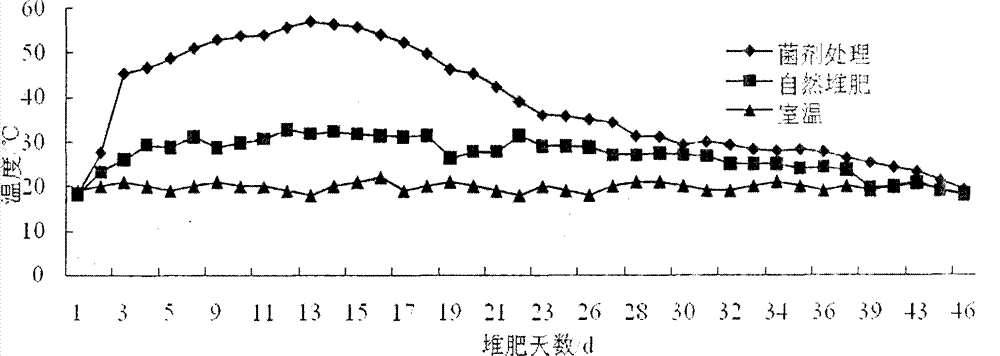
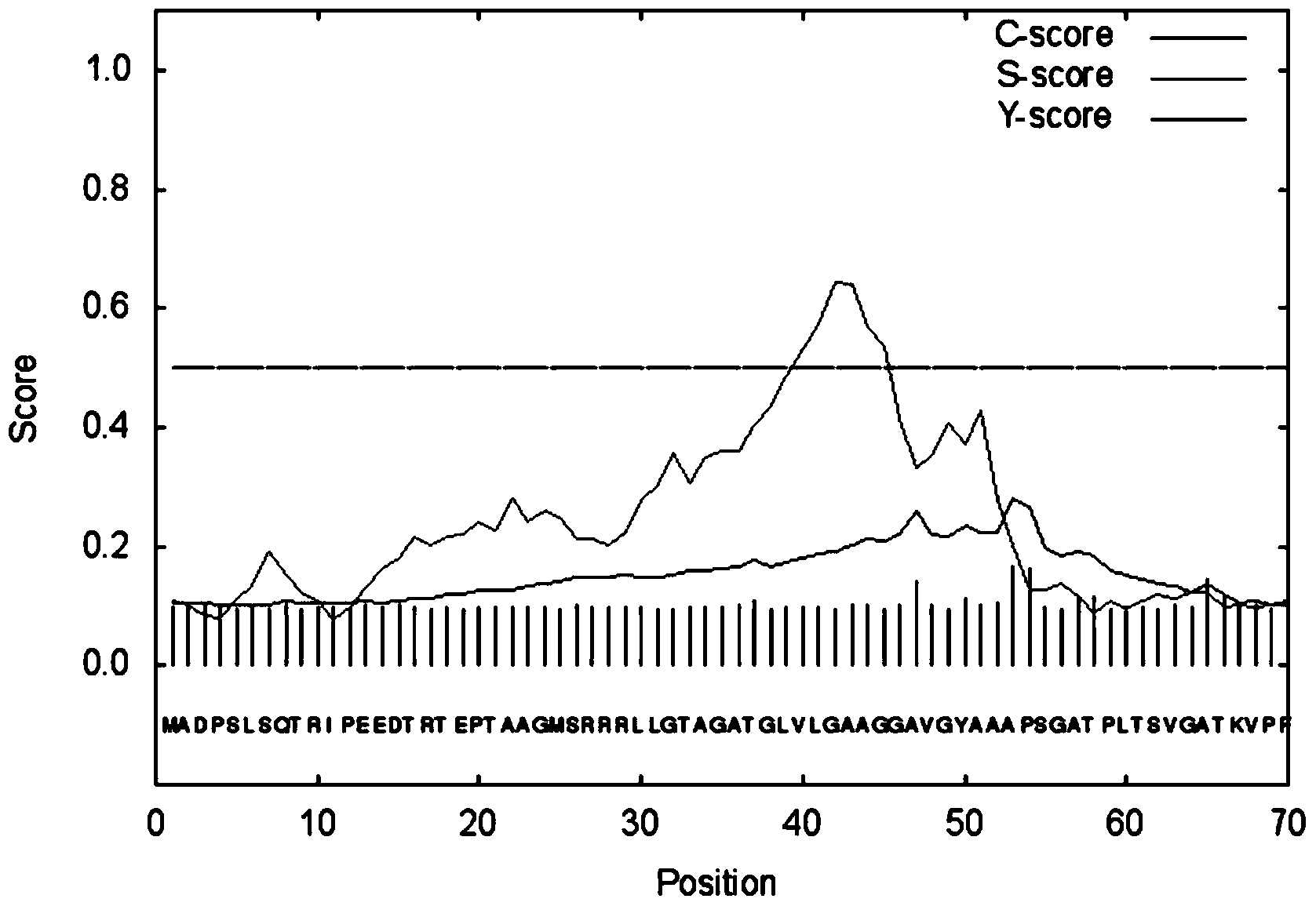
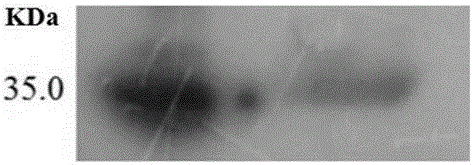
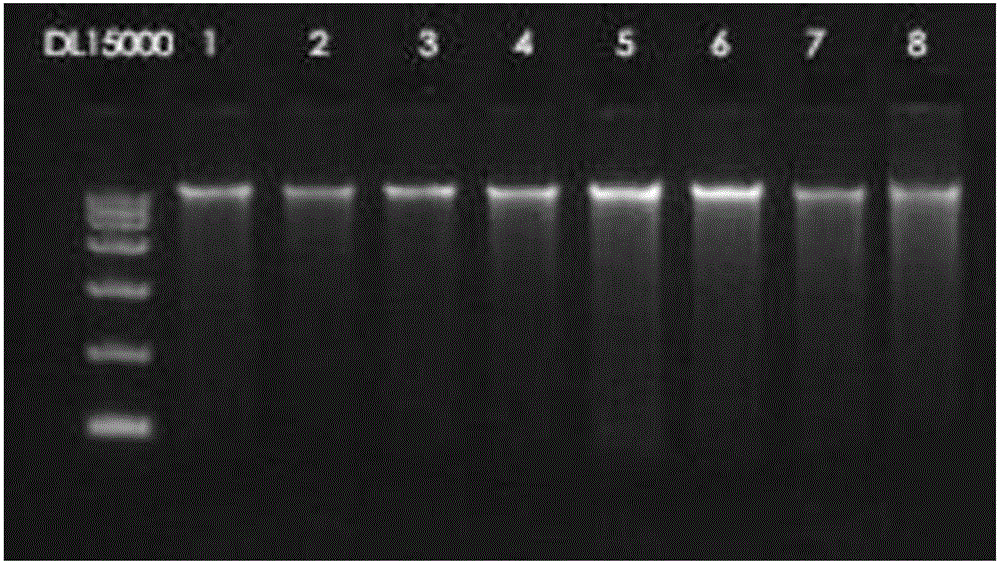
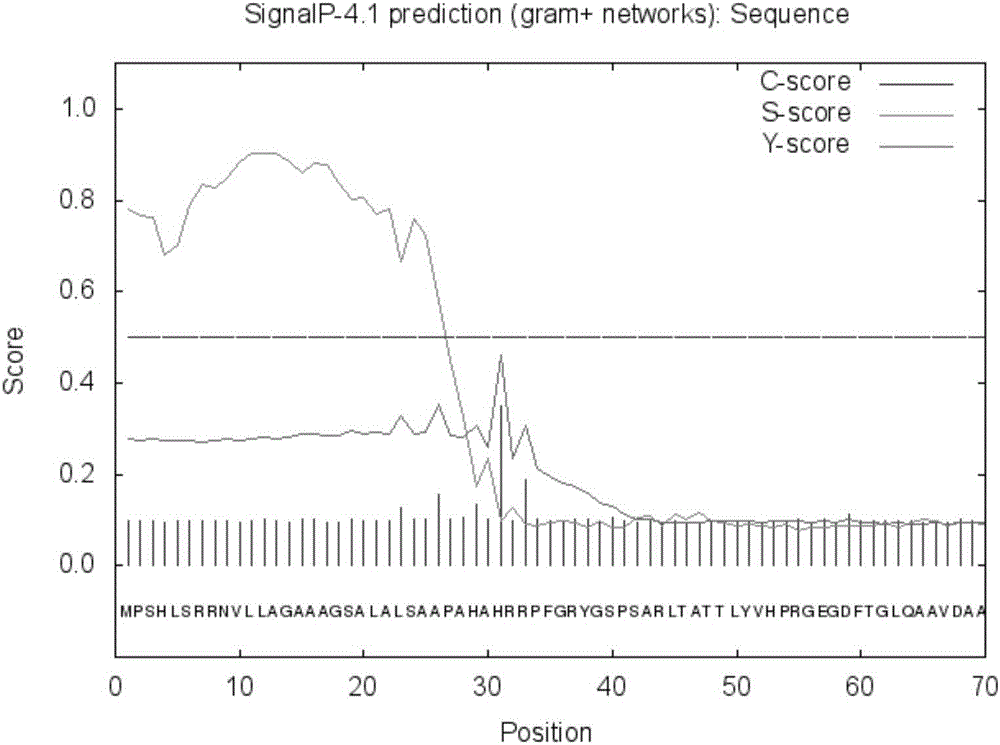
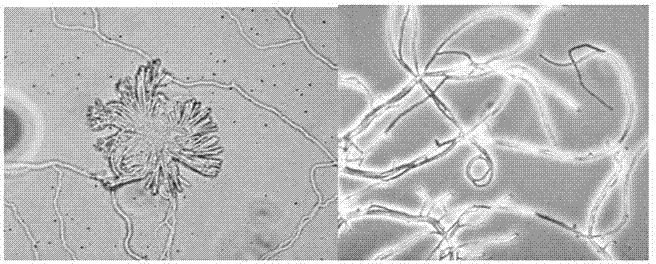
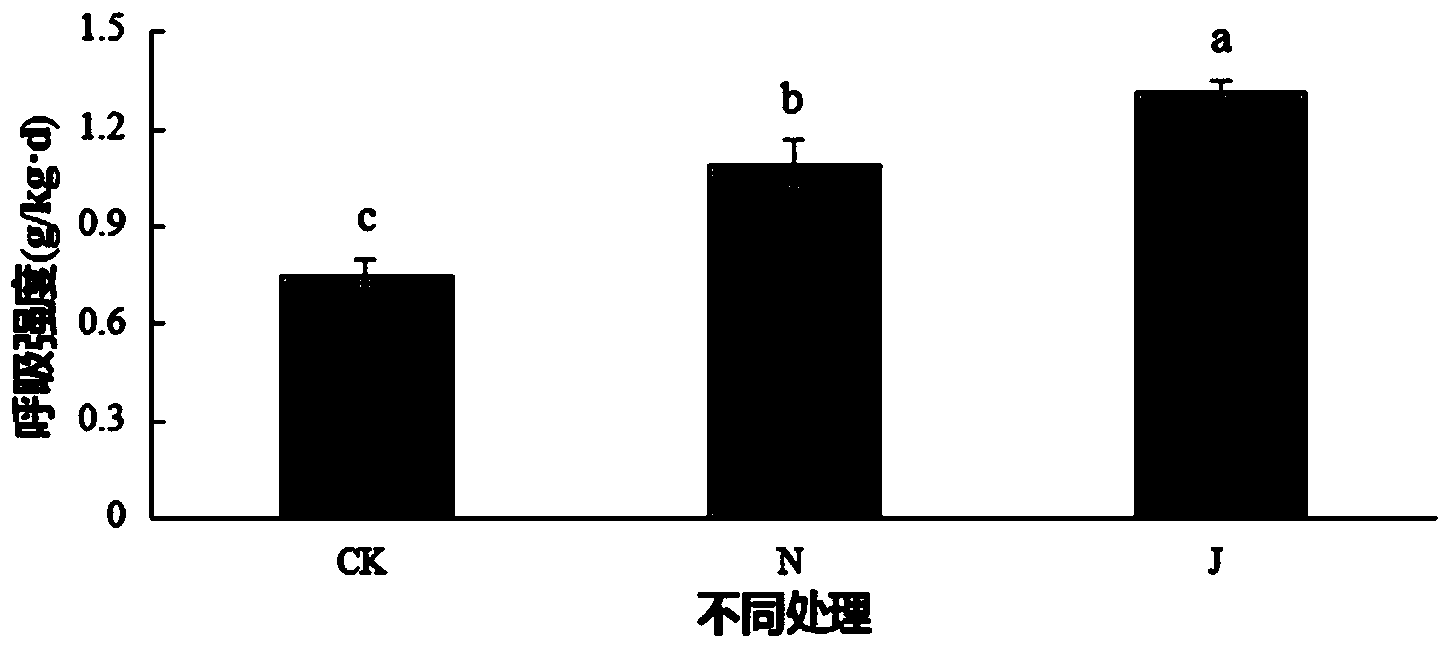
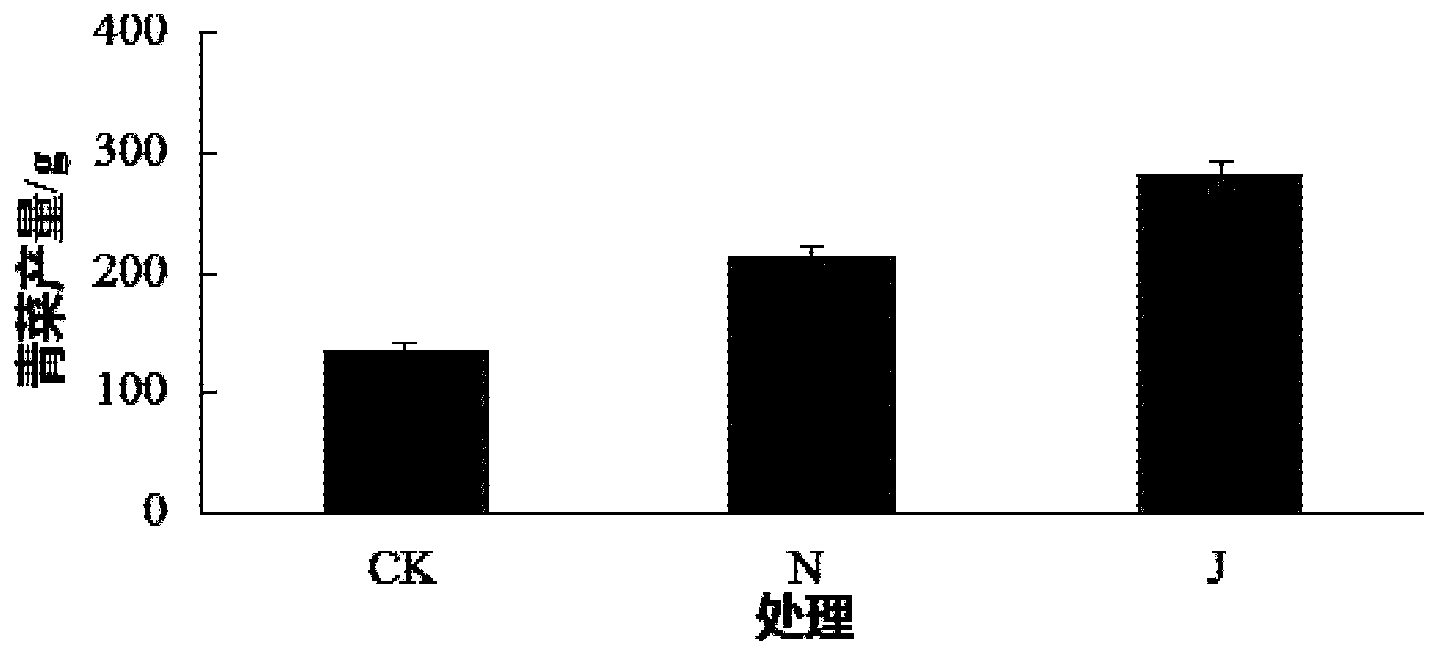
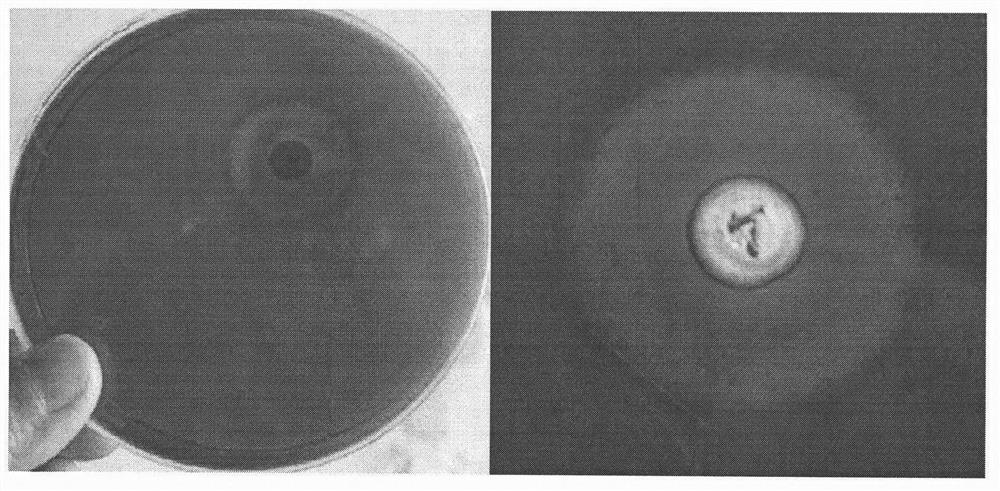
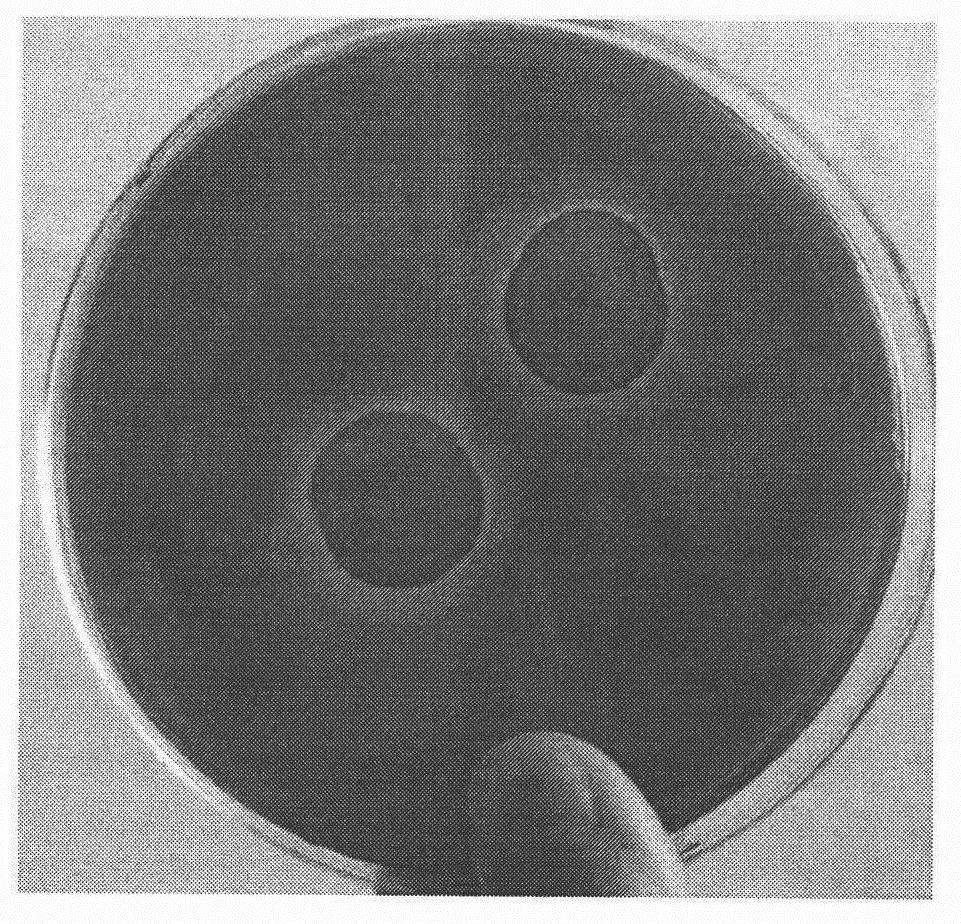
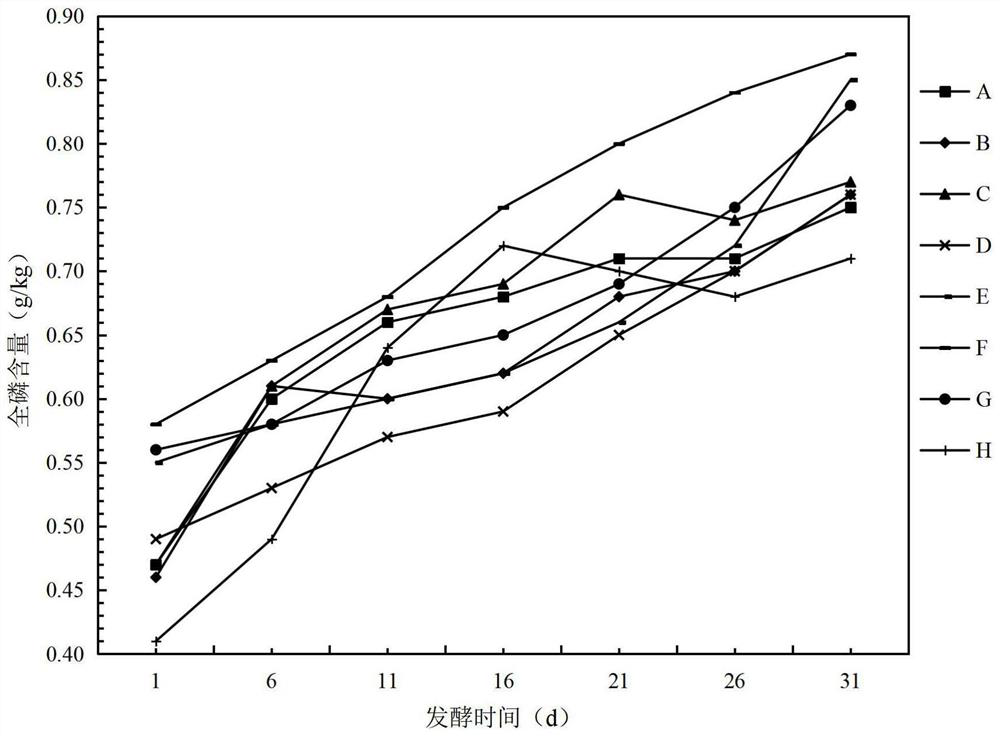
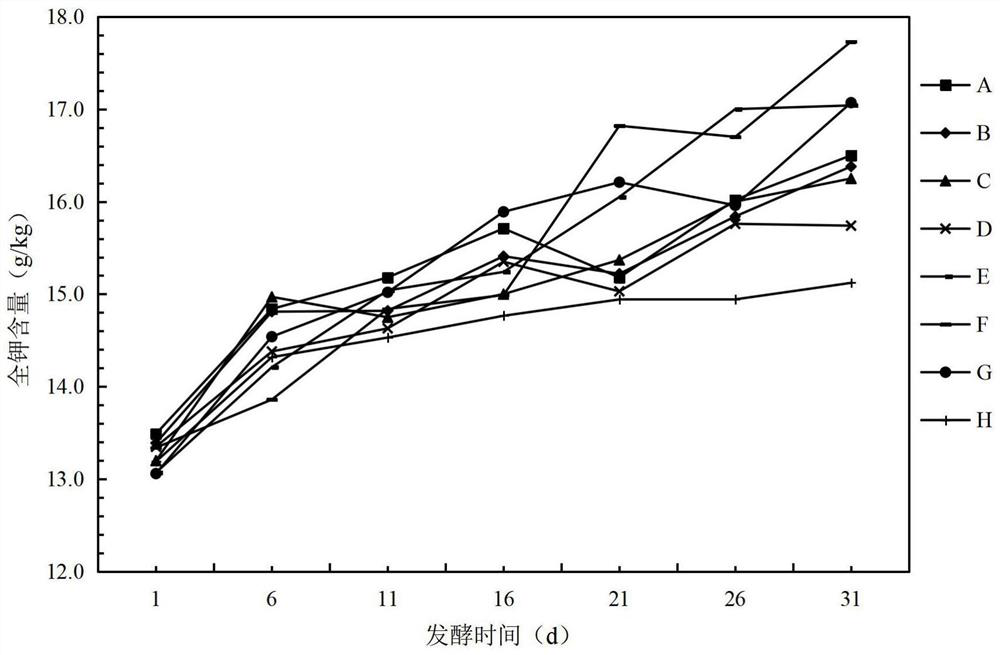
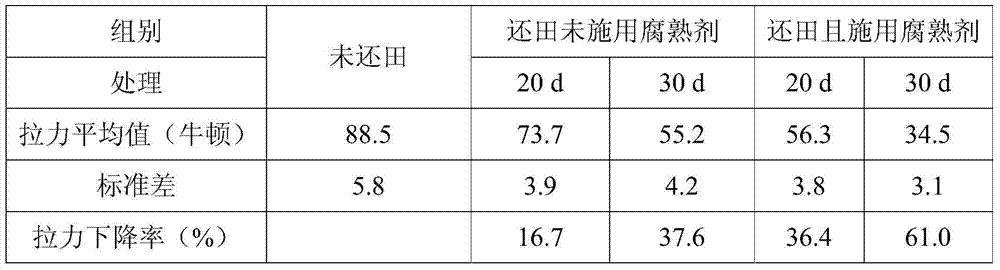
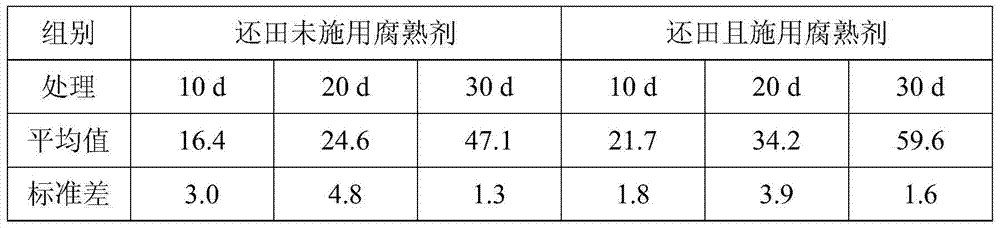
Patents
Literature
44 results about "Streptomyces griseorubens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Streptomyces griseorubens is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil.
Straw degradation actinomycete and application thereof
ActiveCN102703344AIncrease production capacityCause harmBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPectinaseMicroorganism
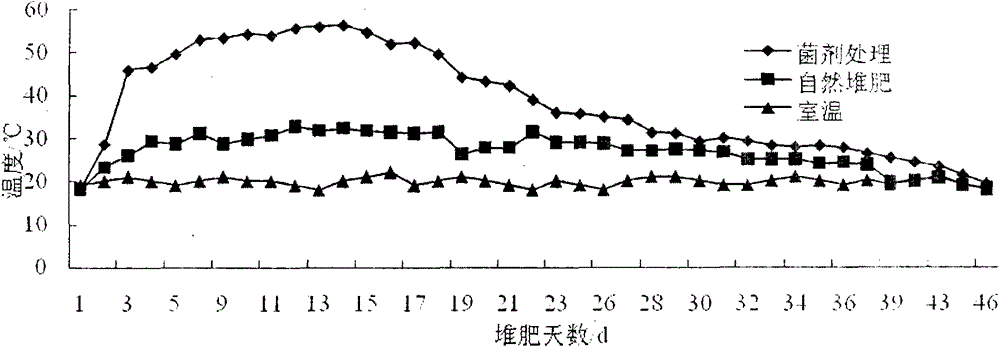
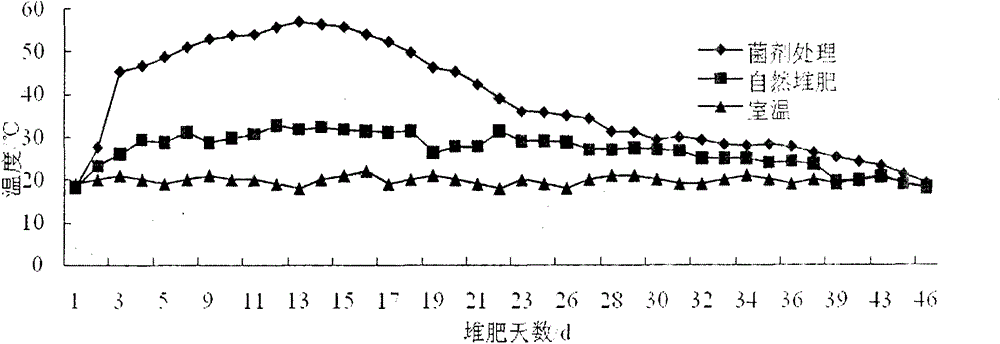
The invention relates to the technical field of straw degradation, in particular to a straw degradation actinomycete and application thereof. The straw degradation actinomycete belongs to streptomyces griseorubens (Streptomyces griseorubens), and the preservation serial number is CGMCC N0.5706. Compared with the prior art, the straw degradation actinomycete and the application have the advantagesthat the streptomyces griseorubens has strong capacity for producing cellulose, hemicellulase, pectinase and ligninase, is free of negative effects on carbon cycling of the nature, and is free of damage to the environment; the streptomyces griseorubens has strong straw degradation capability, enables straw weightlessness rate to achieve 76% after staying in a straw degradation culture medium for 30 days, and is low in culture cost, convenient to operate and easy to industrially apply; and the streptomyces griseorubens has certain antagonism on plant disease microorganism in the soil.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Complex microbial agent for composting fermentation and application thereof
