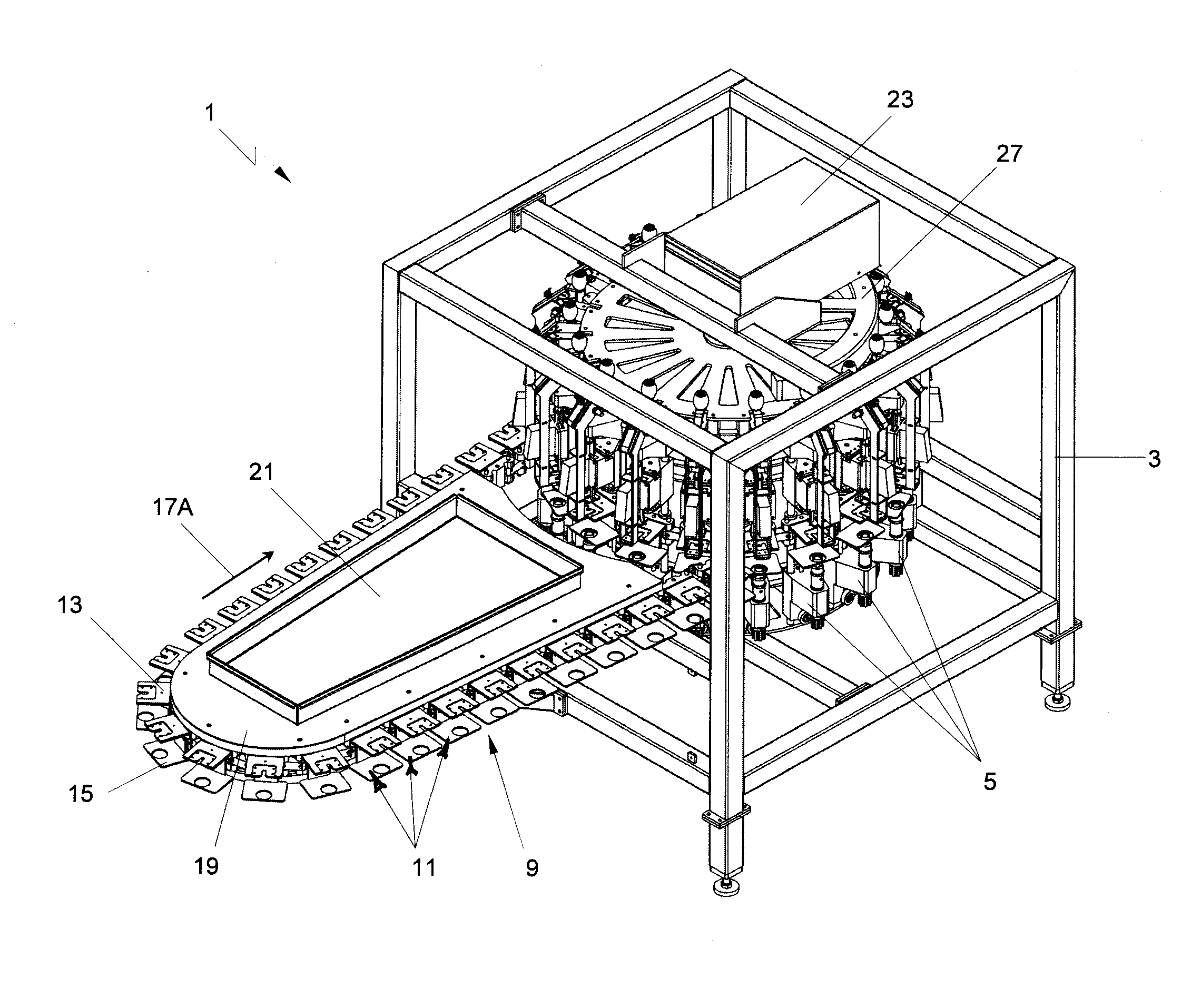
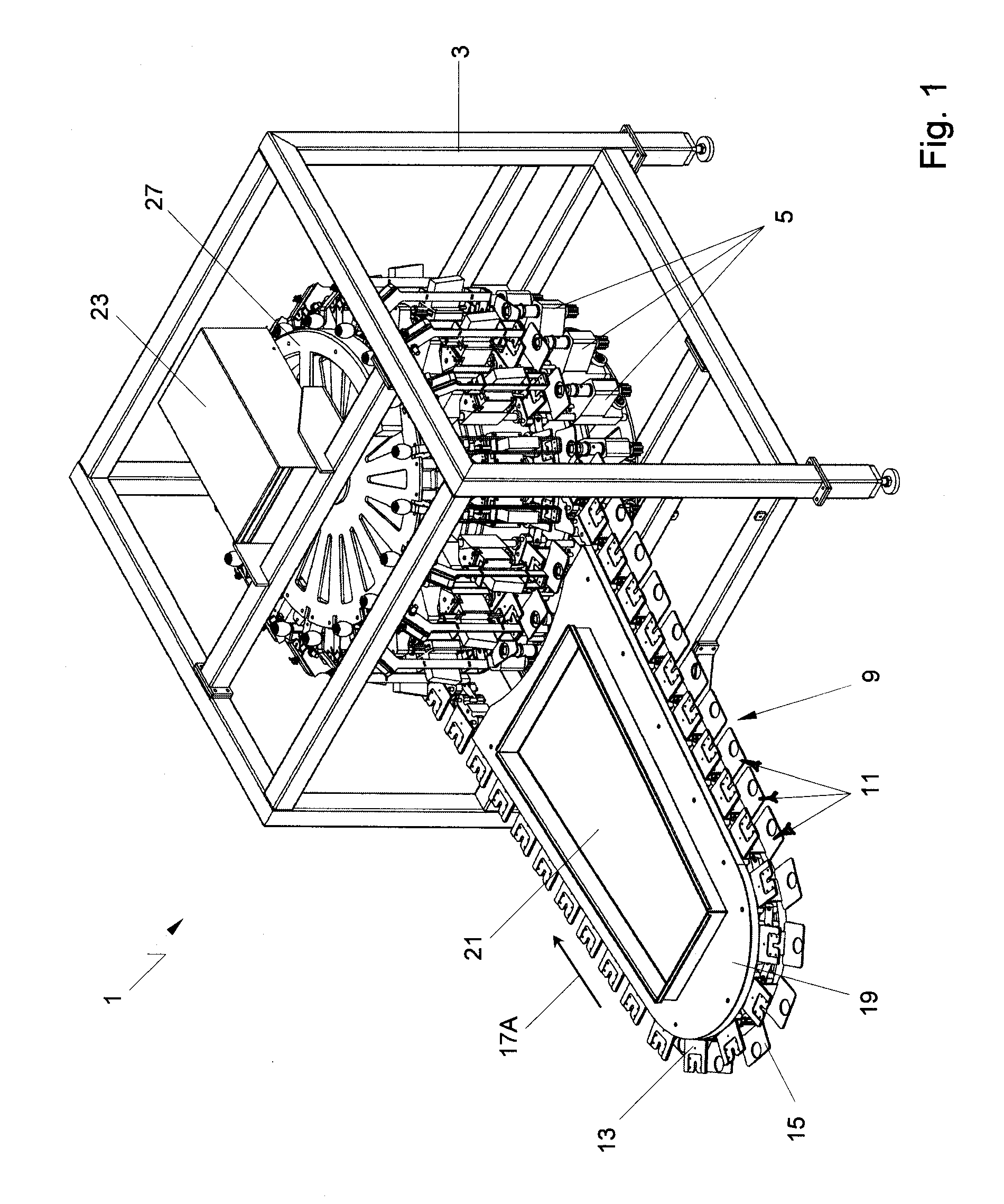
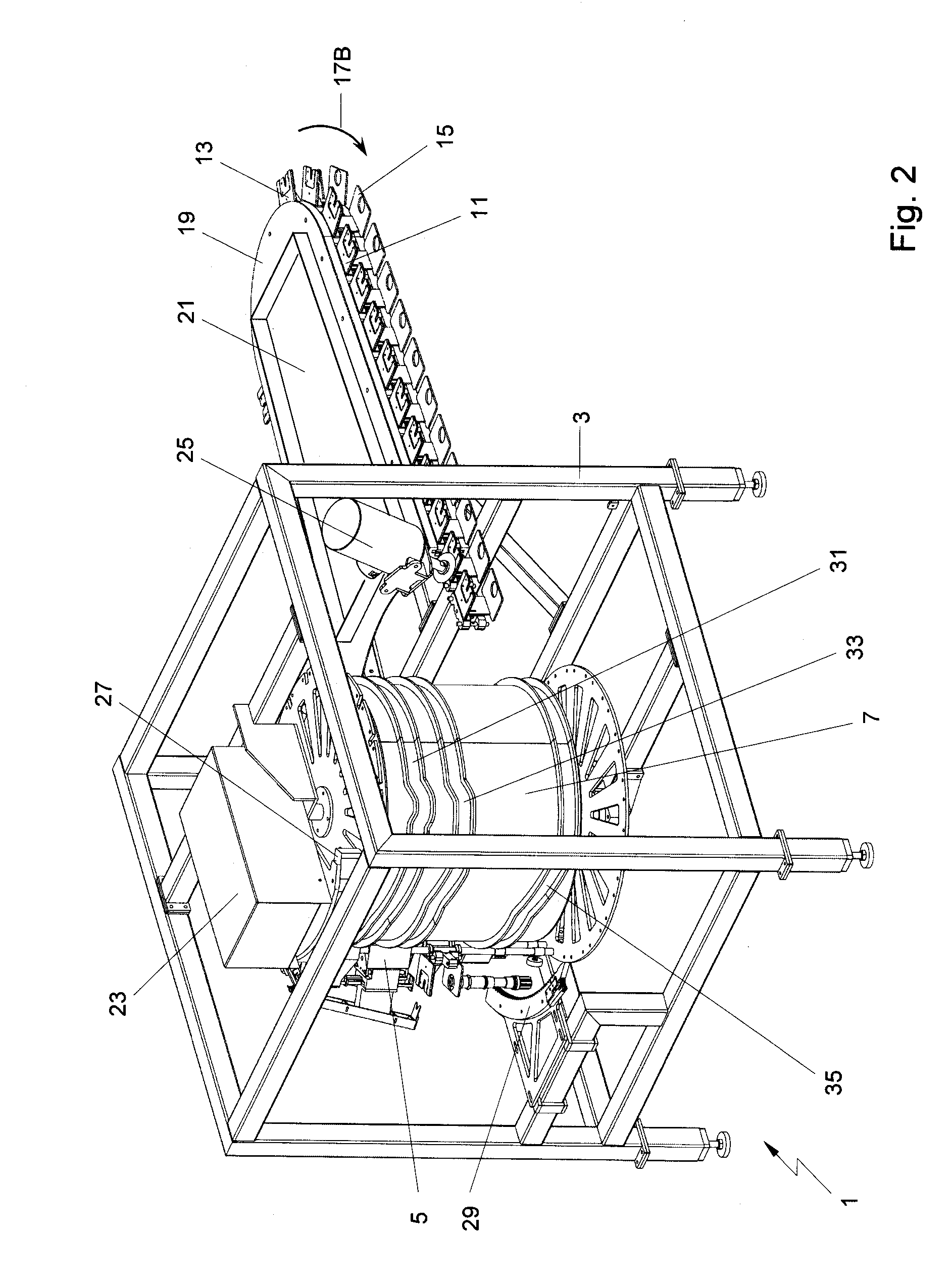
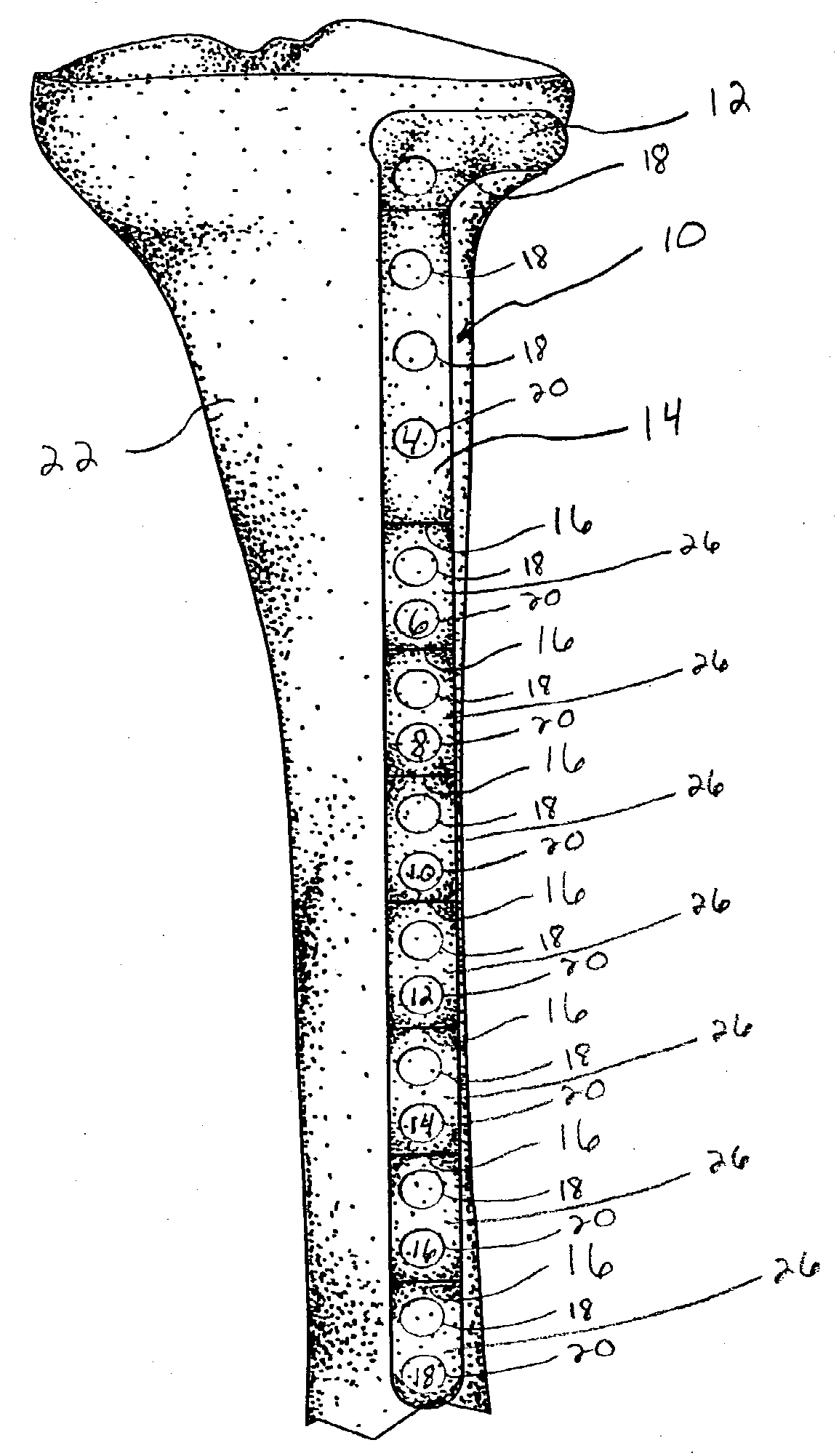
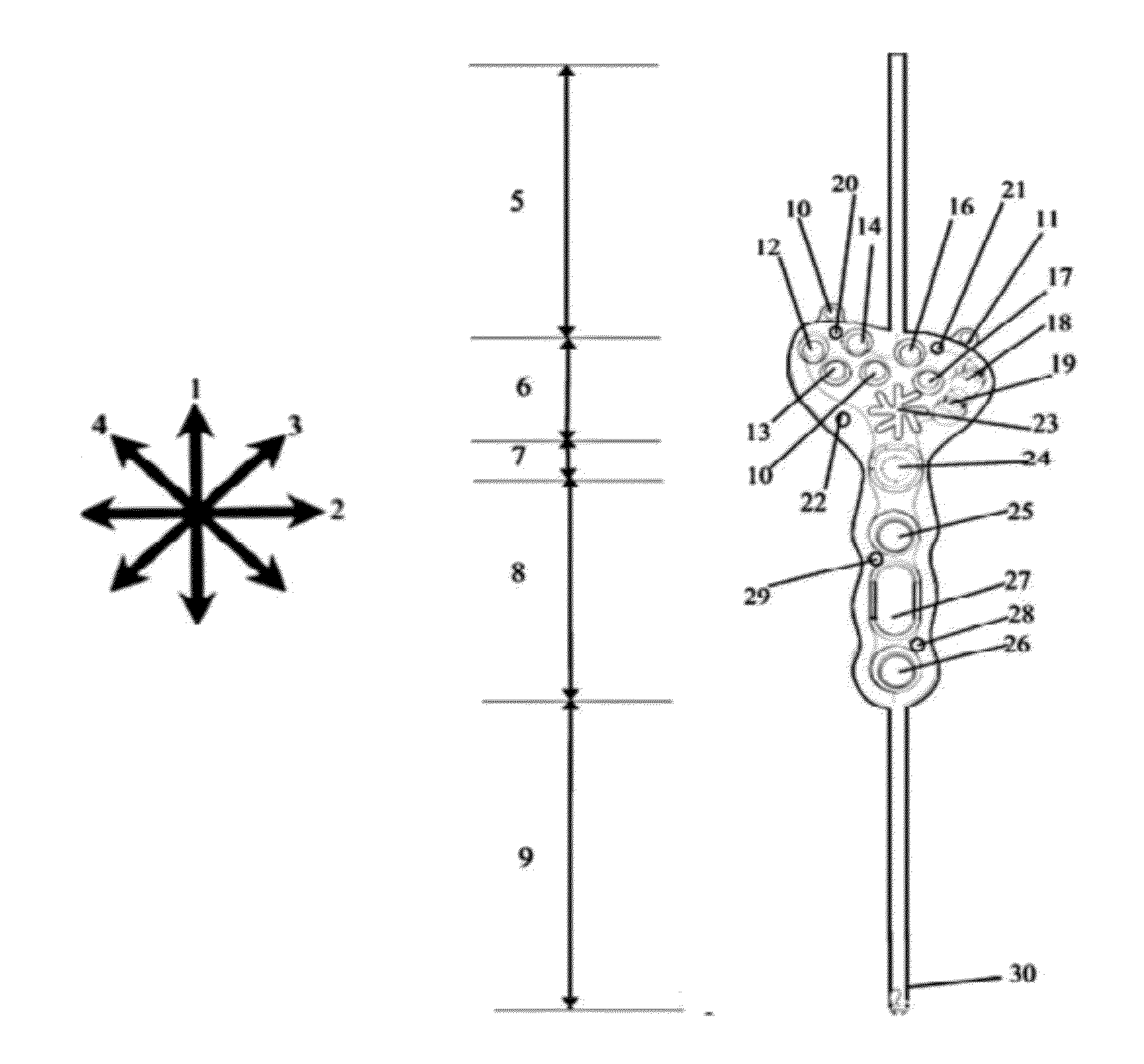
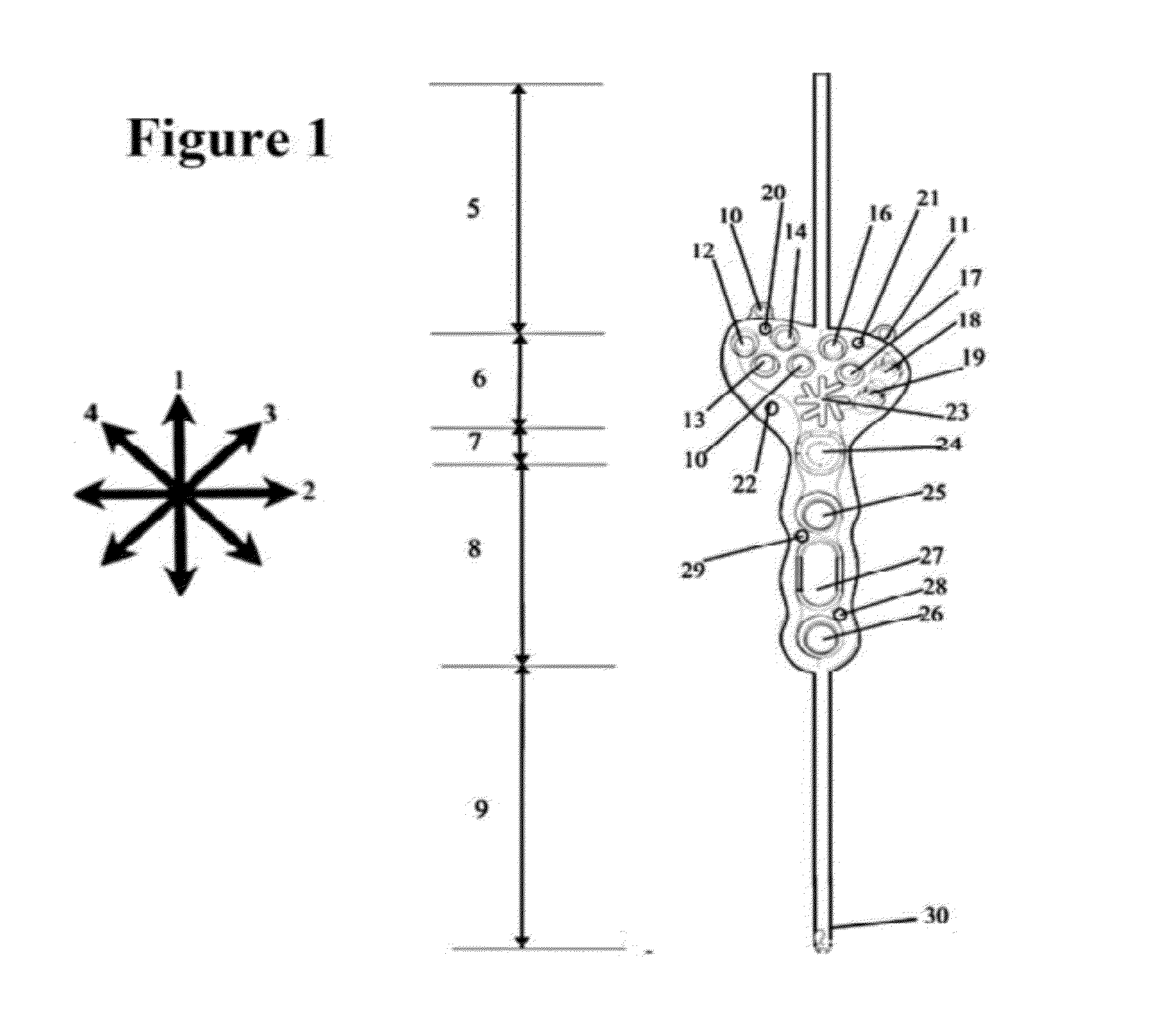
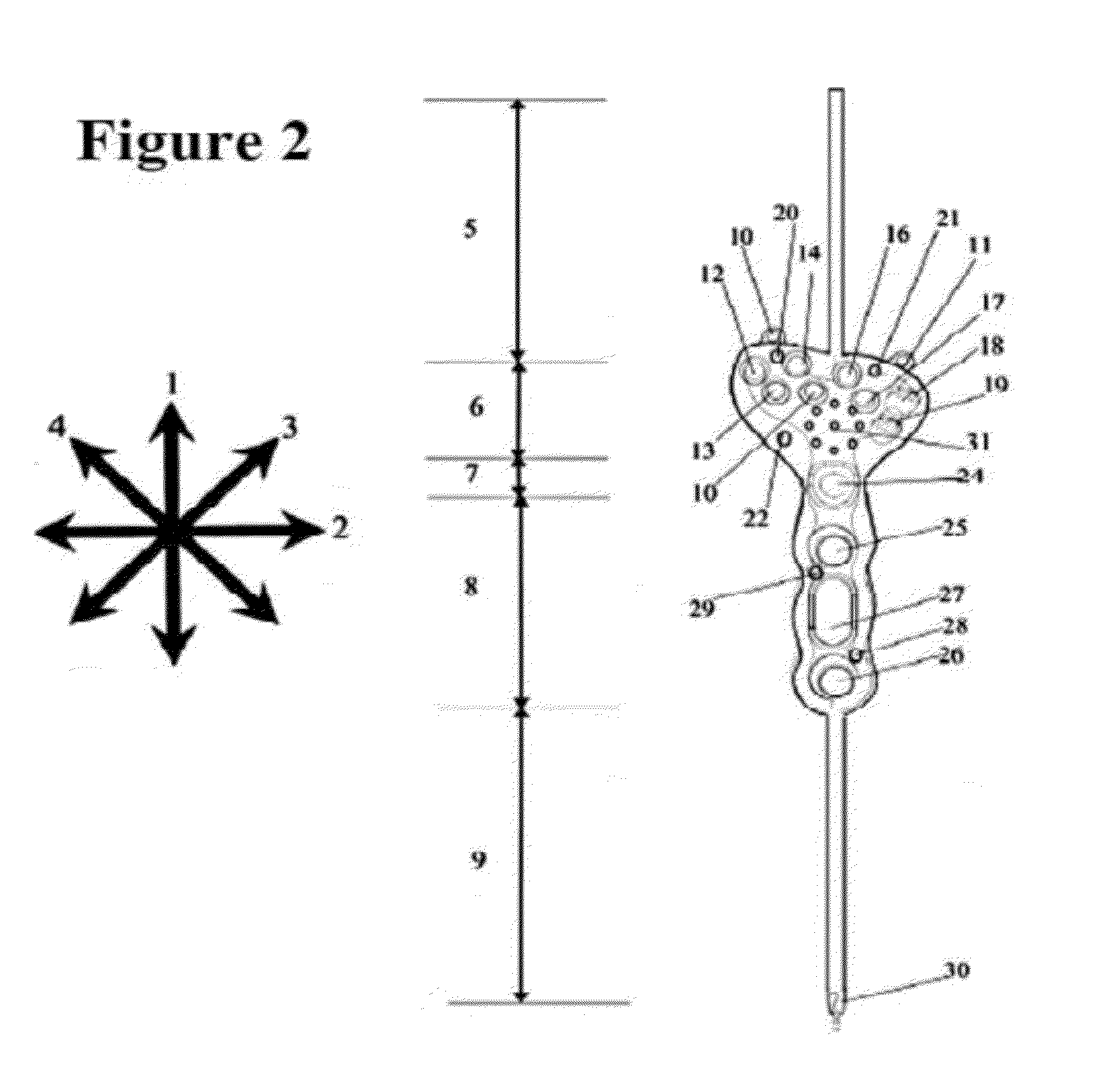
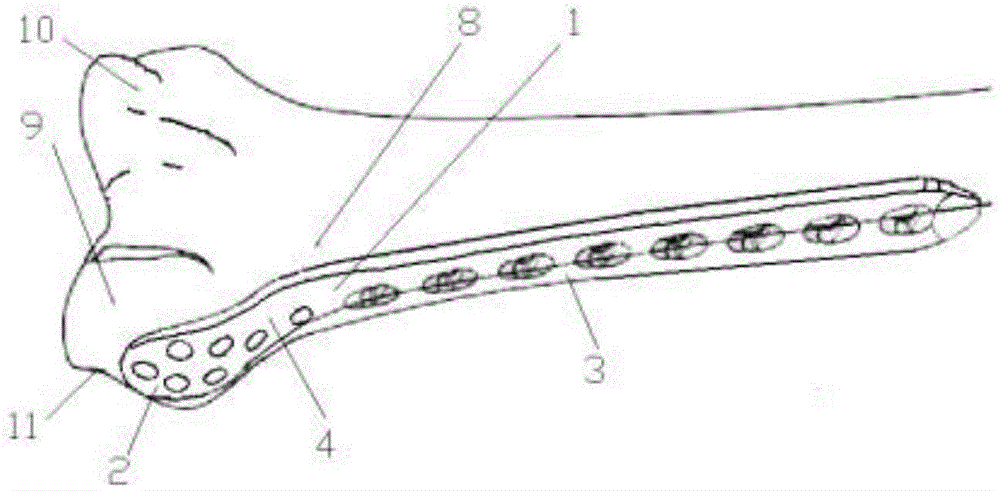
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Bone shaft" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
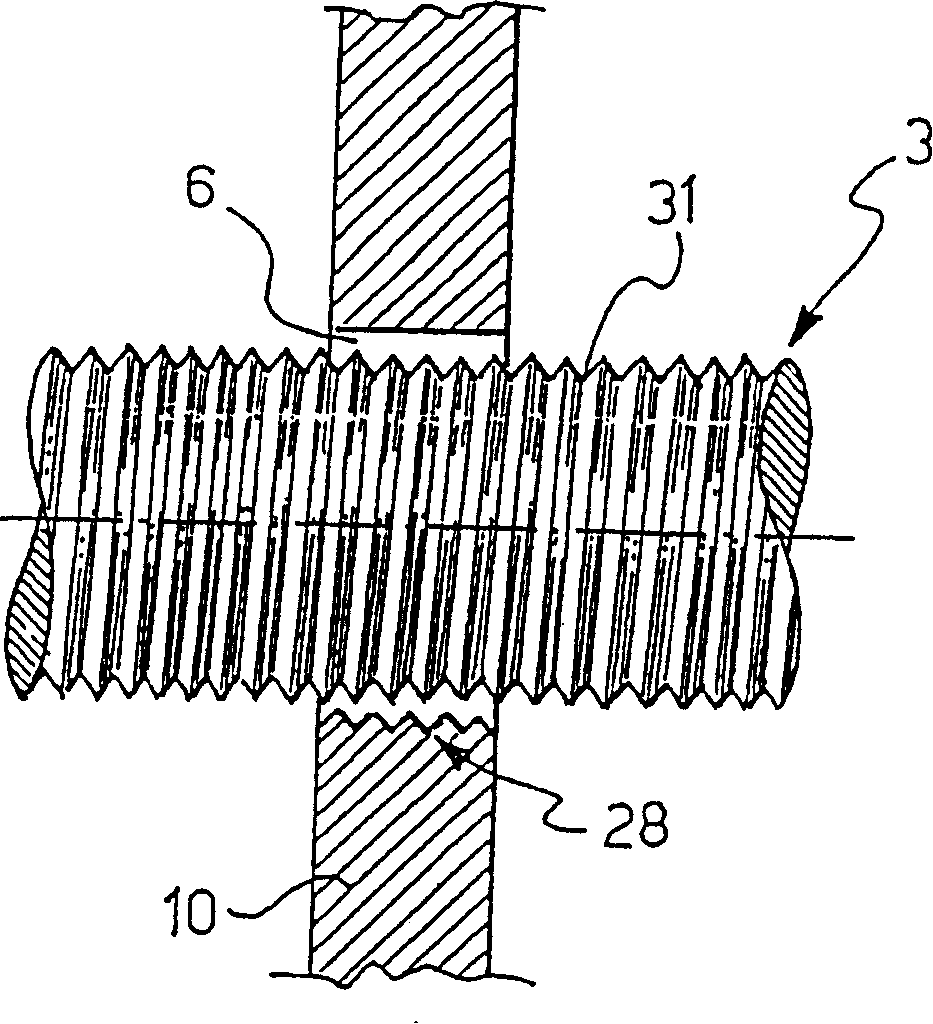
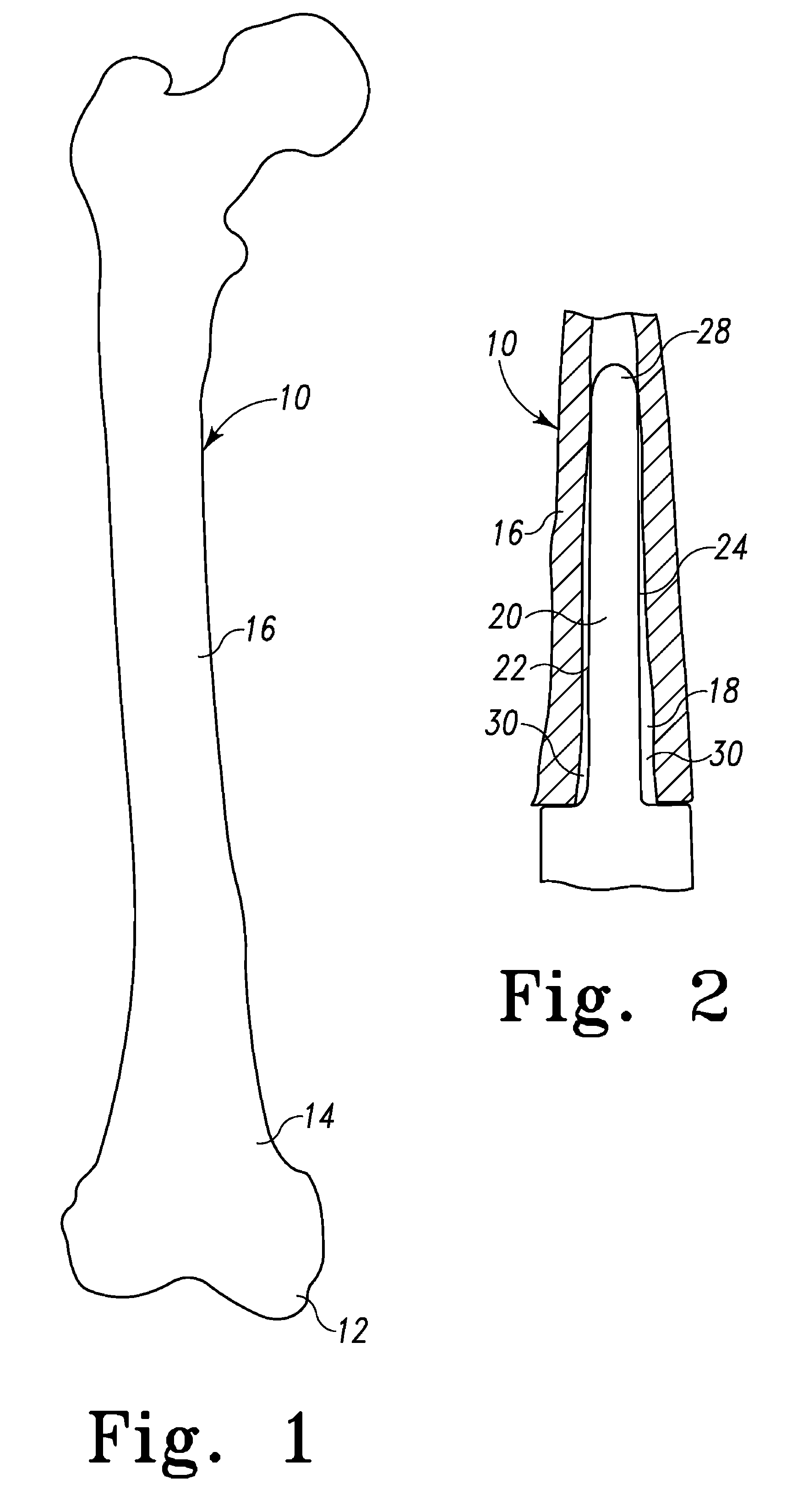
The shaft of a long bone, as distinguished from the epiphyses, or extremities, and apophyses, or outgrowths. Synonym(s): shaft [TA] [G. a growing between] shaft (shaft) a long slender part, such as the diaphysis of a long bone. shaft (shăft) n. 1.
