Method for securing sutures to bones
a technology for securing sutures and bones, applied in medical science, surgery, diagnostics, etc., can solve problems such as jeopardizing a secure repair, and achieve the effects of superior screw fixing, long-term stability, and firm and secure tissue connection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
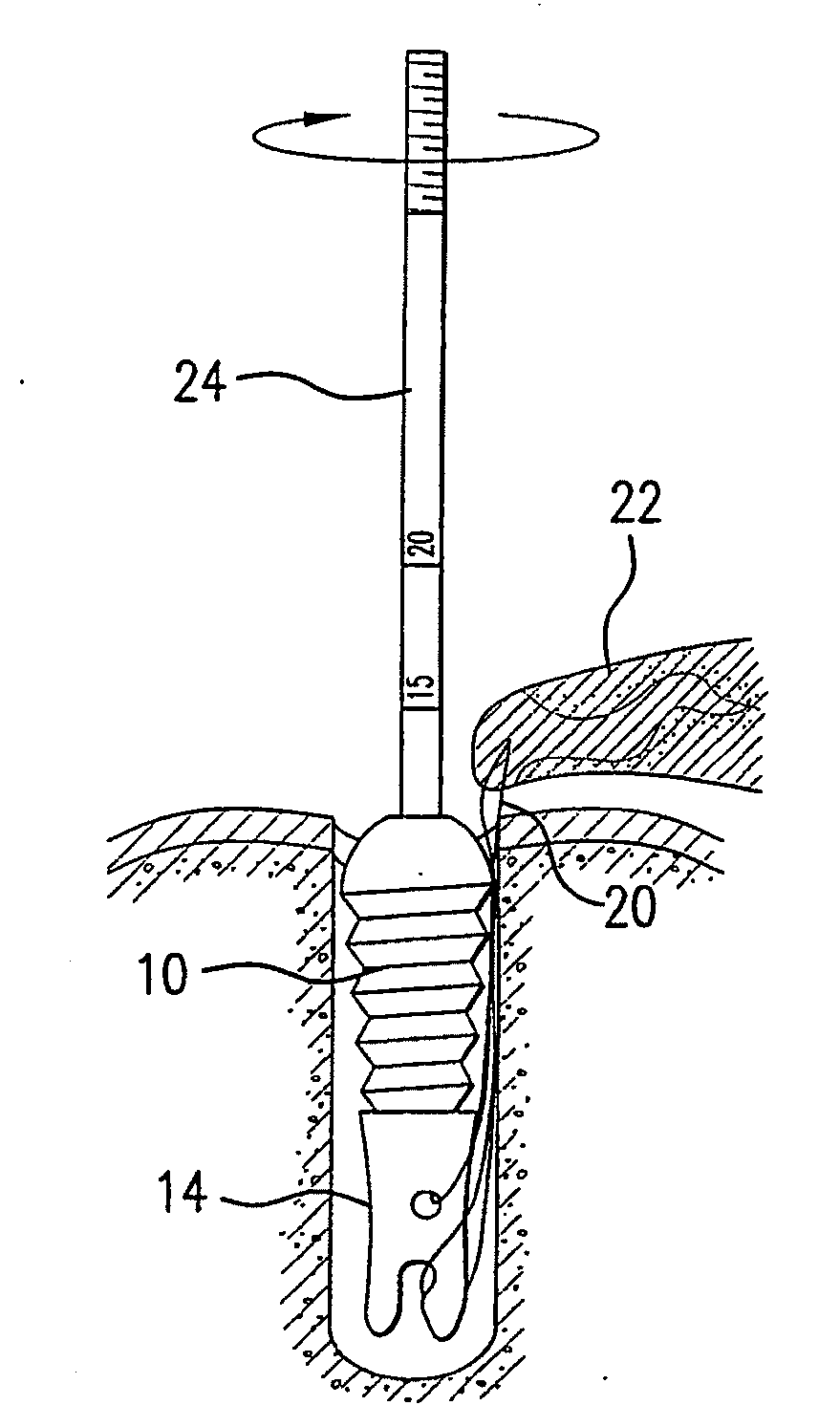
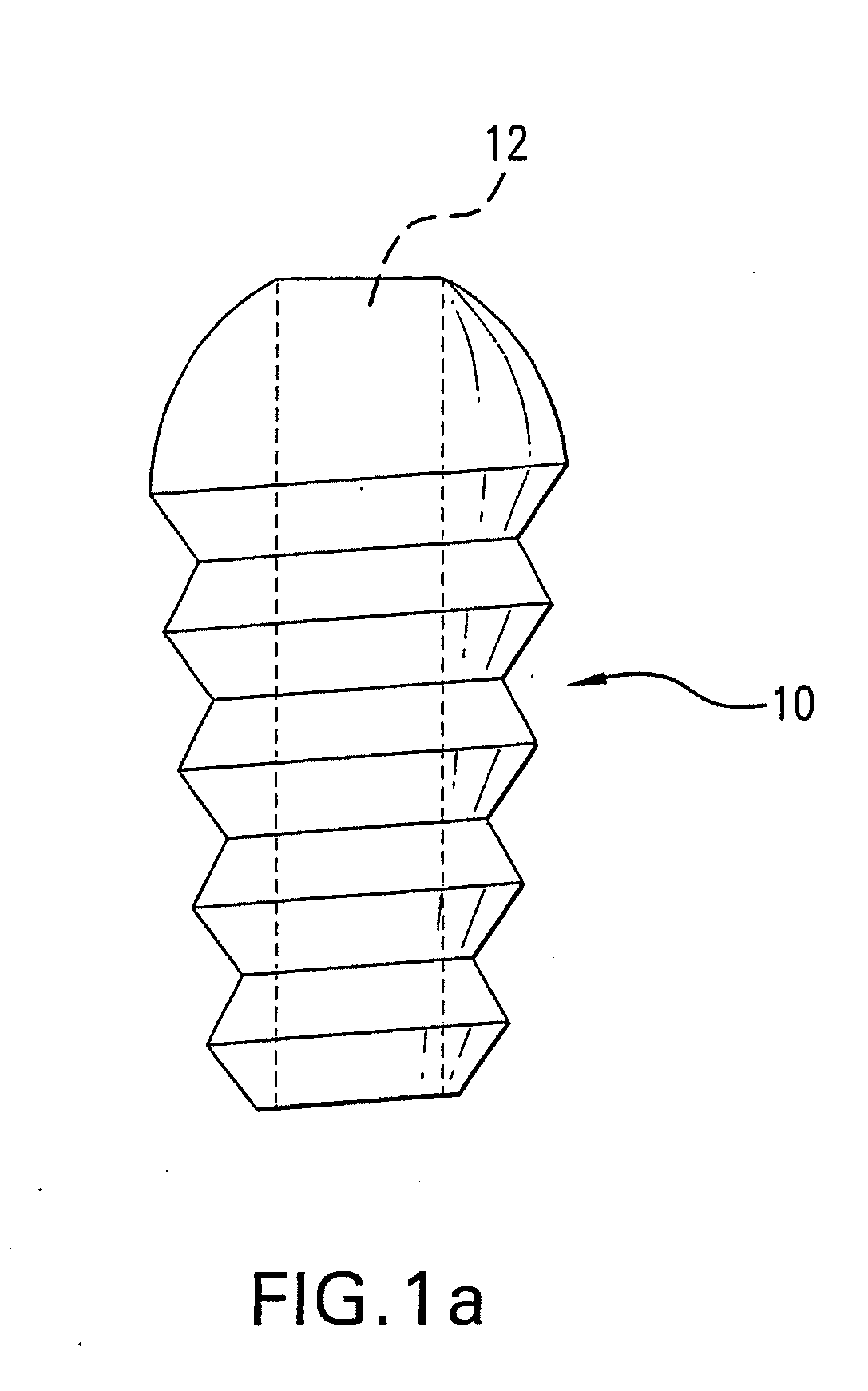
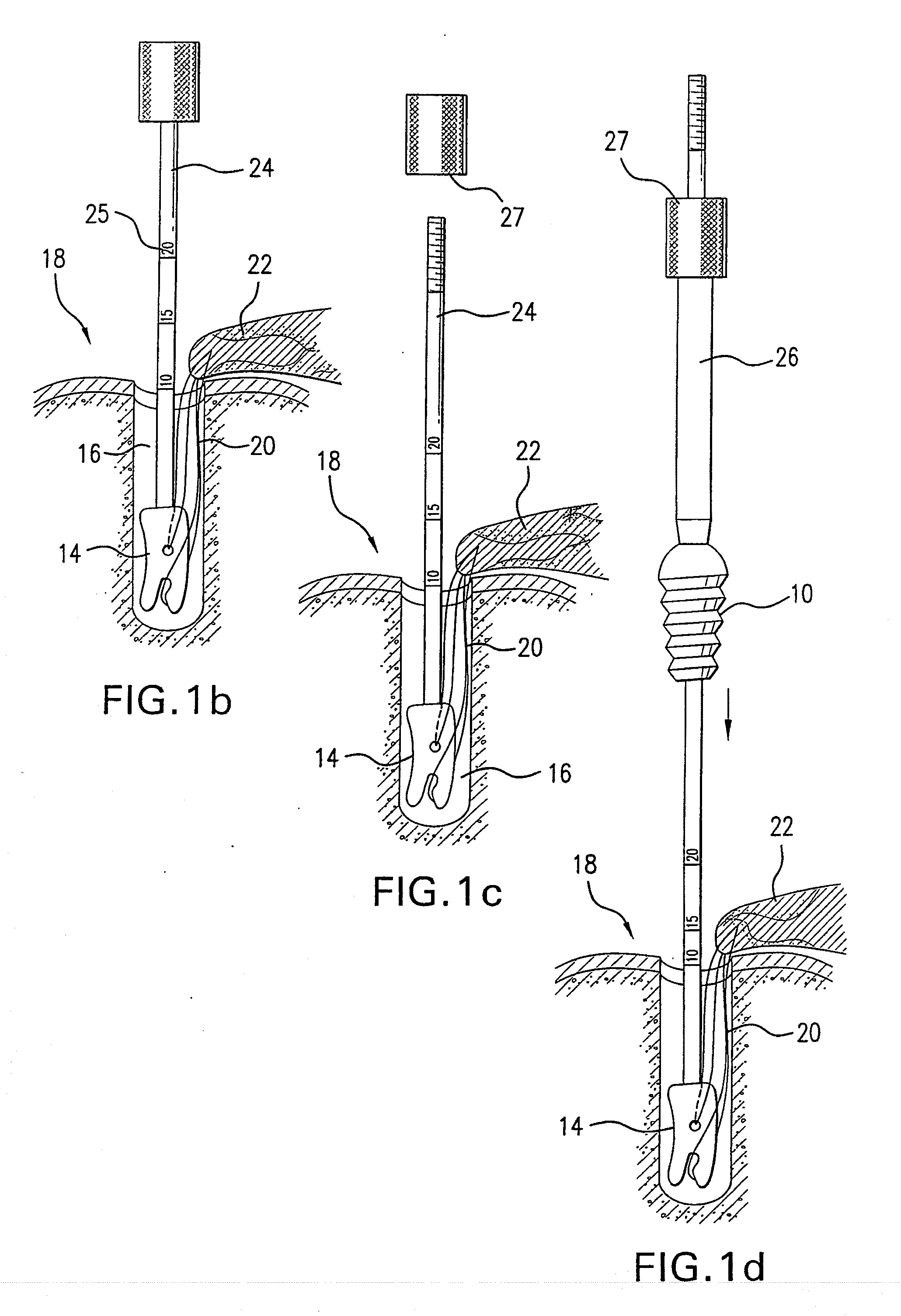
[0010]FIG. 1a shows the cannulated fastener, such as a cannulated bone screw 10 having a central bore 12 extending the entire length of the screw, allowing the screw to move along a bone anchor inserter rod. The fastener may be made of any suitable material, including bioabsorbable material, and may be a barbed fastener which is driven into a bone hole, rather than screwed. The fastener that is inserted need only have a flattened distal aspect to block the fixation anchor from migrating. In FIG. 1b, an anchor 14 has been inserted within a hole 16 in a bone 18. The anchor has a suture loop 20, either fixed or adjustable in length, passing through tissue 22, such as a rotator cuff, to secure the tissue 22 to the bone 18. The anchor has captured the loop, allowing for fixation without needing to tie a knot. As can be seen, there is a distance between the top of the anchor and the top of the opening in the bone. This distance can be measured by markings 25 along the inserter rod 24 seen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com