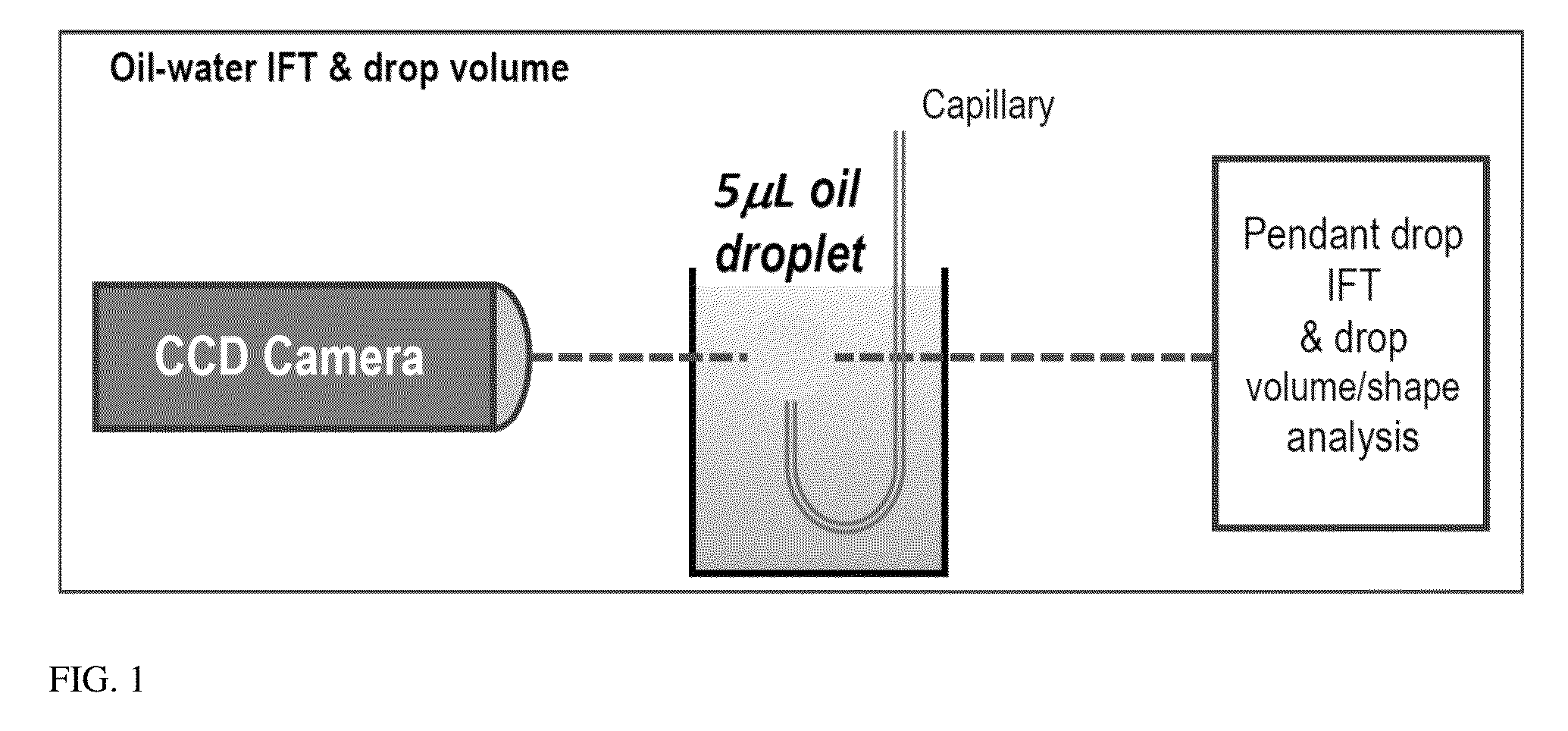
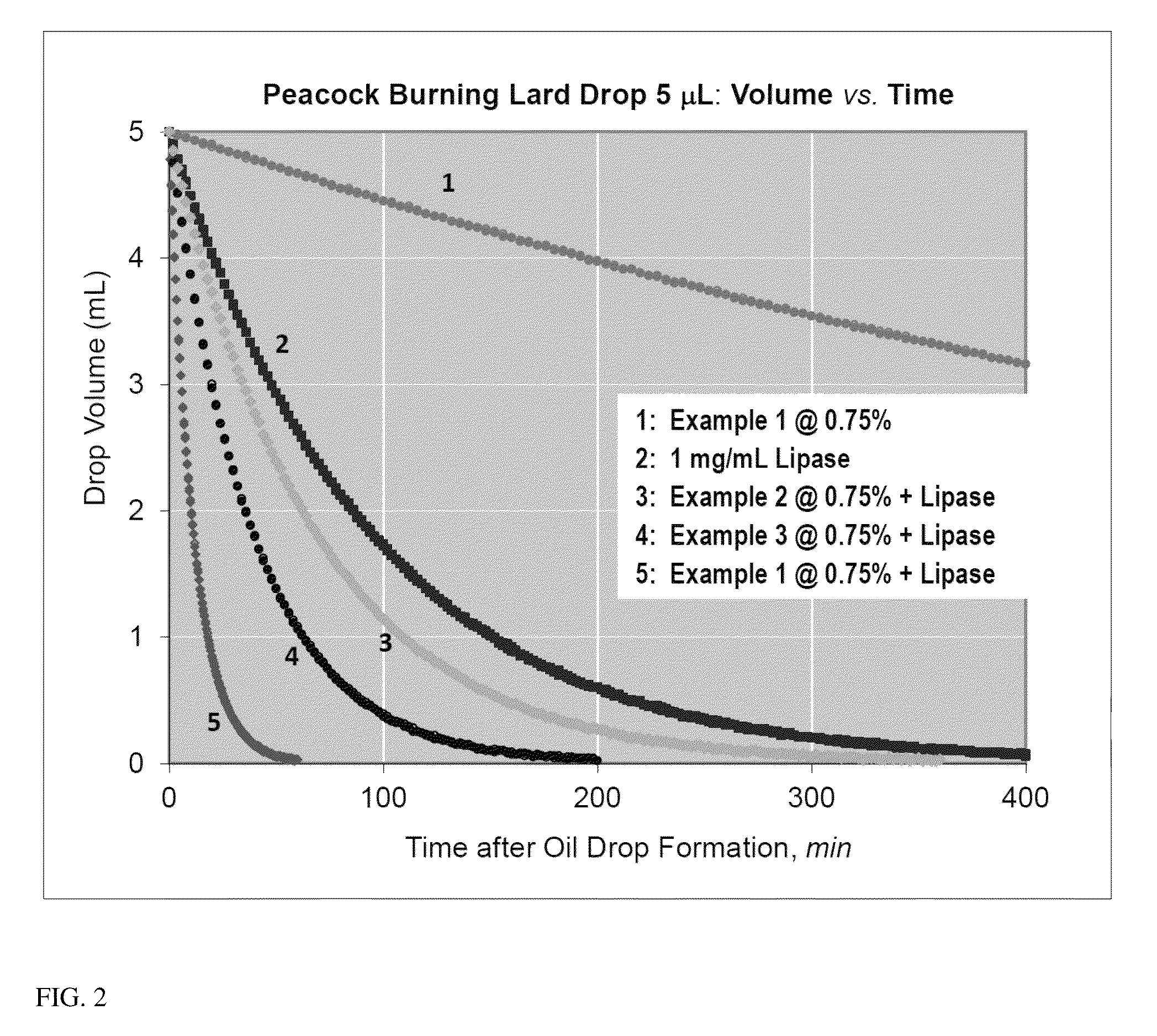
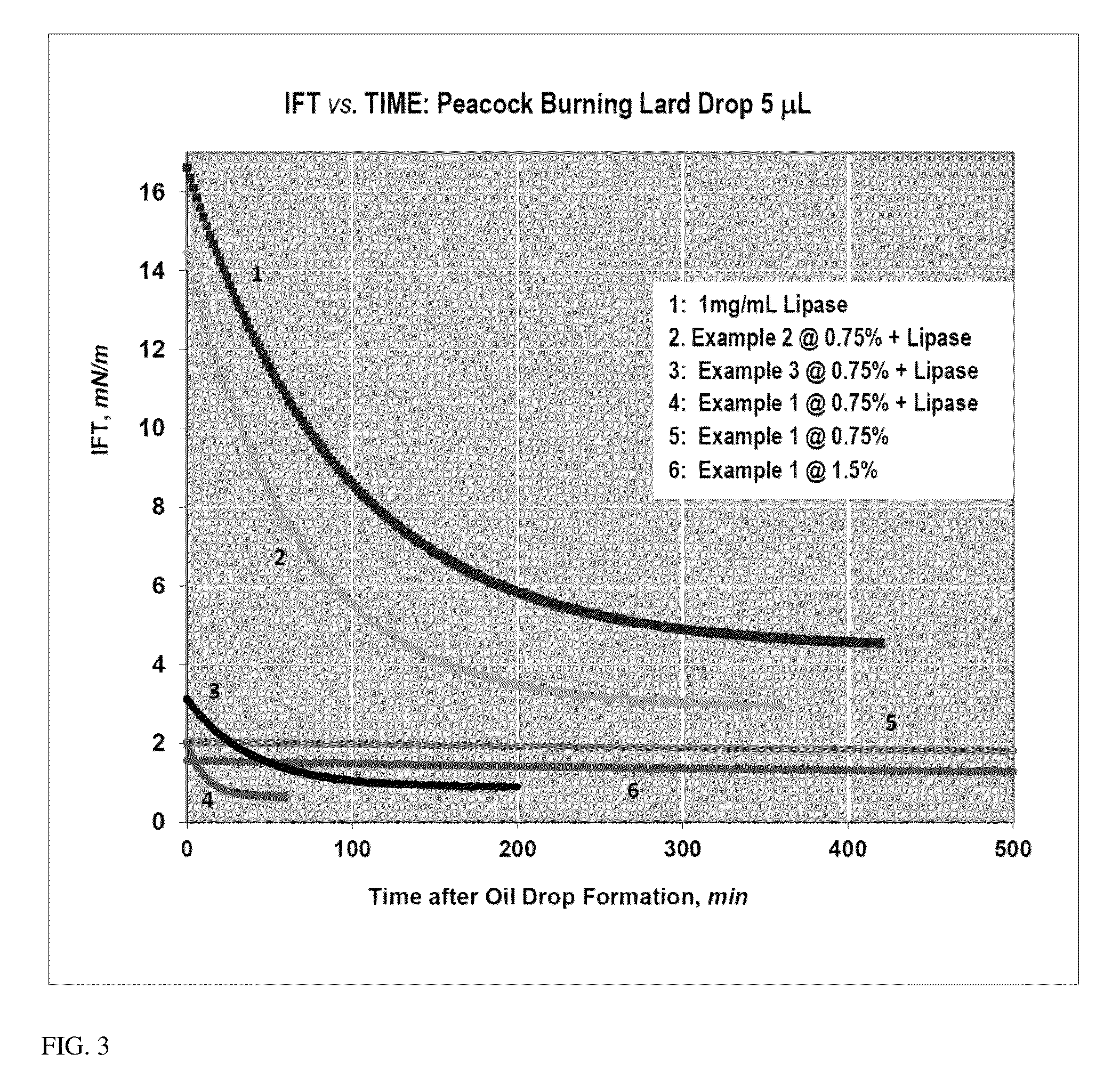
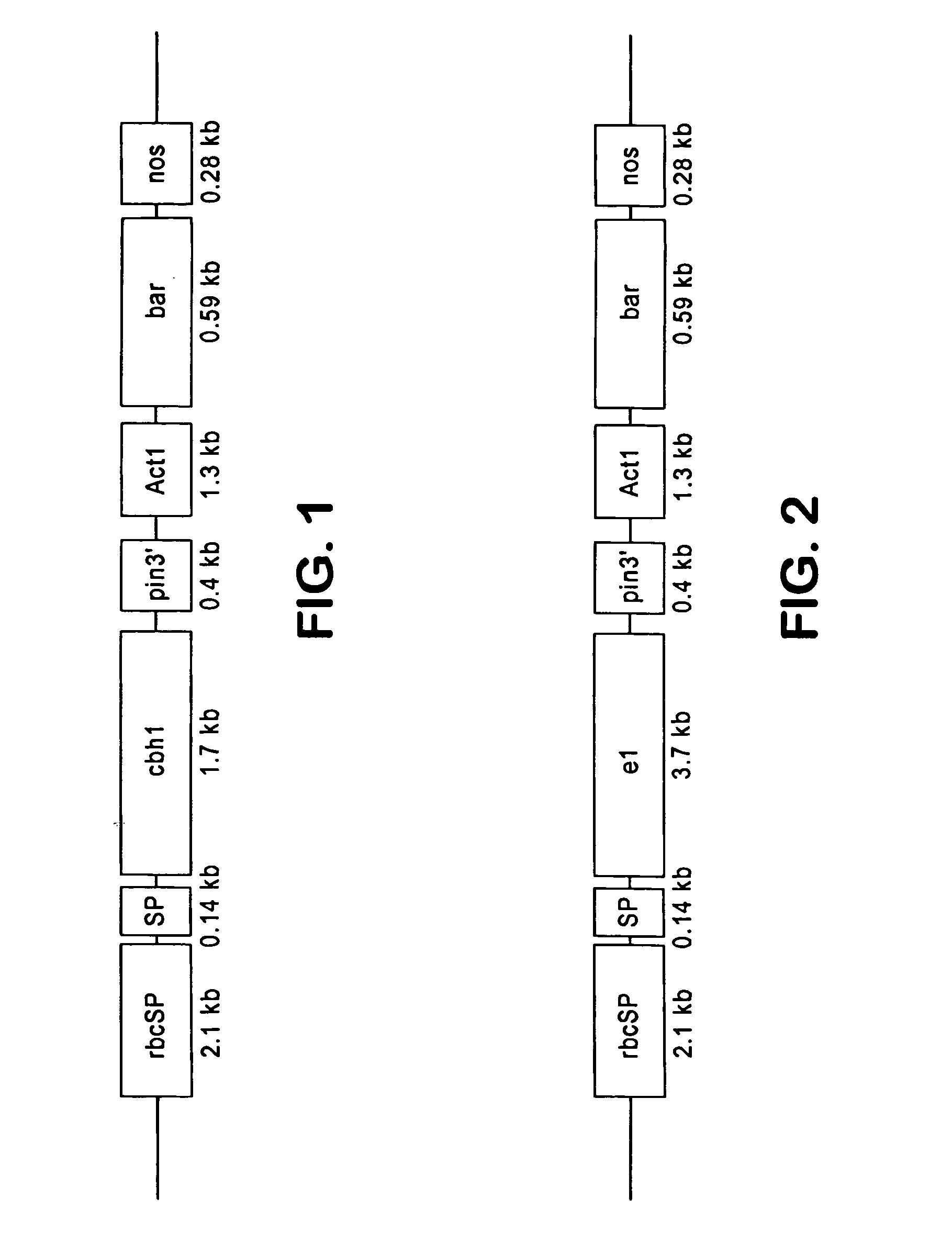
Patents
Literature
84 results about "Lignin-modifying enzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lignin-modifying enzymes (LMEs) are various types of enzymes produced by fungi and bacteria that catalyze the breakdown of lignin, a biopolymer commonly found in the cell walls of plants. The terms ligninases and lignases are older names for the same class, but the name "lignin-modifying enzymes" is now preferred, given that these enzymes are not hydrolytic but rather oxidative (electron withdrawing) by their enzymatic mechanisms. LMEs include peroxidases, such as lignin peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.14), manganese peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.13), versatile peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.16), and many phenoloxidases of the laccase type.
