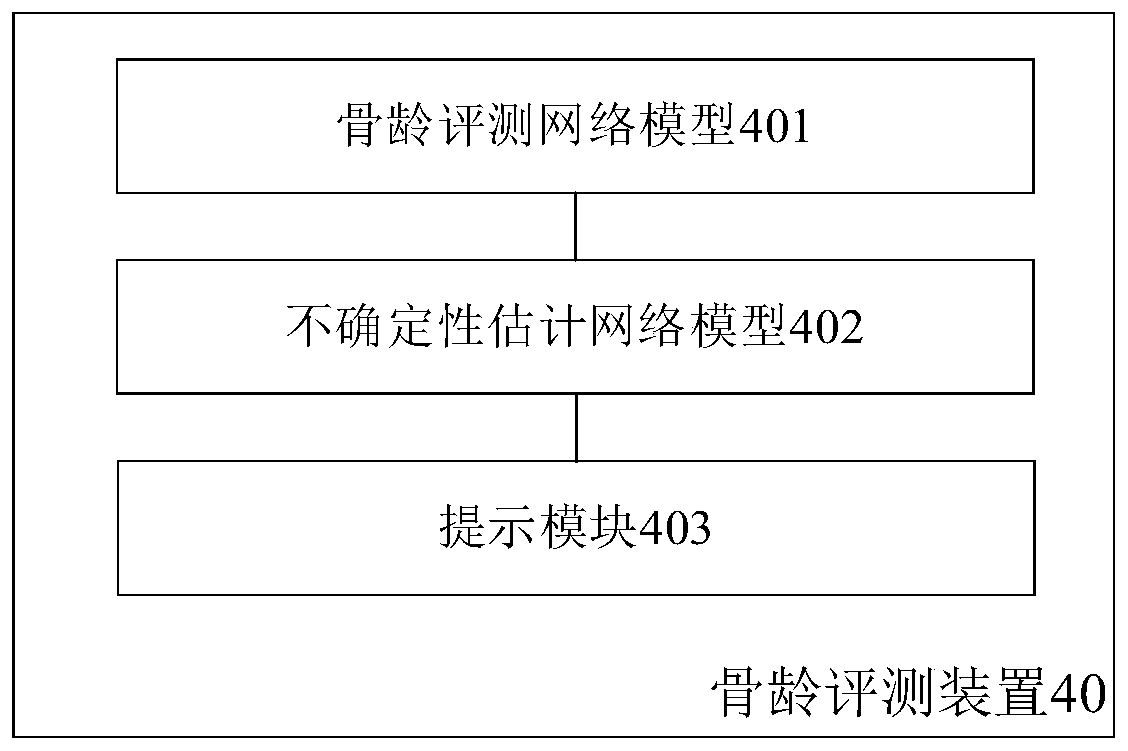
Bone age evaluation method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium
PendingCN111402213AImprove generalization abilityImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisEpiphysisBone age
The embodiment of the invention provides a bone age evaluation method and device, and solves the problems that an existing bone age evaluation method cannot automatically identify difficult bone / epiphysis and cannot effectively intervene in uncertainty of bone age evaluation. The bone age evaluation method comprises the following steps: inputting a bone X-ray image into a bone age evaluation network model to obtain probability distribution data, the probability distribution data comprising a plurality of matching probability values corresponding to a plurality of standard bone age maps, and the plurality of standard bone age maps corresponding to a plurality of bone age standard values; inputting the bone X-ray image into an uncertainty estimation network model to obtain an uncertainty prediction value used for representing the uncertainty of the bone age evaluation value of the bone X-ray image; and when the uncertainty prediction value is greater than a preset threshold, sending keyauditing prompt information. According to the invention, bone / epiphysis with high uncertainty (easy to diverge) can be evaluated according to automatic identification of bone age, and doctors are recommended to focus on auditing.
