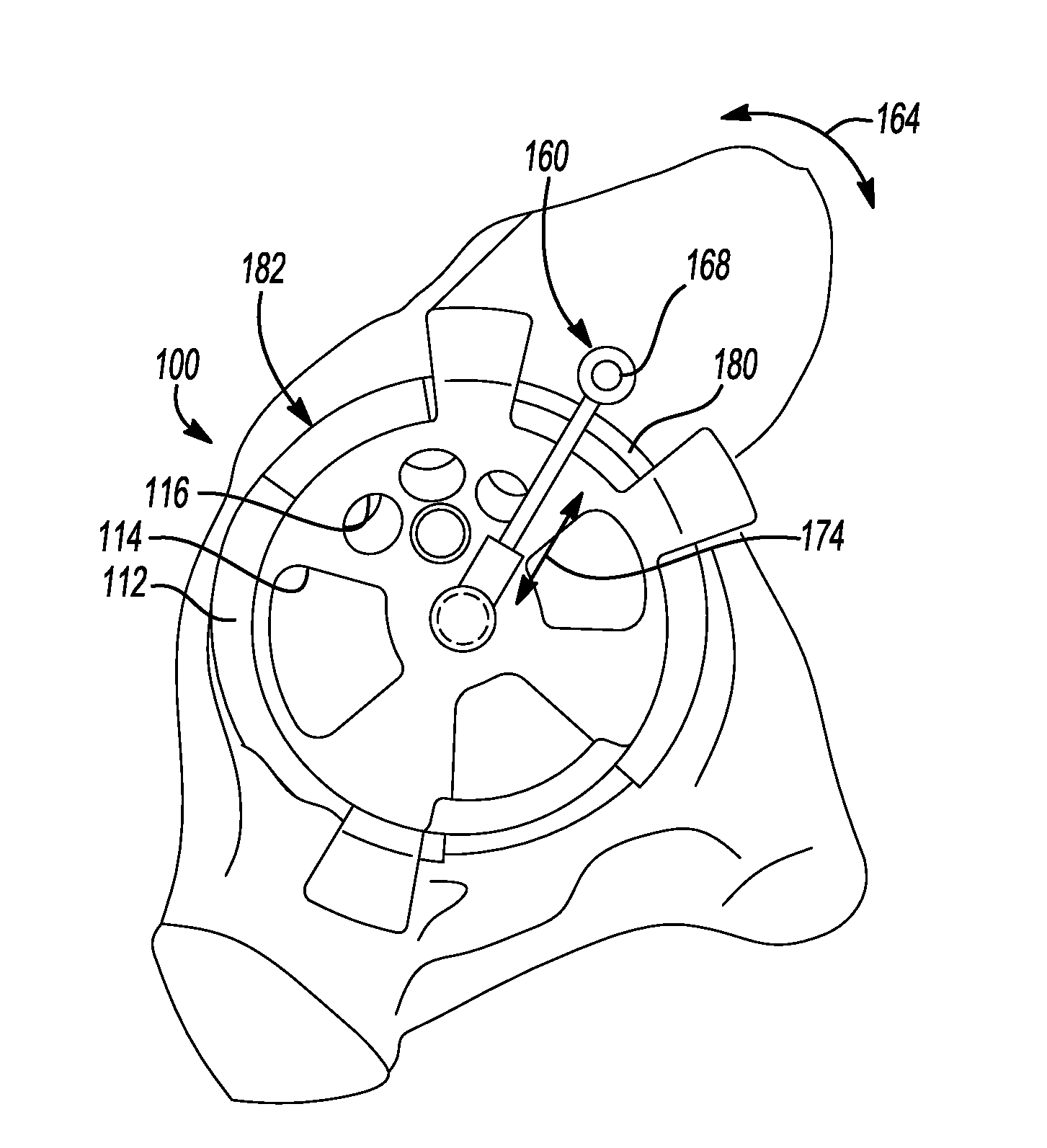
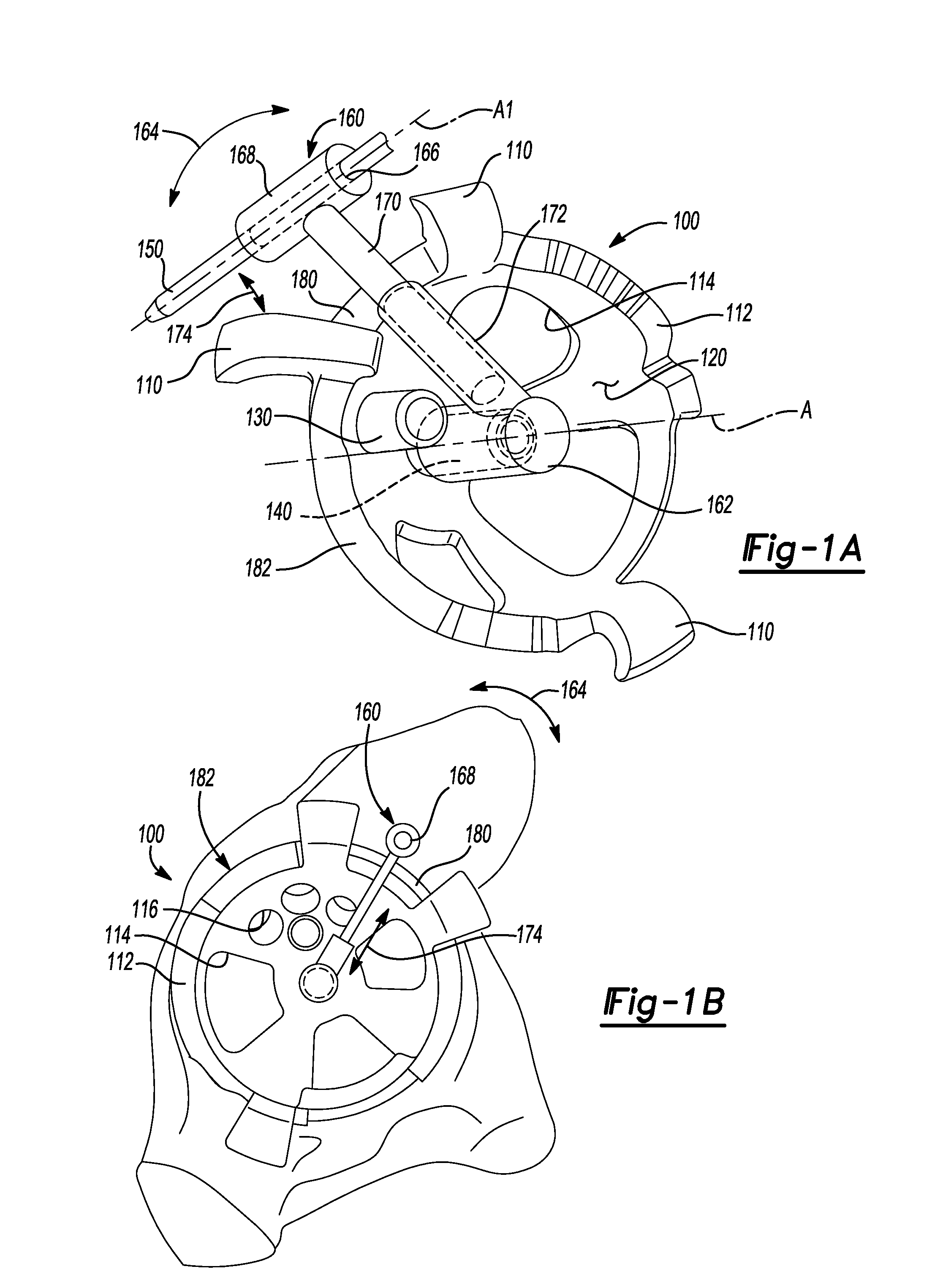
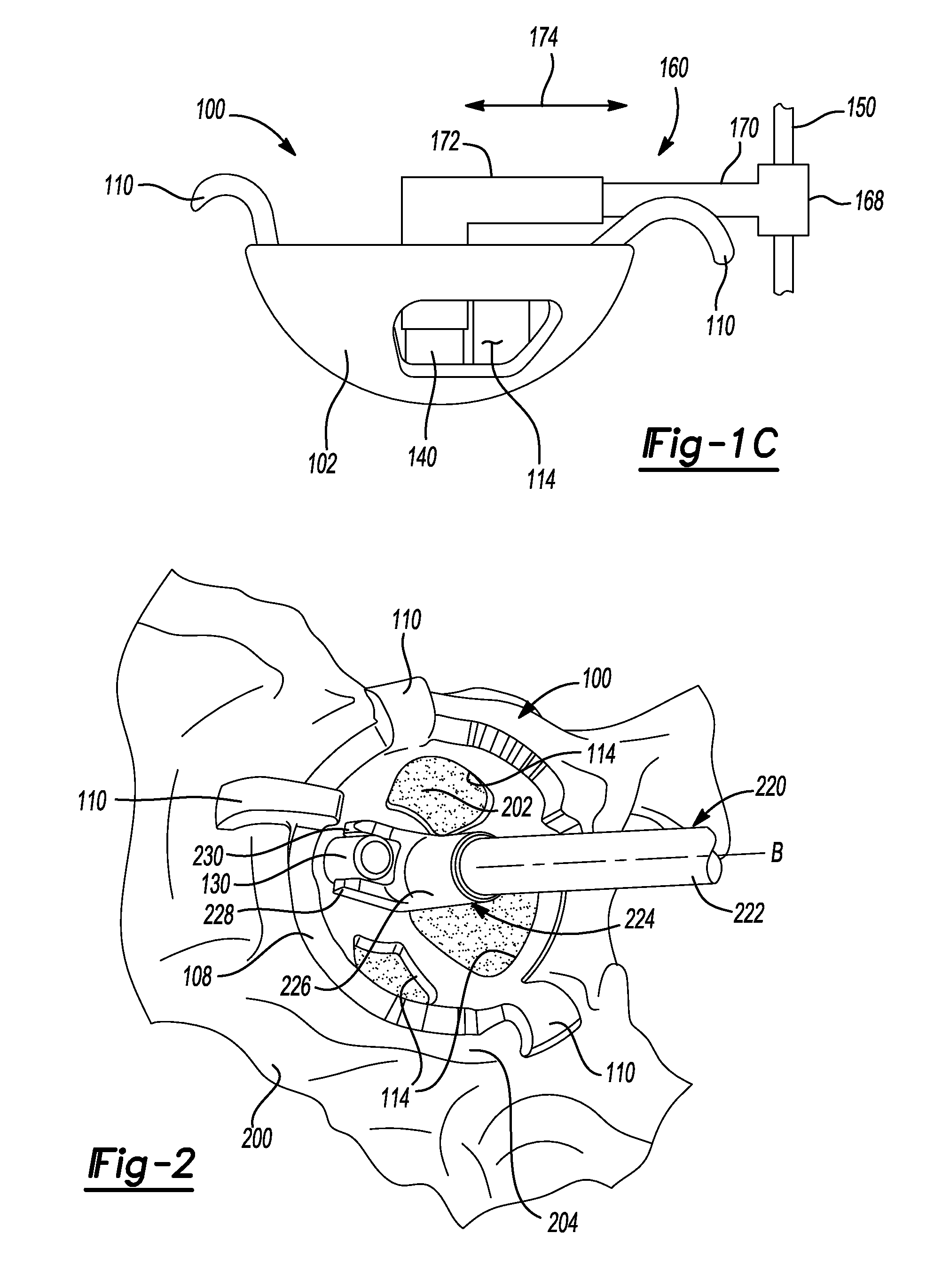
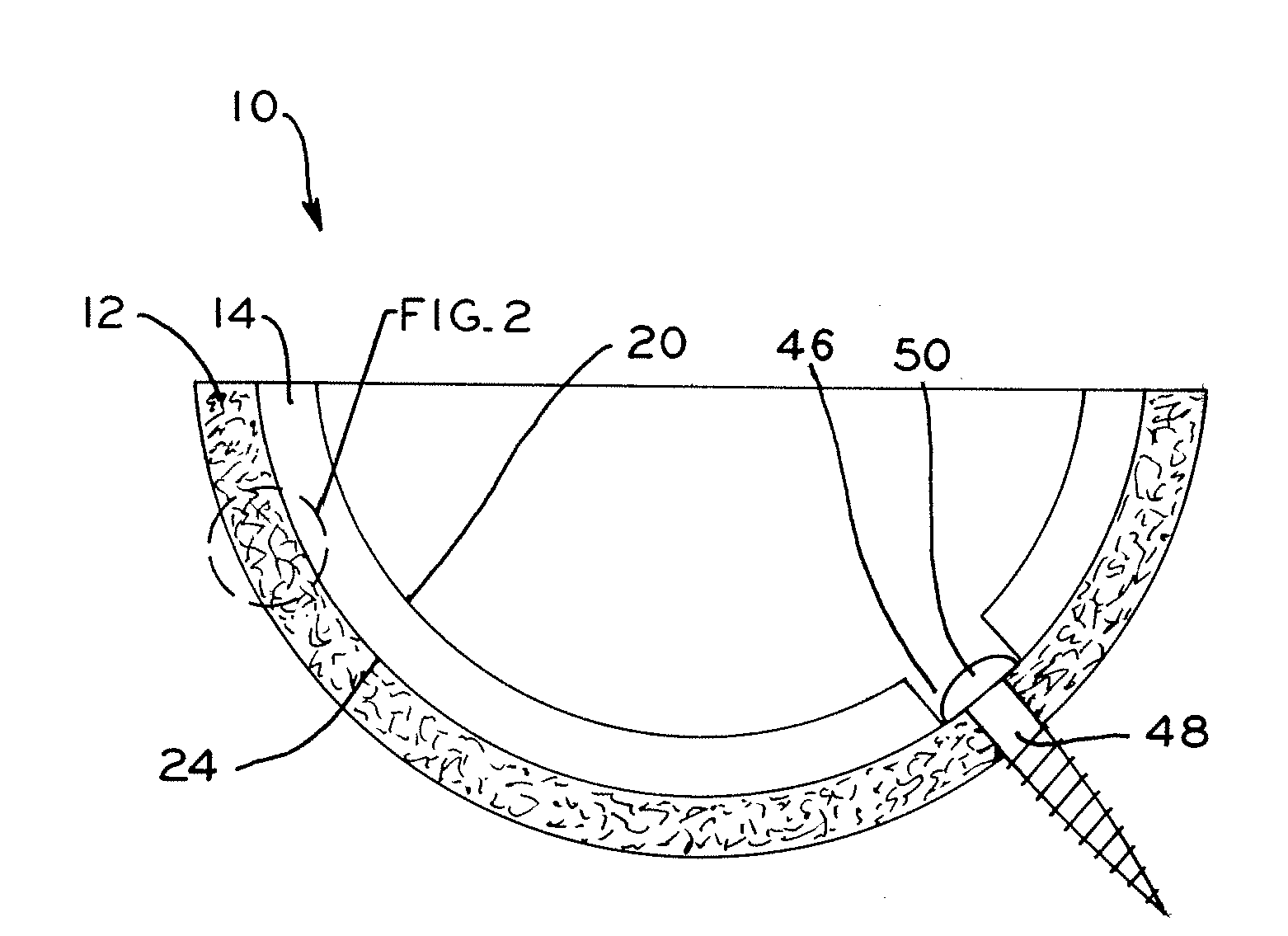
Patents
Literature
1229 results about "Socket hip" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
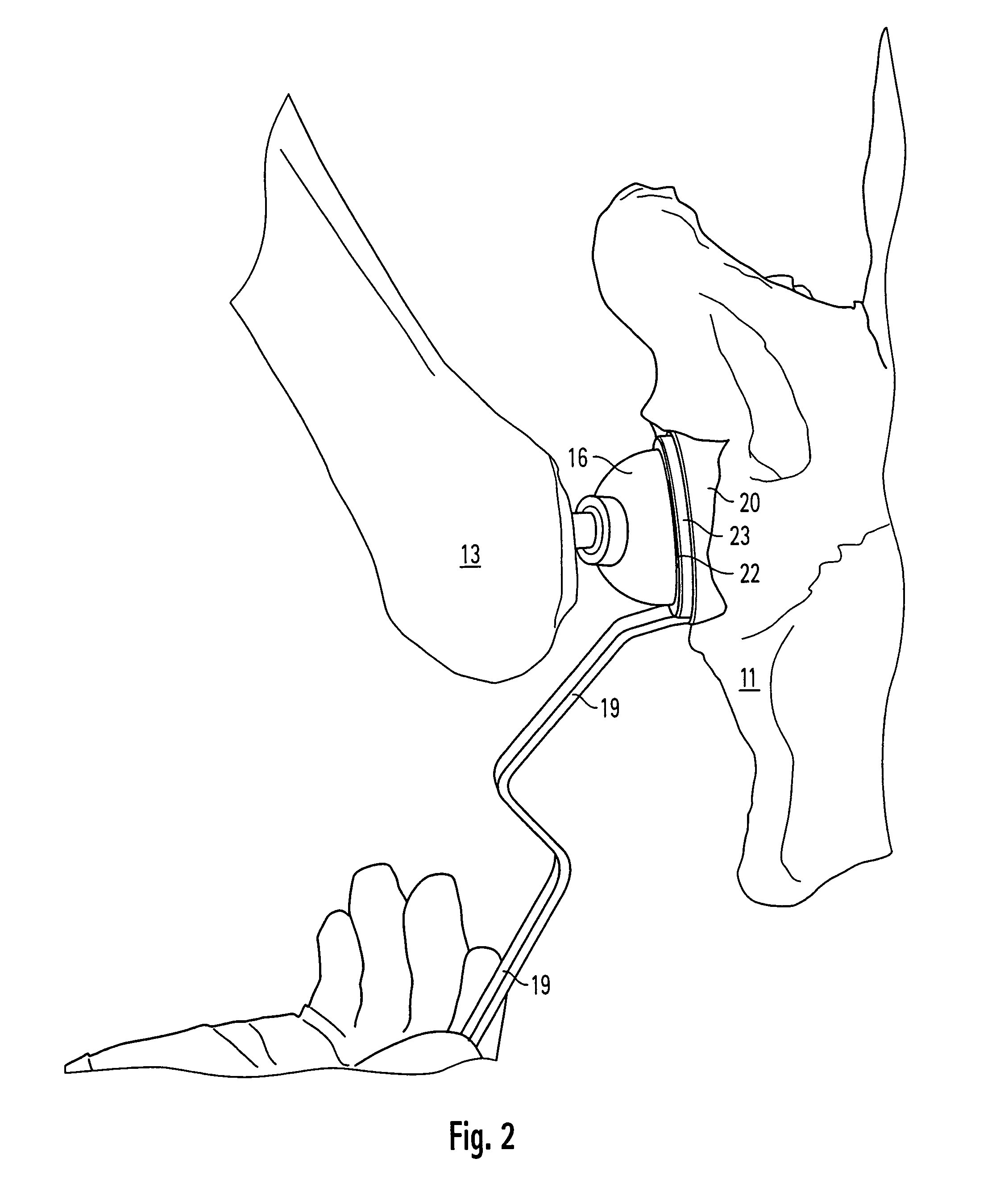
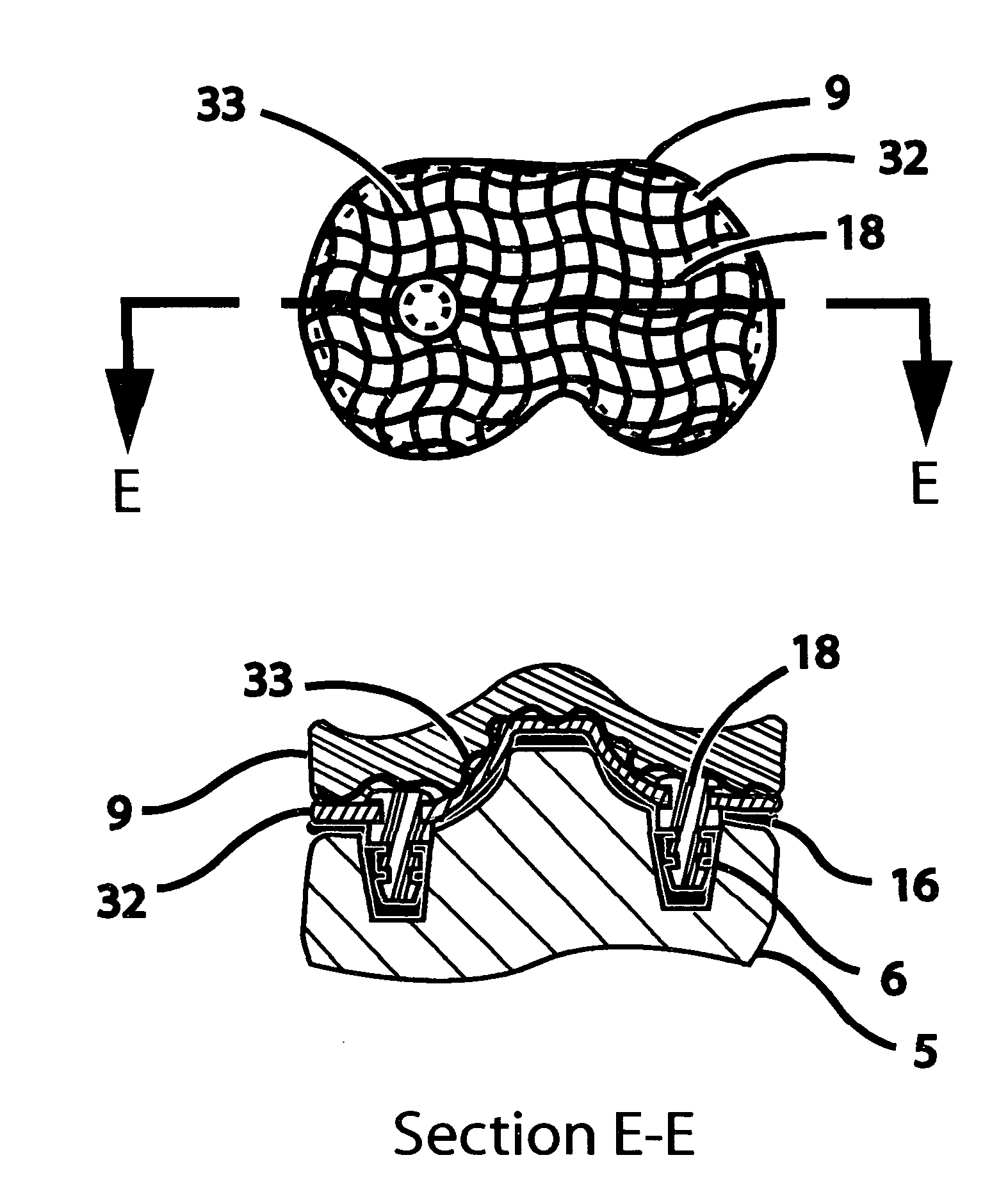
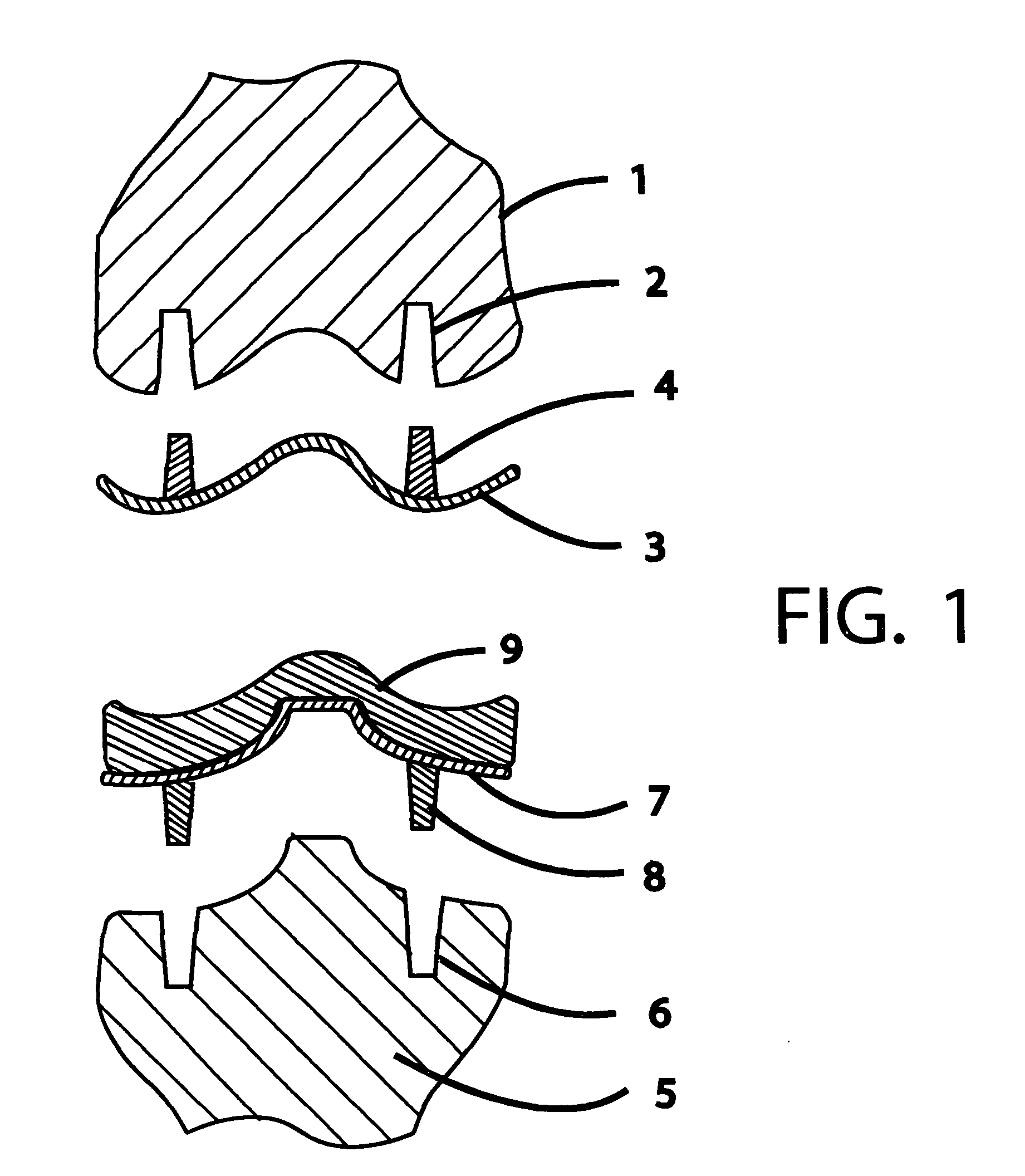
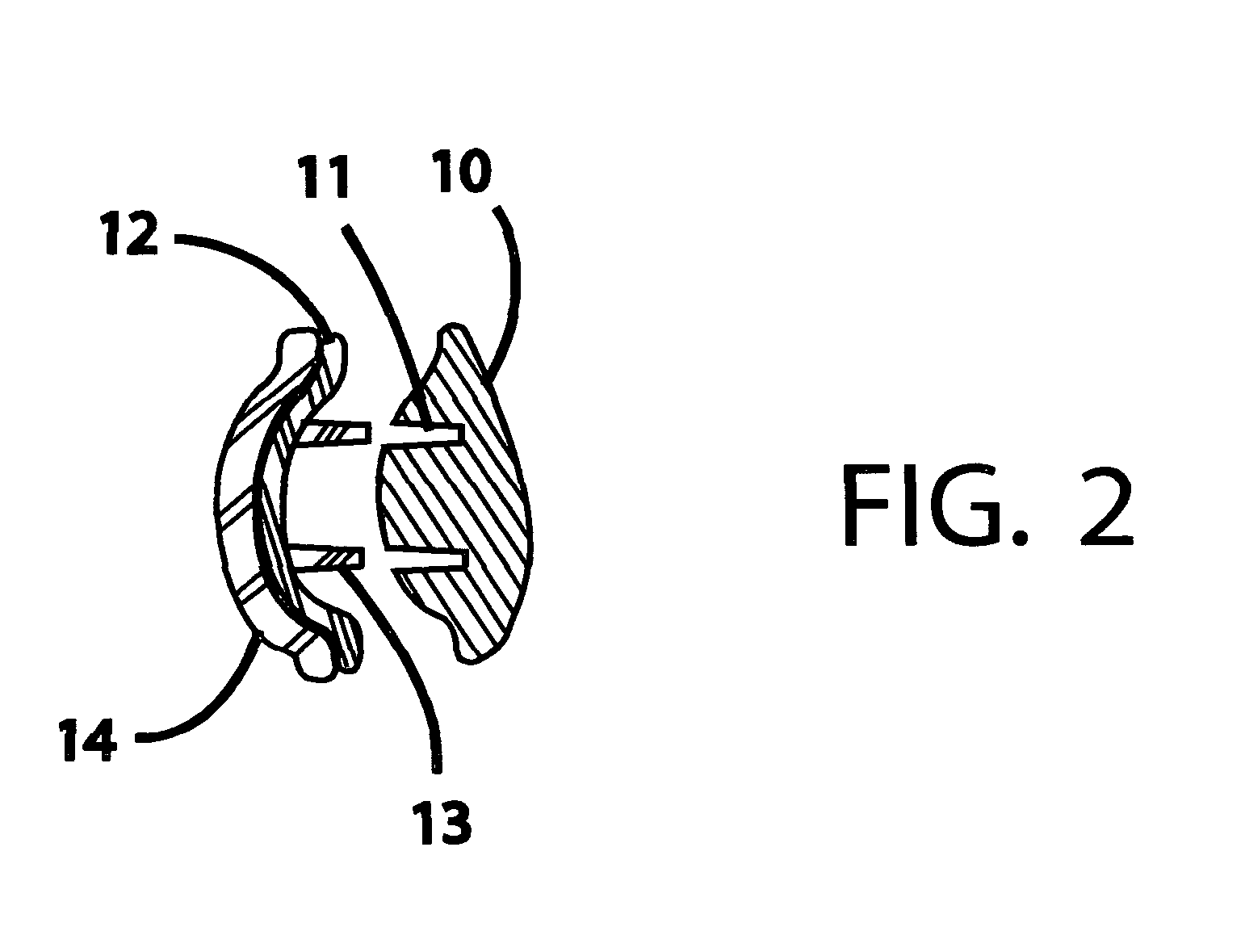
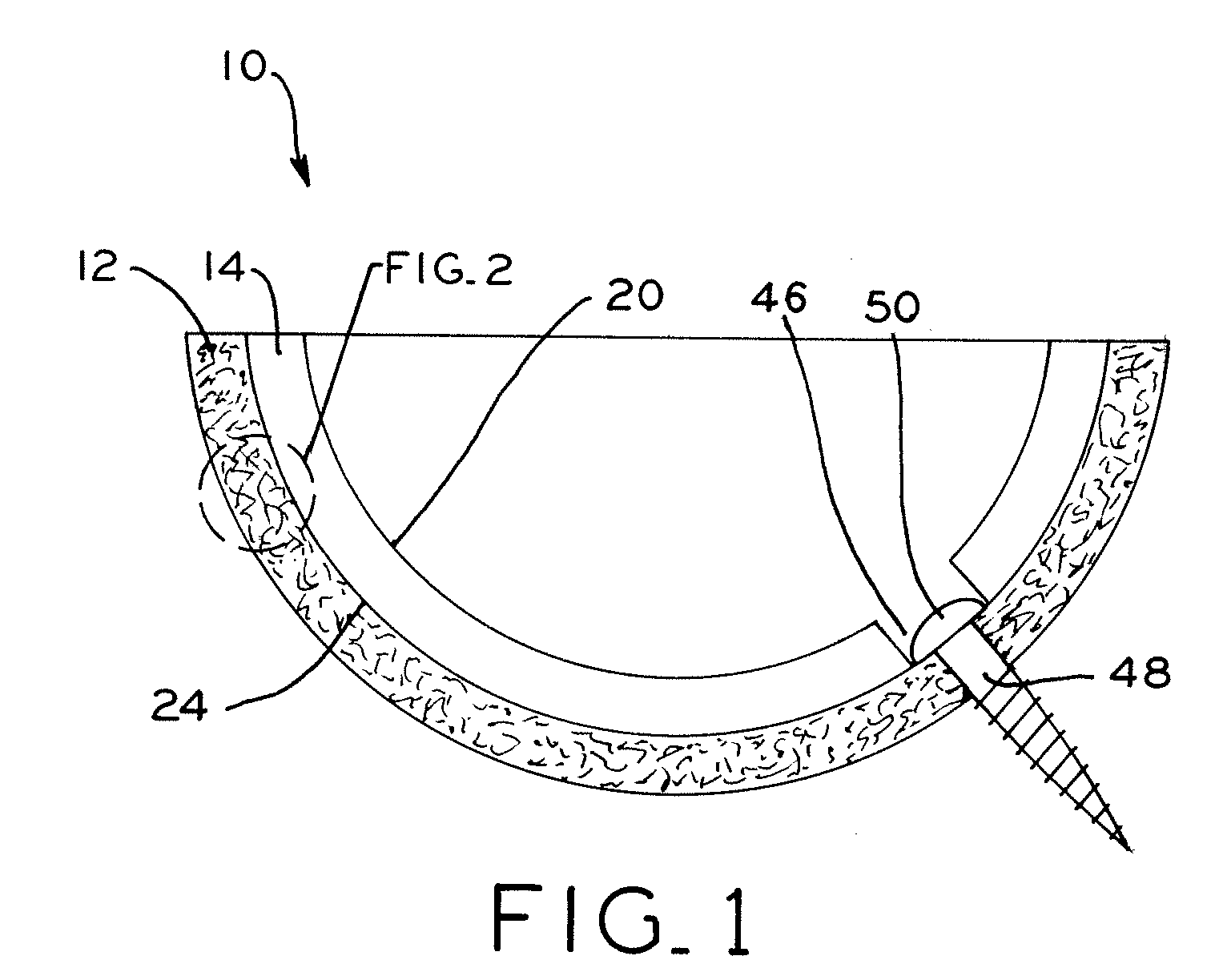
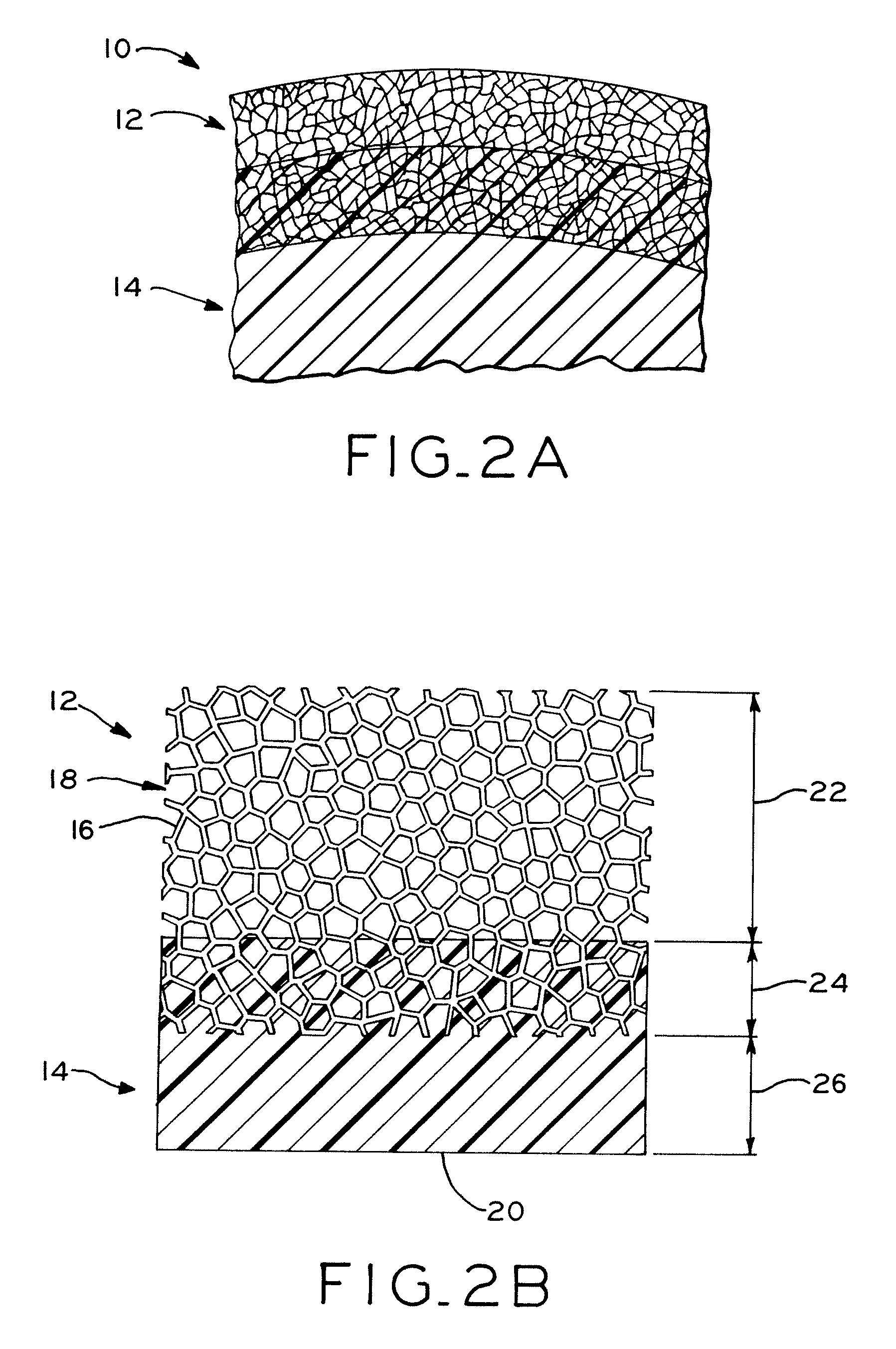
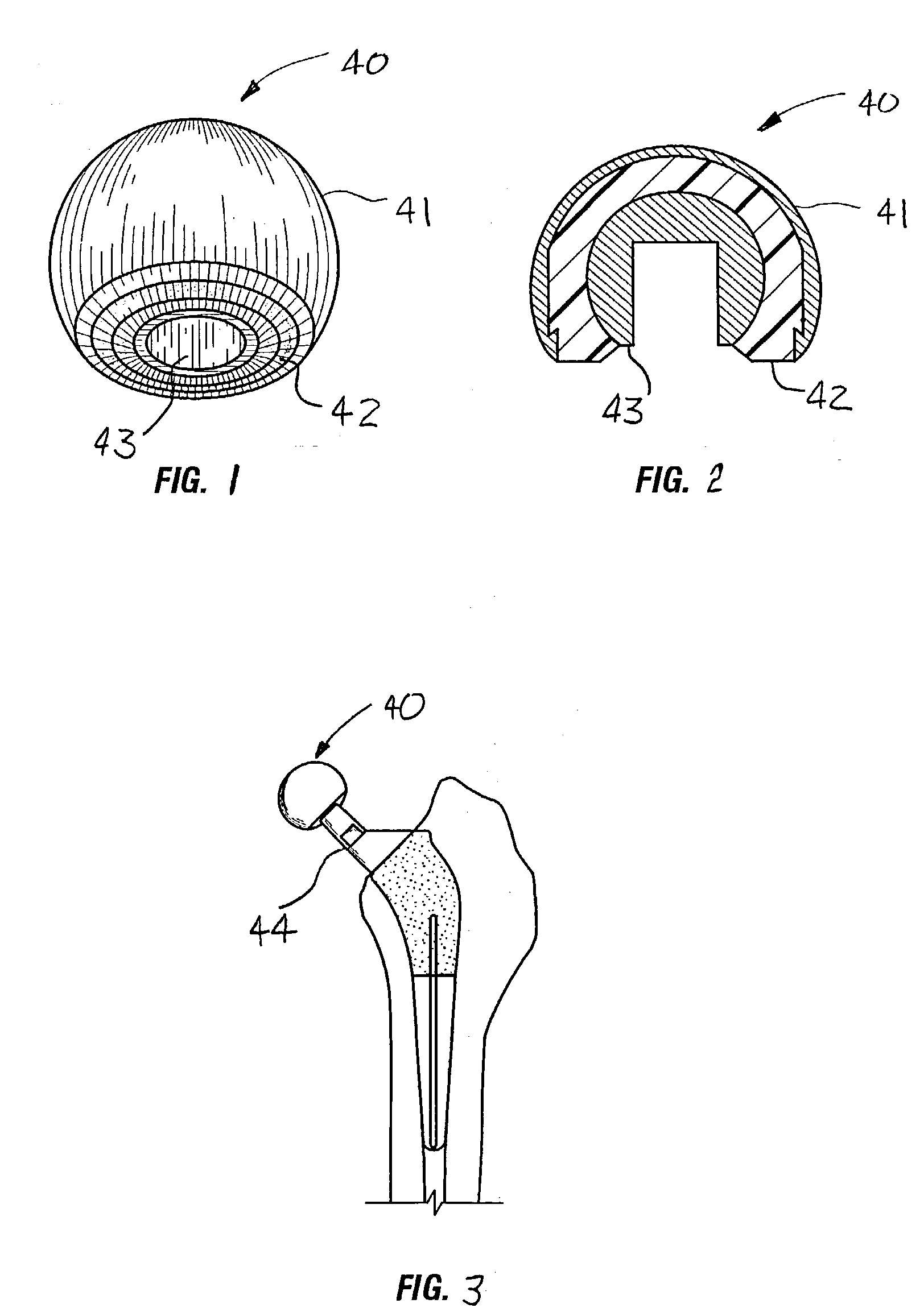
Prosthetic hip joint having sintered polycrystalline diamond compact articulation surfaces
InactiveUS6290726B1Improve wear resistanceReduce coefficient of frictionFinger jointsWrist jointsArticular surfacesProsthesis
Prosthetic joints, components for prosthetic joints, superhard bearing and articulation surfaces, diamond bearing and articulation surfaces, substrate surface topographical features, materials for making joints, bearing and articulation surfaces, and methods for manufacturing and finishing the same, and related information are disclosed, including a prosthetic hip joint having sintered polycrystalline diamond articulation.
Owner:DIAMICRON
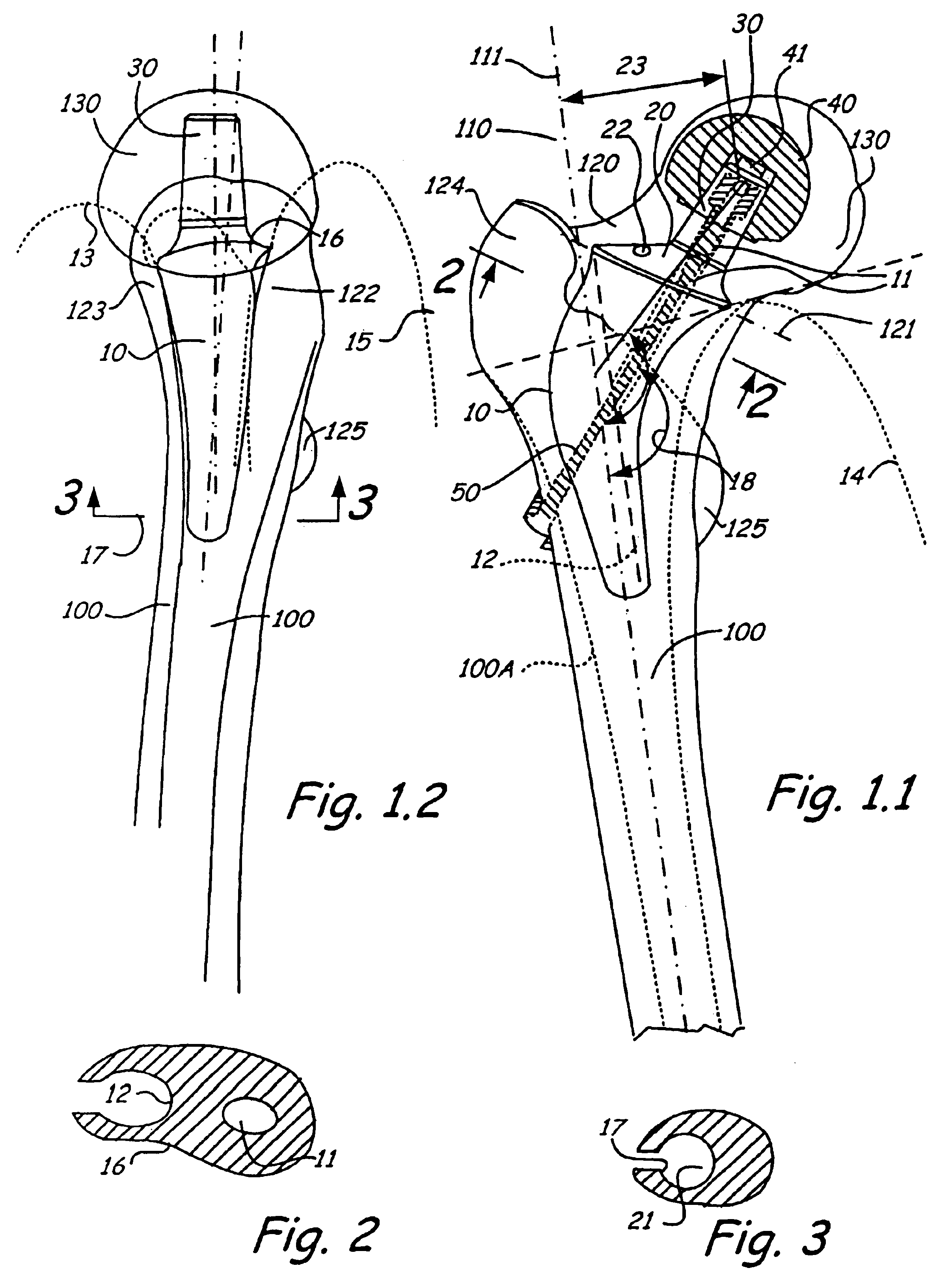
Hip resurfacing surgical guide tool
ActiveUS20090222015A1Increase in sizeProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusArticular surfacesRight femoral head
Disclosed herein is a tool for guiding a drill hole along a central axis of a femur head and neck for preparation of a femur head that is the subject of a hip resurfacing surgery. In one embodiment, the tool includes a mating region and a guide hole. The mating region is configured to matingly receive a predetermined