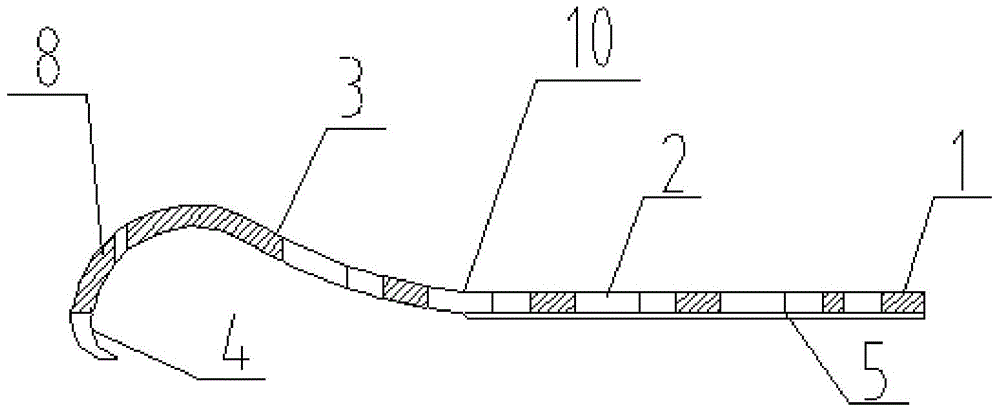
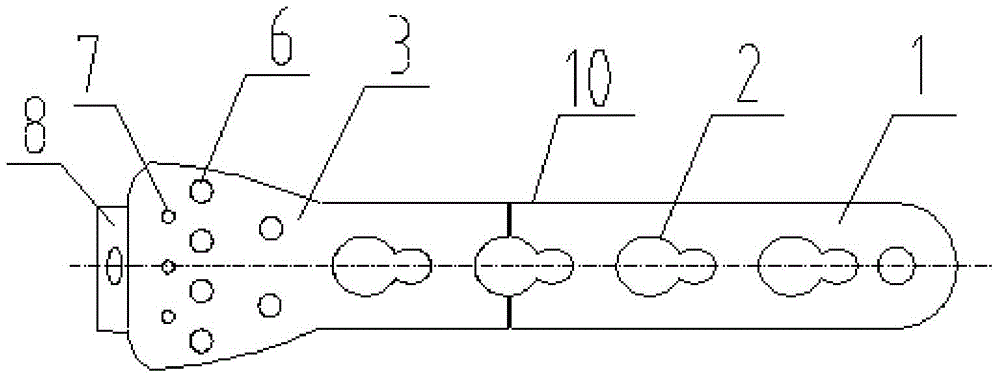
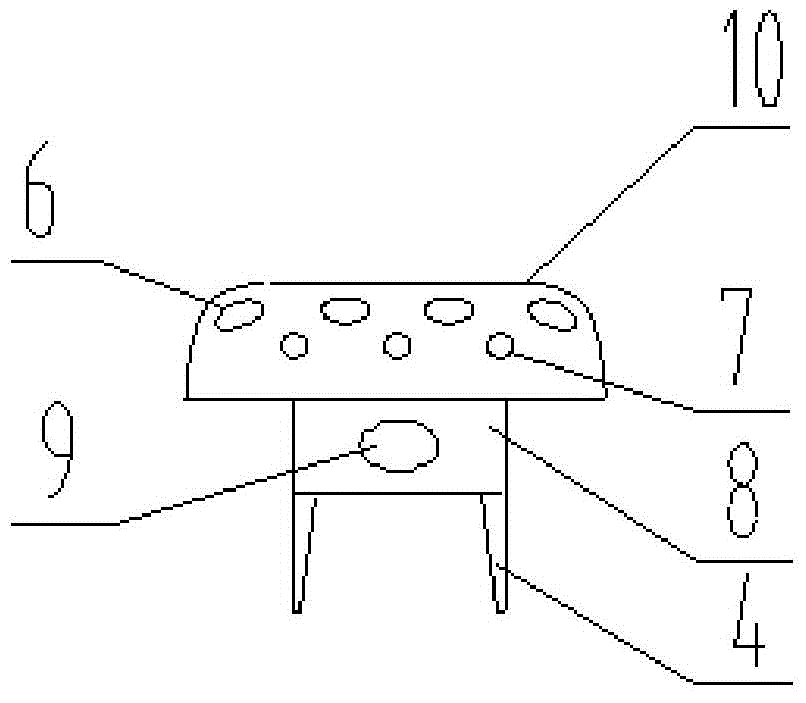
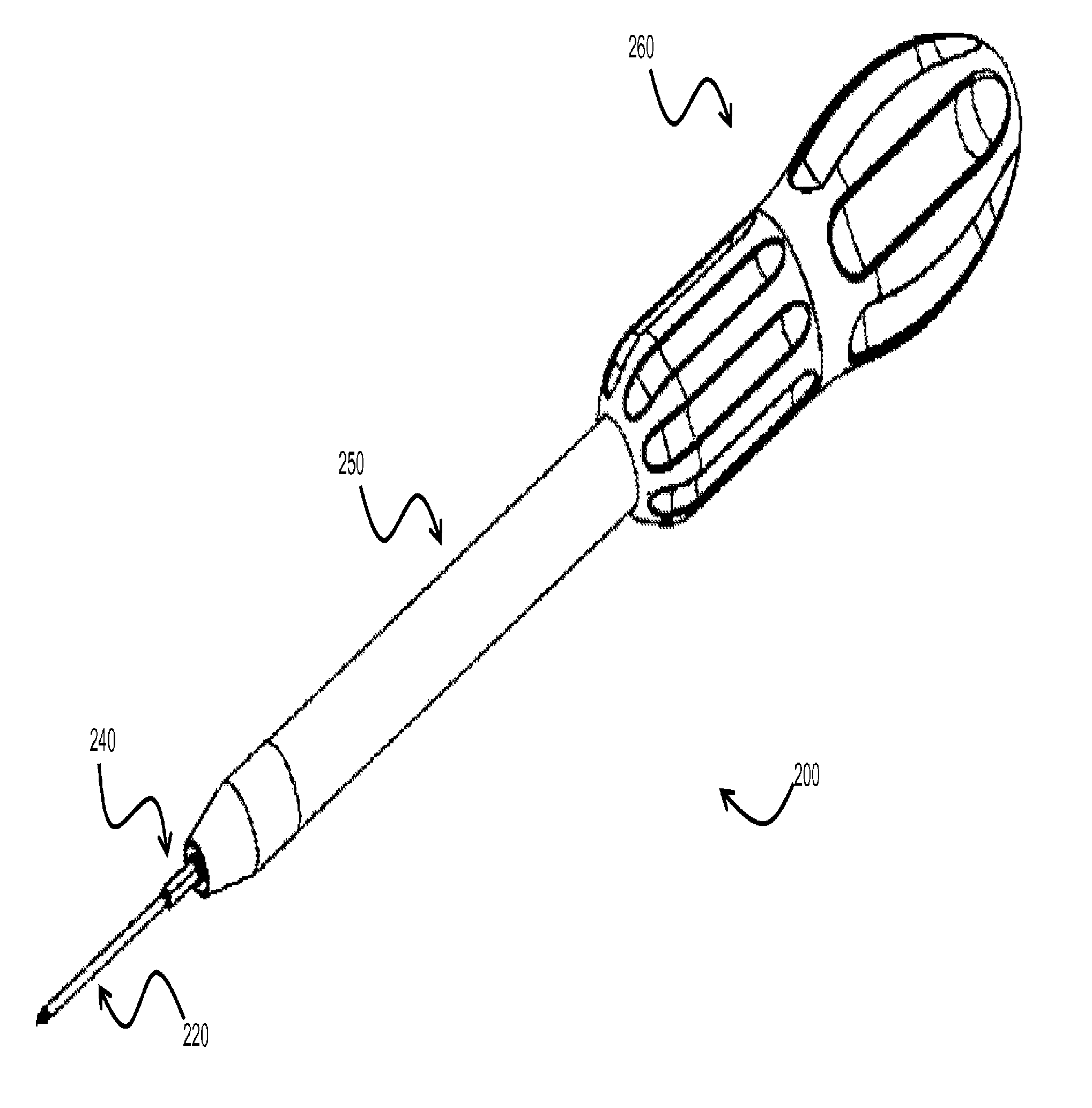
Patents
Literature
126 results about "Cannulated screw" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
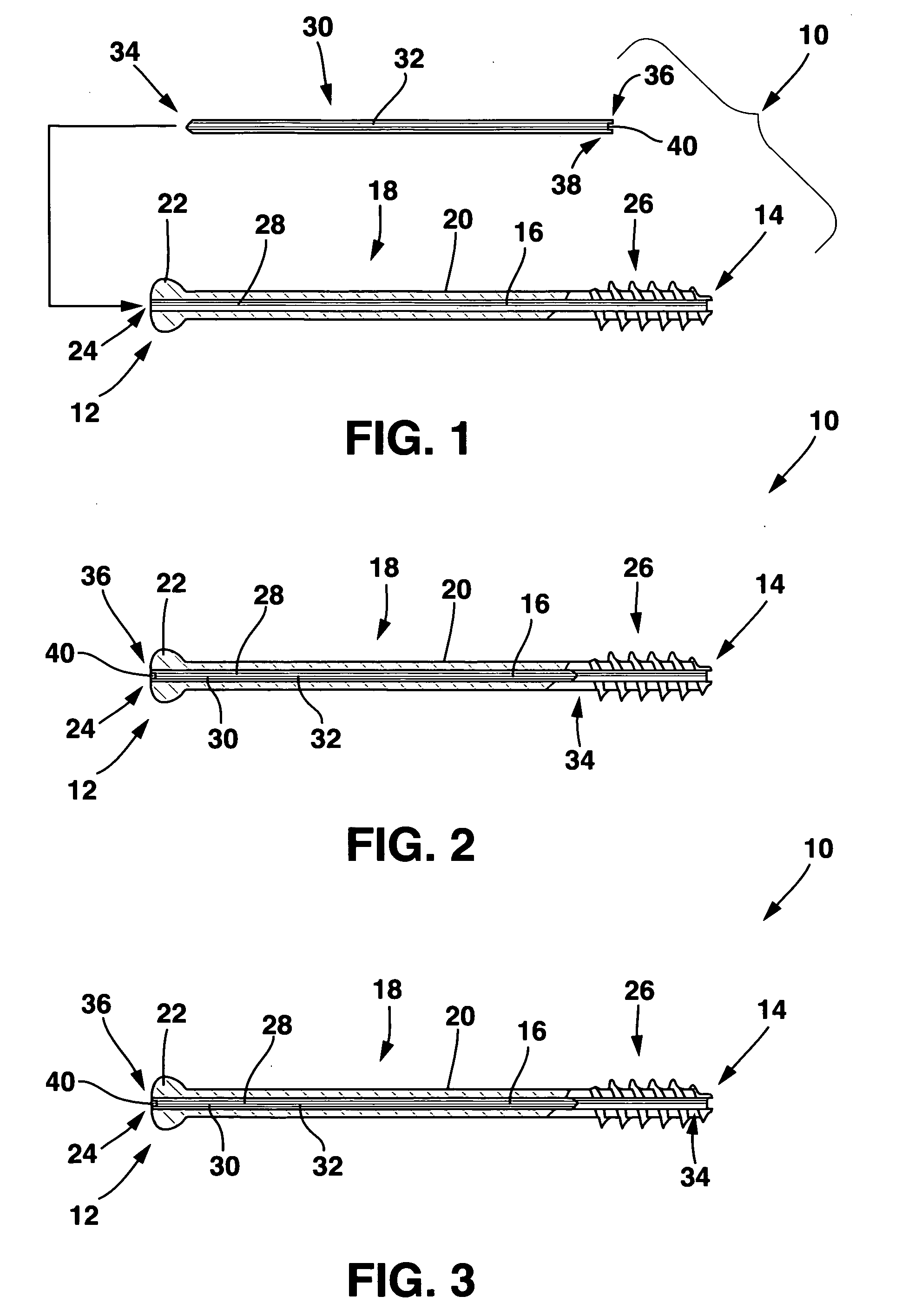
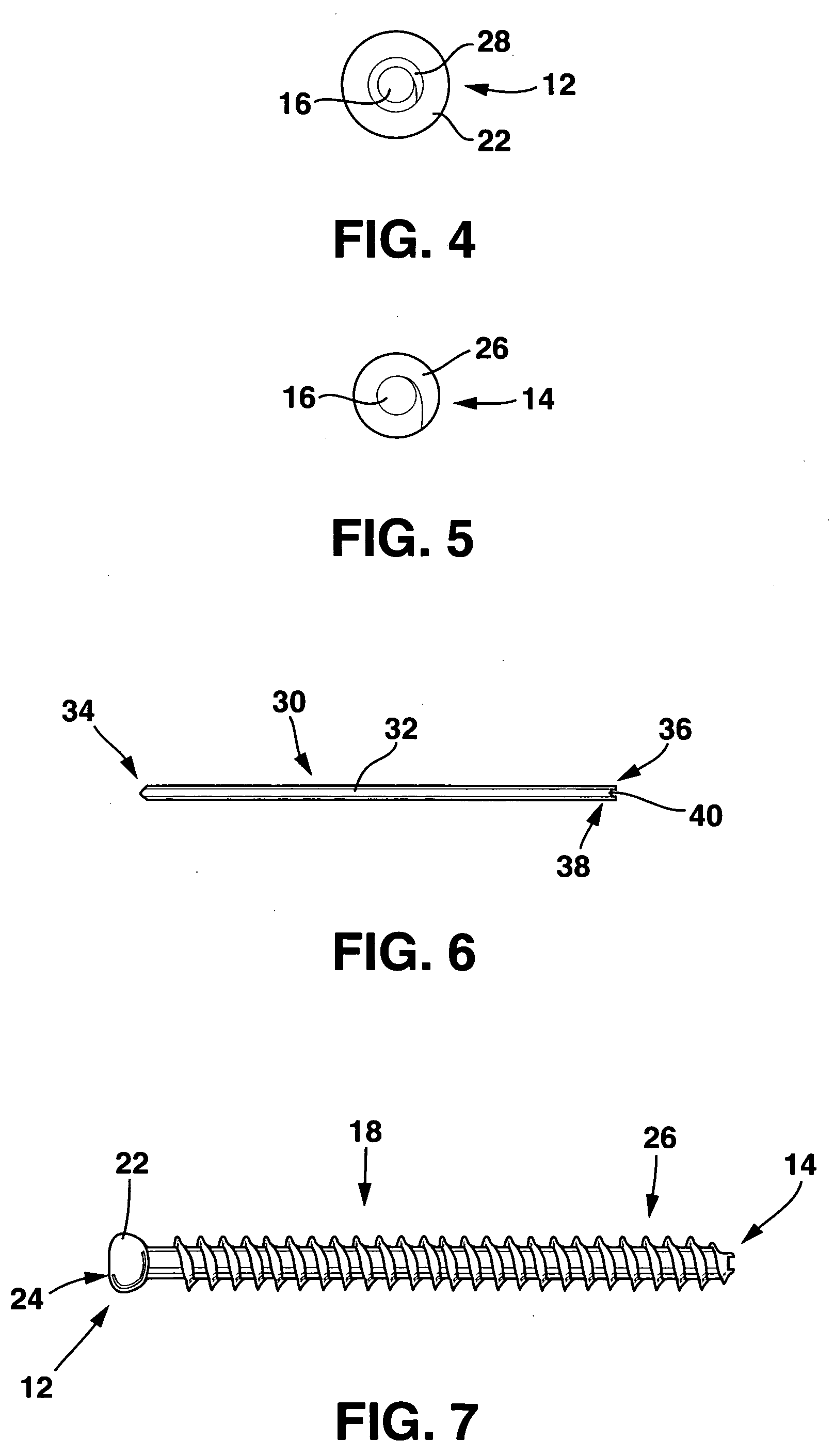
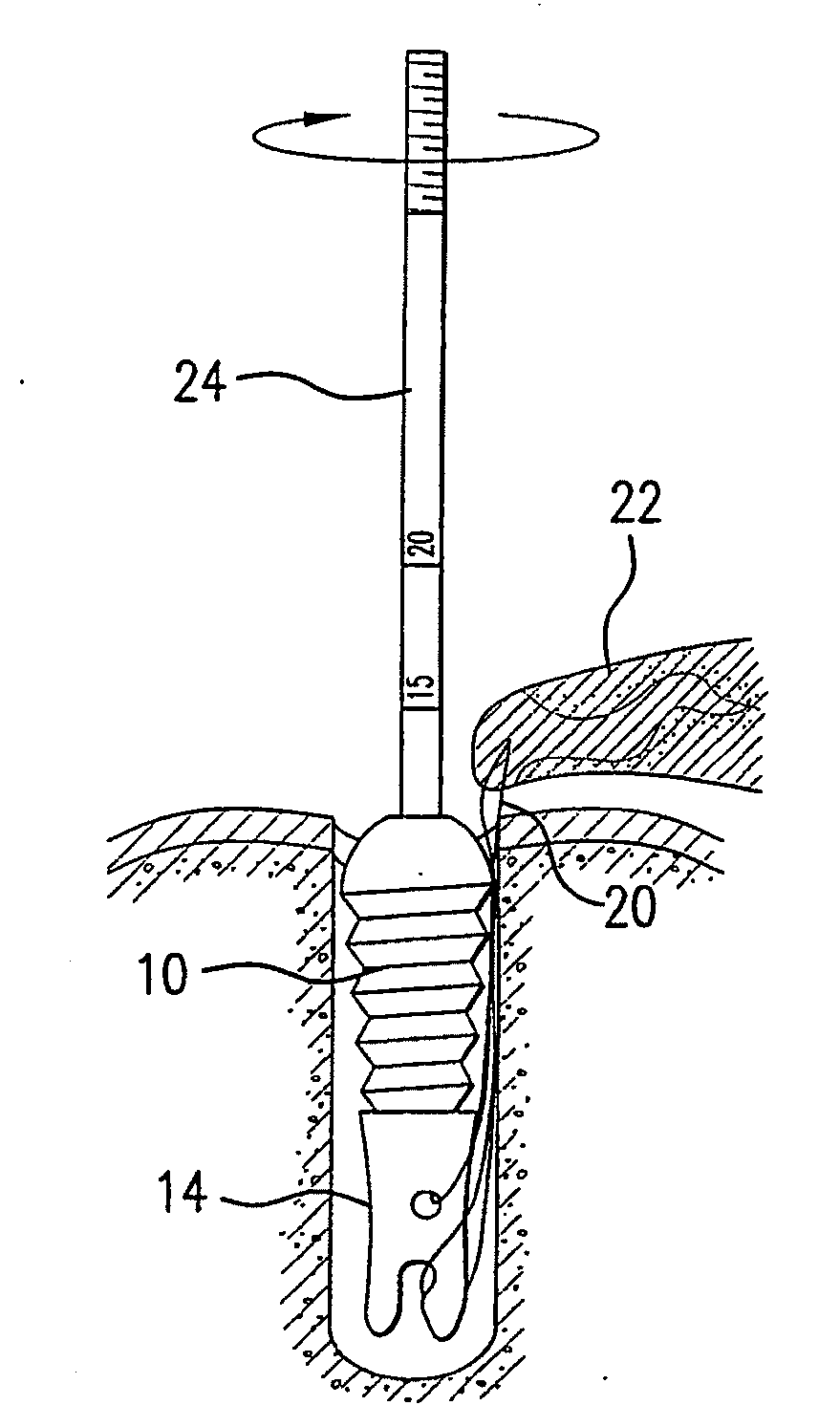
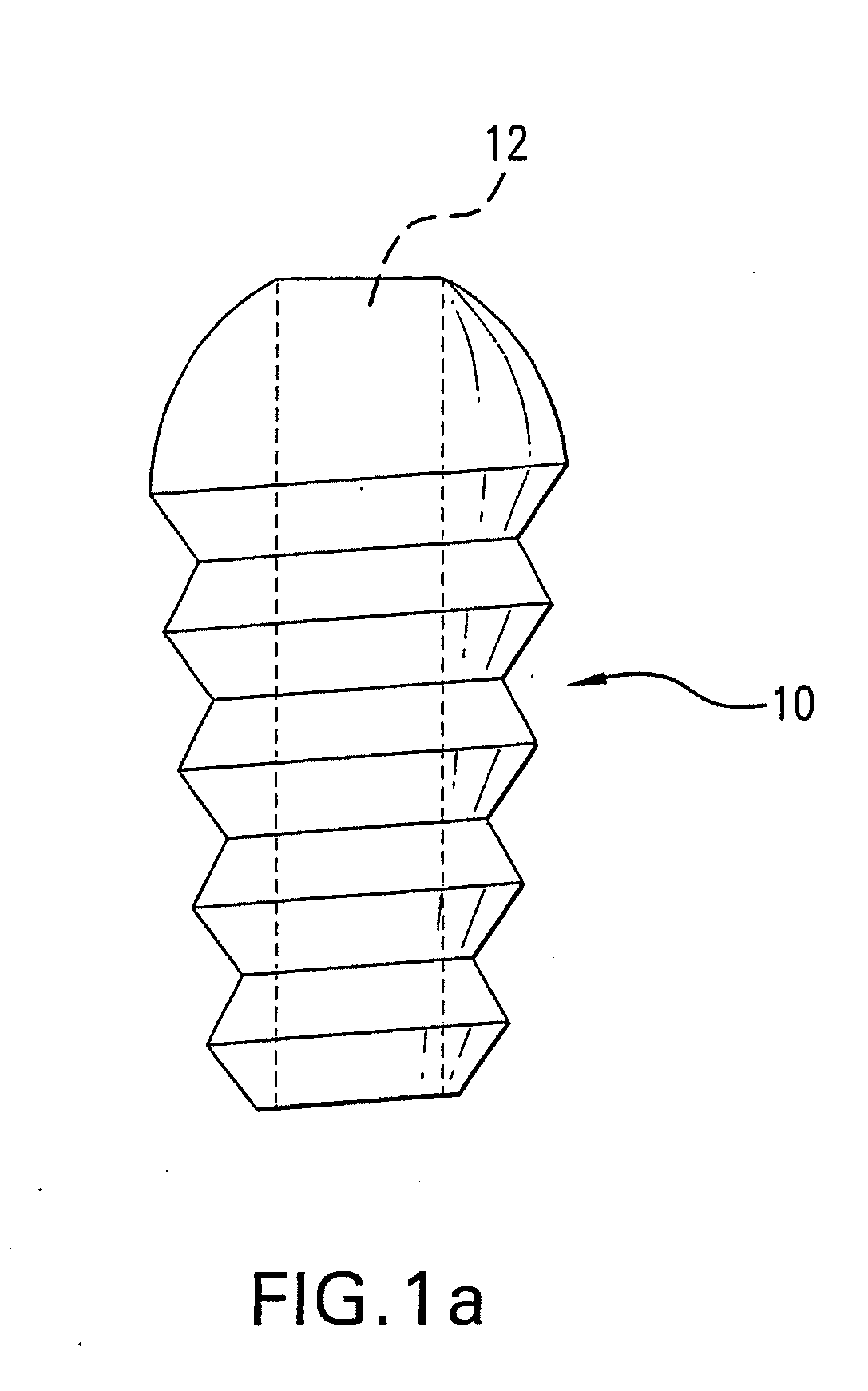
Cannulated screw. A screw with a hollow shaft and a low pullout strength compared to conventional screws, which can be placed with reasonable precision and minimal trauma using Kirscher ("K") wires. CSs may perforate the joint if placed in a bone near subchondral bone.