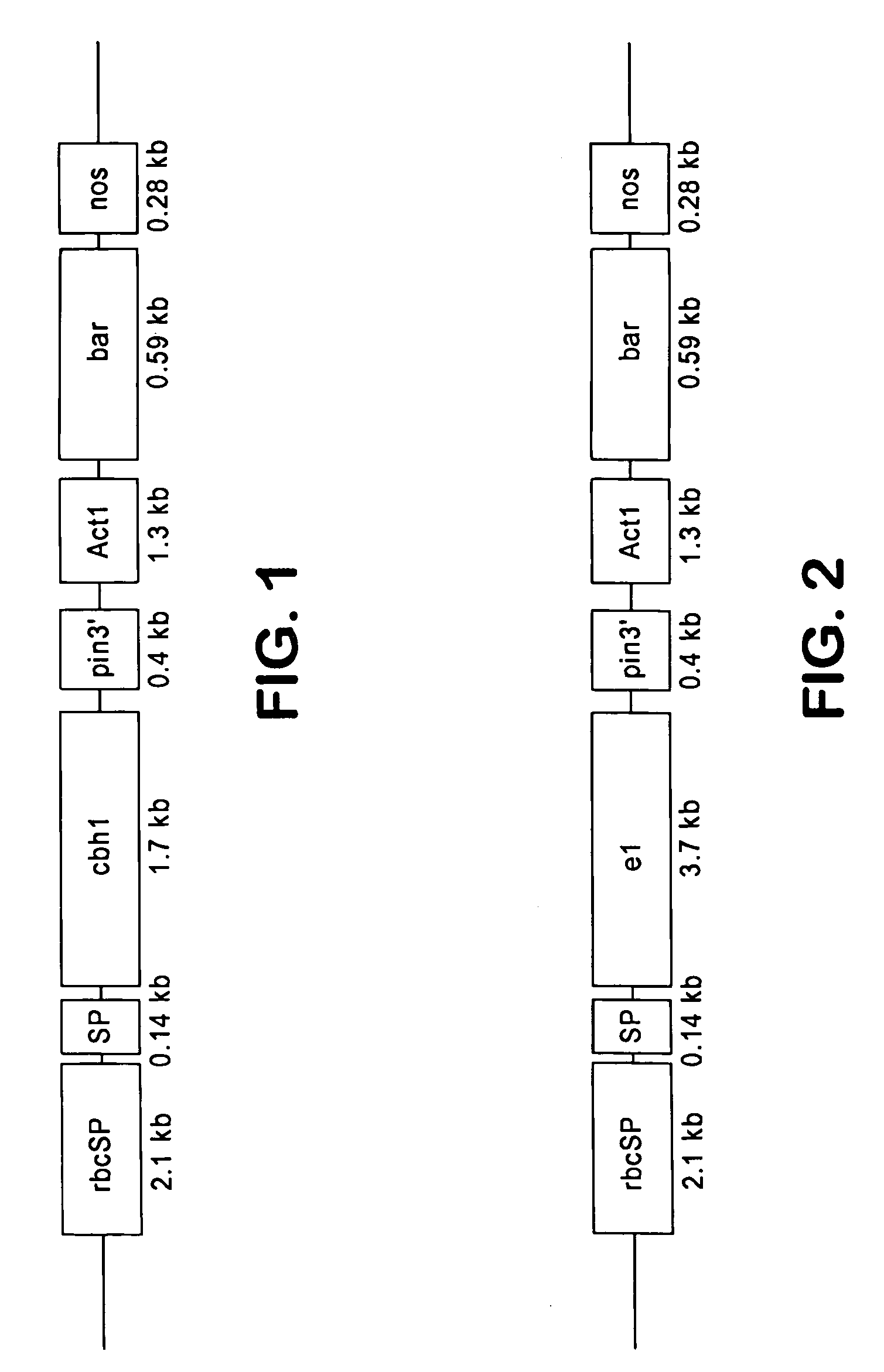
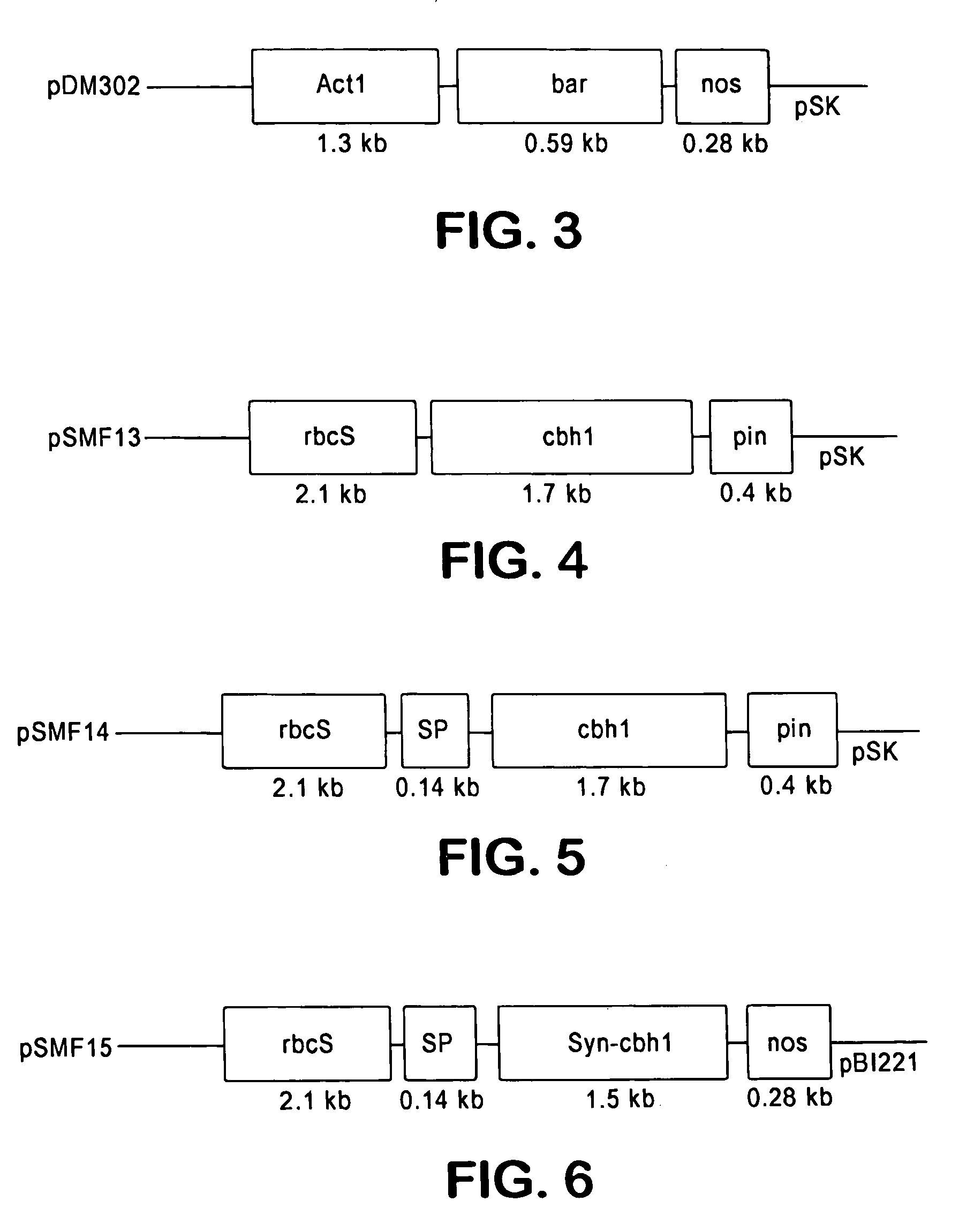
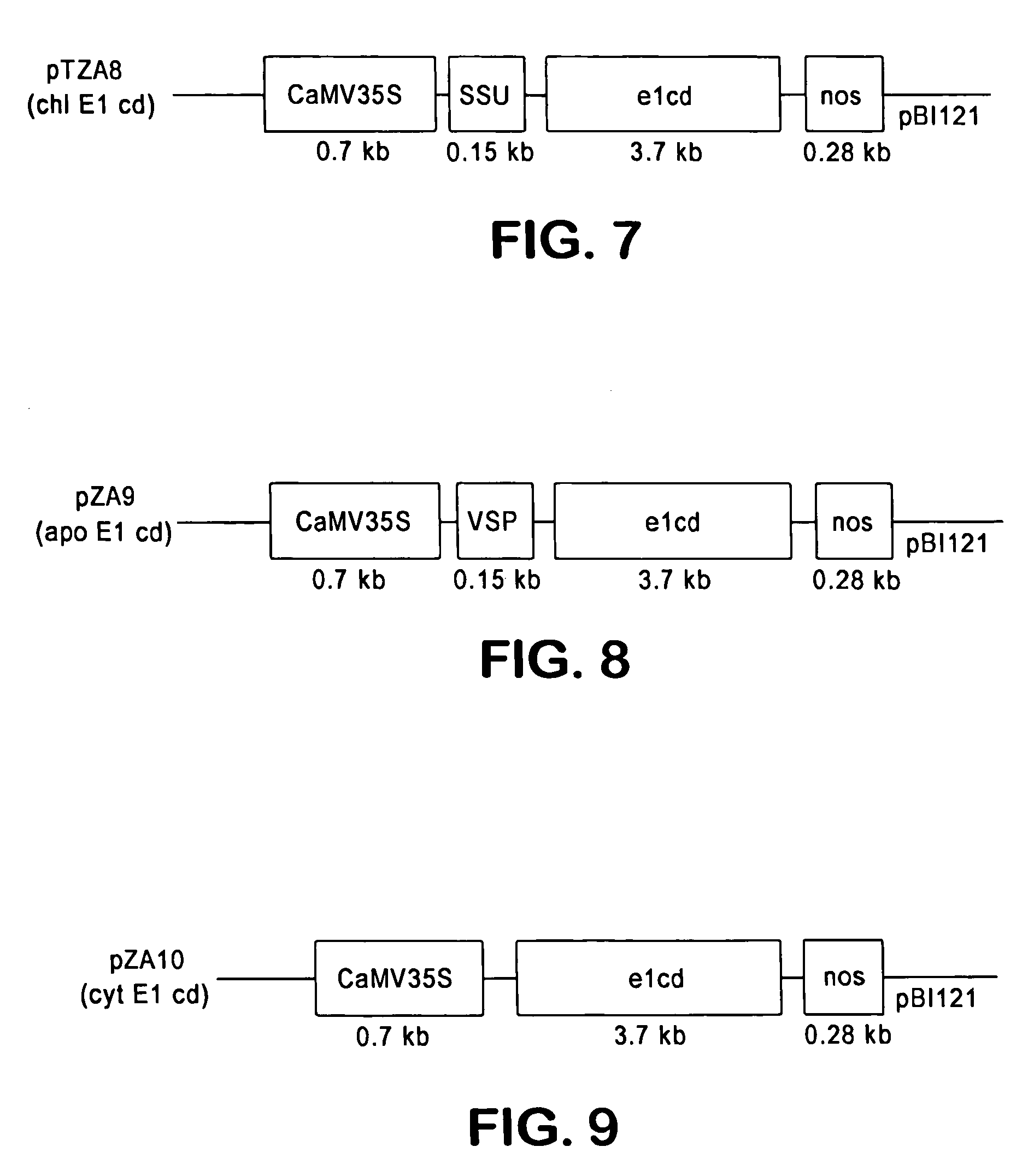
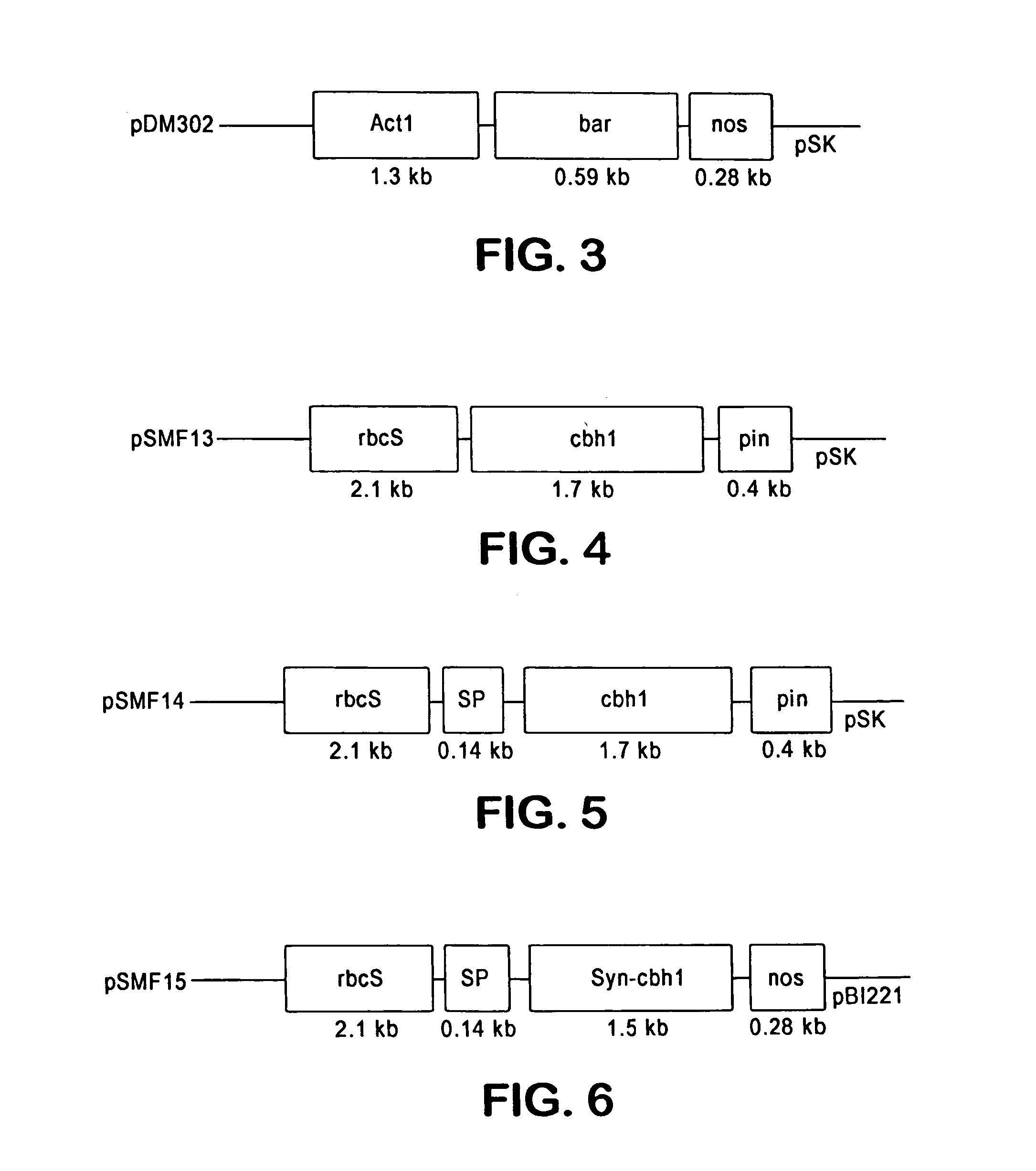
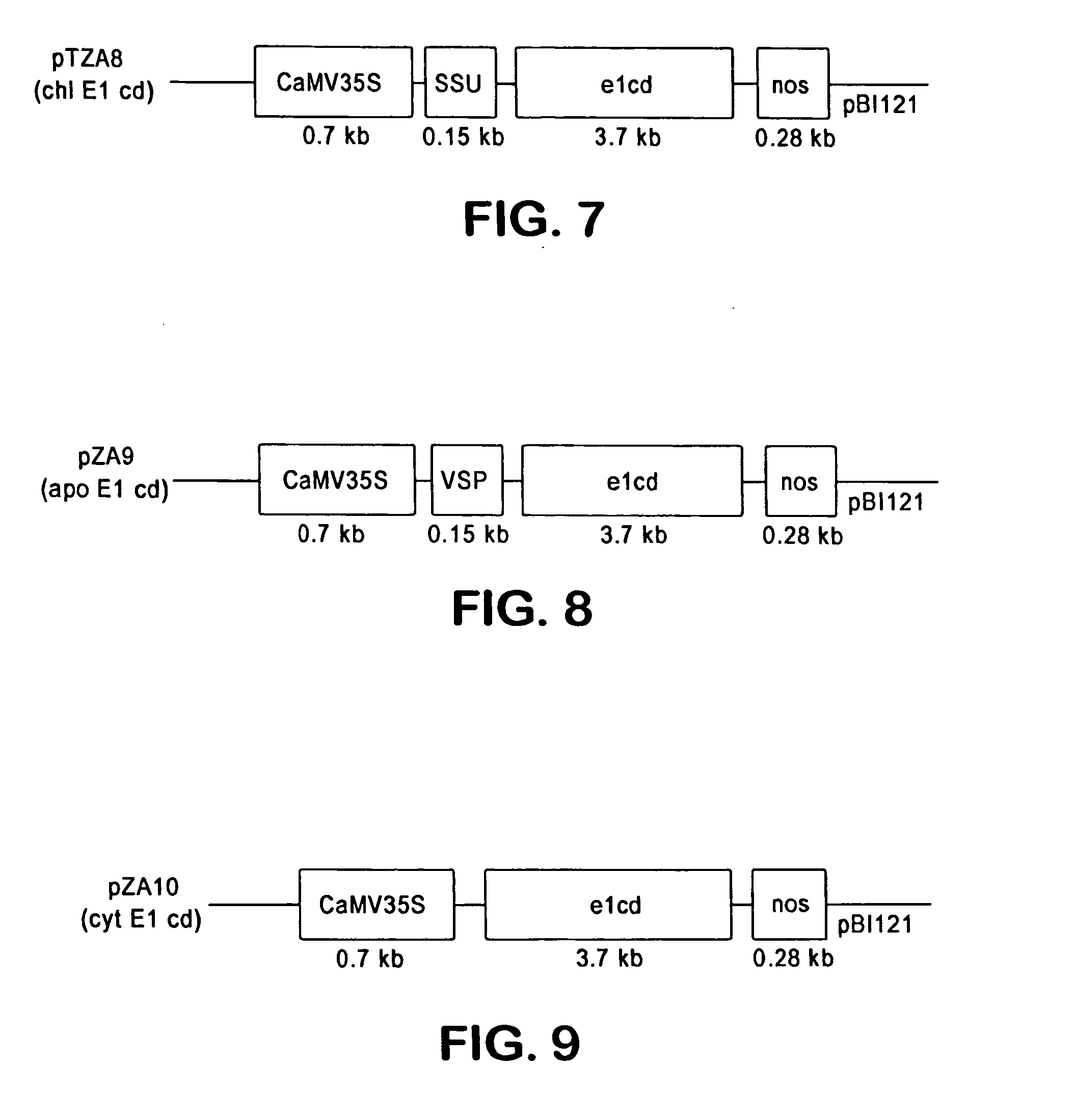
Transgenic plants containing ligninase and cellulase which degrade lignin and cellulose to fermentable sugars
InactiveUS7049485B2Stress resistantConfer resistanceBiofuelsOther foreign material introduction processesLignin-modifying enzymeFermentable sugar
The present invention provides transgenic plants which after harvest degrade the lignin and cellulose therein to fermentable sugars which can further be fermented to ethanol or other products. In particular, the transgenic plants comprise ligninase and cellulase genes from microbes operably linked to a DNA encoding a signal peptide which targets the fusion polypeptide produced therefrom to an organelle of the plant, in particular the chloroplasts. When the transgenic plants are harvested, the plants are ground to release the ligninase and cellulase which then degrade the lignin and cellulose of the transgenic plants to produce the fermentable sugars.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Straw degradation actinomycete and application thereof
ActiveCN102703344AIncrease production capacityCause harmBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPectinaseMicroorganism
The invention relates to the technical field of straw degradation, in particular to a straw degradation actinomycete and application thereof. The straw degradation actinomycete belongs to streptomyces griseorubens (Streptomyces griseorubens), and the preservation serial number is CGMCC N0.5706. Compared with the prior art, the straw degradation actinomycete and the application have the advantagesthat the streptomyces griseorubens has strong capacity for producing cellulose, hemicellulase, pectinase and ligninase, is free of negative effects on carbon cycling of the nature, and is free of damage to the environment; the streptomyces griseorubens has strong straw degradation capability, enables straw weightlessness rate to achieve 76% after staying in a straw degradation culture medium for 30 days, and is low in culture cost, convenient to operate and easy to industrially apply; and the streptomyces griseorubens has certain antagonism on plant disease microorganism in the soil.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Enzyme-bacterium duplex straw decomposing agent and its preparation and application methods
InactiveCN105368744AIncreased degradation rateEasy to separateBio-organic fraction processingFungiMicrobial agentTrichoderma reesei
The invention discloses an enzyme-bacterium duplex straw decomposing agent and its preparation and application methods. The decomposing agent is made by mixing a composite microbial agent and a composite enzyme agent in a weight ratio of 3-4:1. The composite microbial agent includes Trichoderma viride, Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus oryzae, Brevibacillus laterosporus and a fused Saccharomyces cerevisiae, having a weight ratio of (1-2):(1-2):(1-2):(2-3):(2-3). The composite enzyme agent includes cellulase produced by the fermentation of Trichoderma reesei, hemicellulase produced by the fermentation of Bacillus subtilis, and ligninase produced by the fermentation of Pleurotus ostreatus, having a weight ratio of (1-2):(1-2):(1-2). The decomposing agent has a double straw degrading function, allowing more efficient and more thorough biological degradation, increasing the straw degrading speed to a higher extent and shortening degrading time, and can fully decompose crop straw to fields within about a week, without affecting the planting and transplanting of next-stubble crops.