surface of the femur. The mating region and guide hole are positionally correlated or referenced with each other such that when the mating region matingly receives the predetermined surface of the femur, the guide hole will be generally coaxial with a central axis extending through the femur head and the femur neck.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Expandable hip implant
InactiveUS6361565B1Reduce retentionReduce capacitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisProsthesisBody fluid
An implant is formed of an expandable material. An opening is formed in a bone in a patient's body. At least a portion of the implant is positioned in the opening in the bone in the patient's body. The implant is retained against movement relative to the bone in the patient's body by absorbing body fluid with the implant and expanding the implant while the implant is disposed in the opening in the bone in the patient's body. The implant may be a hip replacement member.
Owner:BONUTTI 2003 TRUST A THE +1
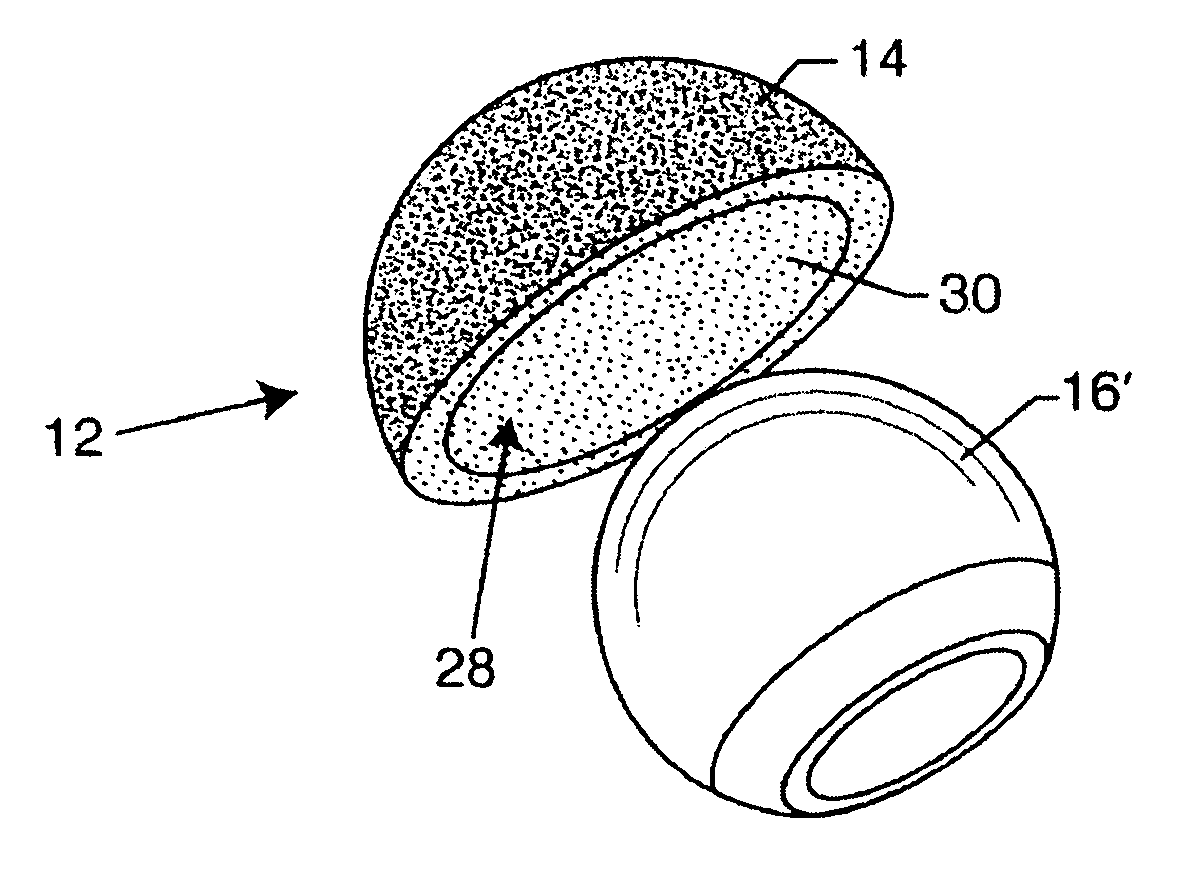
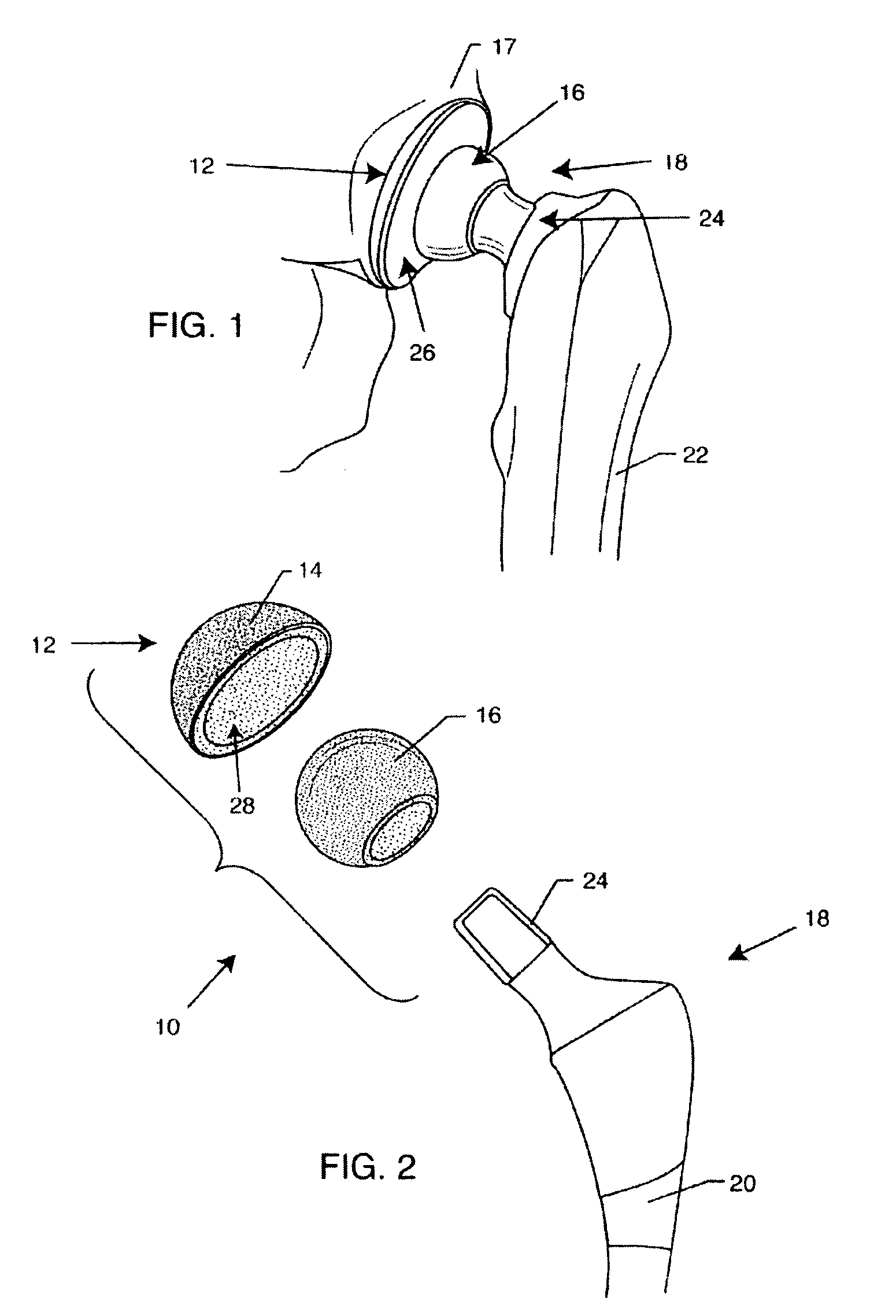
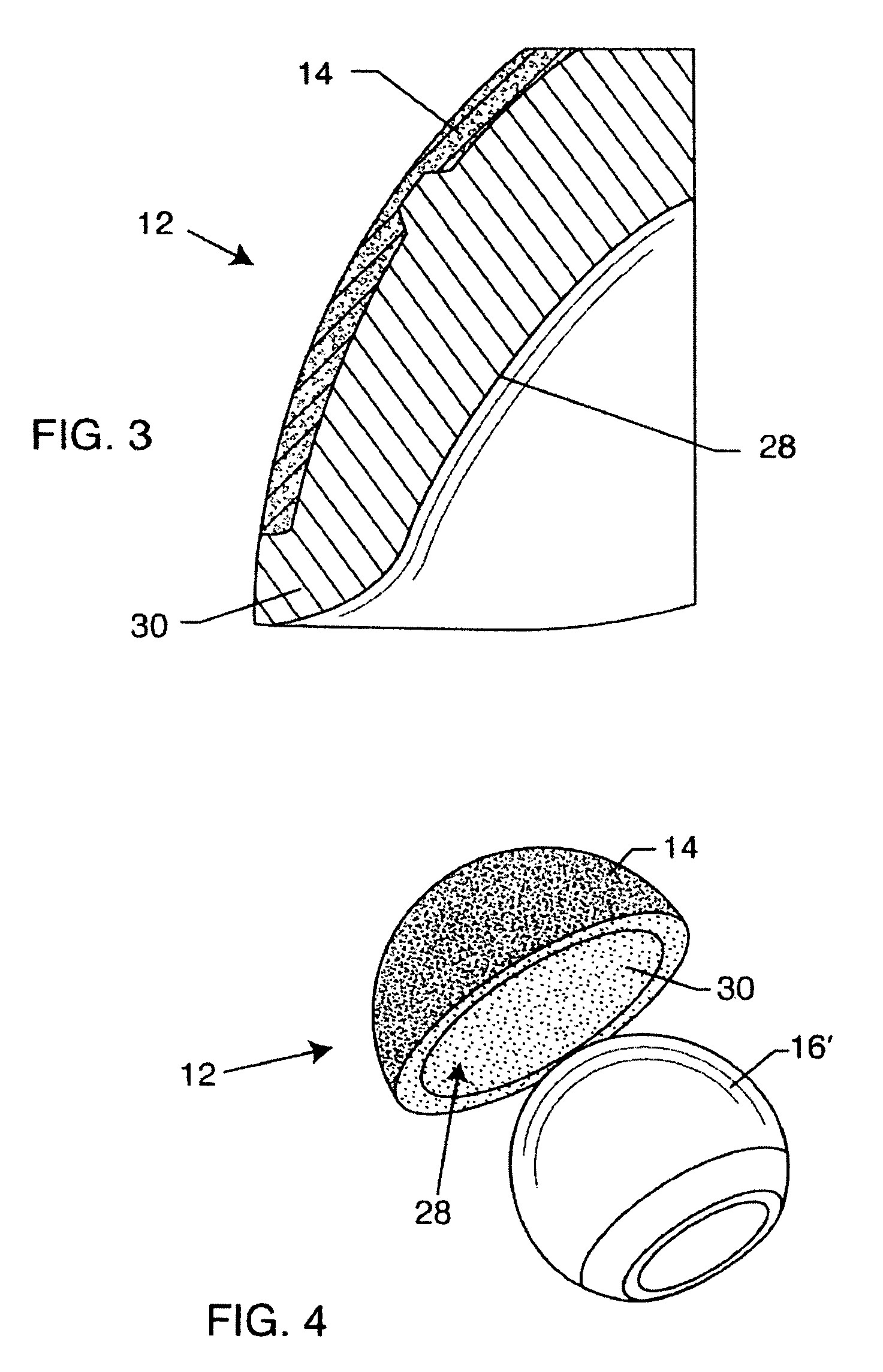
Hip prosthesis with monoblock ceramic acetabular cup
InactiveUS7695521B2High strengthImprove toughnessBone implantJoint implantsRight femoral headMetallic materials
An improved hip prosthesis includes an acetabular cup bearing component constructed from a relatively hard and high strength ceramic material for articulation with a ball-shaped femoral head component which may be constructed from a compatible ceramic or metal material. In one form, the acetabular cup further includes a ceramic porous bone ingrowth surface adhered thereto for secure ingrowth attachment to natural patient bone.