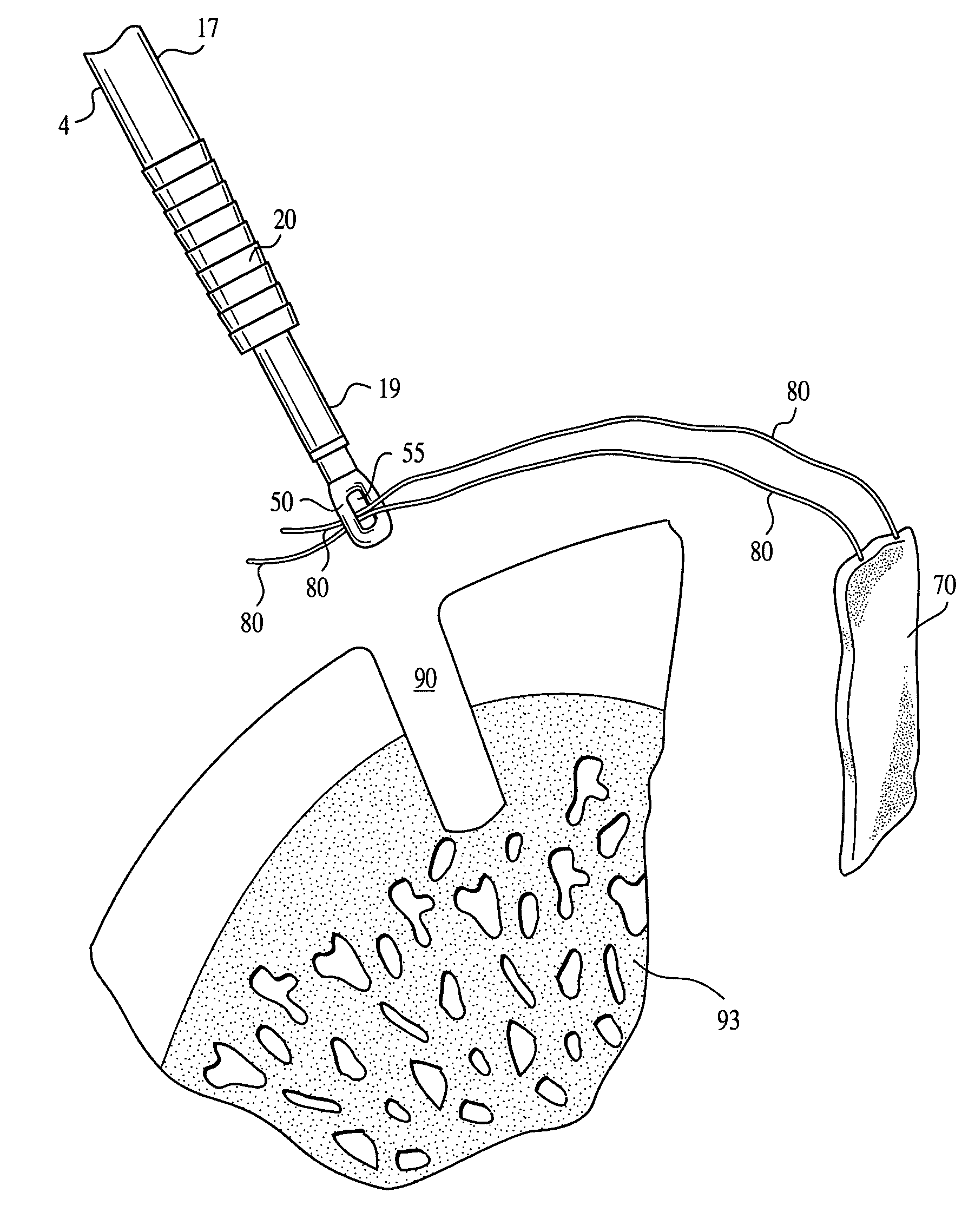
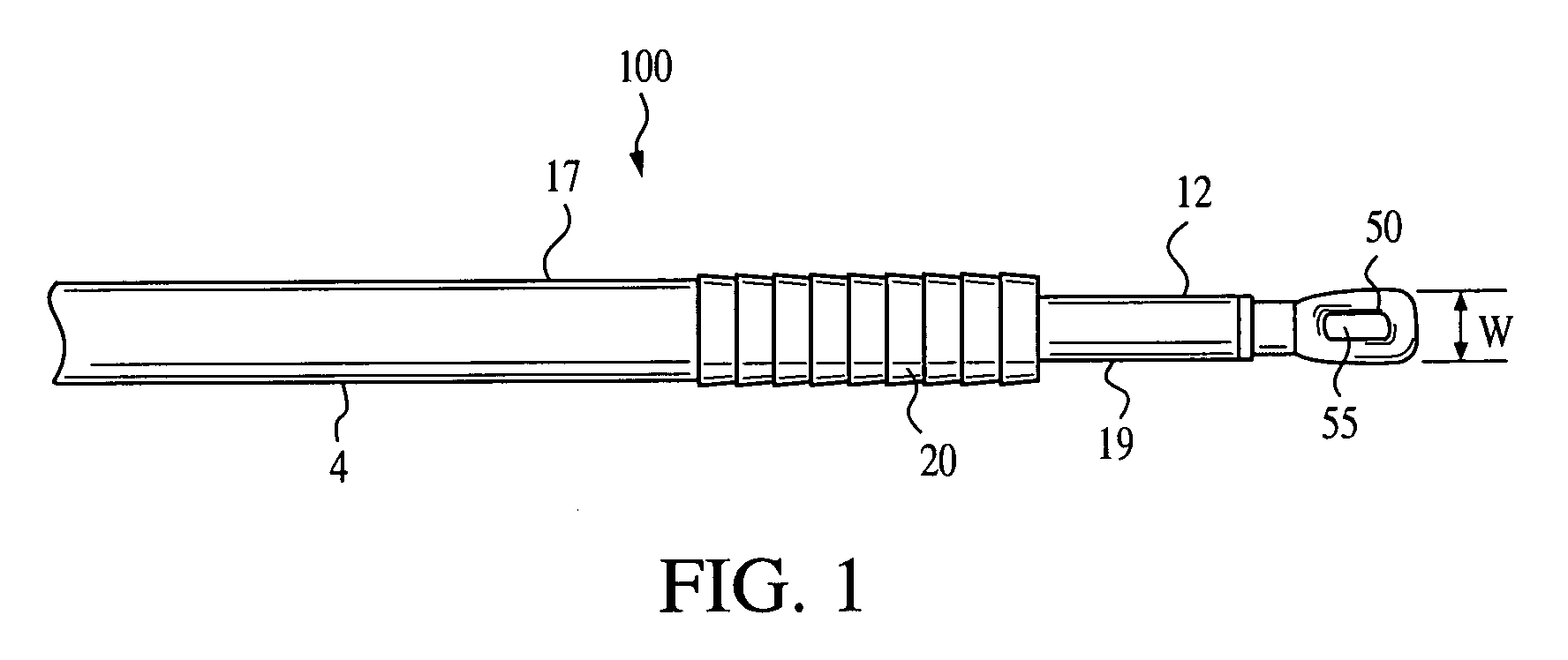
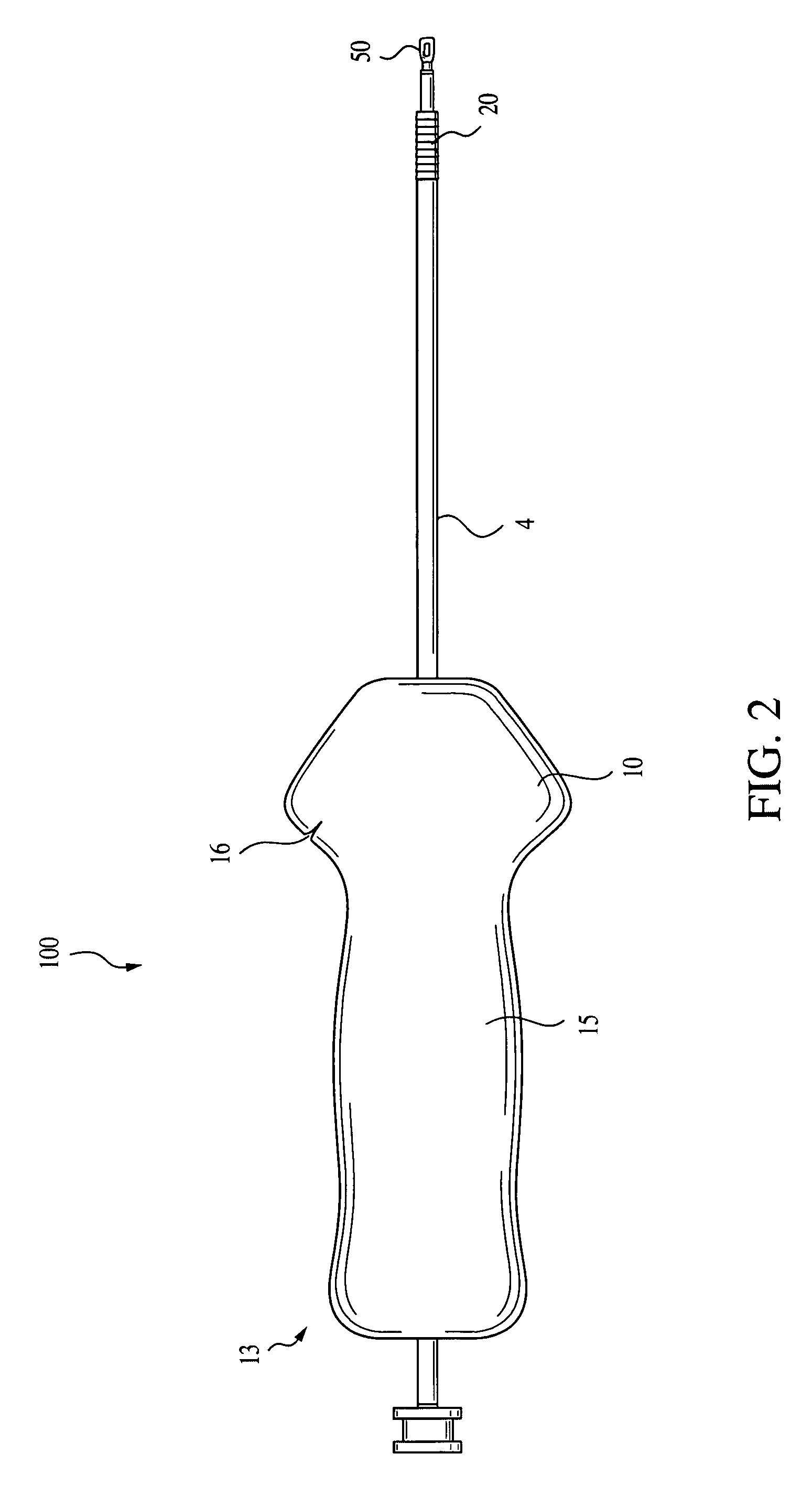
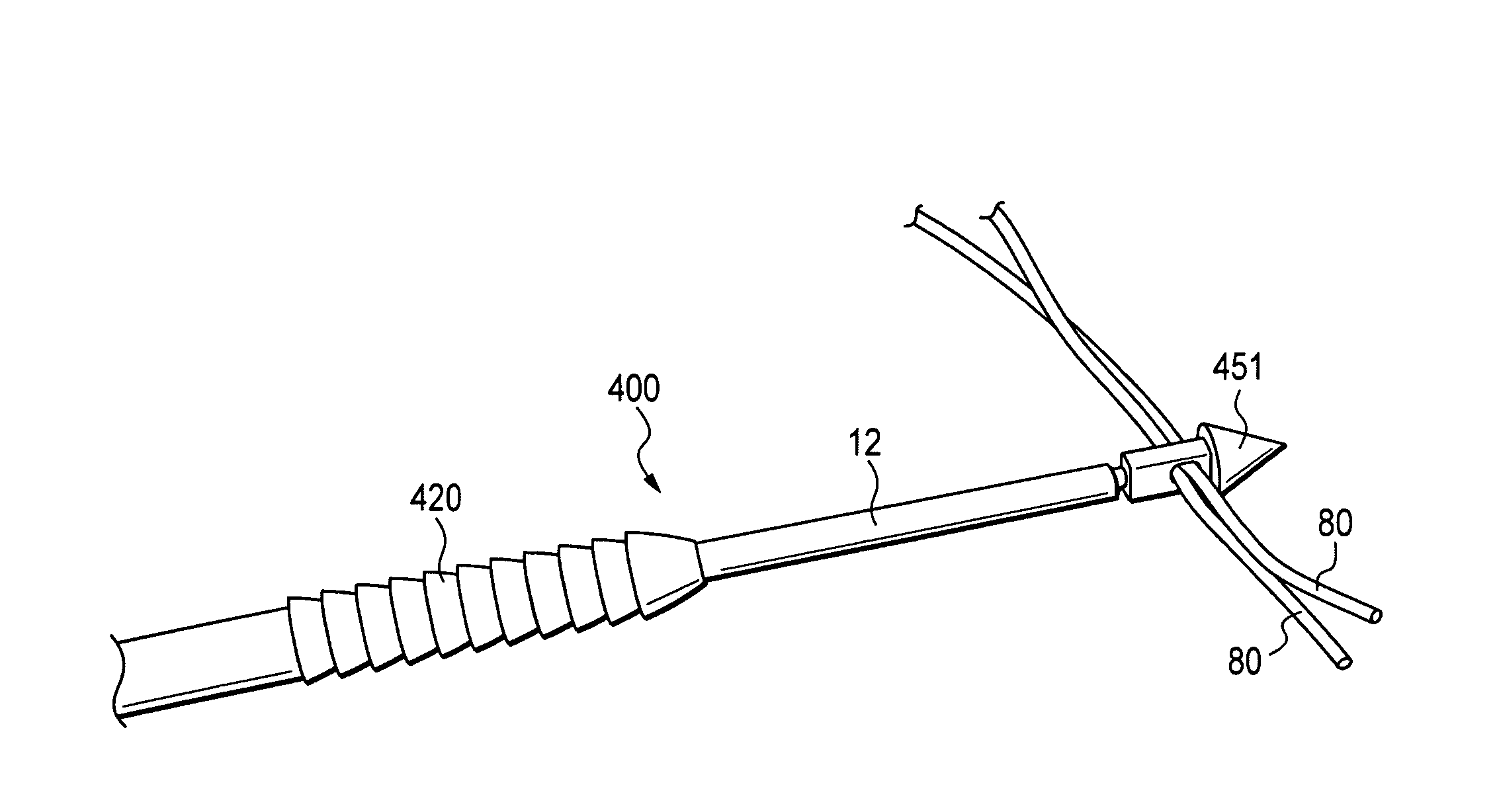
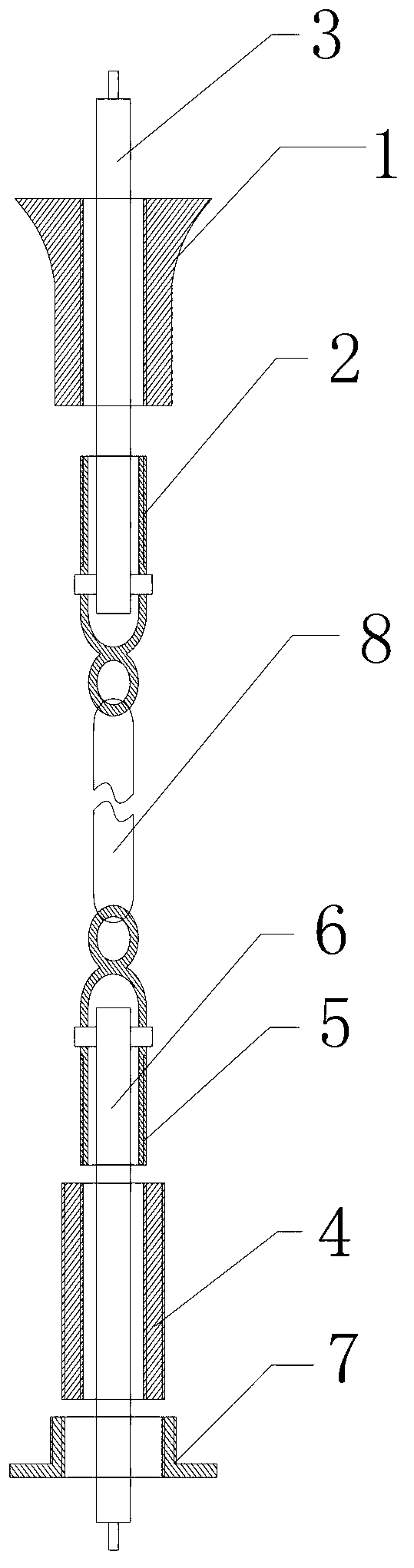
Graft fixation using a plug against suture
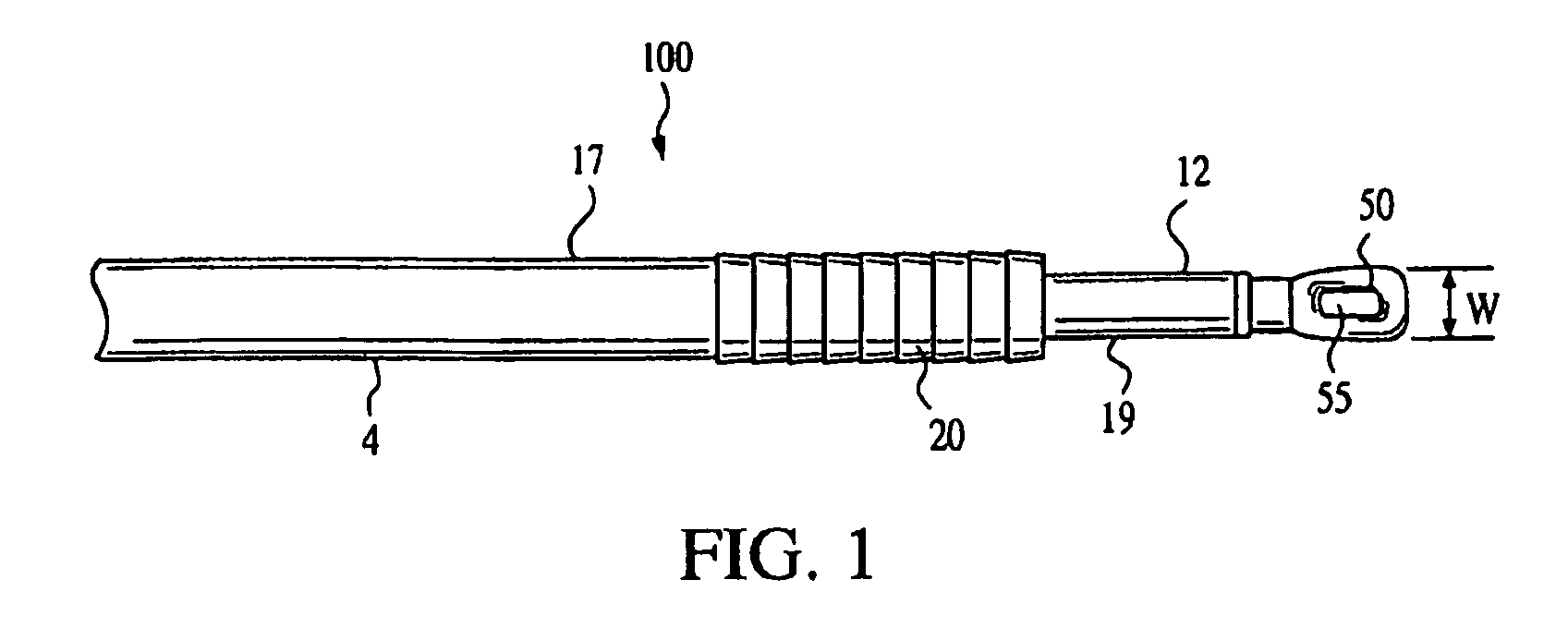
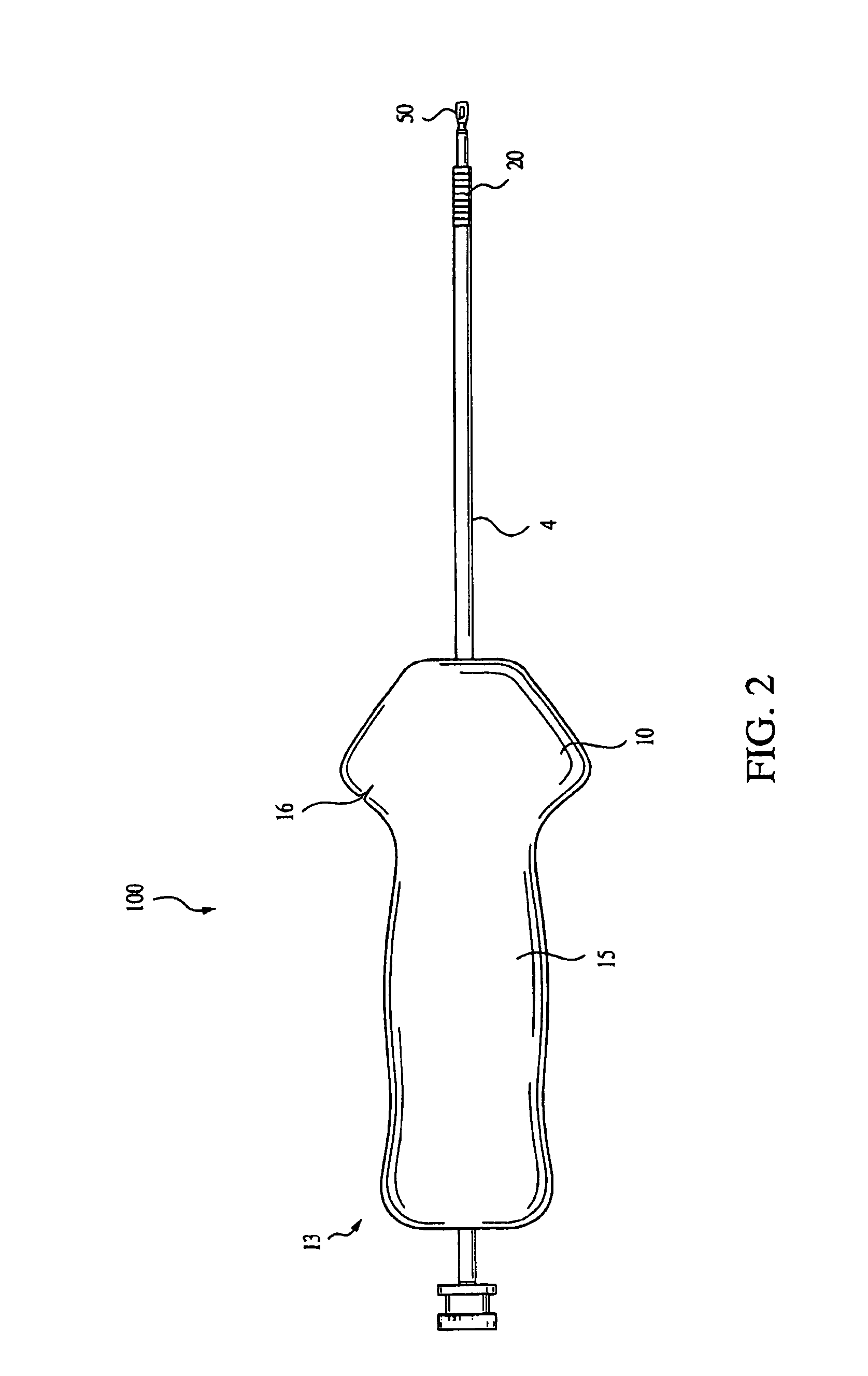
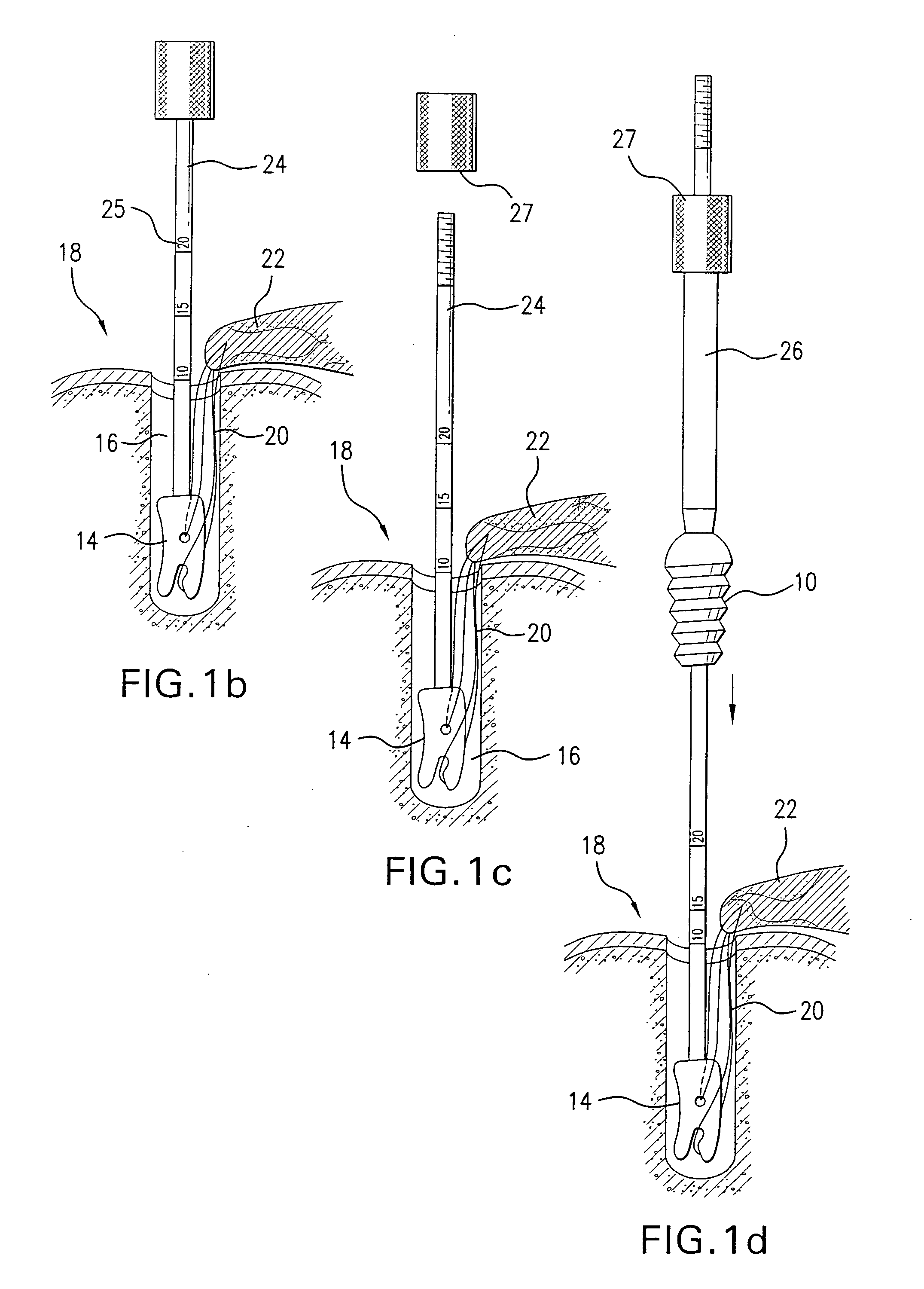
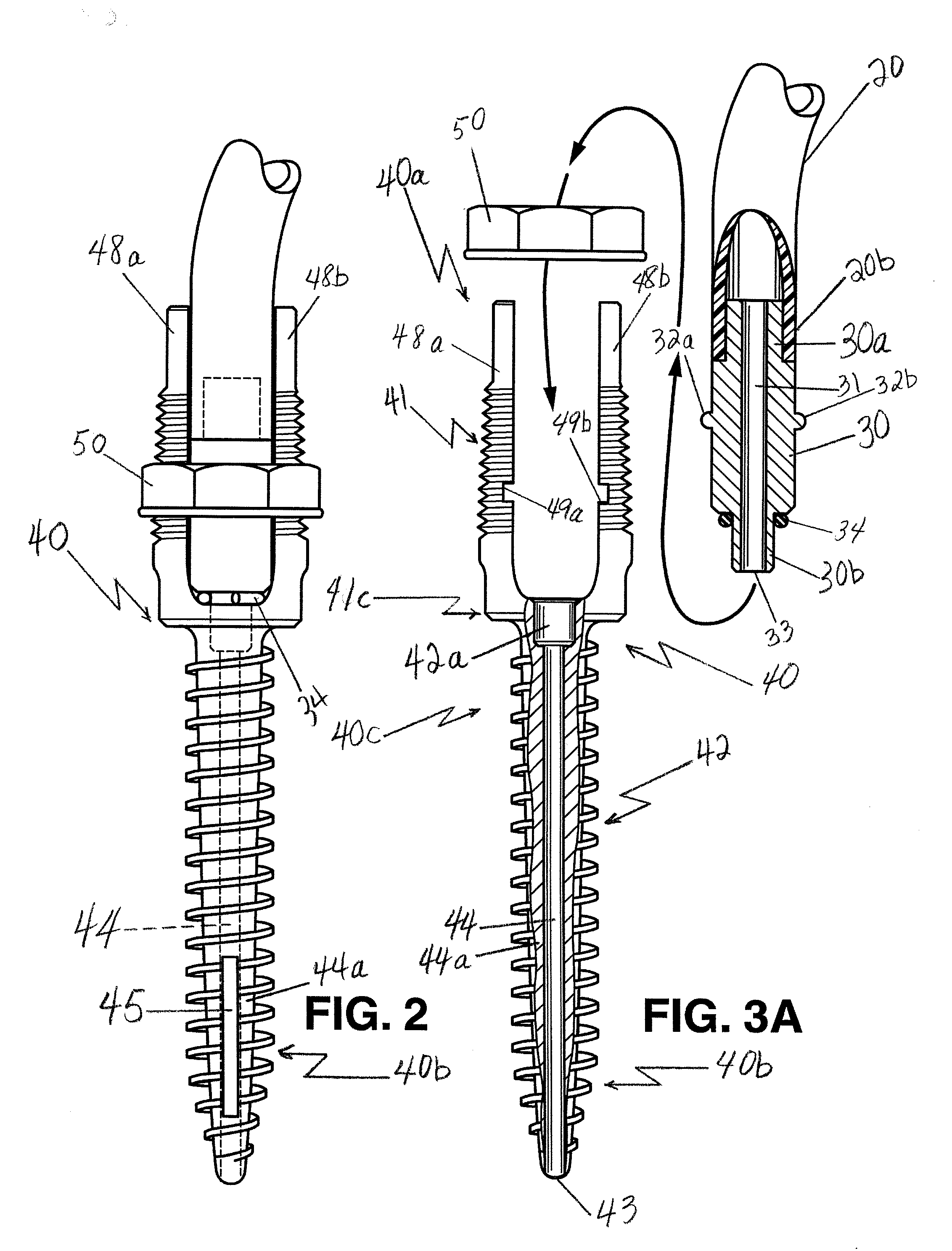
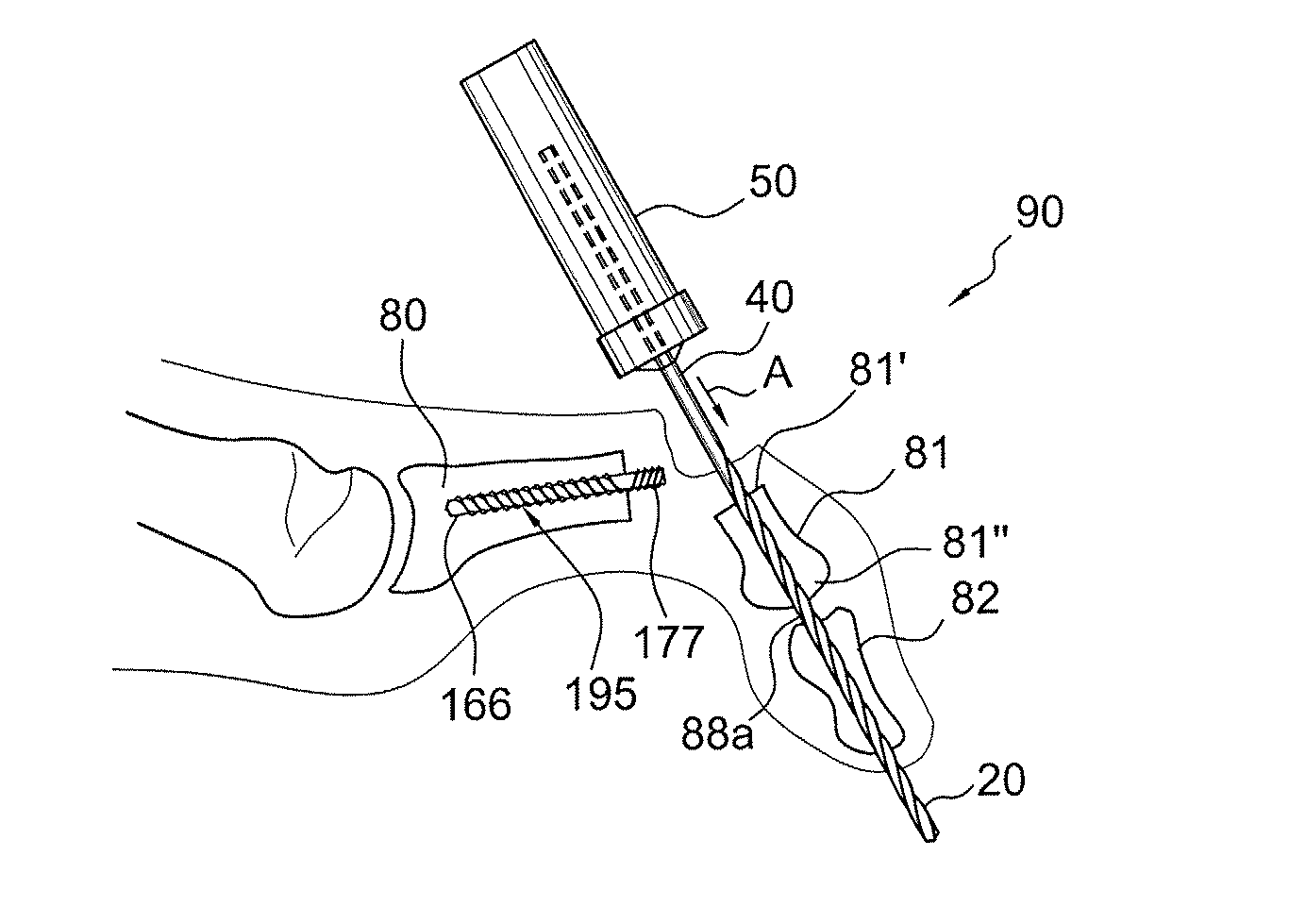
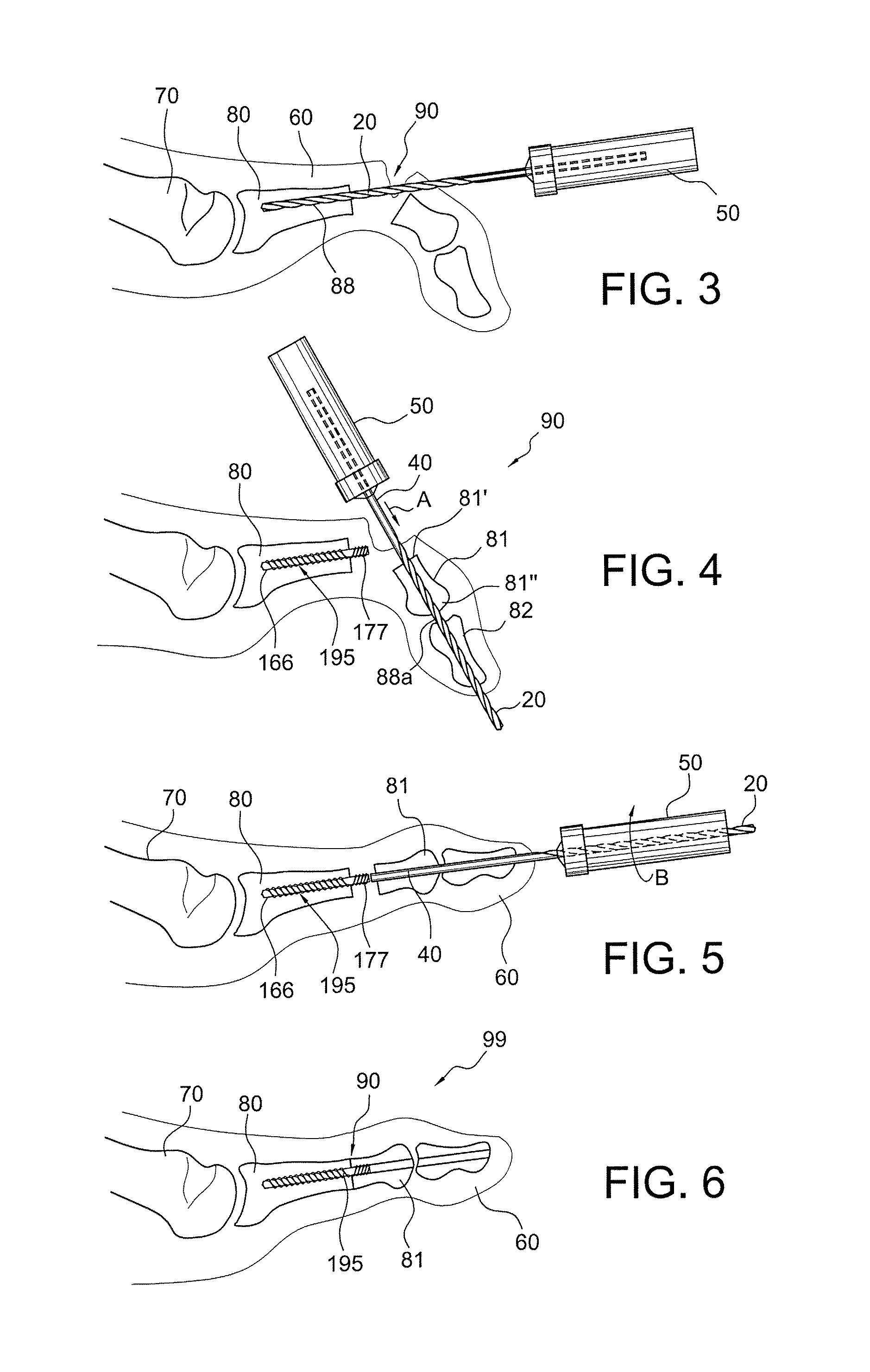
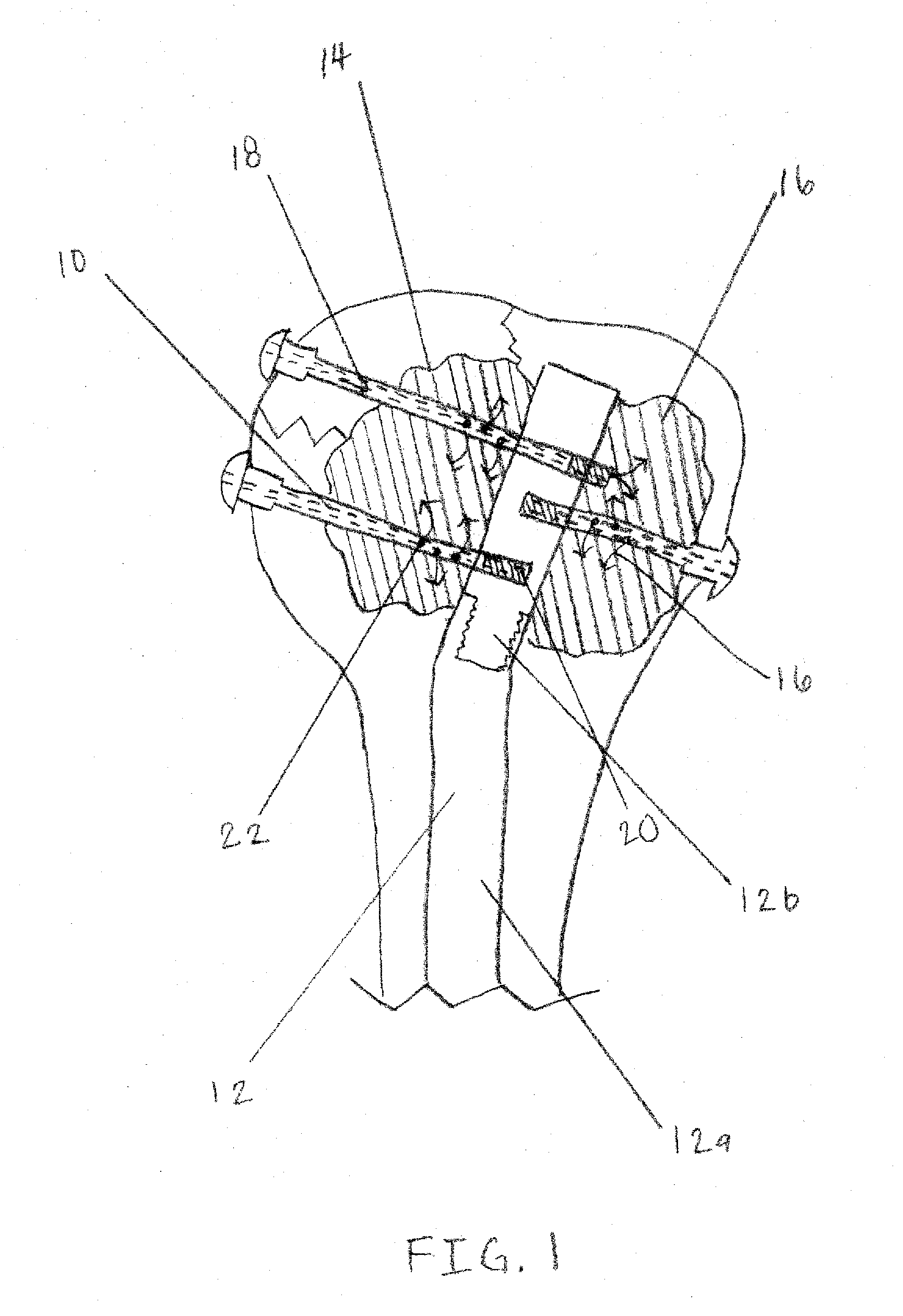
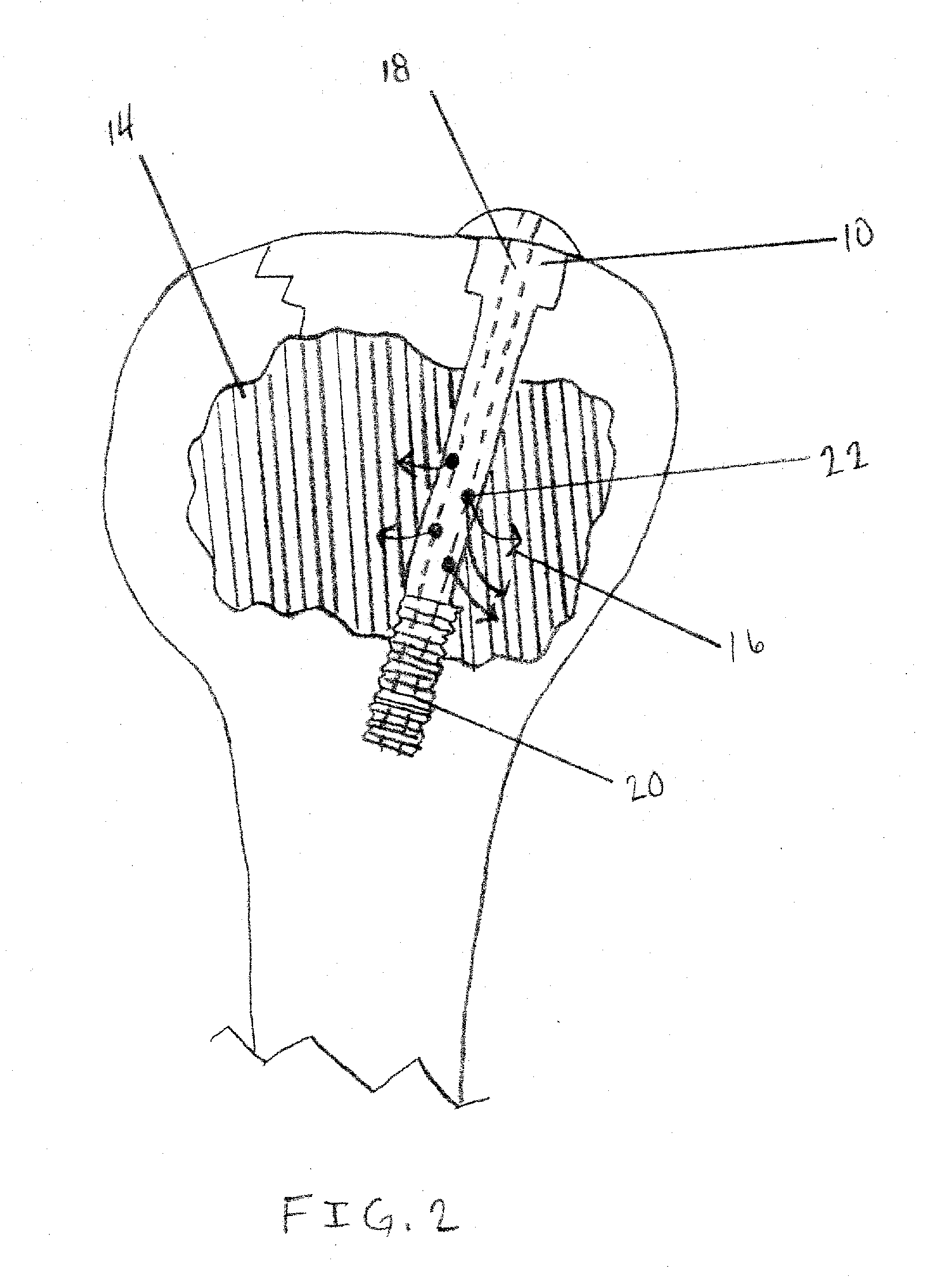
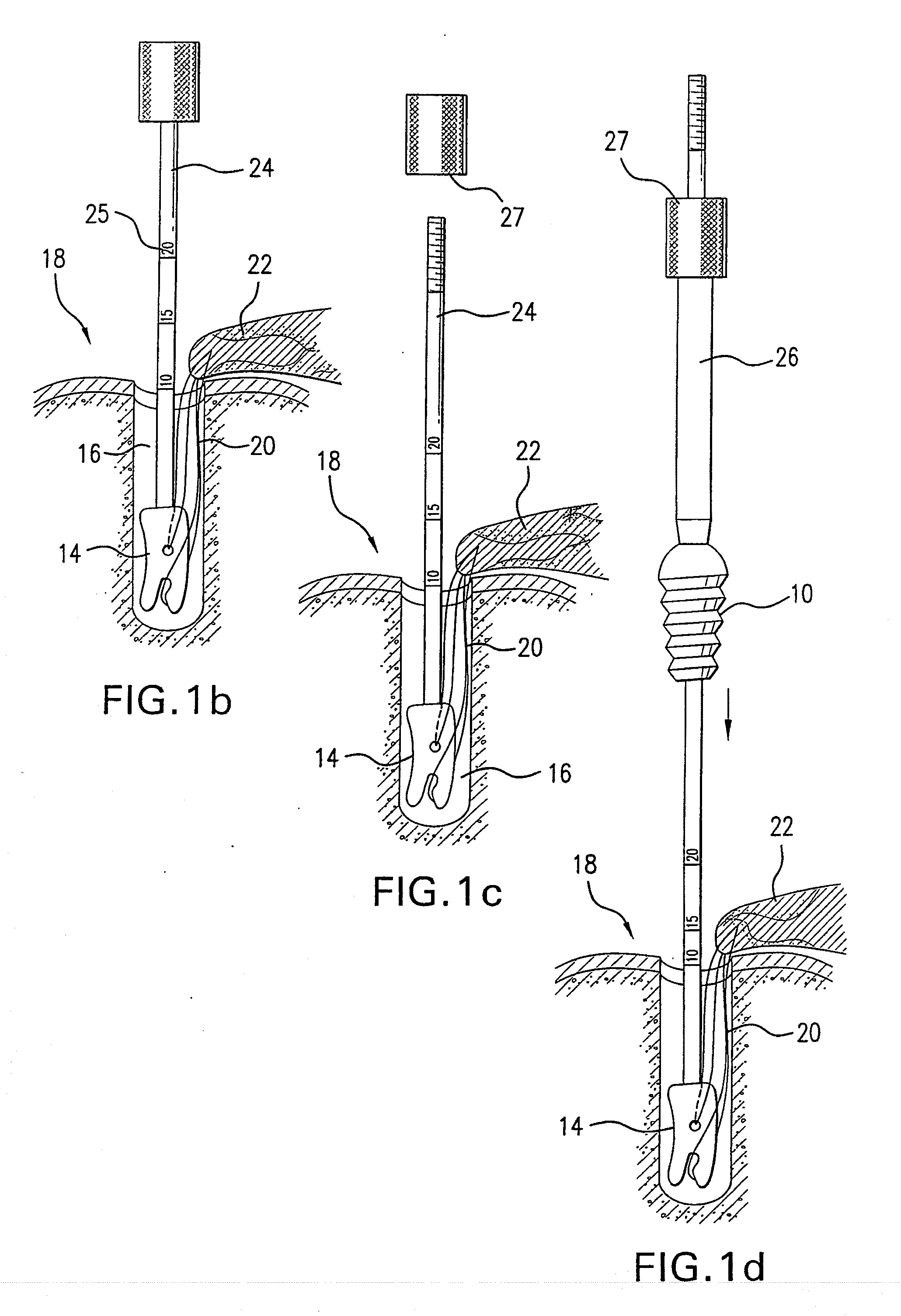
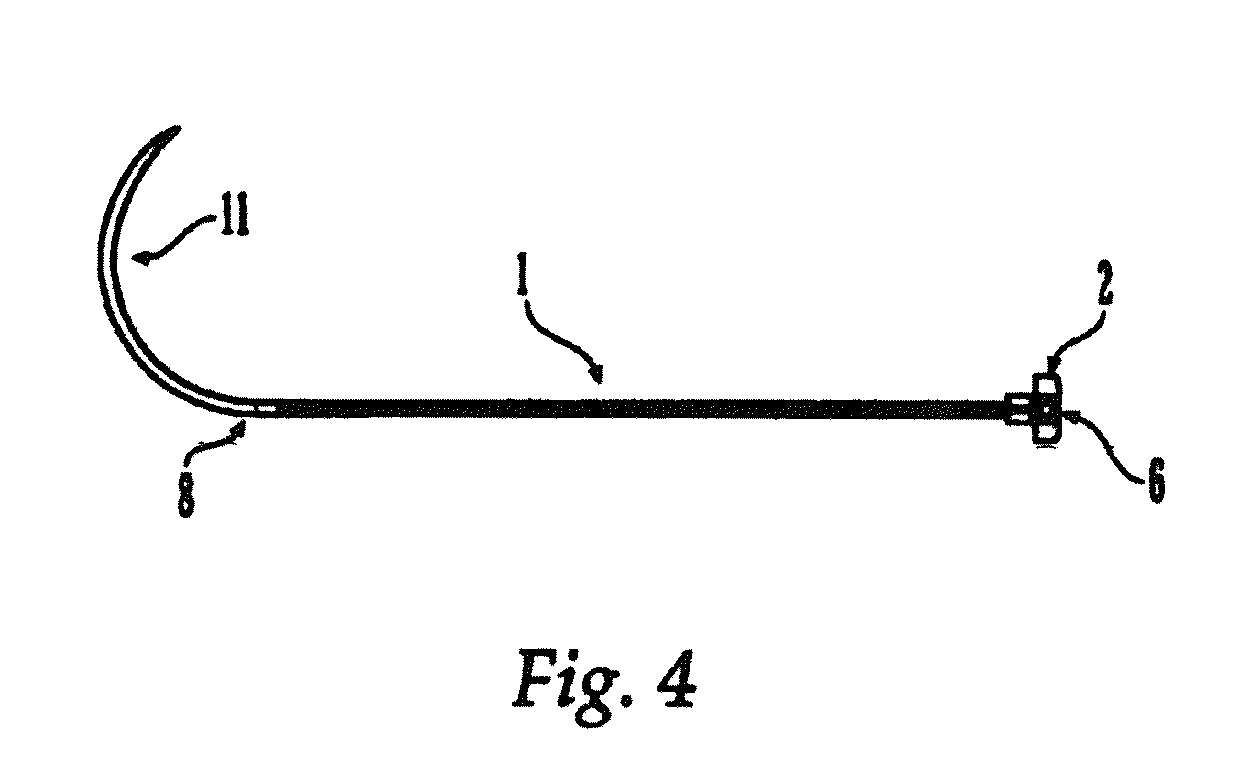
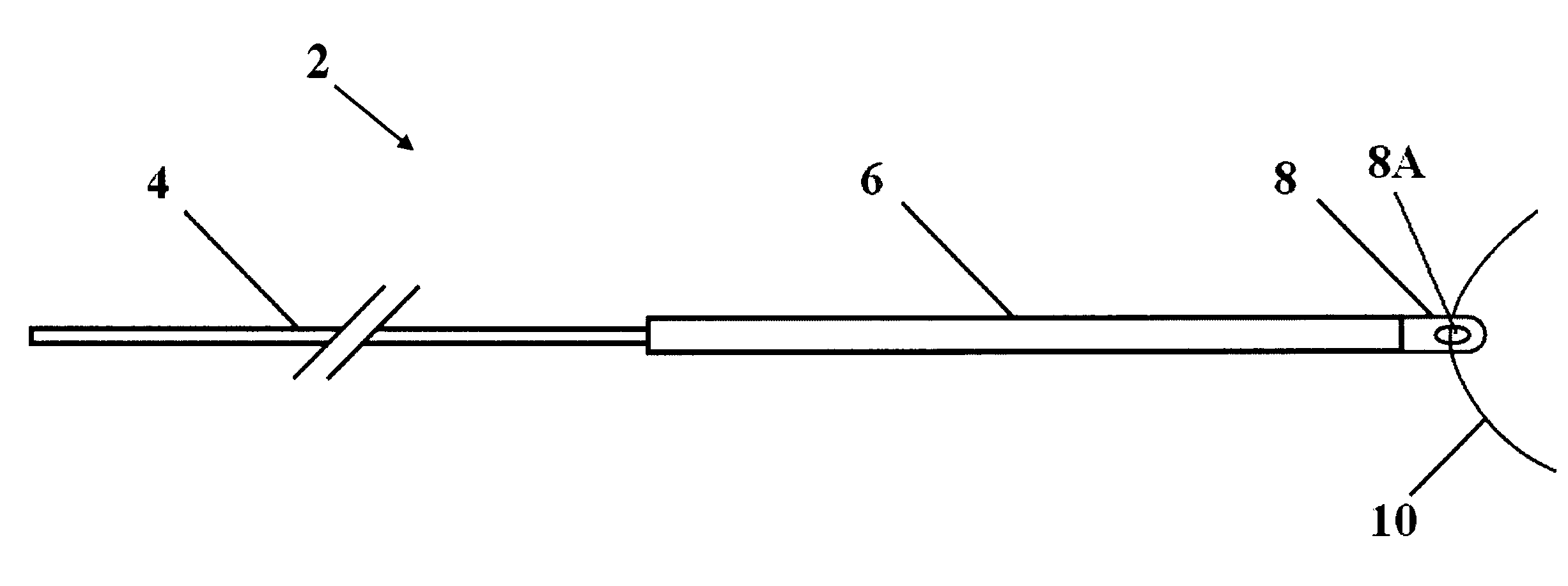
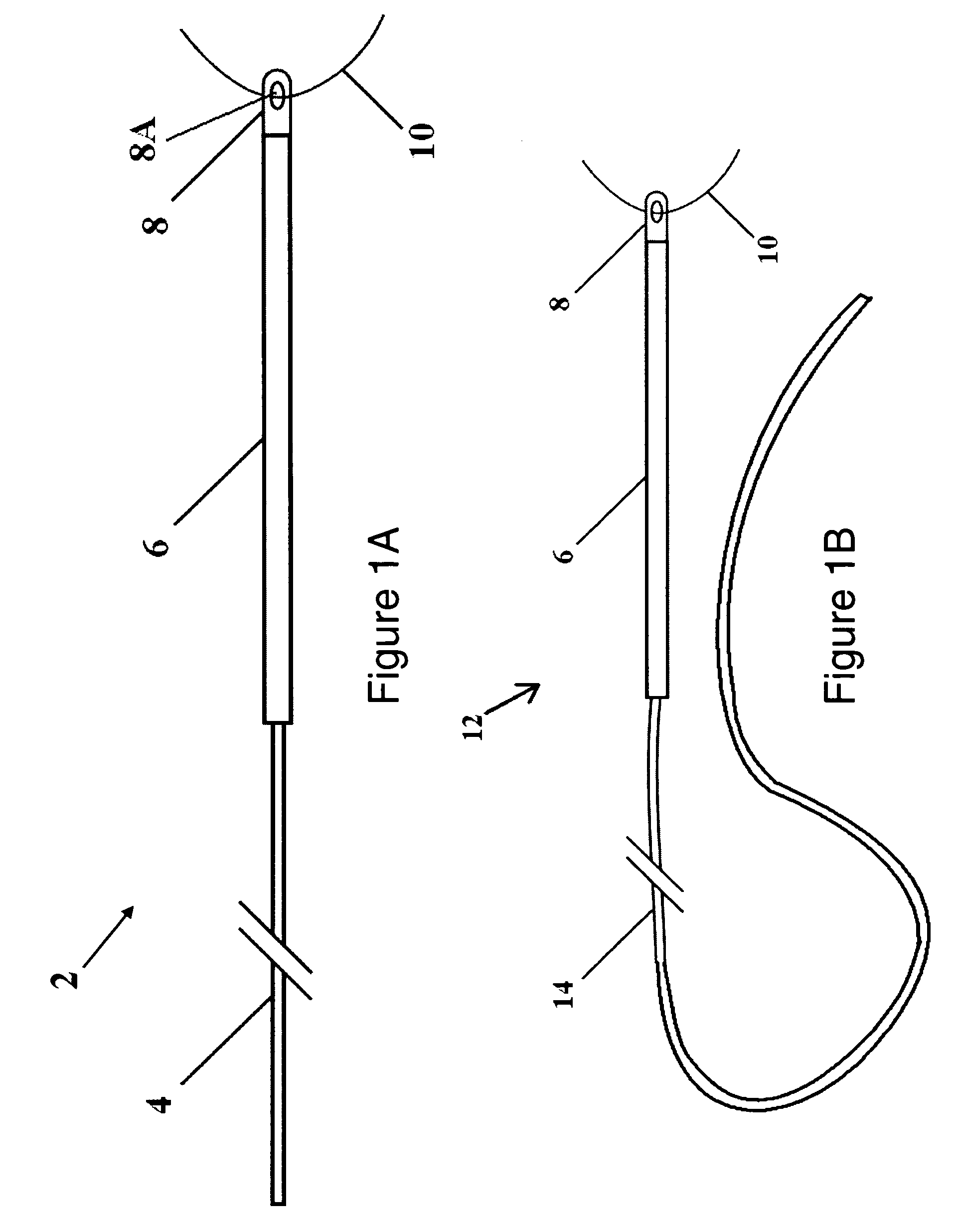
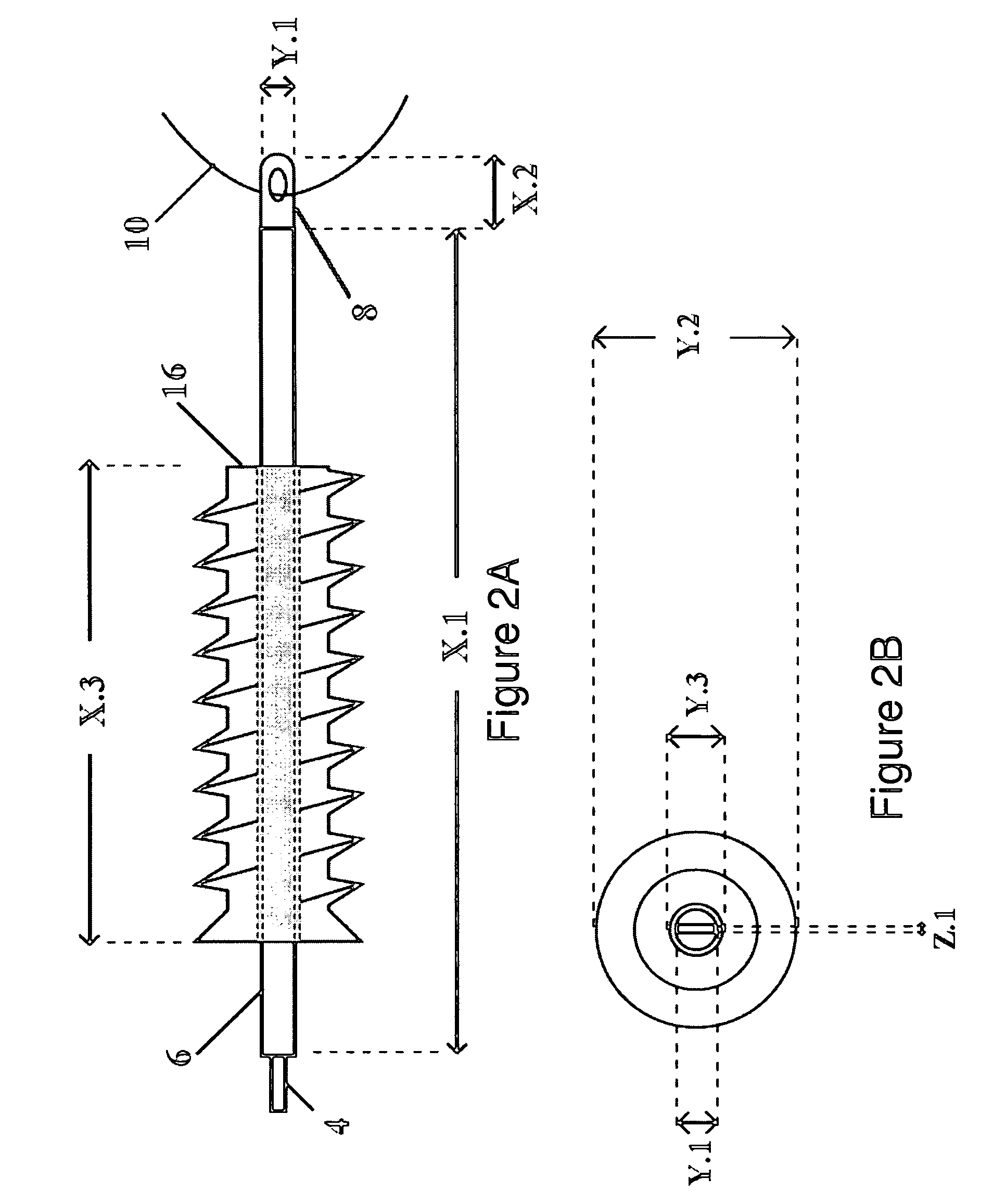
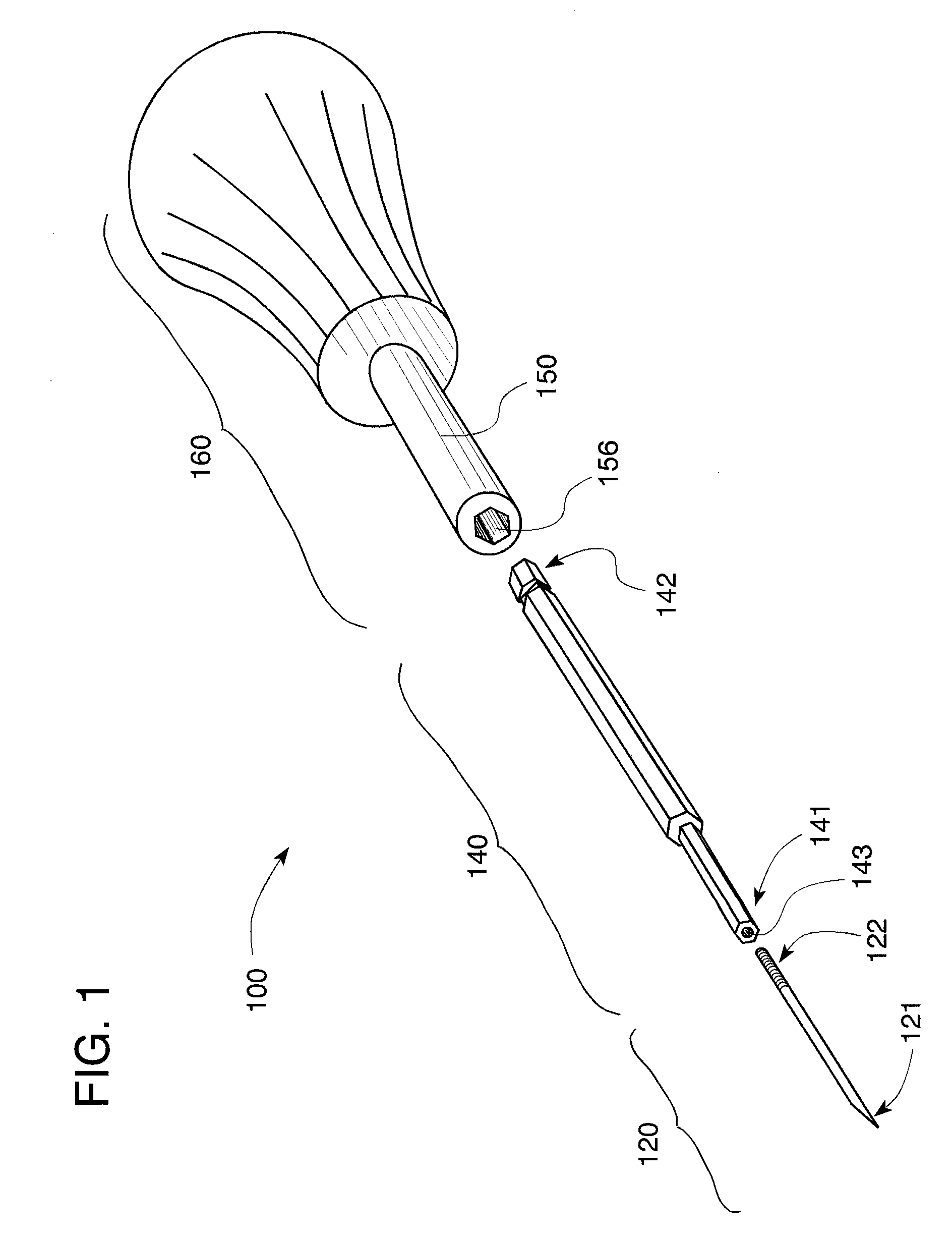
A method for securing soft tissue to bone which does not require the surgeon to tie suture knots to secure the tissue to the bone. A pilot hole or socket is created in the bone at the location that the graft is to be secured. Suture is passed through the graft at desired points. A cannulated plug or screw is pre-loaded onto the distal end of a driver provided with an eyelet implant at its distal end. Suture attached to the graft is passed through the eyelet of the implant located at the distal end of the driver. The distal end of the driver together with the eyelet implant is inserted into the bottom of the hole, with the screw or plug disposed just outside the hole. Tension is applied to the suture to position the graft at the desired location relative to the bone hole. The screw or plug is then frilly advanced into the pilot hole by turning the interference screw or tapping the plug until the cannulated screw or plug securely engages and locks in the eyelet implant, so that the cannulated plug or screw with the engaged eyelet implant is flush with the bone. Once the screw or plug is fully inserted and the suture is impacted into the pilot hole, the driver is removed and any loose ends of the sutures protruding from the anchor site are then clipped short.
