Porous spacers, instruments, and methods for foot and ankle fusion
a technology of porous spacers and fusion joints, applied in the field of foot and ankle fusion, can solve the problems of time-consuming and difficult to reproduce custom shaping, and limited strength of bone grafts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
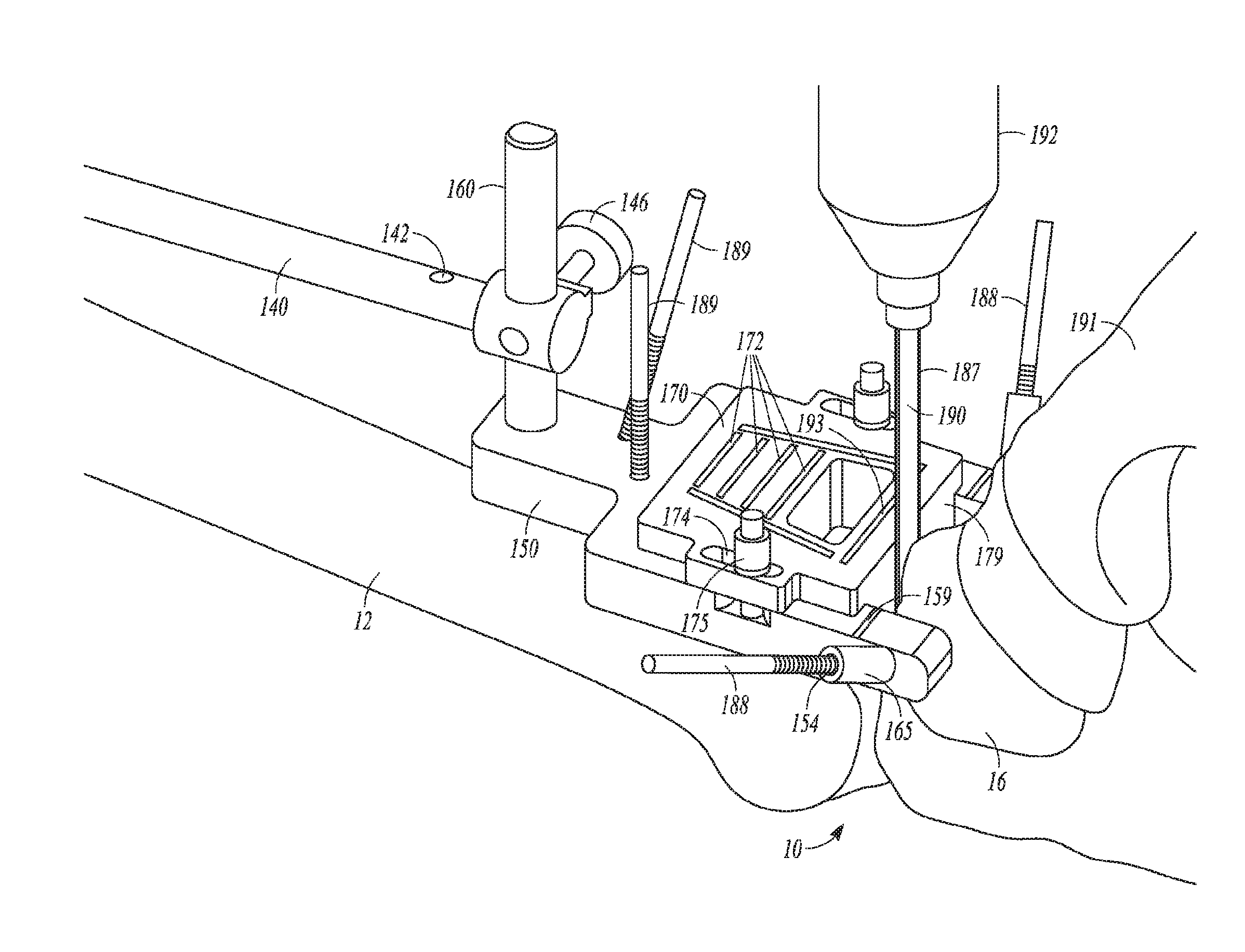
[0085]The present disclosure relates to spacers for foot and ankle fusion. Each fusion spacer is anatomically shaped for implantation in a particular anatomic location of the foot or ankle Each spacer shape may be available in different sizes (e.g., different anterior-posterior dimensions, different medial-lateral dimensions, different superior-inferior dimensions) to accommodate a variety of different patients.
1. Highly Porous Construction
[0086]According to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure, the fusion spacers of the present disclosure are constructed of a highly porous biomaterial. A highly porous biomaterial is useful as a bone substitute and as cell and tissue receptive material. A highly porous biomaterial may have a porosity as low as 55%, 65%, or 75% or as high as 80%, 85%, or 90%.
[0087]An example of such a material is produced using Trabecular Metal™ Technology generally available from Zimmer. Inc., of Warsaw. Ind. Trabecular Metal™ is a trademark of Zimmer. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com