Owner:AMEDICA A DELAWARE
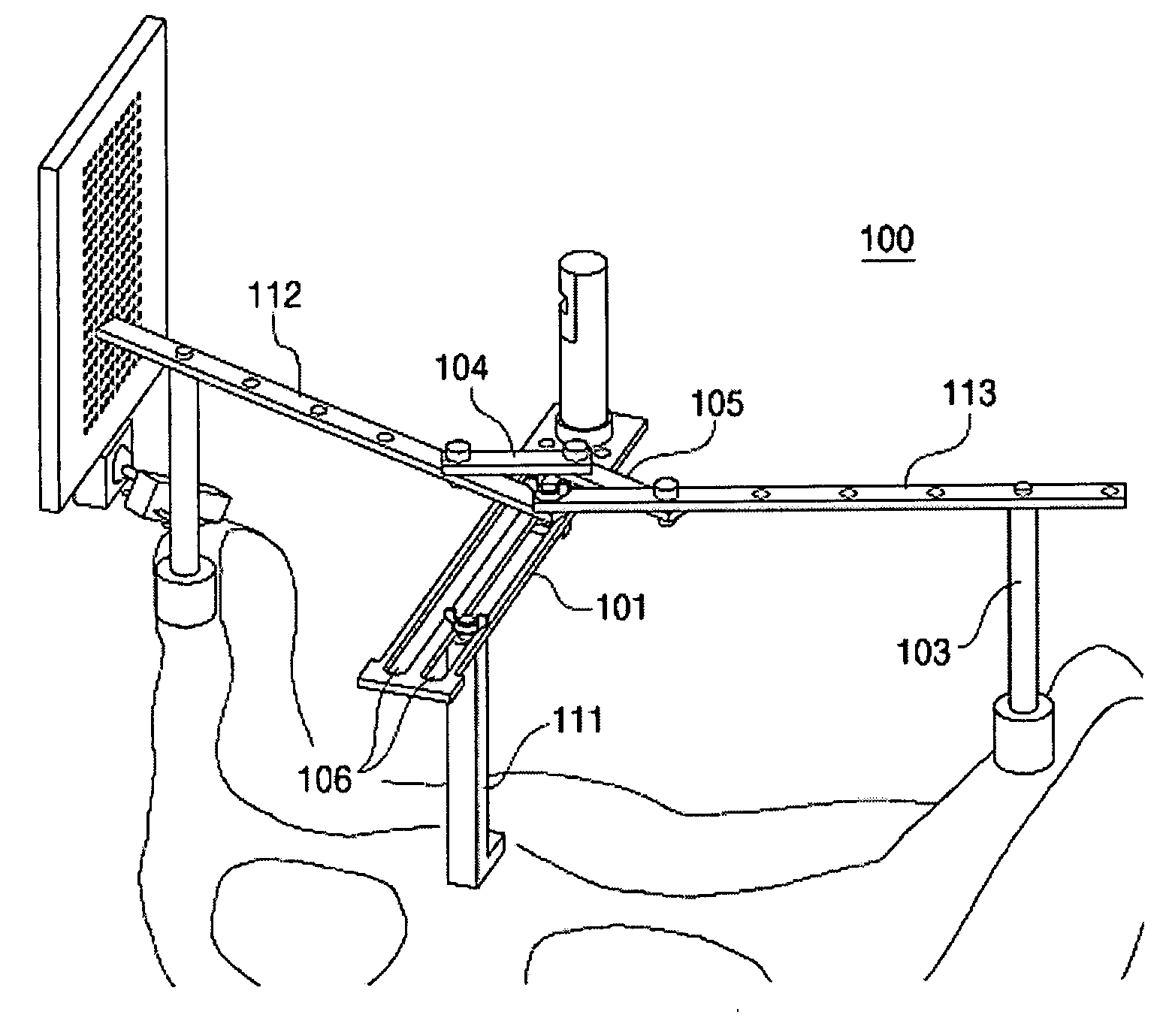
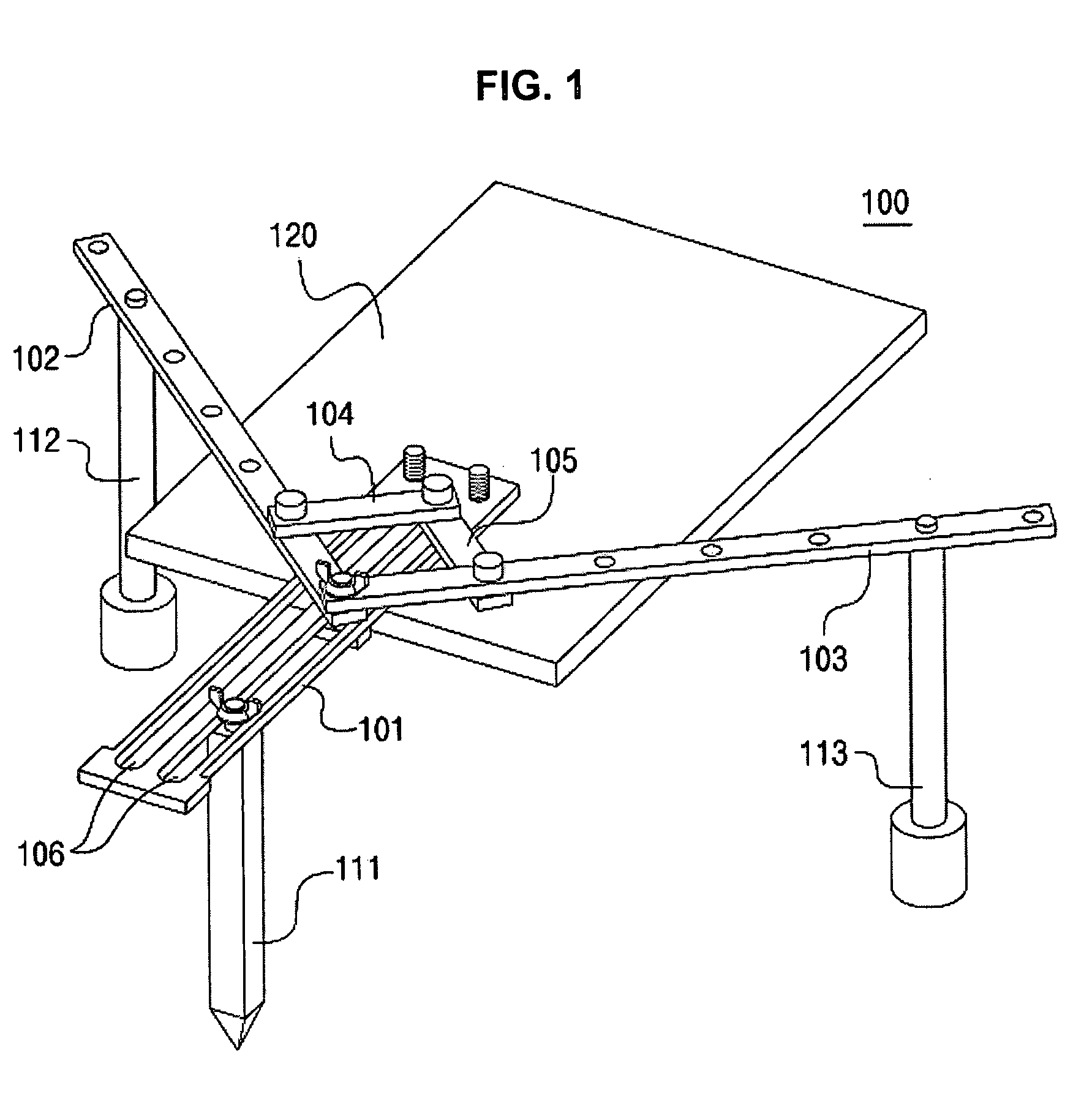
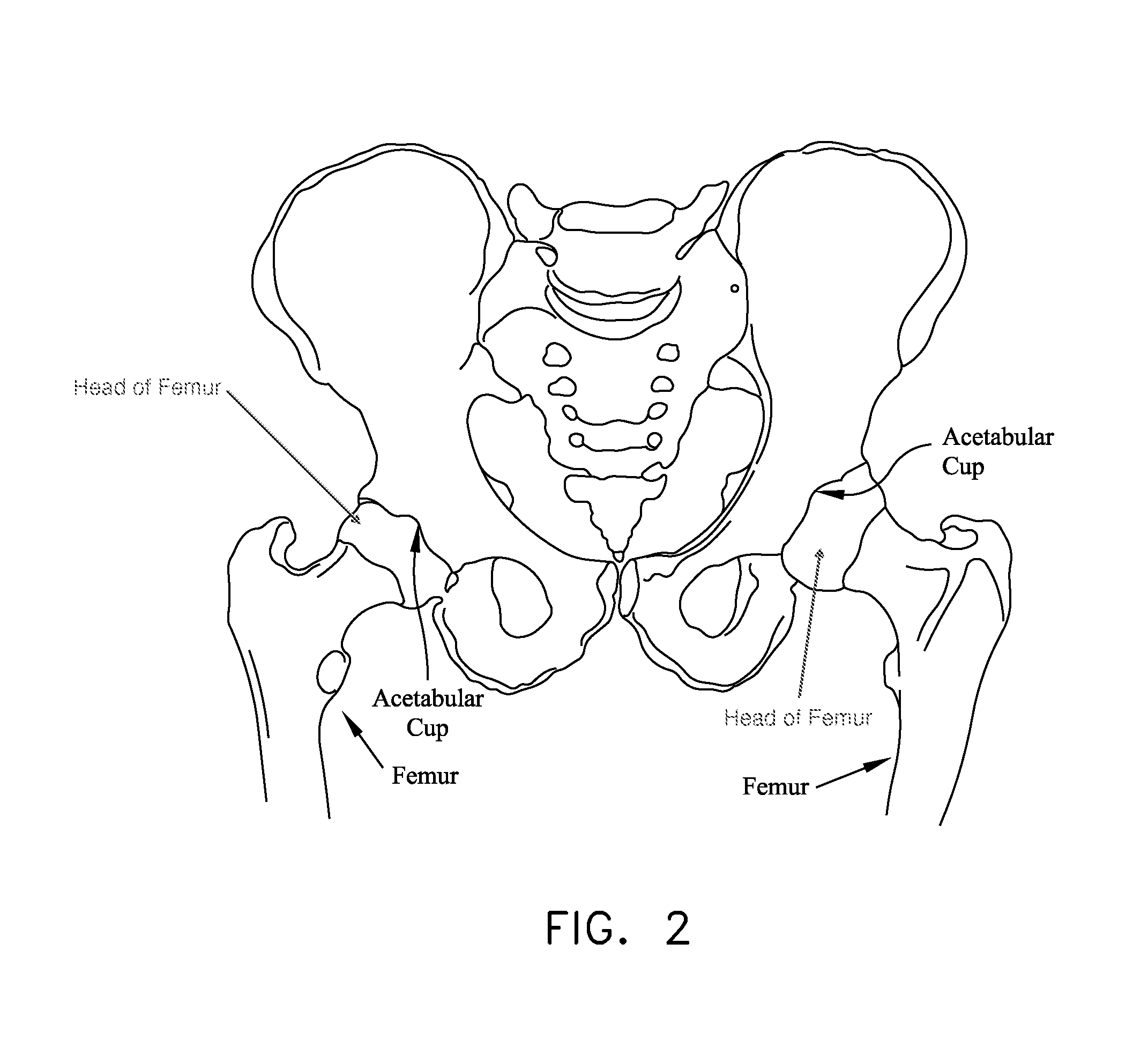
Pelvis level
Instrumentation and method for determining the orientation of the pelvic bone during hip-replacement surgery. Instrumentation includes a pelvis frame and a pelvis level. The pelvis frame is used for performing an operation which provides preliminary information for determining the position of the pelvic bone, and includes pads which are specifically contoured for contact with the pelvic bone. The pelvis level is used in combination with the pelvis frame to determine the exact position of the patient's pelvic bone, and includes a ball level which is capable of withstanding steam sterilization.
Owner:BROYLES JOSEPH E
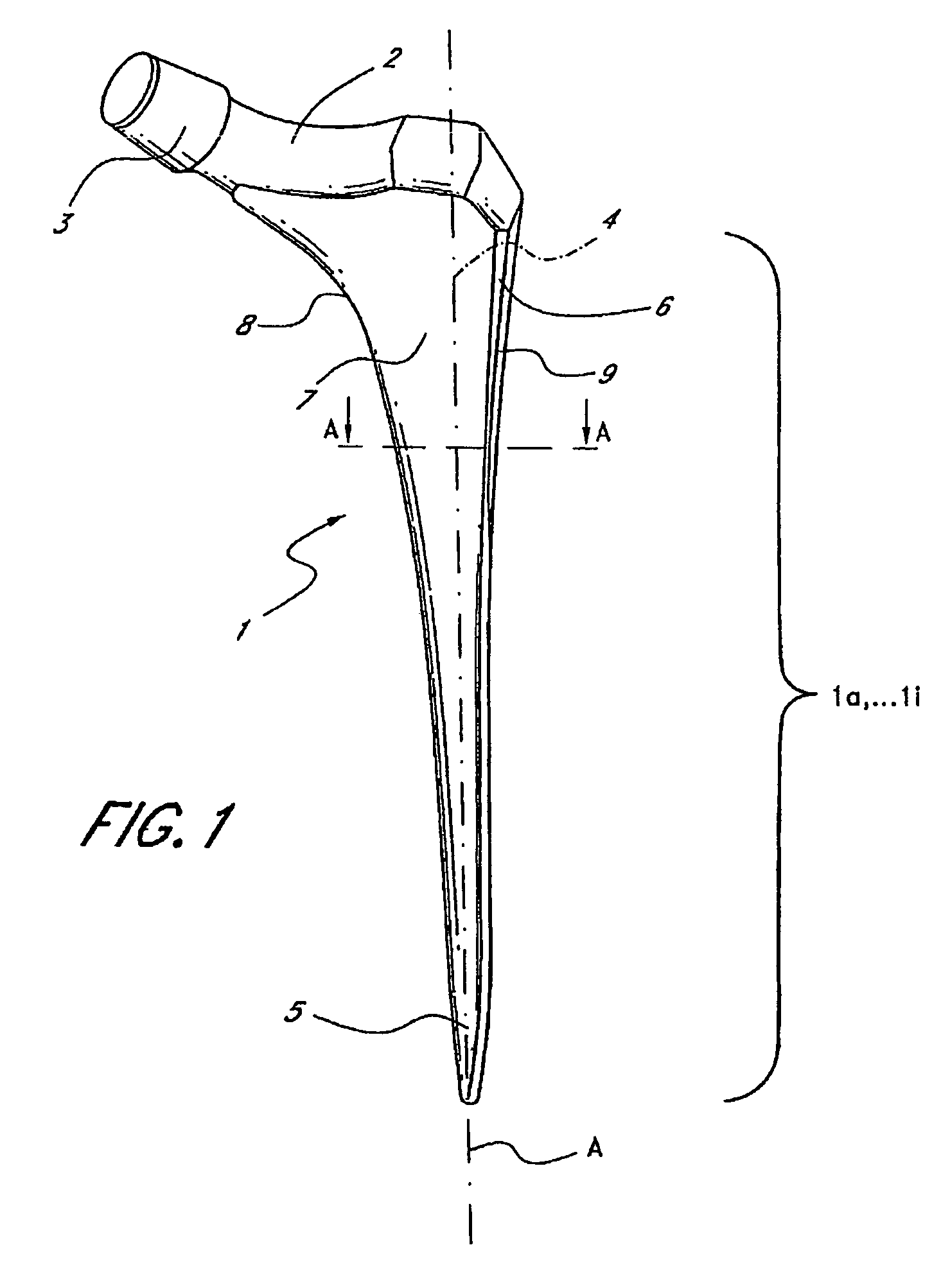
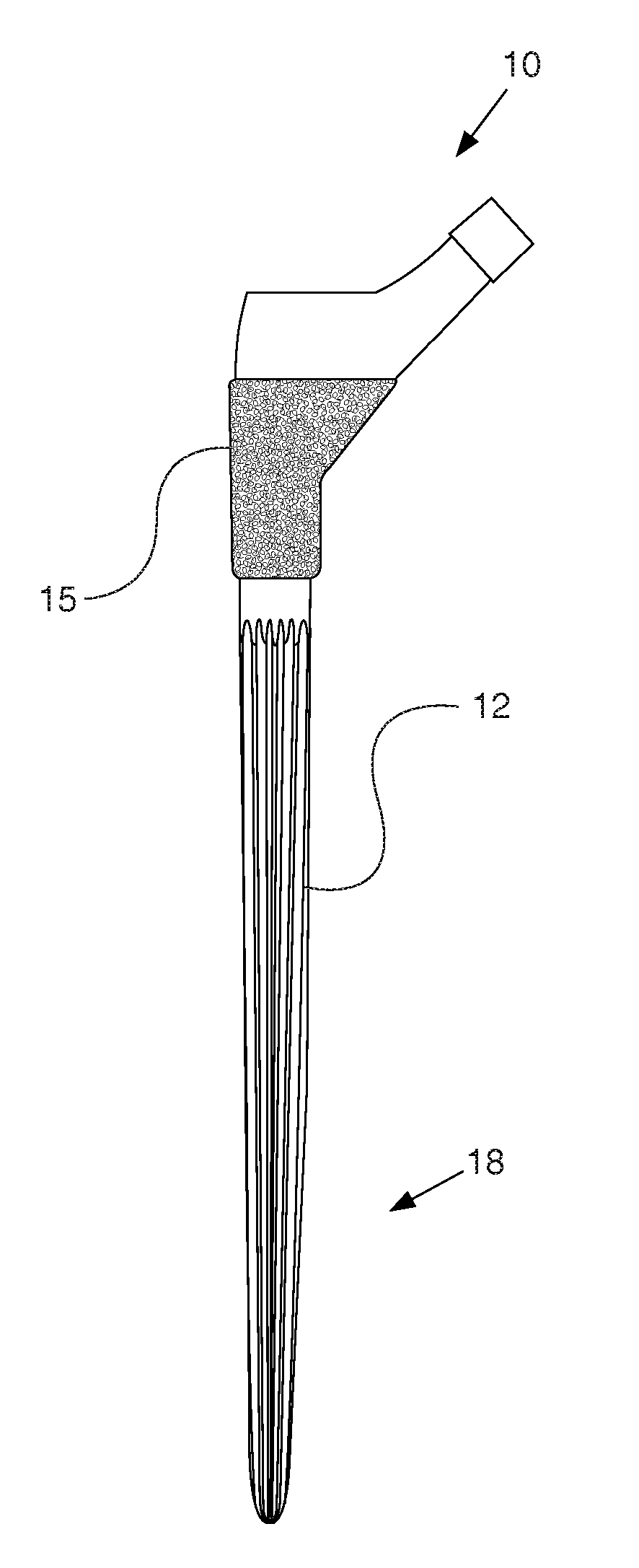
Leaflike shaft of a hip-joint prosthesis for anchoring in the femur
InactiveUS7494510B2Advantageous for revascularizationFacilitate revascularizationSurgeryJoint implantsRaspFemoral shaft
The present invention relates in certain embodiments to components of a hip-joint prosthesis. More particularly, embodiments of the invention relate to a leaf-like femoral shaft for use as part of a hip-joint prosthesis, and instruments (e.g., a rasp) and methods for implanting the shaft. The shaft includes an anchoring section extending between a proximal region and a distal end of the shaft. The shaft has a cross-sectional contour that defines a lateral side, a medial side, an anterior side and a posterior side. A corresponding rasp is preferably provided for each femoral shaft. The rasp is inserted into the femur to form a cavity having generally the same configuration as the rasp. The shaft is configured to be over-dimensioned in at least one of the anterior-posterior direction and medial-lateral direction relative to the rasped femur cavity. In one embodiment, the distance between diagonally opposite corner junctions of the shaft is substantially equal to the distance between corresponding diagonally opposite corner junctions of the femur cavity, so as to inhibit excess stress on the corticalis.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
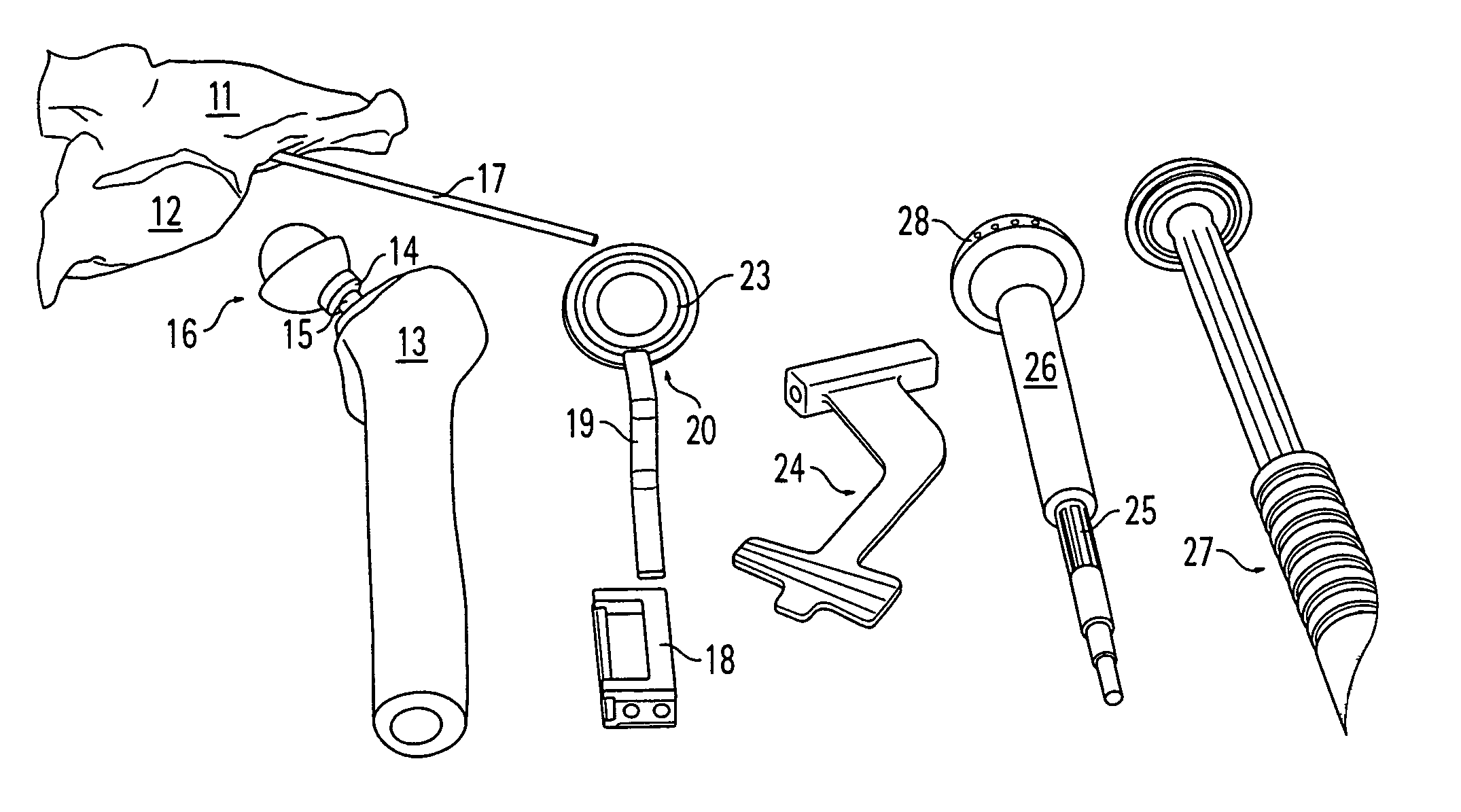
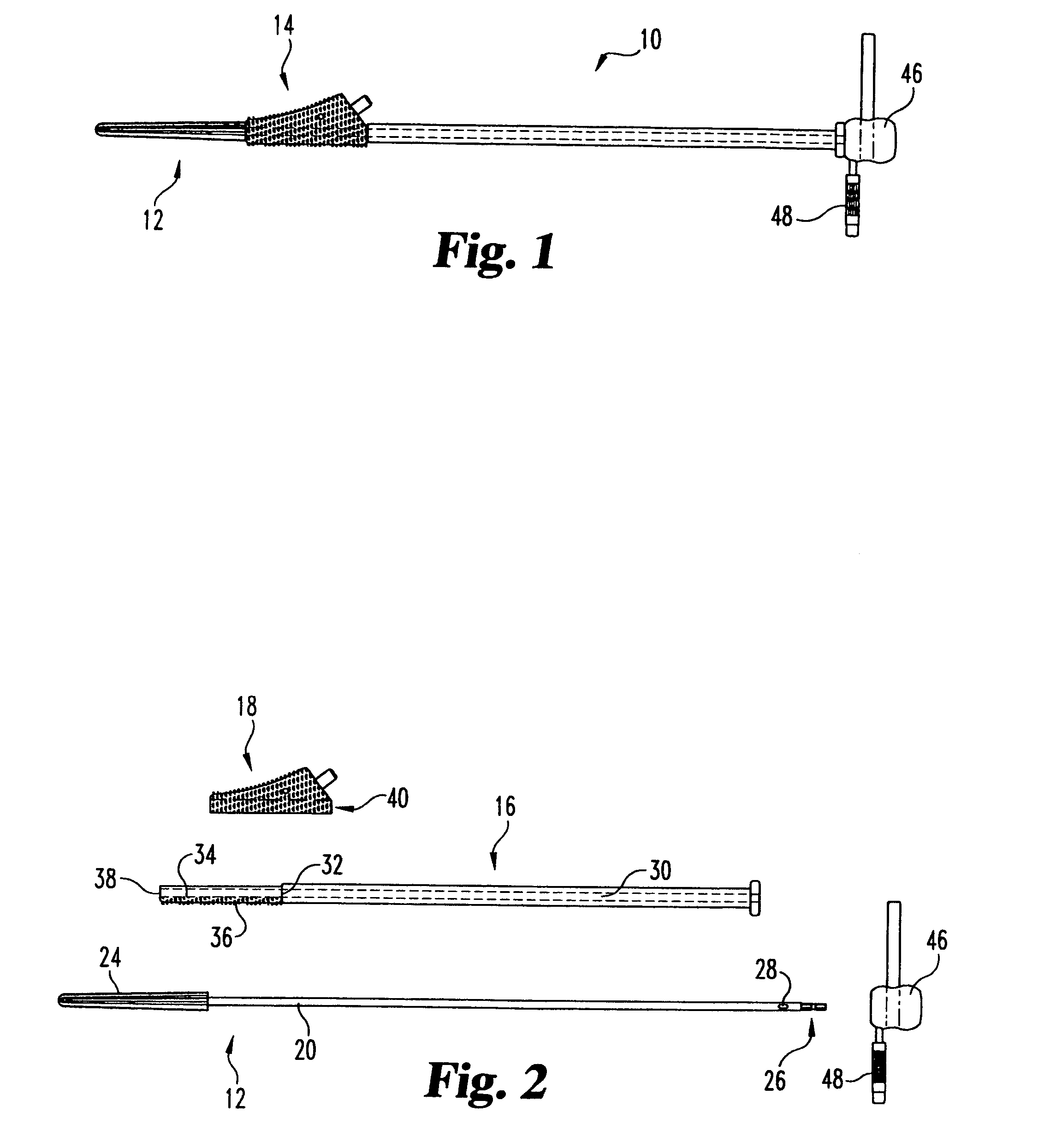
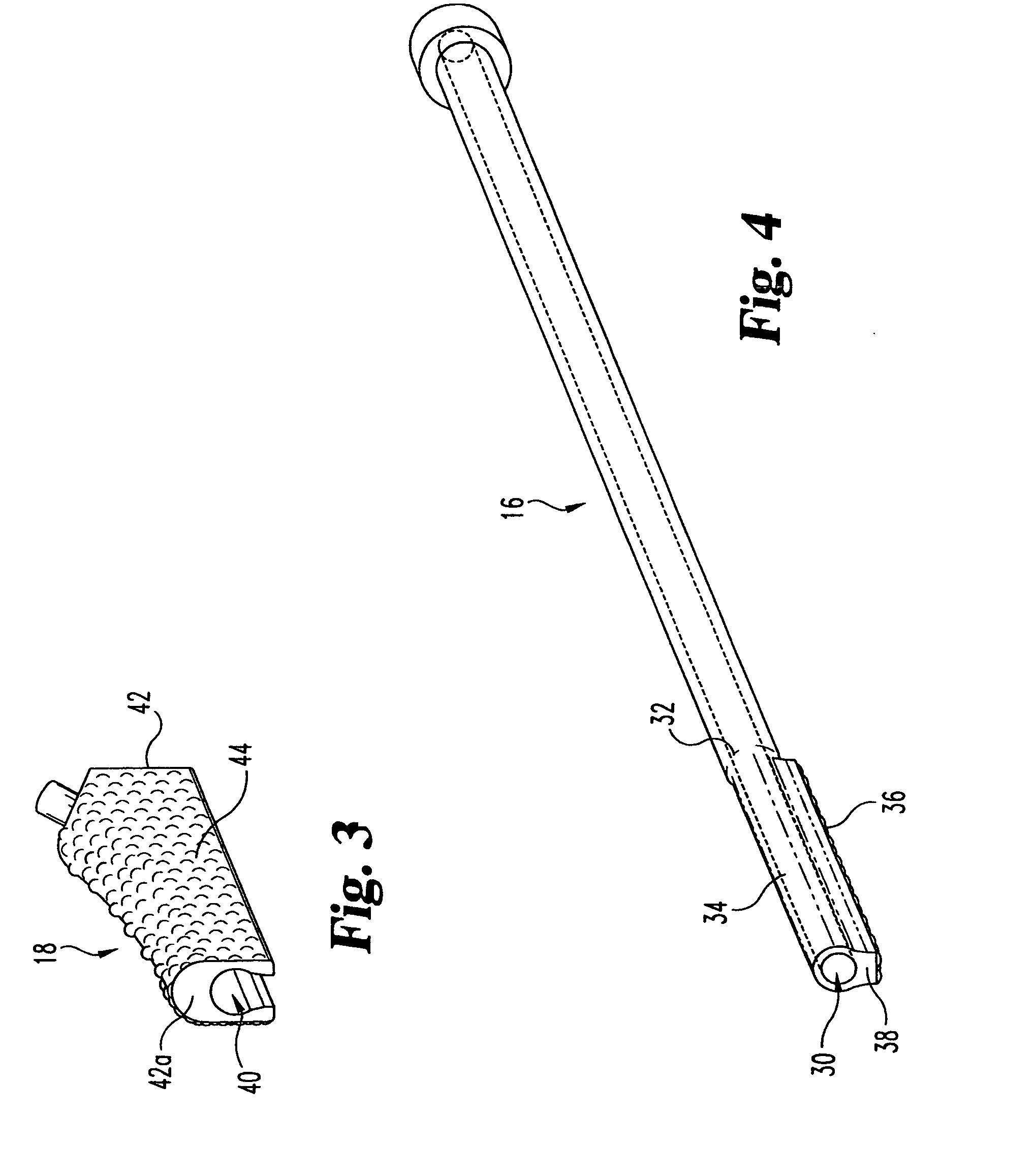
Accessory for implanting a hip endoprosthesis, and method for manipulating the same
Accessory for implantation of a hip joint endoprosthesis, with a manipulation cup, a manipulation joint head with means for orienting the manipulation cup in the acetabulum, and with a device to represent the correctly oriented position of the manipulation cup such that by means of this device a bone-milling cutter and an impact instrument can then oriented appropriately for placement of the prosthesis cup.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Minimally-thick orthopedic prosthesis is disclosed which closely matches the end of a bone of a joint after that bone end has been minimally reshaped and resurfaced by an orbital or lineally oscillating orthopedic resurfacing tool in the minimally invasive orthopedic surgical repair or reconstruction of hip, knee, ankle, shoulder, elbow, wrist, and other joints
InactiveUS20100076571A1Uniform and satisfactoryEvenly distributedBone implantSurgeryThrombusLigament structure
A minimally-thick orthopedic prosthesis is described which closely matches the end of a bone of a joint after that bone end has been minimally reshaped and resurfaced by an orbital or lineally oscillating orthopedic resurfacing tool in the minimally invasive orthopedic surgical repair or reconstruction of hip, knee, ankle, shoulder, elbow, wrist, and other joints. The original ligament tensions and the varus and valgus alignments of the joint are preserved and the marrow cavities of bones are not invaded avoiding the dangers of blood clots, heart attacks, and other complications.