Owner:ARTHREX
Graft fixation using a plug against suture
A method for securing soft tissue to bone which does not require the surgeon to tie suture knots to secure the tissue to the bone. Suture is passed through the graft at desired points. A cannulated plug or screw is pre-loaded onto the distal end of a driver provided with an eyelet implant at its distal end. Suture attached to the graft is passed through the eyelet of the implant located at the distal end of the driver. The distal end of the driver together with the eyelet implant is inserted into the bone. Tension is applied to the suture to position the graft at the desired location relative to the bone. The screw or plug is advanced into the pilot hole by turning the interference screw or tapping the plug until the cannulated screw or plug securely engages and locks in the eyelet implant, so that the cannulated plug or screw with the engaged eyelet implant is flush with the bone. Once the screw or plug is fully inserted and the suture is impacted into the bone, the driver is removed and any loose ends of the sutures protruding from the anchor site are then clipped short.
Owner:ARTHREX
Sternal reconstruction system
A sternal reconstruction system for securing parts of a sternum includes at least one flexible cable with crimp fitting, at least one cannulated screw and at least one reconstruction plate. Circumferential or parasternal fixation may be brought about by use of a sternal reconstruction system including a flexible cable and crimp fitting alone; a sternal reconstruction system including a flexible cable, crimp fitting and cannulated screws; or a system including a flexible cable, crimp fitting, cannulated screws and one or more reconstruction plates. The reconstruction plates are typically planar, having an upper and a lower surface, and containing generally perpendicular and transverse plate holes. The generally perpendicular plate holes are countersunk to better accommodate the heads of the cannulated bone screws. Also provided is a kit for sternal reconstruction.
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
Multi-Axial Expandable Pedicle Screw and an Expansion Method Thereof
ActiveUS20090105771A1Reduce probabilityImprove stabilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisFailure rateUniversal joint
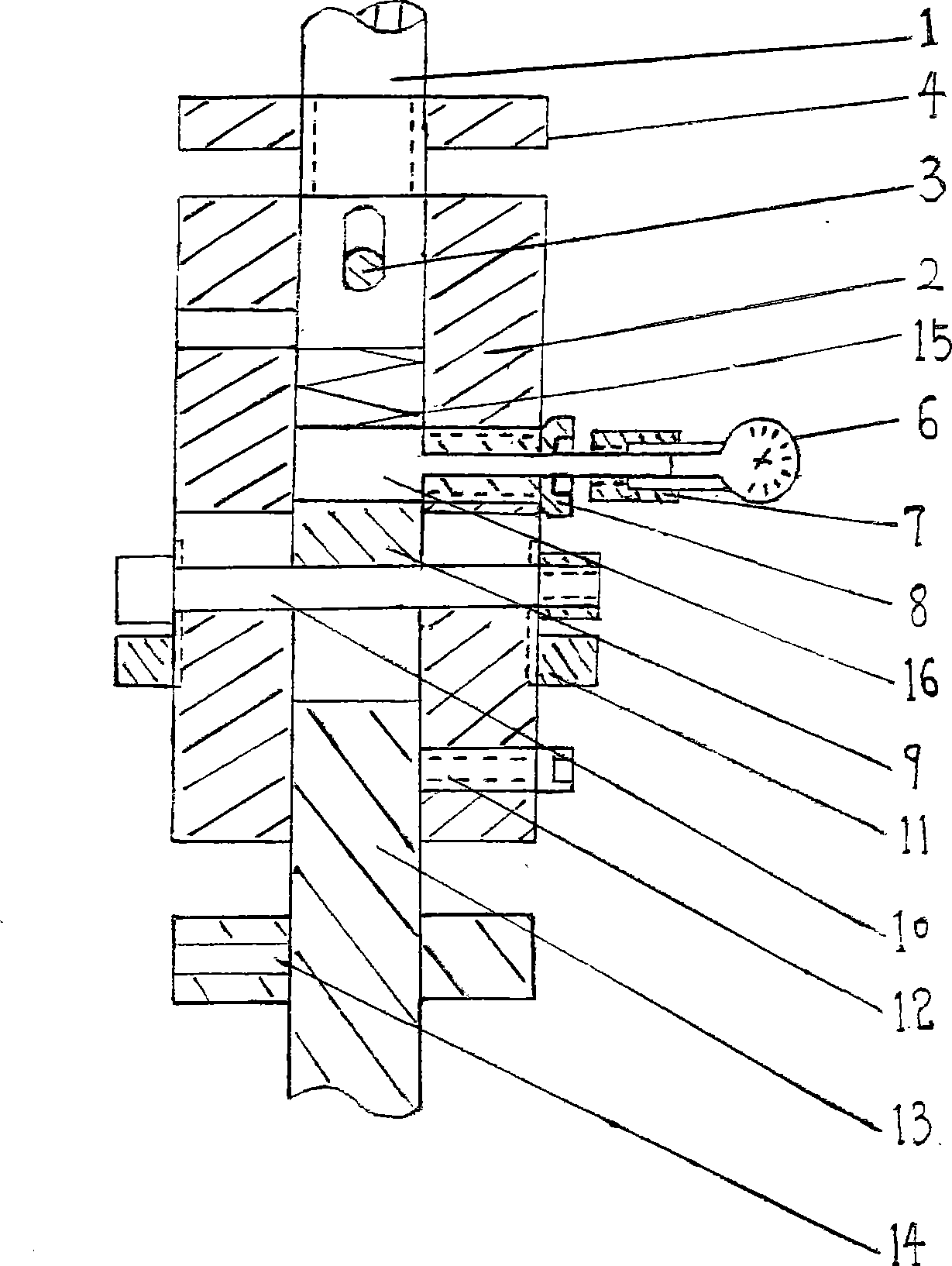
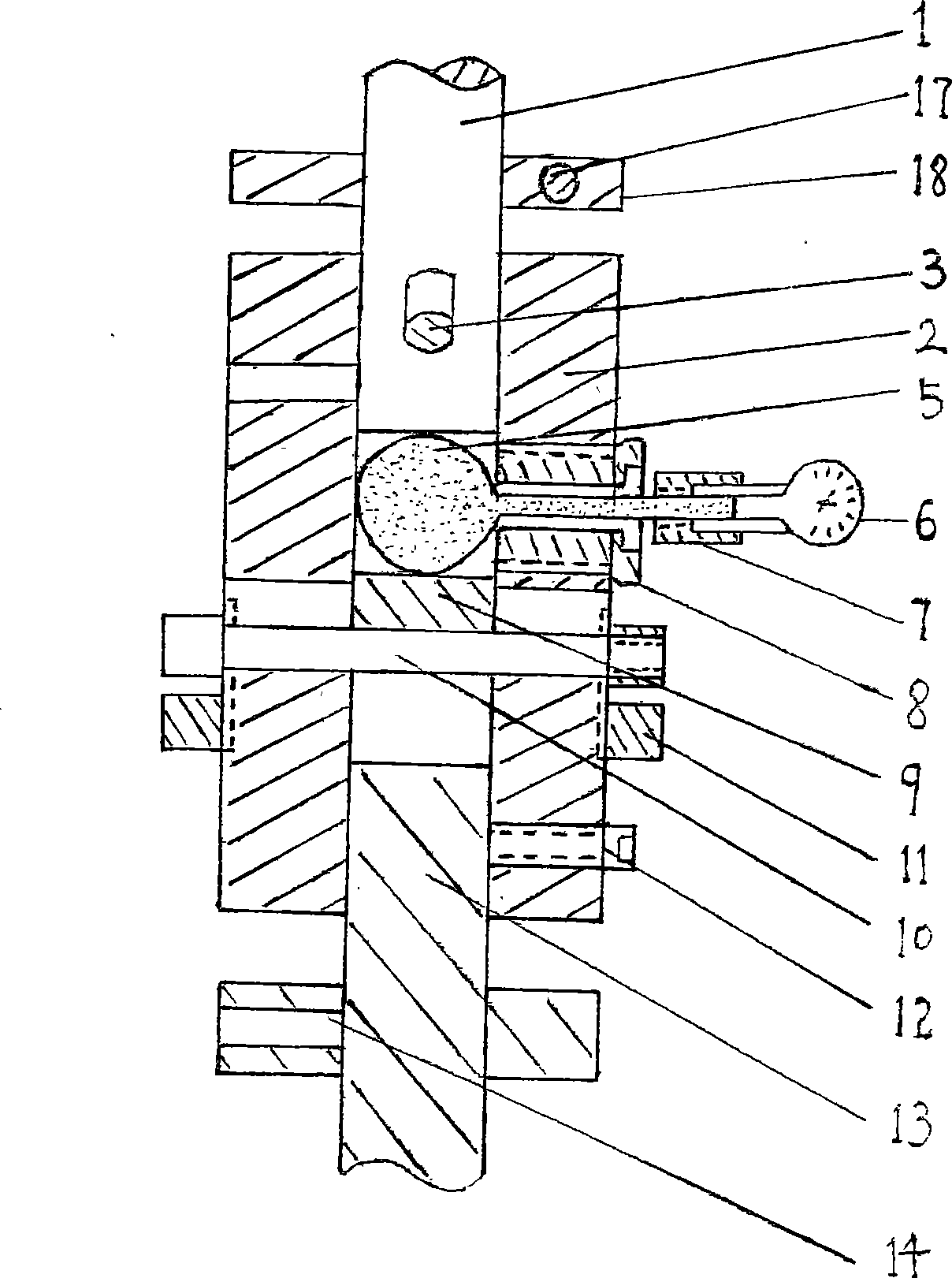
The invention disclosed a multi-axial expandable pedicle screw and an expansion method by using the same. Structure of the screw comprising a hollow screw being spherical shaped end connecting with an adapting piece, which is universal joint structure; an inner wall of the adapting piece connecting a lock bolt through screw threads; the hollow screw with sharp shaped on another end having a bore inside formed hollow structure in its entirety; the bore having taper shaped tip; expansion gaps uniformly setting up two, or three or four or more anterior fins on the hollow screw along its axial direction upward, prolonging from its tip to the bore; the inner needle is disposed in the bore. The invention can reduce the pedicle screw loose and even occurrence ratio of pull-out and increase the stability and reliability and reduce the failure rate of spinal surgeries at the same time. It is also easy to operate, and degree of expansion is of controllable level.
Owner:LEI WEI +1
Method and device for securing sutures to bones
InactiveUS20090281581A1Superior screw in fixationLong-term stabilitySuture equipmentsDiagnosticsSuture anchorsIliac screw
A method, system and device for securing a repair, such as a rotator cuff repair and includes an anchor placed within a hole formed in bone and a cannulated screw inserted into the hole after the anchor has been inserted to effectuate a firm and secure connection of tissue to bone, particularly when the quality of the bone does not permit optimal fixation. The method, system and device allows superior tissue fixation to bone with the ease of knotless suture anchor application.
Owner:LUMACA ORTHOPAEDICS
Fortified cannulated screw
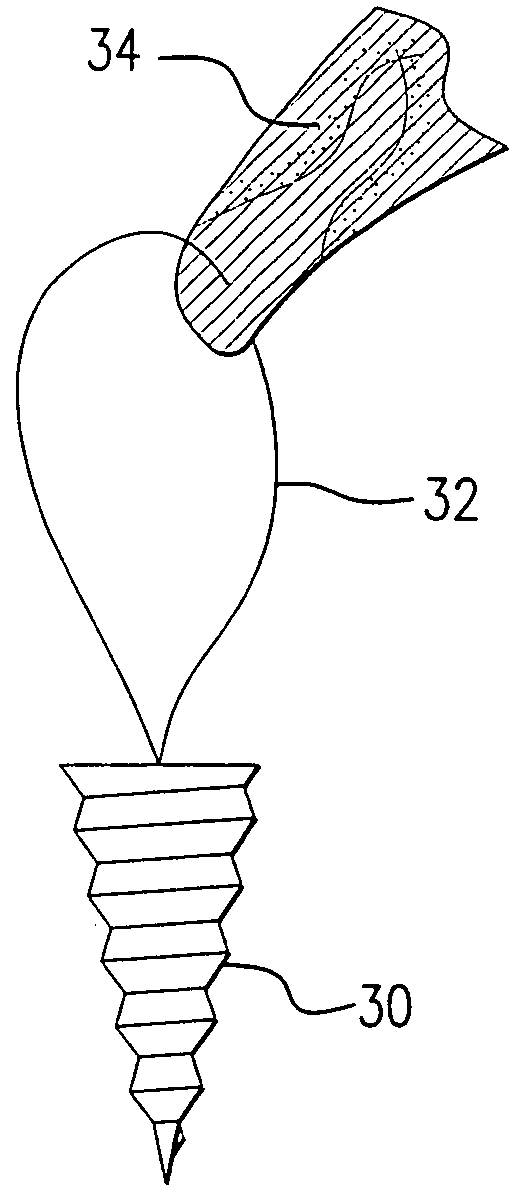
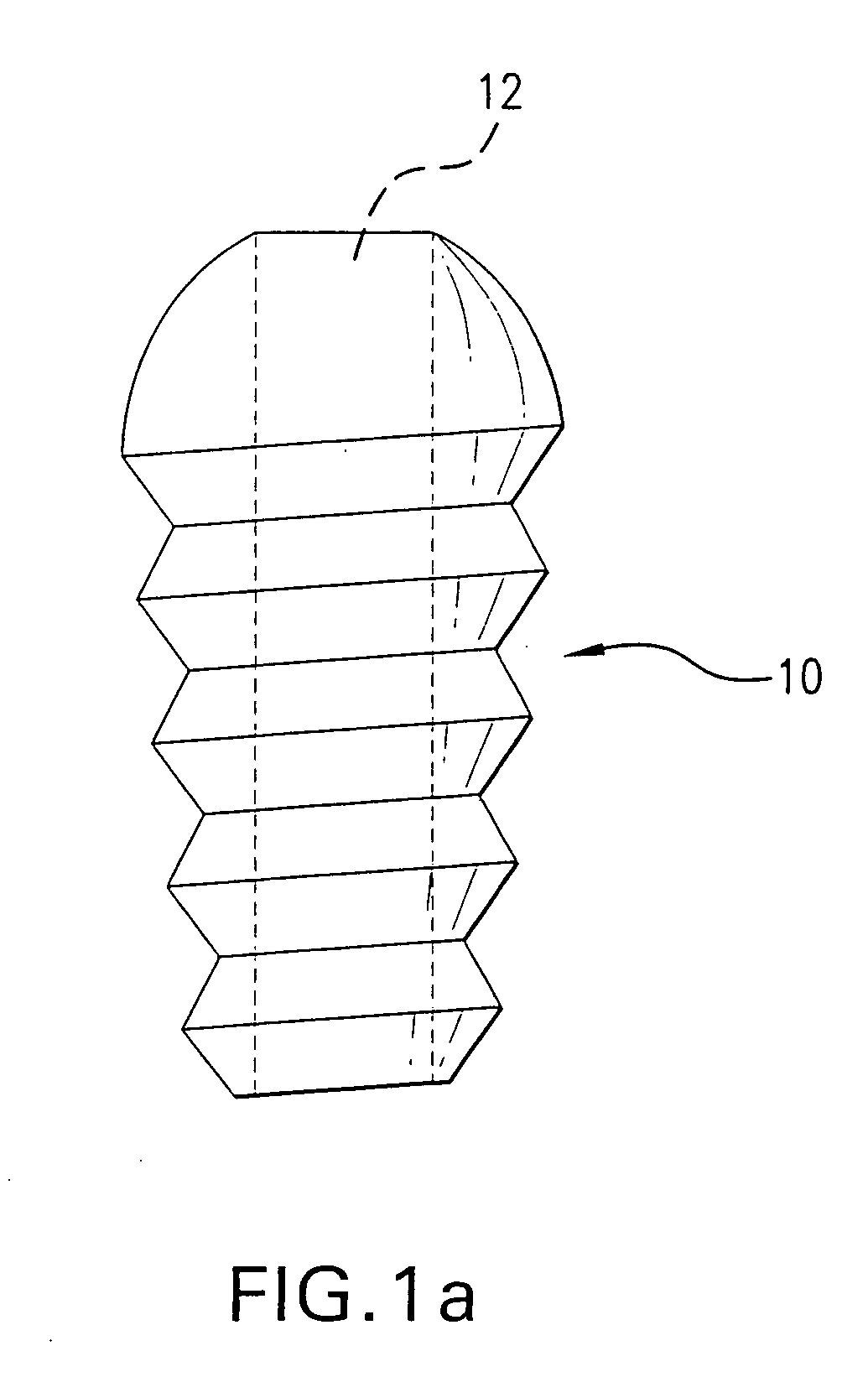
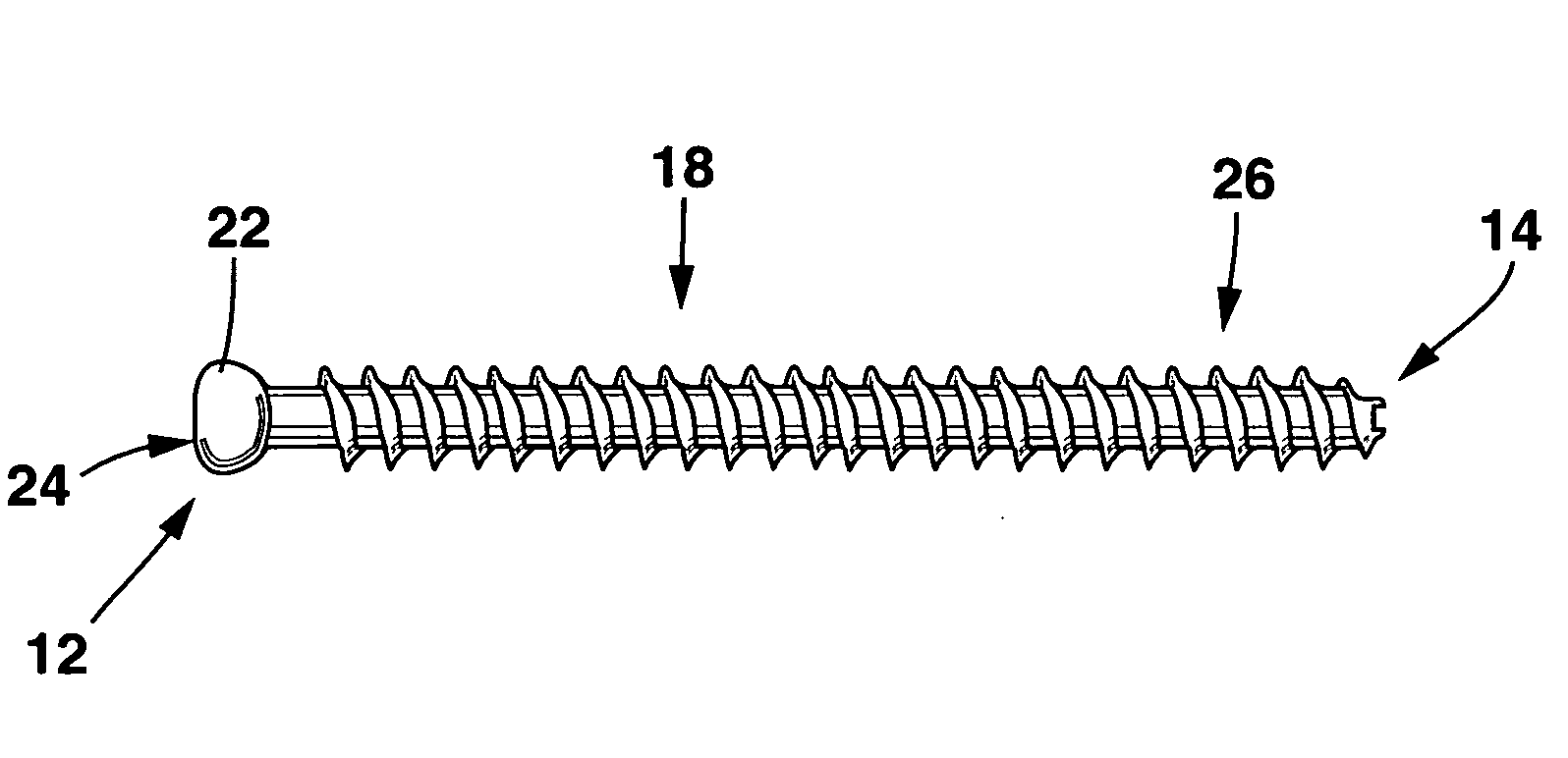
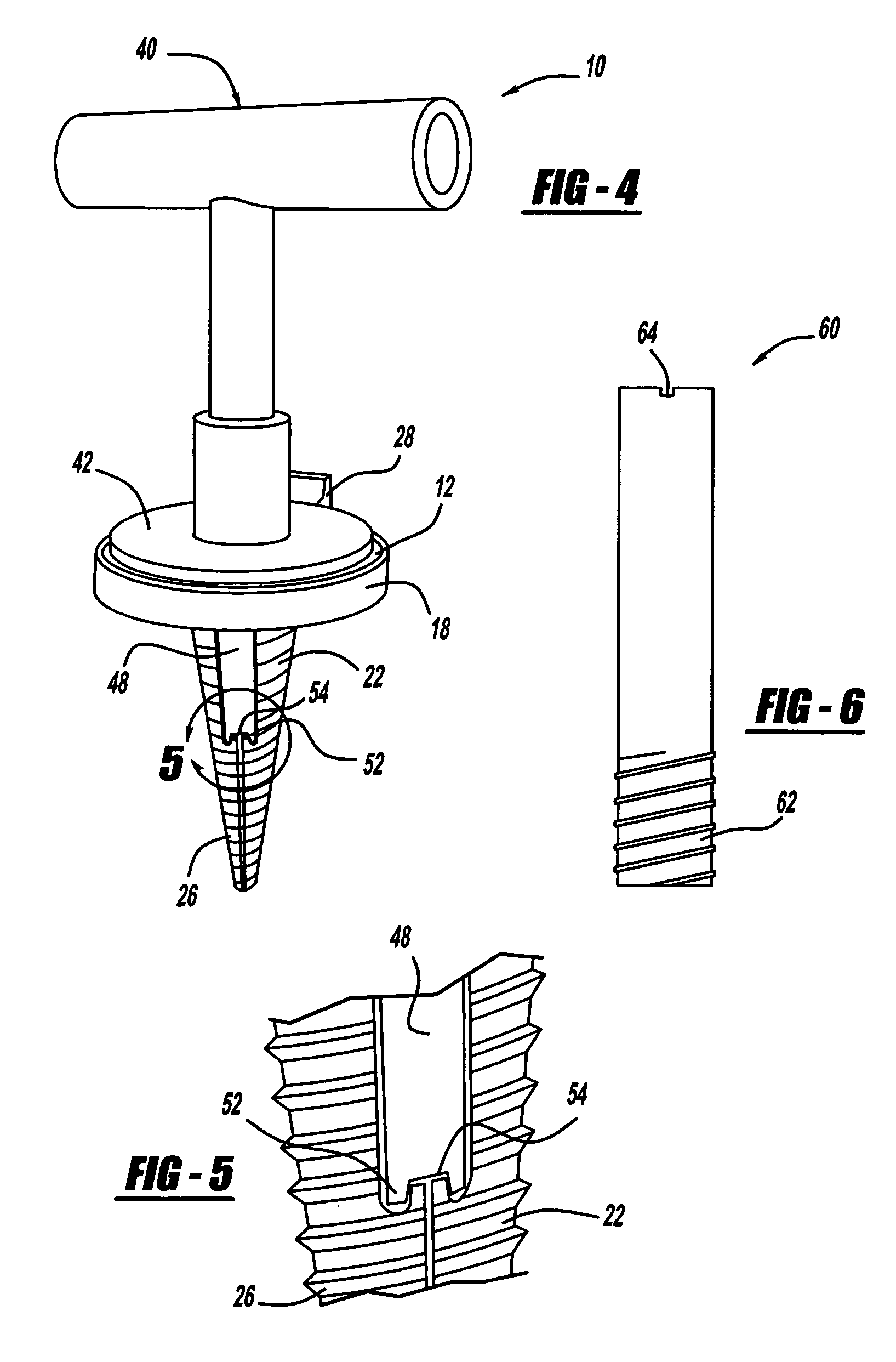
A cannulated screw is provided having internal threads in a lumen to accommodate a fortifying screw. The fortifying screw is screwed into the threads in the lumen of the cannulated screw after the cannulated screw has been accurately placed in the bone by following a guide pin or guide wire to the desired location is as is commonly done with cannulated screws. The fortifying screw fortifies the cannulated screw and gives it strength approximately equal to that of a solid screw.
Owner:MANDERSON EASTON L
Method and apparatus for anchoring bone screws and injecting many types of high viscosity materials in areas surrounding bone
ActiveUS20100030135A1Increase stickinessHigh materialSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisImproved methodHigh pressure
An improved method and apparatus for anchoring bone screws into bones of living beings includes a cannulated screw or bone anchor that is provided with at least one discharge opening in the distal end thereof. The head of the screw is configured to receive therein a material delivery probe in sealing relationship therewith. A fluid insertion device is connected to the material delivery probe and pumps a highly viscous material through the material delivery probe and into the interior of a bone in which the distal end of the screw has been inserted. The screw can be anchored proximally in bone to prevent backpressure from dislodging the delivery cannula and aides in achieving the high pressures necessary to cause the positive effects of materials previously not injectable in the bone or surrounding areas with the current methods and apparatia.
