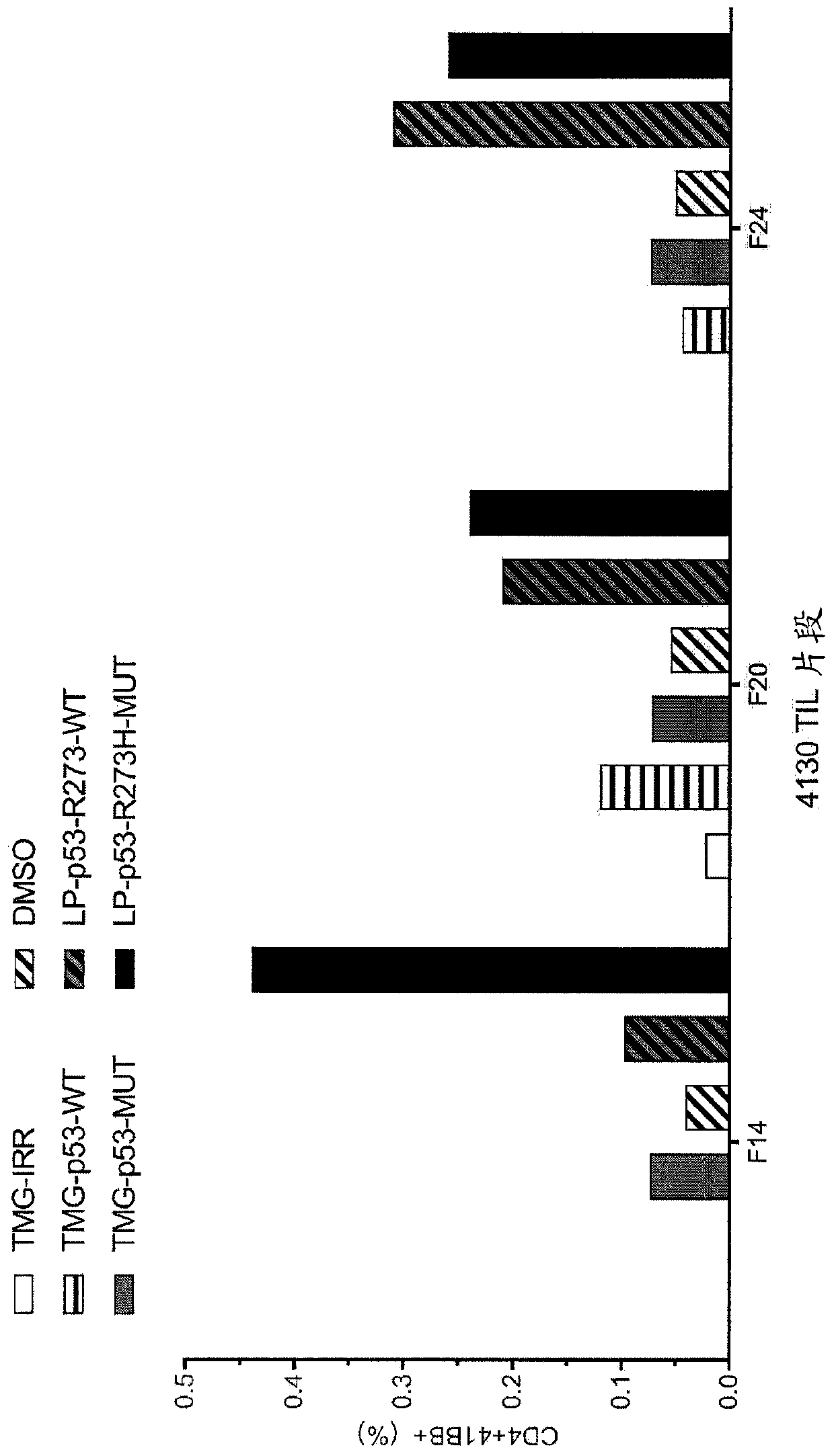
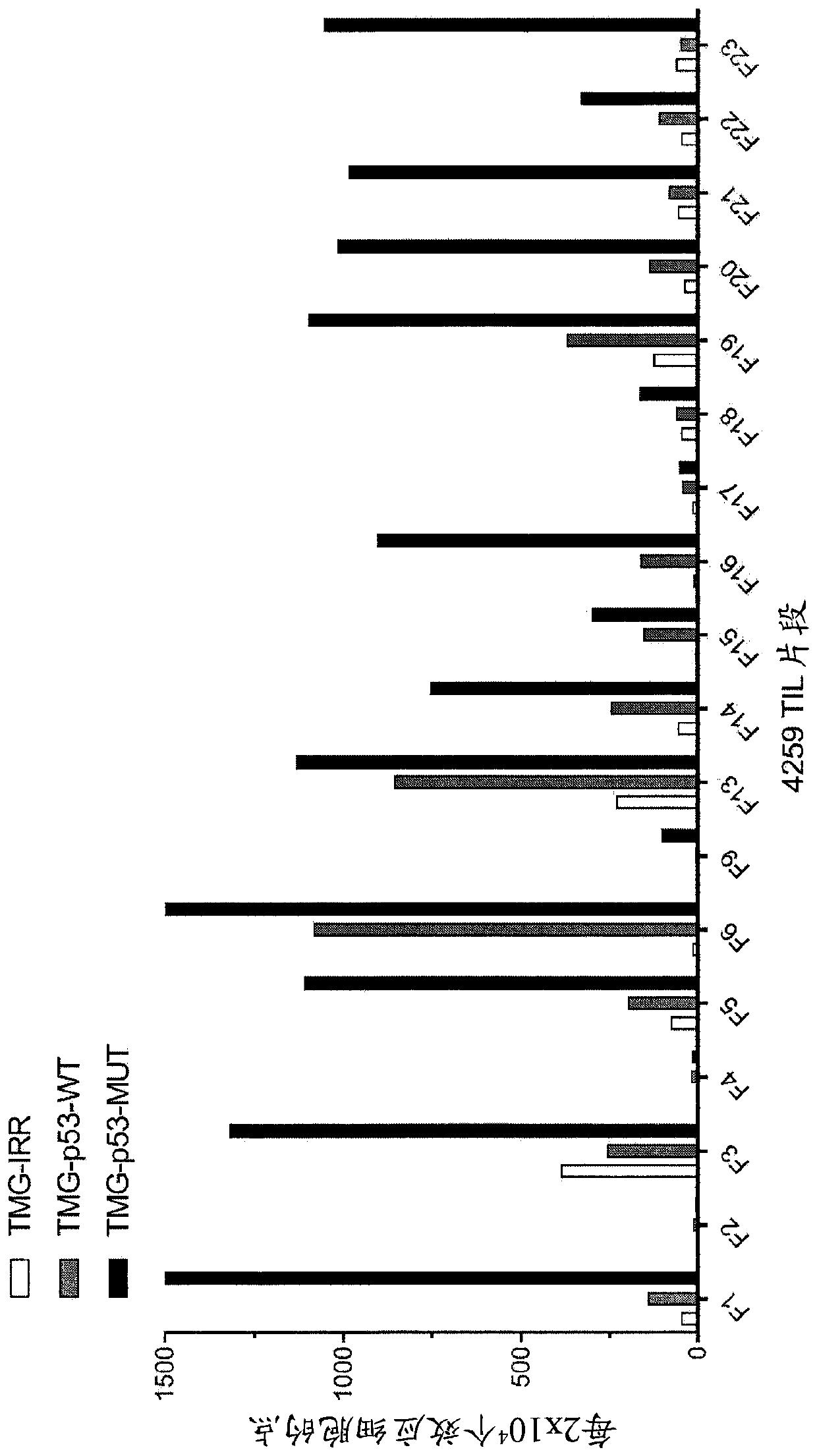
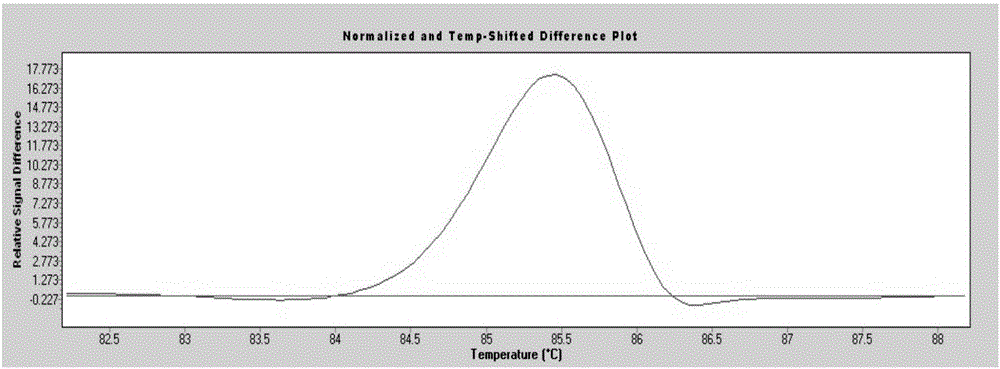
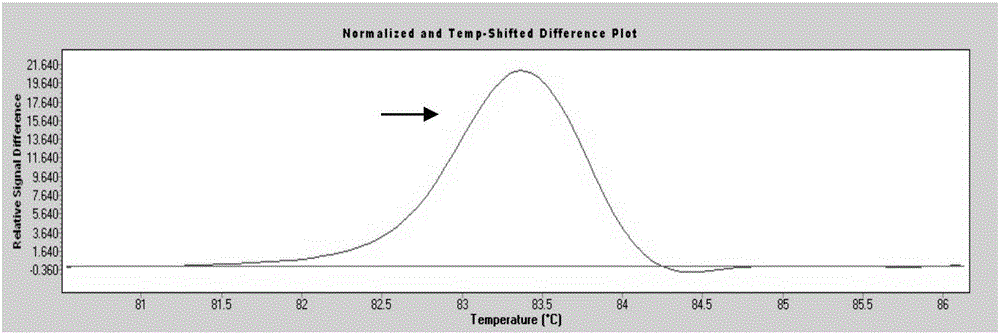
Patents
Literature
52 results about "P53 Mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
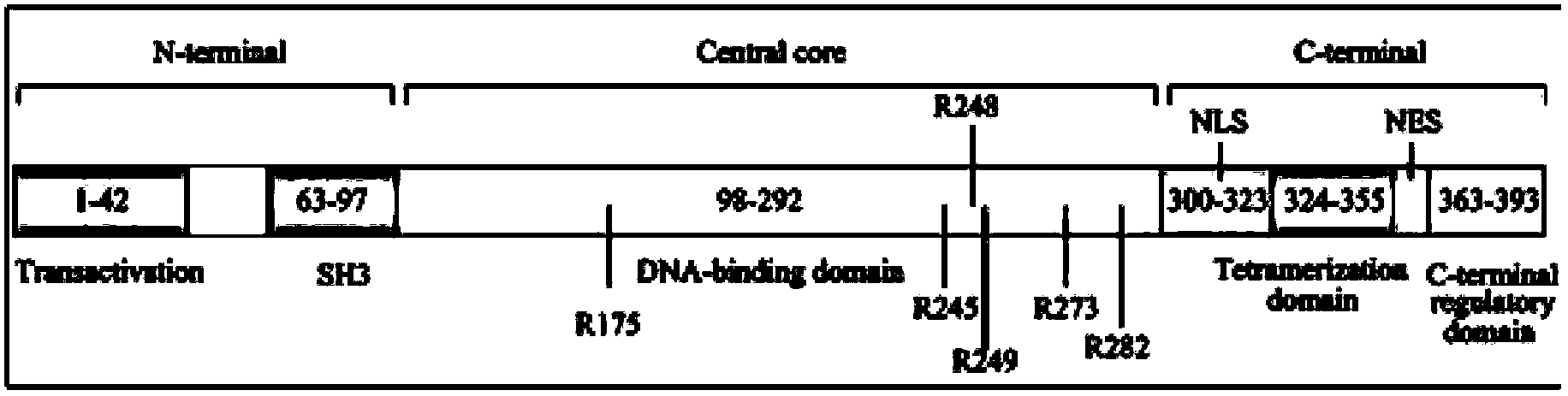
P53 gene mutation have several different effects on the activity of the gene, depending on the location of the alteration. Mutations can occur in regulatory regions also called promoter, that basically control how often, and when, the gene is transcribed. Here mutation can result in a decrease or absence of p53 in the cell.
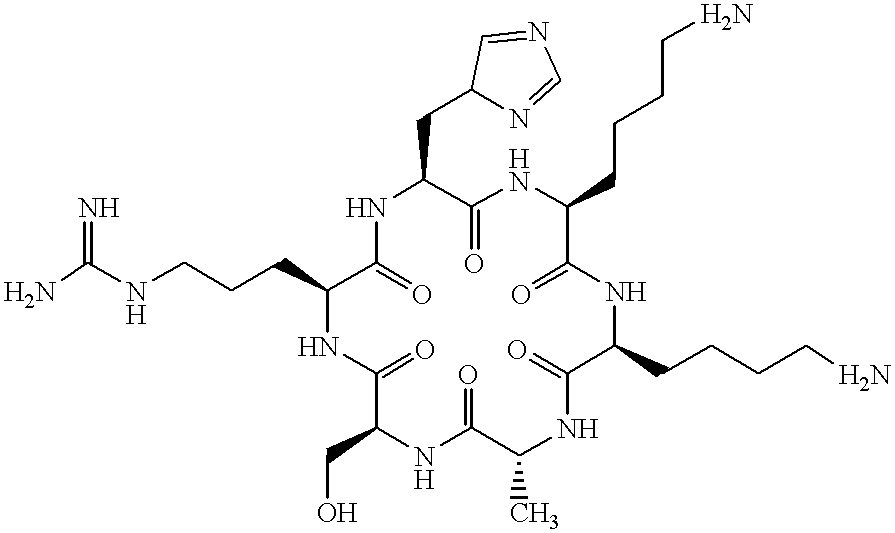
Peptides and peptidomimetics with structural similarity to human P53 that activate P53 function
InactiveUS6245886B1Improve the immunityLow toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsP53 proteinWild typeP53 Mutation
The present invention provides peptides and peptidomimetics corresponding to part or to the entirety of the region encompassed by residues 360-386 of human p53, said peptides and peptidomimetics characterized by the ability to activate DNA binding of wild-type p53 and to select tumor-derived p53 mutants. Pharmaceutical compositions of the compounds of the invention and methods of using these compositions therapeutically are also provided.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC +1
Peptides and peptidomimetics with structural similarity to human p53 that activate p53 function
InactiveUS7189801B2Improve the immunityLow toxicityP53 proteinMicroorganism based processesWild typeP53 Mutation
The present invention provides peptides and peptidomimetics corresponding to part or to the entirety of the region encompassed by residues 360–386 of human p53, said peptides and peptidomimetics characterized by the ability to activate DNA binding of wild-type p53 and of select tumor-derived p53 mutants. Pharmaceutical compositions of the compounds of the invention and methods of using these compositions therapeutically are also provided.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Peculiar p53 mutated protein-p53N236S of ALT tumor caused by progeria syndrome and application thereof
InactiveCN101805738APeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthMutated protein
The invention relates to a mutant gene p53A1243G caused by the point mutation of a tumor suppressor gene p53, encoded protein p53N236S and functions thereof, and application thereof to tumor diagnosis. First, the important functions of p53N236S in an ALT tumor caused by progeria syndrome are disclosed. The invention can be applied to the tumor diagnosis with p53N236S as the target molecule, the screening of anticancer medicine and cancer treatment strategies, and has important significance in preventing tumors caused by aging.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
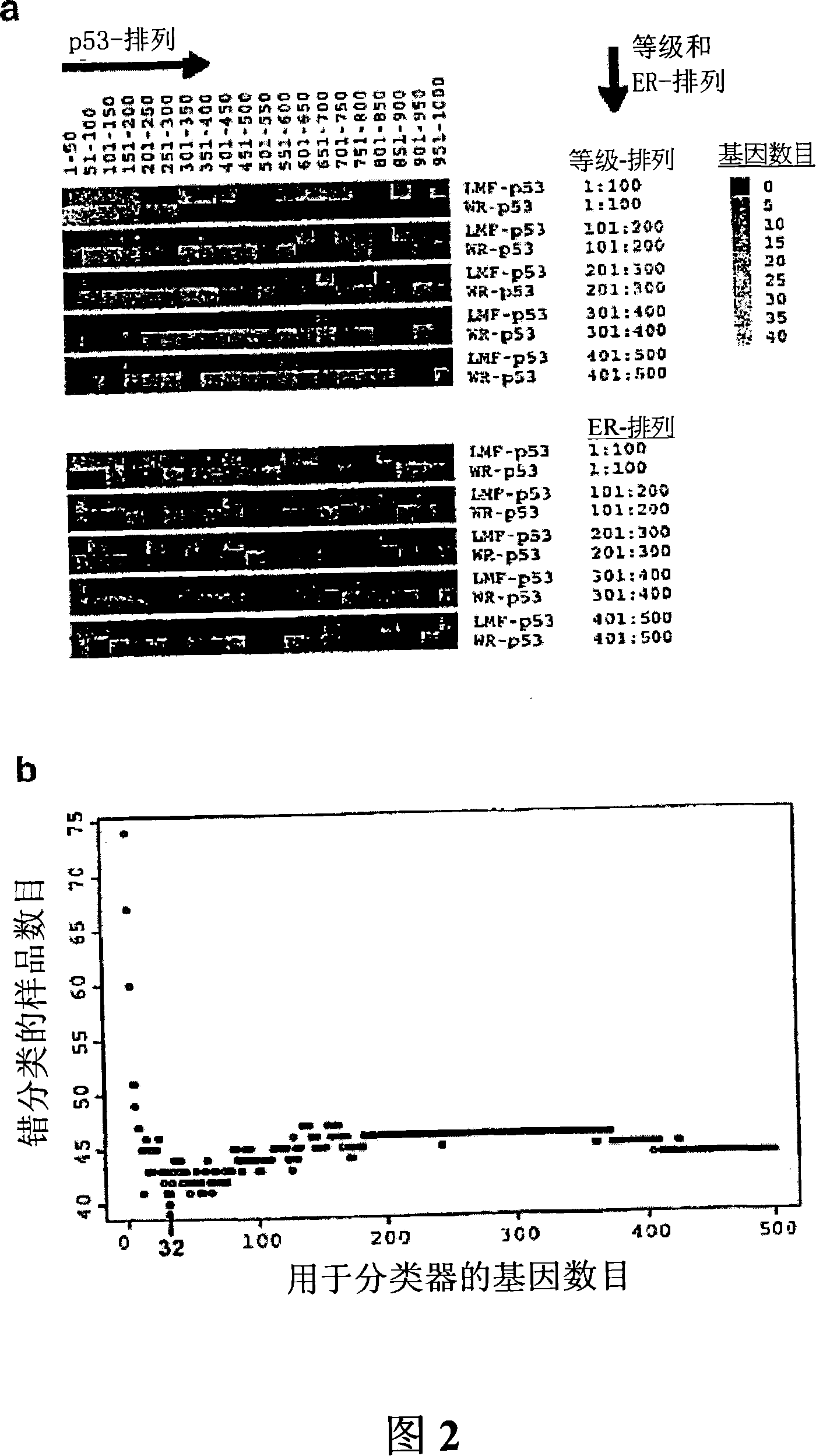