Owner:HATCH EDWIN BURTON
Universal Acetabular Guide And Associated Hardware
An orthopedic device includes a patient-specific acetabular guide that may be used for preparing an acetabulum of a patient to receive an acetabular implant. The acetabular guide has a body with an outer three-dimensional surface configured to match an acetabulum of a specific patient's hip joint designed from data of the patient's hip joint. The acetabular guide may further include a peripheral annular rim.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Orthopedic component of low stiffness
ActiveUS20090192610A1Component can be removedReduce the impactBone implantSynthetic resin layered productsAcetabular linerPlastic surgery
An orthopedic component having multiple layers that are selected to provide an overall modulus that is substantially lower than the modulus of known orthopedic components to more closely approximate the modulus of the bone into which the orthopedic component is implanted. In one exemplary embodiment, the orthopedic component is an acetabular shell. For example, the acetabular shell may include an outer layer configured for securement to the natural acetabulum of a patient and an inner layer configured to receive an acetabular liner. The head of a femoral prosthesis articulates against the acetabular liner to replicate the function of a natural hip joint. Alternatively, the inner layer of the acetabular shell may act as an integral acetabular liner against which the head of the femoral prosthesis articulates.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
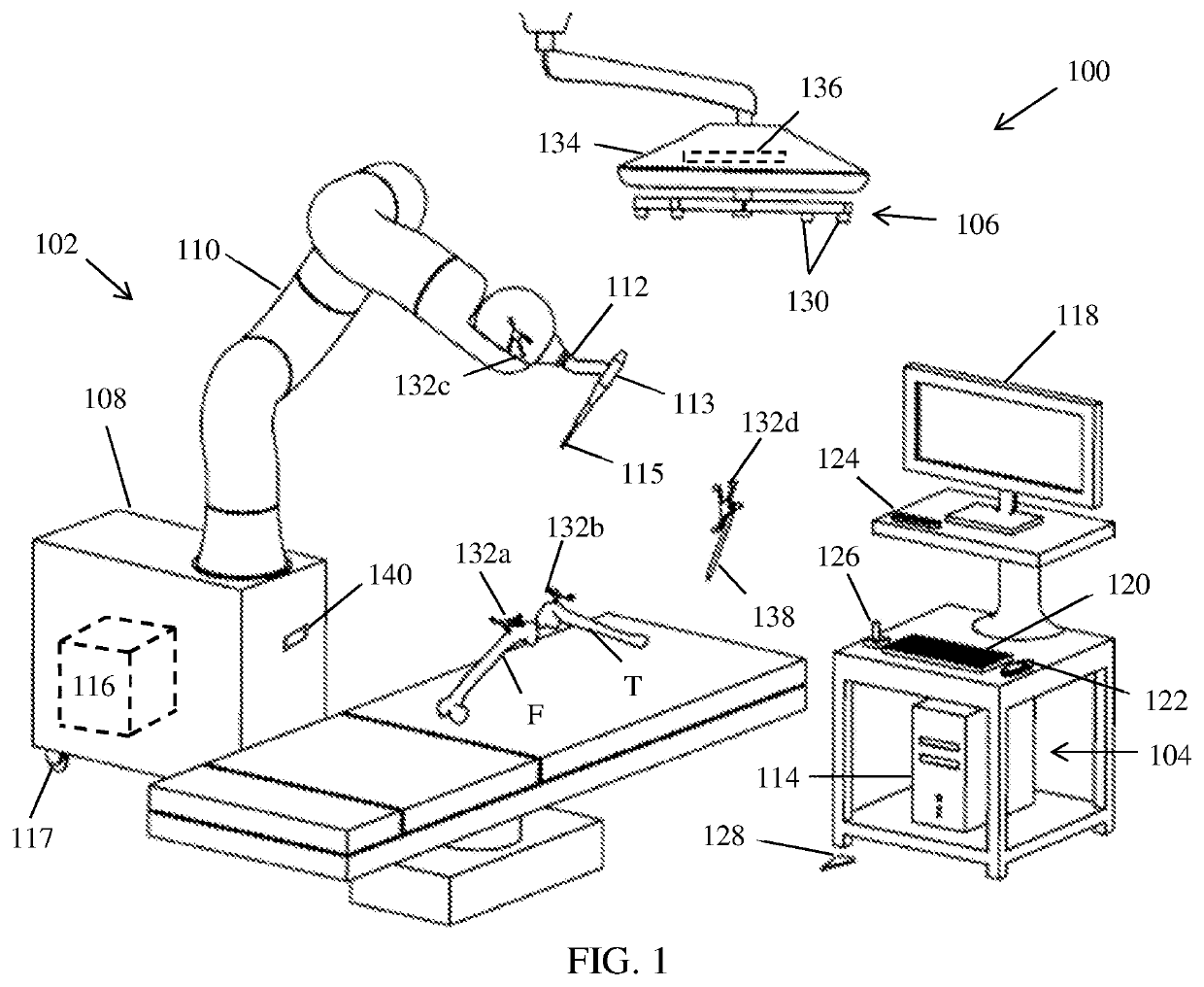
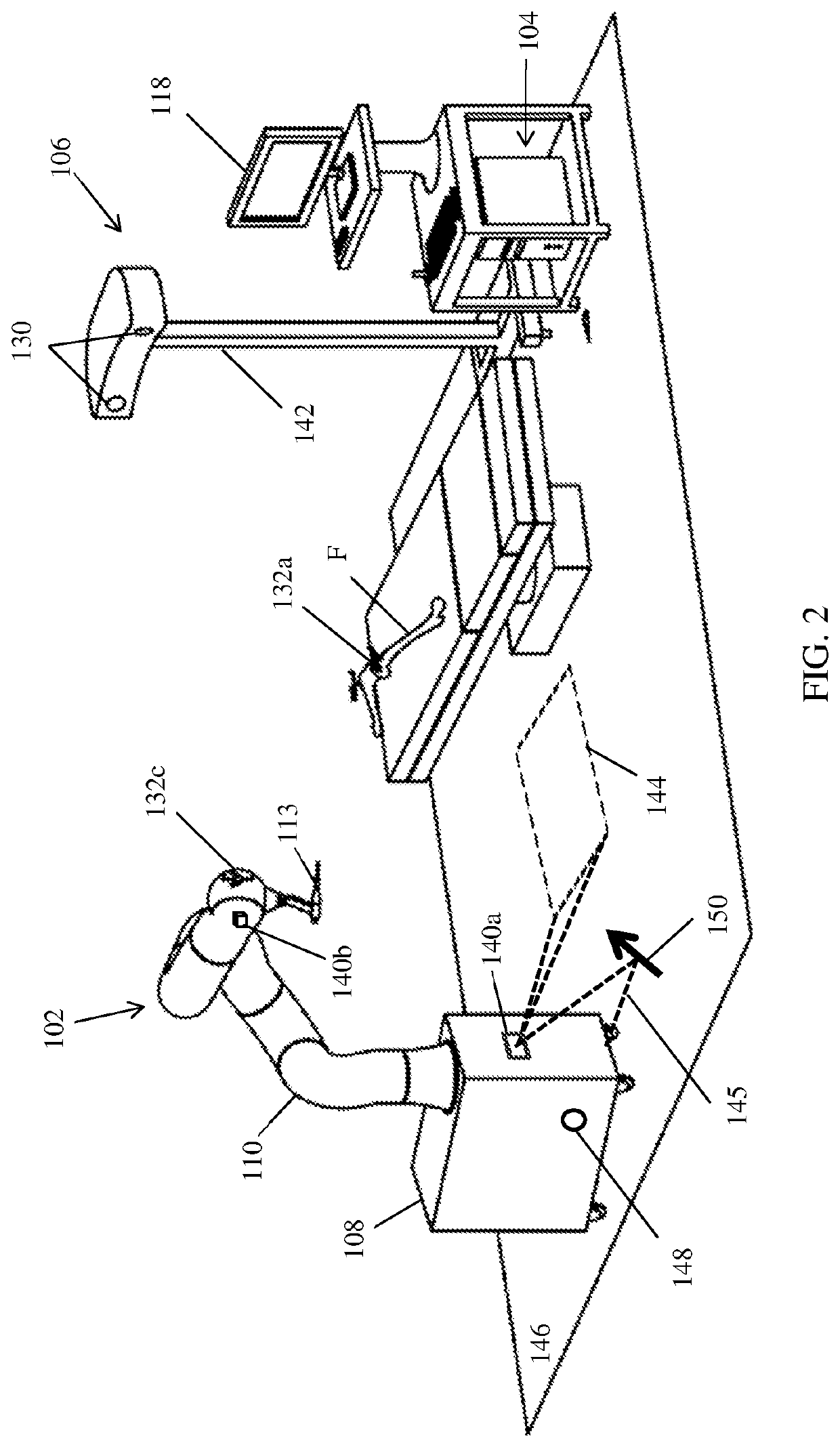
Method and system for guiding user positioning of a robot
ActiveUS10864050B2Surgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceSpinal columnAnatomical structures
A system and process is provided for dynamically positioning or repositioning a robot in a surgical context based on workspace and task requirements, manipulator requirements, or user preferences to execute a surgical plan. The system and method accurately determines and indicates an optimal position for a robot with respect to a patient's anatomy before or during a surgical procedure. Optimal positions for a robot are intuitively indicated to a user, surgical procedures can illustratively include surgery to the knee joint, hip joint, spine, shoulder joint, elbow joint, ankle joint, jaw, a tumor site, joints of the hand or foot, and other appropriate surgical sites.
Owner:THINK SURGICAL
Non-spherical articulating surfaces in shoulder and hip replacement
An orthopedic device and method of use are provided that incorporate complex, non-spherical articulating surfaces to allow a greater available range of motion compared with existing artificial shoulder joint and artificial hip joints. According to some embodiments, complex, non-spherical articulating surfaces can be incorporated on a humeral head and / or glenoid of a shoulder prosthesis. In other embodiments, complex, non-spherical articulating surfaces can be incorporated on the acetabulum and / or femoral head of a hip prosthesis. These non-spherical surfaces can be used to adjust constraint, joint thickness, soft tissue tension, moment and arc of motion, and in doing so, influence motion.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Joint endoprosthesis with ambient condition sensing
ActiveUS20050012610A1Harmful conditionAnkle jointsSurgeryPhysical medicine and rehabilitationProsthesis
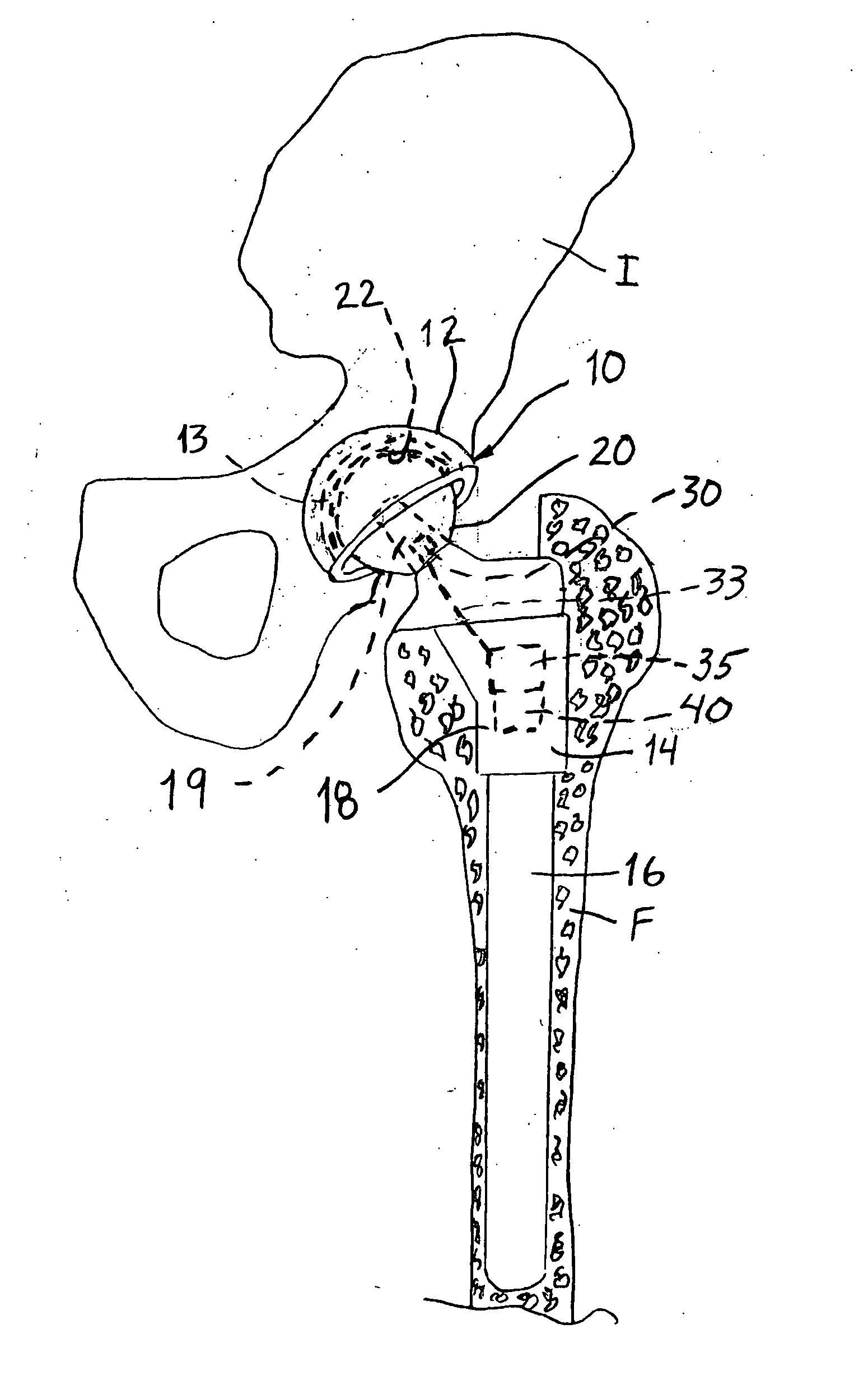
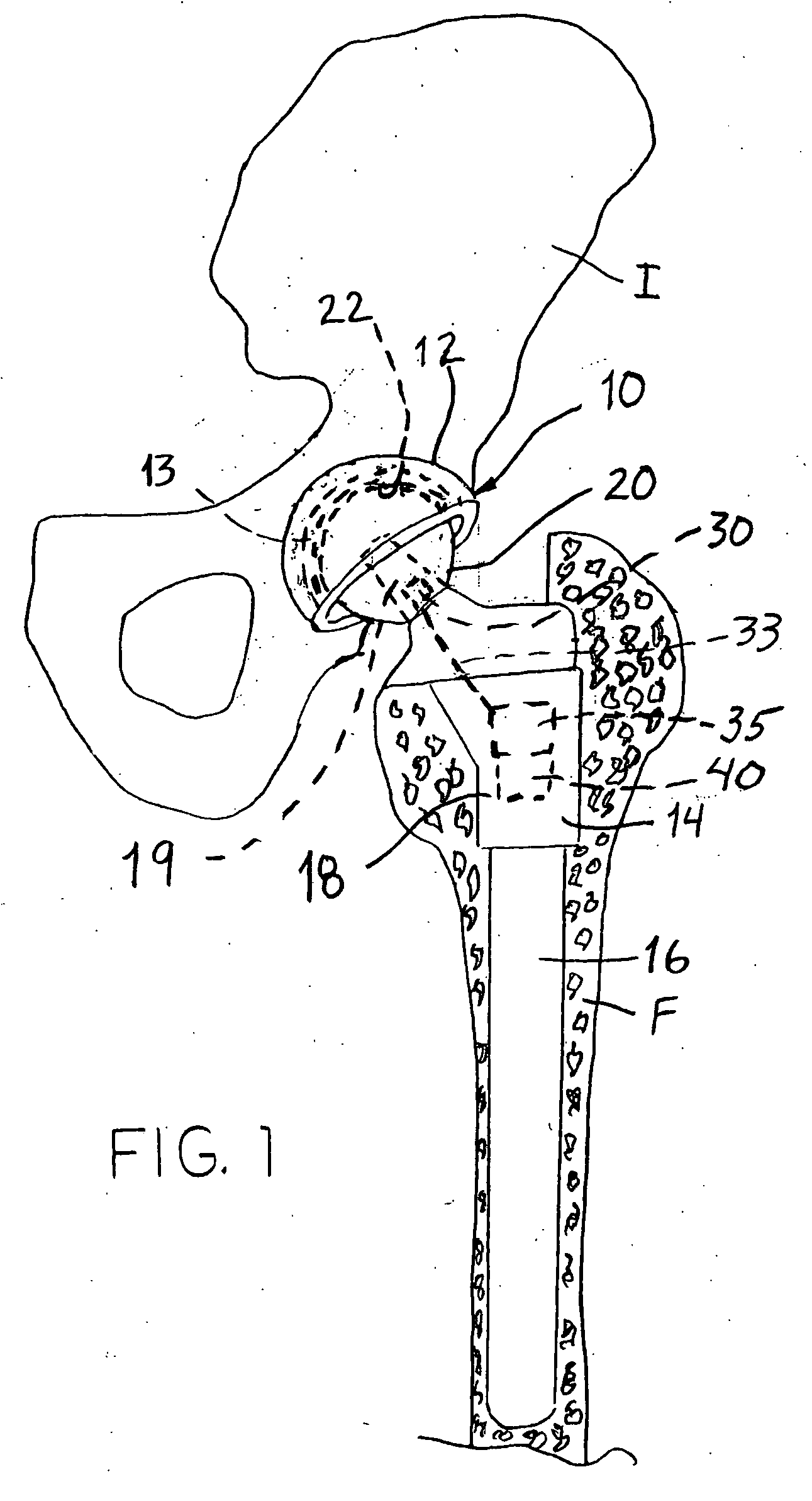
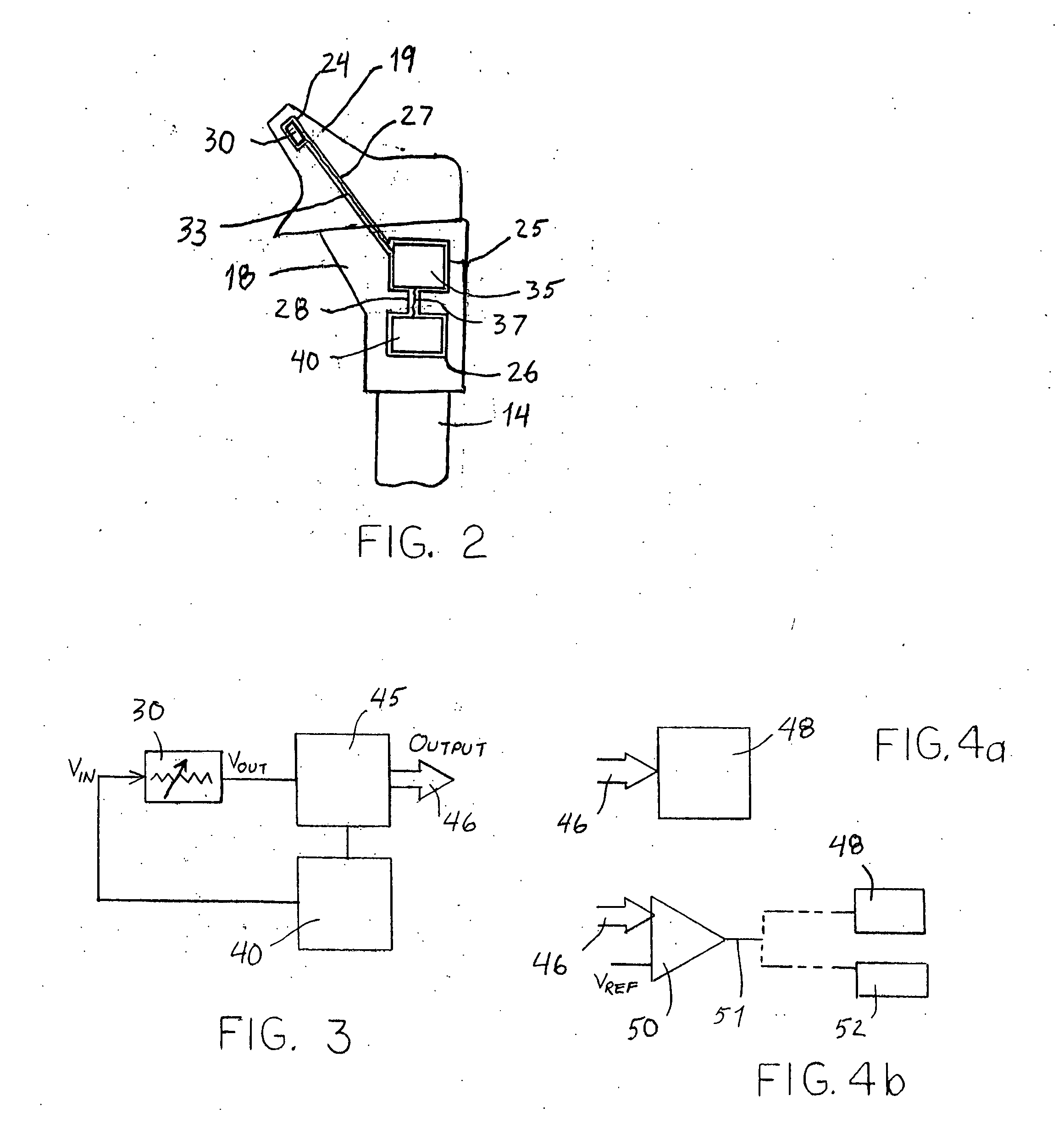
A system for monitoring the ambient conditions of a mammalian joint, and particularly a joint that has been instrumented with a joint endoprosthesis includes a sensor supported by a component of the joint endoprosthesis. The system includes a transmission element that is also supported within the body of the patient, preferably within the endoprosthesis. The transmission element transmits a signal indicative of the sensed ambient condition within the instrumented joint. For example, the sensor can be a temperature sensor used to evaluate the temperature within a joint, such as a hip joint, during activity or exercise by the patient.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
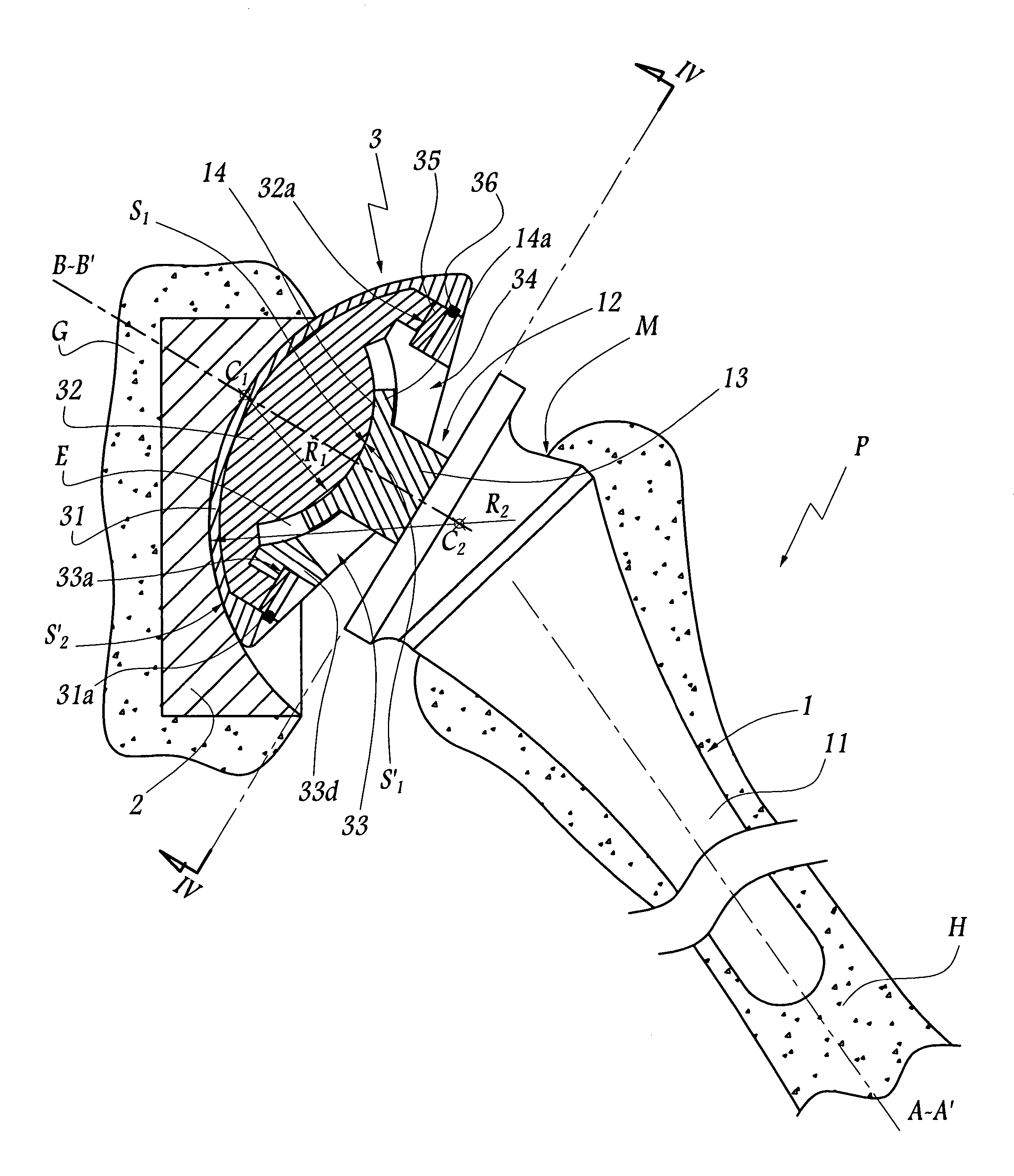
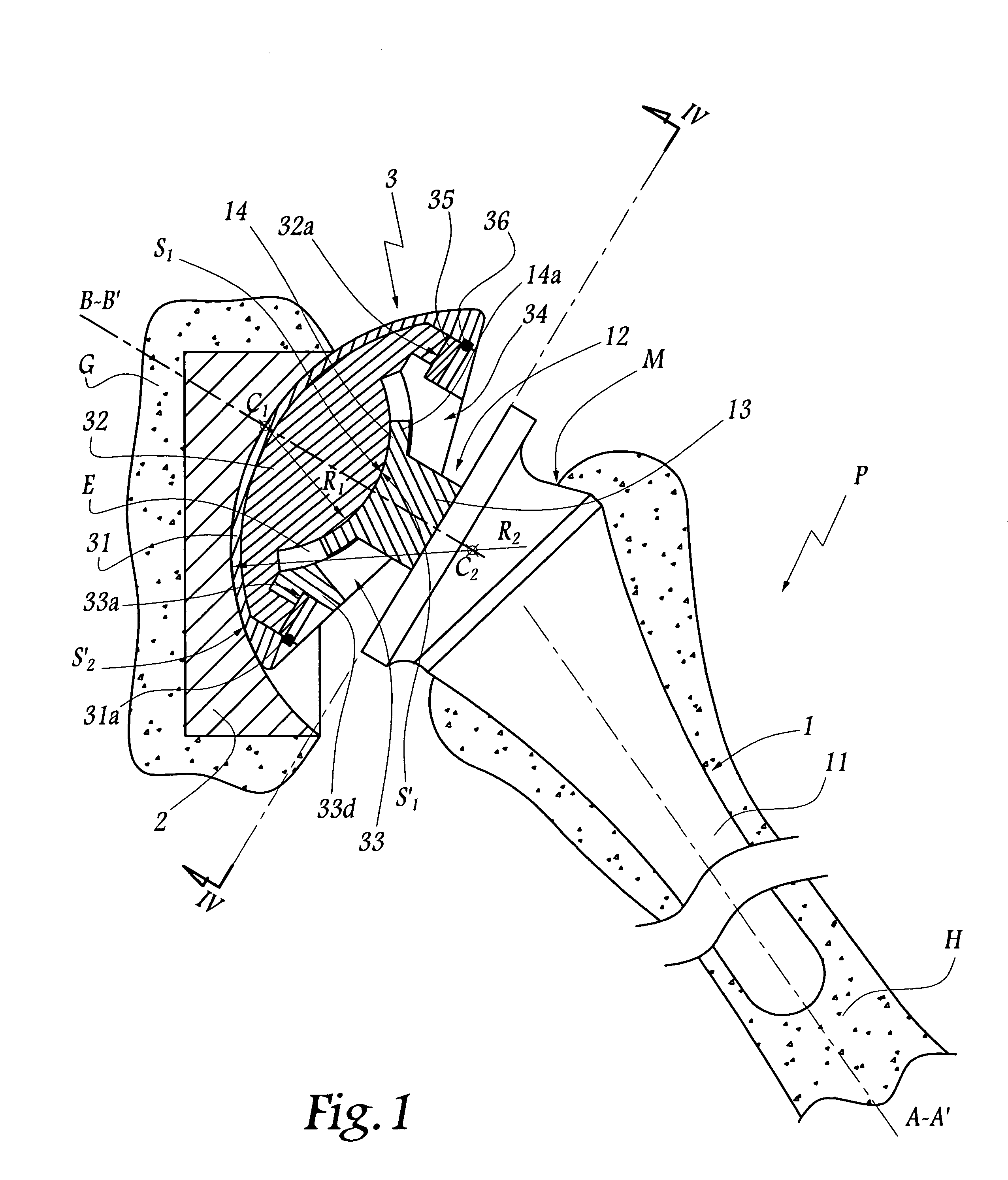
Shoulder or hip prosthesis and process for fitting same
InactiveUS20050165490A1Improve stabilityIncrease amplitudeJoint implantsFemoral headsMedicineAbutment
This prosthesis comprises a humeral or femoral component and an intermediate component. The concave surface of articulation of the humeral or femoral component is formed by a plate connected by a neck to a part of this component adapted to be anchored in the humeral or femoral medullary cavity. The intermediate component is provided with a member for retaining the humeral or femoral component in a position where the plate is in abutment against the first convex surface of the intermediate component. The retaining member defines a non-circular passage in which the neck is adapted to be displaced as a function of the movements of the humeral or femoral component with respect to the other components of the prosthesis. The retaining member defines with the first convex surface of articulation of the intermediate component a volume for receiving a part of the plate projecting radially with respect to the neck.