InactiveCN103497915AQuick breakdownAccelerate the rate of decayBio-organic fraction processingFungiLivestock manureMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a complex microbial agent for composting fermentation and application thereof. The complex microbial agent is a solid inoculant which comprises phanerochaete chrysosporium, streptomyces griseorubens, bacillus subtilis, bacillus methylotrophicus and bacillus amyloliquefaciens. The complex microbial agent is a complex microbial system comprising various microorganisms which have complementary and synergistic functions; the microbial system integrates quick fermentation heat production, biological deodorization and compost material decomposition and degradation and has the effects of a biological fertilizer; the livestock manure compost can be quickly heated to kill off harmful organisms at high temperature; the unpleasant smell is obviously reduced to solve the problem of environment pollution caused by poultry excrement; the microorganisms can be quickly propagated in the poultry excrement fermentation process; the organic matters such as lignocellulose in the excrement can be quickly and effectively decomposed so as to increase the decomposition speed of the compost material and improve the quality of the compost product; the complex microbial agent can be used for producing the biological organic fertilizer so as to reduce the agricultural production cost.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Engineering bacteria based on beta-glucosidase and implementation method thereof
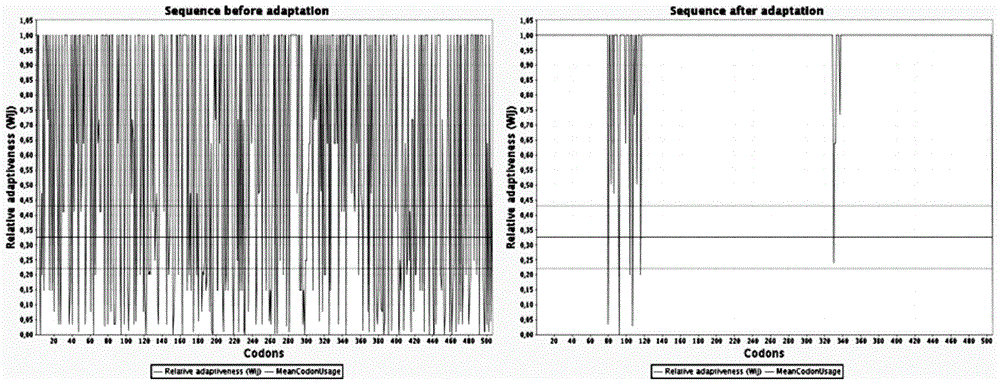
