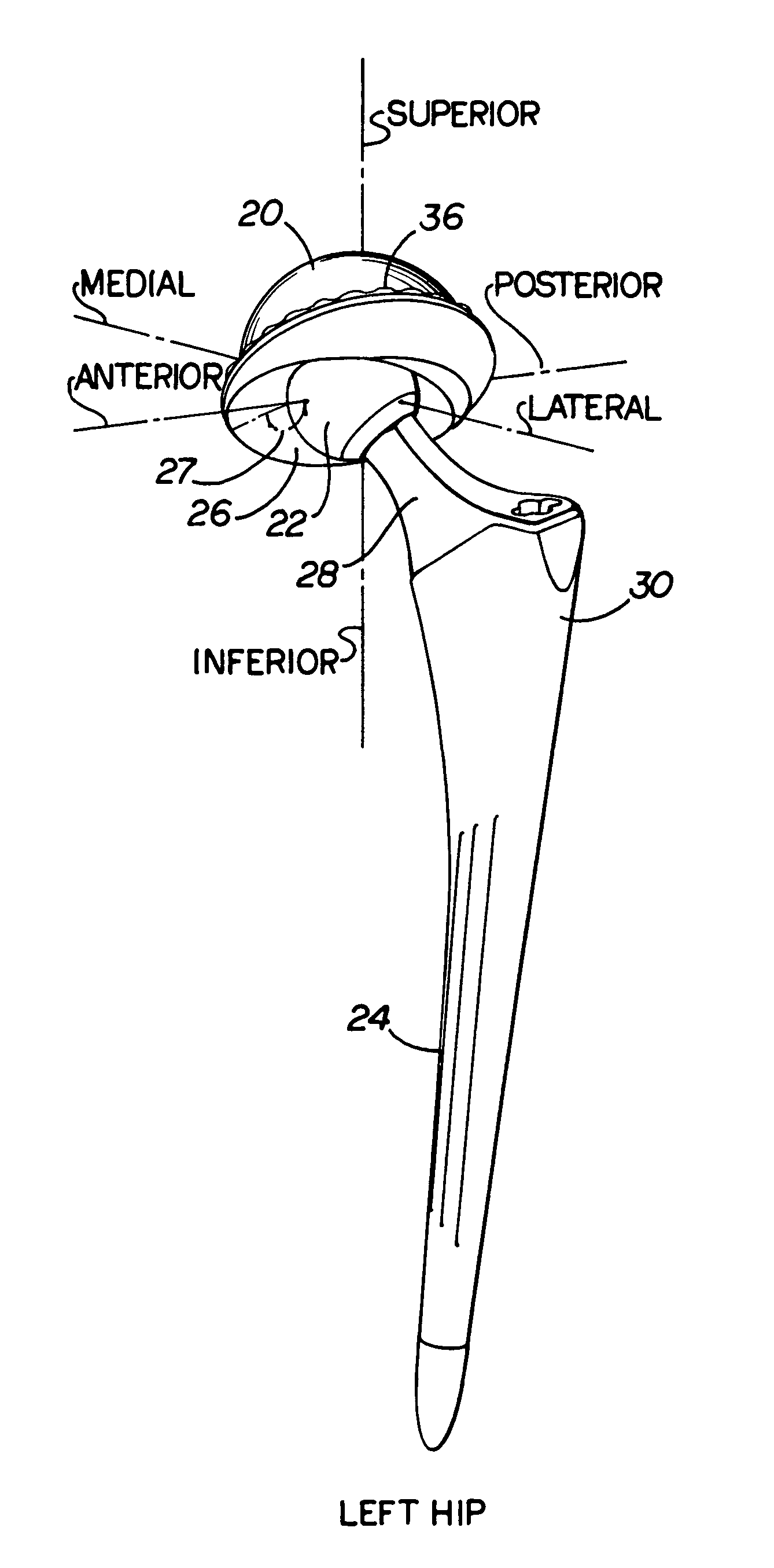
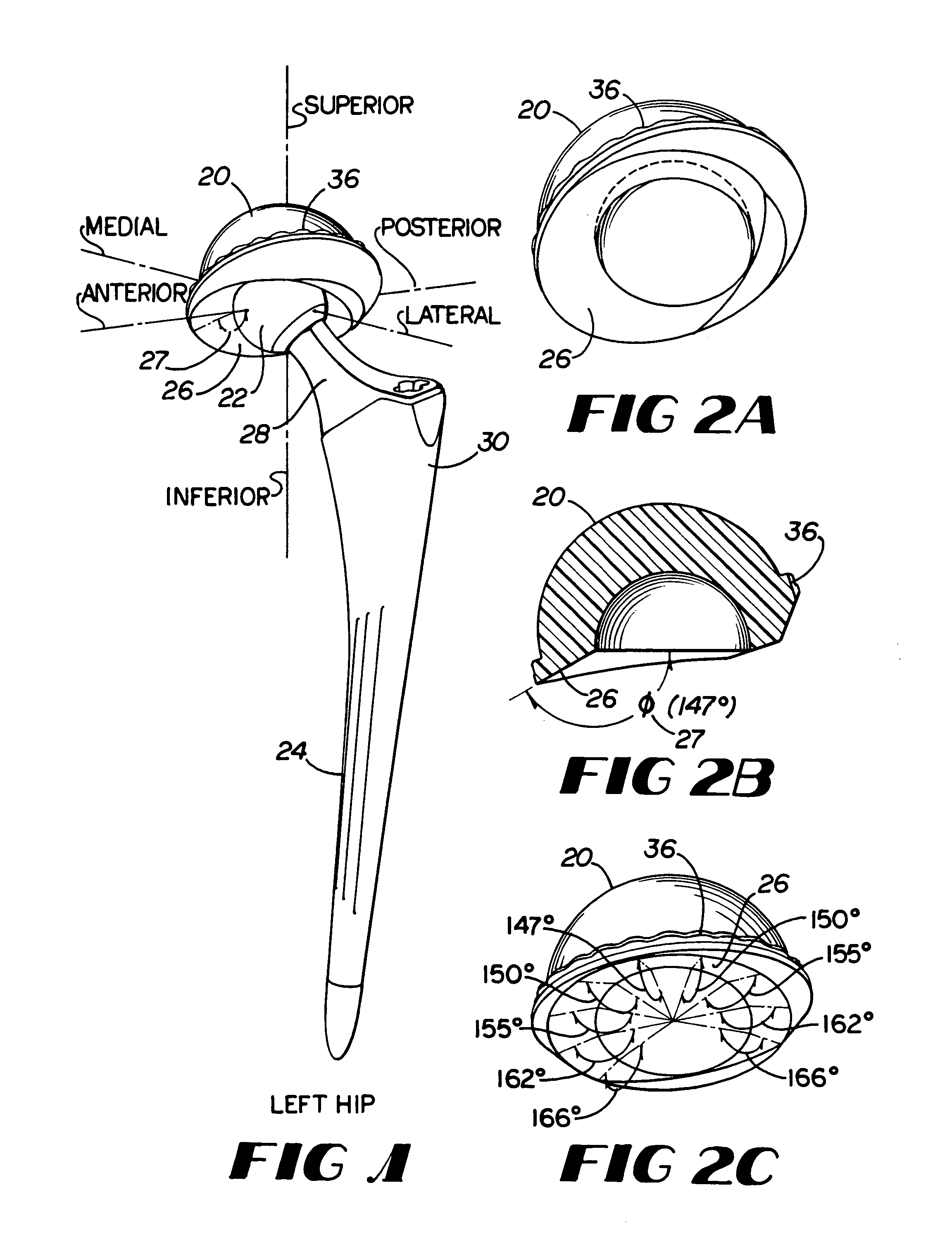
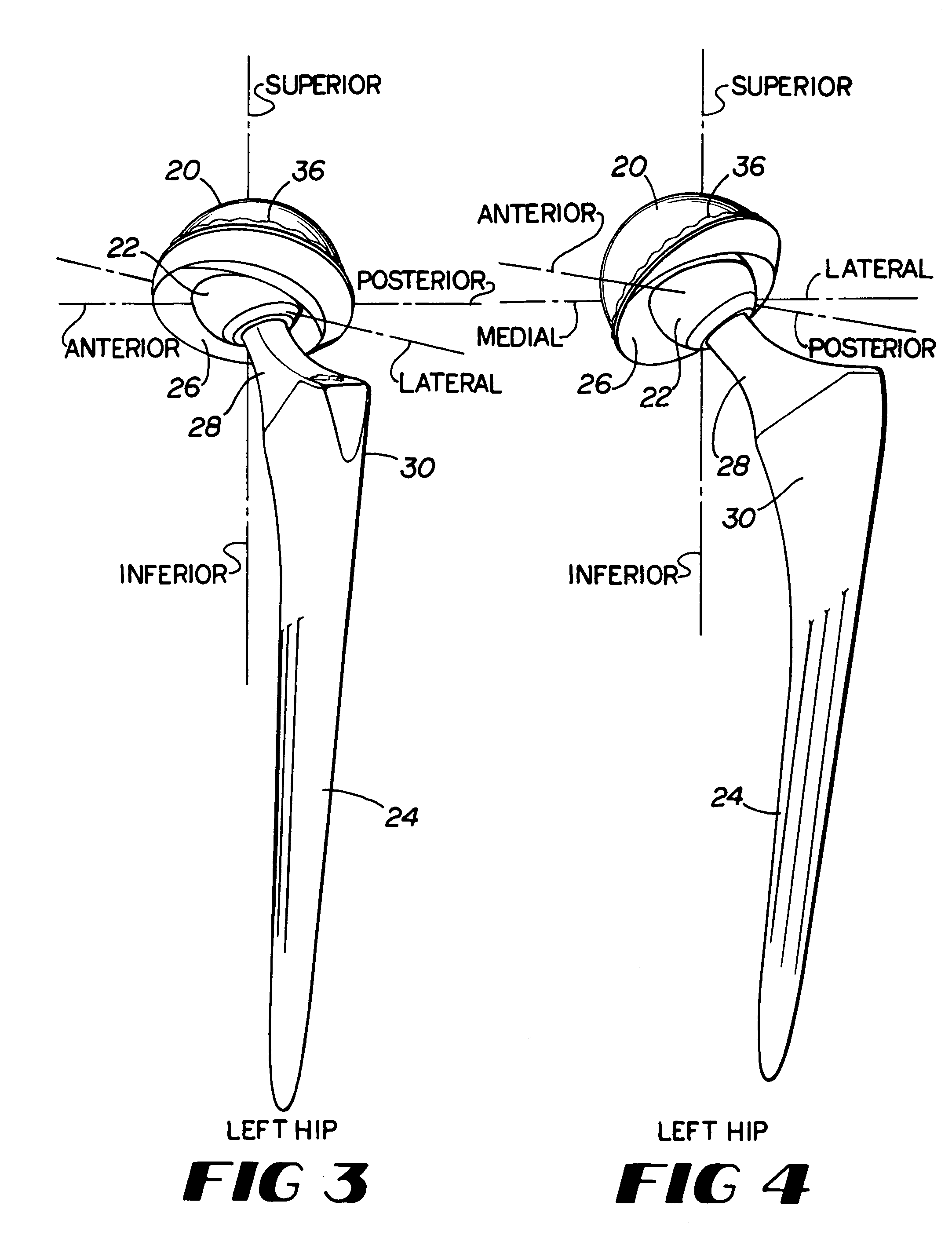
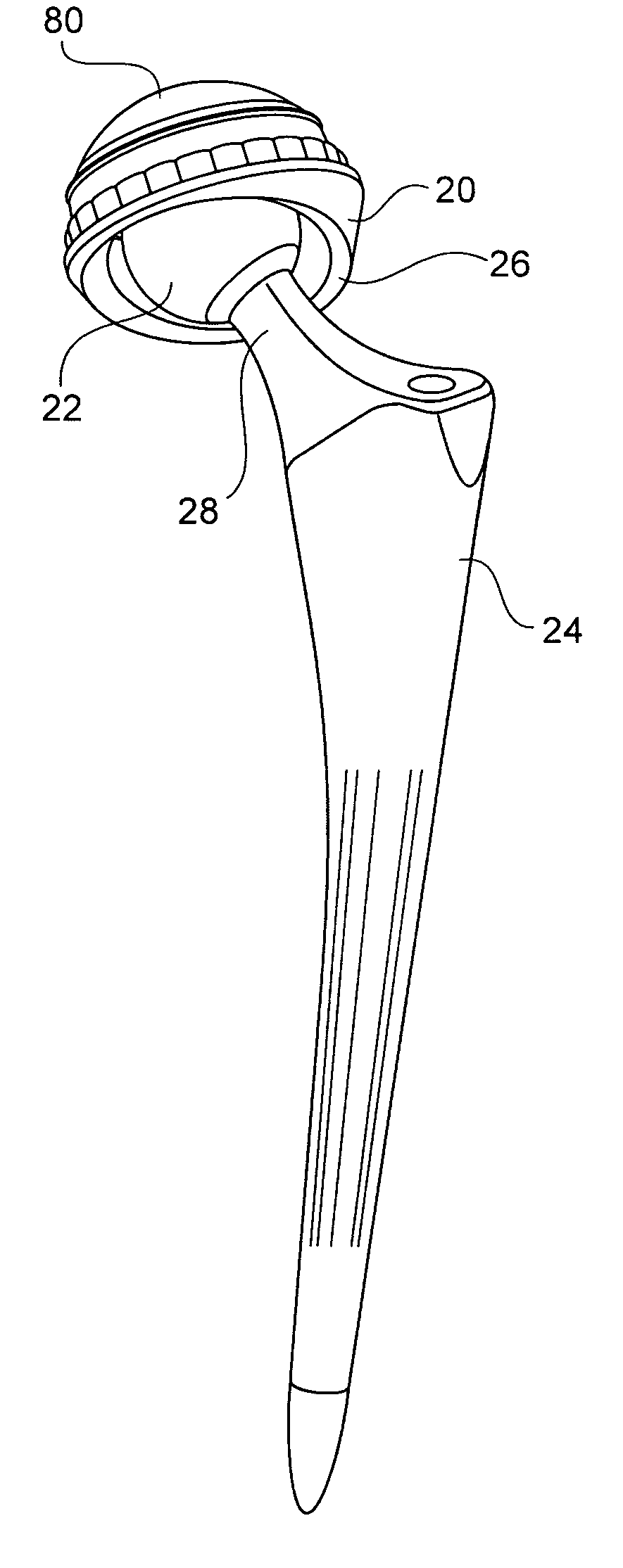
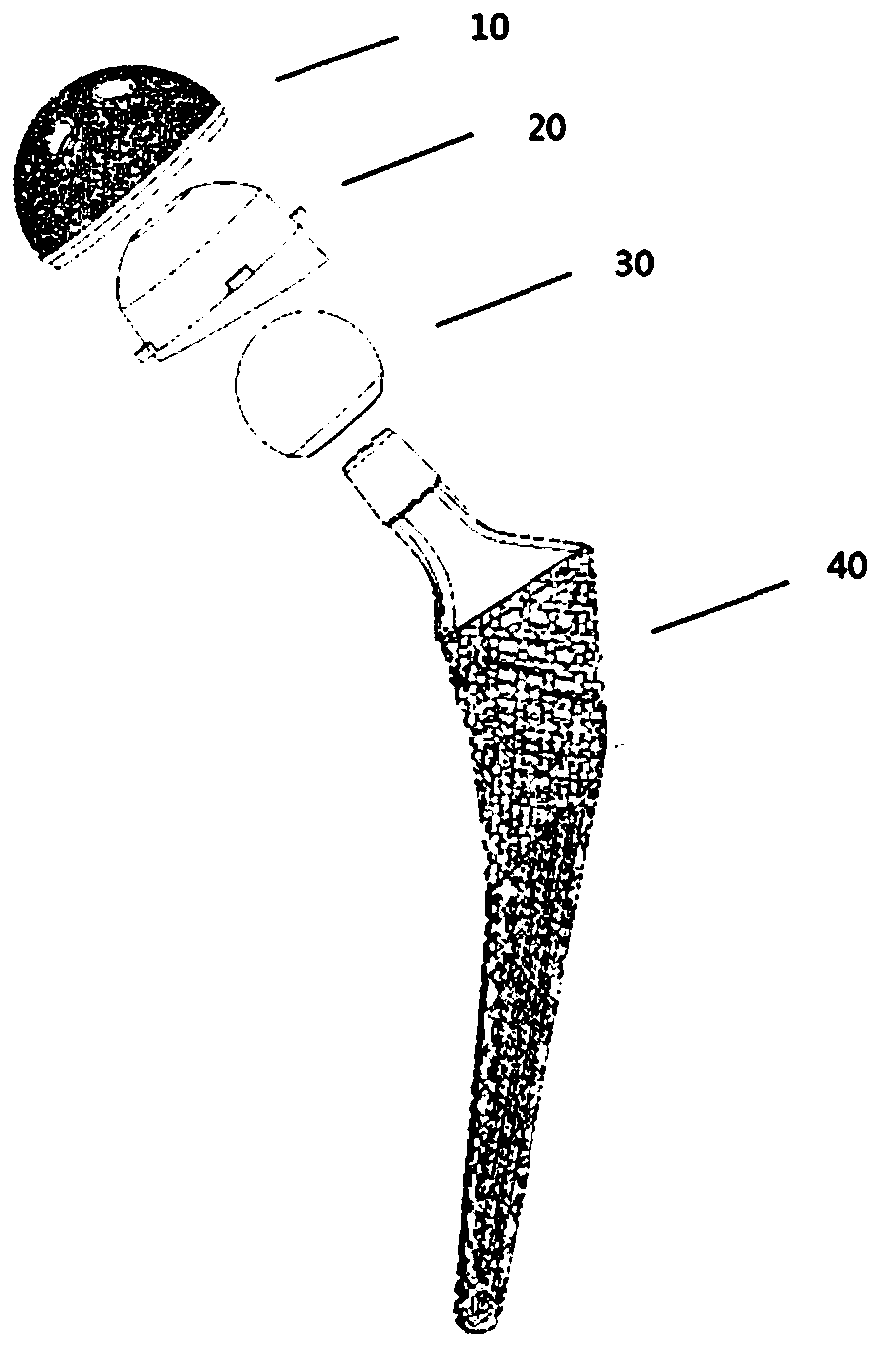
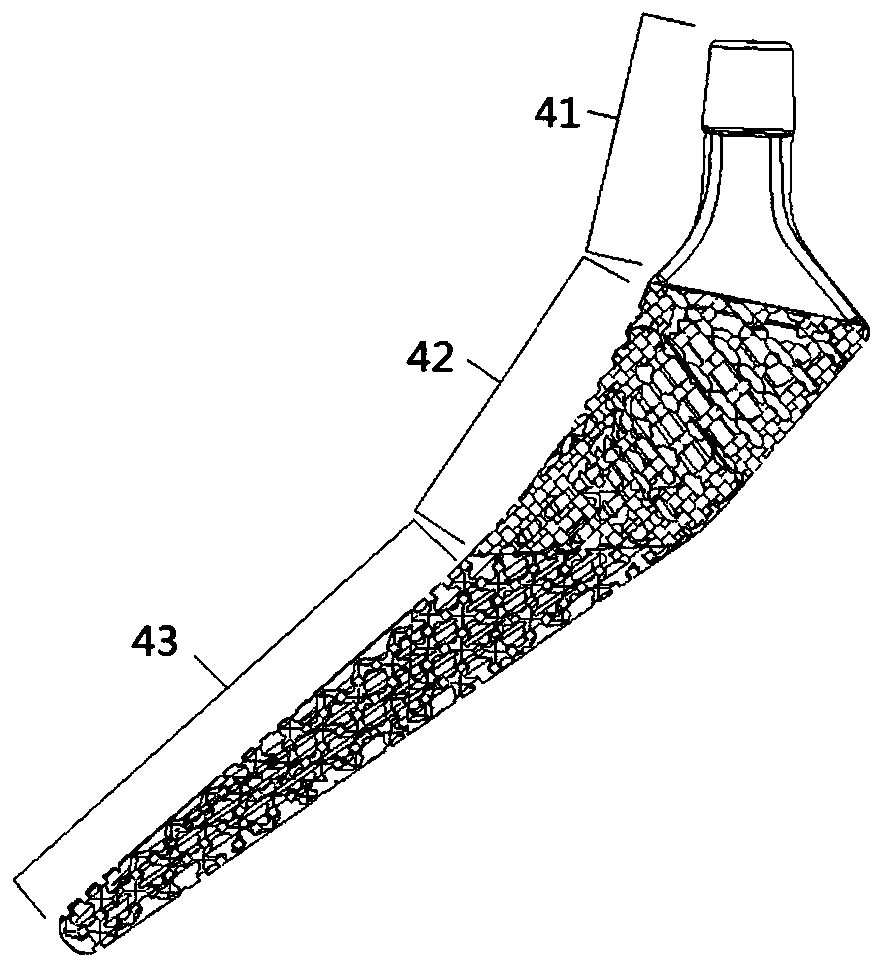
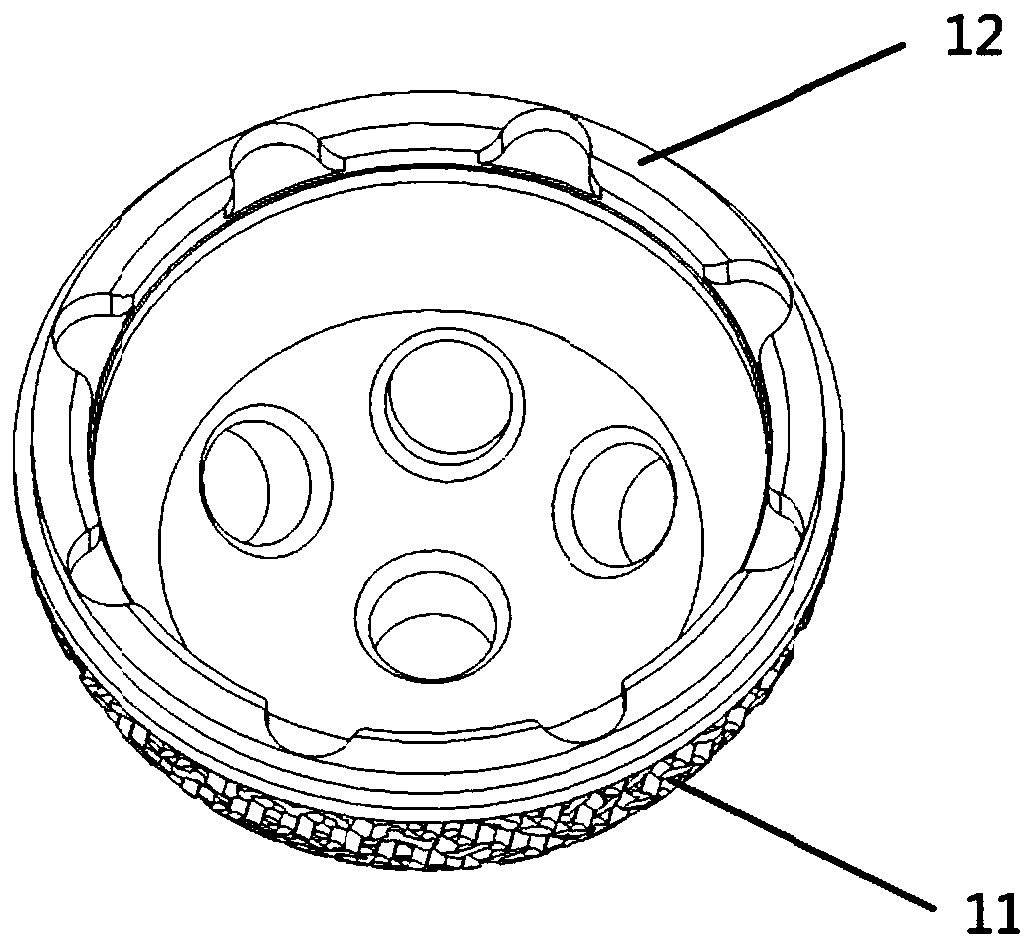
Patents
Literature
172 results about "Hip joint prosthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
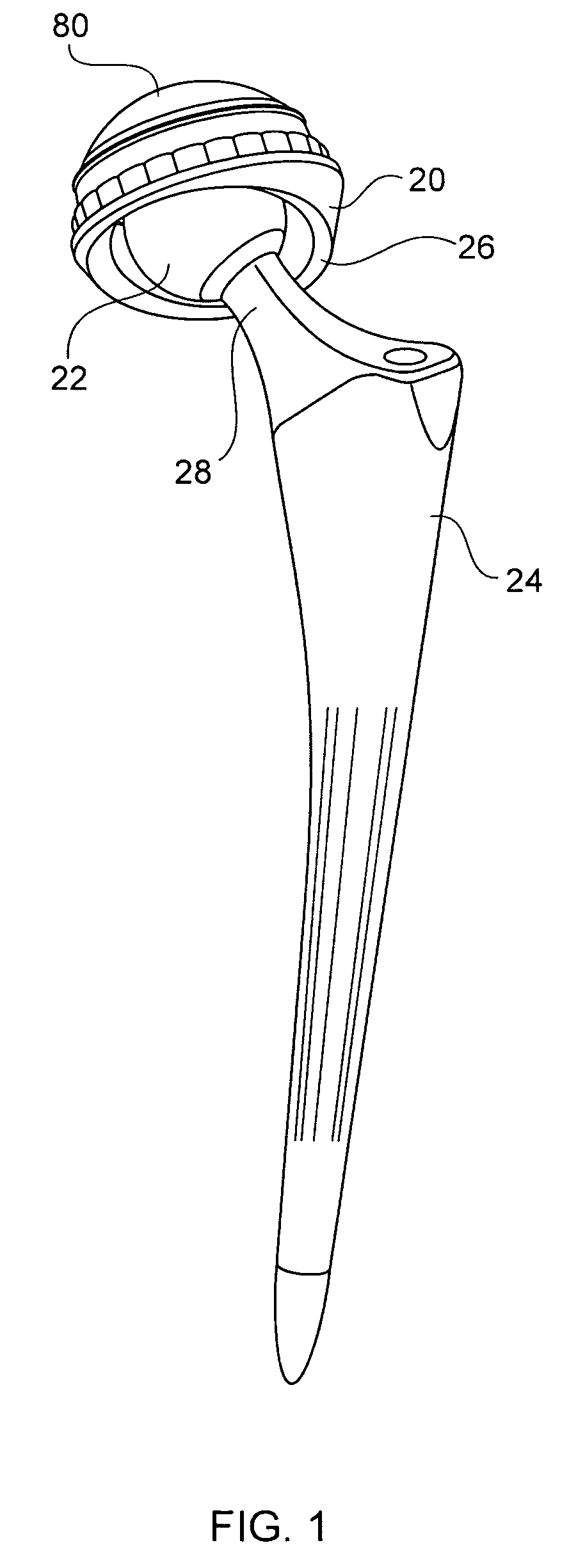
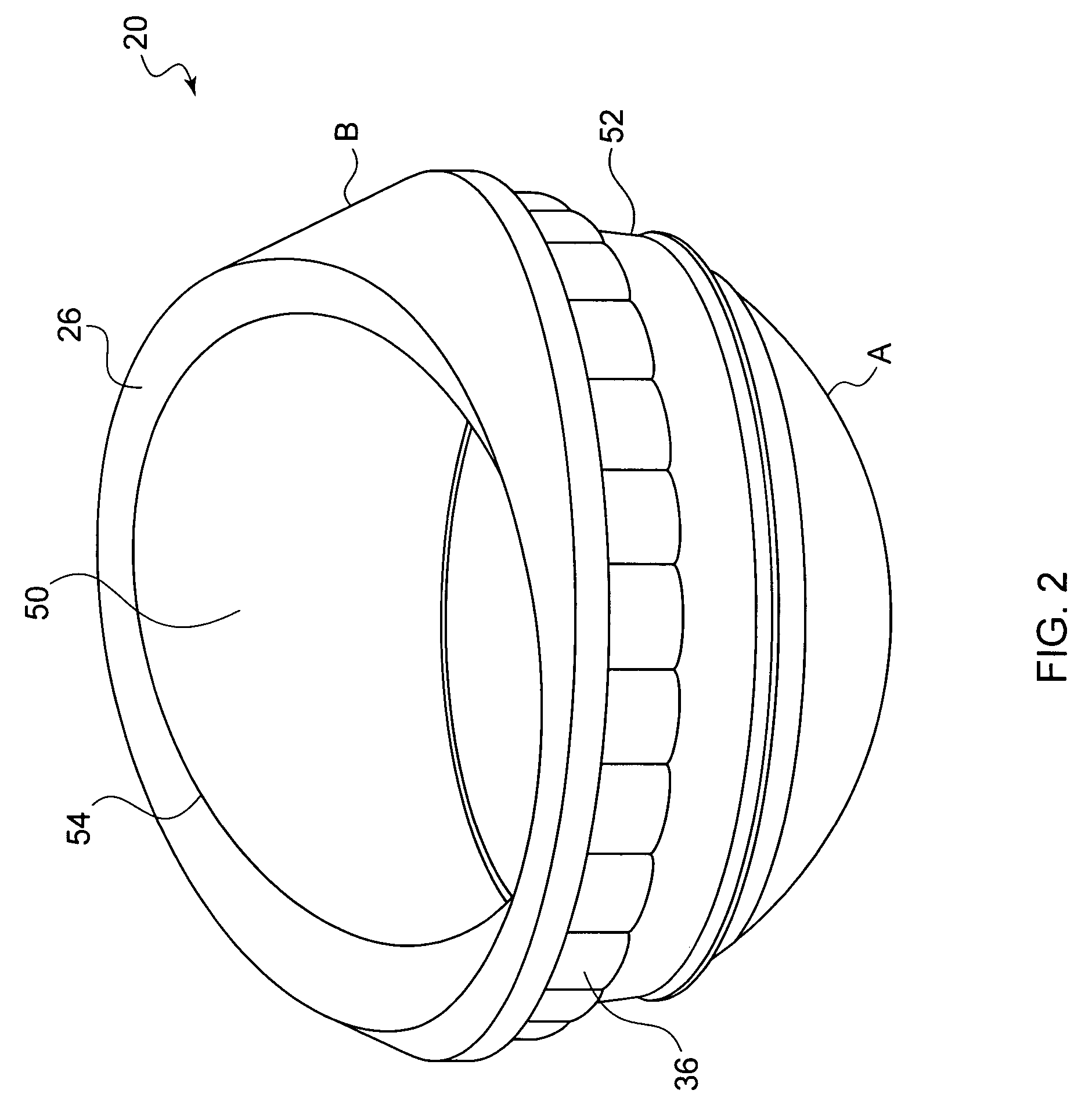
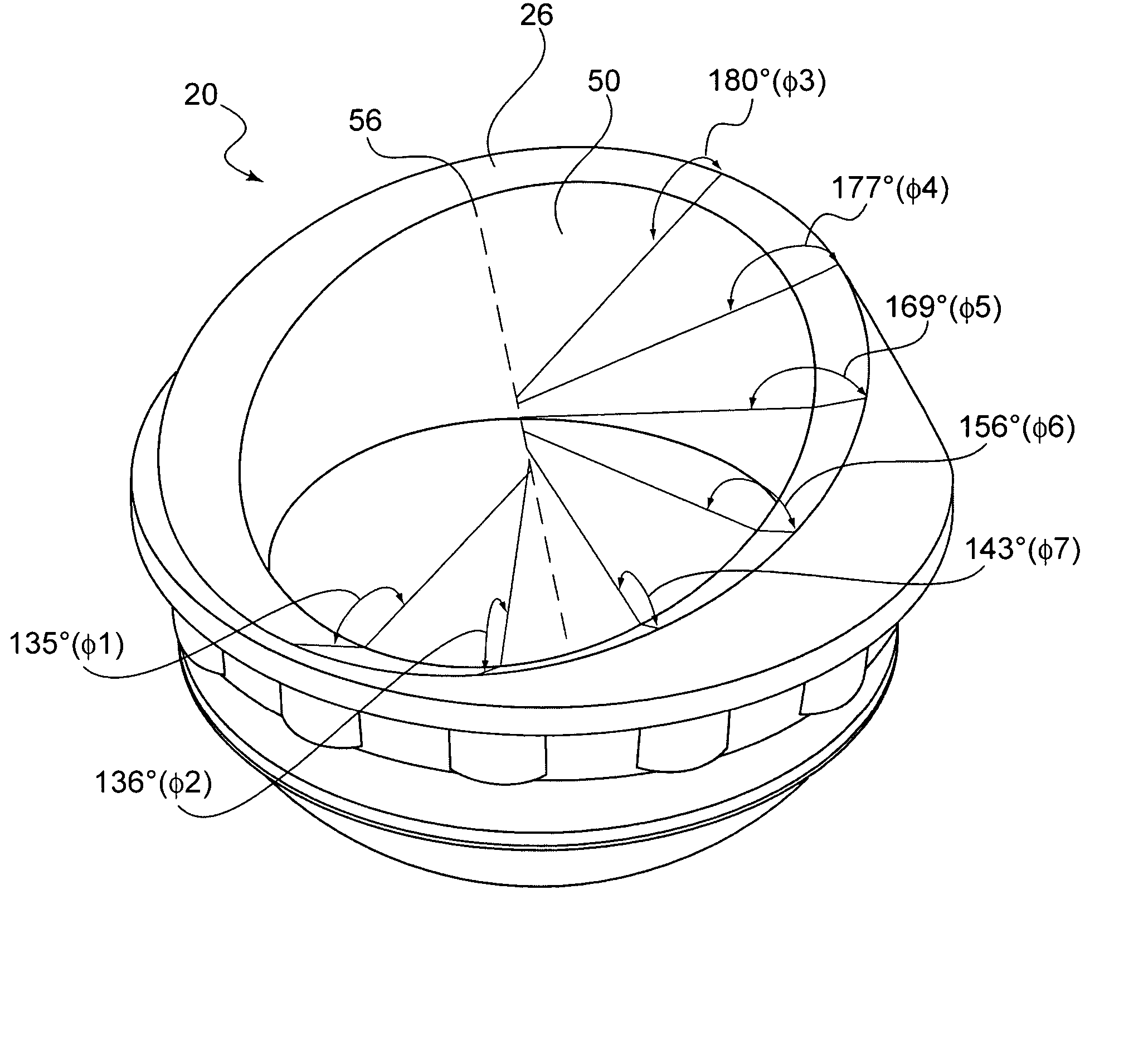
Variable geometry rim surface acetabular shell liner
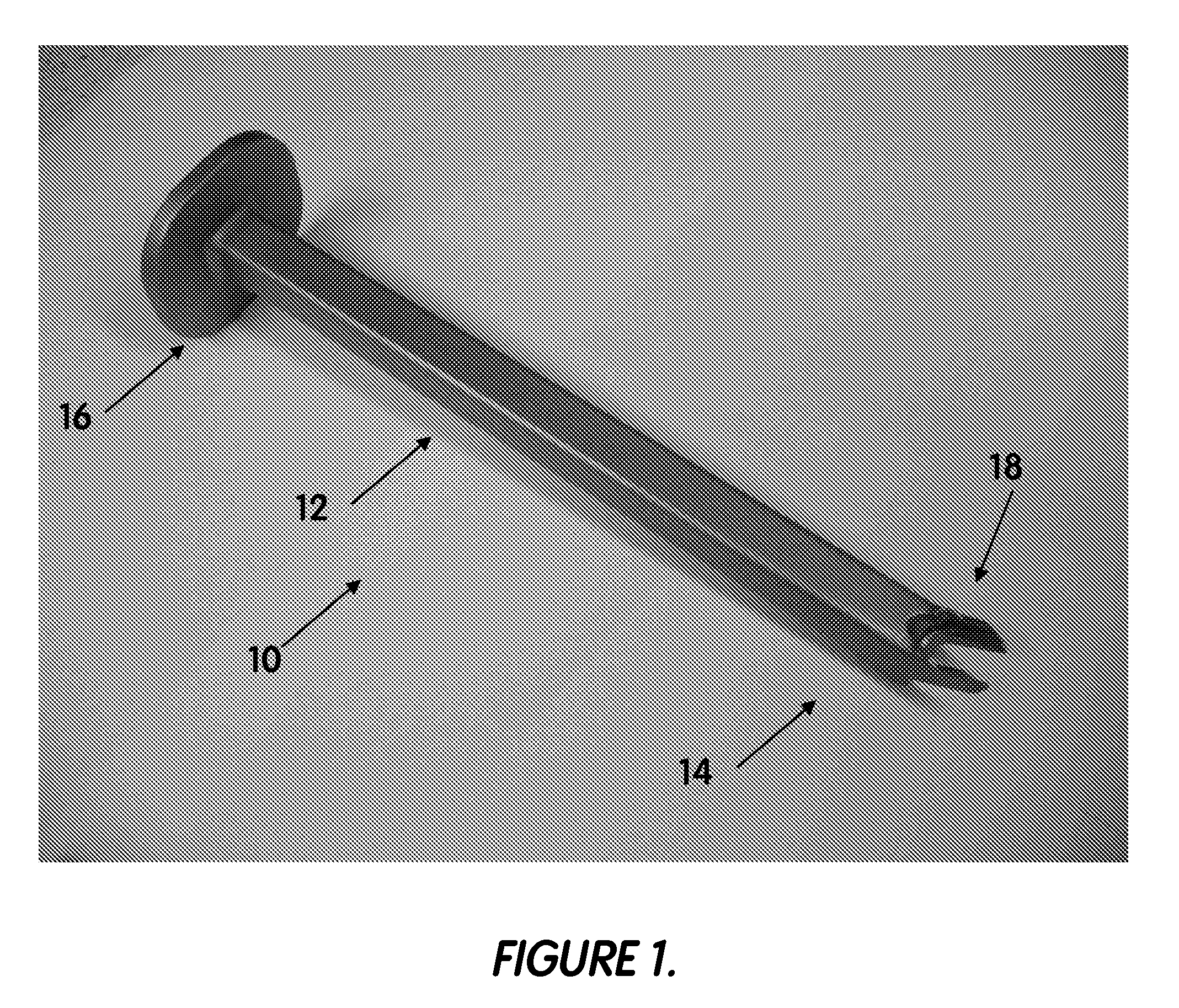
InactiveUS7074241B2Extended range of motionMinimize interferenceJoint implantsFemoral headsEdge surfaceCoxal joint
An acetabular shell liner having a variable rim surface geometry, which improves range of motion of the femoral component within the liner and decreases the incidence of dislocation and subluxation, and methods of making and using the acetabular shell liner. Prosthetic devices, more particularly hip joint prostheses, containing the acetabular shell liner having a variable rim surface geometry are also provided.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Variable geometry rim surface acetabular shell liner
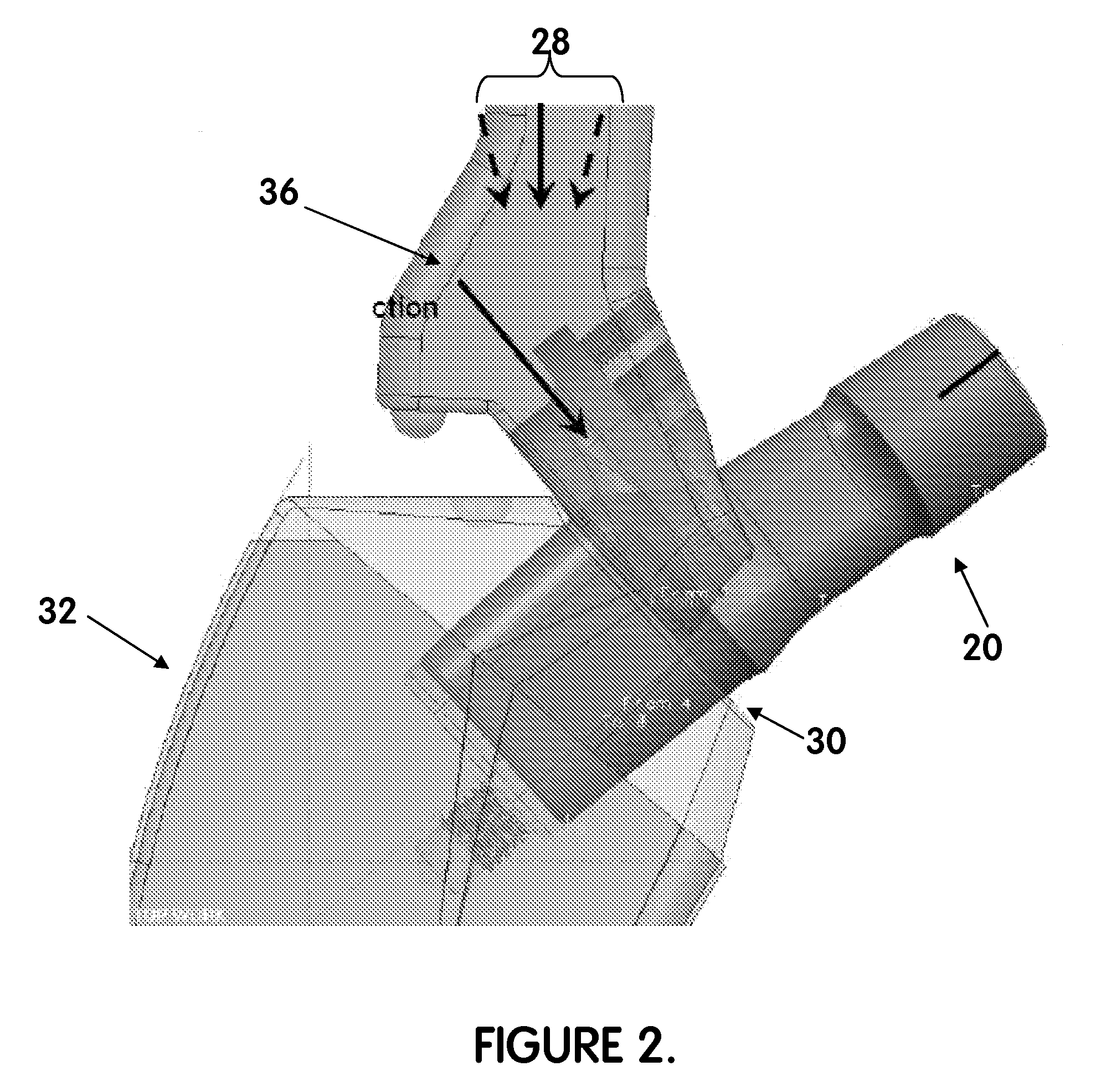
InactiveUS7682398B2Minimize interferenceExtended range of motionJoint implantsFemoral headsEdge surfaceRange of motion
There is provided an acetabular shell liner, and particularly a constrained liner, having a variable rim surface geometry to improve the range of motion of a femoral component within the liner and decrease the incidence of dislocation and subluxation. There are also provided methods of making and using the acetabular shell liner. Prosthetic devices, and particularly hip joint prostheses, containing the acetabular shell liner having a variable rim surface geometry are also provided.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
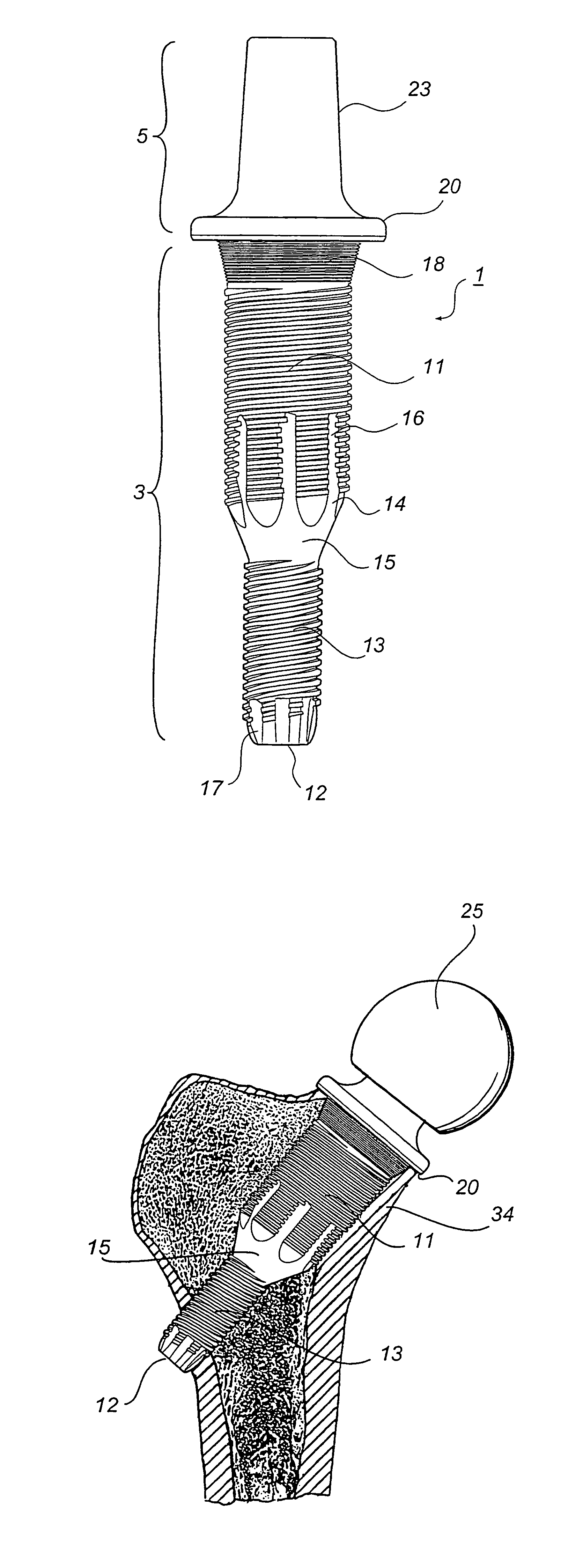
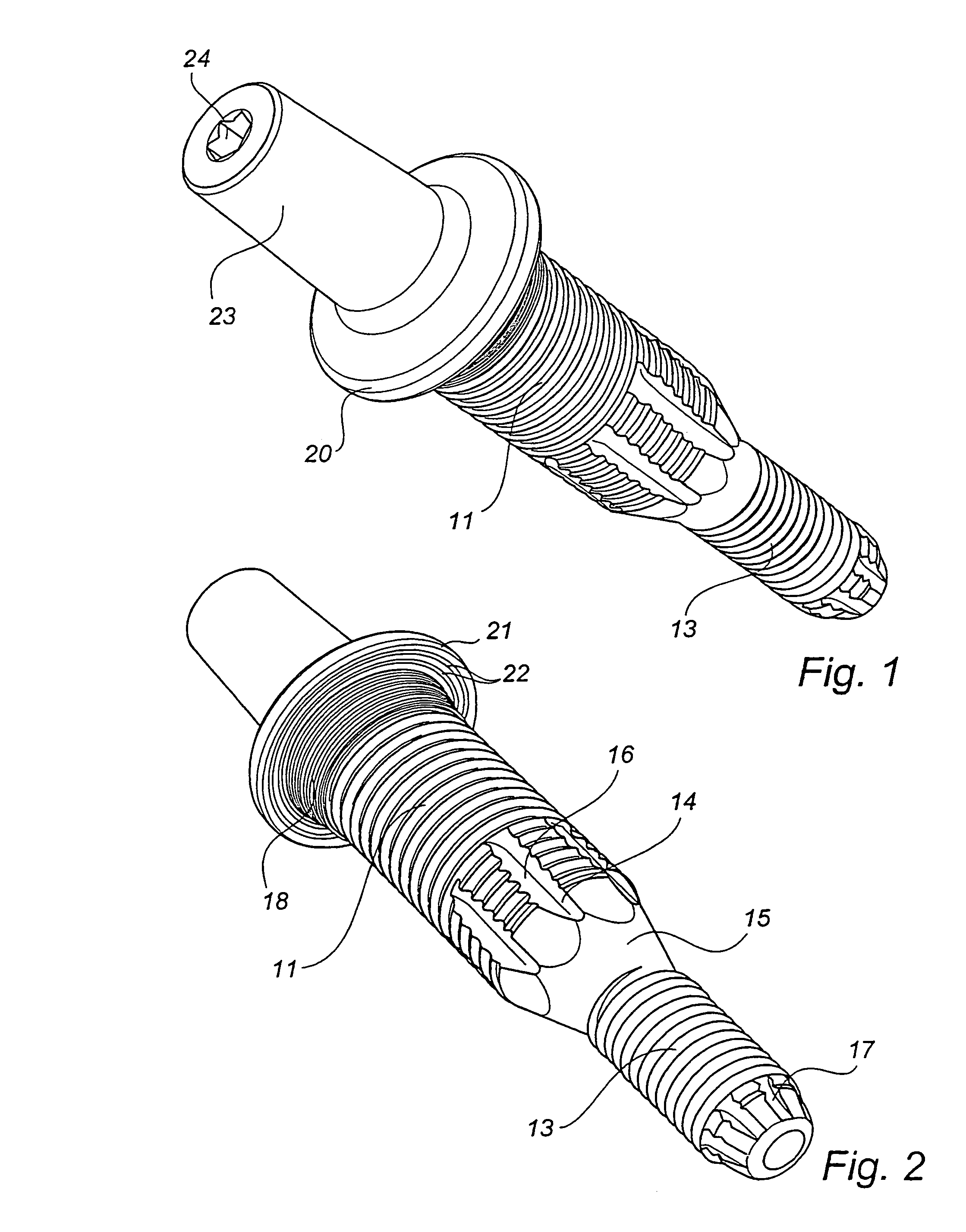
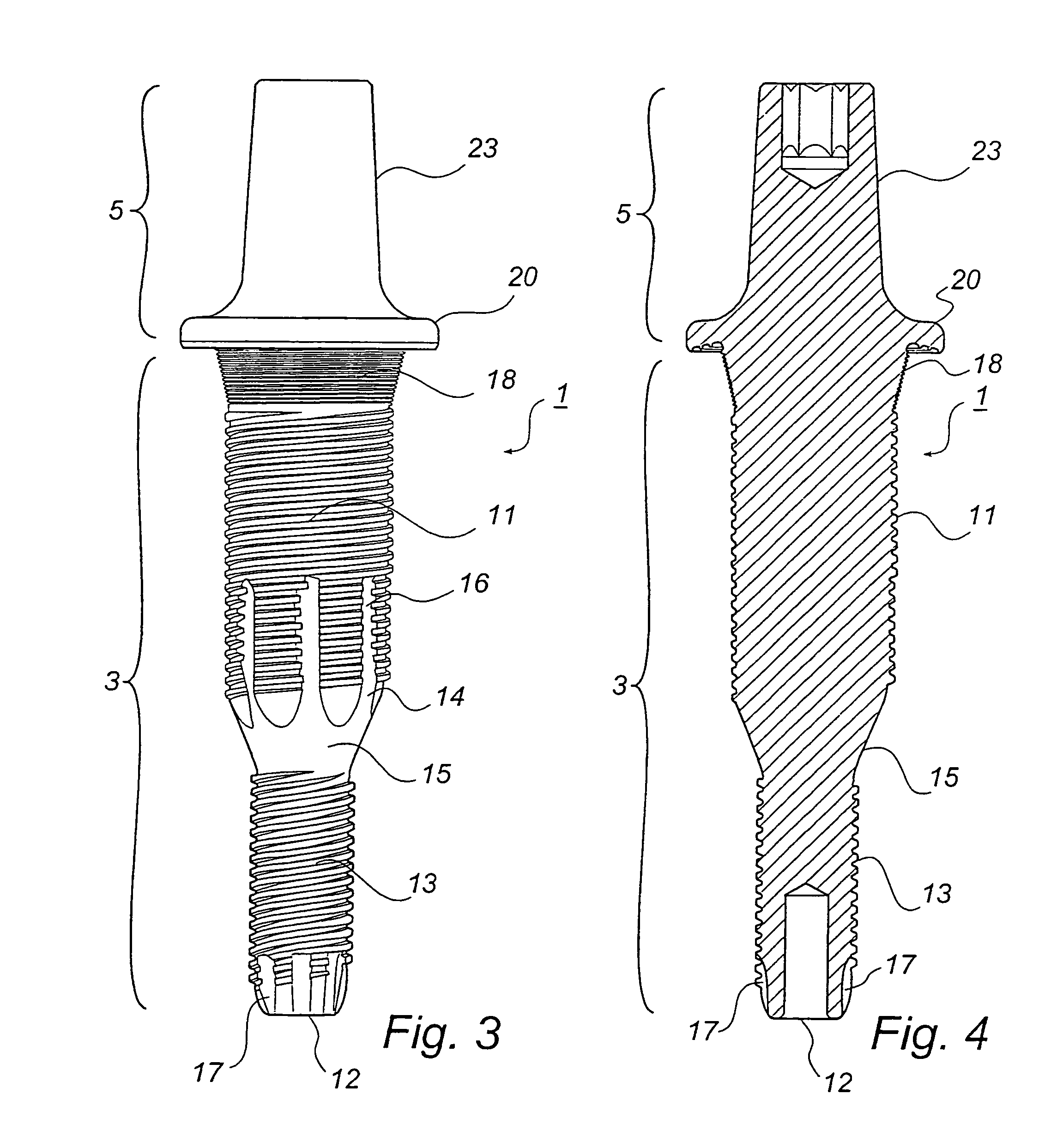
Leaflike shaft of a hip-joint prosthesis for anchoring in the femur
InactiveUS7494510B2Advantageous for revascularizationFacilitate revascularizationSurgeryJoint implantsRaspFemoral shaft
The present invention relates in certain embodiments to components of a hip-joint prosthesis. More particularly, embodiments of the invention relate to a leaf-like femoral shaft for use as part of a hip-joint prosthesis, and instruments (e.g., a rasp) and methods for implanting the shaft. The shaft includes an anchoring section extending between a proximal region and a distal end of the shaft. The shaft has a cross-sectional contour that defines a lateral side, a medial side, an anterior side and a posterior side. A corresponding rasp is preferably provided for each femoral shaft. The rasp is inserted into the femur to form a cavity having generally the same configuration as the rasp. The shaft is configured to be over-dimensioned in at least one of the anterior-posterior direction and medial-lateral direction relative to the rasped femur cavity. In one embodiment, the distance between diagonally opposite corner junctions of the shaft is substantially equal to the distance between corresponding diagonally opposite corner junctions of the femur cavity, so as to inhibit excess stress on the corticalis.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Bi-polar hip prosthetic devices employing diffusion-hardened surfaces
