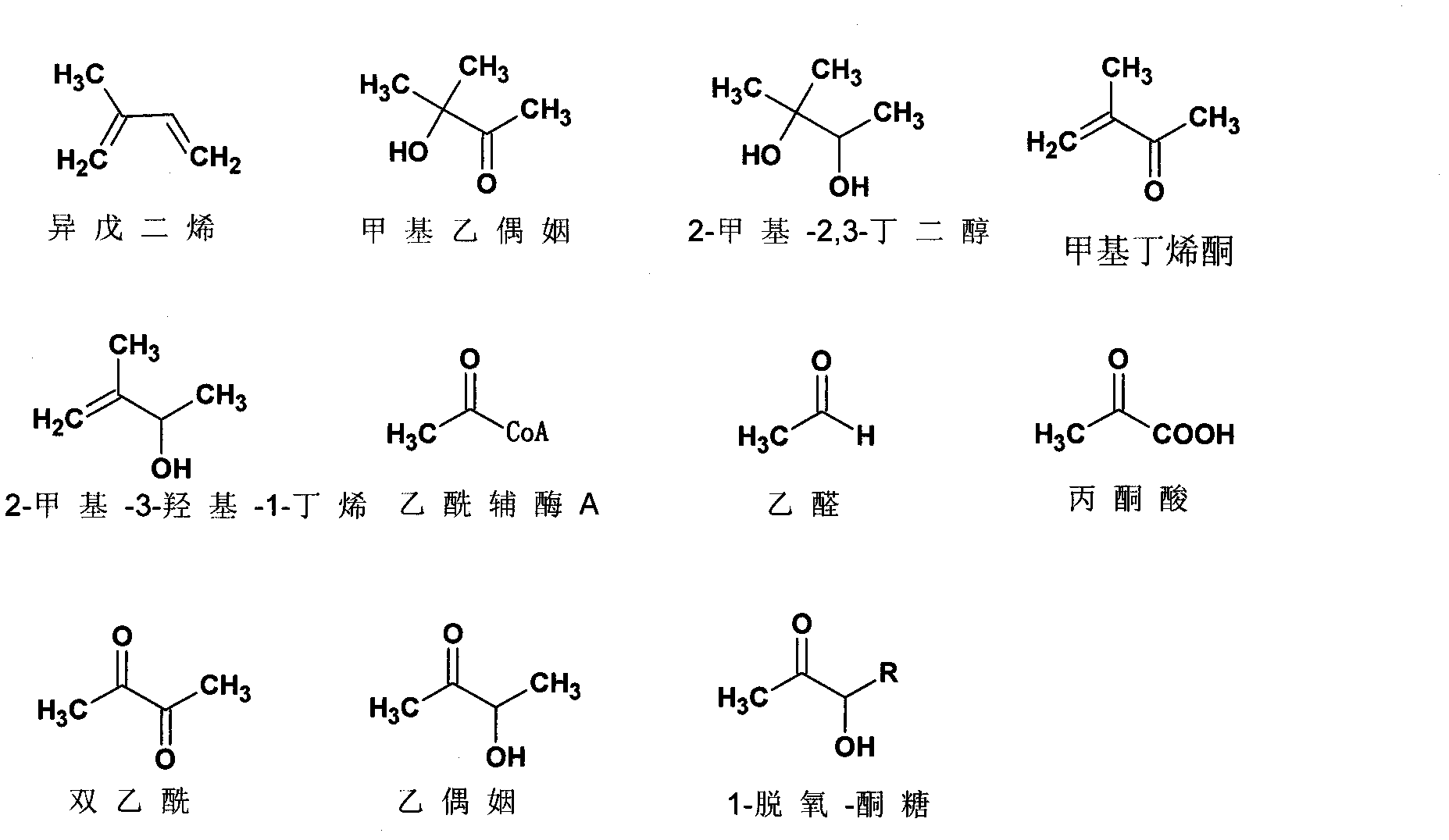
Recombinant cell and method for synthesizing methyl acetoin and derivative compounds thereof by using biological method
A technology of biosynthesis of methyl acetoin, applied in the field of production of methyl acetoin compound, biosynthesis of methyl acetoin compound and its derivative compounds
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
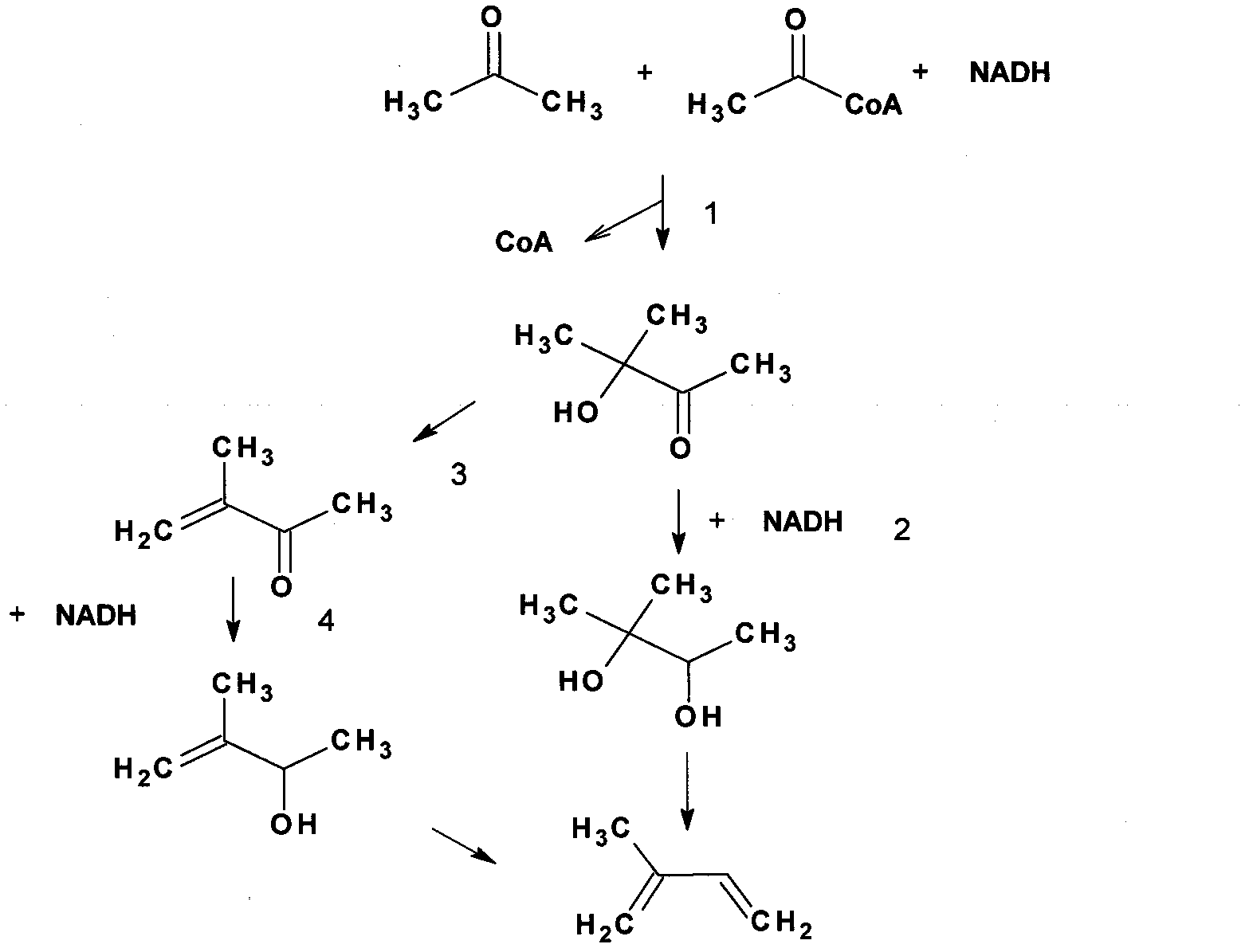
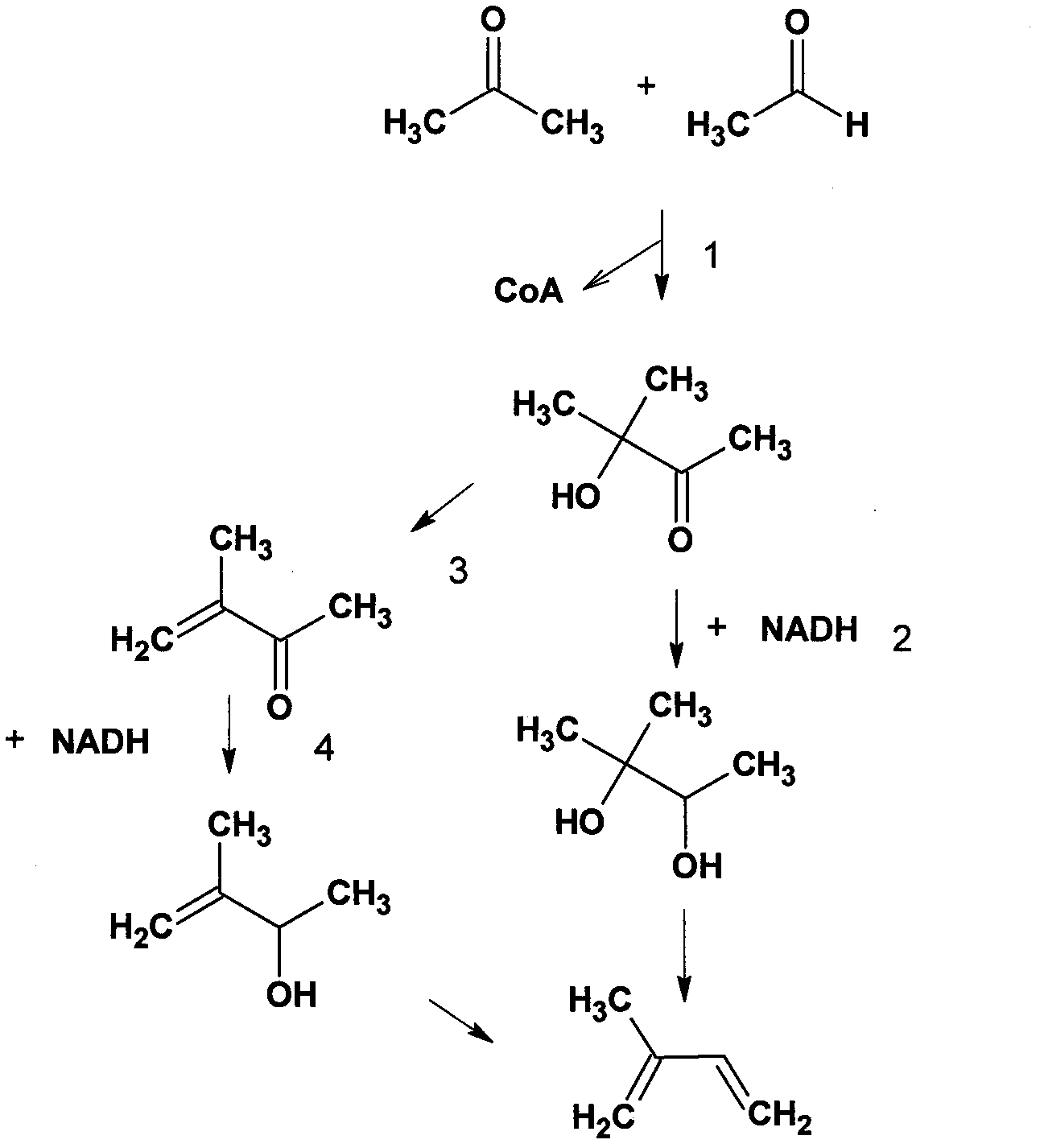
[0065] The acoA and acoB genes (GenBank Accession No.936152; 939697) of Bacillus subtilis were cloned between the NcoI and SalI sites of the pACYduet1 (purchased from Novagen) plasmid, and the constructed pJXL32 plasmid (such as Figure 7 indicated) were electrotransformed into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (purchased from Invitrogen). The constructed cells were cultured in 100ml LB medium (LB medium, 10g sodium chloride dissolved in 1L water, 10g trypsin powder, and 5g yeast powder). The culture temperature was maintained at 30°C. When the cells grow to a certain stage, usually the exponential growth stage, IPTG (50mg / L final concentration) and acetone (1M final concentration) are added to the medium. Causes cells to produce methylacetoin.