The invention provides engineering bacteria based on beta-glucosidase in the technical field of bioengineering and an implementation method thereof. A beta-glucosidase gene is cloned from Streptomyces griseorubens (Streptomyces griseorubens) JSD-1, and then is connected to an expression vector to obtain a recombinant expression vector, and the recombinant expression vector is further introduced into escherichia coli and is induced to synthesize beta-glucosidase. The engineering bacteria provided by the invention overcomes the defects that the beta-glucosidase in the prior art is generally endoenzyme and the expression quantity is very low, and the like, the beta-glucosidase gene of the invention is expressed by genetically engineered bacteria to prepare beta-glucosidase, and a new method is provided for producing beta-glucosidase by industrial fermentation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Straw composting bacterium agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a straw composting bacterium agent as well as a preparation method and application thereof and relates to the straw composting bacterium agent. The straw composting bacterium agent is compounded of 5-15 percent of bacillus subtilis powder, 50-70 percent of trichoderma longibrachiatum powder and 25-45 percent of streptomyces griseorubens powder. The preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively preparing zymophytes of bacillus subtilis, trichoderma longibrachiatum and streptomyces griseorubens and products thereof by adopting a solid fermentation method; drying and crushing to form the bacillus subtilis powder, the trichoderma longibrachiatum powder and the streptomyces griseorubens powder; mixing to obtain the straw composting bacterium agent. The straw composting bacterium agent can be applied to preparation of a straw composting and degrading agent.