InactiveUS20040122524A1Bone implantPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAcetabular componentPlastic surgery
An orthopedic implant having diffusion-hardened surfaces employed at inner and outer load-bearing surfaces. Preferably, the orthopedic implant is a bipolar hip prosthetic device and system where a coating of oxidized zirconium is formed at the articulating, load-bearing surface of the acetabular component and at the articulating, load-bearing surface of the femoral head. The acetabular component has a polymeric cup, made from a bio-compatible material, such as UHMWPE.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Interlocking reverse hip prosthesis and method
ActiveUS8313531B2Reduce wearReduce in quantityBone implantJoint implantsRange of motionFemoral component
An interlocking reversed hip prosthesis including an acetabular cup being implanted in the acetabular cavity having an acetabular articular ball, firmly attached to the central portion of the cup via Morse taper. The femoral component having a hemispherical cup attached to the neck of the implant via Morse taper in a modular fashion thereby allowing use of several length necks. After implantation of the acetabular cup and the femoral cup, the two members are assembled together for relative movement. The acetabular cup secured by several screws or resorbable fixation studs. During range of motion, the edge of the femoral cup becomes inserted into space located between the acetabular cup and the acetabular ball and becomes restrained thus reducing the likelihood of dislocation during extreme range of motion.
Owner:HIP INNOVATION TECHONOLOGY LLC
Fluted sleeve hip prosthesis for modular stem
An intramedullary implant for mounting within an intramedullary canal of a bone is disclosed. The intramedullary implant includes a lower stem portion, an upper stem portion, and a modular sleeve body. The modular sleeve body is connected to one of the lower stem portion or the upper stem portion. The sleeve body includes an inner portion that covers at least a segment of the upper stem portion and has one or more longitudinally extending bone engagement members for engagement with the bone.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Surgical tool holder for facilitated sterilization
ActiveUS20070167952A1Avoid separationEasy to sterilizeControlling membersMechanical apparatusEngineeringSurgical department
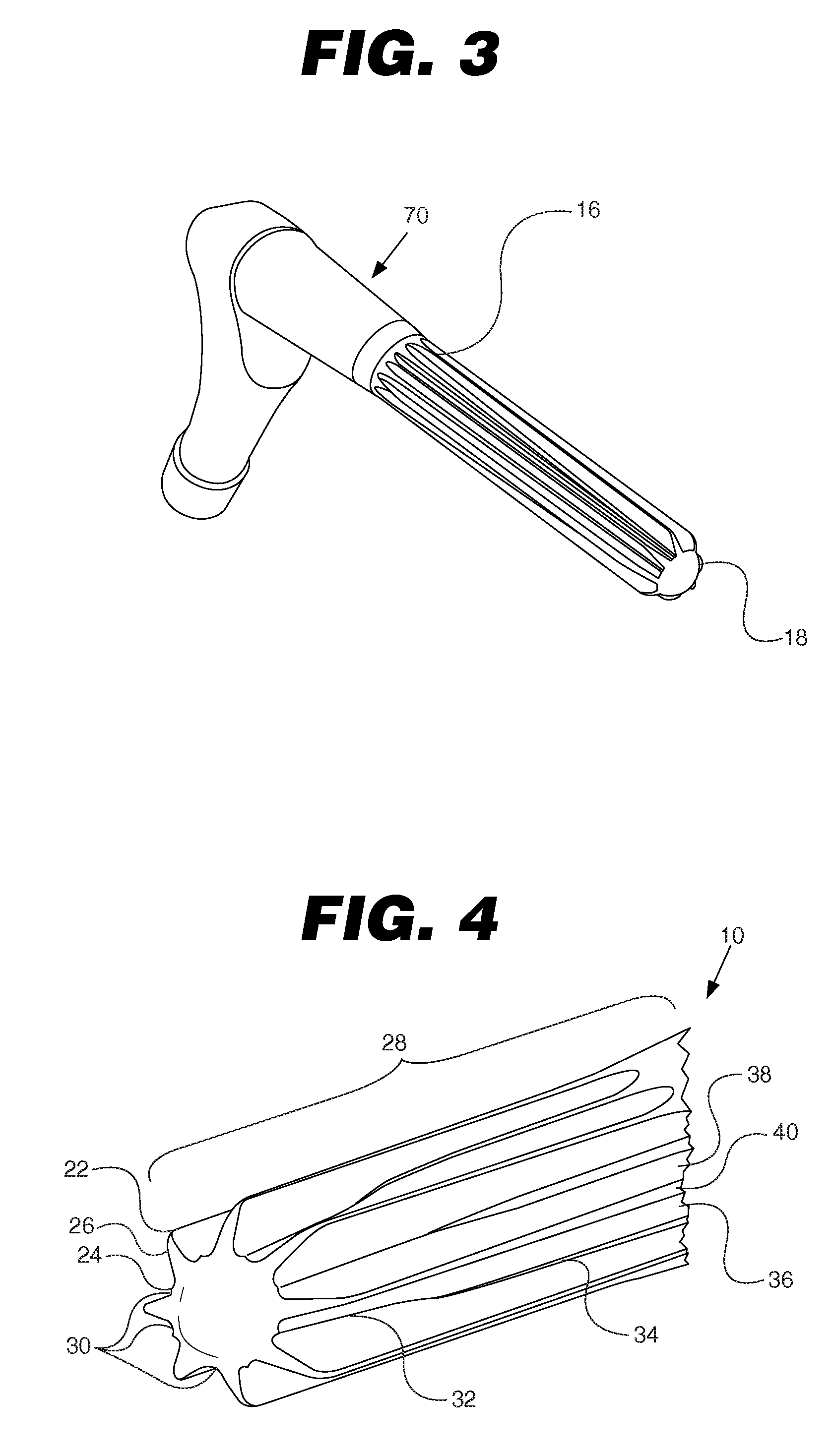
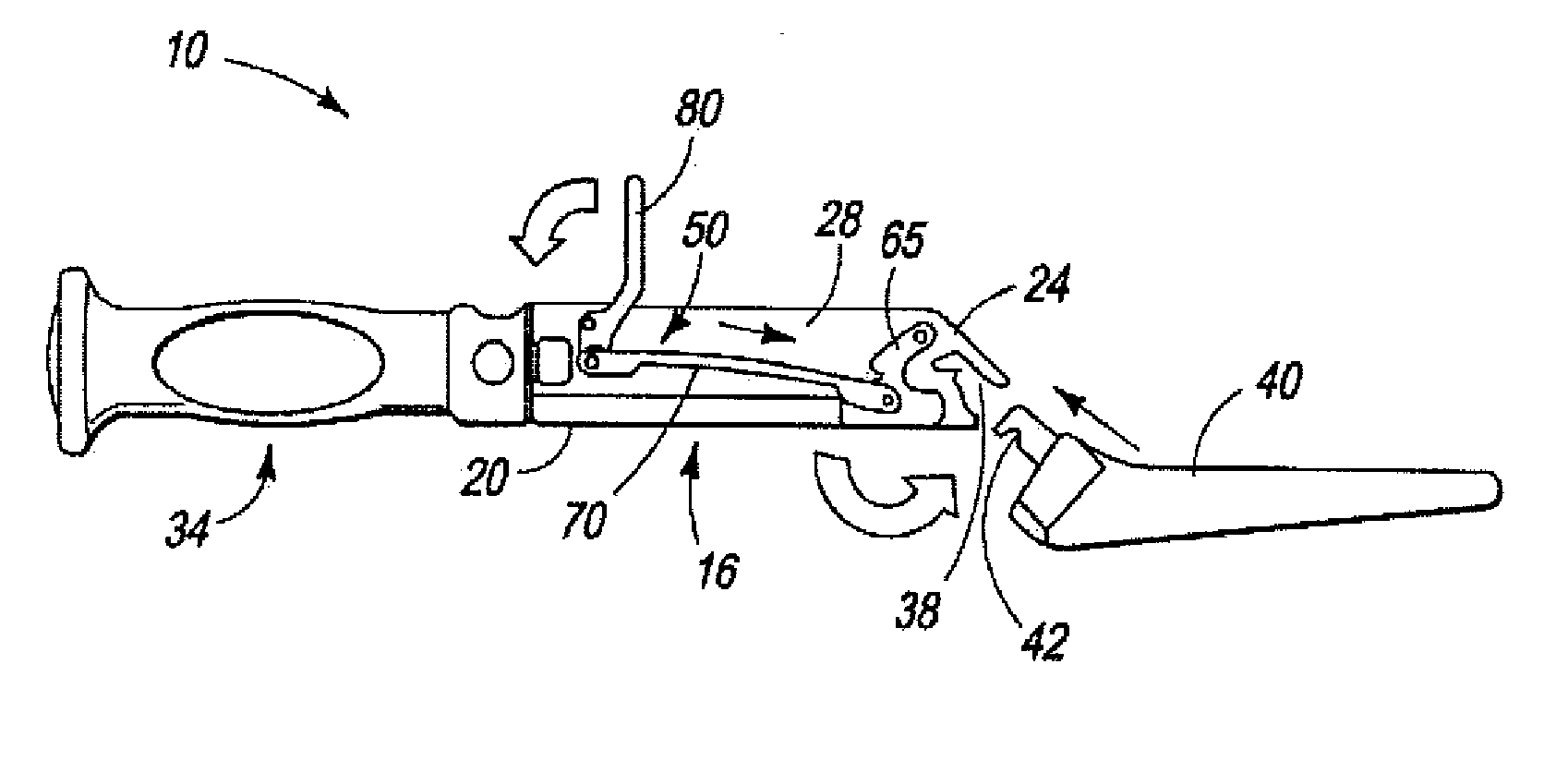
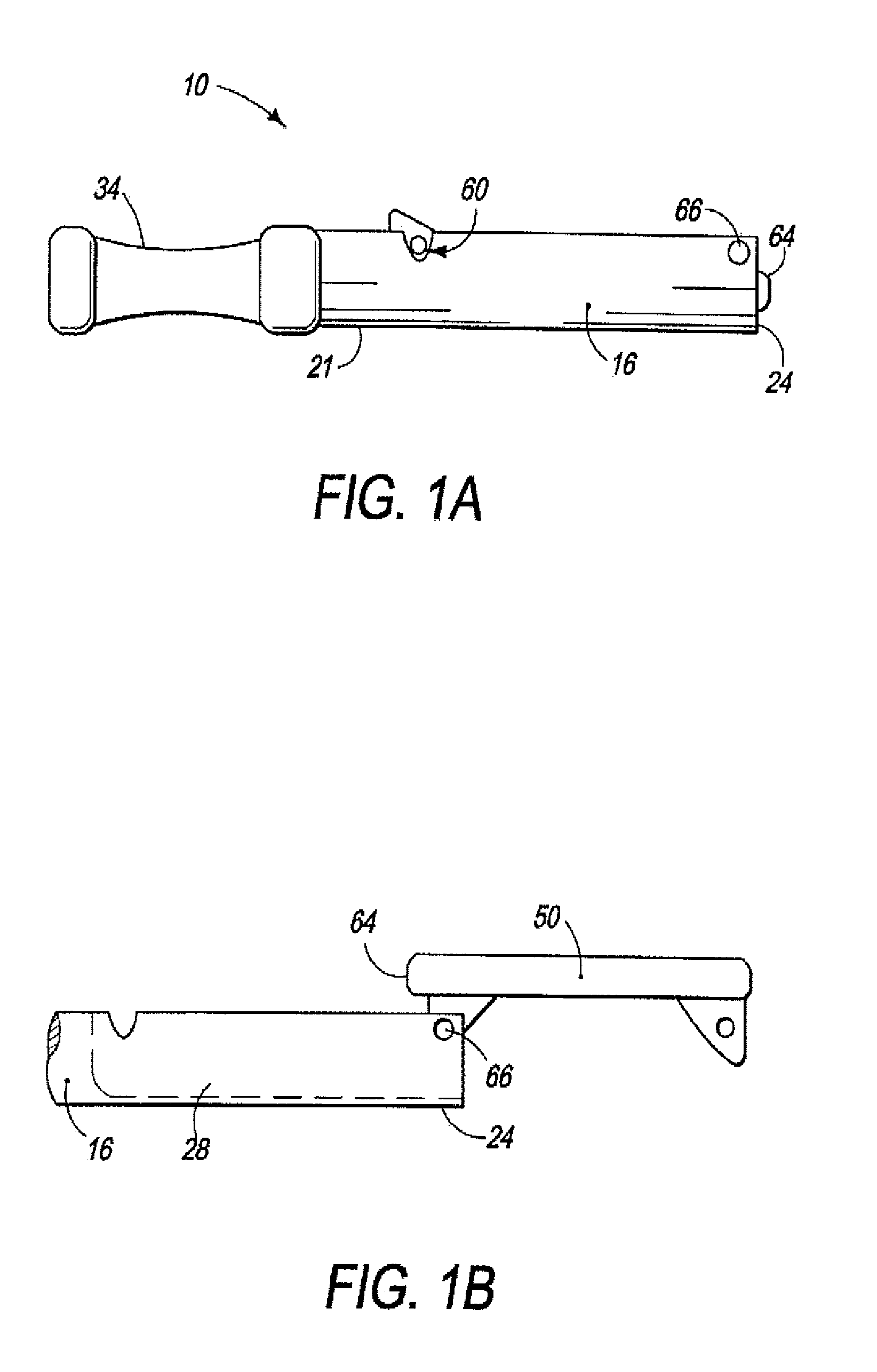
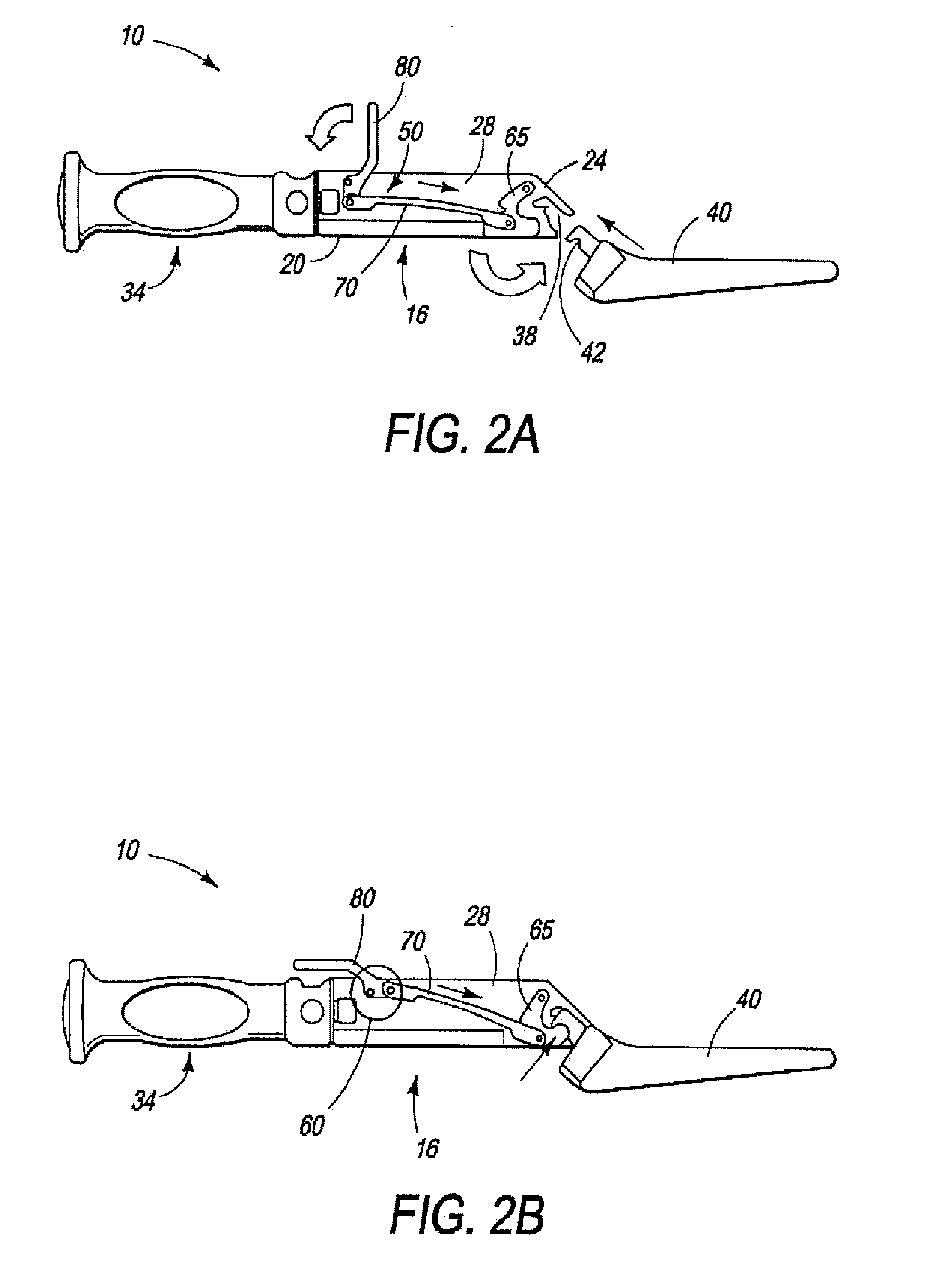
A surgical tool holder aids a surgeon in controlling the use of a tool during, for example, preparation of a femoral cavity for reception of hip joint prosthesis. The holder has a housing that encloses a mechanism having, at a far end, a tool-engaging interface, and at the opposite end, a handle which facilitates manipulation of the tool during use in preparing a bone site by the surgeon. The holder enables easy orientation of the tool attached to its end, which is important because control of the tool is critical in order to accurately prepare a recess for reception and installation of a prosthesis.
