P53R175H specific nucleic acid aptamer and screening method and use thereof
A p53r175h, nucleic acid aptamer technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, to achieve the effect of slowing down the migration rate, small molecular weight, high affinity and specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
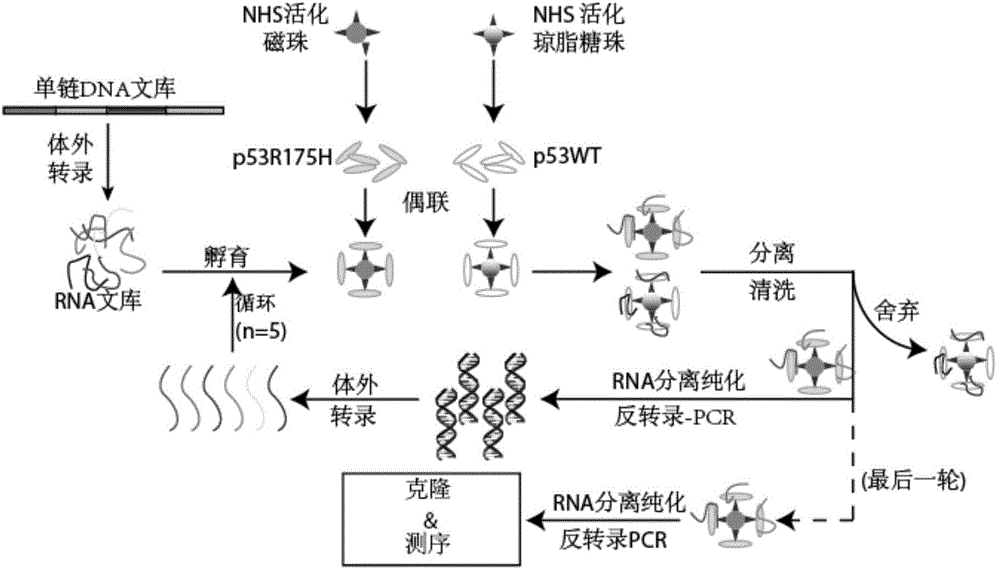
[0067] Embodiment 1, the screening of nucleic acid aptamer
[0068] 1. Design and synthesis of random nucleic acid library
[0069] Design and synthesize single-stranded DNA as shown below, including a random sequence of 25 nucleotides in the middle, which constitutes a nucleic acid sequence library
[0070] TAATACGACTCACTATAGCAATGGTACGGTACTTCC(N25)CAAAAGTGCACGCTACTTTG
[0071] 2. Protein coupled solid phase carrier
[0072] 2.1. Coupling p53R175H protein (Cat. No. AZ-026Abzyme, amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 4) to NHS-activated magnetic beads (28-9940-09 GE Healthcare).
[0073] Put an appropriate amount of magnetic beads from the original tube into a new EP tube, place it on the magnetic stand, and remove the original storage solution;
[0074] Add 500 μl ice-cooled balance solution (1mM HCl (ice-cold)), mix well, and remove the balance solution;
[0075] Immediately after equilibration, add 10 μg of protein, in binding buffer (0.2M NaHCO 3 , 0.5M NaCl, pH 8.3)...
Embodiment 2
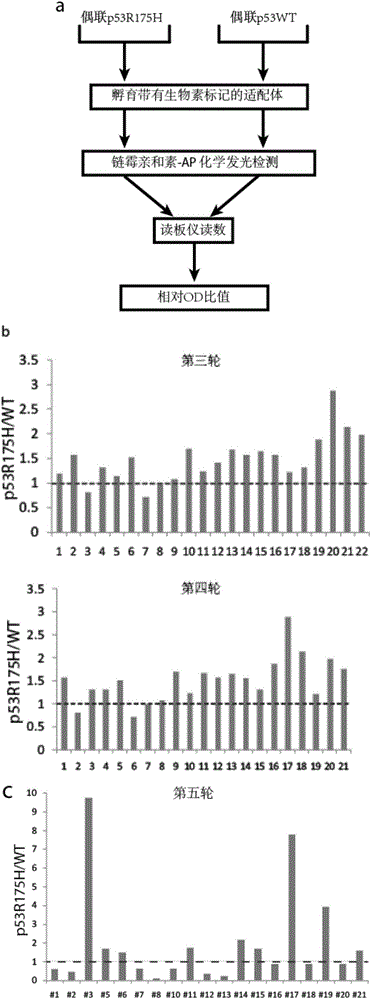
[0143] Embodiment 2, affinity screening method based on ELISA
[0144] Those skilled in the art will understand that the binding ability of the nucleic acid aptamer to the target protein can be detected by other methods than the ELISA method.