Owner:FUJIAN SANJU BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH +1
Marine actinomycetes for generating antineoplastic compound Norharmane
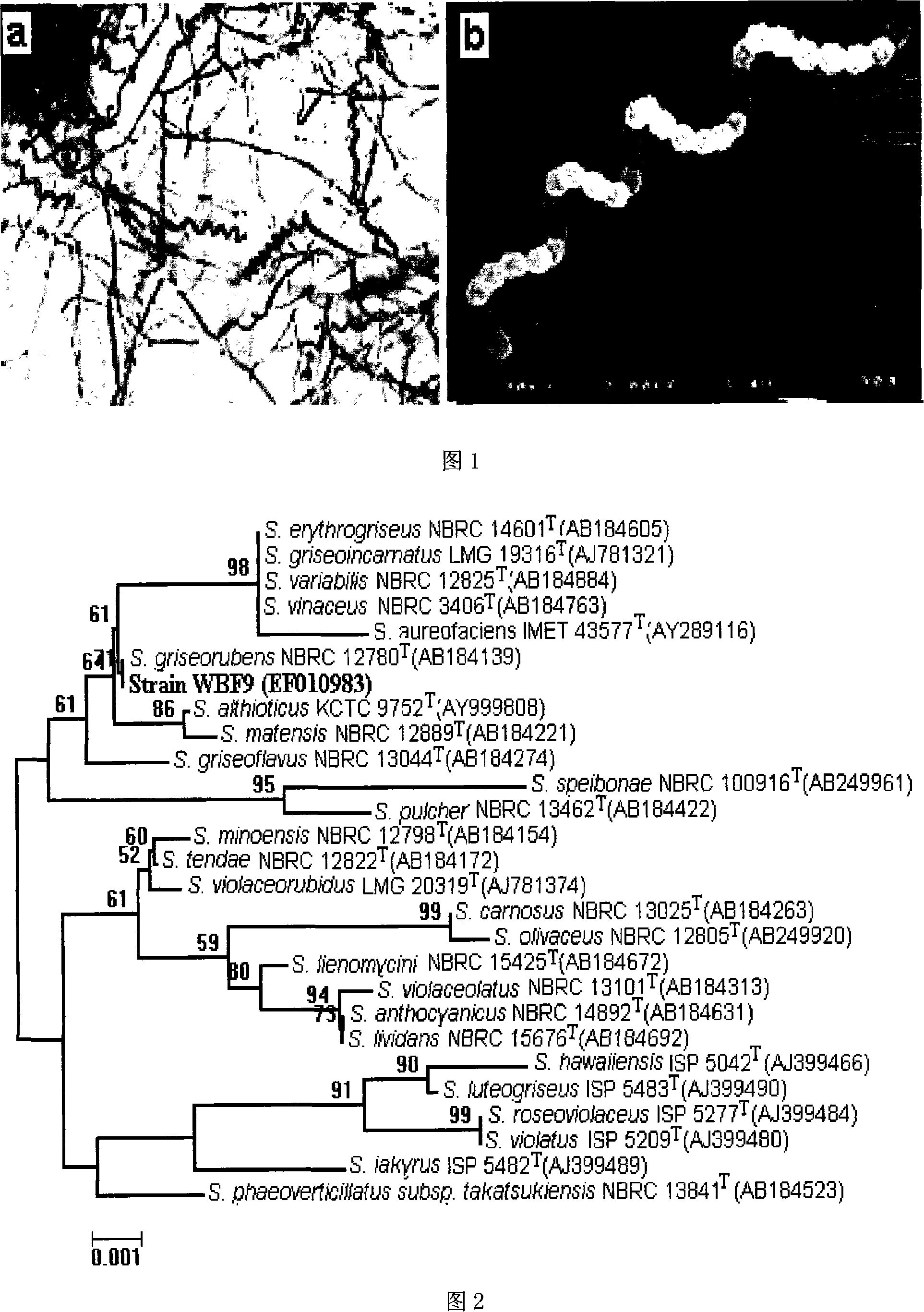
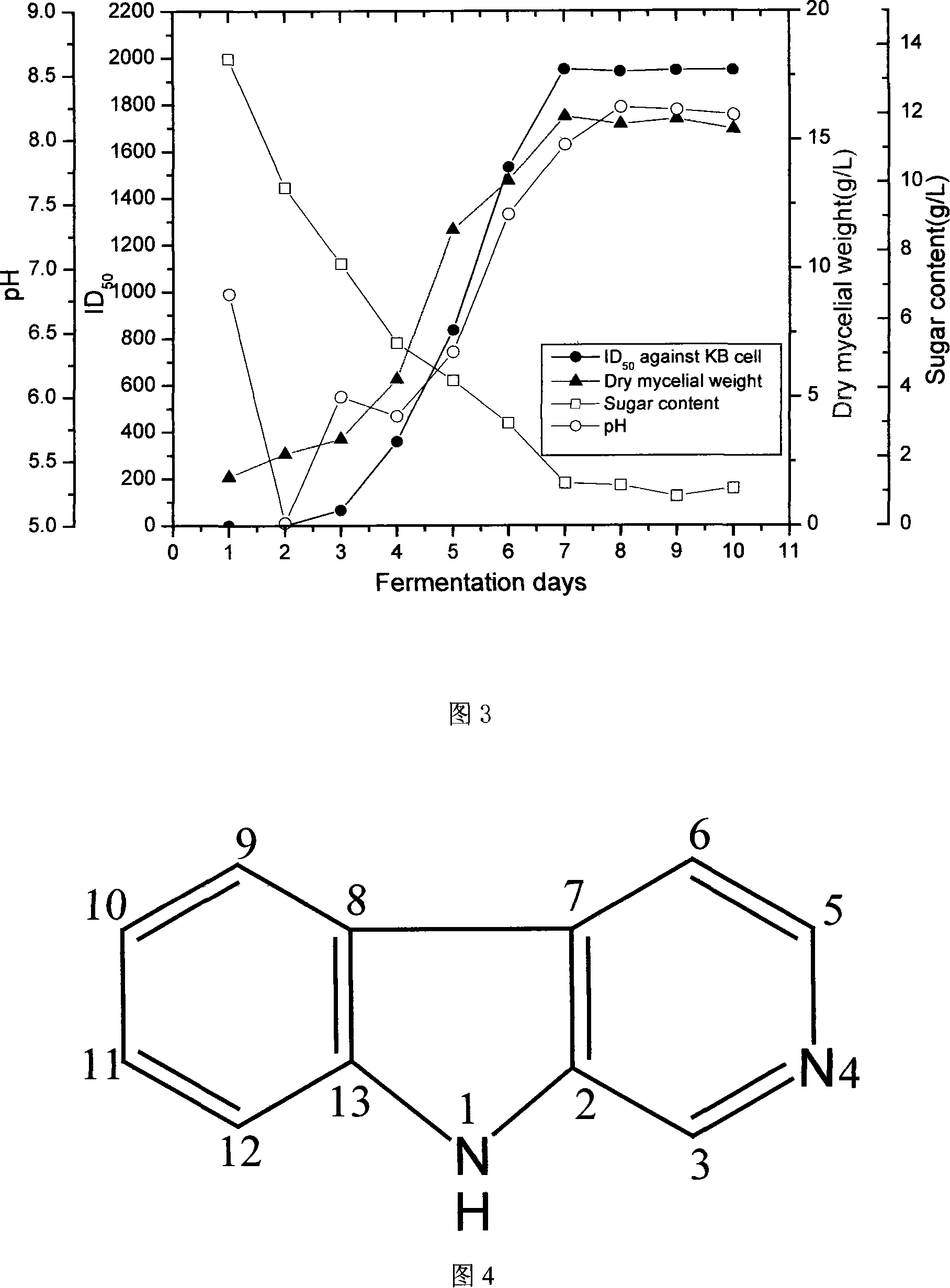
The invention relates to assessment and fermentation of marine actinomycete WBF9 that is used for producing anti-tumor compound and the separation and purification of the anti-tumor compound and the cytotoxic activity, and pertains to the microscopic organisms medicine filed. Bacterial strain WBF9, which is streptomyces griseorubens that is separated from the sea for the first time, is identified as one of the new bacterial strains of streptomyces griseorubens by traditionally classification and 16SrDNA genetic analysis. Culture medium (glucose: 1 percent, potato: 15 percent, yeast powder: 0.6 percent, calcium chloride: 0.12 percent and natural seawater, pH value 7.2) is applied by the bacterial strain for fermentation, and the compound extracted from the fermentation liquor, which has strong anti-tumor activity and identified as Norharmane by MS and NMR technique, is the first compound that is acquired by separating marine actinomycete. According to the MTT method, the compound is found to have cytotoxicity against four tumor cells: KB, BGC 803, Hep G2 and SGC 7901, and is a potential anti-tumor medicine.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
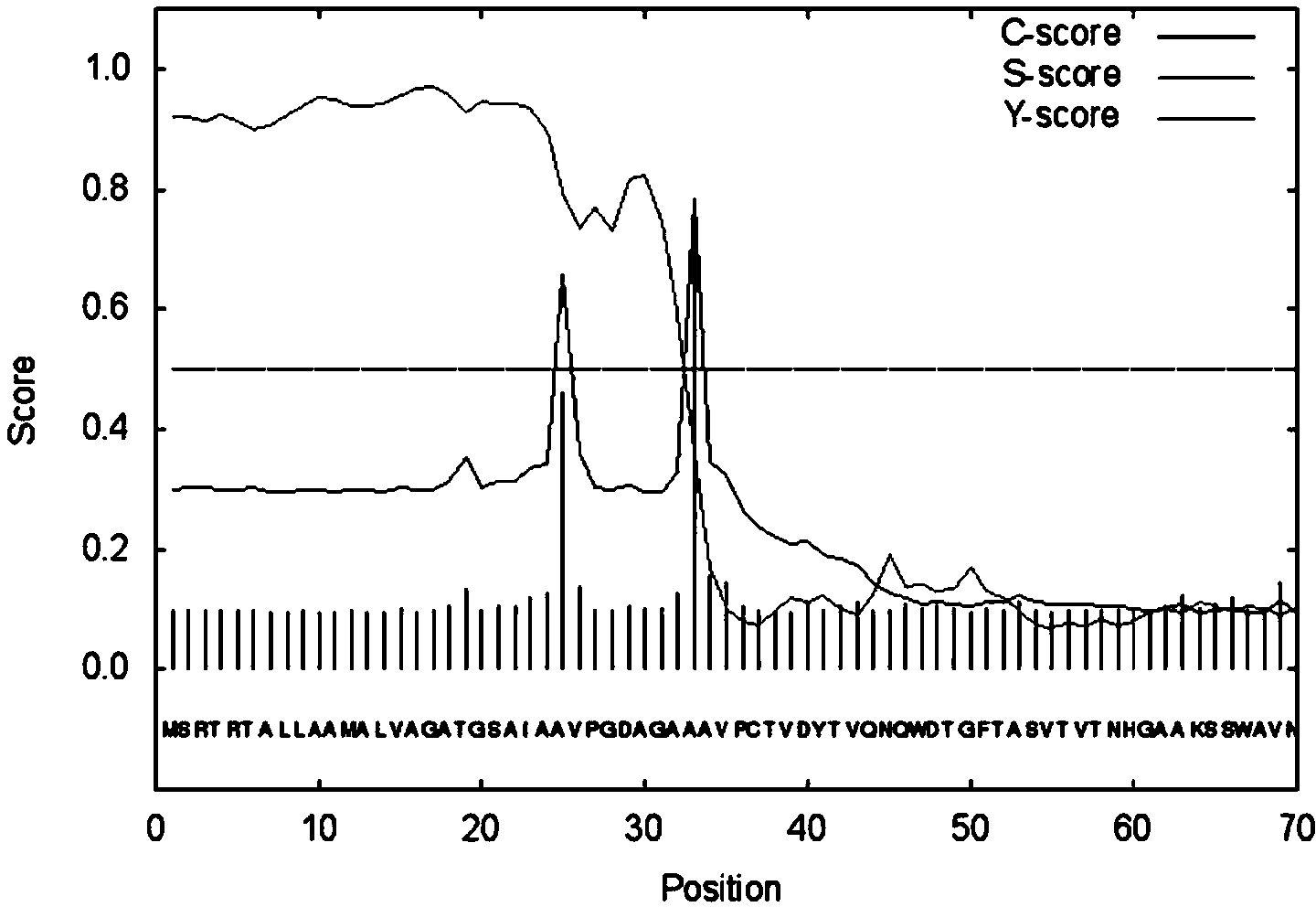
Engineering bacteria based on manganese peroxidase and implementation method of engineering bacteria
InactiveCN104232555AStable enzymatic propertiesAchieve periplasmic space expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme digestionProtein target
The invention provides engineering bacteria based on manganese peroxidase in the field of the genetic engineering and an implementation method of the engineering bacteria. The genome DNA of the streptomyces griseorubens is taken as a template, and PCR amplification is performed on the template and a primer containing an enzyme digestion site and a polyhistidine label so that the nucleotide sequence coding the manganese peroxidase can be obtained; next, the gene sequence obtained by amplification is connected to an expression vector, and then the obtained connection product is transferred into an escherichia coli expressed strain, and finally, the over-expressed recombinant strain of the manganese peroxidase is obtained. The engineering bacteria based on the manganese peroxidase are used for overcoming the shortage of seriously restricted application range and application effect because the manganese peroxidase mostly is an endoenzyme in vivo and is low in expression amount, and in-vitro mass expression and synthesis of the manganese peroxidase are realized by use of a genetic engineering method; besides, the purity of the purified manganese peroxidase is also guaranteed while the protein activity is improved by use of the method of adding the polyhistidine label to the C end of the expressed recombinant protein; in addition, the periplasmic space expression of the target protein is realized by use of a vector signal peptide and the activity of the manganese peroxidase is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Engineering bacterium based on lignin peroxidase and implementation method of engineering bacterium
InactiveCN104232556AEasy to purifyHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideRestriction site
The invention relates to an engineering bacterium based on lignin peroxidase and an implementation method of the engineering bacterium. The implementation method comprises the following steps: with DNA of a streptomyces griseorubens genome as a template, carrying out PCR amplification on the DNA of the streptomyces griseorubens genome and a primer containing a restriction site and a glutathione label to obtain a nucleotide sequence for coding the lignin peroxidase; and then connecting the gene sequence obtained by virtue of amplification to an expression vector, and then transferring an obtained ligation product to an escherichia coli expression strain to obtain a lignin peroxidase expression recombination strain. With the adoption of the implementation method, by virtue of methods of constructing a heterogeneous expression vector, optimizing conditions and fusion tags of protein inducing expression and the like, extracellular over expression of the lignin peroxidase is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Streptomyces lavendulae and application of Streptomyces lavendulae to preparation of algae microbial fertilizer