Method for resecting the knee using a resection guide and provisional prosthetic component
InactiveUSRE39301E1Properly balanceAccurate balanceDiagnosticsJoint implantsAnterior surfaceKnee Joint
A method and apparatus for knee replacement surgery wherein a femoral provisional component is provided which corresponds to a permanent component to be implanted in a human and which includes means for establishing the correct fit and position of such a component, prior to its implantation, in relation to the soft tissues of the knee before final resection of the anterior femoral surface. The provisional component further includes cutting guide means for such anterior surface resection such that accurate cuts may be made with the provisional component in place. The method involves preparing the distal femoral surface using the femoral intramedullary canal as a constant reference point for posterior and distal cutting guides followed by locating the provisional component by means of a provisional intramedullary stem so that the relationship with the soft tissues of the knee may be accurately established.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
Method and apparatus for performing a minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty
A method and apparatus for performing a minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty. An approximately 3.75-5 centimeter (1.5-2 inch) anterior incision is made in line with the femoral neck. The femoral neck is severed from the femoral shaft and removed through the anterior incision. The acetabulum is prepared for receiving an acetabular cup through the anterior incision, and the acetabular cup is placed into the acetabulum through the anterior incision. A posterior incision of approximately 2.5-3.75 centimeters (1-1.5 inches) is generally aligned with the axis of the femoral shaft and provides access to the femoral shaft. Preparation of the femoral shaft including the reaming and rasping thereof is performed through the posterior incision, and the femoral stem is inserted through the posterior incision for implantation in the femur. A variety of novel instruments including an osteotomy guide; an awl for locating a posterior incision aligned with the axis of the femoral shaft; a tubular posterior retractor; a selectively lockable rasp handle with an engagement guide; and a selectively lockable provisional neck are utilized to perform the total hip arthroplasty of the current invention.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
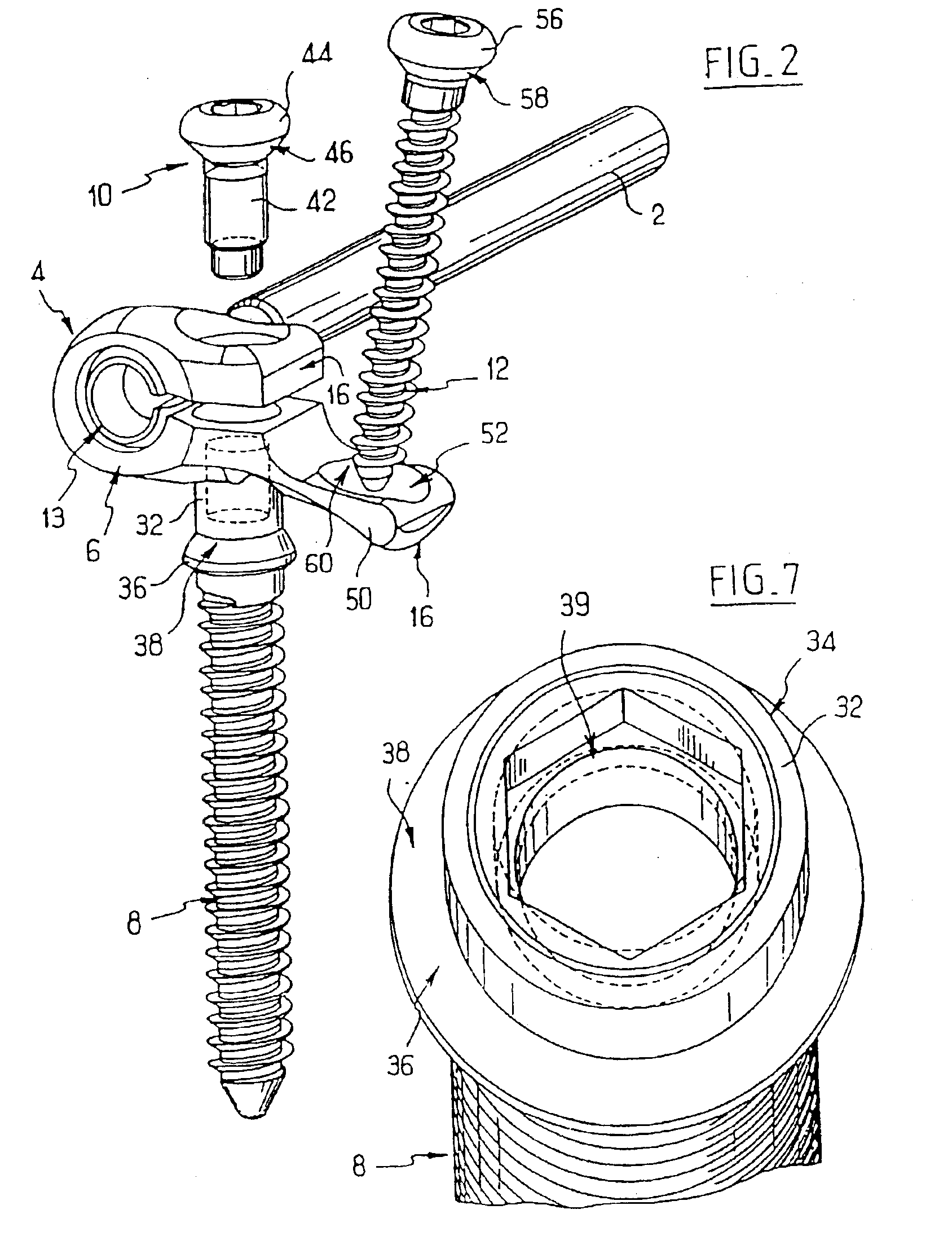
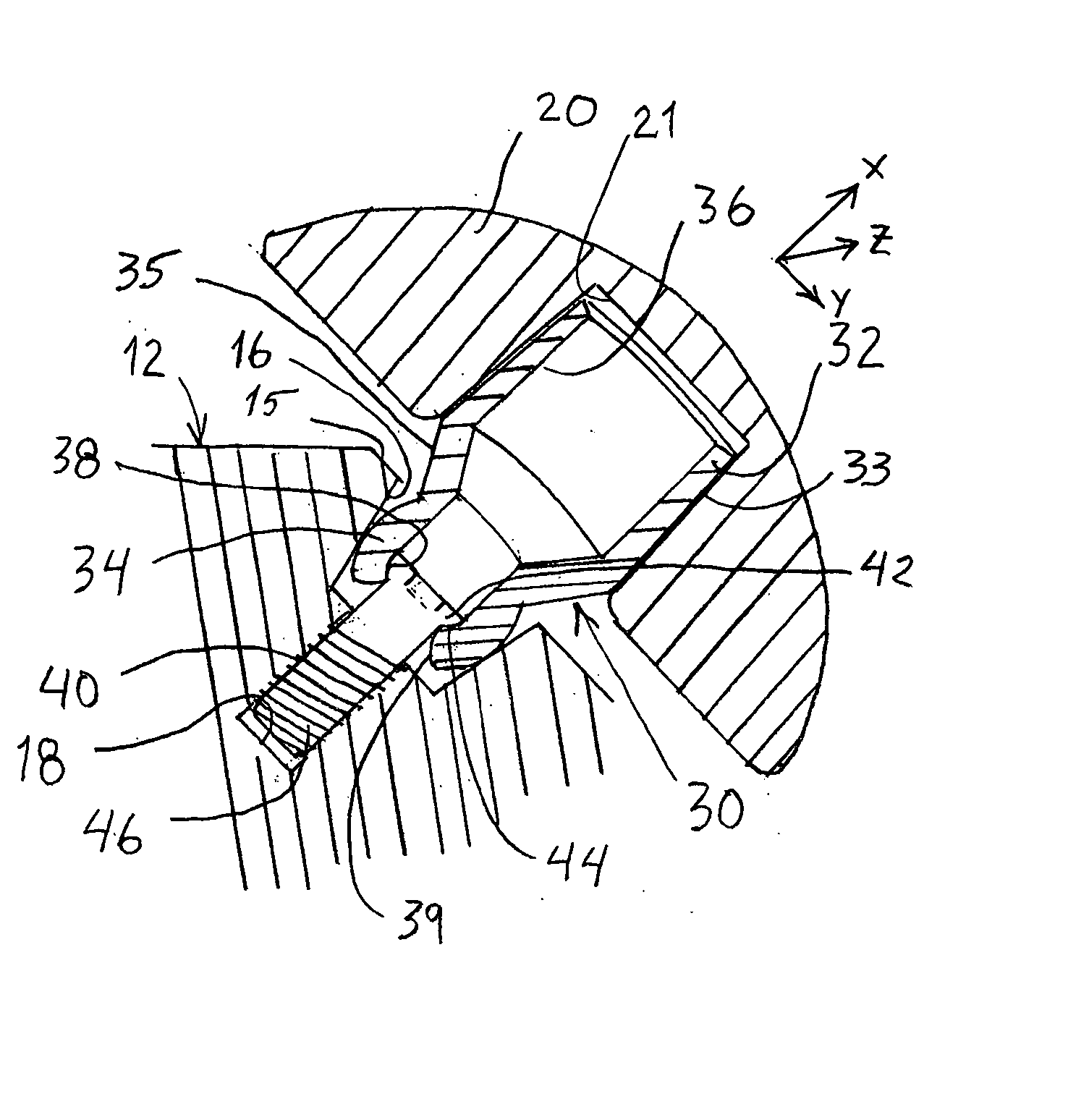
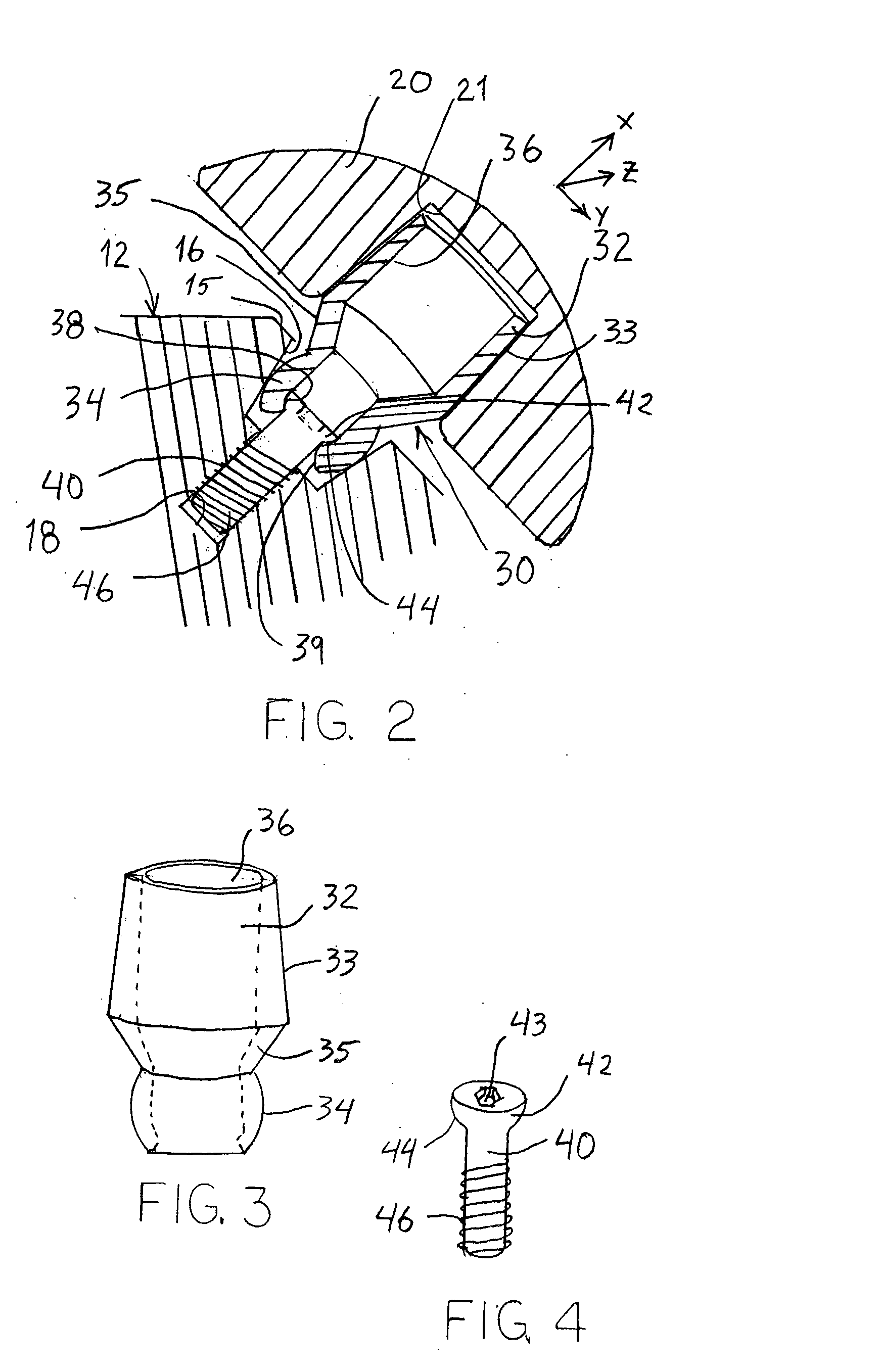
Backbone osteosynthesis system with clamping means in particular for anterior fixing
The invention concerns a backbone osteosynthesis system, in particular for anterior fixing comprising: an elongated linking element; a vertebral screw with a threaded head; a connector comprising two branches capable of being engaged onto the screw and clamping between them the linking element; and a threaded clamping member capable of co-operating with the head for clamping the branches. The head has a threaded orifice, the clamping member comprising a threaded rod capable of being urged to be engaged in the orifice.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
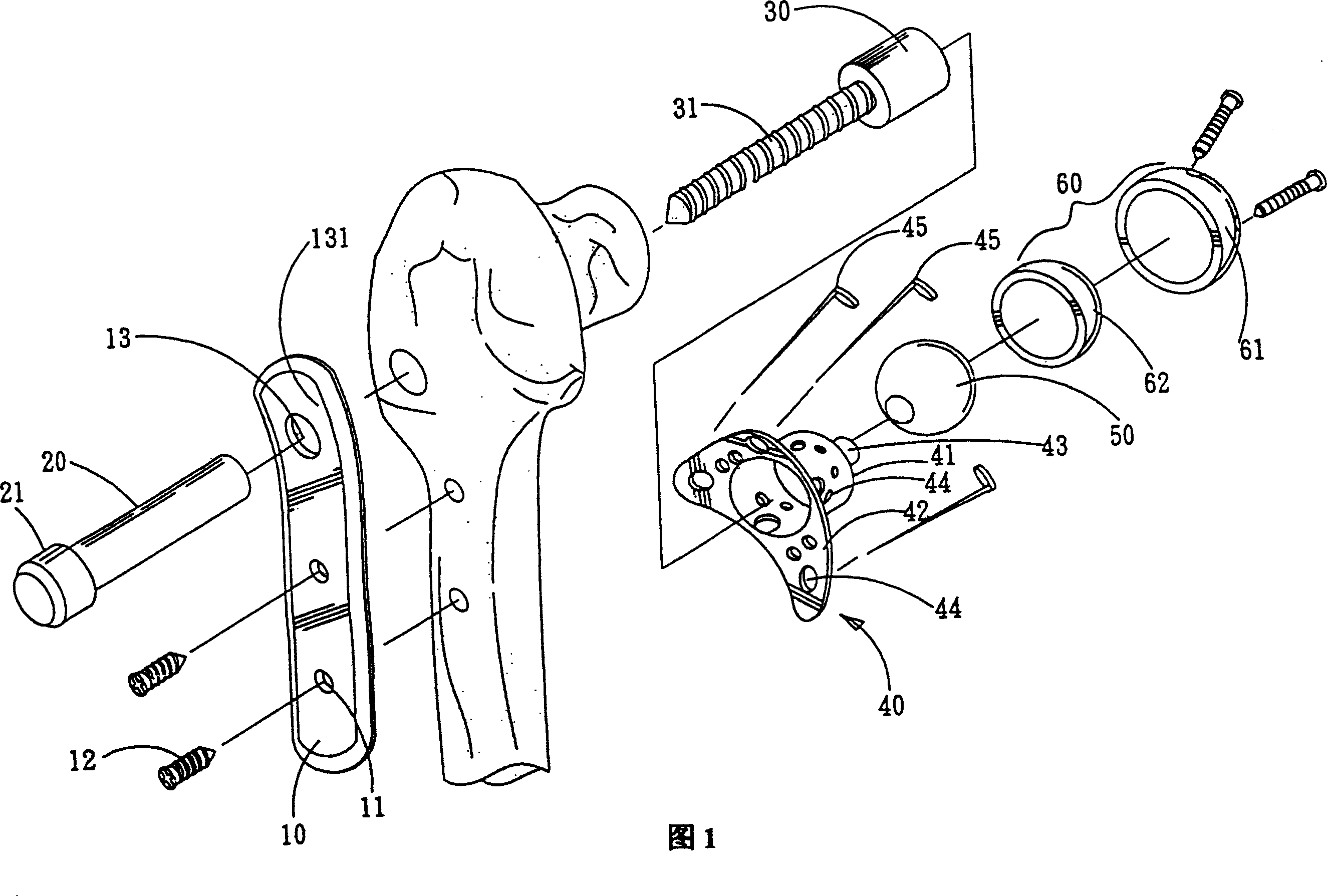
Joint prosthesis with infinitely positionable head
A joint prosthesis includes a head component that is engaged to a bone stem through a mounting element. The mounting element is configured for articulating engagement with the stem to permit angular positioning of the head component in multiple degrees of freedom. The mounting element is fastened to the stem by a press-fit engagement and a separate mechanical fastener.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Modular implant system and method with diaphyseal implant and adapter
A modular implant system includes a set of anatomically-designed diaphyseal fitting and filling modular implant components and adapters for connection to another implant component such as a modular articular component, a segmental component or an intercalary component. The other end of each diaphyseal component is a tapered porous surface. The tapered porous surface is received with a tapered bore in the bone diaphysis that is prepared to match the size and shape of the tapered porous surface. The diaphyseal implant is easy to insert and remove, does not bind before fully seating, and is designed to prevent stress shielding. The diaphyseal sleeve eliminates the long lever arm created when fixation occurs only at the tip of the stem, and should therefore eliminate related stem loosening.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Locking compression hip screw
ActiveUS20070270847A1Avoid relative motionInhibition of translationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFracture reductionIntertrochanteric fracture
A modification to the prototypical compression (dynamic or sliding) hip screw is described which expands the utility and surgical indications of this frequently used fracture fixation device to include the fracture pattern commonly referred to as a “reverse obliquity fracture” of the proximal femur. This fracture pattern is poorly secured with current generation hip screws, frequently necessitating the use of intramedulary fracture fixation devices or external fixation hardware. The described modification blocks telescopic sliding of the femoral head lag screw within the cylindrical barrel of the side plate and allows for secure locking of the lag screw within the side plate, preventing any relative motion between the screw and plate once fracture reduction has been achieved. In a locked mode, the proximal fracture fragment(s) is prevented from displacing laterally relative to the distal (diaphysial) fragment, as occurs commonly when a reverse obliquity fracture or a comminuted intertrochanteric femur fracture is fixed with a conventional hip screw. No change in routine fracture reduction or insertion technique is required to use the Locking Compression Hip Screw. Additionally, the described modification does not preclude use of the Locking Compression Hip Screw in a dynamic or sliding mode, if desired, when used to fix the more common femoral neck or intertrochanteric fracture patterns.
