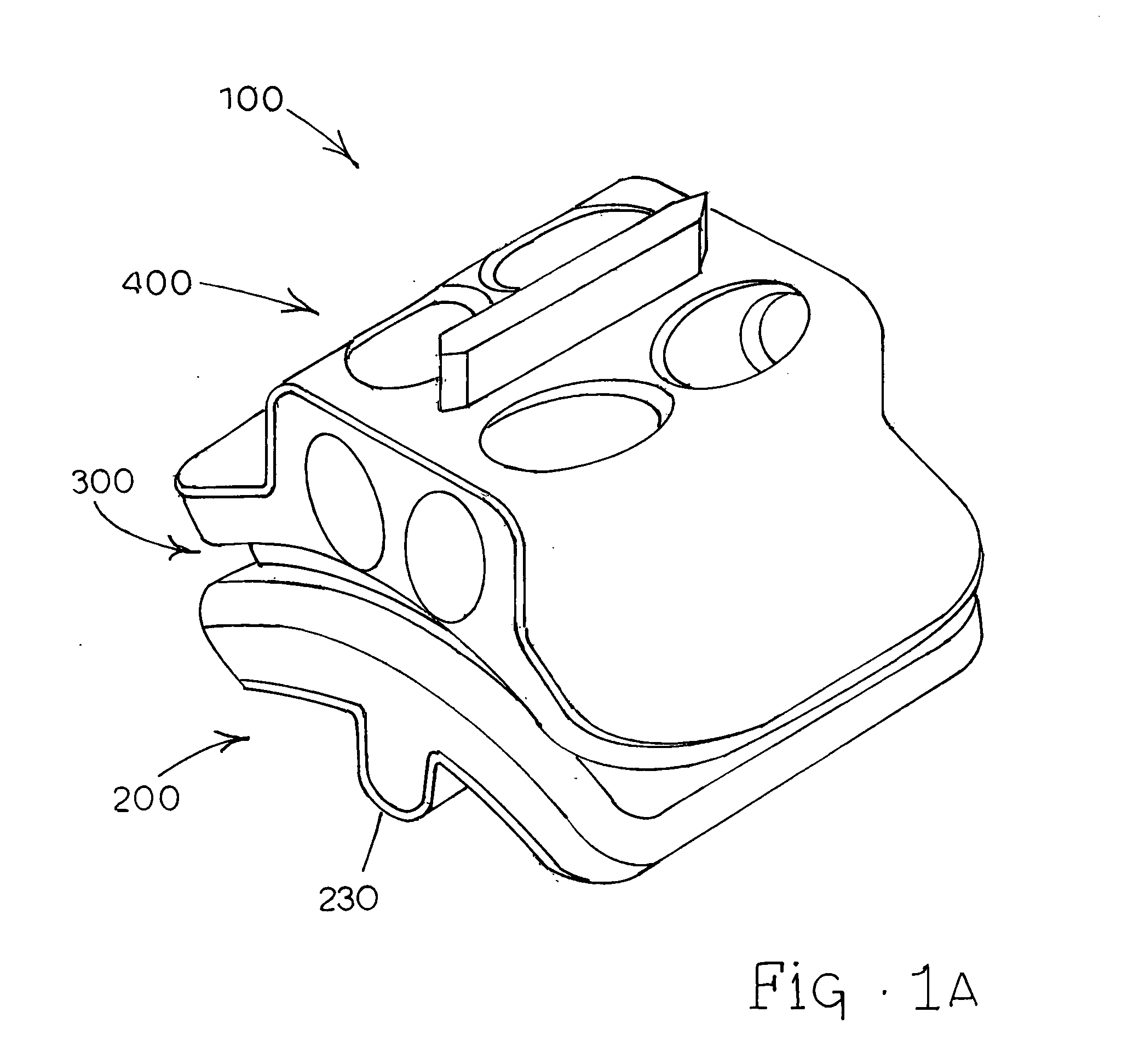
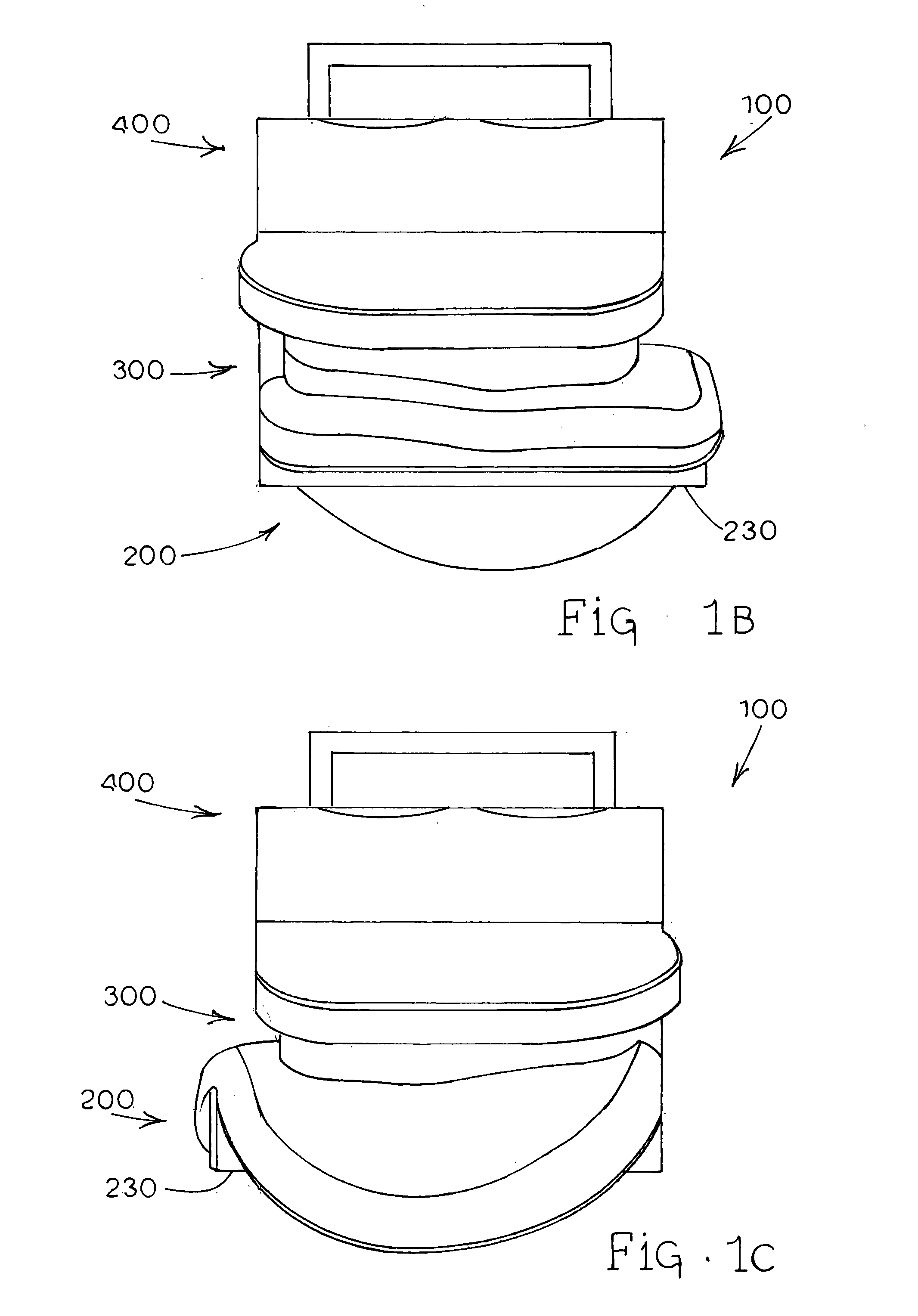
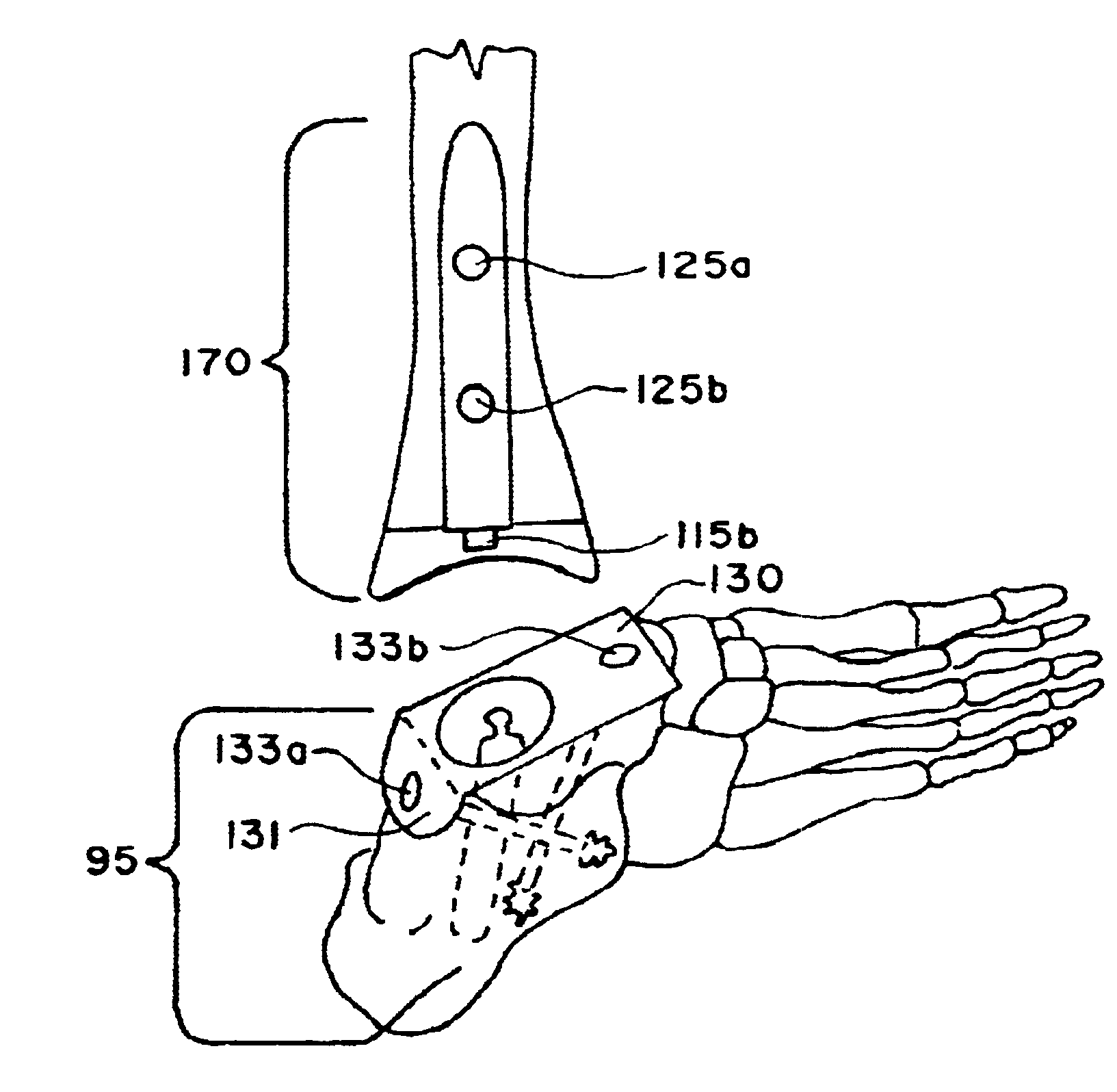
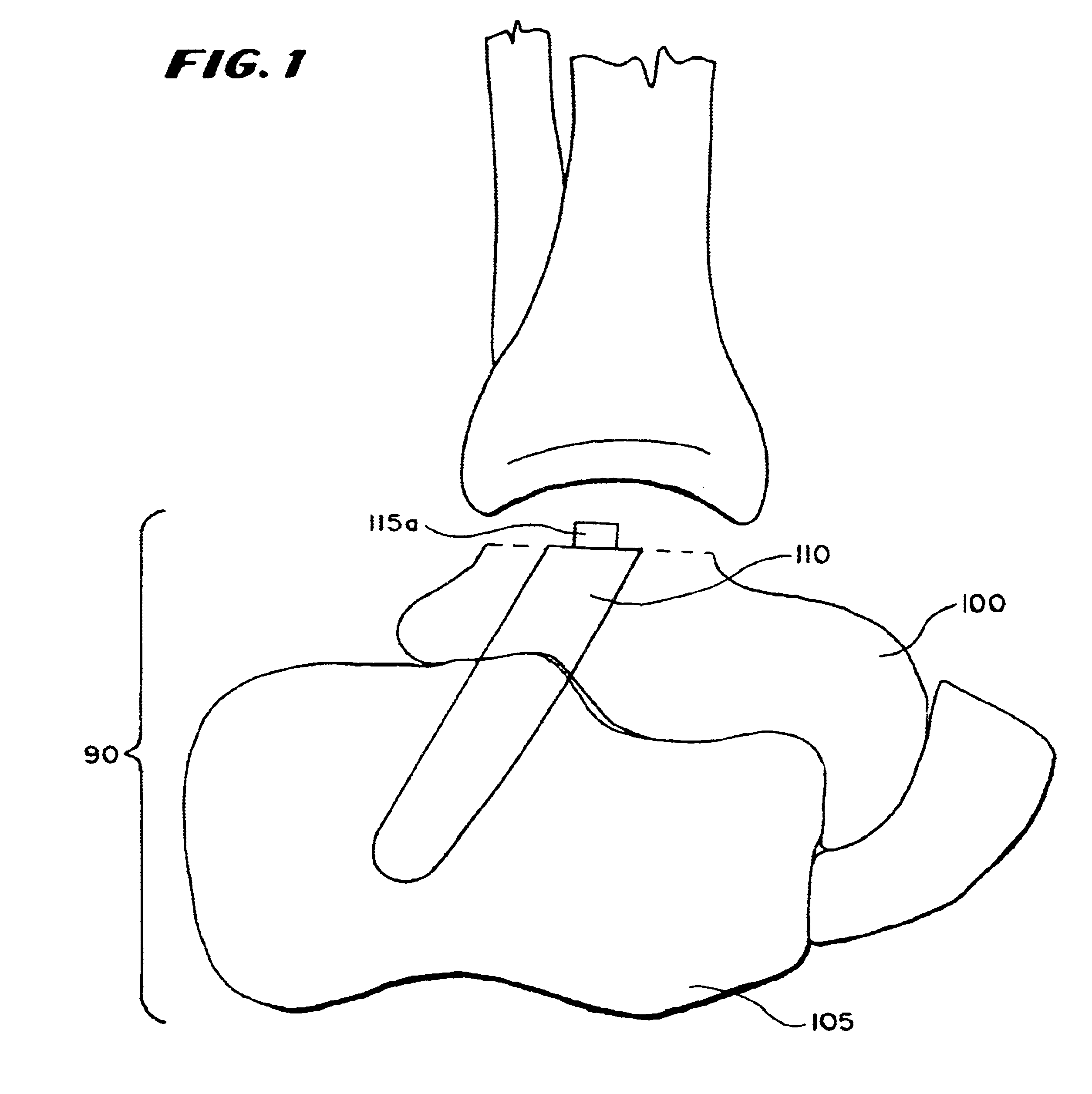
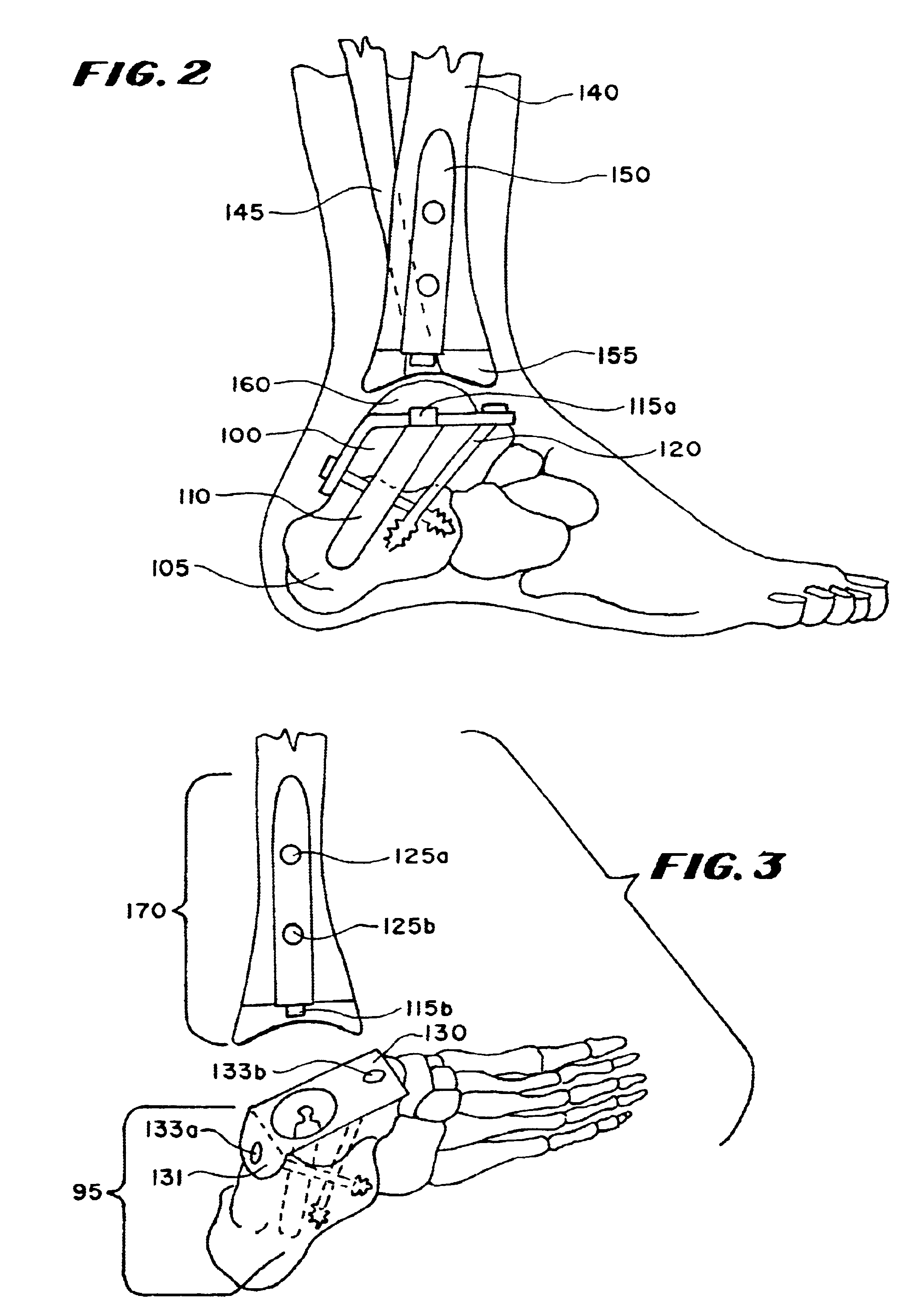
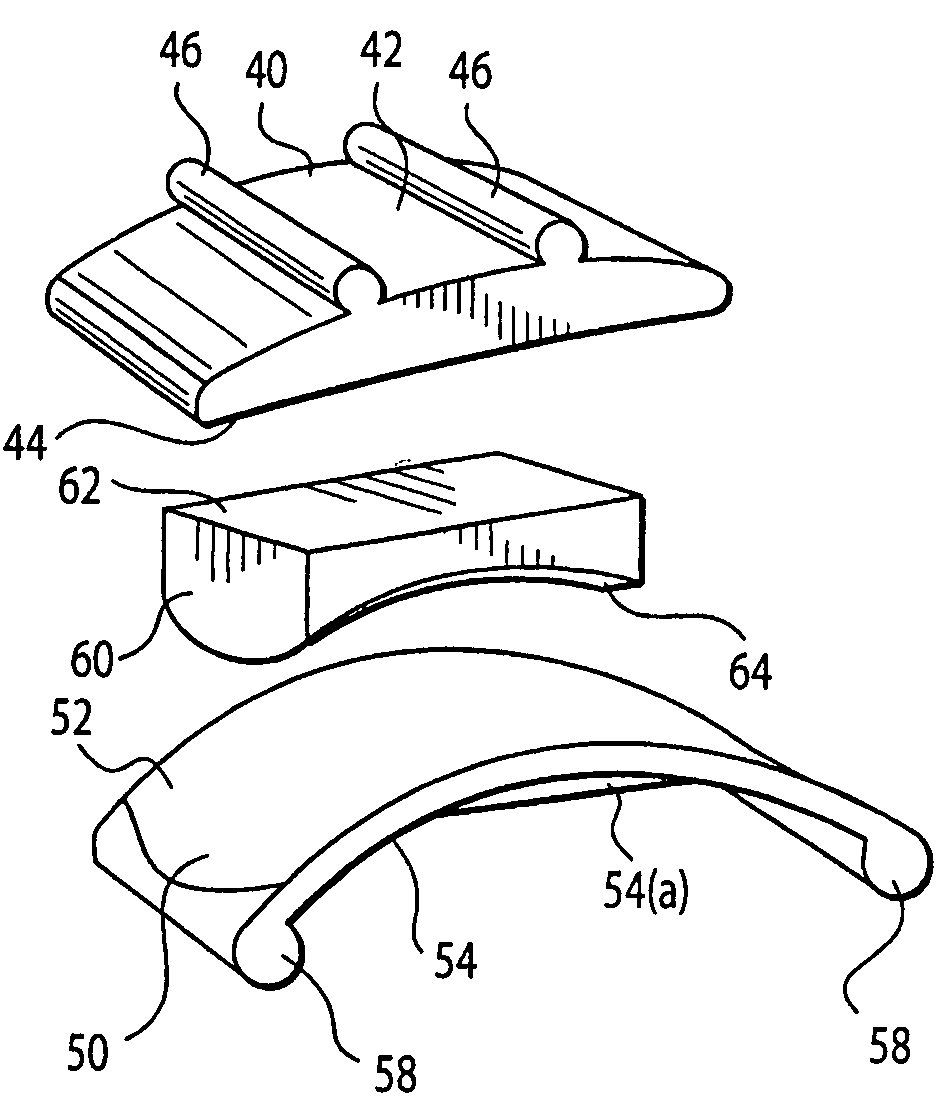
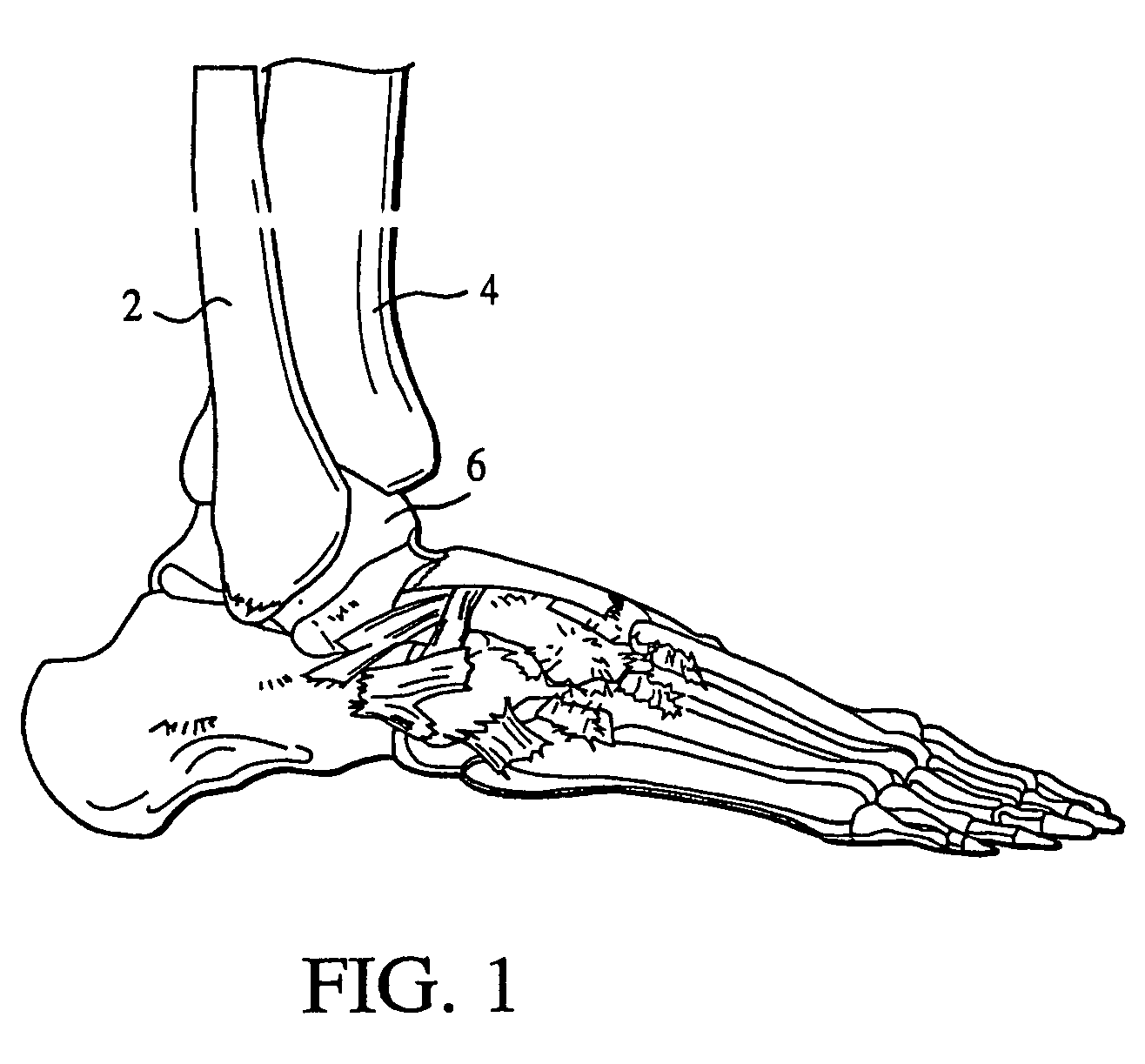
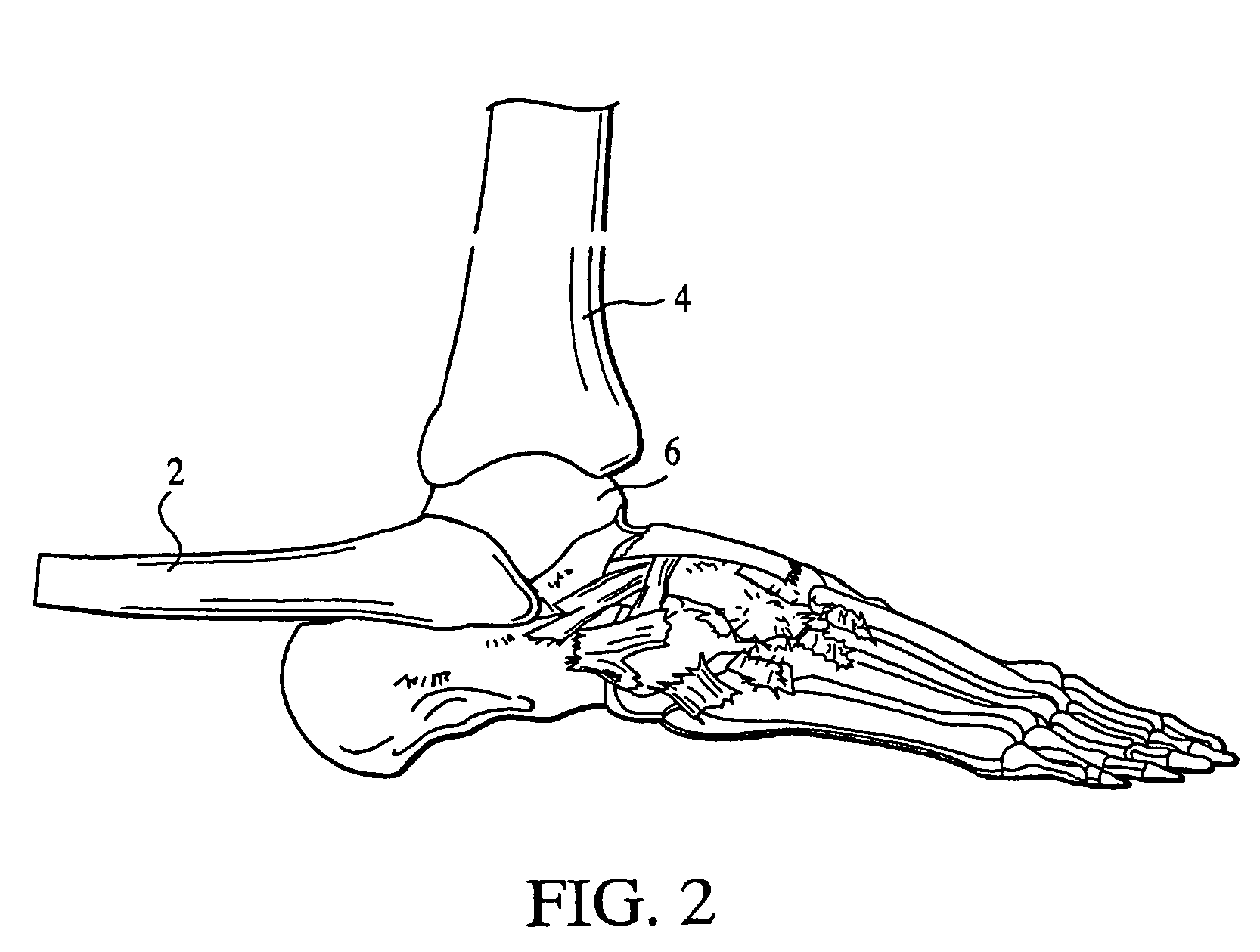
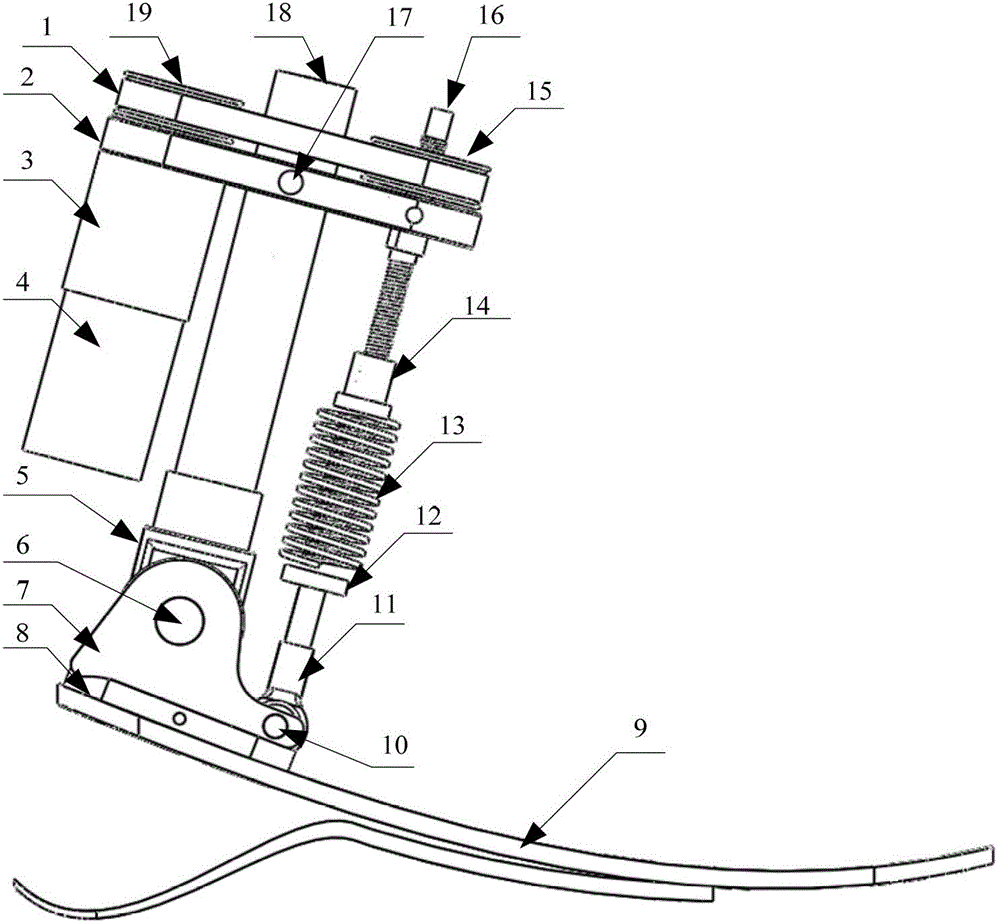
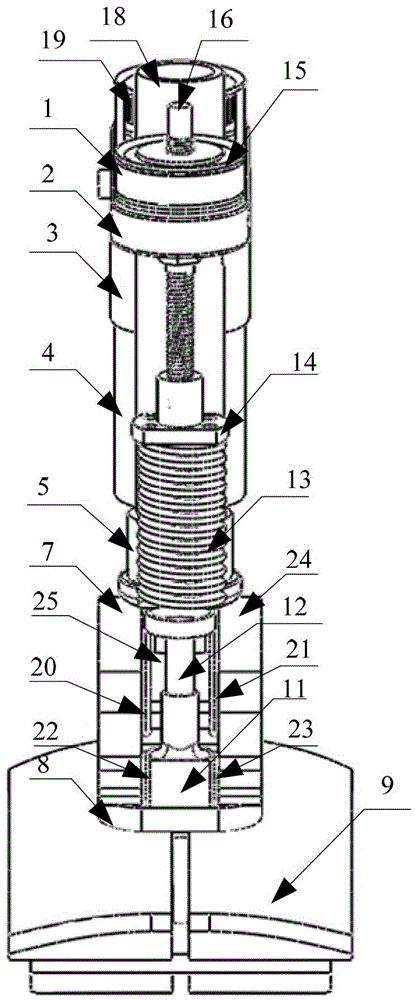
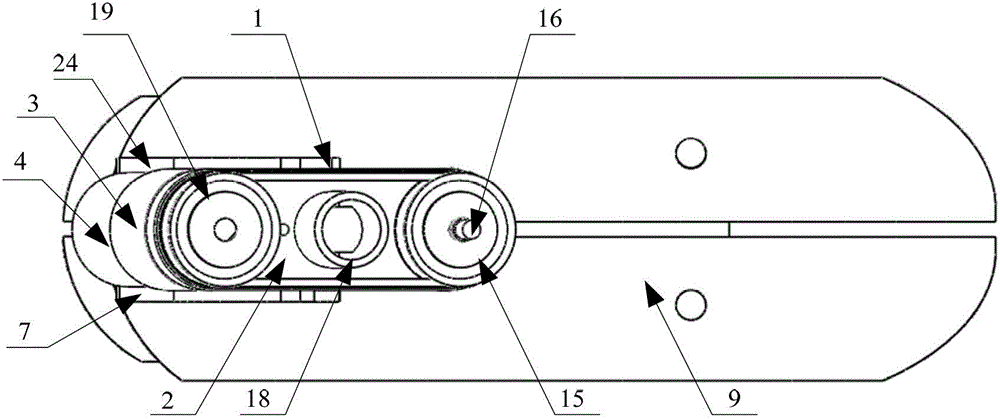