ActiveCN103540556ATo achieve an organic combinationImprove stress resistanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPathogenic microorganismStreptomyces griseochromogenes
The invention relates to a Streptomyces lavendulae strain, which is named as Streptomyces lavendulae in classification. The Streptomyces lavendulae strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with the preservation number of CGMCC No.7548. The invention also relates to application of the Streptomyces lavendulae to preparation of algae microbial fertilizer. The Streptomyces lavendulae strain provided by the invention has a prominent degrading effect on algae residues; waste residues generated after seaweed gel is extracted by the algae processing industry can be recycled, and antibiotic metabolic active substances generated in the fermenting process of the Streptomyces lavendulae can effectively inhibit growth of various pathogenic microorganisms; the Streptomyces lavendulae has excellent effects of promoting growth and increasing yield and has an obvious effect in agricultural production.
Owner:青岛藻源植物营养有限公司
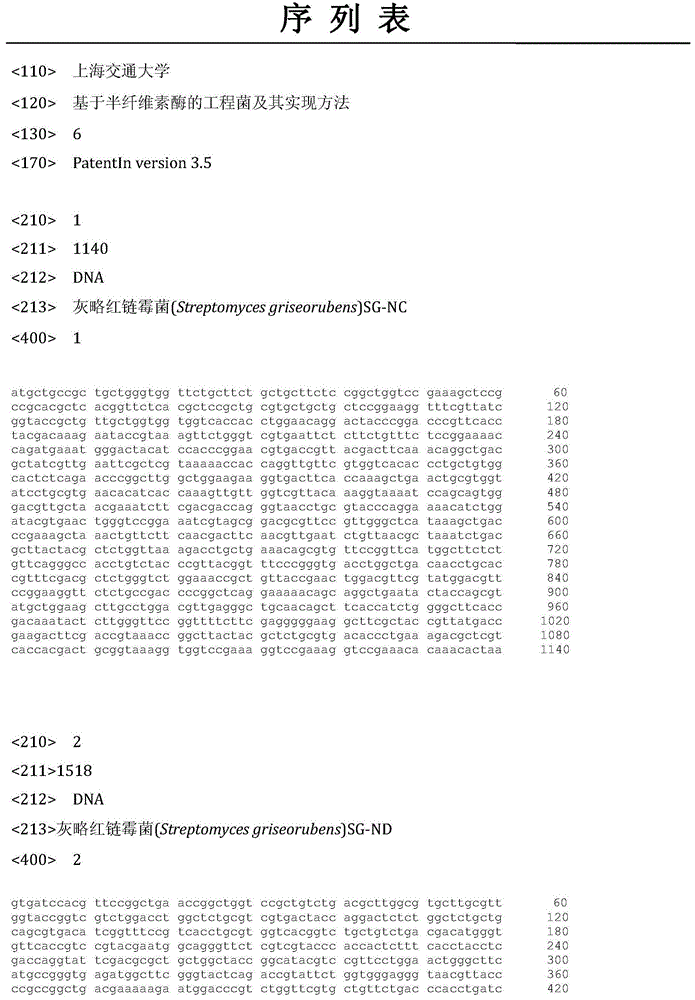
Streptomyces griseorubens pectinesterase as well as coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN106636035AAchieve high expression in vitroMaintain biological activityBacteriaHydrolasesProtein targetNucleotide
The invention discloses streptomyces griseorubens pectinesterase as well as a coding gene and an application thereof. The pectinesterase gene is cloned from streptomyces griseorubens; a nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 or is shown as SEQ ID NO.2 after codon optimization; an amino acid sequence of the coded pectinesterase is shown as SEQ ID NO.3; and the invention also discloses applications of the pectinesterase and the coding gene thereof in degrading pectin. According to the invention, by adding a soluble label to target protein and through peripheral space expression of the target protein, the bio-activity of the protein is guaranteed, and meanwhile, subsequent protein purification is facilitated. The pectinesterase is alkaline and high-temperature resistant, and the enzyme (pectinesterase) has a quite strong resisting capacity to a plurality of metal ions and enzymatic activity inhibitors; therefore, the enzyme has great significance in practical production and application.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Streptomyces murinus and application thereof
ActiveCN104726362AGrowth inhibitionInhibition of germinationBiocideBacteriaLasiodiplodia theobromaeSpore germination
The invention provides streptomyces murinus and application thereof. The streptomyces murinus is named streptomyces murinus FXQ-5B, is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on October 16, 2014, and has a preservation number of CCTCC M2014487. The streptomyces murinus FXQ-5B can be used for effectively inhibiting growth and spore germination of camellia oleifera leaf blight pathogen, has the advantages of remarkable prevention effect, no pollution and good environment safety, and has an excellent effect for inhibiting other bacteria, such as fusarium oxysporum, lasiodiplodia theobromae, diaporthe phaseolorum, bipolaris setariae, pestalotiopsis menezesiana and the like. The streptomyces murinus has broad-spectrum anti-disease, and has an important and profound significance for prevention and treatment of camellia oleifera and other diseases.
