Patents
Literature
209results about How to "High tension" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
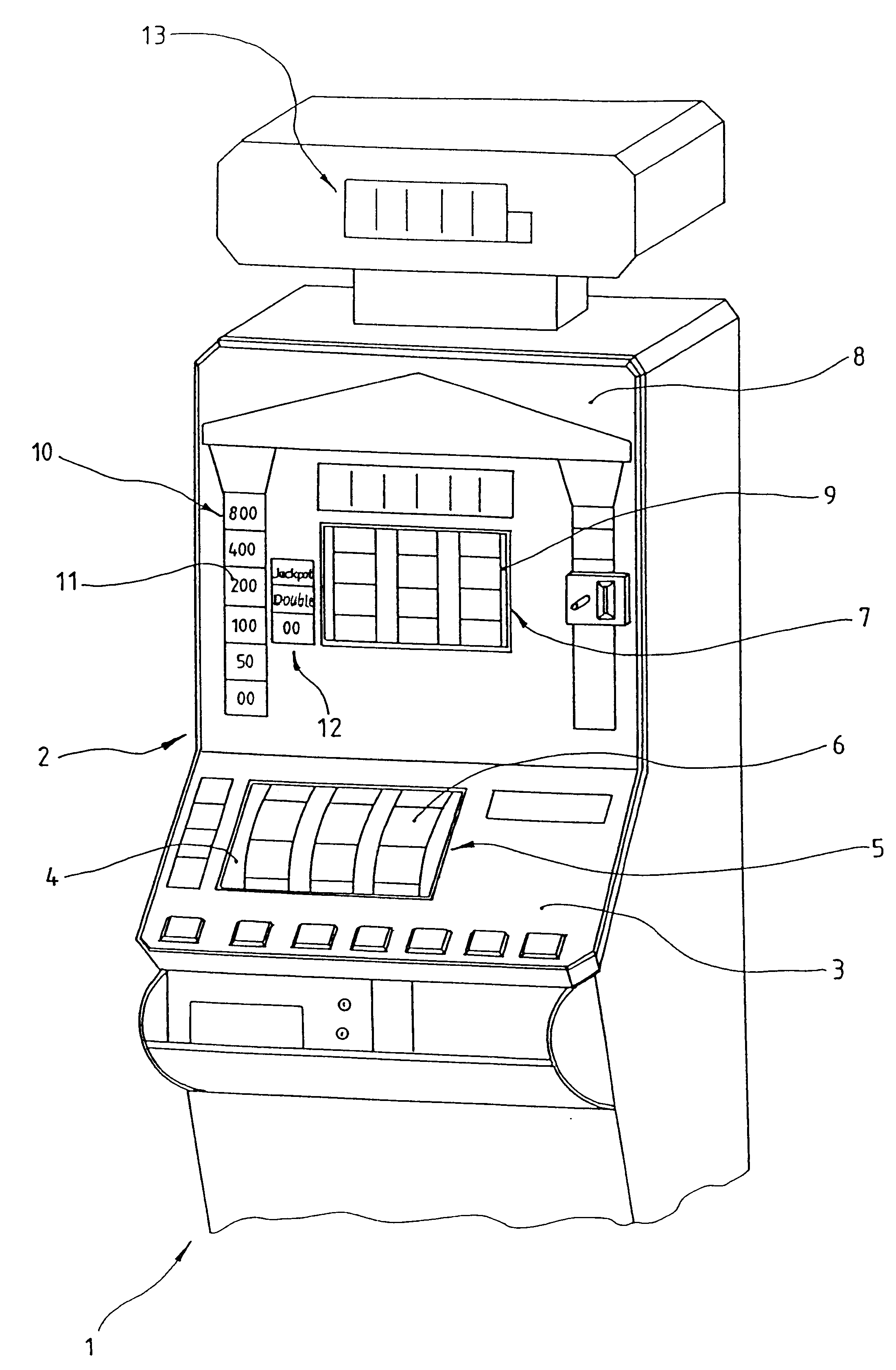
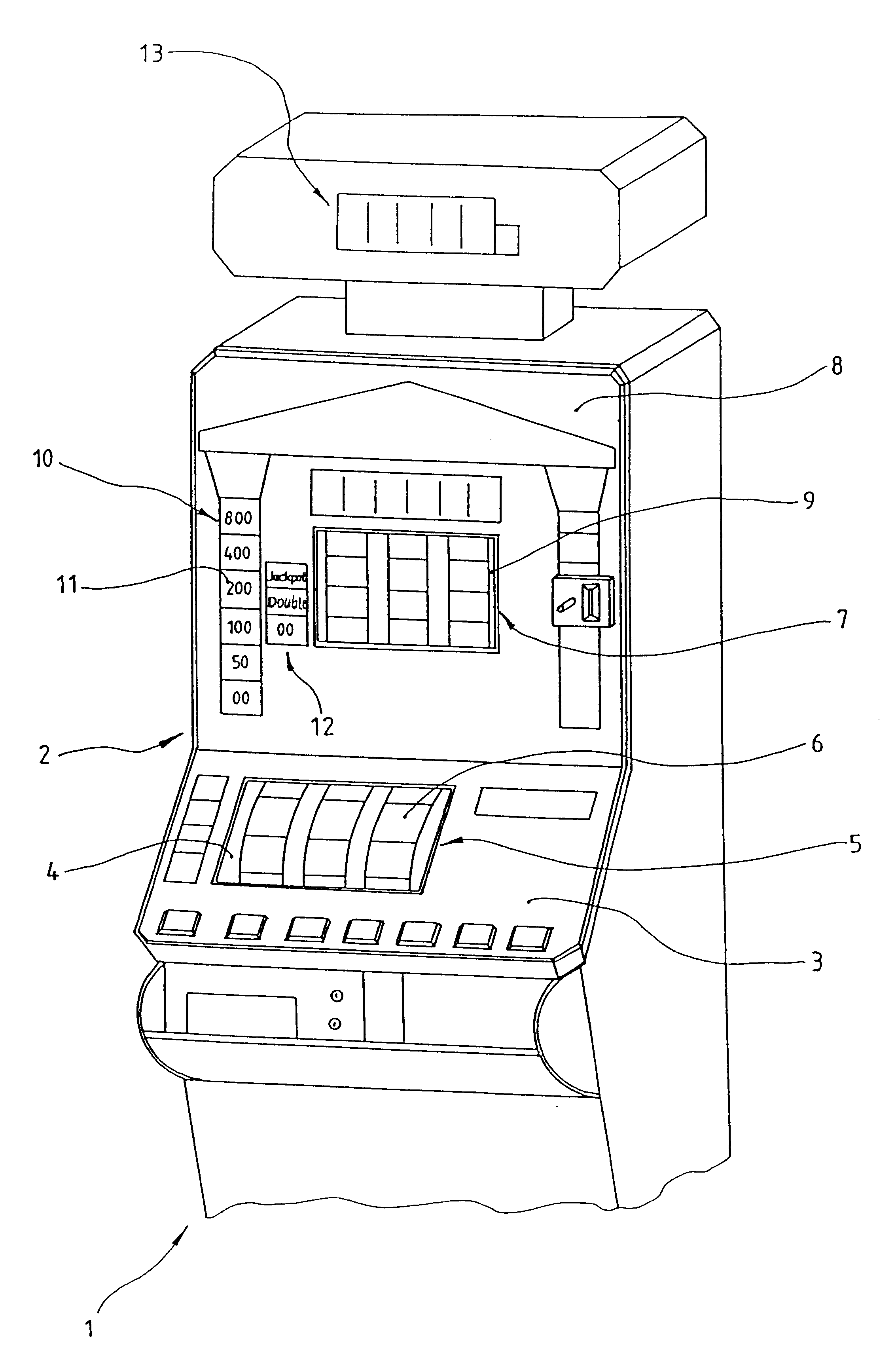
Method for determining the winning value upon reaching of a game result at a coin operated entertainment automat
InactiveUS6491583B1High tensionGame tension can be maintainedApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesEngineeringRest position
Abstract of the disclosure method for the determination of a winning value upon reaching of a game result at a coin operated entertainment automat with a symbol game arrangement. Coin operated entertainment automat comprise a symbol game arrangement where the circulating bodies displays in a rest position of winning or non-winning symbol combination. The winning value associated with the displayed symbol combination can in following under danger of loss in a risk game be staked against a higher winning value. This new feature is to assure that the player always maintains a maximum game tension independent of the amount of the stake. This is accomplished in that at jackpot is continuously filled from the game stake and is present to be released at an unknown point in time. An achieved winning value can be staked in the risk game against the jackpot.
Owner:GTECH GERMANY
Prosthetic device and method of manufacturing the same
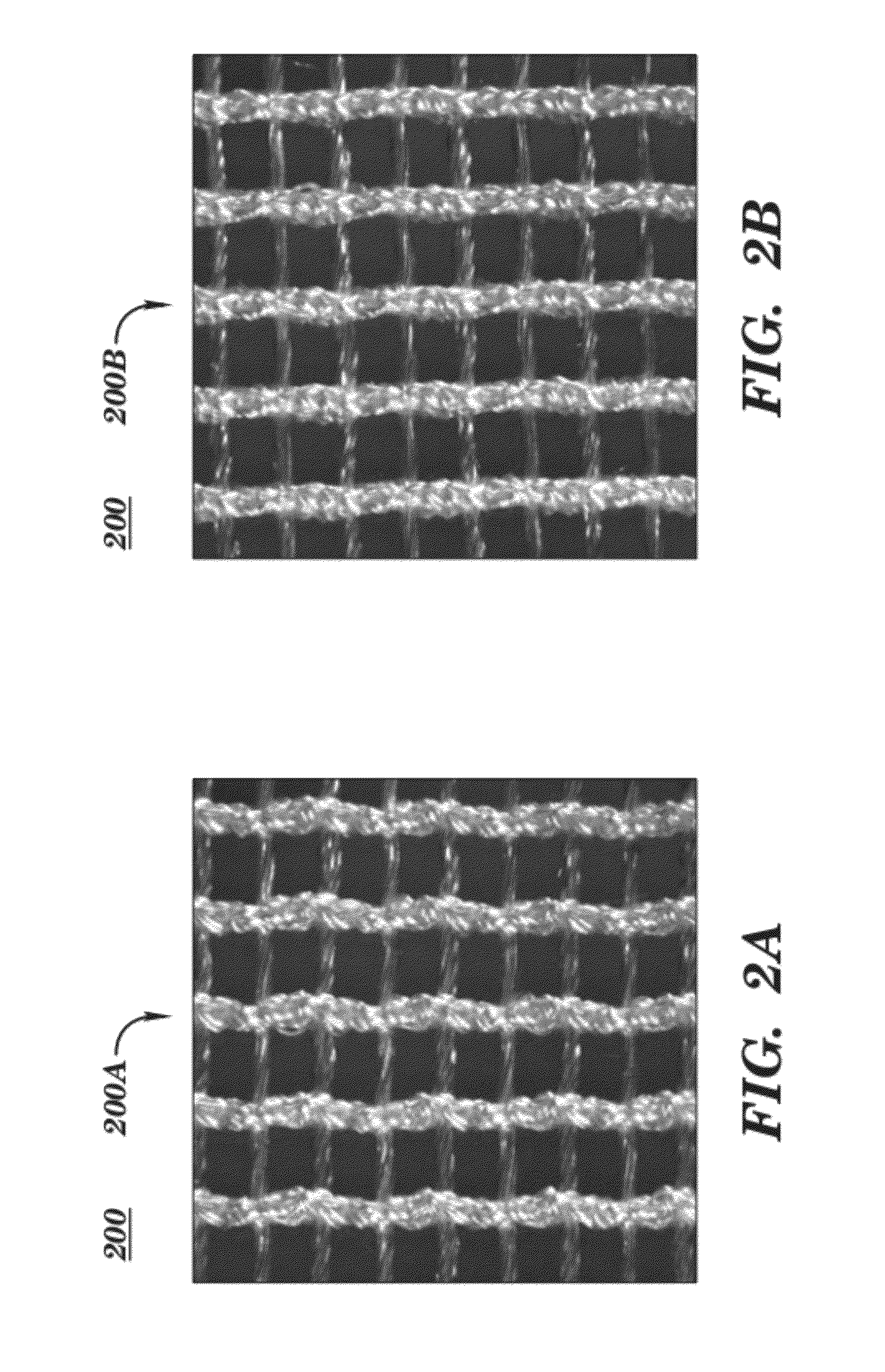
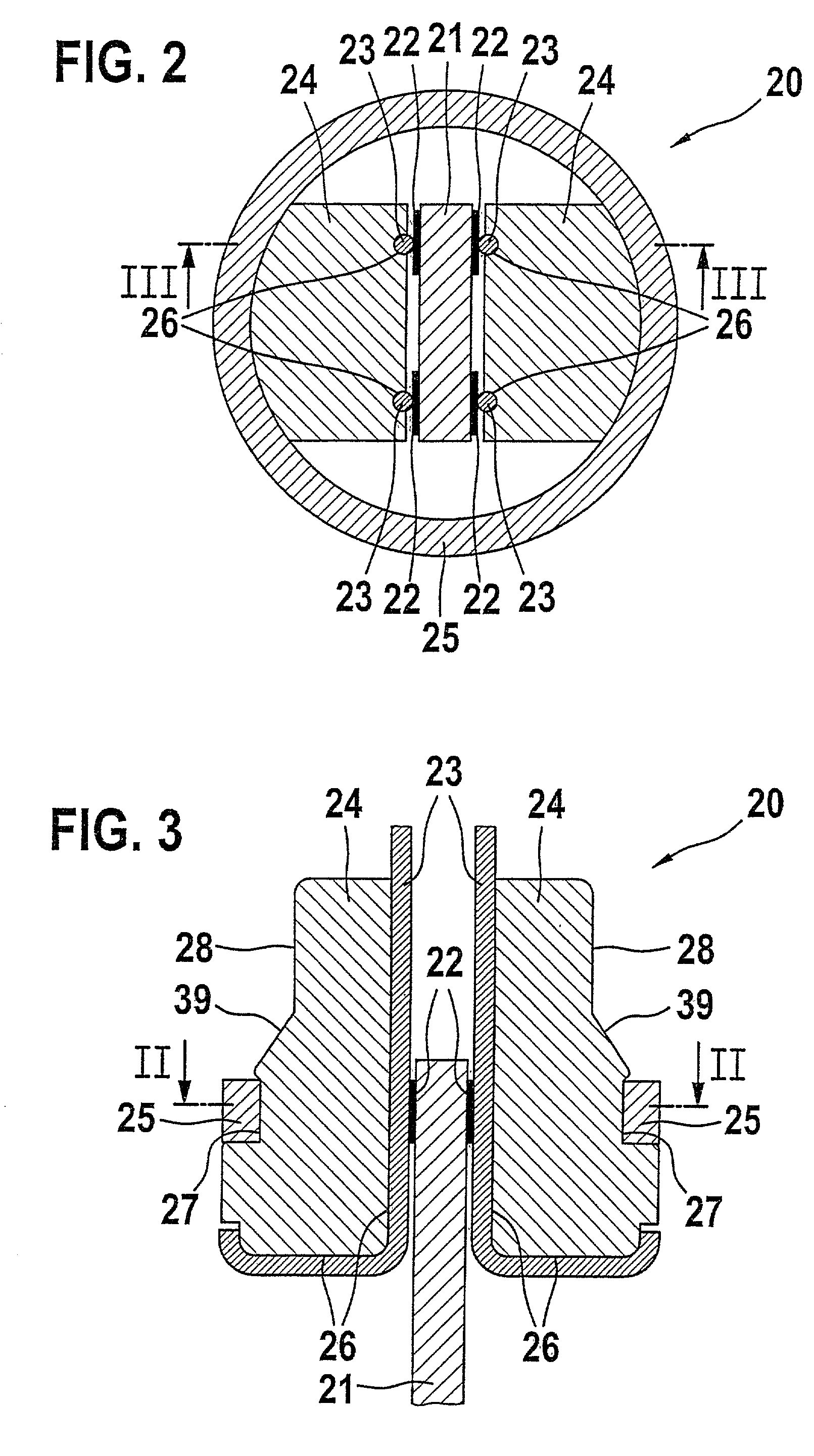
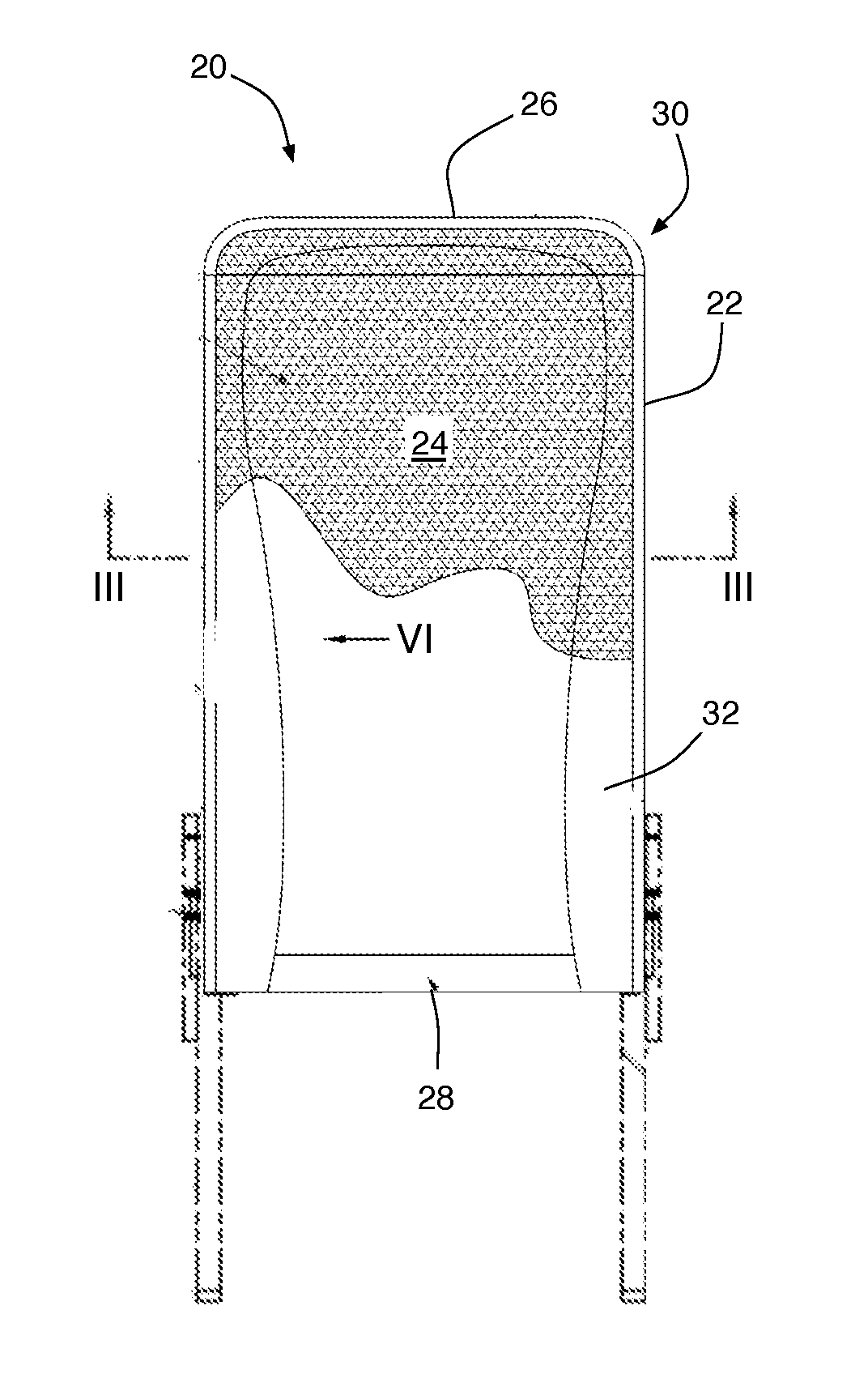
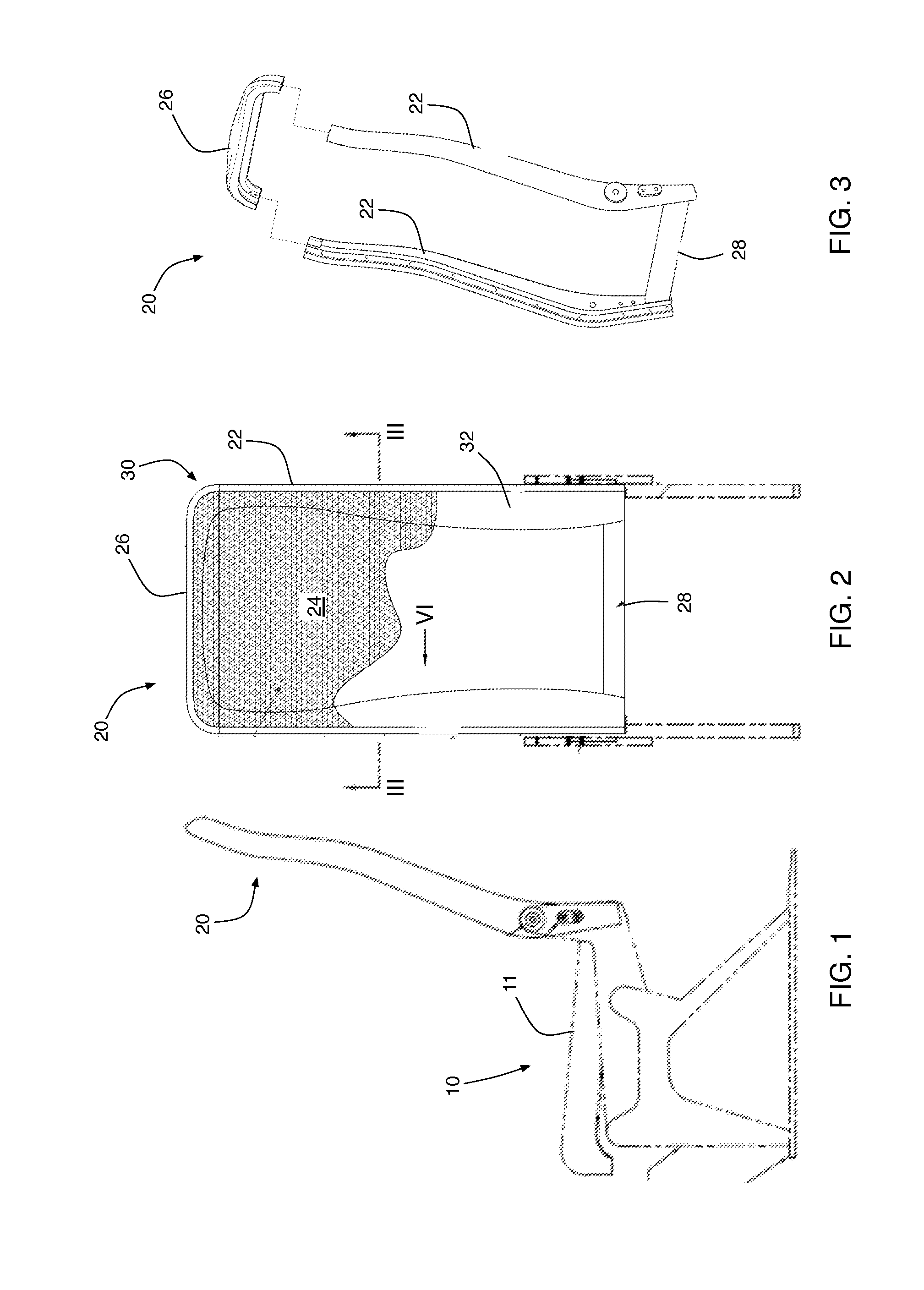
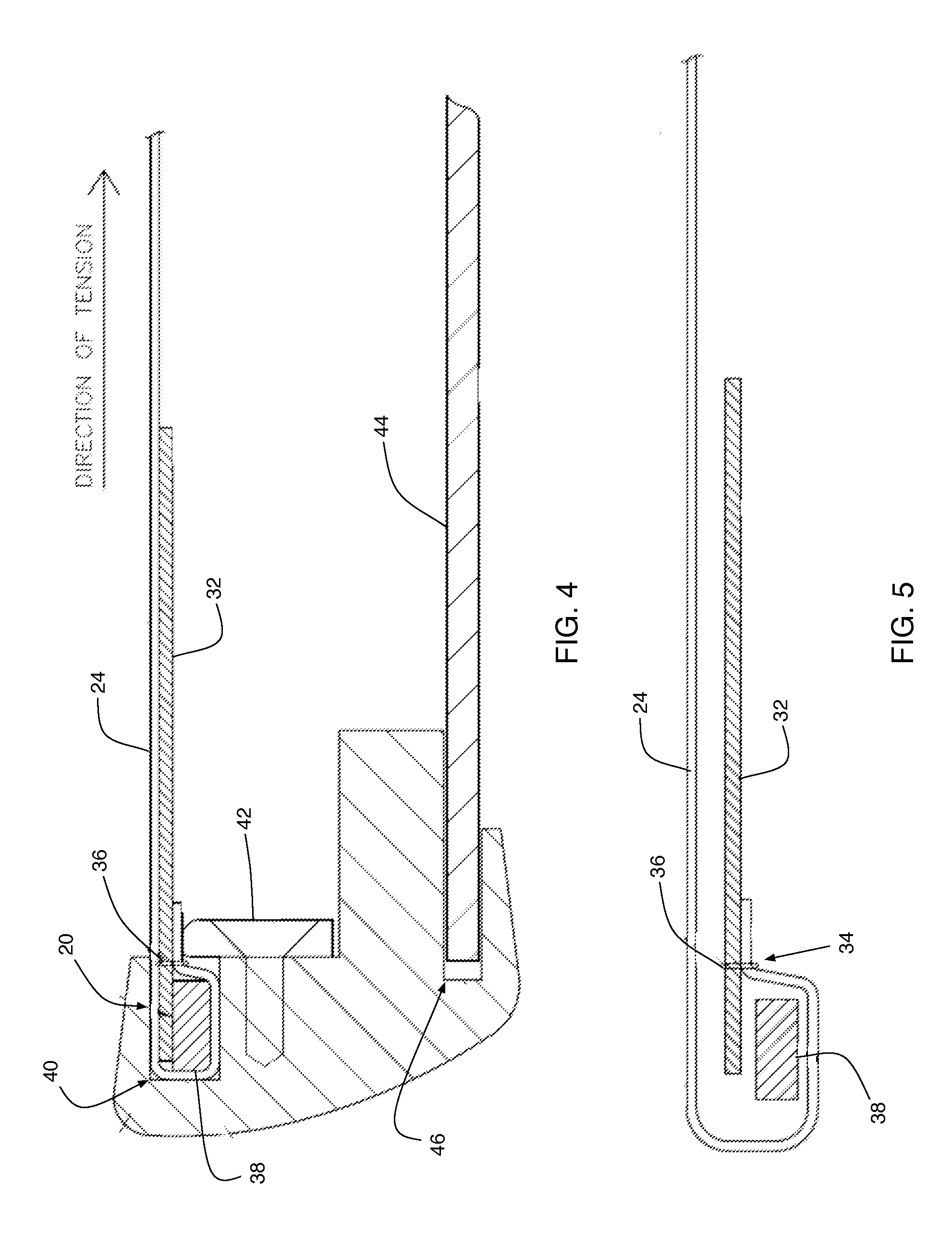
InactiveUS20120029537A1Minimizes tissue erosionMinimizes fistulaMammary implantsWarp knittingYarnDevice prosthetic
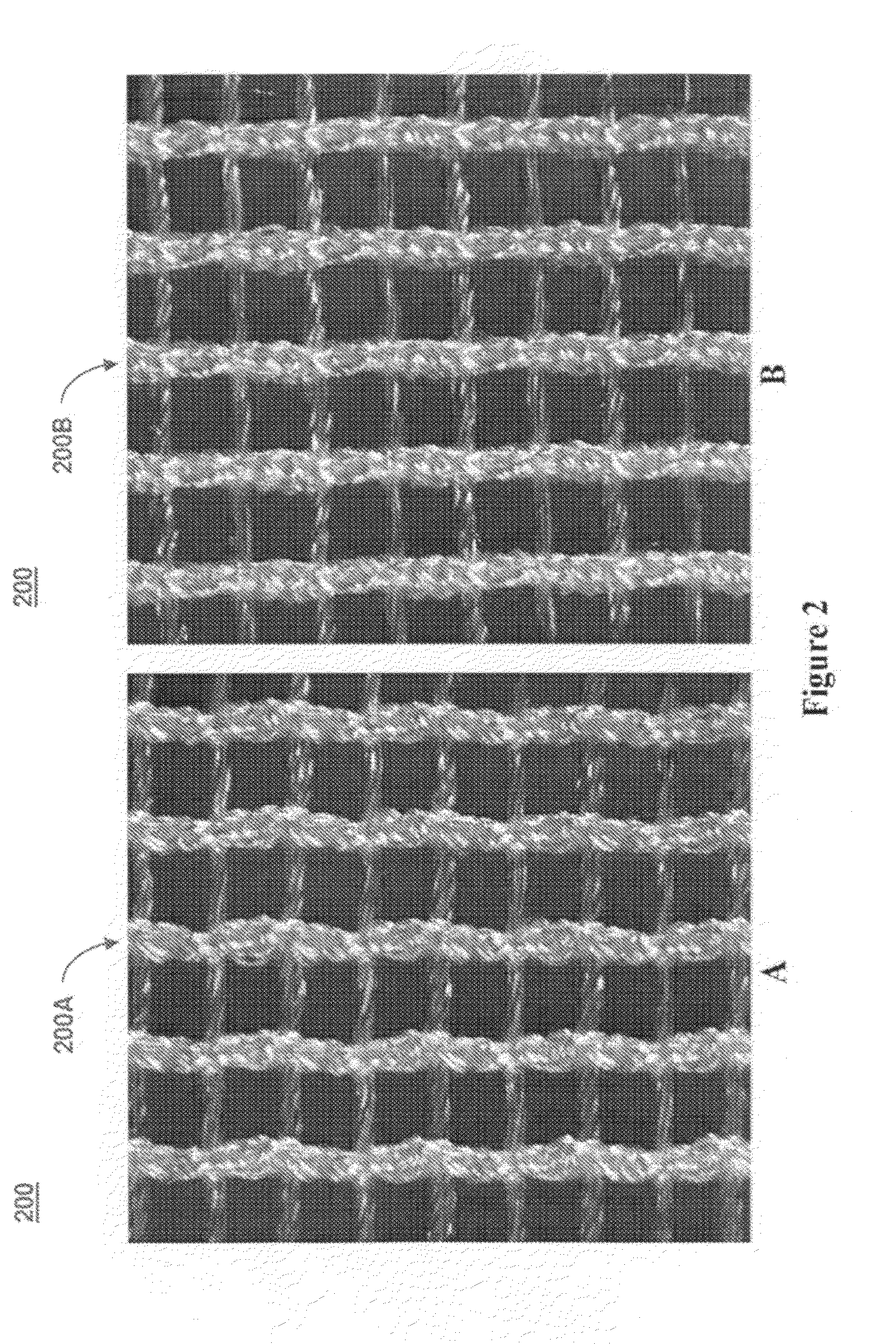
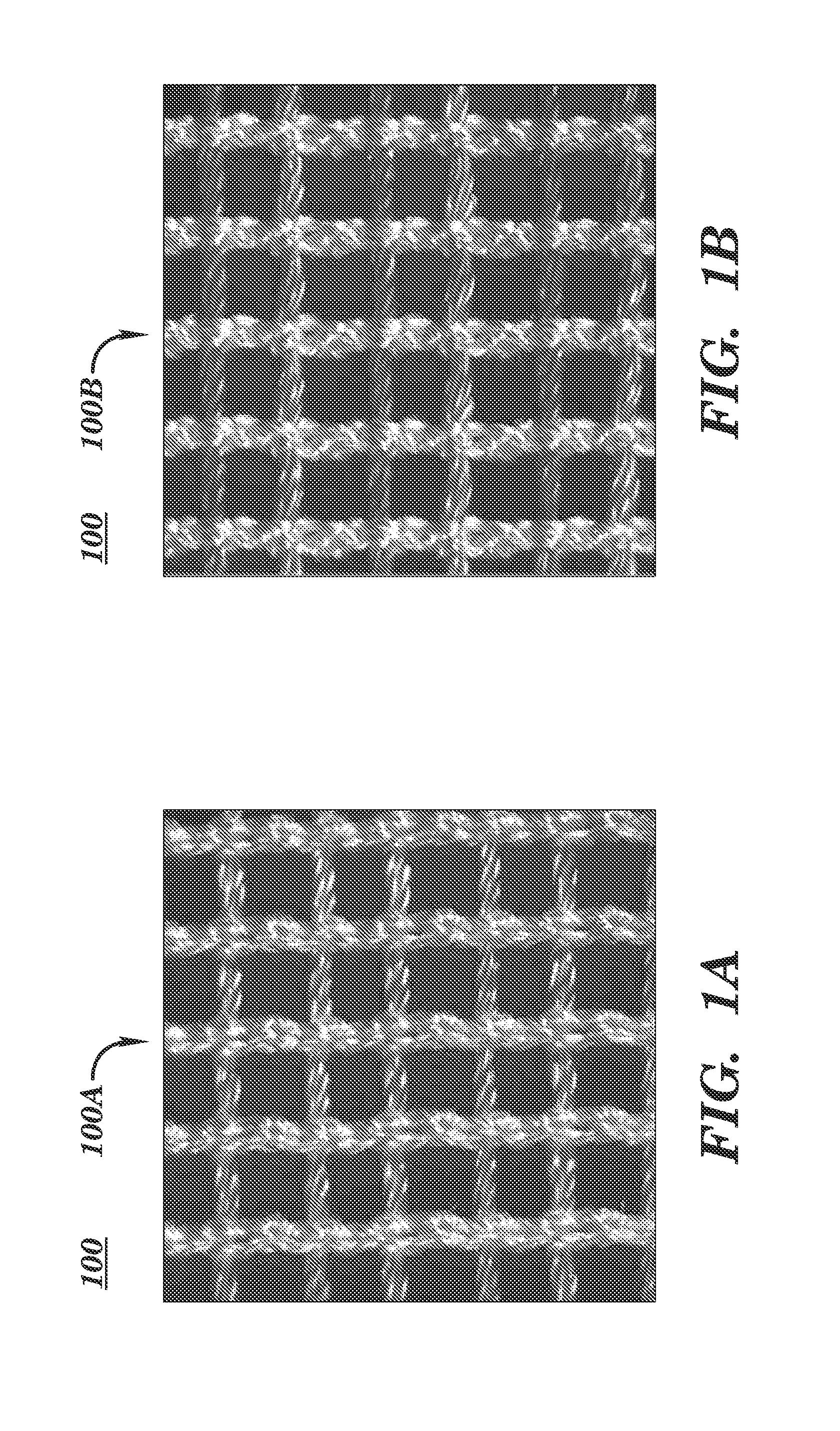
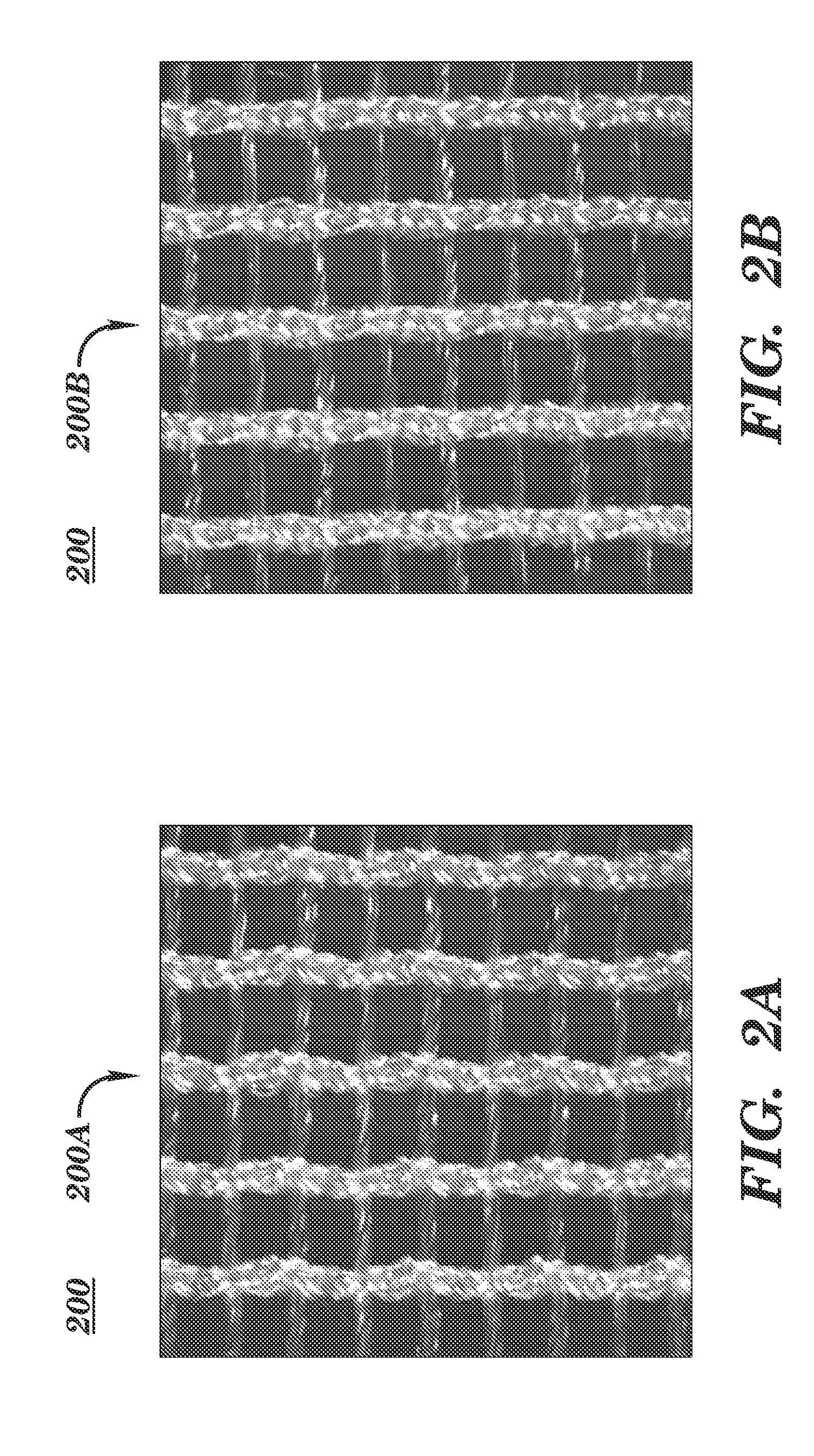
A biocompatible surgical silk mesh prosthetic device employs a knit pattern that substantially prevents unraveling and preserves the stability of the mesh device, especially when the mesh device is cut. An example prosthetic device employs a knitted mesh including at least two yarns laid in a knit direction and engaging each other to define a plurality of nodes. The at least two yarns include a first yarn and a second yarn extending between and forming loops about two nodes. The second yarn has a higher tension at the two nodes than the first yarn. the second yarn substantially prevents the first yarn from moving at the two nodes and substantially prevents the knitted mesh from unraveling at the nodes.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Prosthetic device having regions of varying stretch and method of manufacturing the same