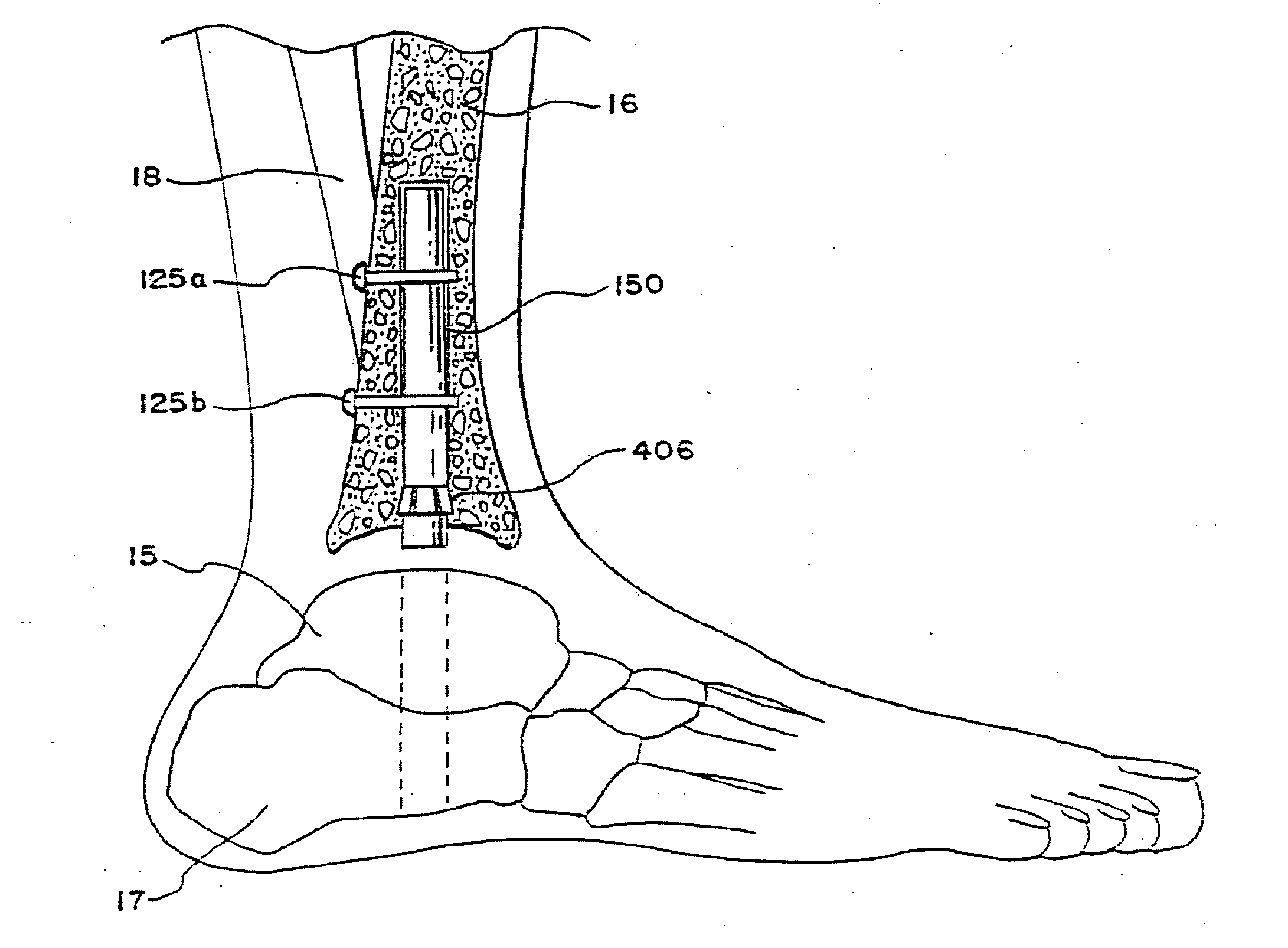
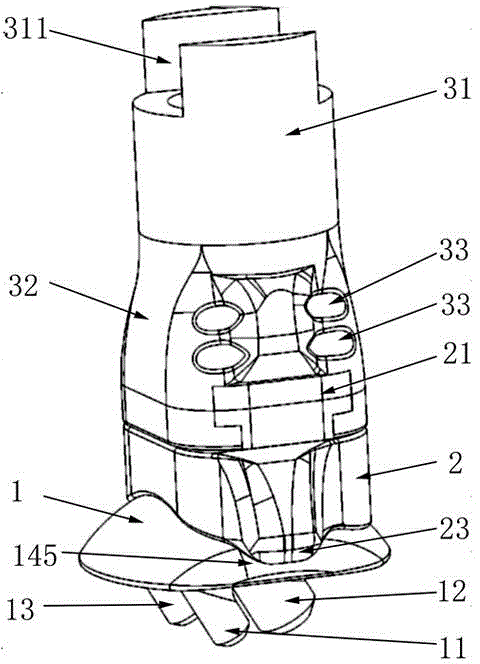
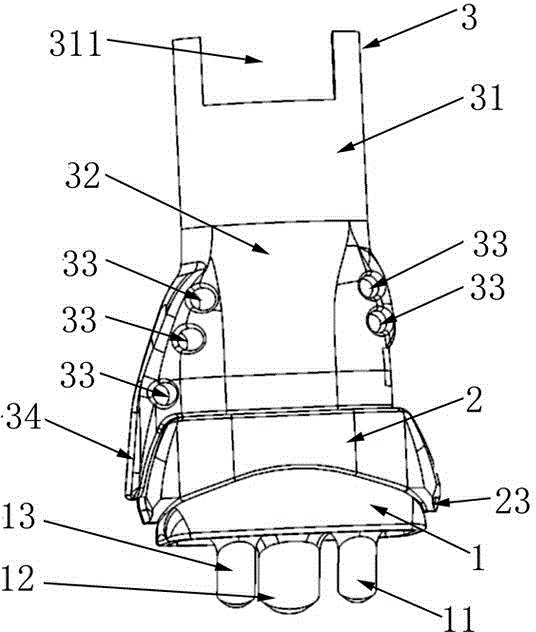
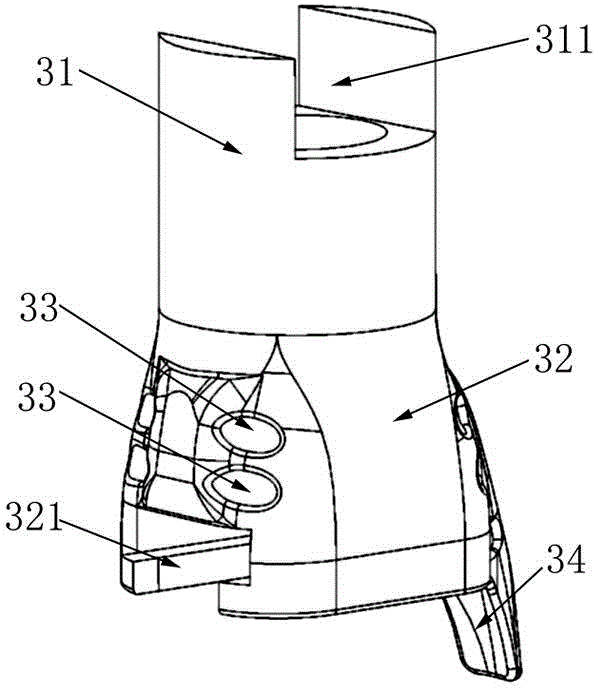
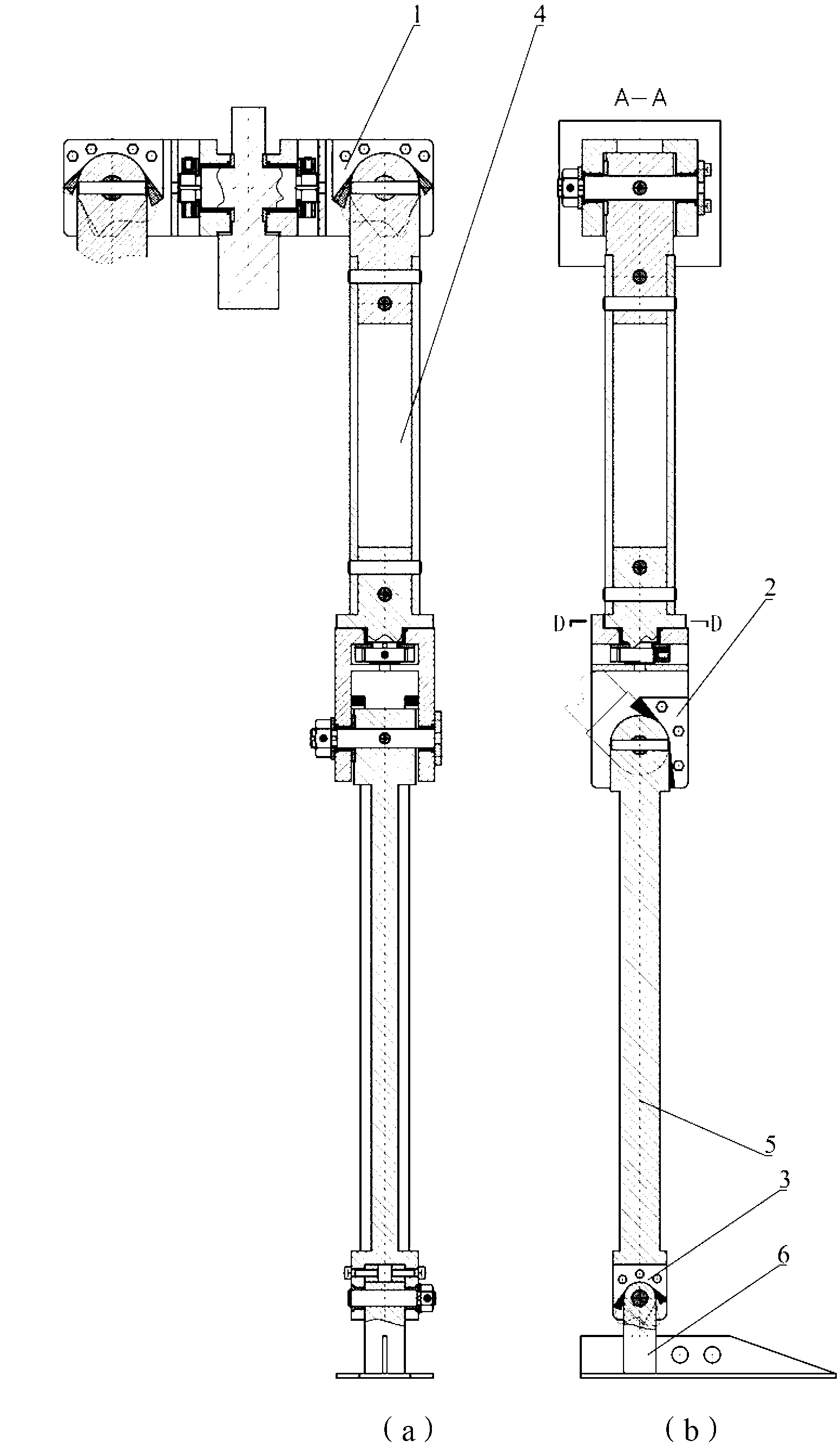
Patents
Literature
88 results about "Ankle joint prosthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
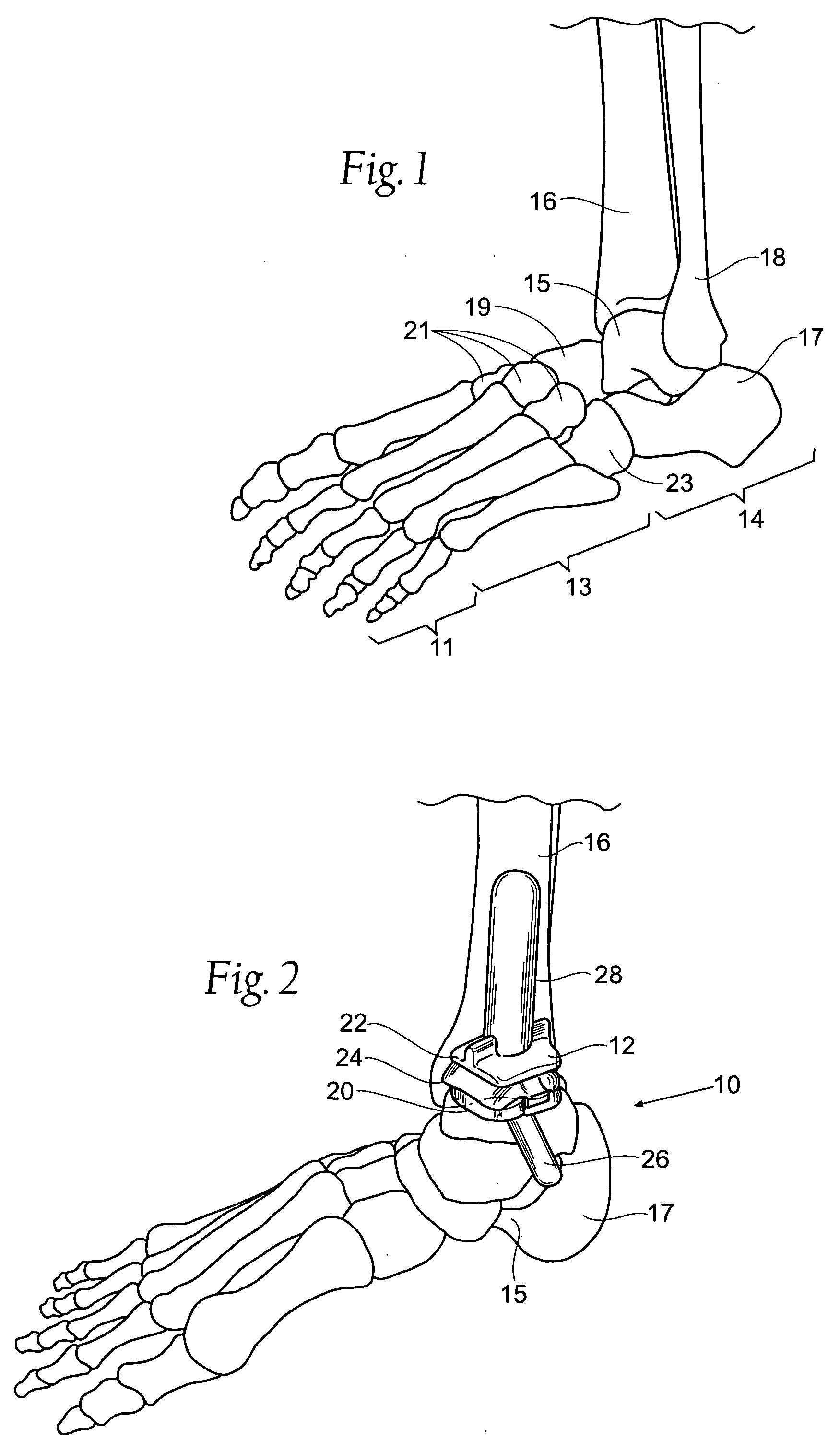
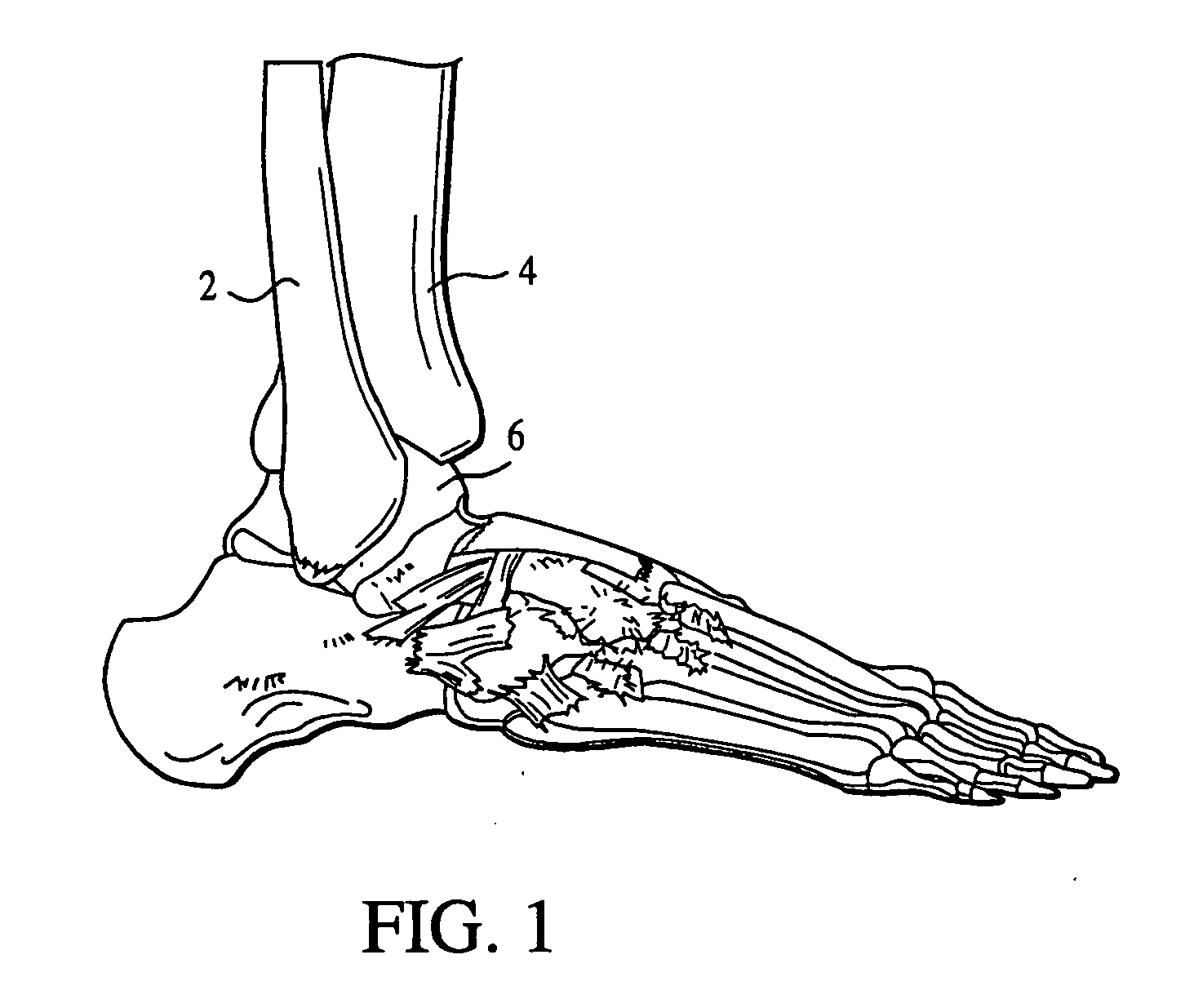
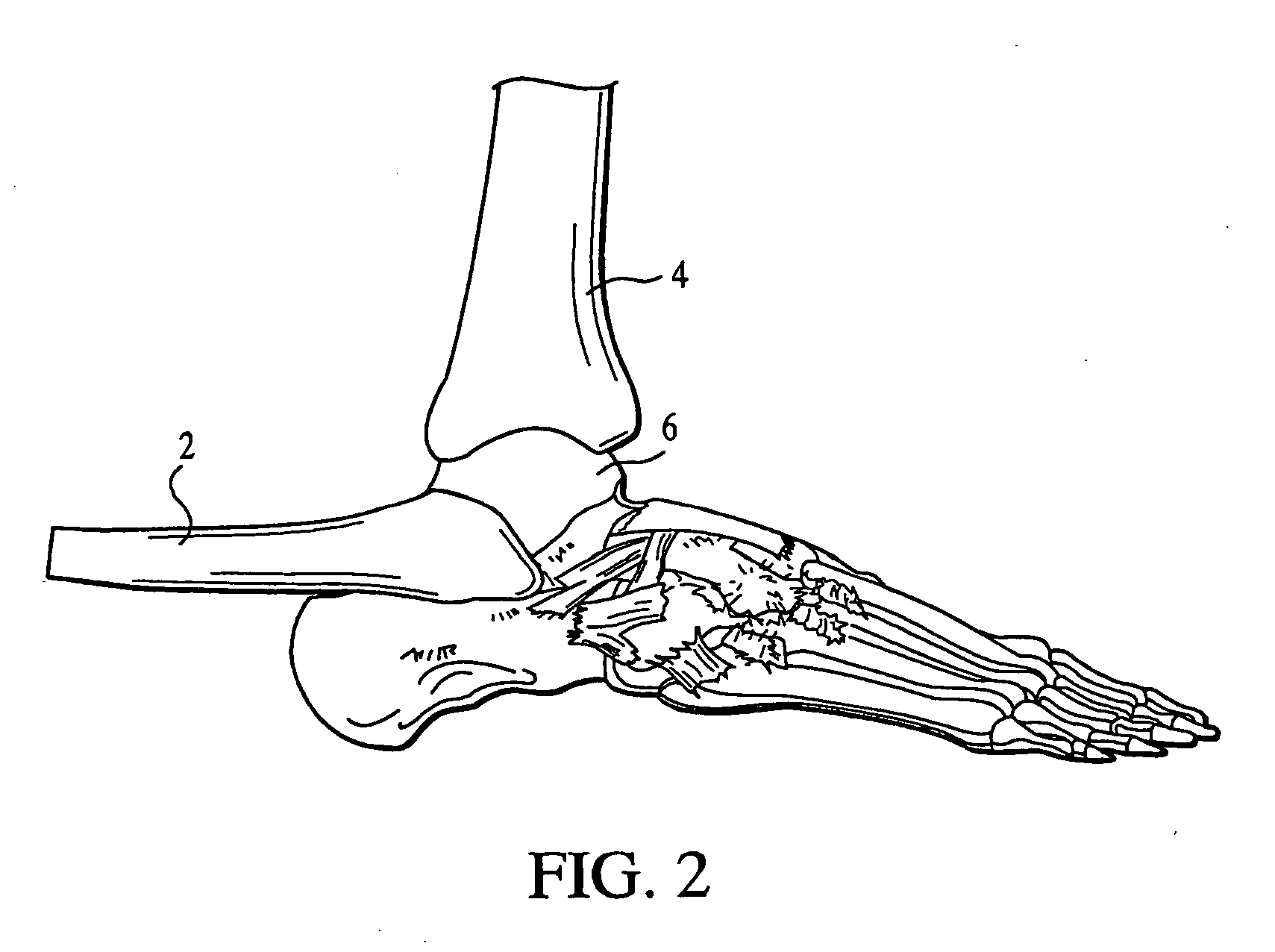