Owner:甘肃明德伟业生物科技有限公司
Lignin degradation solution and preparation method thereof as well as method for degrading lignin by using lignin degradation solution
InactiveCN104894079AEfficient degradationImprove degradation conversion efficiencyOxidoreductasesFermentationCelluloseSodium acetate
The invention discloses a lignin degradation solution and a preparation method thereof as well as a method for degrading lignin by using the lignin degradation solution, and belongs to biochemical and bio-refinery methods to solve the problem that the efficient biodegradation of lignin is difficult to realize by adopting single ligninase of laccase at present. The lignin degradation solution is prepared by the following steps: dissolving laccase and manganese peroxidase into an acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution of which the pH value is 4-6 in an enzyme load ratio of (10:1)-(1:5) to ensure that the enzyme loads of the laccase and manganese peroxidase are respectively 1U / ml-50U / ml and 1U / ml-50U / ml; and then adding 1-10mM of MnSO4 and 0.1-1mM of H2O2, wherein the laccase and manganese peroxidase are obtained by fermenting white rot fungi to obtain extracellular crude enzyme liquid and then performing separation and purification respectively. According to the lignin degradation solution and the methods disclosed by the invention, the synergistic oxidative degradation of macromolecular lignin with rich structural diversity is realized, and compared with a degradation reaction system with single ligninase, the degradation rate of the macromolecules of the lignin can each 30-50%, the degradation conversion efficiency is significantly improved, and the degradation solution and the methods can be applied to the fields of bio-refinery of lignocelluloses, biological pulping or environmental treatment and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Production method and application of complex enzyme liquid for chemi-mechanical pulping
ActiveCN103555702AHigh whitenessImprove qualityHydrolasesOxidoreductasesPectinaseEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a production method of a complex enzyme liquid for chemi-mechanical pulping. The production method is characterized by comprising the following steps: weighing various component enzymes, mixing and compounding the various component enzymes in a compounding tank, preventing corrosion, inspecting, packaging and storing in a storeroom at 5 DEG C, wherein the various component enzymes comprise alkaline pectinase, xylanase, mannose and ligninase. The application of the complex enzyme liquid in chemi-mechanical pulping is realized as follows: before steaming paper-making raw materials, adding the complex enzyme liquid to the paper-making raw materials through a metering pump, uniformly mixing the complex enzyme liquid with the paper-making raw materials for enzymatic hydrolysis under enzymatic treatment conditions that the temperature is 40-60 DEG C and enzymatic hydrolysis duration is 30-240 minutes; after the enzymatic hydrolysis, performing following processes as normal. The production method, through coupling synergistic effect of multiple enzymes of the complex enzyme liquid in chemi-mechanical pulping, can be used for improving the whiteness of pulp by 2-5% and reducing the pulp yellowing under a condition of guaranteeing high yield and low cost of pulping; the production method can be used for reducing the dosage of chemical raw materials by 20-30% and reducing the pulp grinding energy consumption by 18-30%; meanwhile, the production method can be used for reducing pollution and improving the pulp quality.