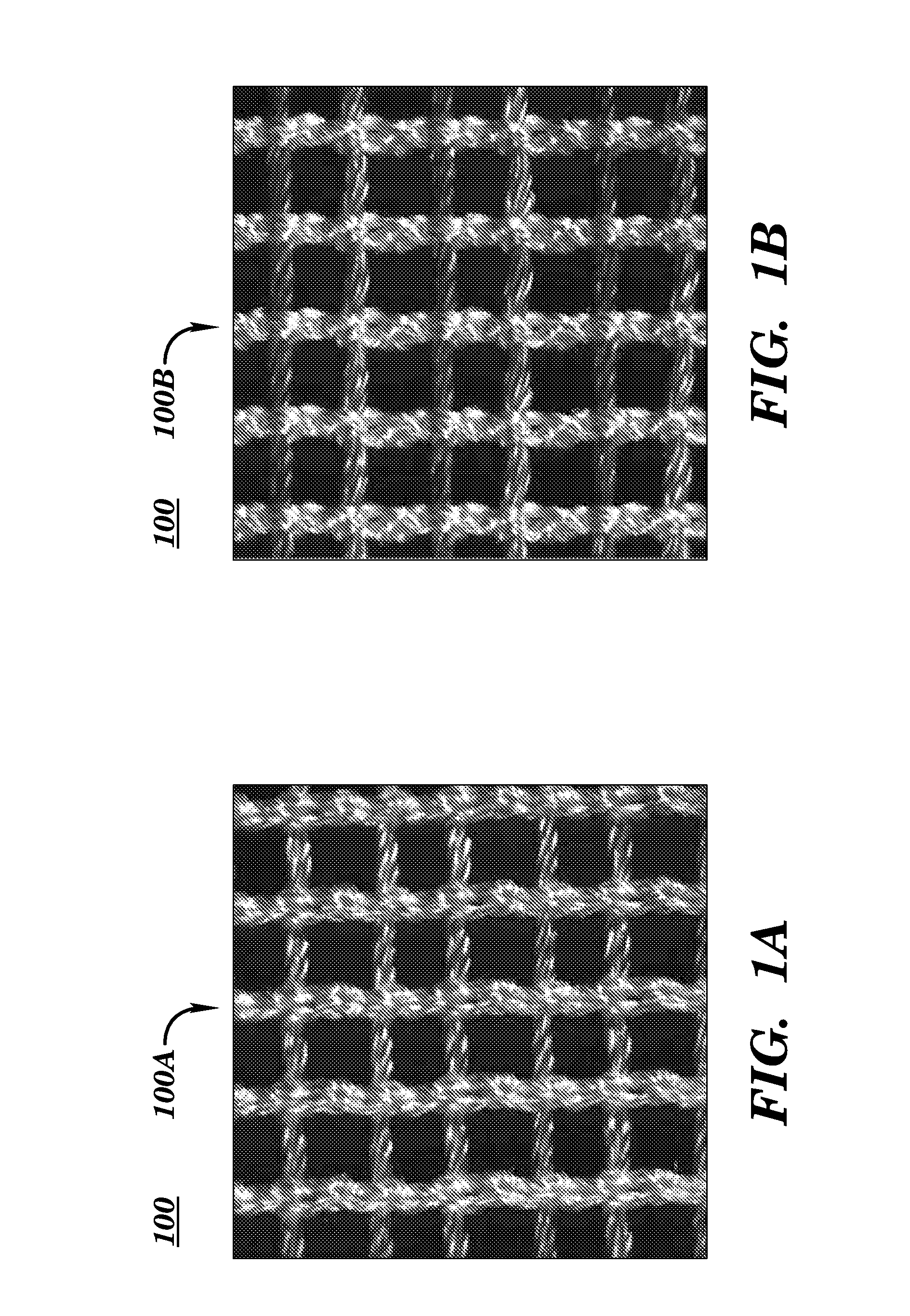
InactiveUS20110257761A1Minimizes adhesionsErosion minimizationMammary implantsWeft knittingYarnMechanical property
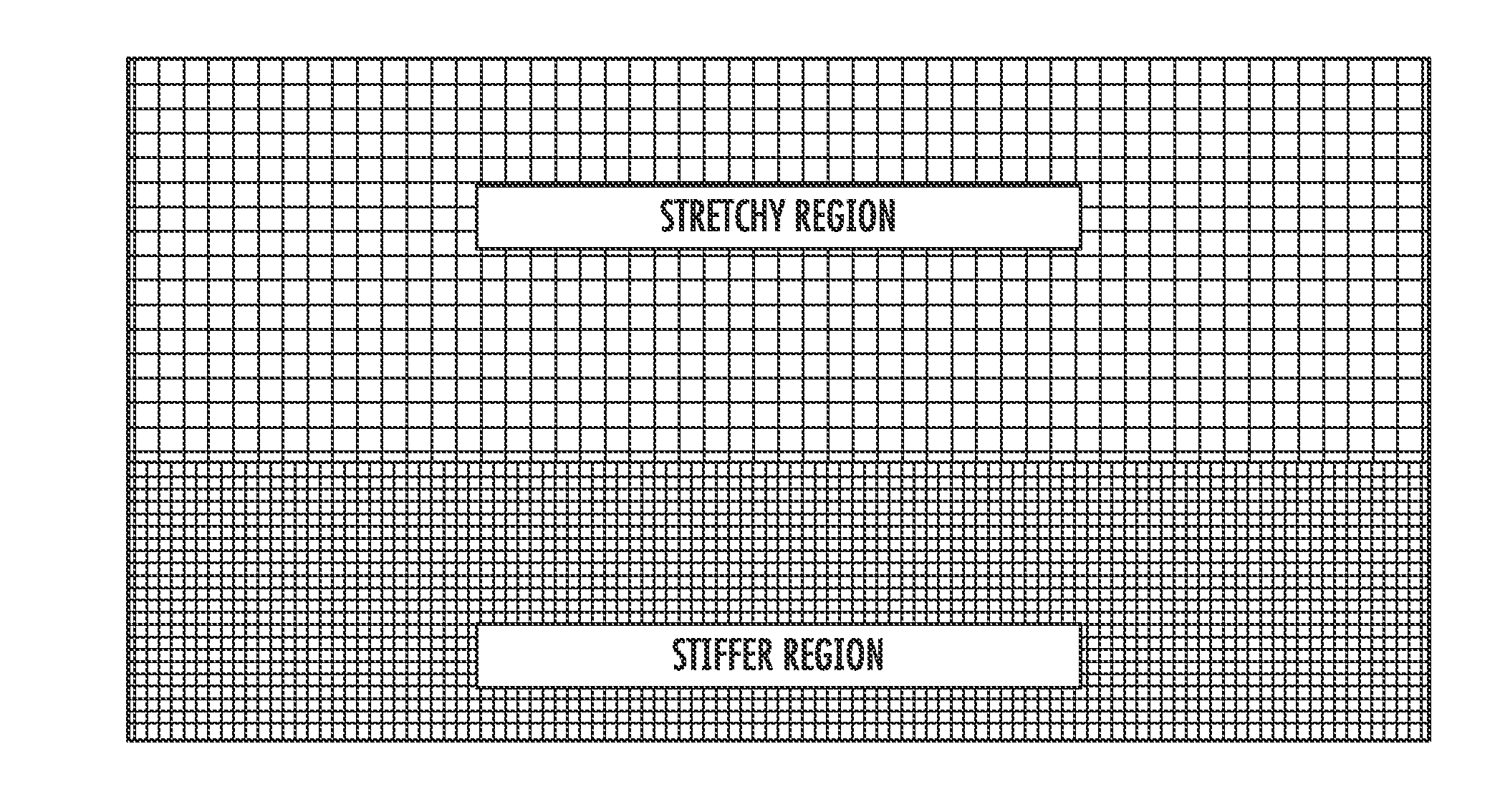
A biocompatible surgical scaffold made from a multi-filament silk yarn for soft tissue reconstruction. The scaffold incorporates regions of varying stretch having different physical and mechanical properties that allow contouring to the required soft tissue shape to be replaced or repaired. The porous structure allows tissue in-growth, while the mesh degrades at a rate which allows for a smooth transfer of mechanical properties to the new tissue from the silk scaffold.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Prosthetic device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110257665A1Minimizes tissue erosion and fistula and adhesionWithstanding stressMammary implantsWeft knittingMesh gridYarn
A biocompatible surgical silk mesh prosthetic device employs a knit pattern that substantially prevents unraveling and preserves the stability of the mesh device, especially when the mesh device is cut. An example prosthetic device employs a knitted mesh including at least two yarns laid in a knit direction and engaging each other to define a plurality of nodes. The at least two yarns include a first yarn and a second yarn extending between and forming loops about two nodes. The second yarn has a higher tension at the two nodes than the first yarn. the second yarn substantially prevents the first yarn from moving at the two nodes and substantially prevents the knitted mesh from unraveling at the nodes.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Hollow-core optical fiber and method of making same
InactiveUS20050185908A1Increase surface tensionReduce surface tensionGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreFiberSurface roughness
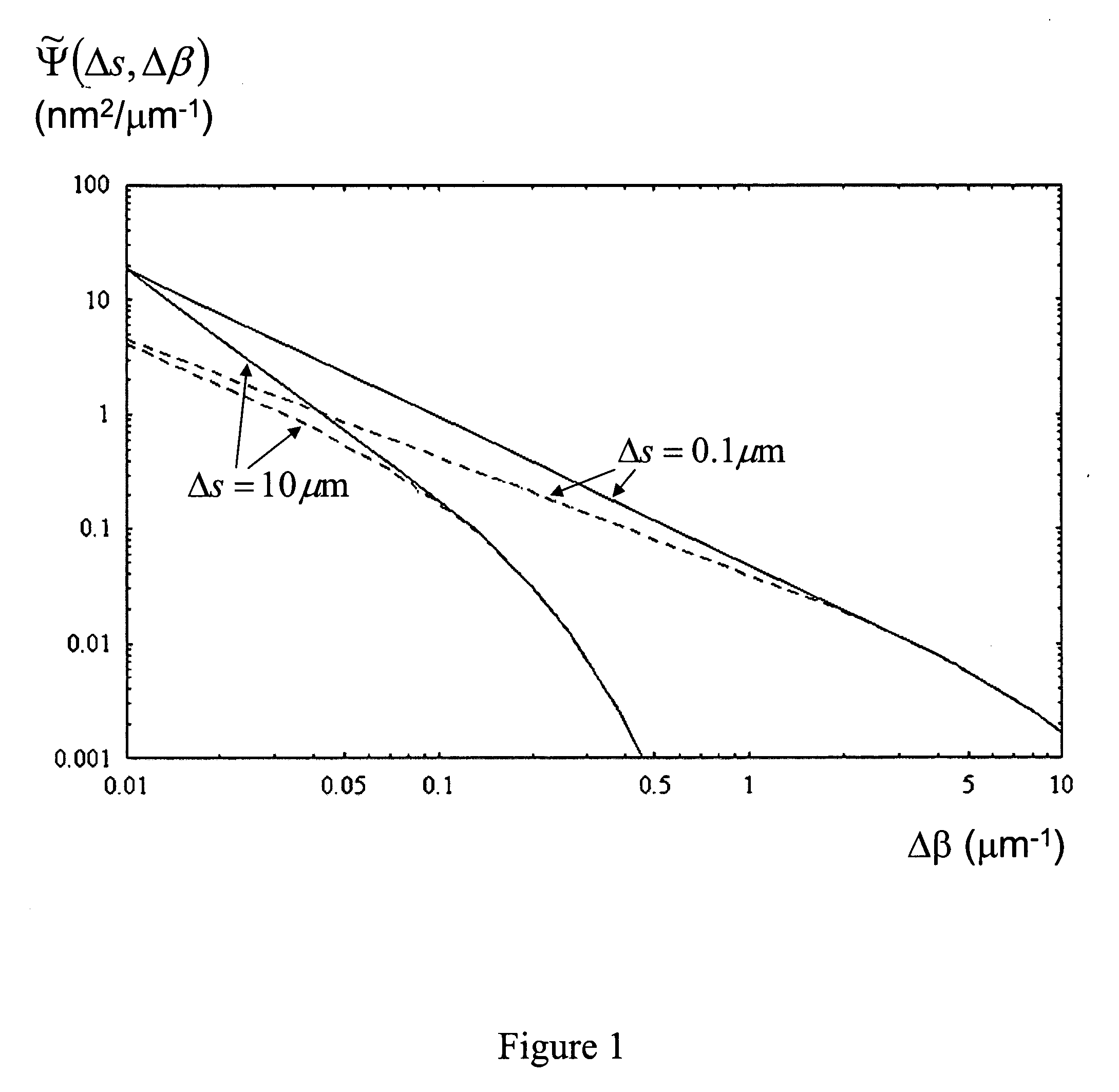
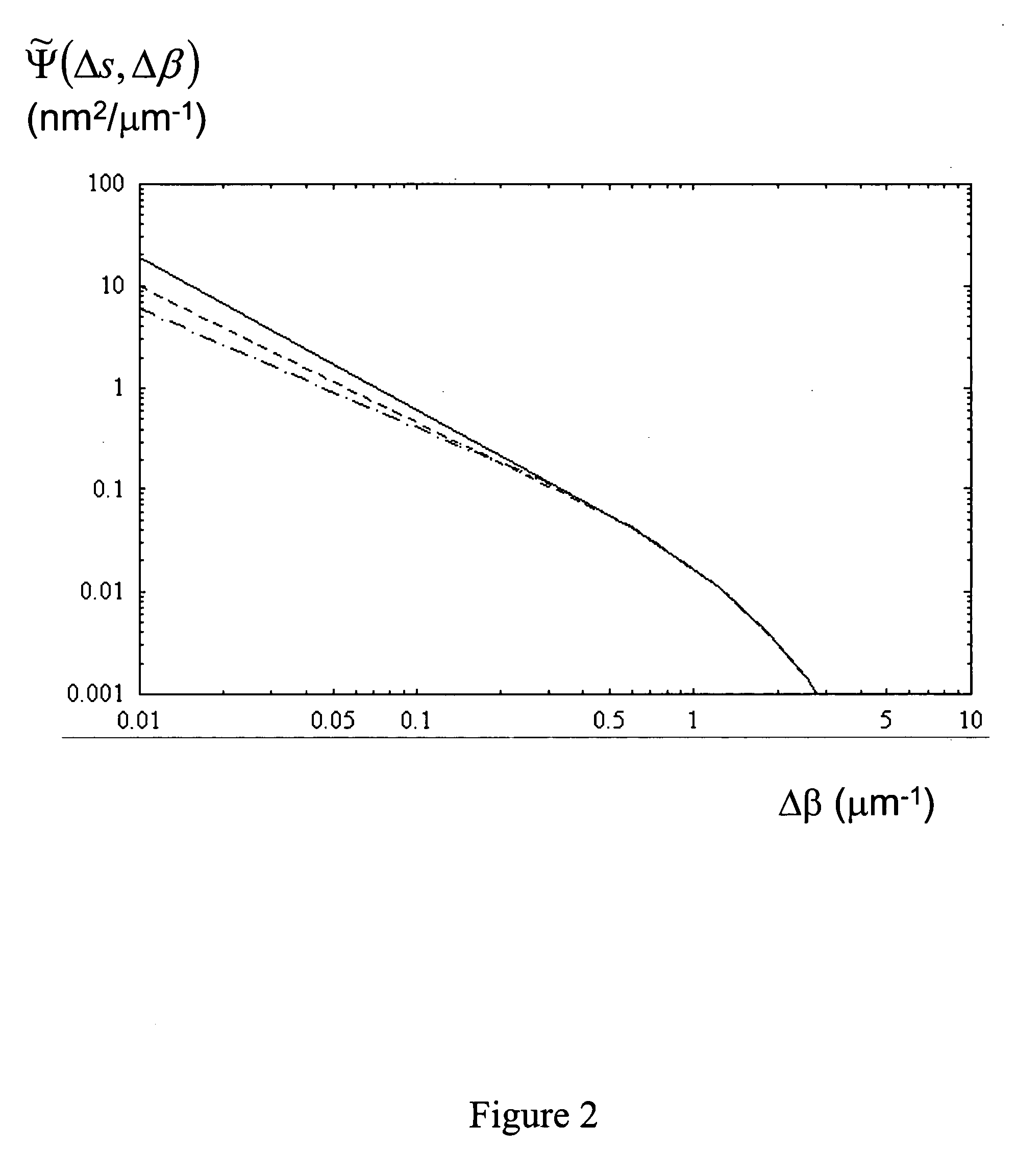
An optical fiber having a cladding region surrounding a core region having an elongate core hole, the inner or outer surface of the core hole having a surface roughness with a spatial period equal to or less than 5 μm by a spectral power below 0.0017 nm2μm−1. A method of making an optical fiber including a cladding region having an arrangement of elongate cladding holes in a matrix material, surrounding an elongate core region having an elongate core hole, the method including the step of increasing the surface tension of the matrix material prior to or during the step of heating and drawing the fiber.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