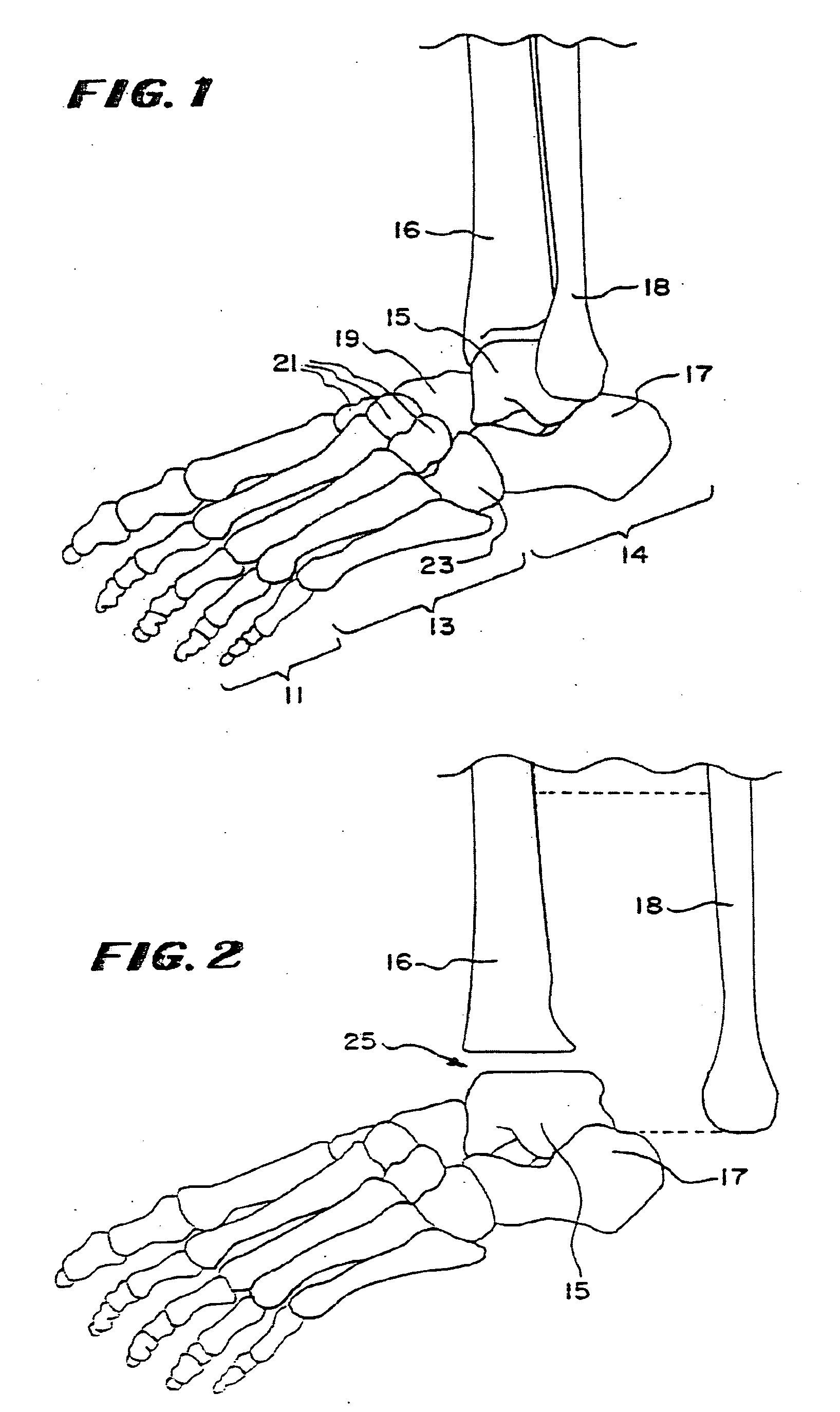
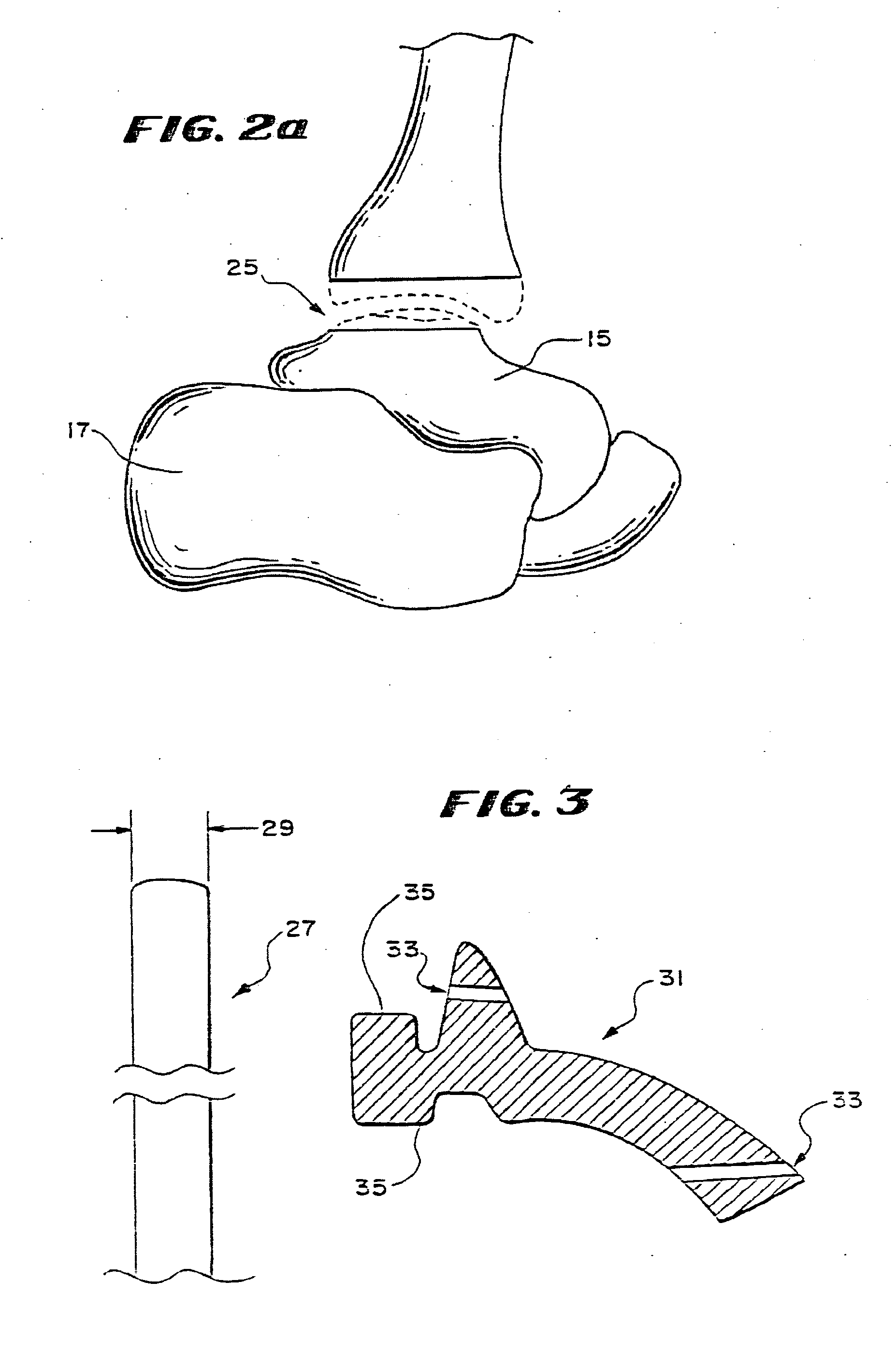
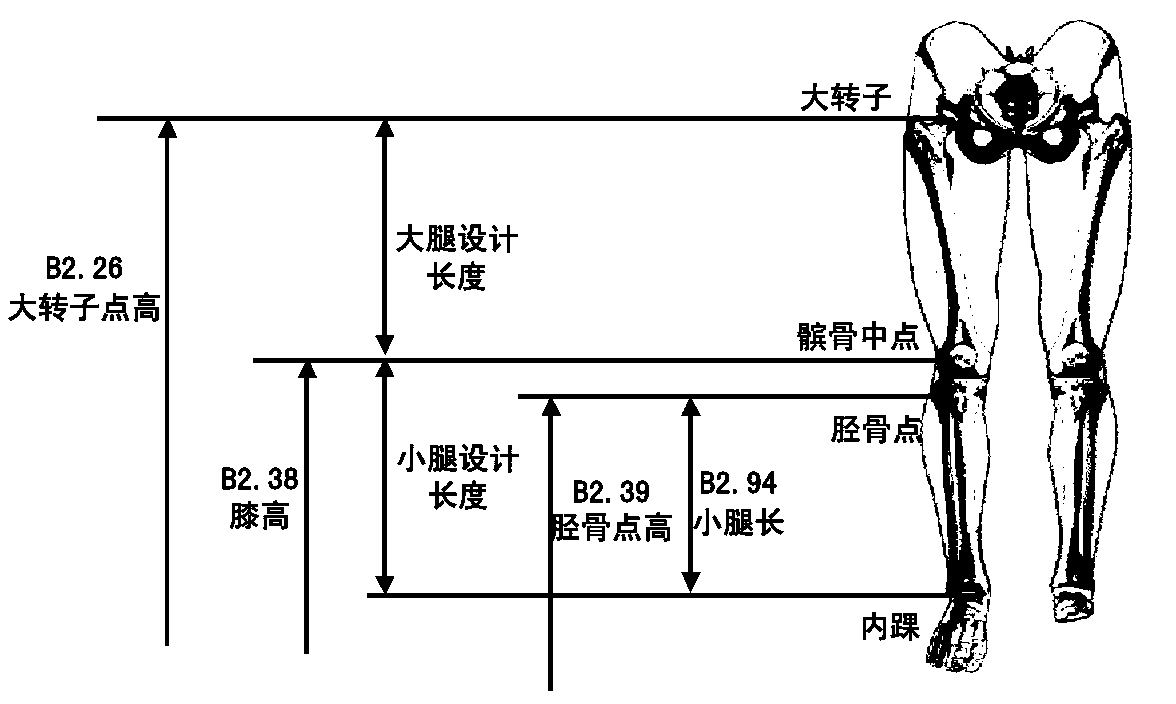
Ankle replacement, or ankle arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to replace the damaged articular surfaces of the human ankle joint with prosthetic components. This procedure is becoming the treatment of choice for patients requiring arthroplasty, replacing the conventional use of arthrodesis, i.e. fusion of the bones.
