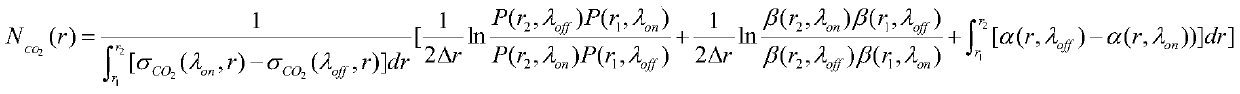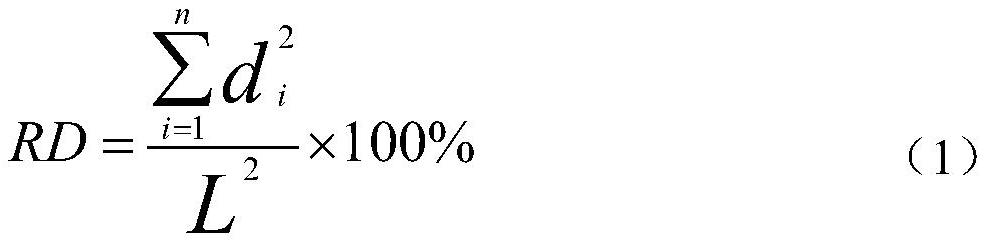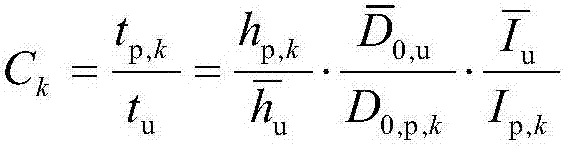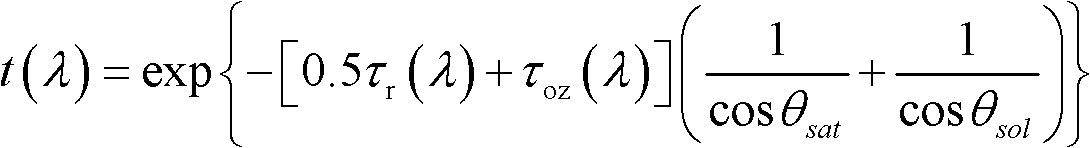Patents
Literature
60 results about "Empirical relationship" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In science, an empirical relationship or phenomenological relationship is a relationship or correlation that is supported by experiment and observation but not necessarily supported by theory.
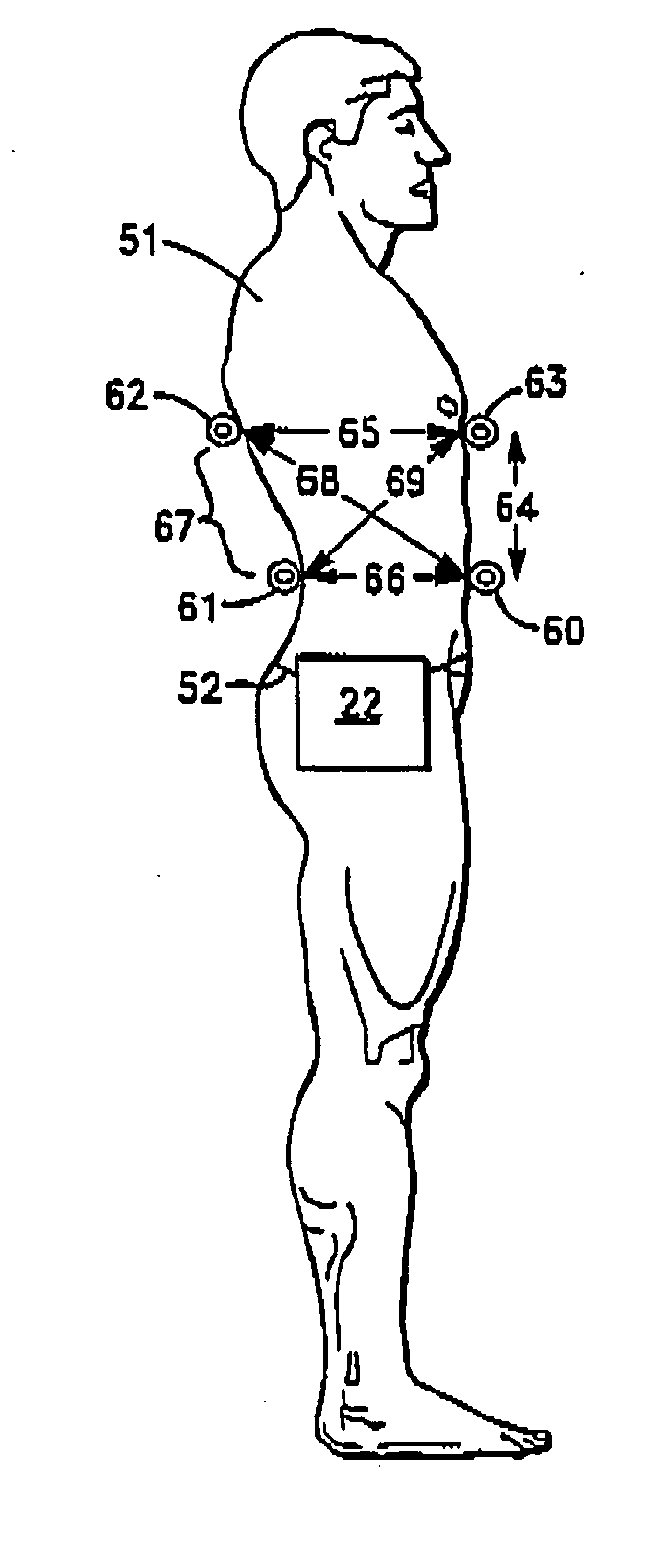
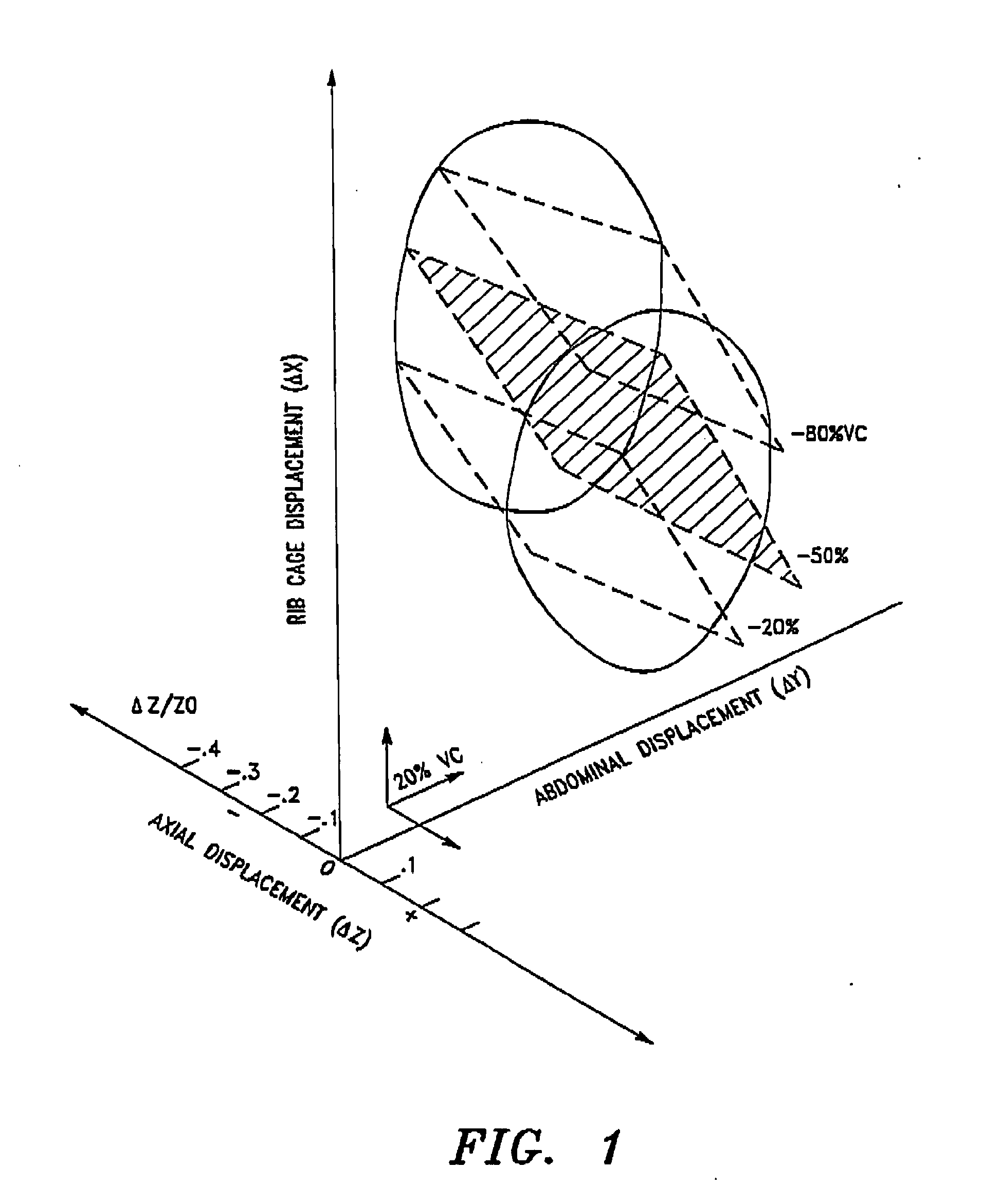
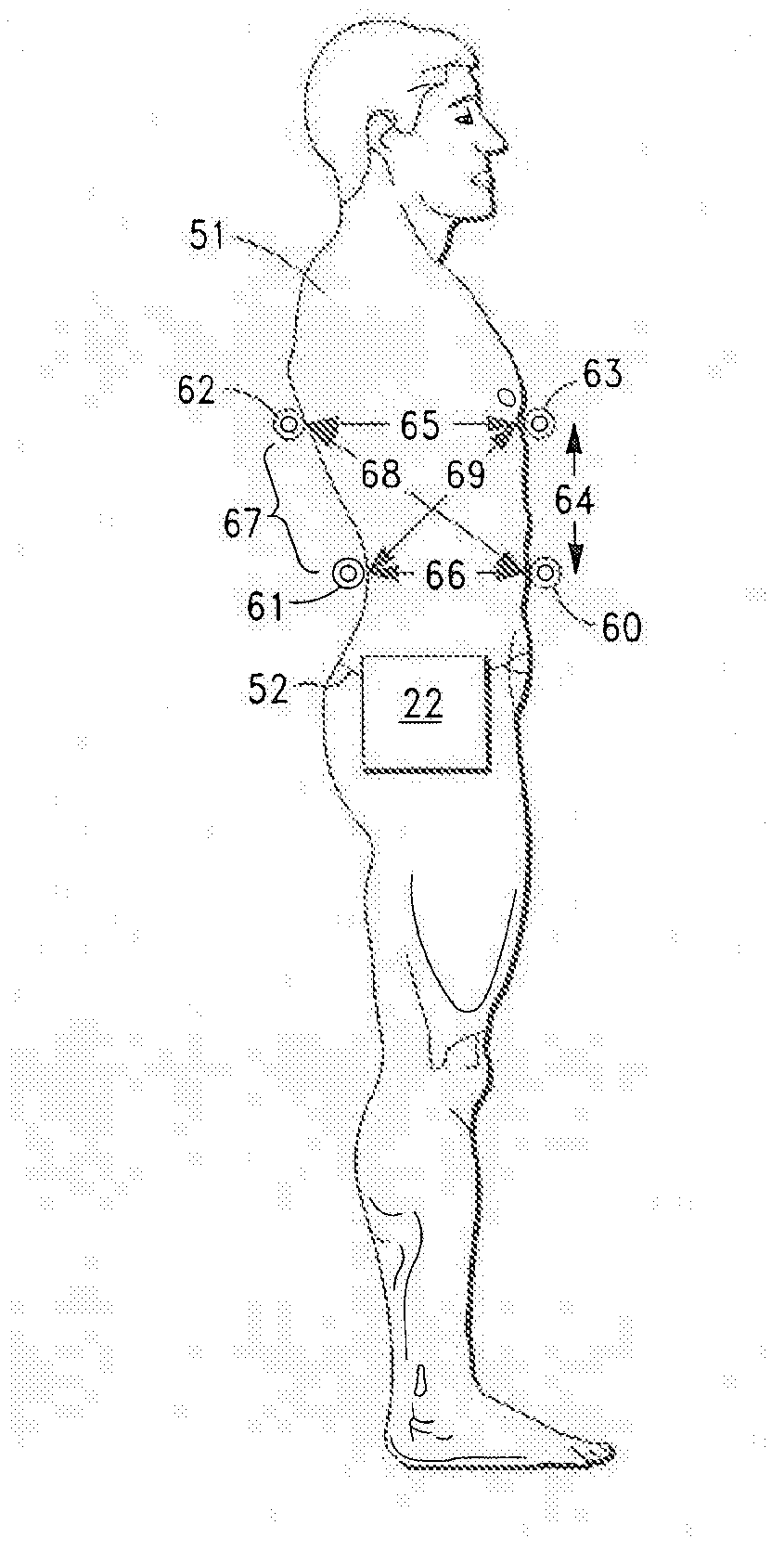
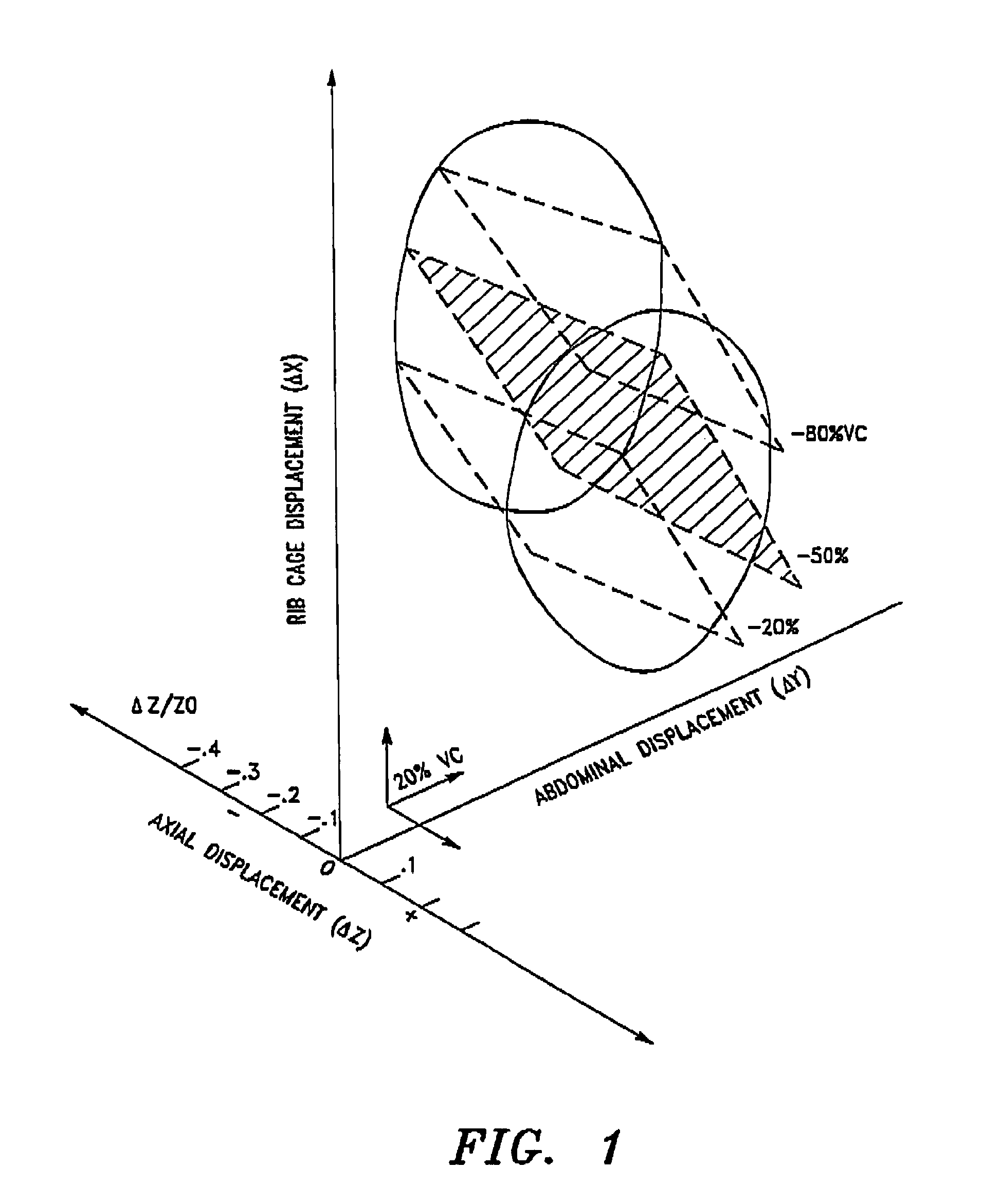
Noninvasive method and system for measuring pulmonary ventilation
ActiveUS20110009766A1Accurate detectionEasily employedRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsEmpirical relationshipIntensive care medicine