Owner:江苏富星纸业有限公司
Human ochrobactrum anthropi and its application in degrading plant stalks and preparing important enzyme
The present invention discloses one kind of human Ochrobactrum anthropi IBL01 (Ochrobactrum anthropi CCTCC M 206046) and its application in degrading plant stalks. Ochrobactrum anthropi IBL01 has high plant stalk degrading effect and can produce high activity cellulase, hadromse and hemicellulase. The present invention also discloses the preparation process of cellulose, xylanase, lignin peroxidase, laccase and manganese peroxidase with the human Ochrobactrum anthropi. The human Ochrobactrum anthropi of the present invention is bacterium with short growth period of about one week, and can produce fiber degrading enzyme as well as hemicellulose degrading enzyme and lignin degrading enzyme.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for producing ligninase by using edible mushroom stick
InactiveCN104694513ALow costReduce manufacturing costOxidoreductasesLignin peroxidaseEdible mushroom
The invention discloses a method for preparing ligninase from mushroom residue. The method comprises the specific steps: crushing the mushroom stick to obtain mushroom residue, adding enzyme-production induced liquid, cultivating under proper condition, recycling crude enzyme and repeatedly adding the enzyme-production induced liquid; the enzyme activity of obtained paint enzyme is 1-10U, the manganese peroxidase is 1-10U, and the lignin peroxidase is 10-30U. compared with other prior art related to the ligninase production method, the method saves the mushroom growth process, saves the energy source and the material, the waste is utilized, the environment is improved, and the cost for preparing the ligninase is effectively reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nano carbon organic compound fertilizer
The invention provides a nano carbon organic compound fertilizer. The nano carbon organic compound fertilizer is composed of following components according to suitable weight parts: urea, monopotassium phosphate, hairs, palygorskite, dimethyl sulfoxide, a boron fertilizer and zinc fertilizer mixture with the weight ratio of 1:0.5, ferrous sulfate, nodule bacteria, azotobacter chroococcum, nano carbon, rhizoma curculiginis, pseudolarix kamepferi, radix sophorae flavescentis, ligninase, plant ash, humic acid, dicyandiamide, animal dung and powdery EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid) chelated manganese. The nano carbon organic compound fertilizer can be good for effective utilization of secondary elements and microelements, is suitable for crops including wheat, rice, corns, soybeans, oilseed rapes and the like, and can enhance the cold-resisting, drought-resisting, and disease and insect pest-resisting functions; the nano carbon organic compound fertilizer can be used on cotton and linen crops to enhance the tension and the strength of fibers and the yield and the quality are obviously improved.
Owner:GUIZHOU TELIDA NANO CARBON SCI & TECH +1
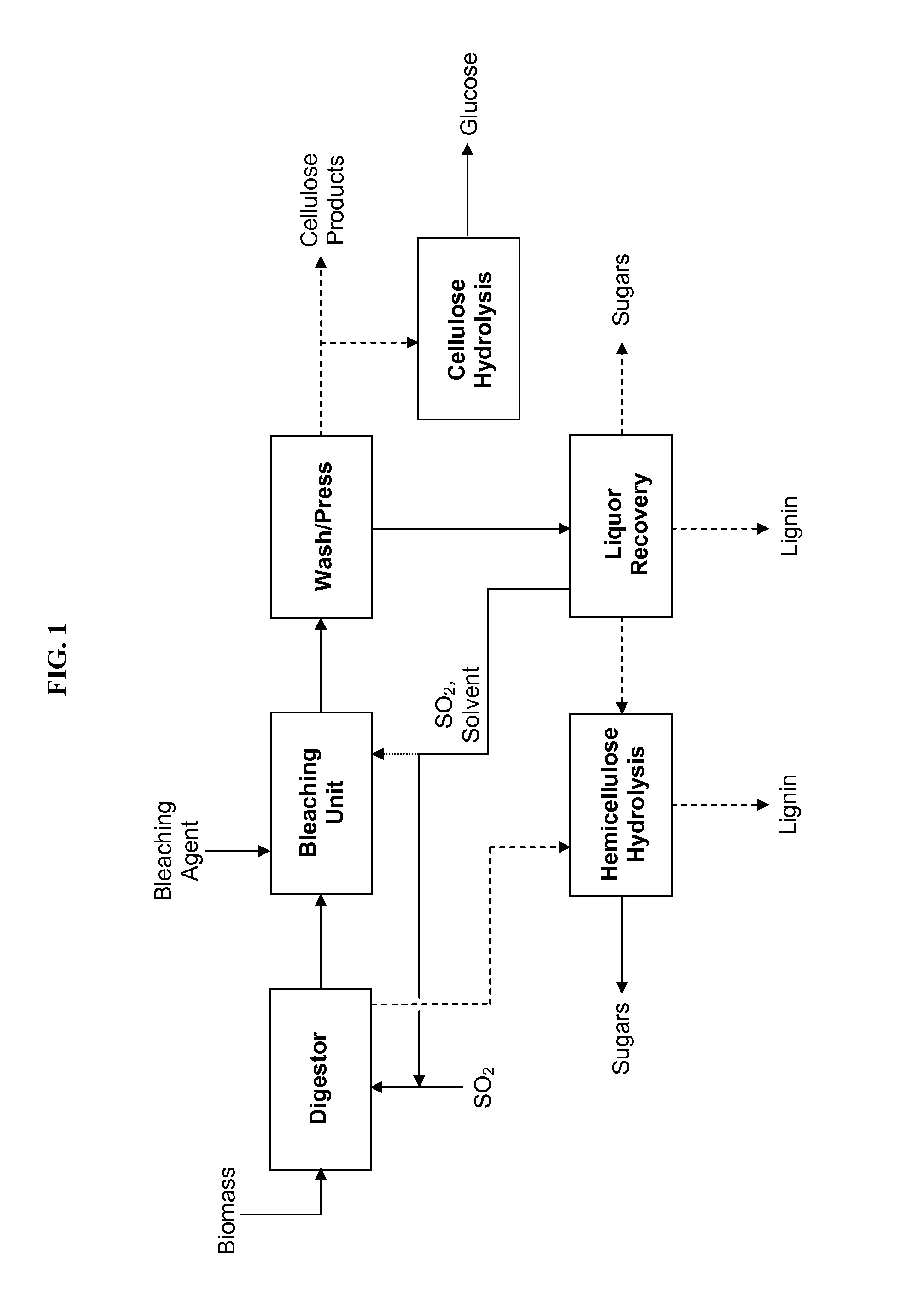
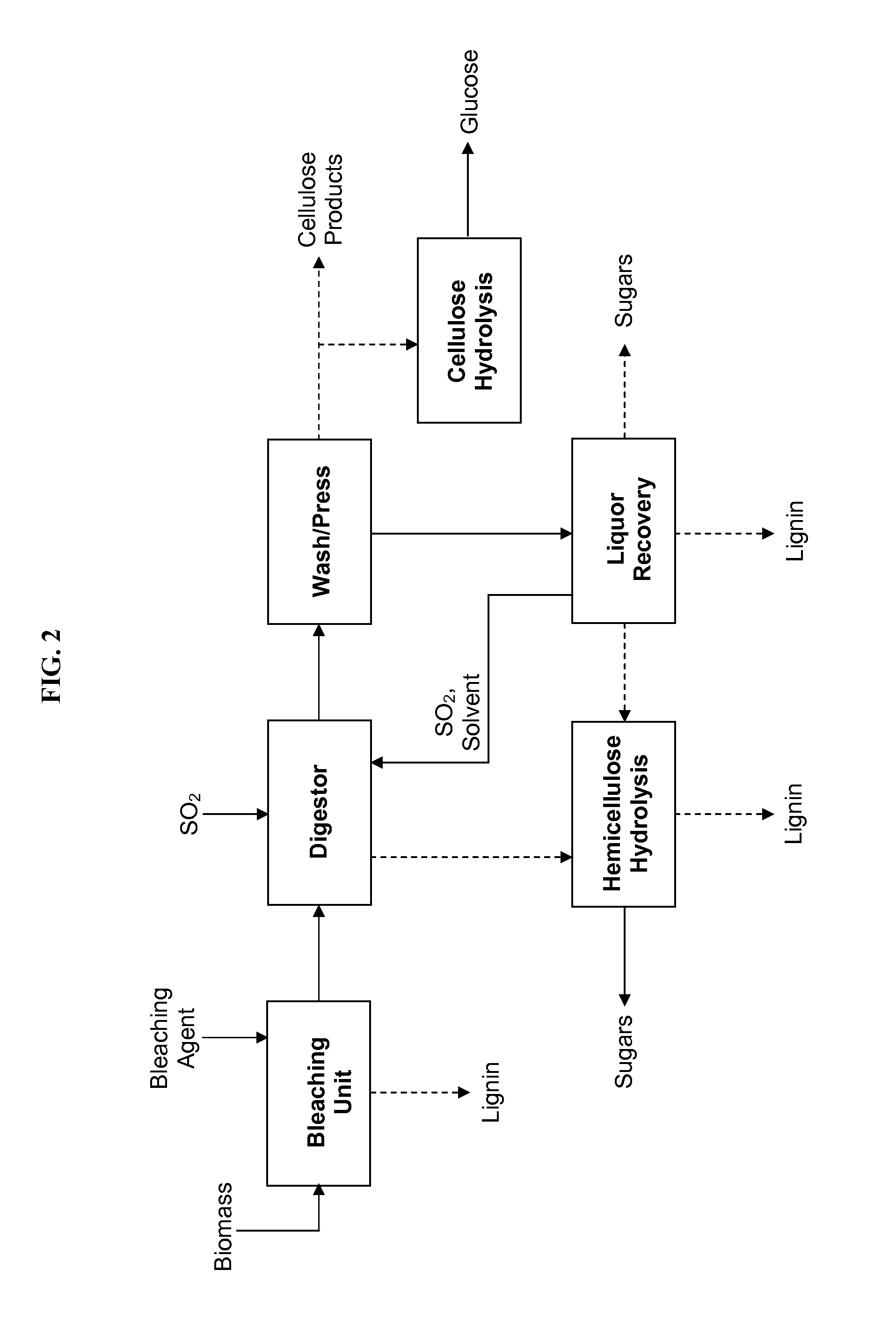
Processes for making cellulose with very low lignin content for glucose, high-purity cellulose, or cellulose derivatives
InactiveUS20140182582A1Reduce lignin precipitationReduce precipitationLignin derivativesGlucose productionBleachFractionation
In some variations, the invention provides a process for producing purified cellulose, comprising: providing a feedstock comprising lignocellulosic biomass; contacting the feedstock with sulfur dioxide, water, and a solvent for lignin, to produce intermediate solids and a liquid phase comprising hemicelluloses and lignin; mildly bleaching the intermediate solids to further delignify the intermediate solids, thereby generating cellulose-rich solids; and washing the cellulose-rich solids to generate purified cellulose with less than 2 weight percent lignin. The bleaching may employ bleaching agents including lignin-modifying enzymes. The bleaching and washing steps may be combined. It is also possible to carry out bleaching prior to, or simultaneously with, biomass fractionation in the digestor, which may help reduce downstream lignin precipitation. The purified cellulose may be utilized for making cellulose materials or cellulose derivatives, or for hydrolysis to produce glucose.
Owner:API INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Preparation method of bioorganic fertilizer
InactiveCN104692844ASpeed up the ripening processHigh activityClimate change adaptationExcrement fertilisersDecompositionPotassium
Owner:DALIAN SANKE BIO ENG
Increased production of secreted proteins by recombinant eukaryotic cells
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Sweet potato plantation bioorganic fertilizer and production method thereof
InactiveCN106397051AAdjust pH valueImprove compactionCalcareous fertilisersBio-organic fraction processingAzotobacter chroococcumLivestock manure
The invention relates to the technical field of bioorganic fertilizers, and concretely relates to a sweet potato plantation bioorganic fertilizer and a production method thereof. The organic fertilizer comprises, by weight, 140-170 parts of sweet potato residues, 90-120 parts of cassava residues, 20-40 parts of Artemisia carvifolia extraction medicine residues, 15-25 parts of isatis root extraction medicine residues, 45-65 parts of livestock manure, 15-35 parts of shell powder, 15-30 parts of slaked lime, 10-25 parts of humic acid, 5-15 parts of a nitrogen fertilizer, 3-8 parts of a potassium fertilizer, 0.2-0.7 parts of cellulase, 0.2-0.6 parts of ligninase, 0.1-0.35 parts of Azotobacter chroococcum, 0.1-1.1 parts of actinomyces and 0.2-0.7 parts of compound sodium nitrophenolate. The bioorganic fertilizer has the advantages of uniform fertility, high absorption and utilization rate, effective improvement of the soil structure, reduction of the use amount of pesticides, enhancement of the resistibility of crops to insect diseases, improvement of the quality and the output of agricultural products, and increase of peasants' income. The invention also provides the production method of the bioorganic fertilizer.