Implantable silk prosthetic device and uses thereof
InactiveUS20120150204A1Minimizes tissue erosionMinimizes fistulaMammary implantsWeft knittingYarnProsthesis
A method of using a biocompatible surgical silk mesh prosthetic device in body aesthetics and body contouring, the surgical mesh employing a knit pattern that substantially prevents unraveling and preserves the stability of the mesh device, especially when the mesh device is cut. An example prosthetic device employs a knitted mesh including at least two yarns laid in a knit direction and engaging each other to define a plurality of nodes. The at least two yarns include a first yarn and a second yarn extending between and forming loops about two nodes. The second yarn has a higher tension at the two nodes than the first yarn. the second yarn substantially prevents the first yarn from moving at the two nodes and substantially prevents the knitted mesh from unraveling at the nodes.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Prosthetic device having diagonal yarns and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110224703A1Minimize erosionMinimizes adhesionsMammary implantsMedical devicesYarnEngineering
A knitted scaffold comprising at least two silk yarns in a knit direction and a yarn member diagonal to the knit direction to thereby provide a knitted fabric or mesh for surgical use that can retain its shape and / or resist collapse when opposing forces are applied at an angle from the knit direction. The knitted scaffold may include at least two yarns laid in a knit direction and engaging each other to define a plurality of nodes. The at least two yarns can include a first yarn and a second yarn extending between and forming loops about two nodes. The second yarn has a higher tension at the two nodes than the first yarn. The second yarn substantially prevents the first yarn from moving at the two nodes and substantially prevents the knitted mesh from unraveling at the nodes.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
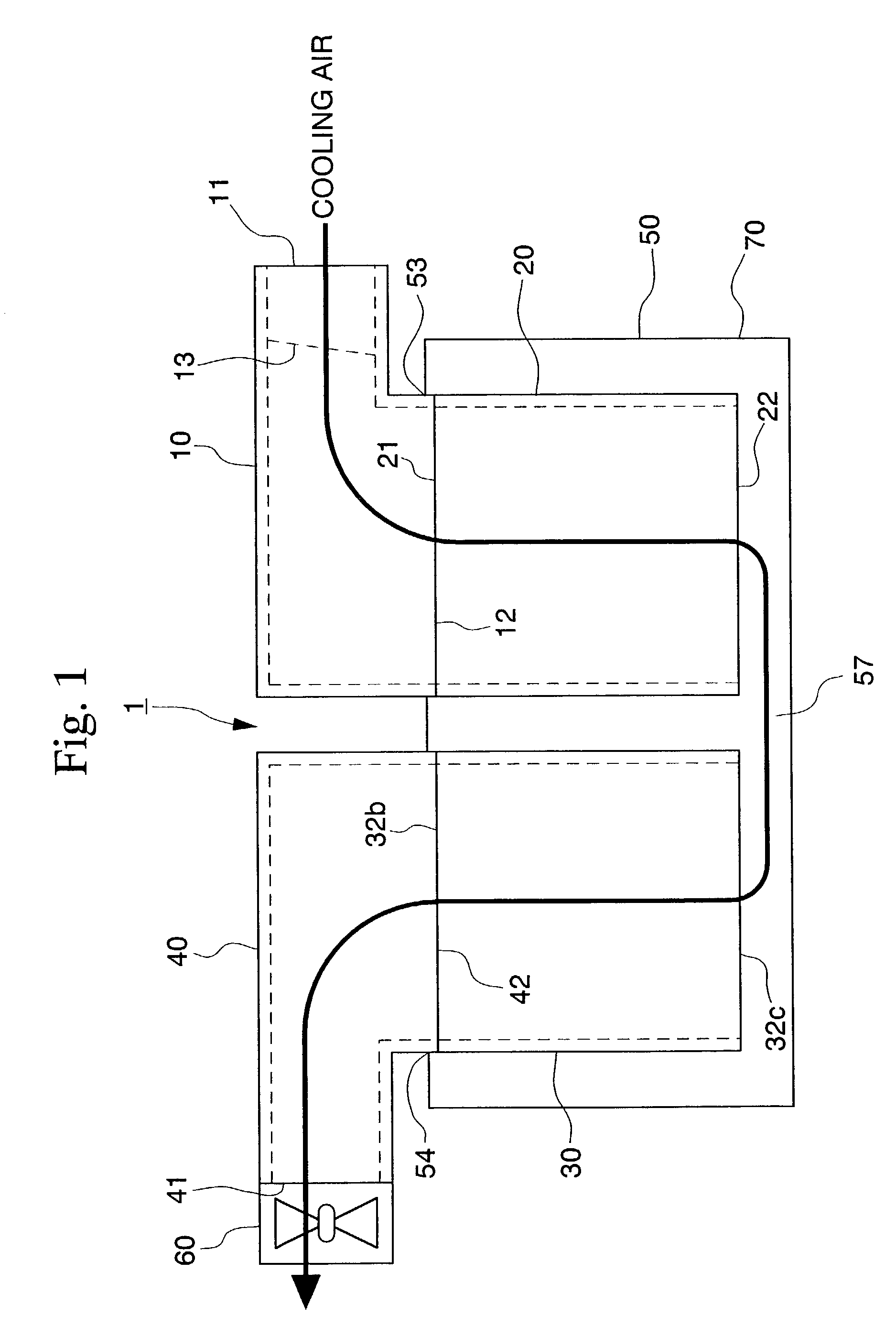
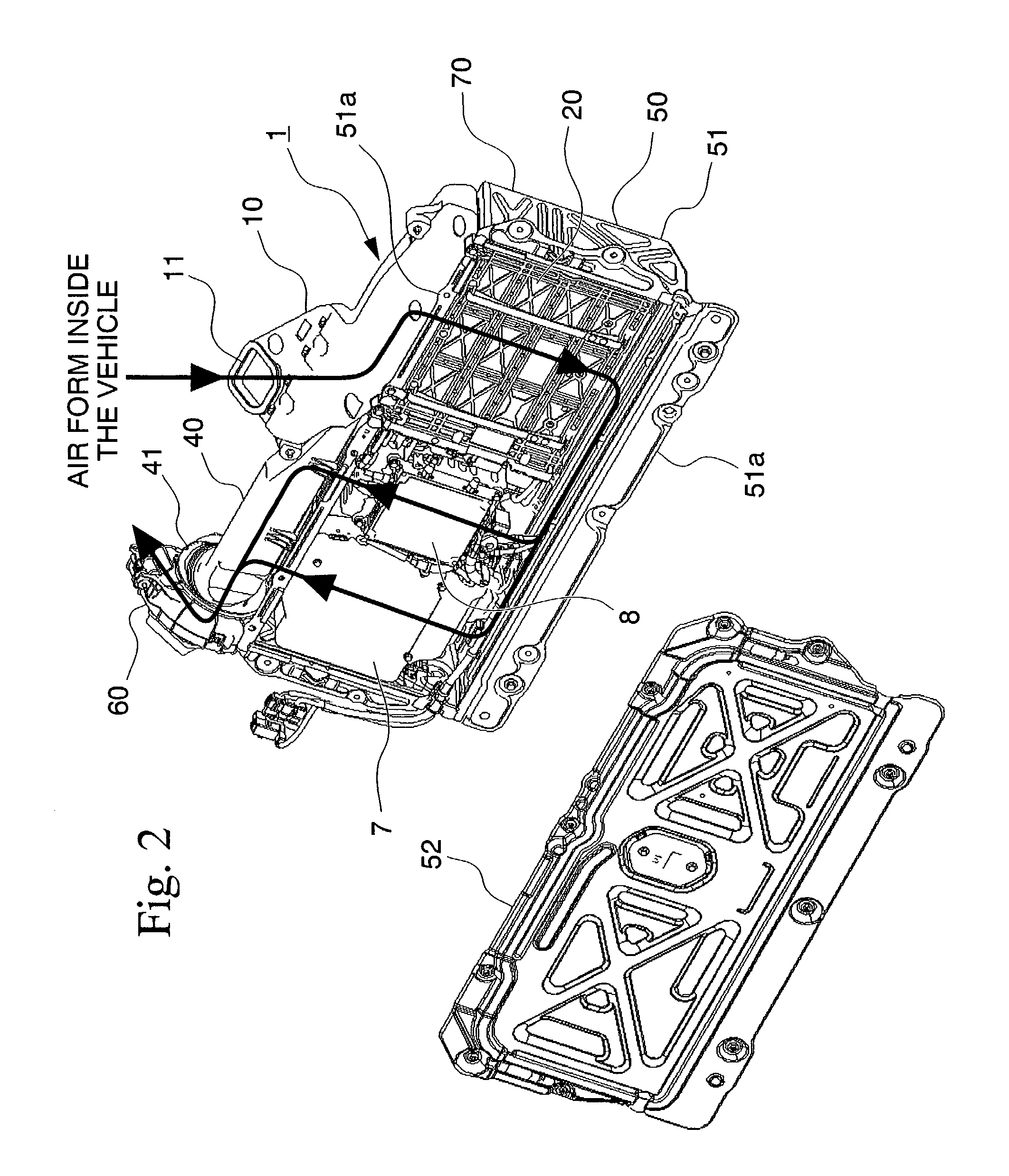
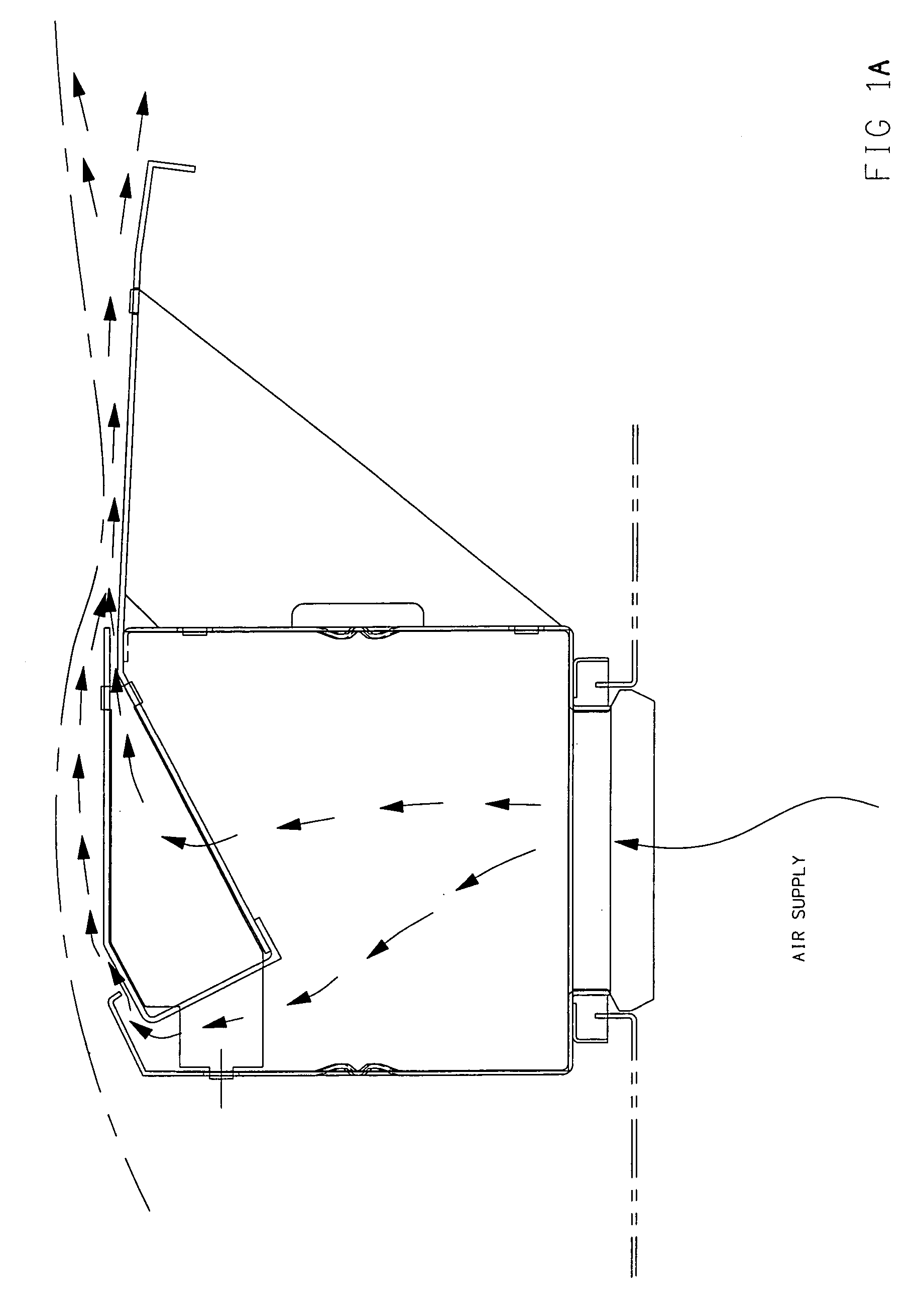
Cooling structure for high tension electrical equipment
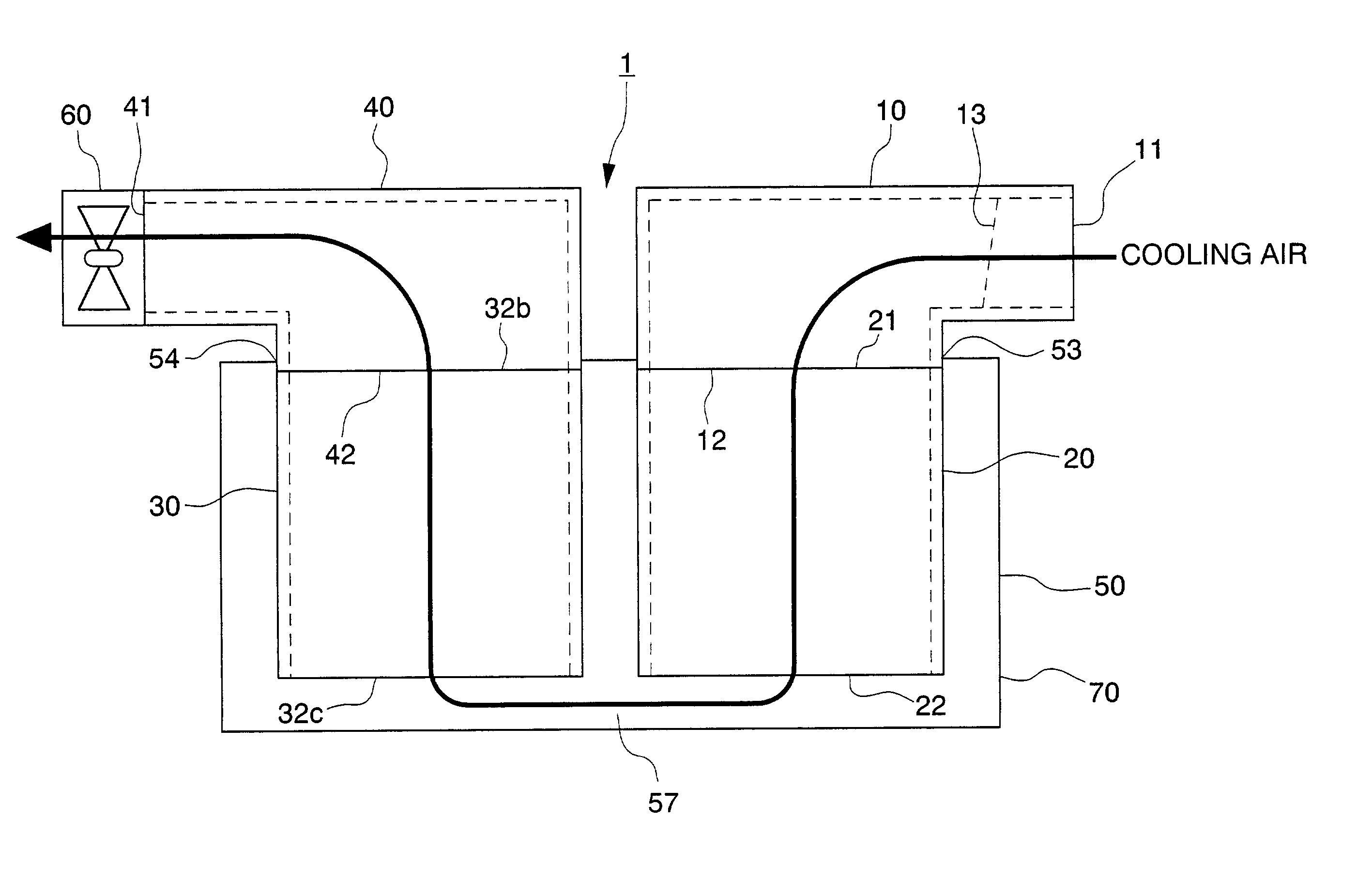
InactiveUS7004233B2Made lighter in weightImprove propertiesDucting arrangementsCell temperature controlElectricityHigh pressure