Ankle prosthesis
InactiveUS6409767B1Preventing uncontrolled deformationImprove the situationInternal osteosythesisAnkle jointsTibiaBase of the sacrum
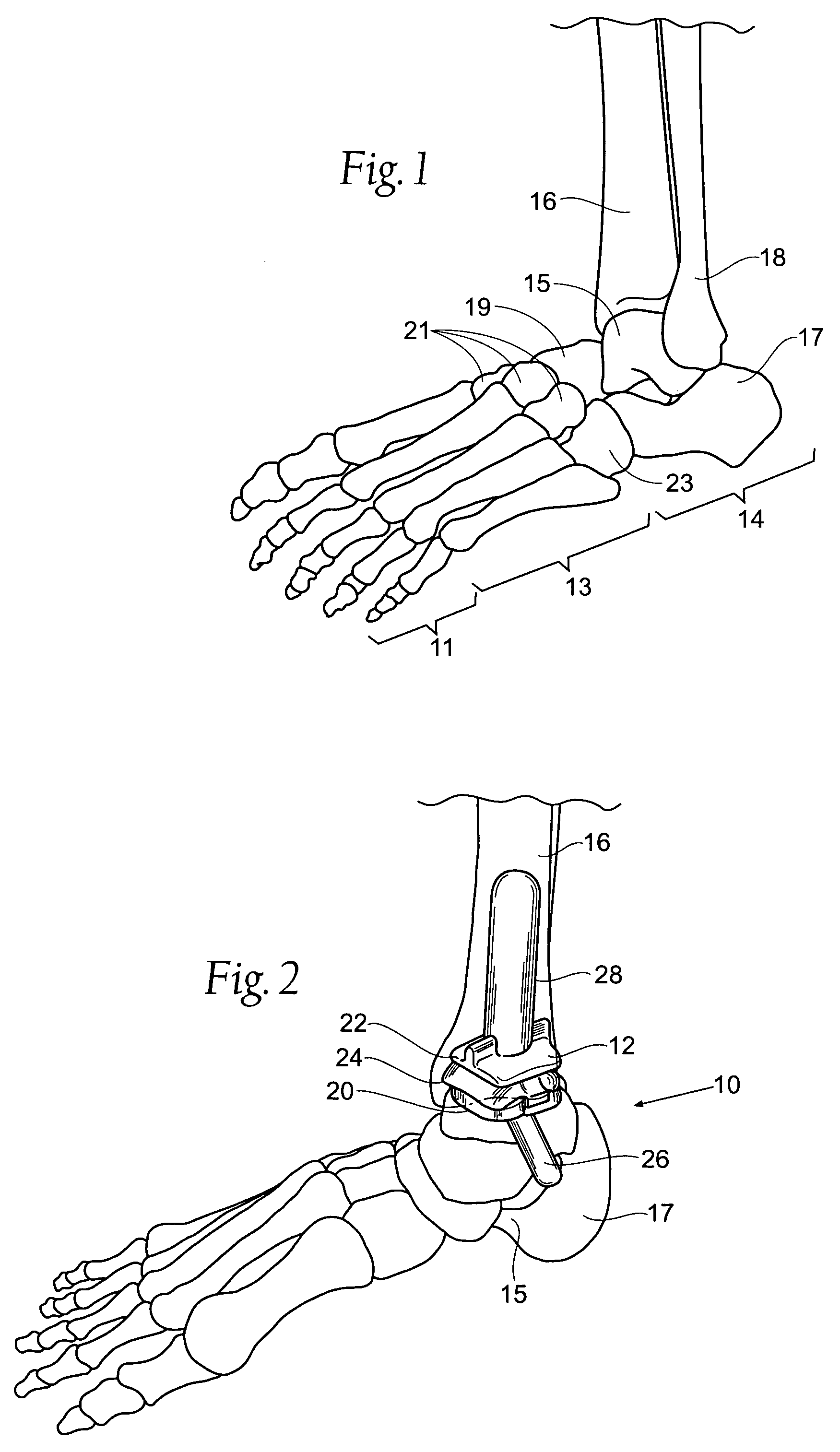
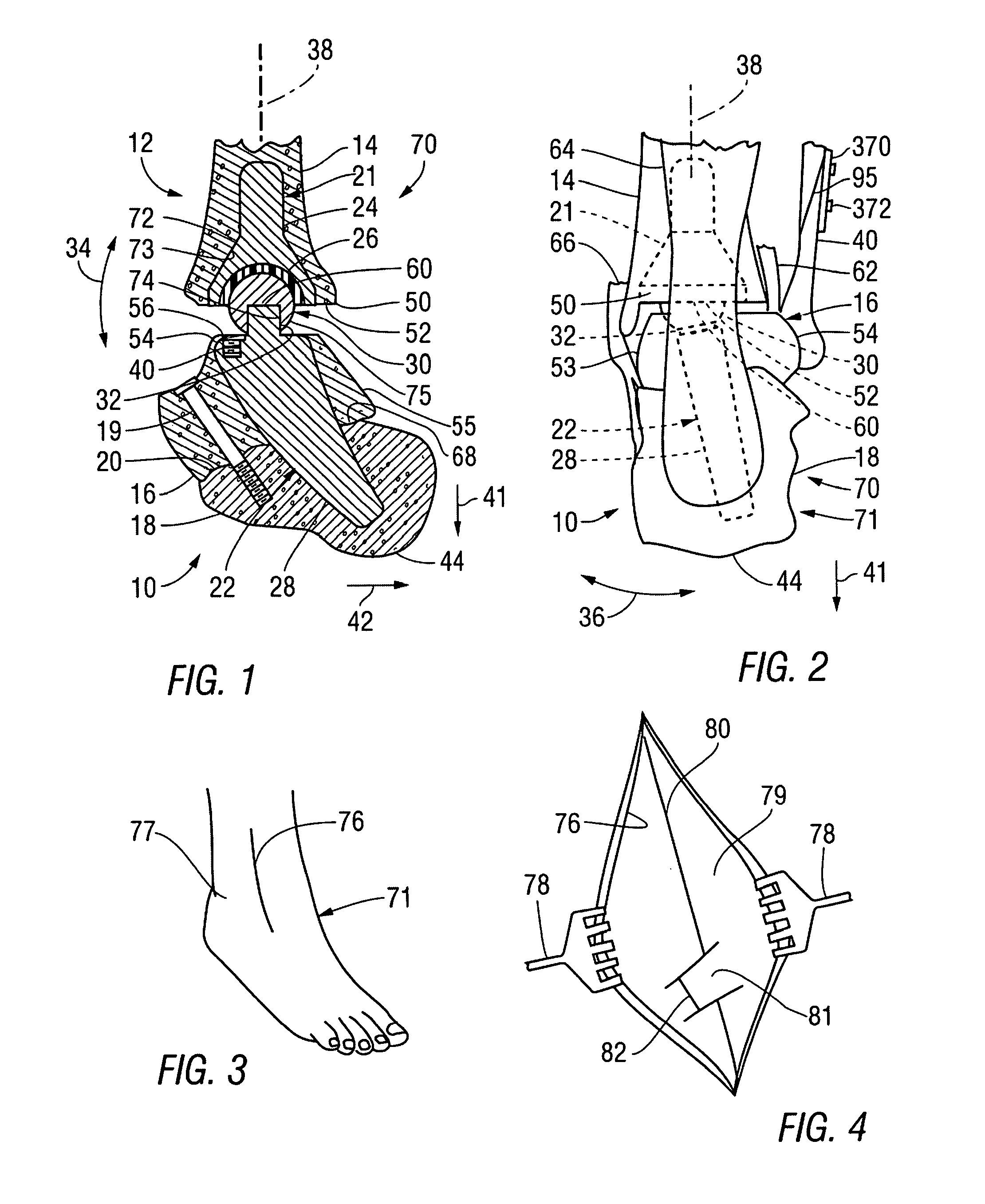
The invention provides an ankle prosthesis for use in the field of orthopedic prostheses comprising a talus implant for implanting in or on the talus and a top element including a tibia implant for implanting in or on the base of the tibia. The top element and the talus implant being mounted to move relative to each other by friction on a contact interface so as to allow the ankle to move. The contact interface presents a friction surface that can be considered as being a fraction of a substantially frustoconical surface. When implanted, the substantially frustoconical surface is oriented so that its larger radius portion is directed substantially towards the outside of the ankle.
Owner:EURON FOOT PLATFORM
Modular total ankle prosthesis apparatuses, systems and methods, and systems and methods for bone resection and prosthetic implantation
Ankle prosthesis apparatuses, systems and methods are provided as disclosed herein. Additionally, systems and methods for bone resection and implantation of prosthetics are provided, including surgical techniques and related instrumentation. An ankle prosthesis apparatus can include a talar component having a lower surface with a bone fixation portion for fixation to a talus bone and an upper surface designed for articulation with a bearing component. The bearing component can have a lower surface for articulation with the talar component and an upper surface for articulation with a tibial component. The tibial component can have a lower surface for articulation with the bearing component and an upper surface with a bone fixation portion for fixation to a tibia bone and / or a fibula bone. The bearing component can have a protrusion on its upper surface adapted for engagement with a recess on the tibial component to allow desired rotational and translational movement. Methods and systems can be used to prepare a bone surface for implantation of a prosthesis including determining a location for a curved cut line on the bone surface and drilling a series of holes tangent to the curved cut line to create a curved bone resection surface. Methods and systems can be used for the implantation of an ankle joint prosthesis including the use of an alignment guide, tibia and talus drill guides, tibia and talus saw guides, and tibia and talus broach guides, all components of which can be placed on and removed from a plurality of alignment anchor pins throughout the implantation procedure. A method for medially to laterally implanting an ankle joint prosthesis can include exposing tibia and talus bones from the medial side, resection of the tibia and talus bones, broaching the tibia and talus bones, and positioning and affixing the ankle joint prosthesis components.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI
Ankle replacement system
A total ankle replacement system, novel surgical method for total ankle replacement, and novel surgical tools for performing the surgical method are described. The total ankle replacement system includes the calcaneus in fixation of a lower prosthesis body, thereby significantly increasing the amount of bone available for fixation of the lower prosthesis body and allowing the lower prosthesis body to be anchored with screws. The total ankle replacement system further includes a long tibial stem which can also be anchored into the tibia with, for example, screws, nails, anchors, or some other means of attachment. The novel surgical arthroscopic method allows introduction of ankle prostheses into the ankle joint through an exposure in the tibial tubercle. Various novel surgical instruments, such as a telescoping articulating reamer and a talo-calcaneal jig, which facilitate the novel surgical method, are also described.
Owner:INBONE TECH
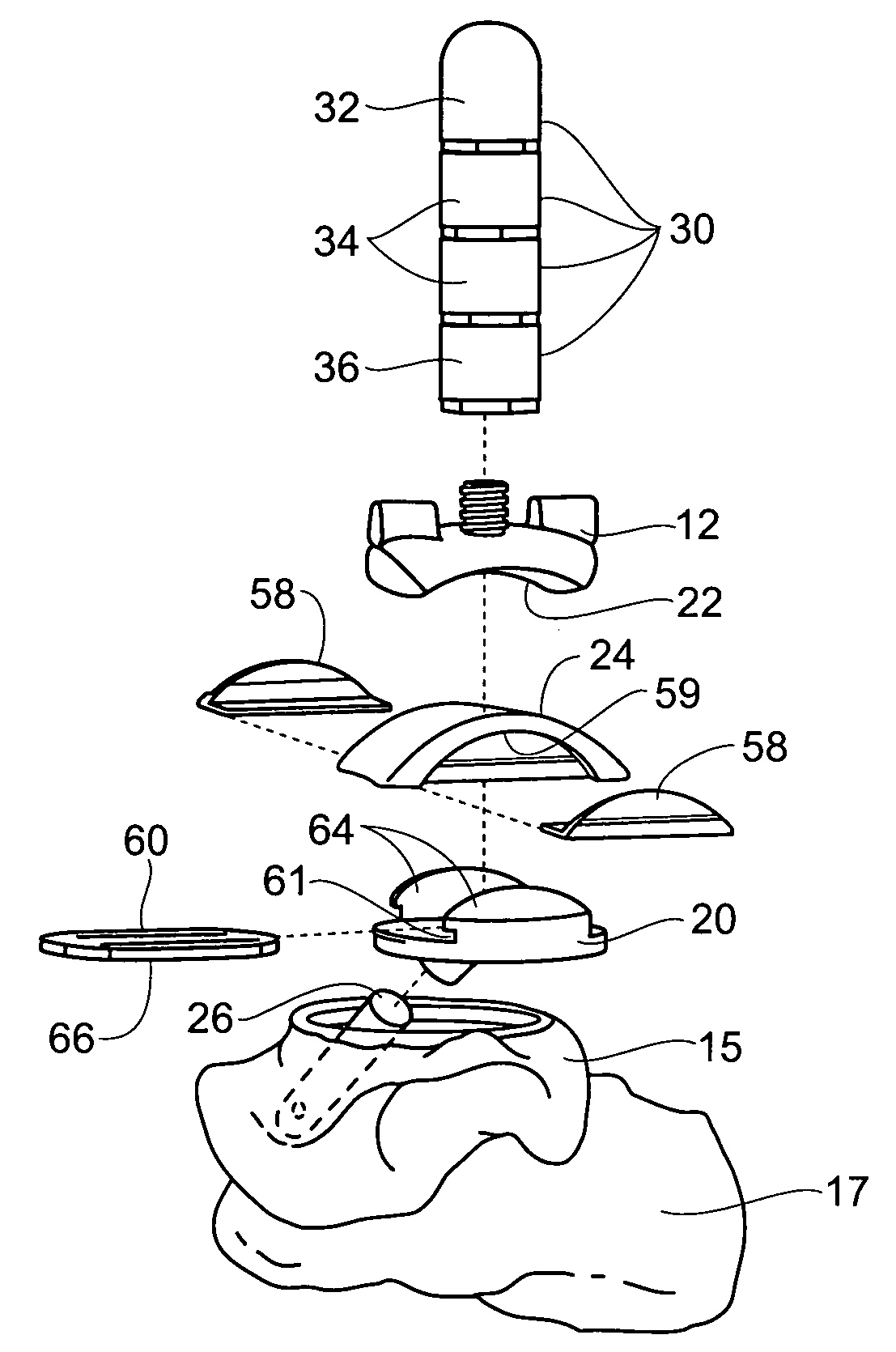
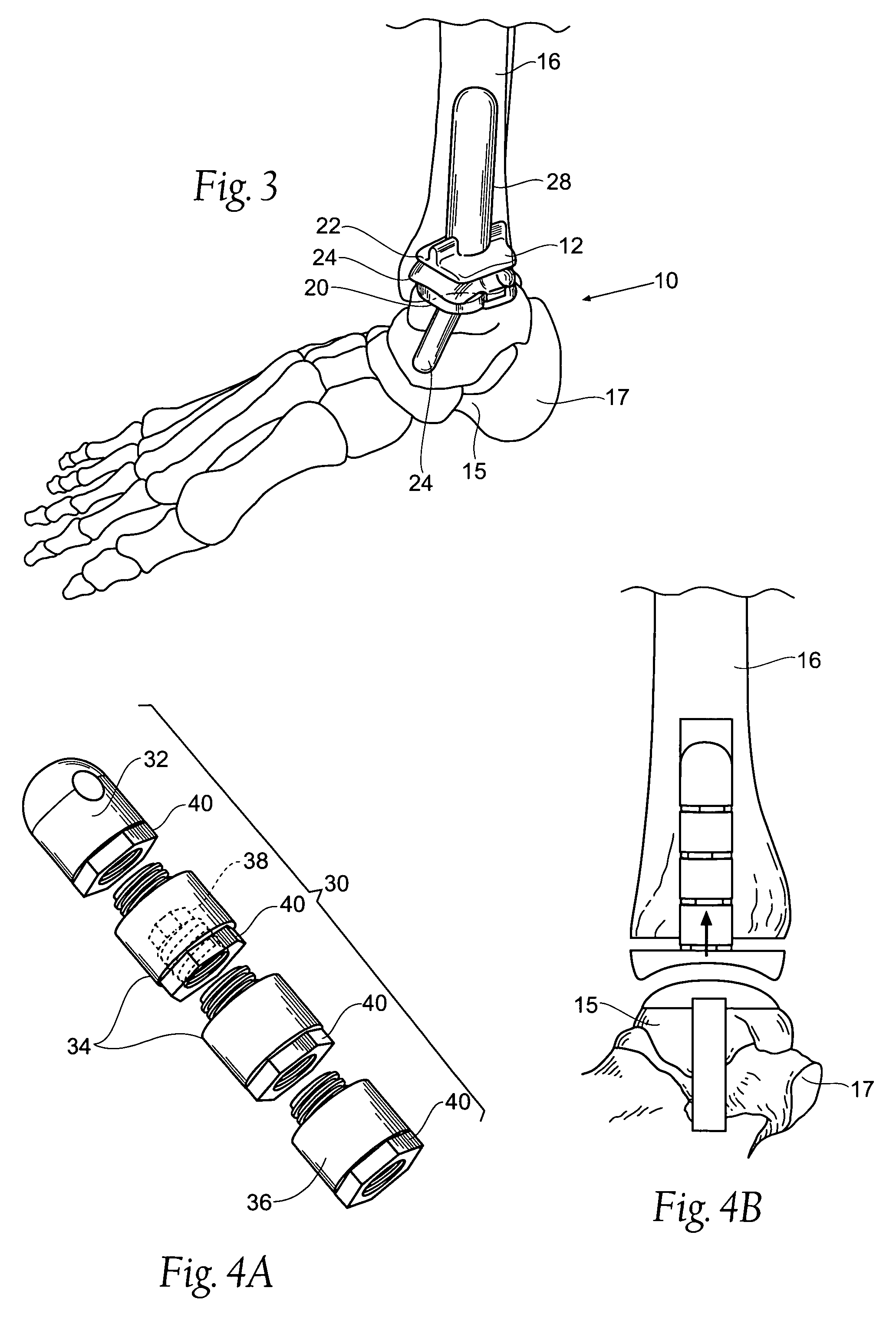
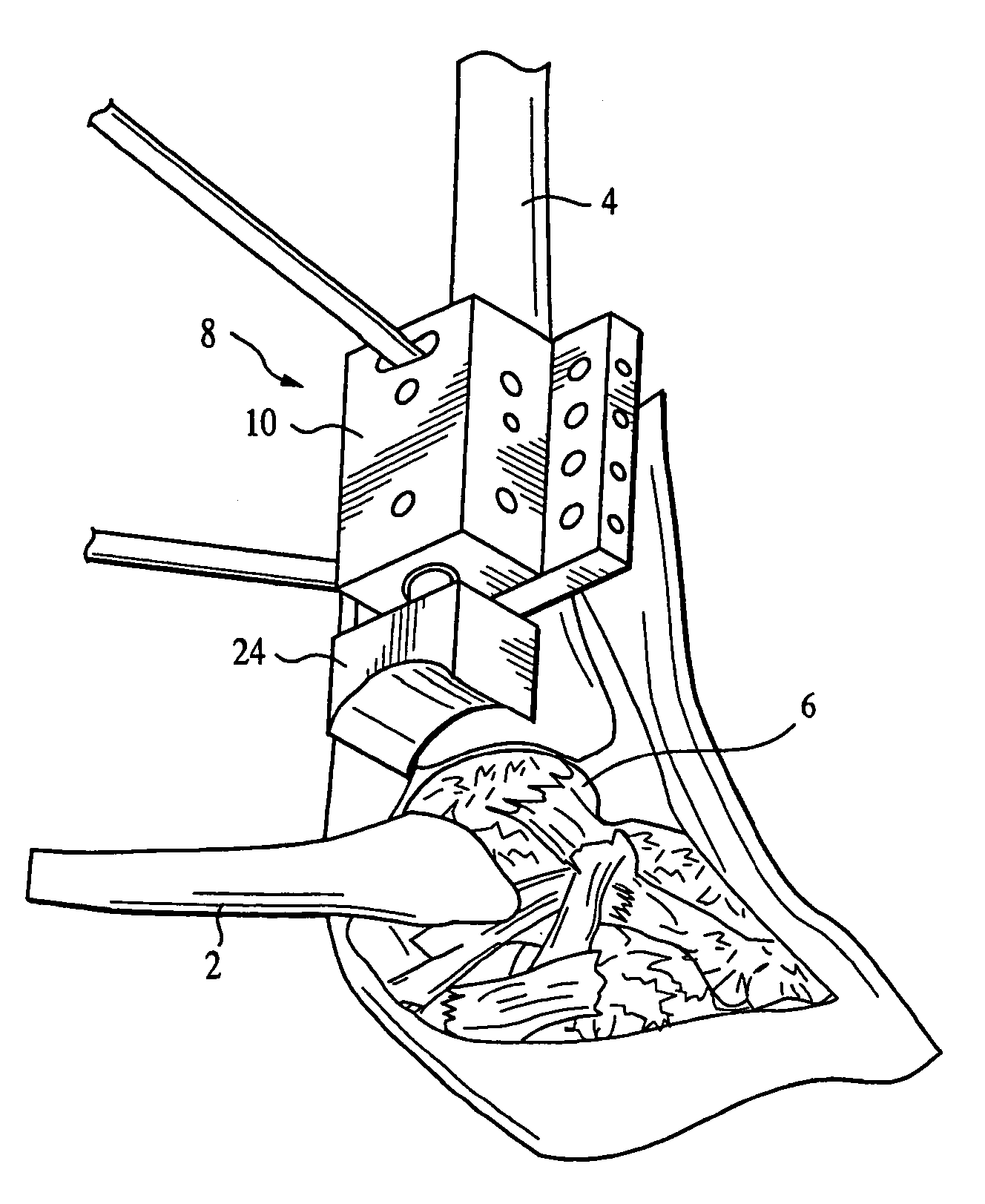
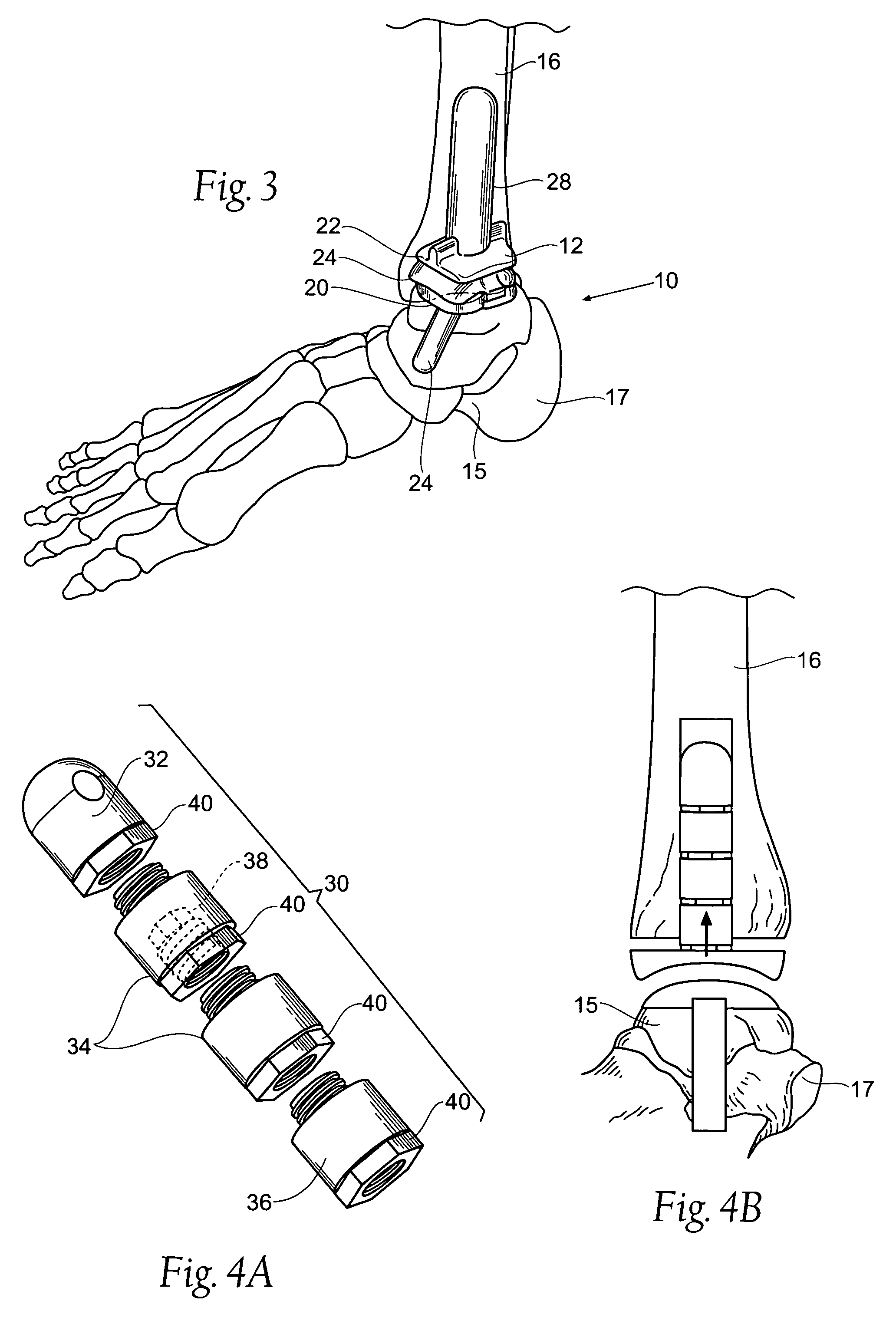
Ankle joint prosthesis and its method of implantation
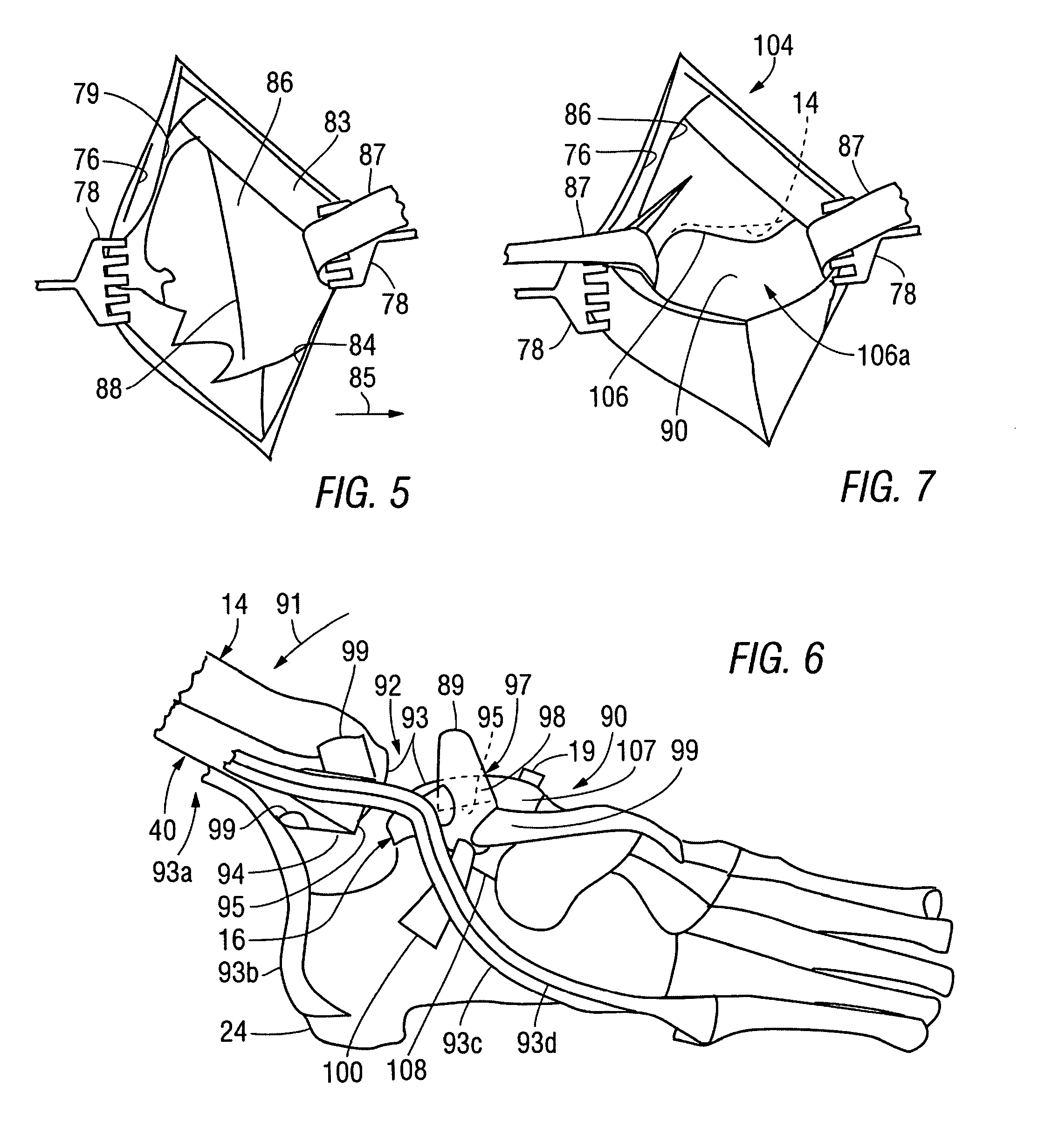
The ankle joint prosthesis adapted to involve the patient's distal tibia and talus has, according to the present invention, tibial, talar and mobile or semi-constrained bearing components that are laterally to medially implanted in the patient. The tibial component's top surface has convex curvature in its anterior to posterior plane and is configured so as to approximate and match with the curvature of a prepared portion of the distal tibia; its bottom surface being approximately flat. The talar component's top surface has saddle-shaped, convex curvature in its anterior to posterior plane, it's bottom surface has concave curvature and is configured so as to approximate and match with the curvature of a prepared portion of the talus. The mobile or semi-constrained bearing components have embodiments that comprise a wide variety of geometric shapes. A method for implanting such a prosthesis is also disclosed.
Owner:CONCEPTS & MEDICINE III
Ankle replacement system
ActiveUS20060229730A1Improved long-term resultPrecise positioningWrist jointsAnkle jointsCalcaneusAnkle joint replacement