Owner:SHAW JAMES ALBERT
Bone alignment implant and method of use
InactiveUS20070093834A1Minimizing chanceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisConvex sideBone growth
A bone alignment implant includes a first bone fastener with a first bone engager that is adapted for fixation into the metaphyseal bone and a second bone fastener with a second bone engager that is adapted for fixation into the diaphyseal bone. A link connecting the two fasteners spans across the physis. Alternatively, the bone alignment implant is adapted for fixation into the diaphyseal sections of two adjoining vertebral bodies. These implants act as a flexible tethers between the metaphyseal and the diaphyseal sections of bone during bone growth. These implants are designed to adjust and deform during the bone realignment process. When placed on the convex side of the deformity, the implant allows the bone on the concave side of the deformity to grow. During the growth process the bone is then realigned. A similar procedure is used to correct torsional deformities.
Owner:AMEI TECH
Supportive device for handicapped people
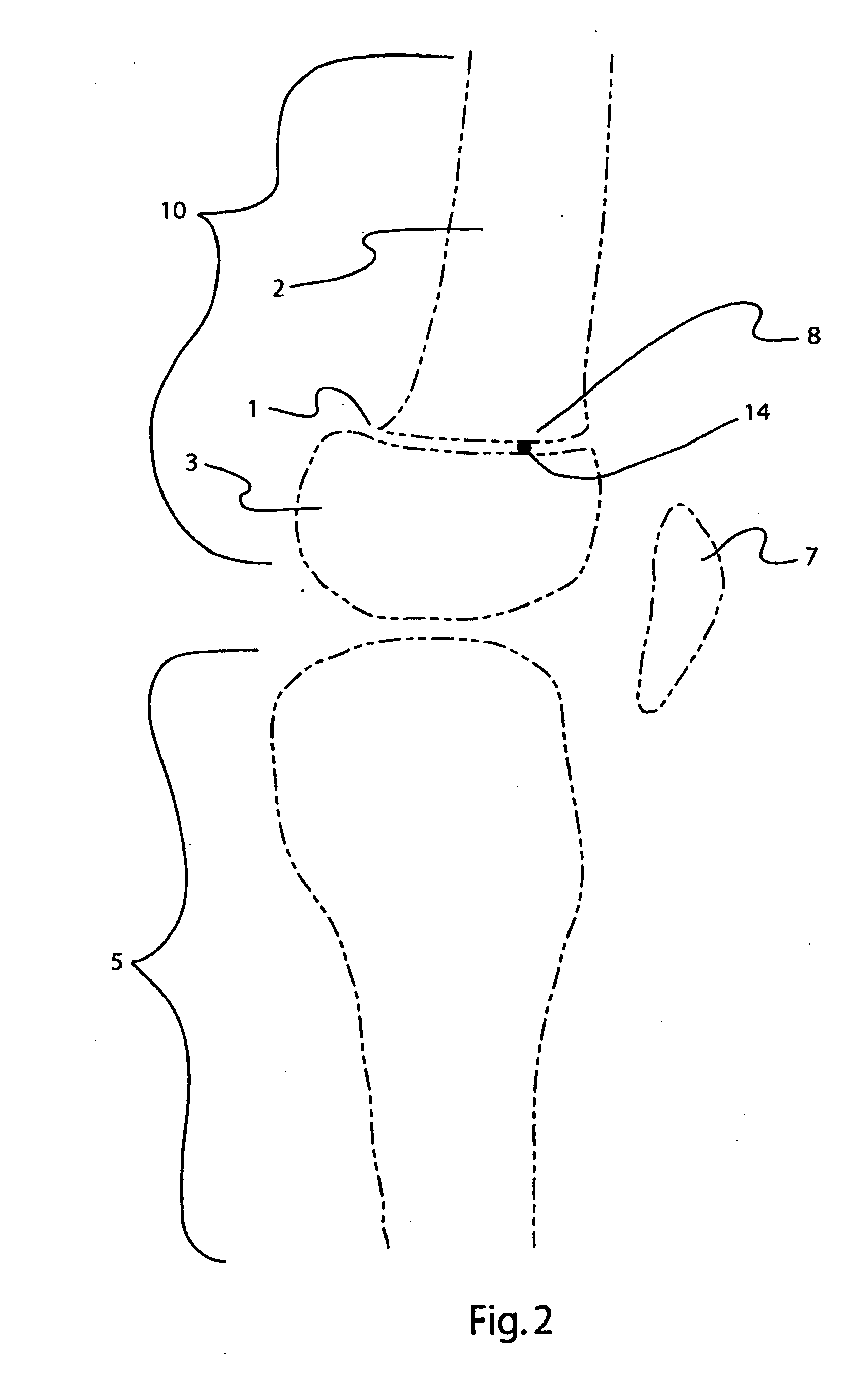
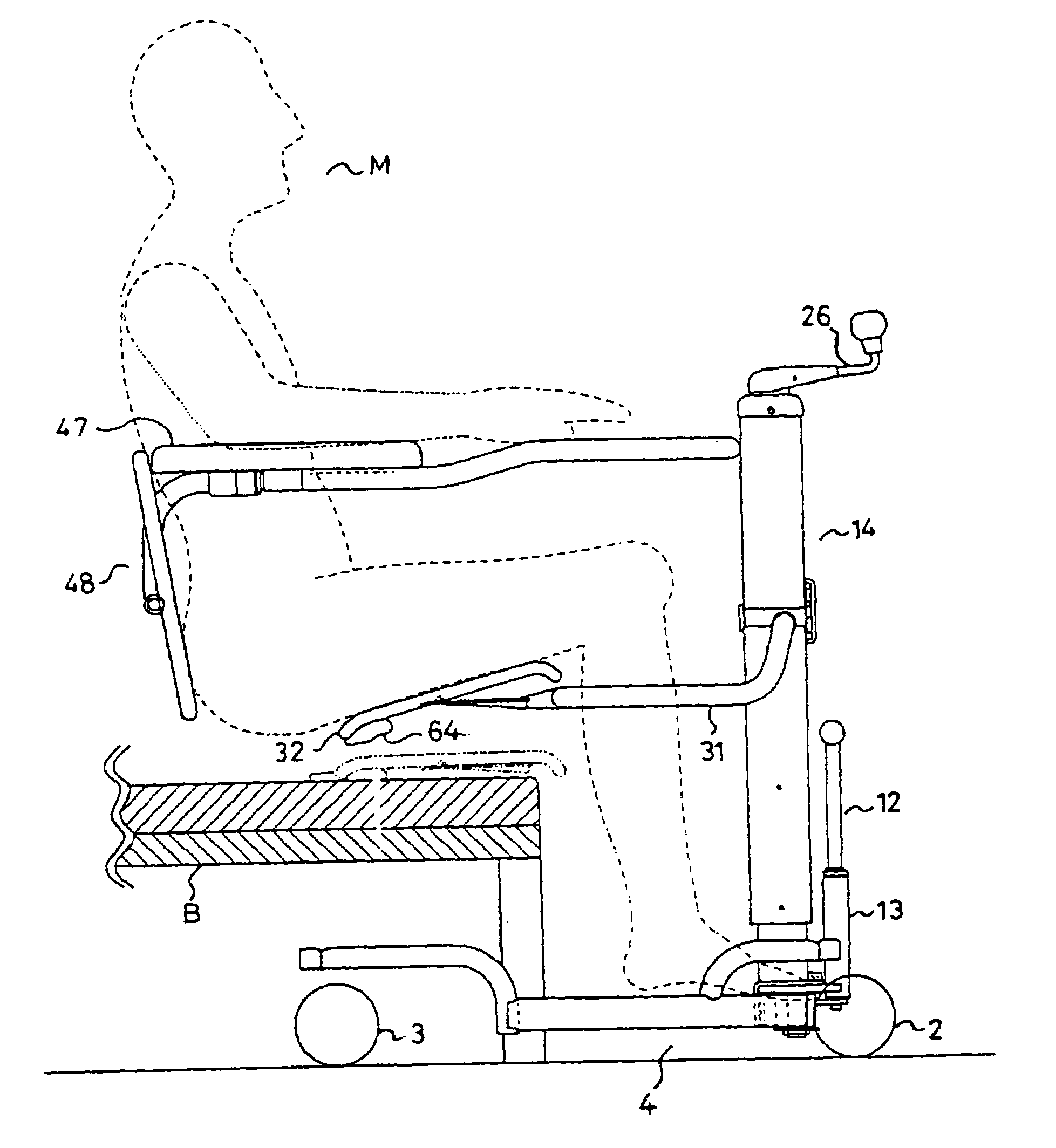
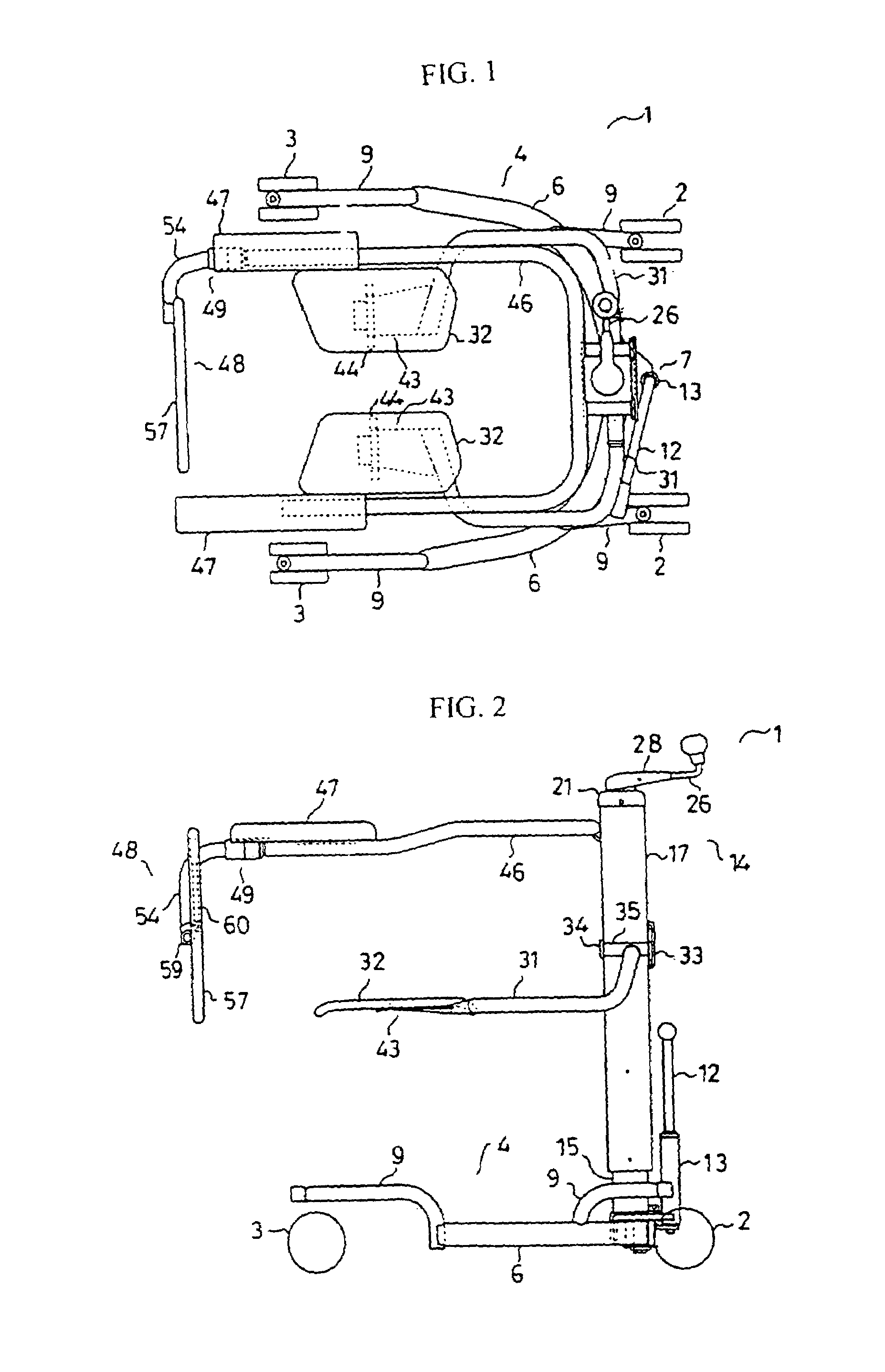
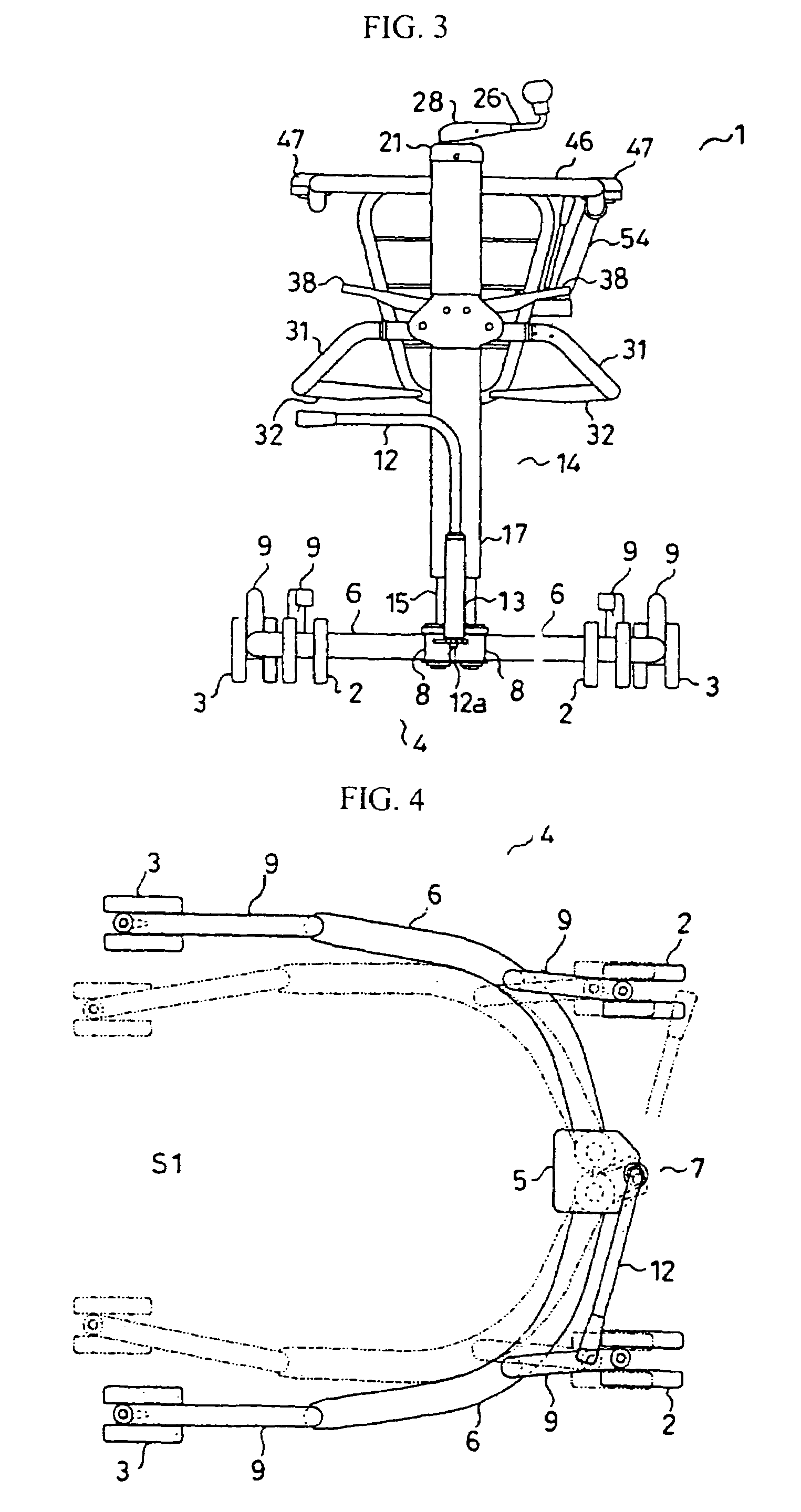