A high tension electrical equipment cooling structure for cooling batteries which supply electricity to the operating motor via an inverter, and the inverter using cooling air, and includes an equipment box for guiding cooling air introduced from a cooling air inlet port into a cooling air outlet port, and a fan for introducing cooling air from the cooling air inlet port. A shutter that includes an elastic material is disposed inside the intake duct. The shutter closes off the cooling air flow path, and when negative pressure is generated downstream of the shutter due to the operation of the fan, the shutter undergoes elastic deformation, and as a result, the cooling air flow path is opened.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Glass roll, and method of manufacturing glass roll
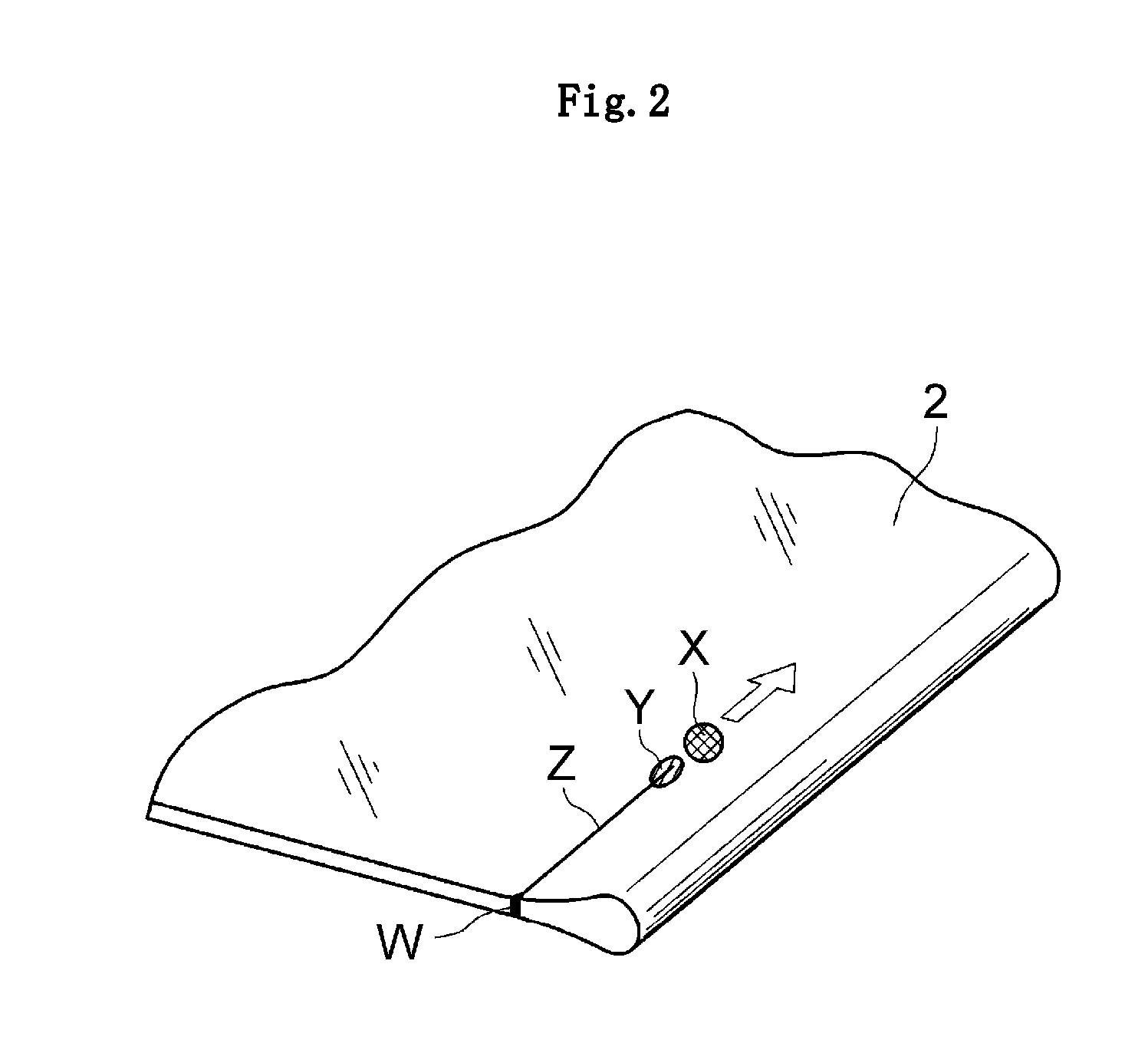
InactiveUS20110217521A1High tensionPrevent changeFilm/foil adhesivesGlass drawing apparatusGlass filmMaterials science
To manufacture a roll body (glass roll) of the glass film, which is subjected to a tension application, and is free from looseness, without adversely affecting the formation of the glass film and causing a problem such as cracks, provided is a method of manufacturing a glass roll (1), including: forming a glass film (2) by a downdraw method; and winding the formed glass film (2) into a roll while superposing the glass film (2) on a protective sheet (3), in which the glass film (2) and the protective sheet (3) are wound while higher tension in a winding direction is applied to the protective sheet (3) than to the glass film.
Owner:NIPPON ELECTRIC GLASS CO LTD
Random rebound practice device
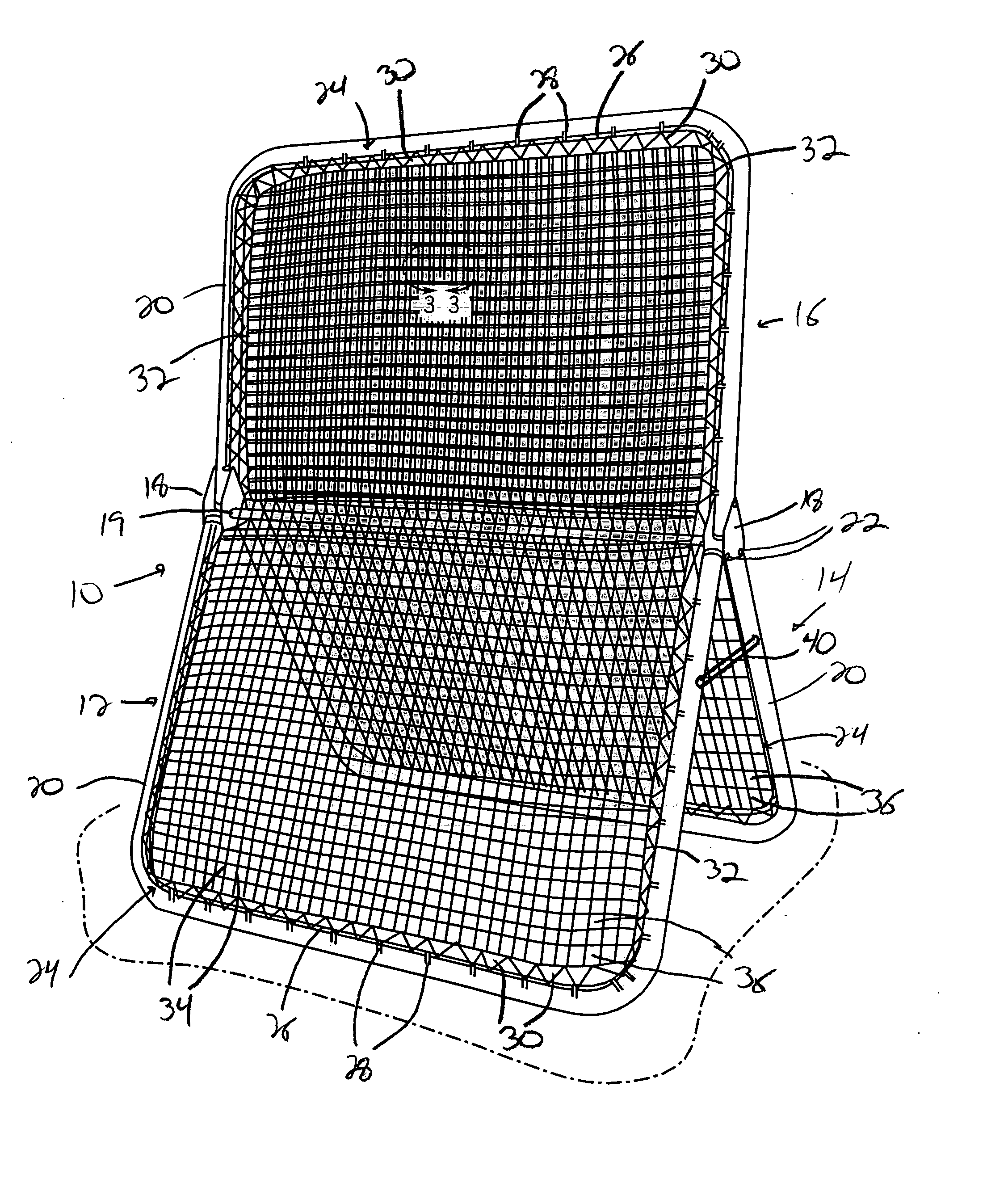
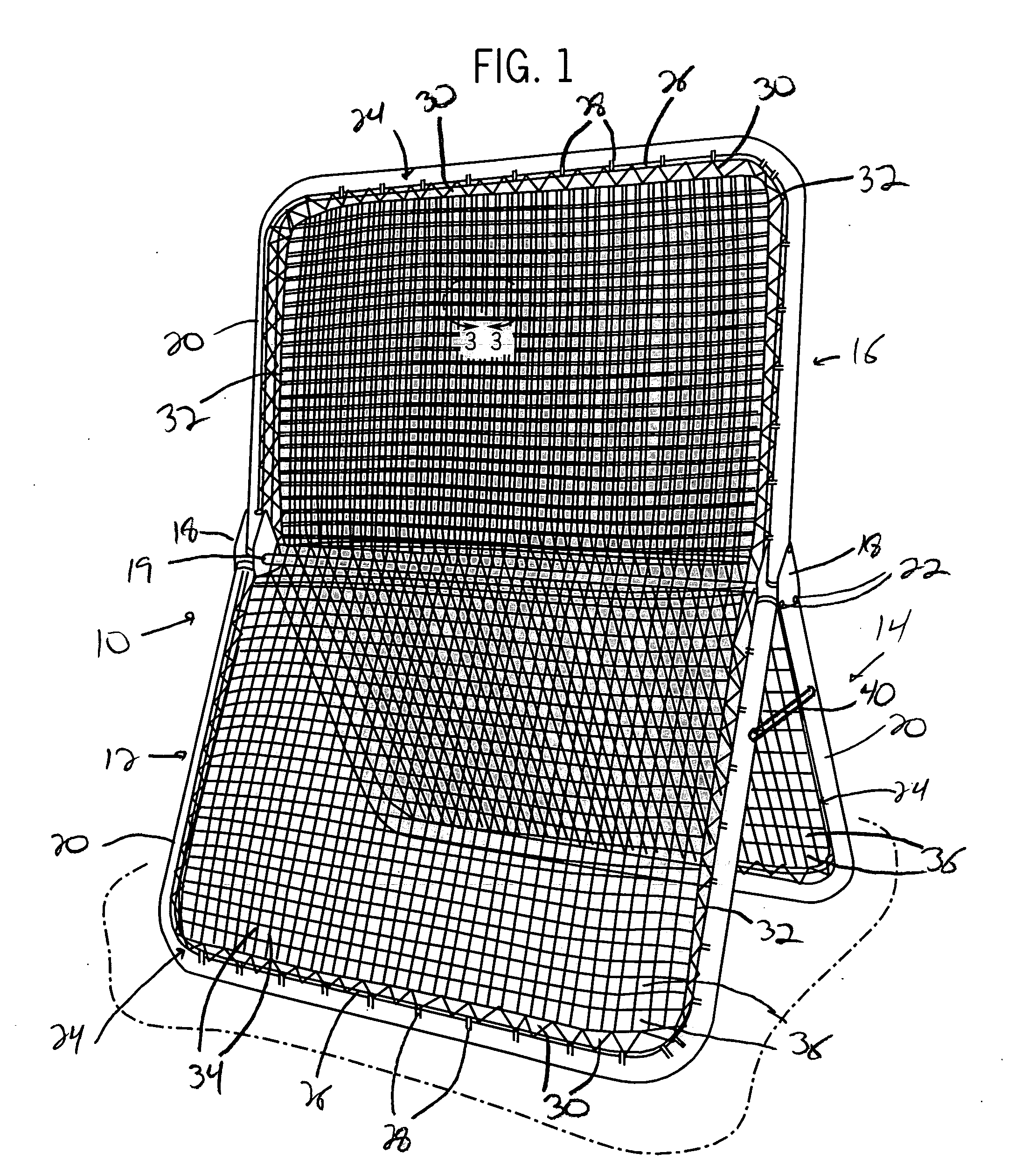
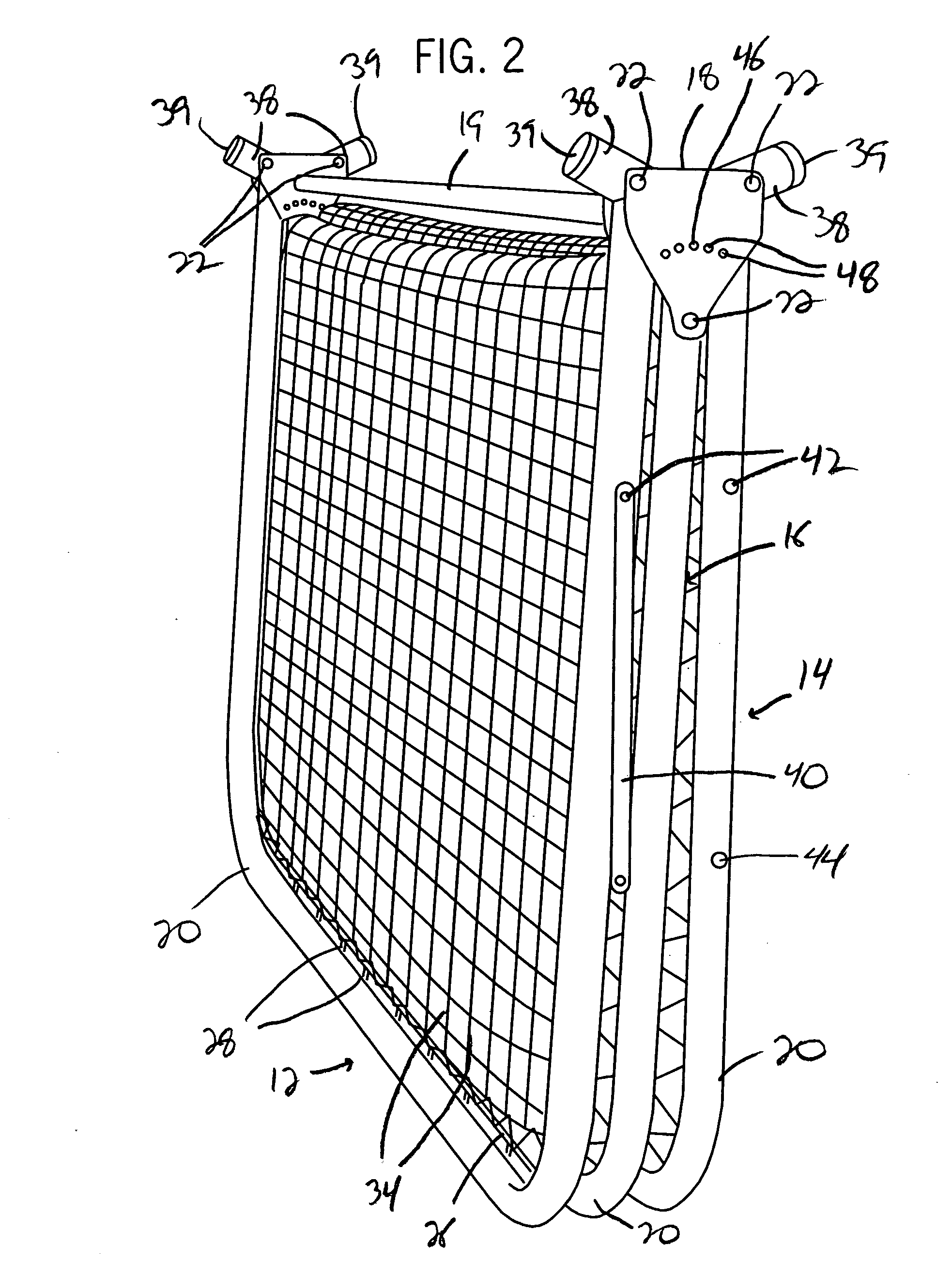
InactiveUS20080067751A1Improve abilitiesHigh tensionBall sportsSpace saving gamesSingle supportBraced frame
A random rebound sports training device is provided which includes a pair of misaligned or offset net structures disposed on a frame that enable a projectile striking the net structures to rebound in a random manner. The structures are secured to a support frame such that the openings formed in the net structure, which are larger than normally utilized, are offset from one another. The offset of each of the net structures greatly reduces the potential for a projectile striking the device from contacting the same portions of the net structures, thereby causing the projectile to rebound in a random manner from the device. The frame on which the net structures are mounted can be easily configured between a use configuration and a storage configuration. Further, each of the net structures can be secured to a single support frame, or can extend from separate frames onto a target frame to provide multiple use sections on the device.