Owner:DM SPINE 2 LLC A TENNESSEE
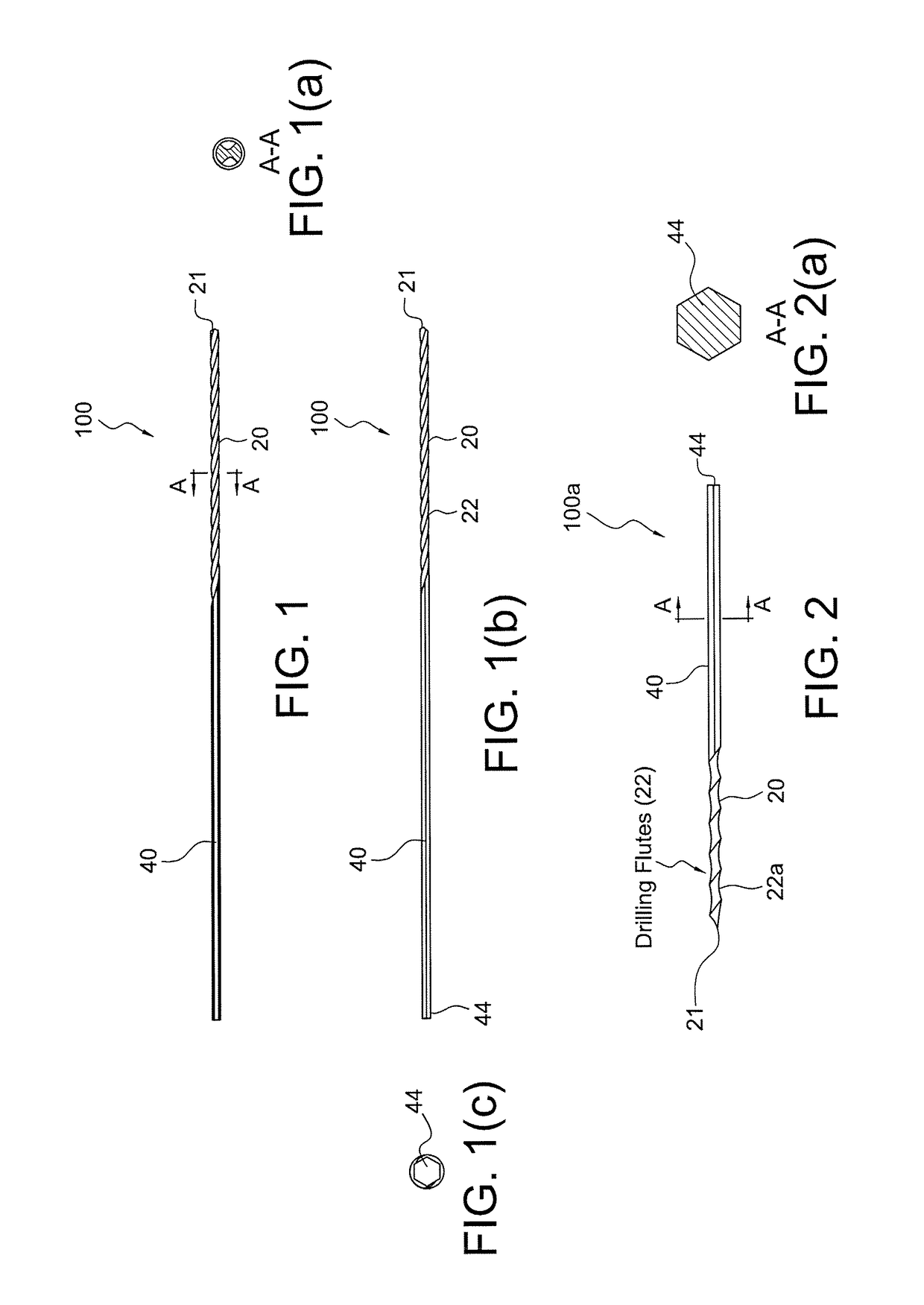
Interference screw driver assembly and method of use
InactiveUS20090248029A1Reduce the possibilityLimitations is associated with assembliesLigamentsMusclesInterference screwsEngineering
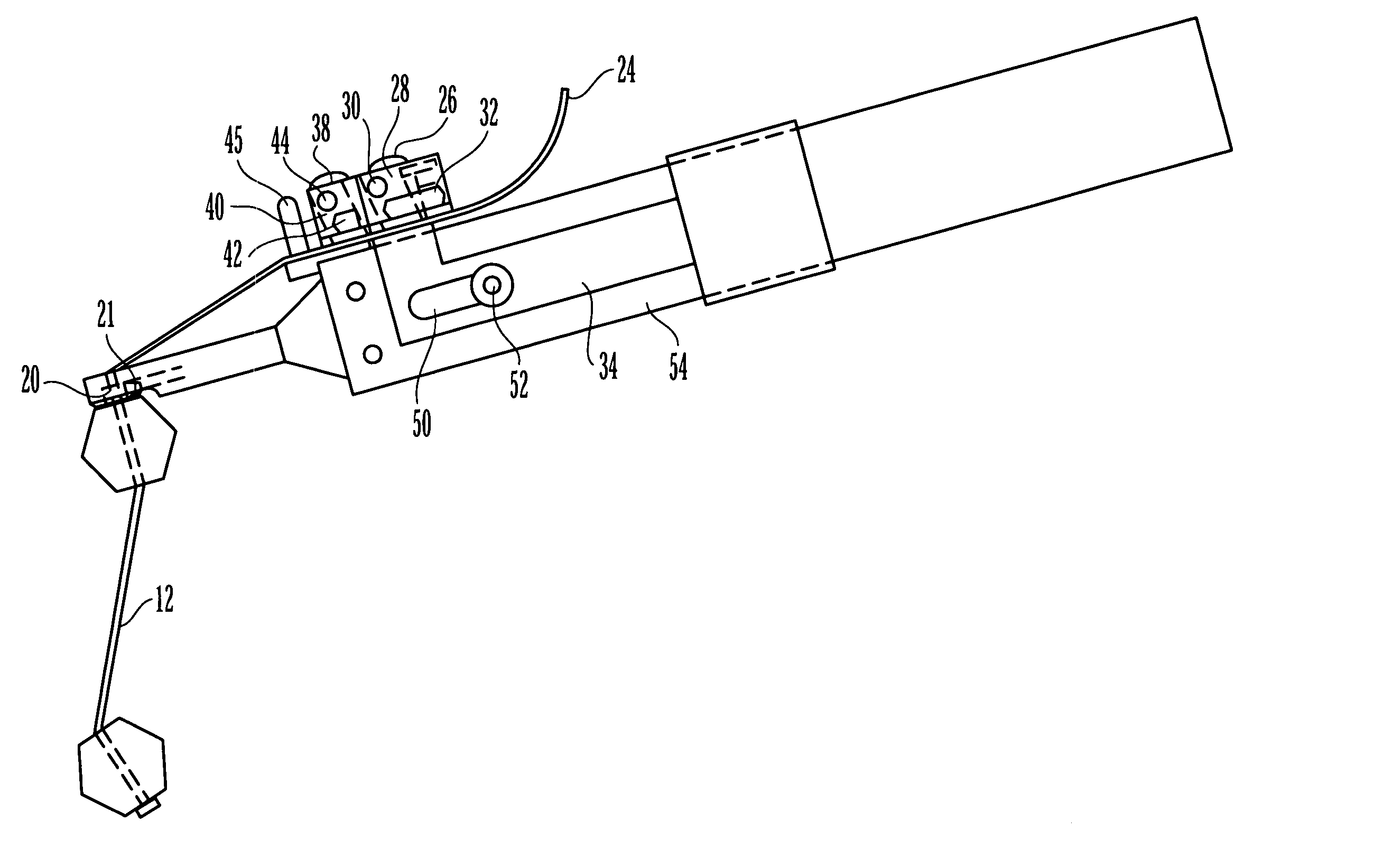
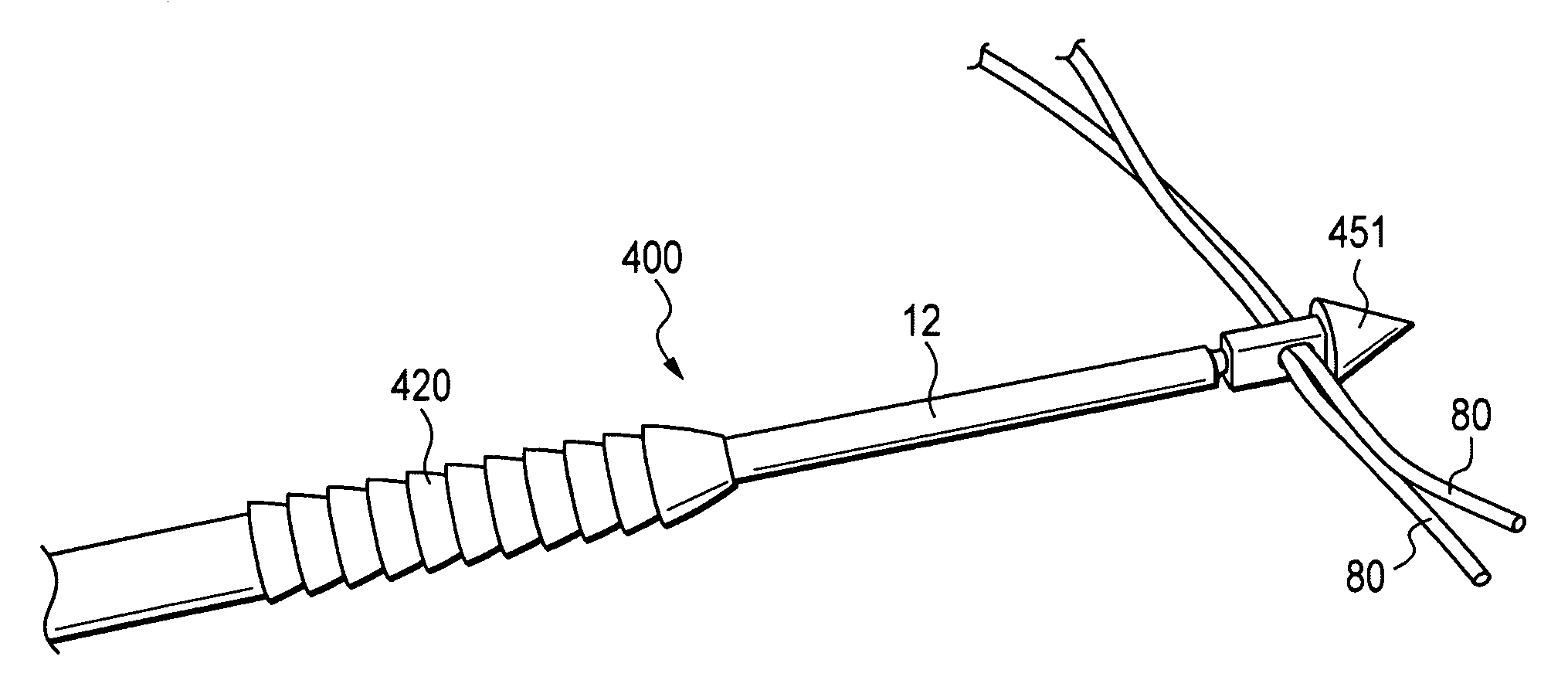
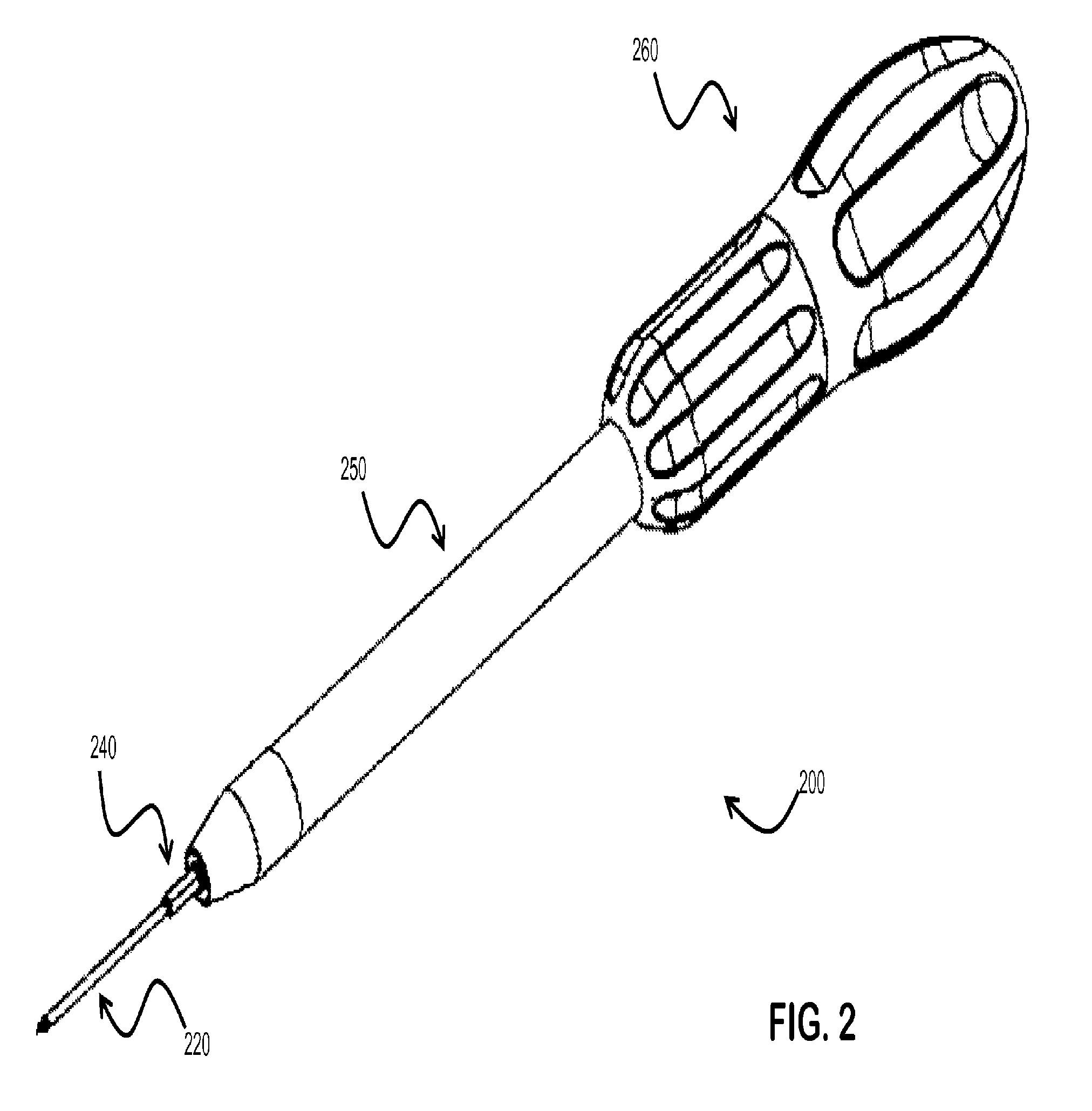
Embodiments of the present invention provide a cannulated screw driver assembly which includes a rigid guide pin such that the assembly can be used to assist the surgeon in inserting and positioning the rigid guide pin and an interference screw within a bone graft tunnel. Once the screw is properly placed, screw driver assembly components to include the rigid guide pin, the driver and the handle can be removed while the screw remains in the tunnel to secure the graft. In one embodiment, the interference screw can be removed from the distal end of the driver and the driver and handle can be removed from the screw's proximal end. Embodiments of the inventions also include an interchangeable driver to mate with different size and types of interference screws.
Owner:THE LONNIE & SHANNON PAULOS TRUST AS AMENDED & RESTATED
Drill/driver hybrid instrument for interphalangeal fusion
Surgical techniques, instruments and systems for bone fusions and repairs (for example, phalangeal fusion) which allow alignment of small bones (for example, phalanges) without the use of guidewire and cannulated instrumentation such as, for example, drills and drivers, and cannulated screws. A drill / driver hybrid instrument (a combined drill / driver device) may be used in fusion of two small bones (for example, in interphalangeal fusion). One end of the hybrid instrument is provided with a plurality of flutes so that the instrument can be used as a drill to remove bone. The other end is shaped to mate with a device to be inserted intraarticularly (for example, interphalangeally), acting as a driver for that device.
Owner:ARTHREX
Apparatus and Methods of Repairing Bone Defects
InactiveUS20090157078A1Fixed securityFortifying the structural integrity of the boneInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBody of femurBone defect
An apparatus and method for repairing osseous defects in such bones as the humerus, femur, ulna and long bones. A first embodiment presents one or more cannulated screws affixed to an intramedullary nail, which is installed in a humerus having an intraosseous void. In a second embodiment, one or more cannulated screws alone are inserted into a proximal humerus having an intraosseous void. Other embodiments teach one or more cannulated screws inserted into a damaged femur and attached to a plate or medullary rod. Another embodiment presents a number of cannulated screws used to attach a plate to a fractured long bone. In a final embodiment, a cannulated screw is installed in damaged ulna. In all embodiments, a bioresorbable or non-bioresorbable cement is injected into a hollow channel of the cannulated screw and extruded into the bone to stabilize the weakened bone and secure the position of a fixation device.
Owner:MIKOL EDWARD J
Graft fixation using a plug against suture
A method for securing soft tissue to bone which does not require the surgeon to tie suture knots to secure the tissue to the bone. Suture is passed through the graft at desired points. A cannulated plug or screw is pre-loaded onto the distal end of a driver provided with an eyelet implant at its distal end. Suture attached to the graft is passed through the eyelet of the implant located at the distal end of the driver. The distal end of the driver together with the eyelet implant is inserted into the bone. Tension is applied to the suture to position the graft at the desired location relative to the bone. The screw or plug is advanced into the pilot hole by turning the interference screw or tapping the plug until the cannulated screw or plug securely engages and locks in the eyelet implant, so that the cannulated plug or screw with the engaged eyelet implant is flush with the bone. Once the screw or plug is fully inserted and the suture is impacted into the bone, the driver is removed and any loose ends of the sutures protruding from the anchor site are then clipped short.
Owner:ARTHREX
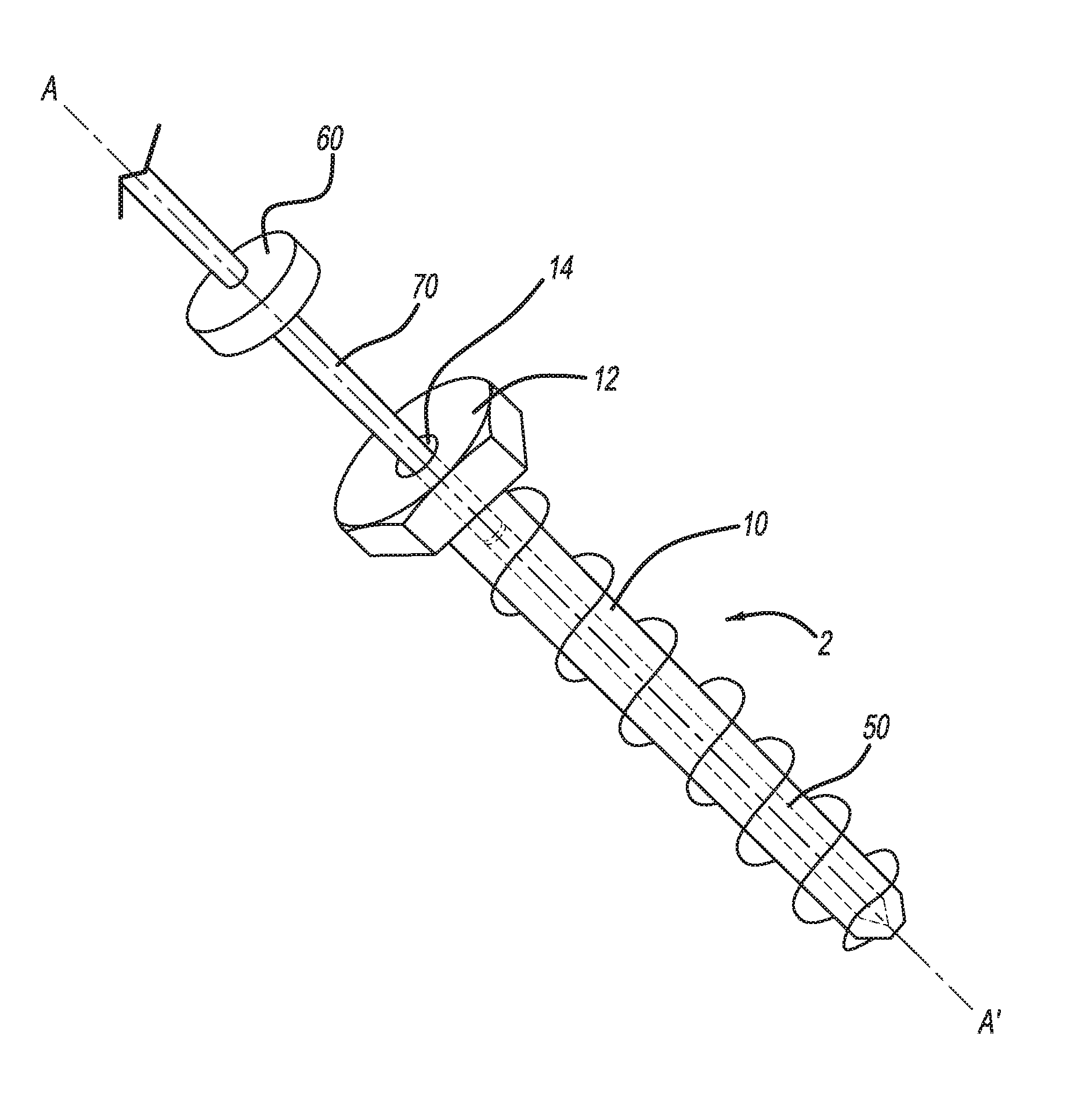
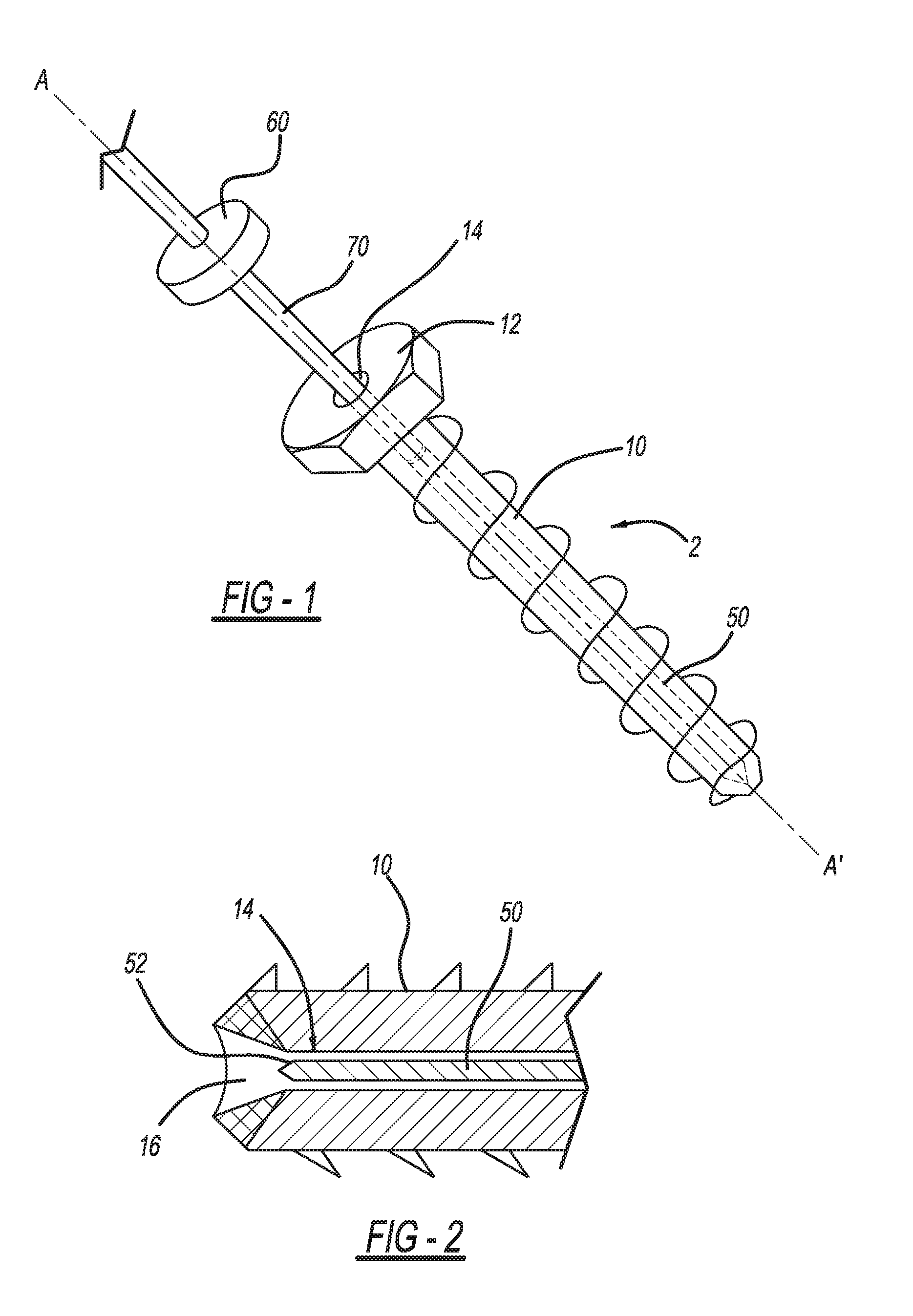
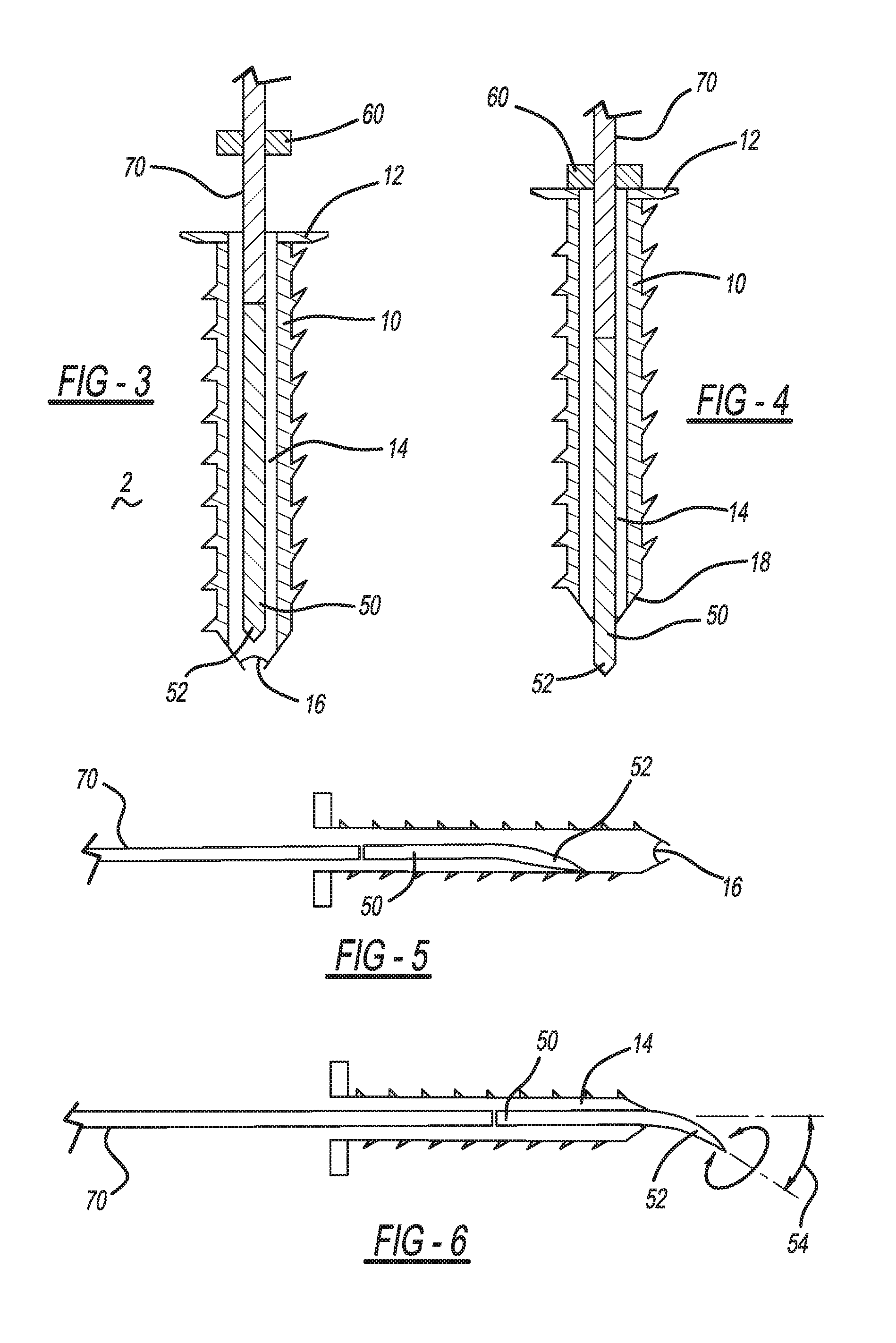
Connecting Cannulated Bone Screws
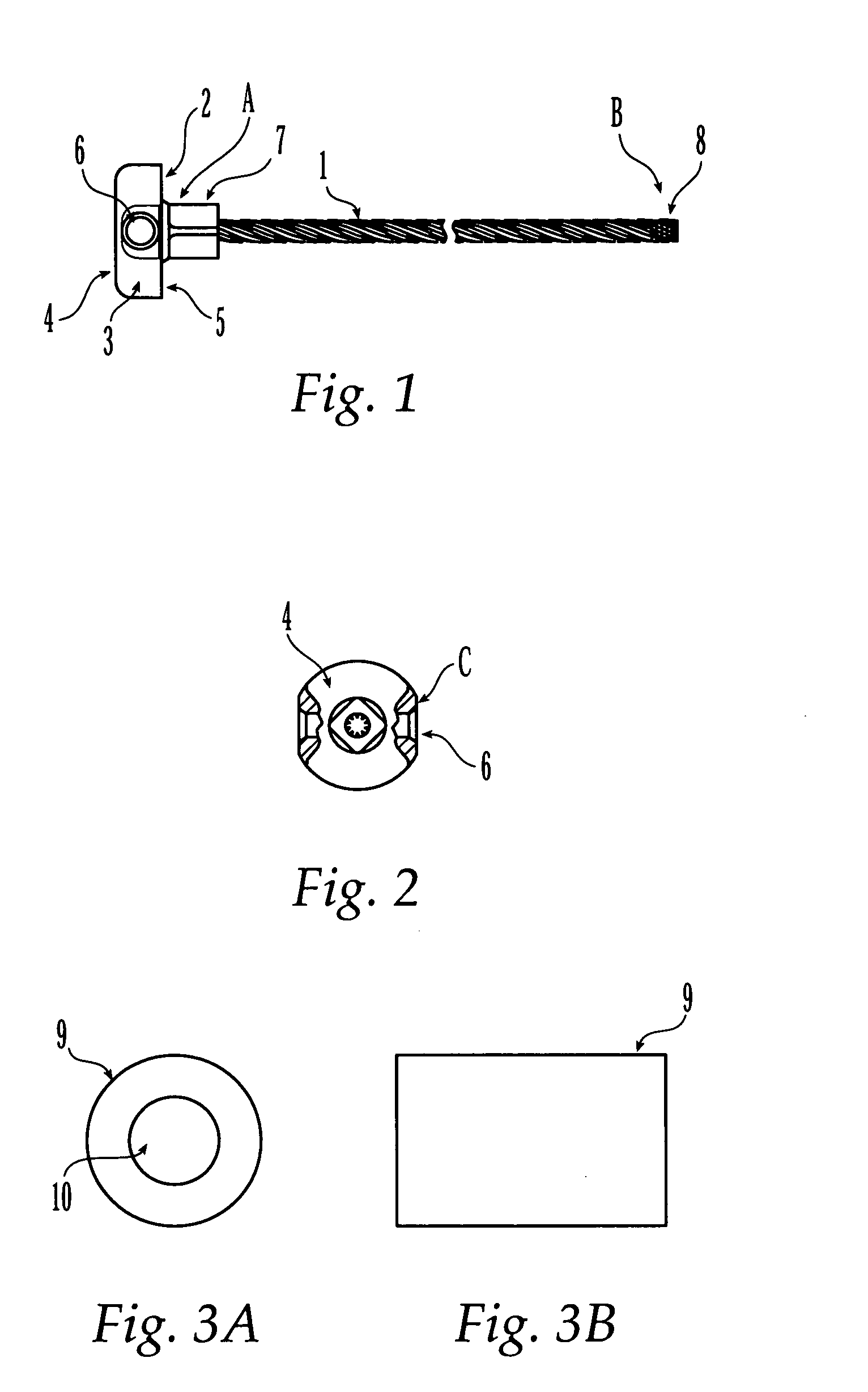
A method of bone fixation comprises engagement of internal threads on an implantable object associated with the bone at one side of the fracture with the external threads on the shaft of another implantable object associated with the bone at the opposite side of the fracture. The preferred embodiment comprises two cannulated screws of different diameters which associate with the bones at the opposite sides of the fracture via their screw heads contacting the bone surfaces, and the screws are screwed into the bones manually or drilled towards each other and engage by means of internal threads of the larger-diameter cannulated screw and the external threads of the smaller-diameter cannulated screw. The engagement of the two cannulated screws is aided by a guiding mechanism.