Owner:广西罗城中科嘉业农业发展有限公司
Ligninase-assisted process for degumming China hemp fiber by freezing and suddenly heating
ActiveCN104178819AReduce total usageMeet the needs of the finishing processBacteriological rettingFibre treatment to obtain bast fibreChemical treatmentEnvironmental resistance
The invention discloses a ligninase-assisted process for degumming China hemp fiber by freezing and suddenly heating. The ligninase-assisted process for degumming China hemp fiber by freezing and suddenly heating comprises the following steps: ultrasonically poaching and pre-pickling; then carrying out UV radiation, freezing and suddenly heating, and processing by the ligninase; and finally degumming at high temperature and high pressure. The gumming effect of the surface of the China hemp fiber processed by the process is superior than that of a chemical method and a mechanical method; the China hemp fiber processed by the process is relatively low in residual gun rate and content of ligninase, so that the requirements of a textile finishing process can be met; good whiteness and softness are obtained; meanwhile, the breakage strength of the fiber is controlled in the spinning requirements; the length and the fineness of the fiber are also improved; the comfortable property is greatly improved; the use amount of chemical treatment reagents can be reduced; the polluted wastewater discharge is relatively low; the ligninase-assisted process for degumming China hemp fiber by freezing and suddenly heating is a green and environment-friendly process.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Production method and applications of compound enzyme liquid used in papermaking and pulping process of wheat straws and rice straws
ActiveCN103540581AImprove catalytic performanceImprove accessibilityMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesCellulosePectinase
The invention discloses a production method of a compound enzyme liquid used in the papermaking and pulping process of wheat straws and rice straws. The production method is characterized by comprising the steps of weighing each component enzyme, mixing and compounding all the component enzymes in a compounding pot, performing corrosion prevention, inspecting, packaging, and storing in a warehouse with the temperature of 5 DEG C, wherein the component enzymes are alkaline pectinase and xylanase, or are alkaline pectinase, xylanase, mannose and ligninase. The application of the compound enzyme liquid in the papermaking and pulping process of wheat straws and rice straws comprises the following steps: papermaking raw materials are pre-treated and then sent into a digester for enzyme treatment, namely the raw materials are soaked with the compound enzyme liquid, wherein the enzyme treatment conditions are as follows: the temperature ranges from 40 DEG C to 60 DEG C, the mass ratio of an absolute dry raw materials to the compound enzyme liquid is 100:(1.2-1.8) and the enzyme soaking time ranges from 20 minutes to 60 minutes; after enzyme treatment, the papermaking raw materials are digested in the digester. Each component enzyme in the compound enzyme liquid is high in activity but has no activity to crystalline cellulose and carboxymethyl cellulose; and compared with the traditional chemical pulping method, the production method has the advantages that the use amount of alkali is lowered by about 50%, the content of COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) in waste water is lowered by over 30%, the production cost is lowered by about 20% and the quality of paper products is enhanced.
Owner:江苏富星纸业有限公司
Scouring and bleaching method of hemp fabric
InactiveCN103882679AEasy to handleHigh whitenessBiochemical fibre treatmentBleaching apparatusPectinaseEngineering
The invention relates to a scouring and bleaching processing method of hemp fabric, aiming at improving the whiteness and the hygroscopic property, meeting the requirements on subsequent dyeing and finishing and alleviating the damage to hemp fiber. The pretreatment of a hemp fiber product comprises the steps of firstly, treating the hemp fabric by a rolling base stacking method to enable the impurities on the fiber to be fully swelled; washing by hot water, and then treating the product by a biological method through pectinase, ligninase, cellulose and the like; combining oxidation bleaching and deoxidizing by an enzymic method. The method comprises the steps of carrying out pad-roll caustic soda stacking treatment on the hemp fabric; carrying out biological enzyme (pectinase, ligninase and cellulose) treatment on the hemp fabric; bleaching the hemp fabric by hydrogen peroxide; deoxidizing the hemp fabric by catalase. Compared with the traditional high-temperature alkaline pretreatment, the scouring and bleaching method has the advantages that the production energy consumption is reduced, and the environmental pollution is alleviated.
Owner:吴江市桃源海润印染有限公司
Boiling assistant for preparing high polymerised pulp
The invention relates to a boiling assistant for preparing high polymerised pulp. The assistant comprises 30-50% of sodium sulfite, 5-10% of alpha-methylanthraquinone (alpha-MAQ), 5-15% of lipase, 1-10% of hemicellulase, 1-10% of ligninase, 10-20% of diethylene triaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) and 20-40% of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate. The assistant can promote the swelling of celluloses, quickly improve the permeation of alkaline liquor on celluloses, accelerate the breakage of primary walls, quickly dissolve out lignin, pectin, wax and other non-fiber impurities, improve the boiling reaction speed, oxidize the reducing groups (aldehyde terminal groups) of the cotton linter carbohydrate into various alkali-stable sugar acid terminal groups, inhibit the peeling reaction, reduce the degradation of celluloses and improve the yield.
Owner:YIBIN GRACE GROUP CO LTD
Protein-enhanced surfactants for enzyme activation
ActiveUS9051535B2Increase ratingsIncreasing catalytic activity of an interfacial hydrolyticOrganic detergent compounding agentsHydrolasesSurface cleaningBiological activation
Disclosed herein are compositions containing enzymes, particularly acting at the interface between two immiscible phases where the rate of enzymatic activity is increased by addition of a blend of surfactant(s) and a mixture derived from yeast fermentation, that contain non-enzymatic exo-proteins released by yeast in response to a non-lethal stress. The enzymes include those that work at the interface between an aqueous solution and a water immiscible phase, liquid or solid, such as oil, fat, cellulose, lignin, etc. including, but not limited to the following or combinations thereof: lipases, polysaccharase, lignase, cellulase and the like, in which the substrate of an enzymatic reaction forms a phase, segregated from the aqueous solution in which the enzymes are typically operating. Disclosed herein are methods for improving a washing solution with the use of these compositions, where the enzyme-protein-surfactant solution can be used in such applications as: laundry, spot remover, pre-laundry, dishes, hard surface cleaning, wastewater treatment, cellulose breakdown as in ethanol production, lignin utilization, environmental remediation, industrial cleaning, and agricultural applications.
Owner:ADVANCED BIOCATALYTICS
Transgenic plants containing ligninase and cellulase which degrade lignin and cellulose to fermentable sugars
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Production method and application of compound enzyme liquid for paper pulp bleaching
The invention discloses a production method of a compound enzyme liquid for paper pulp bleaching, the production method is characterized by weighing component enzymes, mixing and blending in a compound tank, corrosion preventing, checking, packing and then storing in a storehouse at 5 DEG.C, wherein the component enzymes are alkaline pectinase, xylanase, mannose and ligninase; the application of the compound enzyme liquid in paper pulp bleaching comprises the following steps: stocking, pulping, washing and screening a papermaking material, preparing into yellow pulp, adding the compound enzyme liquid in the bleached yellow pulp through a metering pump, uniformly mixing and performing enzymatic hydrolysis, wherein the enzyme treatment condition is as follows: the temperature is 50-55 DEG C, and the enzymolysis time is 40-50 min; performing the chemical bleaching according to conventional process steps after the enzymolysis is finished. The component enzymes in the compound enzyme liquid are high in activity, the aim of bleaching the paper pulp in aid is achieved, the dosage of chemical raw materials in the chemical bleaching process is reduced, the bleaching effect is good, the environment pollution is less, and the component enzymes in the compound enzyme liquid are inactive to crystalline cellulose and carboxymethyl cellulose, so that the paper pulp strength cannot be damaged.
Owner:江苏富星纸业有限公司
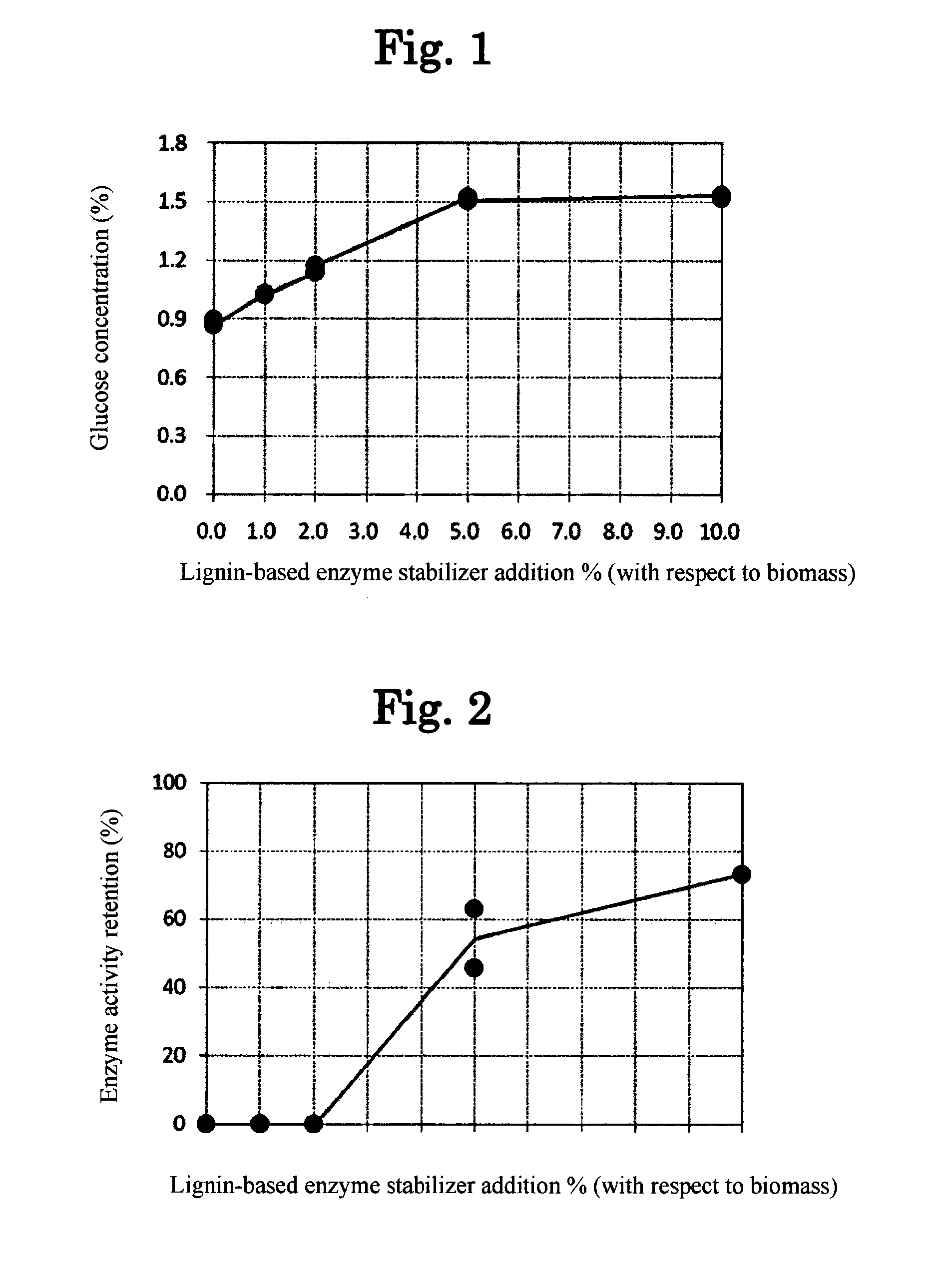
Lignin-based enzyme stabilizer
ActiveUS8911976B2Avoid adsorptionAvoid inactivationBiofuelsEnzyme stabilisationCelluloseLignocellulosic biomass
The invention relates to an enzyme stabilizer comprising a lignin derivative produced by reaction between lignin and a hydrophilic compound, and to a method of saccharifying lignocellulosic biomass which employs the enzyme stabilizer. According to the invention it is possible to accomplish effective saccharification of cellulosic biomass with saccharifying enzymes, by enhancing saccharifying enzyme activity and preventing nonspecific adsorption of saccharifying enzyme onto substrate.