Owner:BEIJING SHENRUI BOLIAN TECH CO LTD +1
Intramedullary nail special for children and use method thereof
ActiveCN112914702APreserve normal growth functionPrevent rotationInternal osteosythesisDistal femur fractureNormal growth
The invention discloses an intramedullary nail special for children, which comprises a nail sleeve and a nail core, the far end of the nail core is provided with a first locking hole, the far end of the nail core is driven into the femoral marrow and penetrates through the growth plate at the lower end of the femur, a kirschner wire or a screw is driven at the epiphysis to enter the first locking hole to lock the nail core, the far end of the nail sleeve is driven into the femoral marrow from the greater trochanter at the proximal end of the femur to reach the metaphysis without passing through the growth plate, the nail sleeve is sleeved on the nail core, the near end part of the nail sleeve is arranged outside the femur, a second locking hole is formed in the nail sleeve, and a screw is screwed into the second locking hole through the skin to lock the nail sleeve. The intramedullary nail is applied to the distal femoral fracture of children, can be extended, prevented from rotating and locked, and can fix the fracture and retain the normal growth function of the growth plate.
Owner:SHANDONG PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
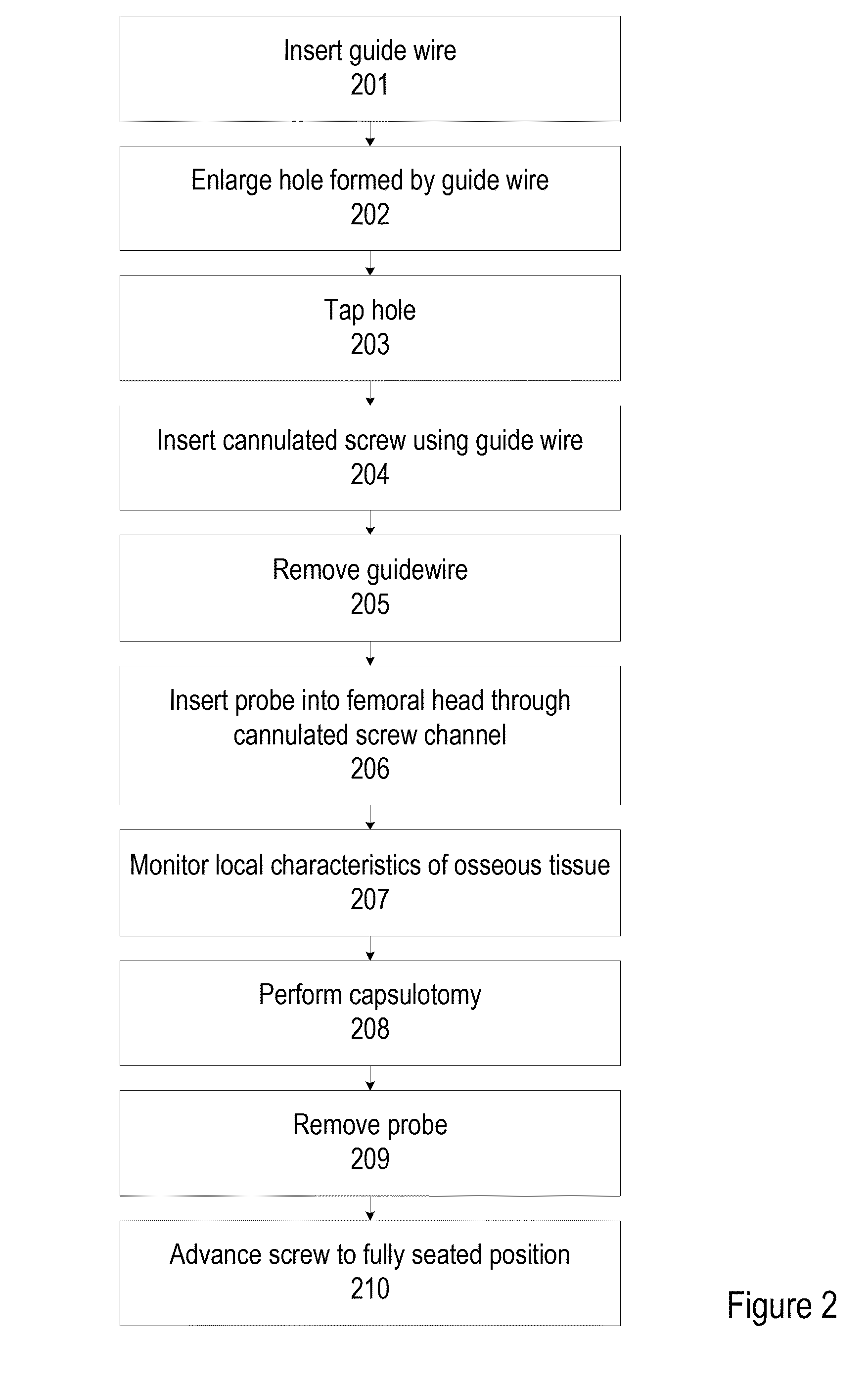
Cannulated screw probe
Concepts for measuring and monitoring characteristics of osseous tissue are presented. In various embodiments, a monitoring probe may be inserted through a hollow passageway within a cannulated screw during an operation in order to measure characteristics of the osseous tissue in which the cannulated screw is inserted. In various embodiments, the cannulated screw may be inserted into a femoral head, through a physis, and into an epiphysis for stabilization of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. During surgical treatment thereof, a pressure transducer may be inserted into the osseous tissue through the cannulated screw in order to monitor epiphysis perfusion through the femoral head.