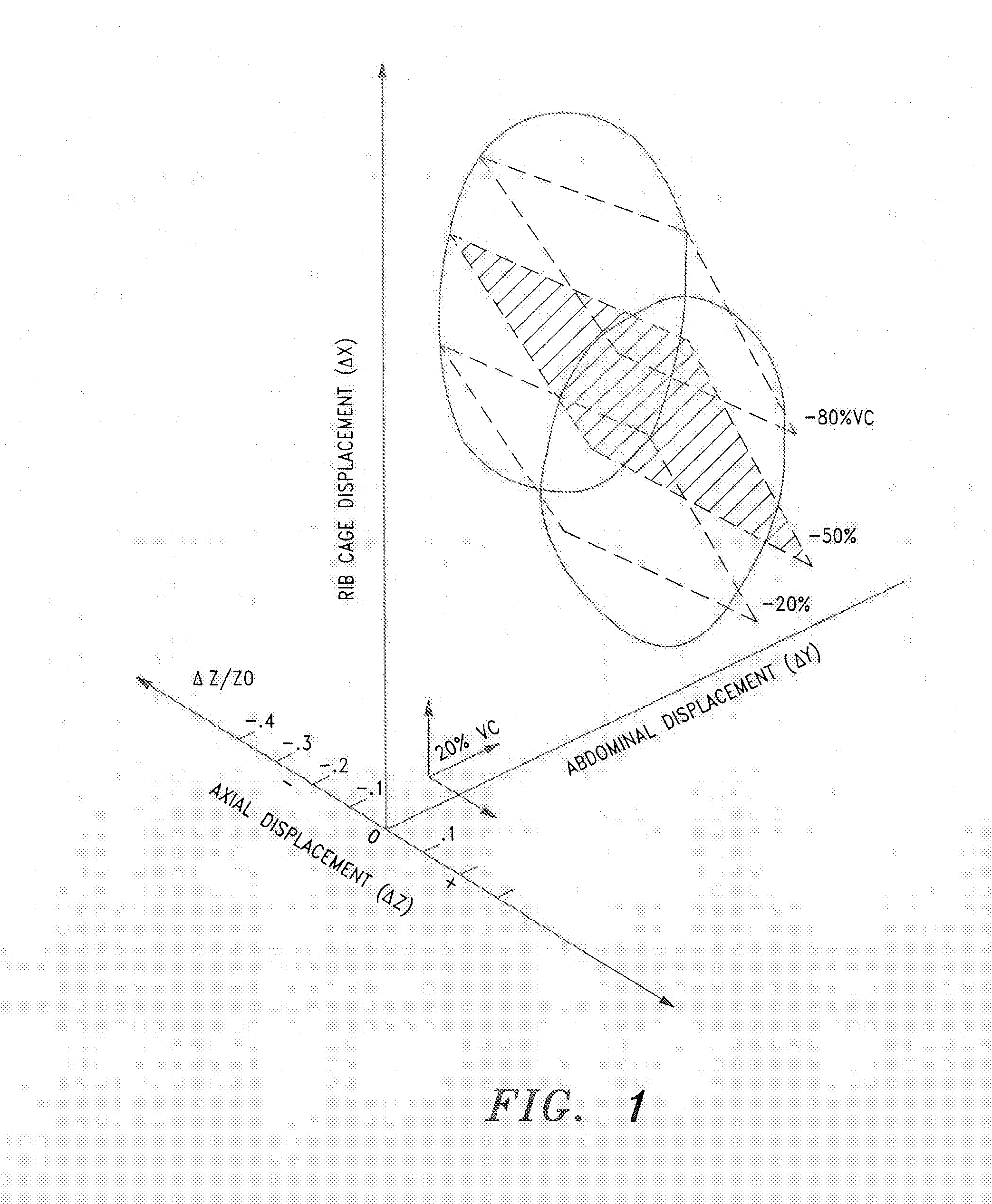
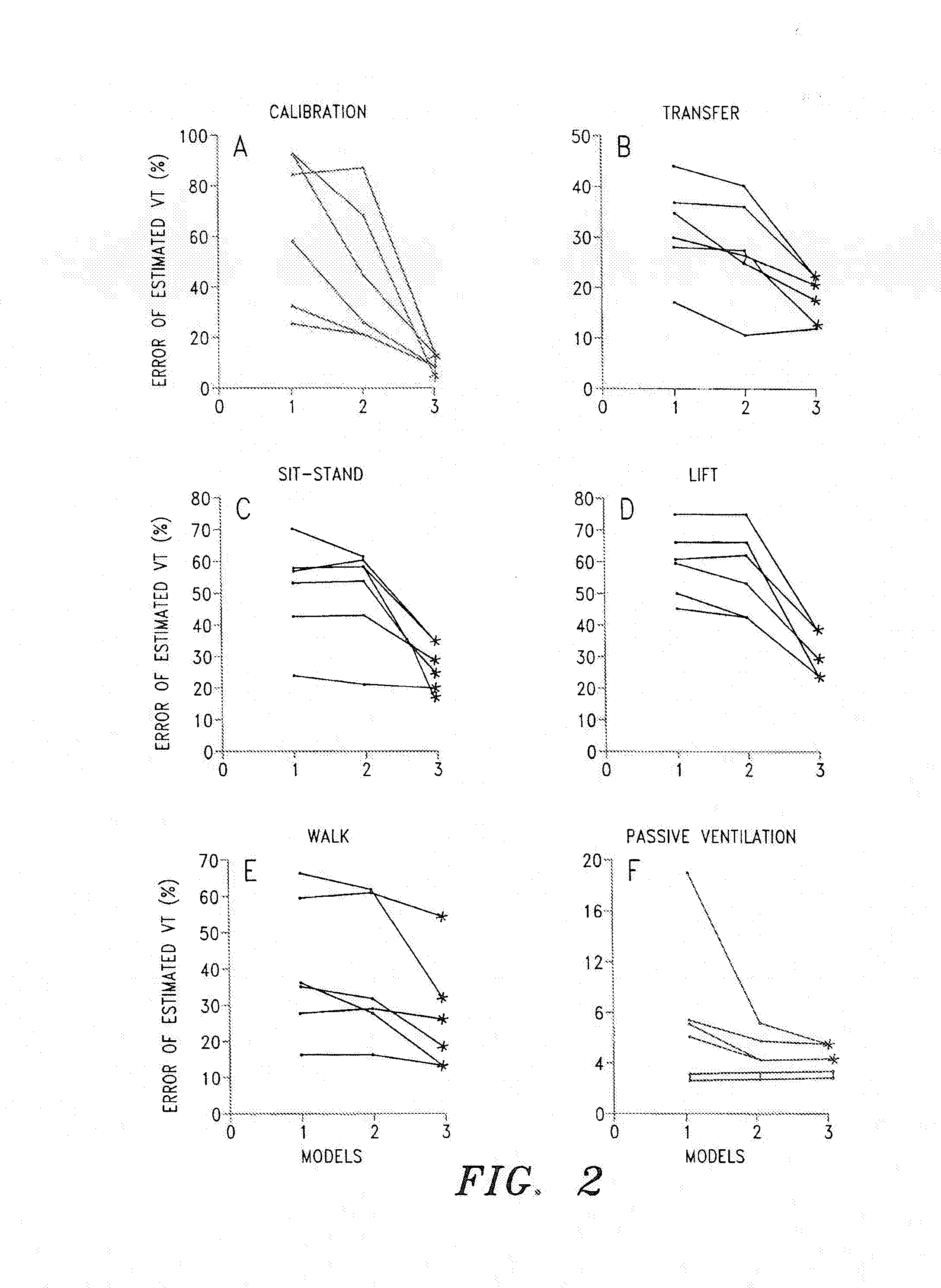
A pulmonary ventilation system comprising means for storing an empirical relationship that is designed and adapted to determine at least one pulmonary ventilation parameter as a function of a plurality of measured anatomical distances and volume-motion coefficients, means for acquiring the anatomical distances, means for determining the plurality of motion coefficients, and processing means for determining the ventilation parameter based on the acquired anatomical distances and determined plurality of volume-motion coefficients. In one embodiment, the system further includes means for acquiring base-line ventilation characteristics and means for correlating the base-line ventilation characteristics to the ventilation parameter determined with the empirical relationship.