Owner:FORESTRY & FOREST PRODS RES INST
Method for producing ligninolytic enzymes
InactiveCN103205403ASave raw materialsSave energyMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesPichia pastorisEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses a method for producing ligninolytic enzymes, and belongs to the biotechnical field. The method comprises the following steps: 1, respectively cloning lignin peroxidase, manganese peroxidase and laccase genes from microbes; 2, constructing a Pichia pastoris expression vector containing the expression cassettes of the above three genes, and a Saccharomyces cerevisiae expression vector containing the expression cassettes, and converting the above vectors to corresponding host bacteria to obtain engineering bacteria; and 3, respectively fermenting Pichia pastoris expression engineering bacteria and Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria to produce recombinant lignin peroxidase, manganese peroxidase and laccase. The method has the following advantages: engineering bacteria are used to substitute natural bacterial strains to produce the lignin peroxidase, manganese peroxidase and laccase, so the enzyme outputs are improved through increasing the copy numbers of the genes; and the engineering bacteria containing three enzyme gene expression cassettes substitute engineering bacteria containing a single enzyme gene expression cassette to produce single enzymes, so the raw material, the energy consumption and the manpower resource are saved.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
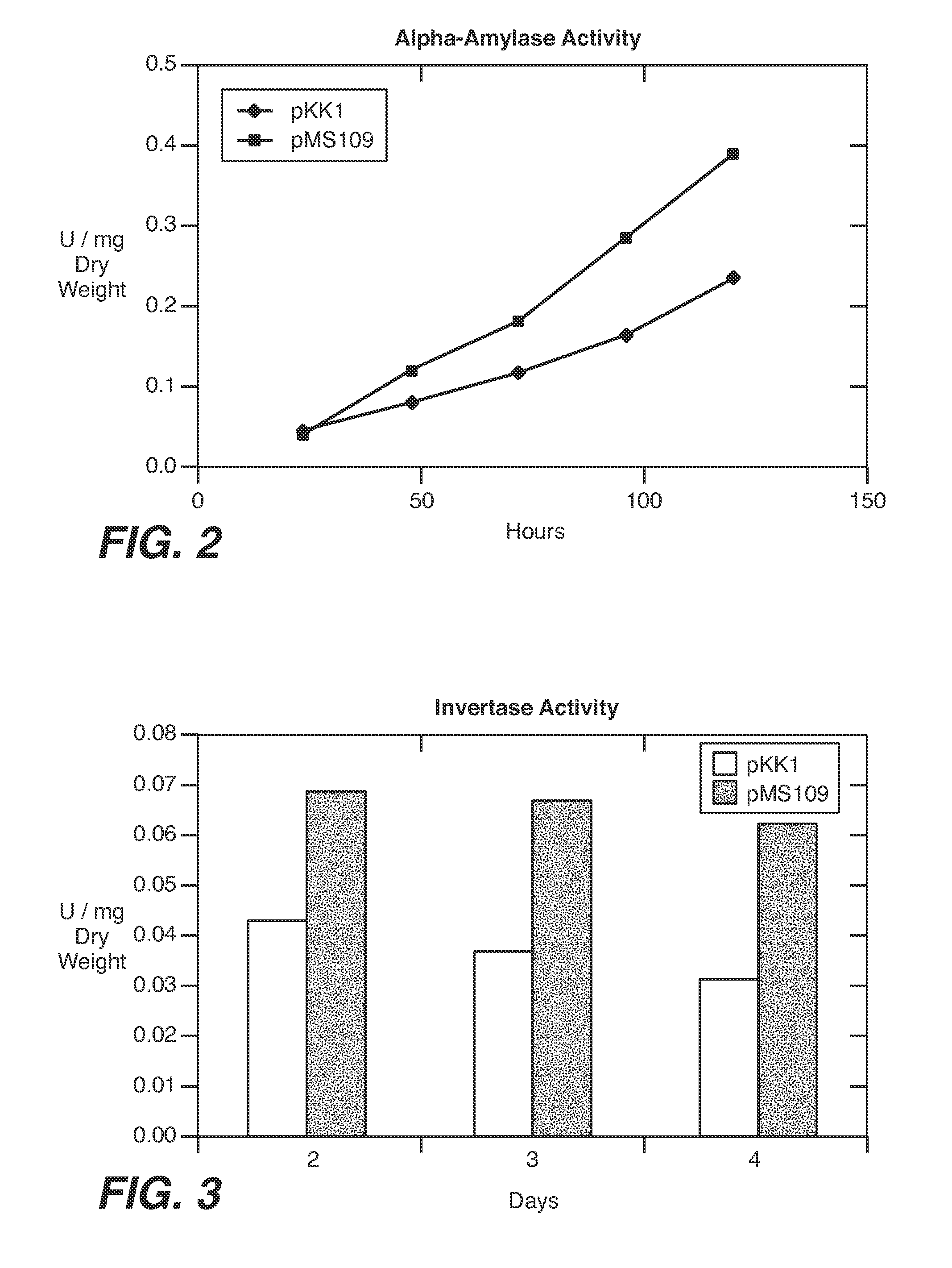
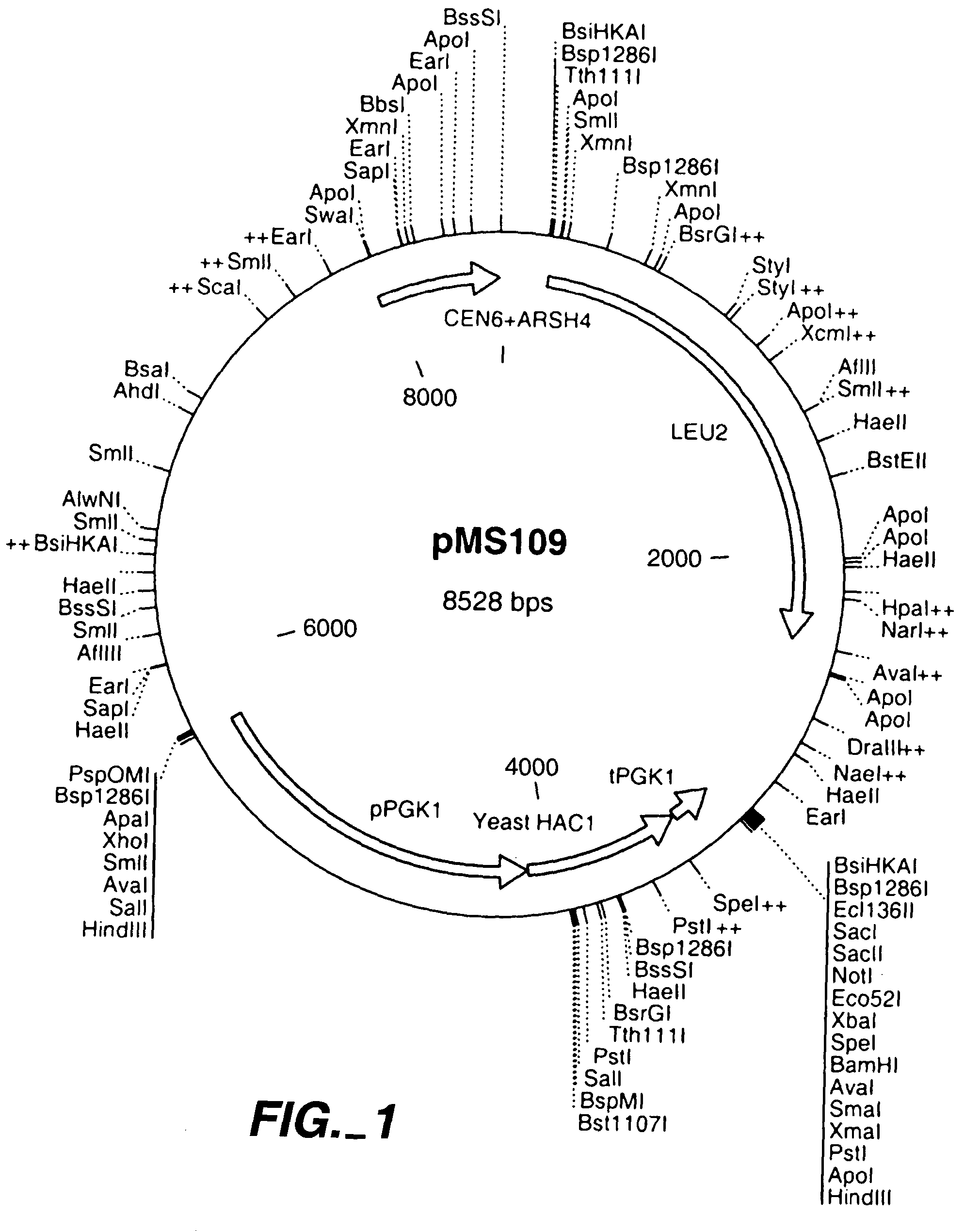
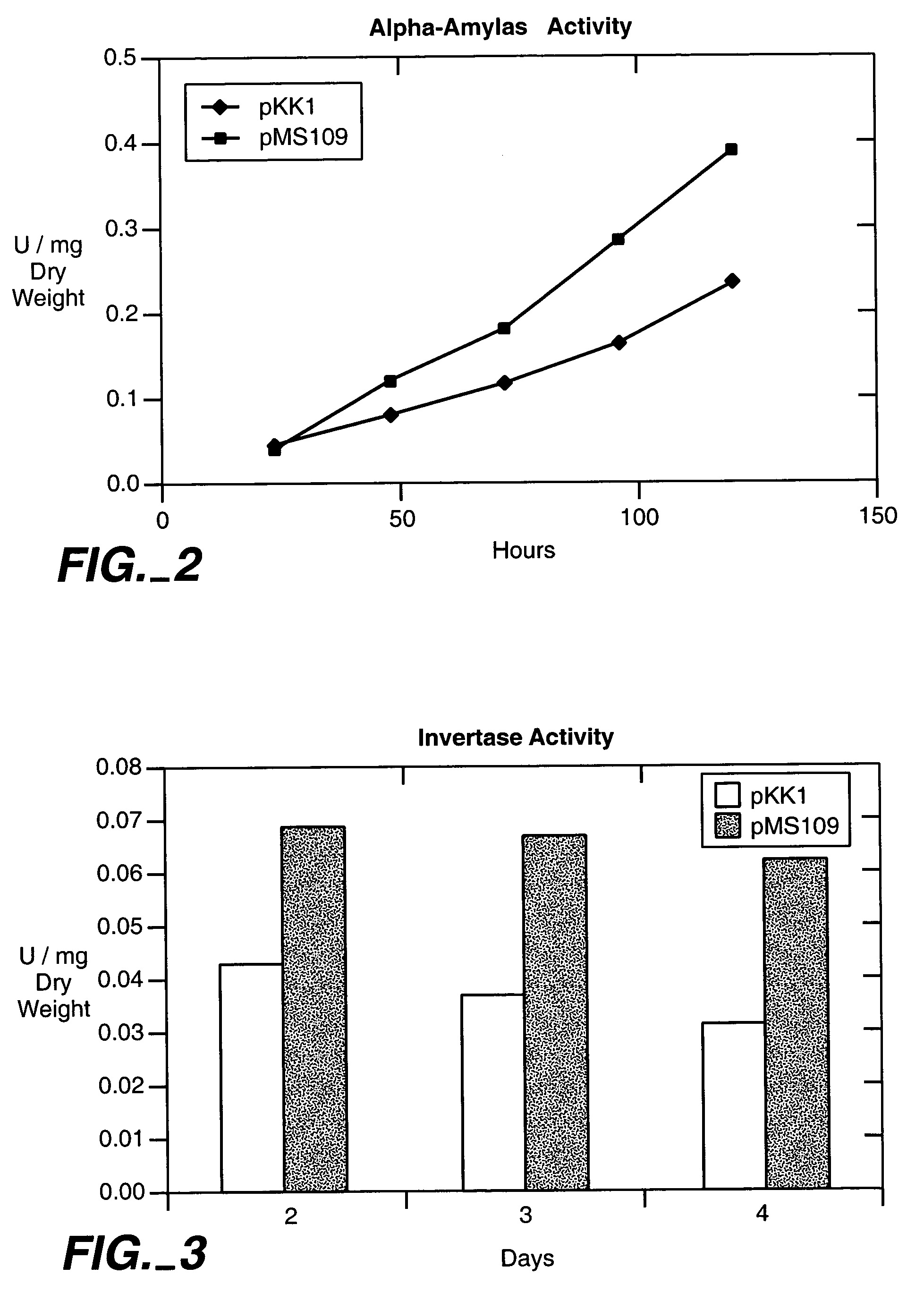
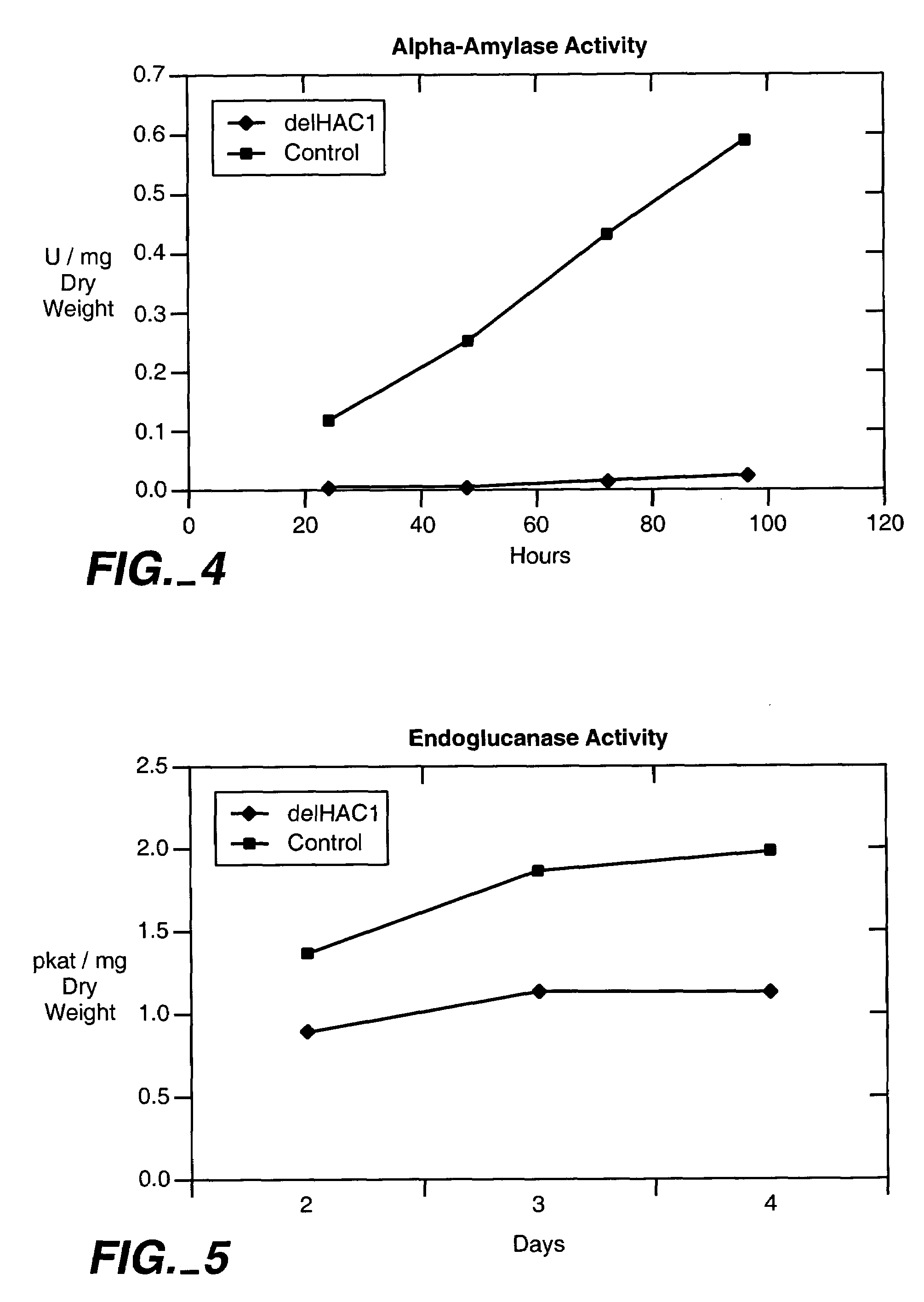
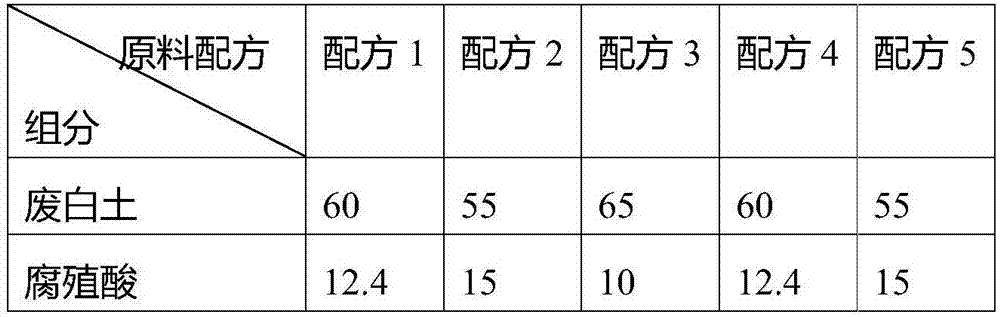
Increased production of secreted proteins by recombinant eukaryotic cells
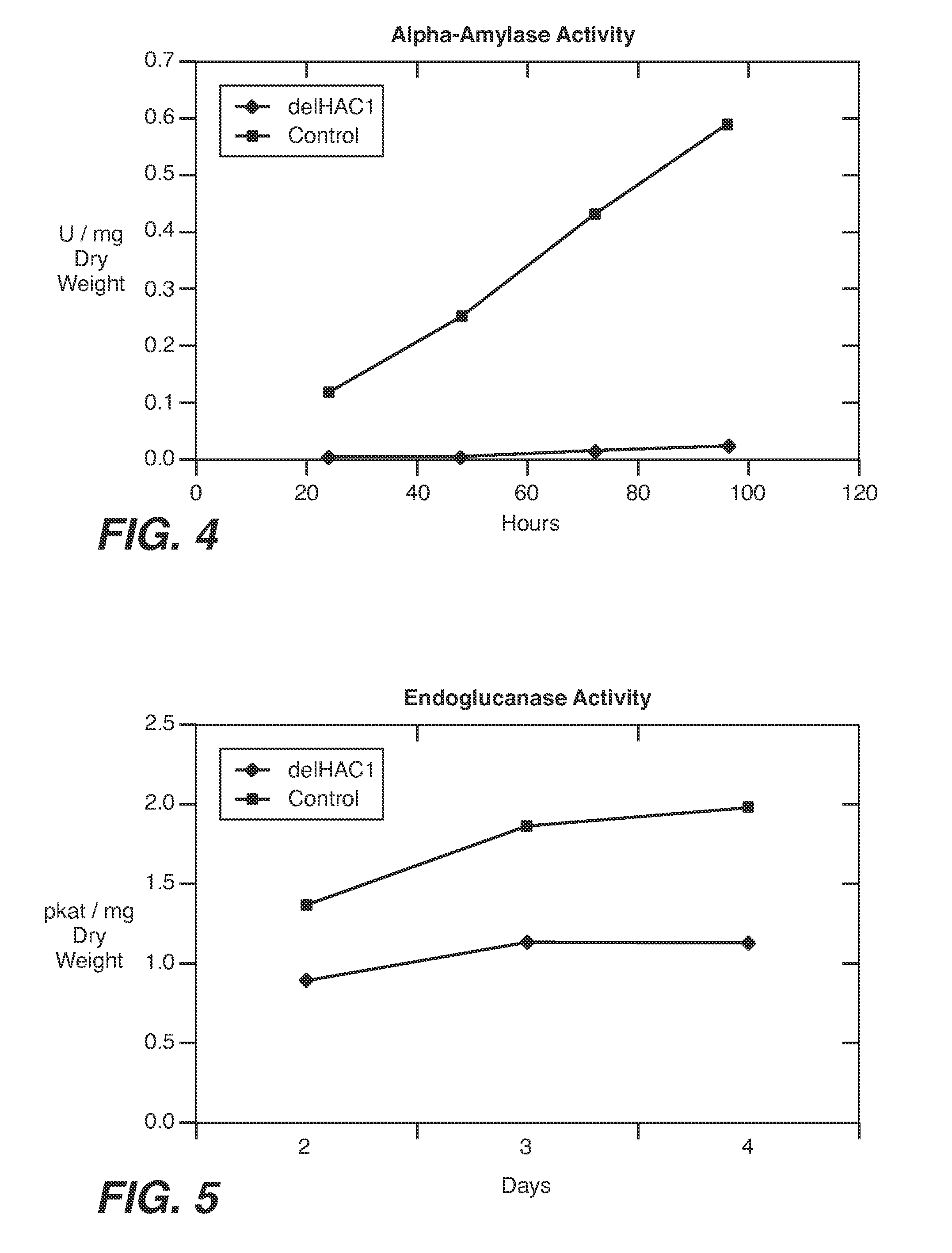
Described herein are methods for increasing the amount of protein secreted by a cell. In one case, a cell is provided which contains a heterologous nucleic acid encoding a protein having unfolded protein response modulating activity and a heterologous nucleic acid encoding a protein of interest to be secreted. In one case, the protein having unfolded protein response modulating activity is selected from the proteins selected from the group consisting of HAC1, PTC2 and IRE1. The protein of interest can be any secreted protein such as a therapeutic or an industrial enzyme. For example the protein can be selected from the group consisting of lipase, cellulase, endo-glucosidase H, protease, carbohydrase, reductase, oxidase, isomerase, transferase, kinase, phosphatase, alpha-amylase, glucoamylase, lignocellulose hemicellulase, pectinase and ligninase.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Composite preparation for degumming of ramie with skins and degumming method