Owner:VIANT AS&O HLDG LLC
Mill and guide apparatus for preparation of a hip prosthesis
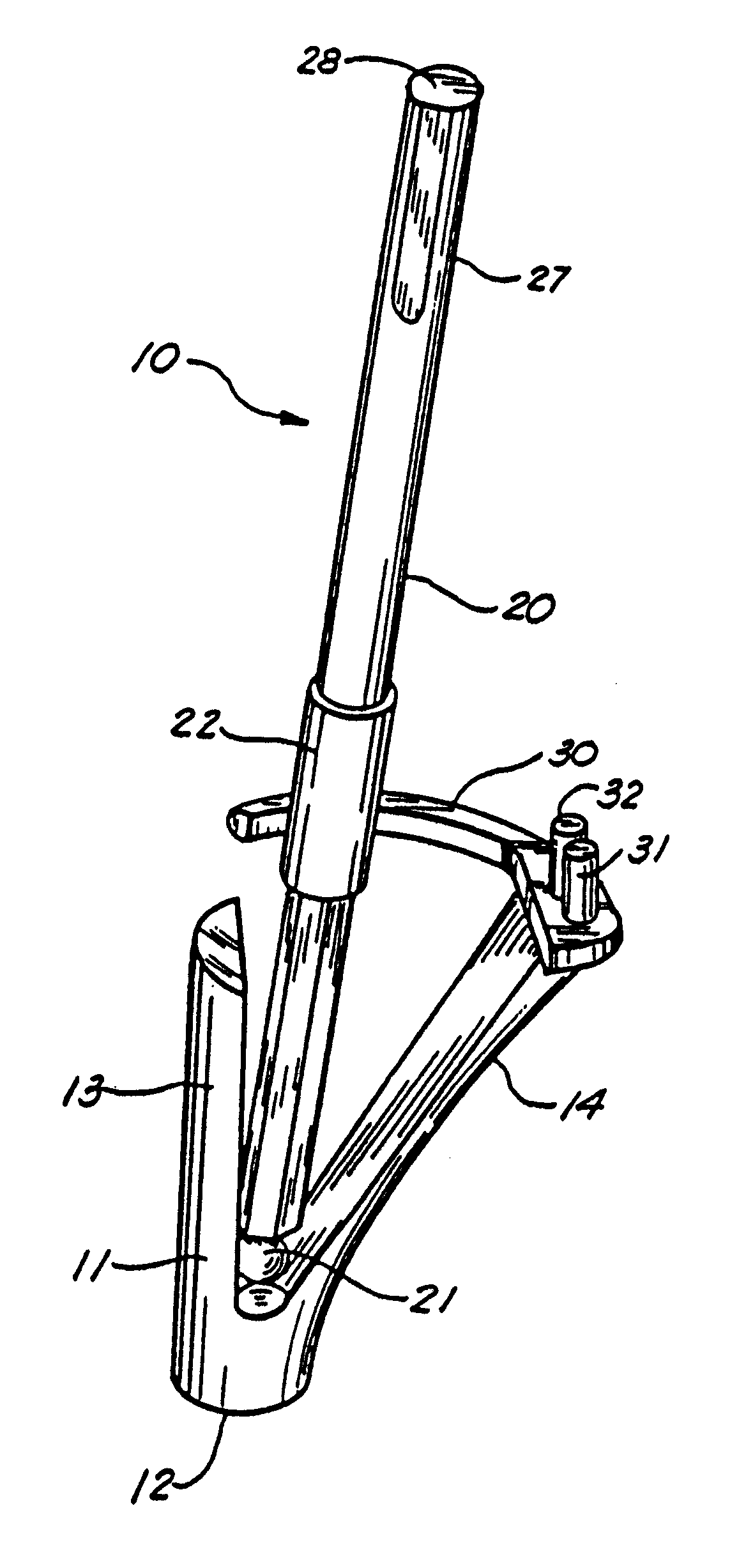
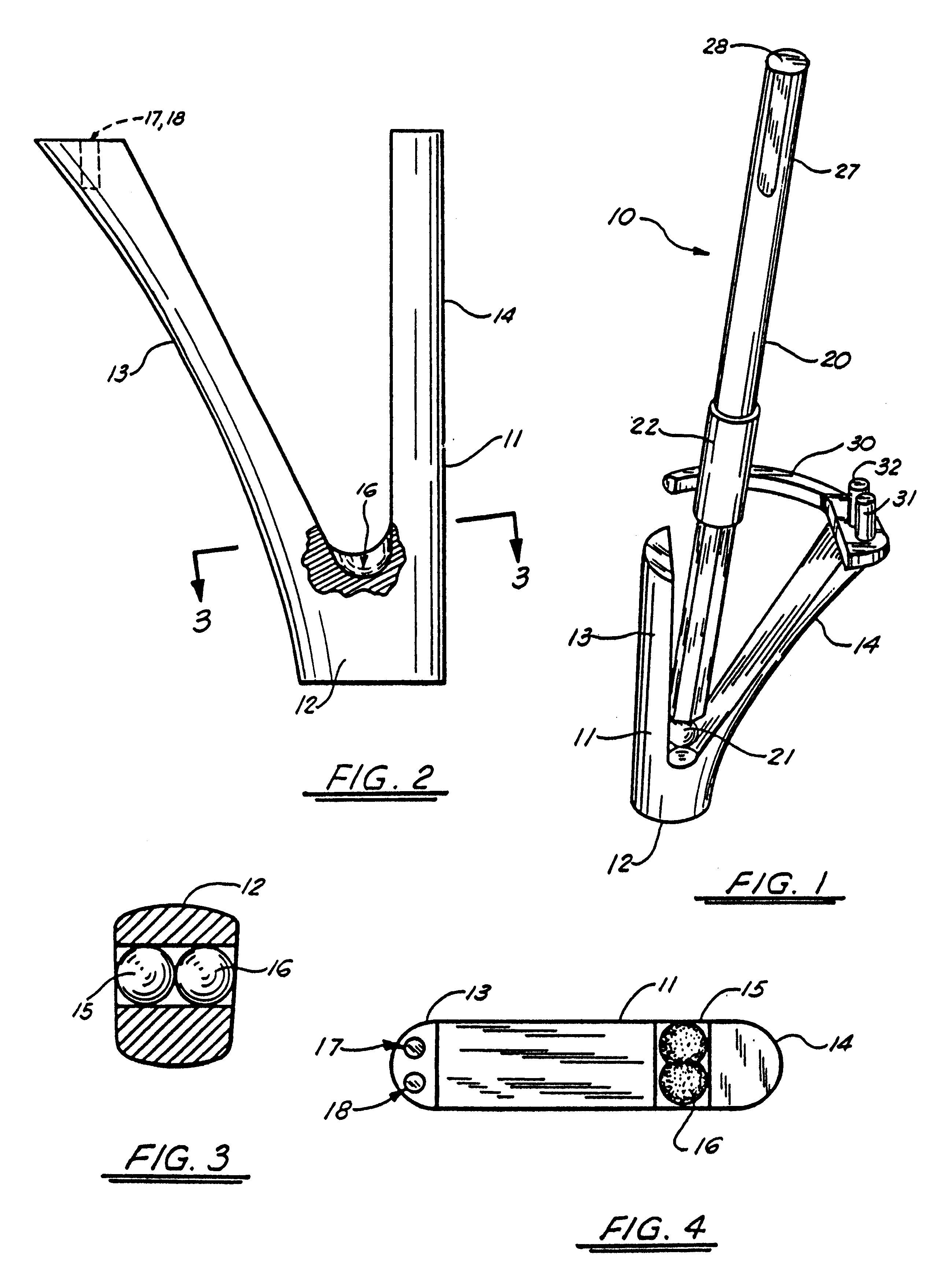
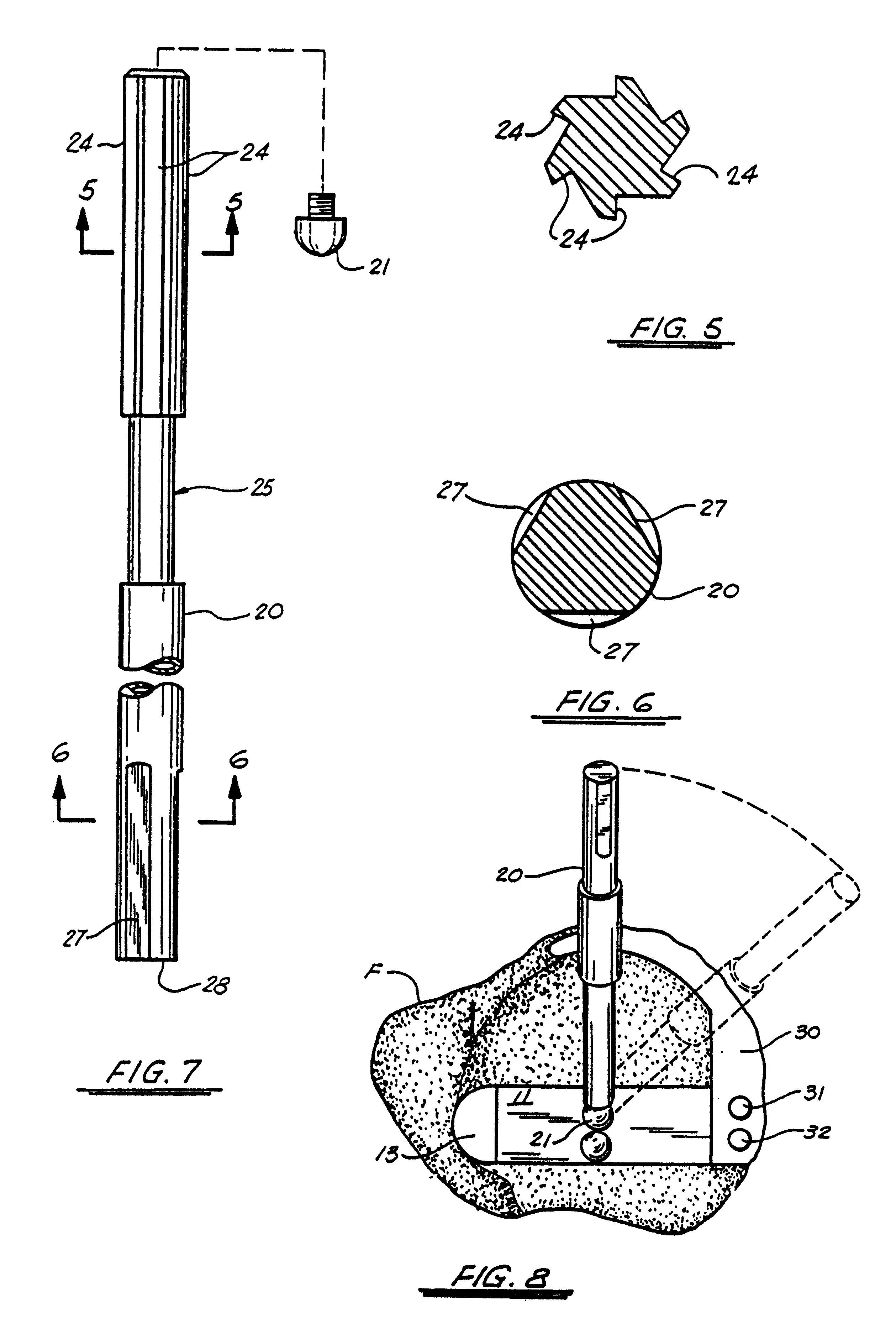
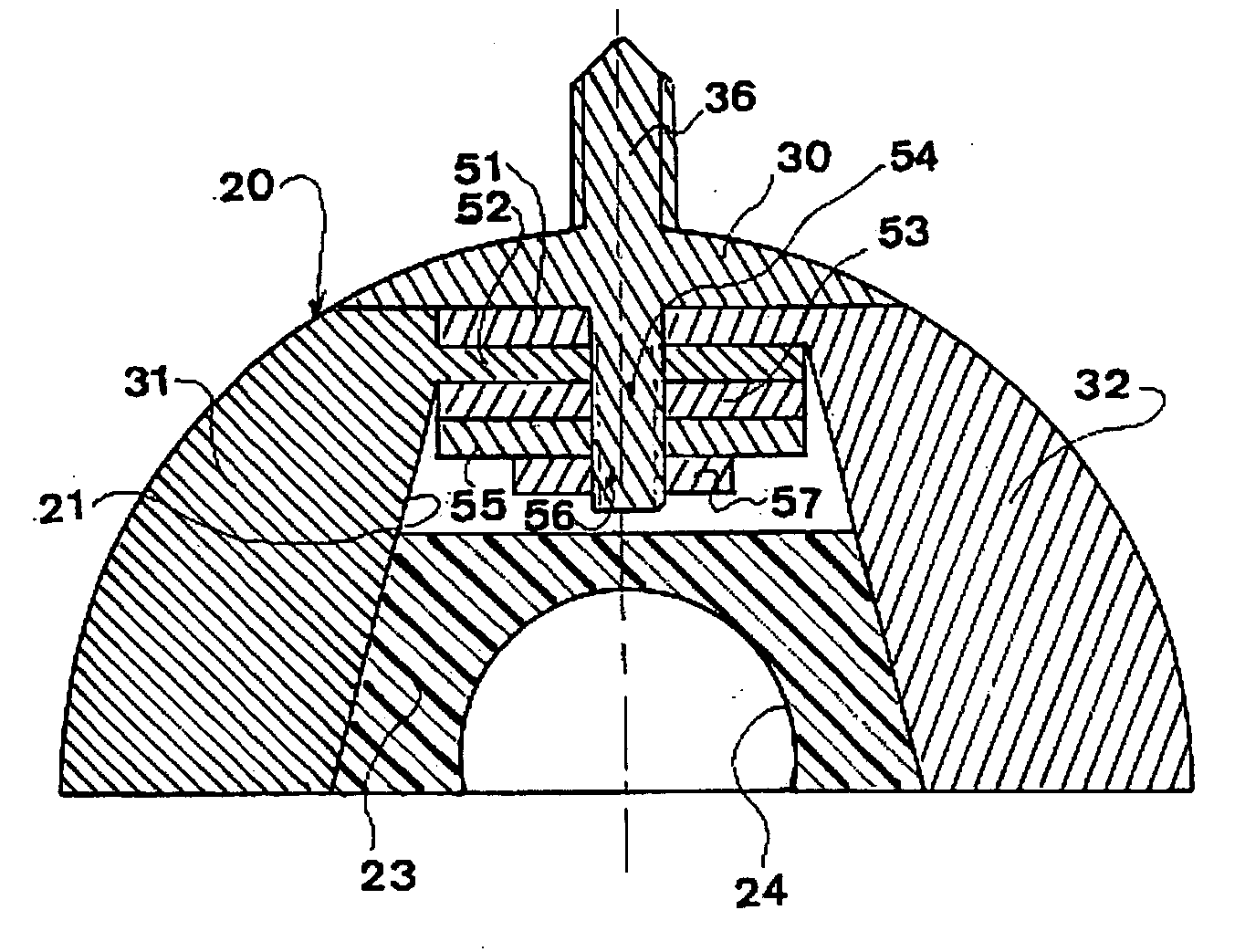
A guide apparatus for preparing the femur of a patient with a rotary mill to receive a femoral hip prosthesis includes a V-shaped guide body having a lower end base portion adapted to extend into the intermedullary canal of the femur and an upper end portion comprised of at least two spaced apart struts so that the overall guide body had a configuration substantially the same as the prosthesis body sought to be implanted in the patient. The lower end of the guide body base provides one or more hemispherical receptacles for holding the hemispherical end portion of a spinning mill bit. A preferably removable transverse guide rail has connection pins at one end portion thereof for forming a connection with the upper end of the guide body at one of the struts, the arm having a curved surface that is adapted to guide the mill bit during preparation of the intermedullary canal of the patient's femur for receiving a hip prosthesis thereafter.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
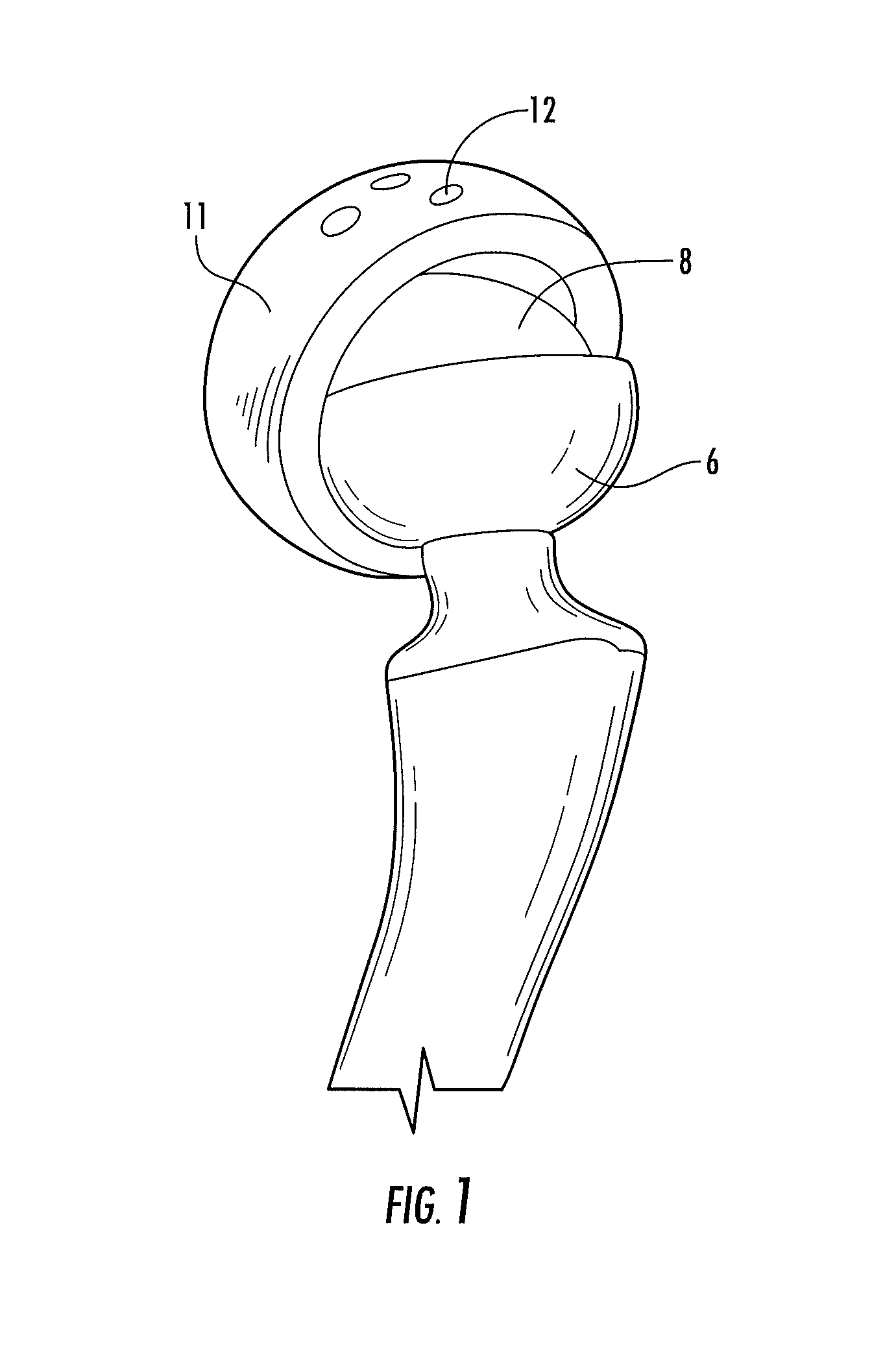
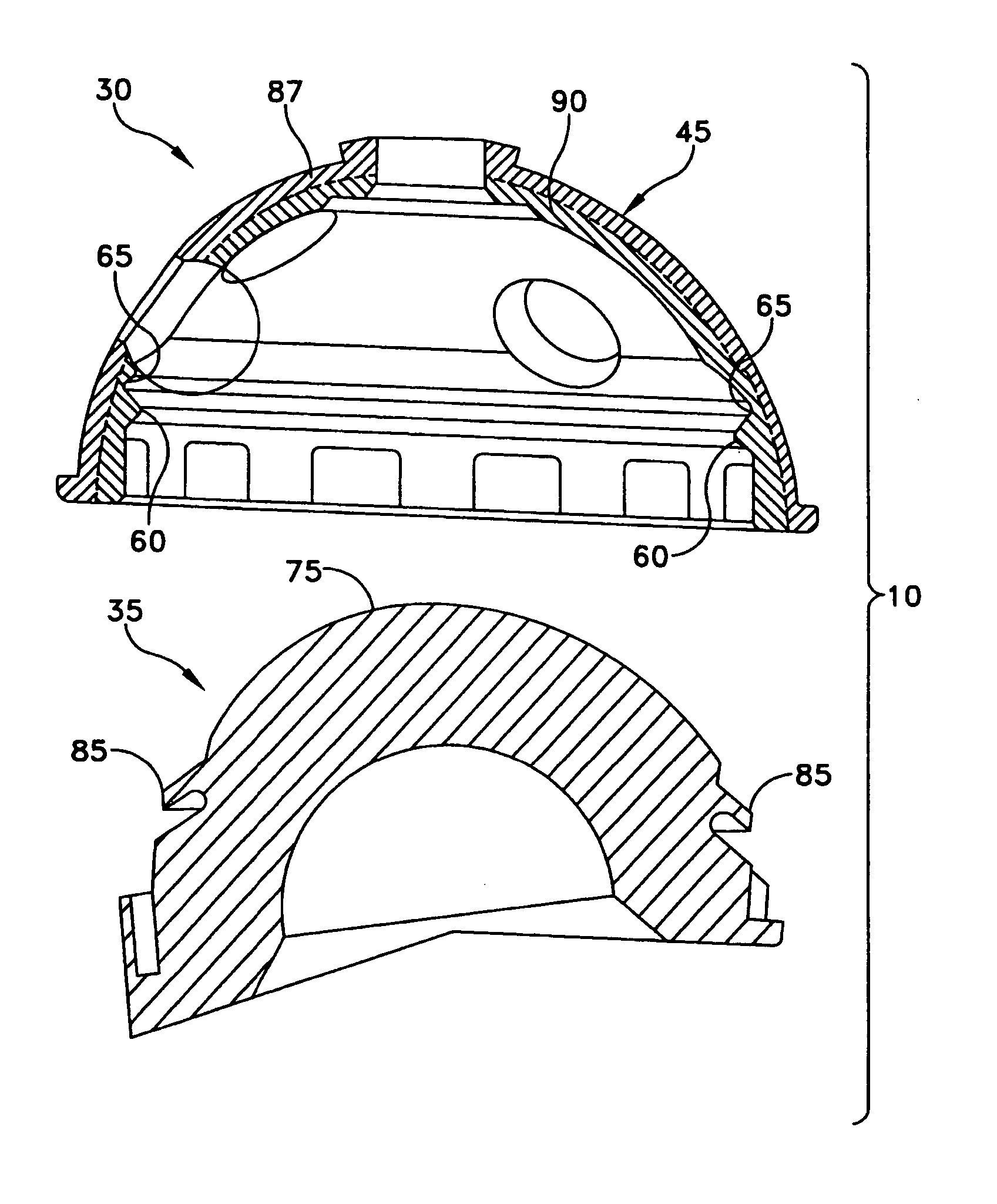
Acetabular cup for hip prosthesis ball-socket or the like
InactiveUS20050010303A1Mitigate such drawbackJoint implantsFemoral headsSacroiliac jointBiomedical engineering
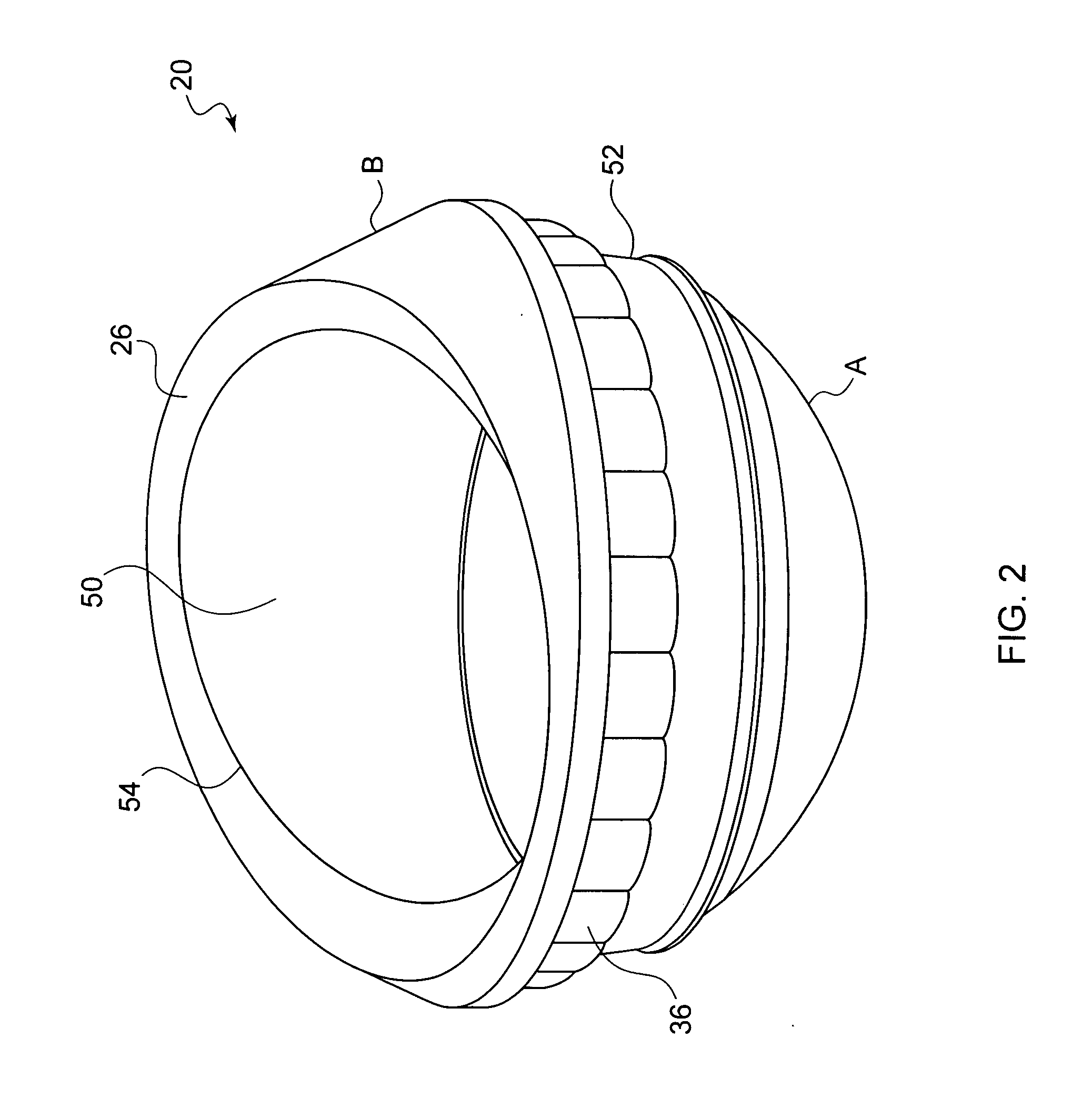
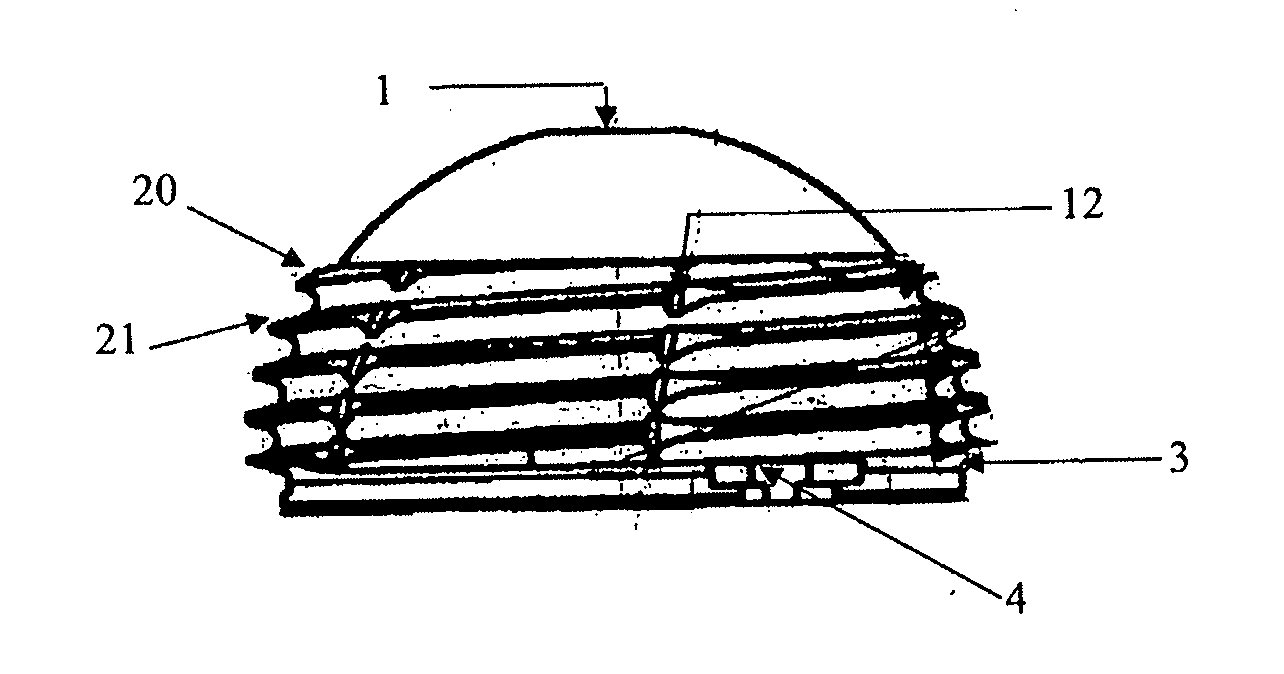
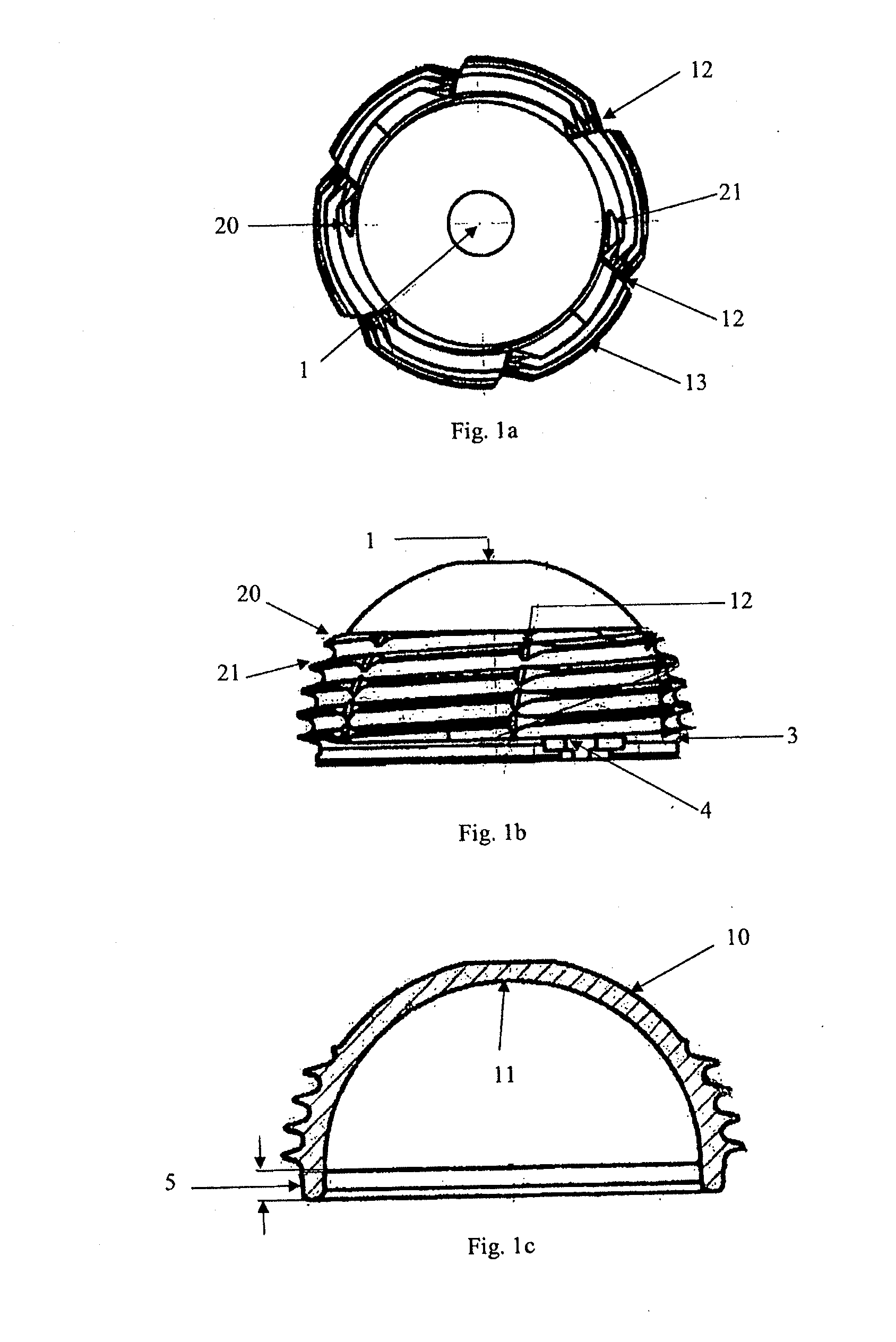
The present invention relates to acetabular cup assemblies for ball-and-socket joint protheses. The acetabular cup assembly is essentially characterized by the fact that it comprises a cup 20 of outside general shape that is substantially hemispherical, the cup including an open hollow housing 21, and an insert 23 in which a hemispherical cavity 24 is made suitable for receiving a spherical head to co-operate in rotation therewith, the insert being of outside shape that is substantially complementary to the housing 21 so as to be capable of being engaged therein, the cup 20 comprising a central base 30 constituting the polar cap of the cup 20, a determined number of cup portions 31-33, and means 34 for associating the cup portions 31-33 at least with the central base 30 to form the cup 20 with its housing 21. The invention is applicable to making a prosthesis, in particular a hip prosthesis or the like.
