Human ochrobactrum anthropi and its application in degrading plant stalks and preparing important enzyme
A technology of Pallidum pallidus and straw, which is applied in the field of Pallidinus pallidus, can solve problems such as difficulties, complex chemical structures, and difficult degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Fermentation test of Pallidum pallidus:
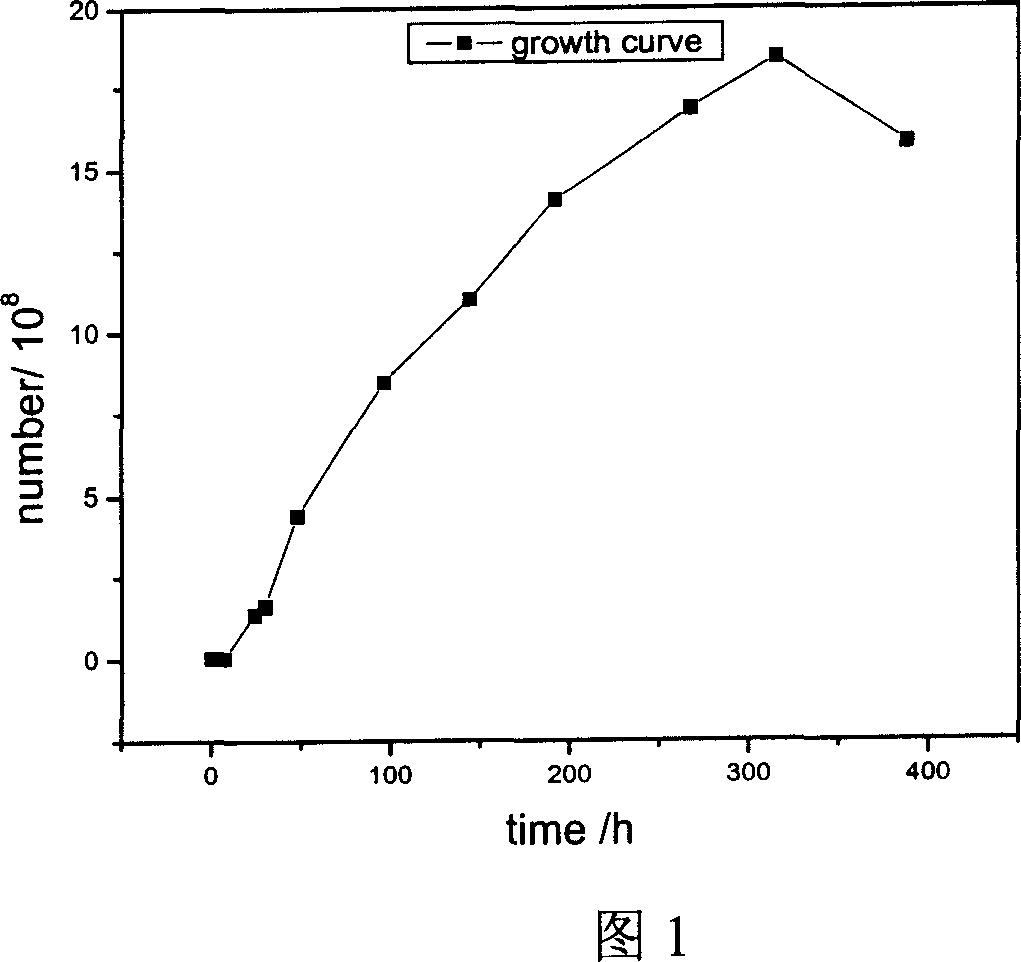
[0065] Pick a single colony of Pallidum human from the plate and inoculate it into the seed medium of M9+ bagasse (5g / L), the pH of the seed medium is 6.7, the filling volume is 50ml / 250ml shake flask, the conditions of 30°C and 200rmp The number of cells can reach 8.0*10 in shake flasks for four days 9 about. Take 0.5ml and inoculate it into the fermentation medium of M9+bagasse (5g / L). The fermentation conditions are the same as those of seeds. After five days of cultivation, the number of cells can reach 1.4*10 10 . The total amount of starch, crude protein, soluble sugar and uronic acid contained in the bagasse we prepared is 102mg / g, and these small molecular substances that can be used for bacterial growth can only be used for bacterial growth up to 10 9 Left and right, it can be seen that the bacteria also utilize macromolecular substances such as lignocellulose. In addition, the bacteria we have tested can produce ce...