Methods, systems, and arrays based on correlating p53 status with gene expression profiles, for classification, prognosis, and diagnosis of cancers
InactiveCN101111604AMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical automated diagnosisP53 MutationWilms' tumor
The present invention provides a method, a system and the composition for forecasting the susceptibility of the patient to the disease, which is based on executing relevancy of p53 mutation state and gene expression profile to a set of predefined gene. The methods for specification, prognosis and diagnosis to the cancer are provided in some execution modes. In other execution modes the present invention provides the statistical method for constructing the categorizer base on gene expression, and the categorizer can be used for forecasting the susceptibility of the patient to the disease, classifying the tumour and doing prognosis to the clinical result.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Dkat cell line, a model for human triple-negative breast cancer
InactiveUS20110085982A1High expressionPrevent proliferationMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug screeningExonP53 Mutation
The present invention provides a human triple-negative breast cancer cell line designated DKAT. The DKAT cell line has a marker profile of high expression of Snail-1 and Snail-2 (Slug); and a p53 mutation in exon 8 at codon 273 (CGT>CAT). The present invention further provides methods of using the DKAT cell line.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Cancer Treatment
InactiveUS20080171051A1Increased apoptosisIncrease resistanceBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsActive agentP53 Mutation
The invention relates to methods and compositions for treatment of cancer. In one embodiment the method involves the use of a c-FLIP inhibitor as the sole active agent. In another embodiment the invention relates to the treatment of p53 mutant cancers using combinations of c-FLIP inhibitors and chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF BELFAST
USE OF FATOSTATIN FOR TREATING CANCER HAVING A p53 MUTATION
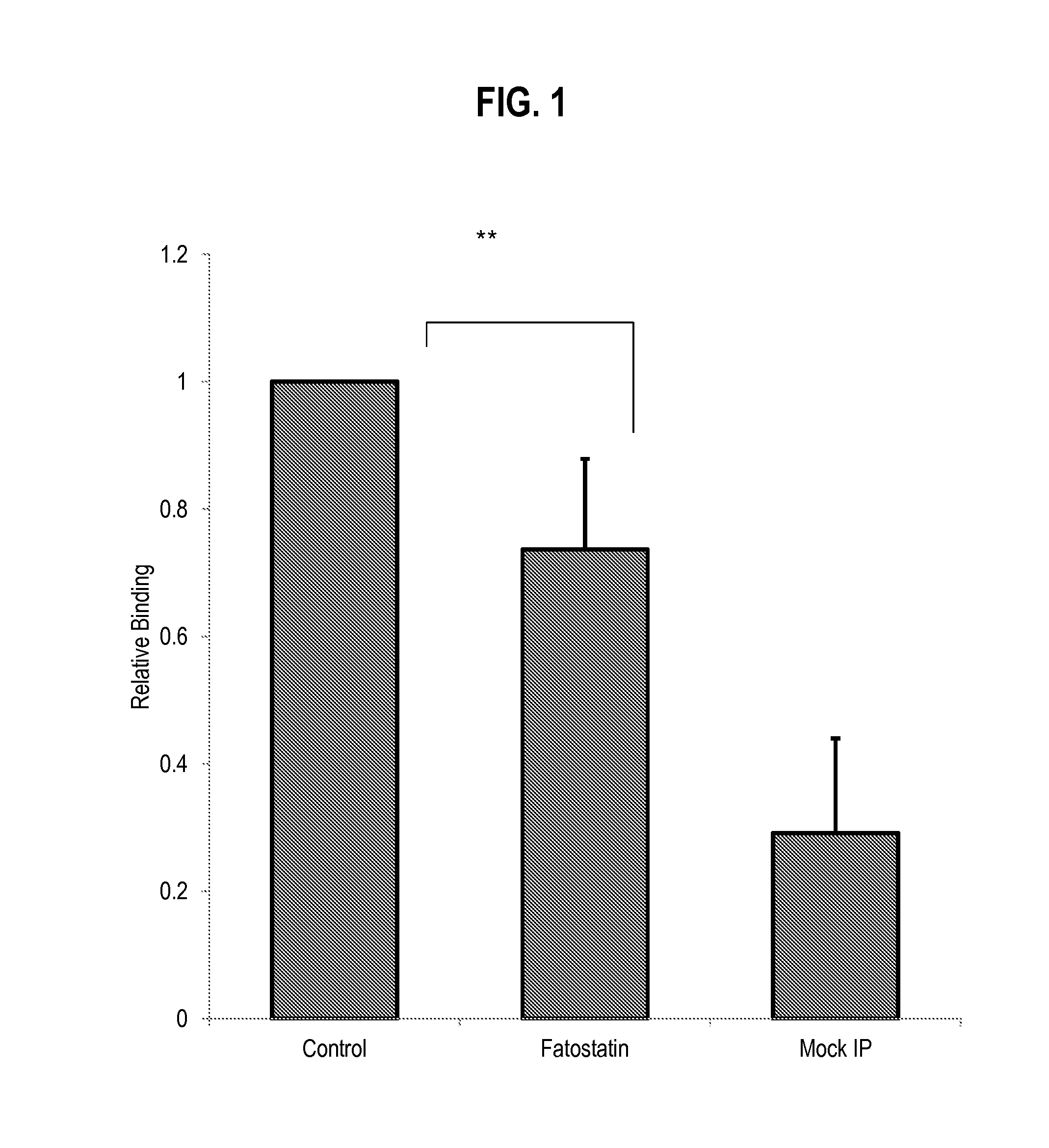
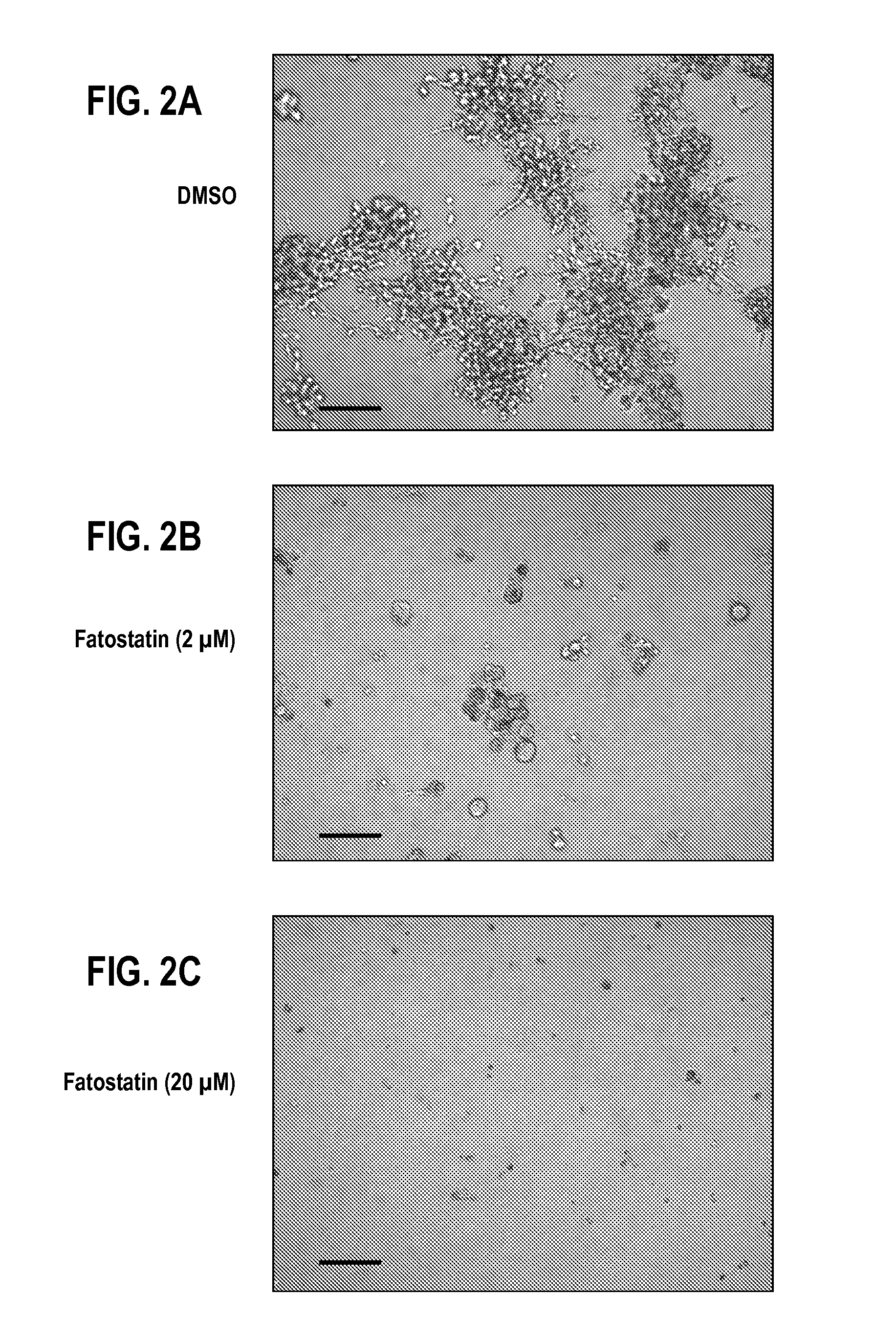
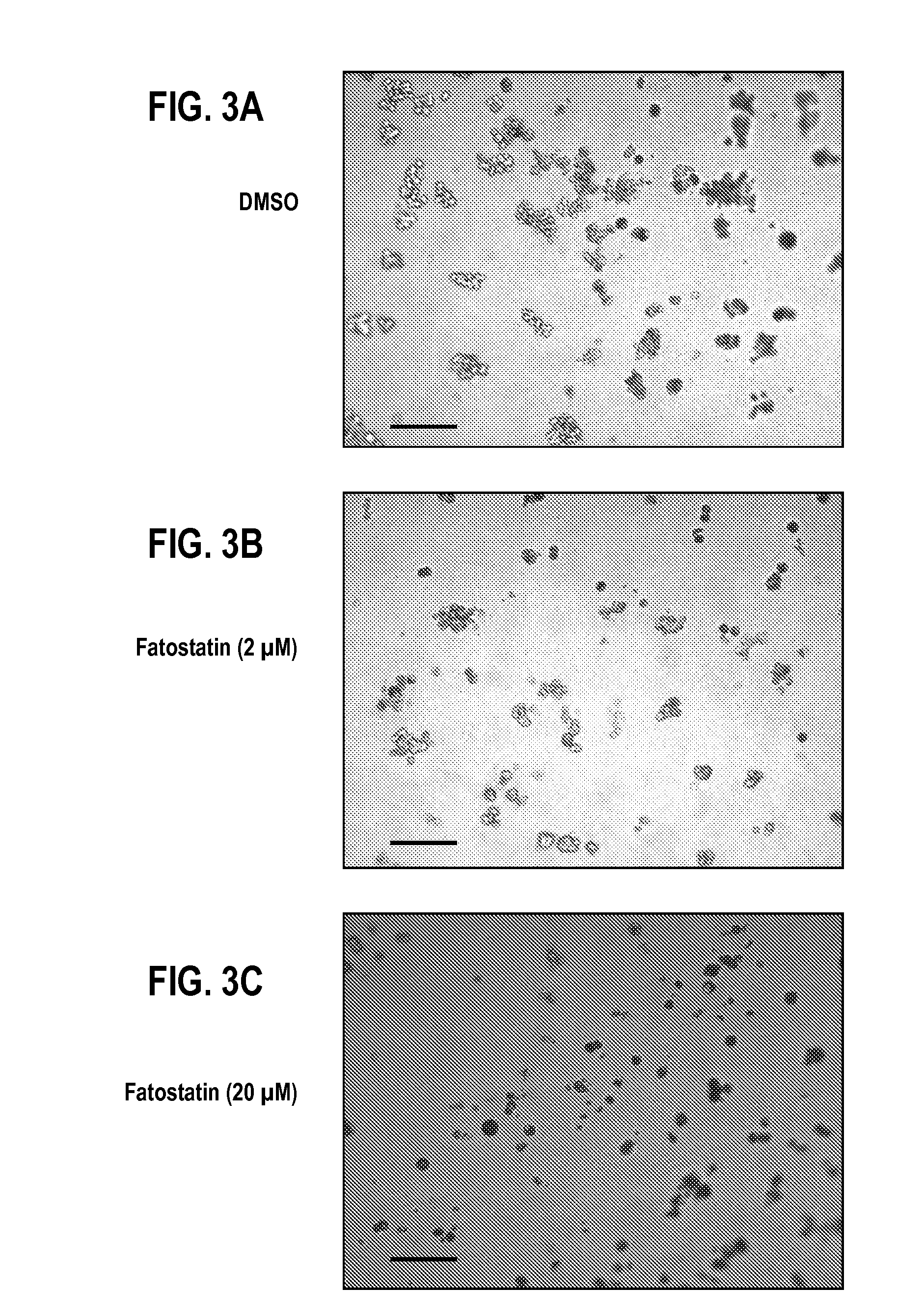
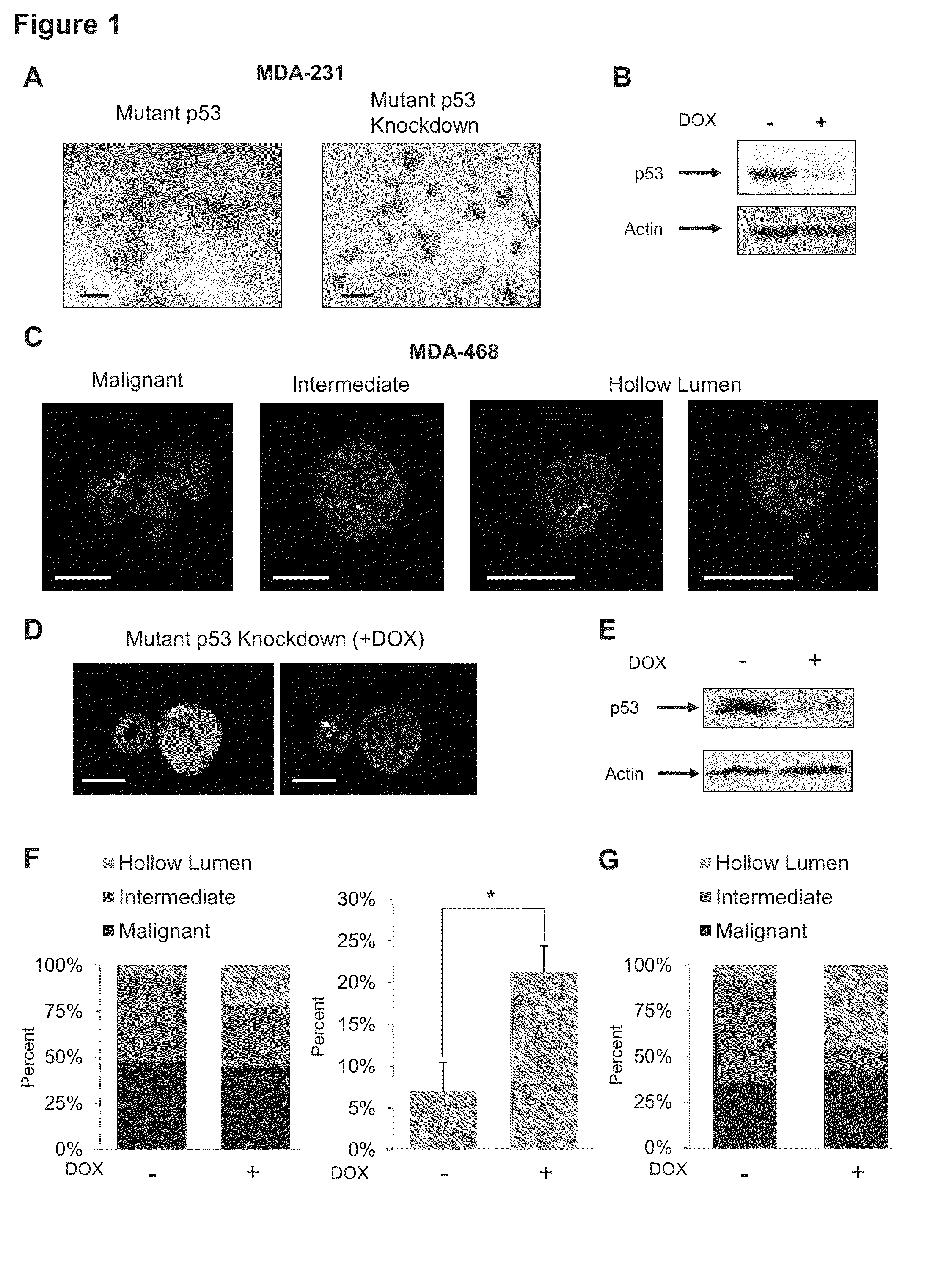
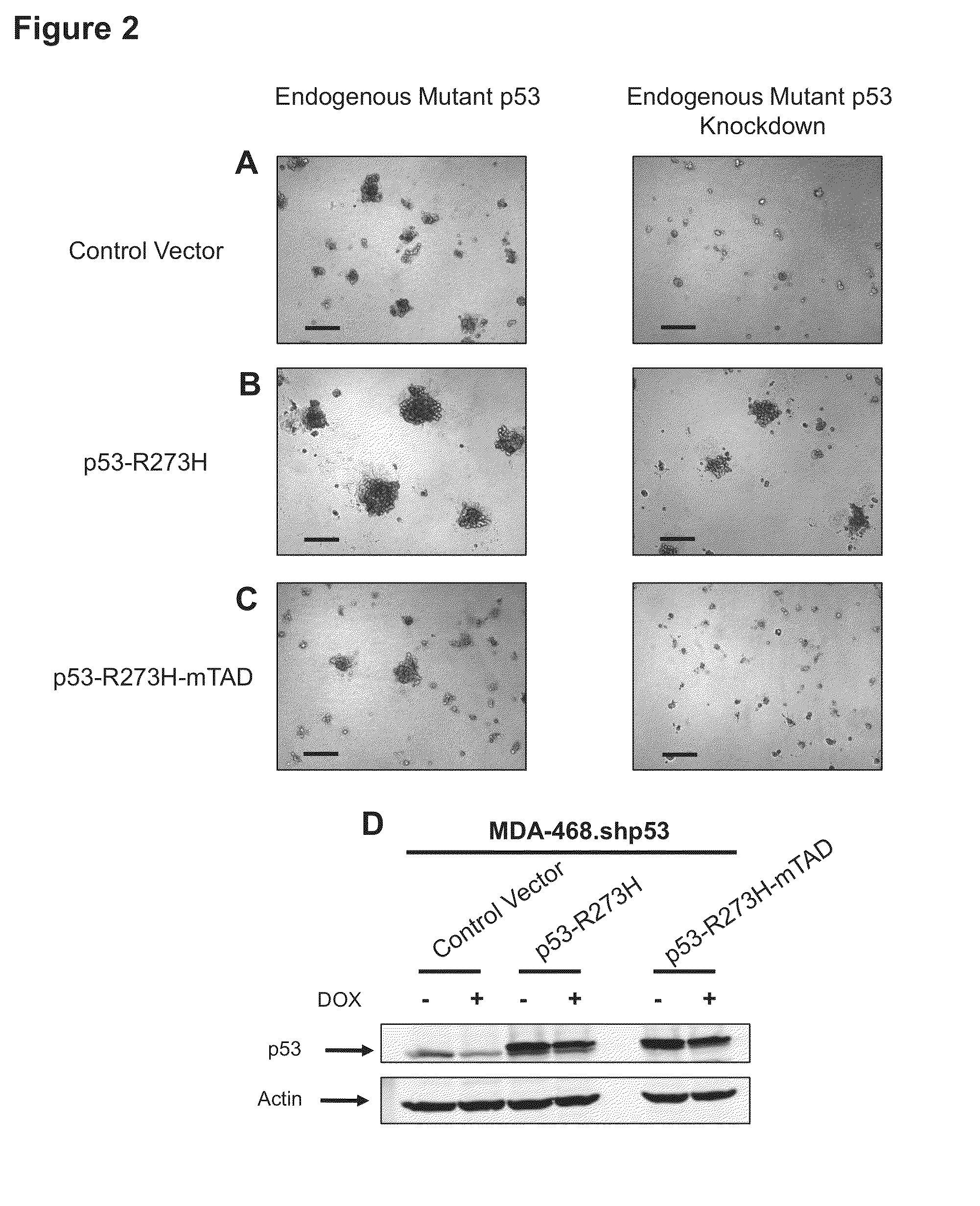
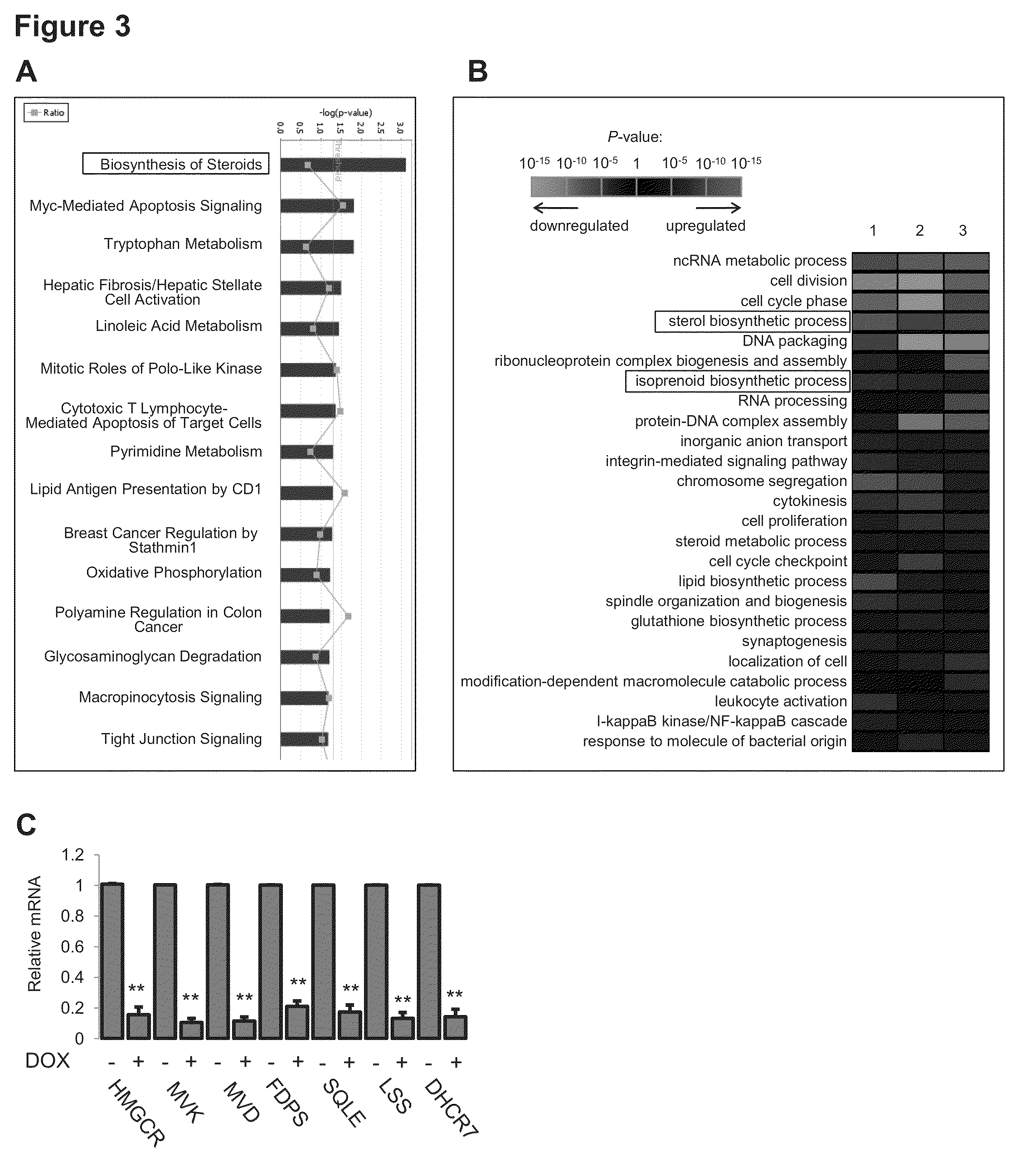
Fatostatin, a recently described inhibitor of SREBP activation, significantly reduces the level of mutant p53 binding to the HMG-CoA reductase gene promoter. Further, fatostatin treatment had a dramatic effect on normalizing the abnormal 3D morphology of 3 strains of breast cancer cells: MDA-468 cells, MDA-231 cells, and SKBR3 cells. The results show a functional interaction with SREBPs as being critical for mutant p53-mediated upregulation of the mevalonate pathway genes. At a clinical level, inhibition of the mevalonate pathway, either alone or in combination with other therapies, offers a novel, safe and much needed therapeutic option for tumors bearing mutant p53.