Owner:PARK SANGDO
Minimally invasive surgical access device
InactiveUS20070219416A1Reduce riskBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesAnatomical structuresLess invasive surgery
A minimally invasive surgical access device that allows access to a pathology being treated while significantly reducing the risk of damaging anatomical structures proximate the pathology. The access device includes a base portion having a central bore extending therethrough, and retractor blades pivotably mounted to the base portion. An insertion handle is coupled to the base portion to thread the retractor blades into the patient. The insertion handle is removed from the base portion, and a core hollow screw is threaded into the base portion to separate the retractor blades to gain access to the pathology through the hollow screw.
Owner:THOMPSON MIS
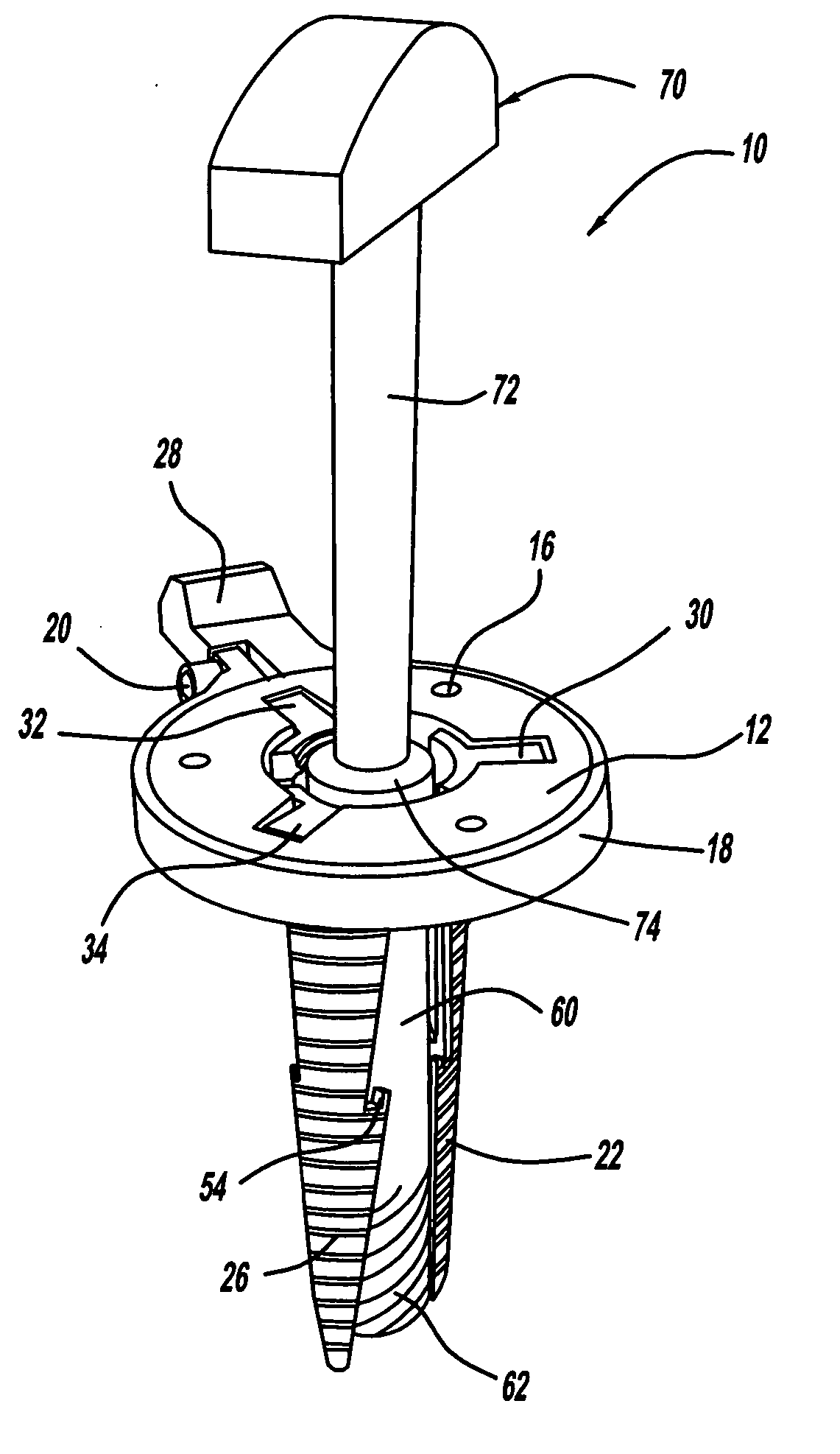
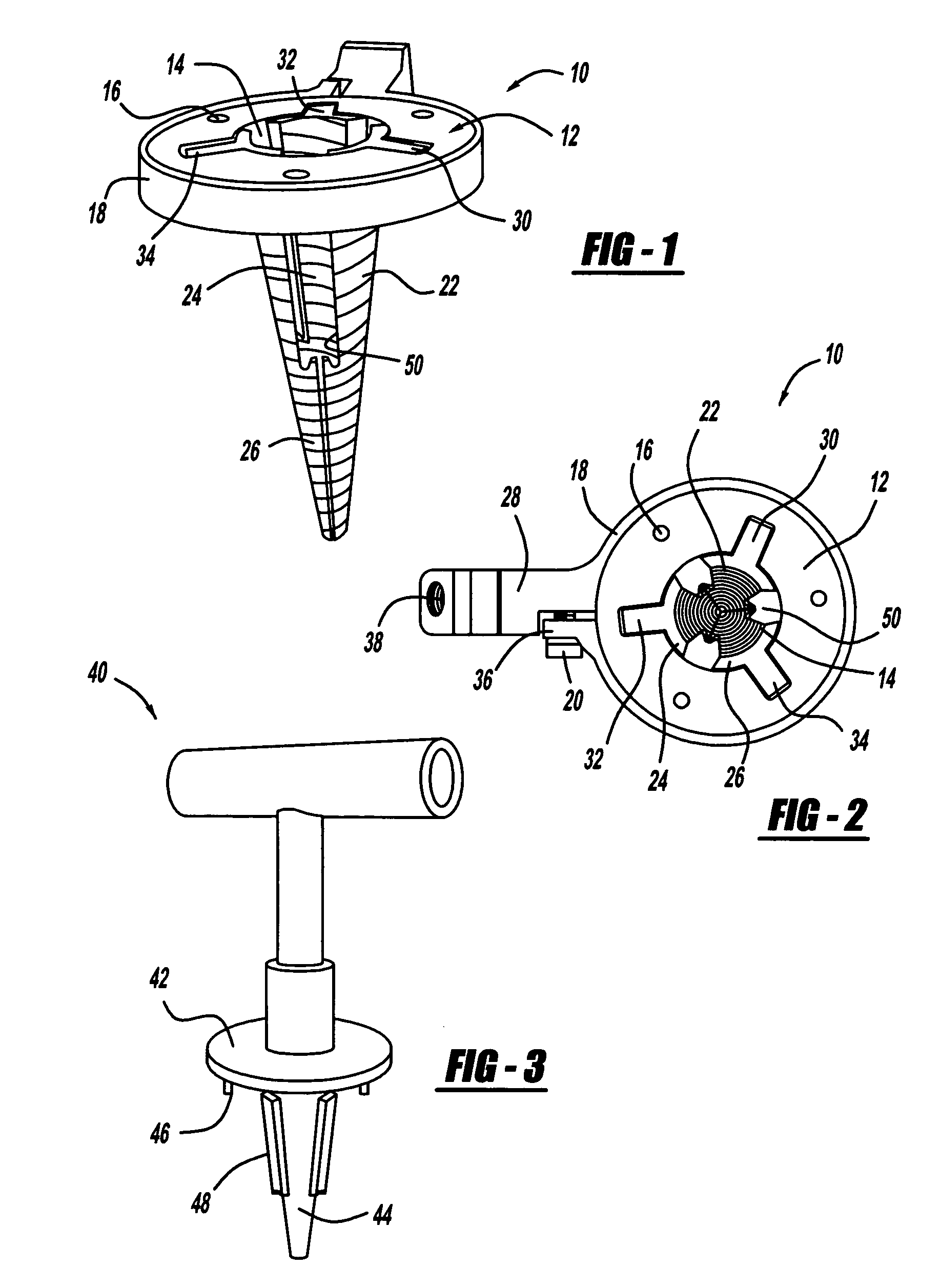
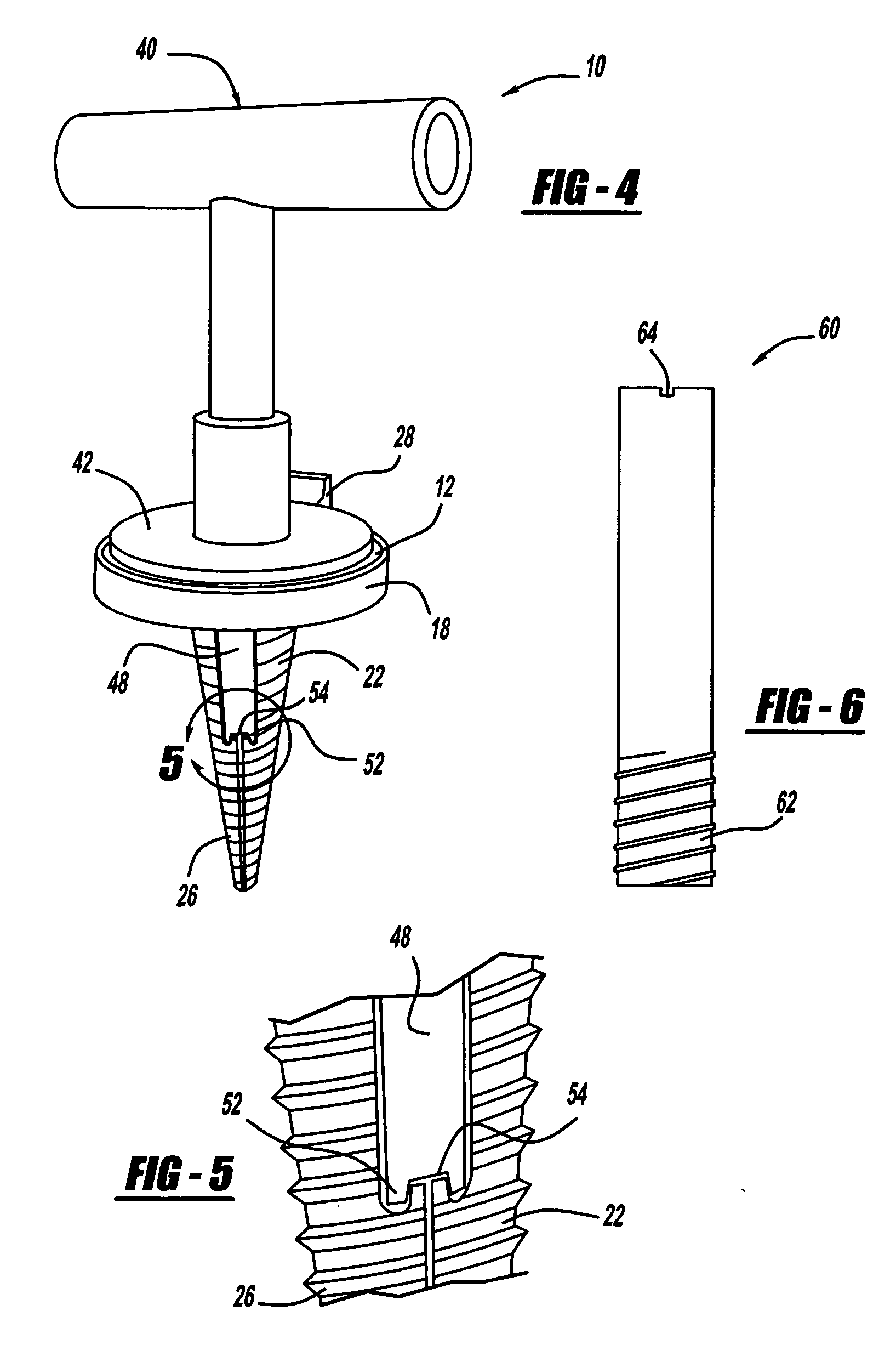
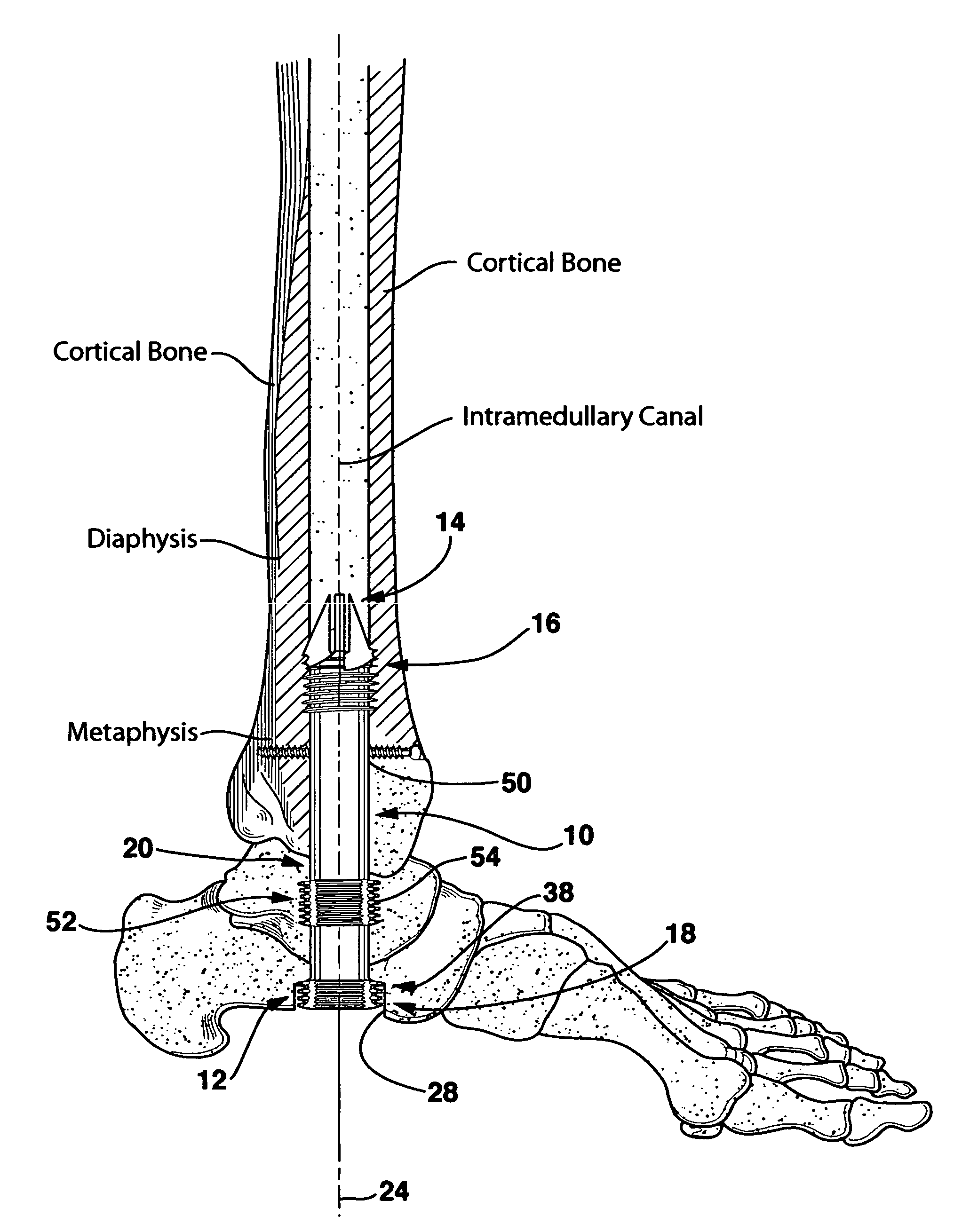
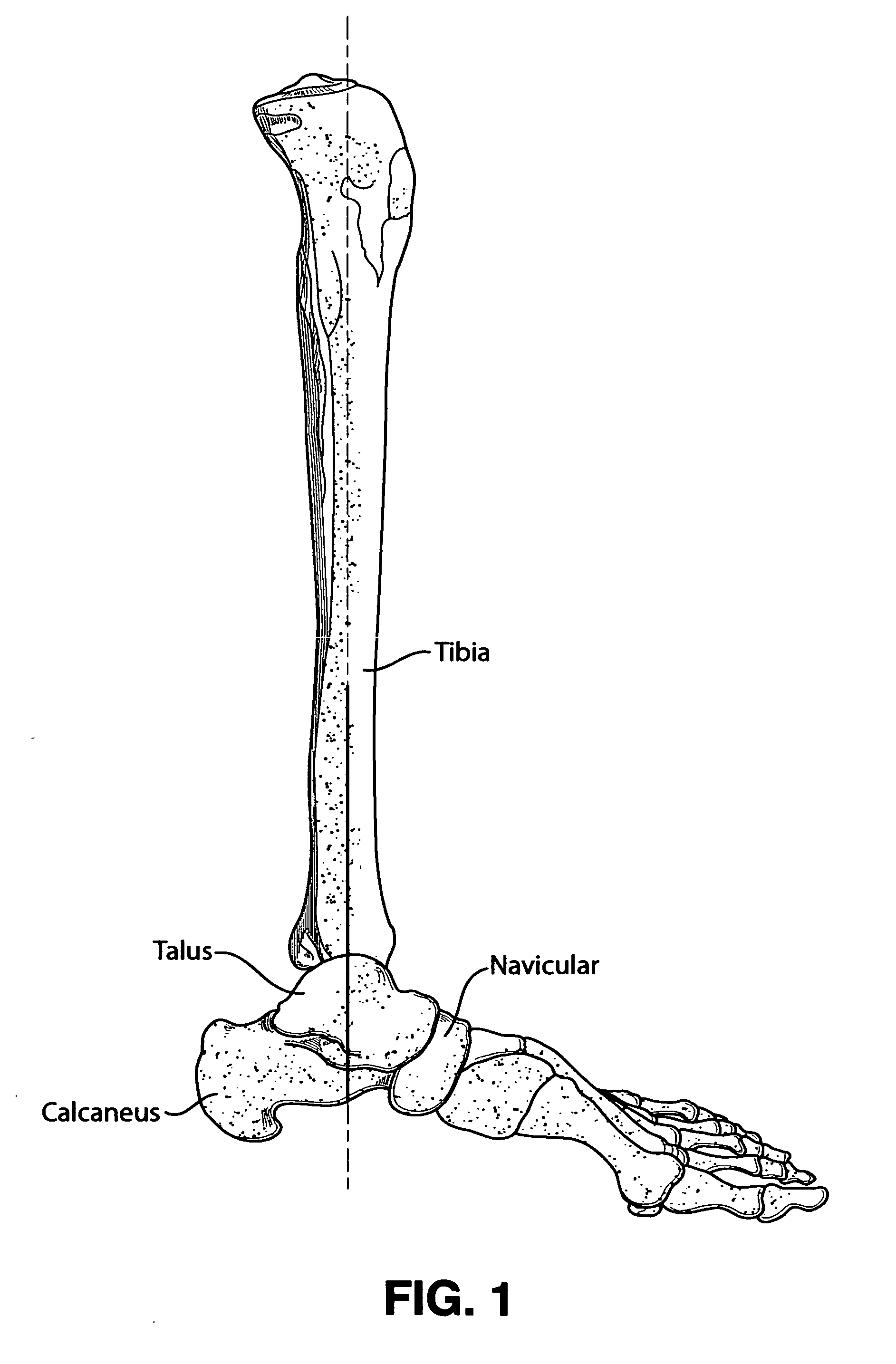
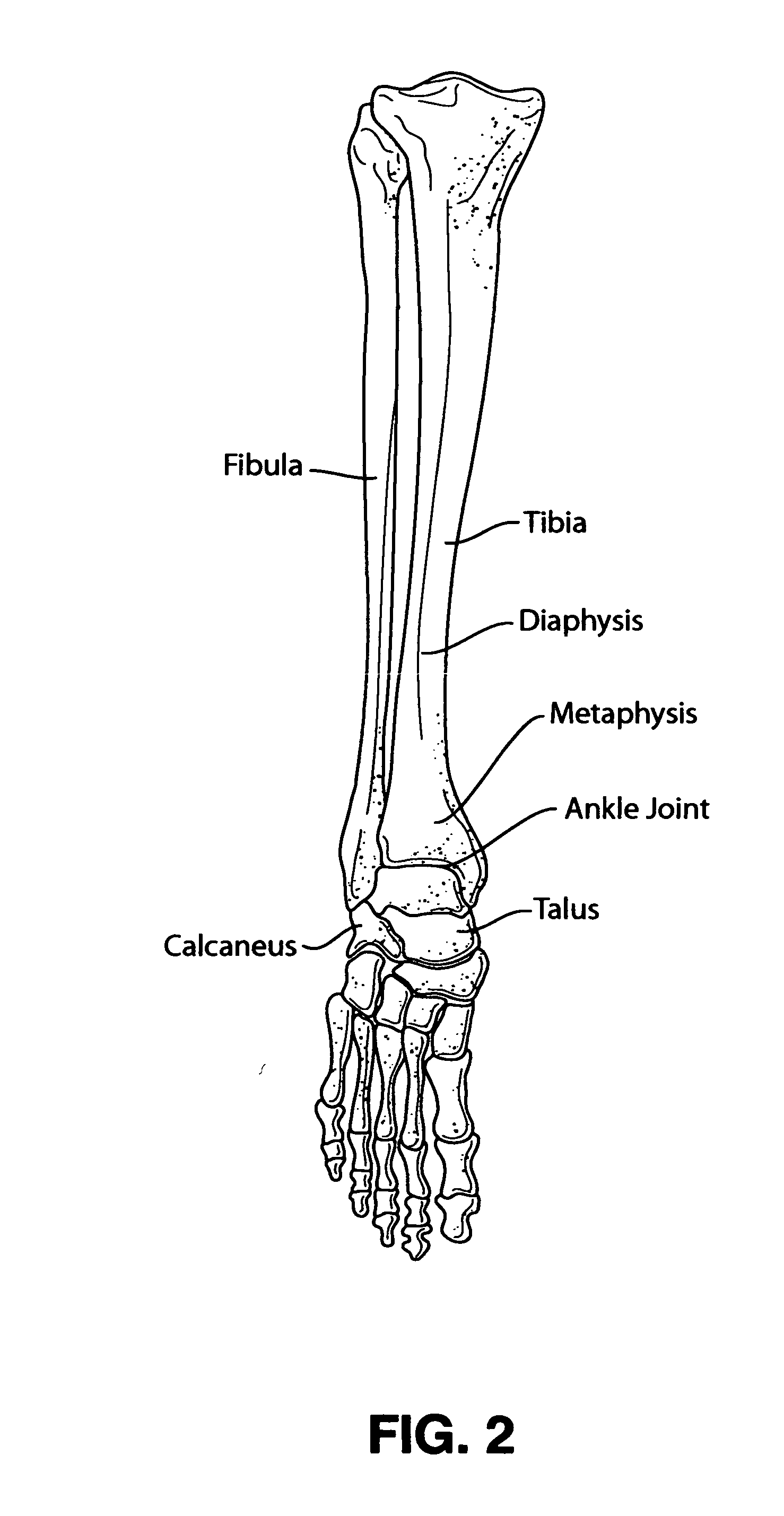
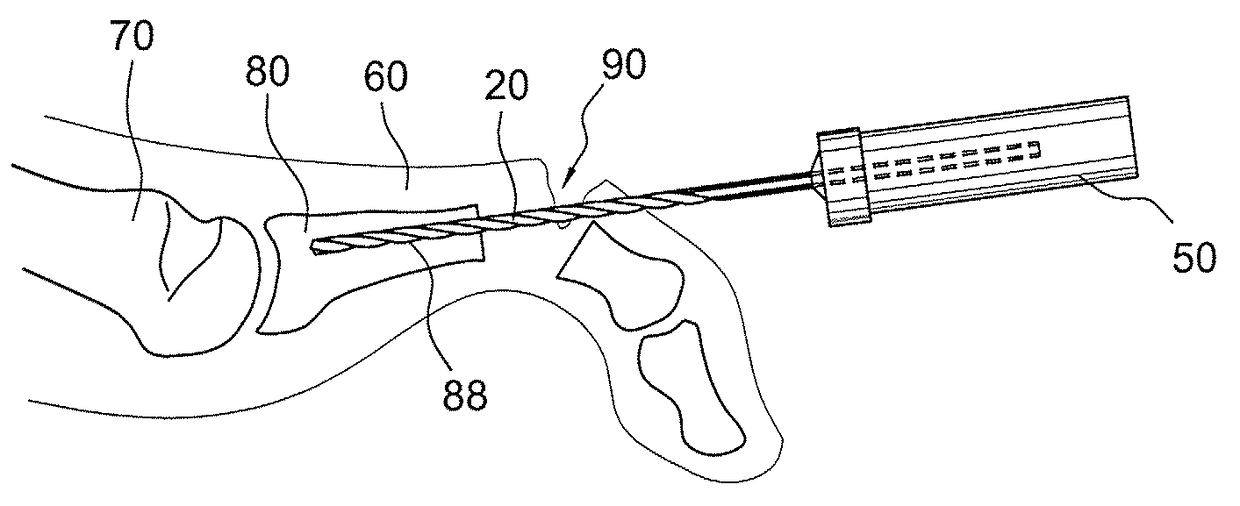
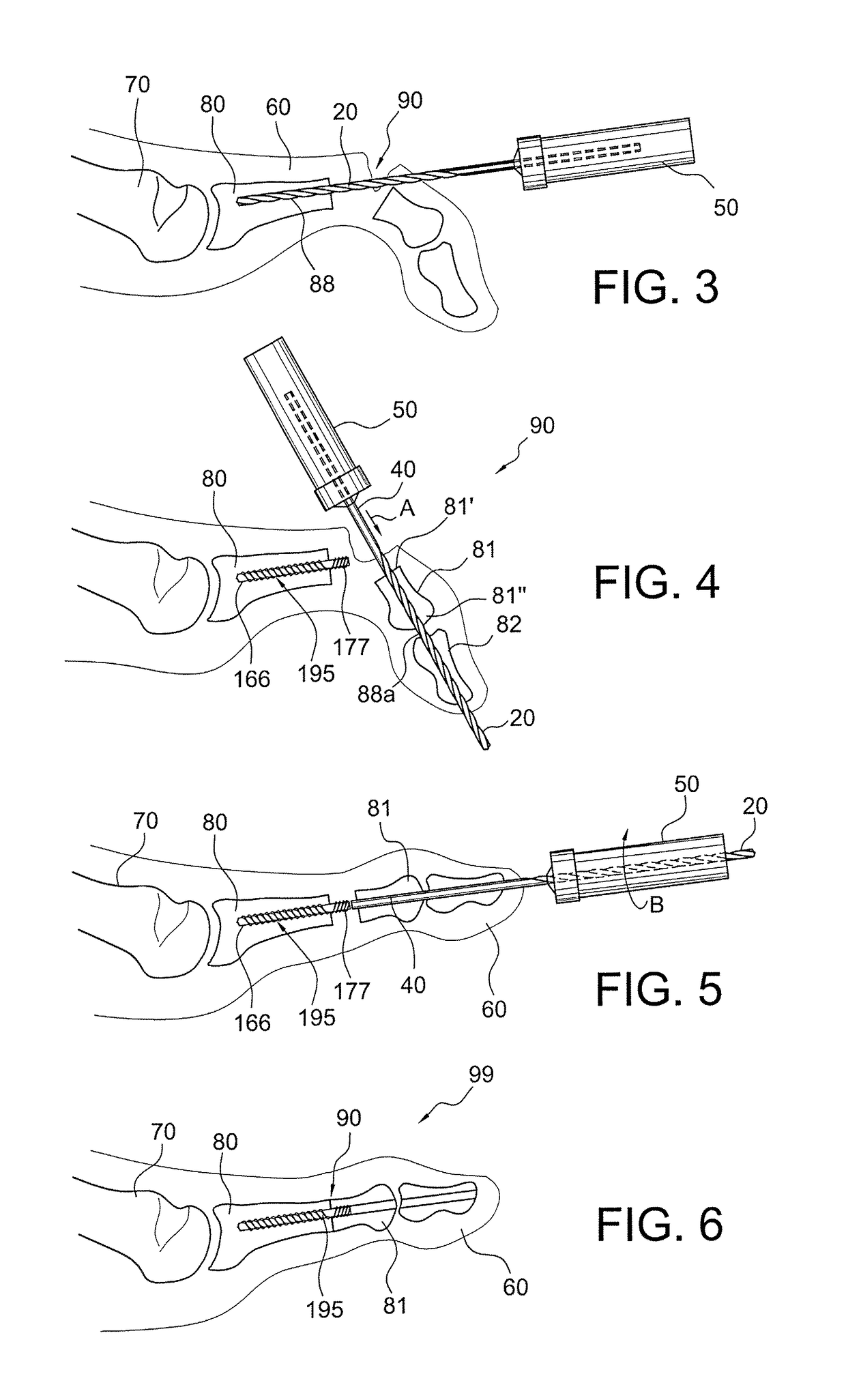
Intramedullary locked compression screw for stabilization and union of complex ankle and subtalar deformities
An implant for causing fusion of bones in an ankle is disclosed. The implant, in a preferred embodiment, is a cannulated screw with threads at the leading end and threads at the trailing end having a a tibial component that interacts with the tibia, a calcaneus component that interacts with the calcaneus and a midsection extending between the tibial component and the calcaneus component. The implant is placed in a borehole formed in the tibia, talus and calcaneus and causes the tibia and talus to be moved into compressive contact with each other. As a result, the ends of the tibia and talus that have previously had the cartilage removed down to bloody bone are coapted together to allow fusion. In another embodiment of the invention, a middle threaded portion is placed between the tibial component and the calcaneus component. The middle threaded portion interacts with the talus to help add compressive force to the fusion process. The invention also includes a method for using the implant to fuse the bones of the ankle together. The method includes steps of producing an implant and then using the implant to apply compressive forces on the bones of the ankle. The invention in one embodiment also includes a method that uses images such as x-ray images preoperatively to determine the length and width of the disclosed implant or any other implant with each patient's unique anatomy will properly allow coaption of the ends of the prepared tibia and talus at the ankle joint. The implant is inserted from the bottom of the foot through a predetermined hole in the calcaneus which extends through the talus into the diaphysis of the tibia. When properly inserted and seated in the bones, the implant is locked by screws.