Owner:TORNIER SA SAINT ISMIER
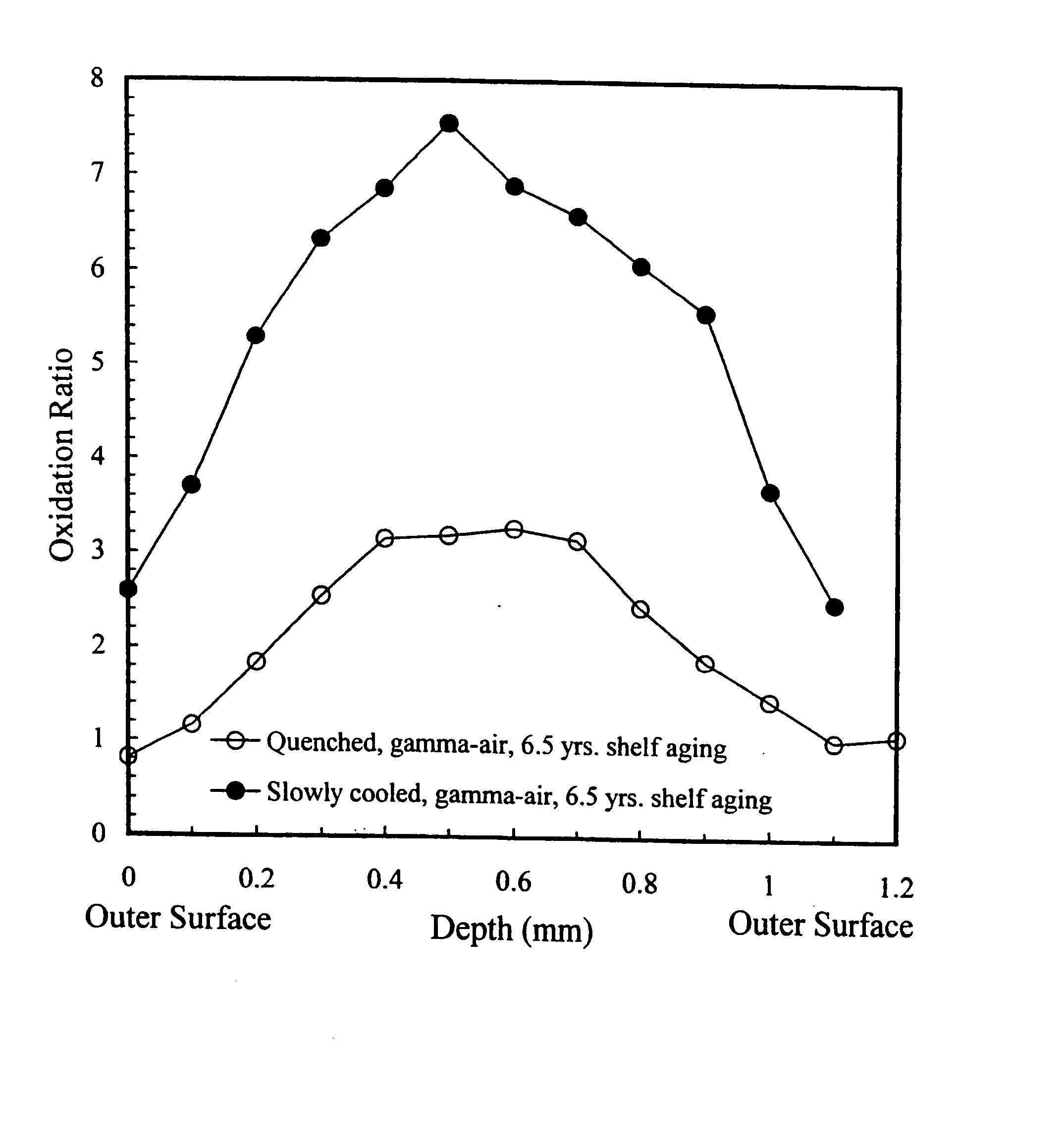
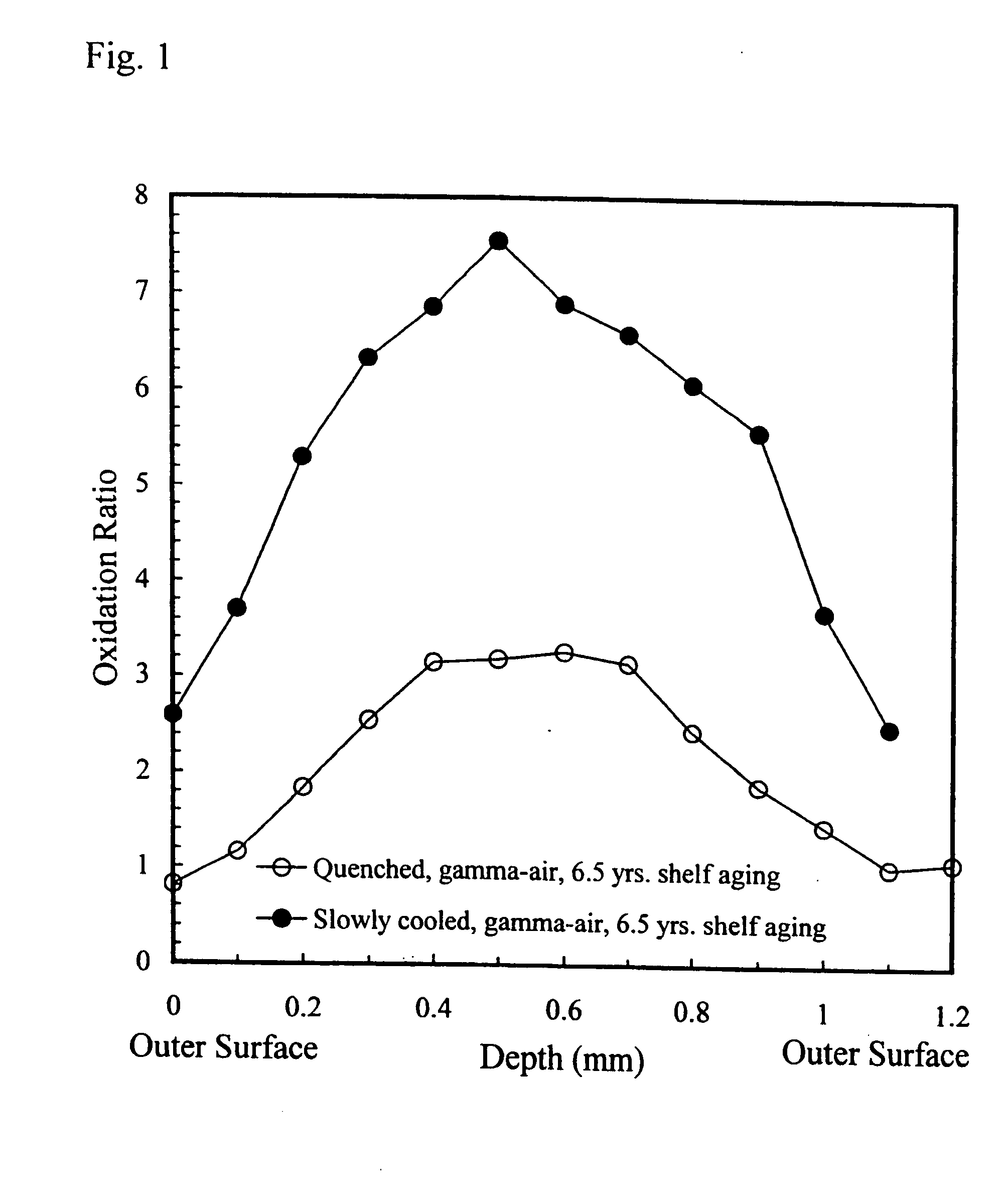
Oxidation-resistant and wear-resistant polyethylenes for human joint replacements and methods for making them
InactiveUS20070293647A1Improve wear resistanceImprove the immunitySurgeryPackage sterilisationPresent methodWear resistant
The present invention presents methods for making oxidation-resistant and wear-resistant polyethylenes and medical implants made therefrom. Preferably, the implants are components of prosthetic joints, e.g., a bearing component of an artificial hip or knee joint. The resulting oxidation-resistant and wear-resistant polyethylenes and implants are also disclosed.
Owner:THE ORTHOPAEDIC HOSPITAL
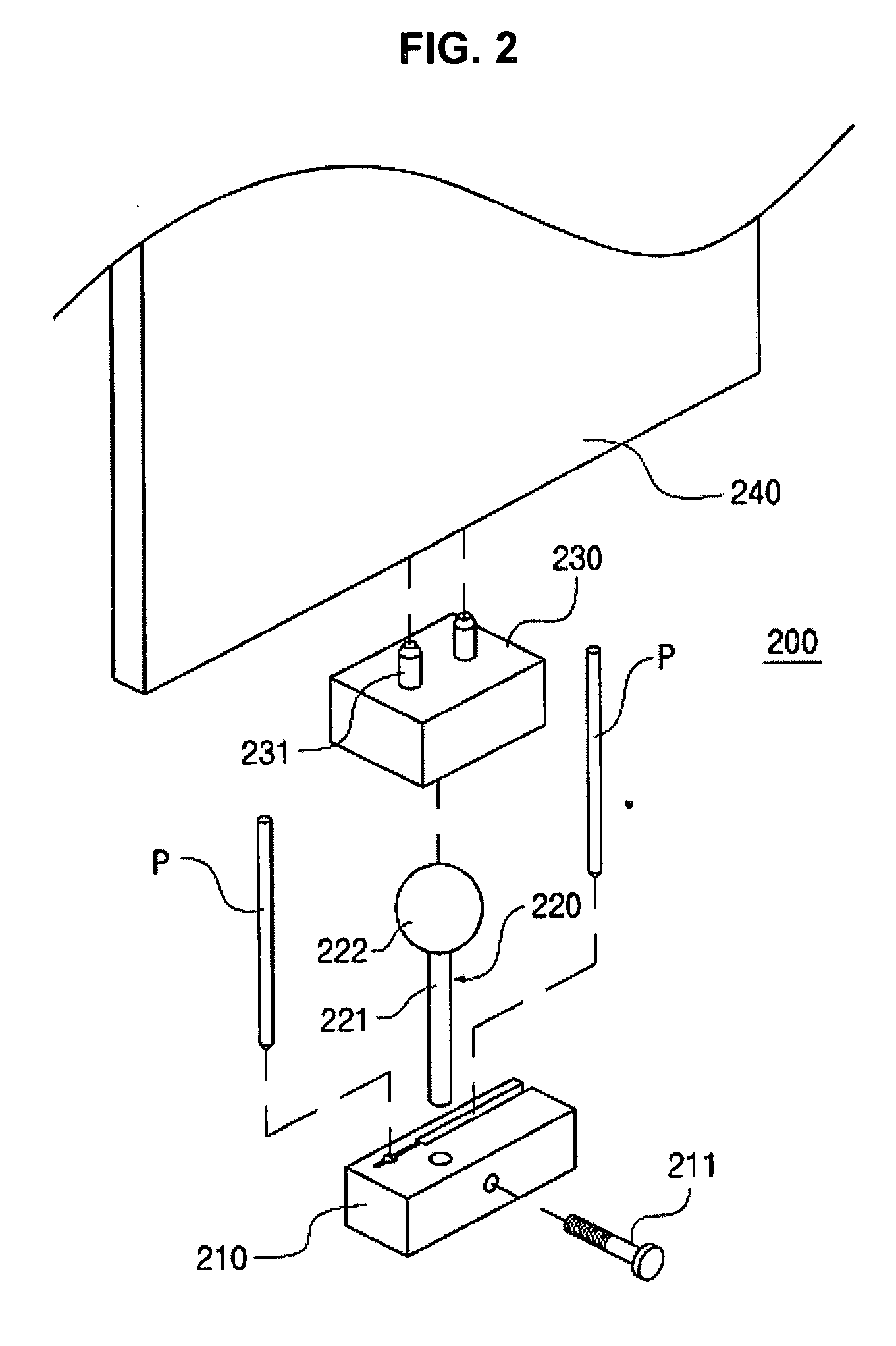
Navigation System for Hip Replacement Surgery Having Reference Mechanism and Method Using the Same
InactiveUS20090171370A1Simple structureDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsAirplaneAnterior pelvic plane
A navigation system for an acetabular cup, which guides an insertion orientation of the acetabular cup inserted into a pelvis during a total hip replacement surgery, includes: a pelvis position tracer which includes probes in contact with three particular points of the pelvis placed on an anterior pelvic plane and a first reference mechanism disposed to indicate a specific reference plane when the probes come in contact with the particular points; and a pelvis position indicator which is fixed to the pelvis, and includes a second reference mechanism that is adjustable to indicate a plane parallel to the specific reference plane indicated by the first reference mechanism, or to indicate a plane perpendicular thereto, or to indicate the both planes. Accordingly, an insertion orientation of an acetabular cup can be guided by using a reference mechanism having a simple structure, and the acetabular cup can be accurately guided regardless of changes in the patient's pelvic position during surgery, because a plane used in the insertion of the acetabular cup can be indicated continuously.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Bi-polar hip prosthetic devices employing diffusion-hardened surfaces
InactiveUS20040122524A1Bone implantPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAcetabular componentPlastic surgery
An orthopedic implant having diffusion-hardened surfaces employed at inner and outer load-bearing surfaces. Preferably, the orthopedic implant is a bipolar hip prosthetic device and system where a coating of oxidized zirconium is formed at the articulating, load-bearing surface of the acetabular component and at the articulating, load-bearing surface of the femoral head. The acetabular component has a polymeric cup, made from a bio-compatible material, such as UHMWPE.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
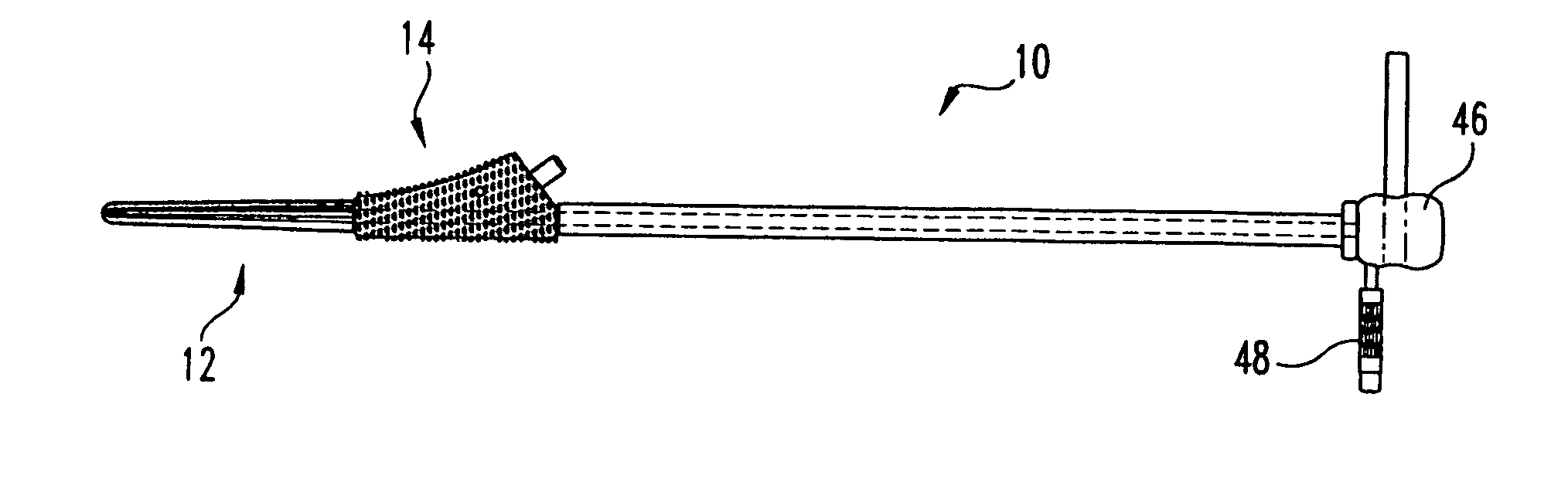
Laterally-expandable access cannula for accessing the interior of a hip joint