Owner:NIH DEITR
Application of iridoid compound to preparation of ovarian cancer resistance medicament
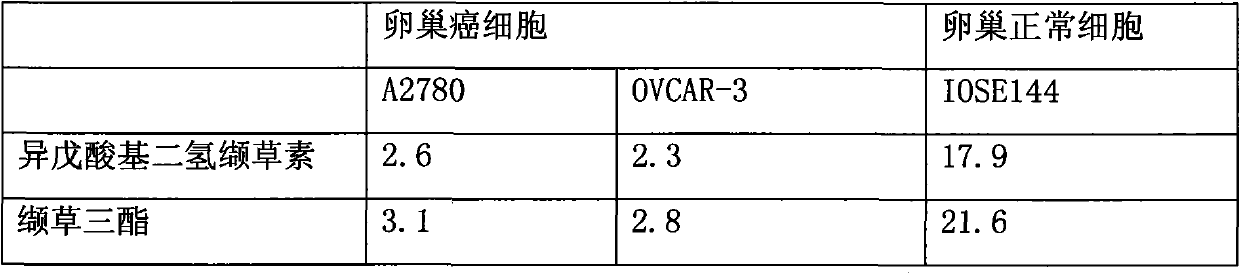
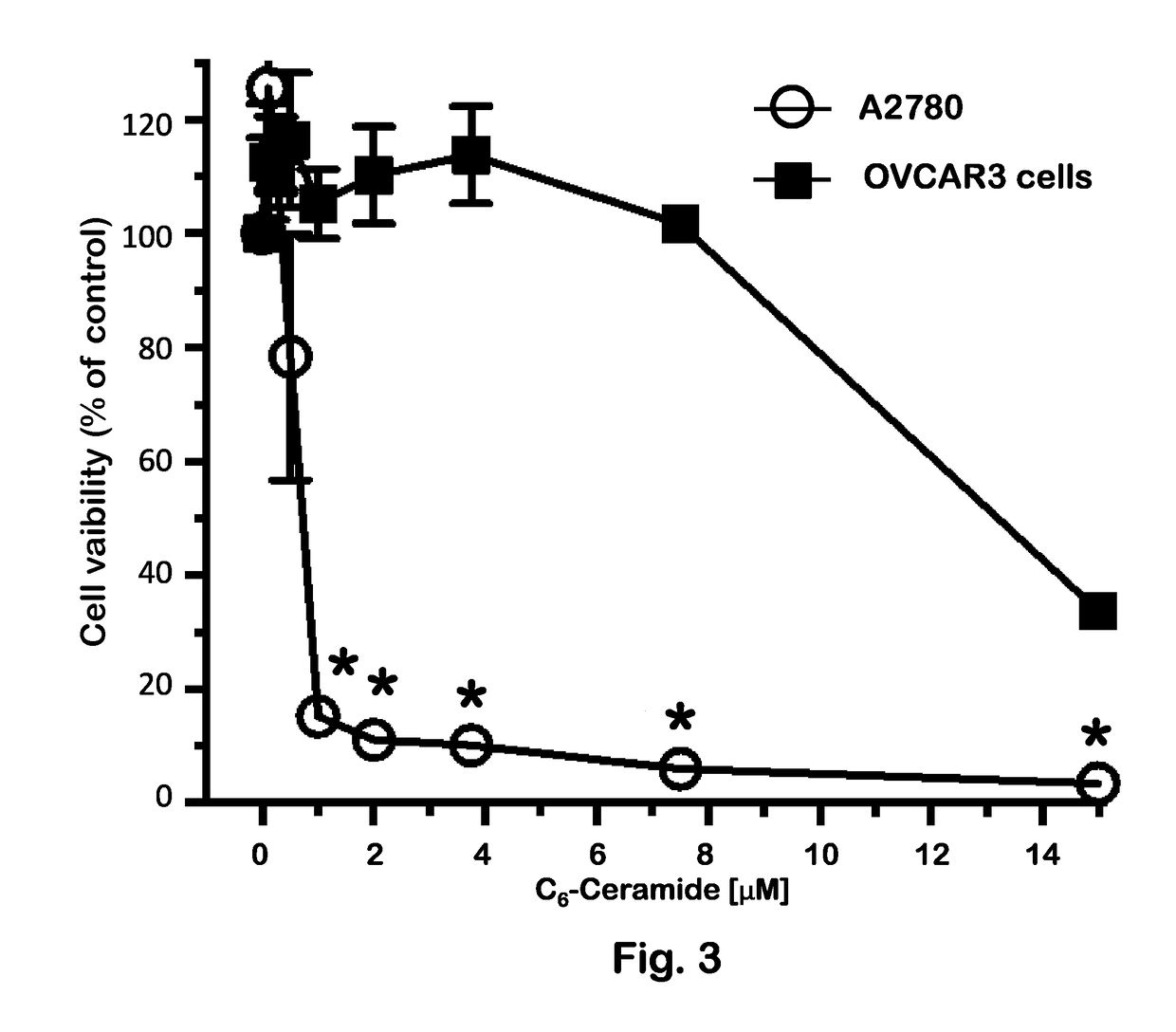
The invention provides the application of iridoid compound to the preparation of ovarian cancer resistance medicament. The iridoid compound is isovaleric acid base dihydro valerian element or isovaleric acid base dihydro valepotriate J which has the following structural formula. The experiments on the toxic and killing effect of the isovaleric acid base dihydro valerian element or the isovaleric acid base dihydro valepotriate J on the p 53 wild ovarian cancer cells A2780, the p53 mutated OVCAR-3 cells and the normal ovarian cells IOSE144 show that the isovaleric acid base dihydro valerian element or the isovaleric acid base dihydro valepotriate J has the selective toxic and killing effect on the ovarian cancer cells and can inhibit the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells and kill the ovarian cancer cells. The iridoid compound can be used as the active component to prepare the ovarian cancer resistance medicament. The invention provides the novel ovarian cancer treatment medicament for the clinical treatment of the ovarian cancer and brings the joyous news to the patients with the ovarian cancer. The iridoid compound has higher application value.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Method for Treating Cancer Harboring a p53 Mutation
InactiveUS20130281493A1Preventing or delaying the onset (or reoccurrence)Reduce the possibilityBiocideOrganic chemistryCancer cellFhit gene
A method for determining if a subject with cancer or precancerous lesions or a benign tumor, will respond to treatment with an inhibitor selected from the group comprising an inhibitor of one or more enzymes in the mevalonate pathway, an inhibitor of geranylgeranyl transferase, an inhibitor of farnesyl transferase or an inhibitor of squalene synthase, by (i) obtaining a sample of the cancer cells, precancerous cells or benign tumor cells from the subject, (ii) assaying the cells in the sample for the presence of a mutated p53 gene or a mutant form of p53 protein or a biologically active fragment thereof, and (iii) if the cells have the mutated p53 gene or mutant form of the p53 protein, then determining that the subject will respond to treatment with the inhibitor or combinations thereof. Some embodiments are directed to treatment with the inhibitors.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
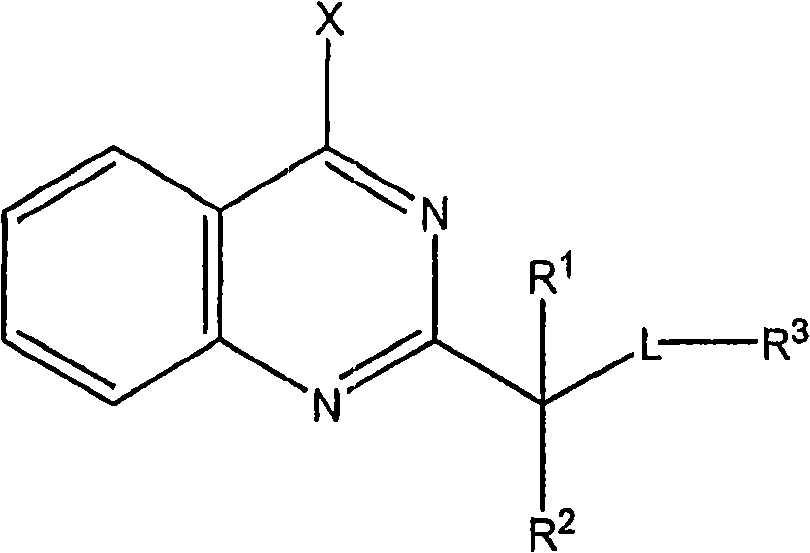
Quinazoline derivatives useful in cancer treatment
The present invention provides compounds of Formula (I) (wherein R<1>, R<2>, R<3>, L, and X are as defined herein), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate or ester thereof. The present invention also provides compositions comprising these compounds that are useful for treating cellular proliferative diseases, disorders associated with activity of mutants of p53, or in causing apoptosis of cancer cells.
Owner:SCHERING AG
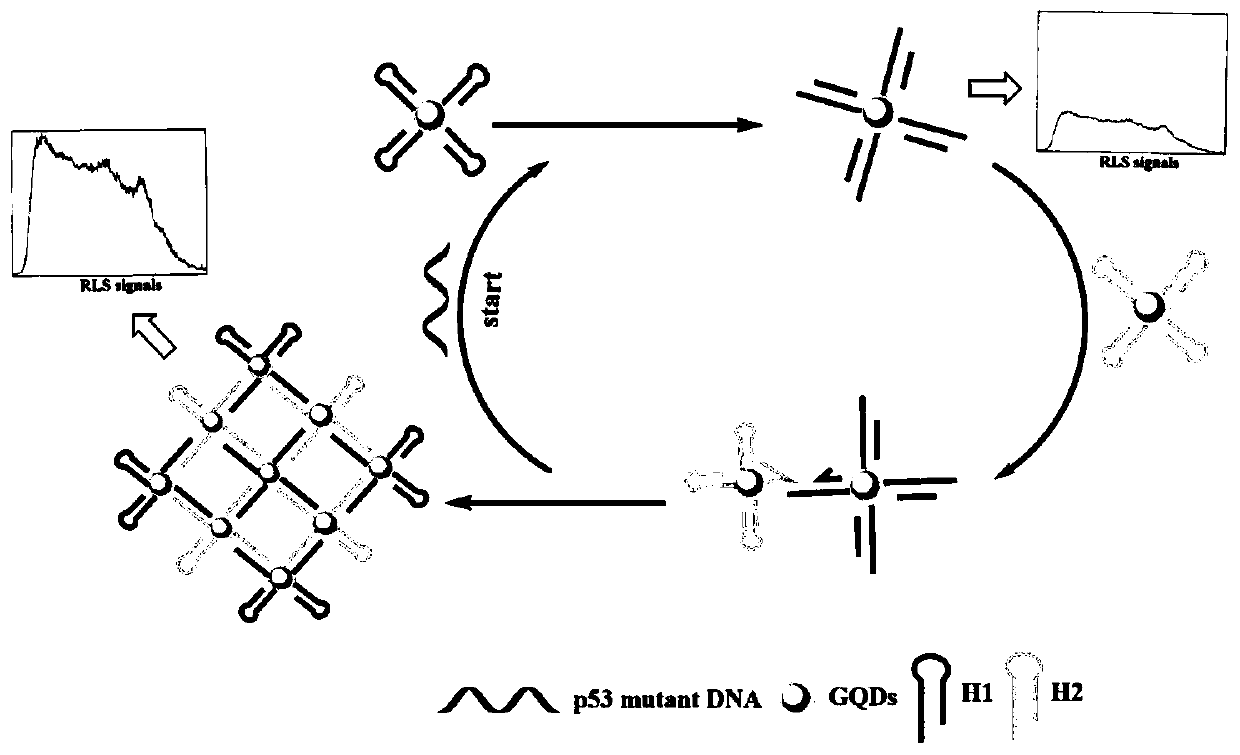
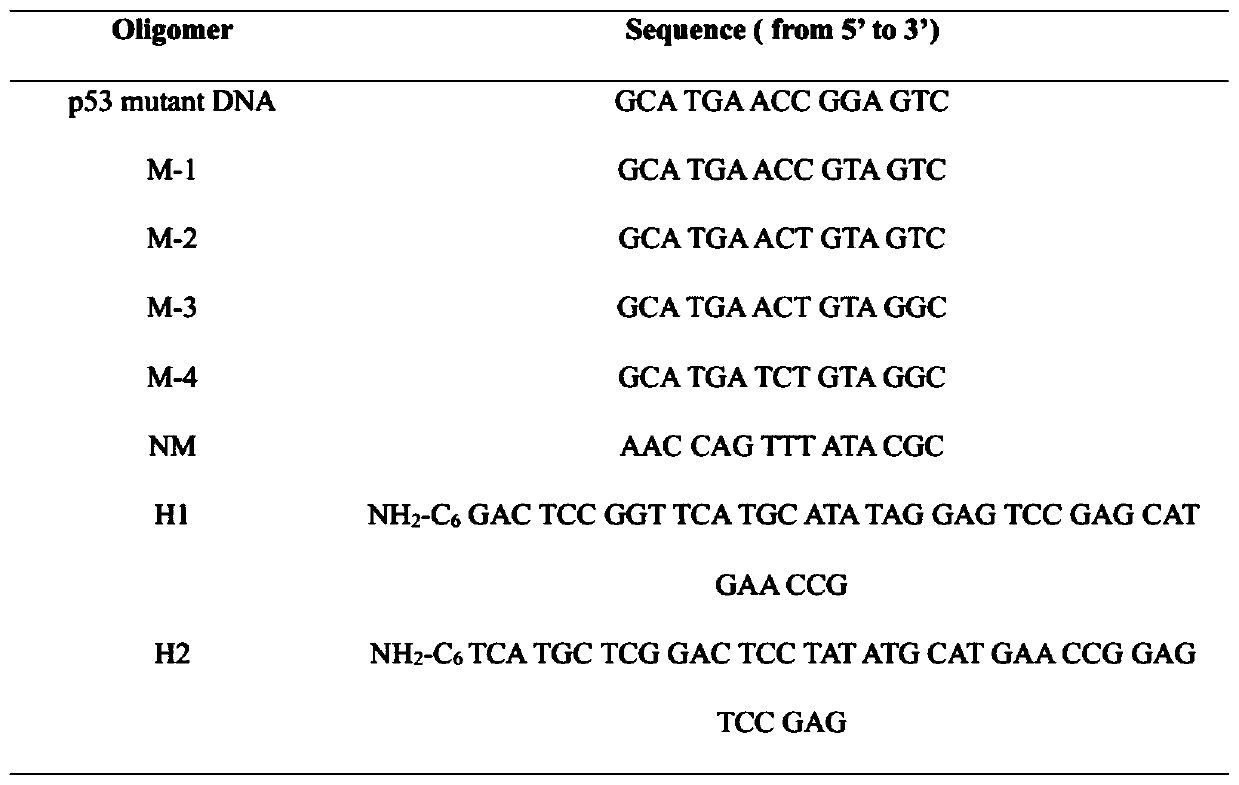
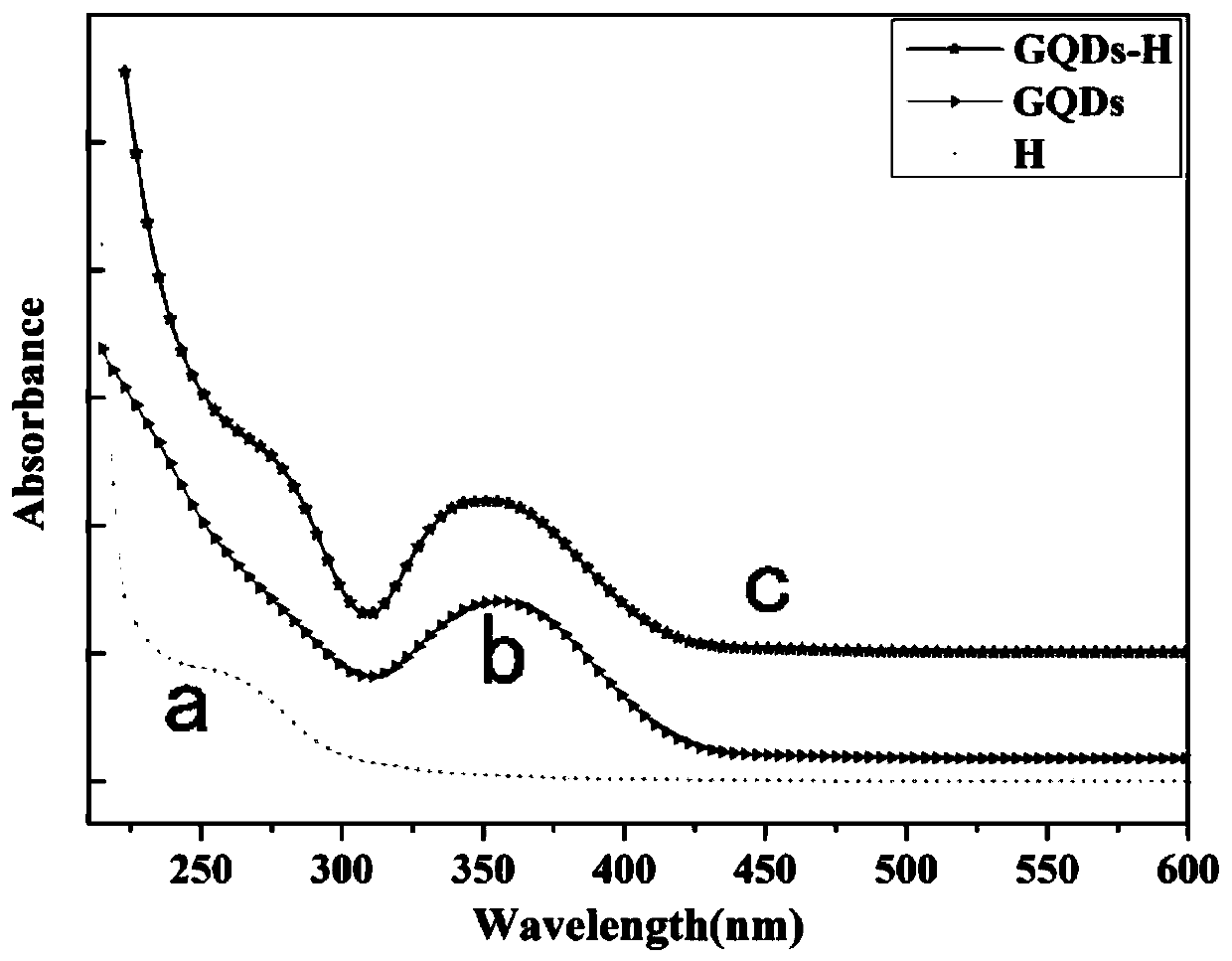
Method for quantified detection of mutation DNA through combination of resonant light scattering probe with CHA technique based on GQDs
ActiveCN109706221AStrong specificitySimple detection equipmentMicrobiological testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsResonanceP53 Mutation
The invention discloses a method for quantified detection of mutation DNA through combination of a resonant light scattering probe with a CHA technique based on GQDs. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, synthesizing graphene quantum dots, designing two harigrip probes H1 and H2 in according to objects, and then preparing two probes GQDs-H1 and GQDs-H2 through a condensation reaction. In a PBS buffer solution reaction system, when p53 mutation DNA is added, aggregation of the GQDs-H1 and GQDs-H2 can be caused, obviously-enhanced resonance light signals are generated, and quantified detection of p53 mutation DNA is realized. The method has high sensitivity and selectivity, the liner scope is 1pM to 50mM, the detection limitation is 0.8pMa, and quantified detection of an object can be realized effectively.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
PEPTIDES CAPABLE OF REACTIVATING p53 MUTANTS
ActiveUS20190315804A1Efficiently reactivatePromote activationPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemDiseaseWild type
The invention provides peptides that can reactivate p53 mutants efficiently and specifically, as well as methods that allow the identification, selection and isolation of such peptides, in a precise, cost and time effective manner. In particular, there are provided mutant p53 reactivating peptides that can restore the native wild type p53 folding, and hence the tumor suppressor activity, to the mutant p53 protein. Such peptides are useful for treating various conditions and diseases in which p53 is mutated.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Rapid detection method for p53 gene mutation
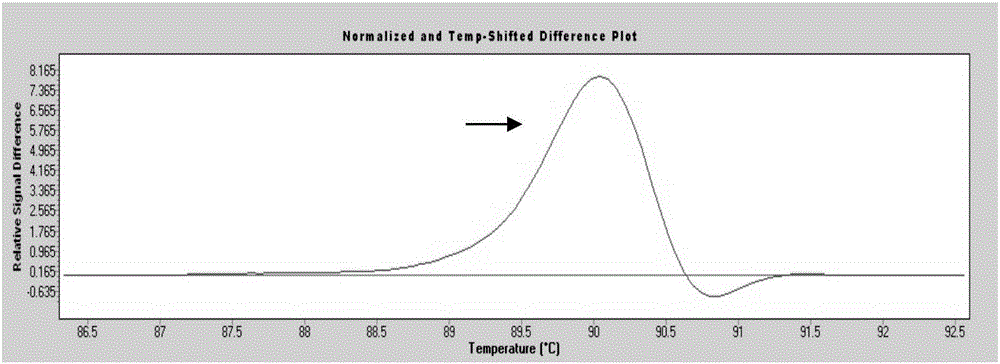
The invention provides a rapid detection method for p53 gene mutation. The rapid detection method comprises the steps of designing wild type primers and mutant type primers of exon 6 (p53-E6) of p53 and exon 8 (p53-E8) of p53; amplifying a corresponding wild type target segment and mutant type target segment respectively; mixing the above two segments according to different proportions so as to make the content of the mutant type target segments being 1 / 10, 1 / 100, 1 / 1,000 and 0; and finally distinguishing by an HRM method. Compared with other methods, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of high specificity and high sensitivity, is convenient and efficient, and has higher throughput and lower cost for single detection.