A moving device (1) capable of being operated easily and safely to move a person between various types of beds and chairs by supporting the femoral region and backbone of a person to be moved instead of by suspending the person to be moved by a belt or supporting the axillas and knees of the person, comprising a body frame (4) having a pair of right and left front wheels (2) and rear wheels (3) and having an open rear side, a column (14) erected on the body frame, a pair of right and left side seat parts (32) provided on a pair of right and left side arms (31) fixed to the column, a handrail frame body (46) fixed to the column and having an open rear side, a backbone supporting part (48) disposed at the rear of the seat parts, and a lifting mechanism capable of lifting the seat parts vertically, wherein the arms are formed in a crank-shape and connected pivotally to the column through longitudinal shafts positioned at the front of the knees of the person to be moved, and the seat parts are rotated eccentrically from the outside upper side to the inside lower side so as to insert the seat parts into the lower side of the femoral region while bypassing the knee parts of the person to be moved.
Owner:IURA CO LTD
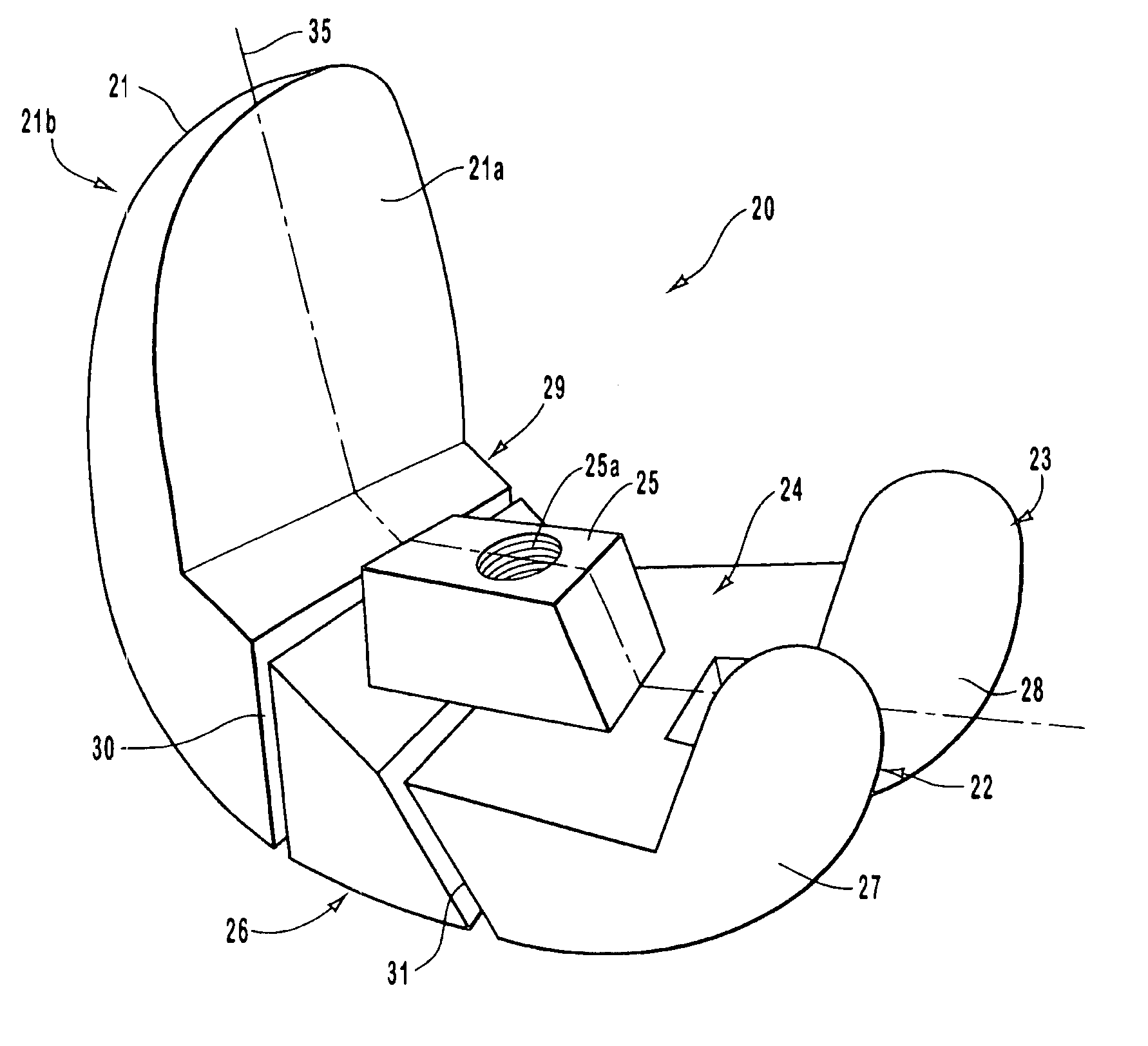
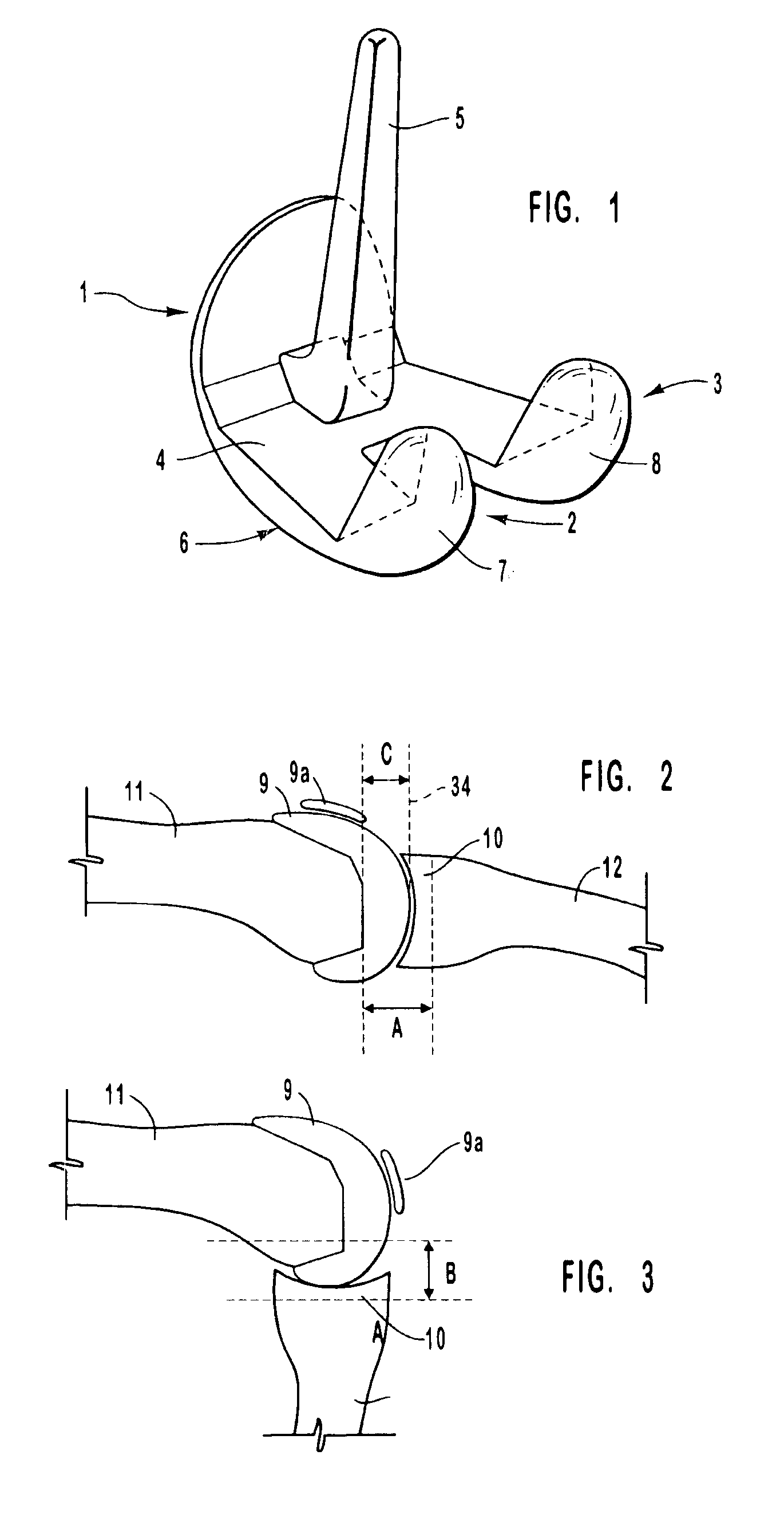
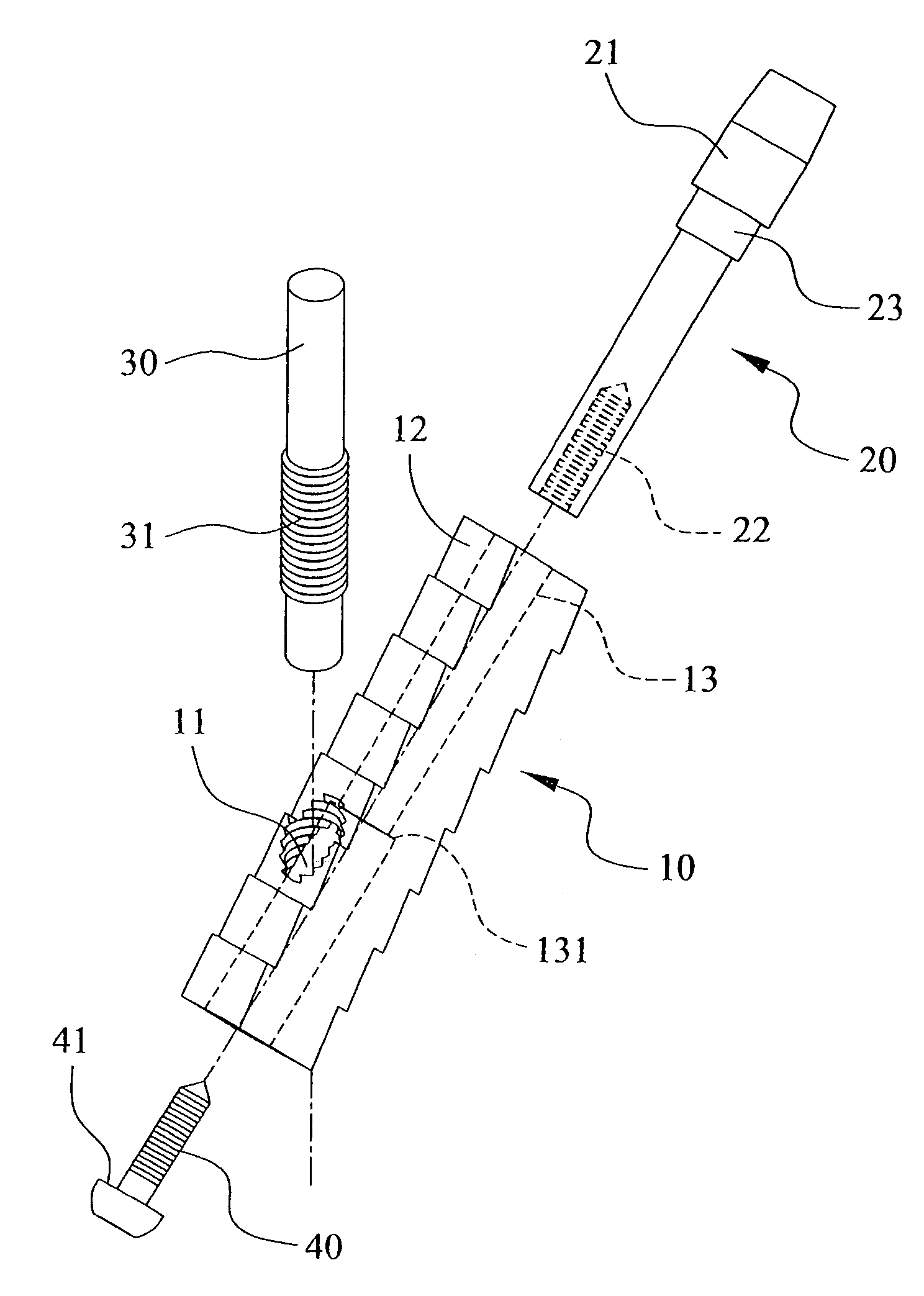
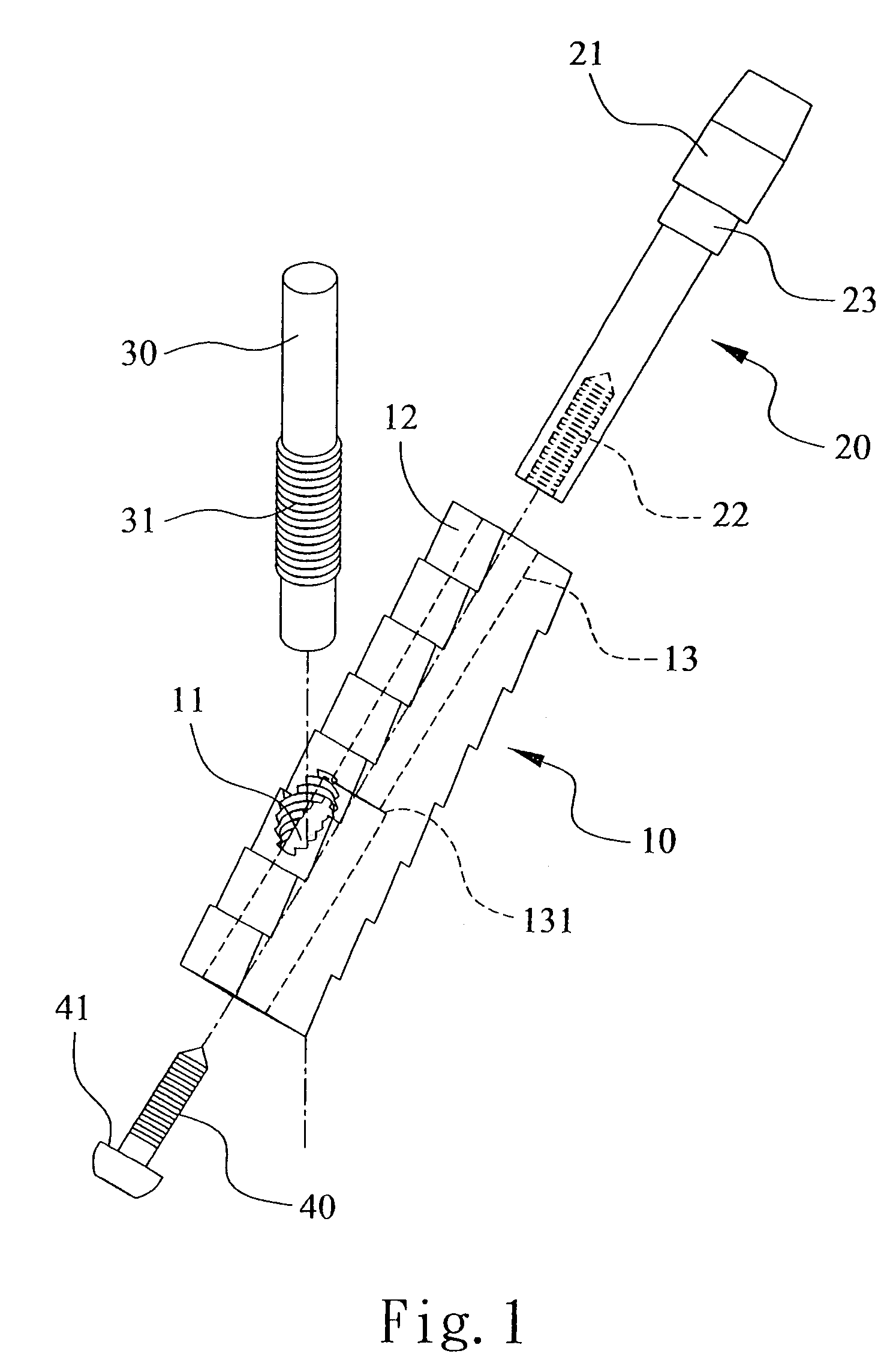
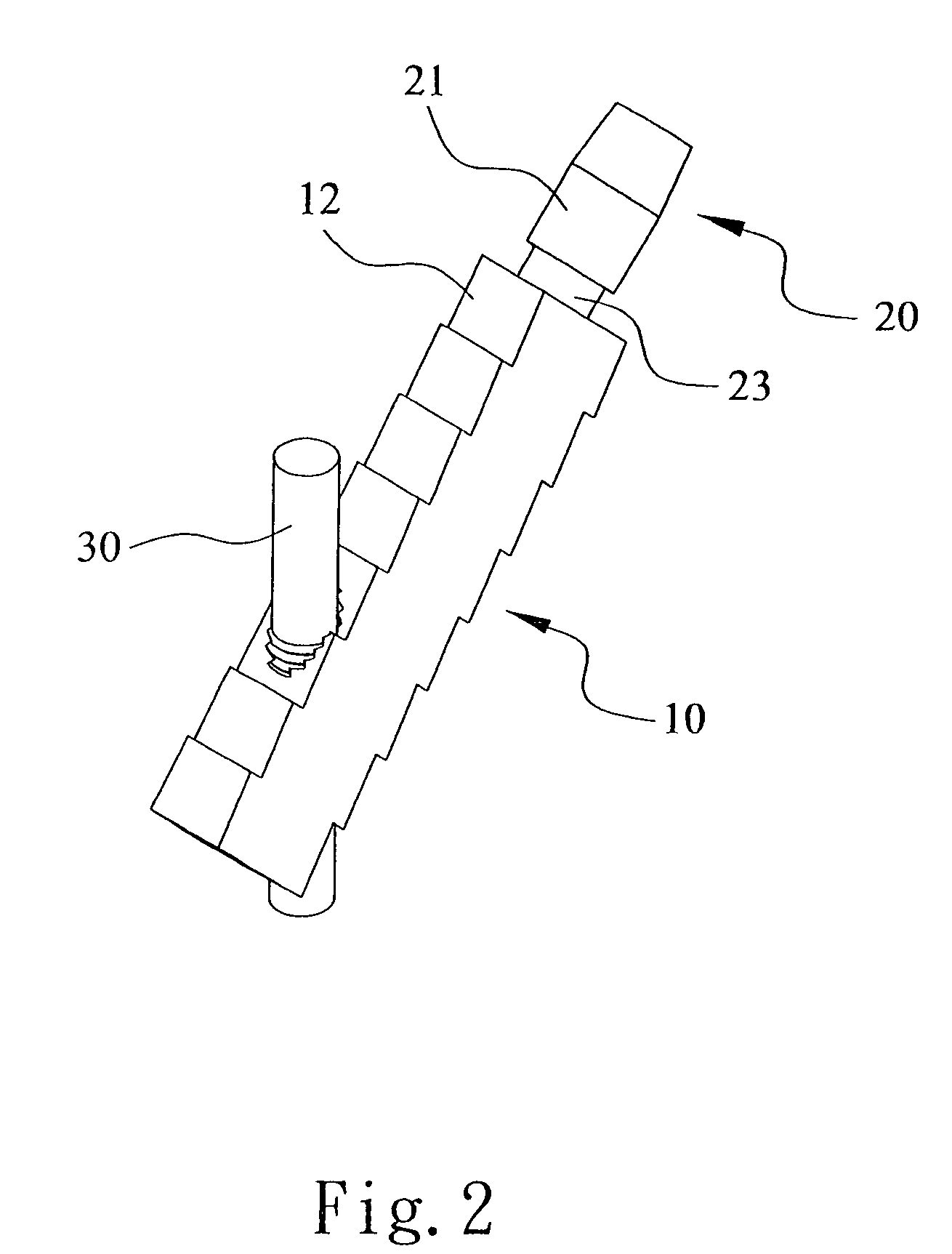
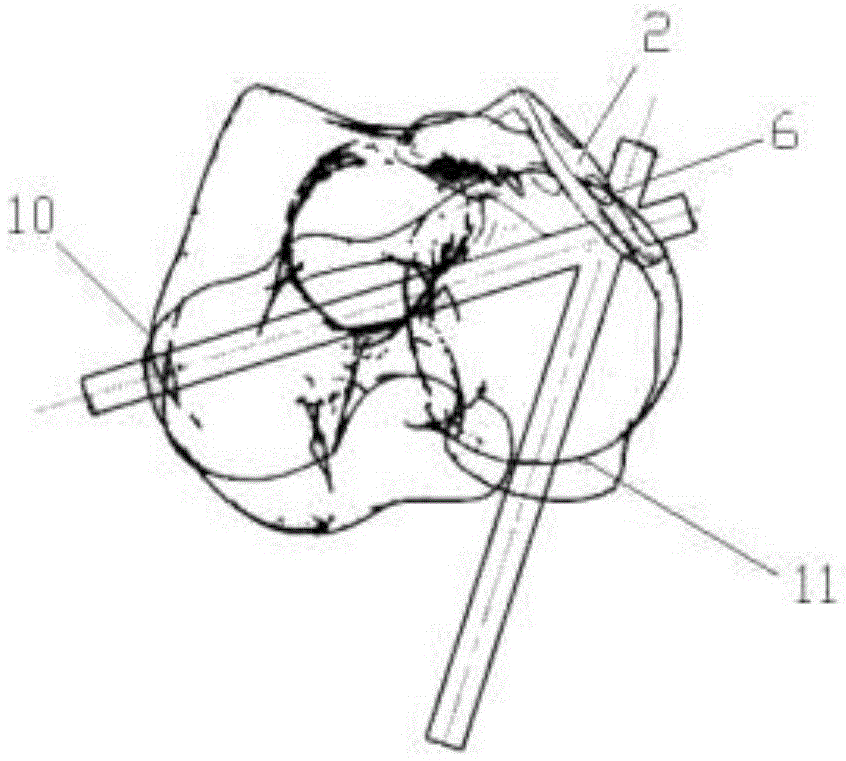
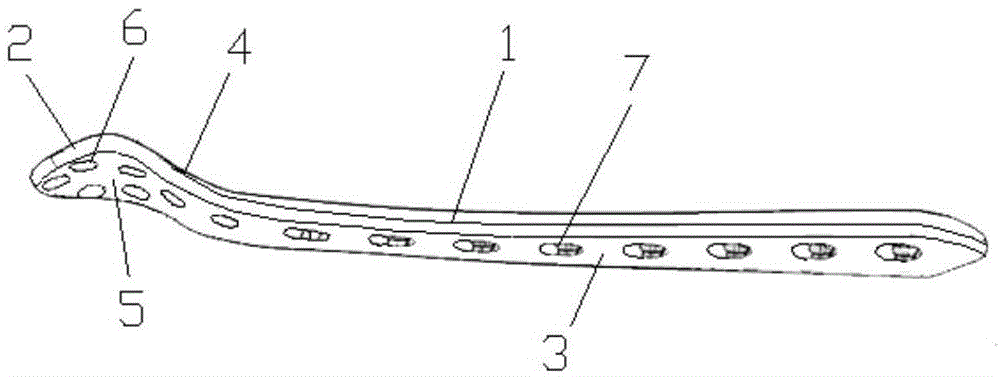
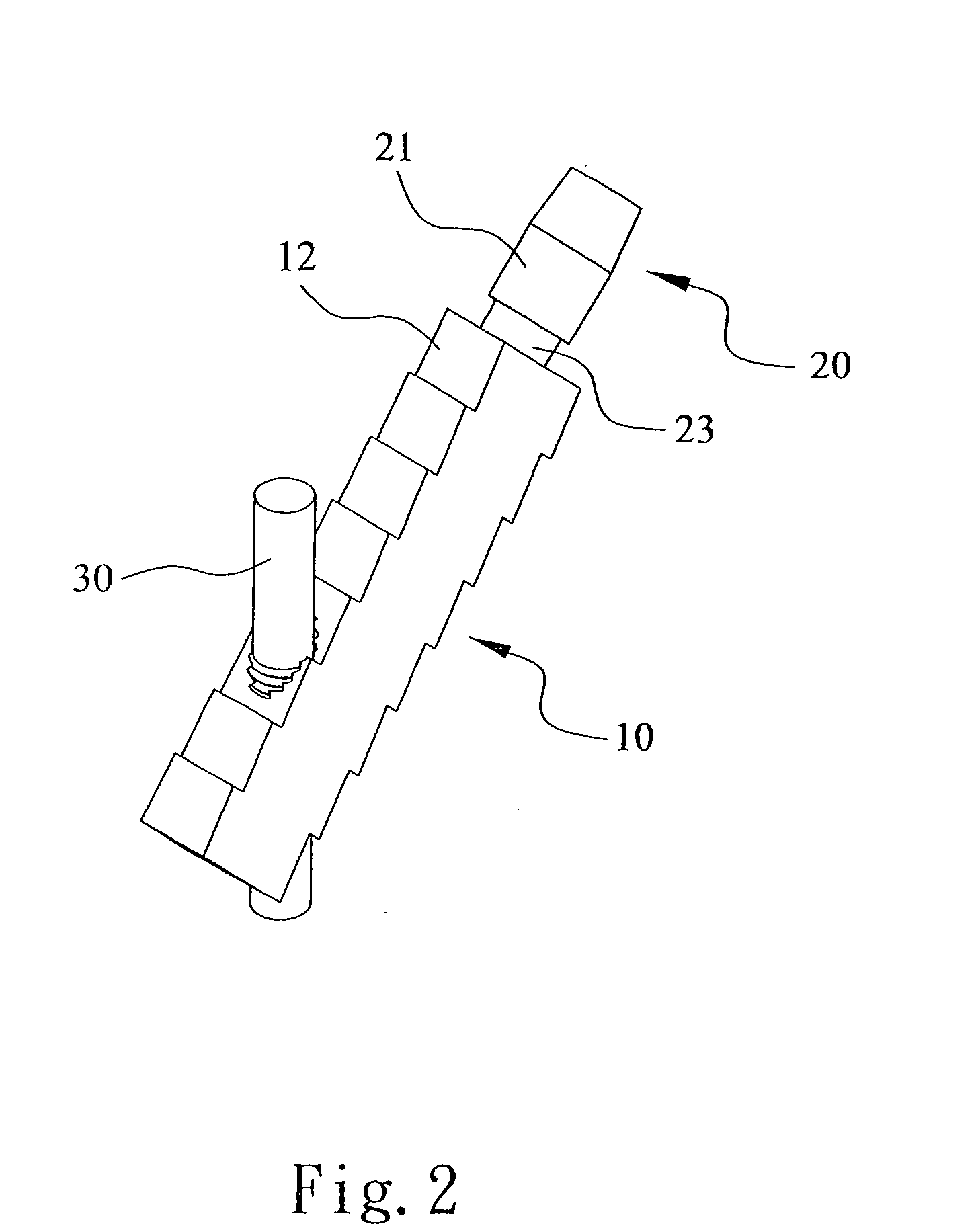