Owner:SOC CHIRURGICALE DAIDE A LA RECH & AUX REALISATIONS
Variable geometry rim surface acetabular shell liner
InactiveUS20070106389A1Extended range of motionMinimize interferenceJoint implantsFemoral headsEdge surfaceRange of motion
There is provided an acetabular shell liner, and particularly a constrained liner, having a variable rim surface geometry to improve the range of motion of a femoral component within the liner and decrease the incidence of dislocation and subluxation. There are also provided methods of making and using the acetabular shell liner. Prosthetic devices, and particularly hip joint prostheses, containing the acetabular shell liner having a variable rim surface geometry are also provided.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
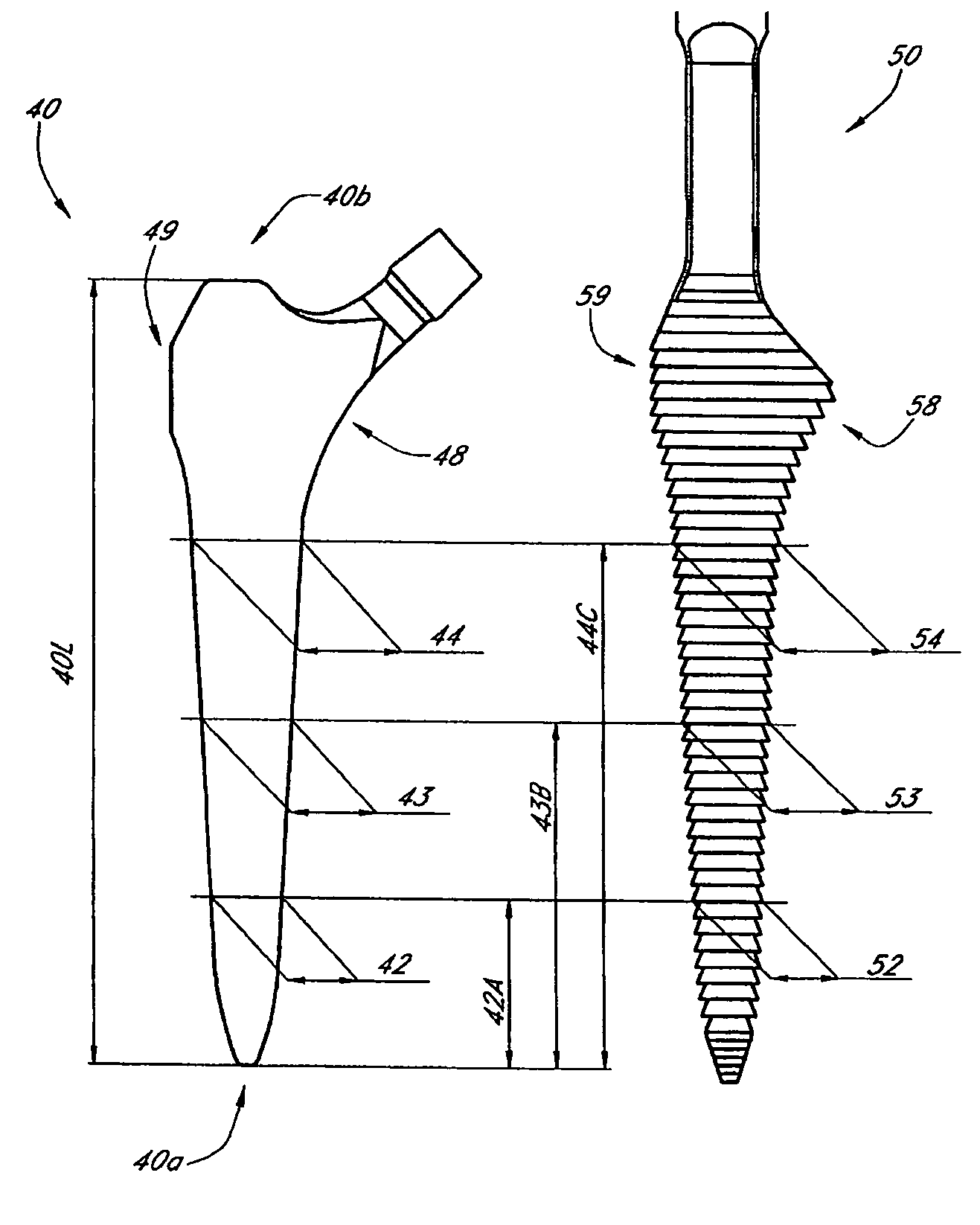
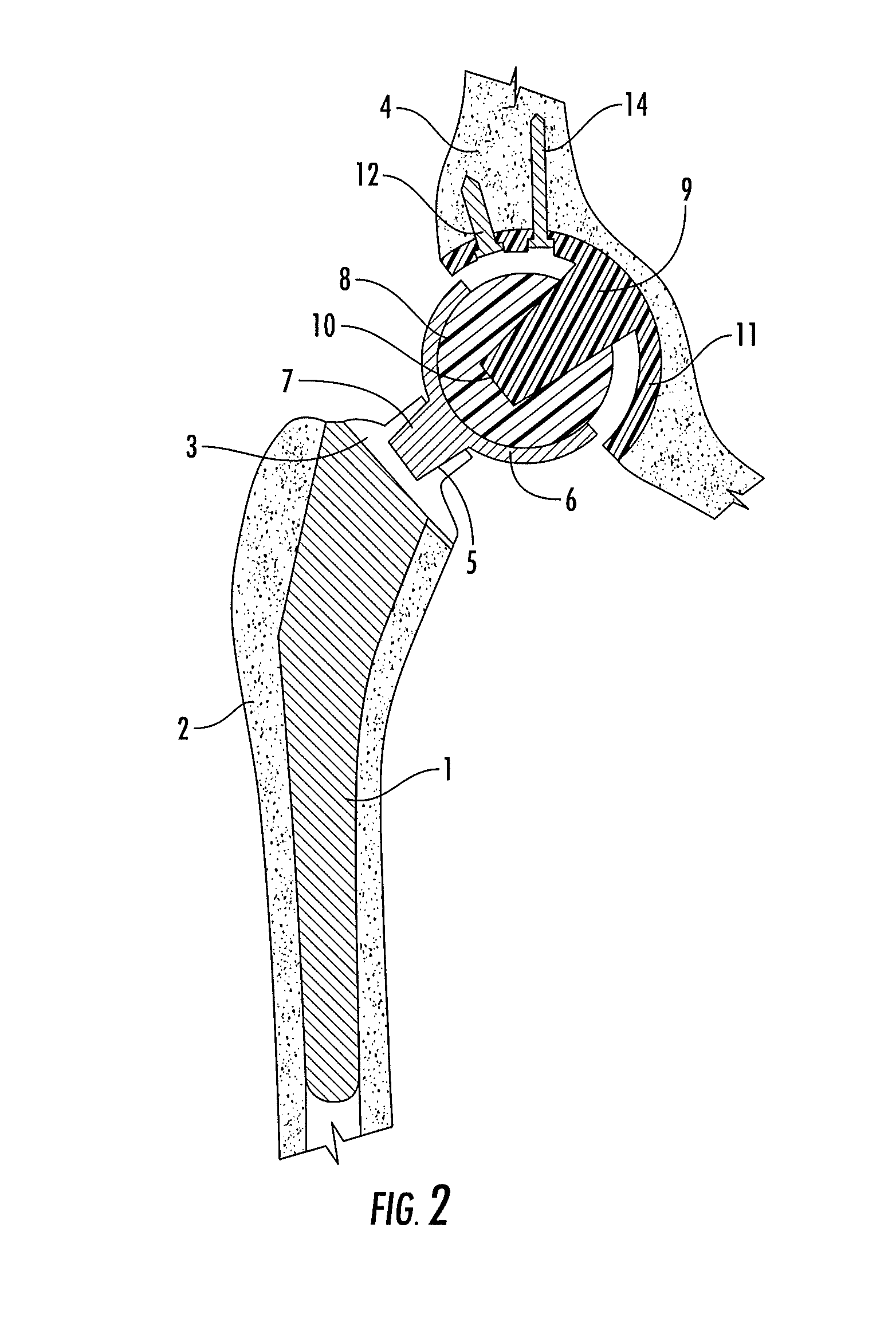
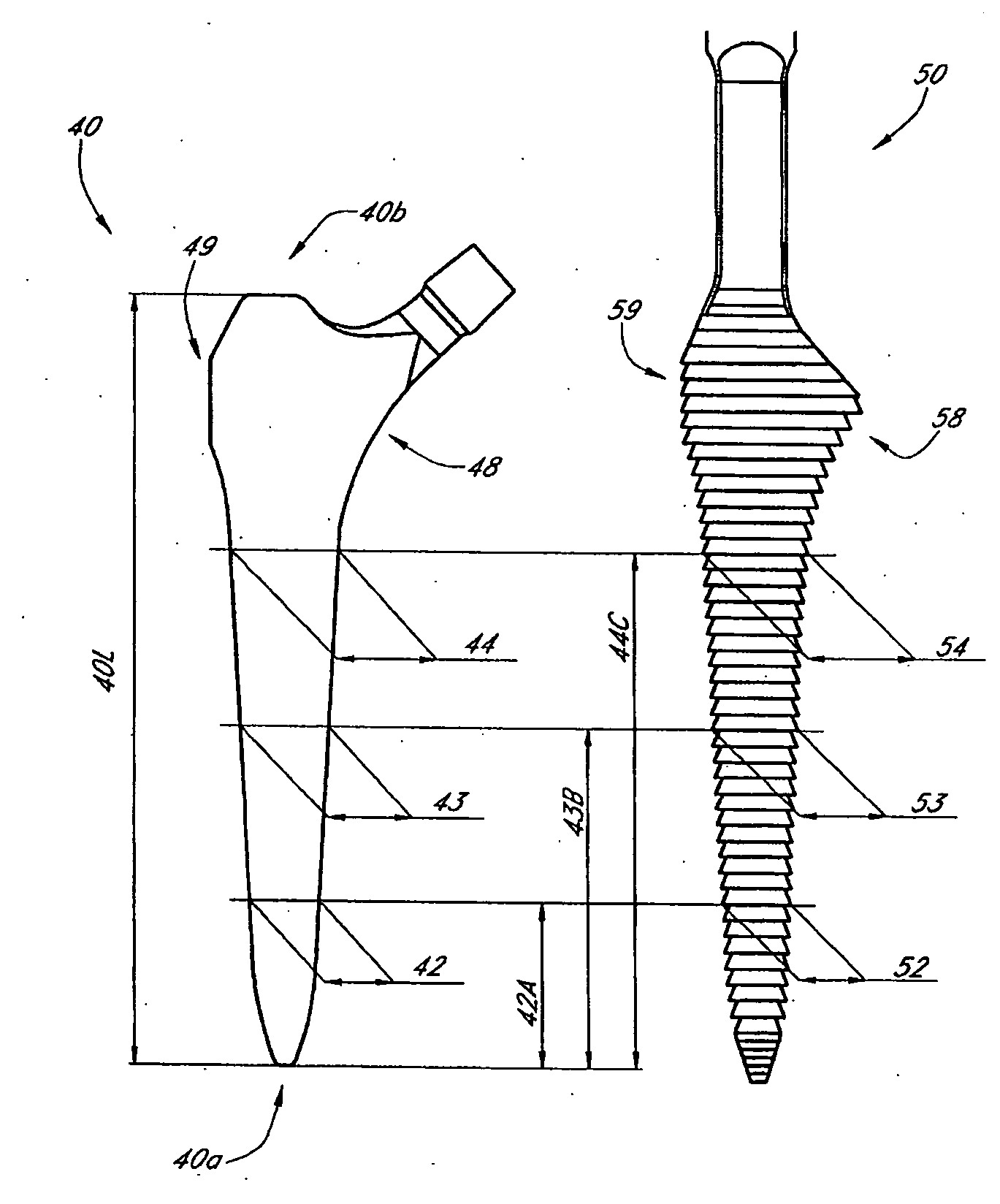
Femur fixture and set of femur fixtures
InactiveUS7156879B1Smooth connectionImprove stabilityInternal osteosythesisBone implantRight femoral headLeft femoral head
A femur fixture for a hip-joint prosthesis comprising an intraosseous anchoring structure of a generally circular cross-section for screwing laterally into a complementary bore drilled laterally into the neck of a femur after resection of the femur head to an anchored position. The intraosseous anchoring structure has a proximal end, a distal end, a relatively short frusto-conical proximal section at the proximal end, and a proximal cylindrical section having a screw thread profile thereon. The proximal cylindrical section extends from the frusto-conical proximal section towards the distal end of the anchoring structure. The frusto-conical proximal section and the proximal cylindrical section each being dimensioned so as to bear against the cortex of the femur neck when the intraosseous anchoring structure is in the anchored position. The invention also relates to a set of such femur fixtures, wherein the frusto-conical proximal section and the proximal cylindrical section of each fixture in the set have different dimensions, whereby the fixture in the set having the frusto-conical proximal section and the proximal cylindrical section of correct size for abutting the cortex of the femur neck of a particular patient can be selected for use in that patient.
Owner:HIP
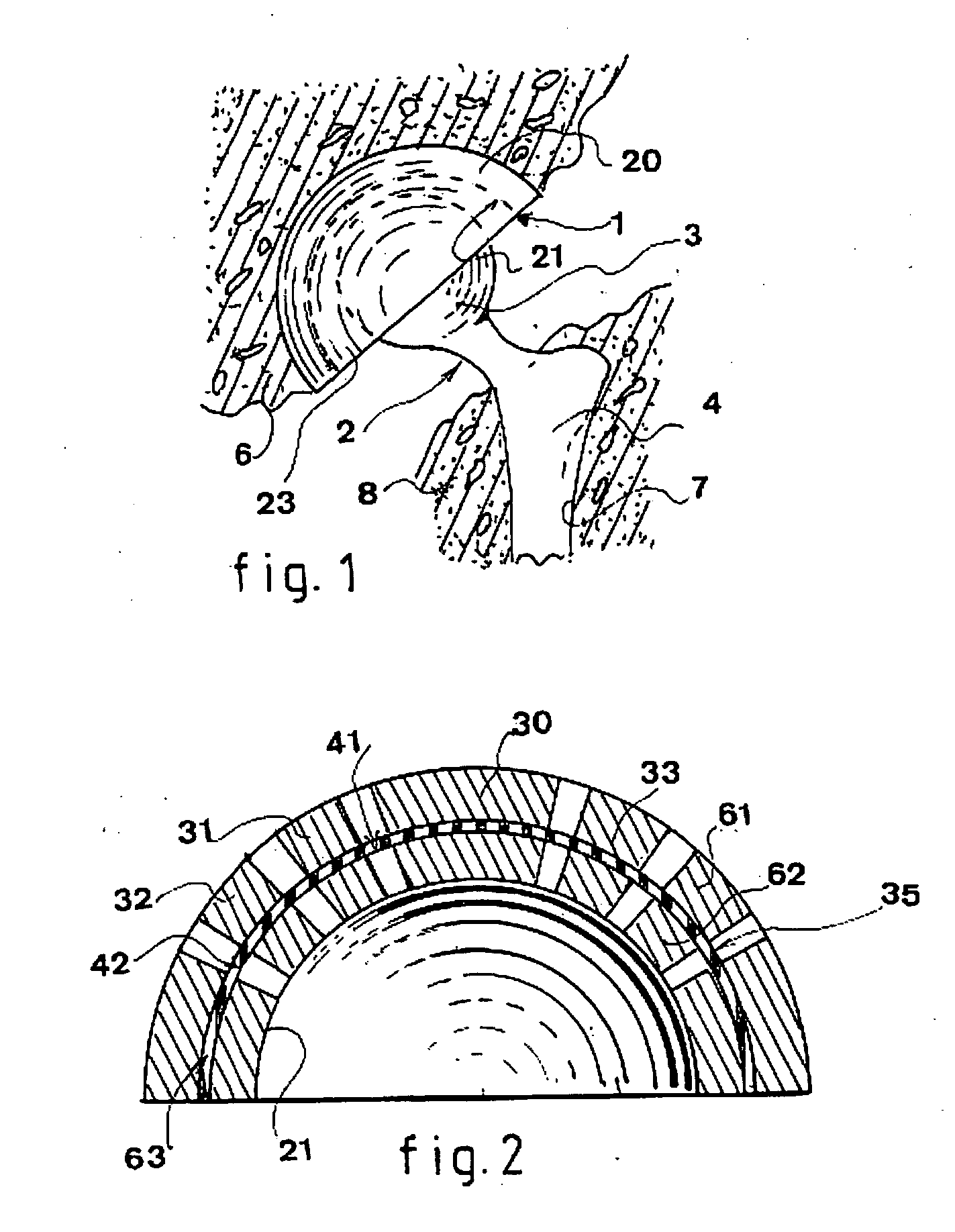
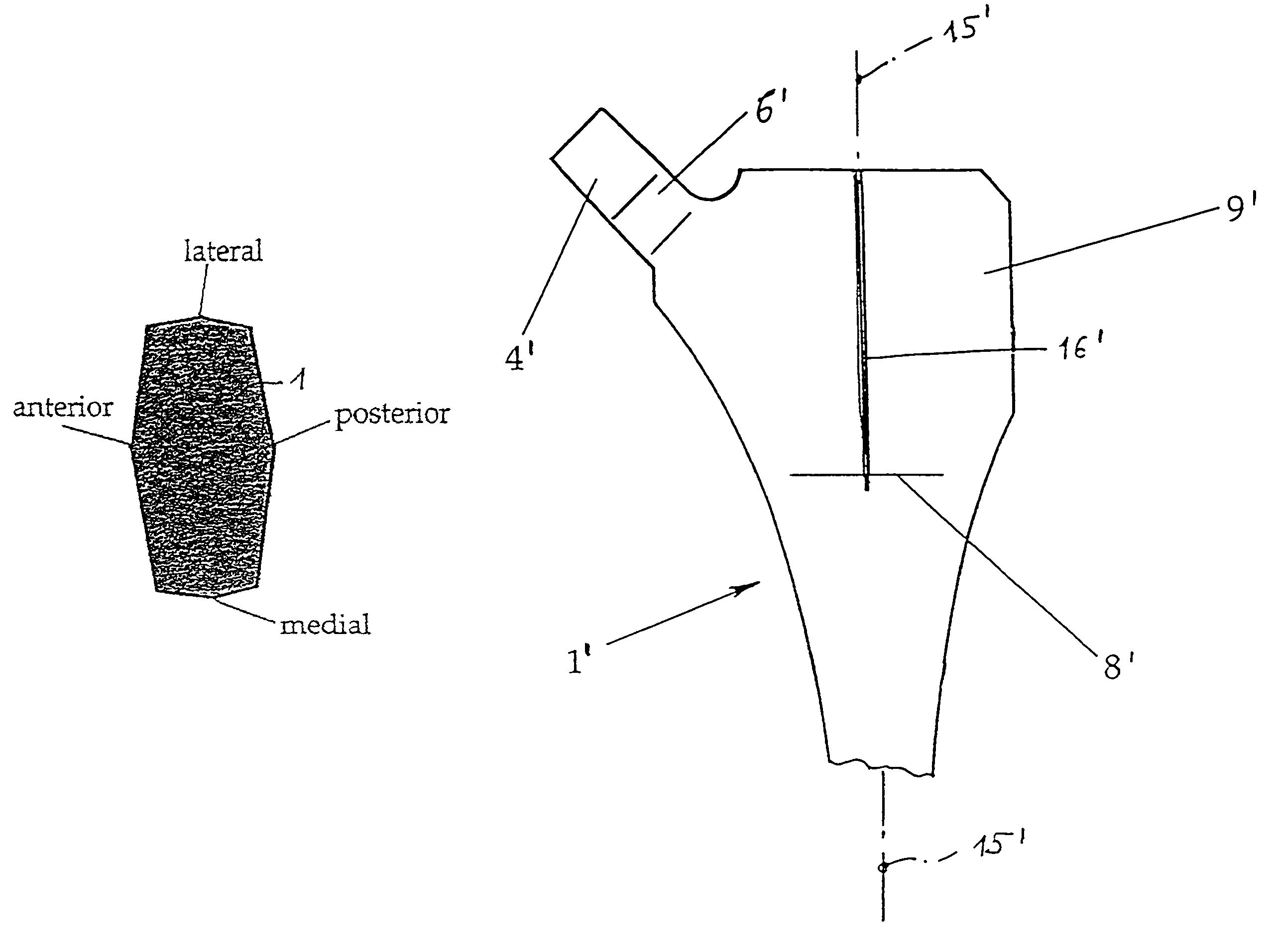
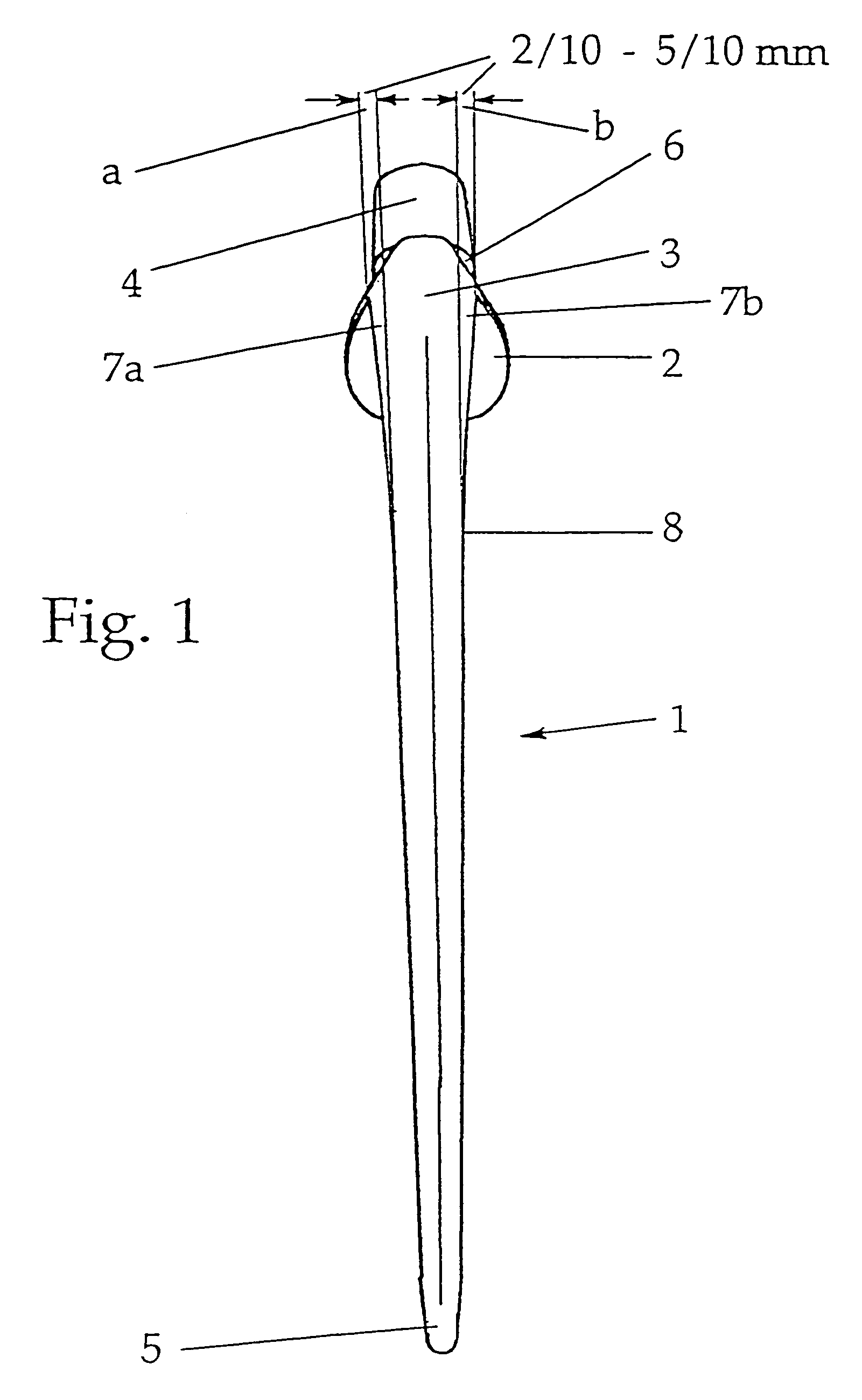
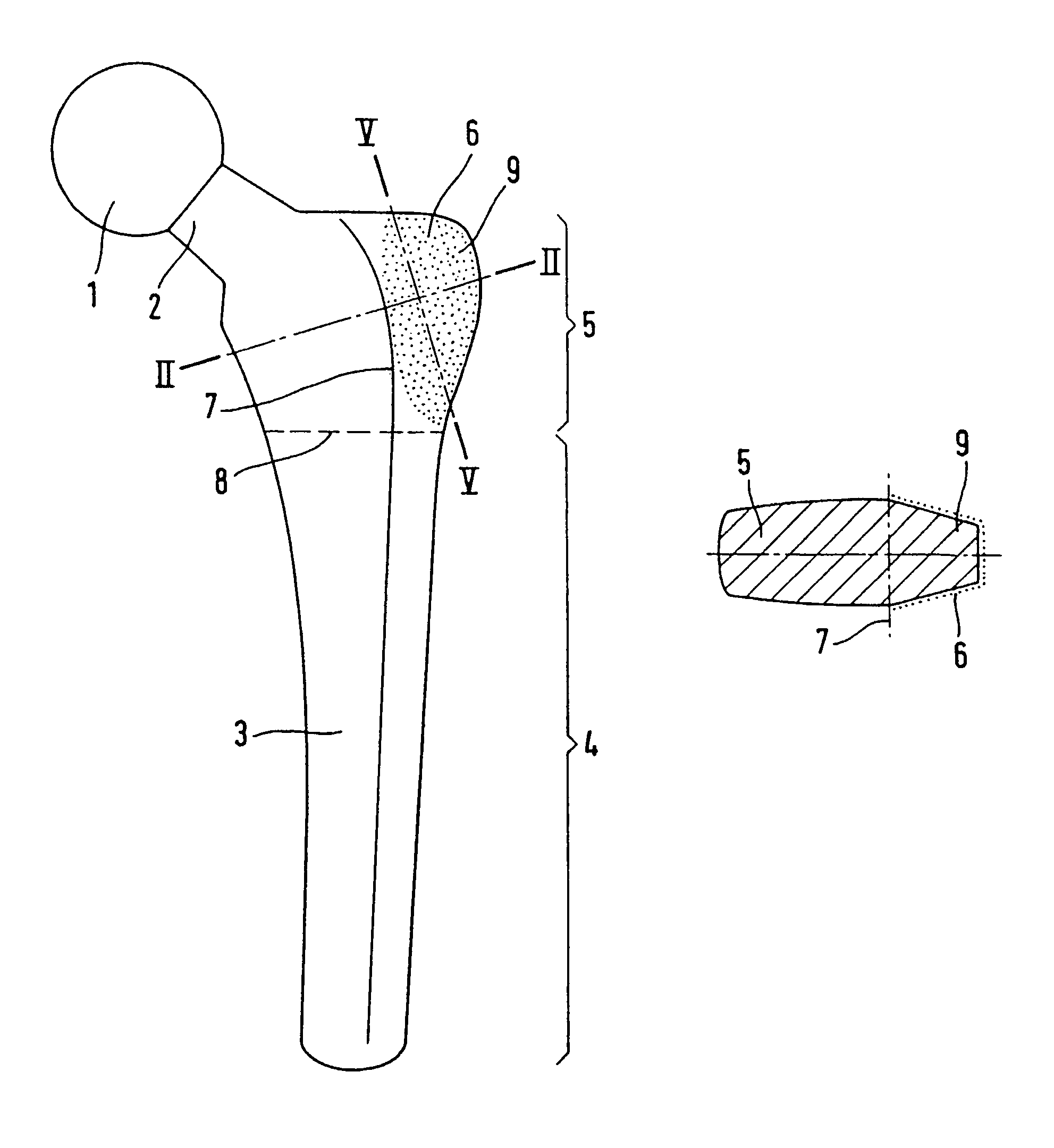
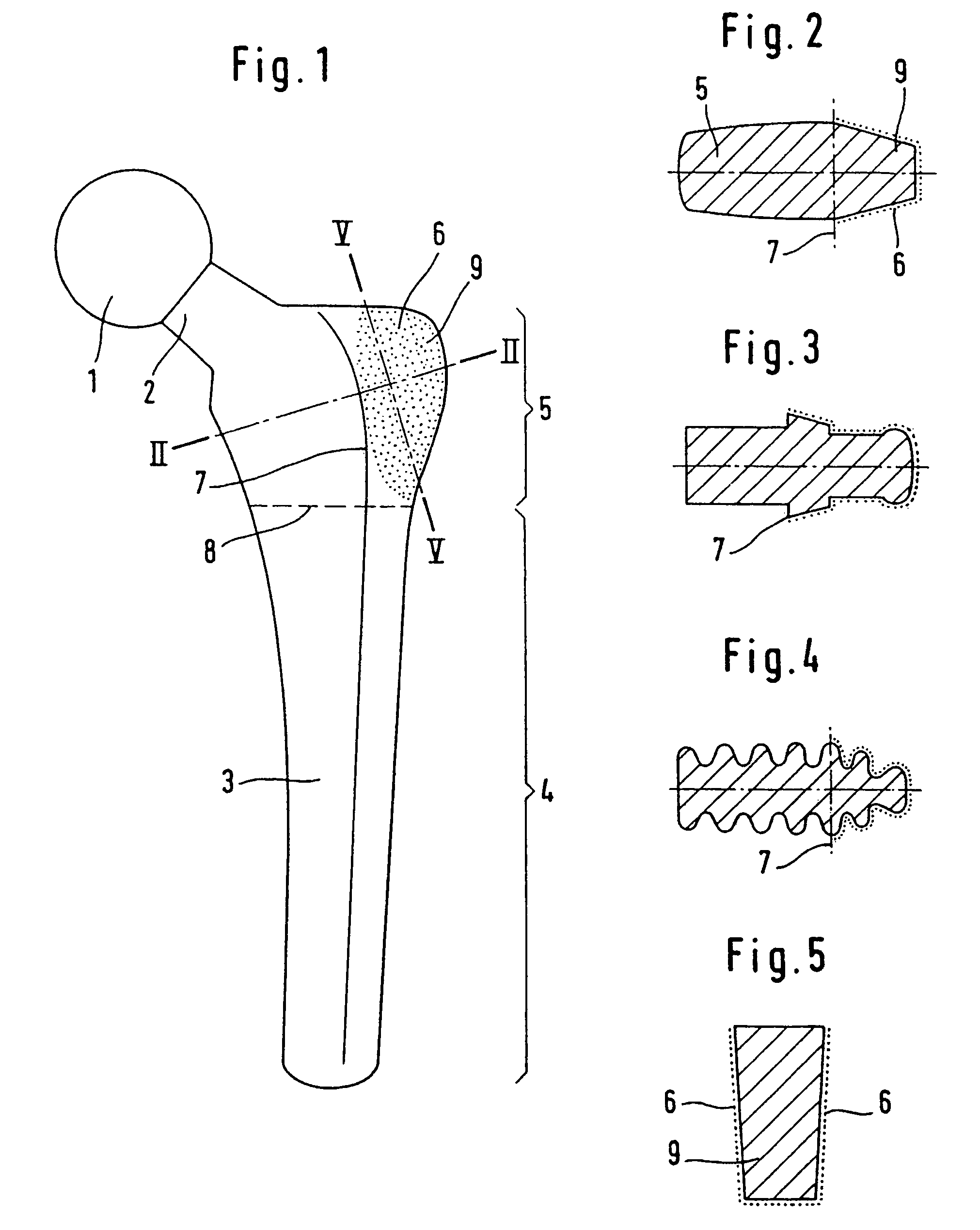
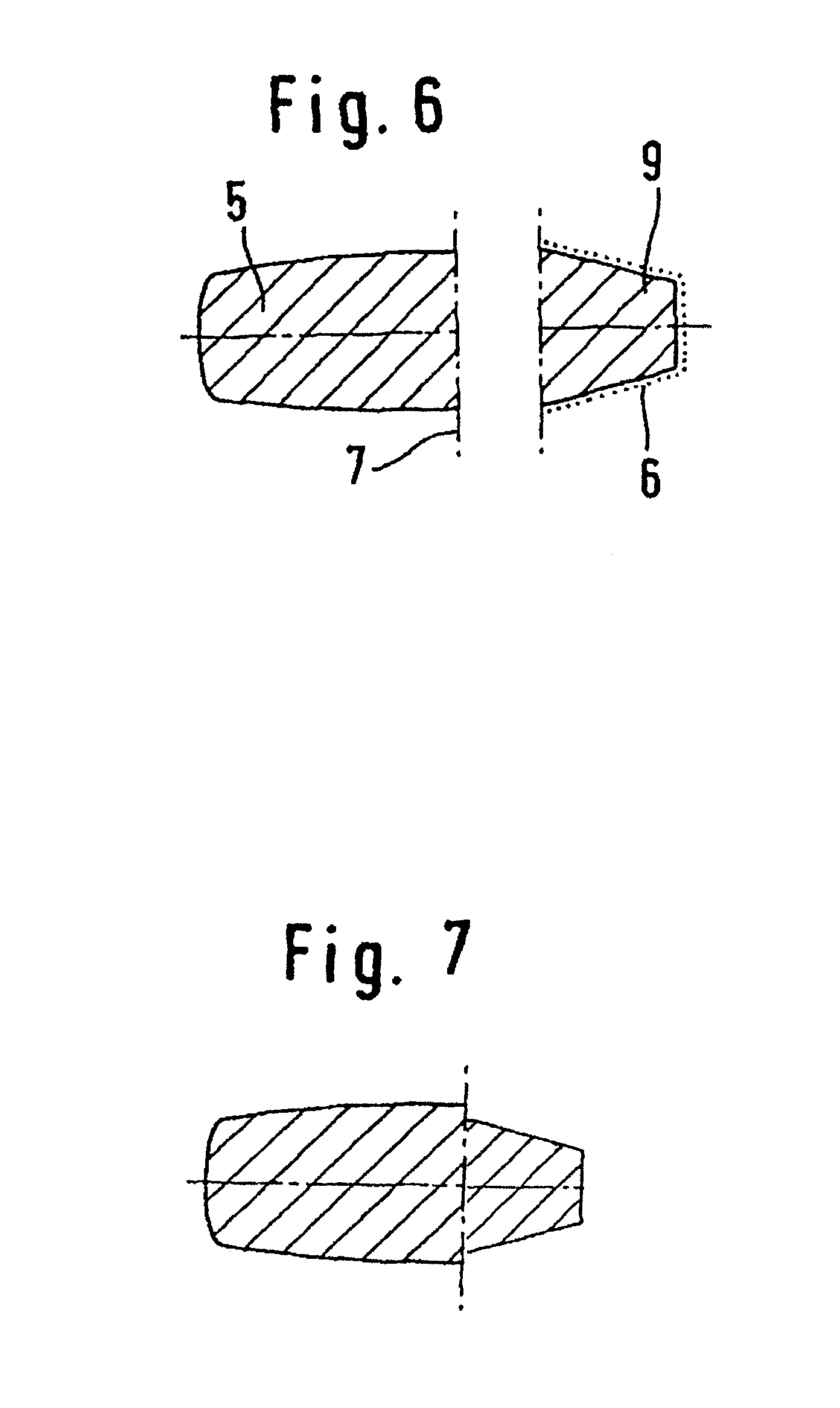
Flat shaft of a hip-joint prosthesis for anchoring in the femur
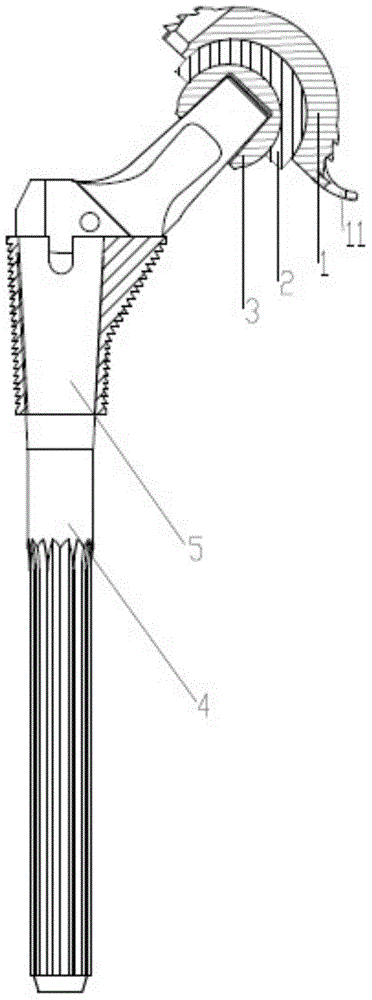
A flat shaft of a hip-joint prosthesis for anchoring in a femur. The shaft expands on all sides towards a proximal end from a distal end of the shaft and medially merges with a curved section that is continuous with a prosthesis neck. The shaft is additionally expanded in a proximal region along a proximal direction on at least one of an anterior and posterior surfaces.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Bimetal acetabular component construct for hip joint prosthesis
InactiveUS20050102034A1Superior bone-engaging faceSuperior polyethylene-engaging faceJoint implantsTissue regenerationAcetabular componentMaterials science
This invention provides a prosthetic acetabular component that comprises two constructs, one being a metal base construct that engages the bone and the other being a polyethylene bearing construct that attaches to the metal base construct and articulates with a femoral stem prosthetic component. The metal base construct is composed of two different metals, one of which engages the bone surface and the other of which engages the polyethylene bearing construct. Each of these metals is selected so that its characteristics are well suited to its particular function. The first metal is selected so as to provide a superior bone-engaging face, while the second metal is selected so as to provide a superior polyethylene-engaging face. By combining the different material characteristics of two different metals in the metal bone construct, it is possible to simultaneously form a superior bone-engaging face and a superior polyethylene-engaging face.