Owner:WILSON HUNT INT
Flat shaft of a hip-joint prosthesis for anchoring in the femur
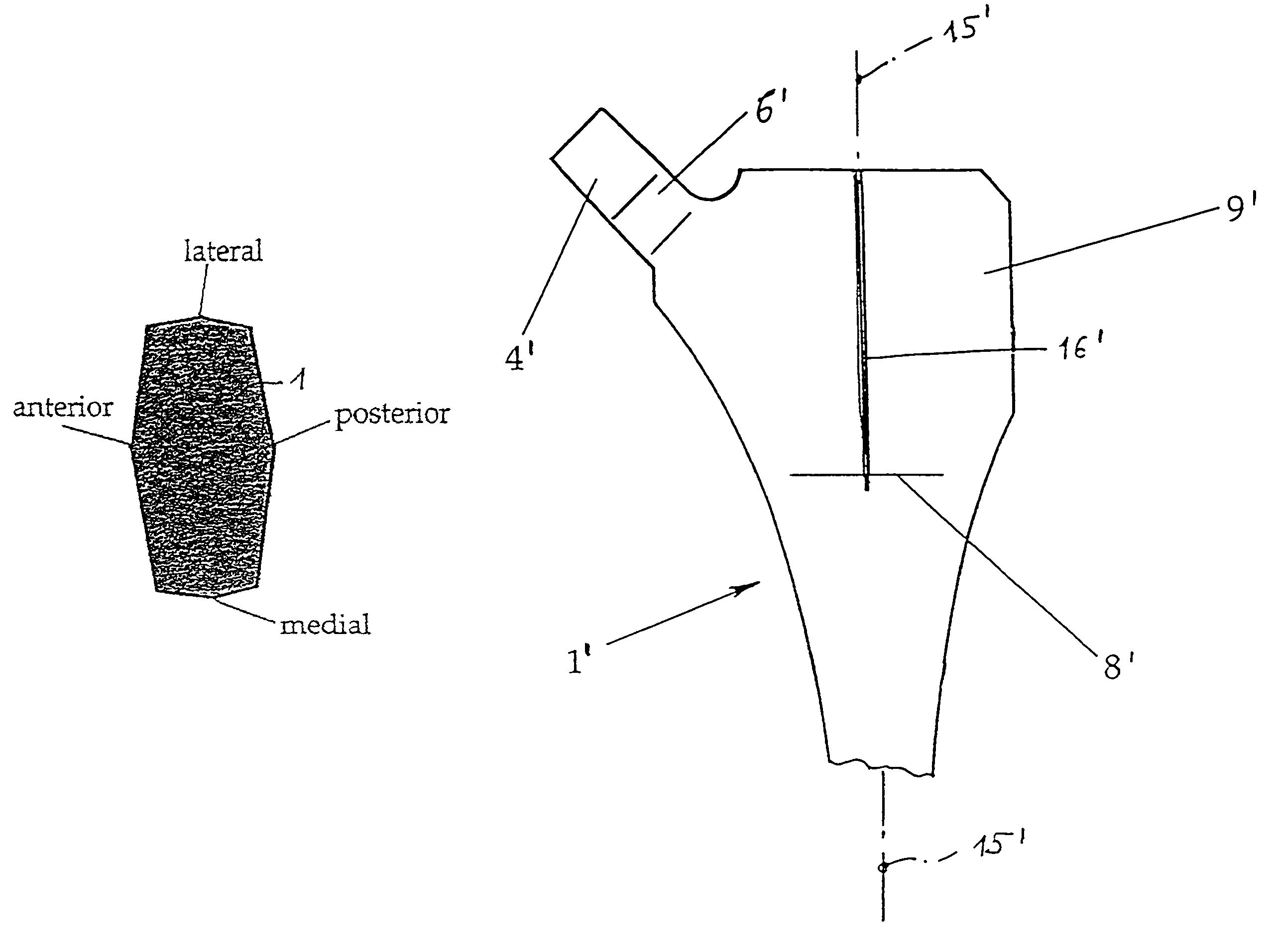
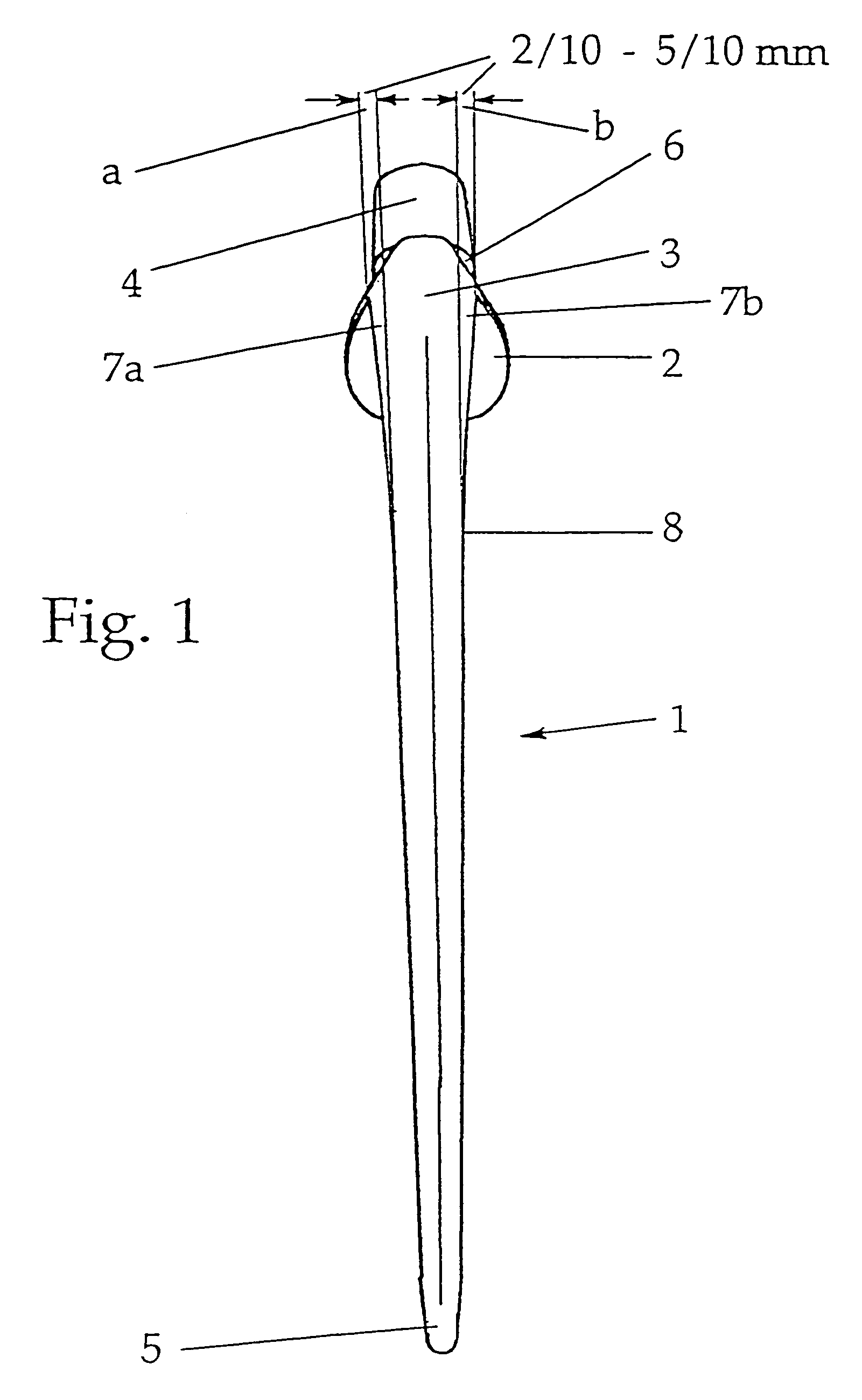
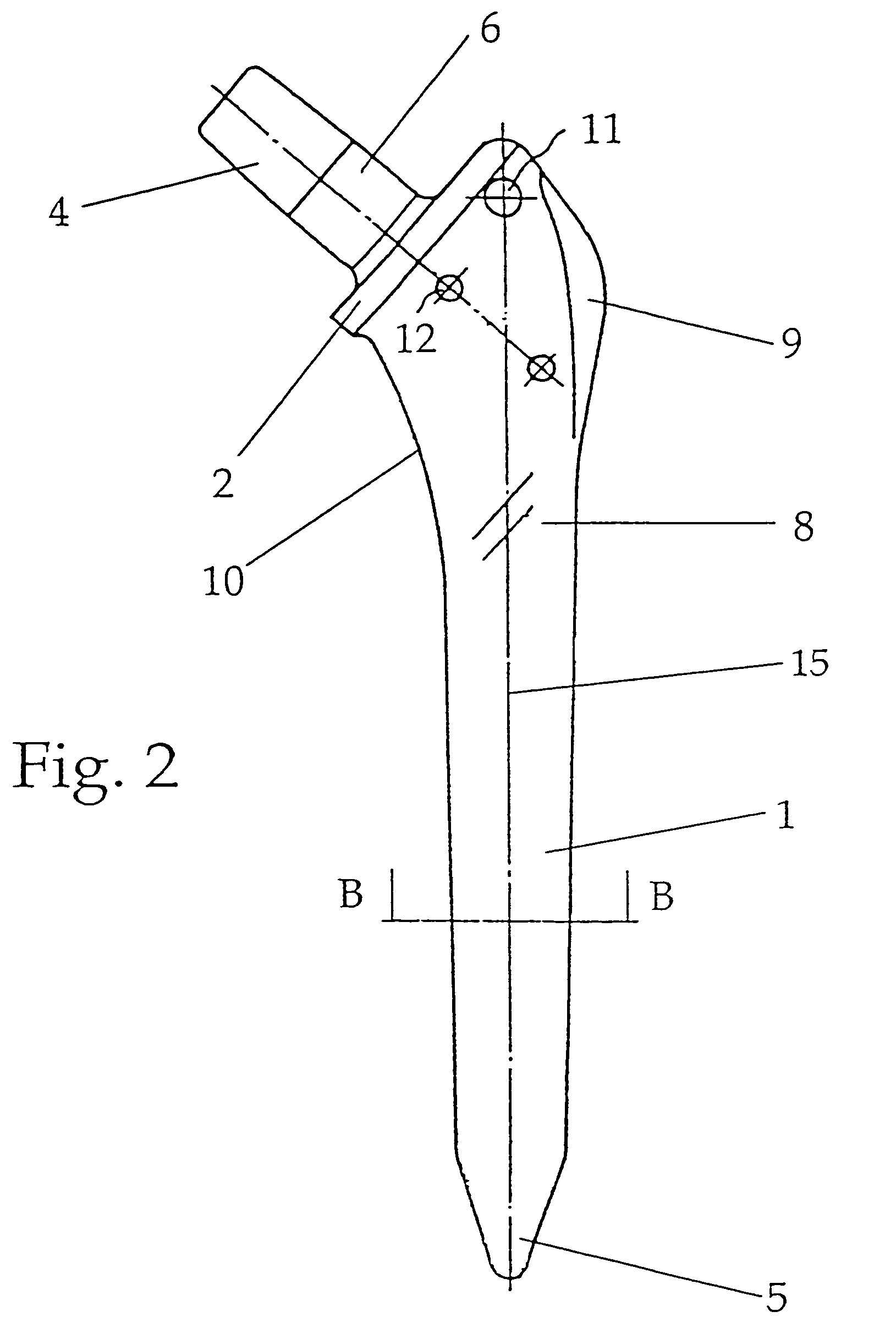
A flat shaft of a hip-joint prosthesis for anchoring in a femur. The shaft expands on all sides towards a proximal end from a distal end of the shaft and medially merges with a curved section that is continuous with a prosthesis neck. The shaft is additionally expanded in a proximal region along a proximal direction on at least one of an anterior and posterior surfaces.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Non-fibrous high modulus ultra high molecular weight polyethylene tape for ballistic applications
ActiveUS20080318016A1High propertySmall incidenceEngine sealsSynthetic resin layered productsStress concentrationFiber
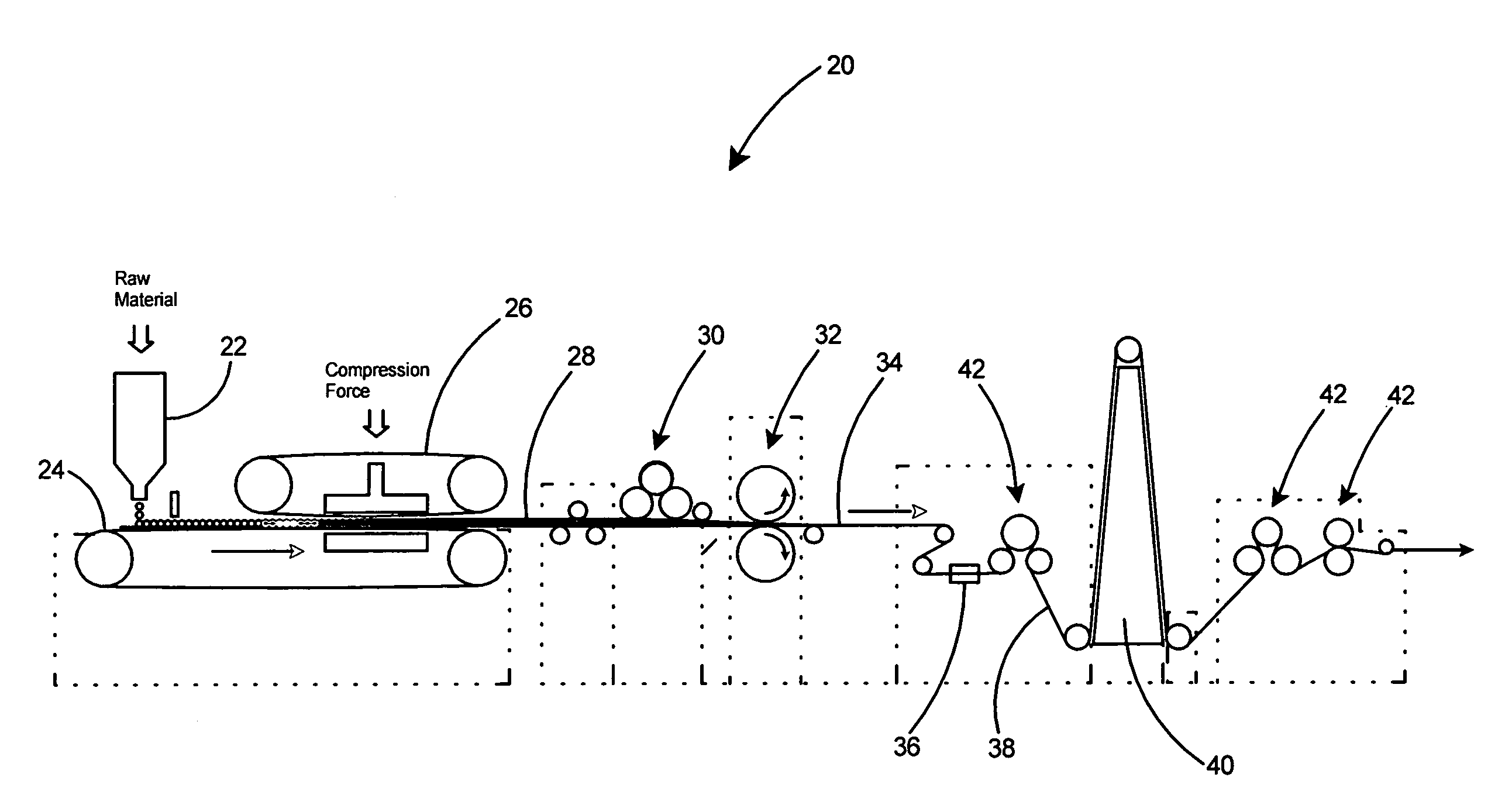
A non-fibrous ultra high molecular weight polyethylene tape having a width of 1-inch or greater and a modulus of 1,400 grams per denier or greater. The non-fibrous UHMWPE tape is obtained by compression molding ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene powder at a temperature below its melting point and then drawing and stretching the entire resultant compression molded UHMWPE sheet, with no slitting or splitting of the sheet, at a draw ratio of at least 100:1. The UHMWPE tape can be produced in weights of 6,000 to 90,000 denier or greater. The UHMWPE tape of the present invention minimizes the effect of stress concentrators that are prevalent with fibers and thereby enables the tape to be drawn at much higher draw ratios than is possible with fibrous UHMWPE. When used in ballistics panels, the high modulus high molecular weight polyethylene tape of the present invention improves ballistic performance by providing enhanced dissipation of the impact energy of a projectile.
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
Feed mechanism for maintaining constant web tension in a wide format printer
InactiveUS20070059078A1Small distanceSuitable for useFunction indicatorsOther printing apparatusPrint mediaControl system
A feed mechanism for feeding a web of print media past a printhead is provided. The feed mechanism comprises a supply spool, a take-up spool, a take-up motor operatively connected to the take-up spool, a take-up control system for controlling the torque of the take-up motor, a drive roller system positioned between the supply spool and the take-up spool and a drive motor operatively connected to the drive roller system. In use, a web fed from the drive roller system to the take-up spool is maintained under substantially constant tension by regulating the torque of the take-up motor using the take-up control system. A wide format printer comprising the feed mechanism is also provided.
Owner:SILVERBROOK RES PTY LTD
Functionally strained optical fibers
InactiveUS6898355B2Eliminating and greatly reducing impactImproved strain distributionCladded optical fibreOptical articlesTensile strainFiber
The present invention introduces a concept of “smart” ribbons, which use functionally tensioned optical fibers during the manufacture of fiber optic ribbons to create fiber ribbons with controlled geometrical configuration, optimized strain distribution and reduced attenuation. The ribbons may have flat or bowed cross section and be straight along the length or curved in its plane, or twisted unidirectionally, or periodically. These shapes and residual stress-strain state are induced and controlled by using tension functions instead of traditional constant-value tension per fiber during the ribbon manufacture. Further, the present invention reduces signal loss and / or attenuation in ribbon fibers caused by an increase in the strain variation from tensile strain to compressive strain along the length of the individual fibers when ribbons are manufactured, stacked, stranded around a strength member or twisted and bent during cable installation. In a first embodiment of the present invention, either a symmetric or non-symmetric load distribution is applied across the fibers being placed or drawn into a ribbon structure to eliminate or control residual twist in a completed fiber ribbon. Additionally, in the present invention, the load distribution on the fibers of a ribbon can be varied (e.g. periodically changed) along the length of the ribbon to provide a ribbon with the required design characteristics for any particular application. In a second embodiment of the invention, a fiber optic ribbon is made up of a plurality of sub-unit ribbons arranged in substantially the same plane. Each sub-unit ribbon includes a plurality of optical fibers coated by sub-unit matrices.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method for coating wire for a musical instrument string, and coated string
InactiveUS20060174745A1Increase line speedMore reliabilityStringed musical instrumentsUltravioletElectron
A musical instrument string having a tarnish resistant exterior surface, comprising a metal wire at least a portion of which has an ultra-violet (U-V) or electron beam (EB) radiation cured polymeric coating defining the exterior surface and having a coating thickness preferably less than 0.0004 inch (0.4 mil). A method of coating a musical instrument string, and a guitar having such coated strings, are also disclosed.
Owner:D'ADDARIO
Step air foil
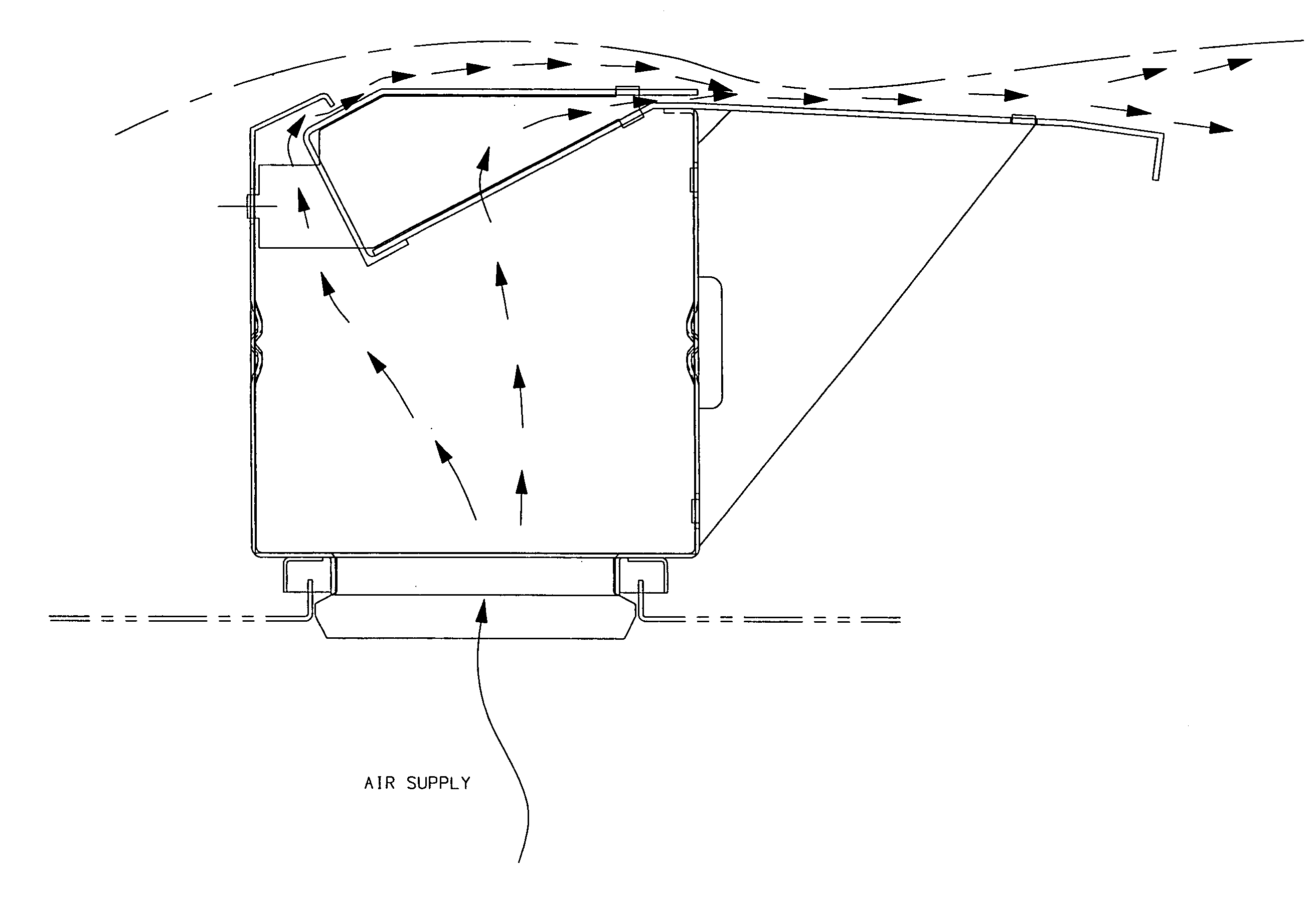
ActiveUS7530179B2Stable supportIncrease downforceProjector film strip handlingCamera film strip handlingWrinkle skinFiber
Step air foil particularly for one-sided flotation of a running web, and web dryer incorporating the same. The air foil includes two discharge slots which allow for increased draw down force, which flattens machine direction wrinkles in a floating web. The air foil includes a primary discharge slot and a second discharge slot spaced from and stepped down from the primary discharge slot, a first web support surface between the primary discharge slot and the secondary discharge slot, and a second web support surface downstream of the secondary discharge slot in the direction of web travel. The air foil is in communication with an air supply which provides a supply of air that is uniformly distributed to the primary and secondary slots. Air discharged from the primary slot is gathered into the air stream of the secondary slot and creates an increased air cushion to provide greater support to the moving web and thereby remove machine direction web wrinkles caused by higher tension in light weight webs.