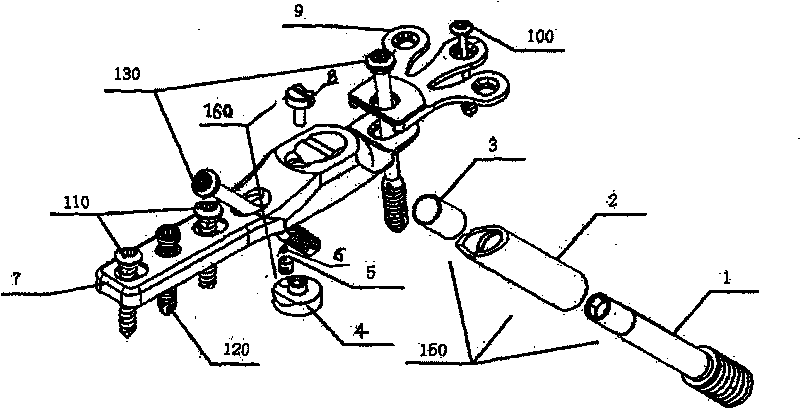
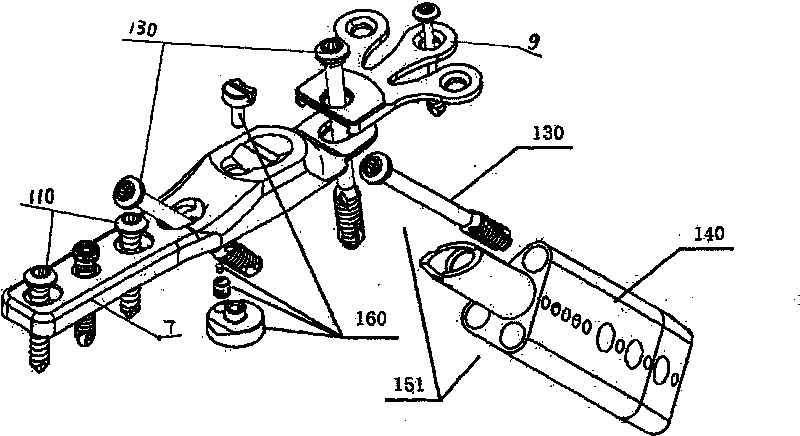
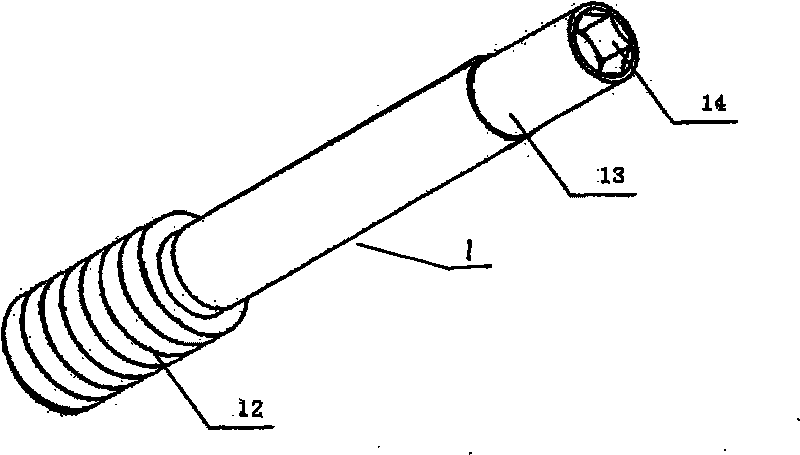
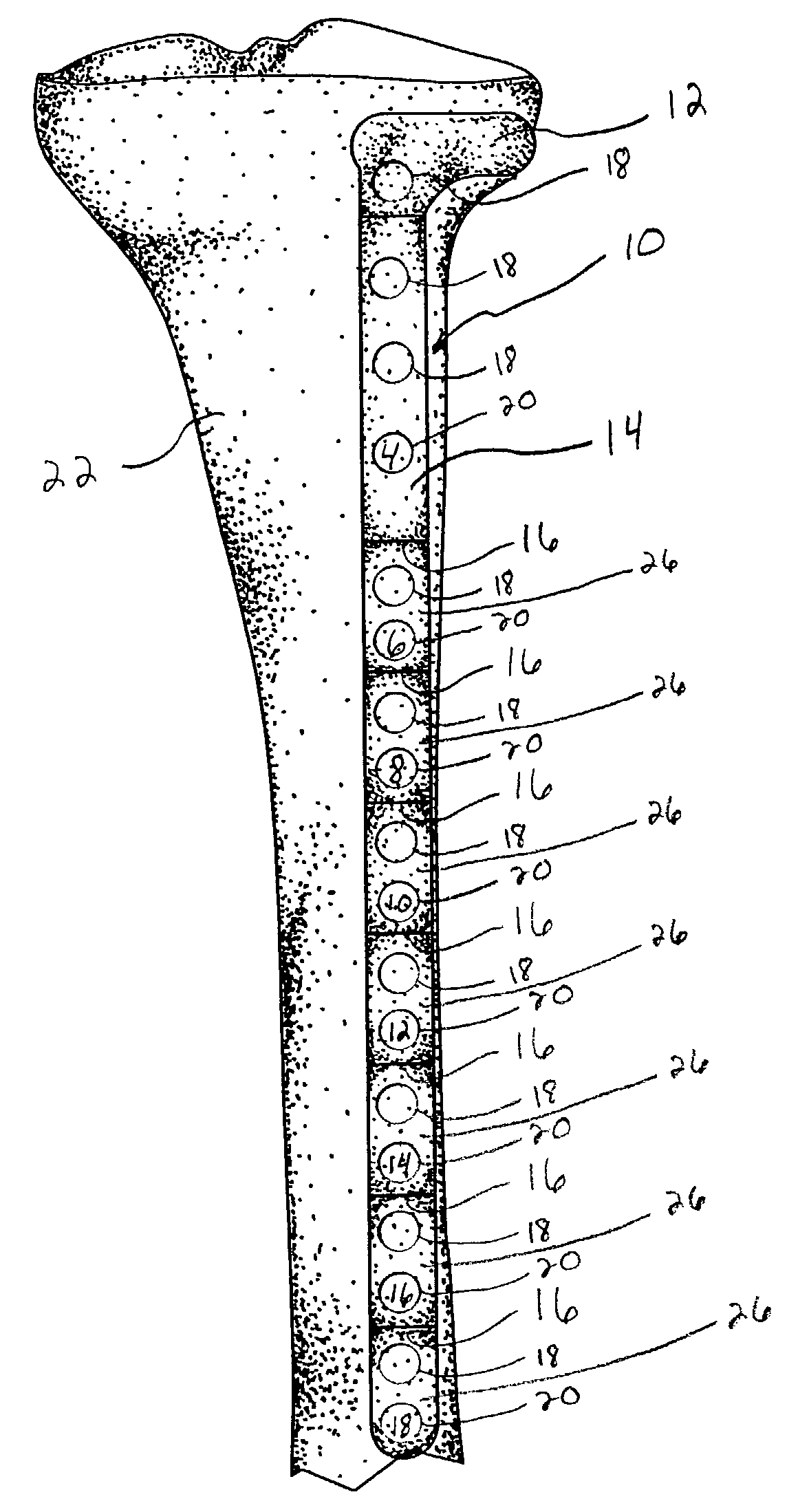
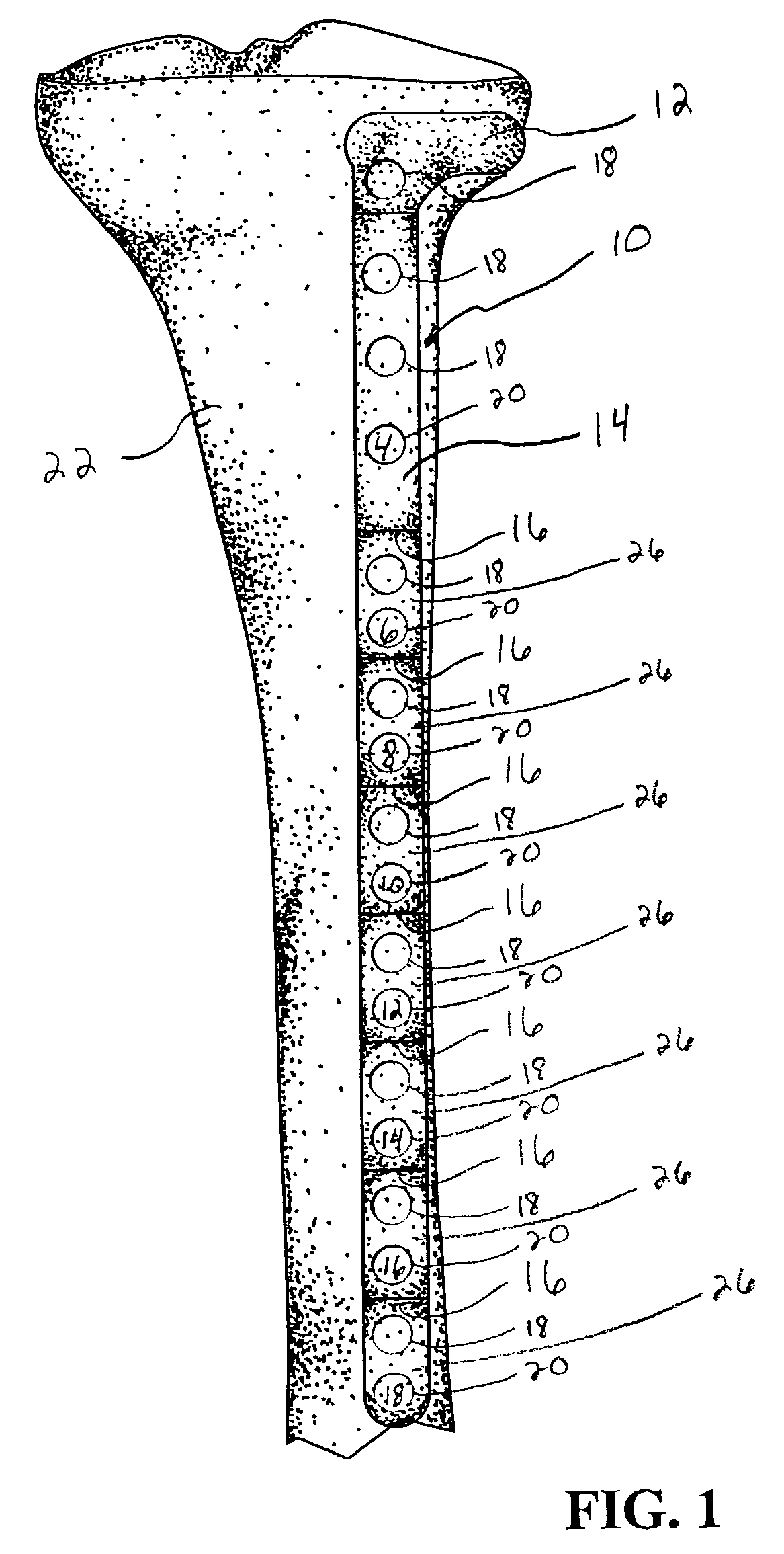
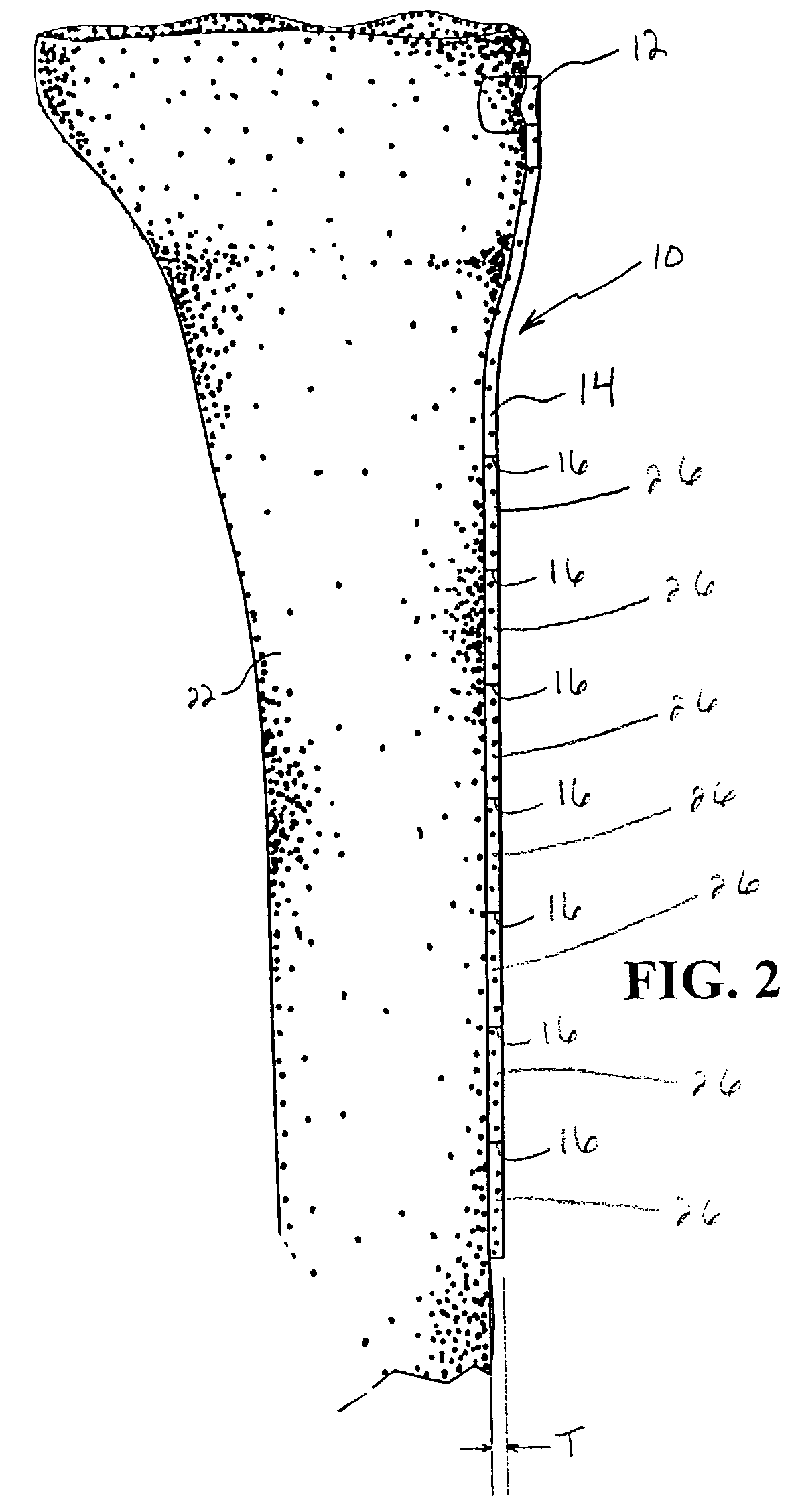
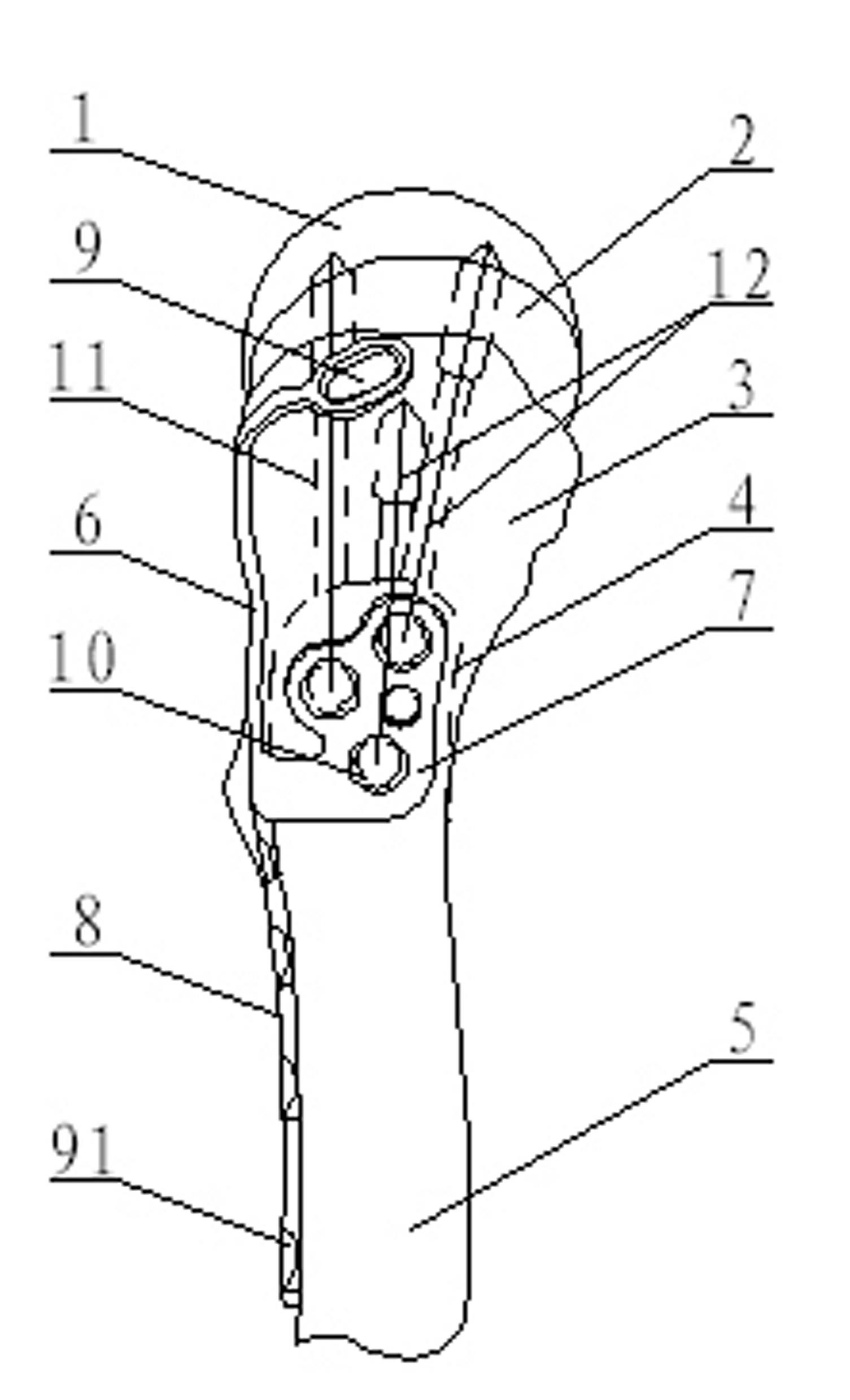
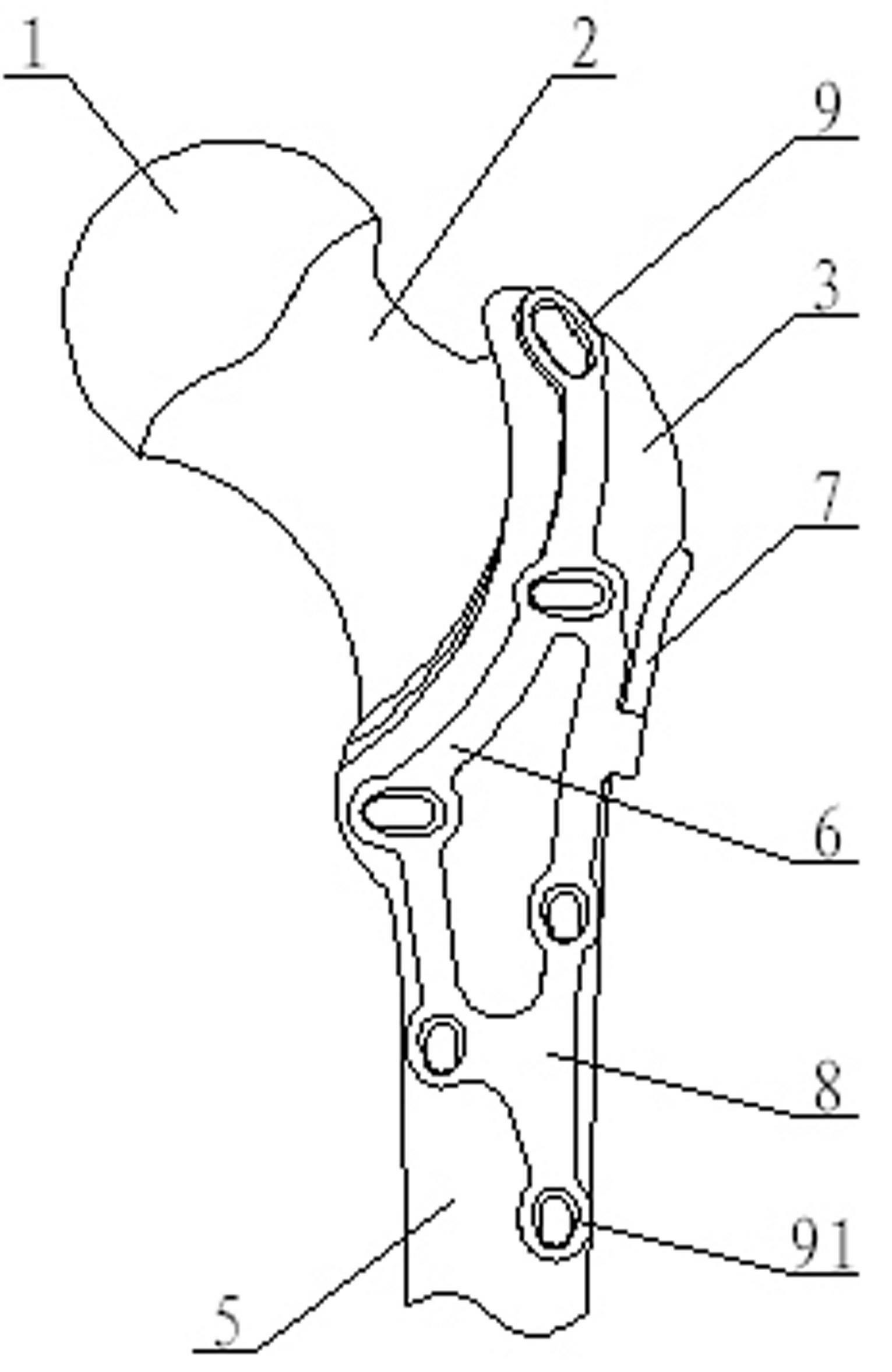
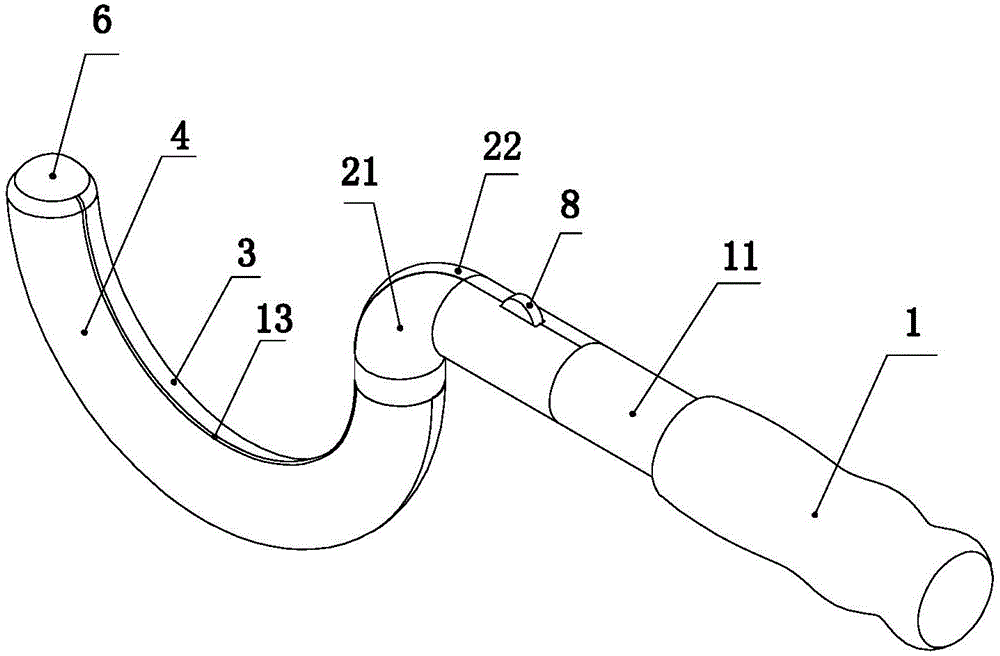
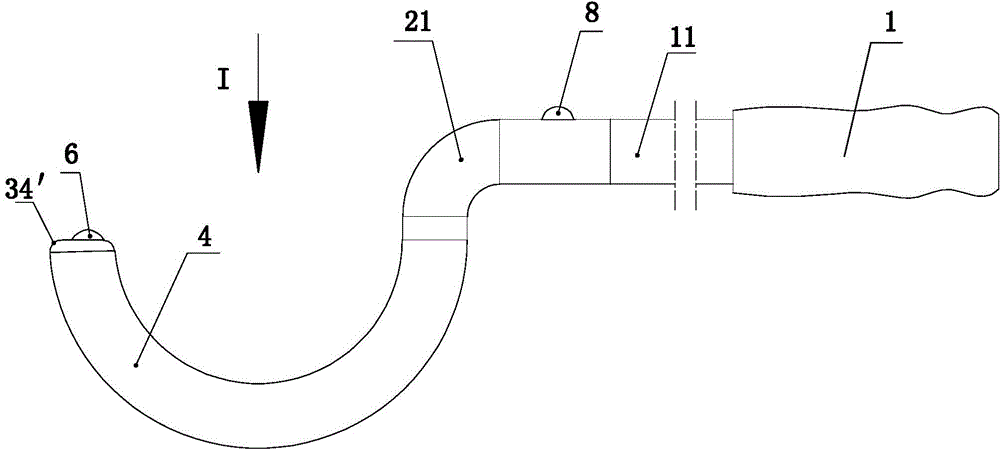
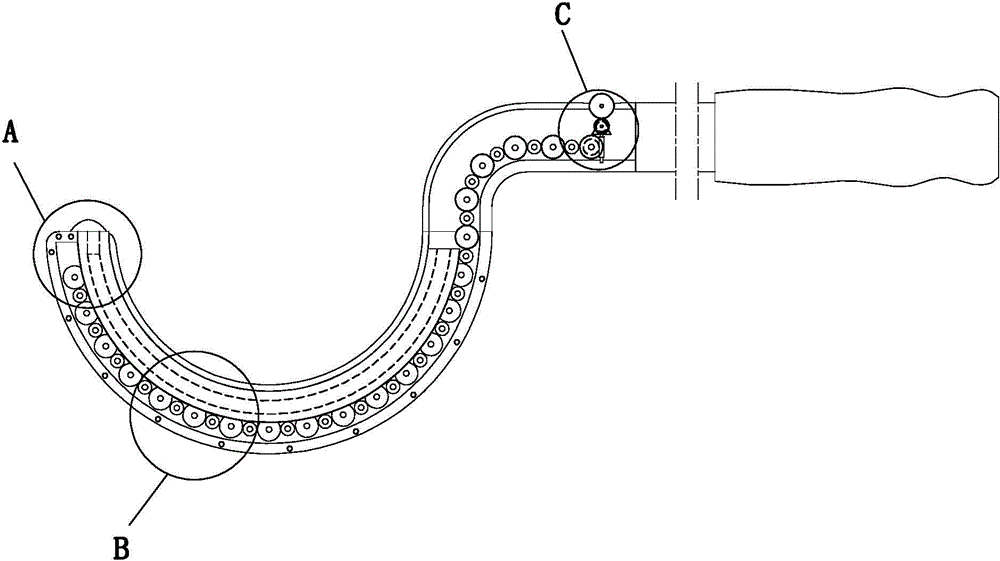
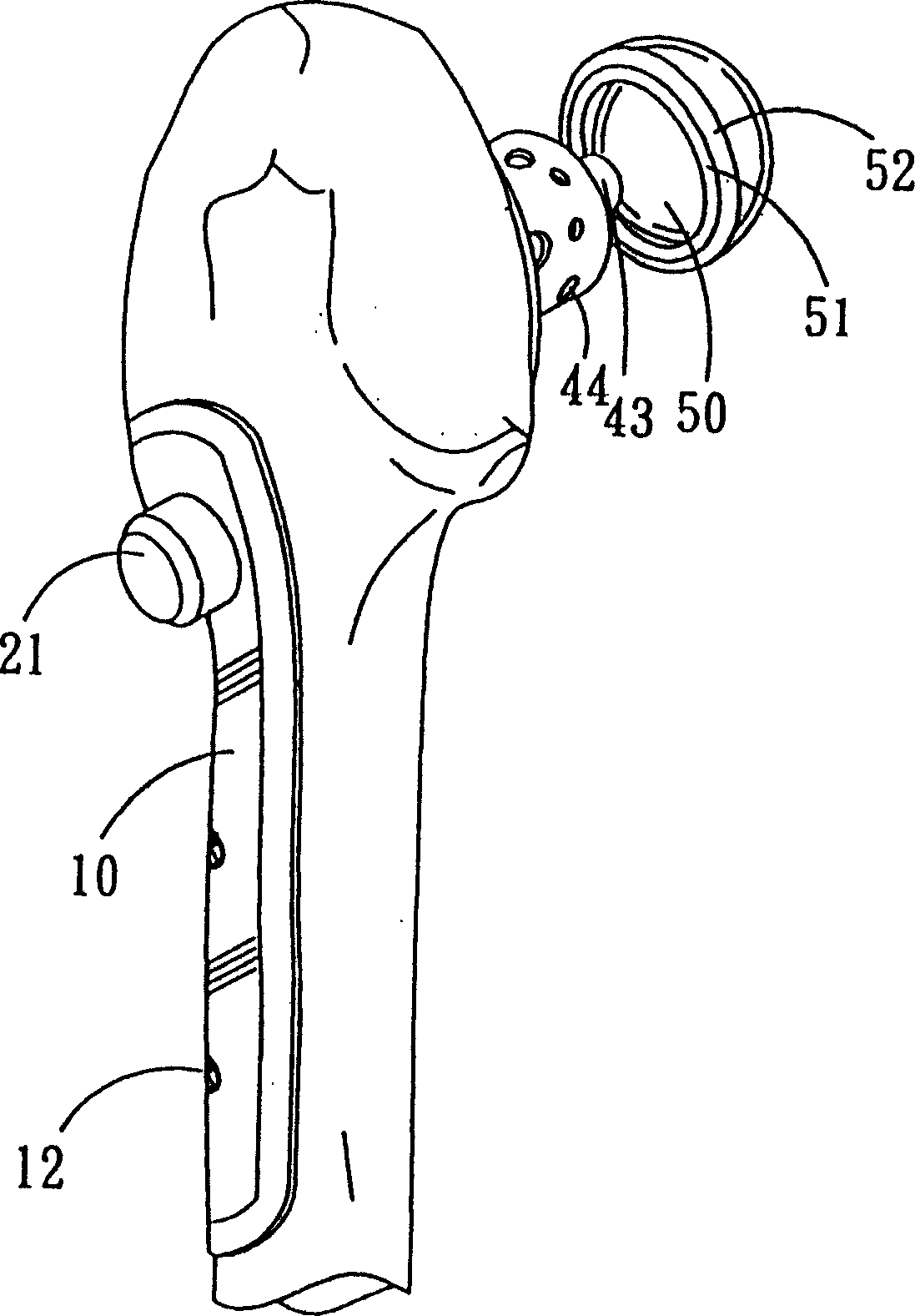
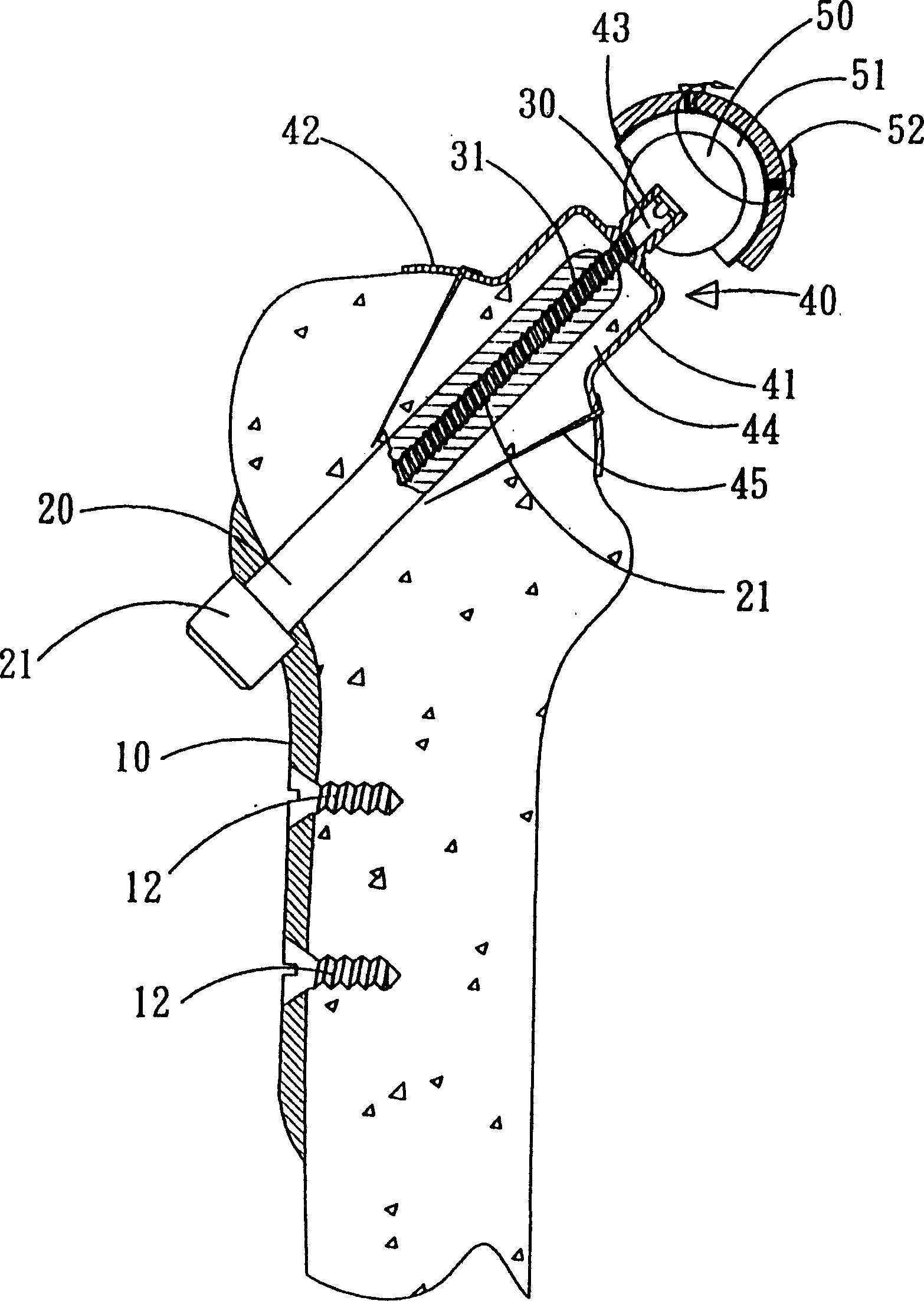
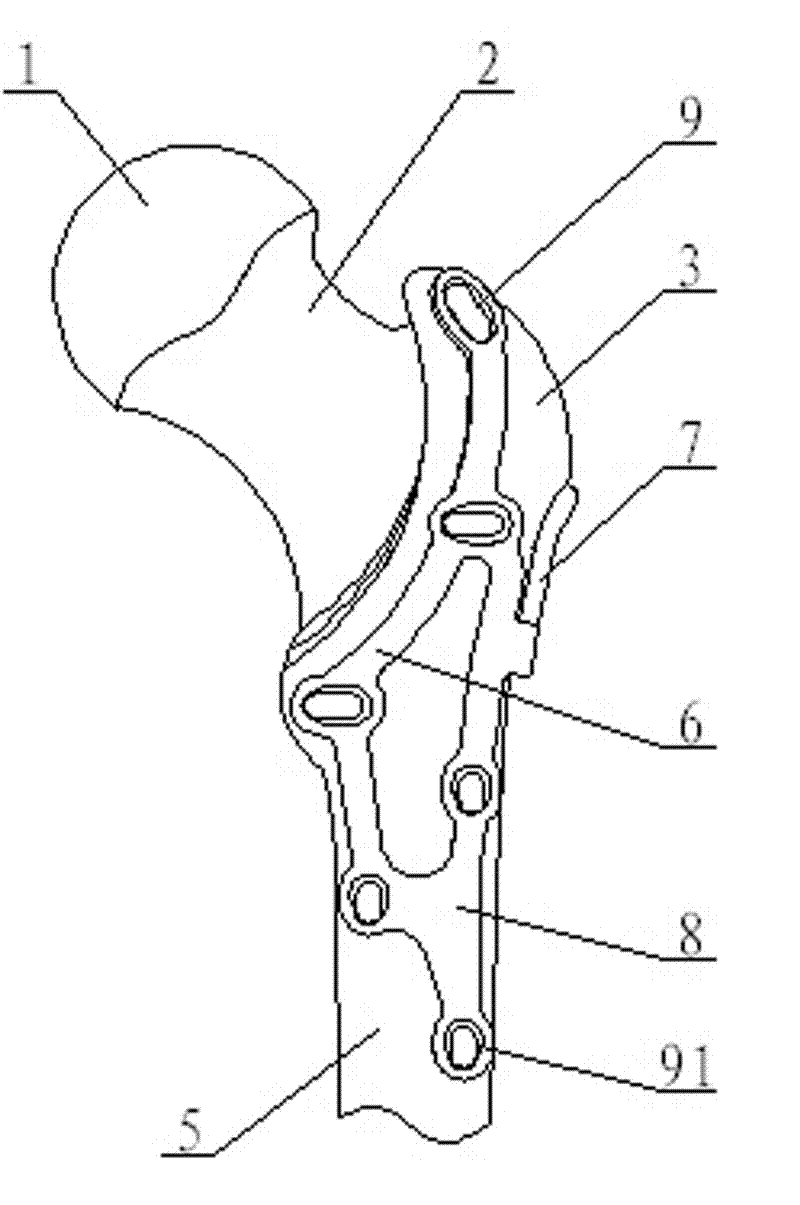
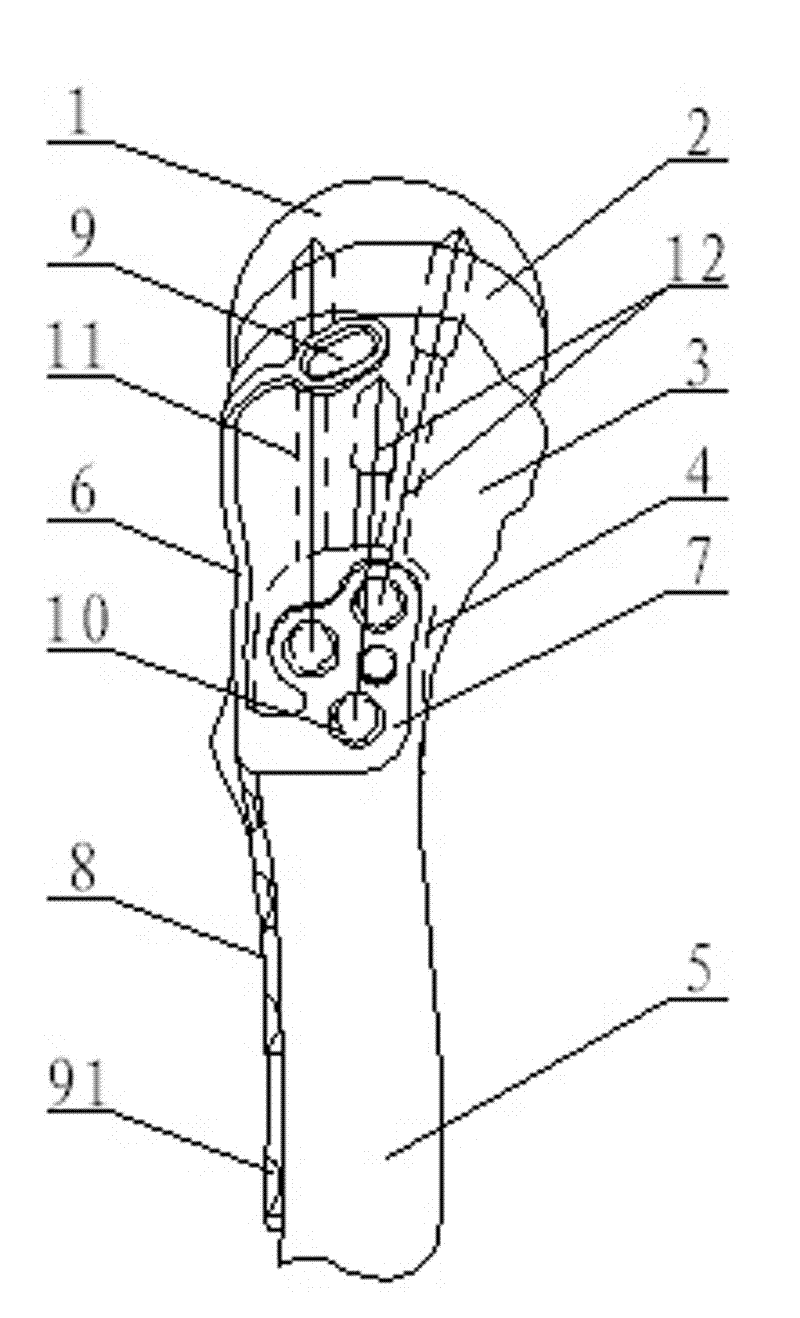
Thighbone shaft
InactiveUS7753961B2Small wound areaReduce planting sizeInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsThighEngineering
Owner:LUNG CHEN YU +1
Modular fracture fixation plate system
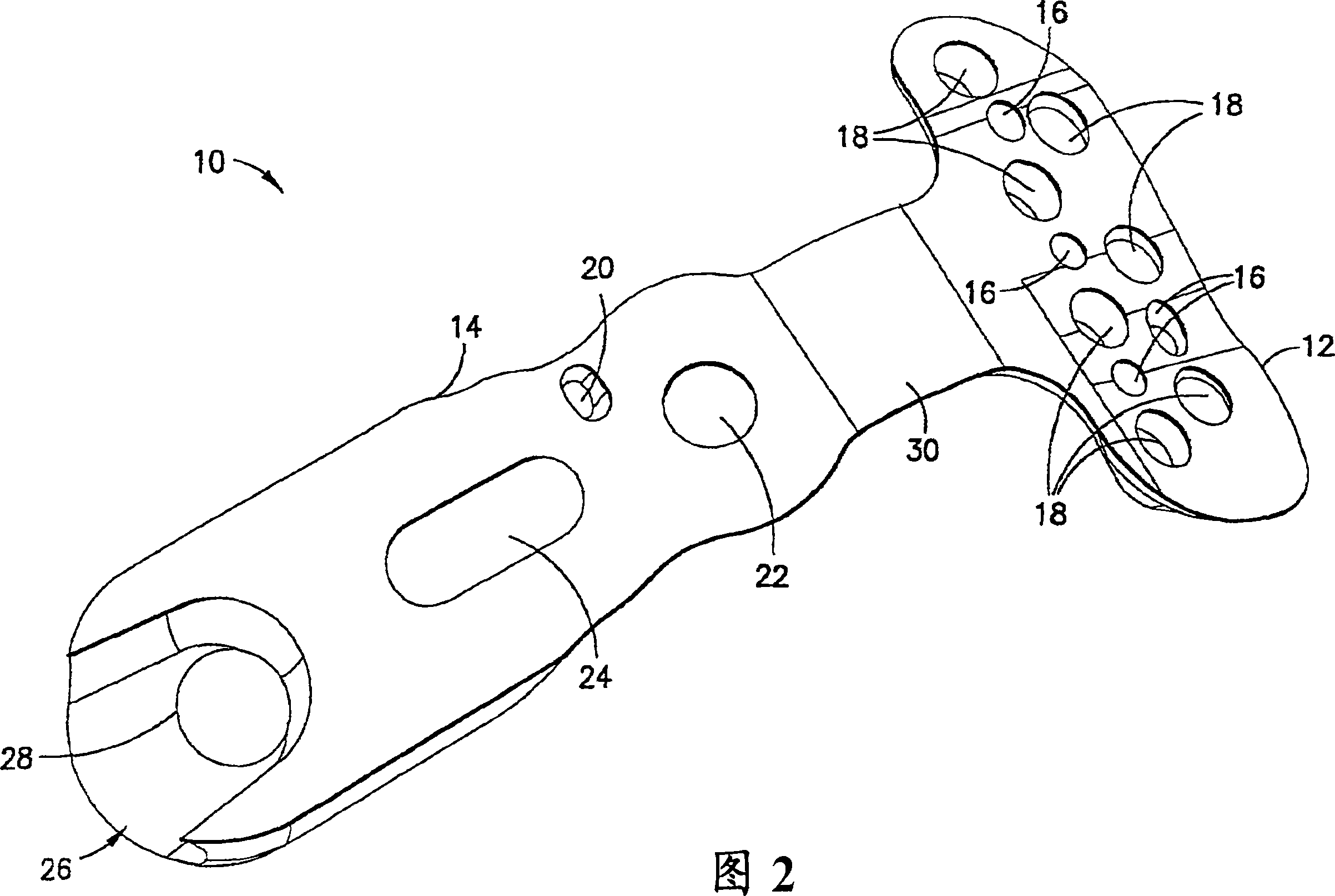
A fracture fixation plate system for use on a long bone having a metaphysis and a diaphysis comprising at least one end plate having a head for the metaphysis and at least one end plate having a first end and a second end A bone plate with a plurality of screw holes between the first end and the second end of the bone plate. The end plate includes mating structure adapted to mate and securely couple with at least one end of the at least one bone plate. The system preferably includes several endplates and bone plates to accommodate anatomical structures of various sizes.