A prosthesis suited for orthopedic implantation possesses a multi-piece stem component that supports an artificial joint surface that can articulate with another artificial joint surface in various ways. The prosthesis can be assembled in a snap fit and / or interlocking fashion that provides positive locking means without the use of screws or other fasteners. The prosthesis can accommodate fitment of a plastic joint surface made, e.g., from ultra high molecular weight polyethylene. The prosthesis is well suited for use in an ankle replacement system that can be installed using minimally invasive intramedullary guidance established with respect to the major axis of the tibia by minimally invasive access through the calcaneus, through an incision in the bottom of the foot. The prosthesis makes possible the installation of a total ankle system using minimally invasive anterior access to the ankle joint for making bony cuts and to install prosthesis components.
Owner:INBONE TECH
Semi-constrained ankle joint prosthesis and its method of implantation
The ankle joint prosthesis adapted to involve the patient's distal tibia and talus has, according to the present invention, tibial, talar and mobile or semi-constrained bearing components that are laterally to medially implanted in the patient. The tibial component's top surface has convex curvature in its anterior to posterior plane and is configured so as to approximate and match with the curvature of a prepared portion of the distal tibia; its bottom surface being approximately flat. The talar component's top surface has saddle-shaped, convex curvature in its anterior to posterior plane, it's bottom surface has concave curvature and is configured so as to approximate and match with the curvature of a prepared portion of the talus. The mobile or semi-constrained bearing components have embodiments that comprise a wide variety of geometric shapes. A method for implanting such a prosthesis is also disclosed.
Owner:SCHON LEW C +4
Ankle replacement system
ActiveUS7534246B2Function maximizationMaximize longevityWrist jointsAnkle jointsArticular surfacesAnkle joint replacement
A prosthesis suited for orthopedic implantation possesses a multi-piece stem component that supports an artificial joint surface that can articulate with another artificial joint surface in various ways. The prosthesis can be assembled in a snap fit and / or interlocking fashion that provides positive locking means without the use of screws or other fasteners. The prosthesis can accommodate fitment of a plastic joint surface made, e.g., from ultra high molecular weight polyethylene. The prosthesis is well suited for use in an ankle replacement system that can be installed using minimally invasive intramedullary guidance established with respect to the major axis of the tibia by minimally invasive access through the calcaneus, through an incision in the bottom of the foot. The prosthesis makes possible the installation of a total ankle system using minimally invasive anterior access to the ankle joint for making bony cuts and to install prosthesis components.
Owner:INBONE TECH
Osteotomy Guide and Method of Cutting the Medial Distal Tibia Employing the Same
InactiveUS20100069910A1Easy to replaceDiagnosticsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesAnkle joint replacementDistal tibia
An osteotomy guide is provided for cutting a bone, such as the medial distal tibia, to facilitate an ankle replacement. The osteotomy guide includes a positioning device having a number of fixation points, a first guide member structured to align with a first portion of the bone, in order to perform a first procedure, thereon, and a second guide member structured to align with a second portion of the bone, in order to perform a second procedure thereon. The fixation points engage the bone and maintain alignment of the first guide member with respect to the first portion during the first procedure, and maintain alignment of the second guide member with respect to the second portion during the second procedure, in order that the first procedure and the second procedure are substantially reproducible.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Ankle prosthesis and method for implanting ankle prosthesis
One embodiment of the present invention relates to an ankle prosthesis. Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a total ankle replacement prosthesis. Another embodiment of the present invention relates to an ankle replacement (partial or total) which is adapted, for example: (a) to treat arthritis of the ankle (e.g., ankle arthritis of any cause: after precious trauma; primary; malalignment induced; after hindfoot fusion; from recurrent ankle instability; rheumatoid or inflammatory arthritis; gout; local growth; dysplasia; growth plate arrest; avascular necrosis; hemophilia; distant septic event); (b) to revise a fused ankle; and / or (c) to treat trauma. The ankle replacement may be carried out by replacing one or more joint surfaces of an ankle joint. Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a method for inserting an ankle prosthesis.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
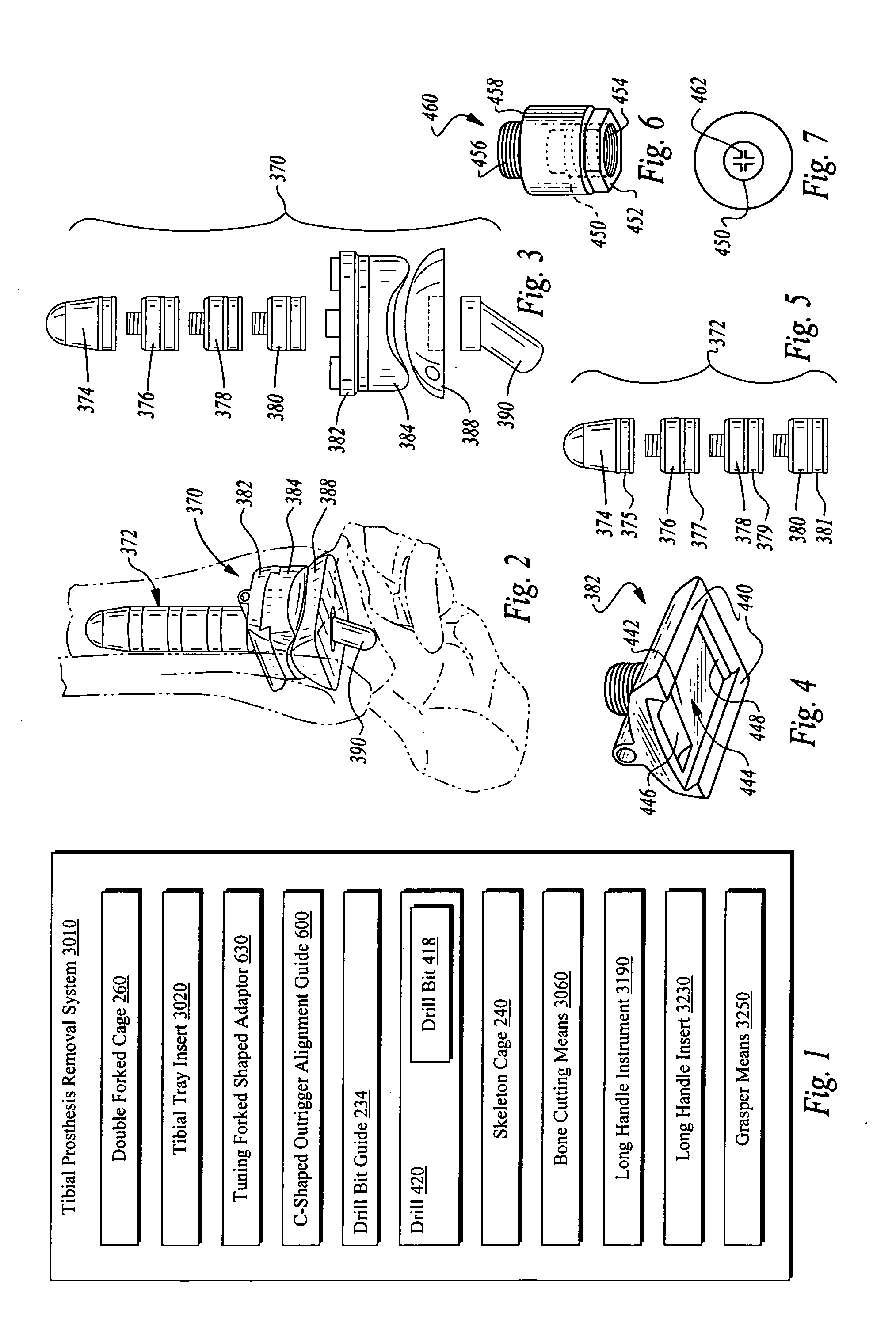
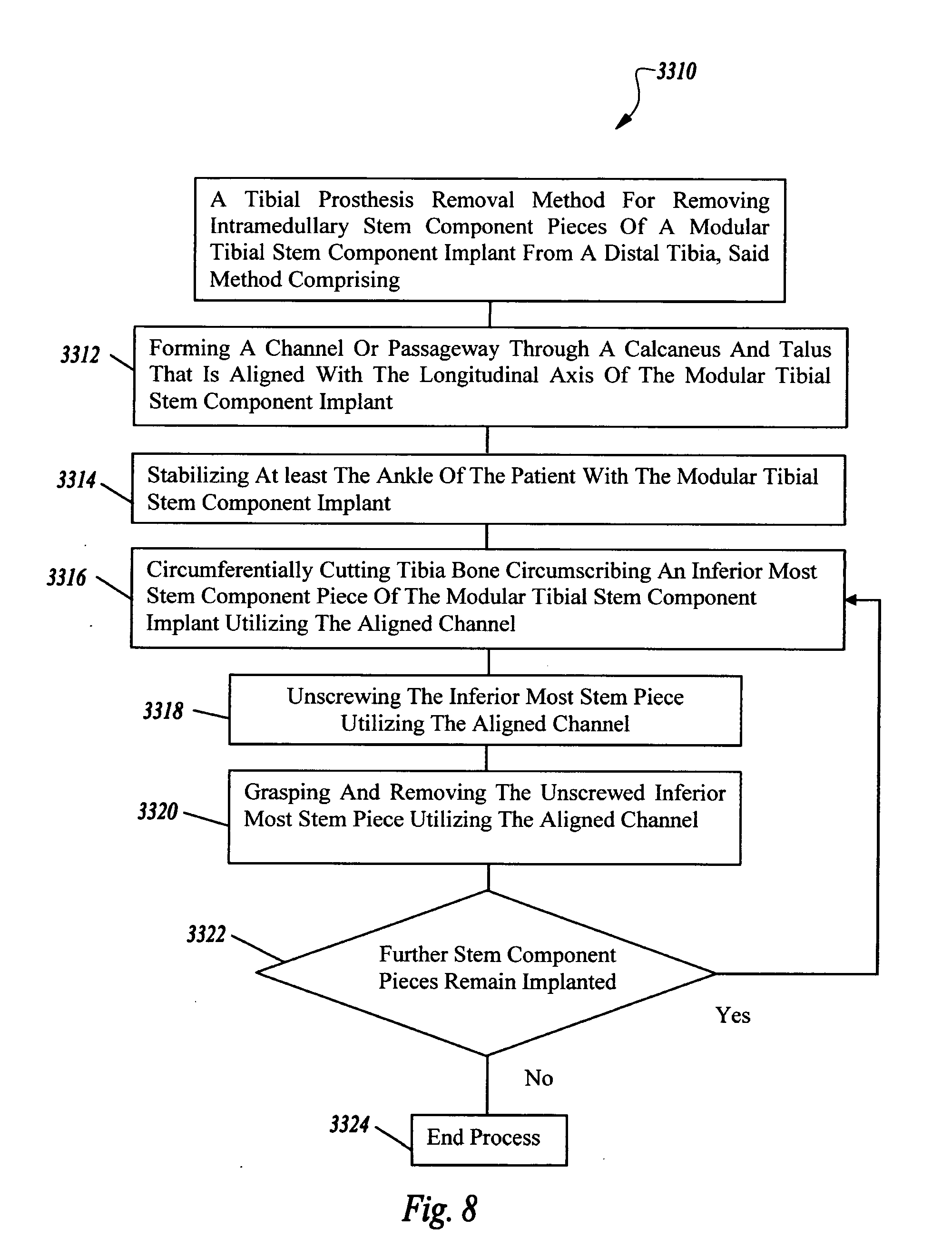
Systems and instrumentalities for use in removal of tibial prostheses of total ankle replacements
A system comprising instrumentalities and methods for removing intramedullary stem component pieces of a tibial implant from a distal tibia.