Owner:DURR SYST INC
Prosthetic device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9326840B2Minimizes adhesionsErosion minimizationMammary implantsWeft knittingYarnEngineering
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Incontinence article in the form of pants
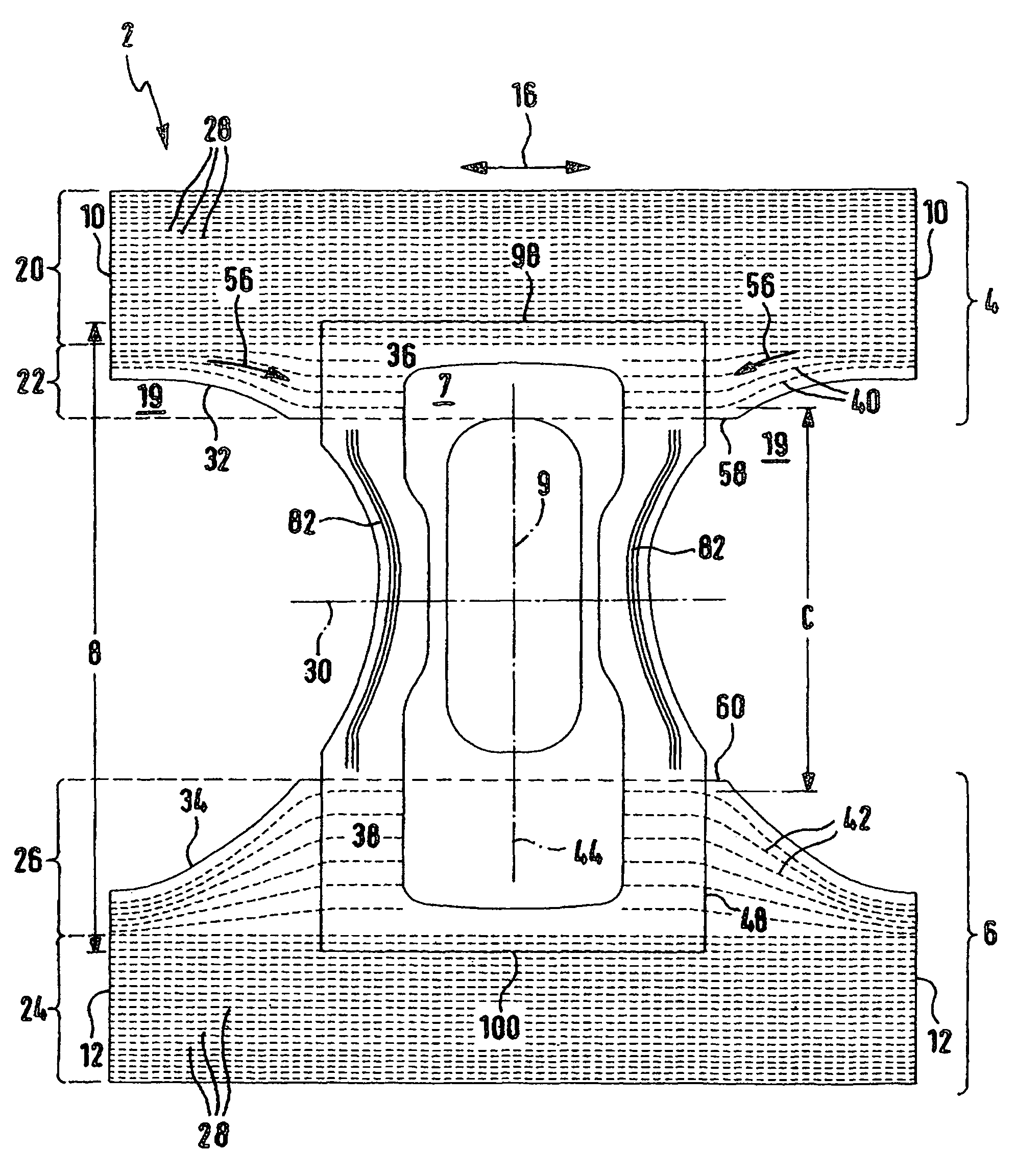
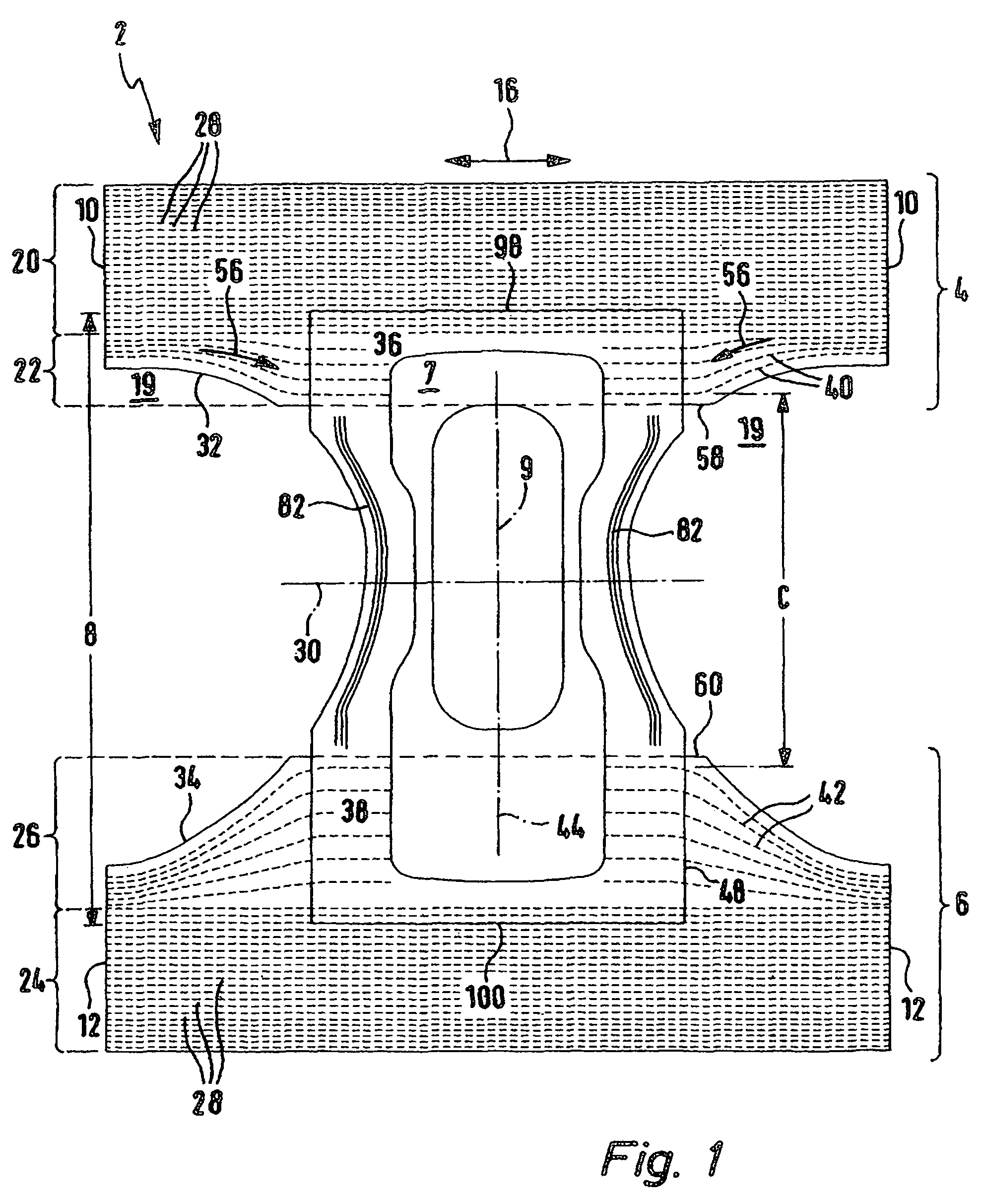
An incontinence article comprising front and back belly sections connected at side seams forming belly and back bands, continuous in the hip direction having a hip opening closed in the hip direction, and a crotch section comprising an absorbent body, extending longitudinally between and permanently attached to the belly and back sections, wherein the crotch, belly, and back sections define leg openings, the belly and back sections have an edge contour extending towards a transverse center axis, wherein first elastification means in the belly and back sections extend parallel to each other in the hip direction and wherein, in the belly and back sections, second elastification means extend from two side seam areas towards a longitudinal center axis of the article in a curved shape, thereby fanning out with increasing separation from each other, where the second elastification means fan out, the restoring force from extensive stretching of this area is smaller than that from extensive stretching of an area on the hip side, having only the first elastification means.
Owner:PAUL HARTMANN AG
Concealed structural post fastening device and method
ActiveUS20170175384A1Improve resistance performanceHigh tensionFencingConnectionsEngineeringThreaded rod
A post fastening device for mounting a post to a construction surface, the device comprising a base having a planar top surface and a threaded rod extending from the top surface, a tubular member for insertion into a longitudinal axial bore on the bottom end of the post, the tubular member having an upper end and a lower end with internal threads complementary to the threads of the rod, and a dowel rod for insertion into a transverse bore extending through a portion of the post and the tubular member when the tubular member is in the longitudinal bore, the dowel rod being sized to pass through the tubular member and a portion of the post on both sides of the tubular member.
Owner:BERGMAN RICHARD
Polishing silicon wafers
InactiveUS20010034197A1High tensile strengthLow elongationEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesYarnHardness
An endless belt for a belt type polishing machine comprises a support fabric and a polymer layer of relatively low hardness. The polymer layer is formed with drainage grooves. The support fabric may comprise a non woven or woven material, or a membrane with oriented reinforcing yarns. A further version comprises a spiral-link fabric supporting a woven or non woven layer carrying the polymer layer. The polymer layer may be a double layer, the upper of which is either harder or softer than the lower layer.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Frictionally driven belted work vehicle
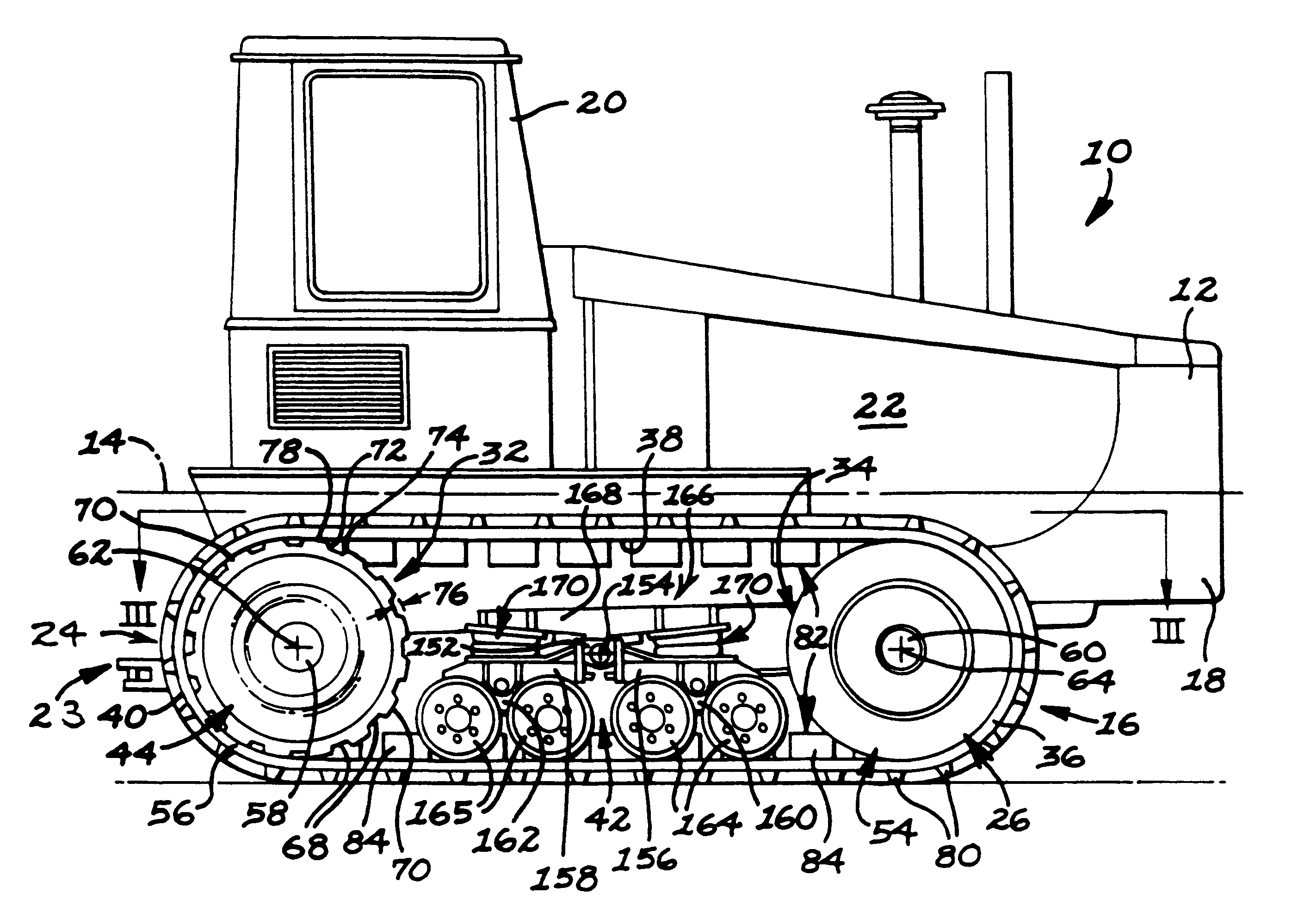
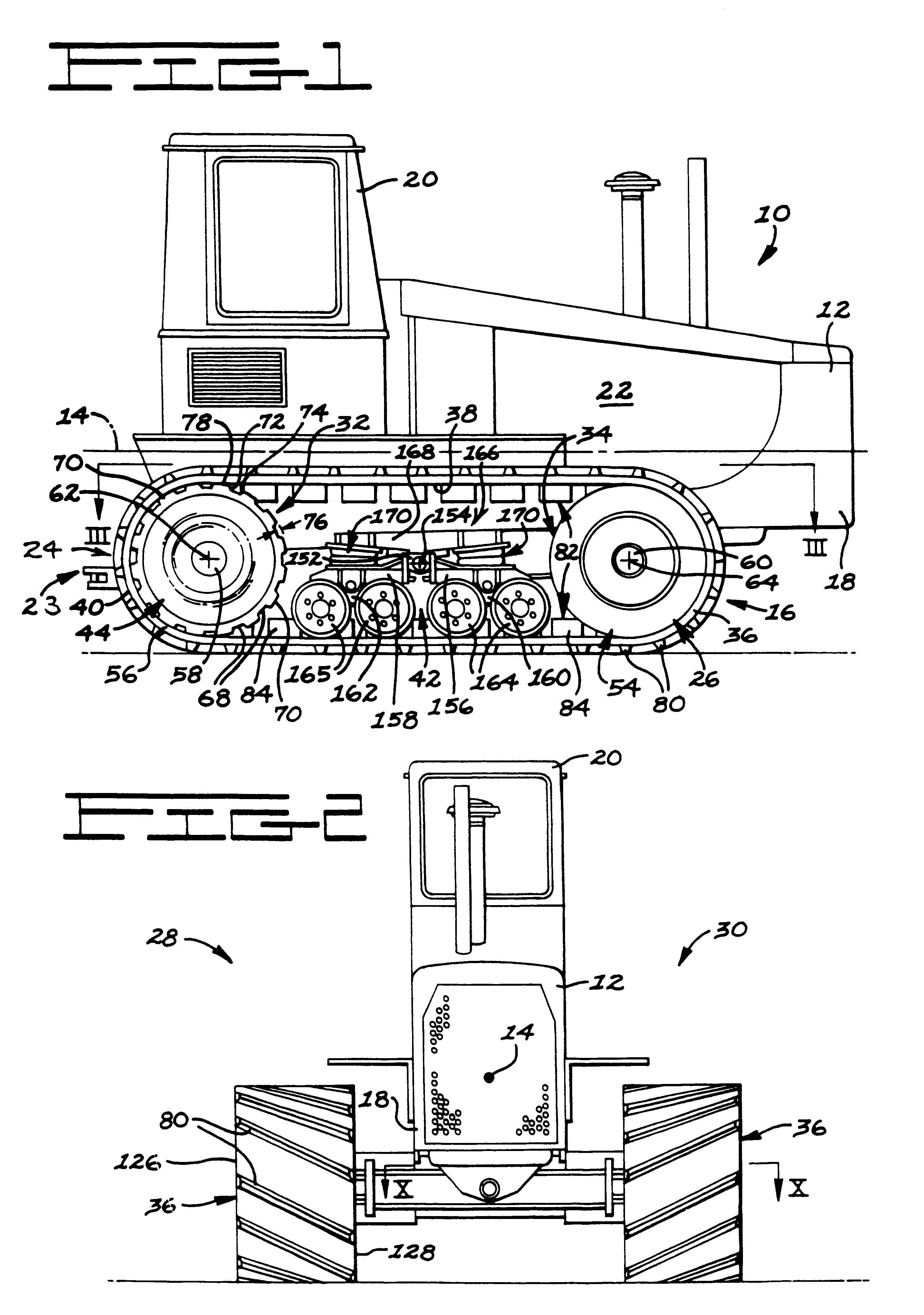
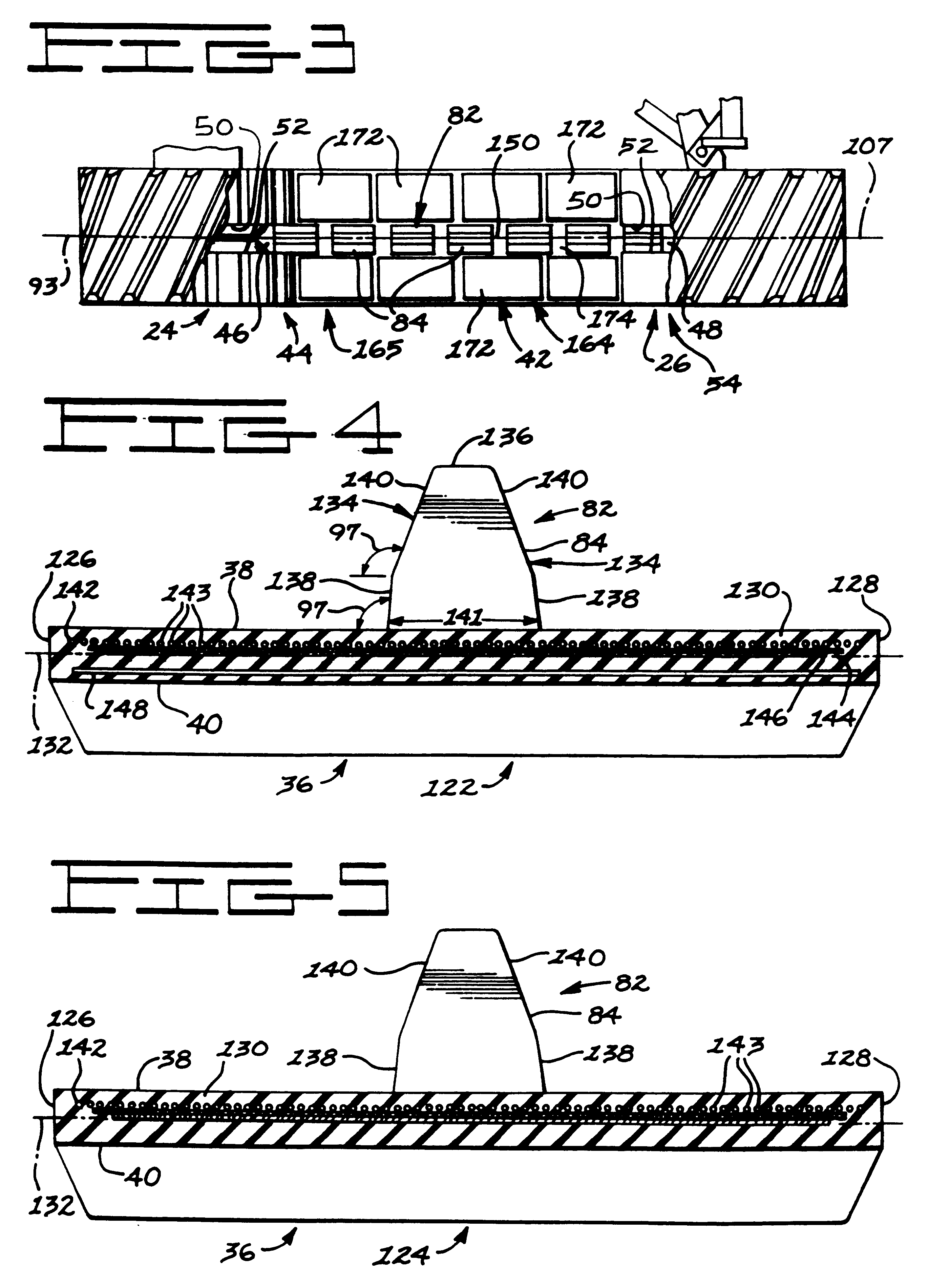
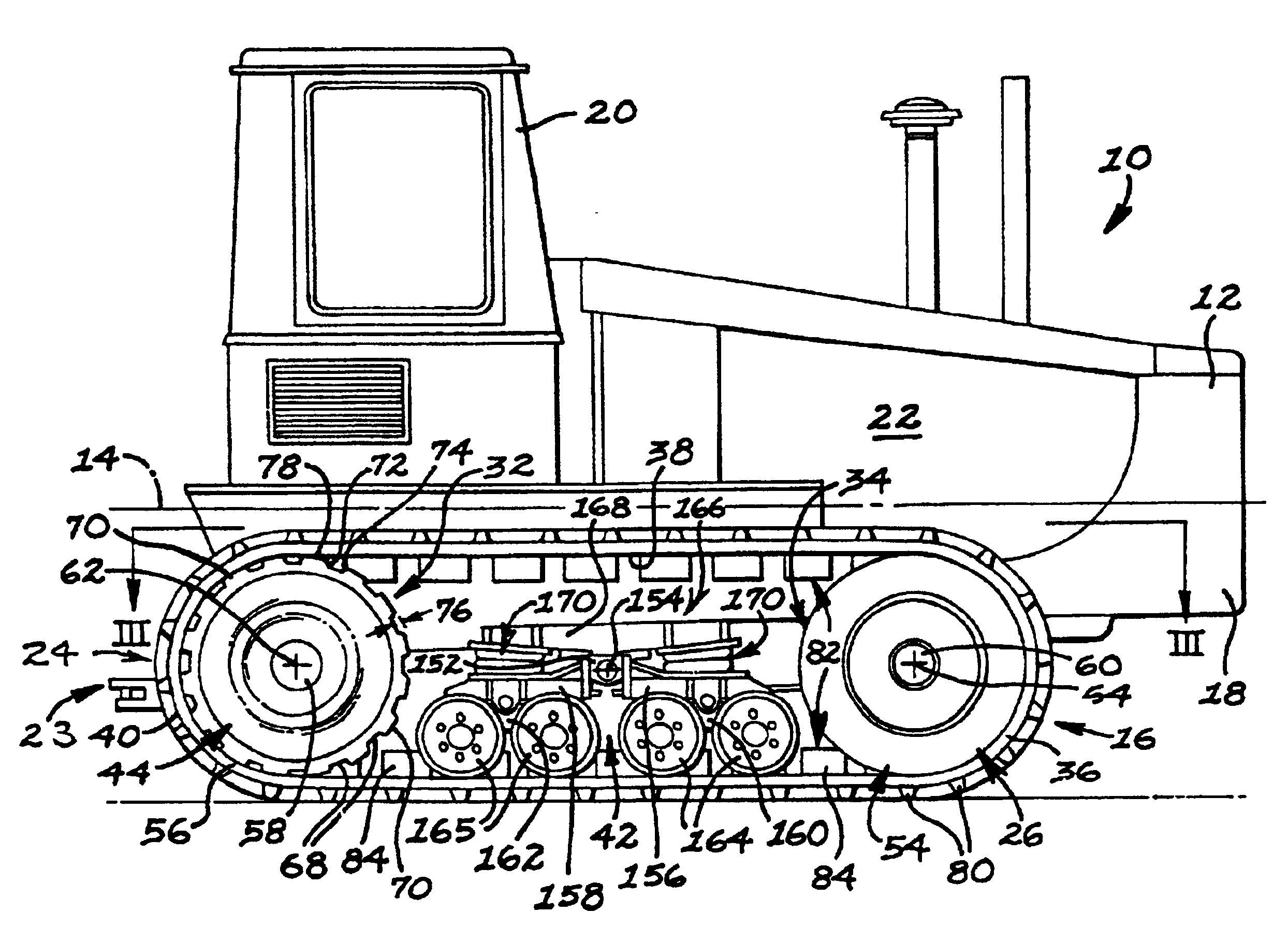
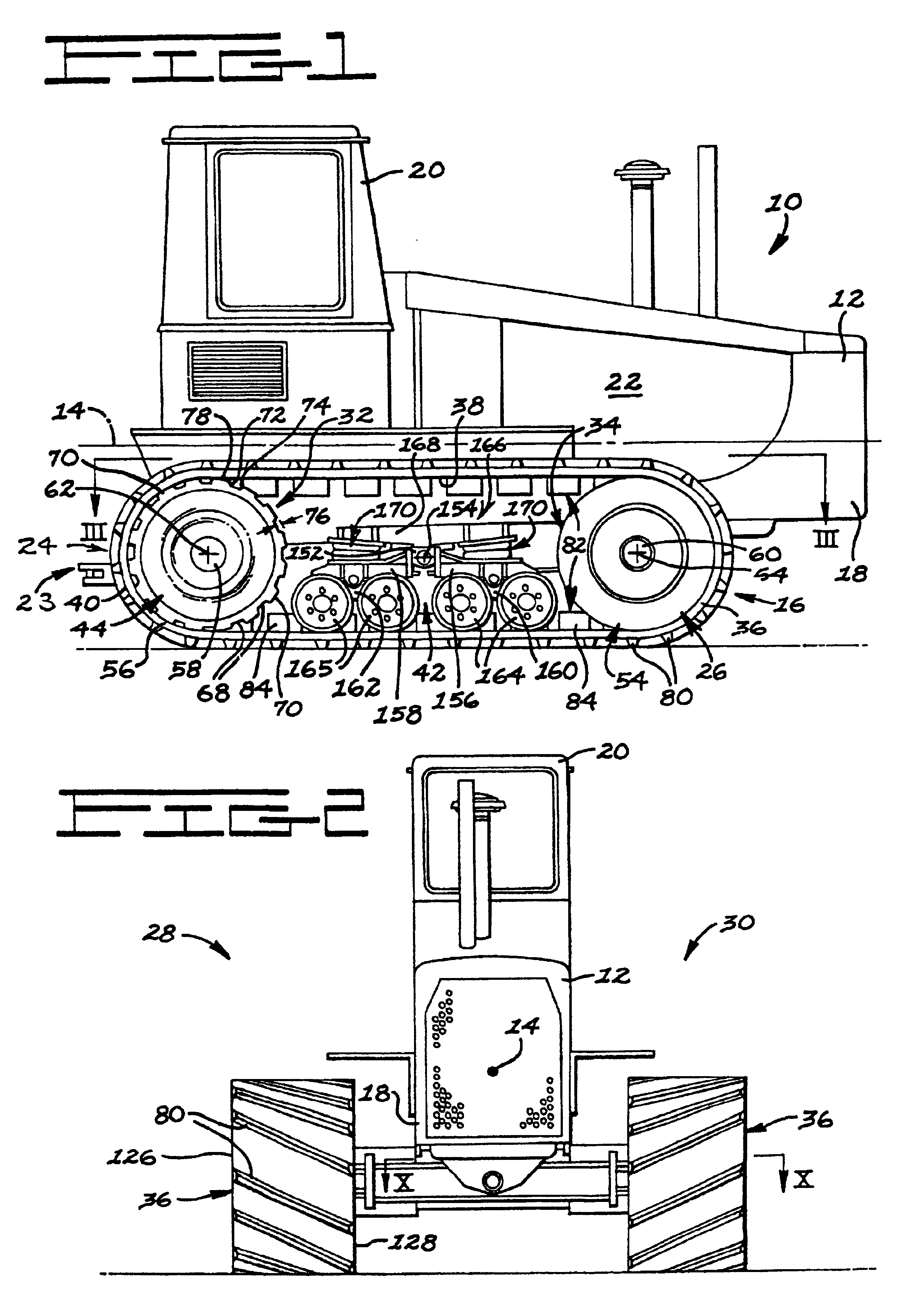
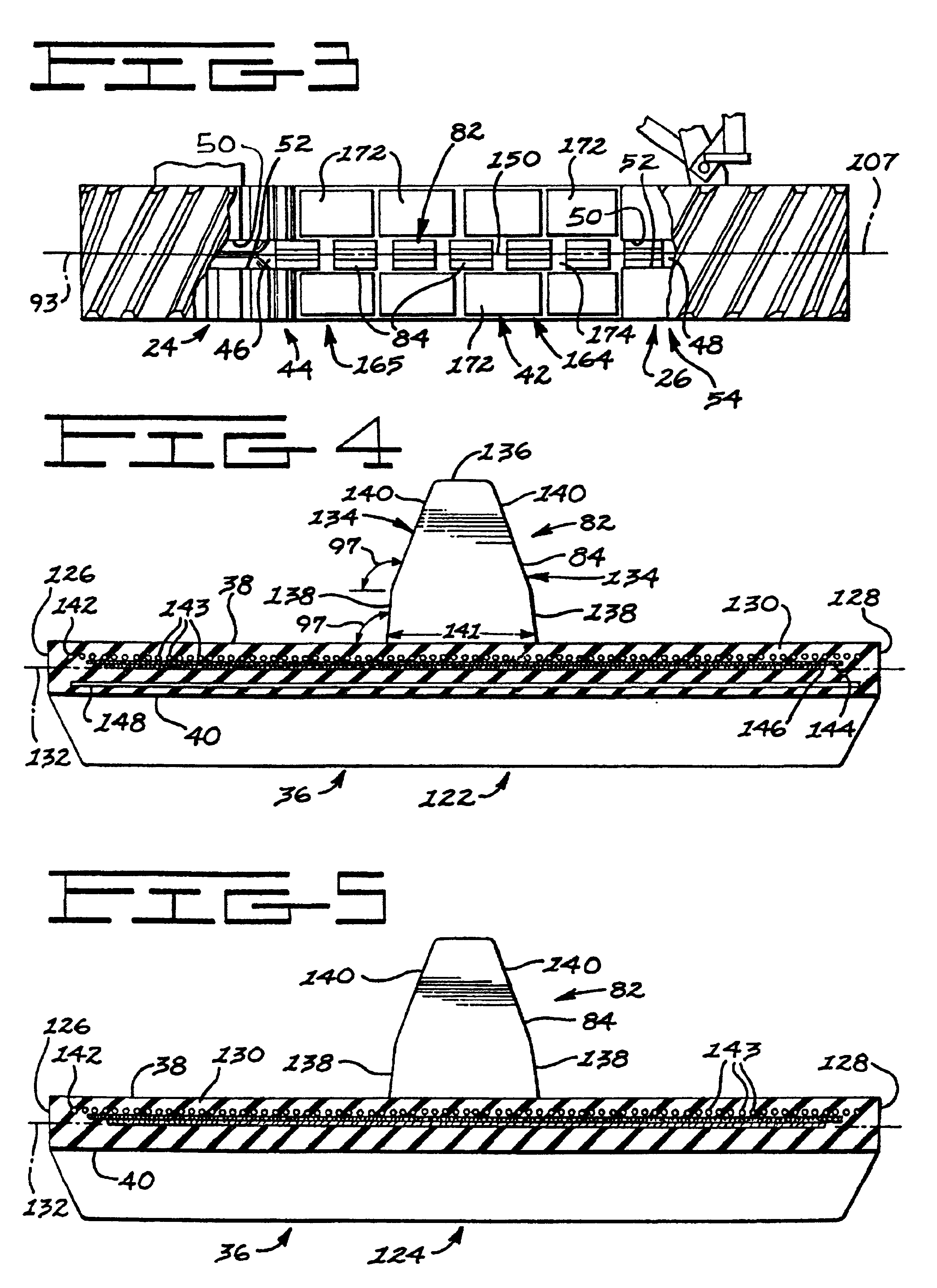
InactiveUSRE37174E1Augments in maintaining lateral beltHigh degree of tensionConveyorsDriving beltsRoad surfaceTractive effort
An elastomeric belt laying vehicle is disclosed for transmitting greater tractive effort to the earth as compared to comparably powered wheel vehicles and being operable at high speed on improved road surfaces without inflicting damage thereto. A pair of the wheels are arranged on each lateral side of the vehicle's chassis for support thereof. An inextensible, endless belt is highly tensioned throughout its length, is entrained about each pair of wheels, and is frictionally, drivingly coupled to at least one wheel of each pair. The structure of the belt, structure of the wheels and cooperating components thereof ensure engagement therebetween, provides long service with minimum maintenance thereof, and supplies the necessary frictional couple to effectively transmit driving torque from the wheels to the belt.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Structure of power transmission apparatus
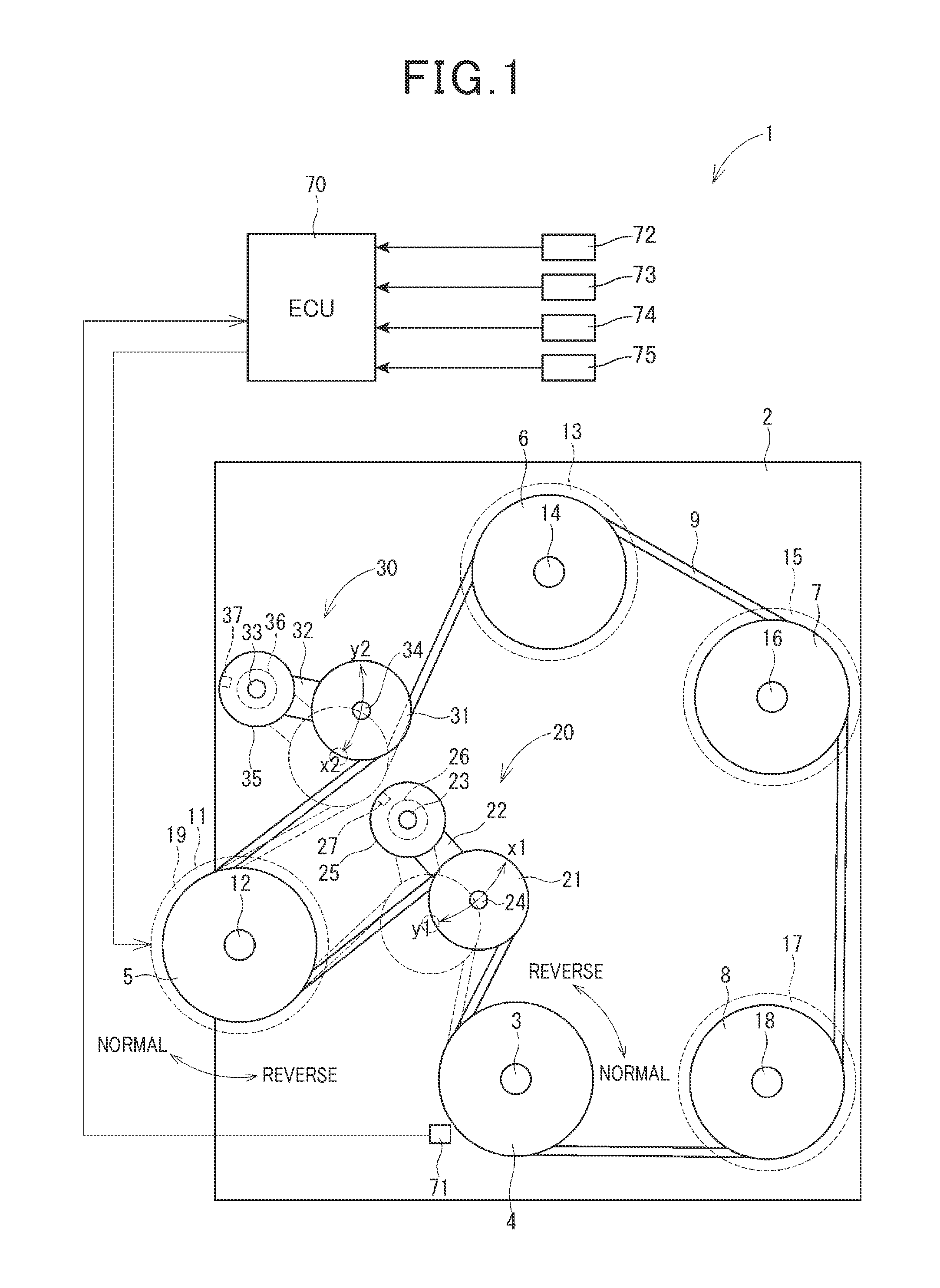