Owner:山东国九堂制药集团股份有限公司
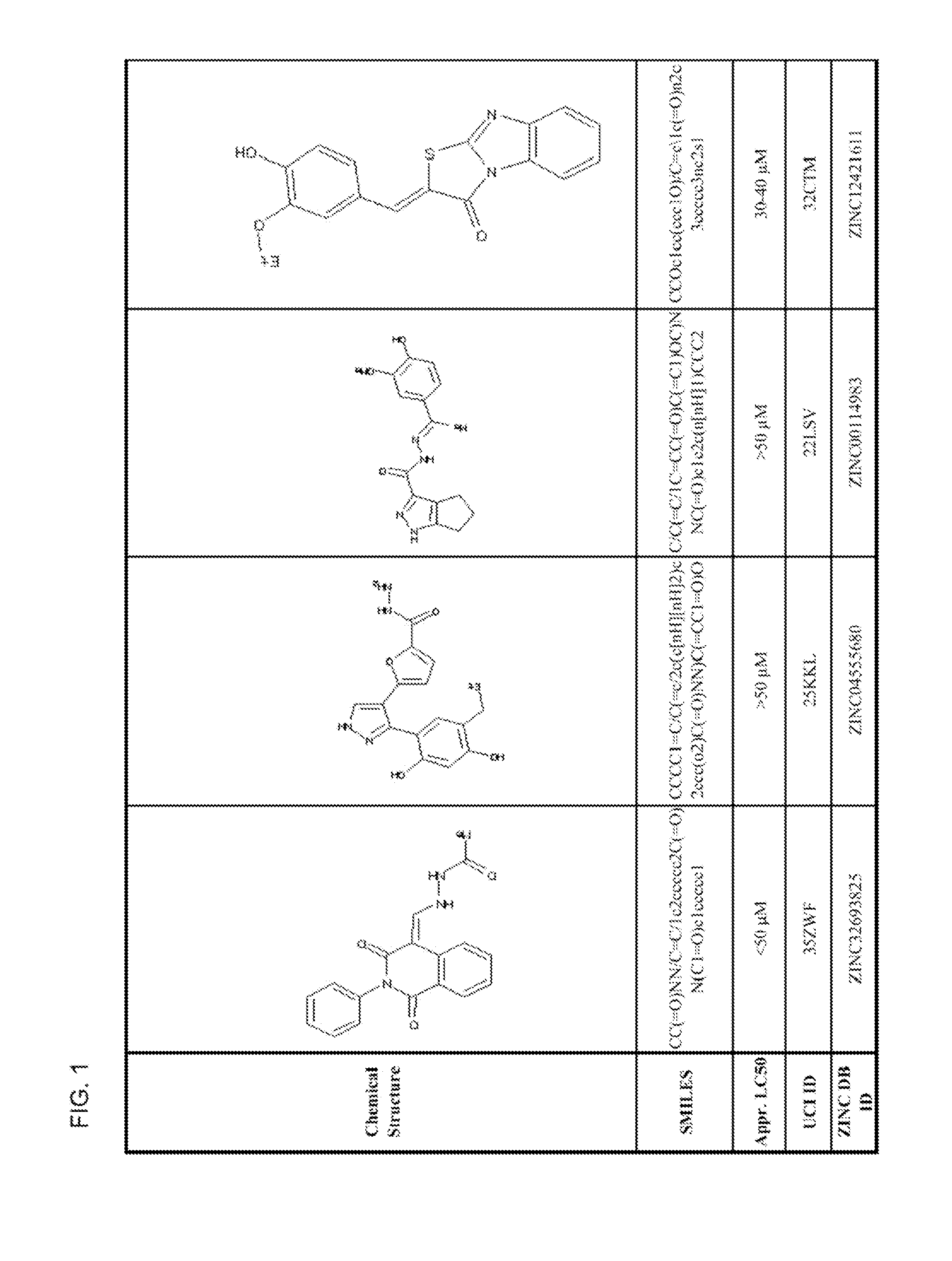
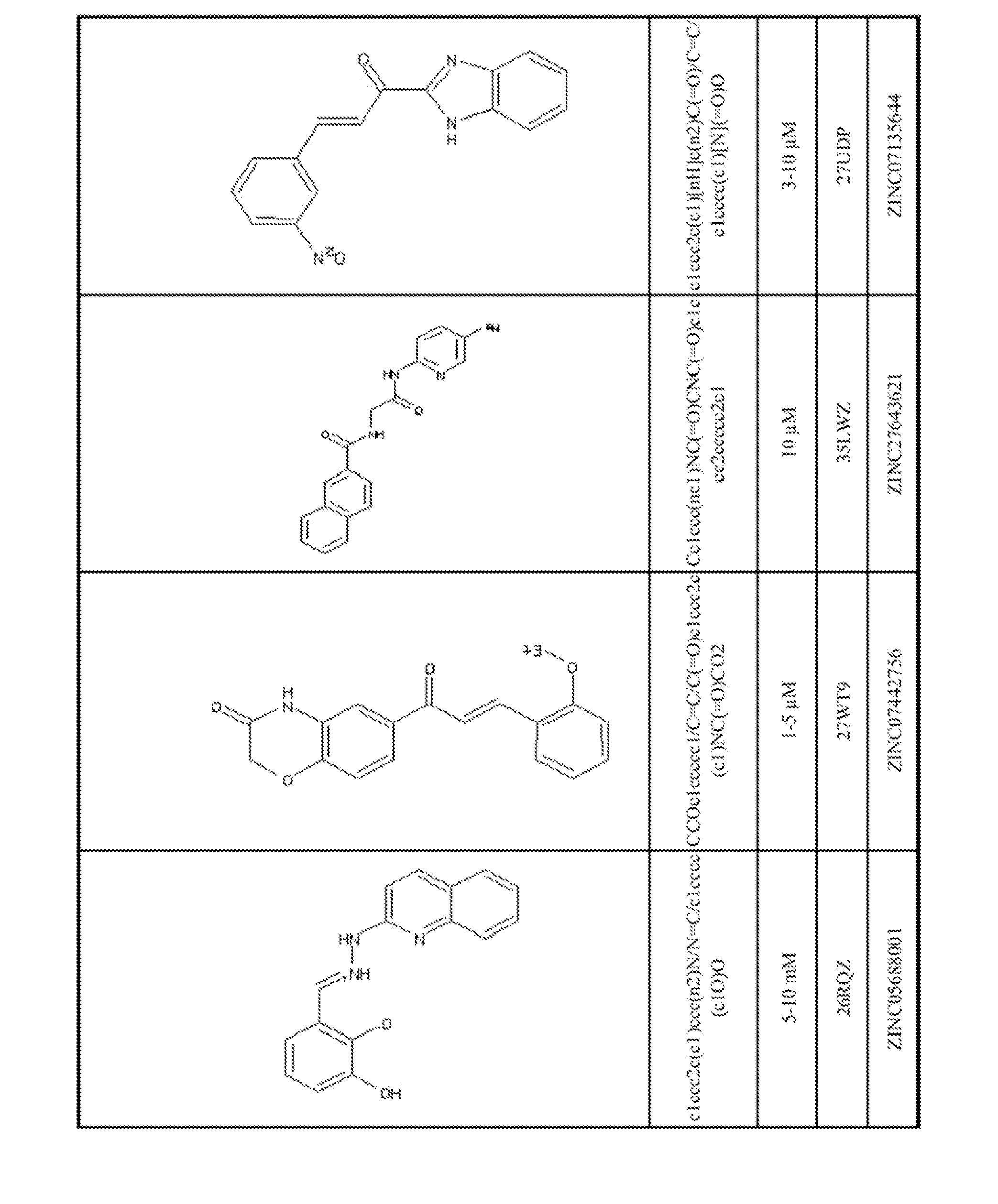
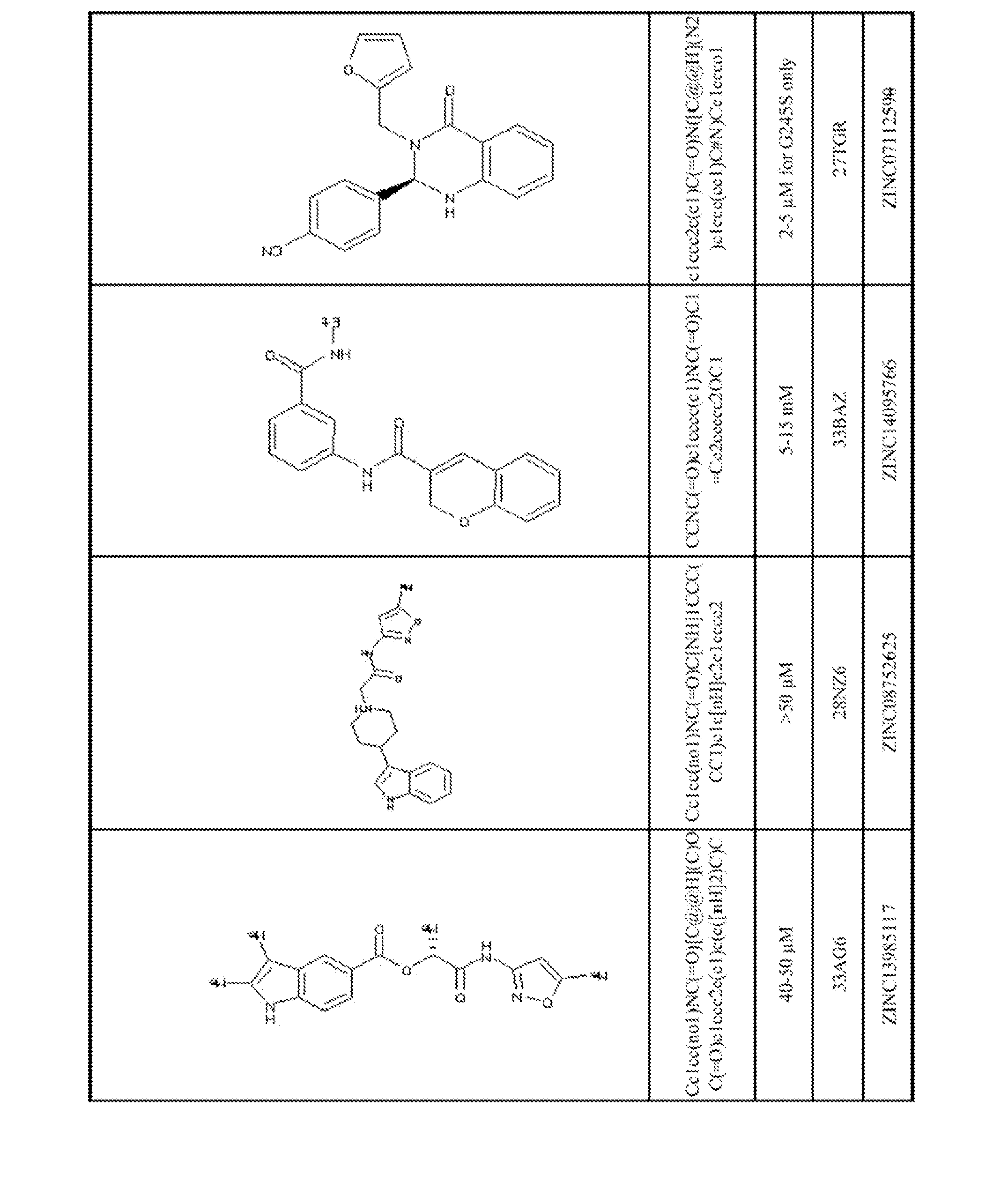
Small molecules to enhance p53 activity
A method of enhancing p53 activity of a p53 mutant polypeptide is provided. The method includes interacting a compound to an open L1 / S3 binding site of the p53 mutant polypeptide, where the p53 activity of the p53 mutant polypeptide is enhanced in the presence of the compound. Compounds were identified from databases of compounds for virtual drug screening. Methods of screening for compounds that enhance p53 activity by binding to the open L1 / S3 binding site, and methods of treatment using the identified compounds, are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
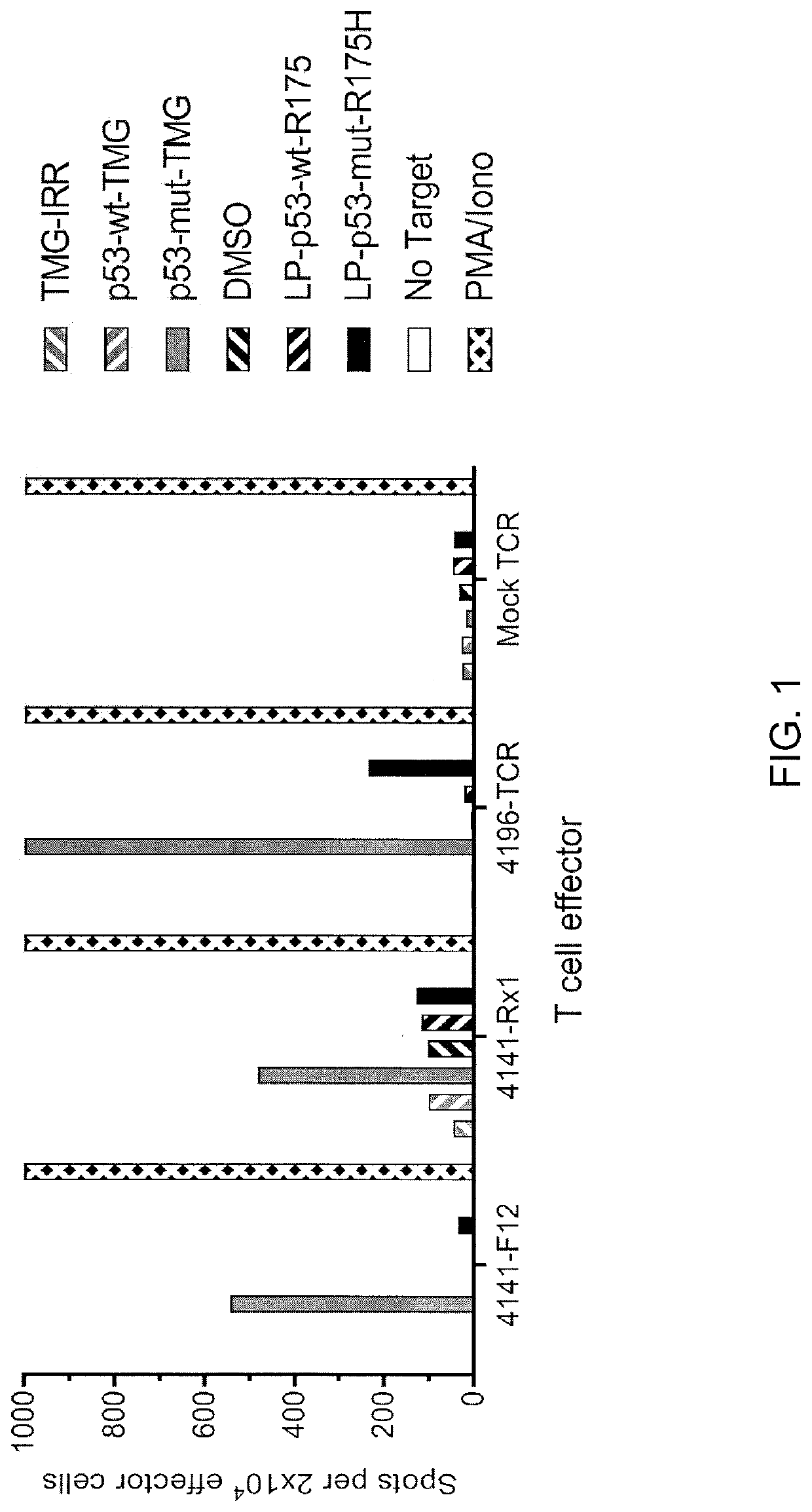
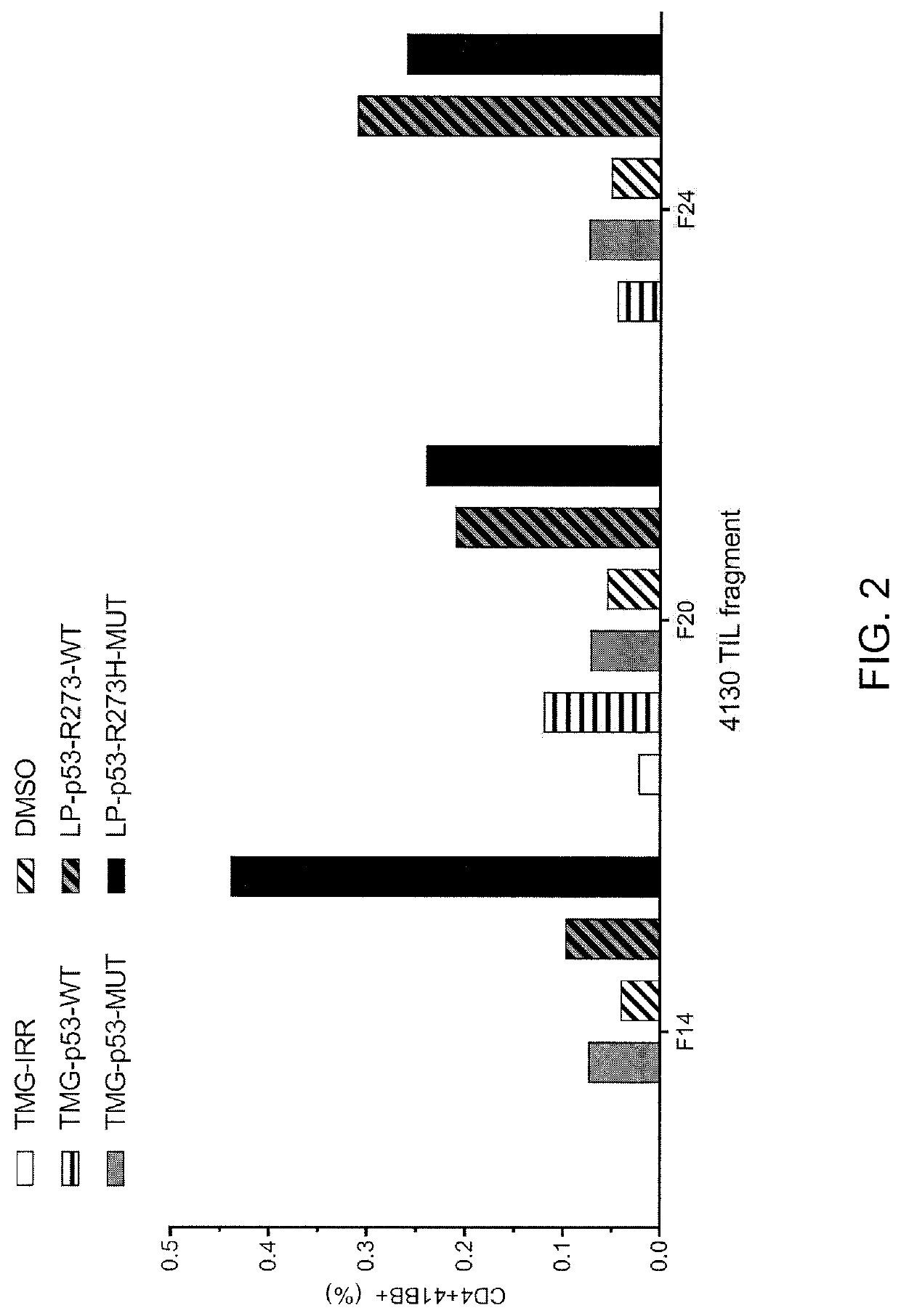
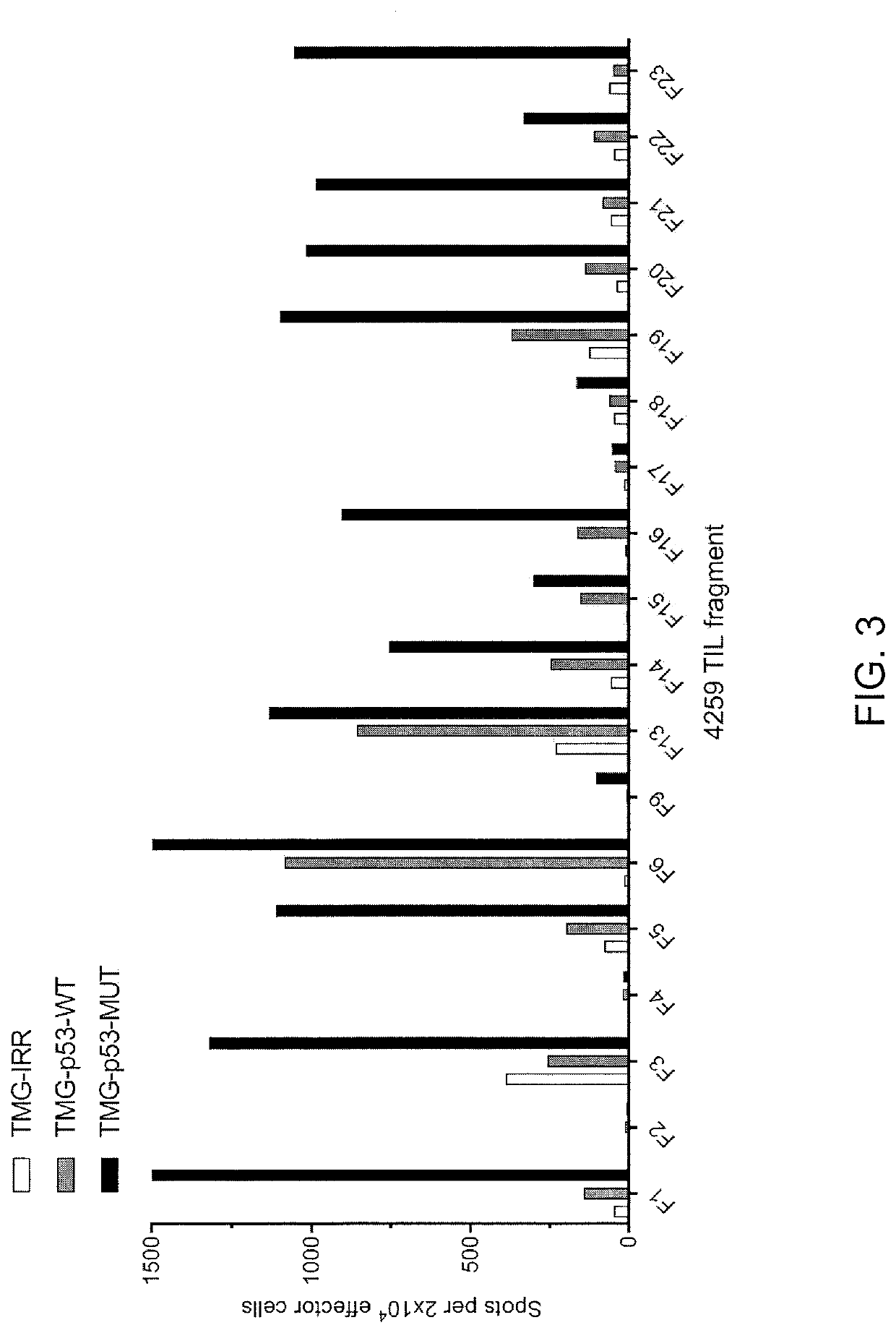
Methods of isolating t cells having antigenic specificity for a p53 cancer-specific mutation
PendingUS20200316121A1Increase the number ofP53 proteinMammal material medical ingredientsMolecular biologyP53 Mutation
Disclosed are methods of isolating T cells having antigenic specificity for a mutated p53 amino acid sequence encoded by a cancer-specific p53 mutation, the method comprising: inducing autologous APCs of the patient to present the mutated p53 amino acid sequence; co-culturing autologous T cells of the patient with the autologous APCs that present the mutated p53 amino acid sequence; and selecting the autologous T cells. Also disclosed are related methods of preparing a population of cells, populations of cells, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of treating or preventing cancer.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
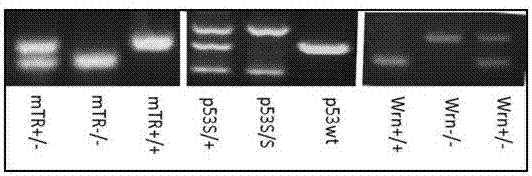
Application of P53 gene mutation and telomere dysfunction
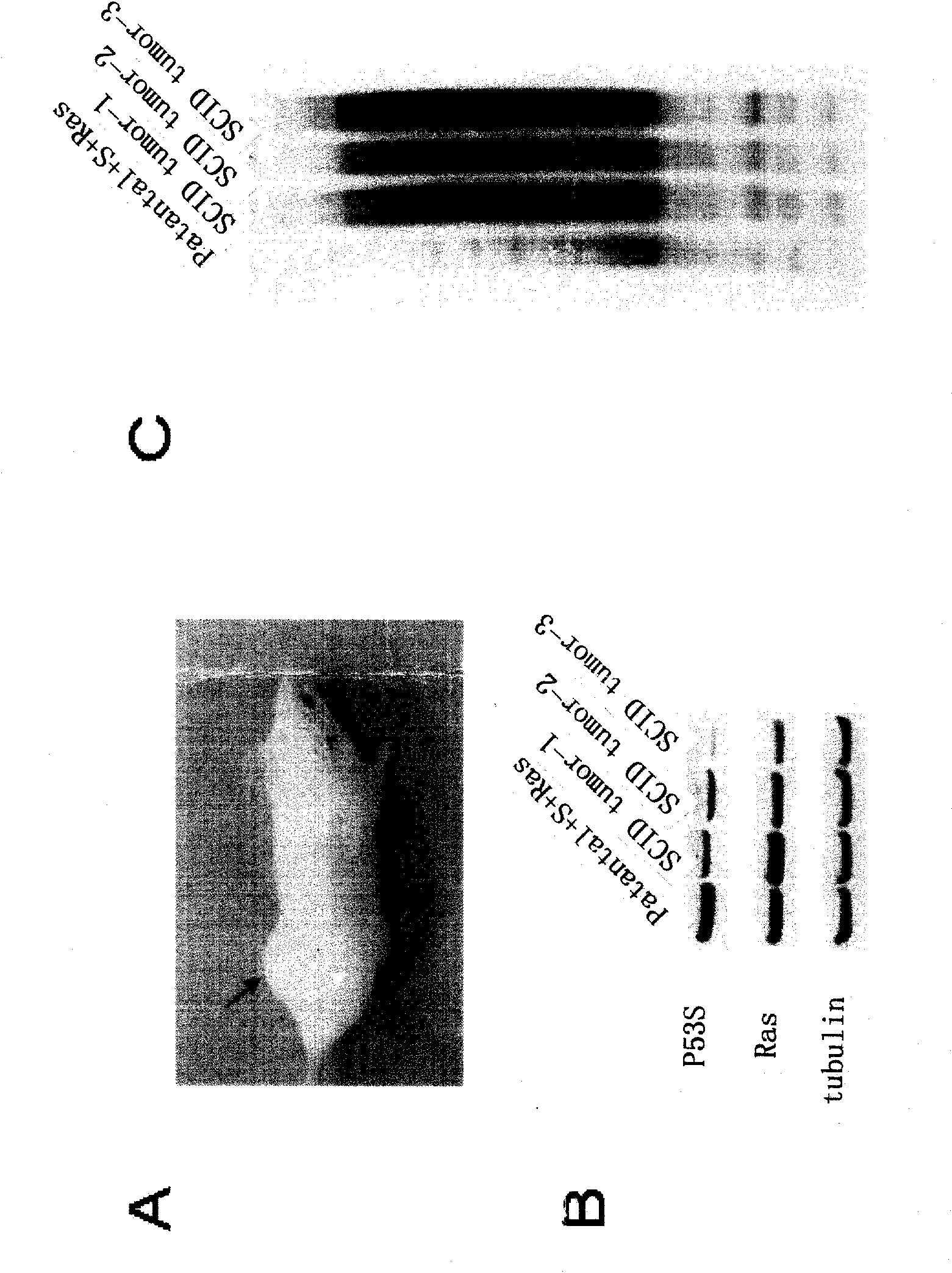
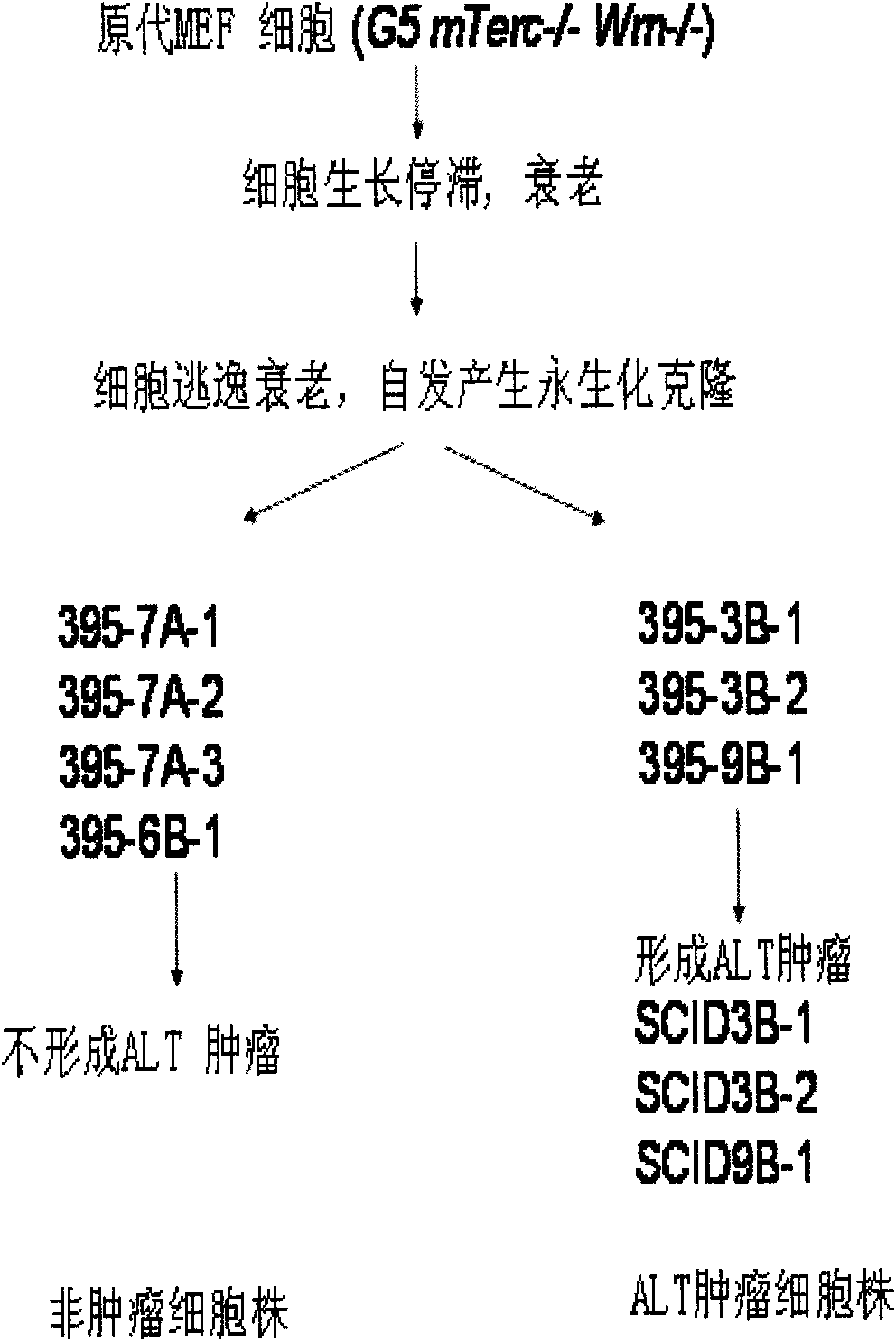
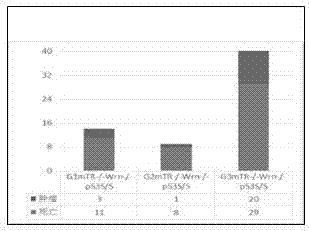
InactiveCN107447005AGood scientific meaningGood clinical valueMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseWerner syndrome
The invention discloses new application of P53 gene mutation and telomere dysfunction, namely, application of a reagent for detecting cancer suppressor gene P53 gene mutation and telomere dysfunction in preparing a reagent for clinical diagnosis of polycystic kidney disease, or the application of P53 gene mutation and telomere dysfunction in screening the therapeutics for the polycystic kidney disease. An experimental result shows that the hybrid descendant of the mice with p53N236S gene mutation and the mice suffering from Werner syndrome (WS) suffers from the polycystic kidney disease so that a novel PKD disease model is acquired. According to