Method for producing acetoin through high-efficiency fermentation by appropriately expressing novel bacillus subtilis NADH oxidizing enzyme
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and oxidase, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering to achieve the effect of shortening the fermentation period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Example 1: Construction of bdhA gene-deleted strains by means of genetic engineering
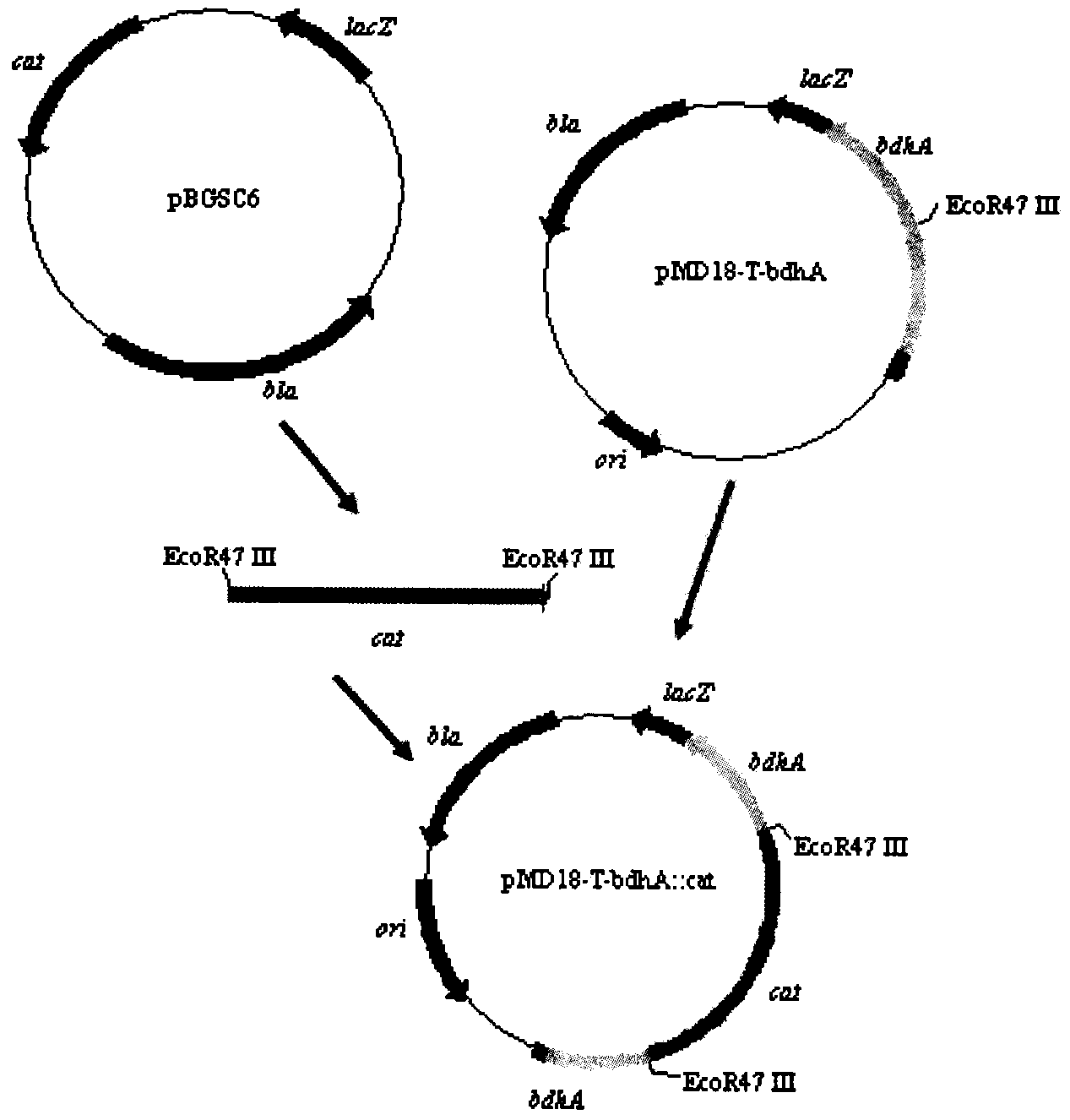
[0017] Construct the bdhA gene fragment of the reporter gene insertion inactivation, use primers P1 and P2 to clone the complete expression gene fragment of the cat gene from the pBGSC6 plasmid, then use EcoR47III to treat the fragment recovered from the gel, and finally treat the gene fragment with alkaline phosphatase and remove Connect with T-bdhA after the same treatment, transform Escherichia coli JM109, and screen positive clones on ampicillin and chloramphenicol double resistance plates. The constructed T-bdhA::cat was transformed into B. subtilis JNA, and the bdhA gene-deleted recombinant strain was screened on a chloramphenicol plate. Colony PCR and enzyme activity verification experiments were performed to confirm whether the bdhA gene was successfully inserted and inactivated.