Owner:BIOMET CV
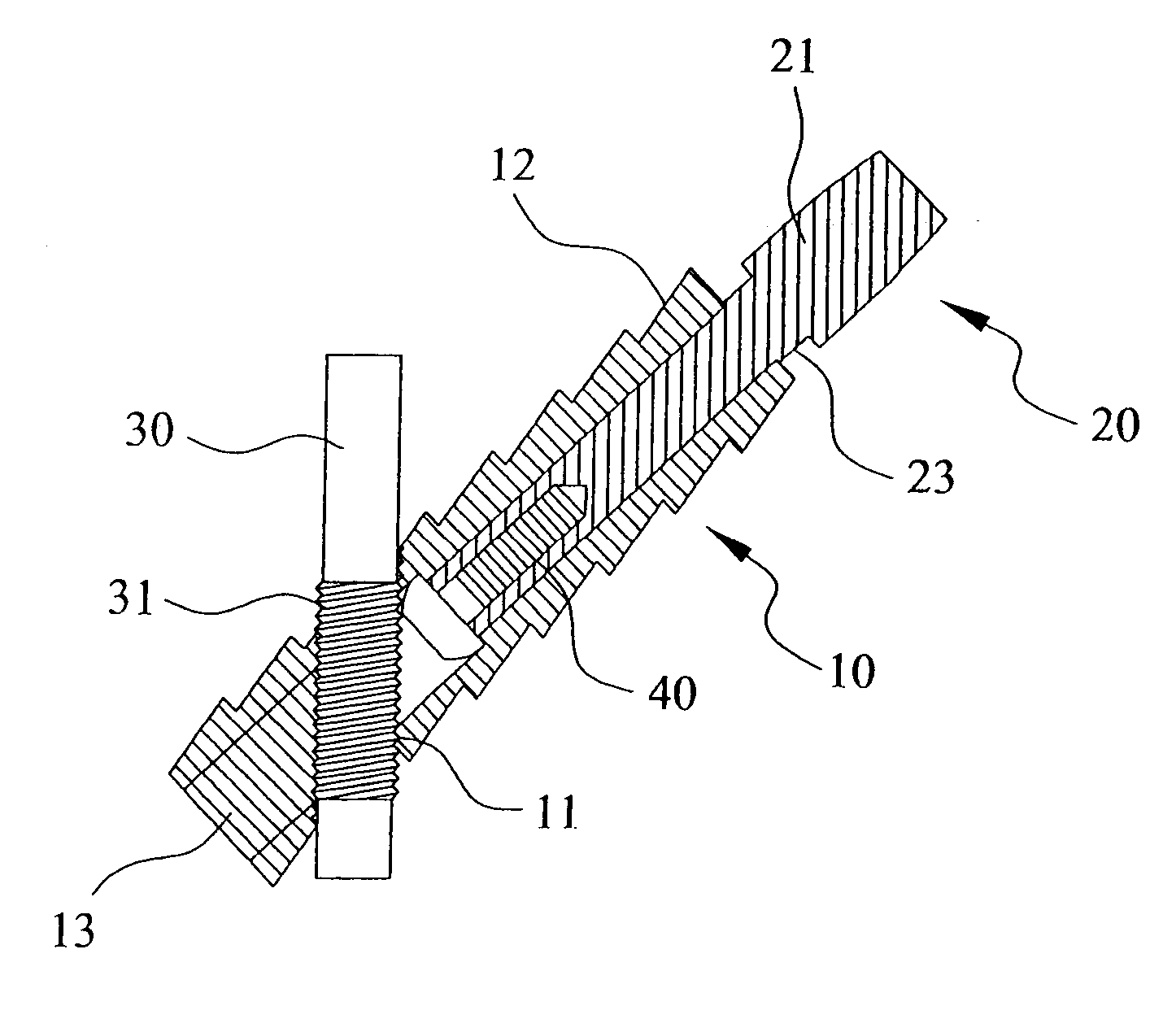
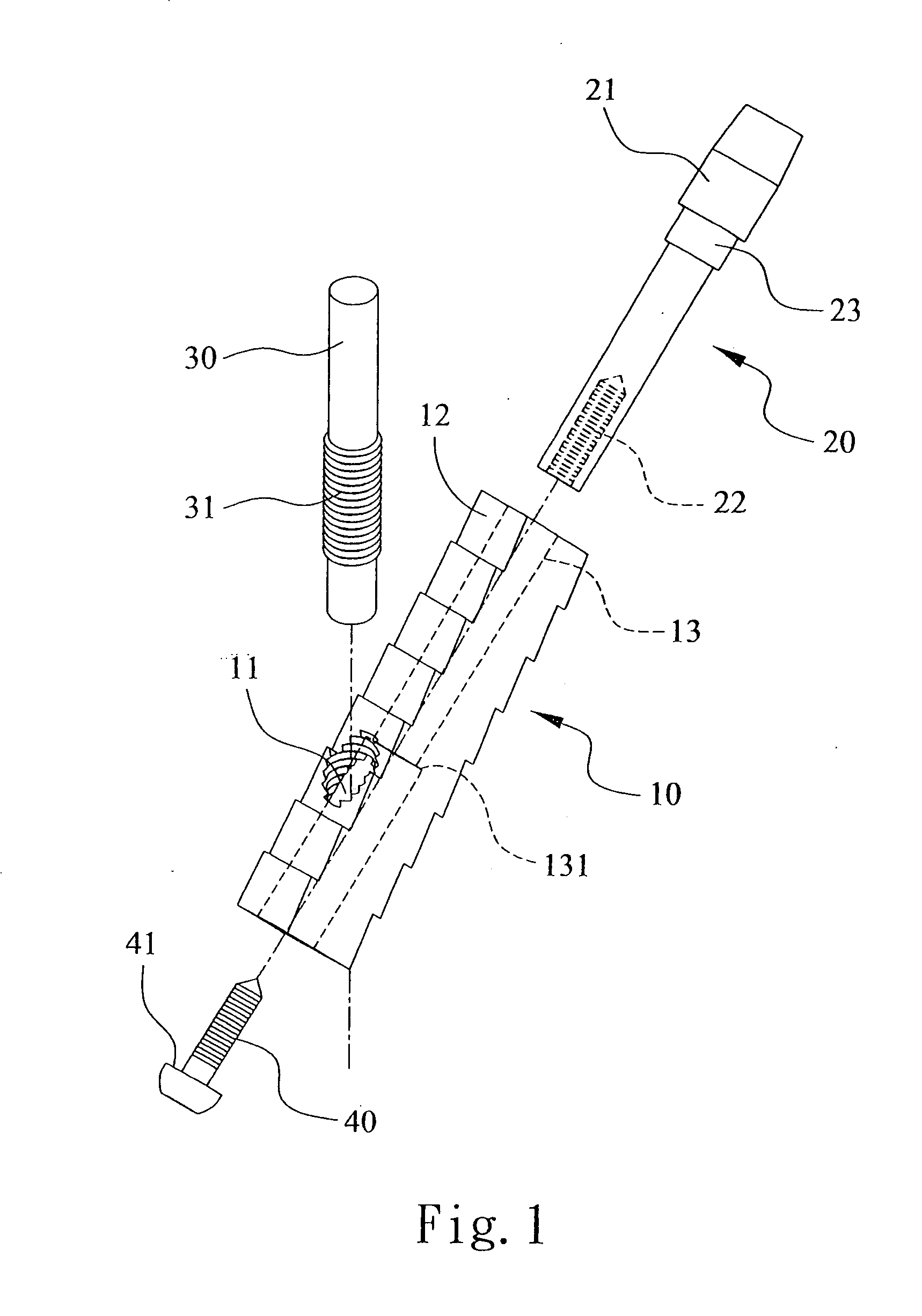
Nail and screw fixation system for improving the fixation of proximal fractures of the humerus
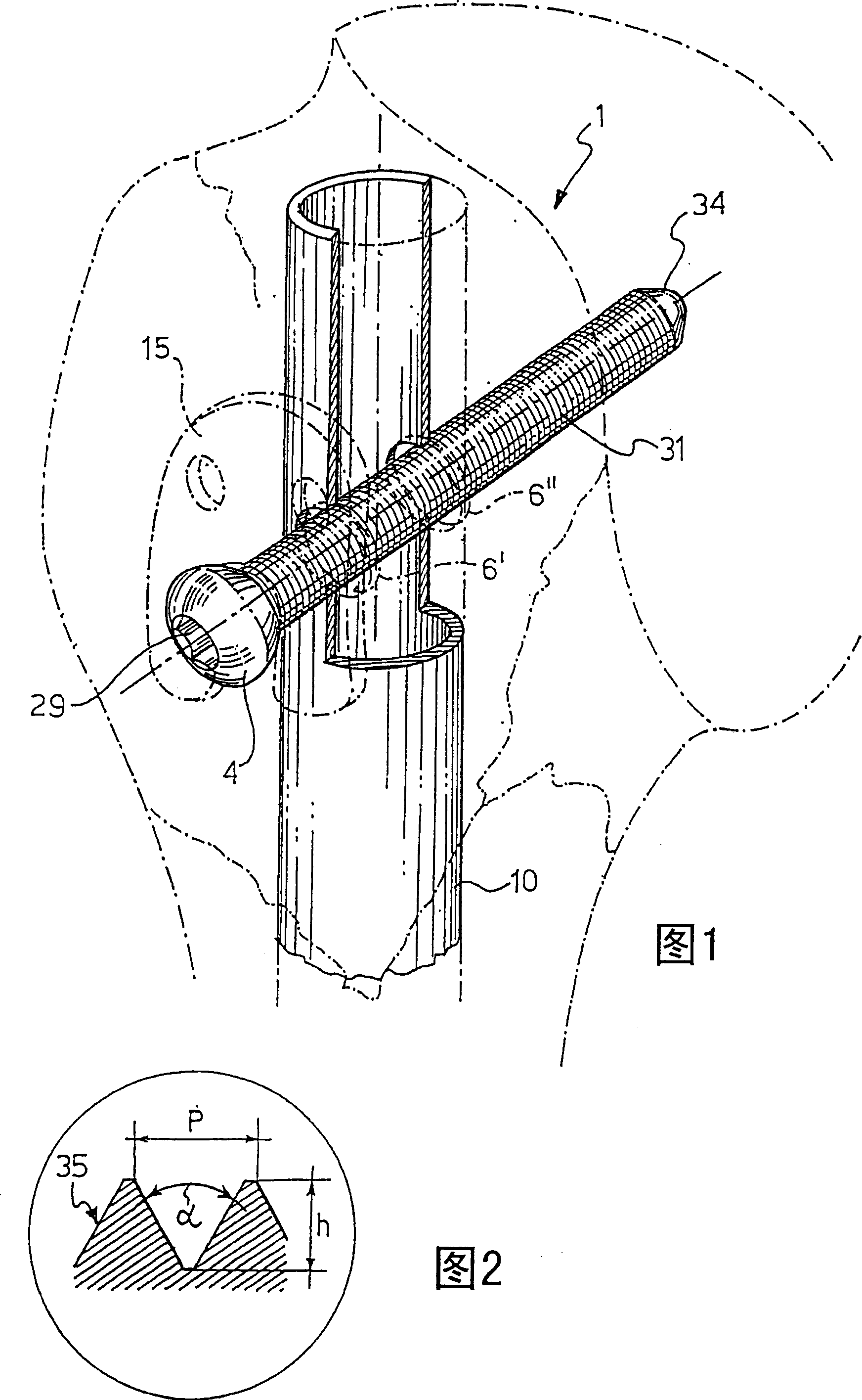
The present invention relates to a nail and screw system (1) for improving the fixation of proximal fractures of the humerus, including at least a Numeral nail (10) to be inserted in a Numeral shaft (9) and comprising at least a proximal transversal hole (5) for the passage of a corresponding locking screw (3), the screw (3) having a screw head (4) and a screw body (31). Advantageously, the nail is cannulated and the transversal hole (5) comprises a couple of opposite holes (6', 6'') on opposite wall of the cannulated nail (10); the hole (6) closer to the screw head (4) has an internal partially threaded portion (28) and the corresponding screw (3) has an outside thread diameter smaller than the diameter of said at least one transversal hole (27) that receives such a screw.
Owner:迪特马尔·彭尼希
Modular implant system and method with diaphyseal implant and adapter
A modular implant system includes a set of anatomically-designed diaphyseal fitting and filling modular implant components and adapters for connection to another implant component such as a modular articular component, a segmental component or an intercalary component. The other end of each diaphyseal component is a tapered porous surface. The tapered porous surface is received with a tapered bore in the bone diaphysis that is prepared to match the size and shape of the tapered porous surface. The diaphyseal implant is easy to insert and remove, does not bind before fully seating, and is designed to prevent stress shielding. The diaphyseal sleeve eliminates the long lever arm created when fixation occurs only at the tip of the stem, and should therefore eliminate related stem loosening.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Method and Apparatus for Removing a Sleeve of Meat from an Animal Part Having Bone with Knuckles on Each of its Opposite Ends
A method of removing a sleeve of meat (D) from an animal part having a bone with a first knuckle (B) on one of two opposite ends of an elongate bone shaft (A) and a second knuckle (C) on another of the two opposite ends. The method includes the steps of engaging the bone of the animal part with a part of a meat stripper (13) between its first knuckle (B) and the sleeve of meat (D) and engaging the bone by a knuckle gripper (71) between the part of the meat stripper (13) and the first knuckle (B). The method continues with moving the meat stripper (13) and the knuckle gripper (71) away from one another, while stripping and gathering the sleeve of meat (D) towards the second knuckle (C). In a subsequent step the method discontinues moving away the meat stripper (13) and knuckle gripper (71) from one another upon the part of the meat stripper (13) engaging the second knuckle (C). A further method step then advances a meat cutter (51) in a direction towards the meat stripper (13) opposite of the knuckle gripper (71) to cut the sleeve of meat (D) gathered by the meat stripper (13) circumferentially around the second knuckle (C). The method finishes by retracting the meat cutter (51), disengaging the knuckle gripper (71), removing the bone from the gathered sleeve of meat (D) and from the meat stripper (13), and collecting the gathered sleeve of meat (D) for further processing. An apparatus for performing the method according to this method is also disclosed.