Owner:ADIDAS
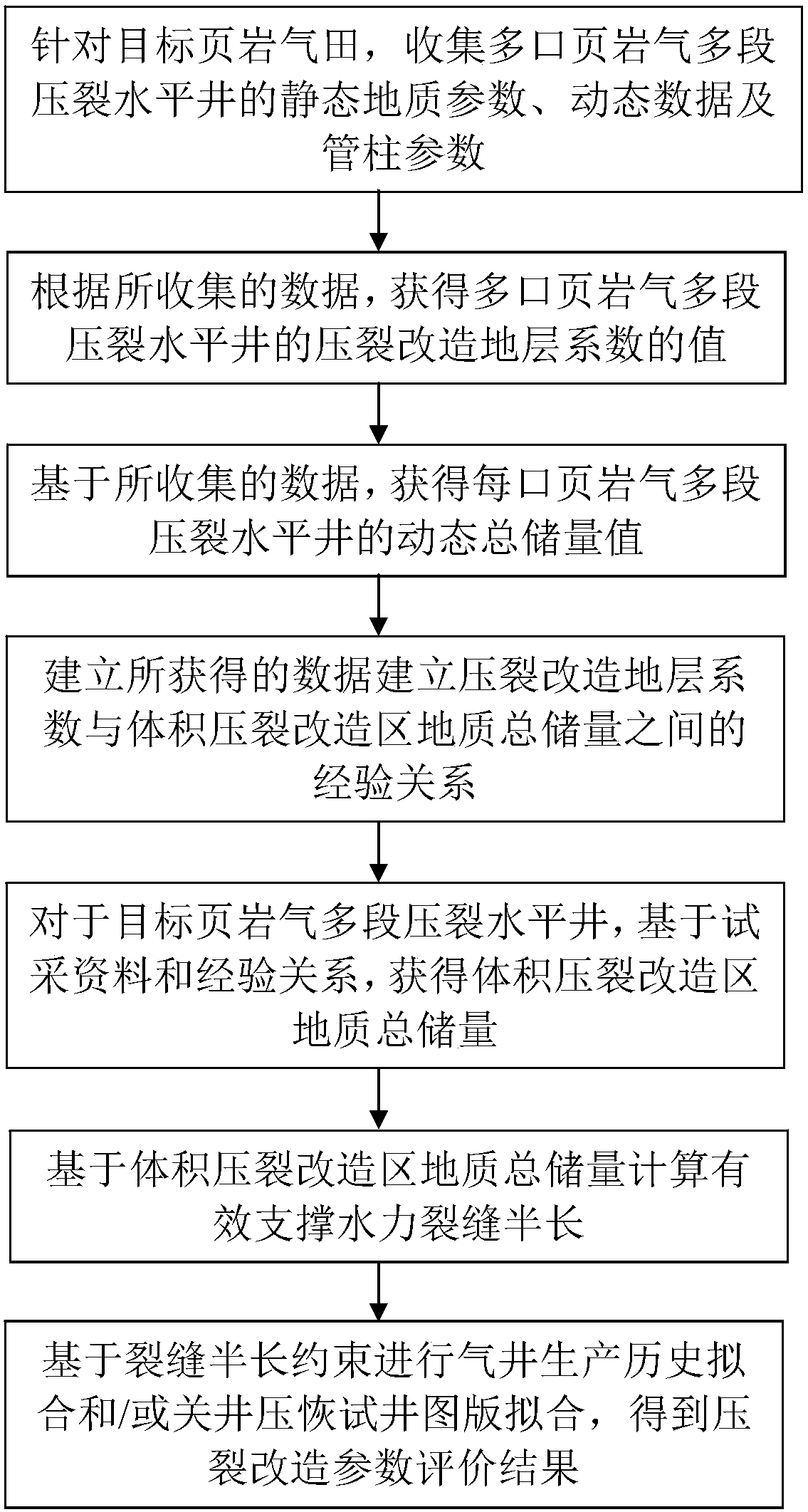
A shale gas multi-stage fractured horizontal well post-fracturing crack parameter evaluation method and system
ActiveCN109594968AReliable interpretation of resultsSolve elusive problemsSurveyFluid removalHorizontal wellsTransformation parameter
The invention discloses a shale gas multi-stage fracturing horizontal well post-fracturing crack parameter evaluation method and system. The method comprises the following steps: 1) aiming at a targetshale gas field, collecting static geological parameters, dynamic data and pipe column parameters of a plurality of shale gas multi-stage fractured horizontal wells; 2) obtaining values of fracturingtransformation stratum coefficients of the plurality of wells; 3) obtaining a dynamic total reserve value of each well; 4) establishing an empirical relationship between the fracturing transformationstratum coefficient and the total geological reserve of the volume fracturing transformation area according to data obtained in the steps 2 and 3; 5) obtaining the total geological reserve of the volume fracturing reconstruction area; 6) calculating the half length of the effective support hydraulic fracture; and 7) performing gas well production history fitting and / or shut-in pressure recovery well test chart fitting based on the crack half-length constraint to obtain a fracturing transformation parameter evaluation result. According to the method, the problem of high historical fitting multiplicity can be solved, a more reliable fracturing transformation parameter interpretation result is obtained, and a basis is provided for predicting the gas well productivity and making a reasonabledevelopment technical policy in the next step.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Distributed optical fiber testing method for porous medium structure seepage
ActiveCN103364320AEnables indirect monitoringPinpoint Linear DependenciesMaterial heat developmentThermometers using physical/chemical changesLinear correlationMathematical model