[0018] P1: 5'-CGCAGCGCTAAAAAAGGATTGATTCTAATG-3' (Eco47III)
[0019] P2: 5'-CGCAGCGCTTAGTGACATTA...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Example 2: NADH oxidase primer design
[0022] First, using the chromosomal DNA of the bacterial strain B. subtilis JNA as a template, using primers P3, P4, P5, P6, P7, P8, P9 and P10, a section of ydfN, ydgI, yodC and yfhC genes were respectively amplified by PCR technology, After the purified ydfN, ydgI, yodC and yfhC genes were digested by restriction endonucleases MluI and BamHI, they were connected with the plasmid pMA5 digested by the above two restriction endonucleases to construct the recombinant plasmid pMA5-bdhA. 4 Under the action of DNA ligase, connect overnight at 16°C, transform the ligation liquid into E. coli competent E.coli JM109, pick positive transformants, extract the plasmids in the transformants, and confirm the recombinant plasmid pMA5-ydfN by enzyme digestion , pMA5-ydgI, pMA5-yodC and pMA5-yfhC were constructed successfully. After verification by double enzyme digestion, it indicated that the recombinant plasmid was constructed successfully. ...
Embodiment 3
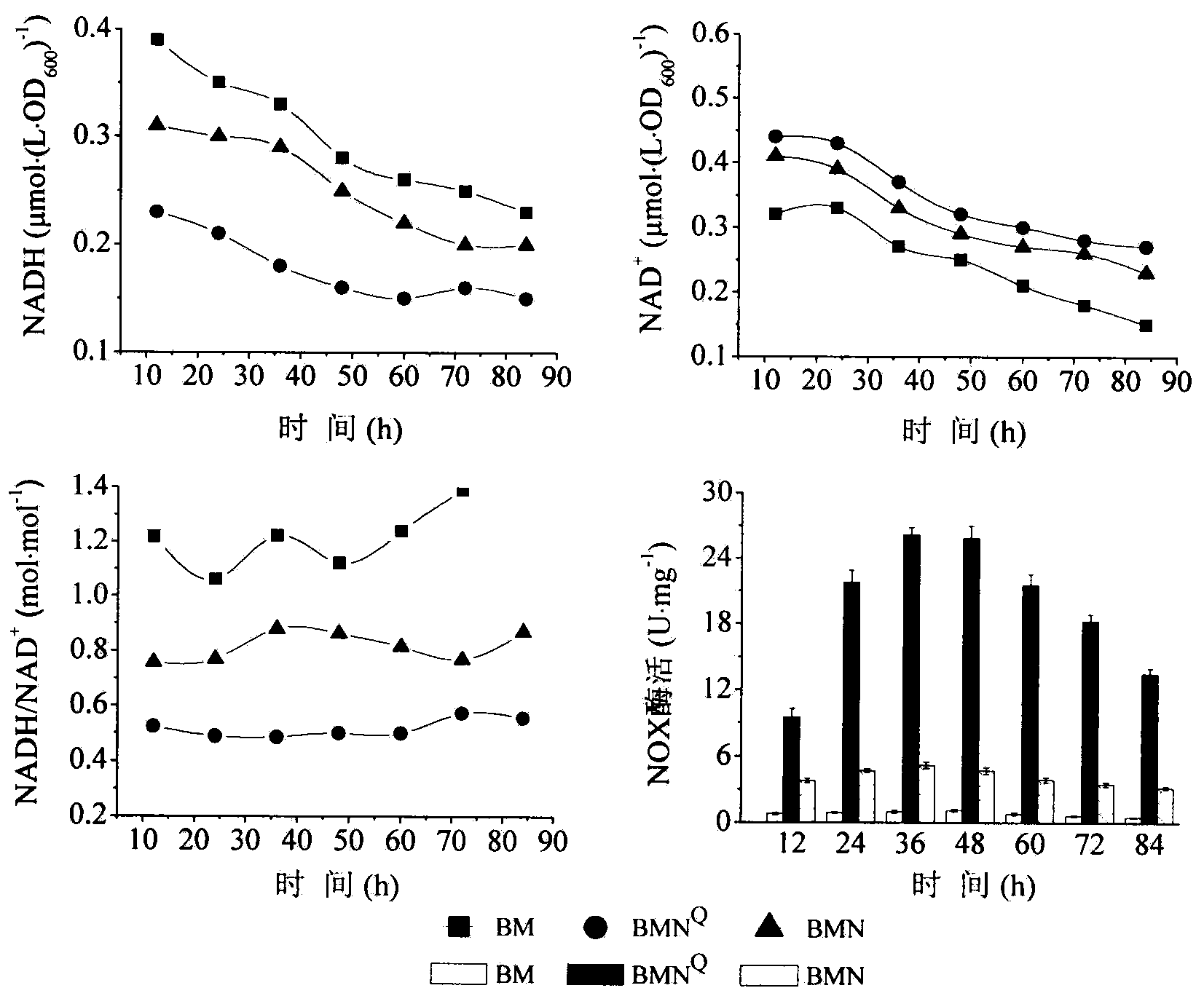
[0032] Embodiment 3: NADH oxidase activity assay
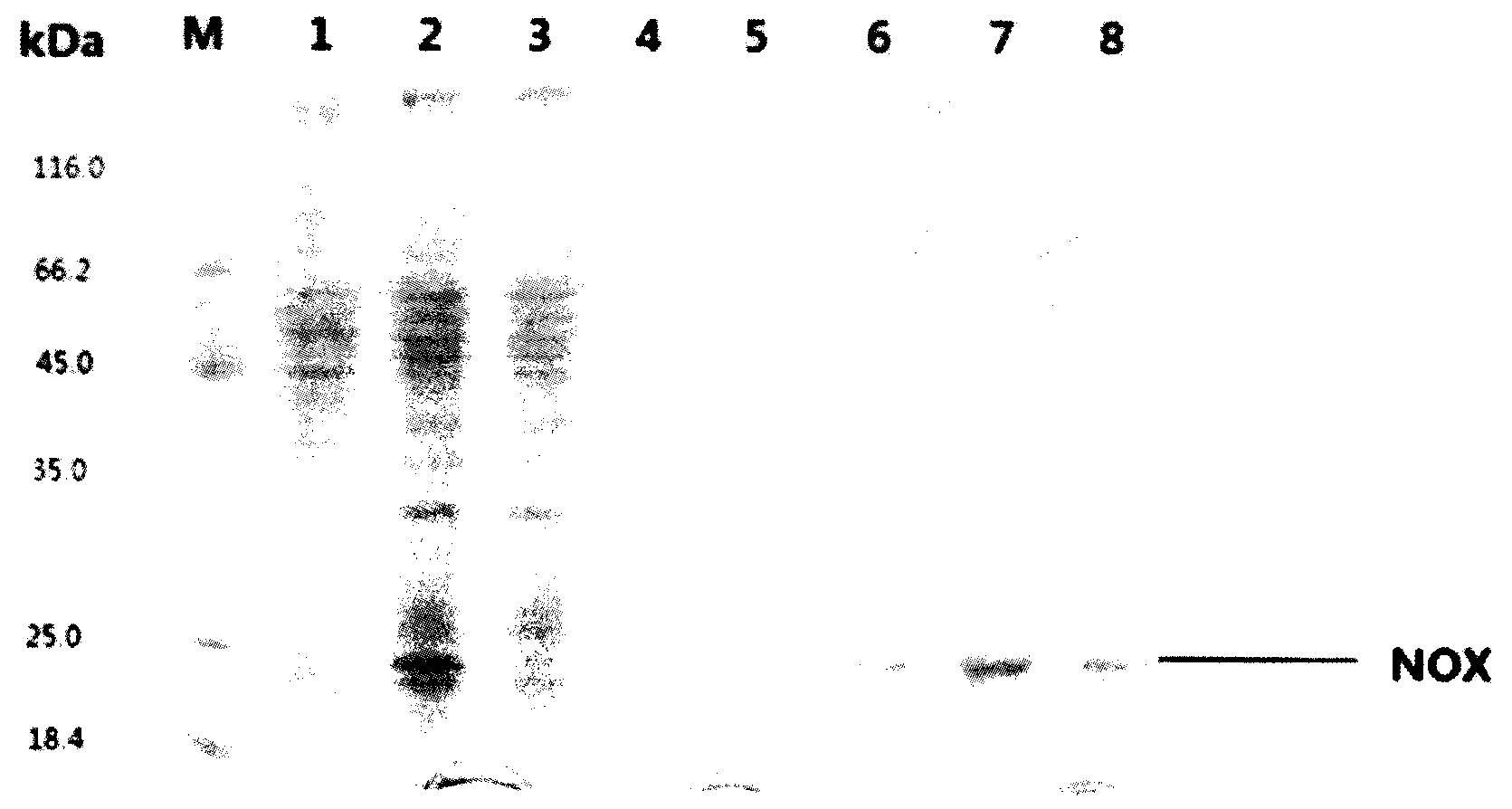
[0033] The recombinant bacteria B.subtilis JNA / pMA5-ydfN constructed in Example 4, B.subtilis JNA / pMA5-ydgI, B.subtilis JNA / pMA5-yodC and B.subtilis JNA / pMA5-yfhC, and the starting strain B.subtilis JNA were respectively inoculated in 10 mL of LB medium containing kanamycin, cultured with shaking at 37°C overnight, transferred to LB medium at 4% inoculum the next day, cultured at 37°C for 24 hours, and the fermentation broth was taken at 4°C. Centrifuge at 10000r / min for 10min, wash with pH7.0 sodium phosphate buffer for 3 times, resuspend the cells in pH6.5 sodium phosphate buffer, then place the liquid in an ultrasonic breaker to treat the cells for 20min, 15000r·min -1 Centrifuge for 30 minutes, and the supernatant is the crude enzyme solution. Add 20 μl of crude enzyme solution to the enzyme activity assay buffer system to detect A immediately 340 Changes in absorbance.
[0034] Determination of NADH oxidase activity: T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com