InactiveUS20090306586A1Simpler and faster and convenient approachEar treatmentCannulasMuscles of the hipCam
A laterally-expandable access cannula comprising:an elongated body have a distal end, a proximal end and a lumen extending between the distal end and the proximal end, the distal end of the access cannula comprising a plurality of fingers tapering inwardly as they extend distally, and the elongated body having an internal thread extending along at least a portion of the length of the lumen; andan inner sleeve disposed within the lumen of the elongated body, the inner sleeve having an external thread extending along at least a portion of its length, the external thread of the inner sleeve being in engagement with the internal thread of the elongated body, such that rotation of the inner sleeve causes the inner sleeve to move distally relative to the elongated body, whereby to cam open the plurality of fingers of the elongated body.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
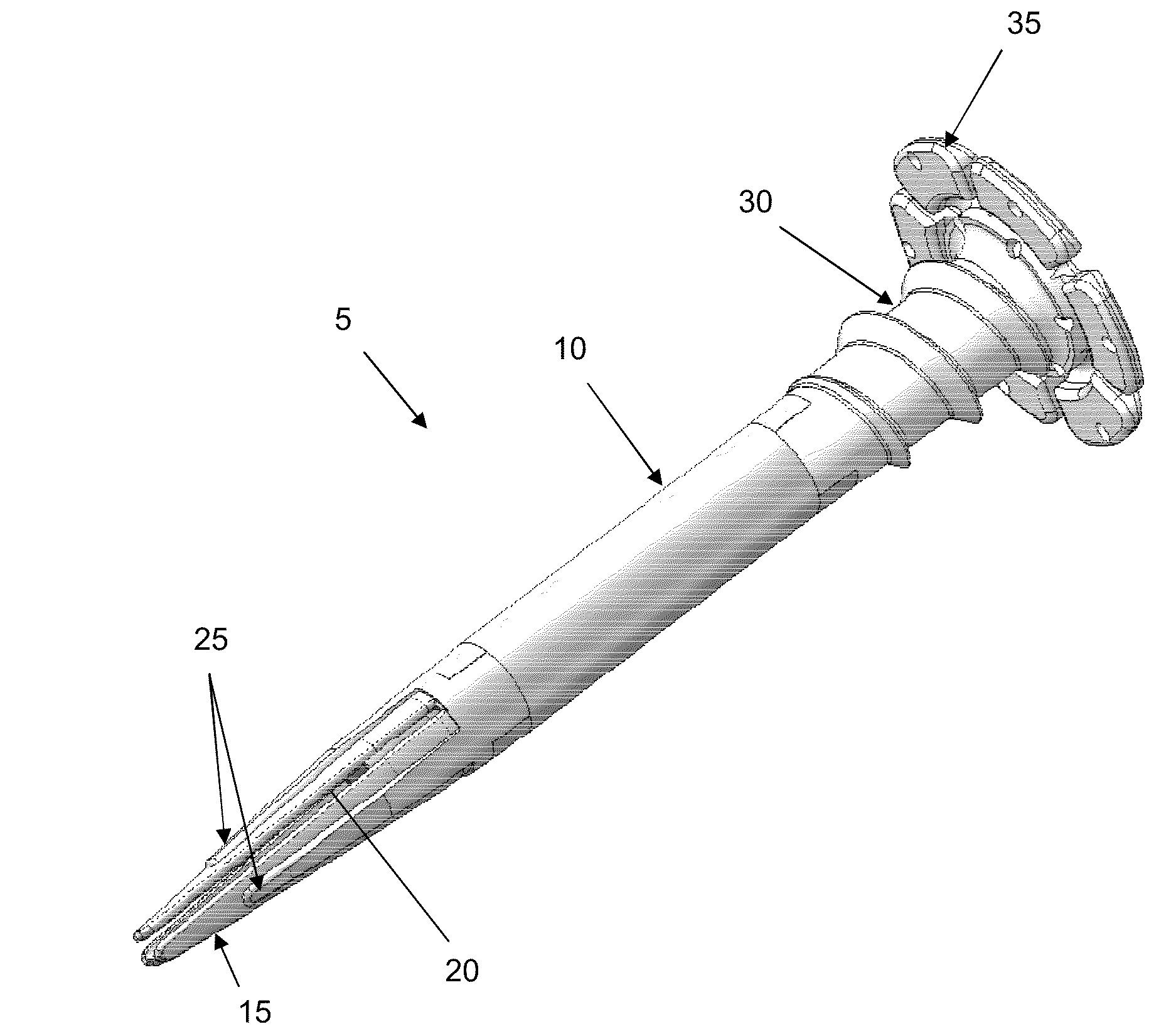
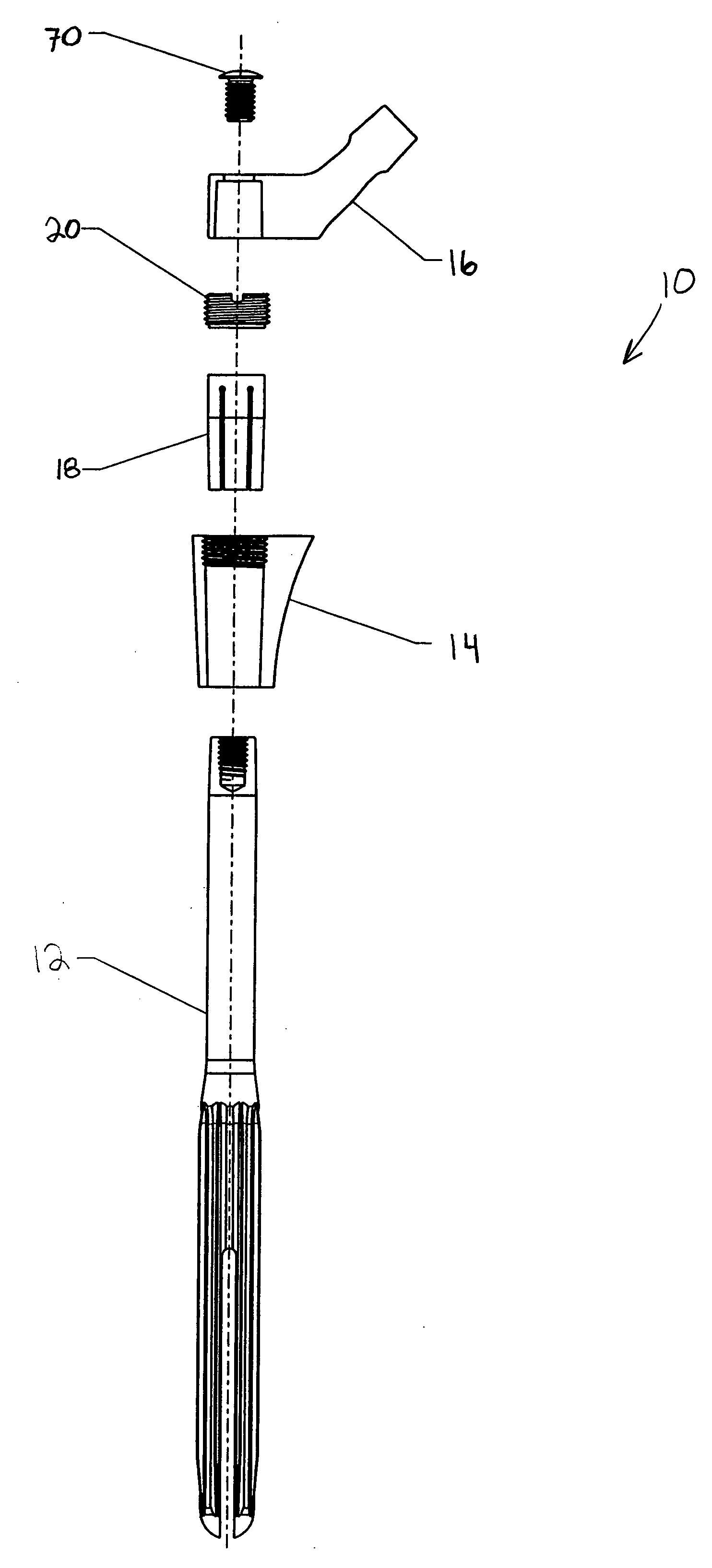
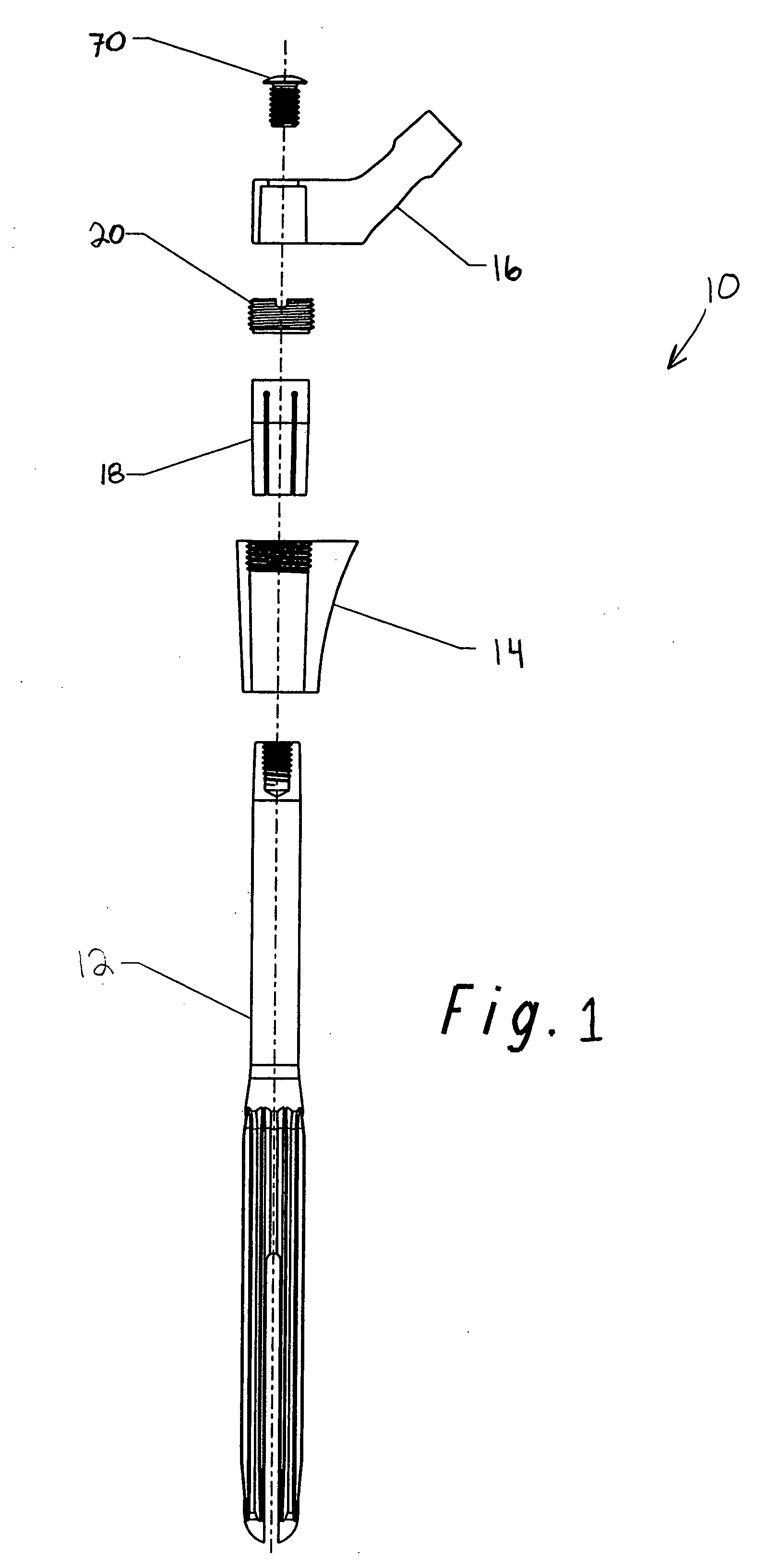
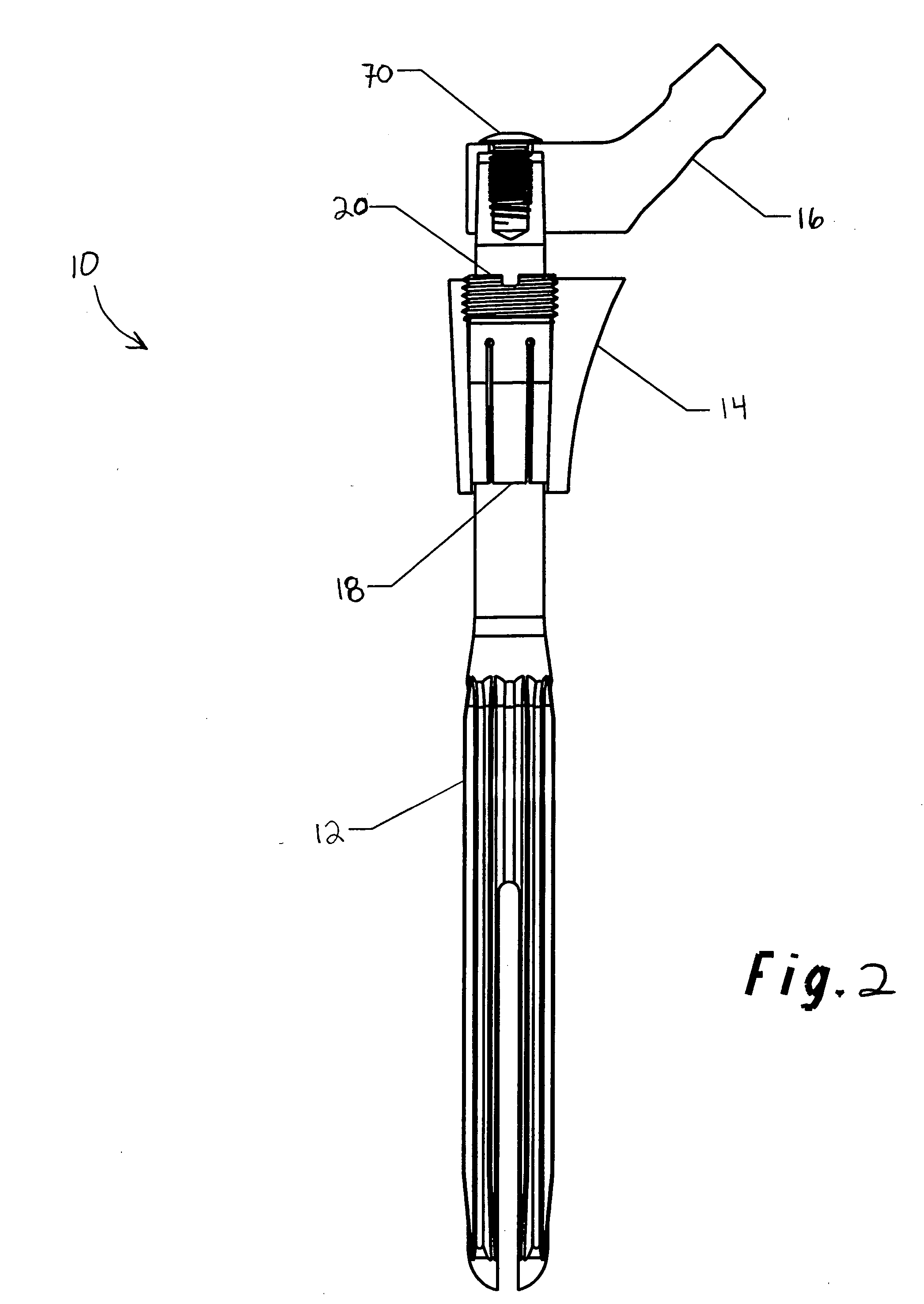
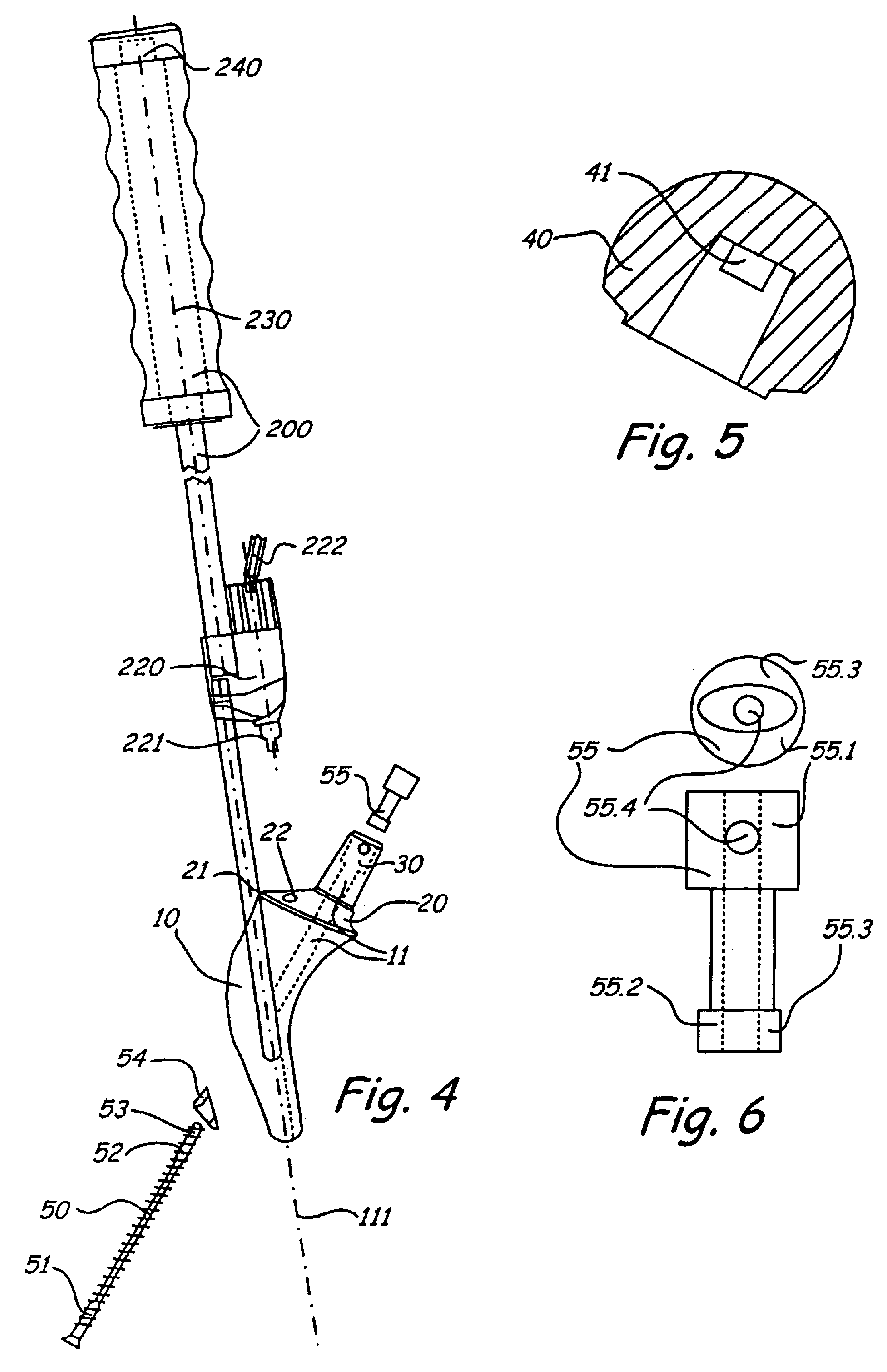
Modular hip prosthesis
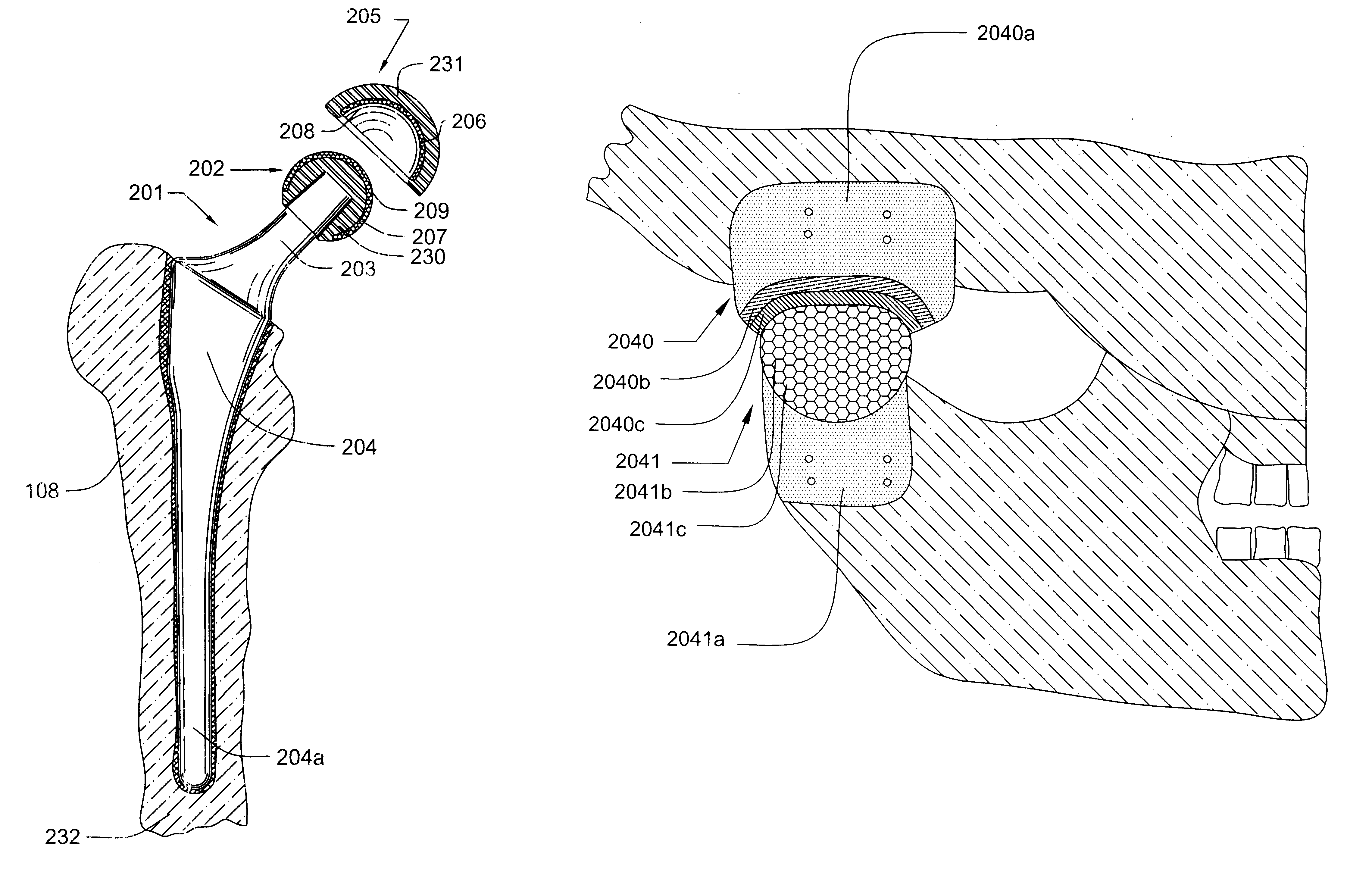
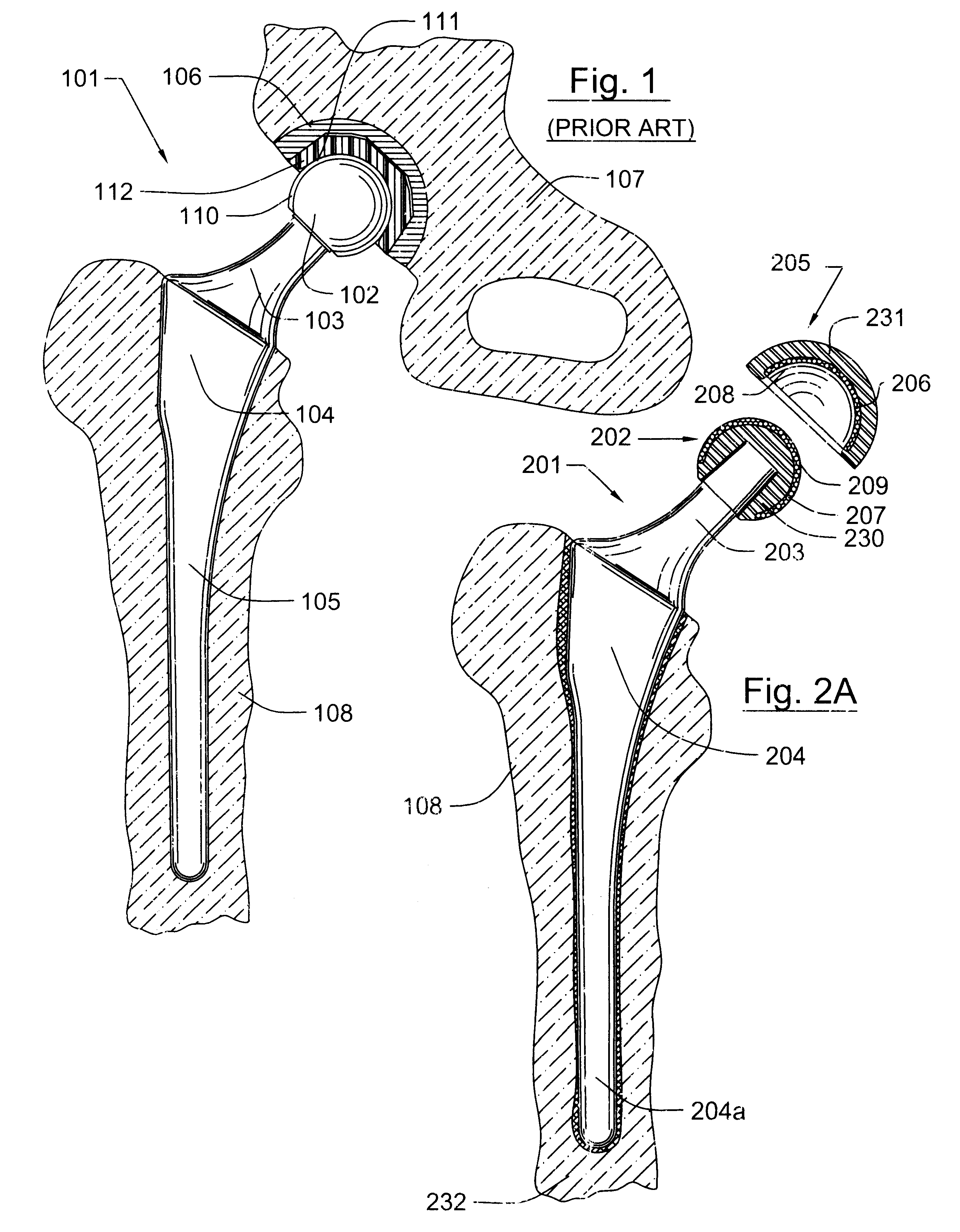
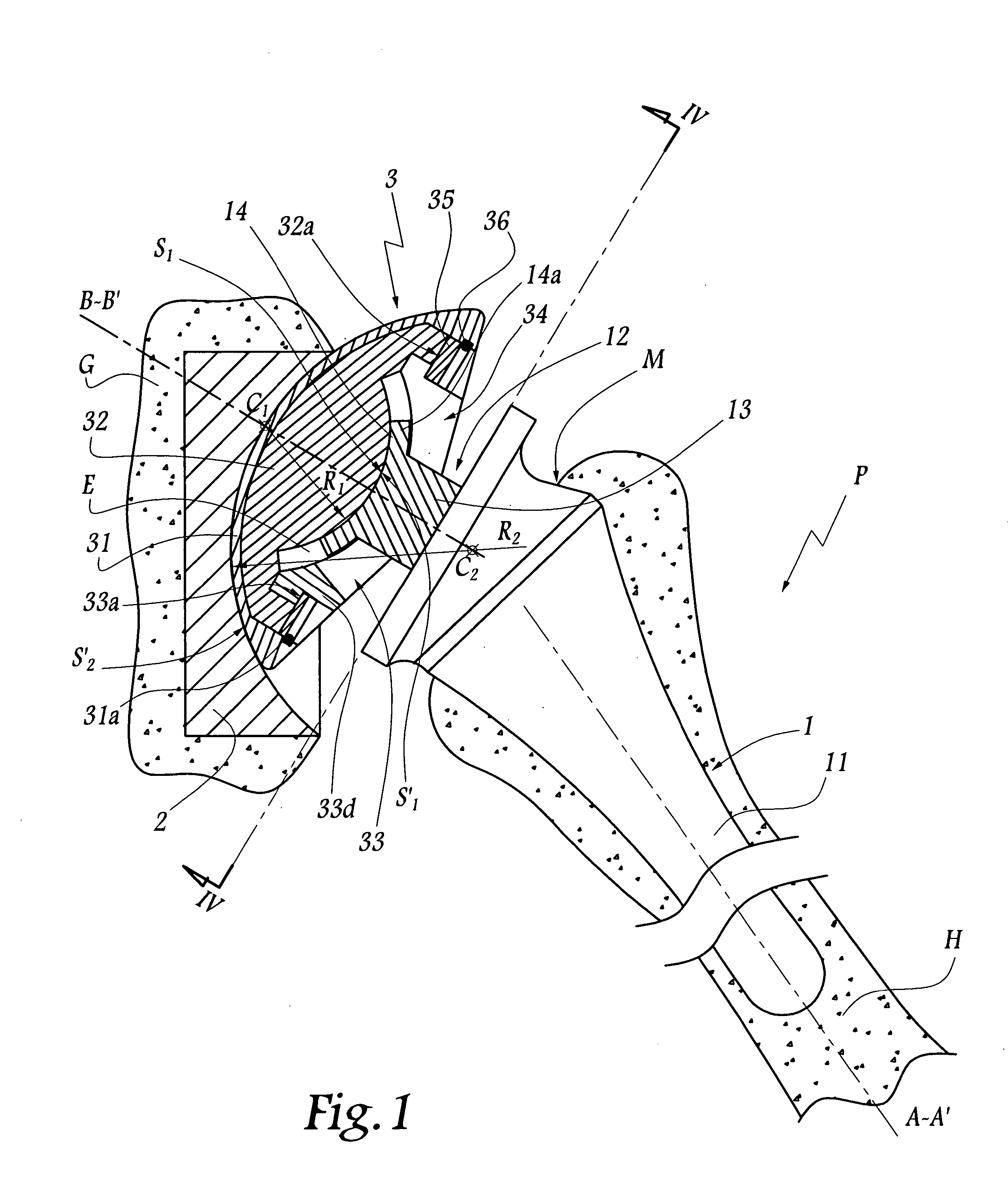
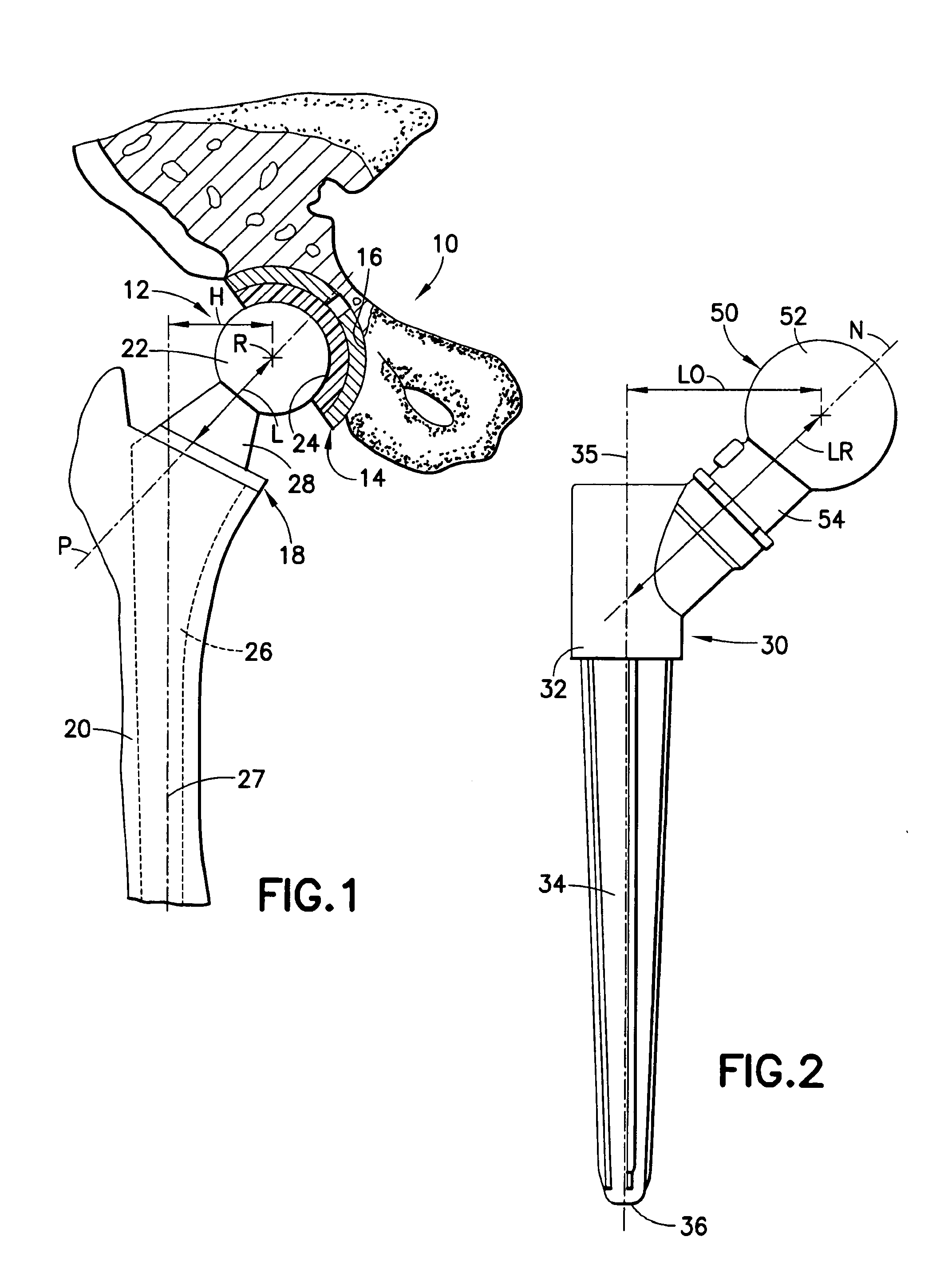
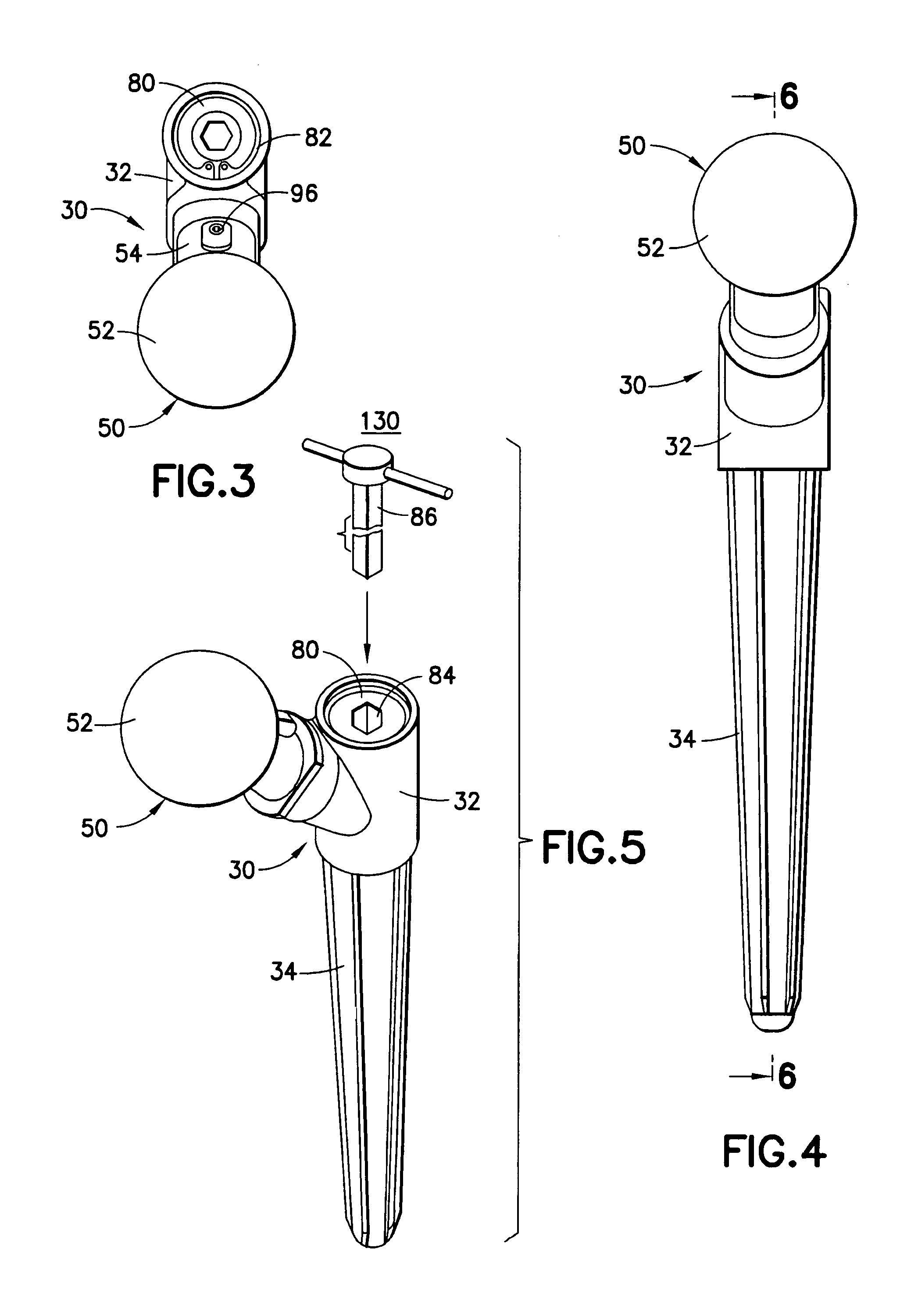
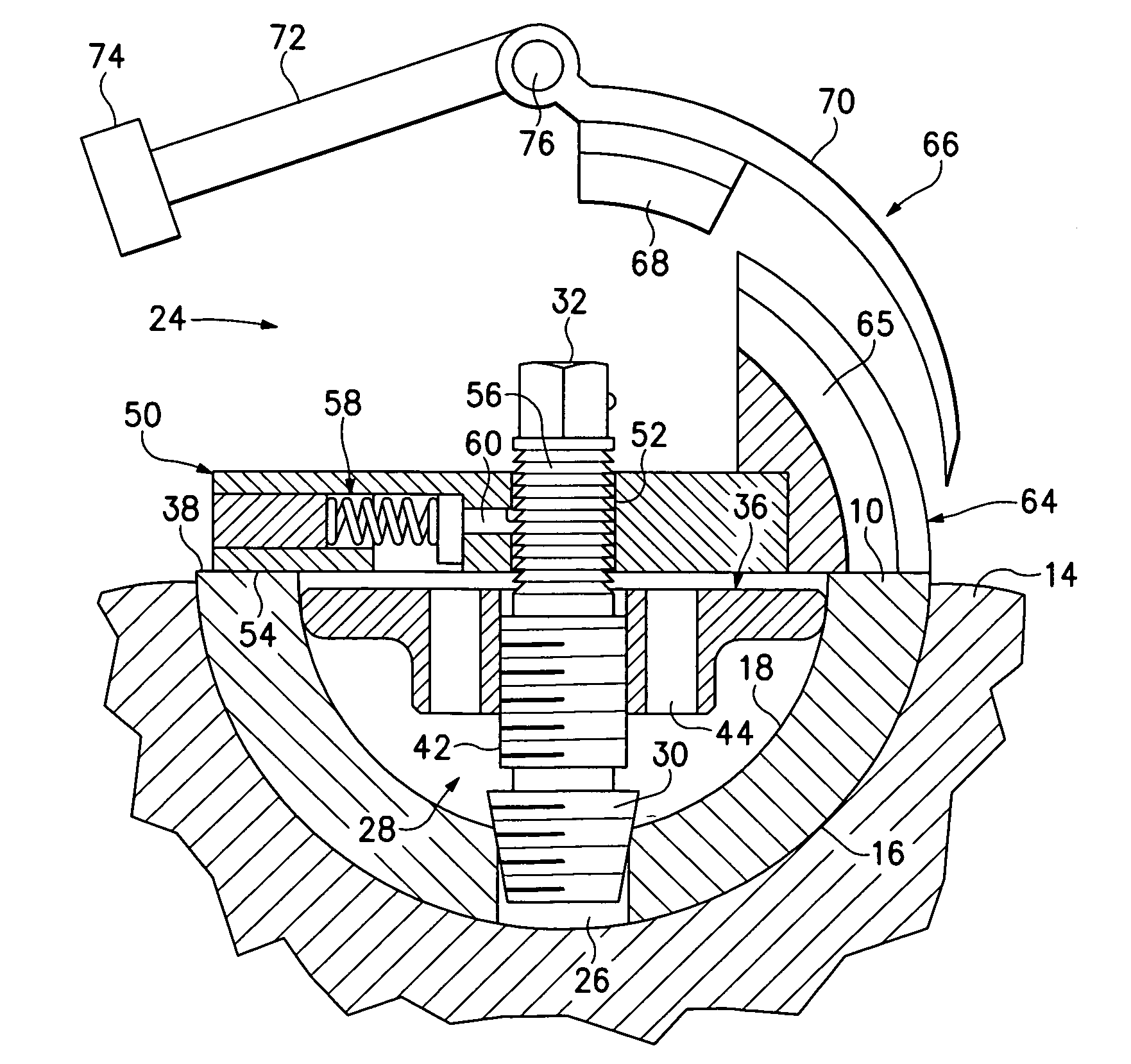
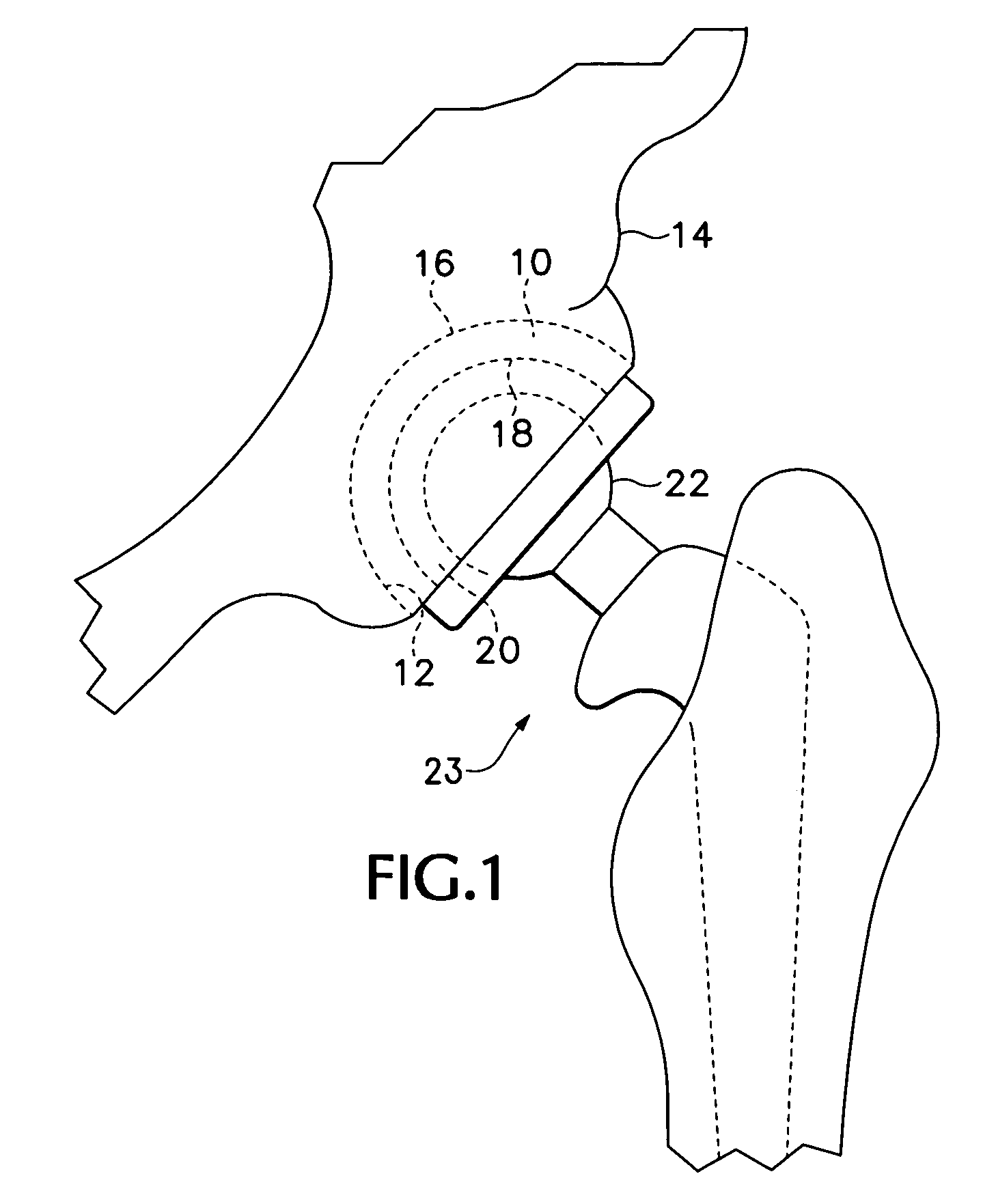
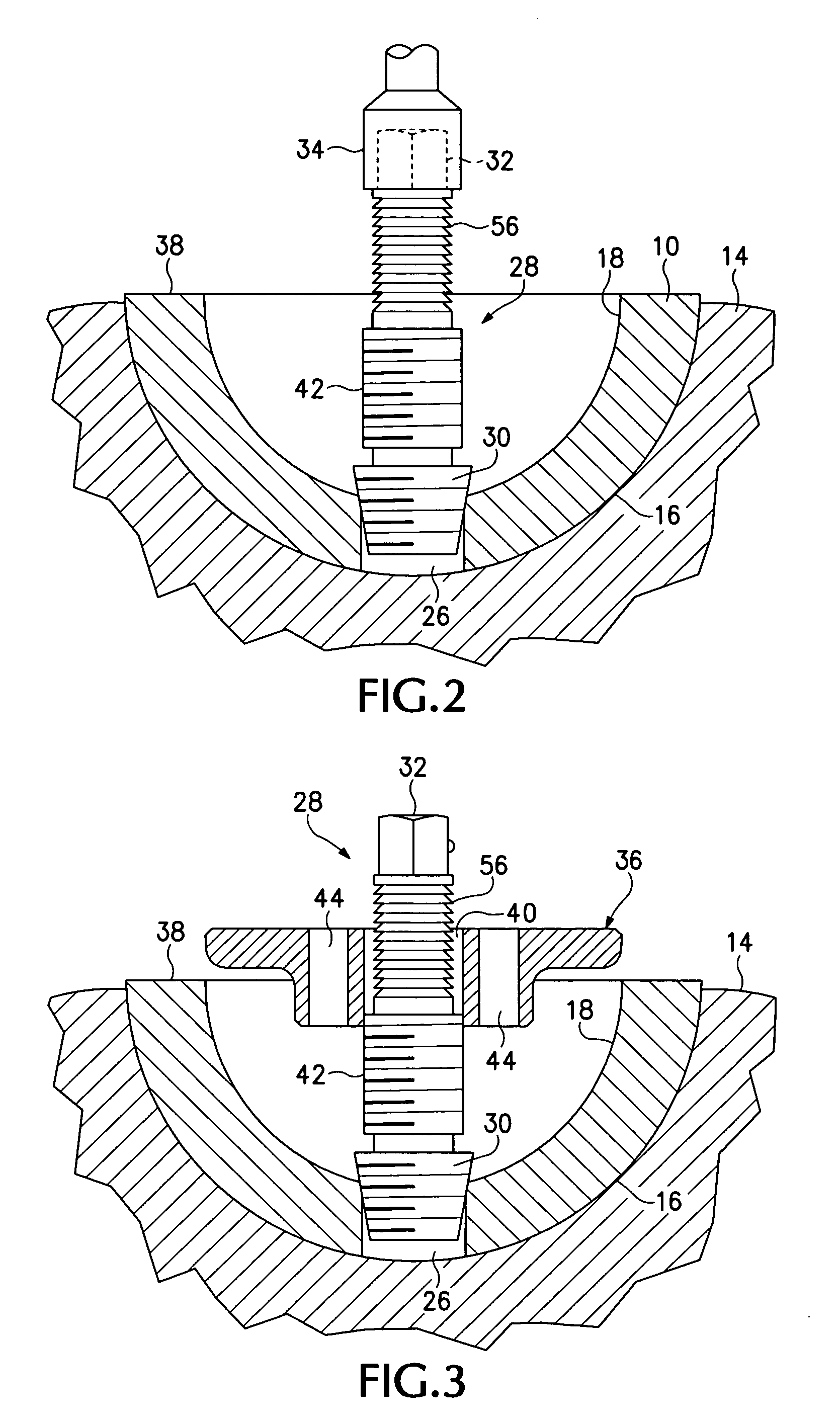
InactiveUS20050004679A1Wide degree of adjustabilityReduced range of motionJoint implantsFemoral headsJoint prosthesisSocket hip
A modular orthopedic hip prosthesis having three main components: a stem, a proximal body, and a neck. The components are removeably connectable and selectively adjustable. The neck is rotationally adjustable about the stem, and the proximal body is both rotationally and axially adjustable about the stem. A collet and locking member hold and lock the proximal body to the stem.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Hip arthroplasty trialing apparatus with adjustable proximal trial and method
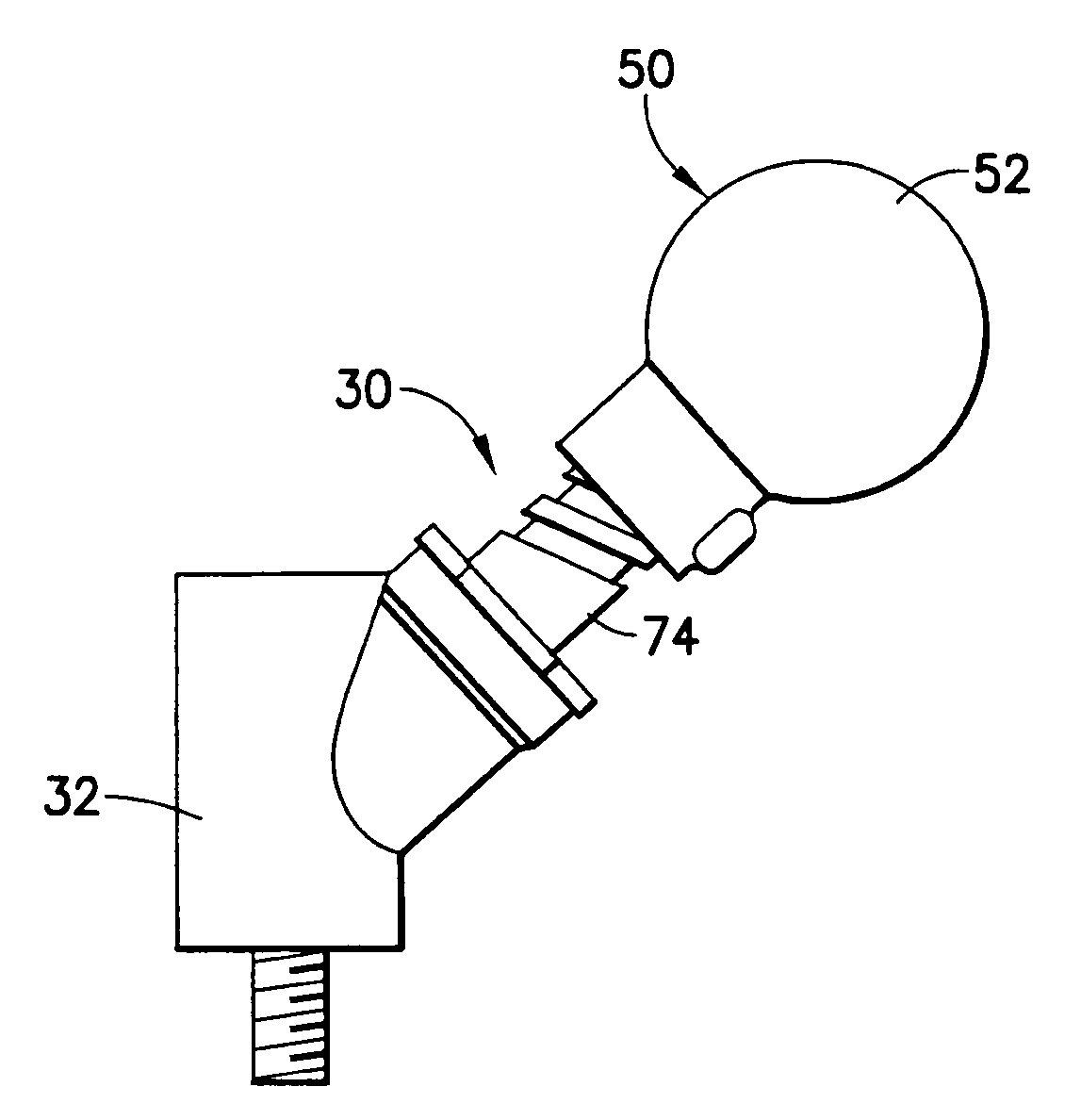
ActiveUS7425214B1Easy to determineOptimal hip mechanicsInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRight femoral headFemoral stem
Apparatus and method are described for interoperatively determining, during a trailing procedure conducted in connection with total hip arthroplasty, a combination of neck length and femoral head offset required in a femoral component for establishing appropriate hip mechanics in a prosthetic hip joint to be implanted at an implant site. A trial femoral head is coupled for selective movement relative to a femoral stem component to move the trial femoral head longitudinally and laterally relative to a predetermined direction among selected combinations of trial distance and trial offset to evaluate hip mechanics and determine interoperatively an appropriate combination of trial distance and trial offset corresponding to the combination of neck length and femoral head offset required in the prosthetic hip joint.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Exoskeleton rehabilitation robot for rehabilitation of lower limb walking function and control system and method thereof