The invention discloses a distributed optical fiber testing method for porous medium structure seepage. The method comprises the steps of: (1) constructing a porous medium structure model groove; (2) forming a uniform and steady seepage field; (3) conducting temperature monitoring on the target optical fiber embedded in the model groove; (4) carrying out ohmic heating operation on the target optical fiber; (5) measuring the temperature rise curves of different heating power under the steady seepage condition; (6) constructing a heat transfer equation of a total heat transfer coefficient of the optical cable; (7) representing the heat transfer between optical fiber and a seepage containing saturated porous medium by the total heat transfer coefficient; (8) measuring the temperature rise curves of different heating power under the condition of different seepage rates; and (9) monitoring the seepage rate. The method provided in the invention establishes an empirical relationship mathematical model of the seepage rate total heat transfer coefficient, accurately pinpoints the linear correlation between the seepage rate and an average total heat transfer coefficient, and reliably guarantees the monitoring precision.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
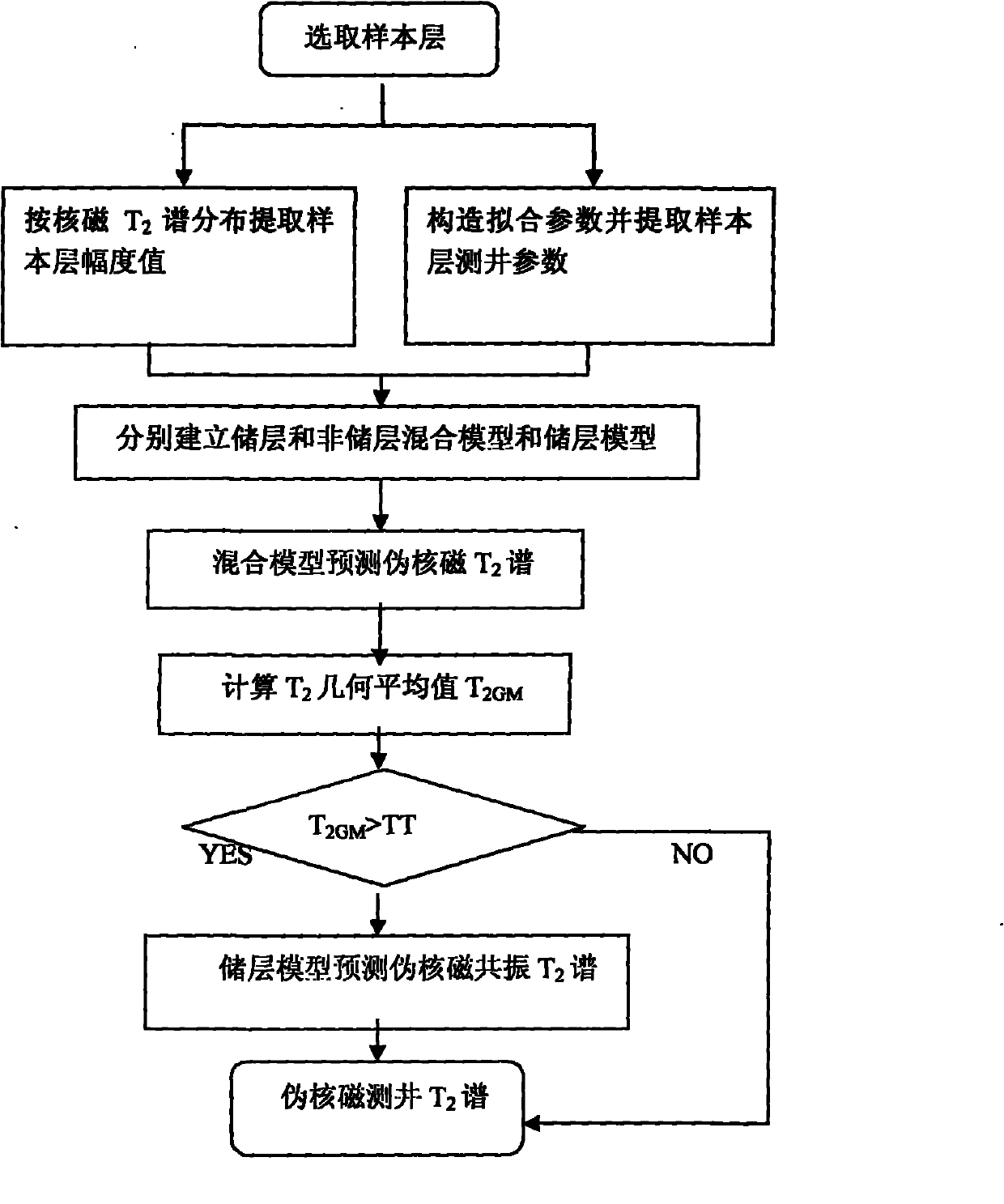
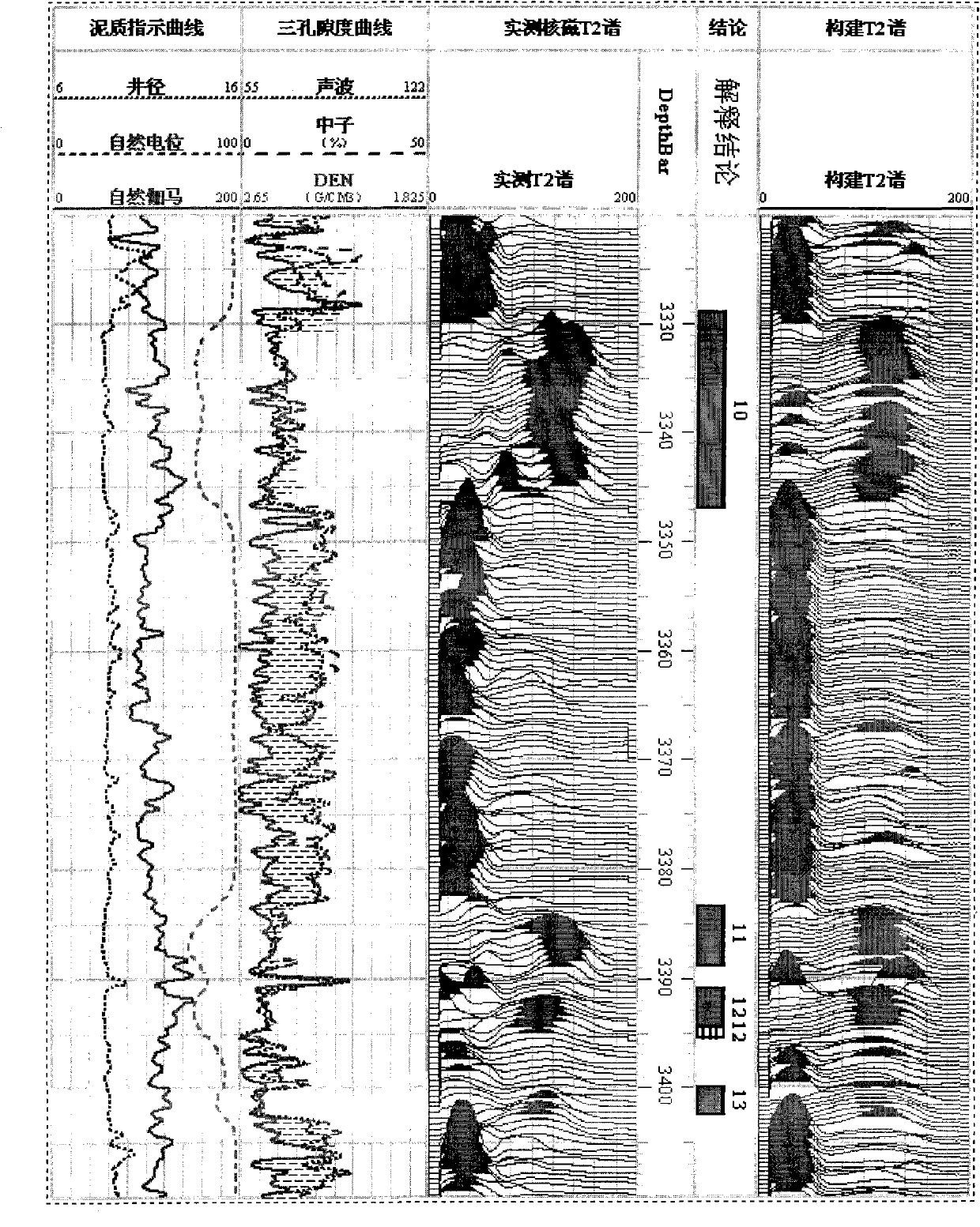
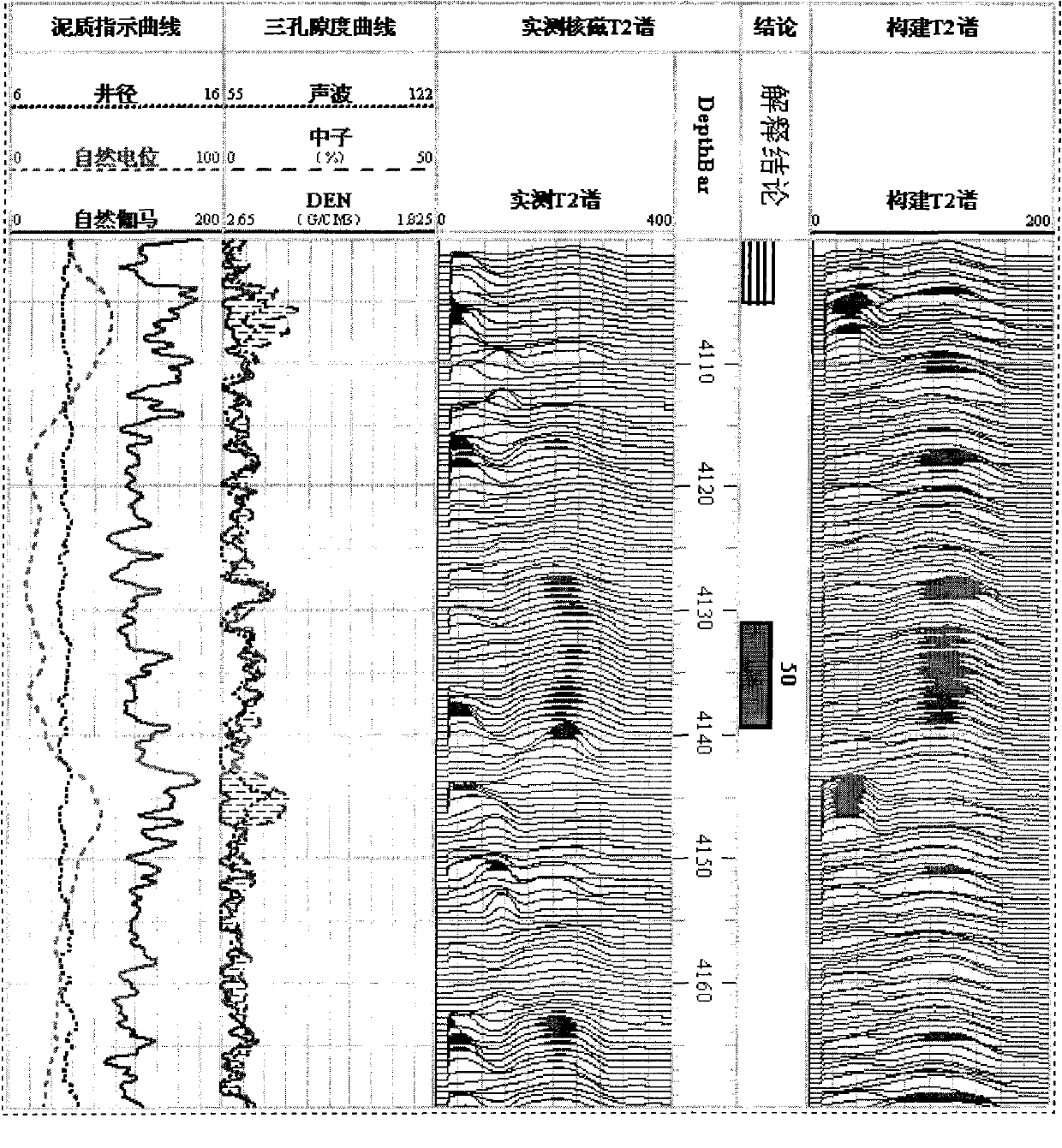
Method for constructing pseudo nuclear magnetic T2 spectrum by using conventional logging data
ActiveCN102042011AGood application effectHigh resolutionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingBorehole/well accessoriesNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceImage resolution
The invention discloses a method for constructing a pseudo nuclear magnetic T2 spectrum by using conventional logging data, which solves the technical problems that the conventional logging technology cannot accurately evaluate hole structure parameters and the nuclear magnetic logging price is high. The method comprises the following steps of: splitting two-dimensional information of a nuclear magnetic T2 spectrum for reflecting a hole structure into one-dimensional information according to the composition, establishing an empirical relationship between the one-dimensional information and the conventional logging data, and then assembling the one-dimensional information and the conventional logging data into corresponding two-dimensional information so as to realize transformation of the logging data from the one-dimensional information to the two-dimensional information, namely construct the two-dimensional nuclear