the application, the condition that the happening of the polycystic kidney disease possibly is a new phenomenon of abnormal proliferation of kidney cells caused by the combined action of mutation p53 and aging signal is discovered for the first time. Through the discovery, the pathogenesis of the polycystic kidney disease is enriched, and a new biomarker for the clinical diagnosis of the polycystic kidney disease is provided.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
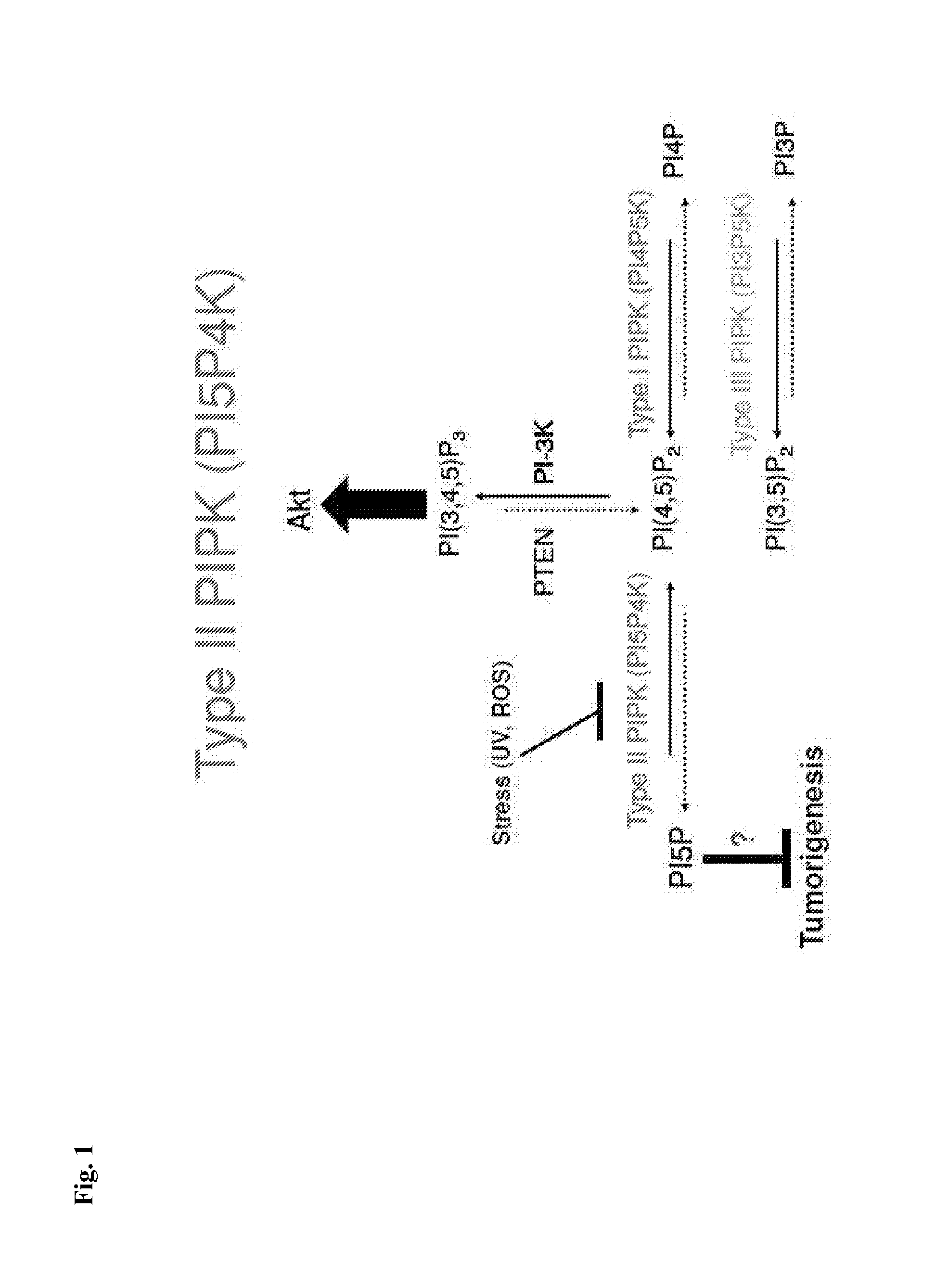
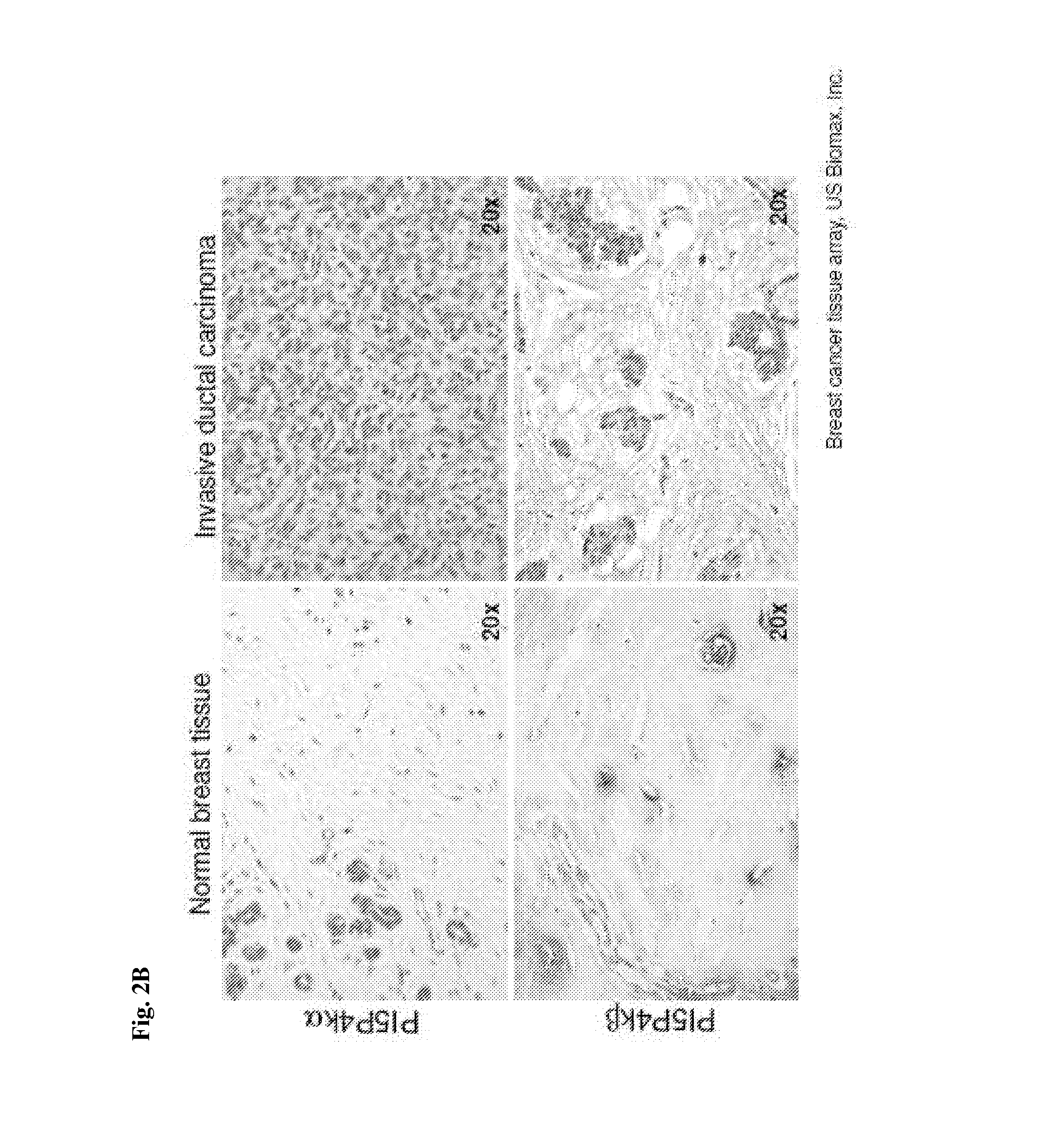
Modulation of phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate-4-kinase activity
ActiveUS20140080893A1Induced deathReduces and prevents tumor cell growthOrganic active ingredientsCompound screeningKinase activityPhosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate
The invention features methods for identifying compounds that modulate the activity of phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate 4-kinase (PI5P4K) Inhibitors of PI5P4K can be used in, for example, the treatment or prevention of cell proliferation dis orders (e.g., the prevention of tumor cell growth in p53 mutated cancers).
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Application of p53 gene mutation in cancer-associated fibroblasts
PendingCN108486248AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisTumor-Associated FibroblastsTumor therapy
The invention discloses application of p53 gene mutation in cancer-associated fibroblasts, and particularly relates to application of p53 gene mutation in the cancer-associated fibroblasts in screening and preparation of cancer therapy medicines. An experimental result shows that the growth of cancer can be promoted by mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) carrying p53N236S mutation, thus it is suggested that p53 mutation activates the cancer-associated fibroblast characteristic of the MEF, and the favorable microenvironment is provided for multiplication, migration and the like of the cancer. Thenew function of p53 mutation in the cancer-associated fibroblasts is disclosed for the first time, through the discovery, the new idea and research direction are provided for p53 mutation in cancer research, a new action target is provided for cancer therapy, and a new strategy is also provided for cancer therapy.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Combination Therapy
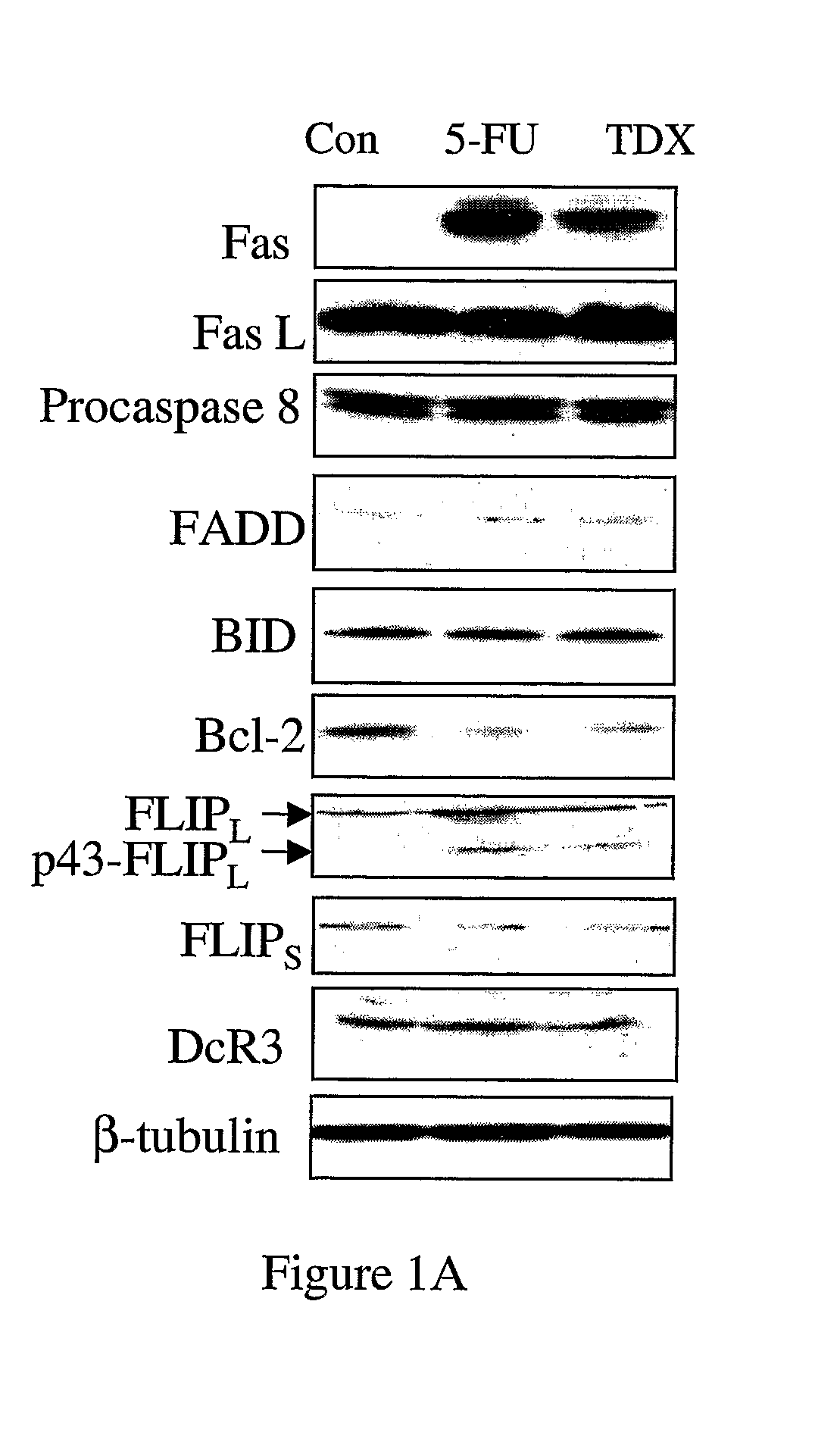
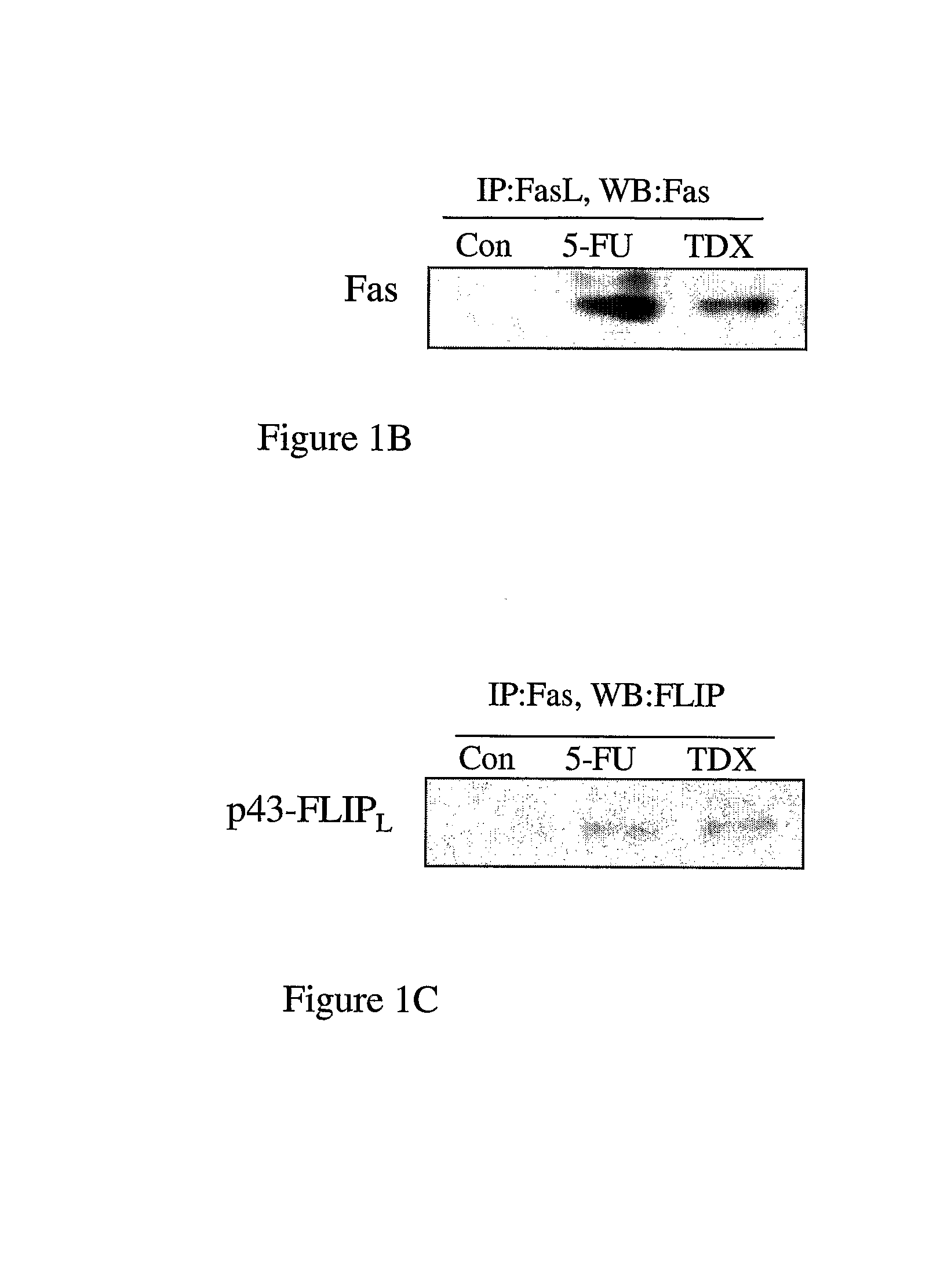
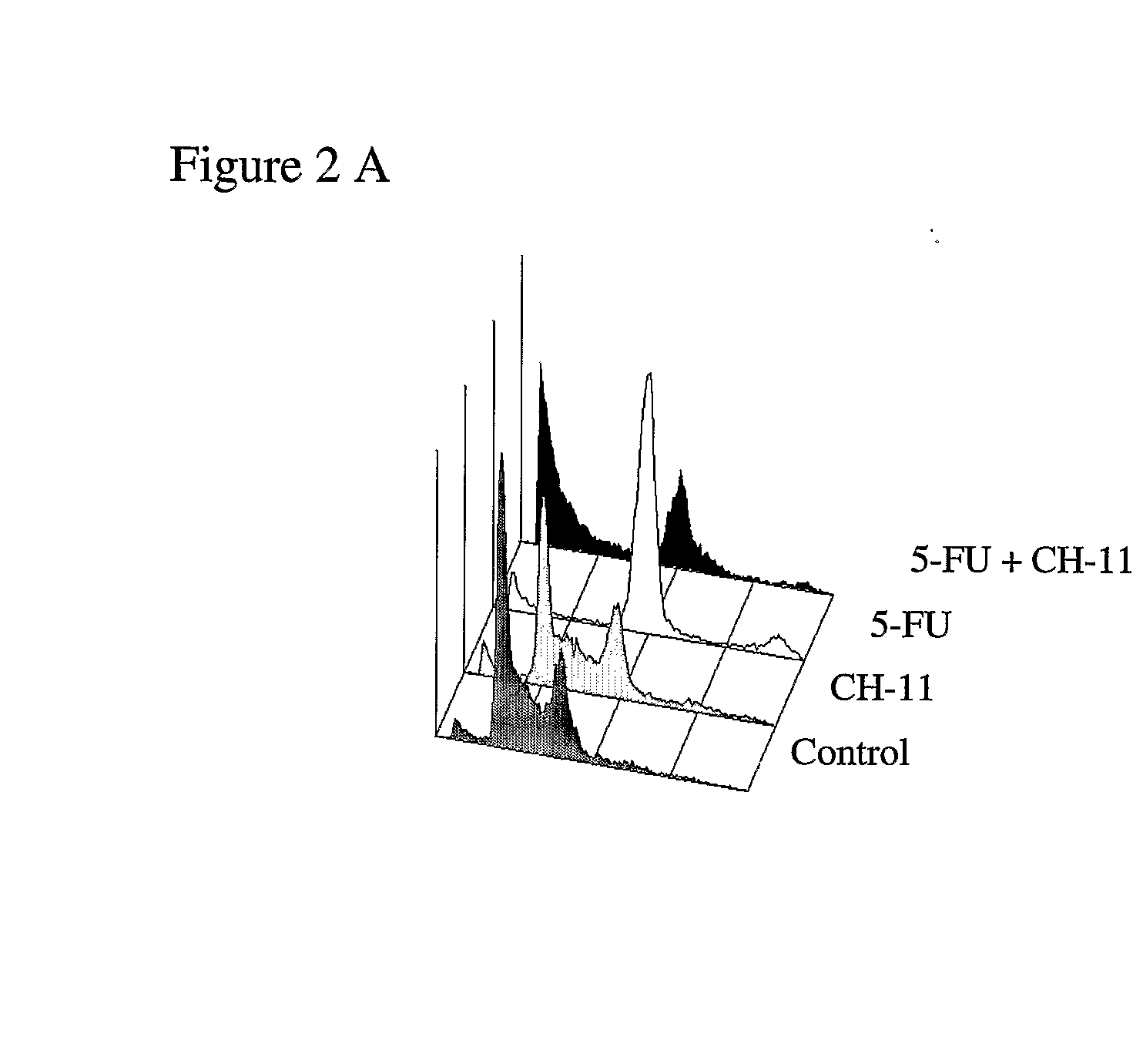
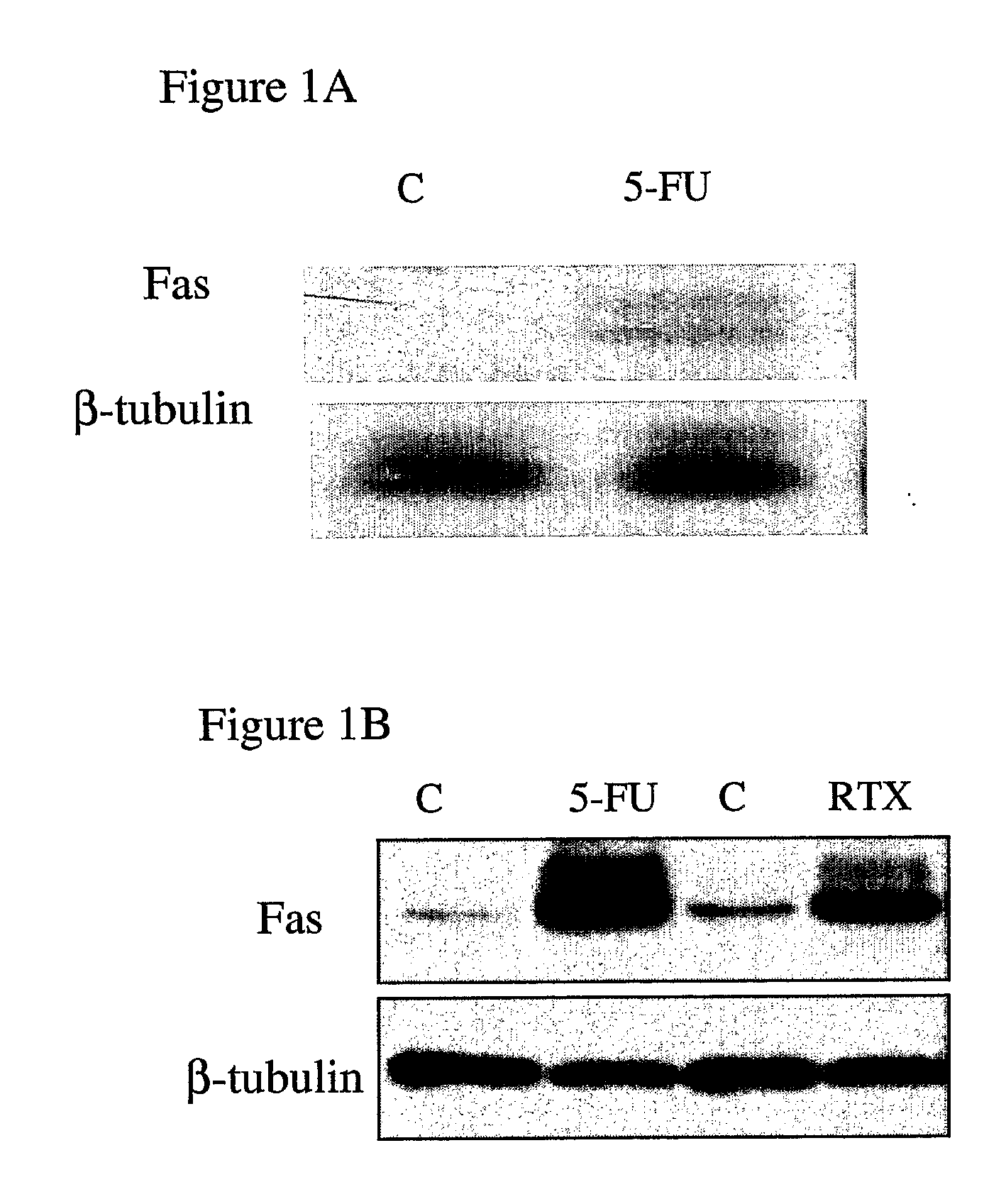
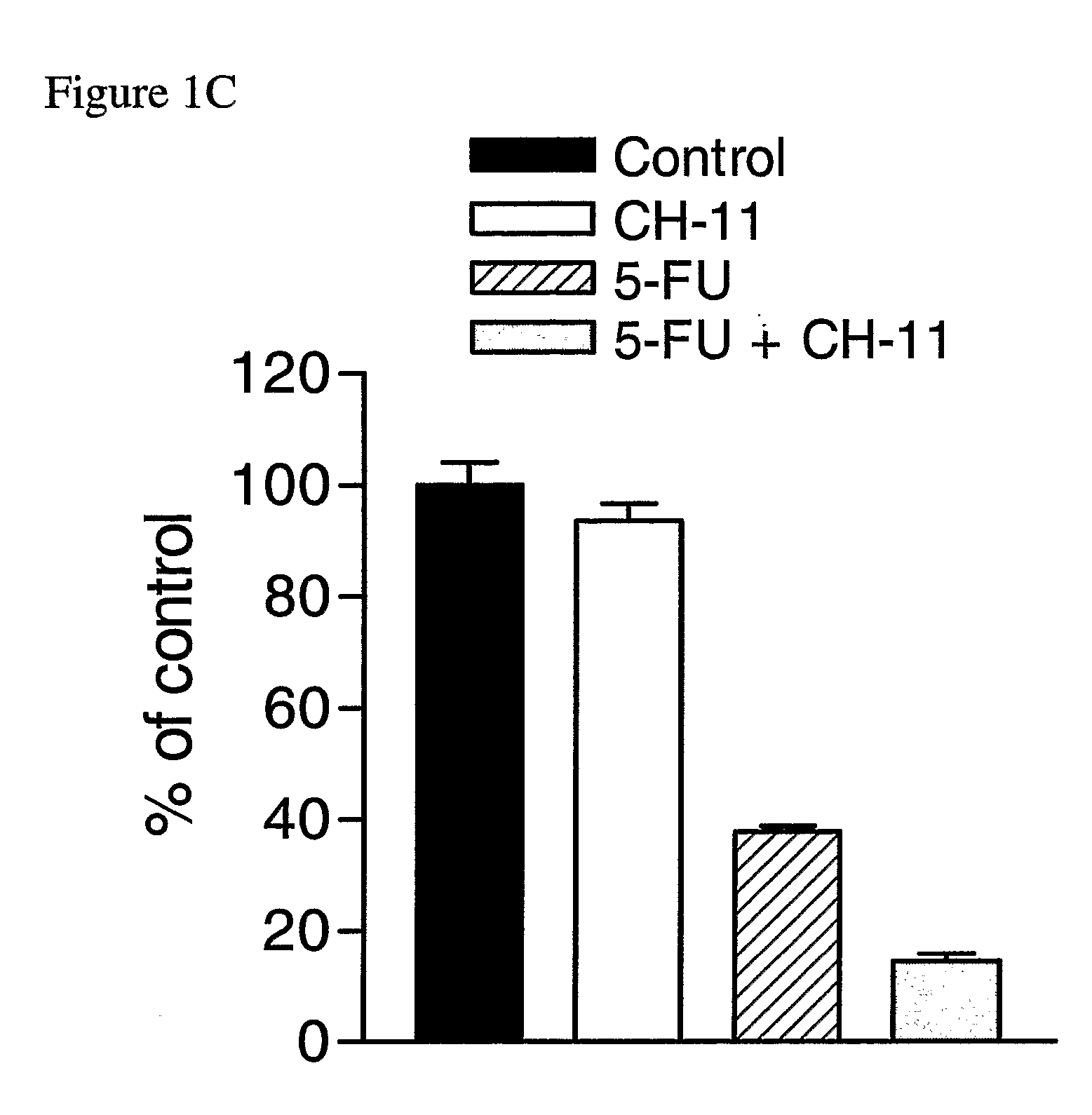
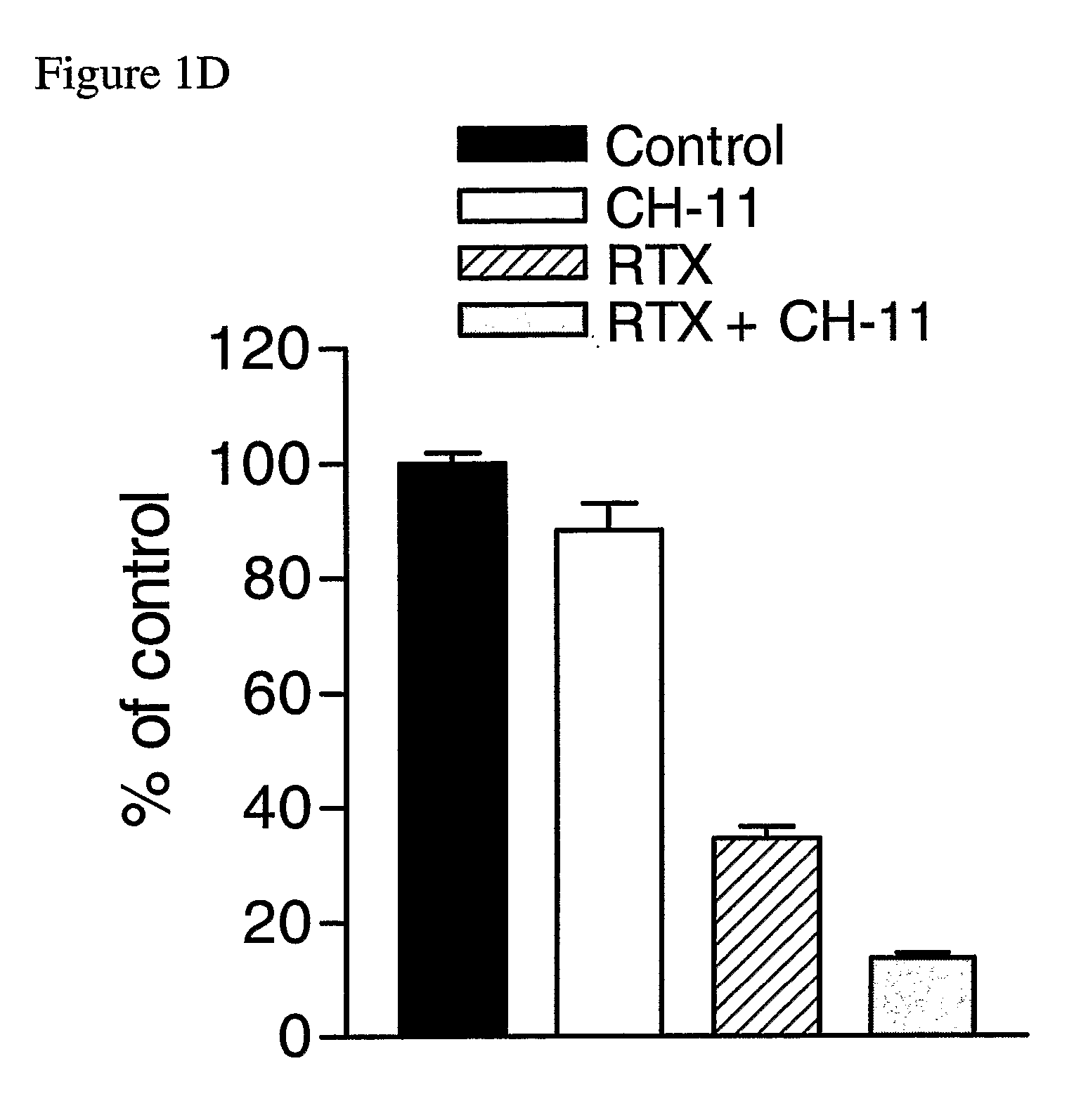
InactiveUS20070286867A1Lower Level RequirementsPromote recoveryAntibody ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDeath ReceptorsTopoisomerase-II Inhibitor