ActiveCN105648544AEfficient removalImproved dry hemp qualityFibre treatment to obtain bast fibreThermal insulationLignin-modifying enzyme
The invention discloses a composite preparation for degumming of ramie with skins and a degumming method. The composite preparation is composed of ligninase, hydrogen peroxide, and catalase. The degumming method comprises the following steps: (1) soaking ramie with skins through adoption of the composite preparation at a temperature of 20-30 DEG C for 12-20 h, wherein the composite preparation comprises 1.5-2.5 g / L of ligninase, 1.5-2.5 g / L of hydrogen peroxide, and 1.0-1.5 g / L of catalase and has a pH value in a range of 4.0-4.5; (2) boiling the soaked ramie in alkali; (3) performing thermal insulation and wet stewing of ramie after alkali boiling for more than 10h; and (4) knocking the obtained ramie. According to the method, skins of ramie can be removed, and pectin and hemicellulose can be effectively removed too. The quality of processed degummed ramie is greatly improved; the problem that ramie is degummed through manual scraping in the prior art is solved; and ramie planting cost is reduced.
Owner:大竹县全畅麻纺有限公司
Spent bleaching clay-based bio-organic fertilizer and applications thereof
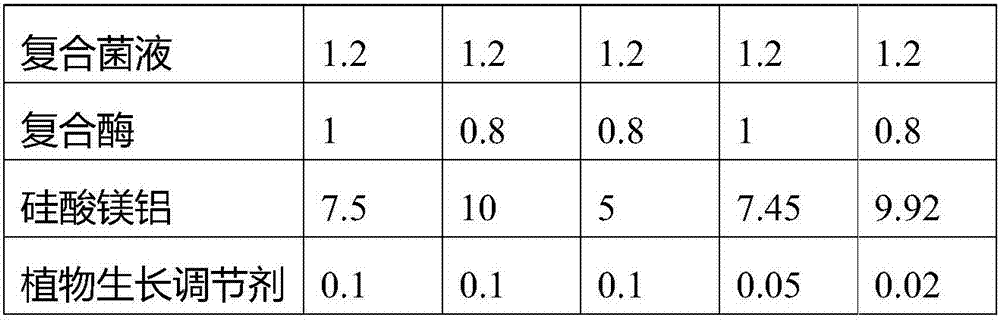
InactiveCN106977304AMaximize utilizationVersatileBio-organic fraction processingMagnesium fertilisersAluminum silicateBacillus cereus
The invention provides a spent bleaching clay-based bio-organic fertilizer, the raw material formula of which includes the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50-70 parts of spent bleaching clay, 10-15 parts of humic acid, 0.5-2 parts of composite bacteria liquid, 0.5-1 part of complex enzyme, 5-10 parts of magnesium aluminum silicate and 0.01-0.1 part of plant growth regulator, wherein the composite bacteria liquid is prepared by mixing pseudomonas, bacillus subtitles, white rot fungi, bacillus cereus, and bacillus thuringlensis according to the volume ratio of nutrient solution being 1 to (1.3-1.6) to (0.5-1.1) to (0.3-0.6) to (0.2-0.4); the complex enzyme is formed by mixing amylase, lipase and ligninase according to the mass ratio of 1 to (1.4-1.6) to (0.3-0.8); and the plant growth regulator is a combination of brassinolide with one or more of cytokinin, thidiazuron, gibberellic acid, indoleacetic acid and naphthalene acetic acid. The bio-organic fertilizer has multiple functions of preventing soil pests, degrading pesticide and chemical residuals in soil, curing and stabilizing heavy metal ions in the soil, is excellent in comprehensive modification effect, has no root burning and seedling burning problems and is low in cost.