magnetic logging T2 spectrum by using the one-dimensional conventional logging data. The method has remarkable actual application effect; the pseudo nuclear magnetic logging T2 spectrum is remarkably similar to the actually measured nuclear magnetic logging T2 spectrum on morphology, succeeds the advantage that the resolution rate of the conventional logging technology is higher than that of the nuclear magnetic resonance technology, and can evaluate the physical property of a reservoir, evaluate the hole structure of the reservoir and perform comprehensive evaluation of the complex reservoir as the actually measured nuclear magnetic T2 spectrum; and the method has great popularization value.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
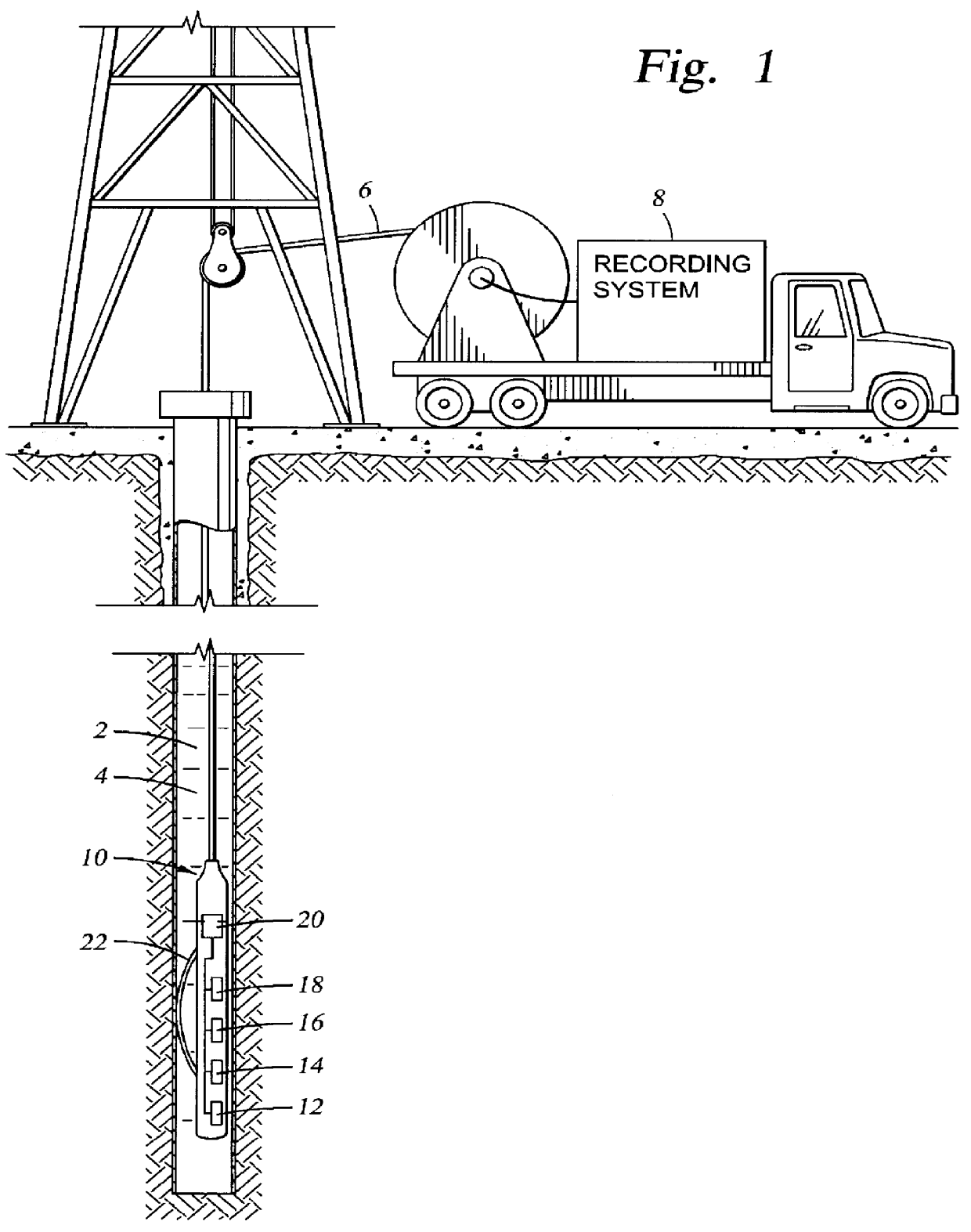
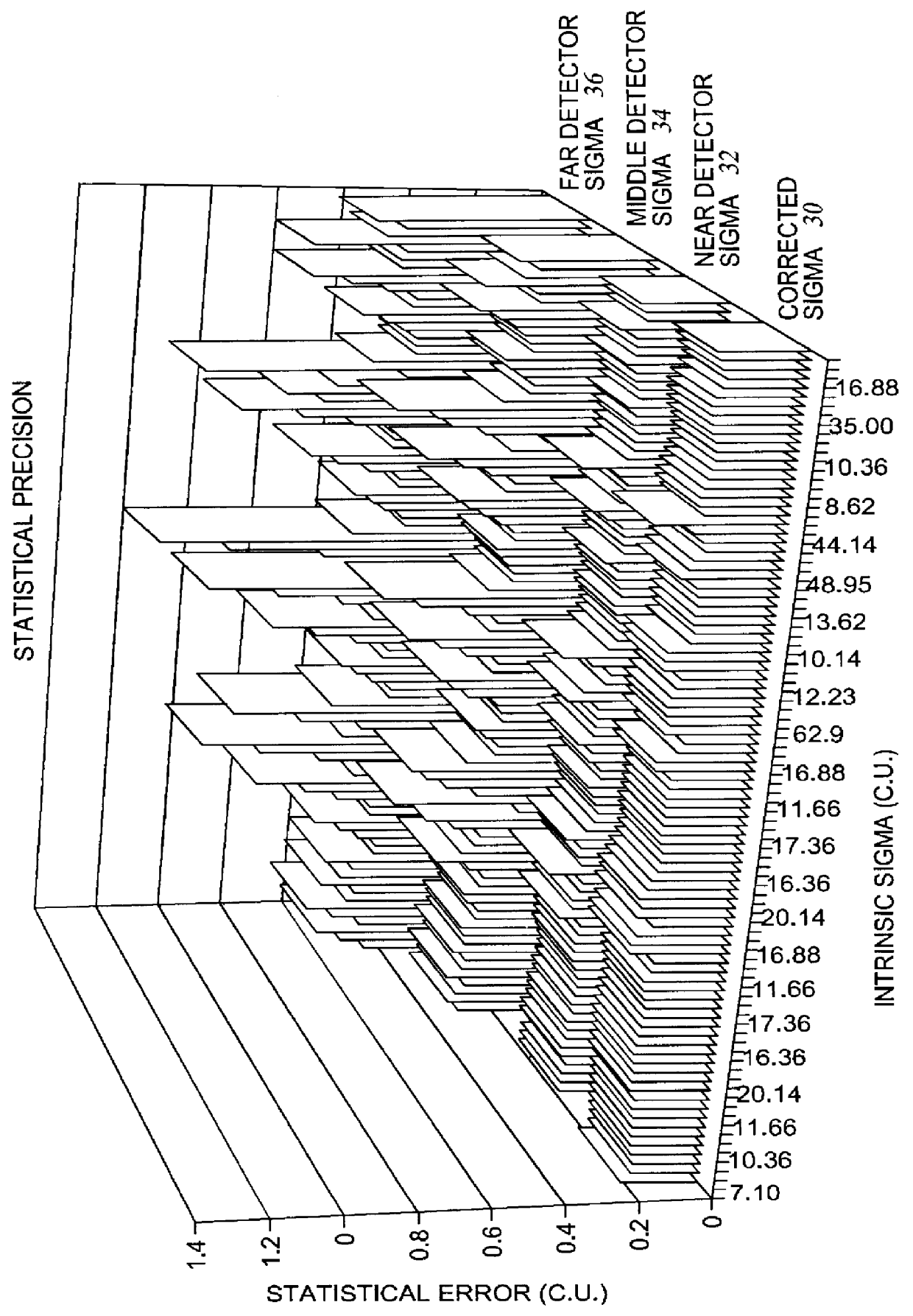
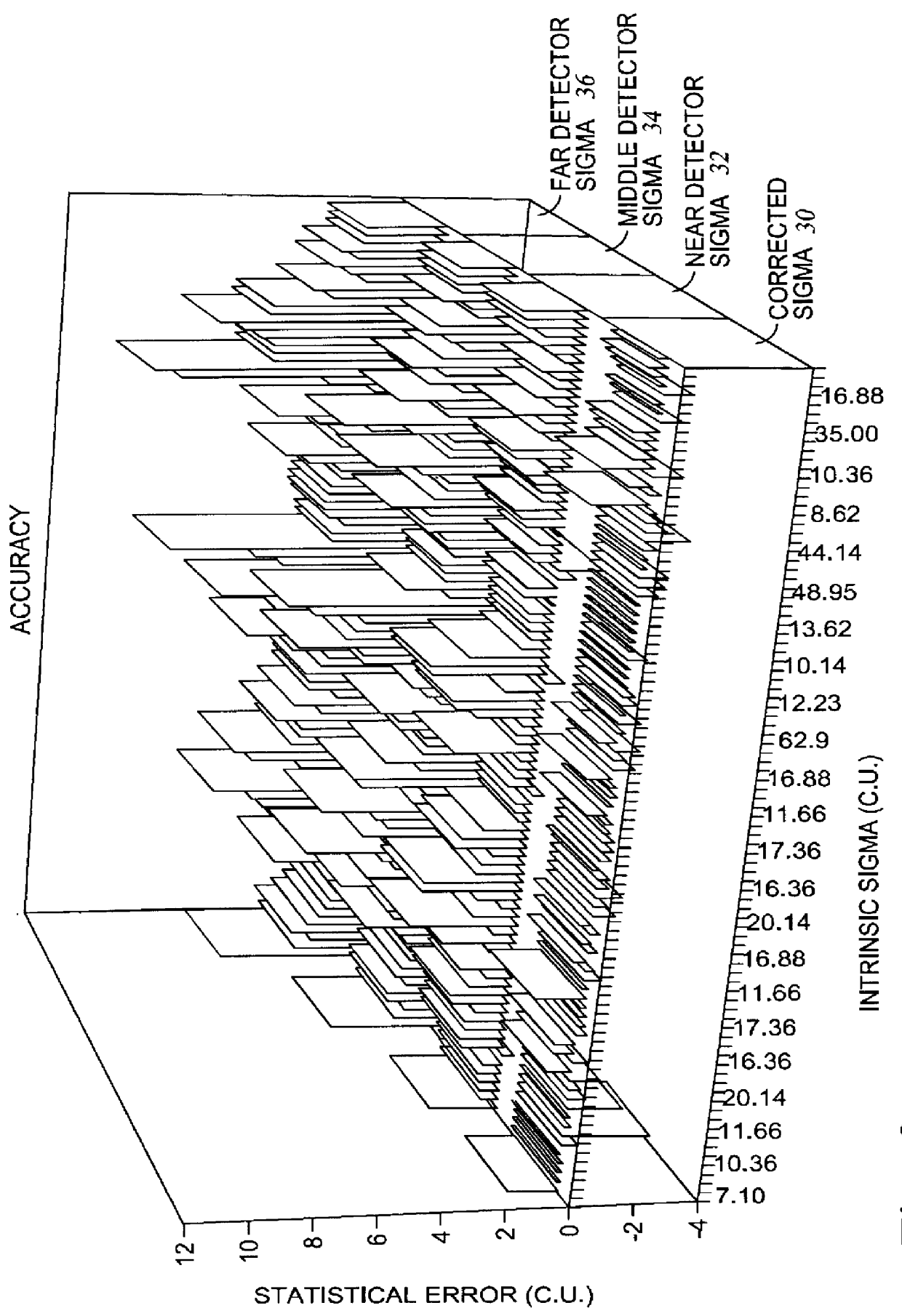
Method for determining thermal neutron capture cross-section of earth formations using measurement from multiple capture gamma ray detectors
A method for determining the thermal neutron capture cross-section of an earth formation penetrated by a wellbore from counts of capture gamma rays. The capture gamma rays are detected at spaced apart locations after bombarding the formations with high energy neutrons. The method includes determining an apparent capture cross-section at each one of the spaced apart locations from the counts of capture gamma rays, determining a difference in the apparent capture cross-sections determined between pairs of the spaced apart locations, and calculating the capture cross-section by combining the apparent capture cross-sections and the differences into an empirical relationship of known values of the capture cross-section with respect to the differences and the apparent capture cross-sections. In the preferred embodiment, the coefficients of the empirical relationship are determined by minimizing a value of an error function including as components: the differences between simulated values of the capture cross-section calculated from simulated gamma ray counts at each one of the spaced apart locations corresponding to known values of the capture cross-section used to perform the simulation, and the known values of the capture cross-section; and the statistical error in the simulated values of capture cross-section.