Embodiment 2~4
[0072] Comparative experiment on the growth of Pallidum hominis in "modified M9 medium" with boiled, acid-treated or alkali-treated bagasse as the sole carbon source
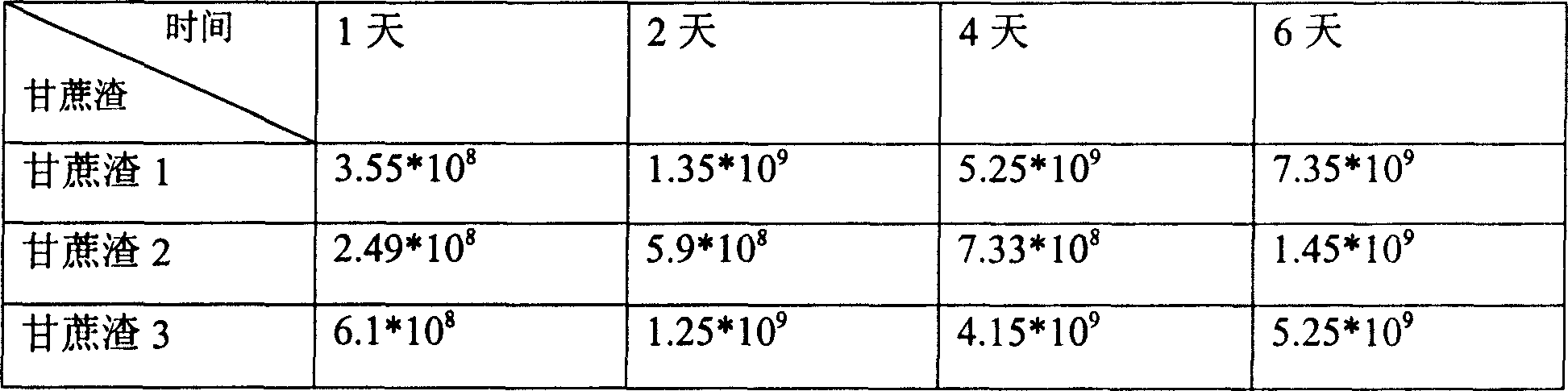
[0073] Bagasse 1: Bagasse—boil for 30 minutes (volume of water: bagasse=2:1) and boil three times continuously—dry at 65°C—crushed—pass through a 40-mesh sieve.
[0074] Bagasse 2: Bagasse—in hydrochloric acid with a weight concentration of 20%, soaking for 3 hours—drying at 70°C—crushing—passing through a 40-mesh sieve.
[0075] Bagasse 3: bagasse—in 2% NaOH by weight concentration, soaking for 2 hours—drying at 70° C.—crushing—passing through a 40-mesh sieve.
[0076] The "modified M9 medium" with bagasse 1, 2, and 3 as the sole carbon source was used as the fermentation medium, and the fermentation conditions were the same as in Example 1.
[0077] After culturing for 1 day, 2 days, 4 days, and 6 days, the following conclusions were drawn by counting:
[0078]
[0079] It can be seen that the acid trea...
Embodiment 5
[0081] Cellulase Qualitative Test
[0082] Solid medium: Na 2 HPO 4 0.6%, KH 2 PO 4 0.3%, NH 4 Cl 0.1%, NaCl 0.05%, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose 1%, agar 2%, balance: distilled water.
[0083] Seed medium: Na 2 HPO 4 0.6%, KH 2 PO 4 0.3%, NH 4 Cl 0.1%, NaCl 0.05%, bagasse 0.5%, balance: distilled water.
[0084] Seed fermentation condition is identical with embodiment 1. After two days of seed fermentation, take 0.1ml of the seed solution and dilute it with an appropriate gradient and spread it on a plate. Place the plate in an incubator at 37°C and cultivate it for a week. After a week of cultivation, the colony is about 1.5mm in size. Add 0.1% Congo red to the plate and stain it with 1 equivalent of NaCl for half an hour. The result of decolorization for 1 minute is shown in Figure 2, and a clear transparent circle appears. Because Congo red can combine with carboxymethyl cellulose, the flat panel appears red. If the bacteria can degrade cellulose, a transpa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com