Owner:FOODMATE
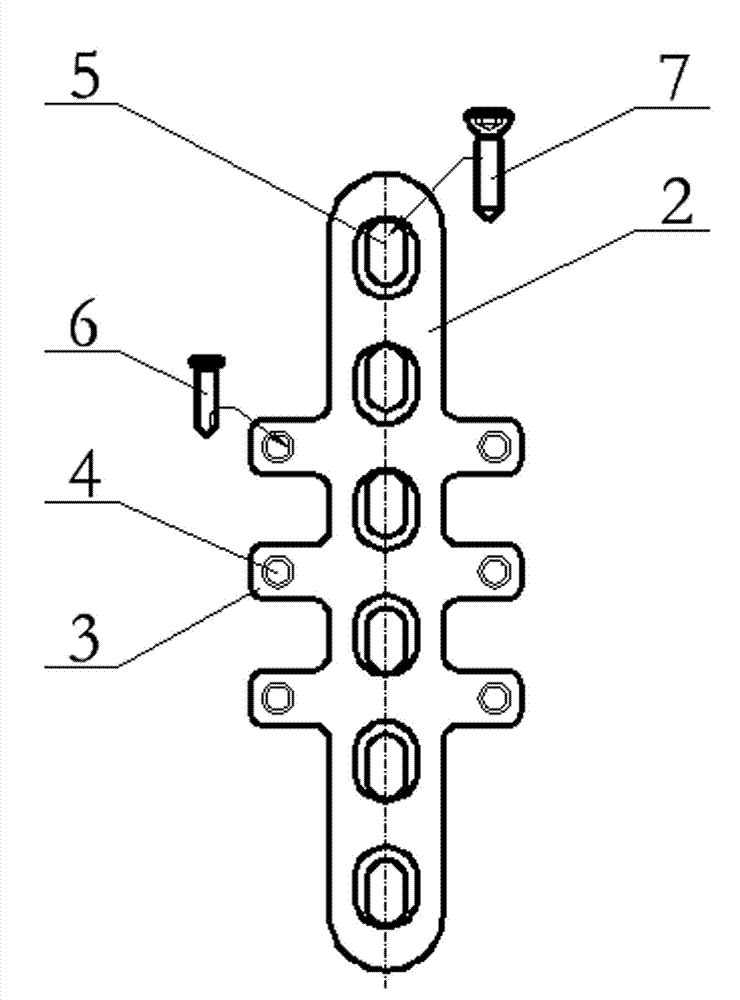
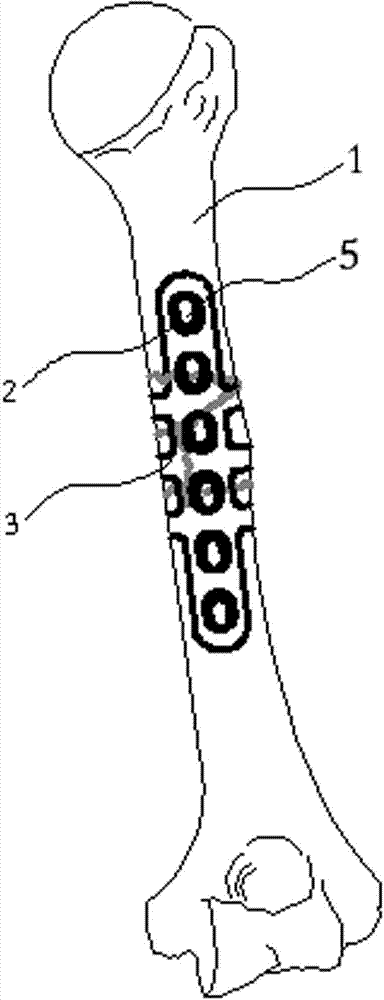
Provisional bone plate
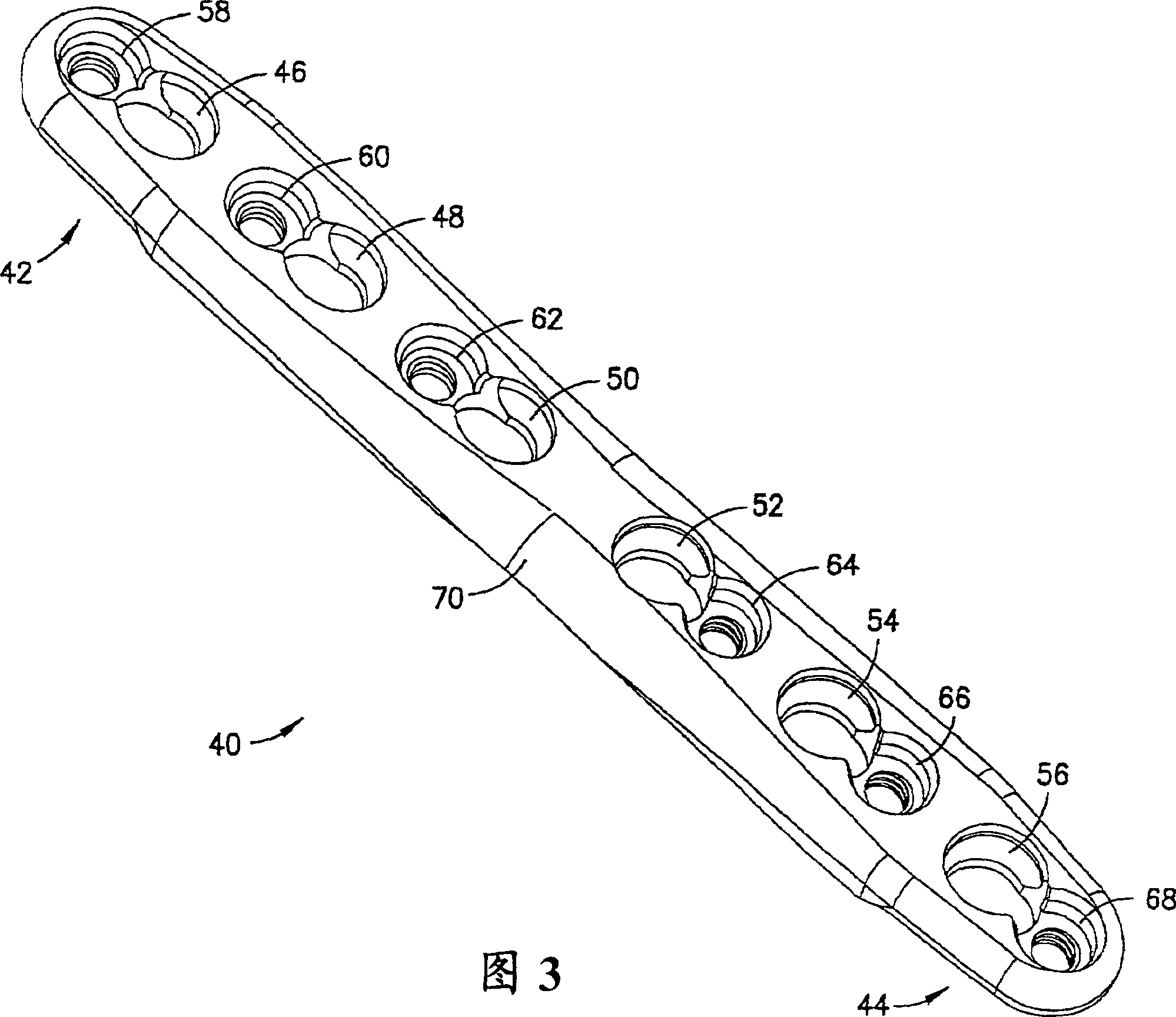
A provisional bone plate formed of an implantable plastic and having a length corresponding to the longest bone plate in a particular family of bone plates. The provisional bone plate includes a head contoured to match the head of a particular bone as well as a shaft for placement adjacent the bone shaft. The provisional bone plate includes a plurality of circumferential notches surrounding the elongate body or shaft of the bone plate. The circumferential notches are substantially transverse to a longitudinal axis of the bone plate and define frangible portions of the bone plate which can be removed from the distal end thereof to alter the length of the provisional periarticular bone plate to correspond to the length of the various bone plates in a family of bone plates. The provisional bone plate is constructed of a biologically suitable plastic, is radiographic, and melts at a temperature less than 200° Fahrenheit.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
Proximal humerus fracture repair plate and system
InactiveUS8968371B2Small surface areaGood for bone healthFastenersBone drill guidesMetaphysisFracture reduction
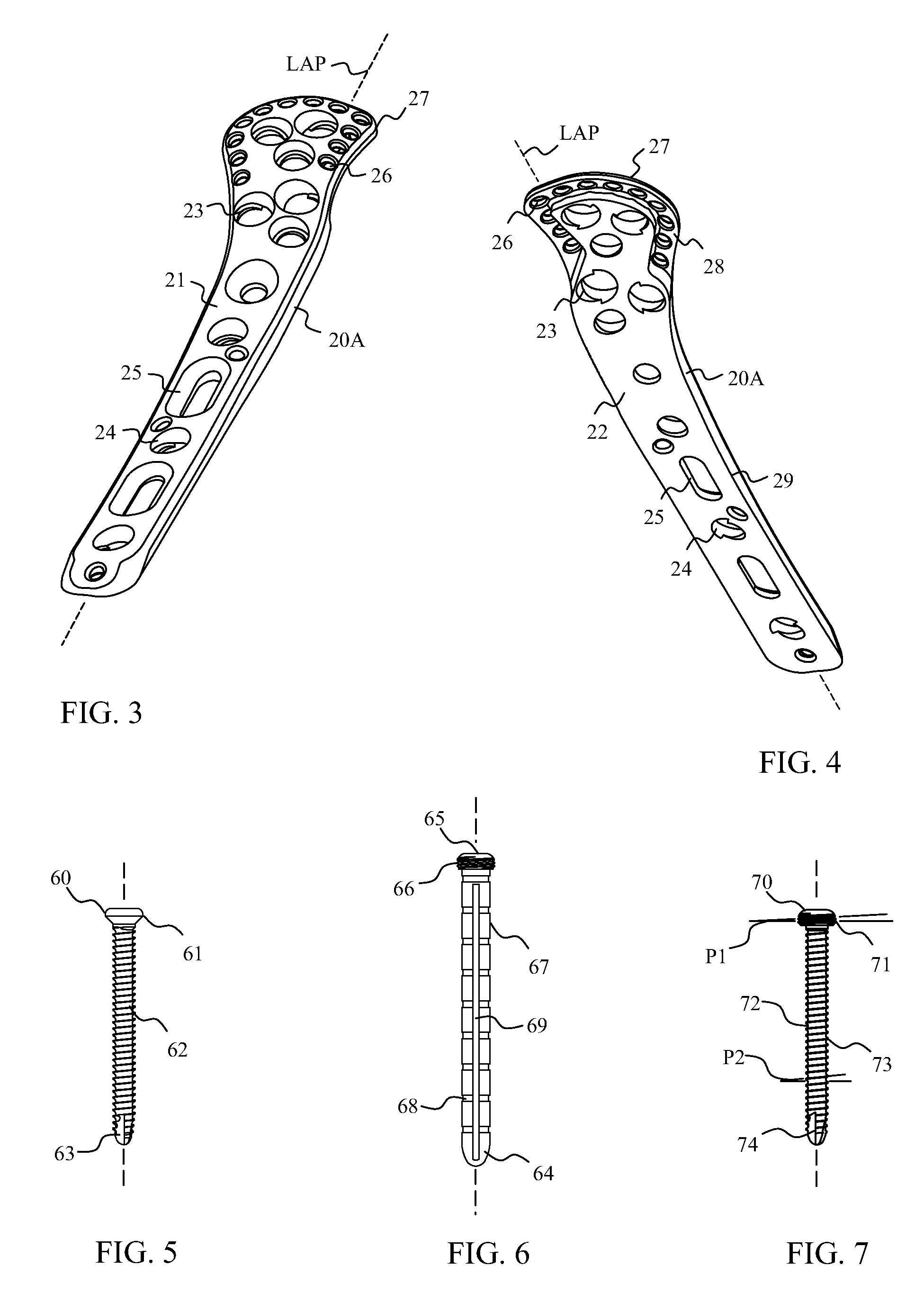
Devices and systems for repairing bone fractures and more specifically a fracture repair plate that provides for fixation of a metaphysis to the diaphysis of a long bone, for instance a fracture between the proximal humerus and the diaphysis of the humerus. The fracture repair system includes an implantable repair fracture repair plate and a bone anchor for fixing the fracture repair plate to a bone. In one embodiment, the fracture repair plate may also be adapted to serve as an anchor for a suture. The fracture repair system may also include a fracture reduction mechanism attachable to the fracture repair plate for imparting a controlled translational movement between two bone segments along a plane that lies substantially parallel to the surface of the bone to which the fracture repair plate is attached and substantially parallel to the longitudinal axis of the bone shaft.
Owner:SHOULDER OPTIONS
Fracture three-dimensionally-intersecting-connecting-locking internal fixing device
InactiveCN105615968APreventing varus displacementSolve the world problem of "stress concentration" that often breaks the plateInternal osteosythesisFastenersStress concentrationIntertrochanteric fracture
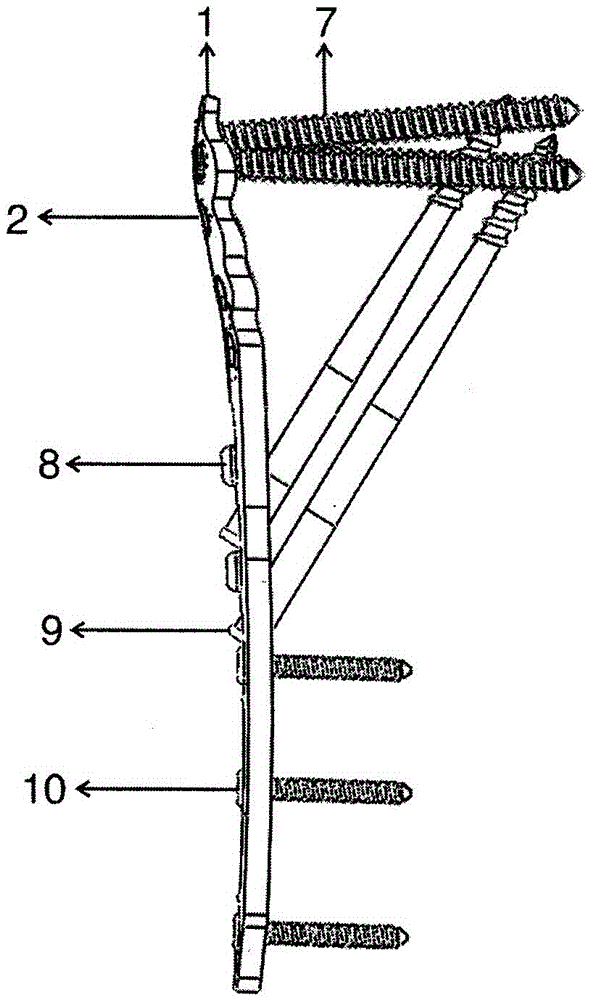
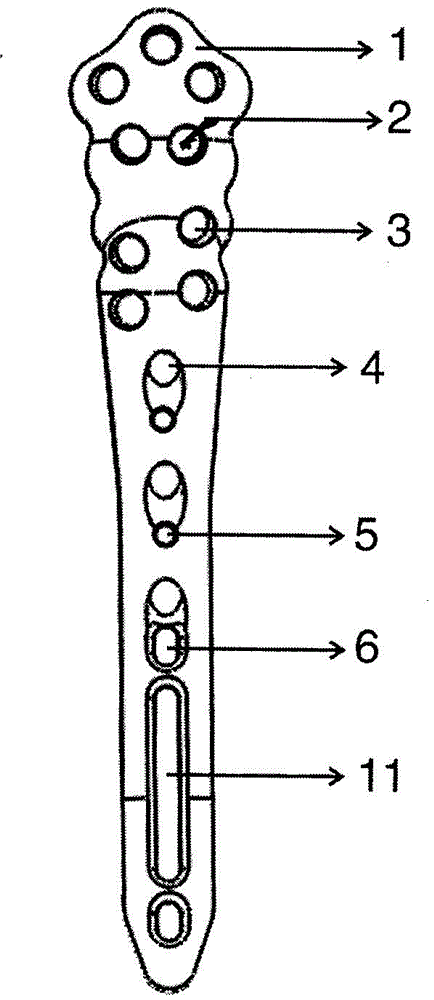
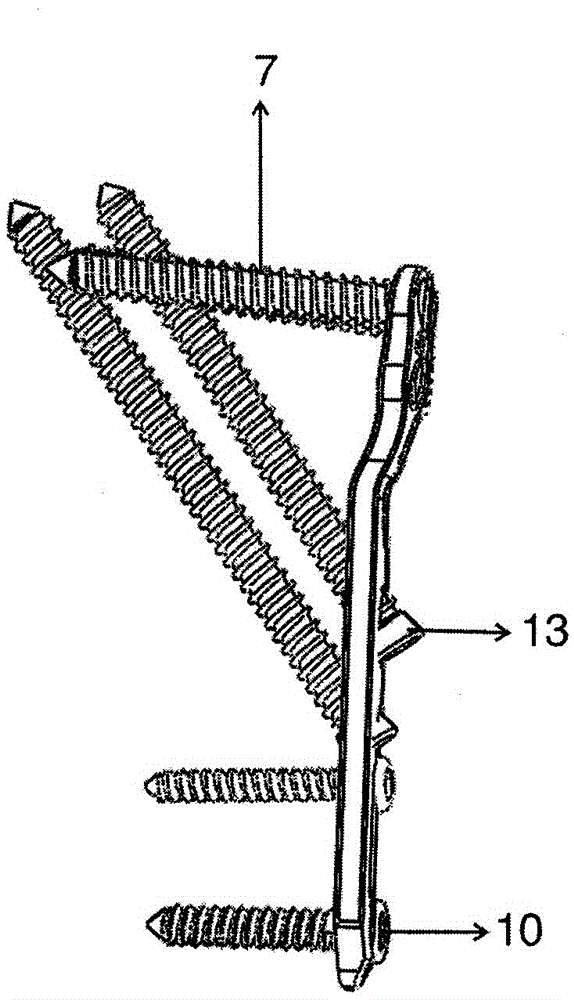
The invention relates to a fracture three-dimensionally-intersecting-connecting-locking internal fixing device. The fracture three-dimensionally-intersecting-connecting-locking internal fixing device is characterized by including the distal-femur fracture three-dimensionally-intersecting-connecting-locking internal fixing device, the proximal-humeral fracture three-dimensionally-intersecting-connecting-locking internal fixing device, the femoral-intertrochanteric fracture three-dimensionally-intersecting-connecting-locking internal fixing device, the femur-neck and proximal-femoral fracture connecting-locking internal fixing device, the backbone intersecting and locking internal fixing device and the backbone sliding-chute locking internal fixing device in a three-dimensionally intersecting, connecting and locking mode. According to the fracture three-dimensionally-intersecting-connecting-locking internal fixing device, the space structure which has the three-dimensional rotation resisting effect and the introversion resisting effect and is optimal and most stable for distal femur fractures is formed; the internal fixing device is tightly attached to the femur inner-side fracture line through high-strength slant cotter pins, the continuity of cortexes of bone is rebuilt to achieve strong spanning supporting, introversion shifting of fractures is effectively prevented, and static force stabilization in structural mechanics is achieved; as locking pins span the two ends of the fracture line to resist bending stress firstly, part of the stress is borne by screws, and the world problem that due to stress concentration of AO locking plates for backbone fractures, proximal femoral fractures, distal femur fractures and proximal humeral fractures, plate breaking often occurs is solved in structure and biomechanics.
Owner:刘明忱
Juxta-articular stabilisation system
InactiveUS20120290016A1For accurate placementPrecise positioningInternal osteosythesisProsthesisJuxtaEngineering
The juxta-articular stabilisation system constitutes of a plate with integral pin and tail part, a plate specific jig, a plate and jig specific drill sleeve, a plate positioner, a slotted head screw, a pin bender, screws and pins.This system can be used for fixation of most types of fractures involving the juxta-articular radius. The plate has a most juxta-articular row of screw holes in individually bendable and detachable extensions especially designed for very distal fractures or the volar lip fractures. The plate and jig assembly have plate positioning apertures in its juxta-articular part to allow adjustment in position of plate in longitudinal, transverse and oblique directions after temporary fixation to the juxta-articular fragment with a pin prior to fixation to diaphyseal fragment. This allows a very precise placement of the plate in the most desirable position. The drill guiding jig can be assembled to the plate prior to surgery thus reducing surgical step and time. The specific orientation of the screws holes in the diaphyseal part of the plate orientates the screws such that when tendons apply forces across the fracture, the plate is wedged between screw and the bone rather than pushed away from the bone. Therefore, more aggressive physical therapy can be commenced earlier and plates with fewer screws in the proximal part can be used without compromising the strength of the fixation. The plate also has bendable and dividable pin part and tail parts on either ends that allows the plate to be used with a chuck or power tool as a pin or drill bit and also have longer purchase into the bone with minimal soft tissue exposure.
Owner:KUMAR DEEPAK
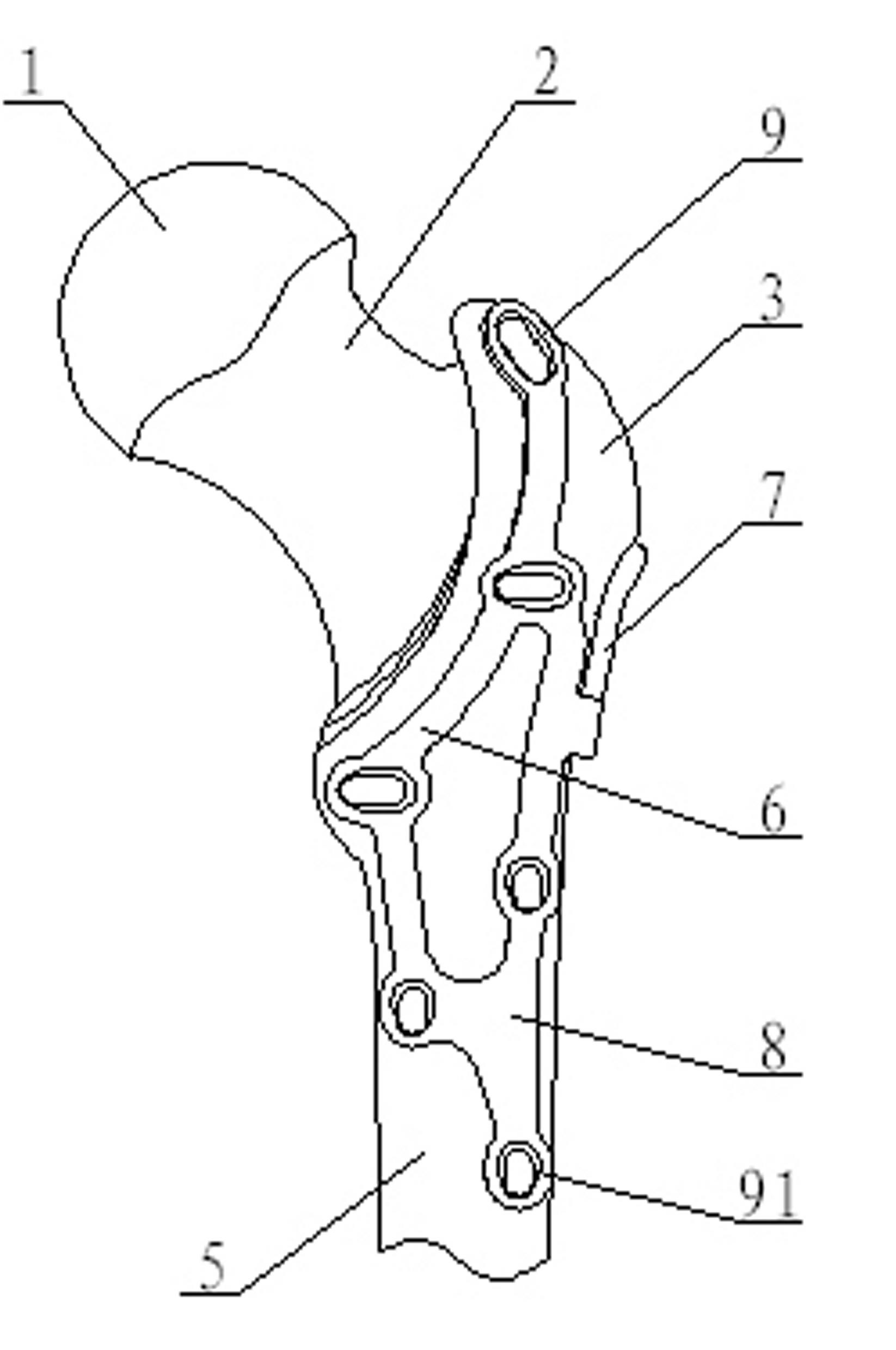
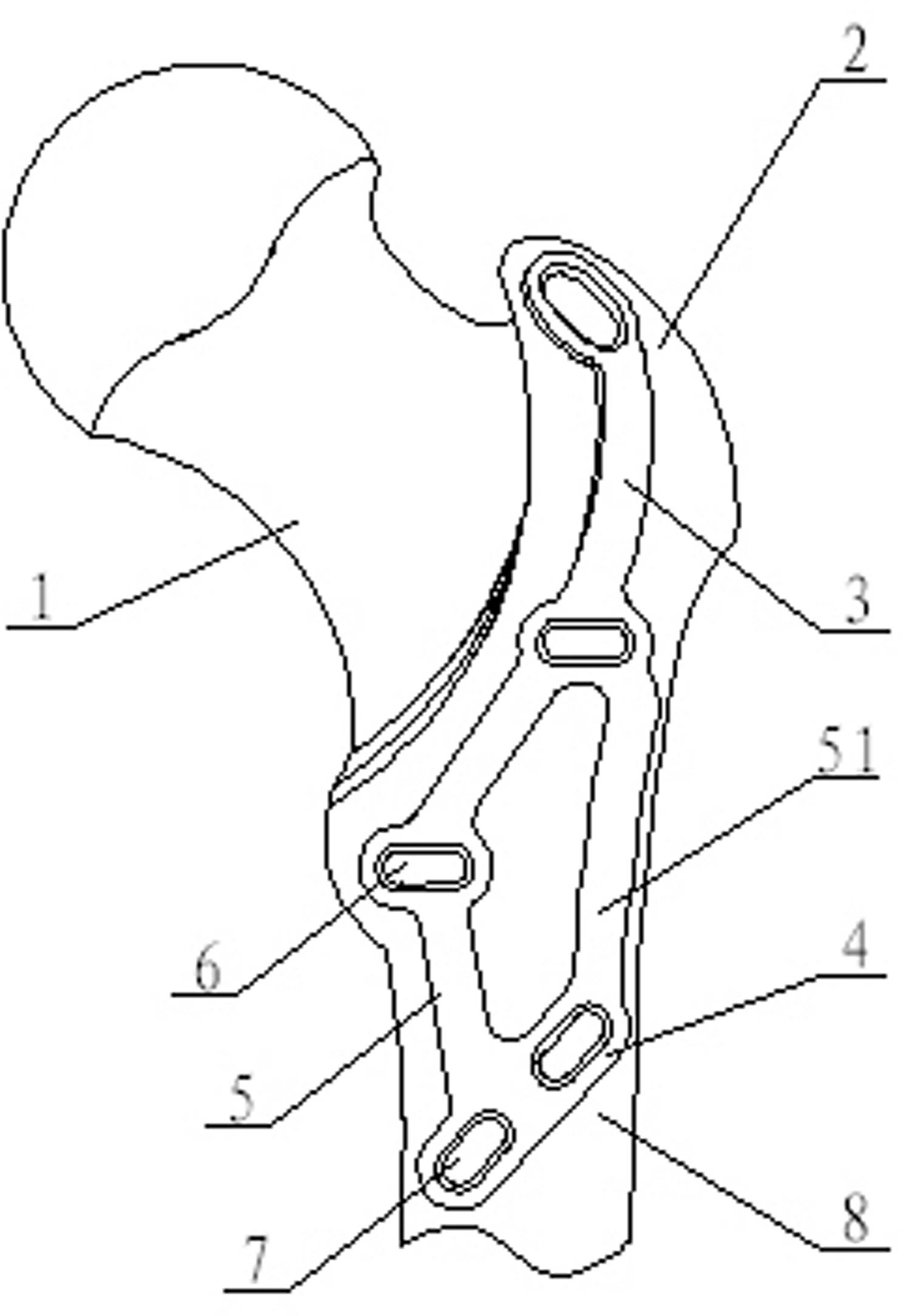
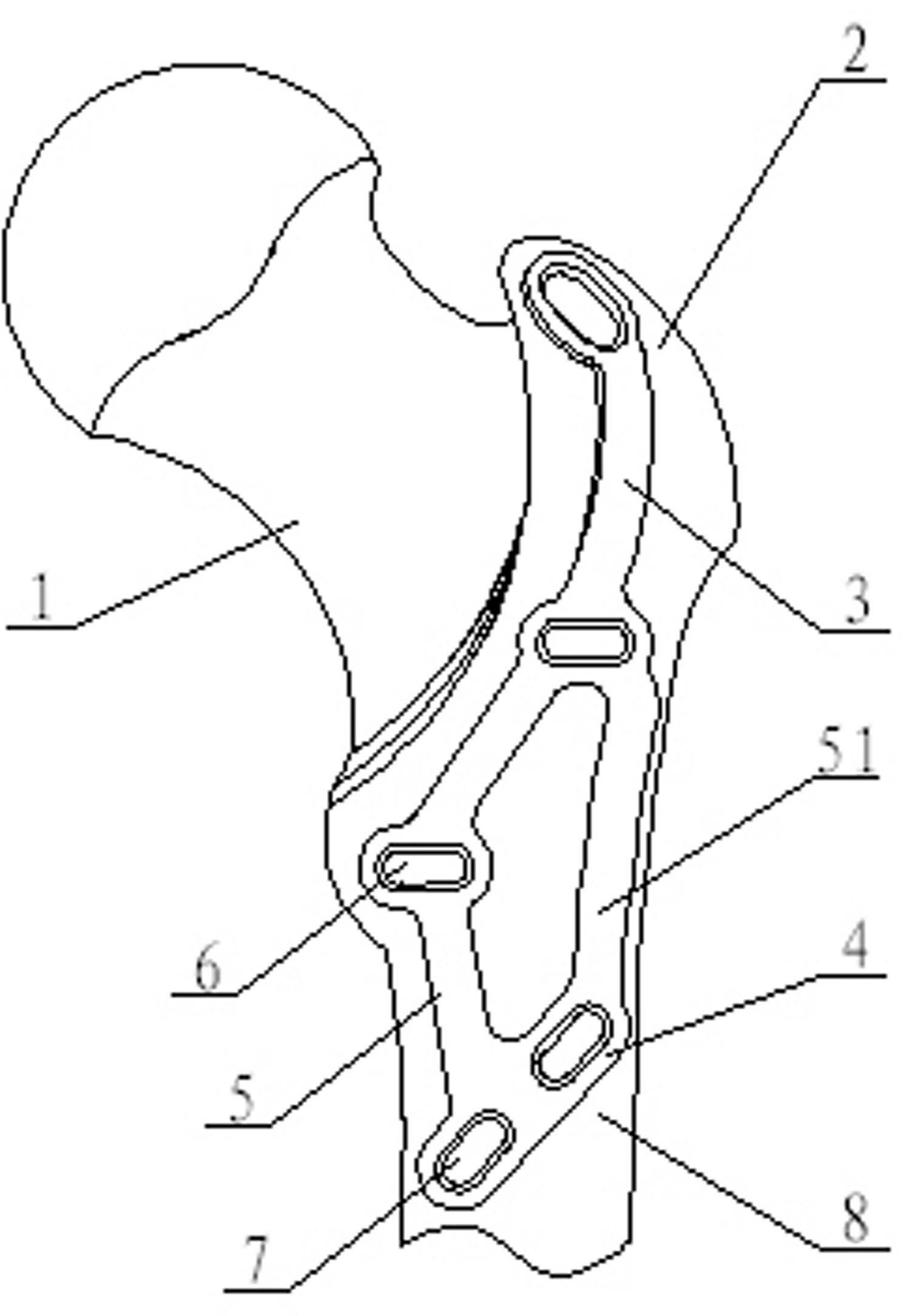
Bone plate implanted from front inner side of distal femur
ActiveCN105520777AGuaranteed to embedImprove gripInternal osteosythesisBone platesBody of femurDiaphyseal fracture
The invention provides a bone plate implanted from the front inner side of the distal femur, belonging to the technical field of medical apparatus and instruments for the department of orthopaedics, and used for treating the condylar fracture and bone shaft fracture of the distal femur. The technical scheme is as follows: the bone plate is composed of a bone plate condylar part, a transitional face and a bone plate shaft part which are connected together, wherein the bone plate condylar part is opposite to the front inner side surface of the condyle of the distal femur, the lower surface of the bone plate condylar part is adaptive to the front inner side surface of the condyle of the distal femur in shape, the bone plate shaft part is opposite to the inner side surface of the distal femur, the lower surface of the bone plate shaft part is adaptive to the inner side surface of the distal femur in shape, and a plurality of fixing holes are uniformly distributed on the bone plate condylar part and the bone plate shaft part. The bone plate provided by the invention belongs to an innovation for the bone plate for the distal femur, therefore, the problem that when the existing bone plate is implanted from the outer side of the distal femur, the fixation for the condyle fracture on the inner side of part of the distal femur is not firm is solved, and the fracture blocks on the inner side of the distal femur can be effectively and firmly fixed, so that the heal of the fracture blocks on the inner side is promoted, and therefore, the bone plate has extremely good promotion and utilization values in the industry.