Owner:WESTERN ATLAS INTERNAIONAL INC
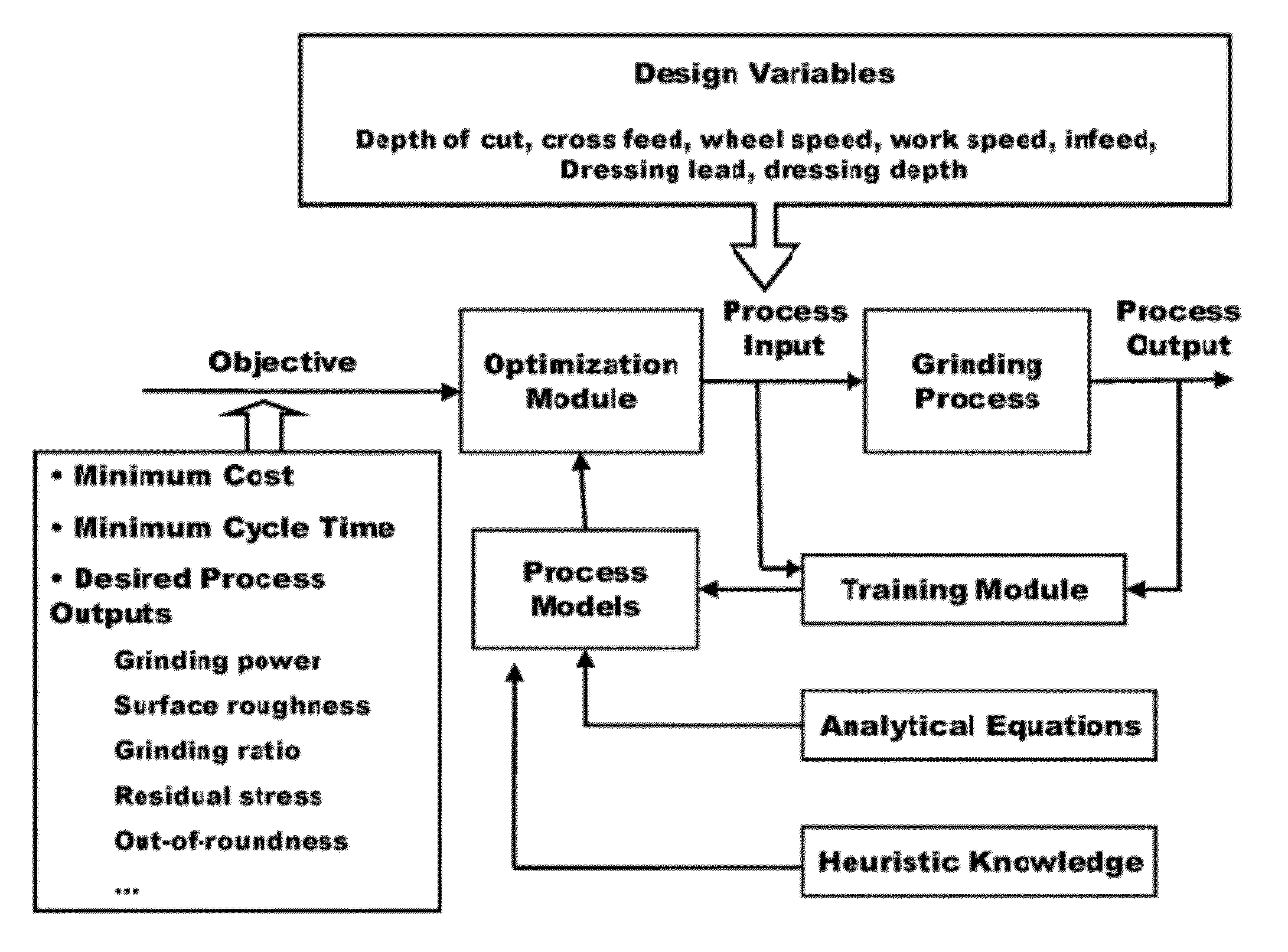
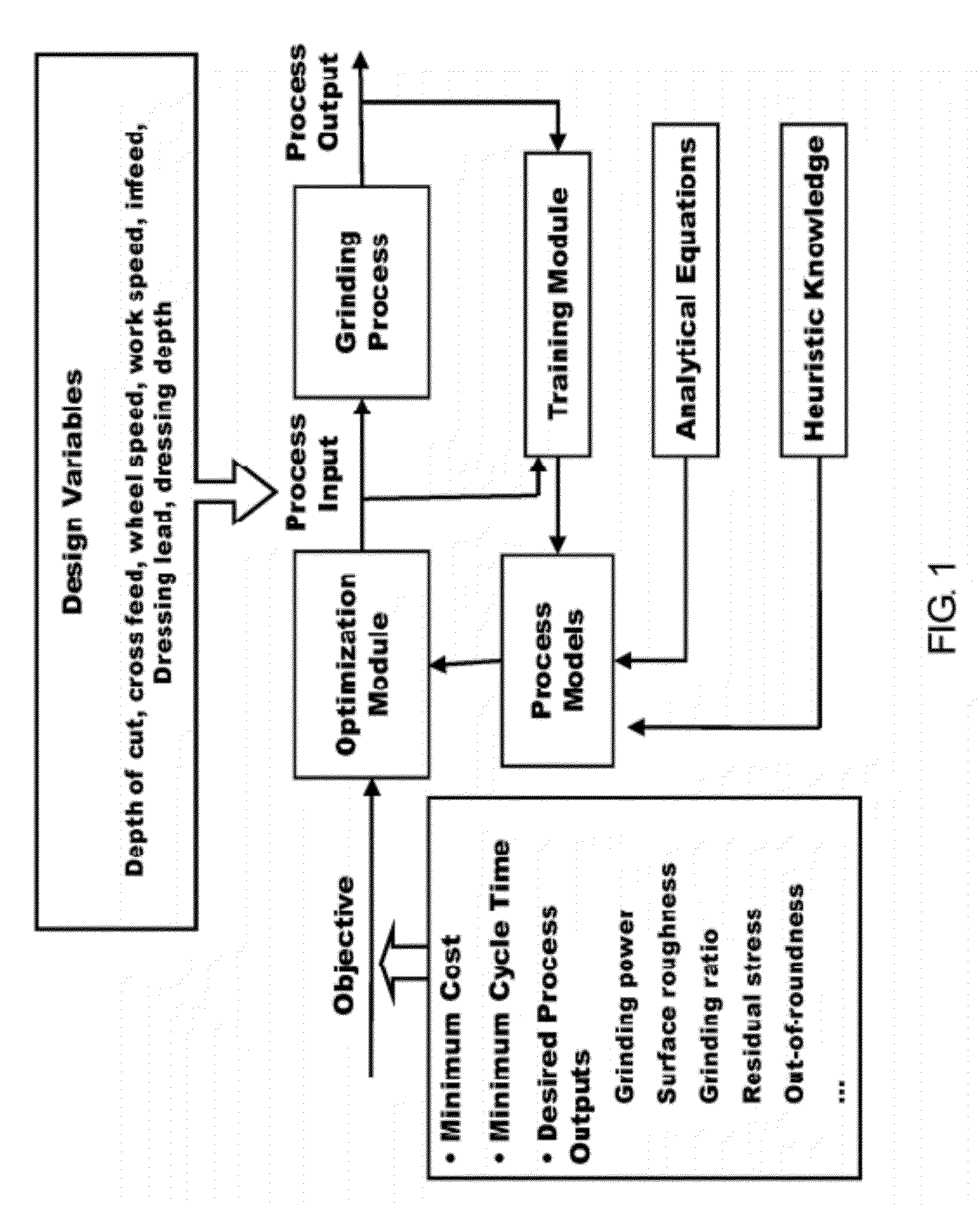
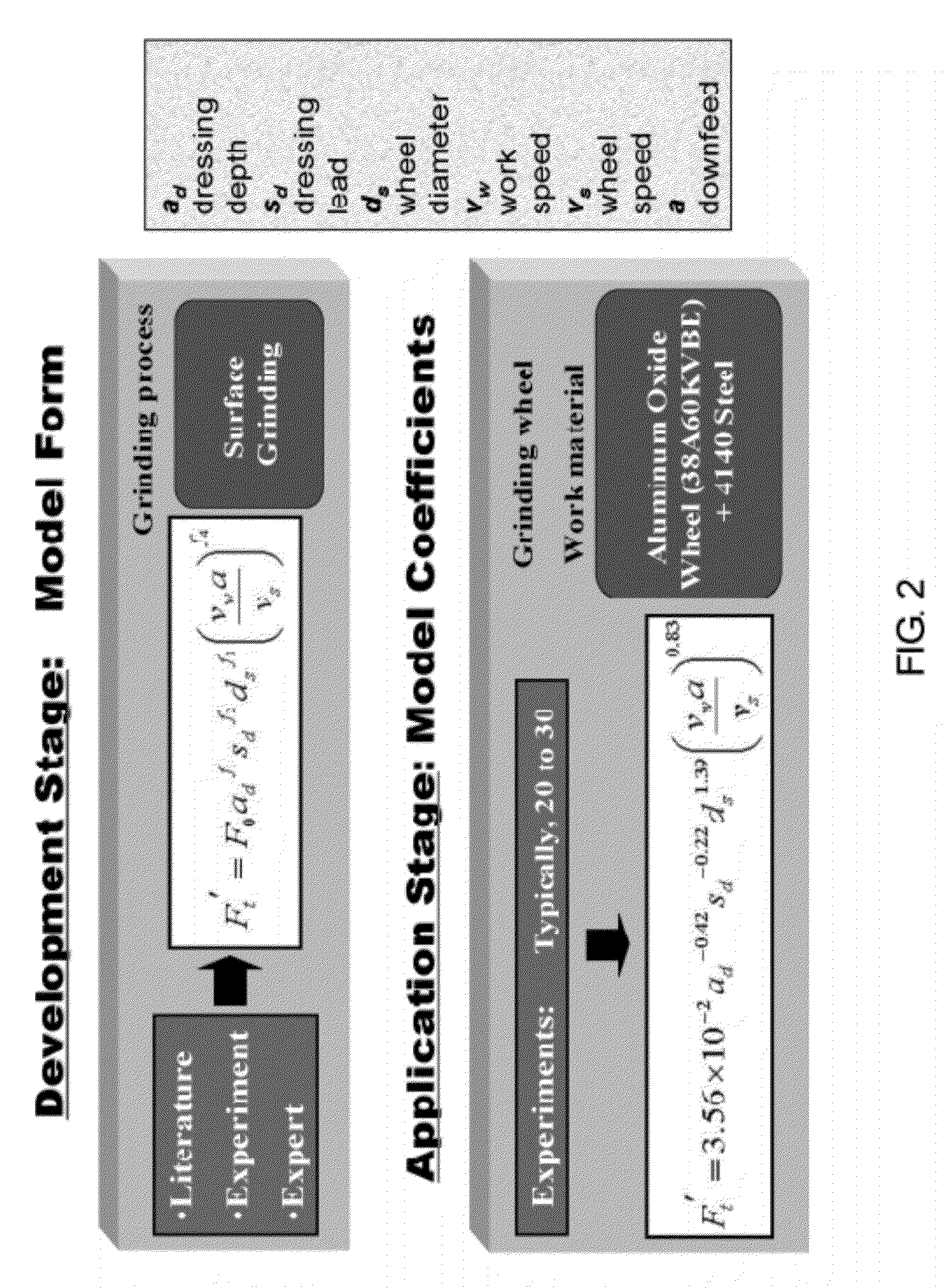
Intelligent optimization method and system therefor
ActiveUS20120191235A1Low costMaximize productivityProgramme controlSimulator controlGraphicsGraphical user interface
A method and system of optimizing a complex manufacturing process performed to achieve one or more processing objectives for the process and / or a component produced by the process. The system includes a graphical user interface, a process module, and an optimization module. The process module includes a training module, an empirical relationships database, an analytical equations database, a heuristic knowledge database, and a process models database. The graphical user interface is used to input one or more processing variables and constraints for the processing objective. The