Owner:MANDERSON EASTON L
Minimally invasive surgical access device
A minimally invasive surgical access device that allows access to a pathology being treated while significantly reducing the risk of damaging anatomical structures proximate the pathology. The access device includes a base portion having a central bore extending therethrough, and retractor blades pivotably mounted to the base portion. An insertion handle is coupled to the base portion to thread the retractor blades into the patient. The insertion handle is removed from the base portion, and a core hollow screw is threaded into the base portion to separate the retractor blades to gain access to the pathology through the hollow screw.
Owner:THOMPSON MIS
Drill/driver hybrid instrument for interphalangeal fusion
Surgical techniques, instruments and systems for bone fusions and repairs (for example, phalangeal fusion) which allow alignment of small bones (for example, phalanges) without the use of guidewire and cannulated instrumentation such as, for example, drills and drivers, and cannulated screws. A drill / driver hybrid instrument (a combined drill / driver device) may be used in fusion of two small bones (for example, in interphalangeal fusion). One end of the hybrid instrument is provided with a plurality of flutes so that the instrument can be used as a drill to remove bone. The other end is shaped to mate with a device to be inserted intraarticularly (for example, interphalangeally), acting as a driver for that device.
Owner:ARTHREX
Method for securing sutures to bones
InactiveUS20120022588A1Secure and stable connectionLong-term stabilitySuture equipmentsDiagnosticsSuture anchorsIliac screw
A method for securing a repair, such as a rotator cuff repair and includes an anchor placed within a hole formed in bone and a cannulated screw inserted into the hole after the anchor has been inserted to effectuate a firm and secure connection of tissue to bone, particularly when the quality of the bone does not permit optimal fixation. The method allows superior tissue fixation to bone with the ease of knotless suture anchor application.
Owner:LUMACA ORTHOPAEDICS
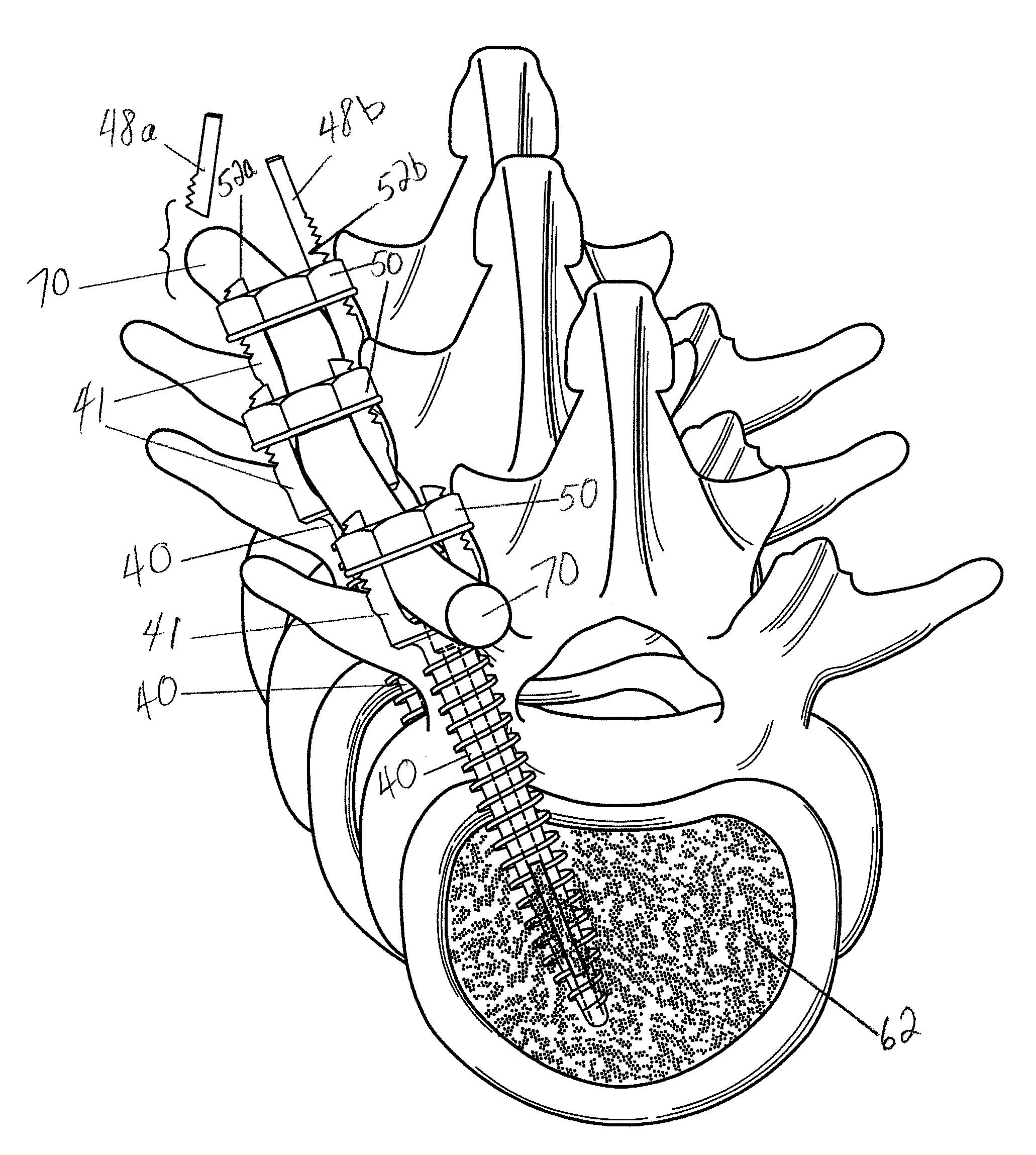
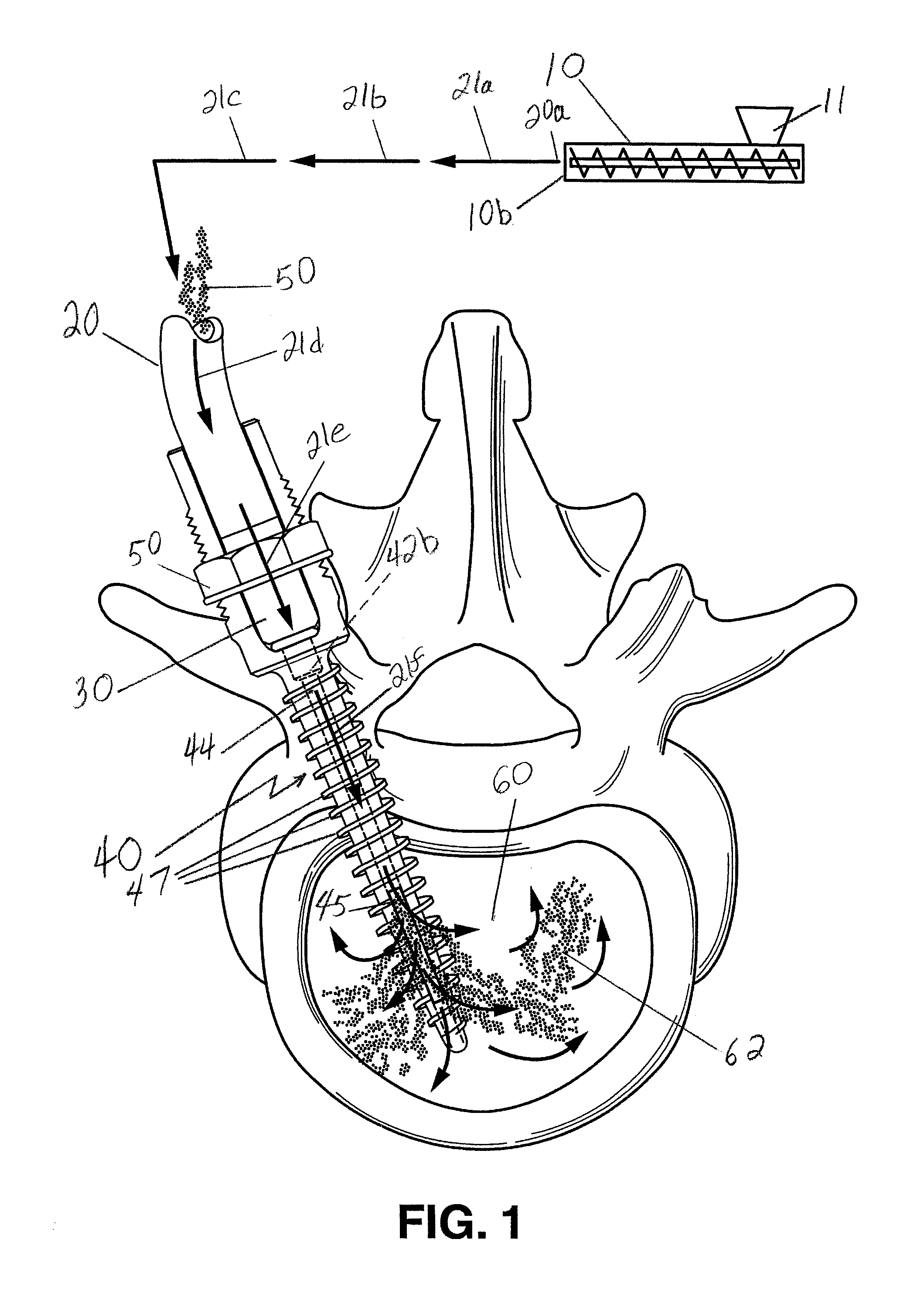
Method for Minimally Invasive Treatment of Unstable Pelvic Ring Injuries with an Internal Posterior Iliosacral Screw and Bone Plate
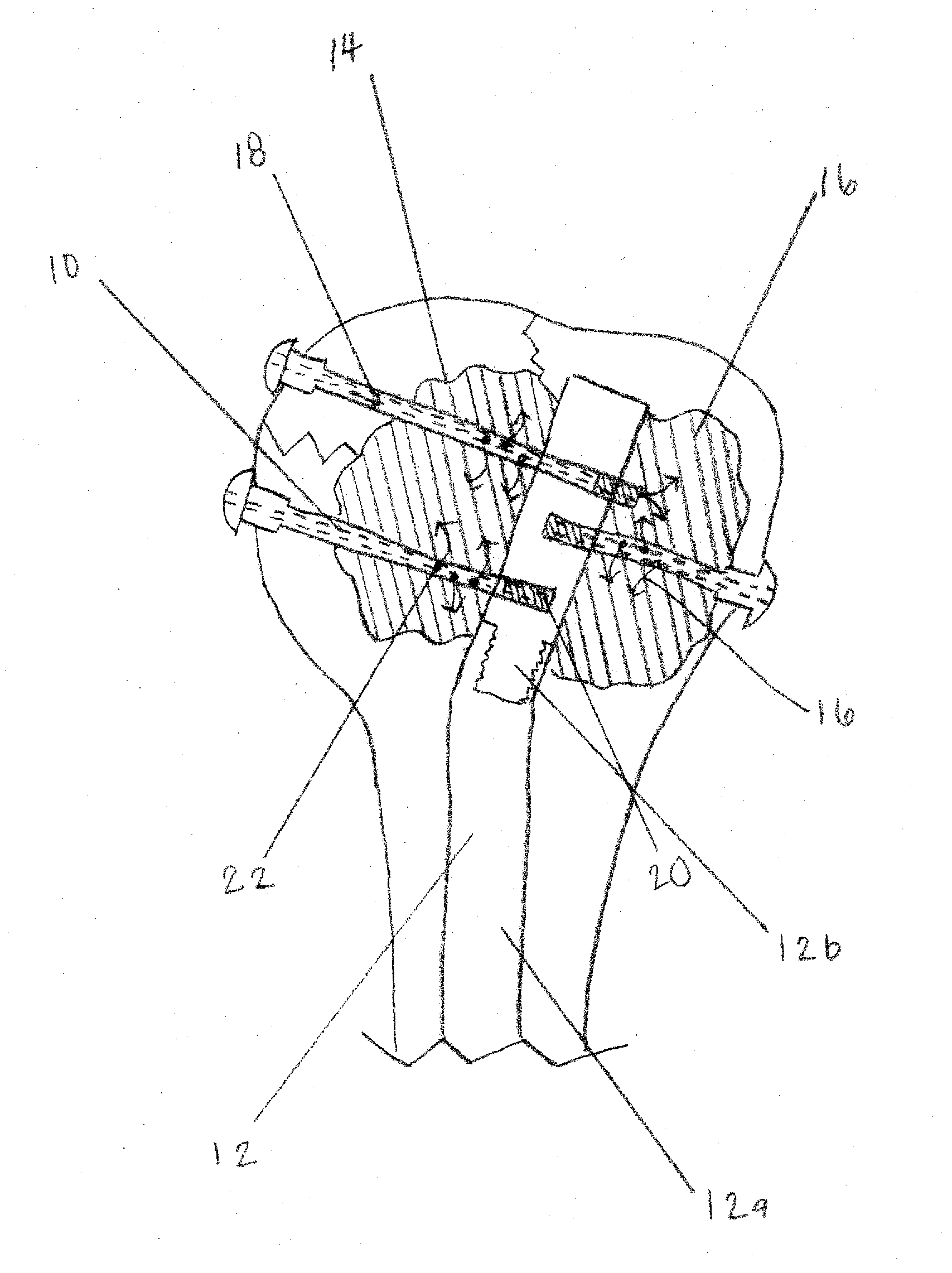
The instant invention is a novel method for stabilization of the posterior pelvis (iliosacral) when treating an unstable pelvic ring fracture. Cannulated screws are inserted through the posterior of the ilium through the sacroiliac joint and into the sacrum. The screws are used to affix the iliosacral joint while it heals. The screws are used in conjunction with a bone plate (through which the screws pass) to provide the construct / fixation with added strength and stability compared to iliosacral fixation using screws alone.
Owner:VAIDYA RAHUL
Sternal reconstruction system
A sternal reconstruction system for securing parts of a sternum includes at least one flexible cable with a fused end fitting, at least one parallel fitting piece and at least one ferrule. Optionally, the system includes at least one cannulated screw. Circumferential or parasternal fixation may be brought about by use of the sternal reconstruction system. Also provided is a method for sternal reconstruction utilizing the sternal reconstruction system. Also provided is a kit for sternal reconstruction.
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
Atraumatic fastener and bone stabilization system and method of use
Atraumatic fasteners involving flexible membranes and tensioning means can be used in conjunction with one or more plates, other fastener types of other materials, particularly locked cannulated screws-plate interfaces providing improved capture and restraint of articular and / or juxta-articular bone fragments. A method of securing bone fragments includes securing or capturing a fragment, at least in part, with an atraumatic foldable and / or expandable device which can be inserted “inside out”, that is, the expandable form is inserted through a channel which has been created in the bone or tissue, from the opposite side of the bone or tissue fragment.
Owner:TRUMAN MARI S
A parallel piezoelectric six-dimensional force sensor
InactiveCN102288334ASimple structureGood symmetryForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesApparatus for force/torque/work measurementMechanical engineeringForce sensor
The invention discloses a parallel piezoelectric six-dimensional large force sensor, which is characterized by comprising an upper cover, force-sensitive elements, wires, a sealing ring, a pretightening screw, a lower cover, screw holes and a hollow screw, wherein the lower part of the upper cover is provided with a circular upper cover groove; the upper part of the lower cover is provided with a circular lower cover bulge; the upper surface of the lower cover bulge is provided with four groups of bosses which are uniformly distributed on the same circle; each boss is provided with a force-sensitive element; the upper cover is matched with the lower cover through the upper cover groove and the lower cover bulge; the upper surface of each force-sensitive element is contacted with the surface of the groove; the side wall of the upper cover is provided with the hollow screw; the upper cover, the force-sensitive elements and the lower cover are fixed to form a whole by the pretightening screw through a through hole; and the upper surface of the upper cover and the lower surface of the lower cover are provided with the screw holes.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
External fixation rack elasticity device
The invention discloses a resilient device of an external fixator in the clinical application of orthopaedics. The resilient device consists of a cylinder, a sliding axle in the cylinder, a flexible apparatus, a sliding nail body and a sliding axle stopper. An anti-spin rivet, a pressure regulation rivet, a pressure regulation nut, a tightening jack bolt, a hollow screw on the cylinder wall and a pressurization hole are arranged in the radial direction on the cylinder wall, wherein, the sliding axle stopper can be provided with a stop jack bolt in the radial direction on the cylinder wall, or a stop nut or a stop fixture block can be arranged on the sliding axle; the cylinder wall can be designed to have equal inner diameters at the upper and lower parts or have the inner diameter of the upper part at the corresponding position of the sliding axle larger than that of the lower part; the flexible device can be made into a flexible capsule or a spring; and the sliding nail body is connected with the cylinder in a sliding manner. The resilient device can match with external fixators of different shapes and structures to form external flexible fixators. When a limb with a fracture suffers axial pressure, the external flexible fixator can have a slight axial movement so that an interaction force can be generated due to the slight movement at the end of fracture so as to stimulate callus to grow at the end of fracture. The resilient device can avoid osteoporosis due to stress shielding of the external fixator, quicken the fracture healing, increase the strength of healed bone and effectively prevent delayed fracture healing or nonunion.
Owner:河南科科生物科技有限公司
Sternal reconstruction system
A sternal reconstruction system for securing parts of a sternum includes at least one flexible cable with crimp fitting, at least one cannulated screw and at least one reconstruction plate. Circumferential or parasternal fixation may be brought about by use of a sternal reconstruction system including a flexible cable and crimp fitting alone; a sternal reconstruction system including a flexible cable, crimp fitting and cannulated screws; or a system including a flexible cable, crimp fitting, cannulated screws and one or more reconstruction plates. The reconstruction plates are typically planar, having an upper and a lower surface, and containing generally perpendicular and transverse plate holes. The generally perpendicular plate holes are countersunk to better accommodate the heads of the cannulated bone screws. Also provided is a kit for sternal reconstruction.
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
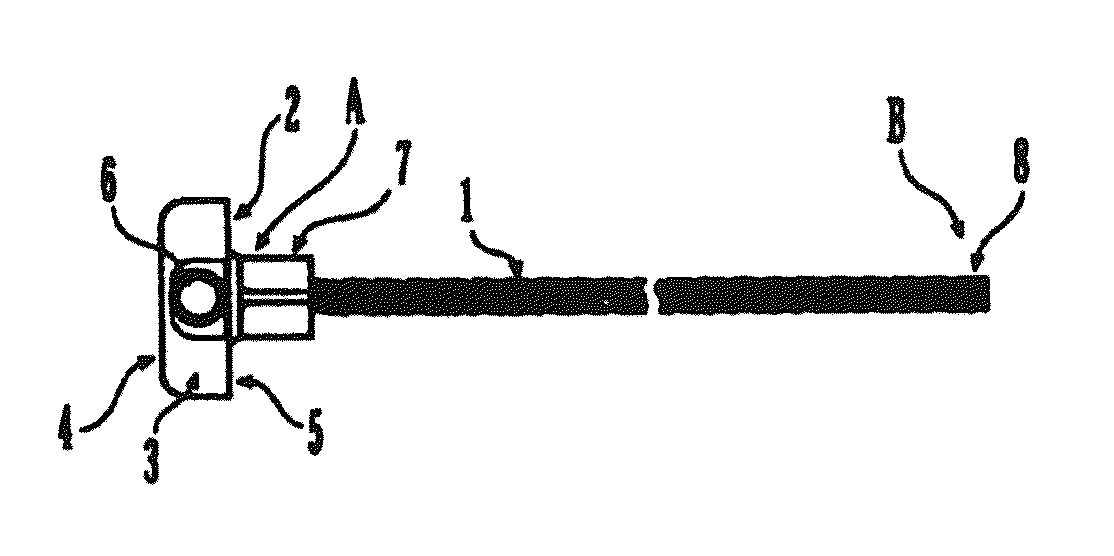
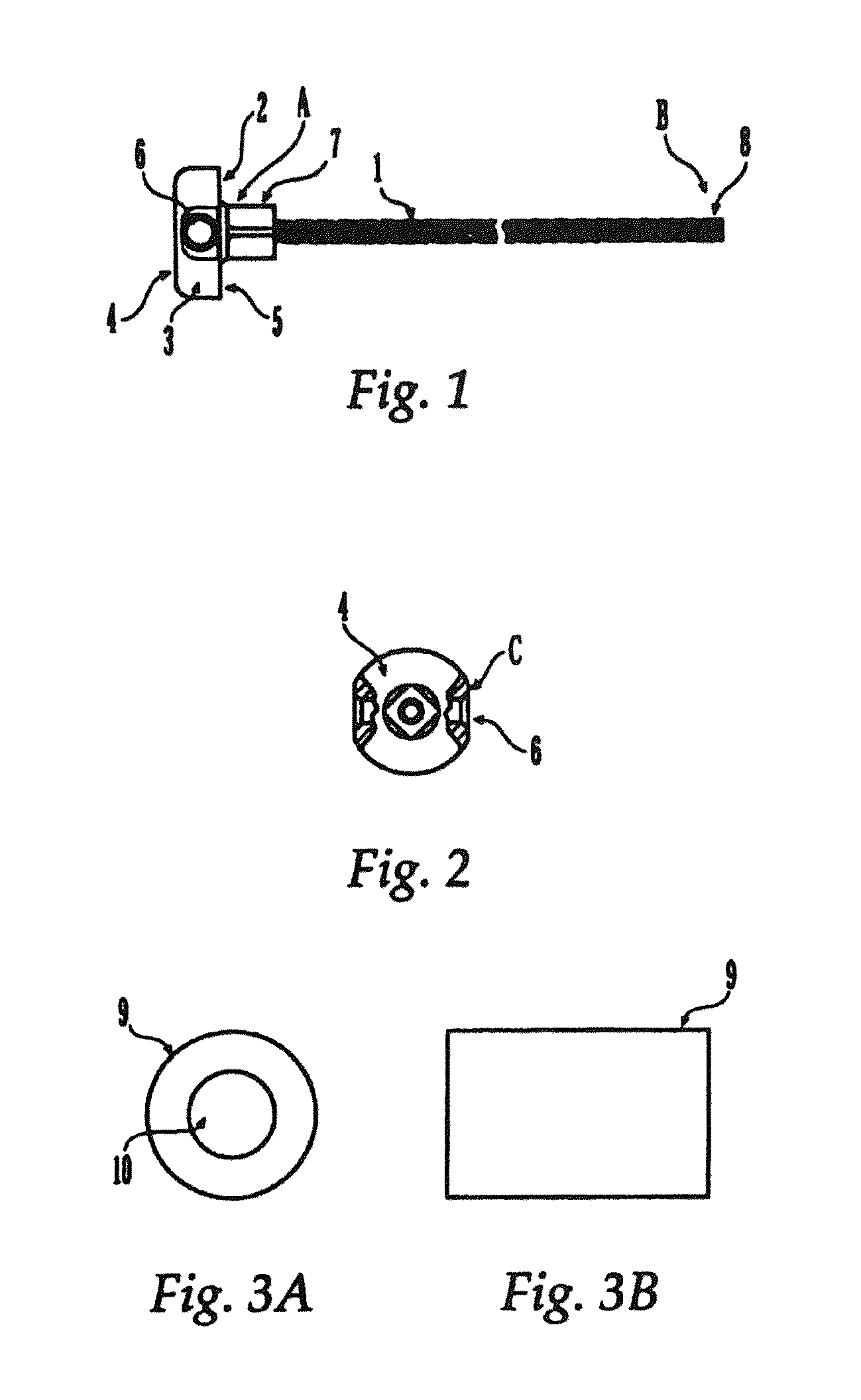
Surgical device and method
A surgical device and method for fixation of a tissue graft into a bone is disclosed. A strand is coupled with the tissue graft. A guide wire is coupled with the strand. The tissue graft is positioned within a socket of the bone and a cannulated screw is driven along the guide wire and into the bone socket to form an interference fixation of the tissue and the tissue graft. The strand attached to the tissue graft is retracted from the bone socket through a strand aperture of the socket. The guide wire is then removed from the bone socket. A loop may be transposed between, and coupling, the tissue graft and the strand. The guide wire may alternatively be coupled with the loop and / or the strand. The tissue graft may be a tendon tissue or a bone-tendon-bone graft.