Owner:HAYES JR DANIEL +1
Modular femoral stem component for a hip joint prosthesis
InactiveUS7097664B2Restoring a hip jointSimple methodSurgeryJoint implantsMuscles of the hipFemoral stem
A prosthetic femoral stem component comprising a body element, a neck element and a stem element, with the body element, neck element and stem element being secured to one another with a modular connection, wherein the modular connection comprises a taper junction and an engaged-fit junction.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
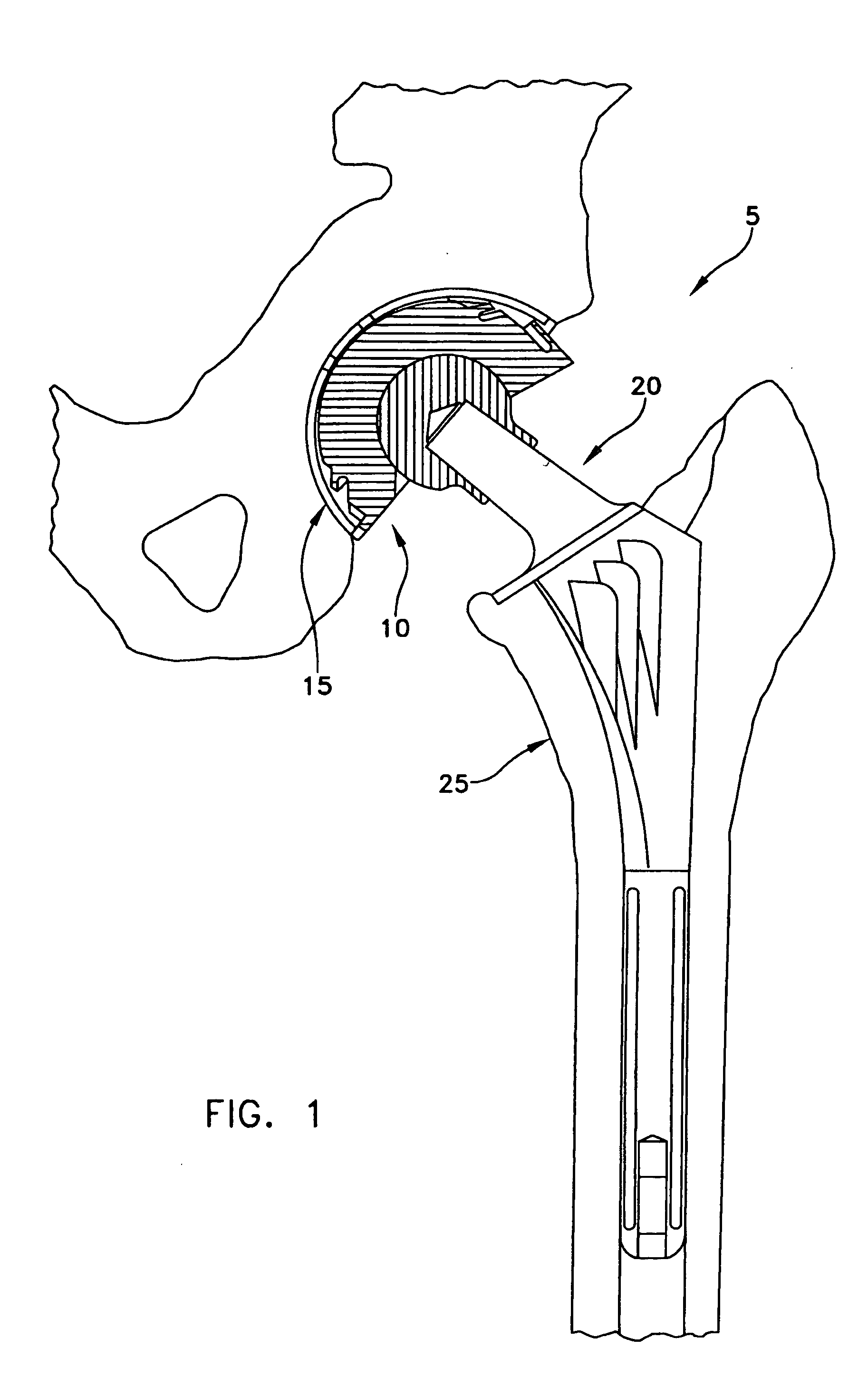
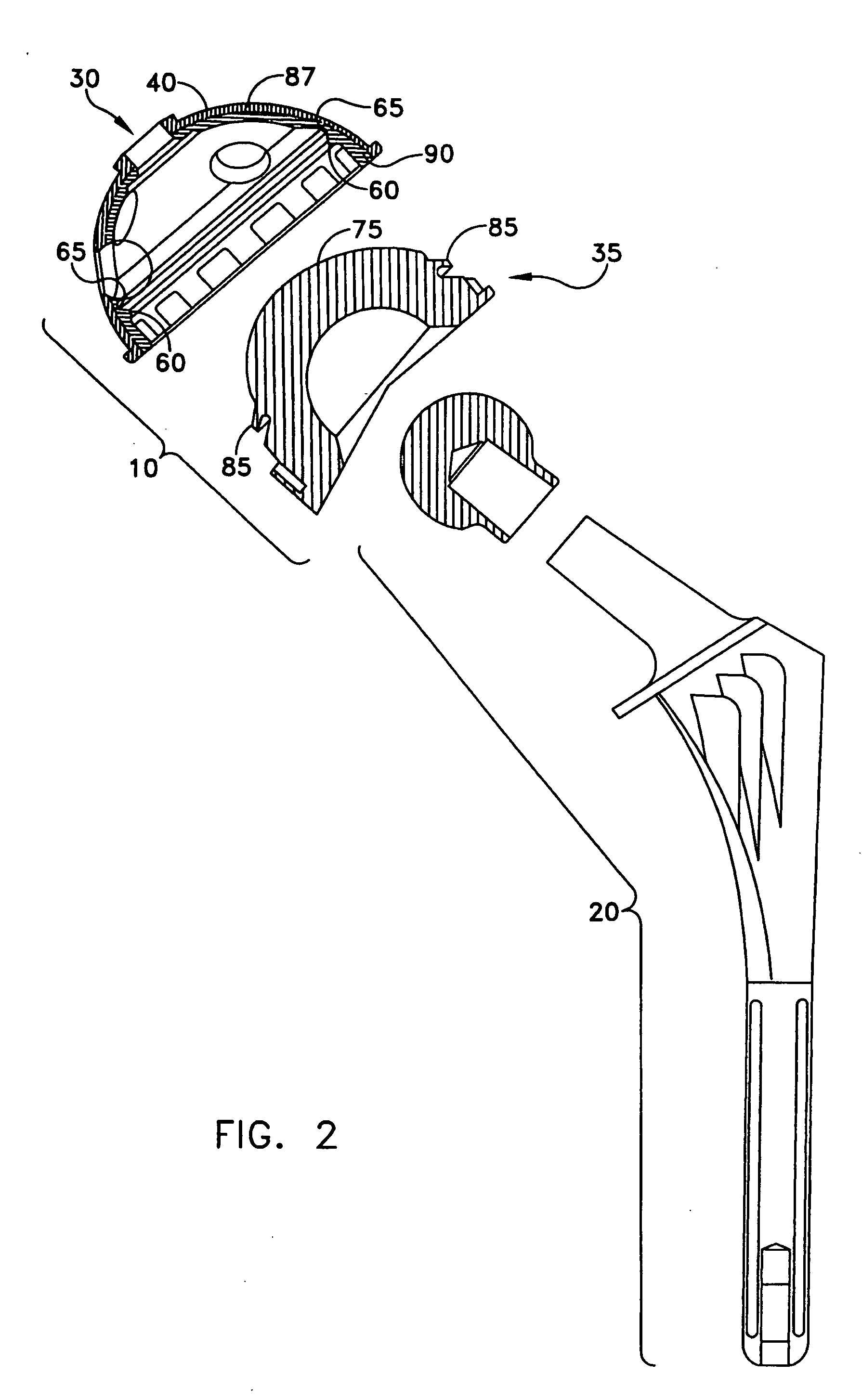
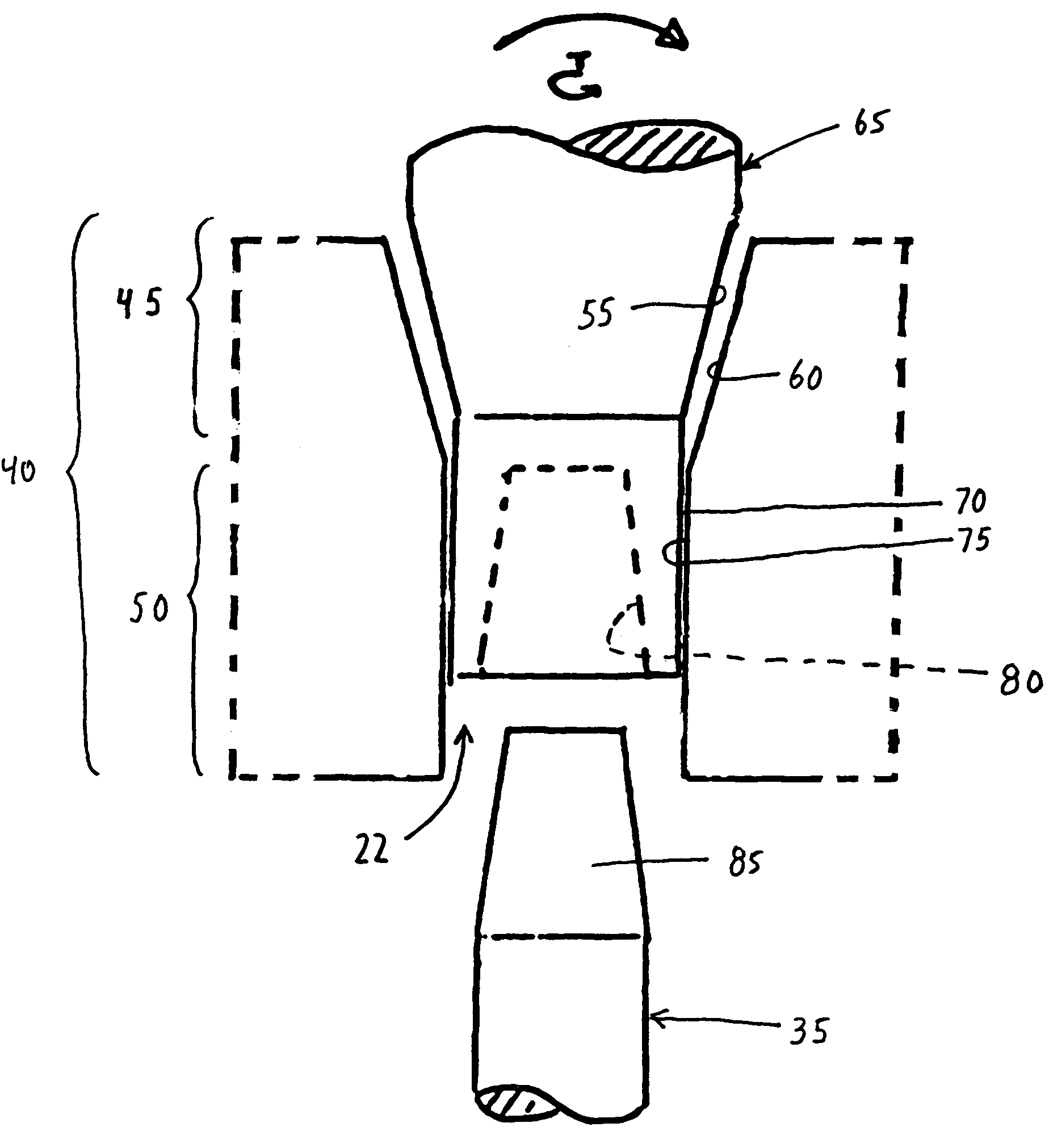
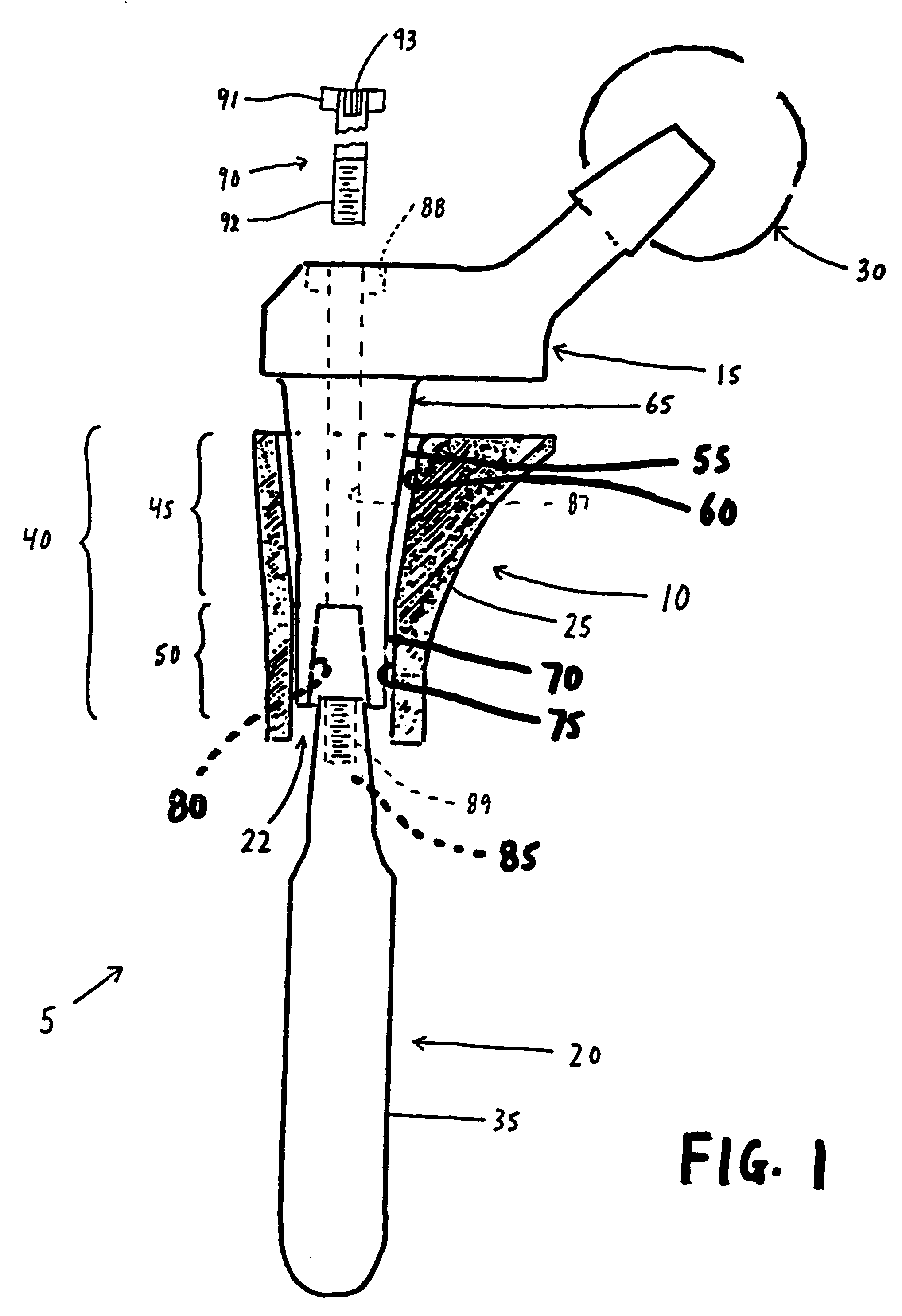
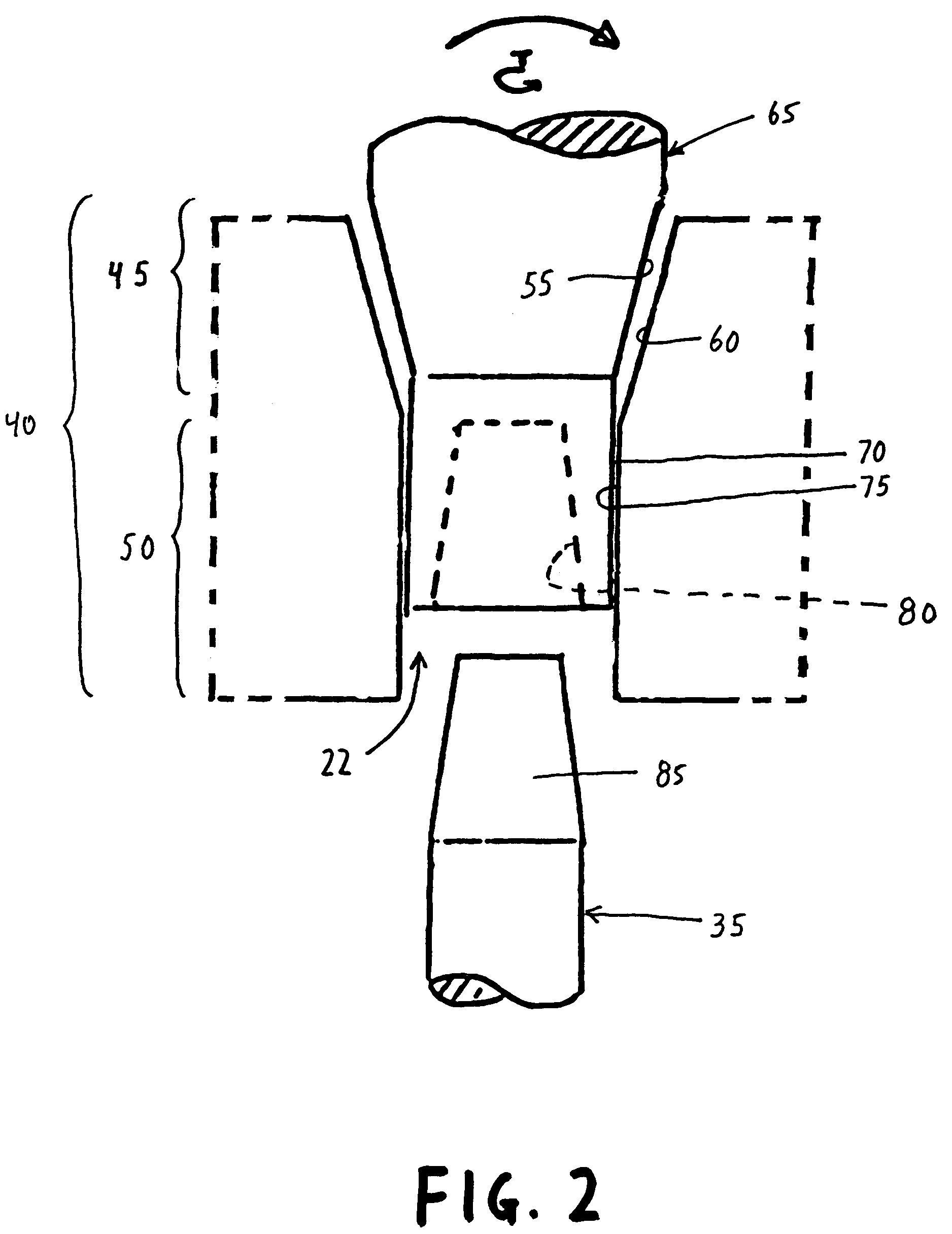
Hip joint prosthesis
InactiveUS20050033445A1Avoid loadPrevent rotationSurgeryJoint implantsBiomedical engineeringHip socket
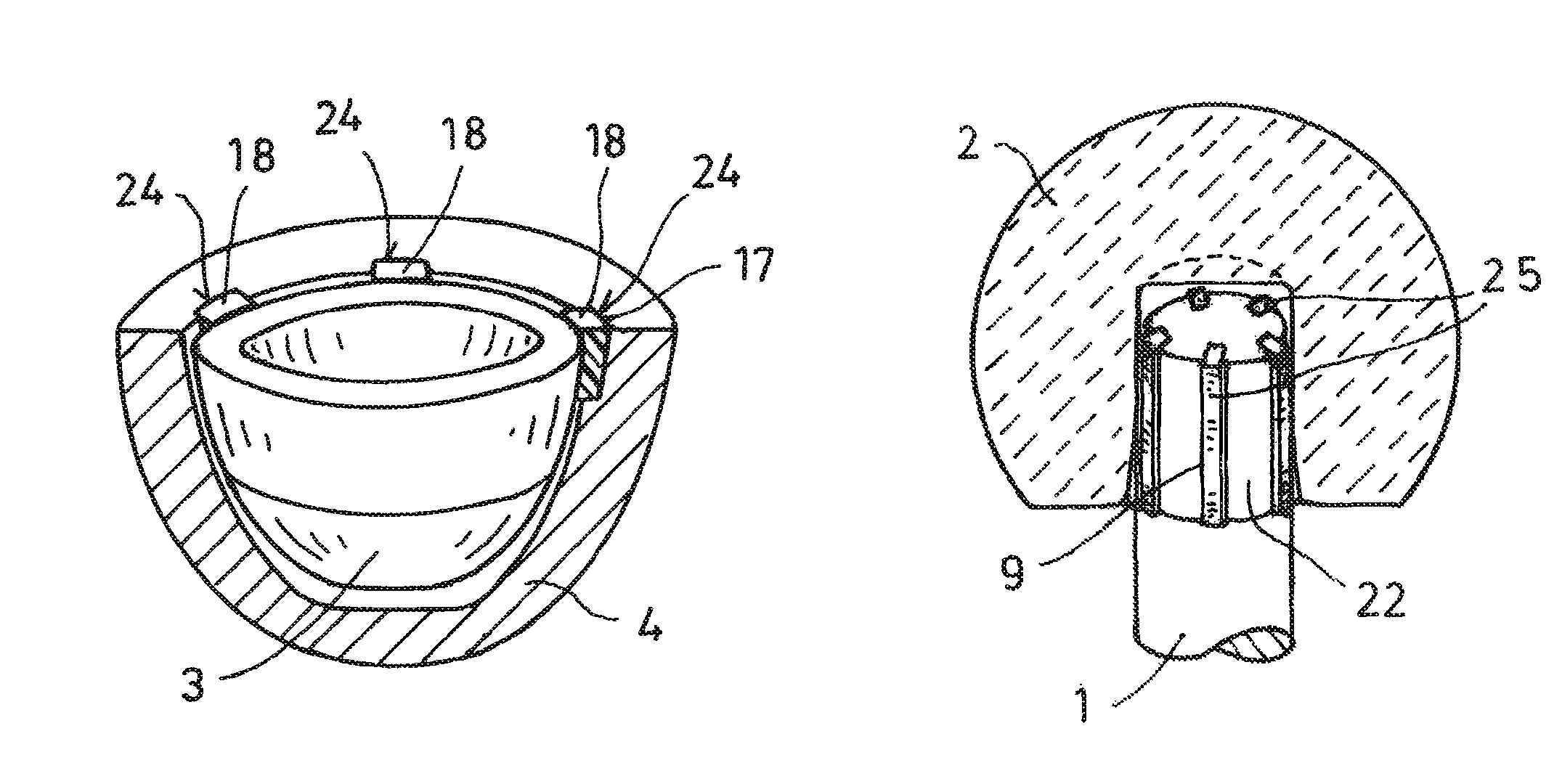
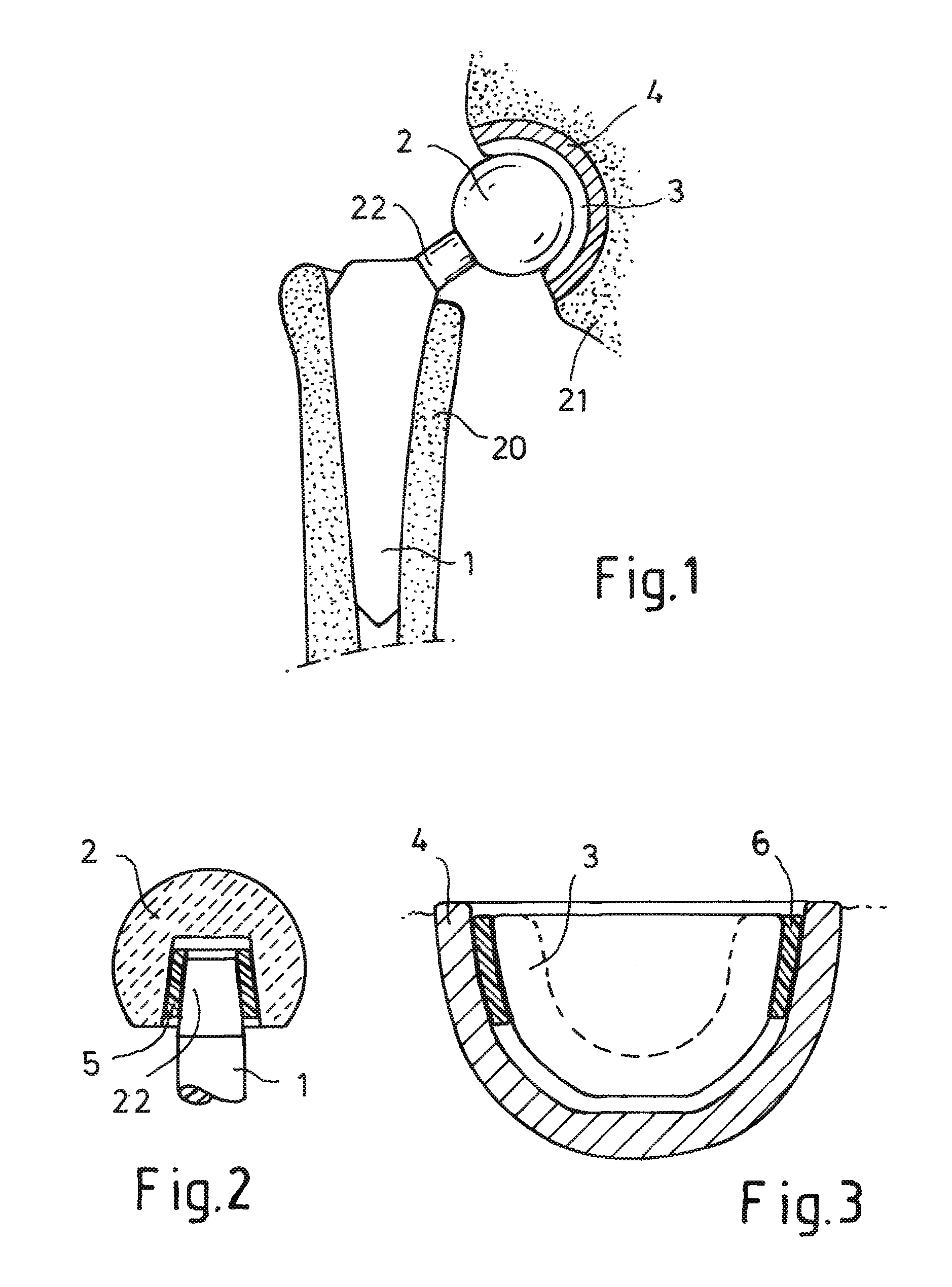
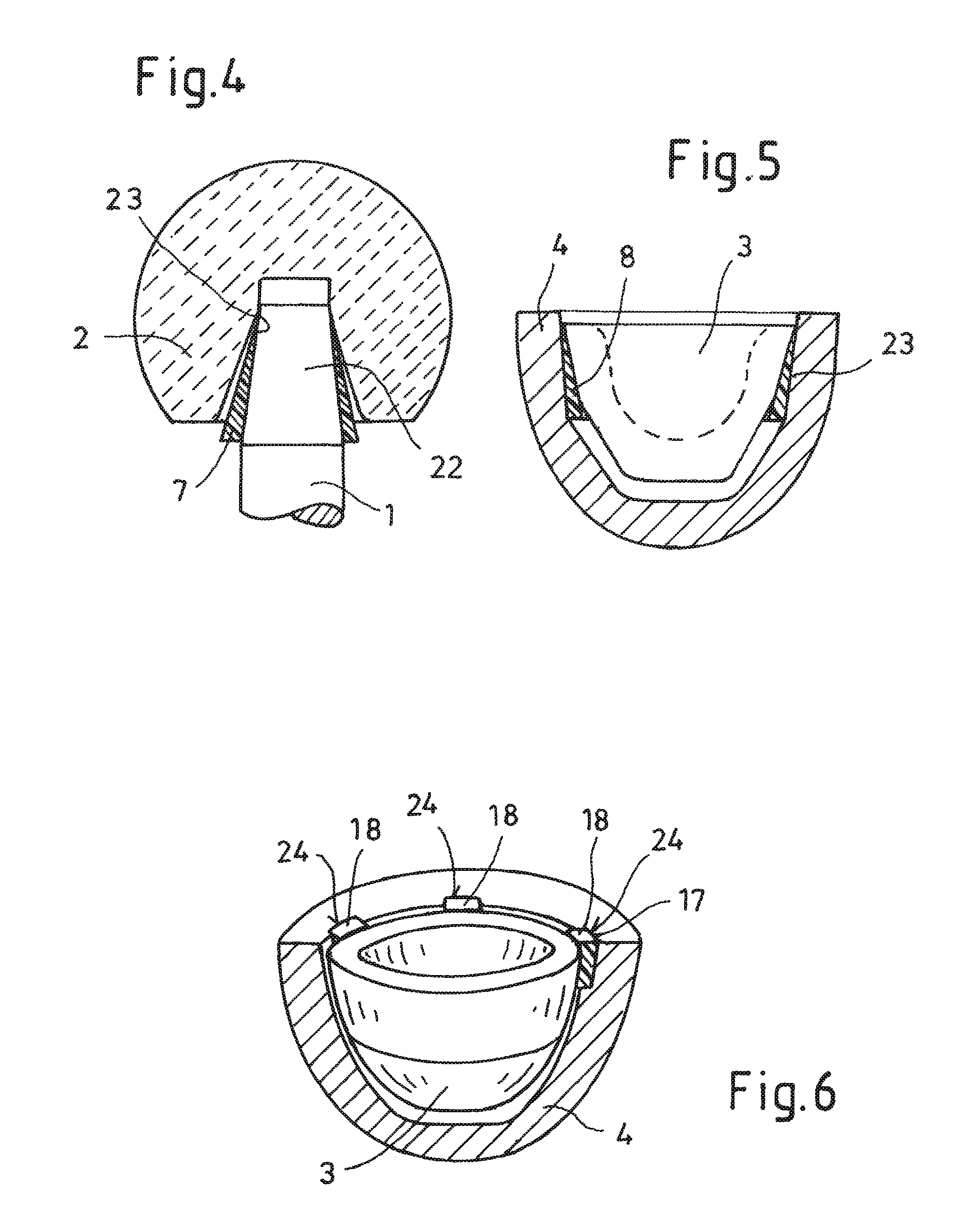
A hip joint prosthesis has a socket part and a head rotatably arranged within the socket part. The socket part has an outer side facing away from the head and the outer side has a gliding surface configured to rotatably support the socket part in a natural hip socket. The socket part is polished on the outer side for forming the gliding surface. A stop is provided on the head or on the hipbone for limiting rotation of the socket part. The socket part has an angled edge portion that is arranged in an edge depression of the hip socket and strikes on the hipbone. The rotation of the socket part is limited in this way.