ActiveCN107126344AIncrease active freedomSpeed up recoveryProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesKnee JointEngineering
The invention discloses an exoskeleton rehabilitation robot for rehabilitation of a lower limb walking function and a control system and method thereof. The robot comprises a backrest, a hip joint power source, a hip joint component, a waist component, a thigh bar component, a knee joint power source, a knee joint component, a shank bar component, an ankle joint component and a foot pedal. According to the lower limb exoskeleton rehabilitation robot, a driving scheme is designed by utilizing a bionics principle, so that the initiative degree of freedom of the ankle joint is increased; through initiatively pulling the heel tendon muscles of the patients, the rehabilitation speed of the ankle joint function is improved; the waist component, a connection rod mechanism and the foot pedal adopt a carbon fiber composite material, so that the structure weights and volumes are lightened while the strength is kept; and a non-polar adjustable function is set for the waist width, thigh length and shank length, and flexible bandages are equipped, so that the wearing comfort level requirement of the users is satisfied to the greatest extent. The robot disclosed by the invention not only can be used as a tool for riding instead of walk for the patients with walking disability, but also can help the stroke patients to obtain walking ability again through initiative training.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Reflex fixation geometry revision and reconstruction system reverse articulation
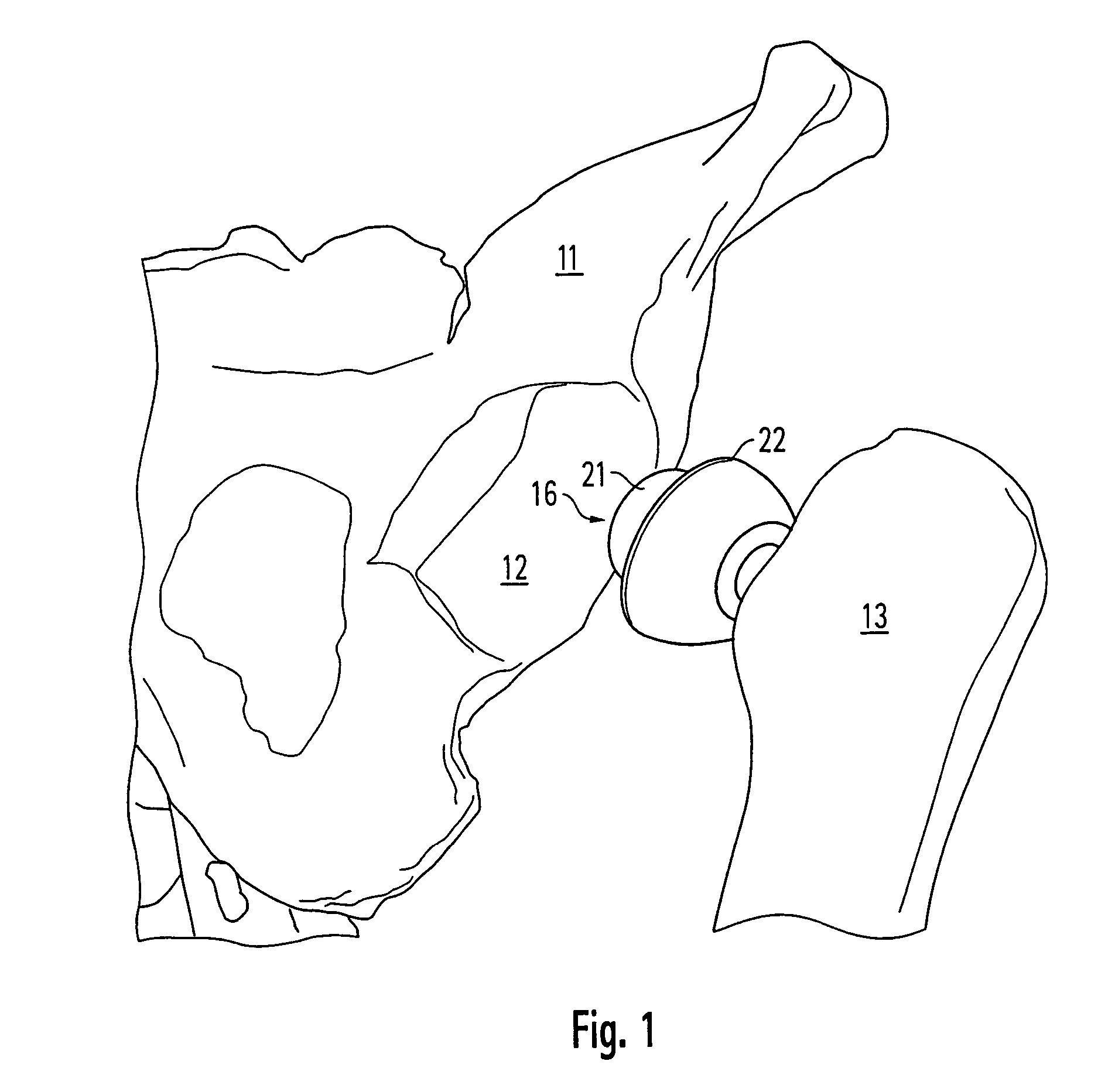
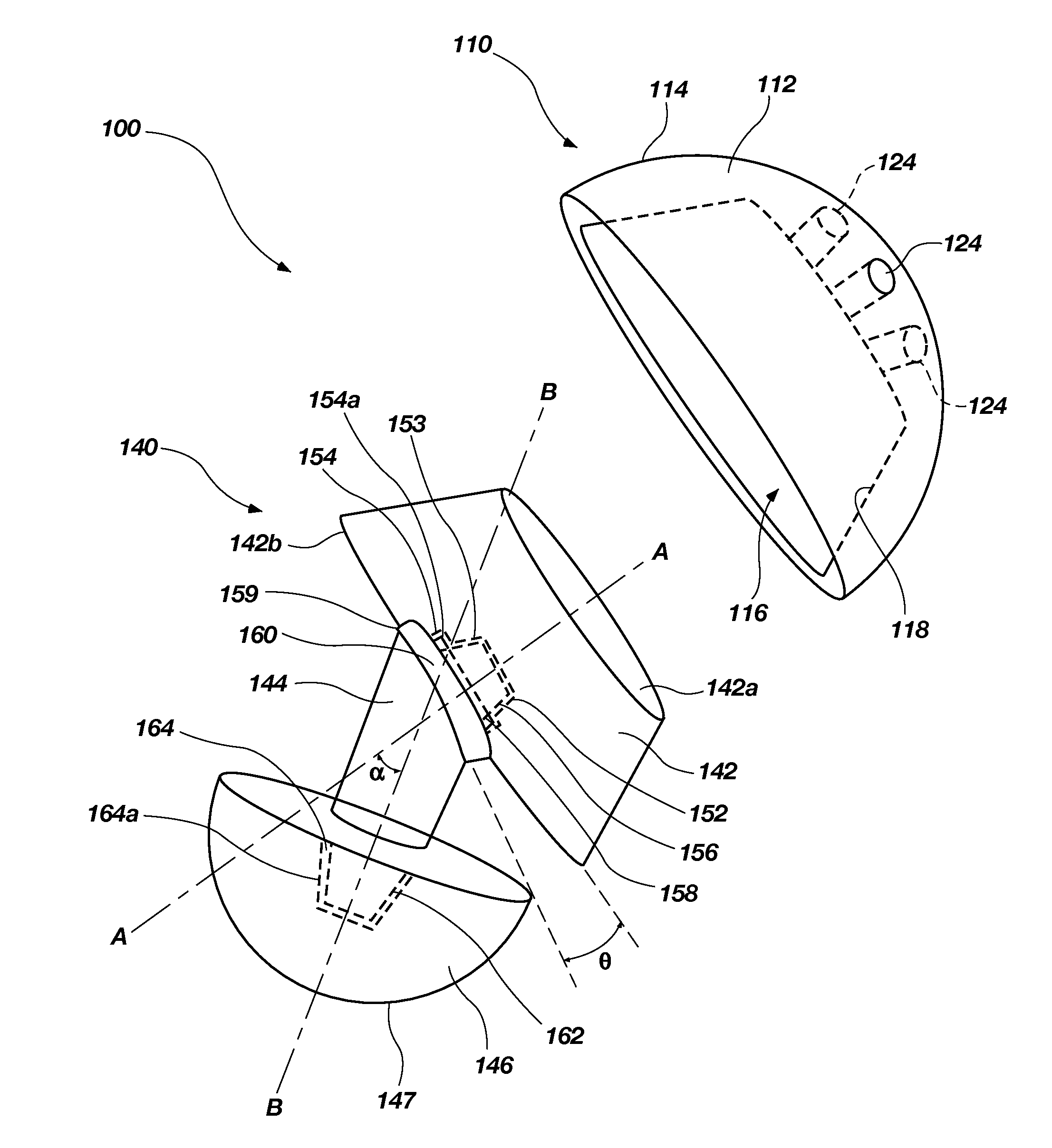
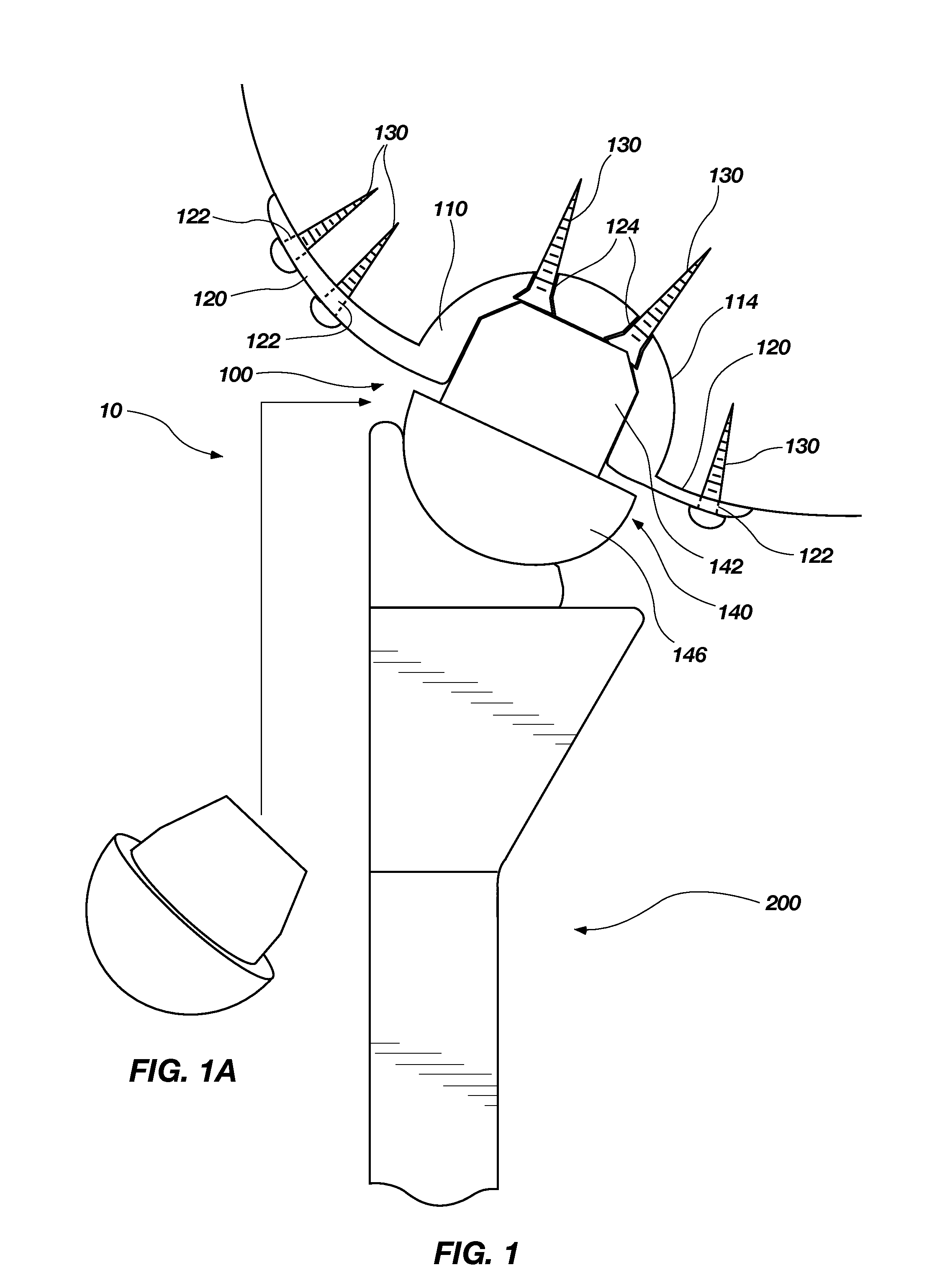
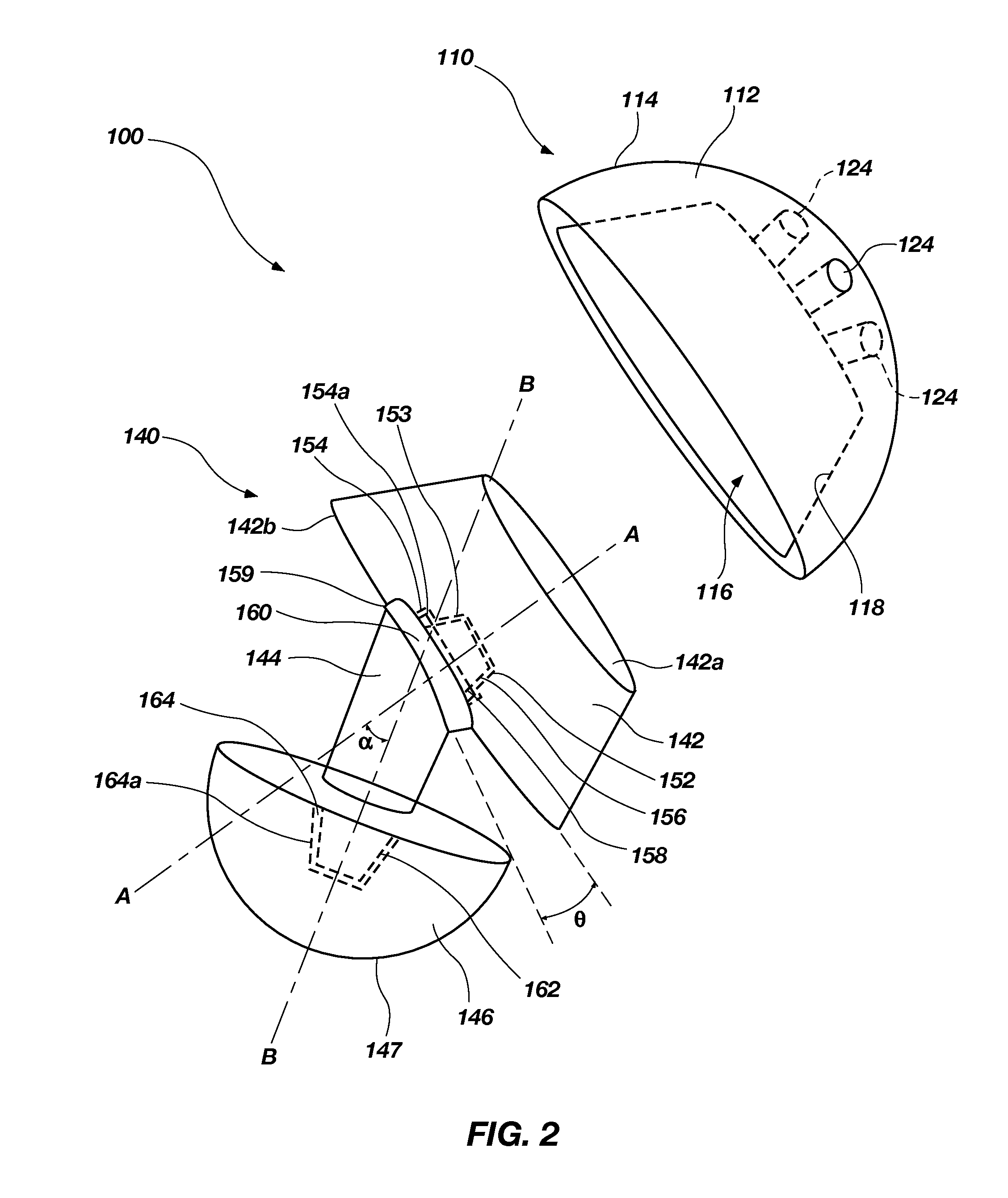
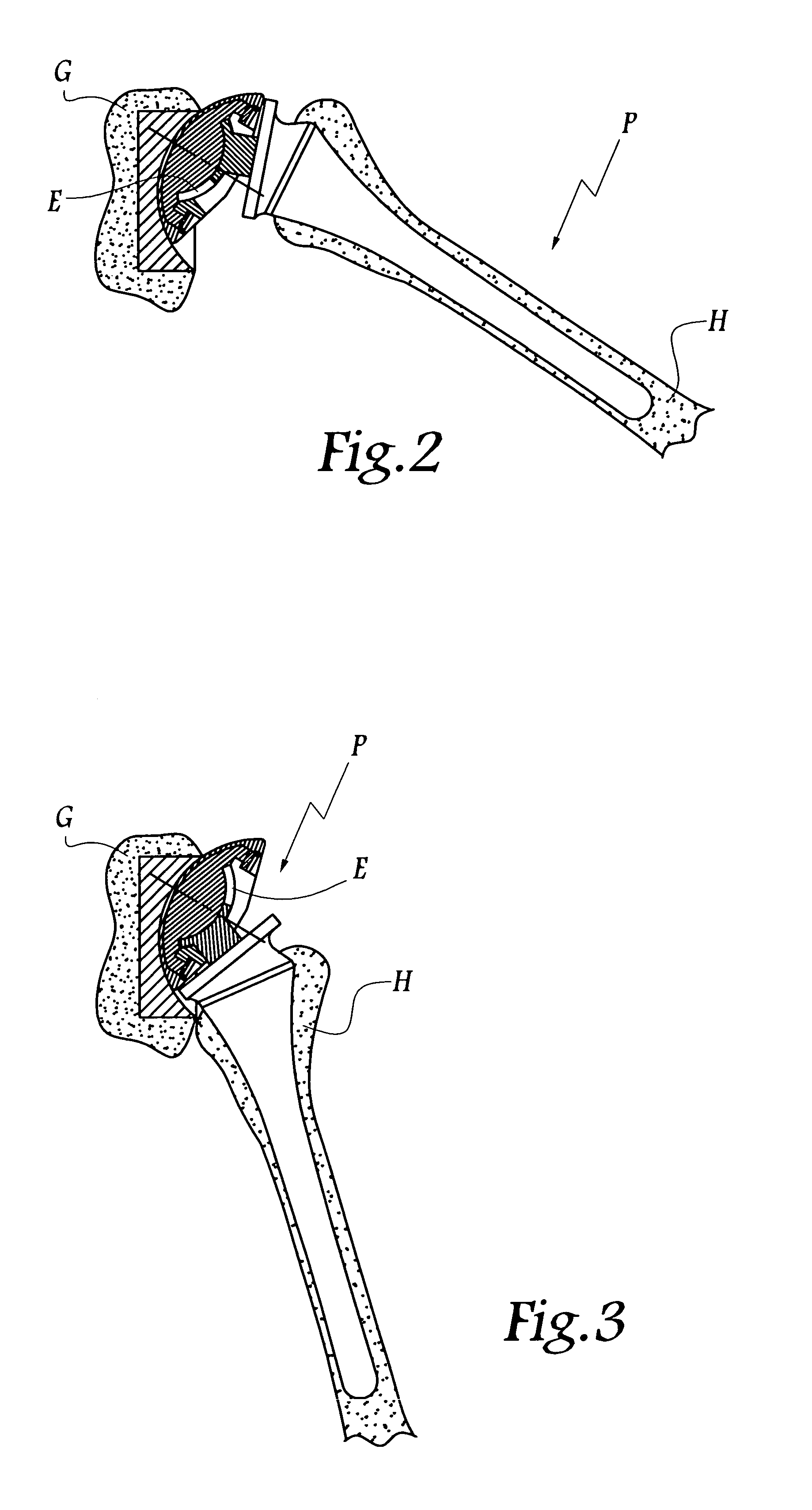
An orthopedic device is disclosed for restoring the normal or natural joint mechanics in, for example, a hip joint. The device includes a first component, such as an acetabular component in a hip implant, that includes a convex articulation surface and a second component, such as a femoral component in a hip implant, that includes a concave articulation surface. It will be appreciated that the convex articulation surface of the device disclosed herein articulates with the concave articulation surface in a mating engagement that may be reversed with respect to the traditional hip implant, in which the concave articulation surface is part of the acetabular component and the convex articulation surface is part of the femoral component.