Owner:LIAN GEORGE JOHN
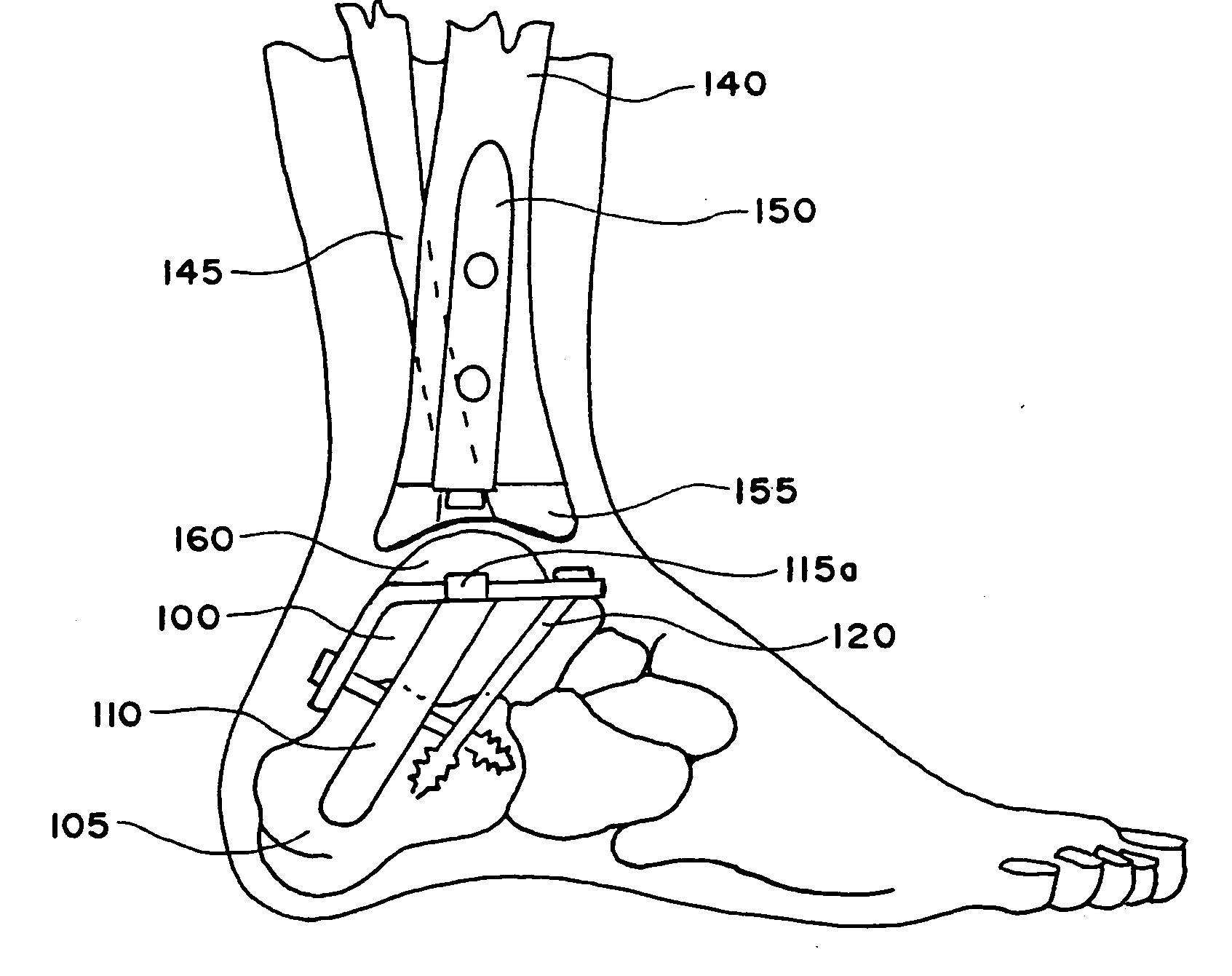
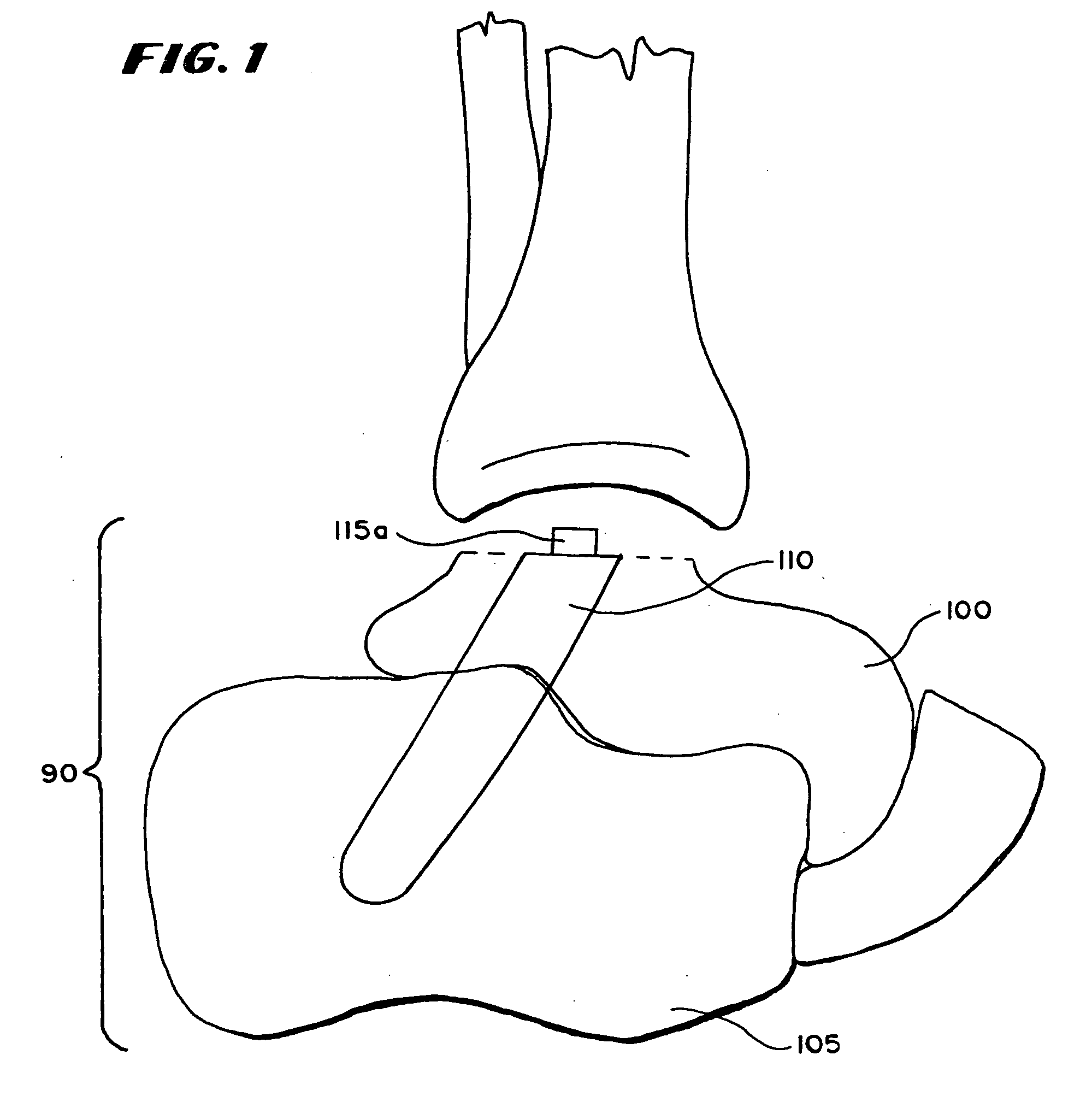
Ankle prosthesis for the arthrodesis of the calcaneum
ActiveUS20080195233A1Relief the painProvide supportAnkle jointsArtificial legsCalcaneusArticular surfaces
A prosthetic ankle assembly including an astragalar component with an upper articular surface that forms part of an ankle joint prosthesis and a lower surface with a shape adapted to engage an upper face of an astragalus. An astragalocalcanean rod is positioned in an astragalocalcanean channel extending from the lower face of the calcaneus to the upper surface of the astragalus. A first end of the astragalocalcanean rod is engage with the lower surface of the astragalar component and a second end of the astragalocalcanean rod is engaged with a lower region of the calcaneus. A distance between the second end of the astragalocalcanean rod is adjustable relative to the lower surface of the astragalar component to adjustably compress the calcaneus against the astragalus.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC +2
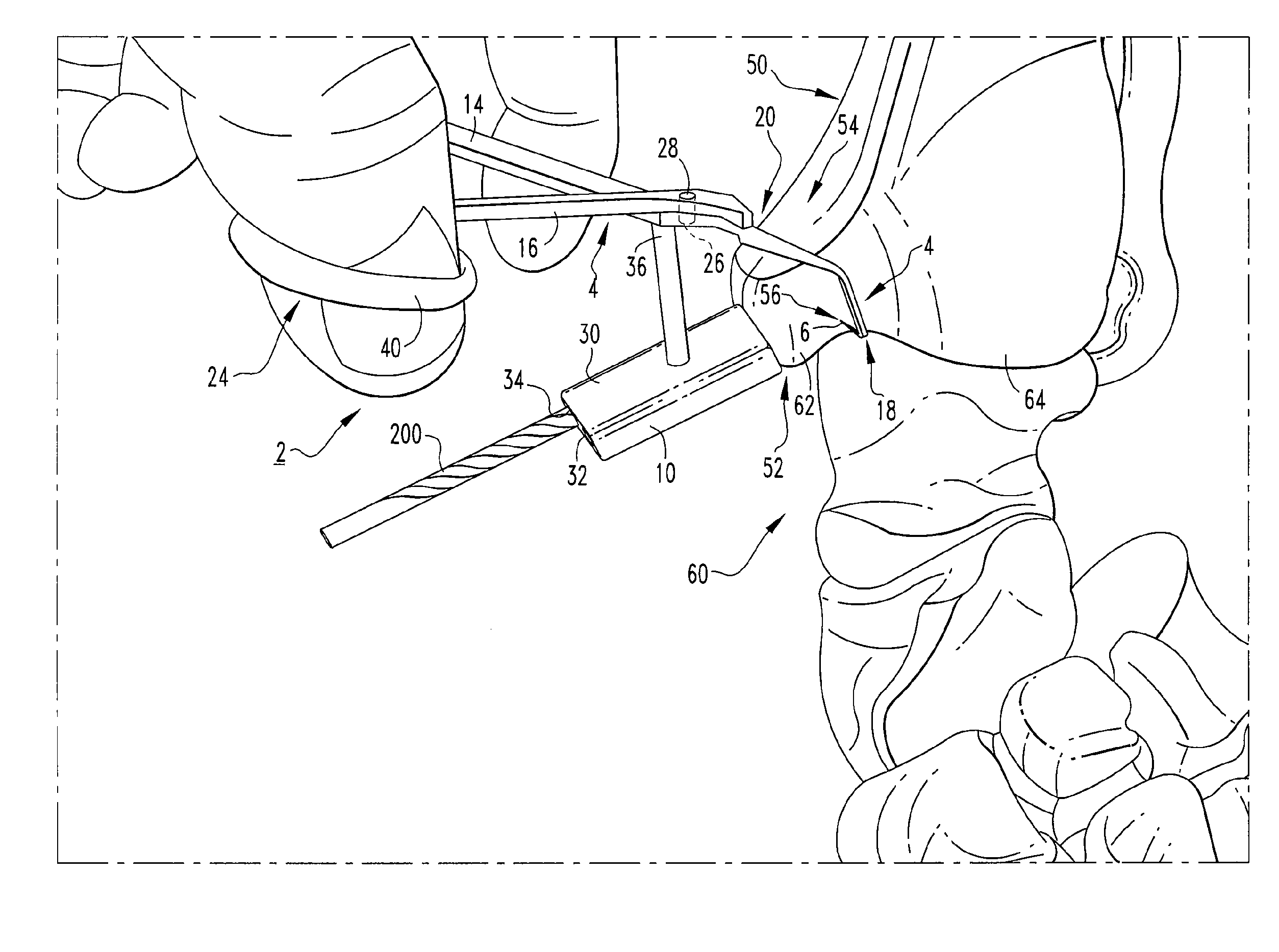
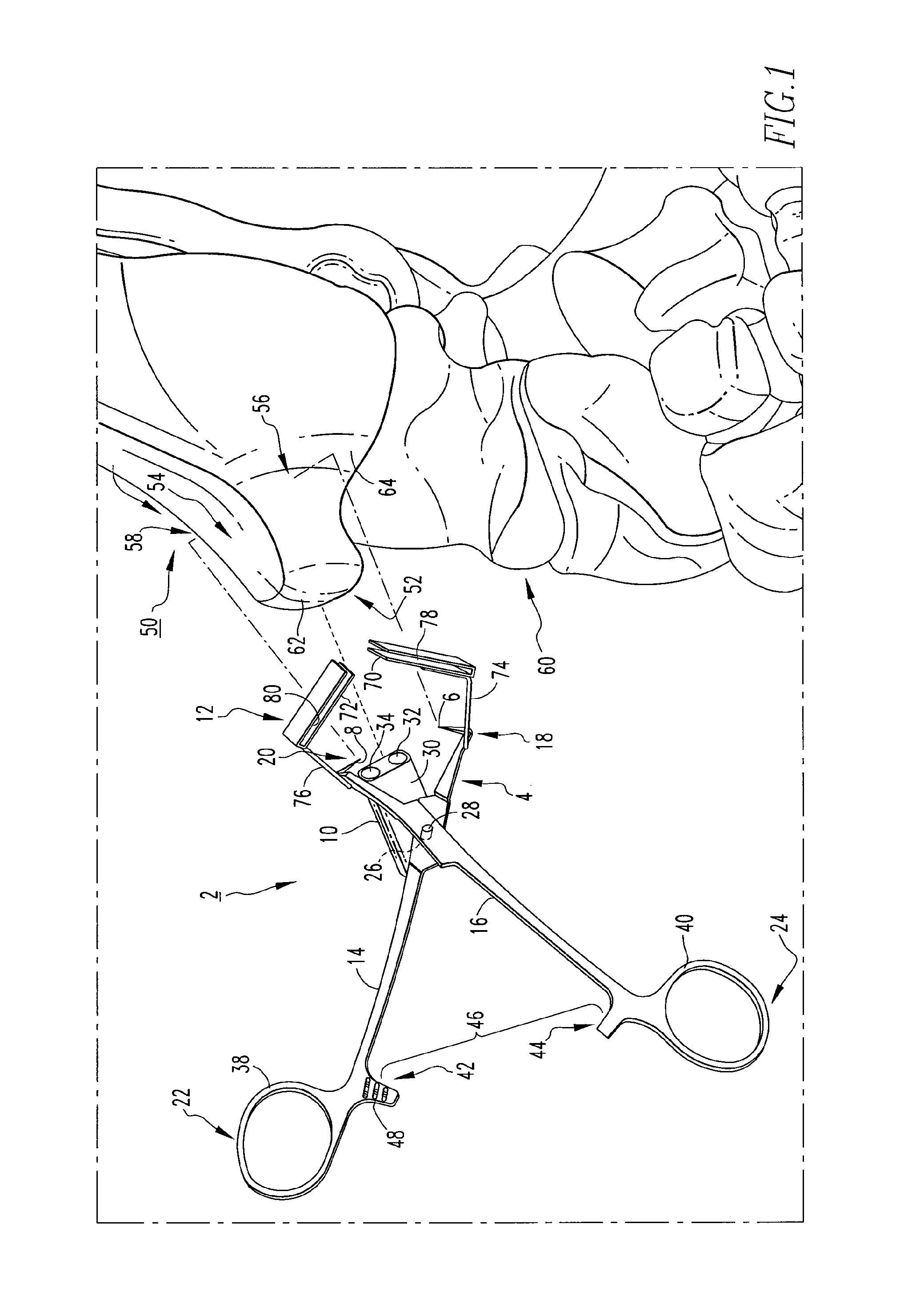
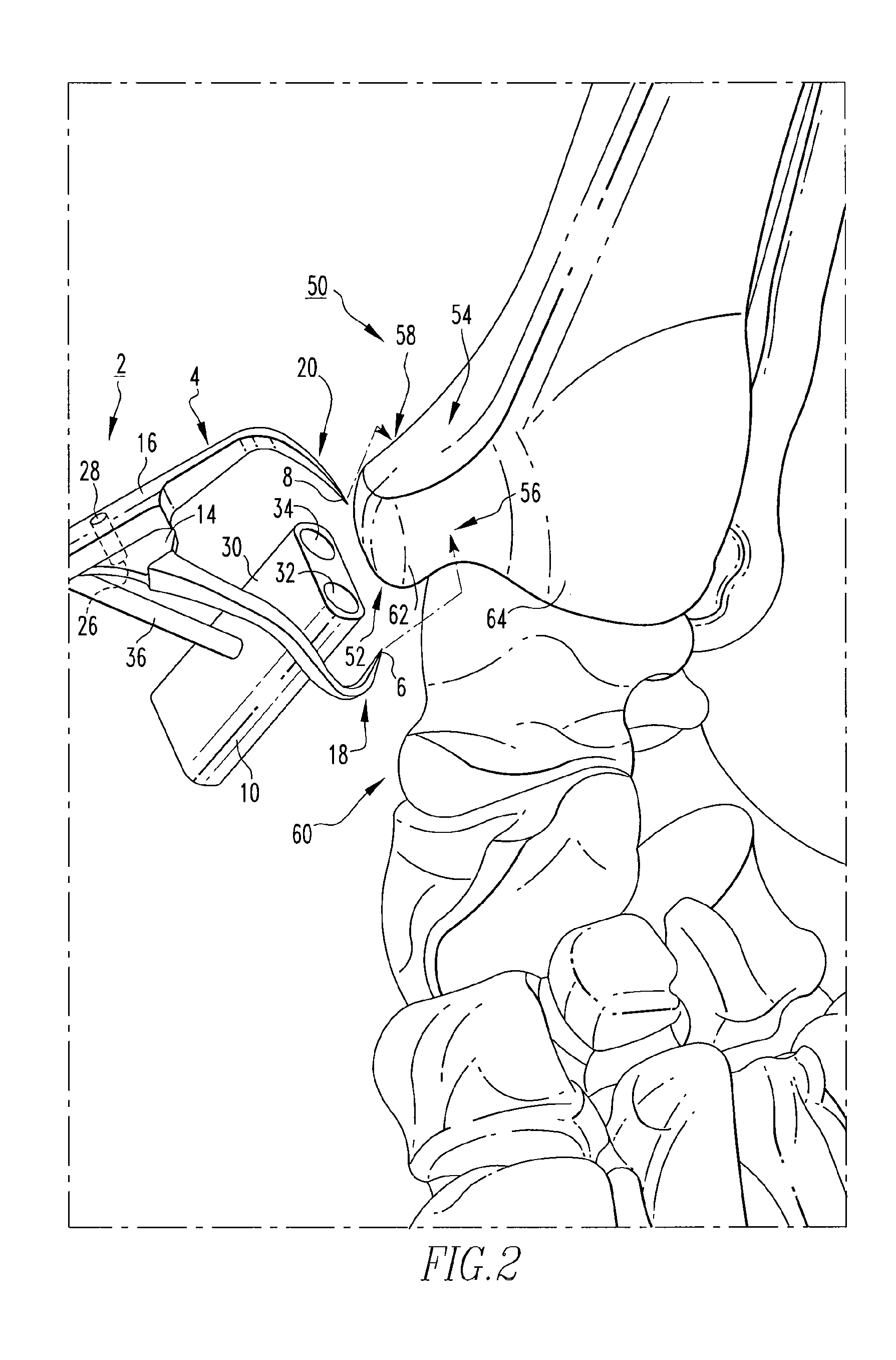
Systems and methods for installing ankle replacement prostheses
An ankle implant for use in ankle arthroplasty in total ankle replacement is provided. The implant includes an upper prosthesis anchored to the tibia and a lower prosthesis anchored to the talus. The lower prosthesis is operable associated with the upper prosthesis. The implant also includes a stem which is rigidly removably connected to the second member. The stem includes a portion for attachment to the calcaneous. The stem is be adapted to be in a first position in the calcaneous when the stem is in a first relative position with respect to the lower prosthesis, and to provide for a second position in the calcaneous when the stem is in a second relative position with respect to the lower prosthesis.
Owner:INBONE TECH
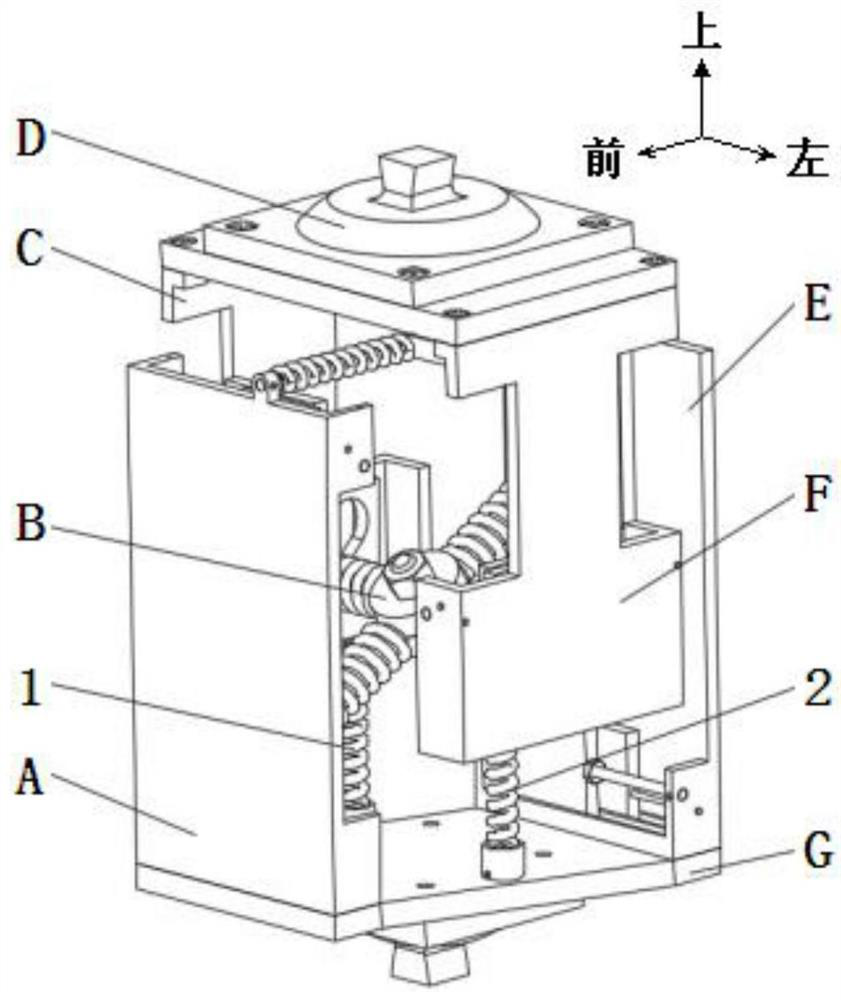
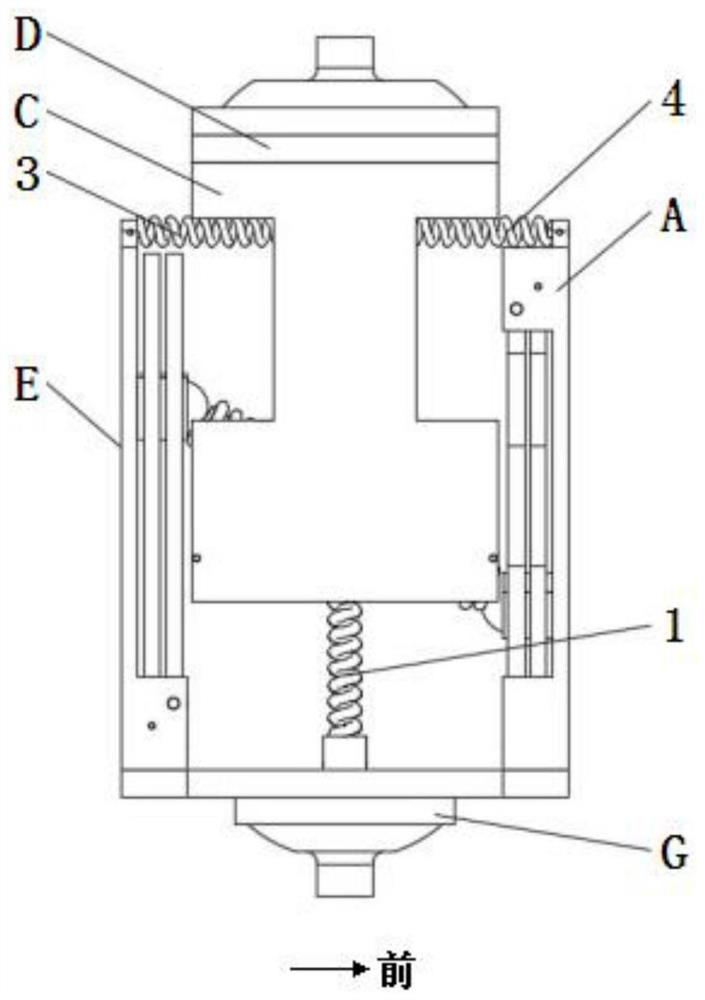
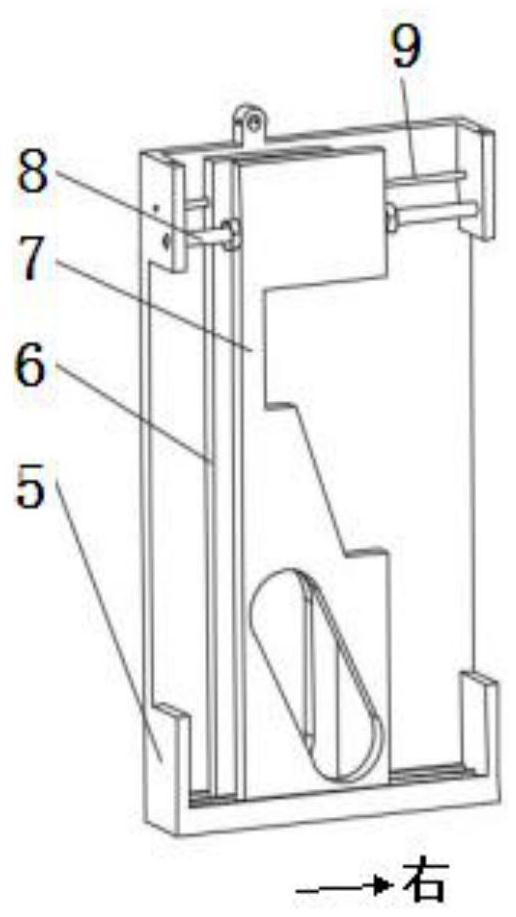
Active-passive type ankle joint prosthesis and movement mode thereof
The invention discloses an active-passive type two-degrees-of freedom ankle joint prosthesis, comprising a carbon fiber energy storage sole, a motor, a speed reducer, a motor fixing supporting seat, a belt pulley transmission device, a carbon fiber pipe, a ball screw, an energy storage springs, joint bearings, energy storage rubber rings and joint supporting seats, wherein the carbon fiber energy storage sole is connected with the carbon fiber pipe through the joint supporting seats; the motor fixing supporting seat is connected with the carbon fiber pipe through an active pin; the motor is fixedly arranged on one end of the motor fixing supporting seat; the ball screw is fixedly arranged on the other end of the motor fixing supporting seat; two ends of the motor fixing supporting seat are connected by the belt pulley transmission device; the energy storage springs areis connected with a ball screw nut; and the energy storage rubber rings are connected with the joint bearings and the joint supporting seats through a shaft. The ankle joint prosthesis provided by the invention not only can completely provide required energy for human gait, but also can adapt to various landforms; in addition, the ankle joint prosthesis can completely imitate movement angles of a human ankle joint on a sagittal plane or a coronal plane; and therefore, the normal walking requirement of an amputation patient can be satisfied better.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Systems and Methods for Installing Ankle Replacement Prostheses
InactiveUS20120010719A1Reduce generationWrist jointsInternal osteosythesisAnkle joint replacementCalcaneus
An ankle implant for use in ankle arthroplasty in total ankle replacement is provided. The implant includes an upper prosthesis anchored to the tibia and a lower prosthesis anchored to the talus. The lower prosthesis is operable associated with the upper prosthesis. The implant also includes a stem which is rigidly removably connected to the second member. The stem includes a portion for attachment to the calcaneous. The stem is be adapted to be in a first position in the calcaneous when the stem is in a first relative position with respect to the lower prosthesis, and to provide for a second position in the calcaneous when the stem is in a second relative position with respect to the lower prosthesis.