[0145] 1. T vector construction and blue-white screening
[0146] a. Configure the T carrier connection system according to the following system:
[0147]
[0148] b. Transforming the ligation product into competent cells;
[0149] c. On the ampicillin-resistant LB plate, coat 100ul IPTG and 200ul X-Gal in advance, and put it in a 37°C incubator to dry. Spread the competent cells cultured at low speed evenly on the plate, and incubate at 37°C for 12-16 hours;
[0150] d. Pick white clones the next day, culture the bacteria and send them for sequencing;
[0151] e. Extract plasmids from samples with successful sequencing, and use them as templates for in vitro transcription in the next step.
[0152] 2. In vitro transcription of ...
Embodiment 3
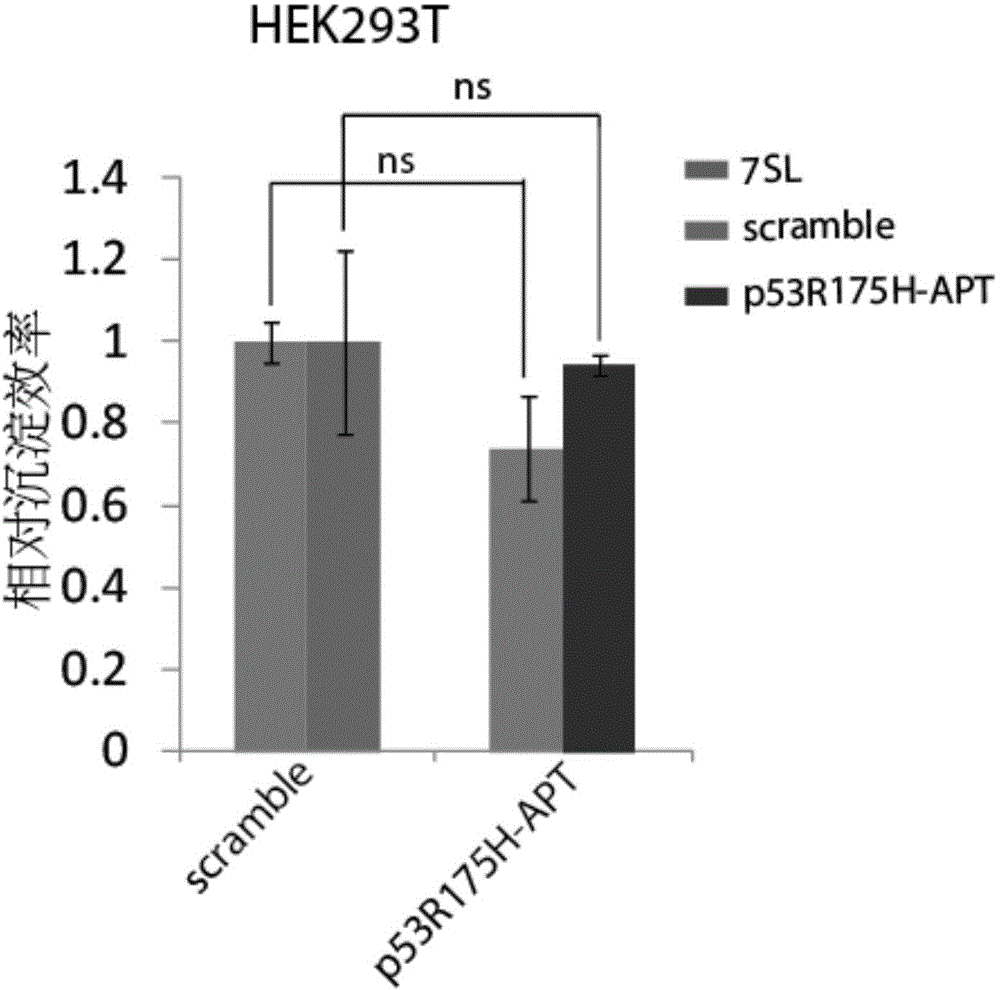
[0179] Example 3, the nucleic acid aptamer obtained by screening has no affinity for p53 wild-type protein
[0180] 1. p53 co-immunoprecipitation experiment
[0181] a. Place HEK293T cells on a 10cm cell culture plate, culture at 37°C for 12-18h under 5% CO2 environment, and use LipofectAmine 2000 system to transfect the sequences screened in Example 1 respectively when the cell density reaches 60-70% The nucleic acid aptamer (p53R175H-APT) shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and scramble (which is a random negative control sequence GCAATGGTACGGTACTTCCGCCTGGCTGGTCTTTGAACTCTTTTTCAAAAGTGCACGCTACTTTG) were continued to be cultured until 48 hours after transfection and subsequent experiments were started;
[0182] b. Cell cross-linking reaction: add methanol with a final concentration of 0.75% to the cell culture dish, and shake gently at room temperature for 10 minutes;
[0183] c. Add a glycine solution with a final concentration of 125 mM, and gently shake for 5 minutes at room temperature t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com