Owner:SCHRADER TIM
Internal plate fixation device
The present invention relates to an internal bone plate fixation device (1) for use as a means of synthesis in anatomical regions or epiphysis / metaphysis with poor coating of soft tissues, of the type comprising a bone plate (2) that is bilobate or having eight-like shape, comprising a pair of portions (23, 24) adapted to be respectively associated to the epiphysis and to the metaphysis of a bone and joined by a central portion (15) and in each of which is formed at least one through hole (3, 4) to receive a corresponding screw (5) for fixing to the bone. Advantageously, the bone plate (2) is flat with almost constant thickness and is delimited by opposite surfaces (6, 7) parallel with a single recess (8) or notch that is transversal to the longitudinal axis of bone plate (2) formed on only one (6) of said surfaces (6, 7), with the thickness (s) of the plate being less than a ninth of its maximum longitudinal extension (L).
Owner:ORTHOFIX SRL
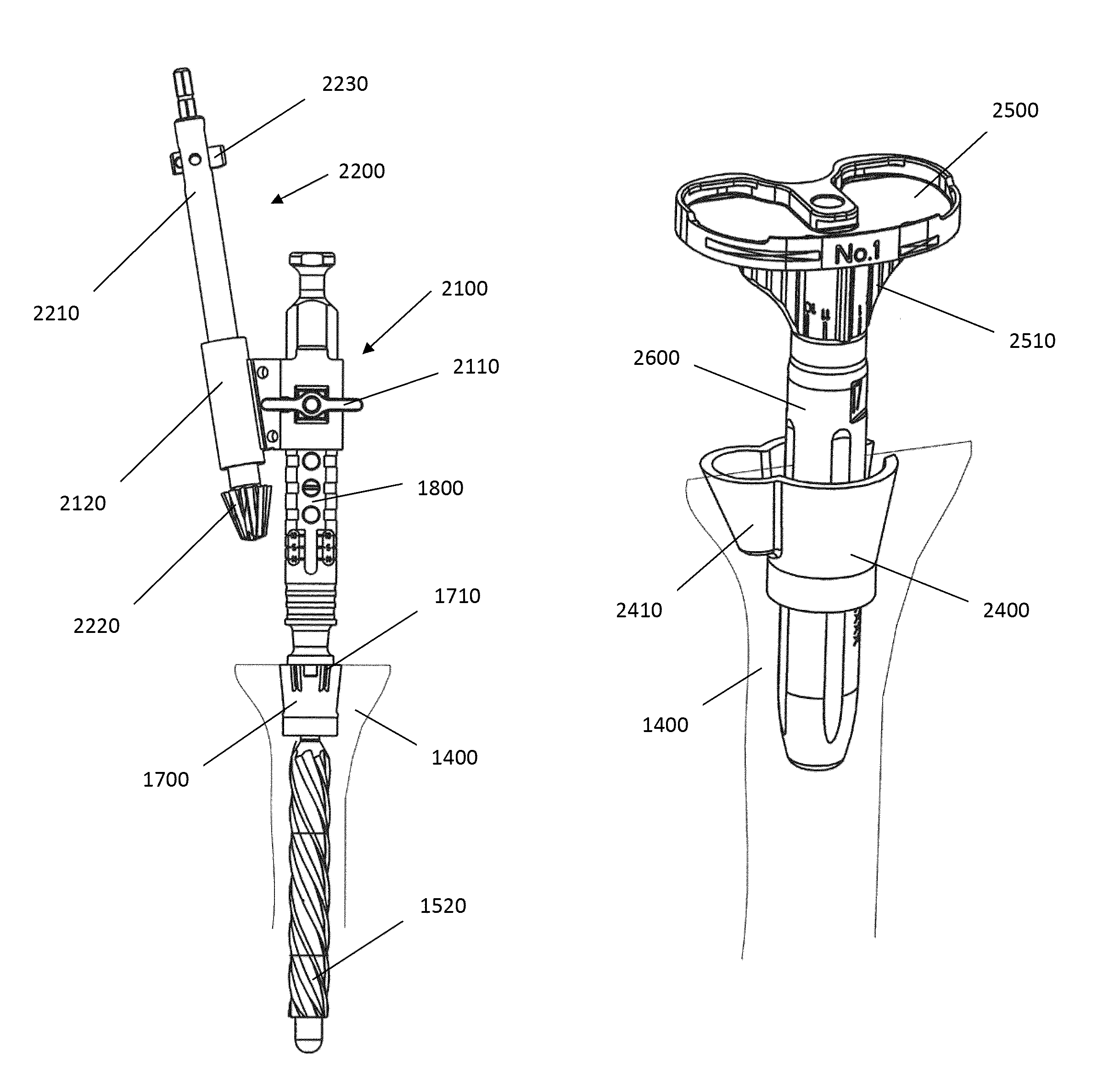
Minimally invasive intramedullary plate system
PendingCN109820585AProtect hematomaRecovery lengthInternal osteosythesisBone platesDynamic fixationFemur intramedullary nailing
The invention discloses a minimally invasive intramedullary plate system comprising an integrally formed intramedullary plate body. The intramedullary plate body is composed of an intramedullary part,an extramedullary part and a transition part connecting the two parts. The intramedullary part is in the long tube type, and the extramedullary part is attached to the epiphysis end and the articularsurface. A main body of the intramedullary part is provided with a locking nail hole, and a main body of the extramedullary part is provided with a locking threaded hole. The system combines the advantages of distal humeral plates, interlocking intramedullary nails and minimally invasive surgery techniques. The intramedullary part can provide static or dynamic fixation for the bone fracture, andsubstantially has