Owner:侯志勇
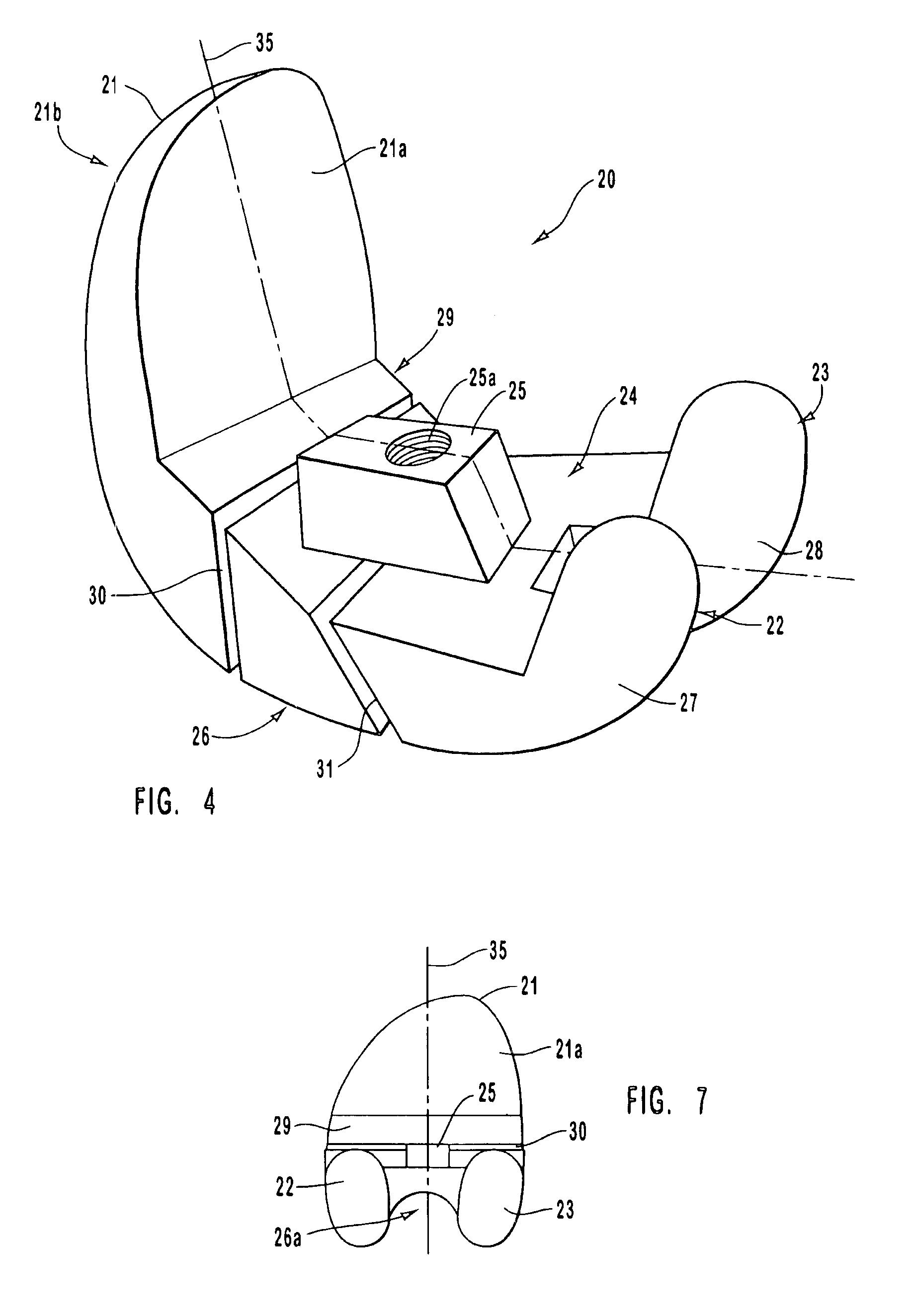
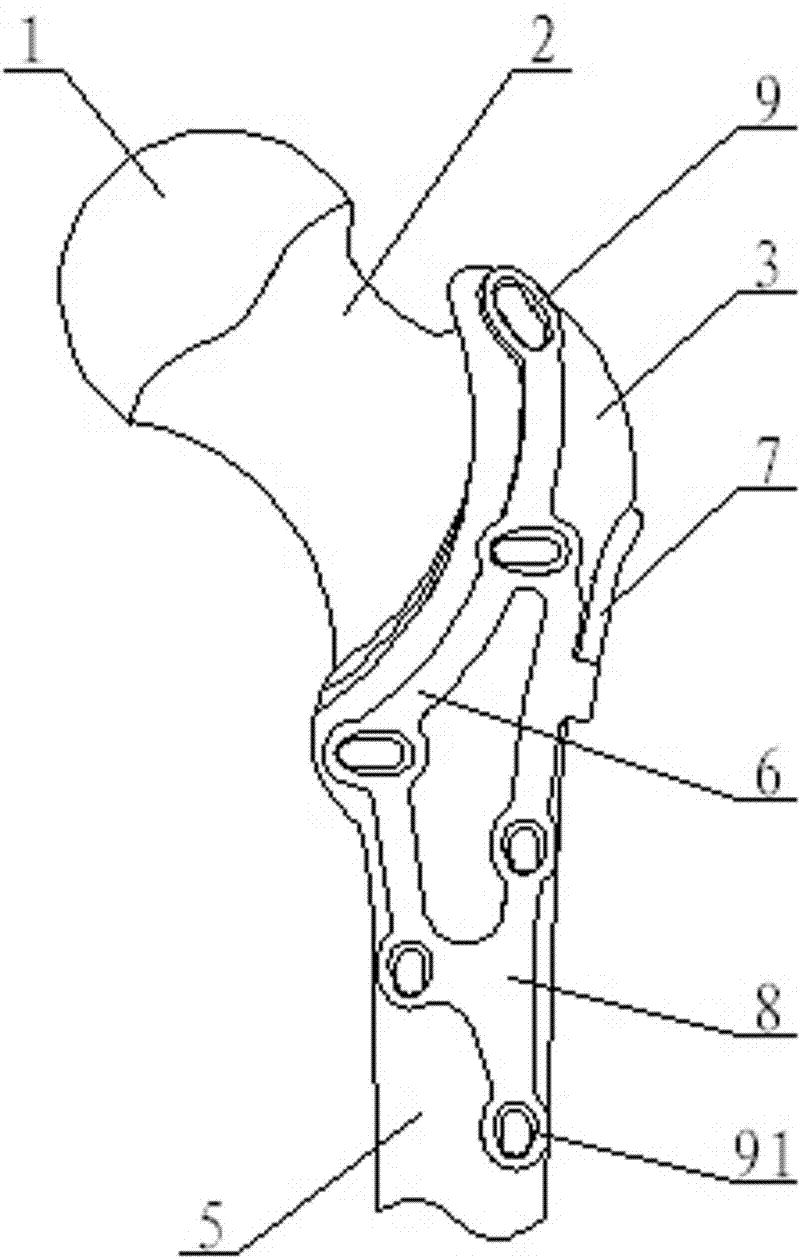
Thighbone shaft
InactiveUS20060161262A1Small wound areaReduce planting sizeInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsThighEngineering
Owner:LUNG CHEN YU +1
Proximal thighbone internal fixation system with minimal invasion
InactiveCN101716093AReasonable designCompact structureInternal osteosythesisBone CortexCortical bone
The invention discloses a proximal femur internal fixation system with minimal invasion, relating to an internal fixation system used for proximal femur comminuted fracture, femoral neck fracture, subtrochanteric fracture and femur backbone fracture. The internal fixation system comprises an internal fixation steel plate, an internal fixation bolt and a locking device, wherein the internal fixation steel plate adopts a dynamic hip screw steel plate or a proximal femur internal steel plate, the dynamic hip screw steel plate is composed of a head part and the rod part, and the proximal femur internal steel plate is composed of a head part and a rod part; the locking device comprises a rotary pin, a sliding pin, a spring and a locking disc; the internal fixation bolt comprises a combined tension force bolt or a combined hollow bolt, a hollow bolt, a spongy bone bolt, a cortical bone bolt and a locking bolt, wherein the combined tension force bolt is composed of a connecting sleeve, a connecting bush and a tension force bolt; the combined hollow bolt is composed of a hollow bolt and a bolt sleeve. The internal fixation steel plate and the internal fixation bolt are connected and fixed by the locking device, which can simplify operation steps, shorten operation time and leave small cut.
Owner:KANGHUI MEDICAL INNOVATION
Provisional bone plate
A provisional bone plate formed of an implantable plastic and having a length corresponding to the longest bone plate in a particular family of bone plates. The provisional bone plate includes a head contoured to match the head of a particular bone as well as a shaft for placement adjacent the bone shaft. The provisional bone plate includes a plurality of circumferential notches surrounding the elongate body or shaft of the bone plate. The circumferential notches are substantially transverse to a longitudinal axis of the bone plate and define frangible portions of the bone plate which can be removed from the distal end thereof to alter the length of the provisional periarticular bone plate to correspond to the length of the various bone plates in a family of bone plates. The provisional bone plate is constructed of a biologically suitable plastic, is radiographic, and melts at a temperature less than 200° Fahrenheit.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Minimal invasive combined pressurizing and locking bone fracture plate for trochanter comminuted fracture and femoral neck fracture
ActiveCN102247205AEasy to operateSmall incisionInternal osteosythesisBone platesTreatment effectFemoral diaphysis
The invention relates to a minimal invasive combined pressurizing and locking bone fracture plate for trochanter comminuted fracture and femoral neck fracture. The bone fracture plate comprises a trochanter rear-side fixing plate and a femoral proximal-end fixing plate, which are connected into an integrated structure for respectively covering the trochanter rear side and femoral proximal end in an annular shape, wherein first locking holes are respectively formed on two ends of the trochanter rear-side fixing plate, and first locking nails which penetrate the rear side of the trochanter crown head end and the rear side of the trochanter crown bottom end are locked in the two first locking holes respectively; three second locking holes, arranged in a regular triangle way, are formed on the femoral proximal-end fixing plate, a second locking nail for locking femoral trochanter, femoral neck and bulb penetrates at least one second locking hole; and the trochanter rear-side fixing plate and the femoral proximal-end fixing plate are connected into an integrated structure for covering the trochanter rear side and femoral proximal end in an annular way. By utilizing a ball lag screw or a locking lag screw, tensioning of the trochanter, the femoral neck and the bulb and positioning lock on the femoral diaphysis are realized, so the minimal invasive combined pressurizing and locking bone fracture plate for the pulverous trochanter fracture and femoral neck fracture has the advantages of simpleness in operation, small cut, good fixing effect, firm tensioning, no potential safety hazards in long term use, no deformation and good treatment effect and is beneficial to accurate diaplasis.
Owner:泰州市中兴医械科技有限公司
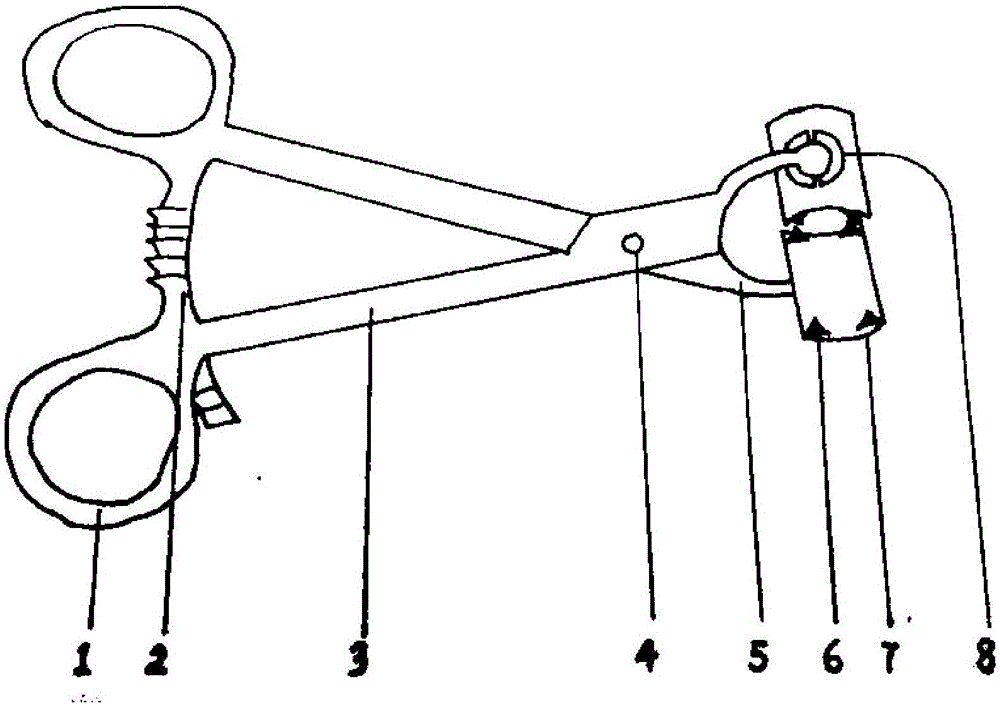
In-situ rotary bone fracture restoration fixer
InactiveCN106175906ADoes not affect screw-inAvoid separationSurgical forcepsOsteosynthesis devicesEngineeringIliac screw
The invention relates to an in situ rotary fracture reduction fixer, comprising two pliers handles hinged to each other and a pair of fixing plates, the pair of fixing plates are used to clamp and fix the fracture site; the rear parts of the two pliers handles are Elastic locks are provided, and the opposite elastic locks are used to lock the distance between a pair of fixed plates. The rear ends of the two pliers handles are provided with ring handles; the front ends of the pliers handles are designed with arc-shaped pliers heads. The end of the pliers head is connected to the fixed plate via a ball-and-socket shaft. When the elastic lock is locked, the two pliers handles can rotate at a certain angle relative to the fixed bone; the inner part of each fixed plate There are no less than two positioning protrusions on the side; the two pliers handles and a pair of fixing plates can be disassembled from the ball-and-socket shaft. The fracture reduction fixer of the present invention can be rotated in situ, leaving room for screw screwing in, and can choose to install fixing plates of different lengths and radians according to the size of the backbone.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Femoral shaft fracture bone fragment fixing steel wire guiding device
InactiveCN104586495ARelieve painEasy to operateInternal osteosythesisFemoral Shaft FractureBody of femur
The invention discloses a femoral shaft fracture bone fragment fixing steel wire guiding device and relates to fixation on a free bone fragment in the femoral shaft fracture and solves the problem of using a steel wire or a suture for carrying out closed reduction and binding fixation on the femur and the free bone fragment. After femoral shaft splintered fracture is subjected to closed reduction interlocking intermeddler nail fixation, under the fluoroscopy of a C arm, an outer tube passes through the muscle and hooks the free bone fragment to enable the free bone fragment to be close to a femoral shaft, then a rotating wheel is rotated to enable an inner tube in an inner cavity of the outer tube to rotate around the circle center of the inner tube, the inner tube is matched with the outer tube to take the effect after extending out of the outer tube so as to loop the free bone fragment and the femoral shaft, and at the moment, a nucleus pulposus tong can be used for extracting a steel wire out of the inner tube and the outer tube; if the bone fragment is fixed by the suture, the suture can be fixed at the tail end of the steel wire to be extracted along with the steel wire. The steel wire or the suture is knotted to implement closed reduction and binding fixation on the free bone fragment and the femur. The guiding device is convenient to operate; compared with open reduction fixation, the closed reduction adopted by the femoral shaft fracture bone fragment fixing steel wire guiding device can avoid destroying blood supply to the free bone fragment, obviously shortens an incision, reduces operation time and relieves pain of a patient.
Owner:SHANDONG PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL
Proximal tibia outer side locking plate
The invention provides a proximal tibia outer side locking plate. The proximal tibia outer side locking plate comprises a main body component and a connecting plate component, wherein the main body component is used for fixing a proximal tibia outer side; the main body component comprises a head part, a rod part and a connecting part for connecting the head part with the rod part; the head part wraps and fixes an outer side column of a proximal tibia platform; the rod part is attached to the outer side surface of a tibial shaft and is fixed; the connecting part is adhered to a tibia surface and is bent; the connecting plate component is connected with the head part and is used for fixing a connecting plate component of a rear side column of the proximal tibia platform. By the main body component, the outer side of a tibia is fixed; by the design of the connecting plate component, fixation to the rear side column of the proximal tibia platform is enhanced, so that the proximal tibia outer side locking plate can be used in surgeries such as proximal tibia fracture, metaphysis fracture, intra-articular fracture and periprosthetic fracture. In addition, the head part of the main body component warps the outer side column of the proximal tibia platform. Compared with an existing curved-surface bone fracture plate, the proximal tibia outer side locking plate is fixed firmly and reliably.
Owner:SHANGHAI KINETIC MEDICAL
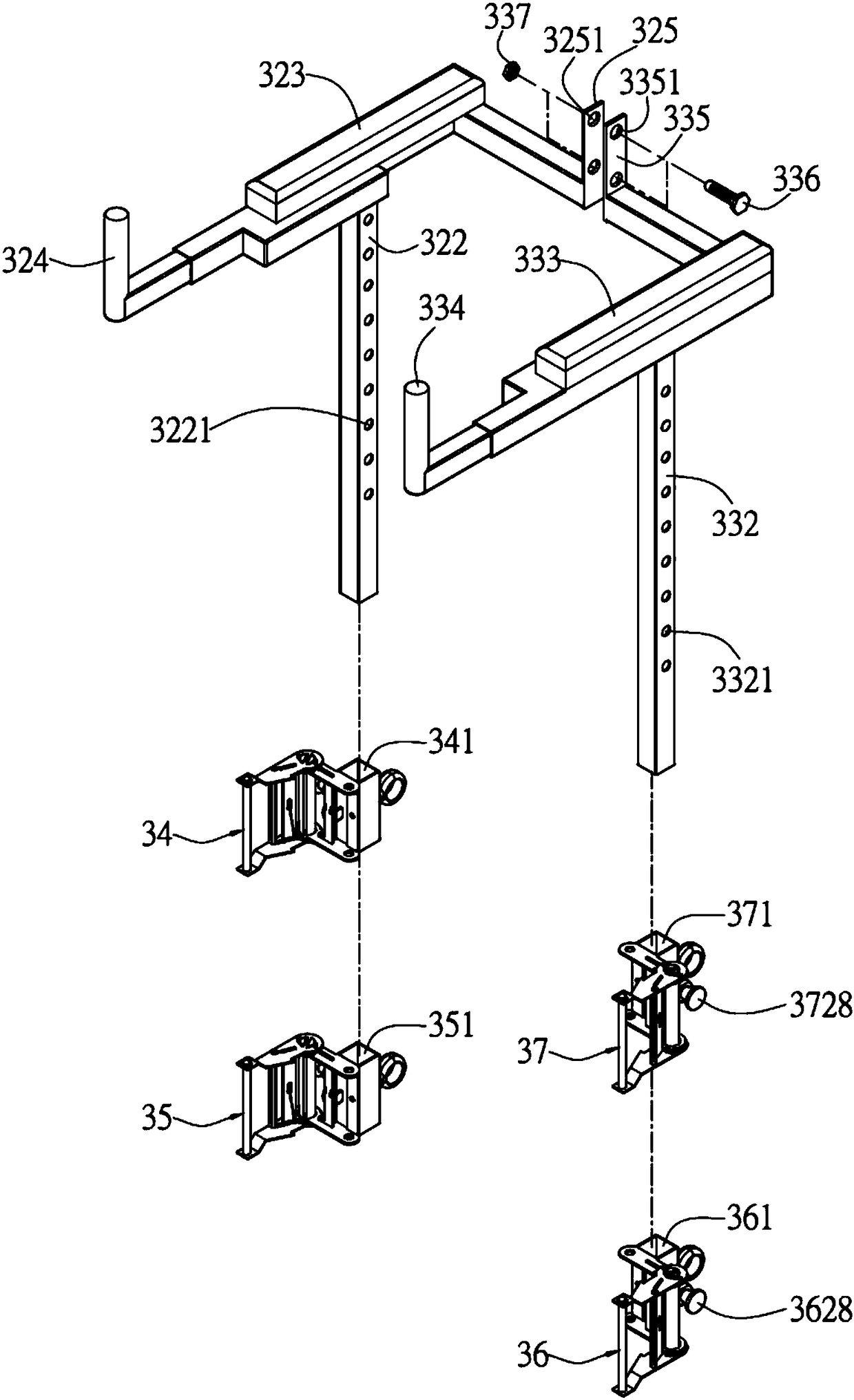
Vertebral column horizontal melodic movement apparatus
ActiveCN108524070ACorrecting symptoms of rotational homingSymptom healingChiropractic devicesVibration massageHuman bodyWireless control
The invention discloses a vertebral column horizontal melodic movement apparatus which at least includes: a T-shaped hanging bracket, a neck traction band, a n-shaped pedestal, a horizontal revolvingdriving platform. One end of the T-shaped hanging bracket is connected to the neck traction band through a drawing tape, while the other end is combined with the n-shaped pedestal by means of an adjusting support tube. The horizontal revolving driving platform is arranged in a space in the n-shaped pedestal. By means of a melodic movement mode, the apparatus is applied to physical threapy on cervical vertebra and vertebral column bone of human body in order to gradually alleviate degree of ache and paralysis, sind bending of thoracic vertebra, rotation and bending of lumbar vertebra, and inclination of pelvis. The recuperation device can achieve gradual regulation and recovery to a normal angle or position. By means of computer program or manual control via wired or wireless control, the apparatus has assistance function of executing regulation on different parts of body of a user can be simultaneously or respectively according to optimum input data. The device can matched with demandsof different users in order to regulate the symptoms of back discomfort such as side bending, obliquity, adhesion, cartilage protruding, etc.
Owner:高睿廷
Minimally invasive tuberositas comminuted fracture back side pressurizing type fixation bone fracture plate
The invention relates to a minimally invasive tuberositas comminuted fracture back side pressurizing type fixation bone fracture plate, which is formed by connecting a tuberositas back side fixing plate and a backbone fixing plate through a connecting plate, wherein the tuberositas back side fixing plate is in an arc-shaped curved surface structure anastomotic with the tuberositas back side surface, both ends of the tuberositas back side fixing plate are respectively provided with locking holes, locking nails penetrating through the tuberositas crown head end back side and the crown bottom end back side are respectively locked in the two locking holes, the backbone fixing plate is in a connecting plate structure anastomotic with the thighbone backbone back side surface, both ends of the backbone fixing plate are respectively provided with locking holes, and locking nails penetrating through the thighbone backbone are respectively locked in the two locking holes. When spherical nails are locked in a waist-shaped spherical groove, the direction and the angle can be adjustable, the tension of the femoral neck and the tuberositas and the tension of the broke bone of the tuberositas are respectively realized, the tuberositas comminuted fracture part is completely fixed, the spherical nails are penetrated and connected onto the backbone fixing plate in a matched way for tightly locking the thighbone backbone, the integral fixation effect is good, the accurate resetting is favorably realized, and the treatment effect is good.
Owner:泰州市中兴医械科技有限公司
Artificial hip joint device without handle
InactiveCN1530080AHigh strengthEasy to fixInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsArtificial hip jointsRight femoral head
A non-handle artificial hip joint unit is composed of a reinforcing plate for supporting femur and with more through holes for inserting the fixing parts through them to fix the reinforcing plate to the surface of femur, a reinforcing bone nail passing through the holes on reinforcing plate and inserted in fermur, a central bone nail screwed with said reinforcing bone nail, and a femur neck protector fixed to another end of said central bone nail. Its advantage is high strength and stability.
Owner:钱本文
Humerus straight protection steel board
InactiveCN103919601AImprove integrityGood treatment effectInternal osteosythesisFastenersSheet steelTherapeutic effect
A humerus straight protection steel board comprises a straight section which is of a structure with the inner side face matched with the humerus backbone, and a plurality of locating holes are formed in the straight section. The humerus straight protection steel board is characterized by further comprising a plurality of protection wings which are symmetrically arranged on the two sides of the straight section and are in a contained shape towards the inner side face of the straight section; when the straight section is fixed to the humerus backbone, the inner side face of the straight section is attached to the front face of the humerus backbone, the two sides of the protection wings wrap the two sides of the humerus backbone in a containing mode, crush bones on the two sides of the humerus can be stably fixed in the mode that screws or fixing needles penetrate through threaded holes or needle penetrating holes, the completeness of the humerus is protected, and the fracture healing and treatment effect of the humerus is improved; countersunk head screws are flat on the surface of the steel board when used, no protrusion exists, implantation is convenient, pains caused by use of the screws are relieved, and postoperative healing is facilitated; the locking firmness is improved through a countersunk forcing screw.
Owner:泰州市中兴医械科技有限公司
Minimal invasive combined pressurizing and locking bone fracture plate for trochanter comminuted fracture and femoral neck fracture
ActiveCN102247205BEasy to operateSmall incisionInternal osteosythesisBone platesFemoral diaphysisTherapeutic effect
The invention relates to a minimal invasive combined pressurizing and locking bone fracture plate for trochanter comminuted fracture and femoral neck fracture. The bone fracture plate comprises a trochanter rear-side fixing plate and a femoral proximal-end fixing plate, which are connected into an integrated structure for respectively covering the trochanter rear side and femoral proximal end in an annular shape, wherein first locking holes are respectively formed on two ends of the trochanter rear-side fixing plate, and first locking nails which penetrate the rear side of the trochanter crown head end and the rear side of the trochanter crown bottom end are locked in the two first locking holes respectively; three second locking holes, arranged in a regular triangle way, are formed on the femoral proximal-end fixing plate, a second locking nail for locking femoral trochanter, femoral neck and bulb penetrates at least one second locking hole; and the trochanter rear-side fixing plate and the femoral proximal-end fixing plate are connected into an integrated structure for covering the trochanter rear side and femoral proximal end in an annular way. By utilizing a ball lag screw or a locking lag screw, tensioning of the trochanter, the femoral neck and the bulb and positioning lock on the femoral diaphysis are realized, so the minimal invasive combined pressurizing and locking bone fracture plate for the pulverous trochanter fracture and femoral neck fracture has the advantages of simpleness in operation, small cut, good fixing effect, firm tensioning, no potential safety hazards in long term use, no deformation and good treatment effect and is beneficial to accurate diaplasis.
Owner:泰州市中兴医械科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com