Owner:USHIBA JAMES
Bone tunnel fixator for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
ActiveCN103315798AReduced longitudinal movement (bungee effect)Reduce lateral movementSurgeryBone tunnelTibia
The invention discloses a bone tunnel fixator for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. The bone tunnel fixator comprises a femur-end internal fixation assembly and a tibia-end internal fixation assembly. The femur-end internal fixation assembly comprises a first hollow screw, a first internal screw and a first guide threaded rod, the diameter of the tail end of the first hollow screw is larger than that of the front end of the first hollow screw, the first hollow screw is in the shape of a combination, the combination comprises an incomplete reverse cone and a cylinder which are connected with each other, internal threads of the first hollow screw are matched with external threads of one end of the first internal screw, a loop used for hanging a transplanted ligament is arranged at the other end of the first internal screw, and the outer diameter of the first guide threaded rod is smaller than the inner diameter of the first internal screw; the tibia-end internal fixation assembly is similar to the femur-end internal fixation assembly. The bone tunnel fixator has the advantages that longitudinal movement (a bungee jumping effect) and transverse movement (a windshield wiper effect) between a transplanted tendon and a bone tunnel can be reduced, loss of the bone mass of a patient is reduced, the bone tunnel fixator is firm in fixation, the contact area of the transplanted tendon and the bone tunnel is large, and healing of the bone and the tendon of the patient is further promoted.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
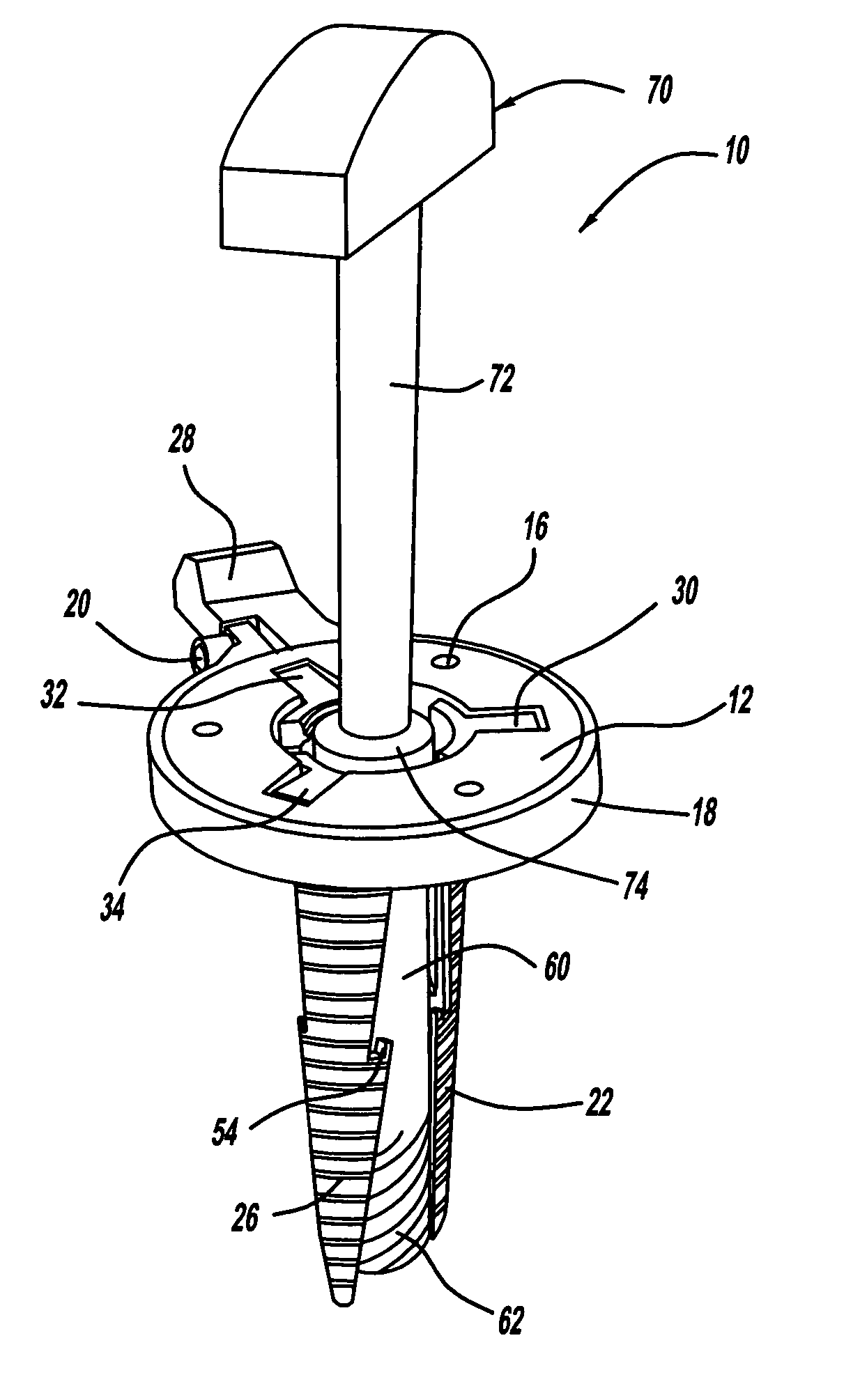
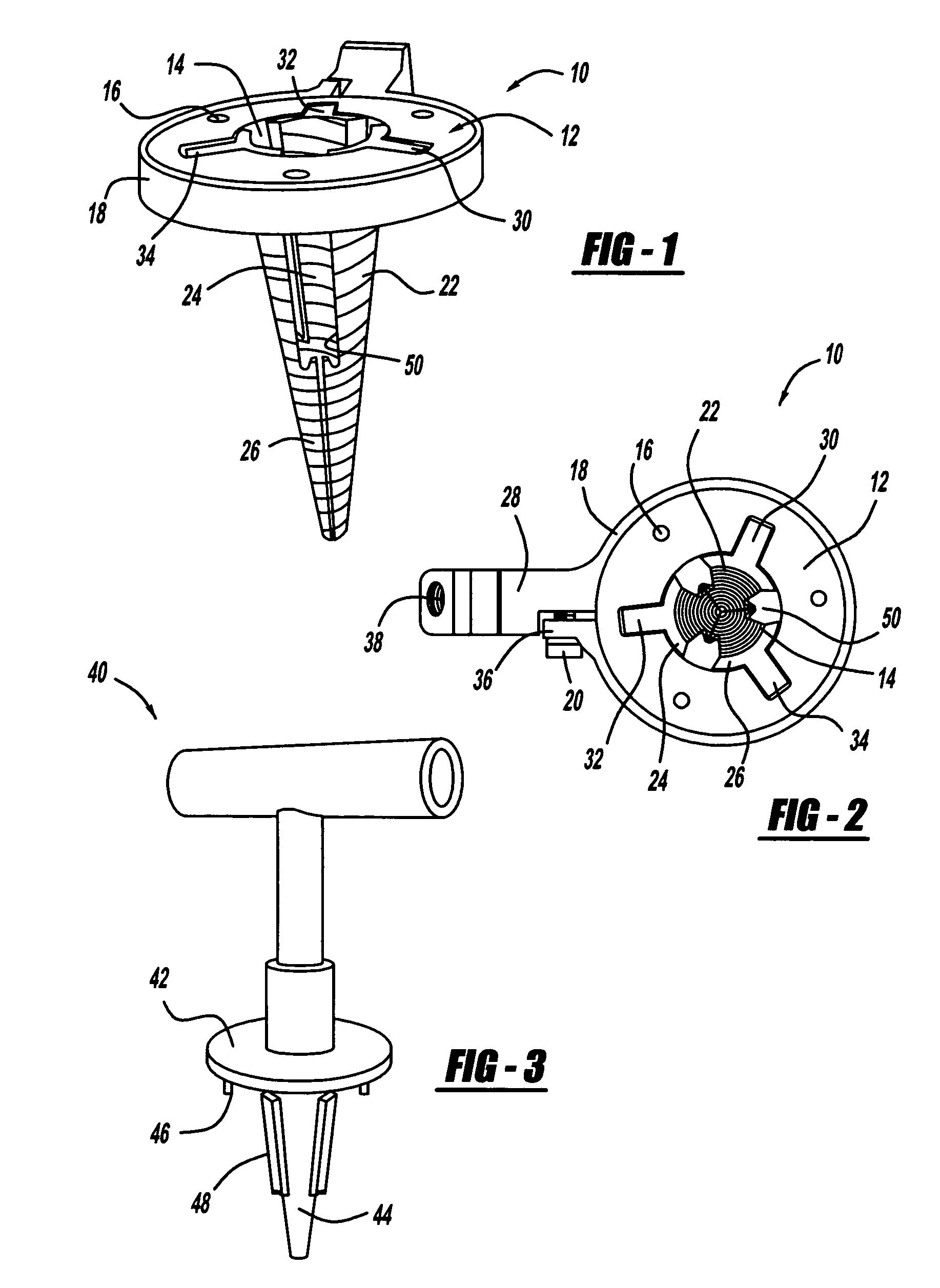
Retractable screw guide
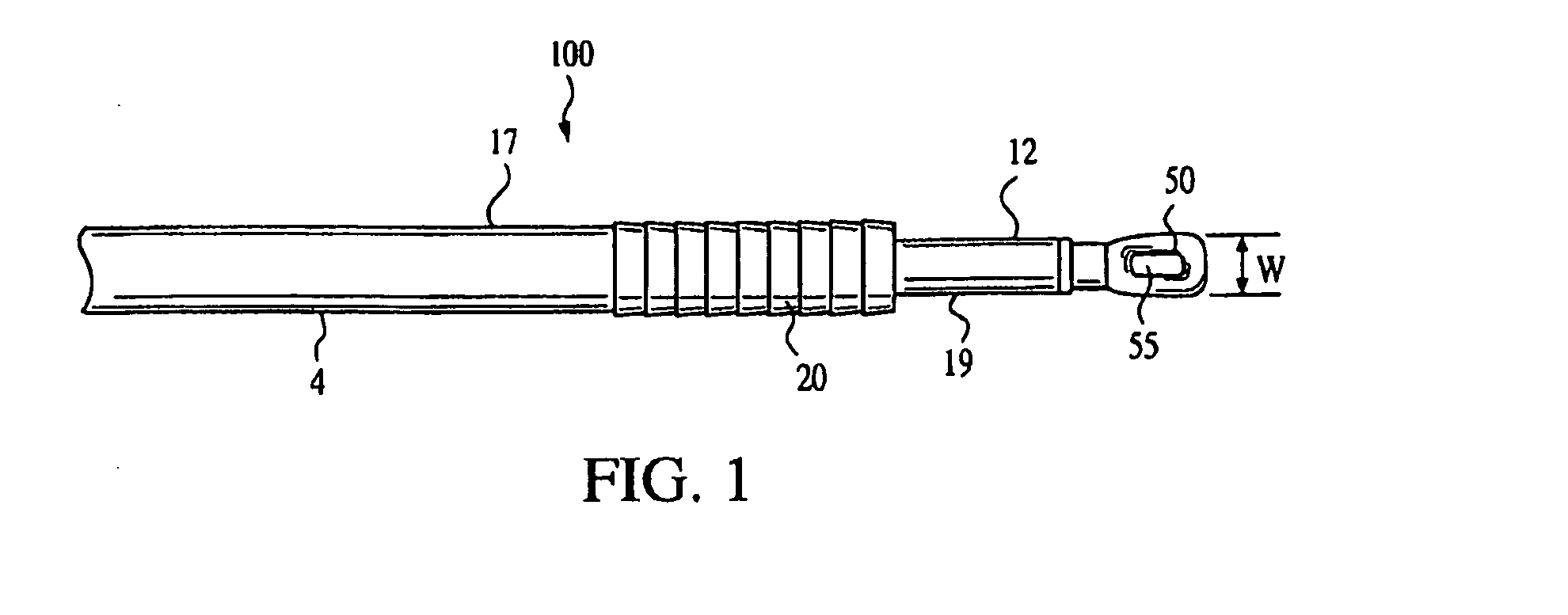
A surgical screw system comprising a cannulated screw, a guide wire and a driver. The screw has a head, a tubular body with a bore, and a tip opposite the head. The guide wire, shorter than the screw, is slidably disposed within the bore of the screw. The guide wire has a working end deployable beyond the tip of the screw, and the working end is sharpened to penetrate the bone and produce a pilot hole when an axial force is applied. The guide wire extends to deploy the working end beyond the tip to create the pilot hole, and fully retracts into the screw upon installation of the screw. The driver passes through the head of the screw into the bore, and applies the axial force to the guide wire. The driver may be used to drive the screw into the bone, and is removable from the screw.
Owner:STERLING THERAPEUTICS LLC
Distal tibia end inner side hook plate
InactiveCN104546104AAvoid displacementPrevent collapseBone platesArticular surfacesArticular surface
A distal tibia end inner side hook plate comprises a plate body and a hook body. The plate body comprises a proximal end portion and a distal end portion wider than the proximal end portion. The plate body is uniformly provided with adjustable screw holes in the axial direction. The hook body is connected to the distal end portion of the plate body and provided with two sharp hooks. The inner side surface of the plate body is recessed inwards. The distal end portion of the plate body is bent outwards. The hook body is bent inwards. The inner side surface of the plate body and the inner surface of the hook body are adapted to distal tibia end inner side bone in shape. The two sharp hooks of the hook body can be pressurized through hollow screws to enter the tip of the medial malleolus bone to form triangular multi-planar three-dimensional fixing at the distal fracture end, strengthen the anti-torsion capability, prevent the distal medial malleolus fracture end from shifting back and forth and reduce the risk of secondary reduction loss. The proximal end portion of the plate body is fixed through screws to serve as an anti-slipping plate for effectively preventing the displacement of the distal end bone. The hook plate used for fixing can also play a role of a supporting plate to prevent secondary collapse of the articular surface for a patient with medial malleolus superior angle articular cartilage lower bone compression.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Interference screw driver assembly and method of use
InactiveUS8814935B2Limitations is associated with assembliesReduce the possibilityLigamentsSpannersInterference screwsEngineering
Owner:THE LONNIE & SHANNON PAULOS TRUST AS AMENDED & RESTATED
Hollow screw for restoring damaged ligaments or muscle tendons
InactiveCN105852951AAvoid rejectionCause psychological burdenSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSuturing needleLigament structure
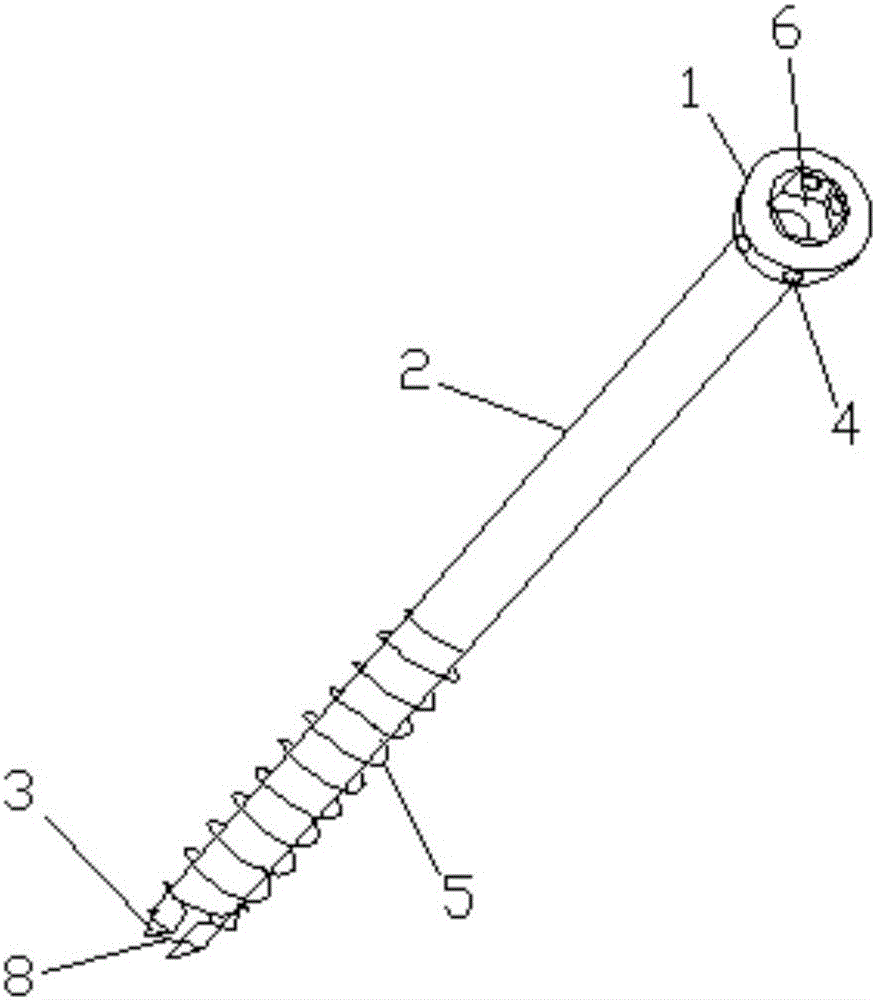
The invention discloses a hollow screw for repairing damaged ligaments or tendons, which comprises a hollow screw body. The hollow screw body is composed of a nail head, a nail body and a nail tail connected in sequence, and a groove is provided in the upper middle of the nail tail. , the outer wall of the nail tail is provided with a suture through hole, and the suture through hole is used for suturing and repairing the damaged ligament or tendon to pass through; the front end of the nail head is open, and the nail head, nail body and groove Interconnected to become a through space for coaxial passage of guide pins. The hollow screw used for repairing damaged ligaments or tendons can not only fix fracture fragments, but also assist in suturing and fixing damaged ligaments or tendons, which not only simplifies operation, reduces operation trauma, but also saves treatment costs.
Owner:高嘉锴
Expanding type spongy bone hollow screw
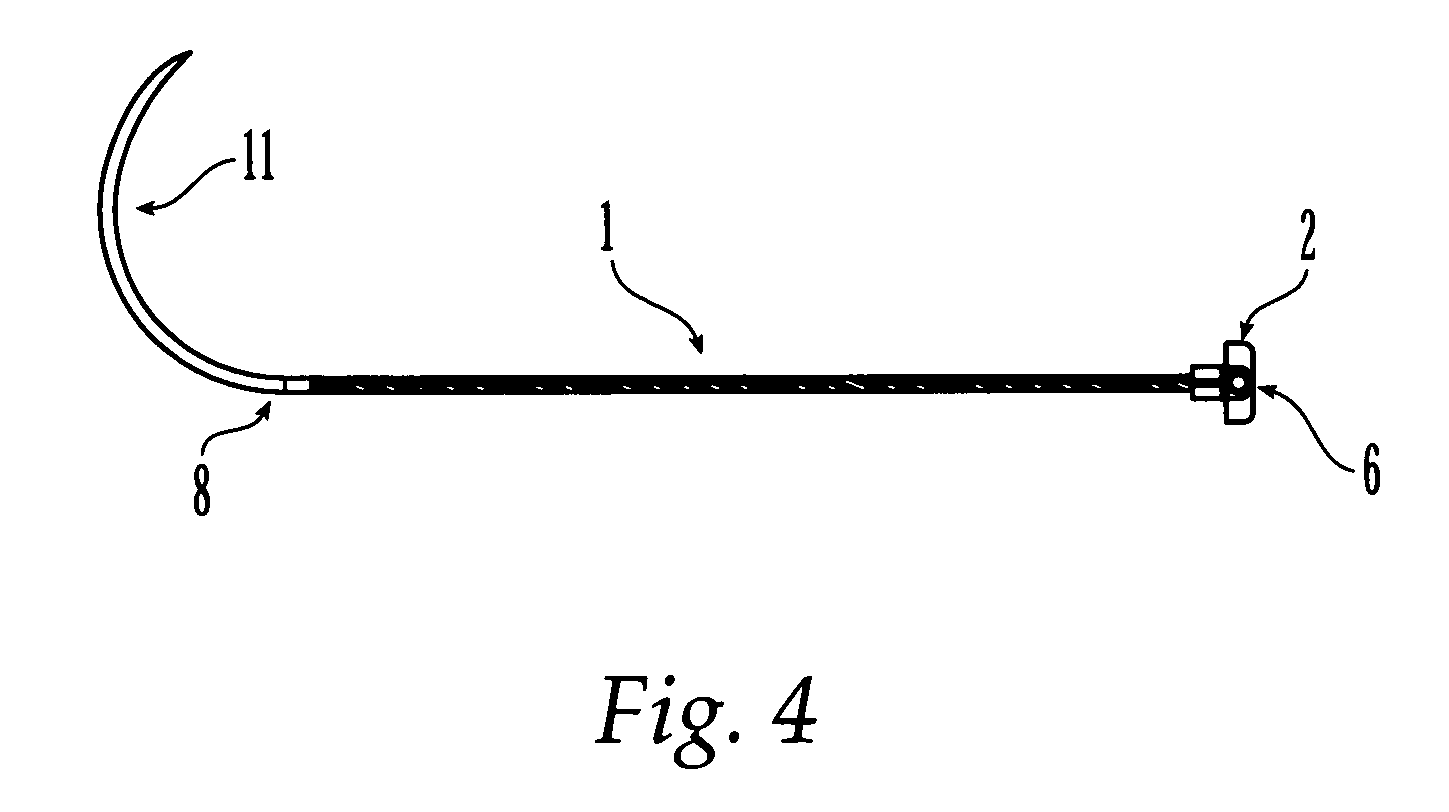
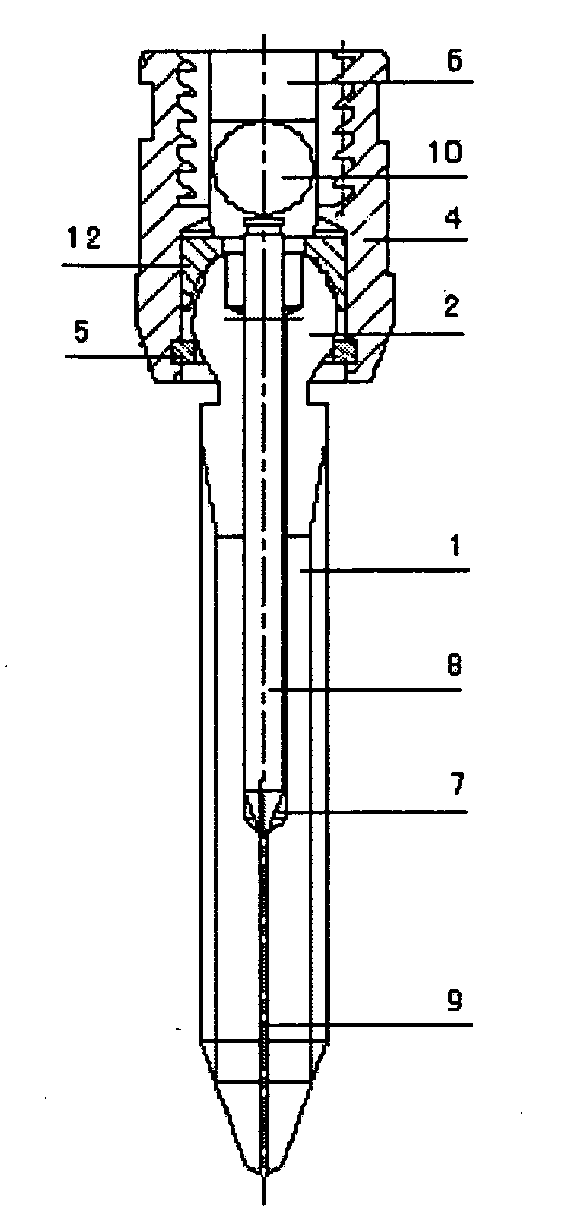
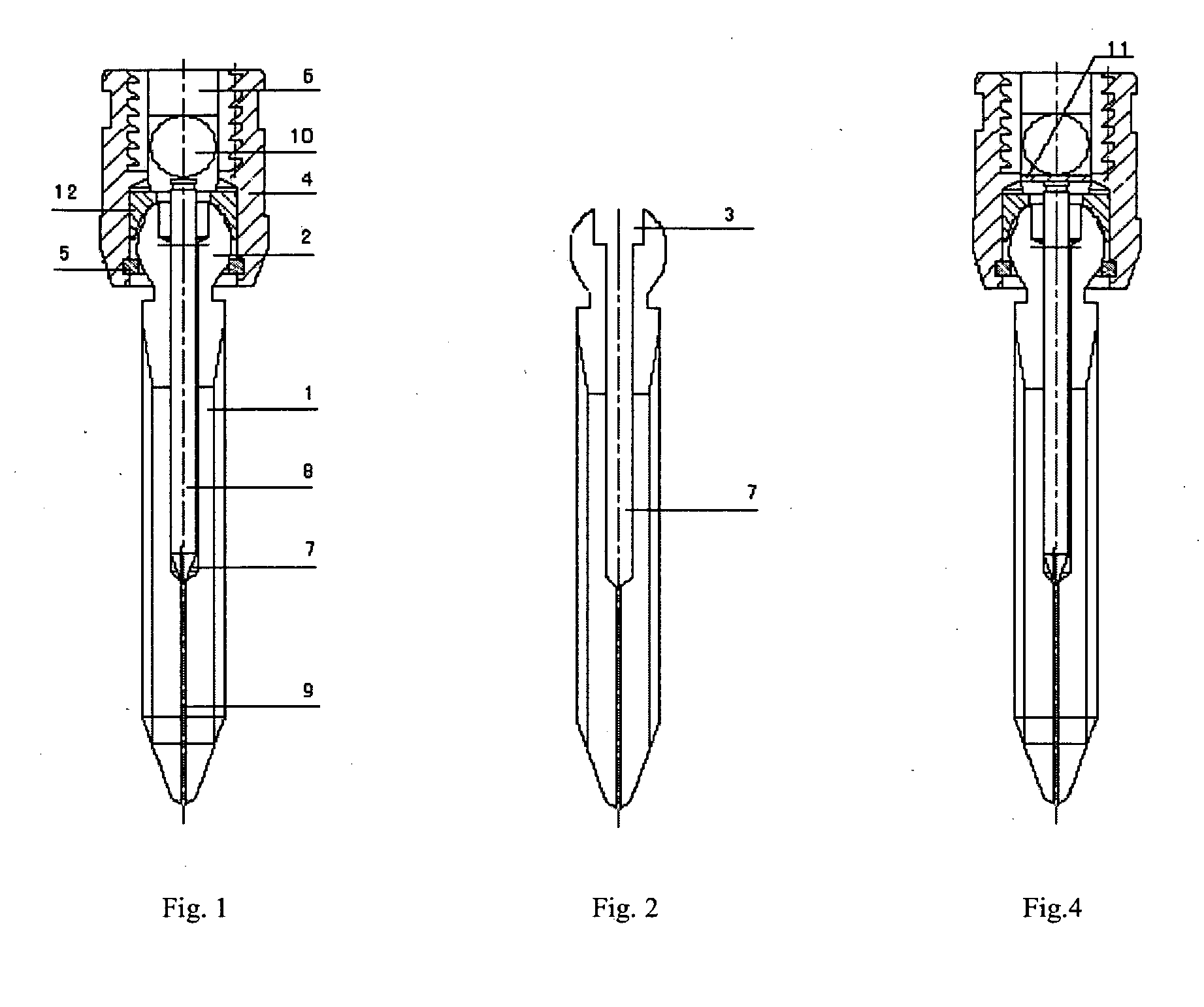
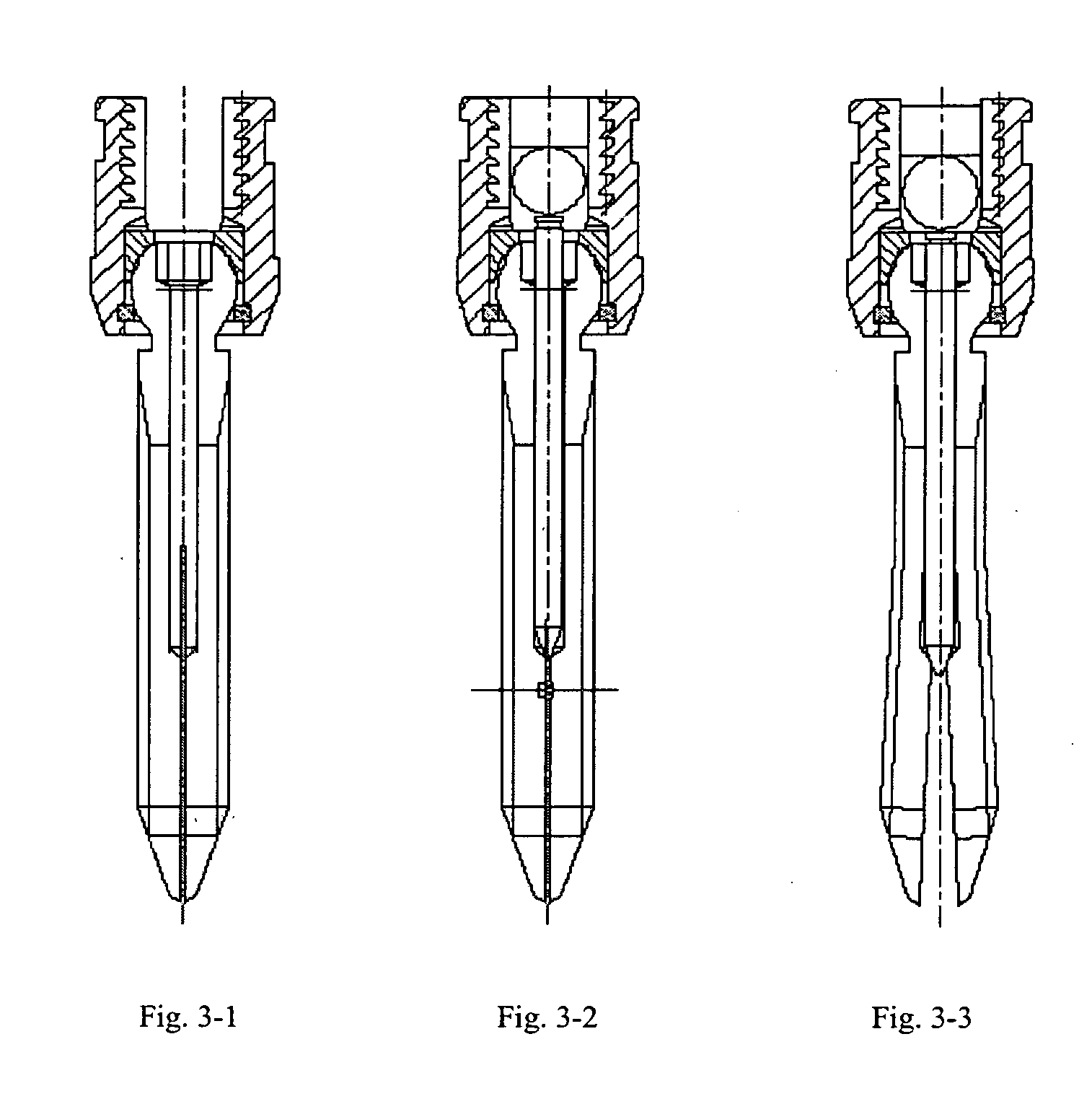
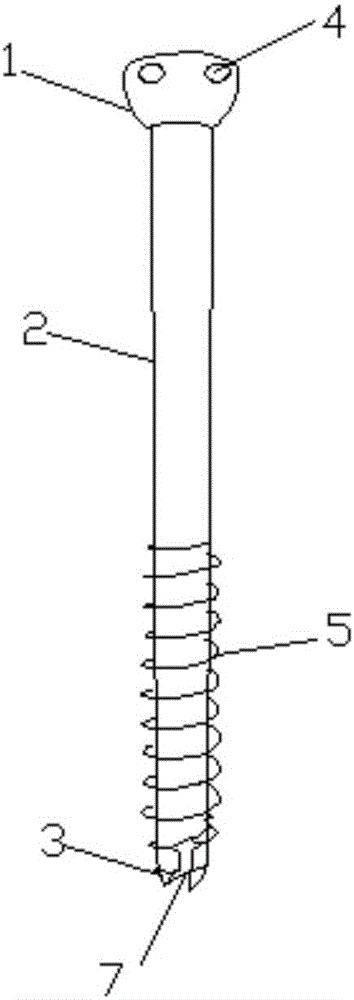
The expanding bolt for use in spongy bone includes one outer screw a one inner screw. The outer screw in integral structure has one tip end, one outer thread section, one spherical end and one inside hole including one front section of small diameter and one back section with inner threads. The front part of the outer screw is cut to form two or four expansion slots. The inner screw matched with the inner treads of the outer screw has one conic tip, threads and socket head for screwing in. There is also one tip steel pin matching the front section of the outer screw. The present invention is for inner fixing of fracture and has high stability and reliability.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com