training module generates empirical relationships from the processing variable and empirical data obtained from the manufacturing process. The process module generates a process model that takes into consideration heuristic knowledge of the manufacturing process, empirical relationships, and optionally analytical equations relating to the manufacturing process. The optimization module employs the process model to optimize the manufacturing process.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
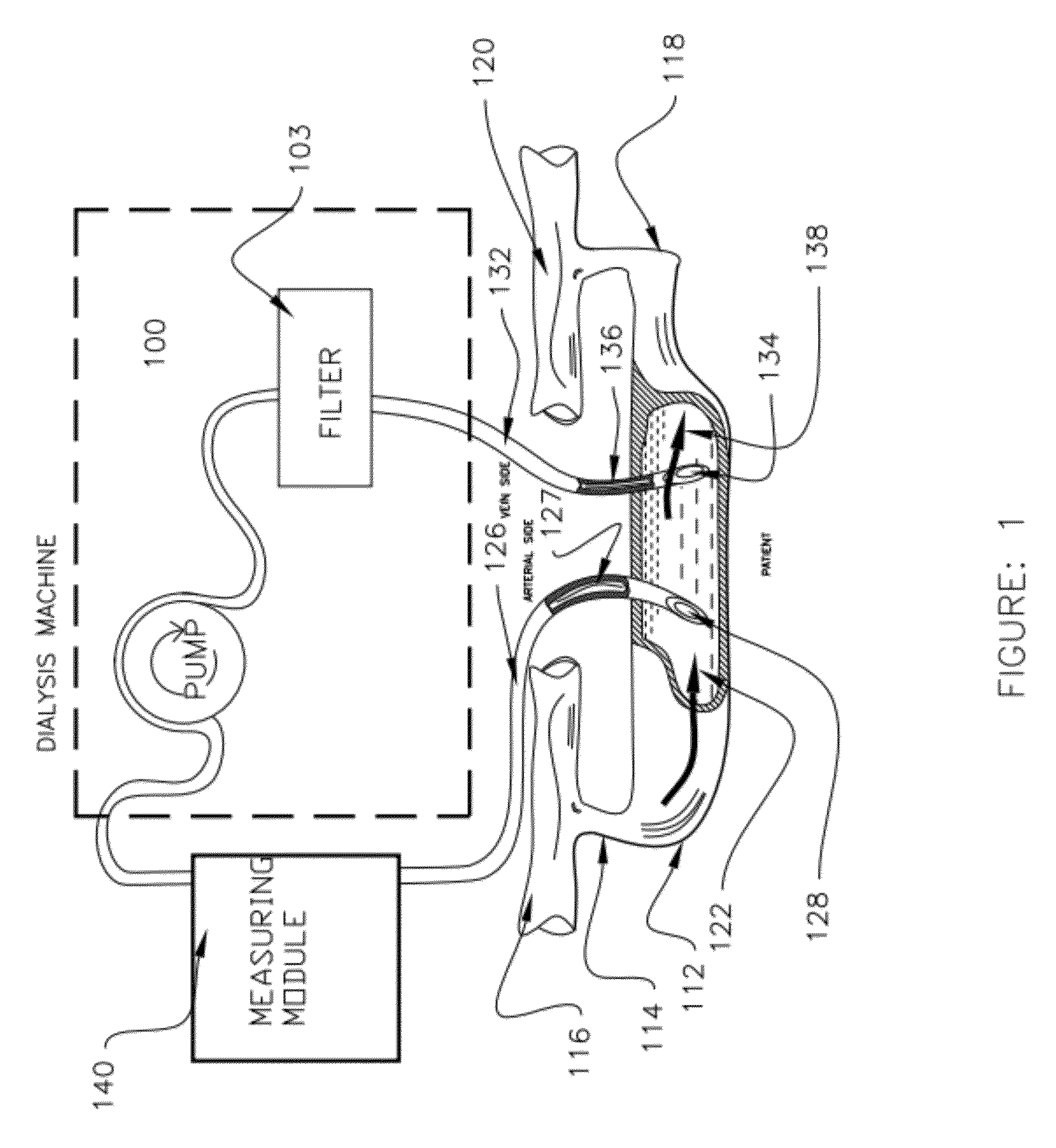
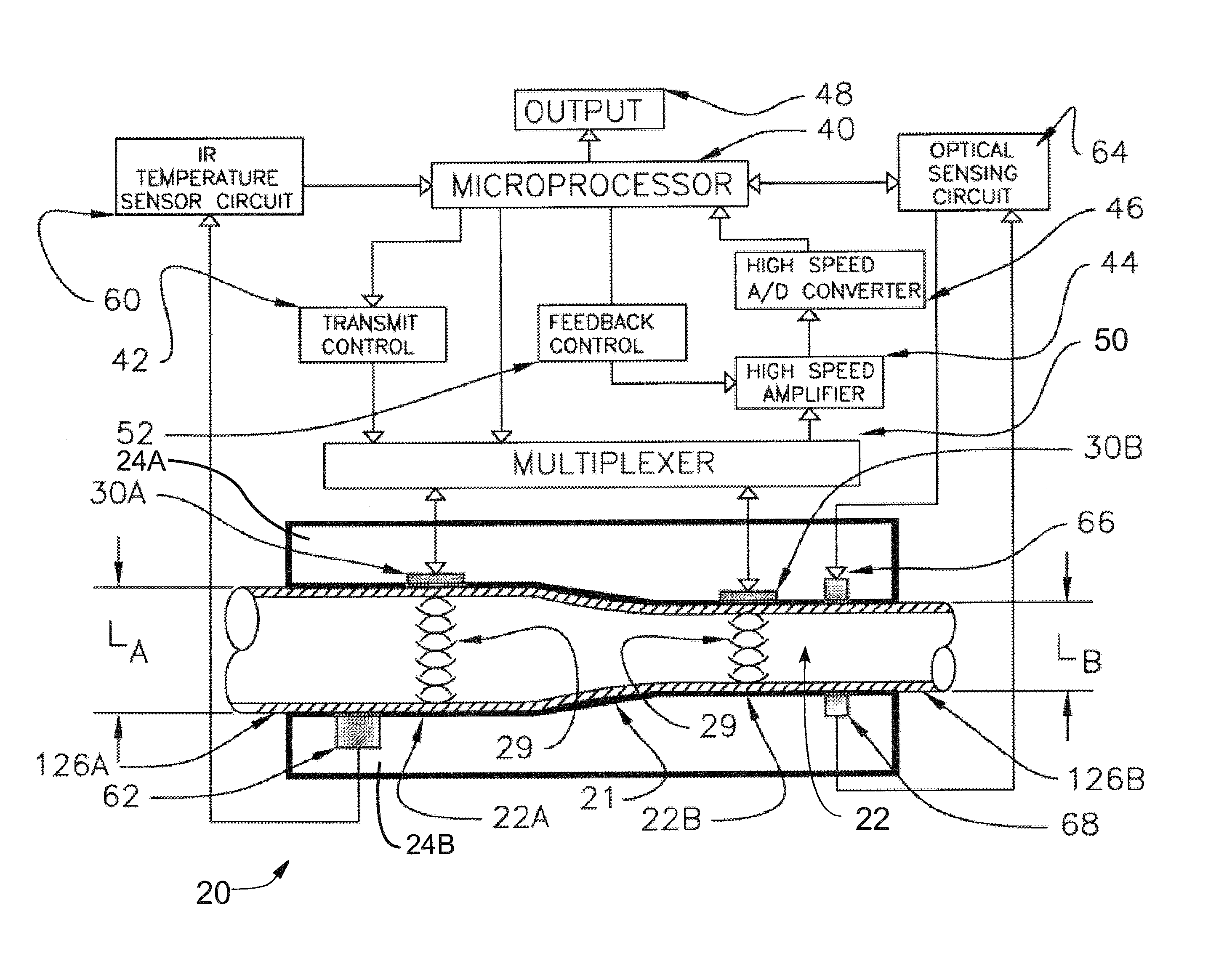
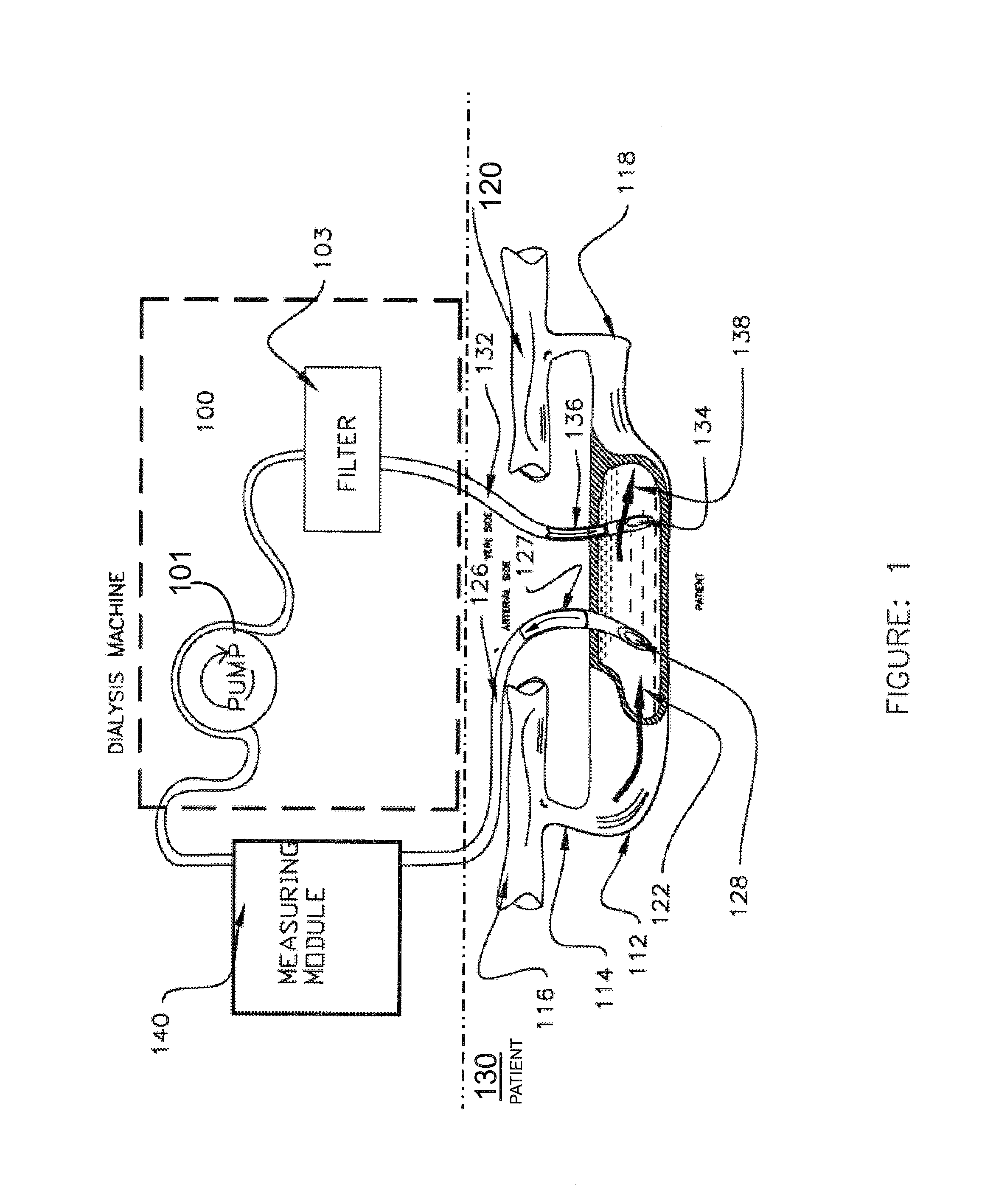
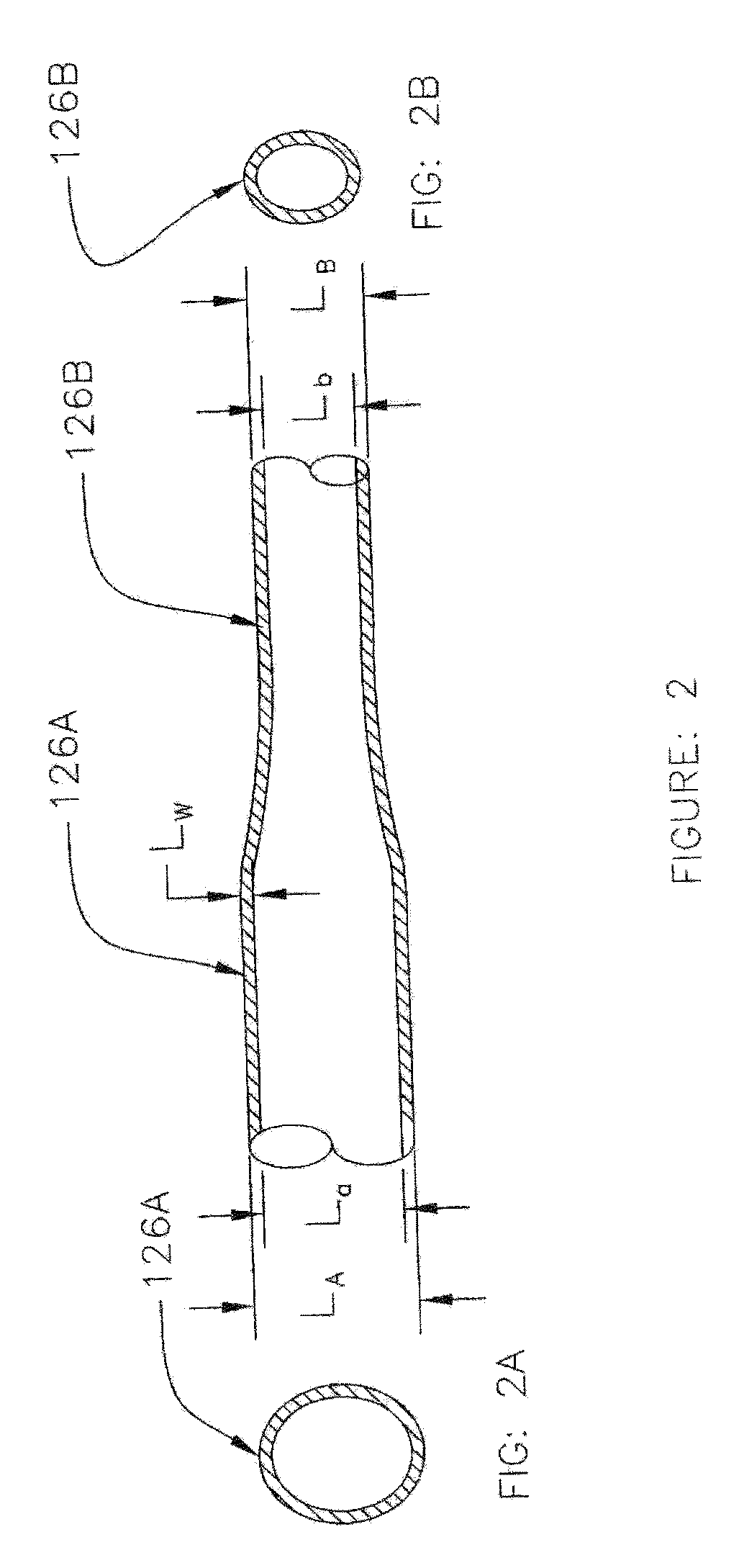
Apparatus and method for real time measurement of a constituent of blood to monitor blood volume
ActiveUS20120203476A1Reliable and accurate measurementEasy to useRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEmpirical relationshipSpeed of sound