Owner:SIEBEL THOMAS
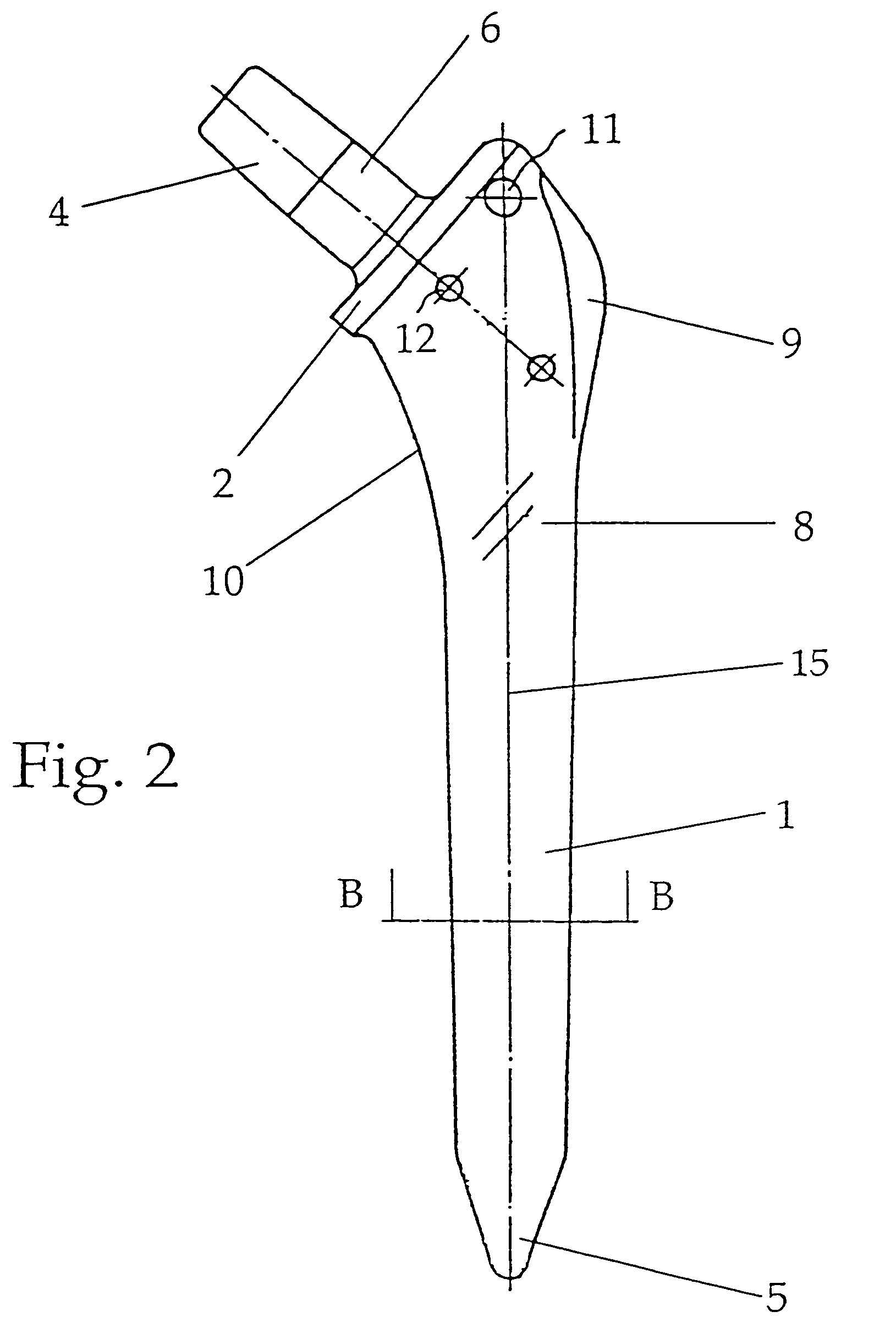
Shaft for anchoring a hip joint prosthesis in the femur
InactiveUS7004973B2Improve fitReduce empty spaceJoint implantsFemoral headsSpherical jointBody of femur
A profiled shaft for anchoring a hip-joint prosthesis in the femur is disclosed, with a shaft section and a fixation section that is formed at the end of the shaft section and that serves for the fixation of a spherical joint head, wherein the shaft section on the lateral surface in the proximal region merges with a trochanter wing at the edges of which beveled surfaces are formed. The essential point of the invention is that the angle formed between the plane of a beveled surface the plane of the adjacent surface is smaller than 135° and larger than 90°. In a construction of this kind the advantage of an improved filling of the empty space in the trochanter-wing region is achieved.
Owner:PLUS ORTHOPEDICS
Minimally invasive surgical tools for hip prosthesis
InactiveUS20120290099A1Effective installationLess invasiveSurgeryJoint implantsMedial partReoperative surgery
Instrumentation for a modular prosthesis having a stem and a neck comprises a handle and an adaptor. The handle extends along an axis. The handle has a distal end and a proximal end. The proximal end has a blunt surface configured to be struck. The adaptor has a male end configured to mate inside the bore of the stem. The adaptor further has a surface configured to mate with the distal end of the handle. The adaptor is configured to have a medial portion and a lateral portion. The medial portion has a relief such that the adaptor is configured to disengage the stem when the adaptor is rotated relative the stem.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
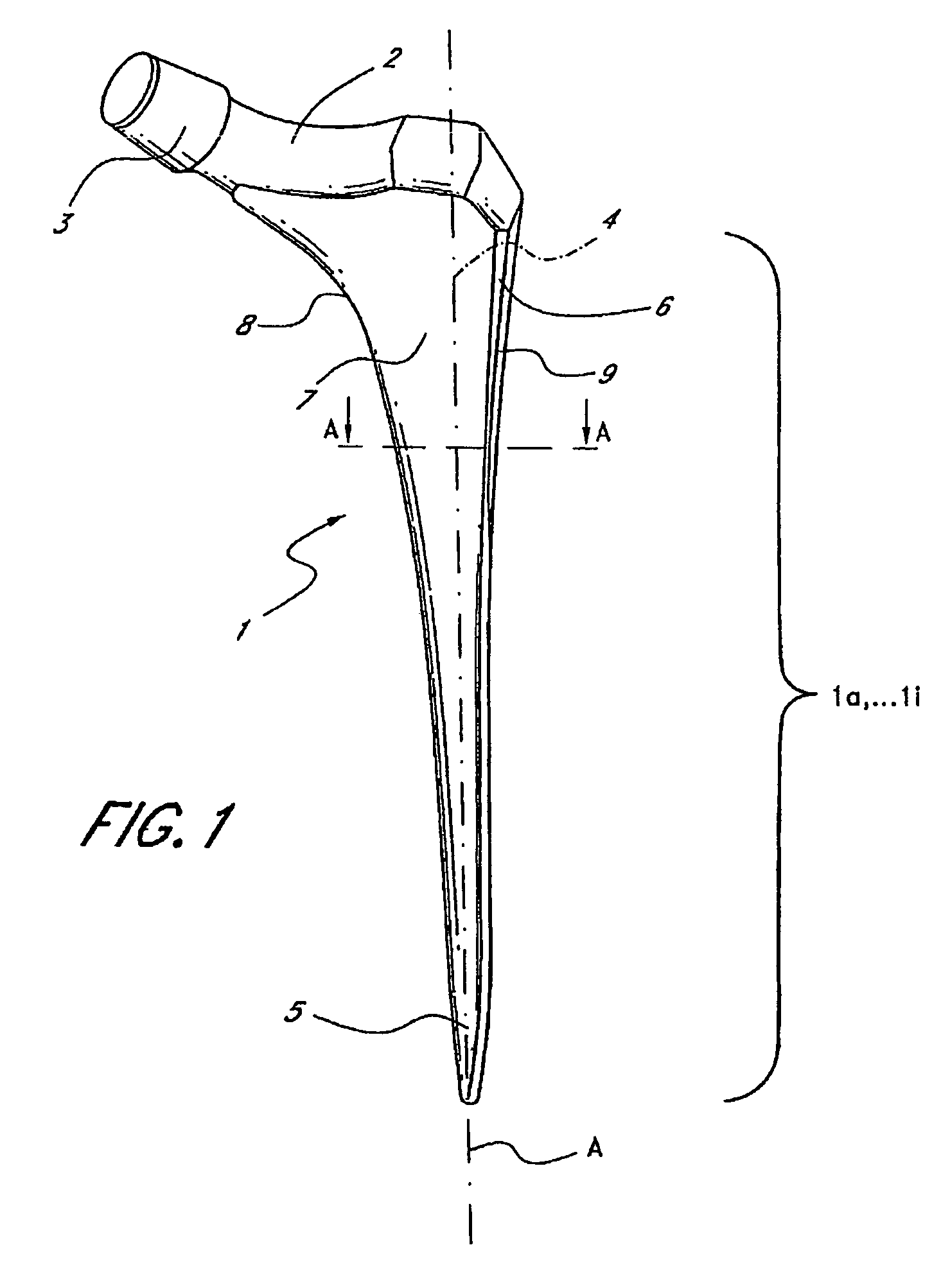
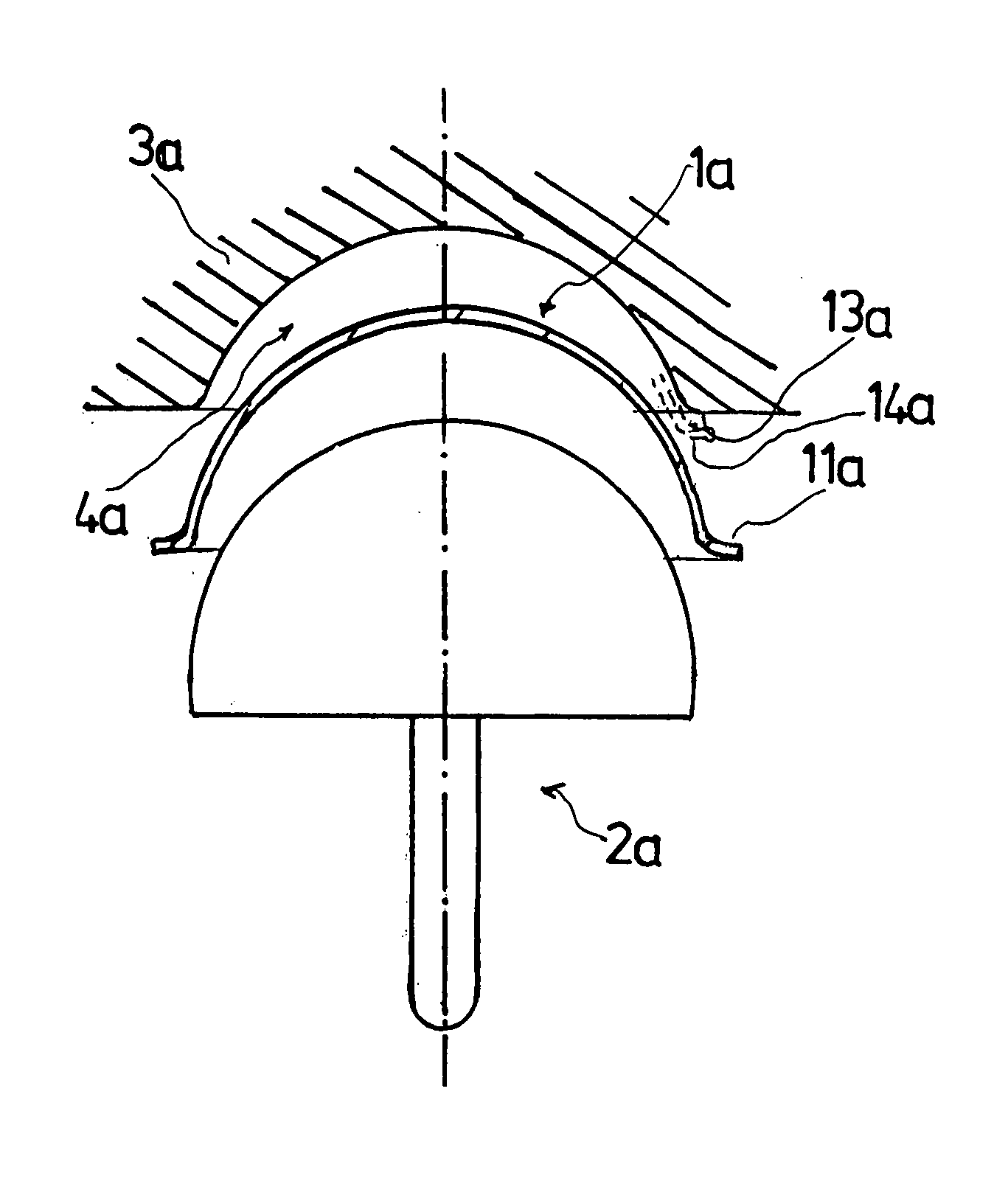
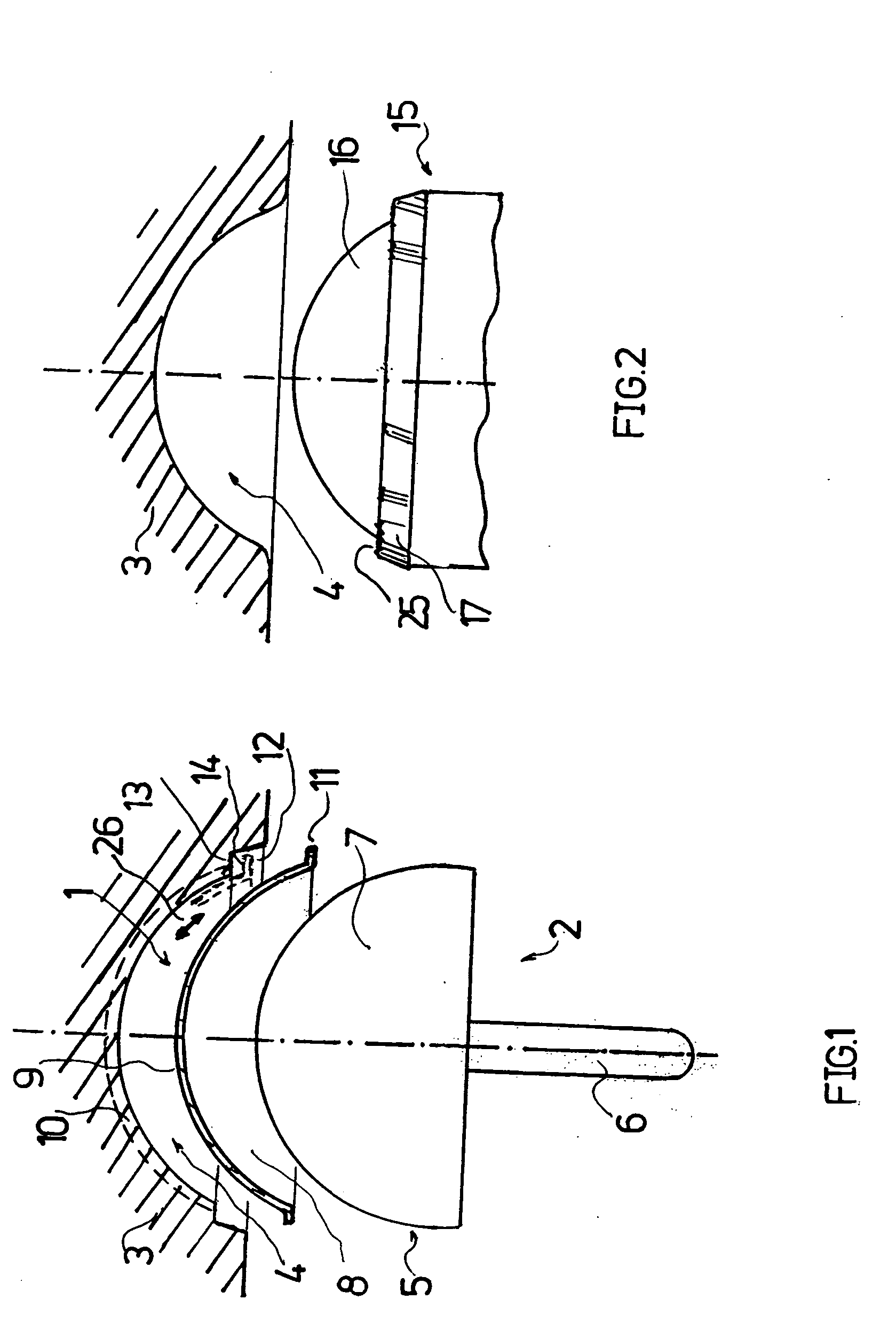
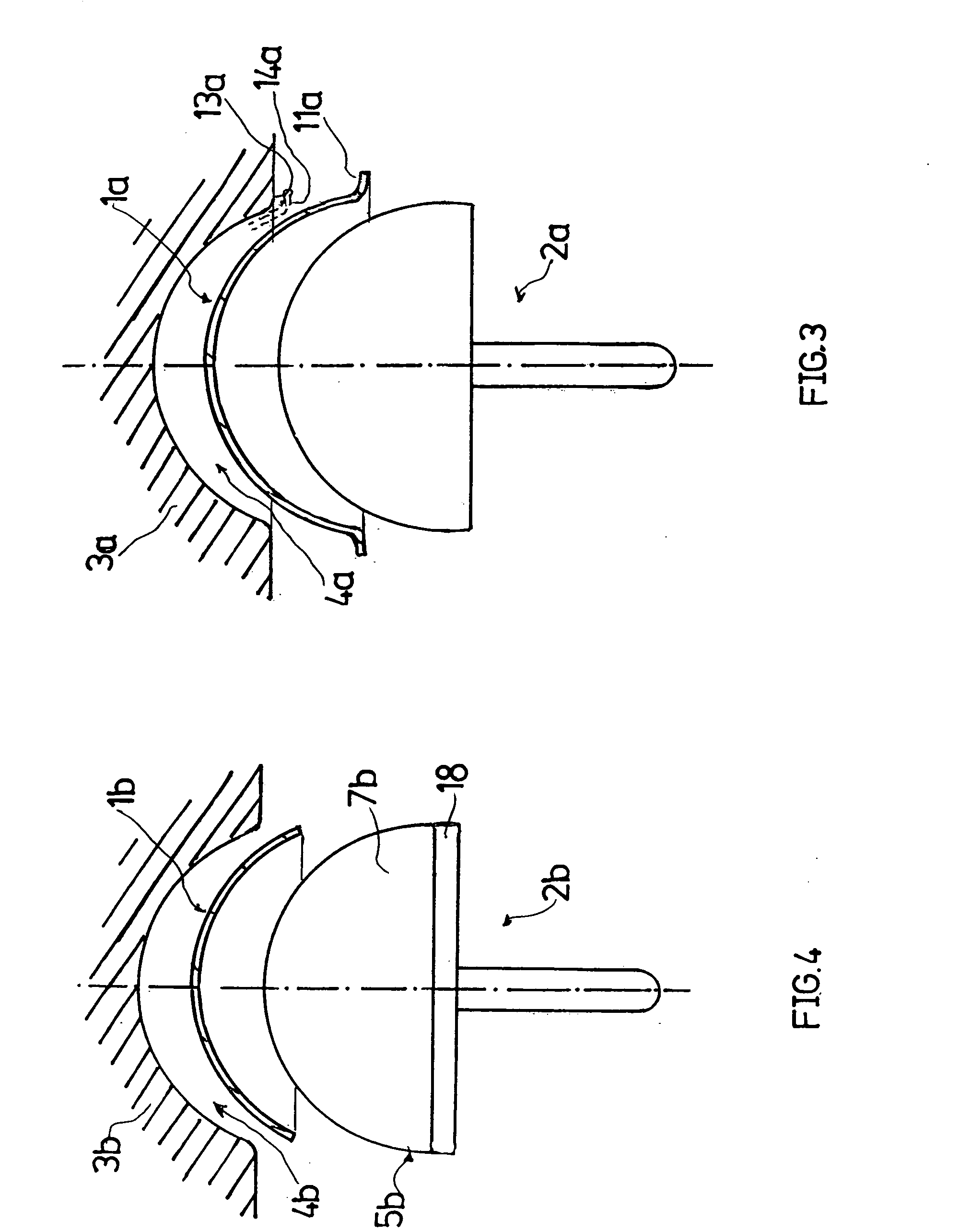
Leaflike shaft of a hip-joint prosthesis for anchoring in the femur
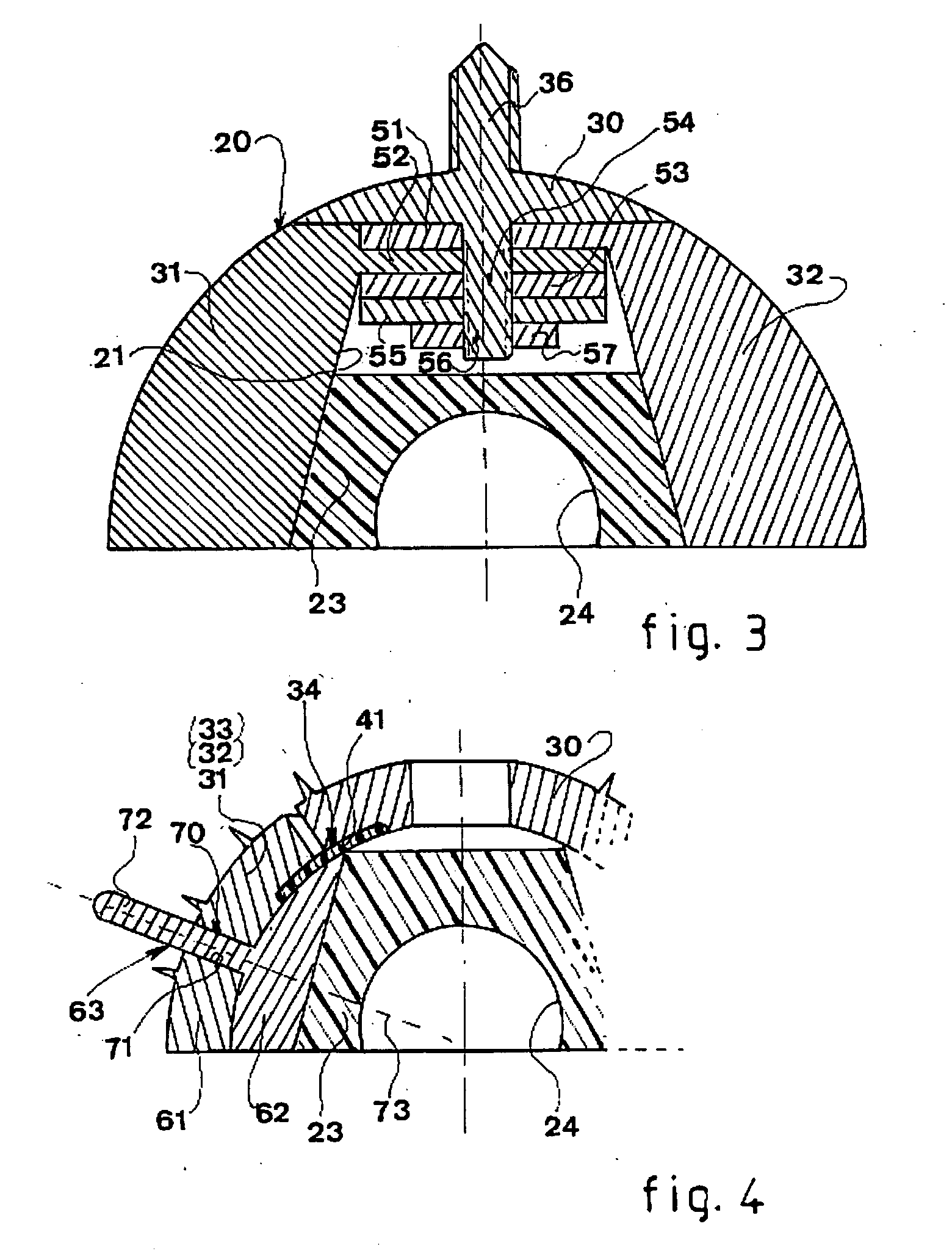
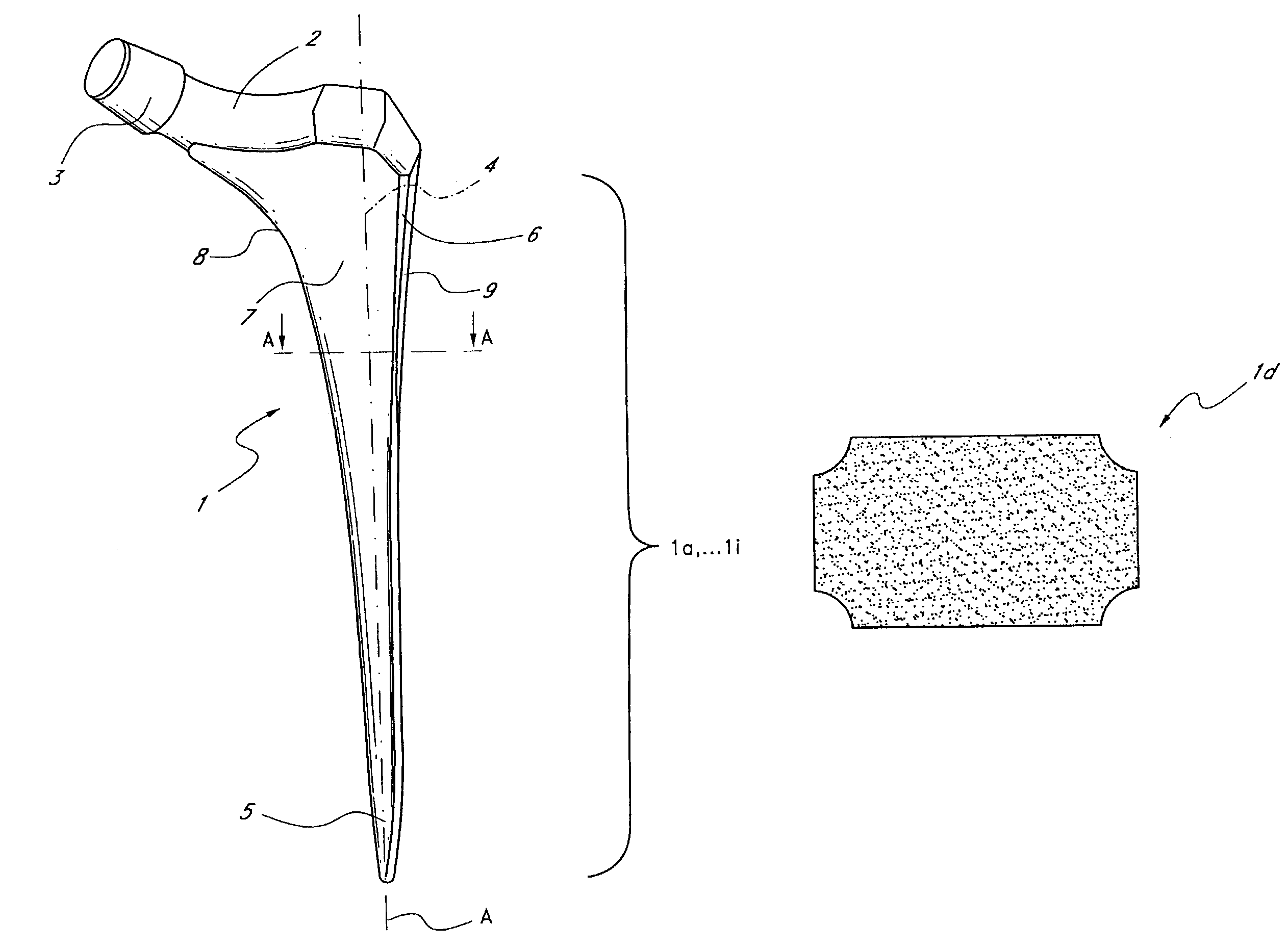
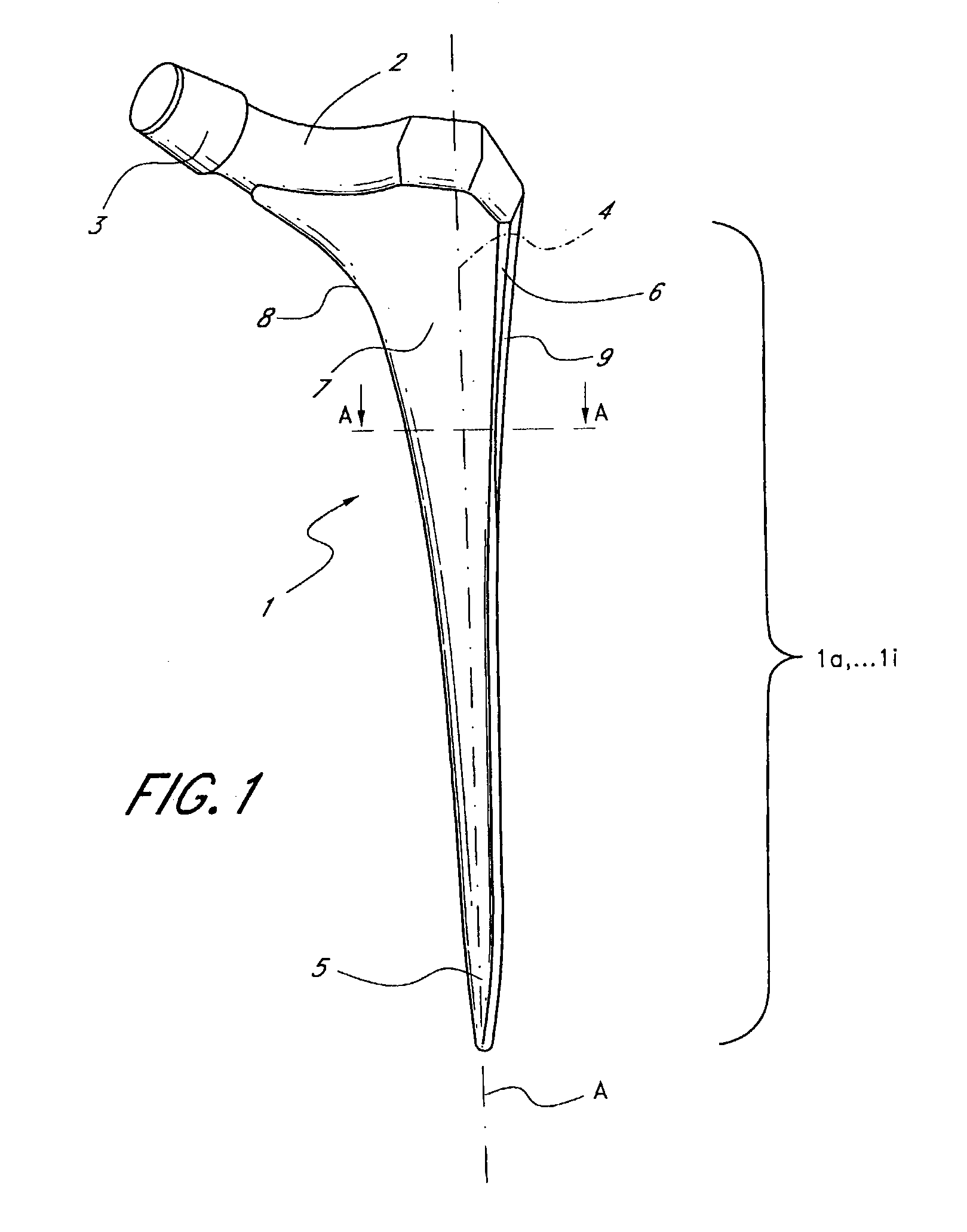
InactiveUS7455693B2Long-term and firm retentionAdvantageous for revascularizationSurgeryJoint implantsMuscles of the hipLong axis
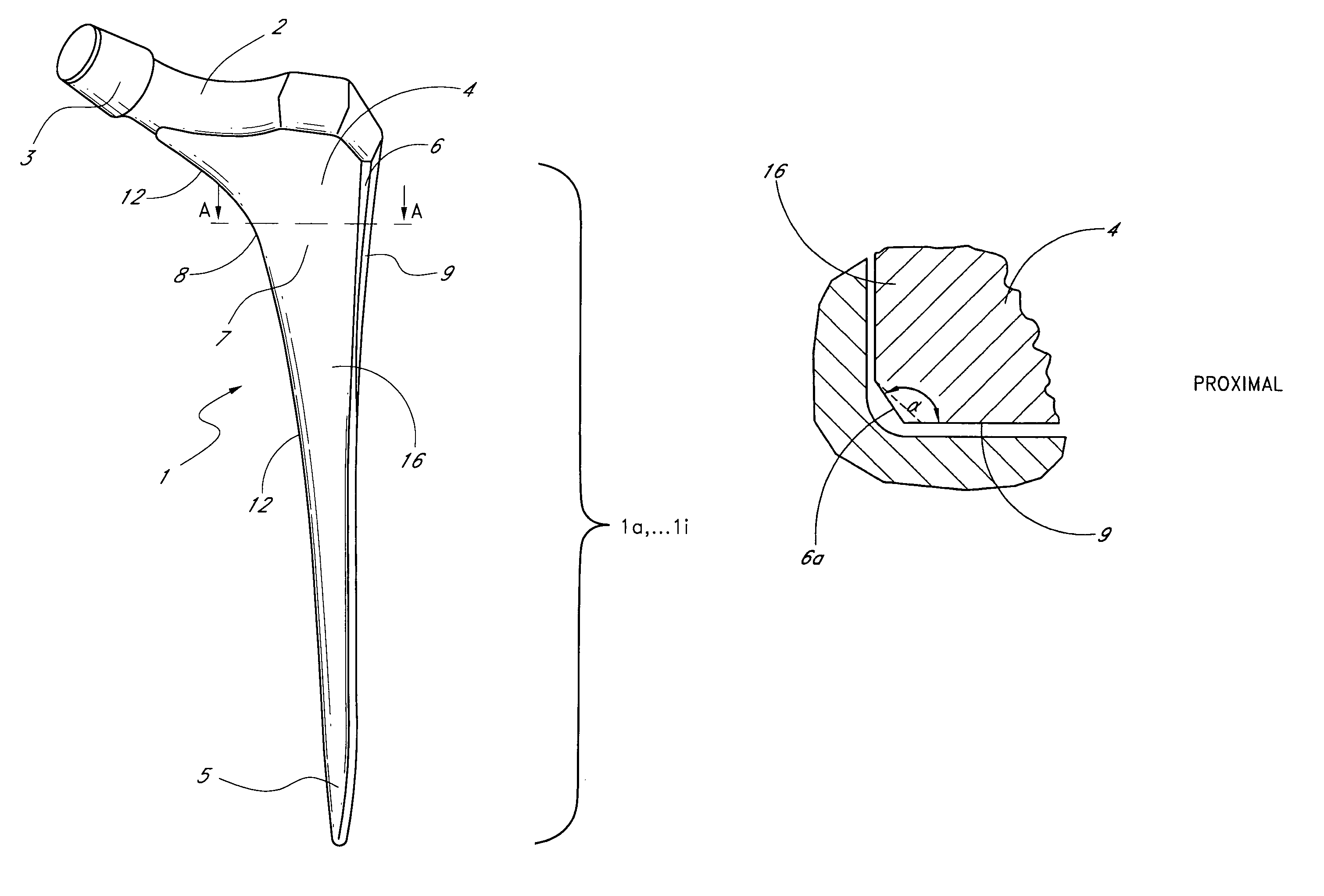
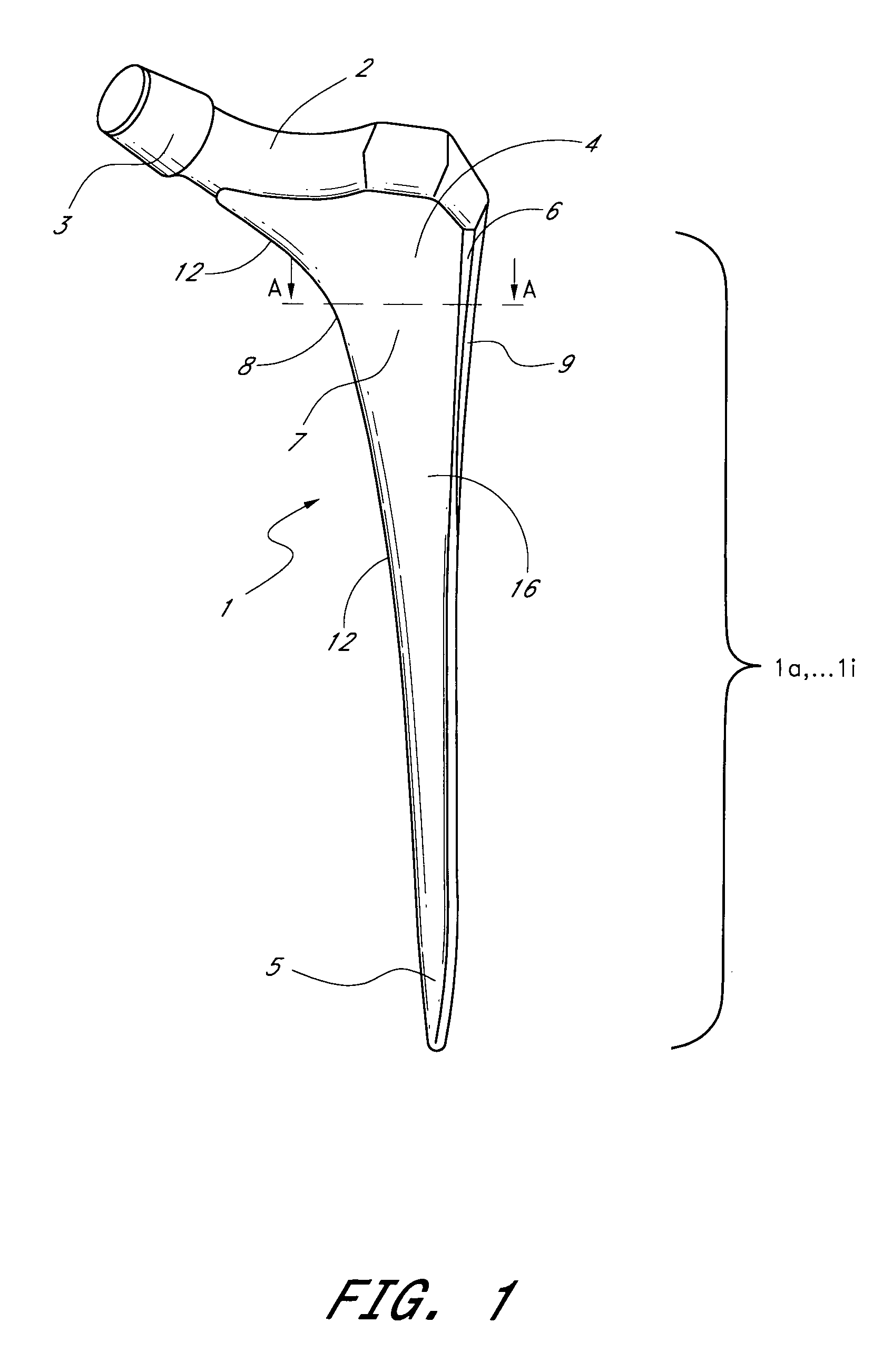
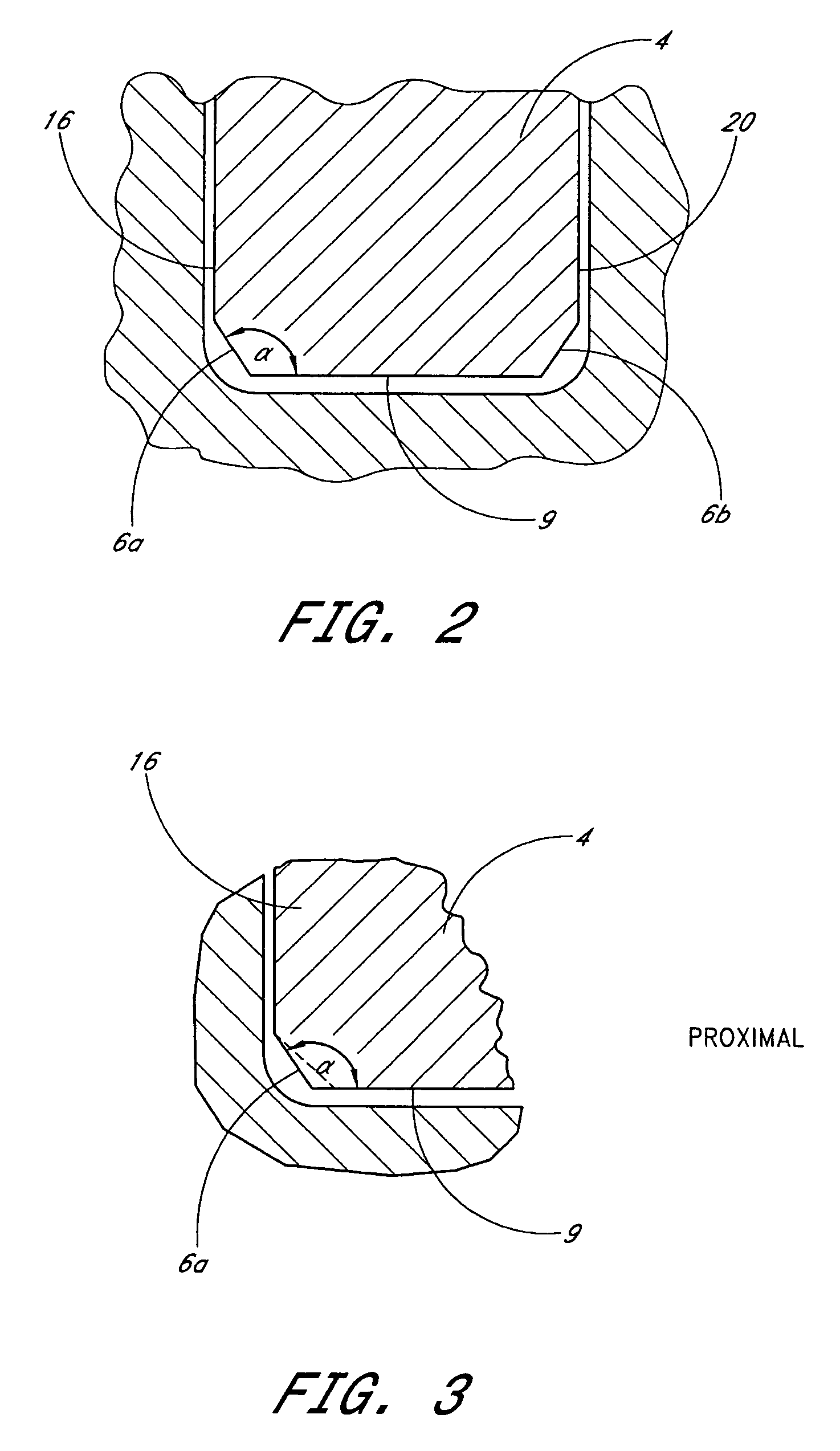
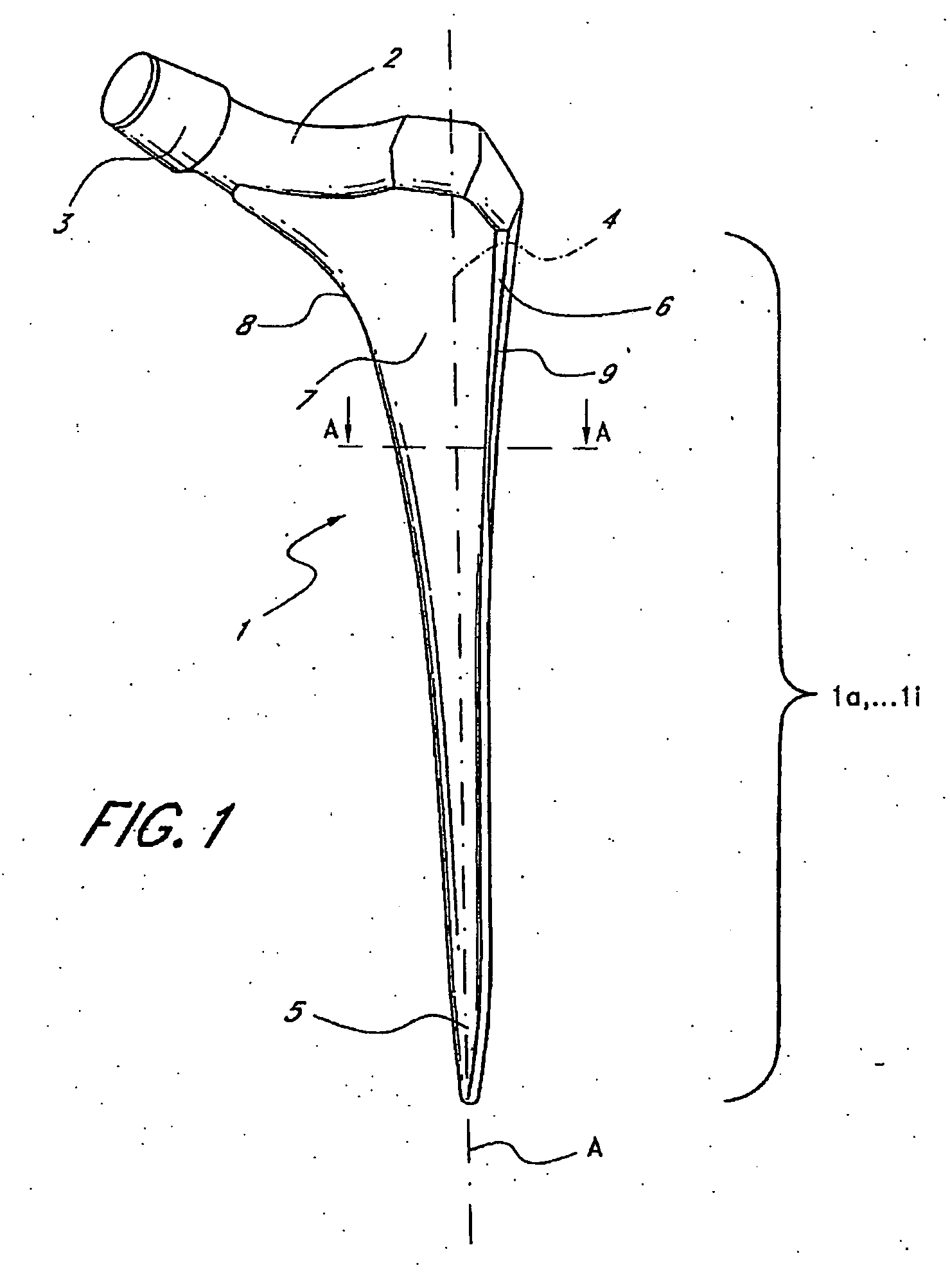
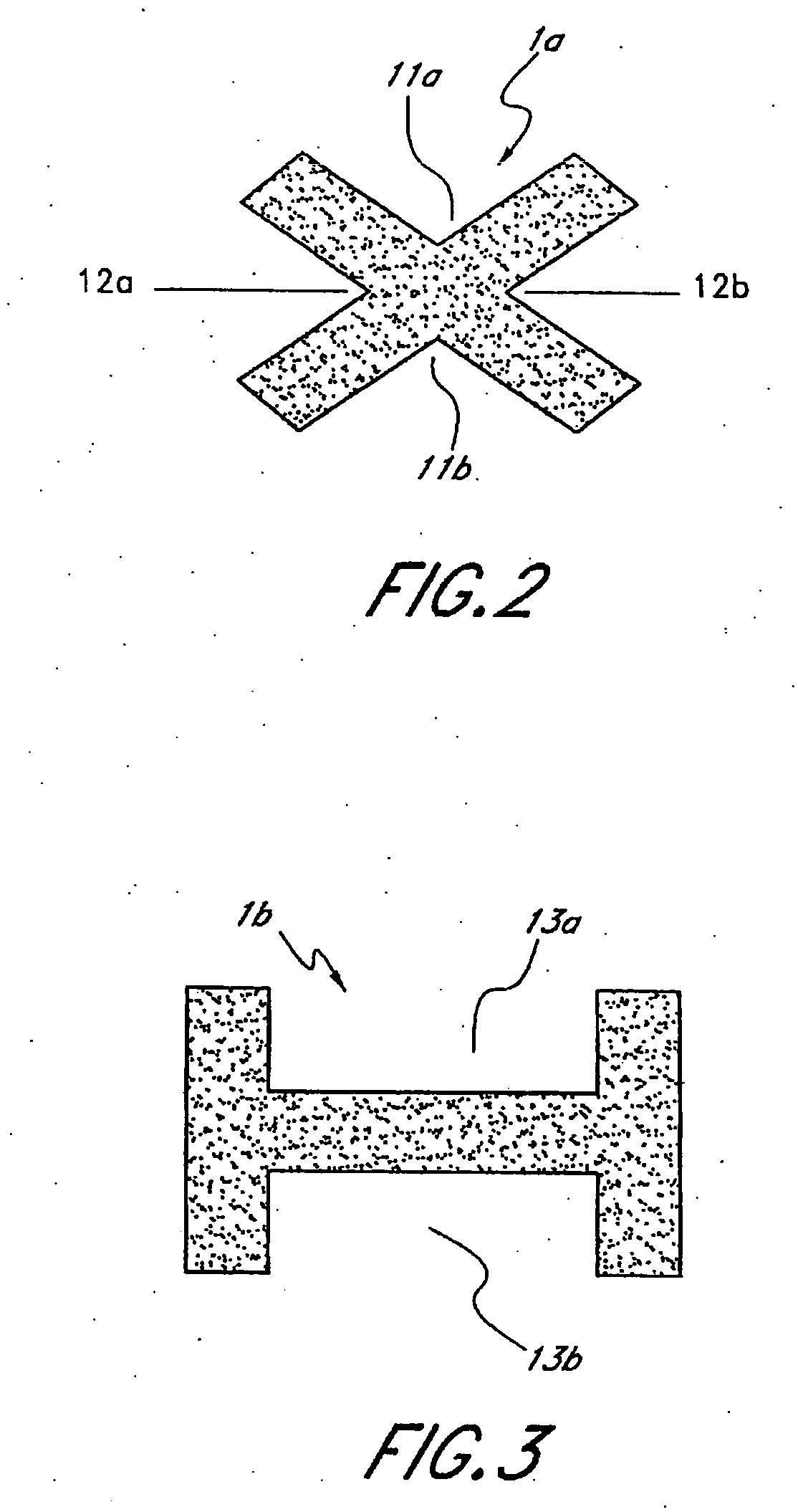
Leaflike shaft (1) of a hip-joint prosthesis for anchoring in the femur, according to a towards a distal end (5), with a femur-anchoring section (1a, . . . 1i) having a long axis (A) and with a prosthesis neck (2), wherein the femur-anchoring section (1a, . . . 1i) has a substantially rectangular external contour in a plane perpendicular to the long axis (A), optionally with recesses in the side edges and / or at the corners.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Surgical tool holder for facilitated sterilization