Owner:甘肃天农一禾农业有限公司
Method for bioenzyme-assisted chlorine dioxide bleaching of bagasse pulp
The invention relates to a method for bioenzyme-assisted chlorine dioxide bleaching of bagasse pulp. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing hemicellulase pretreatment; (2) performing ligninase pretreatment; (3) performing chlorine dioxide bleaching. According to the method, hexenuronic acid and hemicellulose in unbleached bagasse pulp are removed through the hemicellulase pretreatment of the unbleached bagasse pulp, so that more residual lignin is exposed; lignin exposed on the fiber surface is removed by using ligninase, so that less chlorine dioxide is used in a chlorine dioxide bleaching section and AOX (adsorbable organic halogen) generated in the bleaching process is reduced; after the bagasse pulp is subjected to bioenzyme pretreatment, the consumption of chlorine dioxide is saved by 30%-50% and the forming amount of AOX is reduced by 40%-60%.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for production of high protein feed from edible fungus chaff
InactiveCN105146053AReduce manufacturing costFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiomassLignin-modifying enzyme
The invention discloses a method for production of high protein feed from edible fungus chaff. The method specifically includes: breaking a fungus stick to obtain fungus chaff, adding an enzyme production induction liquid, then conducting culture under suitable conditions, eluting the fermentation system to obtain ligninase and efficiently transformed fungus chaff, then adding Tenebrio molitor, fly larvae, earthworms, locusts, silkworm chrysalis and other insect larvae into the remaining material to conduct culture, thus obtaining a high protein feed culture system. Compared with other production processes producing feed from biomass, the method can acquire ligninase, and realizes absorption and utilization of fungus chaff residue by the insect larvae so as to obtain the high protein feed. And pollution generated in the edible fungus production process is reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
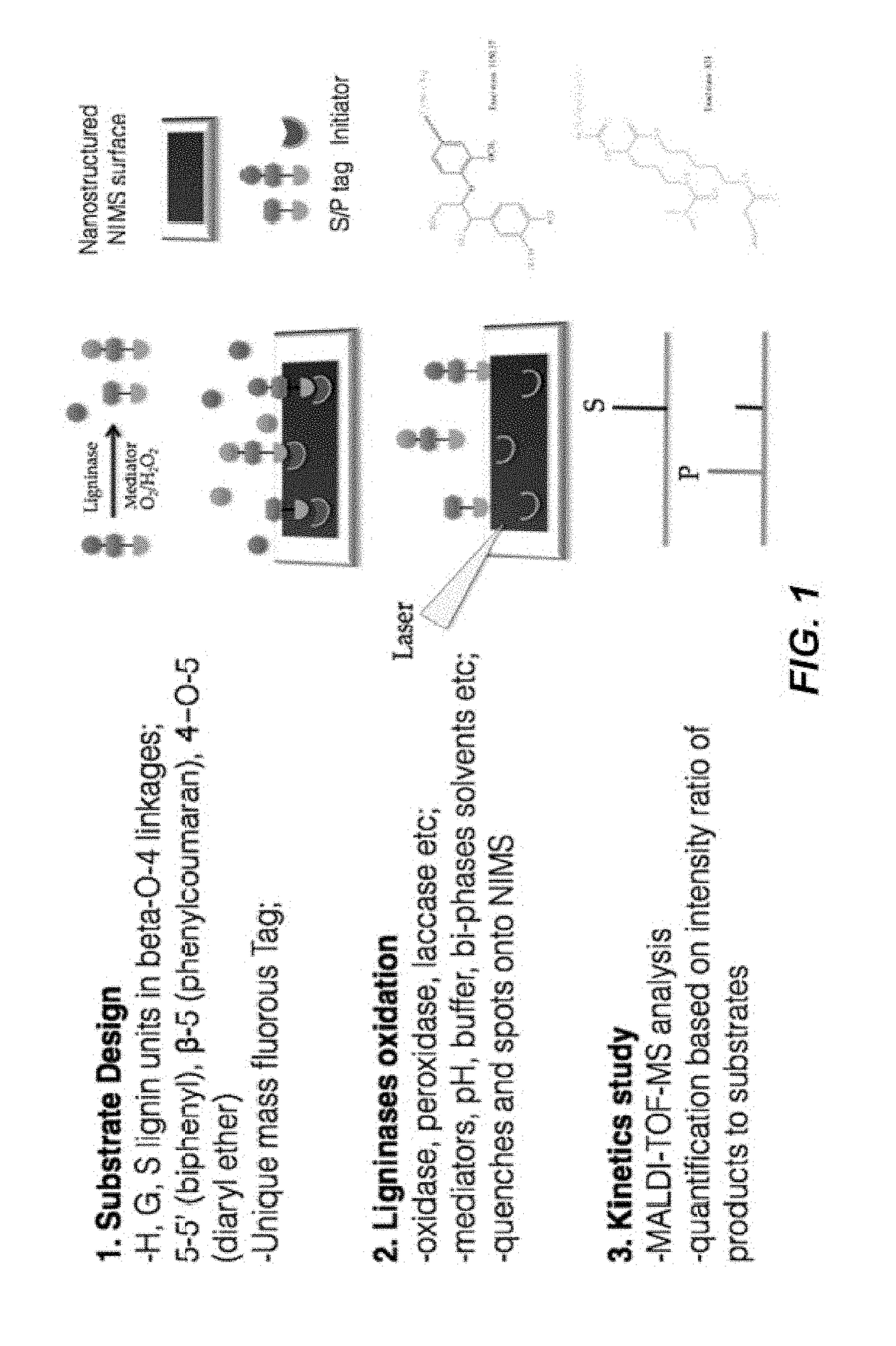
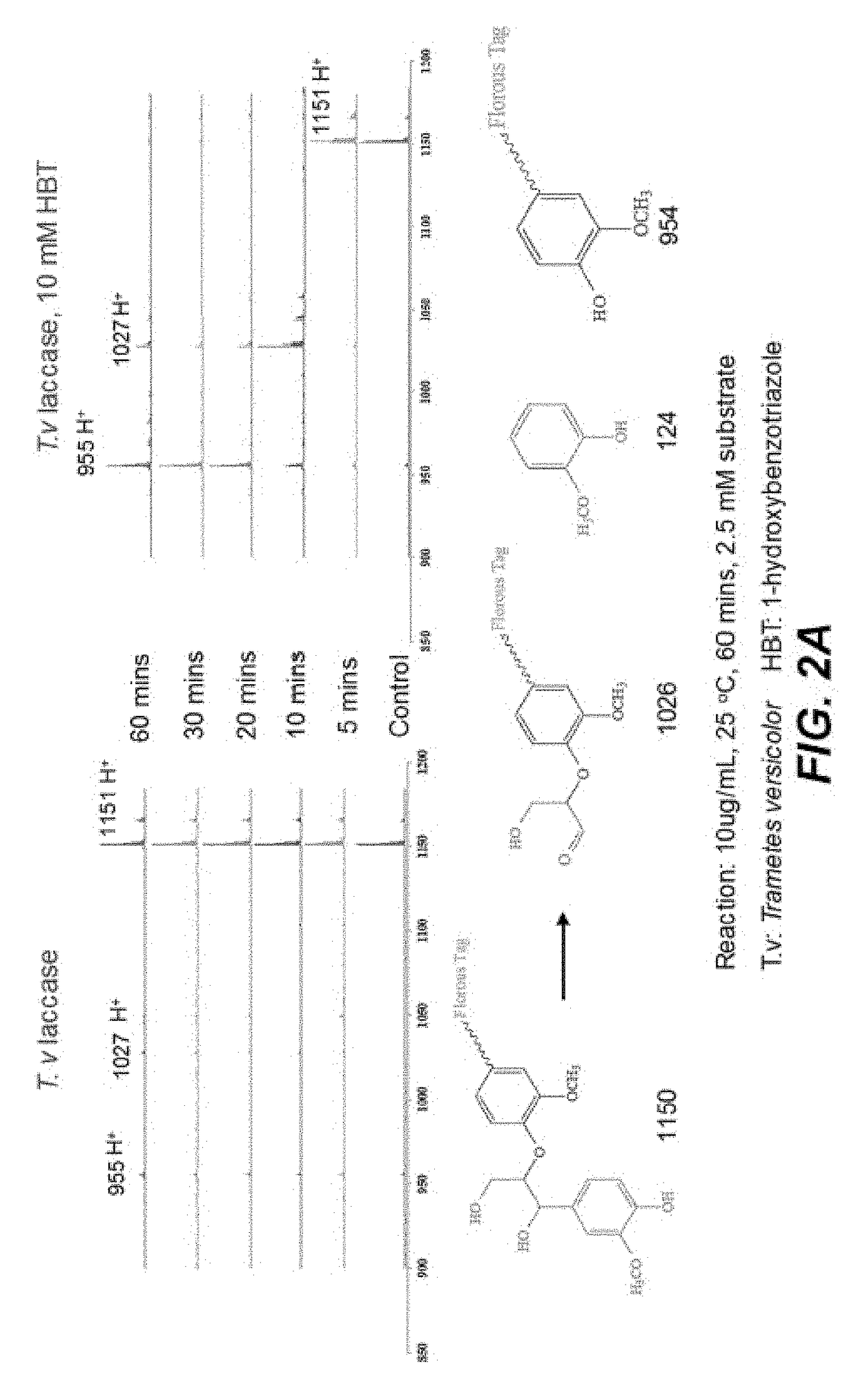
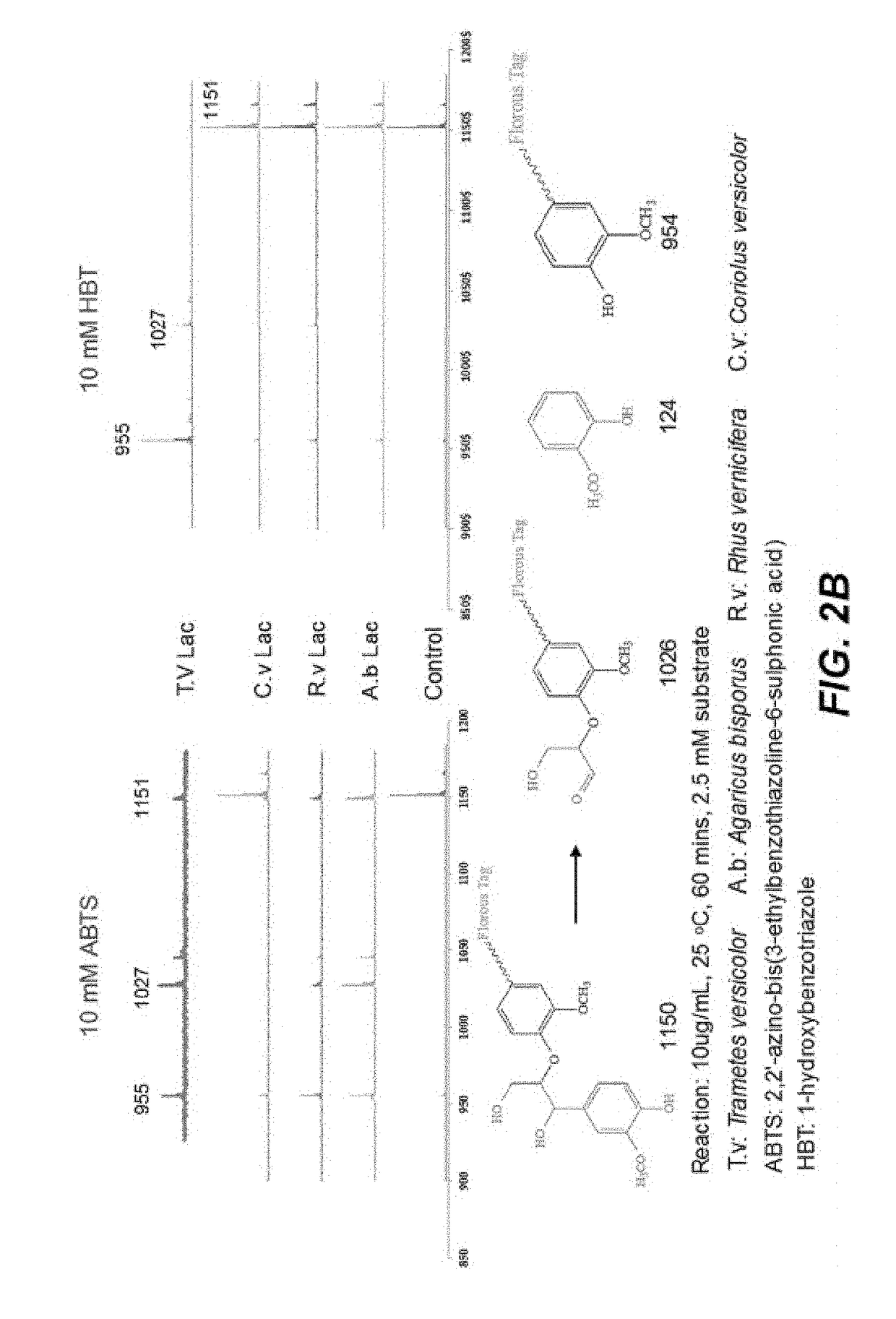
Determination of Ligninases Activities by Nano-structure Initiator Mass Spectrometry
ActiveUS20170314058A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementMass spectrometric analysisNano structuringHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Grape biofertilizer
InactiveCN105985155AImprove applicabilityImprove utilization efficiencyMagnesium fertilisersAnimal corpse fertilisersSodium bicarbonateNutrition
The invention discloses a grape biofertilizer, made from the following materials according to parts by weight: 10-12 parts of rice husk, 25-27 parts of rice chaff ash, 4-5 parts of talc powder, 2-3 parts of potassium selenite, 3-4 parts of ligninase, 2-3 parts of Bacillus subtilis agent, 2.4-2.6 parts of nano silicon, 3-4 parts of sodium bicarbonate, 19-21 parts of nano carbon black, 44-47 parts of organic household waste, 16-18 parts of slaughterhouse pig bone waste, 14-15 parts of slaughterhouse bovine bone waste, 3.5-3.8 parts of citric acid and suitable water; the materials small in scale and high in surface energy activity such as nano silicon and nano carbon black are added to the biofertilizer and cooperate with the added biological enzyme and agent, an enzyme and agent attachment area is provided, the acting time of the enzyme in soil is lengthened, and the absorption of fertilizer particles by grape roots is enhanced, thus improving utilization rate of the fertilizer and reducing nutrition loss during grape planting.
Owner:WUHU CHUANGYUAN NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for preparing forage grass from complex leavening agent and biological yellow corn silage of yellow corn straw
PendingCN110313540ANo pollutionGood workmanshipFood processingAnimal feeding stuffPectinaseBiotechnology
The invention relates to the field of biological agriculture, in particular to a method for preparing forage grass from a complex leavening agent and biological yellow corn silage of yellow corn straw. The forage grass is prepared from, by weight, 20-30 parts of cellulase, 15-20 parts of ligninase, 8-12 parts of protease, 5-8 parts of lipase, 5-8 parts of pectinase, 5-8 parts of a trichoderma viride solution, 8-12 parts of a lactic acid bacterium solution, 8-12 parts of a saccharomycetes solution and 8-10 parts of urea. The method has the advantages that the operation is simple and convenient,the straw degradation utilization rate is high, the cost is low, and the environment is not polluted; the prepared forage grass has high content of protein saccharides, can increase the nutritive value, and can increase the digestive absorption utilization rate of the forage while improving the palatability.
Owner:陕西省生物农业研究所
Production method and application of compound enzyme solution for chemical mechanical pulping
ActiveCN103555702BHigh whitenessImprove qualityHydrolasesOxidoreductasesPectinaseEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a production method of a complex enzyme liquid for chemi-mechanical pulping. The production method is characterized by comprising the following steps: weighing various component enzymes, mixing and compounding the various component enzymes in a compounding tank, preventing corrosion, inspecting, packaging and storing in a storeroom at 5 DEG C, wherein the various component enzymes comprise alkaline pectinase, xylanase, mannose and ligninase. The application of the complex enzyme liquid in chemi-mechanical pulping is realized as follows: before steaming paper-making raw materials, adding the complex enzyme liquid to the paper-making raw materials through a metering pump, uniformly mixing the complex enzyme liquid with the paper-making raw materials for enzymatic hydrolysis under enzymatic treatment conditions that the temperature is 40-60 DEG C and enzymatic hydrolysis duration is 30-240 minutes; after the enzymatic hydrolysis, performing following processes as normal. The production method, through coupling synergistic effect of multiple enzymes of the complex enzyme liquid in chemi-mechanical pulping, can be used for improving the whiteness of pulp by 2-5% and reducing the pulp yellowing under a condition of guaranteeing high yield and low cost of pulping; the production method can be used for reducing the dosage of chemical raw materials by 20-30% and reducing the pulp grinding energy consumption by 18-30%; meanwhile, the production method can be used for reducing pollution and improving the pulp quality.
Owner:江苏富星纸业有限公司
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com