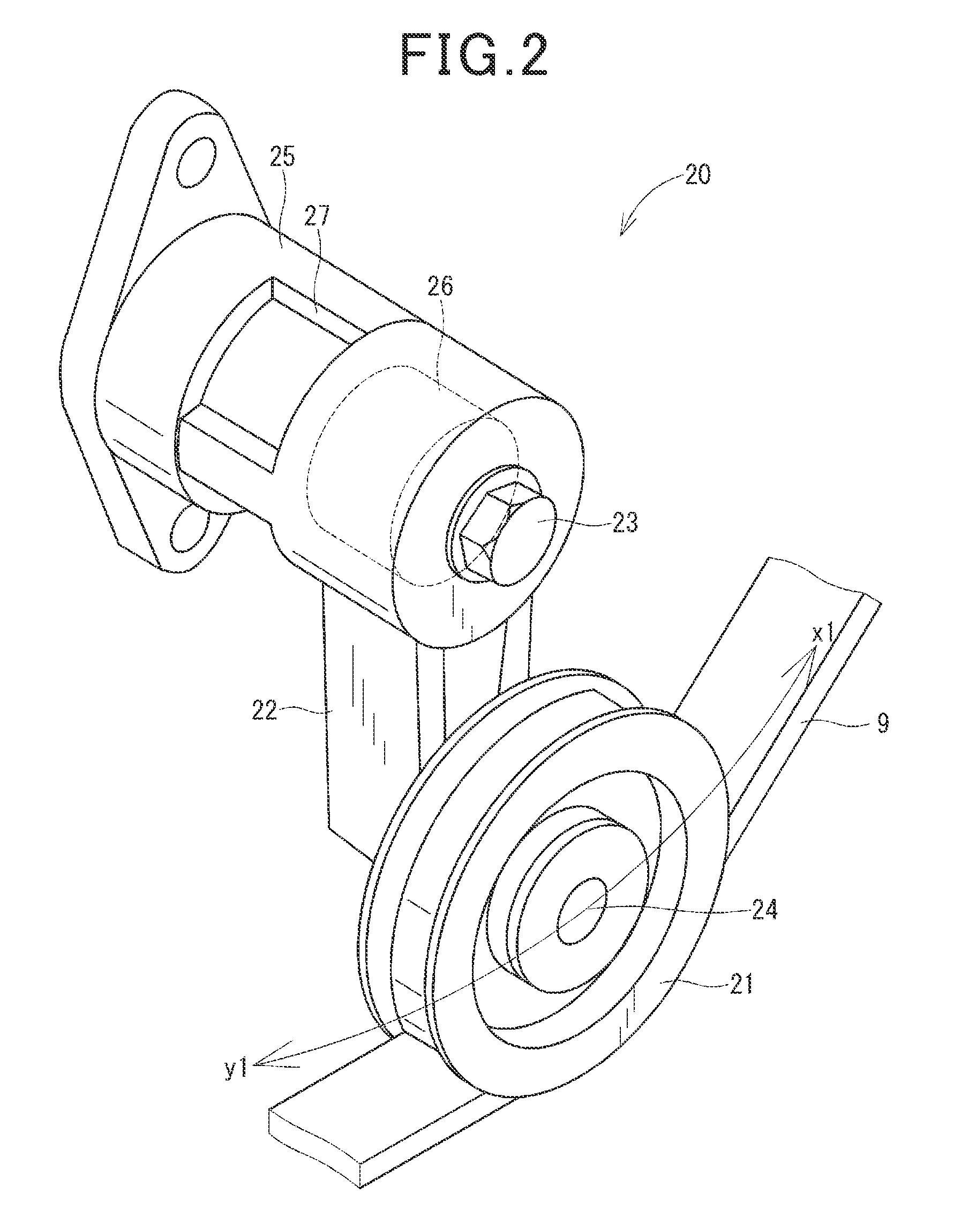
ActiveUS20150167797A1Simple structureMinimize timeHybrid vehiclesPower operated startersTransmitted powerDrivetrain
A power transmission system transmits power from an internal combustion engine to a first and a second auxiliary device through an endless transmitting member. Prior to issuing of an engine start request, the first auxiliary device is actuated to move a tensioner pulley to a given position to increase the degree of tension of the endless transmitting member. The actuation of the first auxiliary device as an engine starter upon the issuing of the engine start request, therefore, enables a drive shaft of the engine to be rotated immediately within a required time to crank the engine. This achieves a quick start of the engine and results in a decrease in amount of time between the issuing of the engine start request and the actual start of the engine.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Washing centers for machinery
InactiveUS6125860AHigh tensionWet surface of machineElectrostatic cleaningCleaning apparatus for vehicle exteriorsComing outFuel tank
PLANT FOR WASHING MACHINERY, which is characterized by being a compact plant which includes a small engine room of approximately 9m3, inside which the different elements such as the following are housed: pressure pumps, electric motors, a diesel boiler, a hot water accumulator, a plant for osmotizing water, an electronic robot mechanism, an electric switchboard, fuel tanks, osmotized water tank, measurement pumps and auxiliary material. The washing liquids come out under pressure through hoses and reach a manual shuttle.
Owner:DE SEBASTIAN FERNANDO GOMEZ
Frictionally driven belted work machine
InactiveUSRE38858E1Augments in maintaining lateral beltHigh degree of tensionConveyorsDriving beltsEngineeringRoad surface
An elastomeric belt laying vehicle is disclosed for transmitting greater tractive effort to the earth as compared to comparably powered wheel vehicles and being operable at high speed on improved road surfaces without inflicting damage thereto. A pair of the wheels are arranged on each lateral side of the vehicle's chassis for support thereof. An inextensible, endless belt is highly tensioned throughout its length, is entrained about each pair of wheels, and is frictionally, drivingly coupled to at least one wheel of each pair. The structure of the belt, structure of the wheels and cooperating components thereof ensure engagement therebetween, provides long service with minimum maintenance thereof, and supplies the necessary frictional couple to effectively transmit driving torque from the wheels to the belt.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
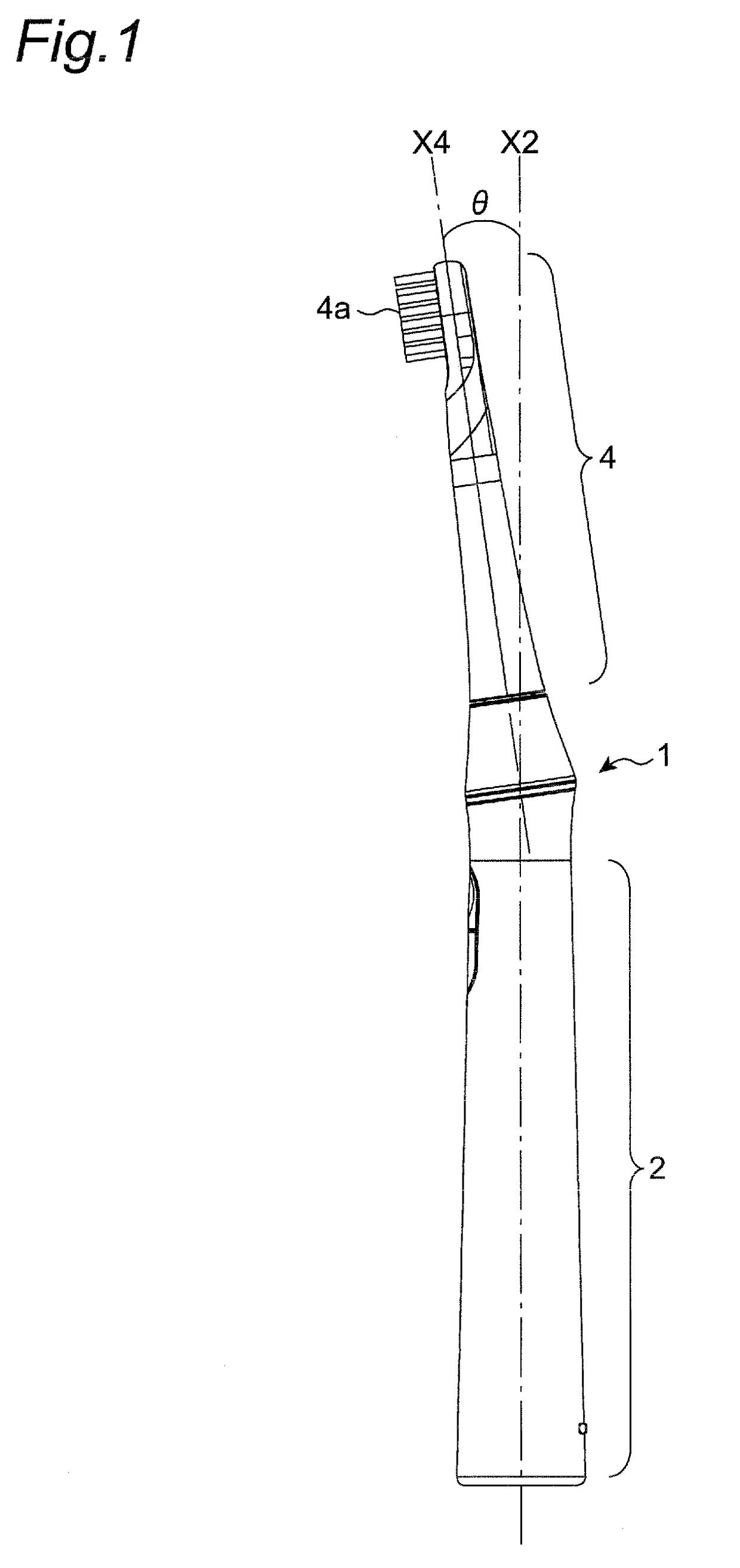
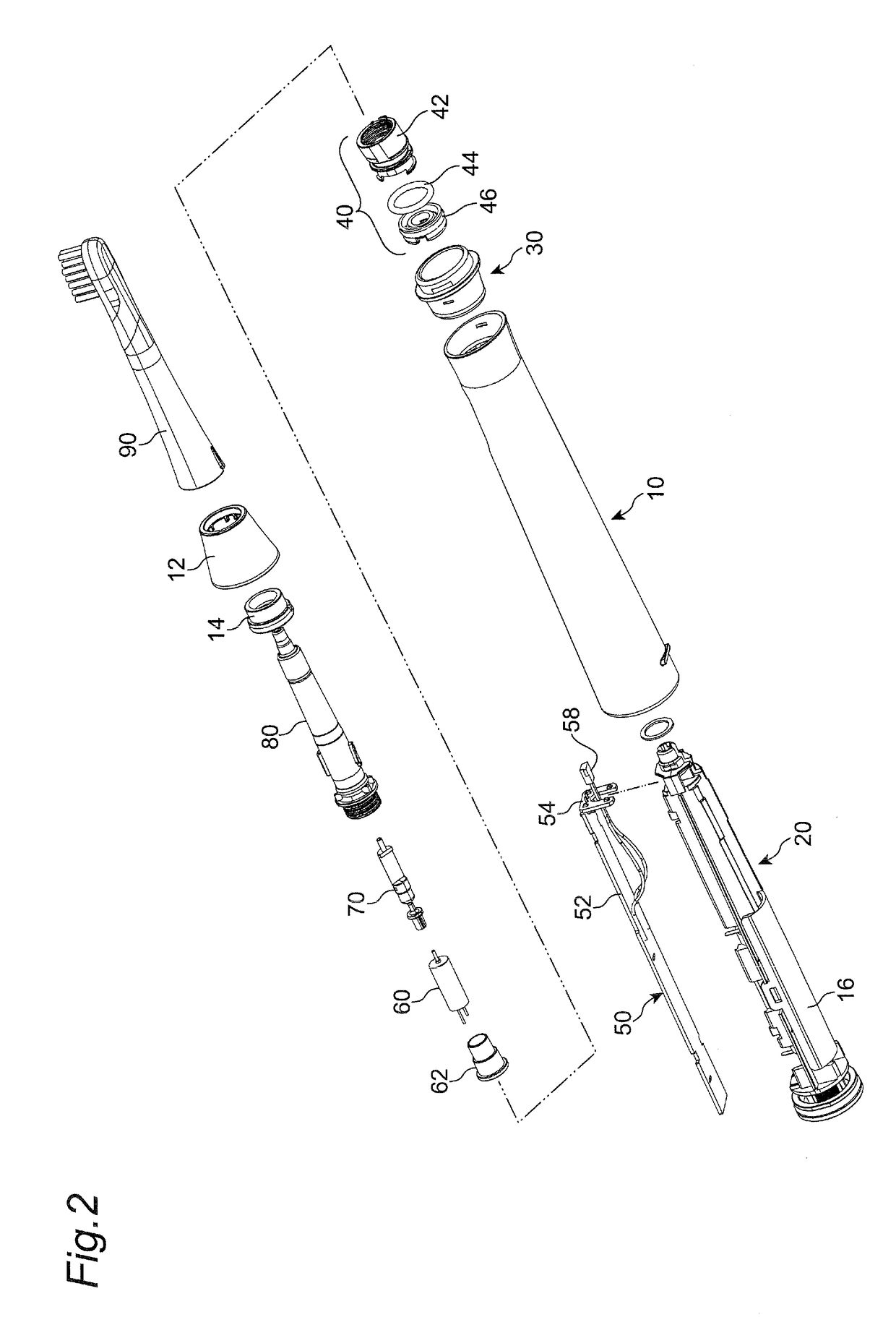
Electric Toothbrush with Rigidly Connected Grip Portion and Brush Portion
ActiveUS20190069978A1TensionHigh tensionTooth cleaningBoring toolsMechanical engineeringPower toothbrush
An electric toothbrush includes a grip portion, a brush portion, and a joint arrangement for connecting the two portions. The joint arrangement has an upper cylinder portion and a lower cylinder portion, with an axis of the upper cylinder portion being inclined a predetermined angle with respect to an axis of the lower cylinder portion. The grip portion is connected to the lower cylinder portion and the brush portion is connected to the upper cylinder portion, so that the grip portion and the brush portion are inclined by the predetermined angle.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO +1
Side curtain air bag
InactiveUS20070164543A1Reduce tensionEasy to controlPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementEngineeringAirbag
The present invention provides a side curtain air bag facilitating the control of tension with the airbag. The side curtain air bag includes chambers expanded by gas supplied from a gas generator, and expands and develops into a curtain shape along a side part of a vehicle so as to protect vehicle occupants. The side curtain air bag includes primary chambers which expand to form the side curtain air bag, and a secondary chamber which expands after the primary chambers to apply additional tension across the expanded side curtain air bag. The secondary chamber includes an opening communicating with the primary chamber.