Owner:COCONUT RES INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Composite microbial agent for cassava residue matrix fermentation and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109749944AIncrease temperatureToxic reductionFungiBacteriaBacillus licheniformisMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a composite microbial agent for cassava residue matrix fermentation and a preparation method and application thereof. The composite microbial agent for cassava residue matrix fermentation comprises bacillus altitudinis, bacillus licheniformis, streptomyces griseorubens and trichoderma viride. The composite microbial agent for cassava residue matrix fermentation can accelerate temperature increase in the early stage of cassava residue fermentation, increase the fermentation temperature and prolong the time of the high-temperature period. The decomposition degree of a fermented product is reduced, the toxic effect on plants is reduced, and the fermentation quality is improved. The method has important scientific significance and application value on cassava residue matrix utilization.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Engineering bacteria based on nitrite reductase and implementation method of engineering bacteria
InactiveCN104152393AGuaranteed purityStable biological activityBacteriaClimate change adaptationNucleotideGenetic engineering
The invention relates to engineering bacteria based on nitrite reductase and an implementation method of the engineering bacteria in the technical field of genetic engineering. The method comprises the following steps: by taking streptomyces griseorubens genome DNA as a template, performing PCR amplification with a primer containing enzyme cutting sites to sequentially obtain nucleotide sequences for encoding nitrite reductase large-subunits and nitrite reductase small subunits; sequentially connecting the gene sequences obtained by amplification to a coexpression vector pETDuet-1, and finally obtaining a recombinant coexpression vector pETDuet-NC-ND; and transforming the nitrite reductase expression vector into an Escherichia coli expression strain. Aiming at the defects that the application range and effect are severely limited because most of the nitrite reductases are intracellular enzymes in a living body and the expression quantity is low in the prior art, the engineering bacteria can realize great in-vitro expression synthesis of the nitrite reductase by using genetic engineering means and has high significance for rapidly repairing secondary salinization soil and realizing precision agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Engineering bacteria based on glutamate synthase and implementation method thereof
InactiveCN104120103AGuaranteed purityStable biological activityBacteriaTransferasesNucleotideGenetic engineering
The invention relates to engineering bacteria based on glutamate synthase and an implementation method thereof in the technical field of genetic engineering. The implementation method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: taking a streptomyces griseorubens genome DNA as a template, and carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification with a primer containing an enzyme cutting site to obtain coded nucleotide sequences of glutamate synthase small subunit and large subunit in sequence; then, sequentially connecting the gene sequences obtained by amplifying to an expression vector pETDuet-1, thereby finally obtaining a recombination expression vector pETDuet-GG-GF; and converting the glutamate synthase expression vector into an escherichia coli expression strain. According to the invention, aiming at the disadvantages of being seriously limited in application range and effect and the like because most of glutamate synthase is intracellular enzyme in living bodies and the expression quantity is lower in the prior art, in-vitro mass expression synthesis is realized by using genetic engineering means; and furthermore, protein purification in the later period is convenient by adding polyhistidine tags in recombinant protein.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Engineering bacterium based on glutamate dehydrogenase and implementation method of engineering bacterium
InactiveCN104498419AGuaranteed purityStable biological activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesStreptomycesRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention relates to a streptomyces griseorubens intracellular glutamate dehydrogenase coding gene and application thereof. The glutamate dehydrogenase coding gene is constructed onto an expression vector, and the recombinant expression vector is introduced into escherichia coli, so that transgenic recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing glutamate dehydrogenase in a fermentation manner is obtained. The defect that application range and effect are seriously restricted as glutamate dehydrogenase is obtained in an intracellular expression manner and expression quantity is low in the prior art is overcome, and in-vitro high expression and synthesis of glutamate dehydrogenase are realized by applying a genetic engineering technique; besides, purification of protein in a late phase is facilitated by adopting a method of adding a histidine tag in recombinant protein. The invention provides a new method for large-scale fermentation production of glutamate dehydrogenase.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Thermostable streptomyce, microbial soil reducing agent, and preparation method and application of microbial soil reducing agent
ActiveCN111004750AAdjust pH valueAutomatic neutralization of pHAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaStreptomyces thermophilusBacilli
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil reducing agent preparation, particularly relates to a microbial soil reducing agent, and a preparation method and an application thereof, and provides a microbial soil reducing agent capable of improving soil acidity and alkalinity imbalance, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The microbial soil reducing agent comprises, by volume, Streptomyces thermophilus, Streptomyces griseorubens and Bacillus subtilis; and the effective viable count ratio of the Streptomyces thermophilus to the Streptomyces griseorubens to the bBacillussubtilis is (5-7):(7-9):(4-6). The microbial soil reducing agent thermostable bacterium can adjust soil nutrient balance and improve soil acidity and alkalinity, and also can inhibit soil-borne diseases, promote crop growth and improve crop quality.
Owner:FUJIAN SANJU BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Hemicellulase-based engineering bacteria and realization method thereof
InactiveCN104152392AAchieve in vitro co-expressionHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideXylanase
The invention relates to hemicellulase-based engineering bacteria in the technical field of genetic engineering and a realization method thereof. The realization method comprises the following steps: firstly, by taking a vector pUC57-XL obtained by whole gene synthesis of streptomyces griseorubens genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) as a template, performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the vector and a primer with an enzyme cutting site to obtain a nucleotide sequence XL for coding xylanase and a nucleotide sequence XO for coding xylosidase correspondingly and respectively; secondly, connecting the gene sequences obtained by amplification to a coexpression vector pETDuet-1 in sequence, and finally recombining a coexpression vector pETDuet-XL-XO; thirdly, converting the recombinant coexpression vector to an escherichia coli expression strain so as to obtain a transgenic coexpression strain. Therefore, a large quantity of xylanase and xylosidase can be expressed and synthesized in vitro by using genetic engineering means, and finally hemicellulose can be quickly degraded in situ.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Engineering bacterium based on exoglucanase and realization method thereof
InactiveCN104232558AEasy to purifyHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesStreptomycesGlucanase
The invention provides an engineering bacterium based on exoglucanase and a realization method thereof in the field of gene engineering. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out PCR amplification on DNA of a streptomyces griseorubens genome serving as a template and primers containing cleavage sites and glutathione tags to obtain a nucleotide coding exoglucanase; then, connecting the gene sequence obtained by amplification to an expression vector; and transferring the obtained connecting product to an escherichia coli expressed strain to obtain over-expressed recombinant strain of exoglucanase. According to the method, extracellular overexpression of exoglucanase is realized by methods of constructing a heterogenous expression vector, optimizing protein induced expression conditions and fusing tag and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Composite bacterial agent for composting fermentation and its application
InactiveCN103497915BQuick breakdownAccelerate the rate of decayFungiBio-organic fraction processingCelluloseLivestock manure
The invention discloses a complex microbial agent for composting fermentation and application thereof. The complex microbial agent is a solid inoculant which comprises phanerochaete chrysosporium, streptomyces griseorubens, bacillus subtilis, bacillus methylotrophicus and bacillus amyloliquefaciens. The complex microbial agent is a complex microbial system comprising various microorganisms which have complementary and synergistic functions; the microbial system integrates quick fermentation heat production, biological deodorization and compost material decomposition and degradation and has the effects of a biological fertilizer; the livestock manure compost can be quickly heated to kill off harmful organisms at high temperature; the unpleasant smell is obviously reduced to solve the problem of environment pollution caused by poultry excrement; the microorganisms can be quickly propagated in the poultry excrement fermentation process; the organic matters such as lignocellulose in the excrement can be quickly and effectively decomposed so as to increase the decomposition speed of the compost material and improve the quality of the compost product; the complex microbial agent can be used for producing the biological organic fertilizer so as to reduce the agricultural production cost.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
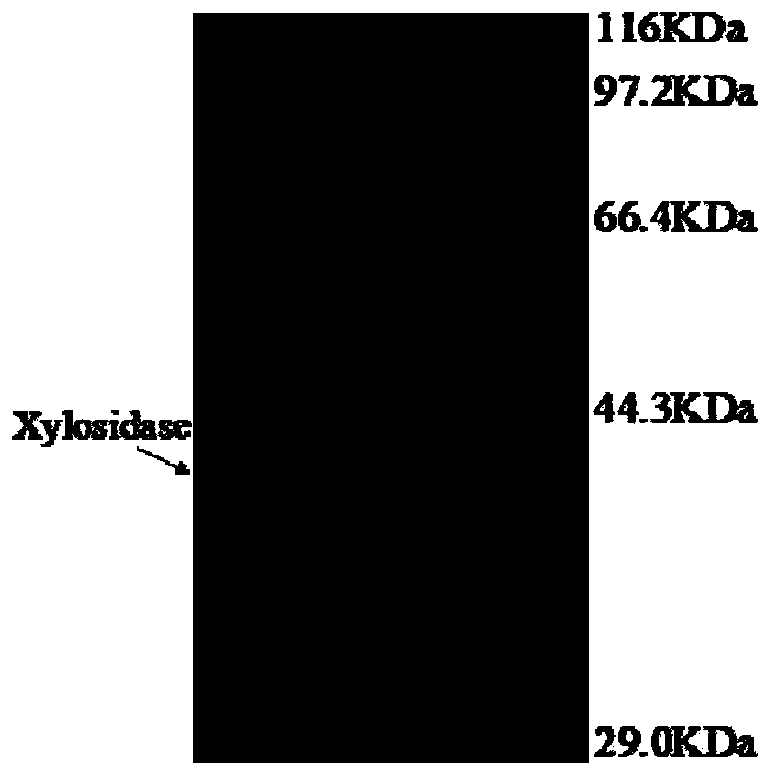
Xylosidase-based engineering bacterium and realization method thereof
InactiveCN104232554AStrong toleranceEasy to purifyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesProtein targetNucleotide
The invention relates to a xylosidase-based engineering bacterium. The realization method of the xylosidase-based engineering bacterium comprises the following steps: by taking streptomyces griseorubens genome DNA as a template, performing PCR amplification together with a primer containing restriction enzyme cutting sites and a poly-histidine tag to obtain a nucleotide sequence for coding xylosidase; then connecting the gene sequence obtained by amplification to an expressive carrier, and transforming the obtained connection product into an escherichia coli expression strain to obtain a xylosidase-overexpressed recombinant strain. Aiming at deficiencies that the majority of xylosidase is endoenzyme in a biological body, and low expression quantity causes seriously limited application range and effect in the prior art, a great amount of expression synthesis of the xylosidase in vitro can be realized by applying gene engineering means; in addition, by adopting a method of adding the poly-histidine tag on the C end of the expressive recombinant protein, the purity of the purified xylosidase can be guaranteed while the protein activity is improved; in addition, expression of periplasmic space of a target protein can be realized by a carrier signal peptide, and the activity of the xylosidase can be enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Compound microbial fertilizer
InactiveCN107266261ARaise the pHPH effectBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersAzotobacter chroococcumNutrient solution
The invention discloses a compound microbial fertilizer. The compound microbial fertilizer is obtained by fully mixing 30-50 mass parts of straw, 20-40 mass parts of chicken manure, and 20-30 mass parts of a mixed bacterial solution, and performing composting fermentation. The mixed bacterial solution is formed by mixing of a mixed inoculant, an EM inoculant and a nutrient solution according to a mass ratio of 2:1:7, and the mixed inoculant is formed by mixing of, by mass, 20% of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, 15% of Streptomyces griseorubens, 5% of trichoderma atroviride, 25% of bacillus subtilis, 10% of azotobacter chroococcum, 10% of aspergillus, 10% of bacillus circulans and 5% of pseudomonas. Through screening of appropriate strain and nutrient solution, the compound microbial fertilizer can effectively improve soil quality and provide nutrients necessary for plants safely and environmentally friendly.