The invention provides combination therapies and methods for the treatment of cancers associates with p53 mutations. The method comprises the separate, sequential or simultaneous administration of a therapeutically effective amount of a) a specific binding member, for example CH-11, which binds to a cell death receptor, for example Fas, or a nucleic acid encoding said binding member and b) a chemotherapeutic agent, wherein the chemotherapeutic agent is a topoisomerase inhibitor, for example CPT-1 or a thymidylate synthase inhibitor, for example TDX. Synergistic cytotoxic effects have been demonstrated using such combinations.
Owner:FUSION ANTIBODIES
Methods of isolating T cells having antigenic specificity for P53 cancer-specific mutation
Disclosed are methods of isolating T cells having antigenic specificity for a mutated p53 amino acid sequence encoded by a cancer-specific p53 mutation, the method comprising: inducing autologous APCsof the patient to present the mutated p53 amino acid sequence; co-culturing autologous T cells of the patient with the autologous APCs that present the mutated p53 amino acid sequence; and selectingthe autologous T cells. Also disclosed are related methods of preparing a population of cells, populations of cells, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of treating or preventing cancer.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
In-vitro detection method for quickly screening exon 5-8 mutation of P53 gene and application
InactiveCN106834487ALow priceLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationExonGene mutation
The invention provides an in-vitro detection method for quickly screening the exon 5-8 mutation of a P53 gene. The method comprises the following steps: (1) extracting the genome DNA of a peripheral blood sample; (2) designing and synthesizing 4 pairs of specific primers for amplifying exon 5-8 of the P53 gene; (3) performing high resolution melting curve analysis and grounding PCR on the genome DNA of the sample by using the primers; and (4) obtaining the sample with a positive result in the curve analysis, meaning occurrence of P53 gene mutation. The detection method is not limited by site or type of mutated base, does not need a sequence specific probe, and can directly run high resolution melting after PCR is completed to complete analysis on the sample mutation. The method is simple, convenient and quick in operation, is low in use cost and accurate in result, can realize truly closed pipe operation. Furthermore, the method has the characteristics of high through-put, high speed, kit availability, low detection cost and the like for quick screening of population.