Owner:INBONE TECH
Active-passive combined low-power-consumption ankle joint prosthesis
InactiveCN103006357AReduce power consumptionMeet the actual requirements of sportsArtificial legsDorsal flexionBiomechanics
The invention discloses an active-passive combined low-power-consumption ankle joint prosthesis, belonging to the technical field of prosthetics and orthotics. The active-passive combined low-power-consumption ankle joint prosthesis comprises a support frame mechanism, an active driving mechanism, an ankle shaft joint mechanism, a series elastic driving mechanism, a parallel spring mechanism and an elastic foot plate mechanism, wherein the support frame mechanism is located above the elastic foot plate mechanism, and the drive part of the ankle joint prosthesis is an active-passive combined drive system formed by combining the active drive mechanism, the ankle shaft joint mechanism, the series elastic driving mechanism and the parallel spring mechanism. According to the invention, the energy storage and energy release functions of the series elastic driving mechanism and the parallel spring mechanism are utilized fully, the active driving mechanism is used for driving only in a proper period in a traveling process, that is, a motor is used for driving only in a dorsal flexion stage, so that the entire ankle joint prosthesis has the advantage of low power consumption; and in addition, the active-passive combined low-power-consumption ankle joint prosthesis is designed according to exercise bionics based on human motion biomechanical studies, can meet the actual requirements of human motion and is simple in structure.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
Intramedullary guidance systems and methods for installing ankle replacement prostheses
InactiveUS20050124995A1Guaranteed long-term resultsEasy to cutInternal osteosythesisAnkle jointsCalcaneusGuidance system
Intramedullary guidance systems and methods introduce some and / or all surgical tools and ankle prostheses components through the tibia, using minimal invasive exposure in the tibia tubercle, or retrograde through the talus, using minimal invasive exposure in planar surface of the calcaneus. The systems and methods align the talus and tibia for the installation of one or more ankle prostheses components, and also maintain that alignment during the installation using intramedullary guidance, e.g., by use of a guide pin to form an intramedullar passage along which surgical tools and prosthetic components are guided.
Owner:INBONE TECH
Combined tumor-type ankle joint prosthesis
The invention relates to a combined tumor-type ankle joint prosthesis which comprises an ankle bone side component, a polyethylene liner and a top component. Three backward down inclined ridges are formed at the bottom of the ankle bone side component in a projecting manner, an arched sliding surface is formed at the top of the ankle bone side component, a T-shaped projection is transversely arranged at the top of the polyethylene liner, the bottom of the polyethylene liner is recessed inwards to form a joint fossa for containing the sliding surface, the top component is provided with an upper connecting surface for connecting the top component with a tibial prosthesis, a T-shaped groove for containing the projection is transversely formed in the bottom of the top component, five through holes for repairing ligaments on the inner side and the outer side of an ankle joint are formed in the top component in a front and rear penetrating manner, the inner side of the top component extends downwards to form a projecting ridge, and the projecting ridge is abutted to the inner side face of the polyethylene liner. The prosthesis is reasonable in structural design, preparation and surgical operation are facilitated, stability of an artificial ankle joint is enhanced, loading and moving functions of the ankle joint are restored, and the prosthesis is suitable for limb salvage treatment of distal tibial malignant tumors.
Owner:SHANGHAI TENTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Dynamic knee joint, dynamic ankle joint prosthesis and dynamic lower-limb prosthesis
InactiveCN102793596AFulfill exercise requirementsFulfilling Geometry RequirementsArtificial legsShock testingPhysical medicine and rehabilitationKnee Joint
The invention discloses a dynamic knee joint, a dynamic ankle joint prosthesis, and a dynamic lower-limb prosthesis containing the dynamic knee joint and ankle joint prosthesis. The dynamic joint prosthesis comprises a U-shaped component, wherein a bottom plate of the U-shaped component is connected with an upper part component to form one rotation pair; two lateral plates of the U-shaped component are connected with a lower part component to form the other rotation pair; hard bosses are arranged on the bottom plate and the lateral plates of the U-shaped component for spacing, and a soft baffle is adhered to the outer side of each hard boss for buffer vibration; and an angular displacement sensor is arranged through a sensor assembly bracket to realize real-time measurement to joint angular displacement. According to the dynamic lower-limb prosthesis, motion in multiple degrees of freedom can be realized, the joint damping is adjustable, the limb posture can be maintained, and the motion angle can be measured in real time.
Owner:AVIATION MEDICINE INST AIR FORCE PLA
Ankle replacement system
A total ankle replacement system, novel surgical method for total ankle replacement, and novel surgical tools for performing the surgical method are described. The total ankle replacement system includes the calcaneus in fixation of a lower prosthesis body, thereby significantly increasing the amount of bone available for fixation of the lower prosthesis body and allowing the lower prosthesis body to be anchored with screws. The total ankle replacement system further includes a long tibial stem which can also be anchored into the tibia with, for example, screws, nails, anchors, or some other means of attachment. The novel surgical arthroscopic method allows introduction of ankle prostheses into the ankle joint through an exposure in the tibial tubercle. Various novel surgical instruments, such as a telescoping articulating reamer and a talo-calcaneal jig, which facilitate the novel surgical method, are also described.
Owner:INBONE TECH
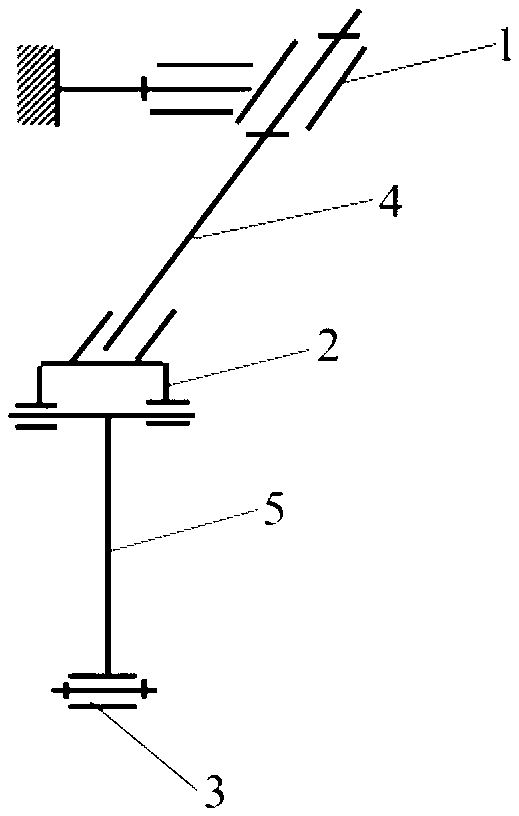
Polycentric powered ankle prosthesis
Systems and methods are disclosed for a powered ankle prosthesis. The prosthesis may comprise a polycentric mechanism having a defined path for an instantaneous center of rotation. The path of the instantaneous center of rotation may be defined by a trajectory substantially equal to an arc positioned over a joint of the polycentric mechanism.
Owner:REHABILITATION INST OF CHICAGO
Joint axis angle adjustable type multi-axis ankle joint prosthesis
ActiveCN111714259AImprove fit lowHigh energy consumptionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsProsthetic limbBiomedical engineering
The invention discloses a joint axis angle adjustable type multi-axis ankle joint prosthesis, and belongs to the technical field of bionic human prostheses. The joint axis angle adjustable type multi-axis ankle joint prosthesis is composed of a front part, a joint axis part, a left part, an upper cover, a rear part, a right part, a bottom cover and four springs, wherein the joint axis part is positioned in a space defined by the front part, the left part, the upper cover, the rear part, the right part and the bottom cover; the space angle of the joint axis below is adjusted by adjusting the positions of groove plates in the front part and the rear part; and the space angle of the ankle joint axis is adjusted by adjusting the positions of groove plates in the left part and the right part, and therefore the prosthesis can be attached to the human ankle joint structure to a larger extent. Different ankle joint axis angles can be adjusted for different wearers, and therefore the comfort degree of the wearers is improved, the movement coordination of the affected side limb and the normal side limb of the wearers is improved, the environment adaptability is improved, the joint axis angleadjustable type multi-axis ankle joint prosthesis can adapt to different road surface changes, and the energy consumption of the wearers is reduced.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
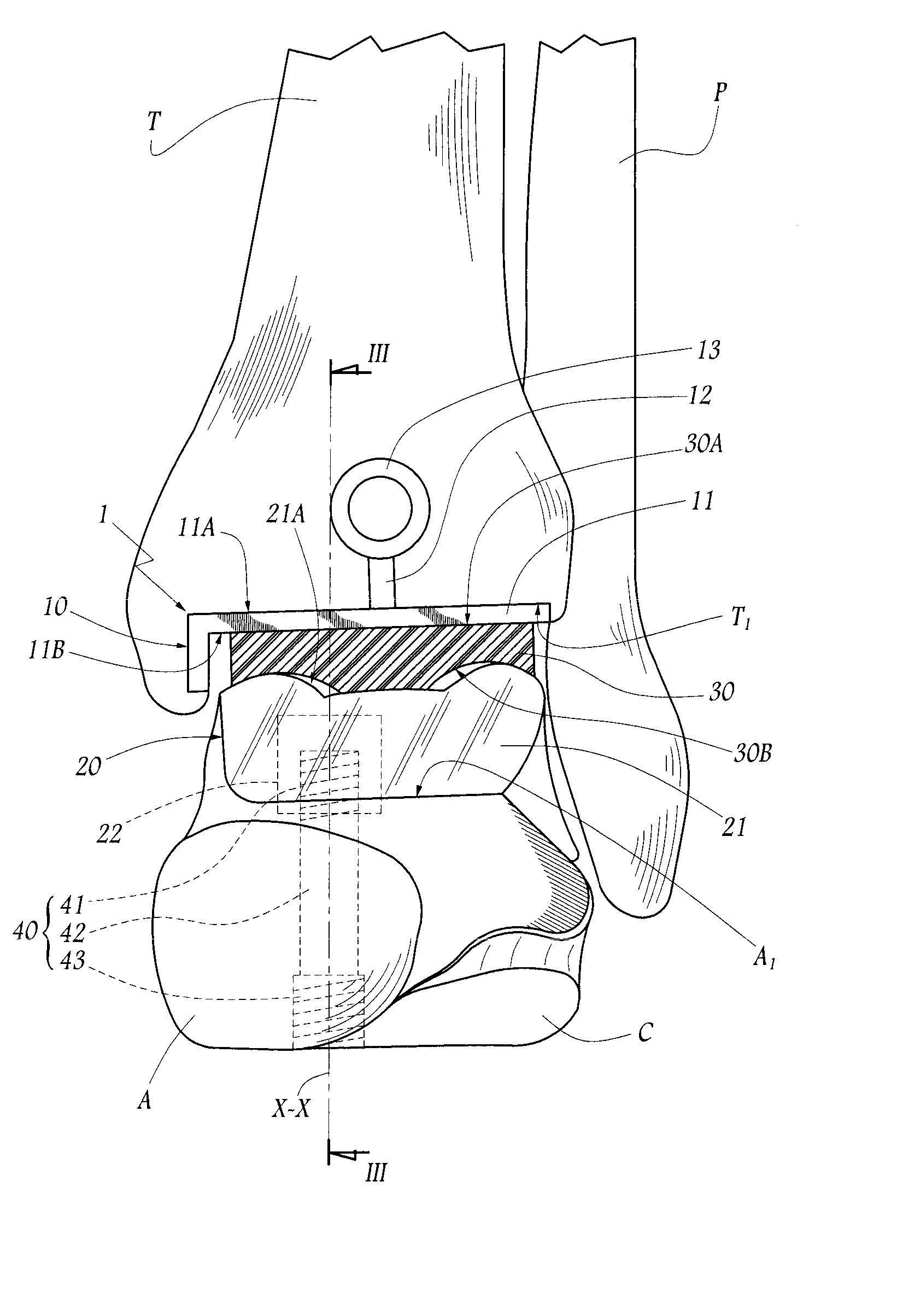
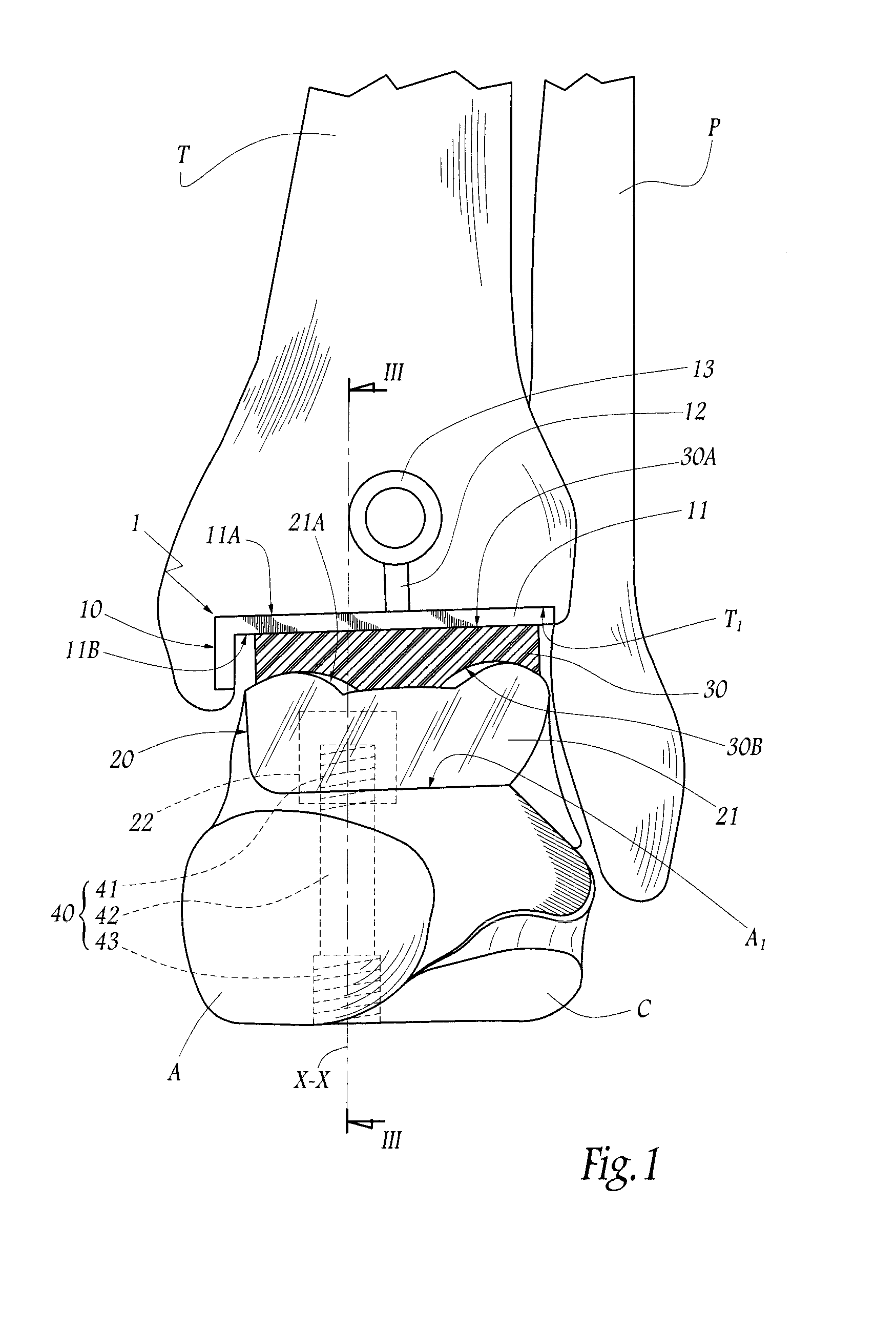
Total ankle replacement
ActiveUS9132018B1Avoid bendingIncrease pressureAnkle jointsJoint implantsCalcaneusAnkle joint replacement
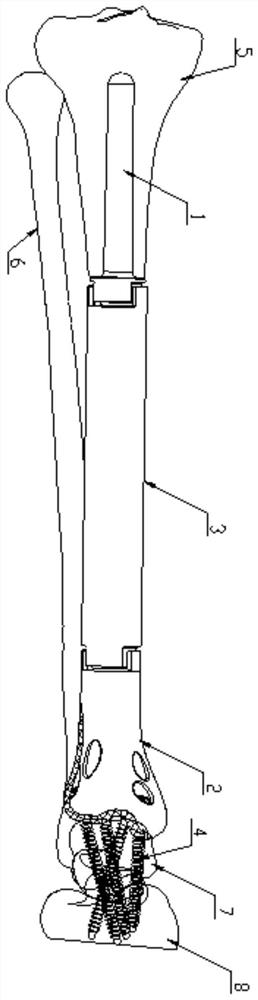
An ankle replacement prosthesis includes a tibial component, attached within a cavity formed in the tibia, and a talocalcaneal component, attached within a slot formed within a talocalcaneal compound, previously formed by fusing the talus and the calcaneus. Preferably, the talocalcaneal component includes a neck, to which a head, having a contact surface engaging a contact surface within the tibial component, is adjustably attached. These contact surfaces may both be spherical, with the contact surface of the talocalcaneal component being formed as a ball fitting within a socket formed by the contact surface of the tibial component, or these contact surfaces may include mating feature that limit inversion / eversion rotation of the foot, while providing for dorsal / plantar rotation thereof.
