Flora for degrading corn straw to produce polysaccharide and microbial ratio of flora
A technology for corn stalks and stalks, which is applied to microorganisms, isolated microorganisms, microorganism-based methods, etc., can solve problems such as poor degradation effect, and achieve the effects of high degradation efficiency, high polysaccharide yield, and high cellulose-degrading enzyme activity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1: Screening of degrading straw-producing polysaccharide-degrading bacteria and the construction of bacterial colonies
[0040] (1) Enrichment
[0041] Add 50g of straw powder to a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask, sterilize at 121°C for 40min, add 2g of soil sample, and incubate at 30°C for 20 days.
[0042] (2) Primary screening of cellulose degrading bacteria
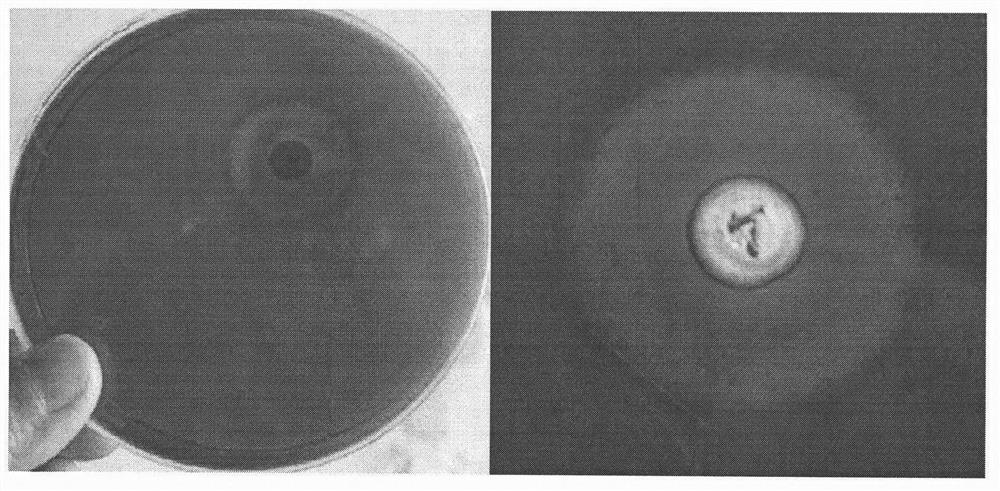
[0043] Take 1g of the enriched material in (1) in a Erlenmeyer flask filled with 99ml of sterile water, incubate on a constant temperature shaker for 45 minutes with shaking at a speed of 120 times per minute, and apply the supernatant to sodium carboxymethylcellulose On a solid medium, culture at a constant temperature of 30°C. After colonies grow out, pure colonies are isolated by streaking.
[0044] Place the single strains screened for the first time in the cellulose Congo red medium, culture at 30°C for 3 days, measure the ratio of the transparent circle to the colony diameter, select the strain with a la...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Example 2: Degradation efficiency of the constructed flora to corn stalks
[0070] (1) Quantitative determination of corn stalk cellulose
[0071] Dry corn stalks (hereinafter referred to as: stalks) to constant weight, add 0.5 g of stalks to the Erlenmeyer flask, and then add 50 mL of enzyme-producing medium, place the high-efficiency flora constructed in Example 1 in sodium carboxymethyl cellulose Activated in the medium for 2 days, transferred to the enzyme-producing medium at 30°C, 120r / min, and cultivated for 8 days. On the 8th day, the straw was taken out and the weight loss rate and the content of each component of the straw were measured.
[0072] (2) Determination and change trend of each component content of straw
[0073] The content of each component (cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin) in straw was determined by differential gravimetric method.
[0074] The result is as follows:
[0075] Such as image 3 As shown in Table 3, the contents of the three majo...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Example 3: Determination of the content of polysaccharides produced by degrading corn stalks by the constructed flora
[0083] The mensuration method of polysaccharide content adopts 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid method (hereinafter referred to as: DNS method) to draw glucose standard curve, and contrast standard curve asks sugar content, concrete steps are:
[0084] (1) Activation of bacteria
[0085] Use an inoculation loop to inoculate the strain into 50ml of activation medium, activate at 30°C, 120r / min for 48h.
[0086] The activation medium formula is: 15g CMC-Na, 1g yeast extract, 1g NH 4 NO 3 , 1g KH 2 PO 4 , 0.5gMgSO 4 , 0.5g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 20g agar, 1000mL distilled water, natural pH.
[0087] (2) Treatment of fermentation broth
[0088] Add 50 mL of straw fermentation medium into the Erlenmeyer flask, and sterilize at 121 °C for 20 min. Then inoculate it with 4% (2ml) of the flora suspension described in (1), and cultivate it at 30°C for 2 days at 120r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com