Owner:北京青航基因科技有限公司
Drug liposome capable of efficient and highly specific killing of P53 gene mutation type of breast cancer cells
InactiveCN102716498AEfficient killingNo killing effectOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSide effectWhole body
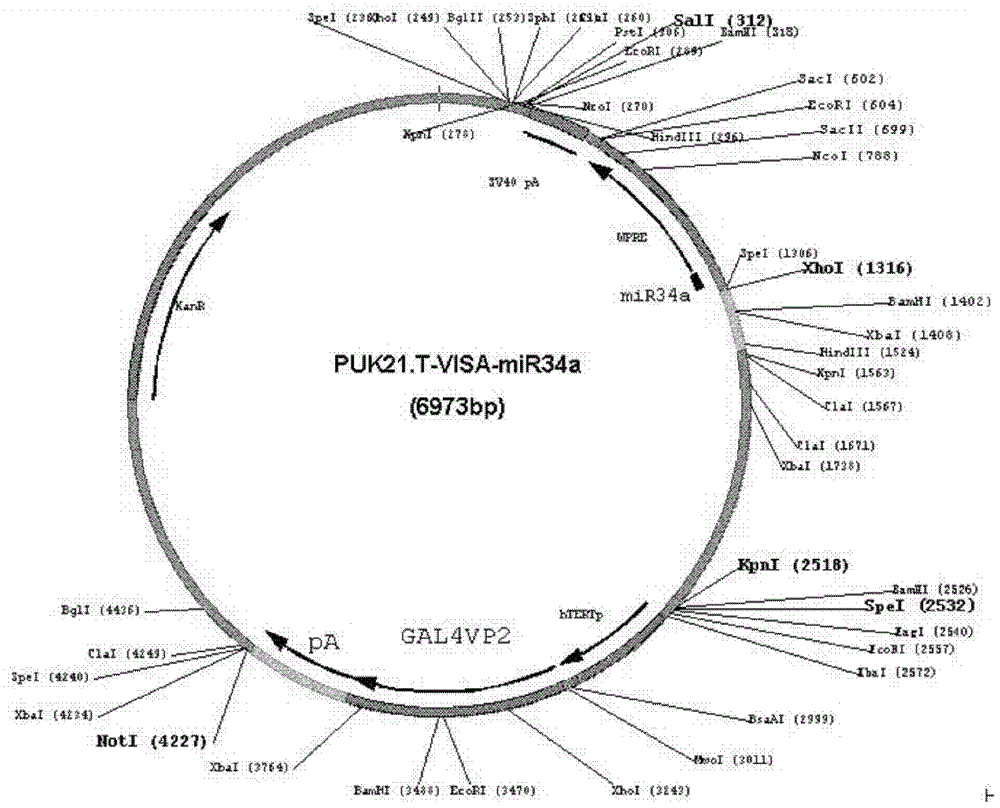
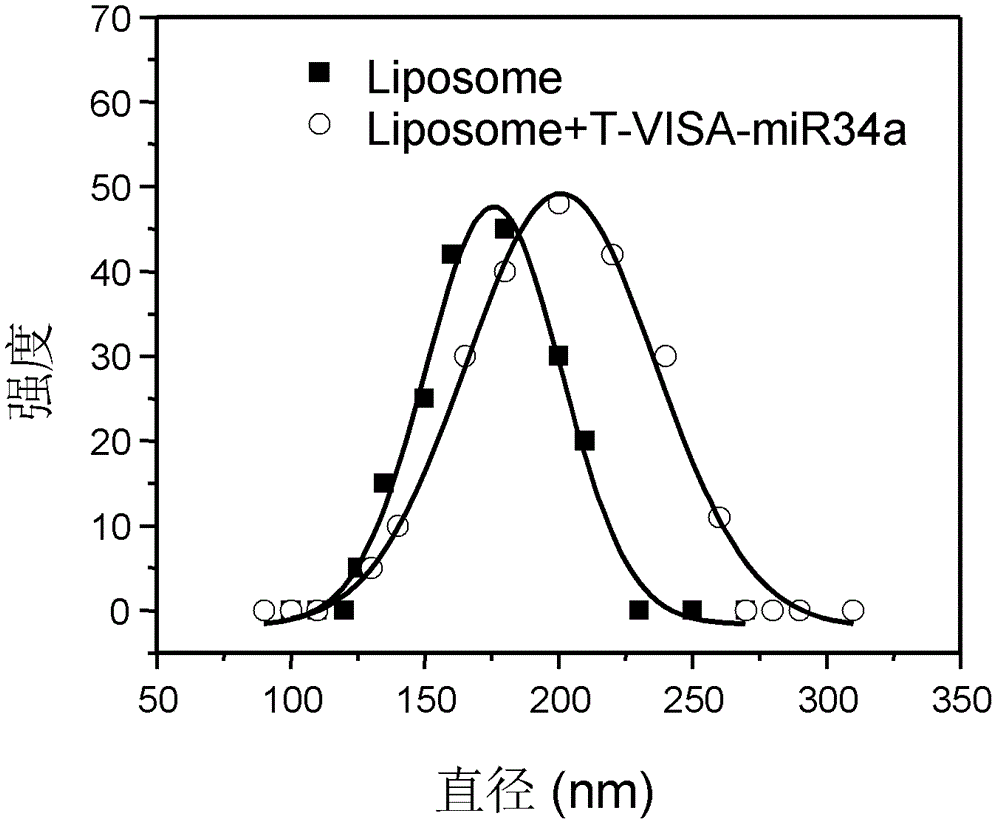
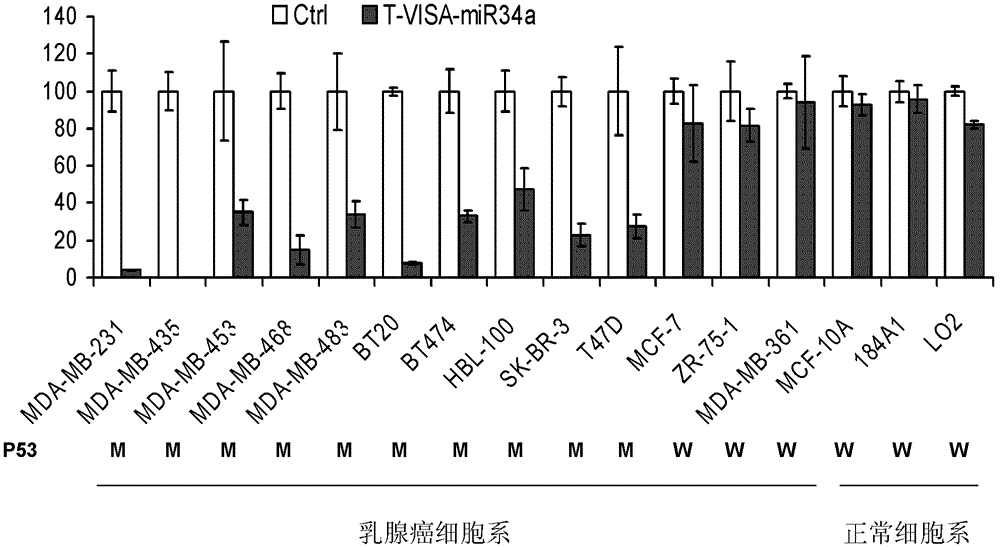
The invention discloses a drug T-VISA-miR34a liposome capable of efficient and highly specific killing of P53 gene mutation type of breast cancer cells. A T-VISA-miR34a treatment carrier capable of efficient and highly specific killing of P53 gene mutation type of breast cancer cells has a nucleotide sequence shown as a SEQ ID NO.1. The drug T-VISA-miR34a liposome capable of efficient and highly specific killing of P53 gene mutation type of breast cancer cells includes a liposome and a T-VISA-miR34a treatment carrier encapsulated by the liposome; and the T-VISA-miR34a treatment carrier has a nucleotide sequence shown as a SEQ ID NO.1. Encapsulated and delivered by the liposome, the T-VISA-miR34a treatment carriers of the invention enrich in the breast cancer site, and can efficiently target breast cancer BCL-2 and CD44 targets, completely or incompletely pair with 3 ' UTR, degrade mRNA of the target gene or inhibit its translation and lead to apoptosis of breast cancer cells without killing the normal cells. The drug can be delivered systemically, has advantages of high gene expression amount, long time, high efficiency, exact efficacy, low toxicity and side effect, no toxicity on kidney or liver, and has broad prospects in the treatment of P53 mutation type breast cancer.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV CANCER CENT
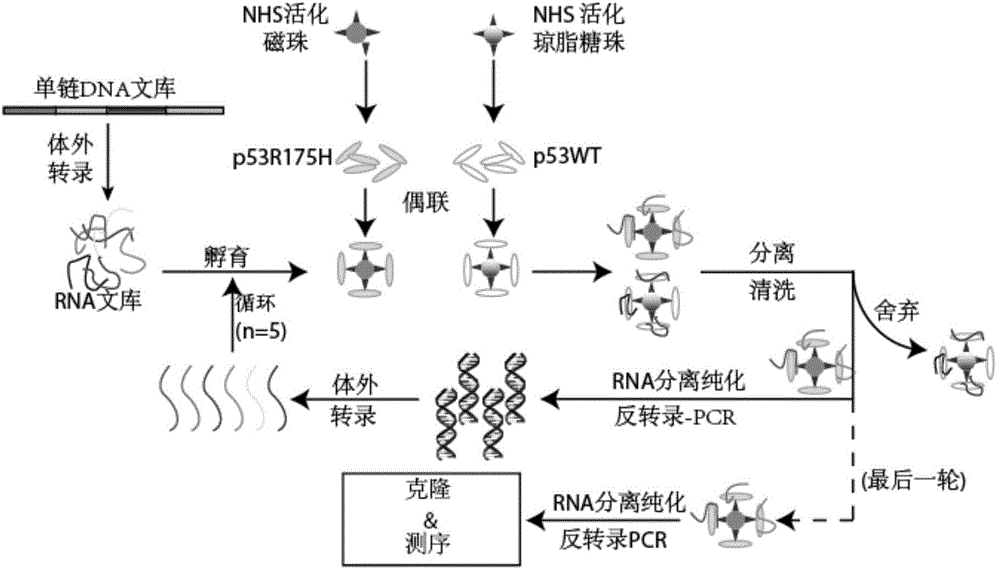
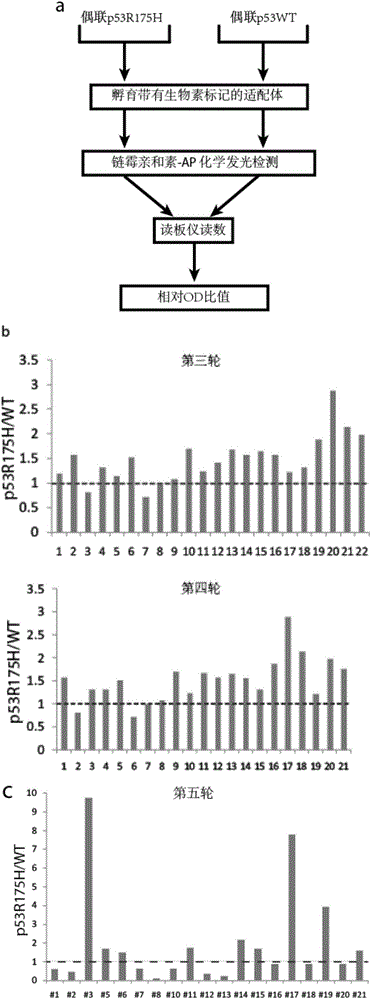
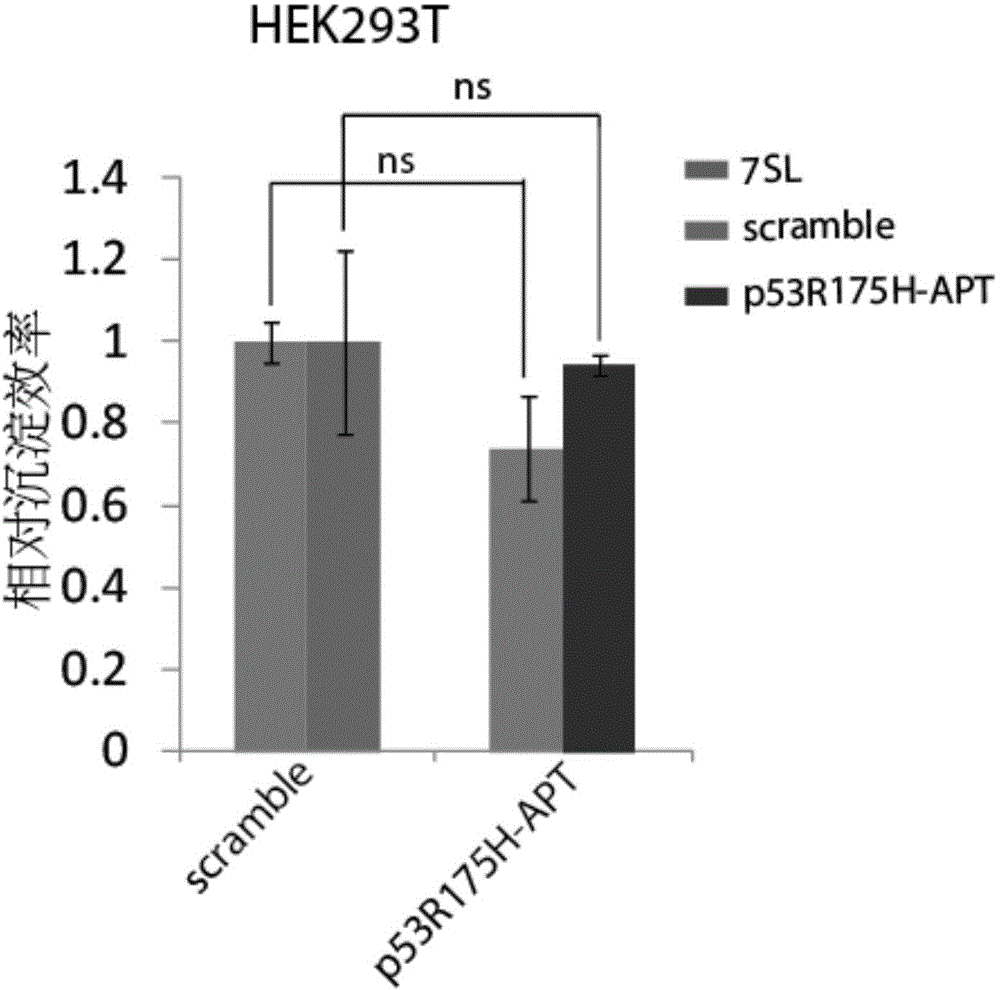
P53R175H specific nucleic acid aptamer and screening method and use thereof
ActiveCN104988156AHigh affinityImprove featuresOrganic active ingredientsBiological testingMutated proteinScreening method
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer specifically binding to a p53 mutant protein p53R175H, wherein the nucleic acid aptamer comprises a sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The invention also discloses a derivative of the nucleic acid aptamer, a screening method of the nucleic acid aptamer and a use of the nucleic acid aptamer in treating tumor.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
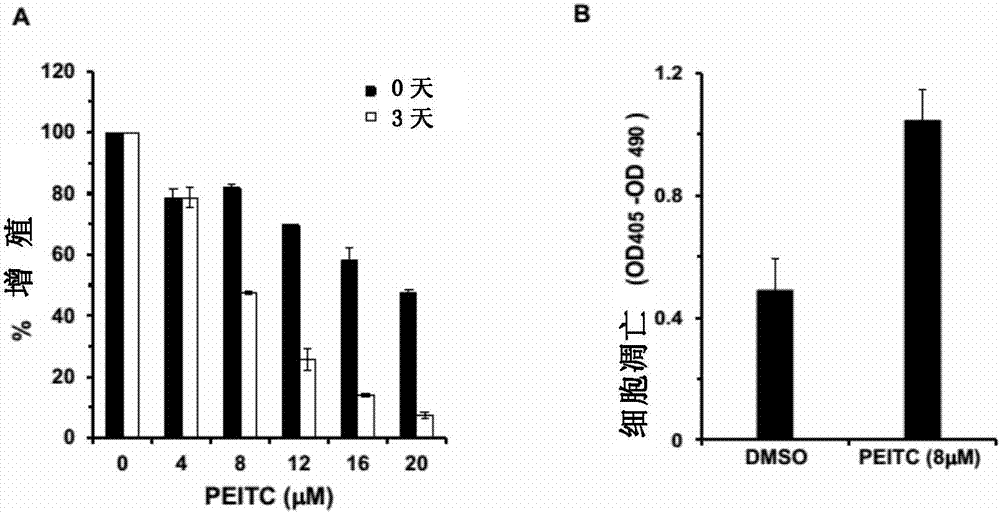
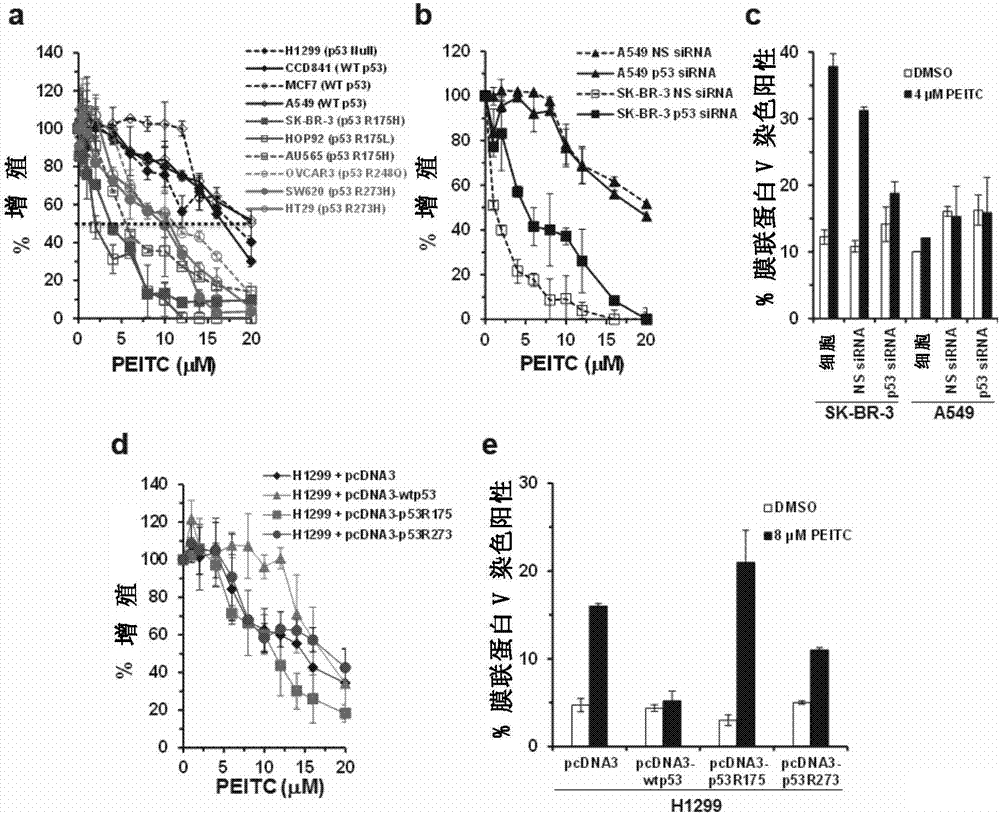
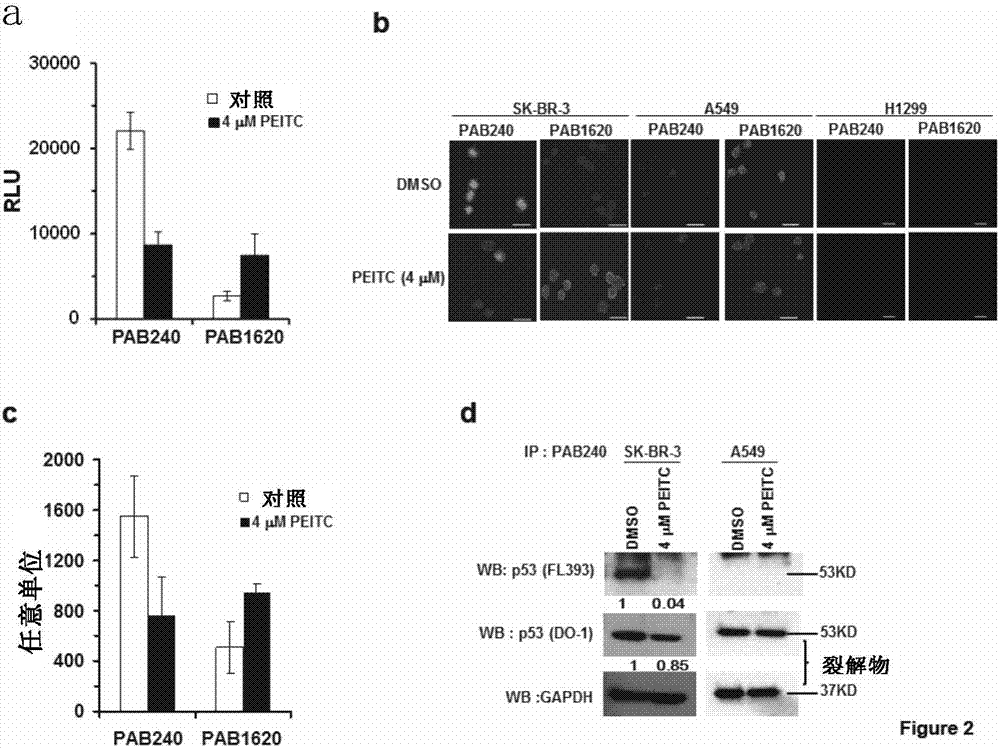
PEITC-containing pharmaceutical composition and application thereof in cancer therapy
The invention provides an application of PEITC for preparing a preparation of a composition. The preparation or the composition is used for (a) changing a mutant p53 to restore the wild activity, (b) inhibiting tumor cell proliferation caused by the mutant p53, (c) inducing tumor cell apoptosis of the mutant p53, and / or (d) preventing or treating a disease caused by p53-based mutation. The invention further provides an application of a p53 gene detection reagent, a kit comprising the PEITC and the p53 gene detection reagent and a method for in vitro non-therapeutic inhibition of tumor cells.
Owner:JC (WUXI) CO INC
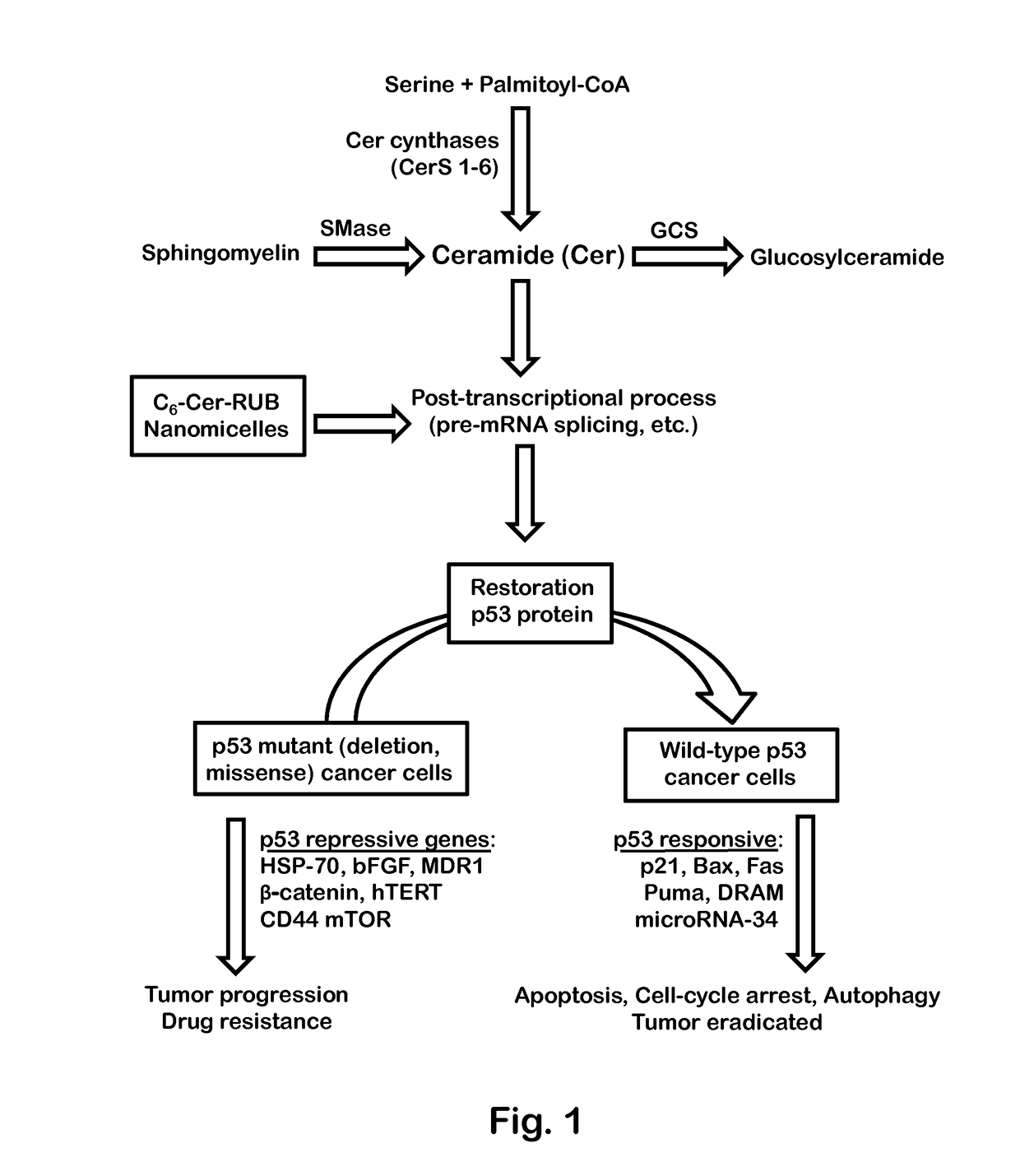
Ceramide-Rubusoside Nanomicelles and Their Use in Cancer Therapy
InactiveUS20170216329A1Good water solubilityWithout adversely affecting bioavailability and efficacyPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilityWild type
Water-soluble, cell-permeable nanomicelles containing ceramides and a steviol glycoside, such as rubusoside, are disclosed. The ceramide-steviol glycoside complex has high water solubility, and can be used for treating cancers with p53 mutations. Preliminary results have shown that the Cer nanomicelles are effective in restoring p53 protein expression, and that they are functionally dominant over p53 mutants. The novel nanomicelles restore a wild-type phenotype, and have very low toxicity to noncancerous cells. The novel Cer nanomicelles may be used in treating p53-associated cancers.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LOUISIANA AT MONROE +1
Specific cancer treatment regimes with ganetespib
Methods of treating certain types of cancer with ganetespib are disclosed. Also provided are methods of treating certain types of cancer with ganetespib in combination with a taxane derivative, and a platinum-containing anticancer agent. Also provided are methods of treating certain types of cancer with p53 mutation by a combination of ganetespib with a taxane derivative, and a platinum-containing anticancer agent. Also provided are methods of treating certain types of cancer with ganetespib in combination with a platinum-containing anticancer agent, and an antimetabolite. Also provided are methods of treating certain types of cancer with ganetespib in combination with a taxane derivative, an anthracycline derivative, and an alkylating antineoplastic agent. Also provided is a pharmaceutical composition comprising ganetespib and one or more other anticancer agents as described above.