no stress shielding effect. At the same time, the closed nailing operation mode is adopted to avoid exposure to the fracture end, protect the fractured part from hematoma, reduce damage and improve the fracture healing rate. The extramedullary part can provide a good supporting effect, and achieve the purpose of restoring the length of the fractured part, correcting the rotational displacement and correcting the force line at the same time to ensure early activities of a patient.
Owner:HEBEI RUIHE MEDICAL DEVICES CO LTD
Thighbone far-end prosthesis capable of preserving epiphysis
PendingCN111888055ANot easy to dislocateAvoid damageJoint implantsTomographyHuman bodyBone Trabeculae
The invention relates to the technical field of medical apparatus and instruments, and provides a thighbone far-end prosthesis capable of preserving epiphysis. The thighbone far-end prosthesis comprises a thighbone far-end prosthesis body and a myeloid needle sleeve, wherein the thighbone far-end prosthesis body and the myeloid needle sleeve are in taper fit. The thighbone far-end prosthesis bodyis provided with a lower end face; a lower end protrusion is arranged on the lower end face, and a third bone trabecula structure is arranged on the surface of the lower end protrusion; and the myeloid needle sleeve is provided with a solid inner wall, and a second bone trabecula structure is arranged on the surface of the solid inner wall. The beneficial effects lie in that the lower end protrusion is customized in size according to the medullary cavity of a patient and matched with the medullary cavity of the patient, rapid intraoperative positioning can be achieved, the postoperative prosthesis is prevented from deviating front and back, and the prosthesis is prevented from damaging the bone of the patient. The third bone trabecula structure is arranged on the surface of the lower end protrusion, so that the contact area between the prosthesis body and human bones is increased, the bone ingrowth places can be increased, and the prosthesis body is more stable and firmer and is not easy to dislocate.