[0066] The produced methyl acetoin is detected by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and the results are as follows: Figure 12 , as shown in 13.
[0067] Methylacetoin or methylbutenone is separated from bacterial cultures by gas stri...
Embodiment 2
[0069] The bdhA (GenBank Accession No.939490) gene of Bacillus subtilis is cloned between the SalI and aflII sites on the pJXL32 described above, and the pJXL37 plasmid (such as Figure 8shown) were electrotransformed into E. coli BL21(DE3). The constructed cells were cultured in 100ml LB medium. The culture temperature was maintained at 30°C. When the cells grow to a certain stage, usually the exponential growth stage, IPTG (50mg / L final concentration) and acetone (1M final concentration) are added to the medium. Causes cells to produce 2-methyl-2,3-butanediol. The 2-methyl-2,3-butanediol that produces is detected by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry as Figure 10 , as shown in 11.
[0070] 2-Methyl-2,3-butanediol was separated from bacterial cultures by distillation. 2-Methyl-2,3-butanediol is catalyzed by lithium acetate to generate prenylation at 200 degrees Celsius, the specific operation reference (2).
Embodiment 3
[0072] The thl gene of Clostridium acetobutylicum (GenBank Accession No. 1119056 ), the atoAD gene of Escherichia coli (GenBank Accession No. 947525 ; 946719 ), and the abc gene of Clostridium acetobutylicum (GenBank Accession No. 1116170 ), connected together by overlap extension PCR, and then cloned on pET28a by homologous recombination (3). The constructed plasmid is called pJXL40 (such as Figure 9 shown). pJXL40 and pJXL32 were simultaneously electrotransformed into E. coli BL21(DE3). The constructed cells were cultured in 100ml LB medium. The culture temperature was maintained at 30°C. When the cells grow to a certain stage, usually the exponential growth stage, IPTG (50 mg / L final concentration) and glucose (20 g / L final concentration) are added to the medium. The cells produced methyl acetoin as analyzed by mass spectrometry.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com