Owner:AUTOLIV DEV AB
Gas sensor
InactiveUS20020148280A1Reduce lossesLoss of tensionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpecific gravity measurementElectrical conductorGaseous detectors
The invention relates to a gas probe (10) for installation in a measurement gas chamber, having a metal housing (30) in which a planar sensor element (21) is disposed, electrically insulated, with at least one contact face (22) that is conductively connected to a metal conductor element (23). For the conductor element (23), an electrically insulating contact holder (24) is provided, which presses the conductor element (23) onto the contact face (22) by means of a spring element (25) that engages the contact holder (24). The conductor element (23) is disposed in an indentation (26) of the contact holder (24), which indentation is oriented toward the contact face (22) of the sensor element (21), and by way of a region protruding out of the indentation (26) of the contact holder (24), the conductor element is in contact with the contact face (22).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Aircraft seat back assembly
The seat back portion of a passenger aircraft seat is built of an elastomer mesh type diaphragm without conventional cushions or dress covers, in order to maximize space available to the passenger while reducing costs and weight. The diaphragm is attached and tensioned into a structural frame, which also supports a slide-in rear shroud closeout. The frame is designed to remain exposed, showing a decorative finish.
Owner:FRANKLIN PRODS
Step air foil web stabilizer
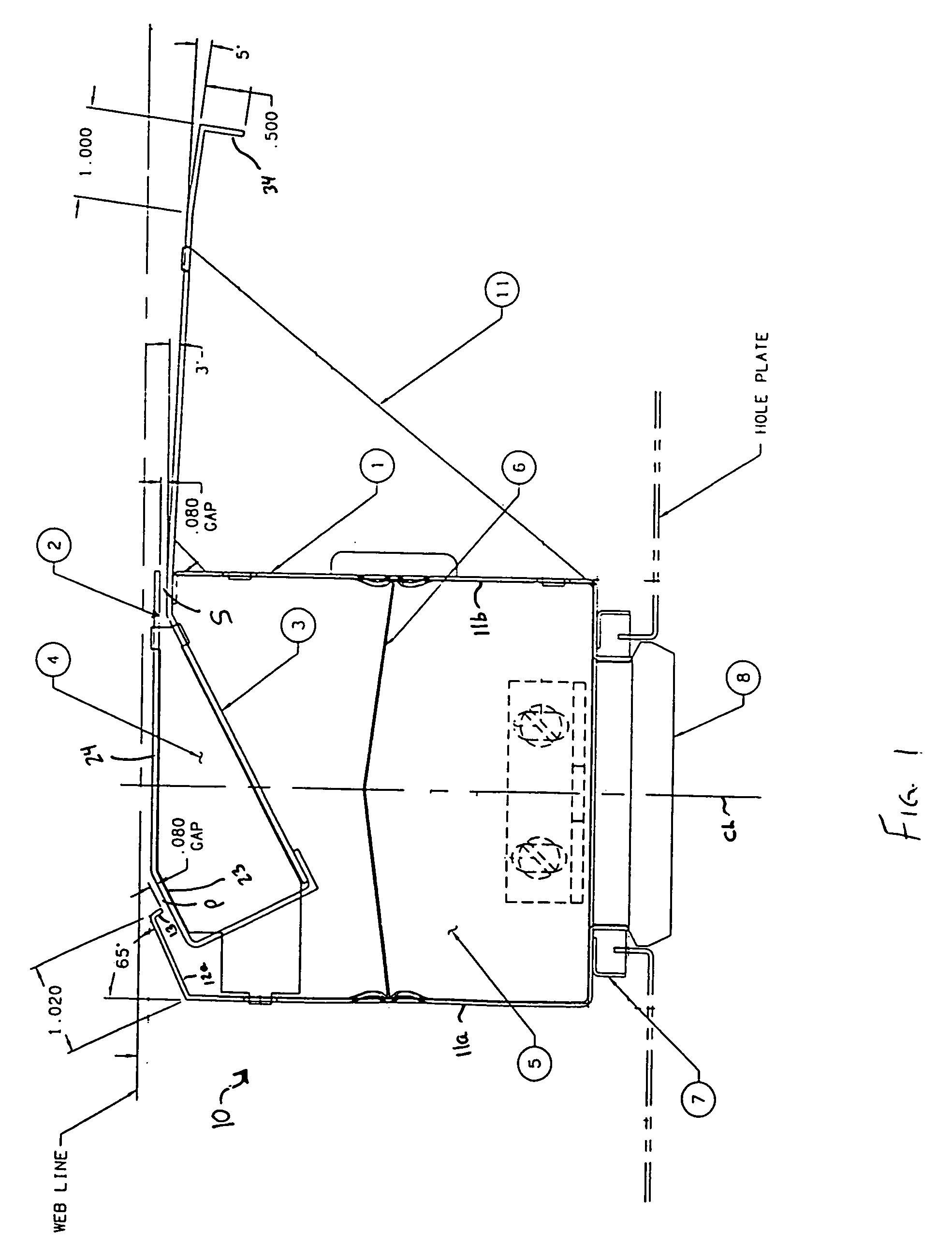
ActiveUS20080276488A1Stable supportHigh tensionNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperWrinkle skinFiber
Web stabilizer particularly for one-sided flotation of a running web. The device includes two discharge slots which allow for increased draw down force, which flattens machine direction wrinkles in a floating web. There is a primary discharge slot and a second discharge slot spaced from and stepped down from the primary discharge slot, a first web support surface between the primary discharge slot and the secondary discharge slot, and a second web support surface downstream of the secondary discharge slot in the direction of web travel. An integral blower provides a supply of air that is uniformly distributed to the primary and secondary slots. Air discharged from the primary slot is gathered into the air stream of the secondary slot and creates an increased air cushion to provide greater support to the web and thereby remove machine direction web wrinkles caused by higher tension in light weight webs.
Owner:DURR SYST INC
Industrial fabric with wear resistant coating
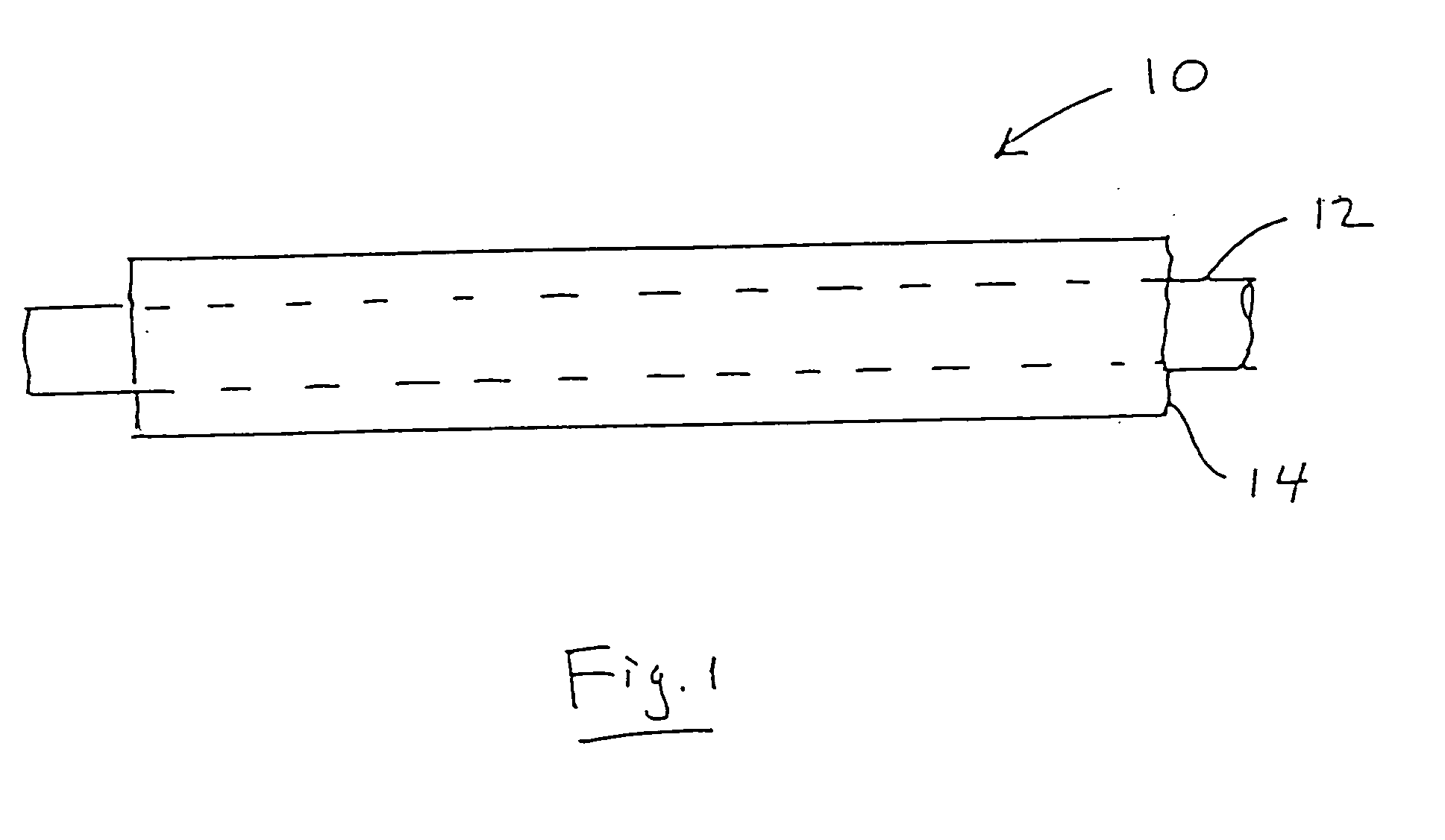
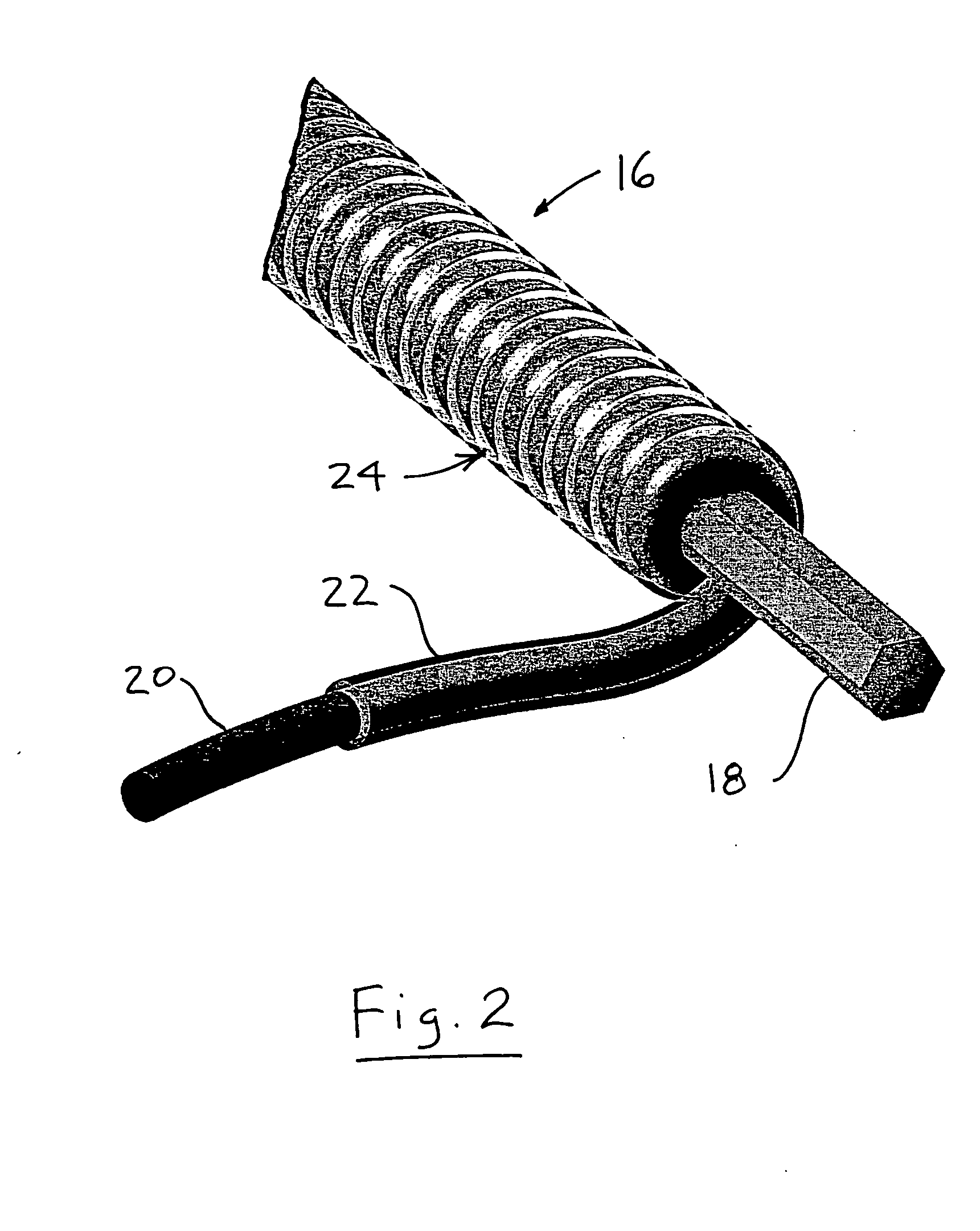
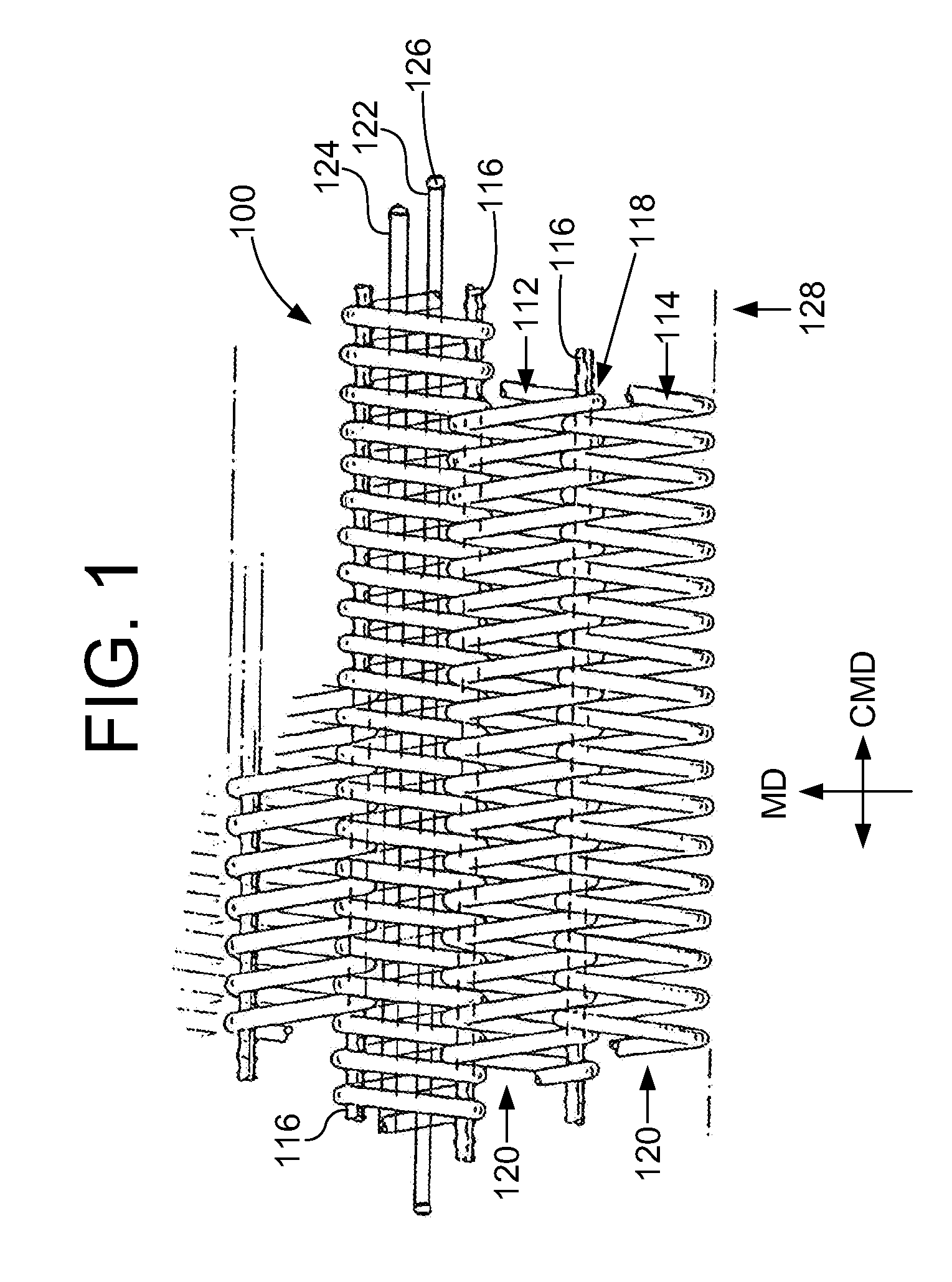
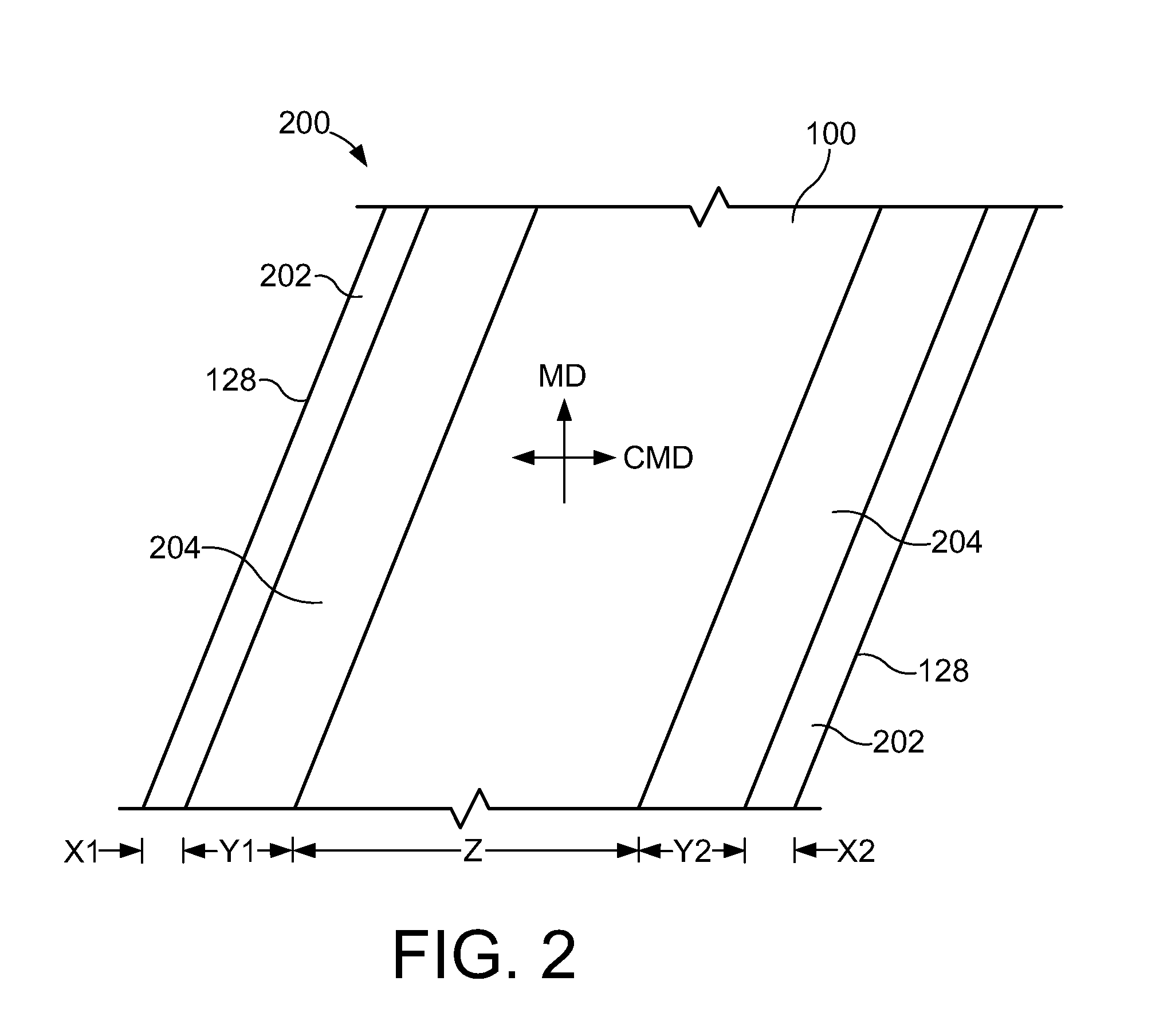
InactiveUS20110146913A1High strengthPrevent “shocking” of nearby personnelMechanical working/deformationLaminationYarnWear resistant
An industrial fabric used in the manufacture or processing of at least one material web includes a base fabric having a board side and a machine side. The base fabric includes a plurality of spirals extending in a cross machine direction (CMD). The spirals are interconnected together with each other along adjacent peripheral edges to form a spiral link fabric. The base fabric has opposite lateral side edges extending in a machine direction (MD). One or more electrostatic control yarns are positioned within a corresponding spiral and extend in the CMD direction to the lateral side edges. A pair of conductive edge coatings are applied to at least the board side of a respective lateral side edge for a predetermined width. The conductive edge coatings and the one or more electrostatic control yarns form an electrostatic grid. A pair of wear resistant coatings are applied to an area adjacent a respective conductive edge coating such that a substantially constant spacing between the wear resistant coatings corresponds to a minimum expected working width of the industrial fabric. The wear resistant coatings are wear resistant with a hardness of between approximately 50 to 66 Shore A Durometer Hardness, and a coefficient of friction greater than approximately 2 on the board side. The industrial fabric has a completely non-marking seam because of its integral nature with the base fabric and the equal amount of the wear resistant coating at the seam and the edges.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com