Owner:BEIJING CHUNLIZHENGDA MEDICAL INSTR
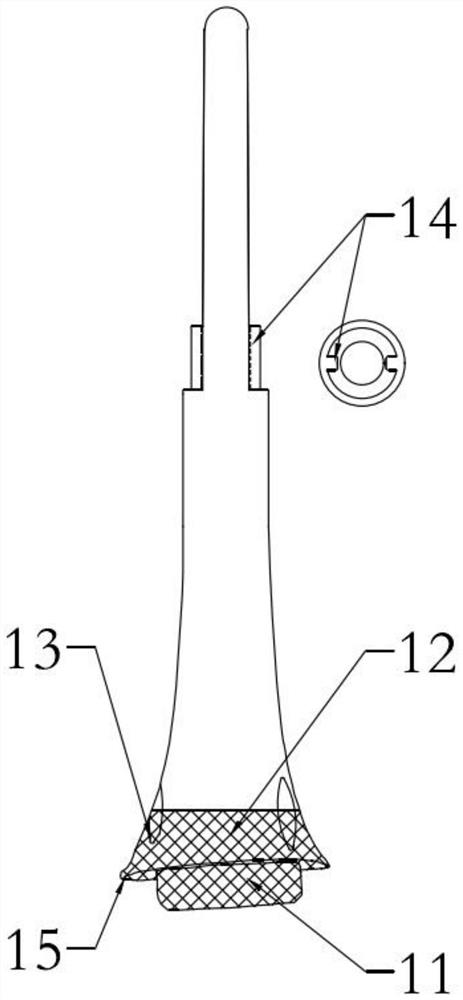
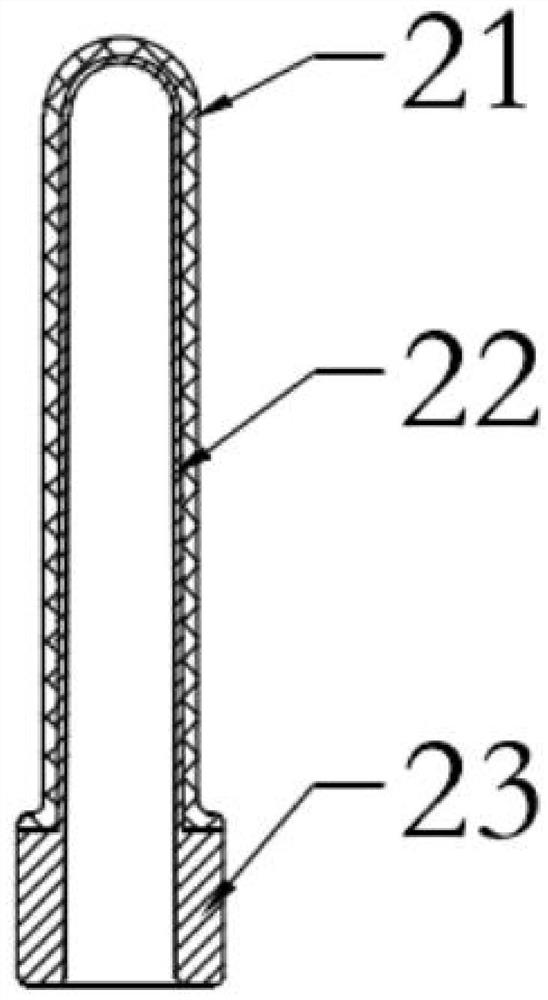
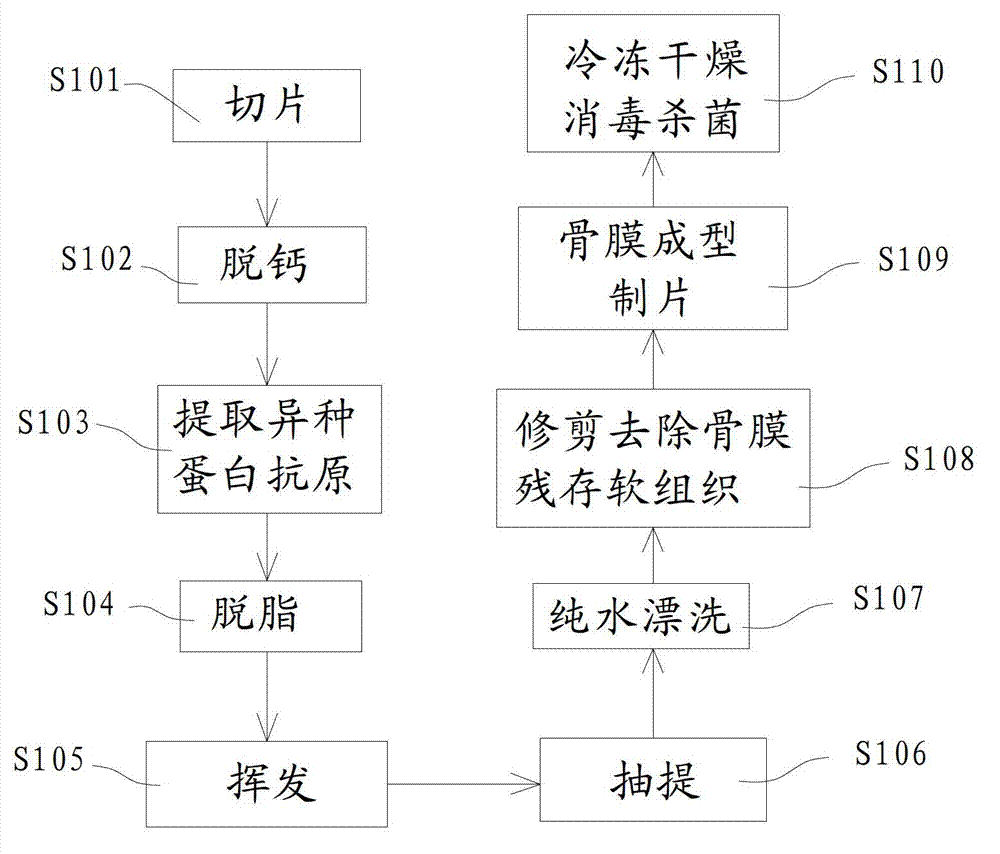
Manufacturing method and application of inductive artificial periosteum
ActiveCN102727934ASimplify the manufacturing processPromotes fracture healingProsthesisCooking & bakingFracture line
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of an inductive artificial periosteum. The method comprises the steps that: animal bone epiphysis is adopted, and is cut into bone slices with thicknesses of 0.5-1mm; the bone slices are decalcified in a hydrochloric acid solution, until the bone slices turn soft; the softened bone slices are cleaned by washing, and are placed in an oxidation liquid; under a baking environment, foreign protein antigen is extracted; the bone slices with the foreign protein antigen extracted are cleaned by washing, and are defatted in a chloroform-methanol liquid; the defatted bone slices are cleaned by washing, sufficiently volatilized, and cleaned by using clear water; the cleaned bone slices are extracted again in the oxidation liquid; the extracted bone slices are cleaned by using clear water, and are cleaned by rinsing by using purified water; the bone slices are trimmed, and residual soft tissues on periosteum are removed; the periosteum is shaped, and periosteum slices are manufactured. The invention also discloses an application of the inductive artificial periosteum. The periosteum slice provided by the invention can be directly applied on a fracture line for achieving a fracture healing promoting purpose.
Owner:SHANGHAI XIAOBO TECH DEV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com