ActiveUS7976548B2Avoid separationEasy to sterilizeControlling membersMechanical apparatusEngineeringSurgical department
Owner:VIANT AS&O HLDG LLC
Insertion of vibration-damping elements in prosthetic systems for the manipulation and damping of natural frequencies
InactiveUS8226728B2Reduce sound pressureLess disturbingAnkle jointsJoint implantsSpherical recessHip socket
Owner:CERAMTEC
Temporary, modular, hip joint with neck-length modification mechanism
InactiveUS20160262912A1Increase pressureIncrease or decrease lengthJoint implantsFemoral headsCoxal jointPinion
A temporary neck for a hip joint prosthesis comprising a mechanism that will allow the length of the temporary neck to be varied while in place, during implant surgery and after the stem and base of a permanent prosthesis have been positioned. In one best mode the variation in length is driven by rotating a pinion gear that engages a rack gear connected to the interior of the side walls of a moveable unit, and the ball is connected by a stud to the front wall of the moveable unit; thus the ball moves the same distance as the moveable unit, and that distance is a direct function of gear tooth spacing and number of rotations of the gear. In an alternative mechanism, a threaded drive axle (worm gear) moves in response rotation an adjustment base (wheel gear) in which the base comprises a drive disk with a female, threaded bore. The axle is secured to the pressure disk at one end and free at the other. The position of the drive disk (hence bore) is static; thus as the drive disk rotates and the threads are engaged, the pressure disk moves and the ball moves with it. Both devices include visual references to determine precisely the distance that has been traveled (generally in mm).
Owner:BURNIKEL BRIAN G +1
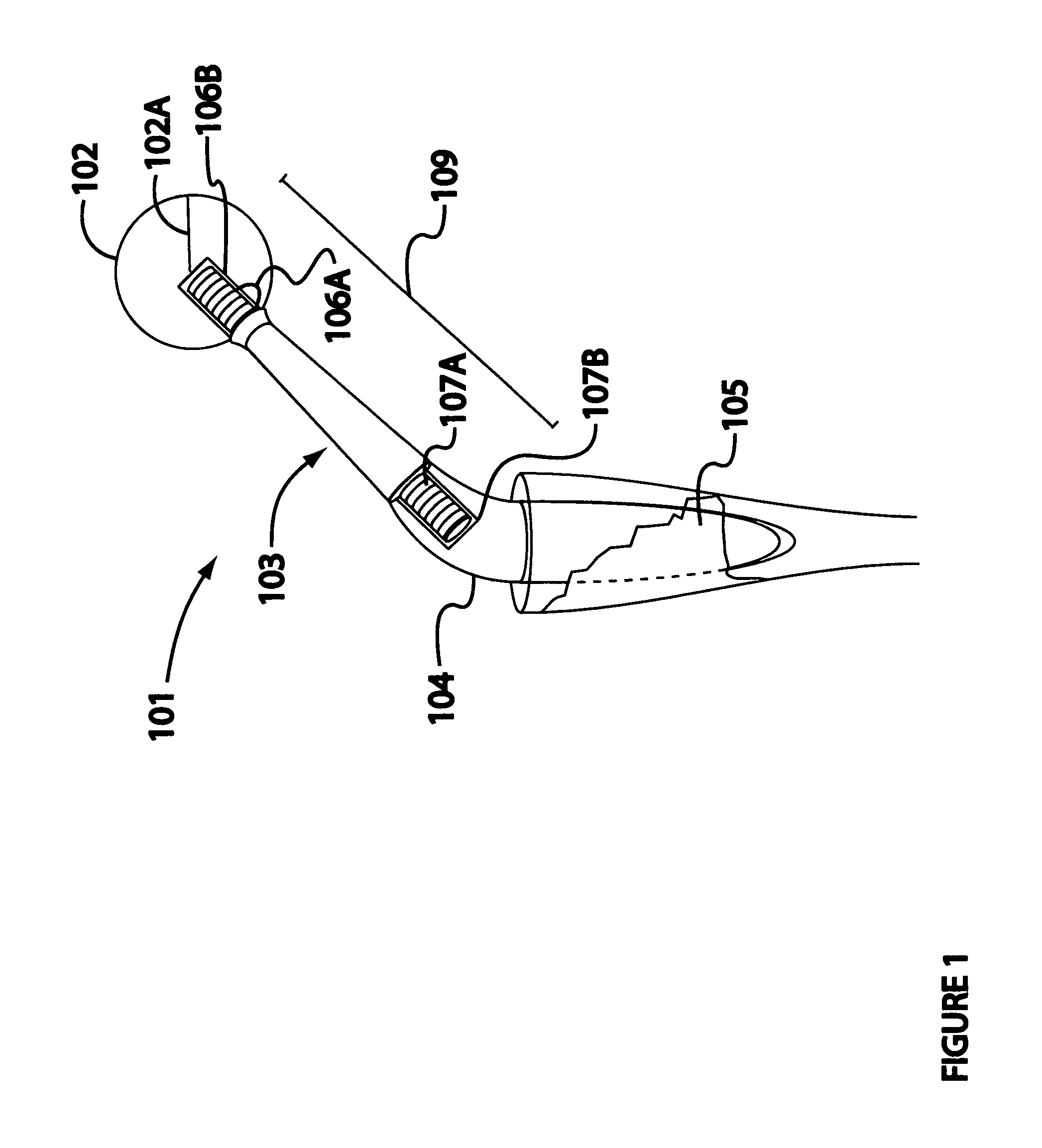
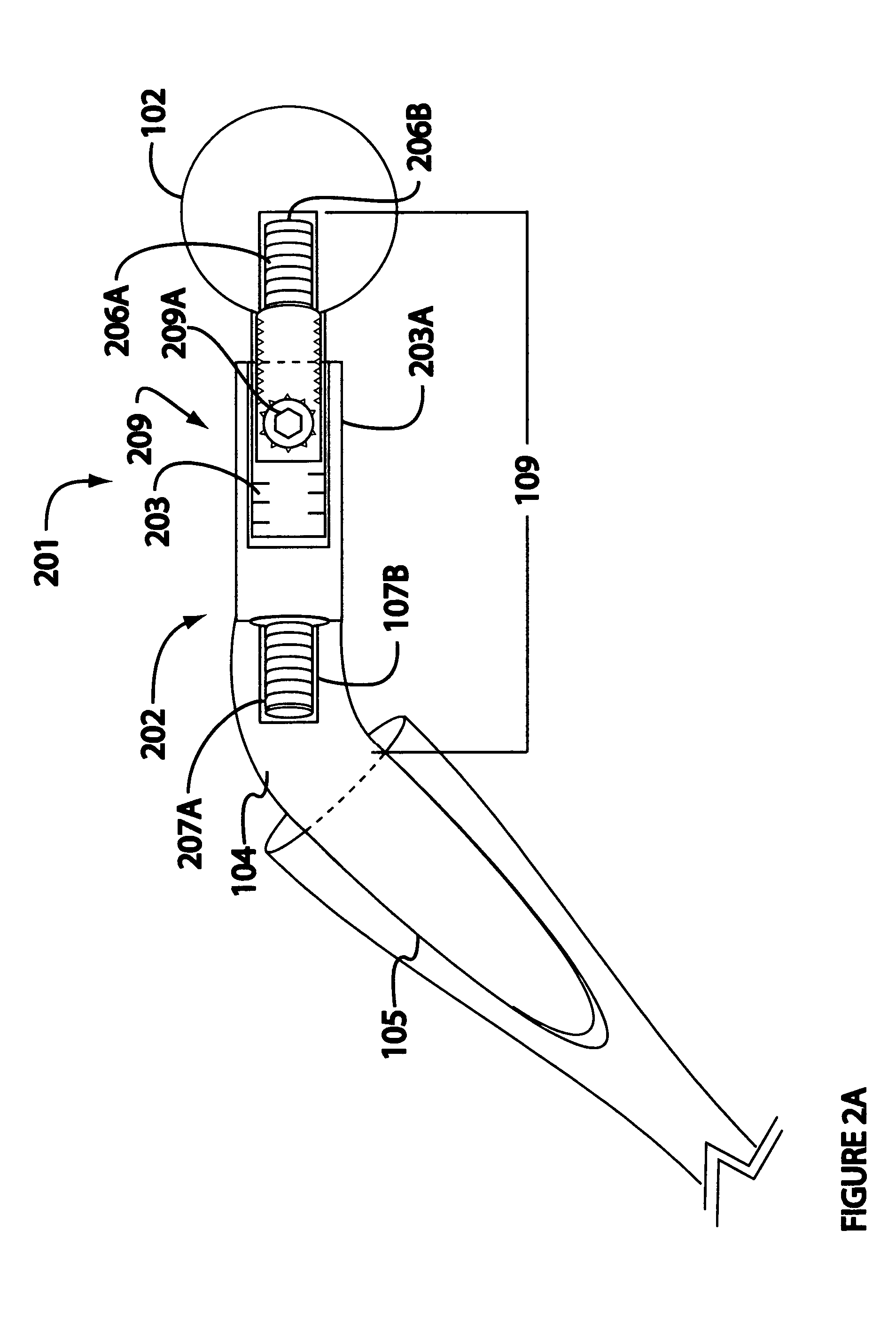
Set of mobile necks for inserting into the stem of a hip prosthesis
ActiveUS8357204B2Meet the requirementsLow costJoint implantsFemoral headsMuscles of the hipProsthesis
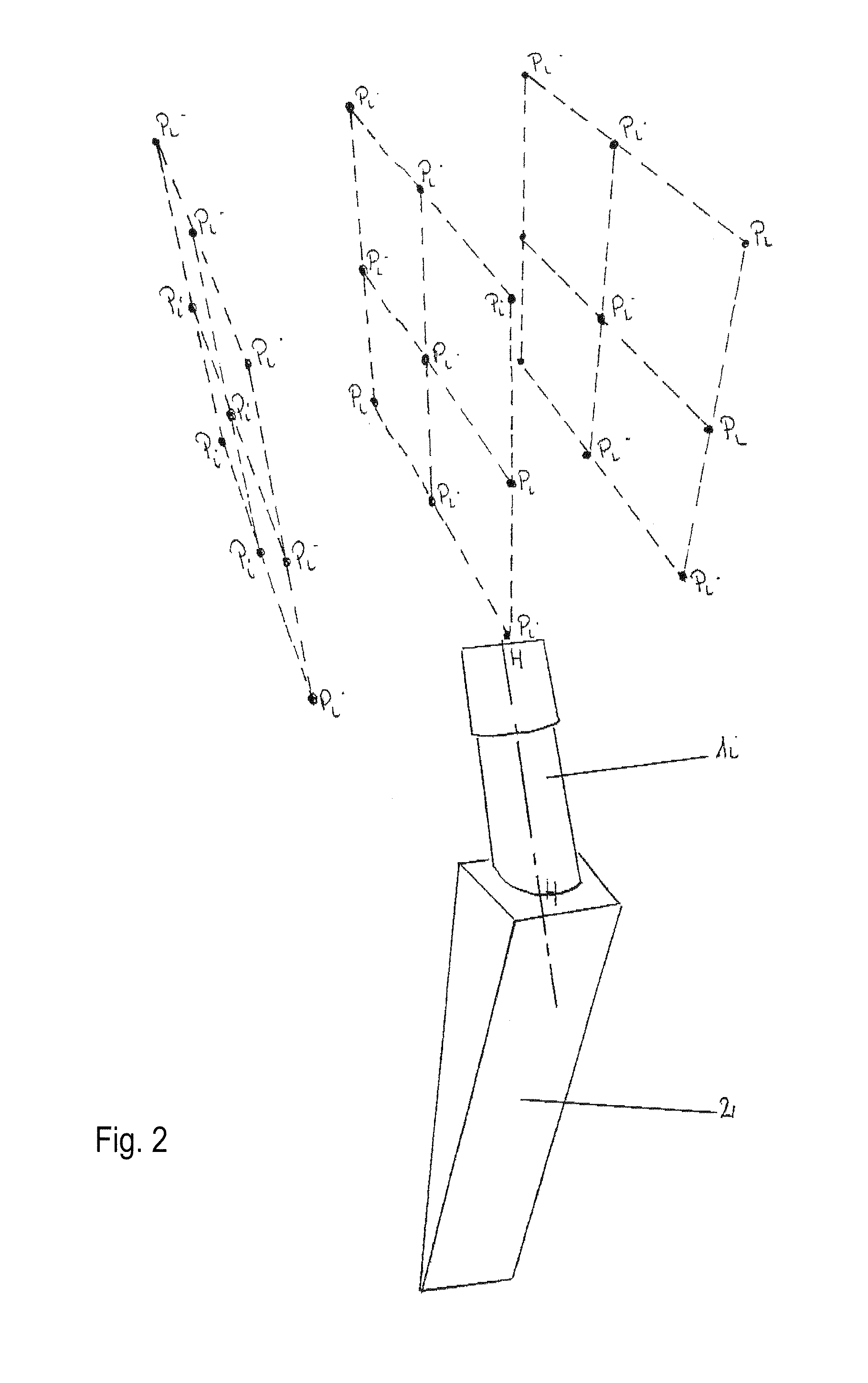
A set of mobile necks for inserting into the stem (2) of a hip prosthesis, in which the mobile necks are produced with different inclinations and lengths in such a way that their free ends (3i), when inserted in the stem, terminate at nine mutually equidistant points (Pi) arranged in three parallel horizontal rows (R0) in such a way that the lines joining the outermost points delineate a square (Q), the length of whose sides is approximately 15 mm, the diagonal (D) of this square coinciding with the axis (H-H) of a mobile neck (1) set at a neutral inclination, that is neither varus nor valgus, with respect to a plane (ss) essentially perpendicular to the axis of the abovementioned stem (2).