Owner:长沙小新新能源科技有限公司
Extract with nematode inhibiting effect, streptomyces and applications of extract and streptomyces
The invention discloses an extract with a nematode inhibiting effect, streptomyces and applications of the extract and the streptomyces. The invention provides a method for preparing a streptomyces griseorubens fermentation product. The method comprises the following steps: fermenting streptomyces griseorubens MS180023 to obtain a fermentation product. The invention also provides a method for preparing the streptomyces griseorubens extract. The method comprises the following steps: taking a supernatant of the fermentation product, performing extracting with an organic reagent, and collecting an extracting solution; and carrying out reduced pressure distillation on the extracting solution to remove an organic solvent so as to obtain the extract. The invention also protects the streptomyces griseorubens MS180023. The invention also protects the applications of the streptomyces griseorubens MS180023, the fermentation product, the supernatant of the fermentation product or the extract: the application of the streptomyces griseorubens MS180023 in preparation of a nematode inhibitor; and (b) the application of the compound in inhibition of nematodes.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Engineering bacteria based on glutamine synthetase and implementation method of engineering bacteria
InactiveCN104140945AGuaranteed purityStable biological activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIn vivoBacterial strain
The invention discloses engineering bacteria based on glutamine synthetase and an implementation method of the engineering bacteria in the genetic engineering technical field. The method includes the steps of firstly, conducting PCR amplification on primers containing enzyme cutting sites with the streptomyces griseorubens genome DNA serving as a template so as to obtain glutamine synthetase encoding genes; secondly, inserting the genes into the escherichia coli expression vector pET-22b(+) to obtain a recombinant expression vector containing the glutamine synthetase encoding genes; thirdly, introducing the recombinant expression vector into escherichia coli expression bacterial strains, and conducting screening to obtain the engineering bacteria of glutamine synthetase. In order to overcome the defects that in the prior art, due to the fact that glutamine synthetase is generally endoenzyme in vivo and the expression quantity is low, the application range and the effect are seriously limited, a large amount of glutamine synthetase can be expressed and synthesized in vitro through the genetic engineering means.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Marine streptomyces griseorubens HN60 and application thereof
ActiveCN111748489AGood antitumor activityEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyStaphylococcus
The invention belongs to the field of marine actinomycete resource development and utilization, and particularly relates to marine streptomyces griseorubens HN60 and an application thereof. The marinestreptomyces griseorubens HN60 is used as a production strain of actinomycin V and actinomycin D, a pH value of the culture medium is 7.2-7.4, and a culture medium comprises 10g of malt extract powder, 4g of glucose, 4g of yeast extract powder and 1L of natural seawater. The extracted actinomycin V and actinomycin D have good anti-staphylococcus aureus activity.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
Prokaryotic expression method of streptomyces murinus AMP (Adenylate) deaminase gene and application of expression product of gene
InactiveCN103773792AIncrease enzyme activityImprove thermal stabilityHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesThiogalactosidesAMP deaminase
The invention discloses a prokaryotic expression method of a streptomyces murinus AMP (Adenylate) deaminase gene. The method comprises the following steps: amplifying AMP deaminase gene sequence by designing a specific primer by taking a streptomyces murinus genome as a template, adding cleavage sites at two ends of the sequence, performing subcloning to an expression carrier to construct recombinant plasmids, further converting the recombinant plasmid into escherichia coli competence, and finally performing IPTG (Iisopropyl-beta-d-Thiogalactoside) inducible expression and purifying to obtain a final AMP deaminase expression product. According to the method, AMP deaminase from the streptomyces murinus is successfully expressed in escherichia coli for the first time, the experimental result shows that a recombinant enzyme is high in enzyme activity, stable in enzyme activity and easy to purify, can be applied to the fields of foods and medicines, and lays the foundation for industrial production of the AMP deaminase.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
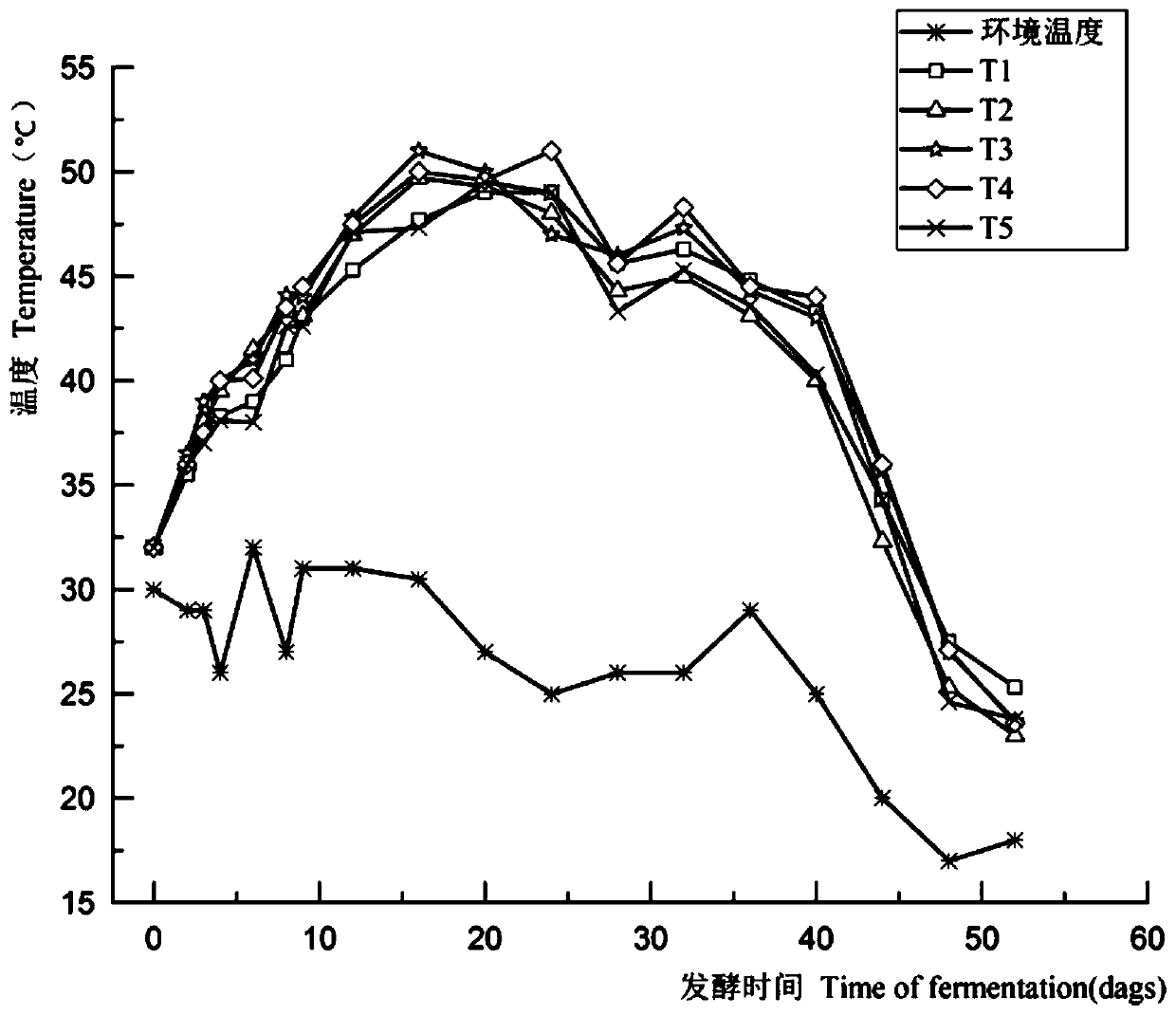
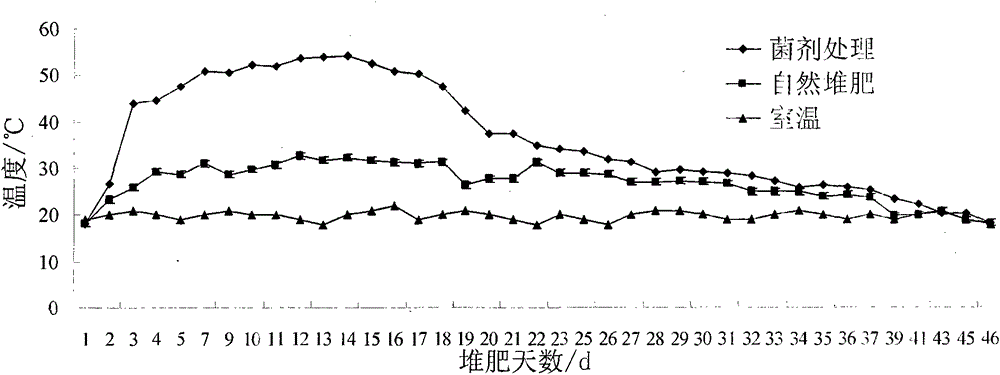
Application of high-temperature-resistant streptomycete in agricultural waste compost
InactiveCN104355690APromote degradationImprove conversion abilityBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention discloses a high-temperature-resistant actinomycete which can efficiently degrade and convert rice straw and nitrogen in pig manure. The actinomycete disclosed by the invention belongs to streptomyces griseorubens with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 5706. The actinomycete can strongly degrade methyl cellulose in the rice straw, further can quickly convert nitrate nitrogen and organic nitrogen in the pig manure, and tolerates the high temperature of more than 70 DEG C; the actinomycete can be added to the mixed compost of rice straw and pig manure to obviously rise the compost temperature, shorten the fermentation cycle, and improve the quality and the yield of the organic fertilizer; in addition, the organic fertilizer inoculated with the solid bacteria agent can quickly fertilize soil, so as to increase the content of the organic fertilizer, total nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen, activate the soil enzyme activity, and finally increase the yield of the crop.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Flora for degrading corn straw to produce polysaccharide and microbial ratio of flora