Owner:ZOYA
Tibia far-end ankle joint prosthesis
PendingCN111870409AImprove stabilityPromote ingrowthAnkle jointsJoint implantsEntire tibiaBone marrow cavity
The invention provides a tibia far-end ankle joint prosthesis. The tibia far-end ankle joint prosthesis comprises a medullary cavity extension handle, a far-end ankle joint and a backbone extension section, wherein the backbone extension section is mounted between the medullary cavity extension handle and the far-end ankle joint, the medullary cavity extension handle is connected with a medullarycavity at the near end of a tibia, and a 3D printing bone trabecula structure is arranged on the contact surface of the far-end ankle joint, talus and fibula. A locking nail is inserted into the nailhole of the far-end ankle joint to be connected with the talus and the fibula, so that the far-end ankle joint is fixedly connected with the talus and the fibula. The tibia far-end ankle joint prosthesis is suitable for ankle joint prosthesis replacement of a tibia far-end tumor excision patient, the 3D printing bone trabecula structure can effectively promote bone ingrowth, the prosthesis is morestable in combination with a locking nail, and the ankle joint prosthesis is high in initial bone ingrowth speed and good in medium and long term stability; And when the tibia far-end ankle joint prosthesis is used, the whole tibia does not need to be replaced, the intact tibia is reserved, only the tibia with a focus is replaced, the length of the prosthesis is suitable for each patient due to the arrangement of the backbone extension section, and the manufacturing cost is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING LIDAKANG TECH
Ankle replacement devices and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS9144500B2Minimizing length variation of the lower extremitiesReliable replacementAnkle jointsJoint implantsAnkle replacementBiomedical engineering
Owner:HARDING JR MICHAEL G
Anatomical ankle prosthesis with fixing pad
ActiveCN107374788ALight in massQuality improvementAnkle jointsJoint implantsArticular surfacesIsosceles trapezoid
The invention discloses an anatomical ankle prosthesis with a fixing pad. The anatomical ankle prosthesis comprises a tibia side component, the fixing pad and a talus side component and is characterized in that the top end of the tibia side component is provided with an upper supporting surface, four projection first dowels are fixedly arranged at four corners of the upper supporting surface respectively, and the middle of the tibia side component is fixedly connected to the bottom middle of an amputated tibia far end through a recess screw. The anatomical ankle prosthesis has advantages that the middle of the tibia side component is fixedly connected to a talus far end through the recess screw while the upper supporting surface are fixedly connected with the tibia far end through the four first dowels respectively, the four first dowels are in isosceles trapezoidal arrangement, stability in connection between the tibia side component and the amputated tibia far end is achieved, a lower slide surface at the bottom end of the fixing pad is in slide connection with an upper slide surface at the top end of the talus side component, and the upper supporting surface, the lower slide surface and the upper slide surface are all arc and matched with an articular surface of the tibia far end in radian to make the prosthesis better accord with a real human ankle structure.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Ankle Replacement Devices and Methods of Making and Using the Same
ActiveUS20140180427A1Minimizing length variation of the lower extremitiesReliable replacementAnkle jointsJoint implantsAnkle joint replacementBiomedical engineering
Owner:HARDING JR MICHAEL G
All-organic high molecular material ankle joint prosthesis
The invention relates to an all-organic high molecular material ankle joint prosthesis which comprises a tibia support prosthesis, a tibia pad and an anklebone prosthesis. The tibia support prosthesis is connected with the tibia pad, the tibia pad is connected with the anklebone prosthesis, and the tibia support prosthesis and the anklebone prosthesis are both formed by poly(ether ether ketone) (PEEK) or derivatives of the poly(ether ether ketone) (PEEK); the tibia pad is formed by ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE). According to the all-organic high molecular material ankle joint prosthesis, inner plant parts are composed of high molecular materials, and therefore the problems of metal corrosion and the allergy and toxicity which are possibly caused by metal are solved; the elasticity modulus of the PEEK materials is matched with that of the natural bones, and therefore stress shieding problem is solved; the abrasion of the prosthesis on the sliding friction surface of the cartilago articularis is reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU SINOMED BIOMATERIALS CO LTD
Ankle replacement system and method
Various surgical devices and methods are disclosed herein. Also disclosed is multi- component prosthesis, which can be used as an ankle prosthesis. One of the disclosed surgical alignment systems includes a guide arm, a ratchet arm frame configured to be coupled slidably to the guide arm, a ratchet arm configured to be coupled to the ratchet arm frame, and a sagittal sizing guide body configured to be coupled to the ratchet arm. The sagittal sizing guide body includes a first radiopaque object disposed at a first position and a second radiopaque object disposed at a second position that is spaced apart from the first position.
Owner:WRIGHT MEDICAL TECH
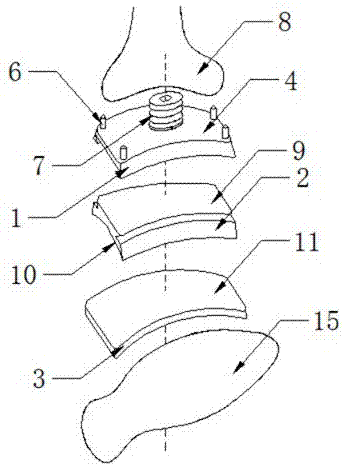
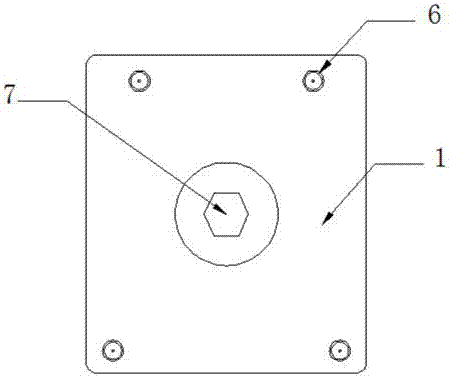
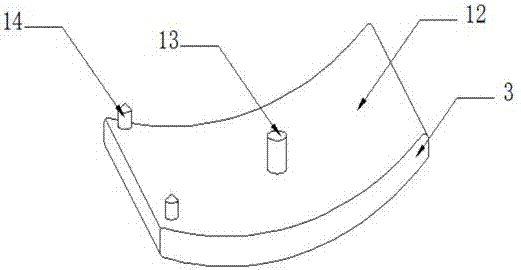
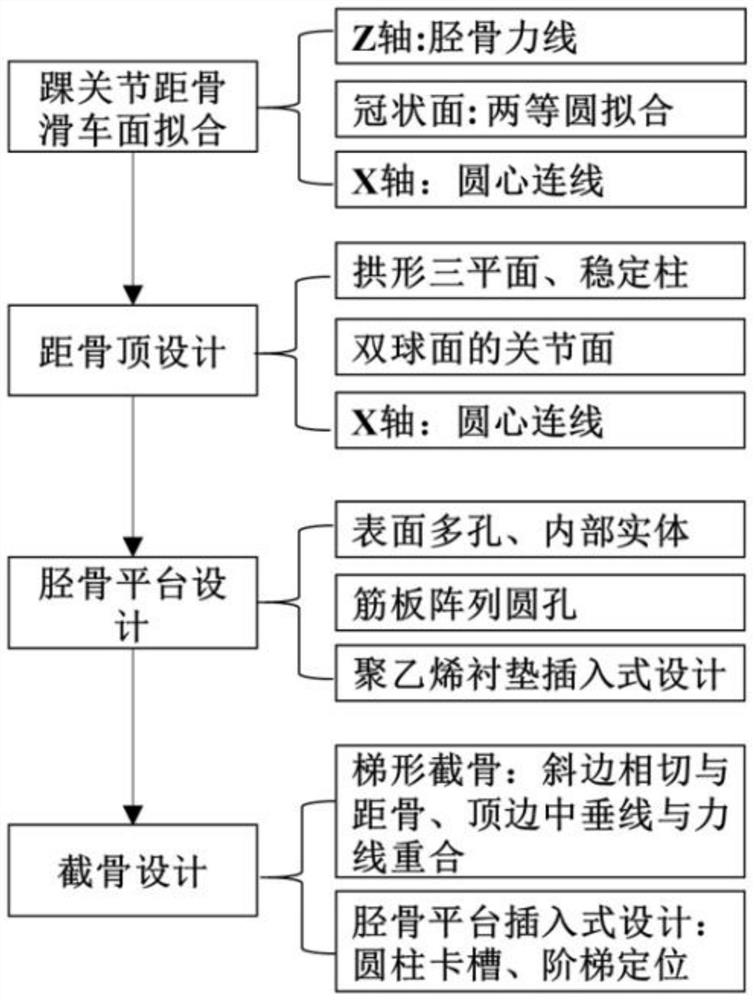
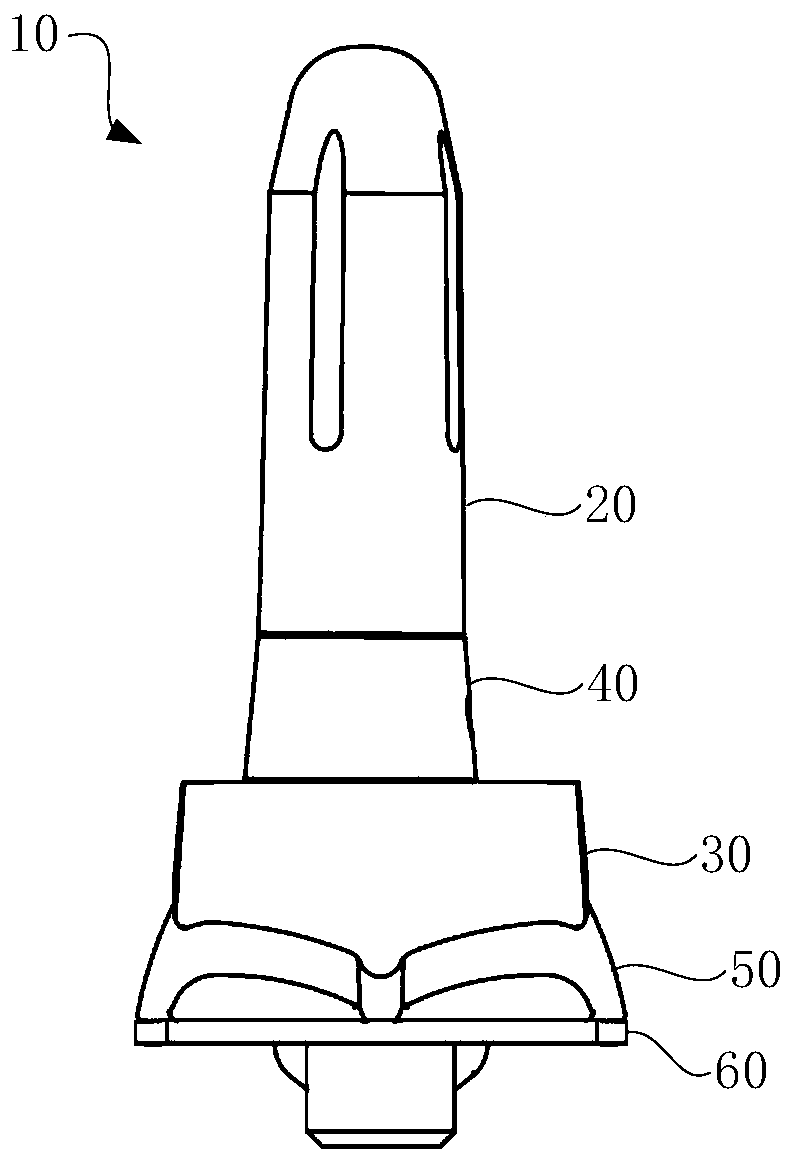
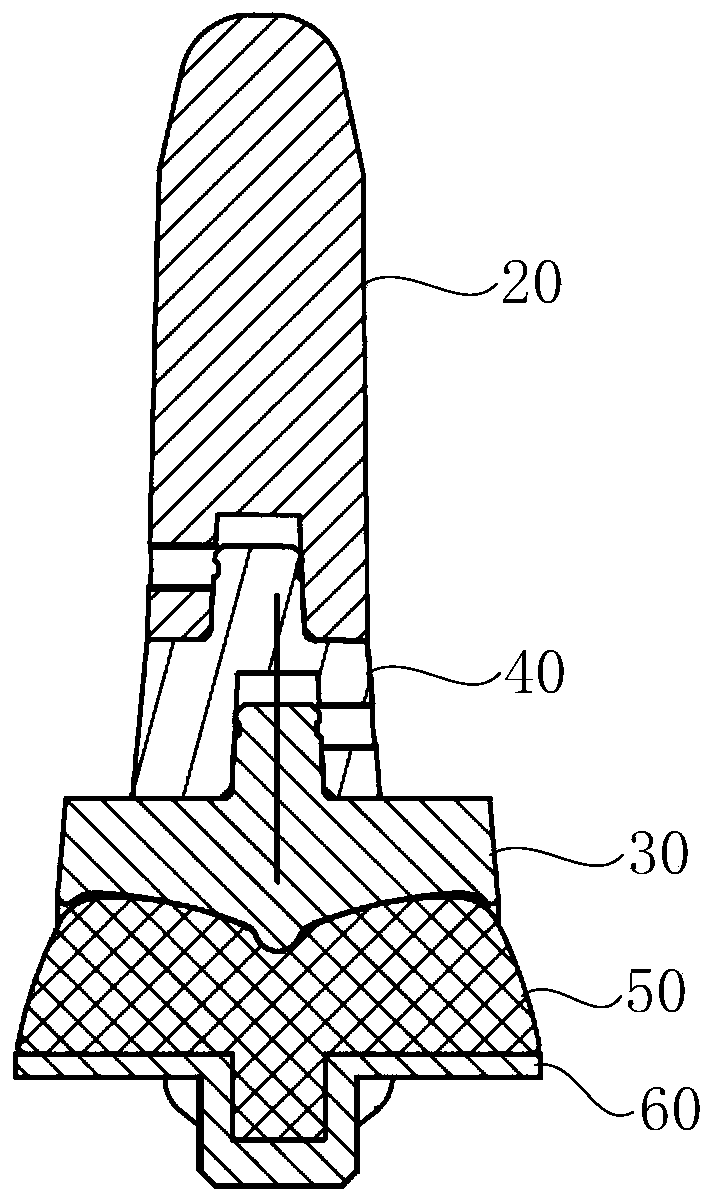
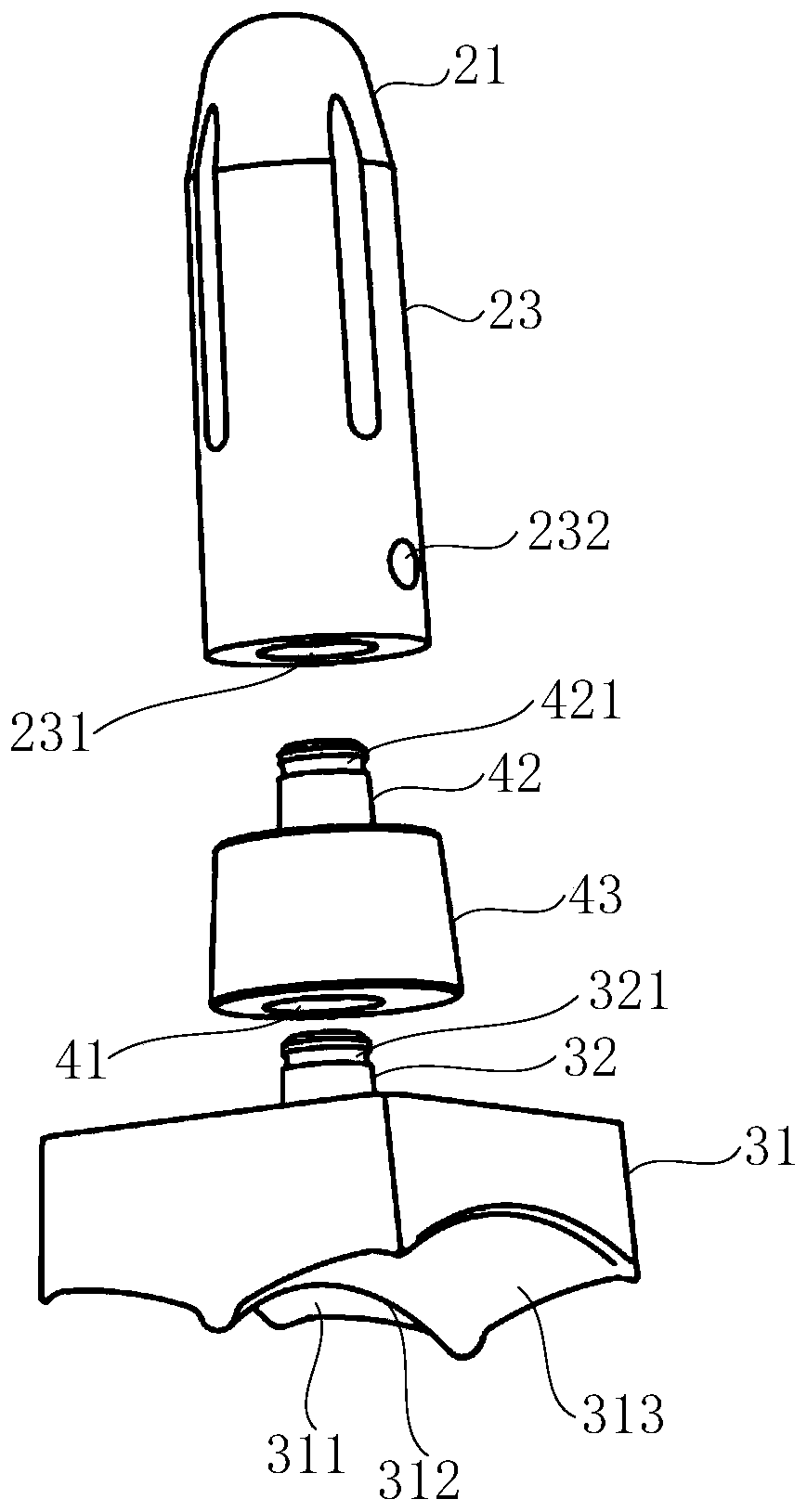
Ankle joint prosthesis and design method
PendingCN113616393ABiomechanical structureHigh forming precisionAnkle jointsJoint implantsHuman bodyBiomechanics
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, and particularly discloses an ankle joint prosthesis and a design method. The ankle joint prosthesis comprises a tibia platform, a polyethylene liner and a talus top, the polyethylene liner is arranged at the lower end of the tibia platform, the talus top is arranged below the polyethylene liner, and the tibia platform and the talus top are formed through powder bed metal additive manufacturing. According to the ankle joint prosthesis and the design method, the tibia platform and the talus top which are manufactured and formed through powder bed metal additive manufacturing are high in forming precision, good in surface quality and excellent in performance, the tibia platform, the polyethylene liner and the talus top are matched with one another to form the ankle joint prosthesis, and the ankle joint prosthesis and the design method has the advantages of being more in line with the human body biomechanical structure, good in adaptability, capable of avoiding stress shielding. Bone tissue growth lacks stress stimulation and force conduction, and long-term implantation is facilitated.
Owner:重庆熙科医疗科技有限公司
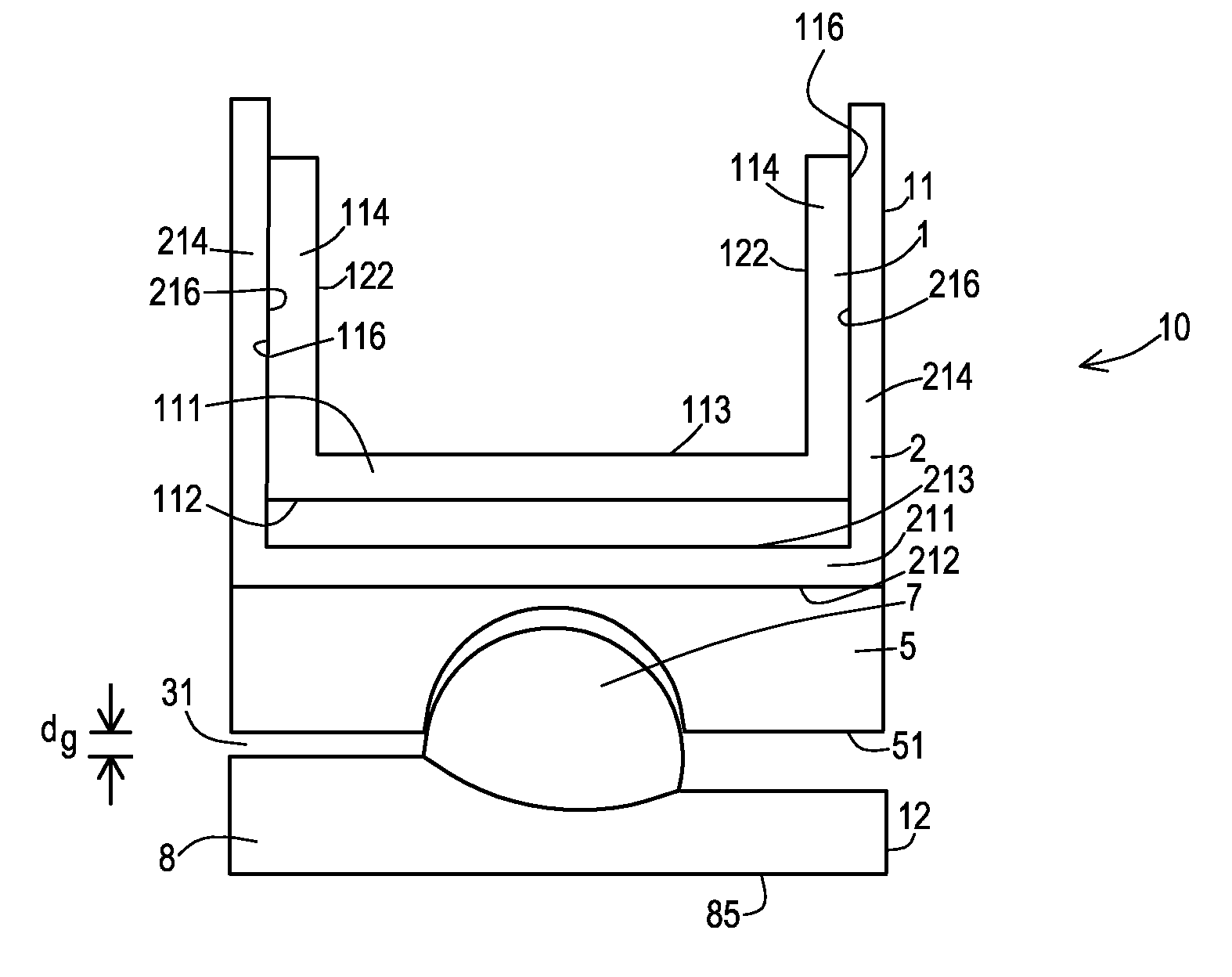
Ankle joint prosthesis
PendingCN110840635ASolve the problem of not being able to adapt to different tibial medullary cavity shapesImprove stabilityAnkle jointsJoint implantsHuman bodyPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention provides an ankle joint prosthesis. The ankle joint prosthesis comprises a tibial stem, a distal tibial prosthesis and a tibial connector. The tibial stem is used for being disposed in atibial marrow cavity of a human body. The tibial connector is disposed between the tibial stem and the distal tibial prosthesis, so as to connect the tibial stem with the distal tibial prosthesis through the tibial connector. The tibial connector comprises a first connection portion and a second connection portion, the second connection portion is used for being connected with the tibial stem, and the first connection portion is used for being connected with the distal tibial prosthesis. A first center line of the first connection portion is parallel to a second center line of the second connection portion, the tibial connector is rotated relative to the distal tibial prosthesis to adjust the position of the second center line relative to a center line of the distal tibial prosthesis, theposition of the tibial stem relative to the distal tibial prosthesis is further adjusted, and accordingly, the tibial stem can well adapt to different bone marrow cavity shapes.
Owner:BEIJING AKEC MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com