Owner:GLOBAL ORTHOPAEDIC TECH
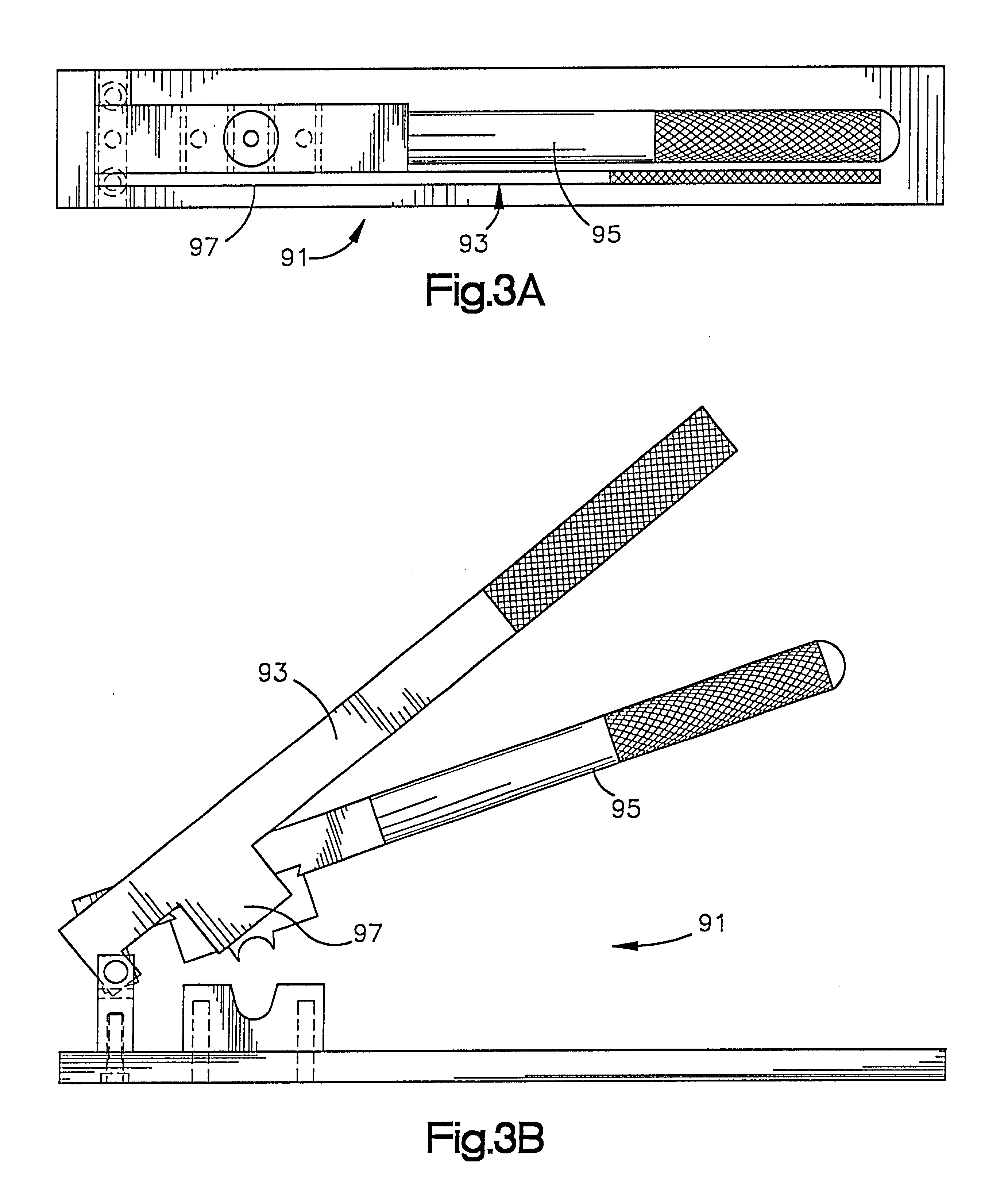
Acetabular shell removal tool
A tool for separating an acetabular shell of a hip prosthesis from the surrounding pelvic bone includes a fixture which attaches to the acetabular shell and has a chisel guide mounted on it. A chisel associated with the chisel guide is curved to conform to the outer periphery of the acetabular shell, and the chisel guide causes the chisel to circumscribe the acetabular shell as the chisel is inserted between the acetabular shell and the pelvis.
Owner:STEVEN M TEENY M D
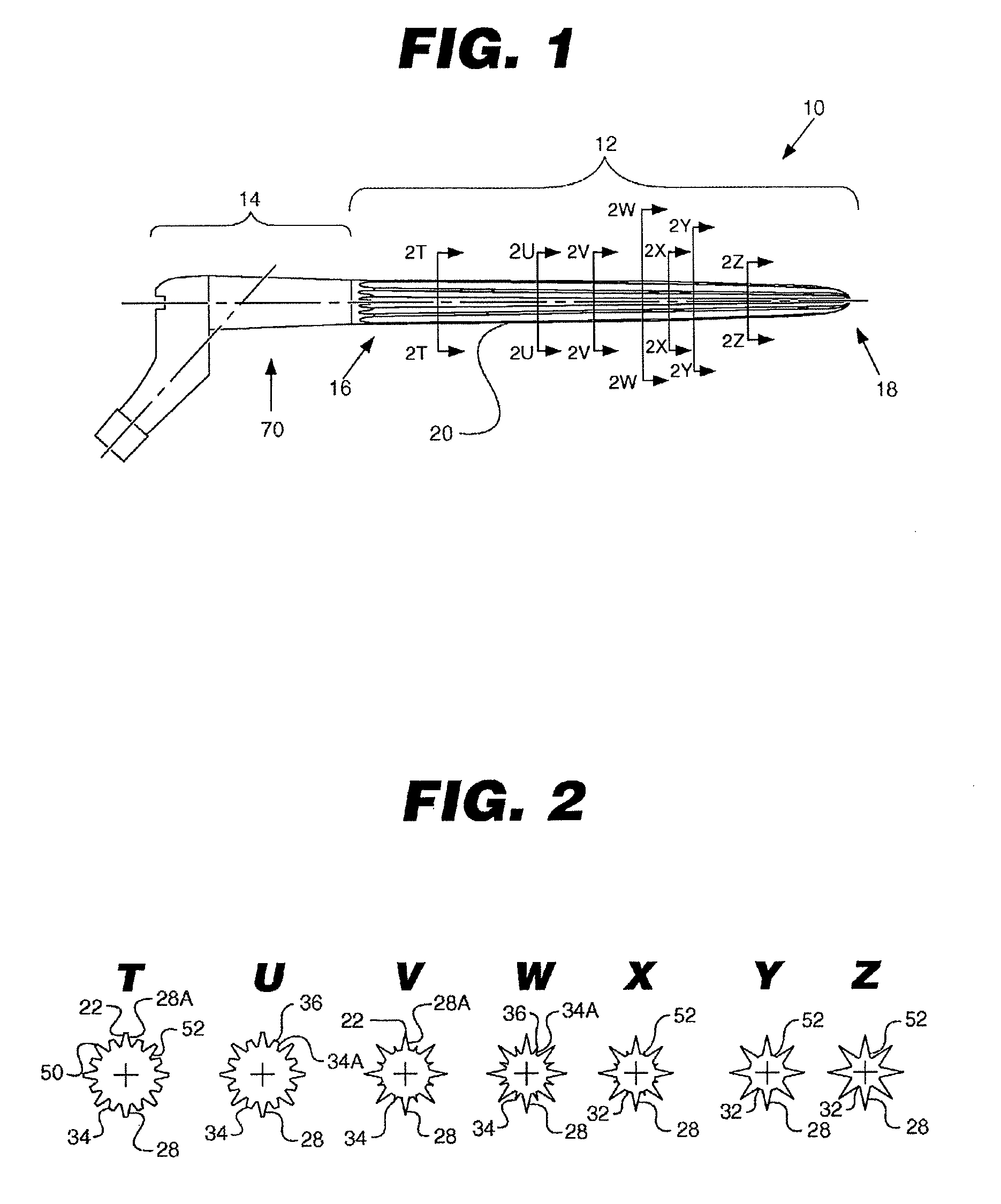
Method and instrumentation for performing minimally invasive hip arthroplasty
InactiveUS20050234463A1Reduce incision sizeSmall sizeJoint implantsFemoral headsTotal hip arthroplastyInterconnection
Broaching instruments divided into multiple parts to reduce the size of incisions necessary to perform a total hip arhroplasty, minimizing trauma to tissue surrounding the hip joint. One approach is to divide the broach head into first and second segments for insertion through posterior and anterior incisions, respectively, and interconnection within the patient. Methods of preparing the proximal medullary canal of a femur for receiving a hip stem implant utilize the multi-part broaching instruments and two-incision techniques to introduce the broaching instruments into the patient for broaching the canal in preparation for receiving the implant.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Shoulder or hip prosthesis and process for fitting same
This prosthesis comprises a humeral or femoral component and an intermediate component. The concave surface of articulation of the humeral or femoral component is formed by a plate connected by a neck to a part of this component adapted to be anchored in the humeral or femoral medullary cavity. The intermediate component is provided with a member for retaining the humeral or femoral component in a position where the plate is in abutment against the first convex surface of the intermediate component. The retaining member defines a non-circular passage in which the neck is adapted to be displaced as a function of the movements of the humeral or femoral component with respect to the other components of the prosthesis. The retaining member defines with the first convex surface of articulation of the intermediate component a volume for receiving a part of the plate projecting radially with respect to the neck.
Owner:TORNIER SA SAINT ISMIER
Method and apparatus for performing a minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty
InactiveUS20050177172A1Less scarringHastens patient recoveryCannulasOperating tablesAcetabular componentProsthesis
A method and apparatus for performing a minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty including an acetabular cup inserter is provided. The cup inserter is utilized for securing a prosthetic acetabular component thereto for implantation into a hip joint. The acetabular cup inserter includes a frame having an offset frame leg to allow for placement of an acetabular cup in the correct anteversion and abduction without interference from soft tissue.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
Method and device for treating osteoarthritis and cartilage disease, defects, and injuries in the human hip
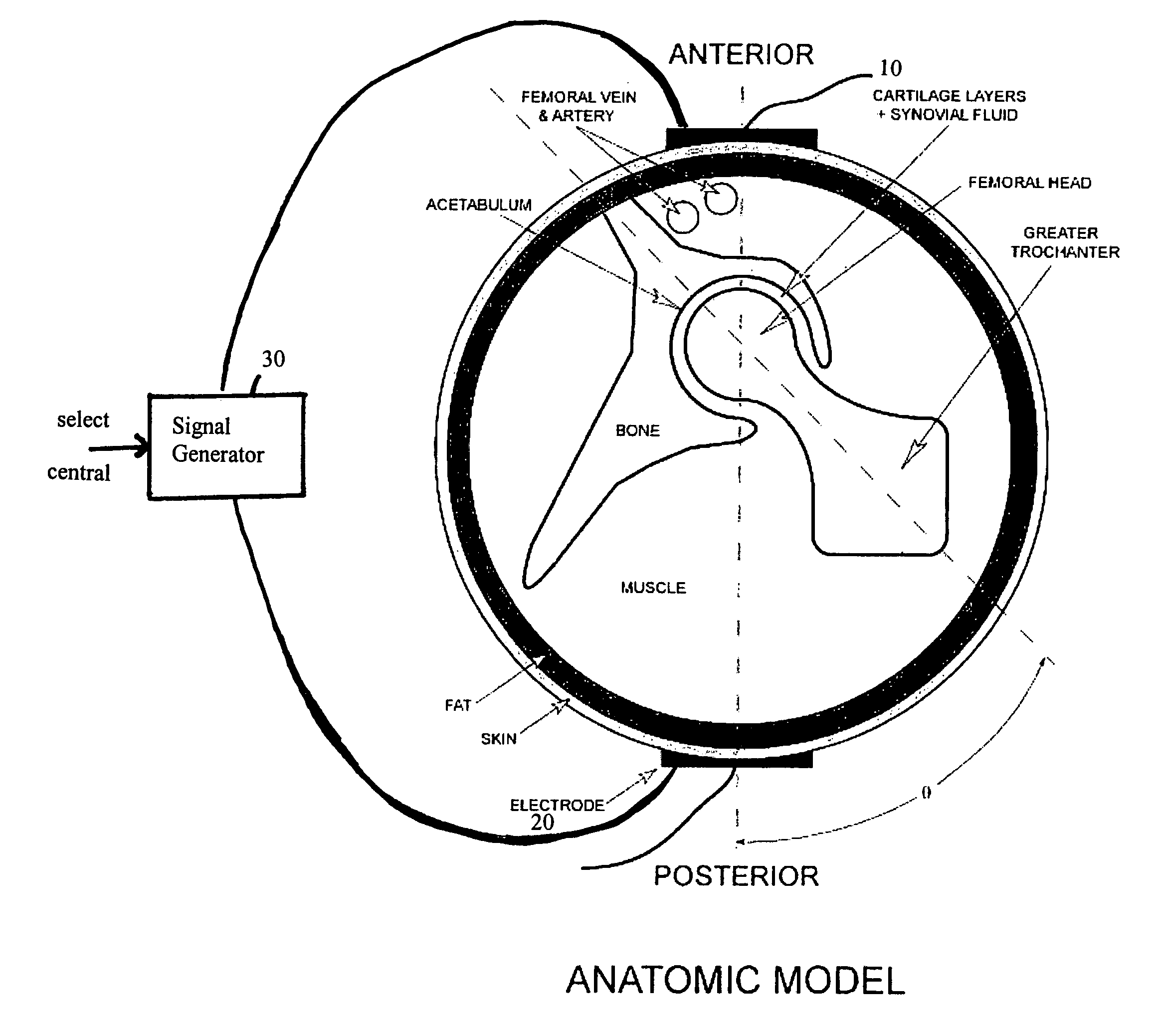
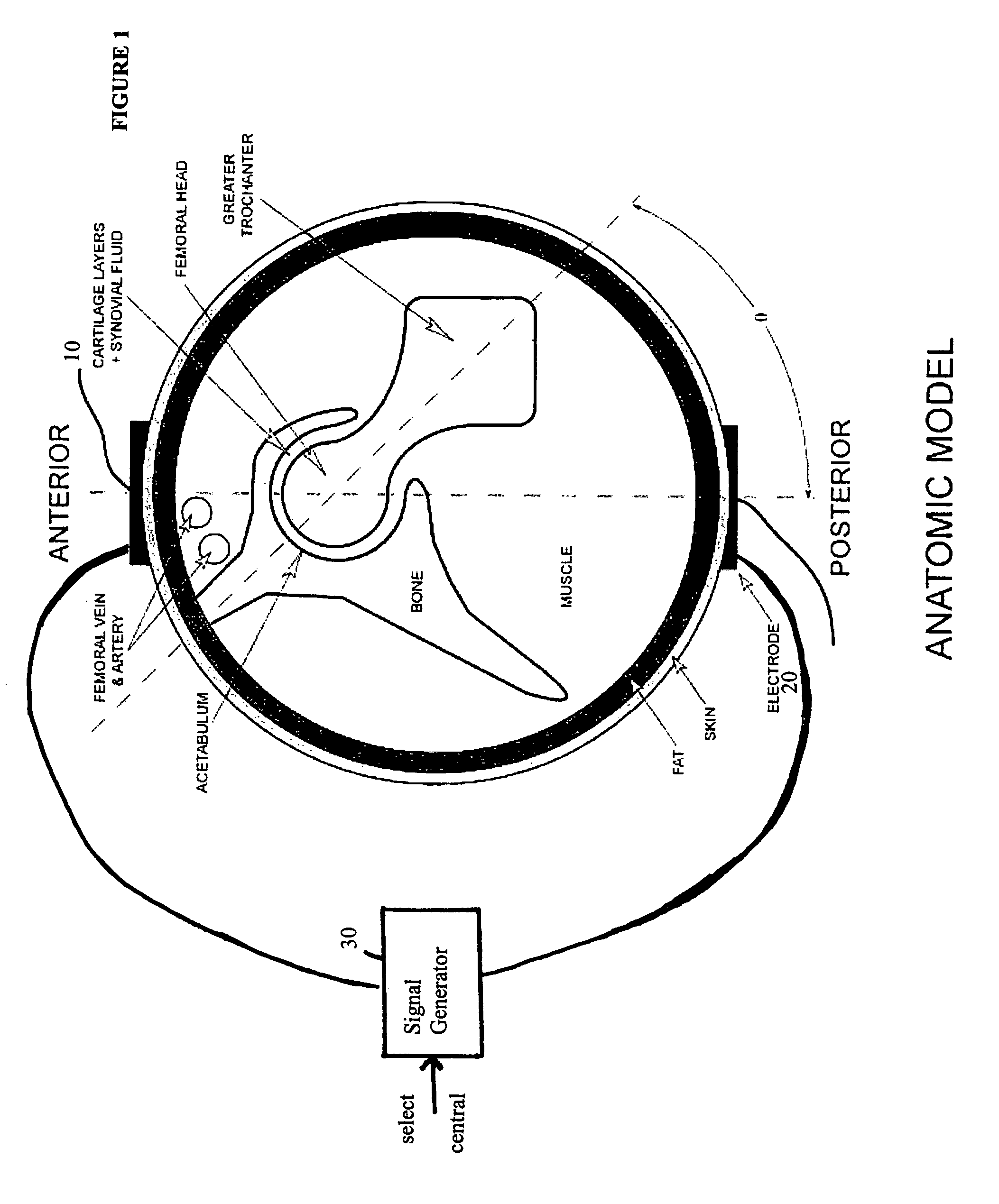
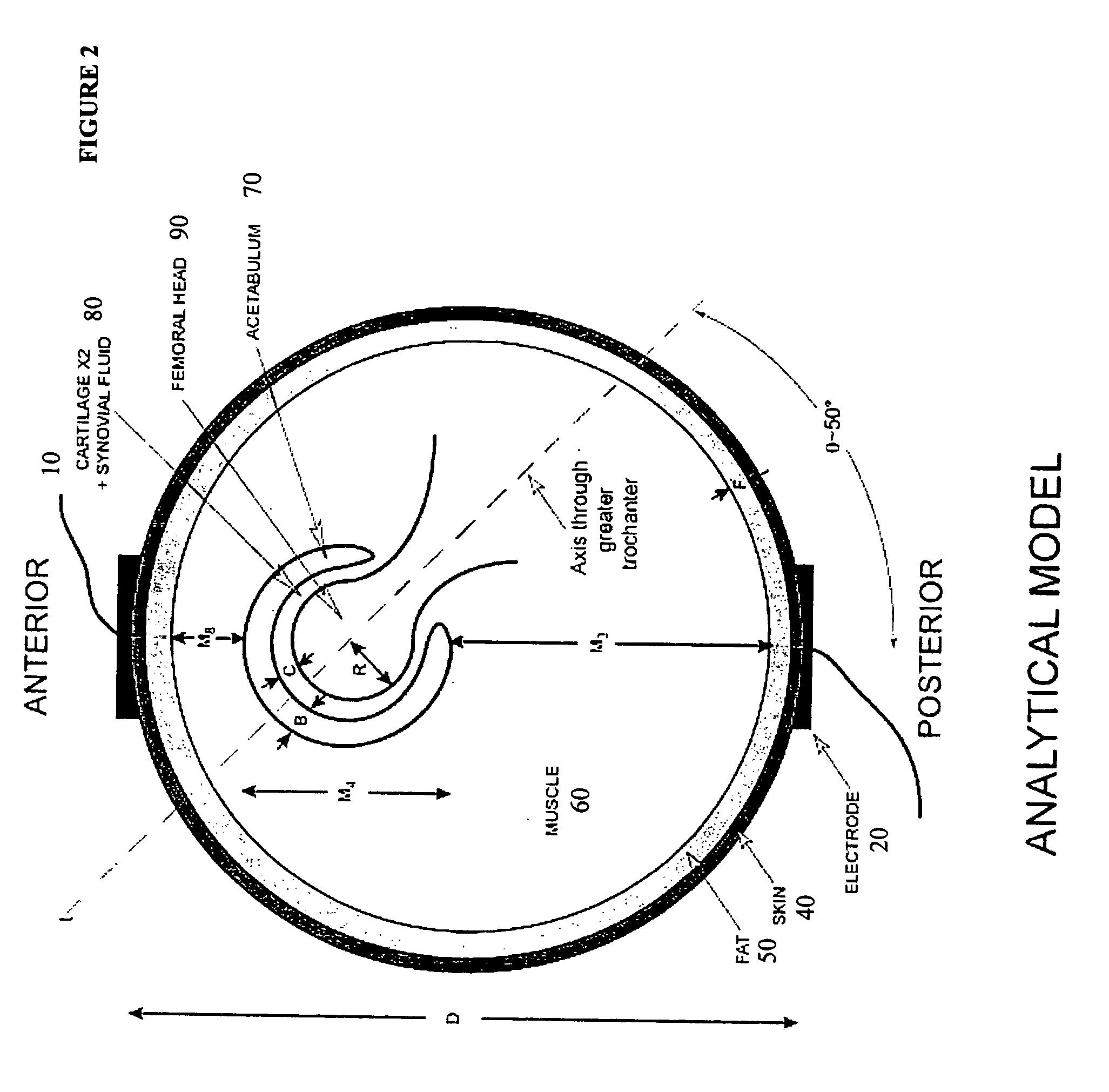
A method of determining the voltage and current required for the application of specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals to diseased articular cartilage in the treatment of osteoarthritis, cartilage defects due to trauma or sports injury, or used as an adjunct with other therapies (cell transplantation, tissue-engineered scaffold, growth factors, etc.) for treating cartilage defects in the human hip joint and a device for delivering such signals to a patient's hip. Anatomic, analytical, and planar circuit models are developed to determining the impedances, conductivities, and current flows in the human hip joint and its surrounding soft tissues and skin that are required to produce a 20 mV / cm electric field in the synovium and articular cartilage of the human hip. The voltage of the signal applied to the surface electrodes or to a coil(s) or solenoid is varied based on the size of the hip joint; larger hip joints require larger voltages to generate the effective electric field.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Neck-slip-prosthesis
A hip prosthesis constructed to transfer forces to the femur without relative movements that cause failures. The prosthesis stem has an open sided central bore. The proximal end of the prosthesis is configured to seat against interior surfaces of the femoral canal and support a femur head on a prosthesis shoulder that seats on the stem proximal end while maintaining the neck of the femur intact.
Owner:THURGAUER KANTONALBANK A CHARTERED IN & EXISTING UNDER THE LAWS OF SWITZERLAND THAT MAINTAINS ITS PRINCIPAL OFFICES AT
Fluted sleeve hip prosthesis for modular stem
An intramedullary implant for mounting within an intramedullary canal of a bone is disclosed. The intramedullary implant includes a lower stem portion, an upper stem portion, and a modular sleeve body. The modular sleeve body is connected to one of the lower stem portion or the upper stem portion. The sleeve body includes an inner portion that covers at least a segment of the upper stem portion and has one or more longitudinally extending bone engagement members for engagement with the bone.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Modular femoral prosthesis with on-axis junction
ActiveUS7776098B2Easy and inexpensive to manufactureEasy to implantJoint implantsFemoral headsFemoral stemModularity
A modular hip prosthesis includes a femoral stem, a spherical head and a coupling member extending from the head defining a neck whose lower end forms a base which plugs into a socket at the top of the stem to form a tapered neck / stem junction. That junction is aligned with the stem axis and has a cross-section with opposite sides that extend generally parallel to the sides of the stem. With such an arrangement, that junction may be relatively long and have a relatively large cross-sectional area thus making a strong junction even in smaller femoral implants.
Owner:MURPHY STEPHEN B
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com