Owner:SYNTA PHARMA CORP
Compound having radiosensitization function and application of compound
ActiveCN106045932AUniversal applicabilityInhibit expressionOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsAbnormal tissue growthMutant
The invention discloses a compound having a radiosensitization function and an application of the compound. The compound has an anti-proliferation effect on p53 wild tumor cells and p53 mutant tumor cells and can reduce TG2 gene expression of two kinds of cells while no remarkable change occurs to p53 gene expression. The compound and IR are subjected to combined treatment, two kinds of cells have remarkable cell apoptosis increasing and remarkable cell cycle arresting, the radiosensitivity is remarkably improved, and the TG2 gene expression is remarkably reduced. Therefore, the compound has a remarkable radiosensitization function on the p53 wild tumor cells and the p53 mutant tumor cells and is expected to substantially improve the tumor radiotherapy effect after being applied to tumor radiotherapy as an active ingredient of a radiosensitizer and particularly applied to p53 signal path activation enhanced tumor radiotherapy after excessive activation of a p53 signal path and ionizing radiation induction.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CANCER HOSPITAL
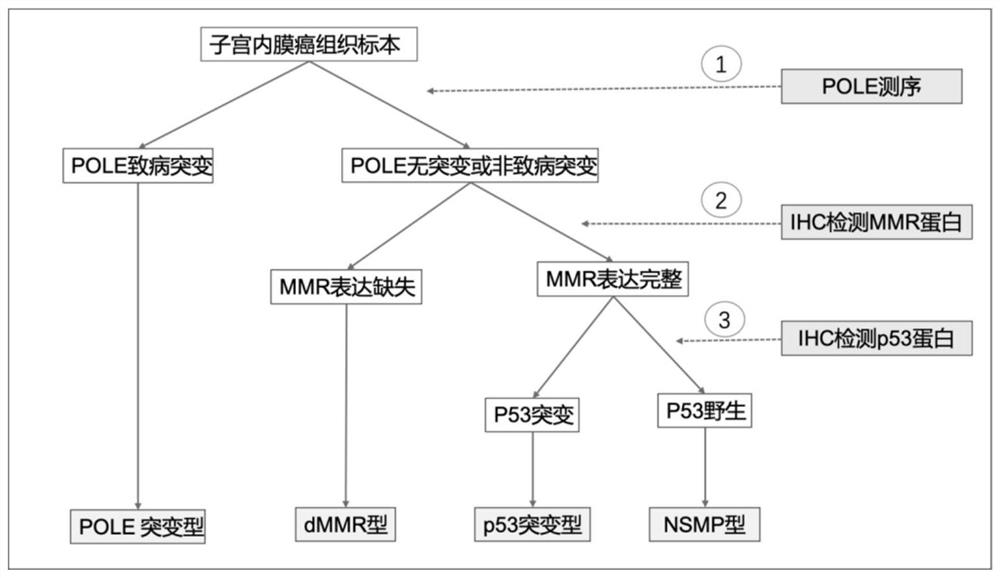
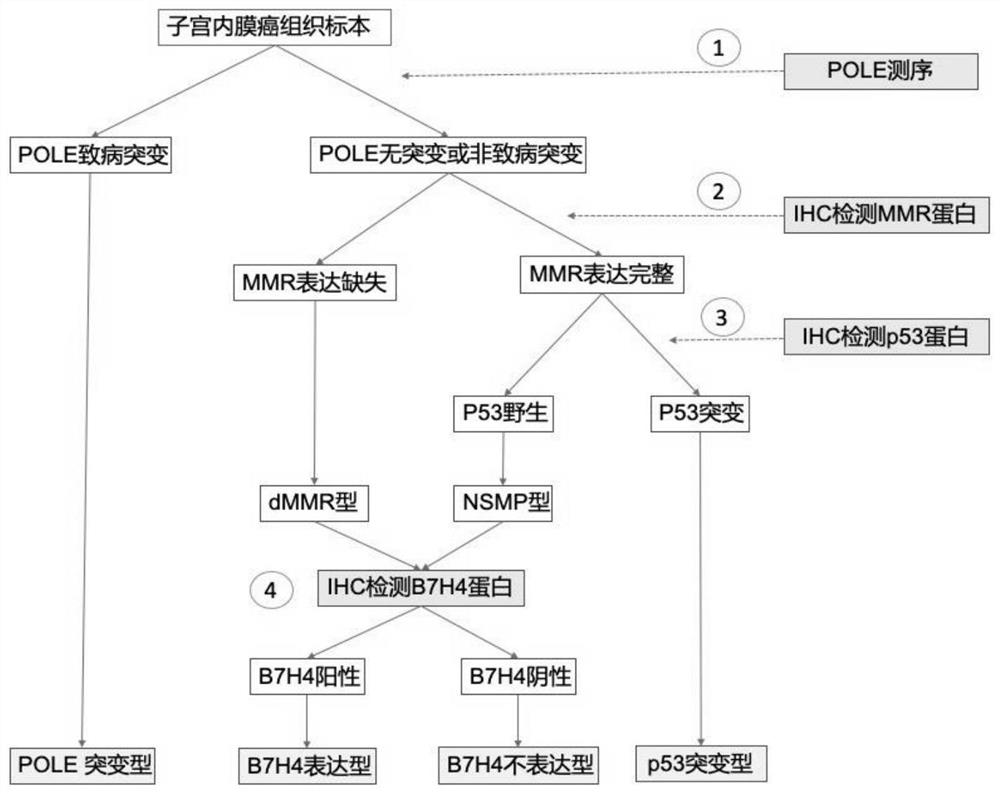
Application of B7H4 in preparation of endometrial cancer molecular typing reagent and system
ActiveCN113156120AImprove survival rateImprove predictive performanceSystems biologyMaterial analysisEndometrial CarcinomasMismatch Repair Protein
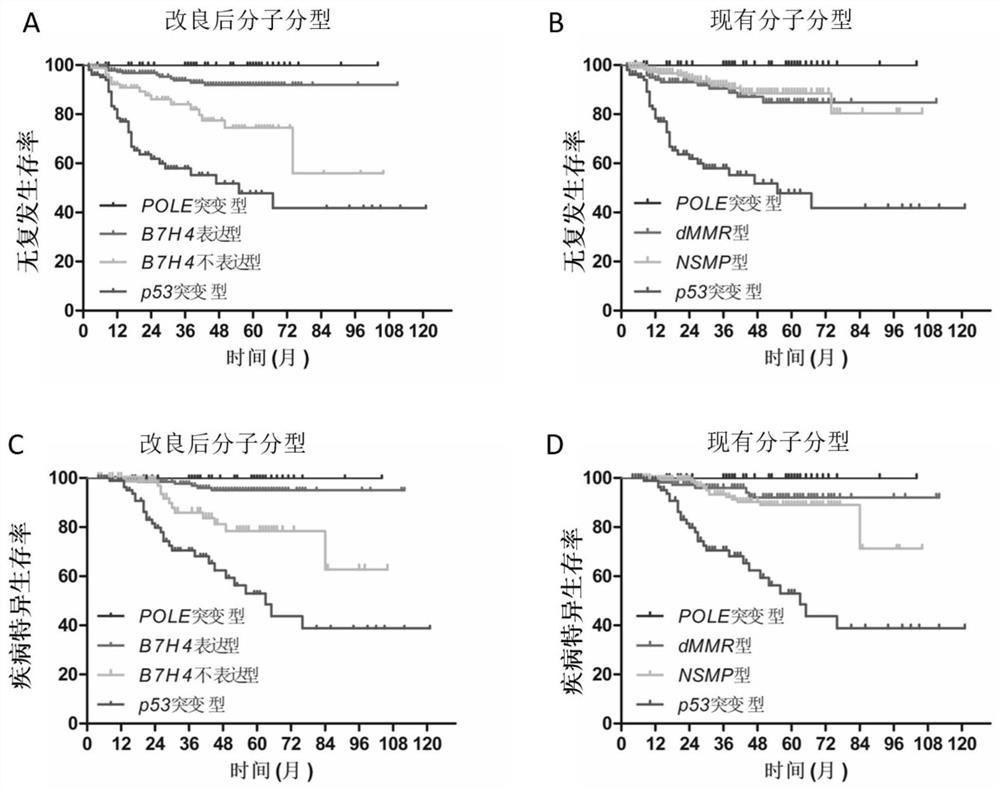
The invention relates to application of B7H4 in preparation of an endometrial cancer molecular typing reagent and system. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, screening out a POLE mutant by a sequencing method; detecting four kinds of mismatch repair proteins on a specimen without pathogenic mutation, and screening out a dMMR type; screening out a p53 mutant from a sample without dMMR by means of immunohistochemical detection of p53 protein; if the p53 mutation does not exist, determining that the p53 mutation is an NSMP type; and for specimens for interpreting the dMMR type and the NSMP type, detecting expression of protein B7H4 through immunohistochemistry, wherein B7H4 coloring in more than 1% of tumor cells is judged as a B7H4 expression type, and B7H4 non-expression types are judged in the rest. According to the invention, endometrial cancer is divided into a POLE mutant type, a B7H4 expression type, a B7H4 non-expression type and a p53 mutant type; and the improved molecular typing is still based on molecular pathology, has the characteristics of relative objectiveness, high repeatability and clinical feasibility of the existing molecular typing, but has higher predictive ability than the existing model, and is beneficial to avoiding excessive treatment and insufficient treatment.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Application of tanshinone IIA in preparation of medicament for treating p53 mutational or deficient tumor
InactiveCN102579461ARaise the ratioLower potentialOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCaspaseTanshinone IIA
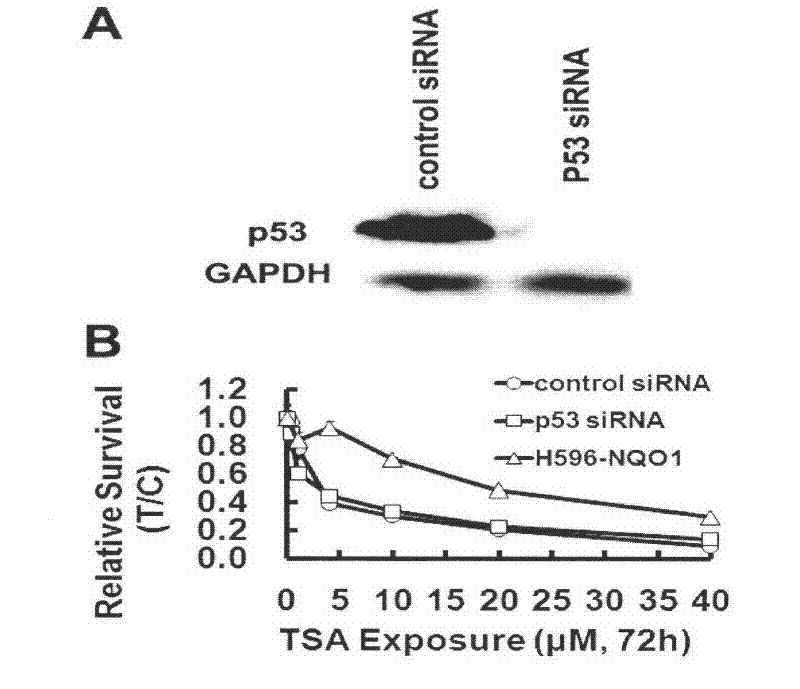
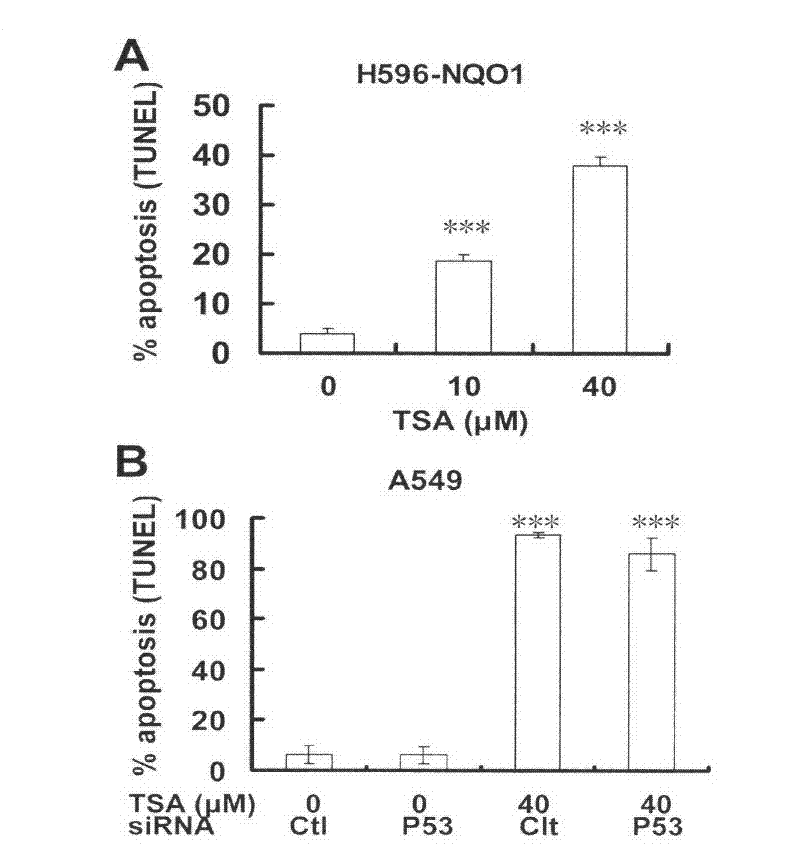
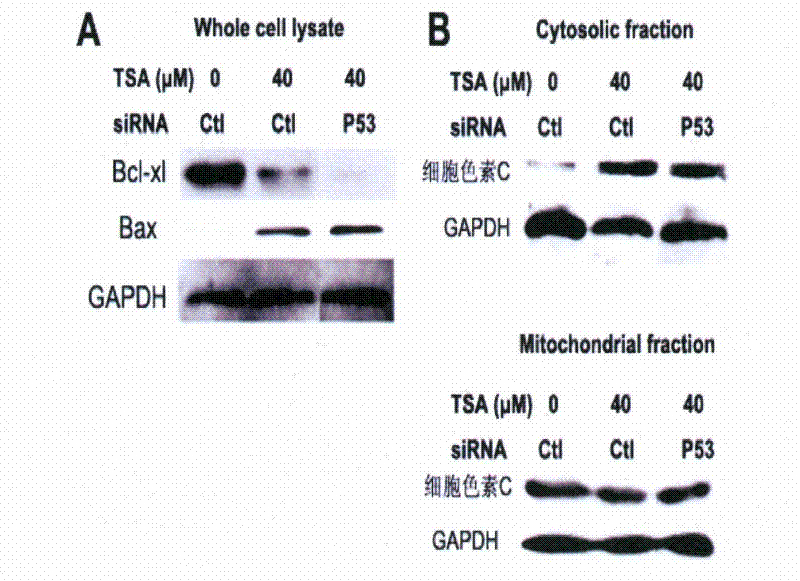
The invention relates to the field of natural medicaments, in particular to the application of tanshinone IIA in preparation of a medicament for treating p53 mutational or deficient tumor. The tanshinone IIA can induce cellular poison and apoptosis of p53 mutational H596-NQO1 non-small cell lung cancer cells; and simultaneously, in wild A549 cells of p53, when P53 small interfere ribose nucleic acid (siRNA) silences endogenous P53 genes, the tanshinone IIA can still induce the cellular poison and apoptosis of the A549 cells, reduction in the mitochondrial membrane potential of the A549 cells induced by the tanshinone IIA is not influenced in the process of treating the P53siRNA, the ratio of BAX / Bcl-x1 is increased, cytochrome C is released, and Caspase is activated, so that an anti-tumor effect which does not depend on the p53 is generated.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Culture method for screening tumor organoids based on P53 mutation
PendingCN113186163AObvious cost price advantageHigh sensitivityCell culture active agentsTumor/cancer cellsMatrigelBiochemistry
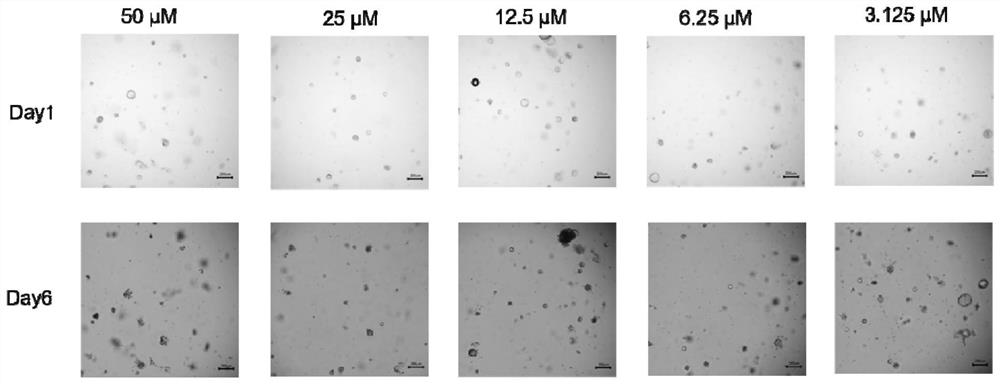
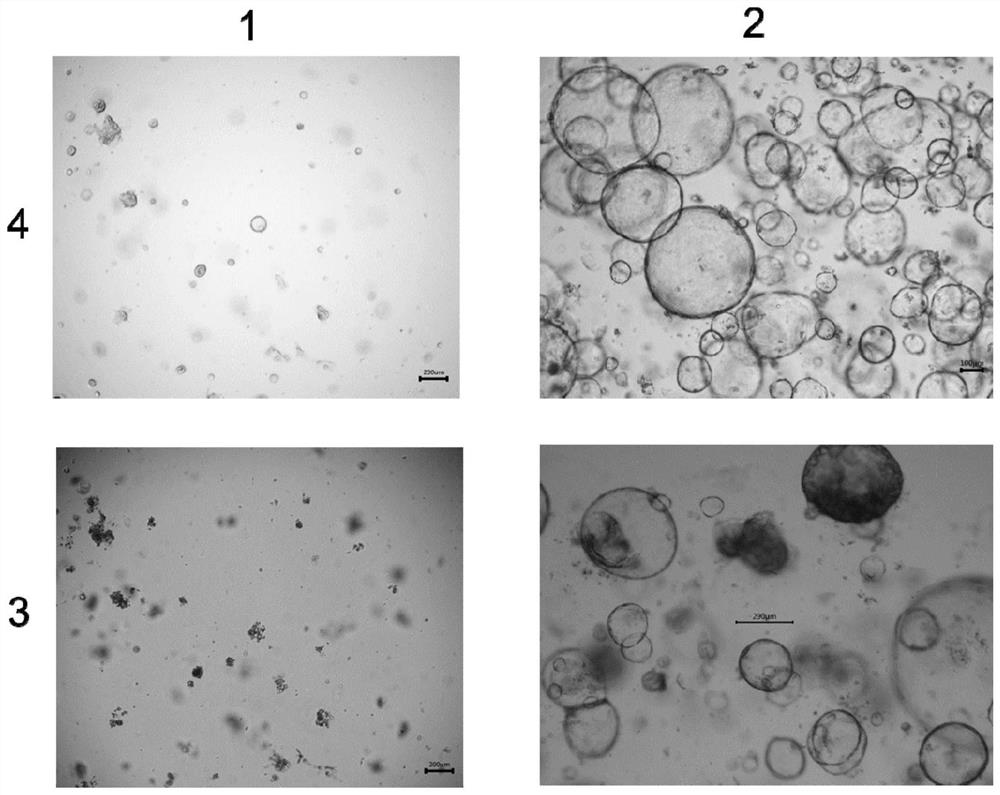
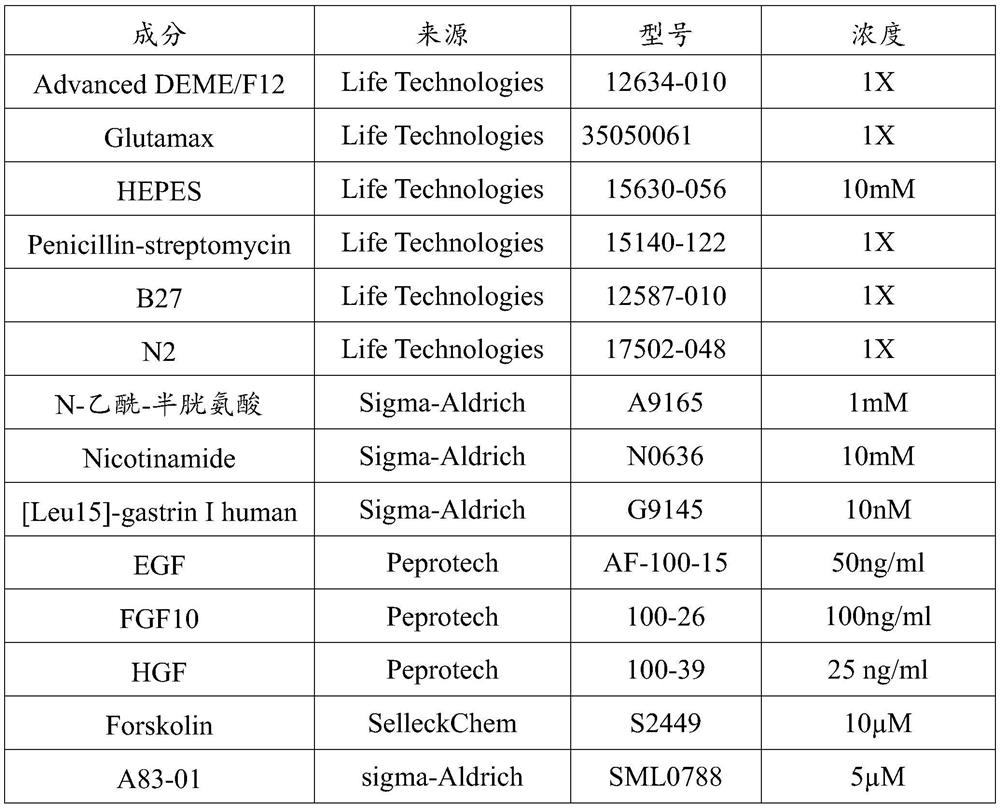
The invention relates to the technical field of organoid culture, and particularly discloses a culture method for screening tumor organoids based on P53 mutation. The culture method comprises the following steps: S1, unfreezing untreated tumor organoid to generate a cell suspension, adding the cell suspension into a basic culture medium, uniformly conducting mixing and centrifuging, and removing supernate to obtain a tumor organoid mixture; S2, adding matrigel to resuspend the tumor organoid mixture, and after resuspending, inoculating the organoid mixture into an organoid culture medium containing y27632 for culturing; and S3, after the liquid of the tumor organoid mixture is changed for the first time, absorbing and removing the organoid culture medium, and then adding a culture medium containing Nutlin3A for continuous culture. The culture method is low in cost and price, sequencing is not needed, the detection cost is saved in the early stage of culture of the tumor organoids, and accurate and simplified culture of the tumor organoids is achieved.
Owner:南昌五元生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com