Owner:ADLER ORTHO
Hip stem
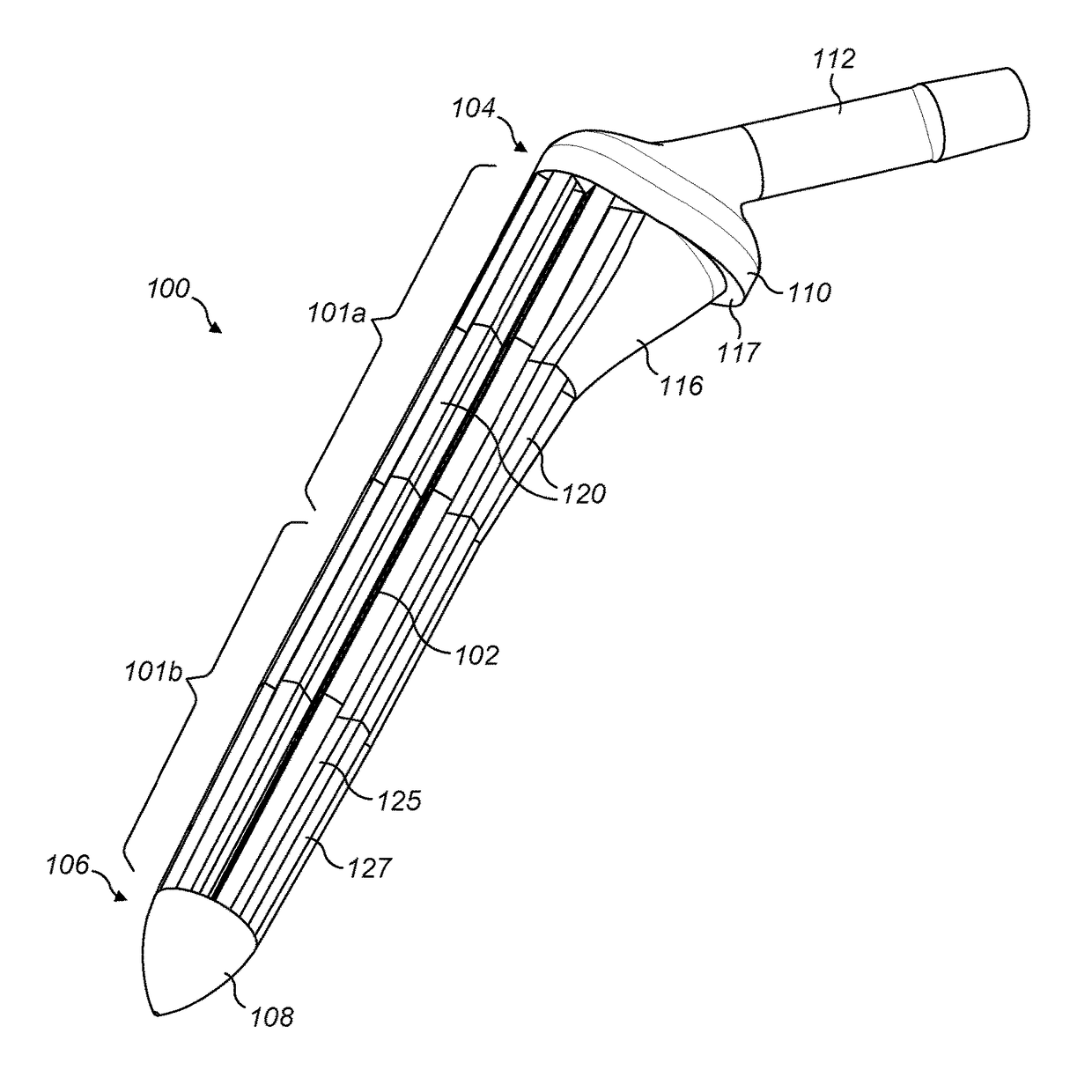
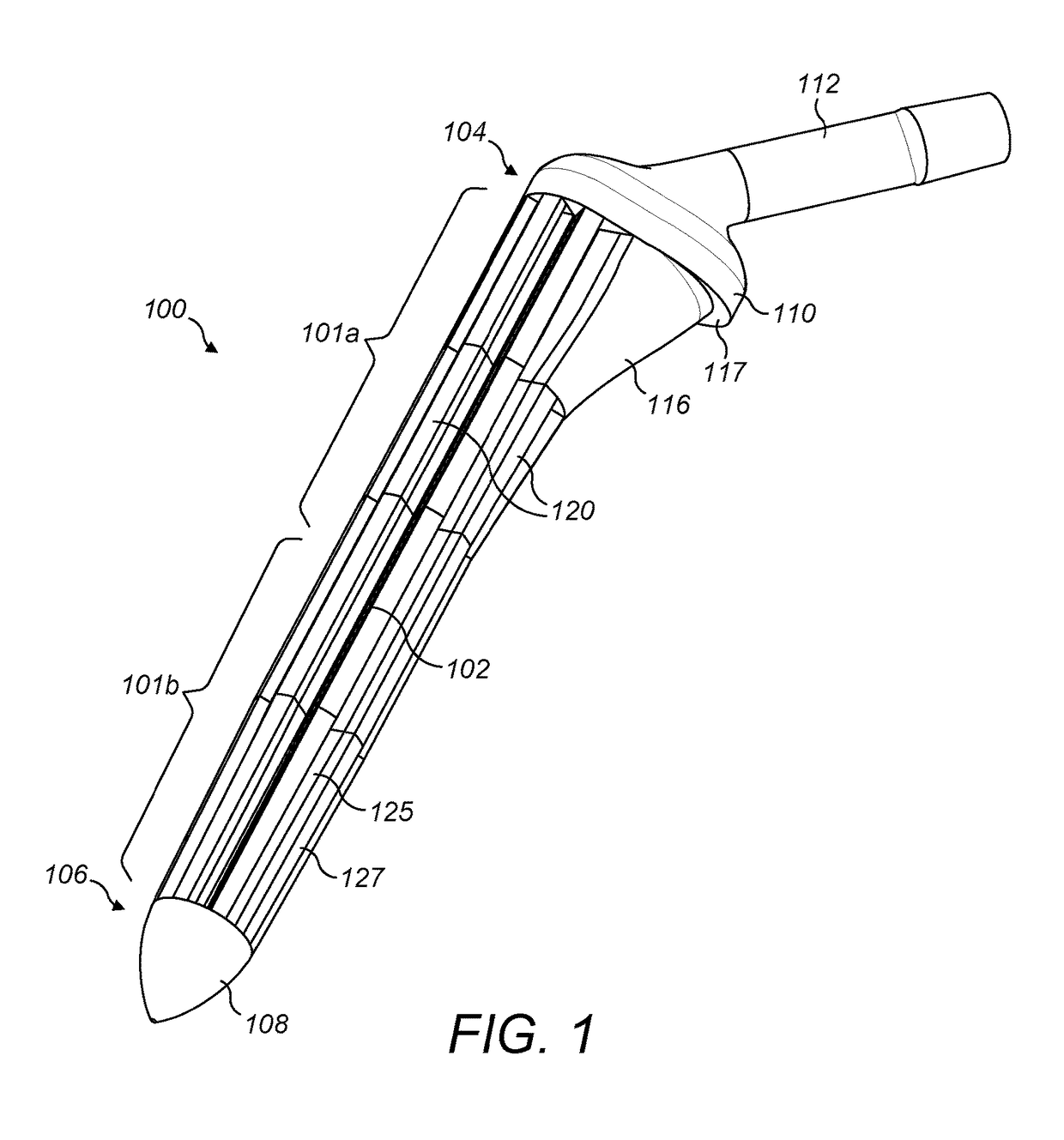
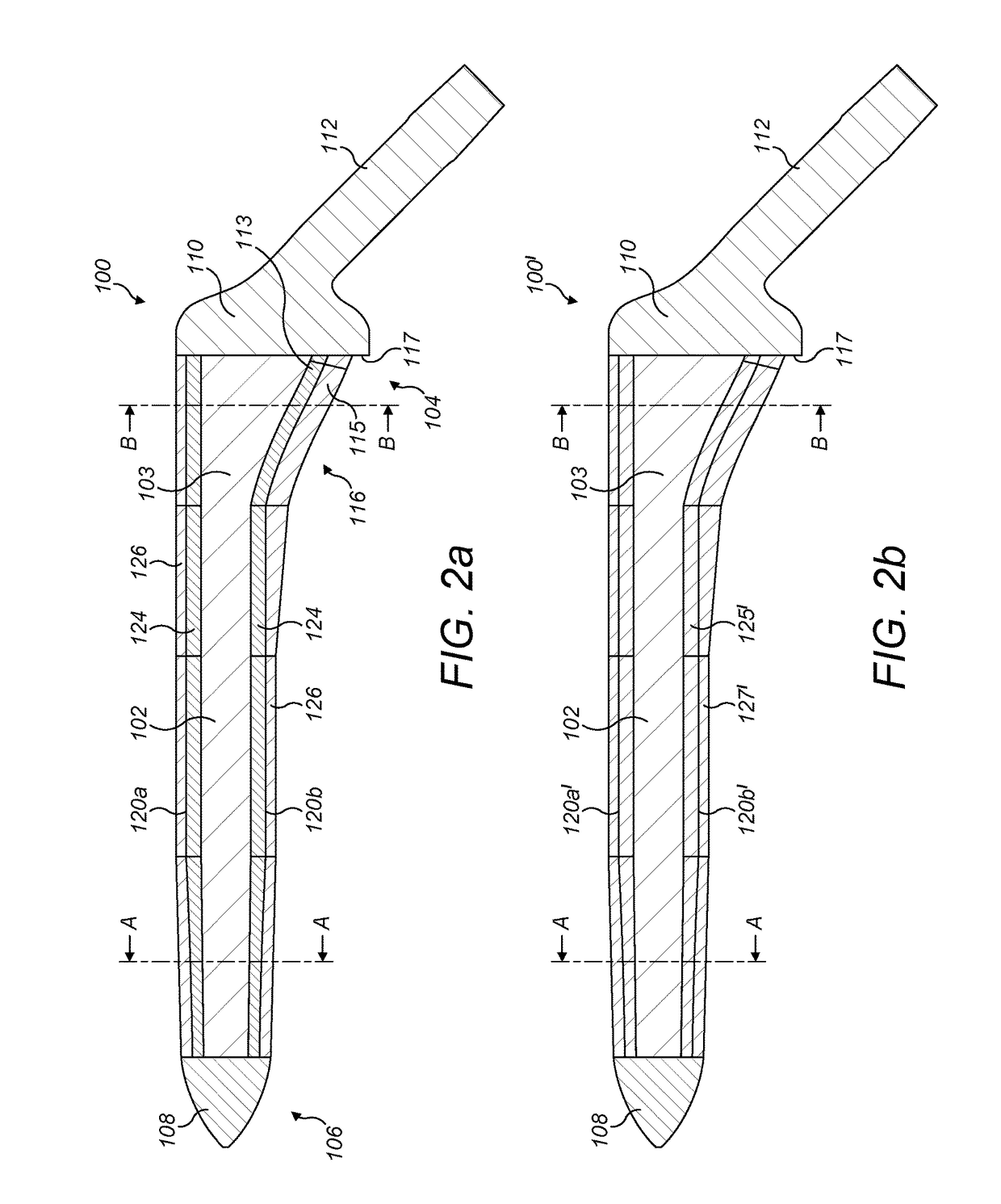
InactiveUS20180000598A1Less invasiveReduce manufacturing costBone implantJoint implantsDistal portionIntraoperative fracture
A stem (100) for use in a joint prosthesis, such as a femoral stem for a hip joint prosthesis, the stem comprising: a solid central core (102); a proximal outer layer (127) disposed over a proximal portion (101a) of the central core, wherein the proximal outer layer comprises a set of longitudinal ribs (120), defining slots (130) there between; and a distal outer layer made of a deformable porous material disposed over a distal portion (101b) of the central core. The arrangement is such that the stem (100) can be made with a relatively large diameter yet without being excessively stiff, for cementless fixation in osteoporotic patients. The deformability of the distal outer layer also mitigates against the risk of intraoperative bone fractures.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
Hip joint prosthesis
ActiveCN103598933AAvoid interferenceJoint implantsFemoral headsPeriacetabular osteotomyRight femoral head
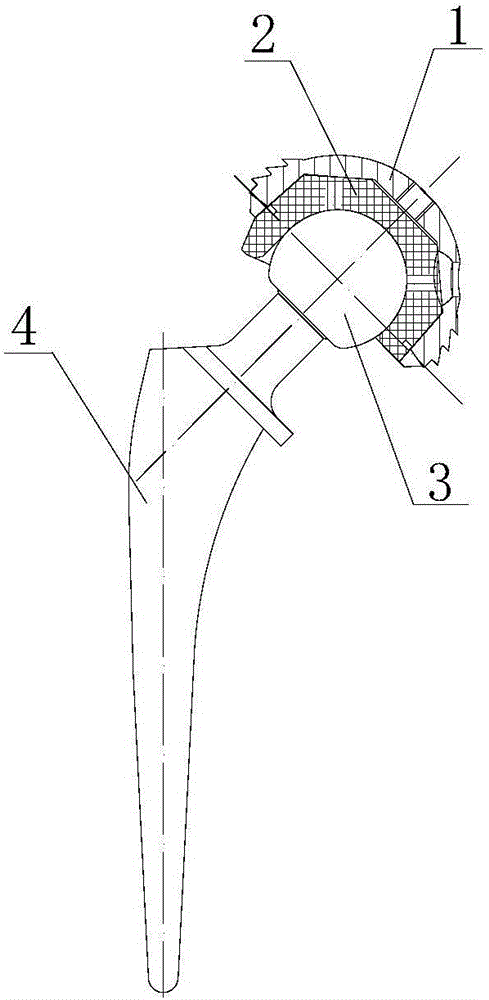
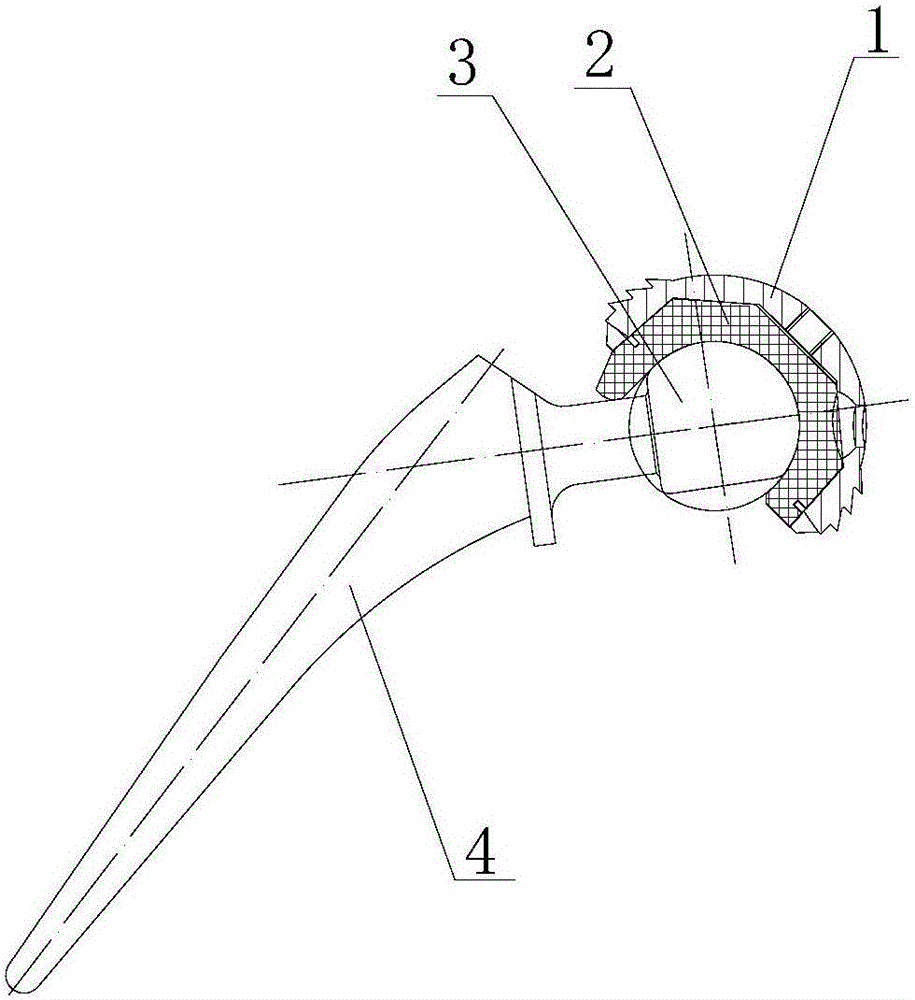
The invention provides a hip joint prosthesis and solves the problems that parts of fastening nails of bone grafts in periacetabular osteotomy interfere with a hip joint prosthesis to cause fixing inconvenience of the bone grafts or the hip joint prosthesis and further to cause the impossibility of reaching an optimum fixing position in the prior art and that an existing total hip femoral prosthesis is not applicable to all DDH (Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip) patients. The hip joint prosthesis comprises an acetabular cup for fixing inside an acetabulum, an eccentric acetabular liner for increasing the range of motion of the hip joint prosthesis and arranged inside the acetabular cup, a ball heat playing the role of a femoral head and arranged inside the eccentric acetabular liner and a stable femoral stem for being fixed onto a cuboid and connected with the ball head. By means of the above technical scheme, the hip joint prosthesis can be arranged in the optimum fixing position and meets the requirements on prostheses required by operations of the DDH patients.
Owner:JIASITE HUAJIAN MEDICAL EQUIP (TIANJIN) CO LTD
Cotyloid element of a hip prosthesis, and total hip prosthesis comprising same
The invention relates to a cotyloid component of a hip prosthesis, said cotyloid component being hollow and in the form of a cup whose outer part has a thread allowing it to be fixed in the iliac bone, said thread being a discontinuous self-cutting double thread (20, 21), and said cotyloid component having a flattened upper pole (1), a coating that promotes osseointegration on its outer face (10), and a concave, substantially hemispherical and polished inner surface (11), characterized in that: (a) the pitch of the threads (20, 21) decreases from the upper pole (1) towards the equatorial periphery (3) of the cotyloid component, (b) the thicknesses of the threads (20, 21) increase from the upper pole (1) of the cotyloid component towards its periphery (3), (c) the crest of the threads (20, 21) is sharp towards the pole (1) of the cotyloid component and rounded or substantially trapezoidal towards the equatorial periphery (3) of the cotyloid component.
Owner:THEILLEZ BORIS +9
Hip joint prosthesis with a shaft to be inserted into the femur
ActiveUS7947084B2Promote rapid accumulationRapid incorporation of boneJoint implantsFemoral headsCoxal jointFemur
A hip-joint prosthesis includes a shaft which is configured to be inserted into the femur and whose surface has an osteoinductive finish. This finish is provided exclusively in the metaphyseal portion of the shaft and laterally from the line delineating the maximum antero-posterior dimension of the shaft cross section. This ensures a better involvement of the metaphyseal spongiosa in the flow of forces, without compromising the ability to perform follow-up surgery on the prosthesis.
Owner:WALDEMAR LINK GMBH & CO
Leaflike shaft of a hip-joint prosthesis for anchoring in the femur
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Non-metal ball hip joint prosthesis
InactiveCN105748174APreserve bone massReduce thicknessJoint implantsTissue regenerationFemoral head prosthesisSacroiliac joint
The invention relates to the field of medical apparatus and instruments, in particular to a non-metal ball hip joint prosthesis.The non-metal ball hip joint prosthesis comprises an acetabulum cup prosthesis body, a non-metal femoral head prosthesis body and a femoral stem prosthesis body.According to the non-metal ball hip joint prosthesis, an original acetabulum cup and liner are changed into a metal cup, and meanwhile a traditional metal or ceramic ball is changed into a high-crosslinking polyethylene ball with a metal core.On the premise that compatibility of the original metal-polyethylene joint surface is maintained, the thickness of the acetabulum cup is greatly decreased, and the large-diameter ball can be used when the small-diameter joint cup is available.Connection among components is reduced, meanwhile, the wear probabilit is greatly lowered, and the defects that a traditional complete hip joint prosthesis is small in movement angle, prone to dislocation and high in acetabulum side bone removal amount are overcome.
Owner:JIASITE HUAJIAN MEDICAL EQUIP (TIANJIN) CO LTD
Dynamic hip joint prosthesis
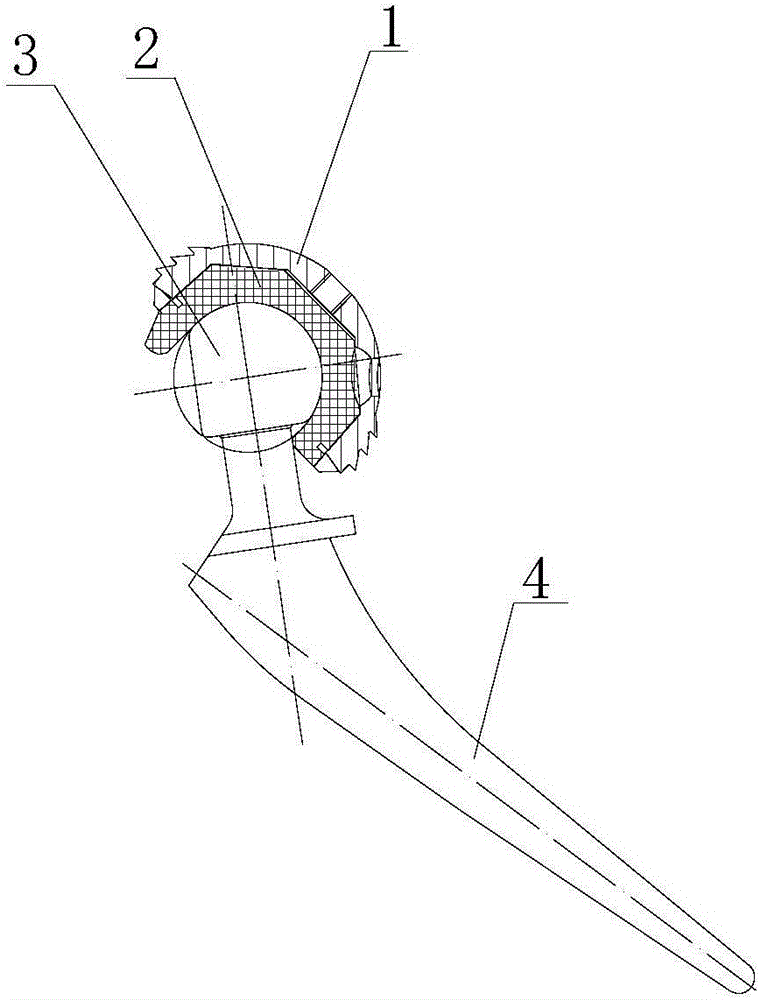
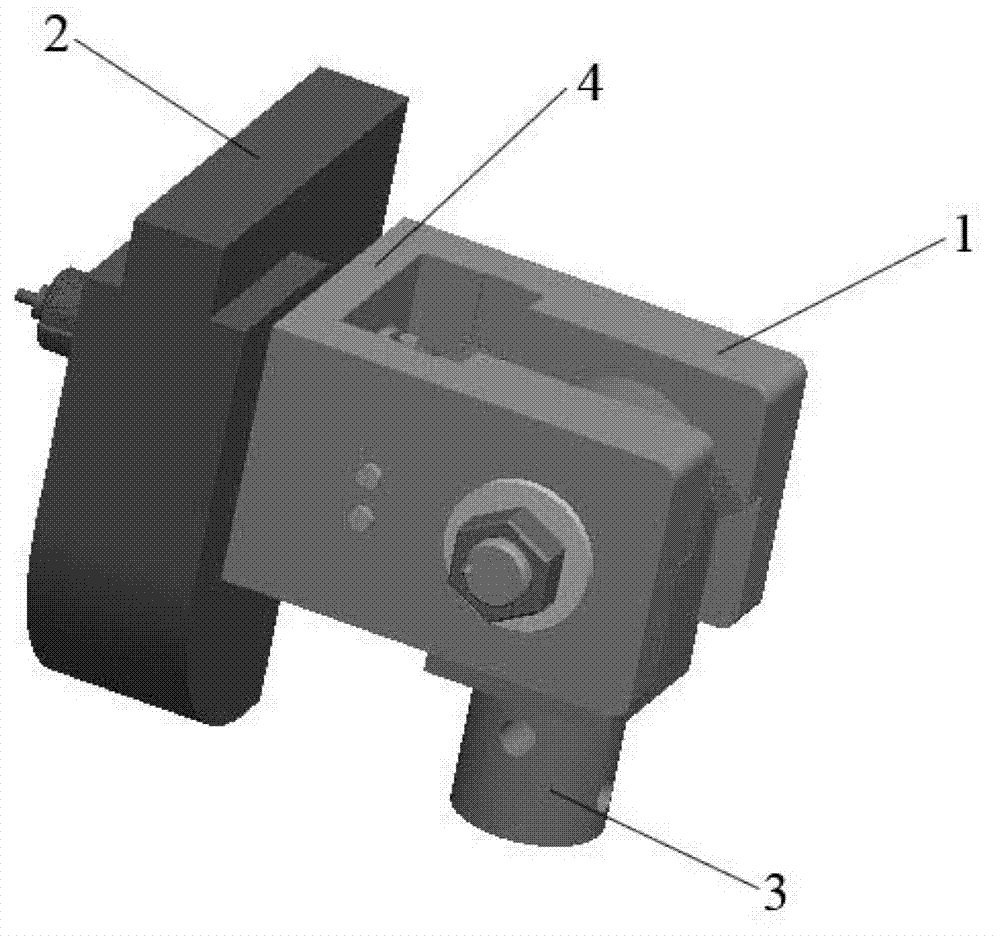
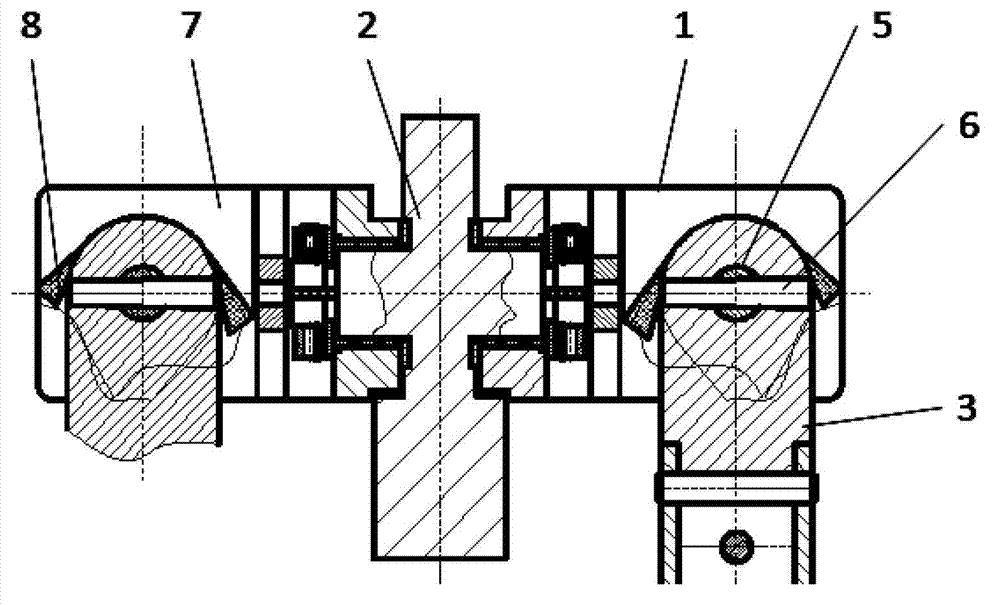
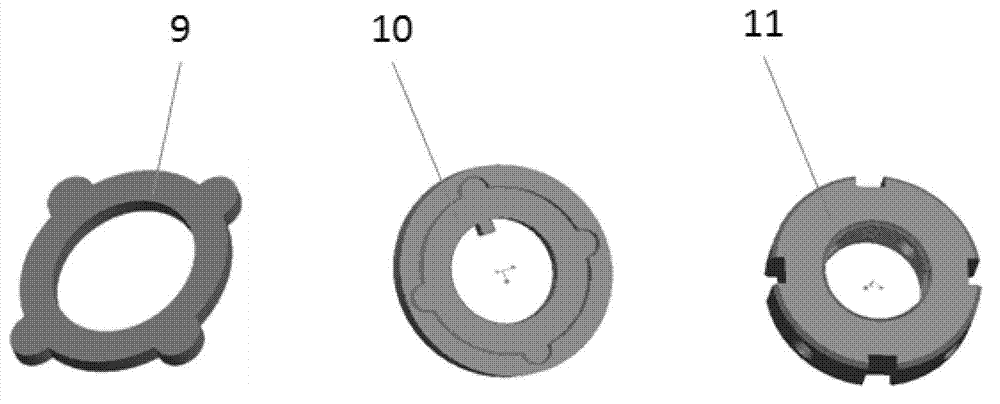
InactiveCN102758994AAchieve freedom of movementAchieve range of motionStands/trestlesPivotal connectionsMultiaxial jointCoxal joint
The invention discloses a dynamic hip joint prosthesis, and adopts an MDOF (multi-degree of freedom) multi-shaft joint design scheme. The dynamic hip joint prosthesis includes U-shaped components (1), a trunk part (2) and thigh end parts (3), which form a hip forward and backward swing joint and a hip side swing joint. The joint moving range is ensured through bosses (7) on side plates of the U-shaped components (1), the impact when the joints reach limit positions are absorbed through soft baffle blocks (8), the friction force is adjusted through lock nuts (11) and further the joint damping is adjusted; and a sensor (12) is mounted through a sensor support (13), so that the joint angular displacement can be measured in real time. The simulated hip joint model can realize hip joint forward and backward swing and inward and outward swing, the joint damping can be adjusted, a trunk can keep a posture under the condition of no external force, and the motion angle can be measured by the sensor in real time.
Owner:AVIATION MEDICINE INST AIR FORCE PLA
Metal hip joint prosthesis with porous layer structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111297519APromote ingrowthHigh manufacturing stabilityJoint implantsTomographyBone tissueFemoral stem
The invention provides a metal hip joint prosthesis with a porous layer structure. The metal hip joint prosthesis comprises an acetabulum outer cup, an acetabulum lining, a femoral ball head and a hipjoint femoral stem, wherein the hip joint femoral stem comprises a femoral stem neck part, a femoral stem near end and a femoral stem far end; the upper end of the hip joint femoral stem neck part issleeved by the femoral ball head in cooperation with the acetabulum lining for use; the acetabulum outer cup sleeves outside the acetabulum lining; the contact surfaces of the metal hip joint prosthesis and host bone tissue are of porous structures similar to human bone trabecula in three-dimensional communication; the metal hip joint prosthesis specifically comprises the hip joint femoral stem with a pore layer and the porous acetabulum outer cup; the femoral stem far end is of a whole or surface porous structure; and the pore diameter of the pore layer of the femoral stem far end is smallerthan the pore diameter of the pore layer of the femoral stem near end. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the hip joint femoral stem and the acetabulum outer cup by integrated molding with a 3D printing technology. The metal hip joint prosthesis with the porous layer structure provided by the invention facilitates ingrowth of new bone tissues, and reduces the risk that a pore layer prepared through a surface treatment method is prone to falling off.
Owner:赵德伟 +4
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com