PendingCN112662577AWide variety of sourcesEasy to buildBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention discloses a flora for degrading corn straw (hereinafter referred to as straw) to produce polysaccharide, and belongs to the technical field of solid waste disposal. The mixed flora comprises streptomyces griseorubens, streptomyces carpaticus and streptomyces rochei, and the inoculation amount is 1:1:1. The degrading strains are respectively named ye-9, er-72 and se-93, and are preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), the preservation numbers are respectively 18289, 18290 and 18291, and the preservation date is July 24th, 2019. According to the invention, a single strain is primarily screened from a sample, and the primarily screened single strain is secondarily screened by taking the activities of four enzymes, namely cellulose whole enzyme, incision enzyme, excision enzyme and beta-glucosidase, as indexes. The strains which are obtained by secondary screening and have a good degradation effect are obtained through screening, the enzyme activity is determined, and efficient mixed flora is picked out. The straw degradation effect of the mixed flora is better than that of a single strain, and the polysaccharide yield is as high as 2159.23 mg / L under the optimized fermentation condition. A basis is provided for microbial degradation of the straws, and resource utilization of the straws is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Composite microbial agent for efficiently converting crop straw and preparation method and application of composite microbial agent
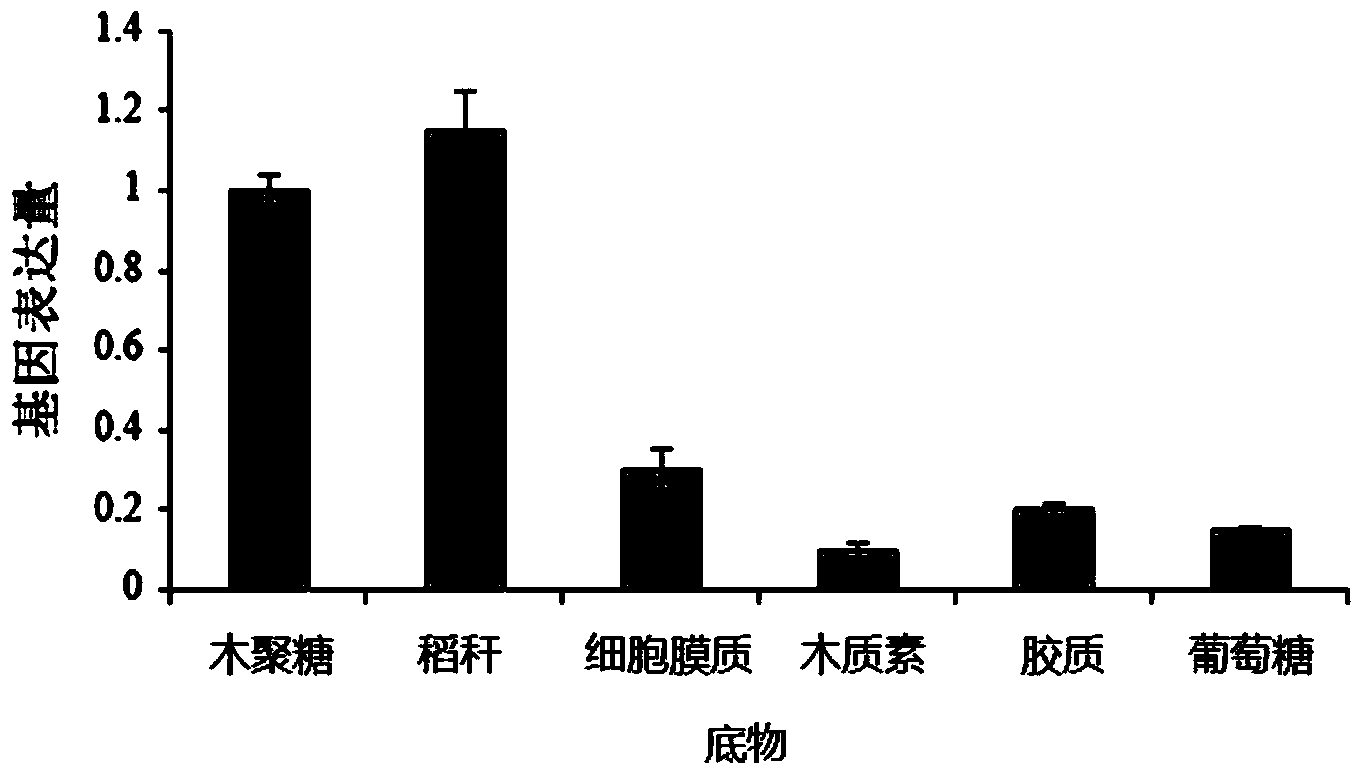
The invention relates to a composite microbial agent for efficiently converting crop straw and a preparation method and application of the composite microbial agent and belongs to the technical fieldof biological agriculture. The problems are solved that in the prior art, the crop straw resource recycling utilization efficiency is low, and the conversion effect needs to be improved. The compositemicrobial agent for efficiently converting the crop straw is prepared by mixing composite flora and a fixing agent, and the composite flora is prepared from, by mass, 37-43% of streptomyces griseorubens, 27-33% of aspergillus niger and 27-33% of trichoderma viride. According to the application, the composite microbial agent is dissolved in water to prepare a composite microbial solution, and thesurface of the crop straw is sprayed with the composite microbial solution for conversion. In order to meet the growth demand of the composite flora in the continuous fermentation process, by generating cellulase and ligninase, all the components of the crop straw are converted to generate small molecule reducing sugar such as glucose and xylose. The selected composite flora can stably achieve a conversion function and has a good effect.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Engineering bacteria based on nitrate reductase and implementation method of engineering bacteria
InactiveCN104140944AGuaranteed purityStable biological activityBacteriaClimate change adaptationNucleotideIn vivo
The invention relates to engineering bacteria based on nitrate reductase and an implementation method of the engineering bacteria. The method includes the steps of firstly, conducting PCR amplification on primers containing enzyme cutting sites with the streptomyces griseorubens genome DNA as a template to sequentially obtain the nucleotide sequence of encoding nitrate reductase catalysis subunits and the nucleotide sequence of electron transfer subunits; secondly, sequentially connecting the gene sequence obtained through amplification to the co-expression vector pETDuet-1; thirdly, obtaining the recombination co-expression vector pETDuet-NB-NA; fourthly, converting the nitrate reductase expression vector into escherichia coli expression strains. In order to overcome the defects that nitrate reductase is generally endoenzyme in vivo and the expression quantity is low, the application range and the effect are seriously limited, a large amount of nitrate reductase can be expressed and synthesized in vitro through the genetic engineering means. The engineering bacteria and the method have great significance in rapid repair of secondary salinization soil and even the achievement of precision agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Agricultural straw waste aerobic zymophyte combined fungus bag
PendingCN114752521AEfficient degradationImprove degradation efficiencyFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyTotal nitrogen
The invention provides an agricultural straw waste aerobic zymophyte combined fungus bag which comprises trichoderma koningii, aspergillus oryzae, bacillus subtilis and streptomyces griseorubens, the ratio of the trichoderma koningii to the aspergillus oryzae to the bacillus subtilis to the streptomyces griseorubens is (4-15): (3-12): (2-8): (5-10) in terms of CFU, and the number of colonies contained in any zymophyte in the combined fungus bag is not lower than 5 * 10 < 9 > CFU / g. By applying the combined fungus bag provided by the invention, the temperature of a straw pile body can be increased, the synthesis and degradation of substances in the pile body can be enhanced, the fermentation time can be effectively shortened, the loss of total nitrogen in the pile body can be reduced, the nutrient level in a decomposed pile material can be increased, and the fertility of straw compost can be maintained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG YIBAO BIOTECH CO LTD
A straw decomposing bacterial agent and its preparation method and application
The invention discloses a straw composting bacterium agent as well as a preparation method and application thereof and relates to the straw composting bacterium agent. The straw composting bacterium agent is compounded of 5-15 percent of bacillus subtilis powder, 50-70 percent of trichoderma longibrachiatum powder and 25-45 percent of streptomyces griseorubens powder. The preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively preparing zymophytes of bacillus subtilis, trichoderma longibrachiatum and streptomyces griseorubens and products thereof by adopting a solid fermentation method; drying and crushing to form the bacillus subtilis powder, the trichoderma longibrachiatum powder and the streptomyces griseorubens powder; mixing to obtain the straw composting bacterium agent. The straw composting bacterium agent can be applied to preparation of a straw composting and degrading agent.
Owner:FUJIAN SANJU BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com