Apparatus and method for non-invasively determining the level of a constituent of a patient's blood drawn though an elastomeric tubing to a dialysis machine deforms the tubing in the slot of a measuring head having two points of different transverse length with a transmit / receive sensor at each point that transmits a signal through the tubing and the blood and is reflected back to it from the tubing internal wall. The round trip transit time of the signal at each sensor is measured and the blood sound velocity is calculated from the two round trip transit times and the differential of the transverse lengths at the two points. Blood hematocrit level, which is related to blood volume, is calculated from the calculated sound velocity and an empirical relationship.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
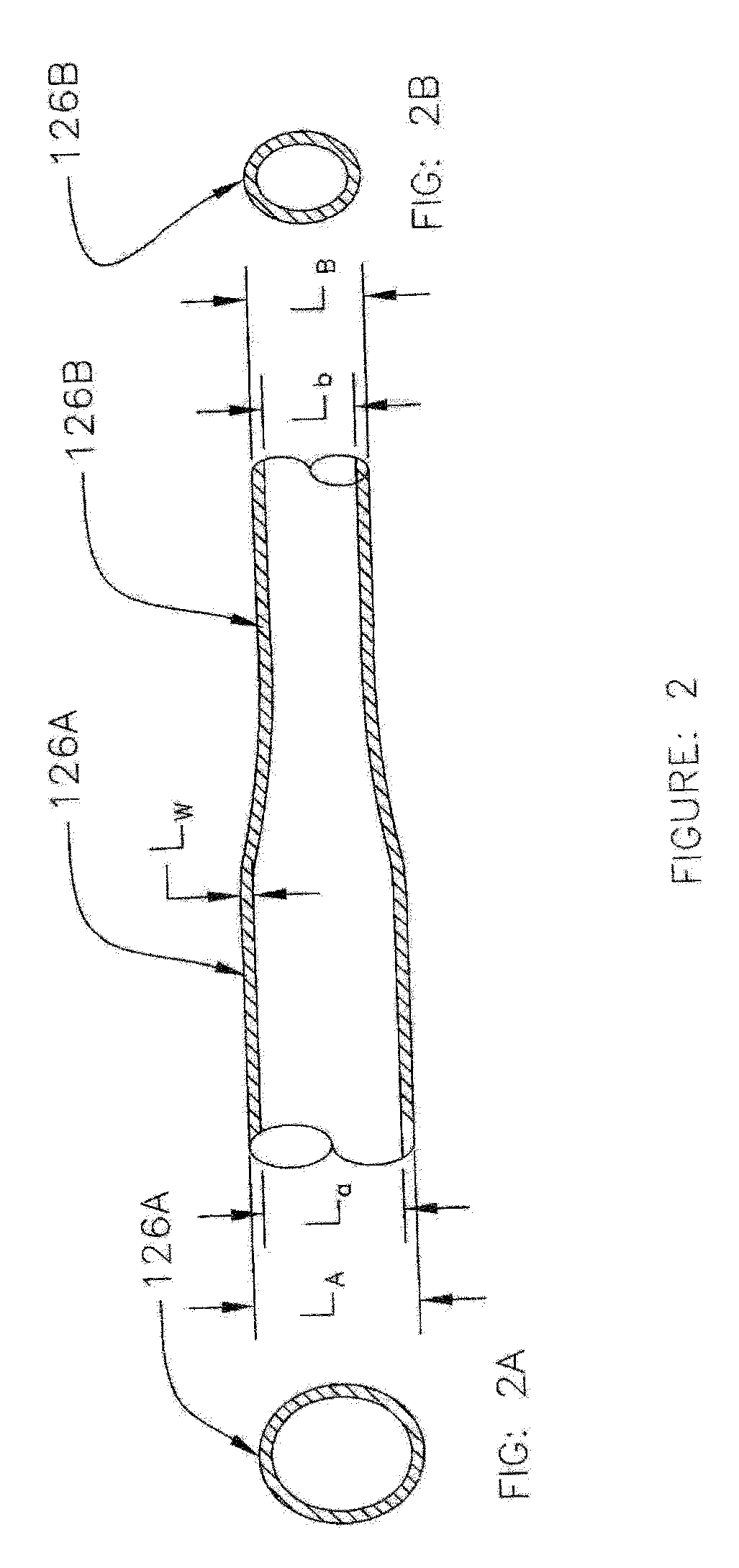
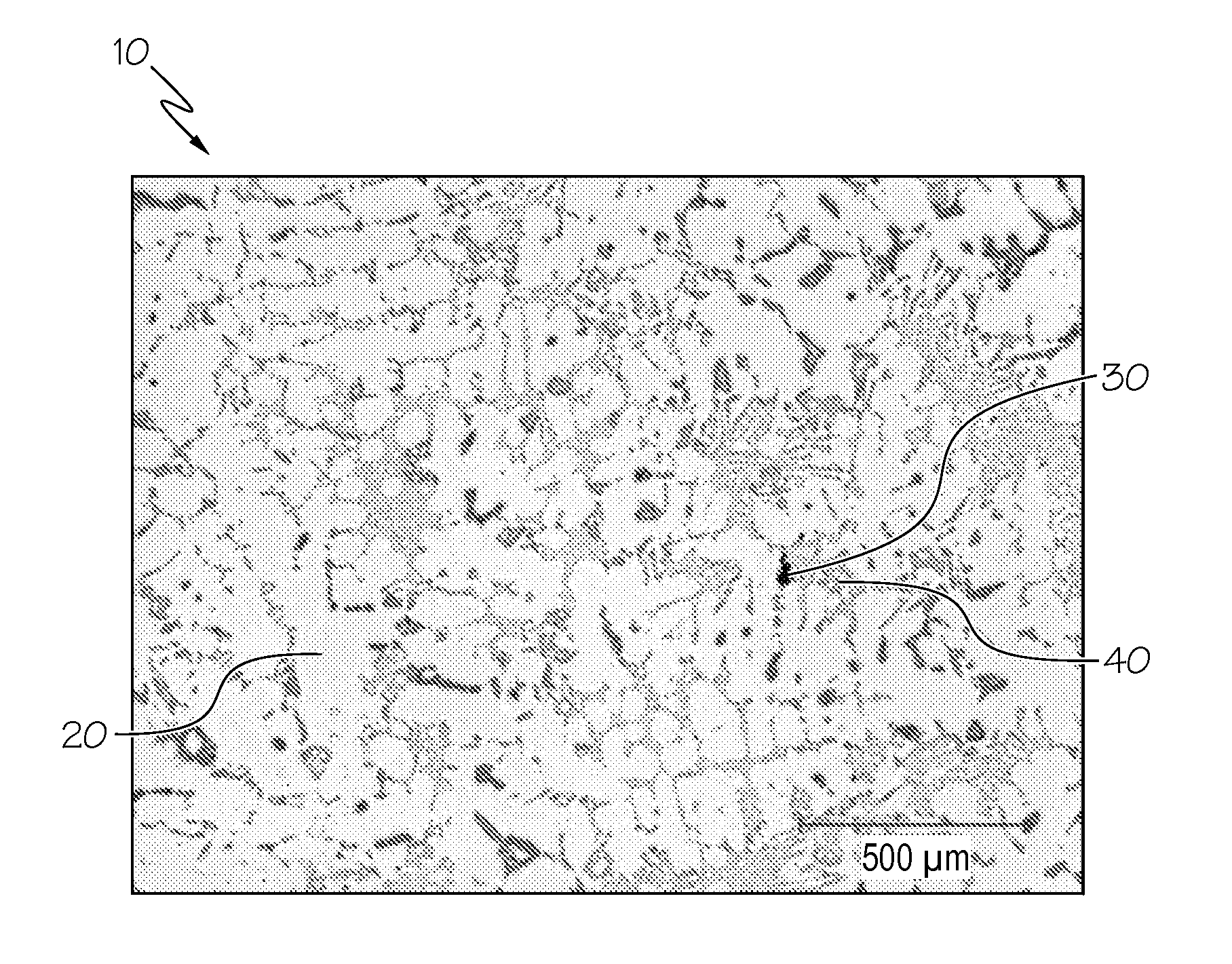
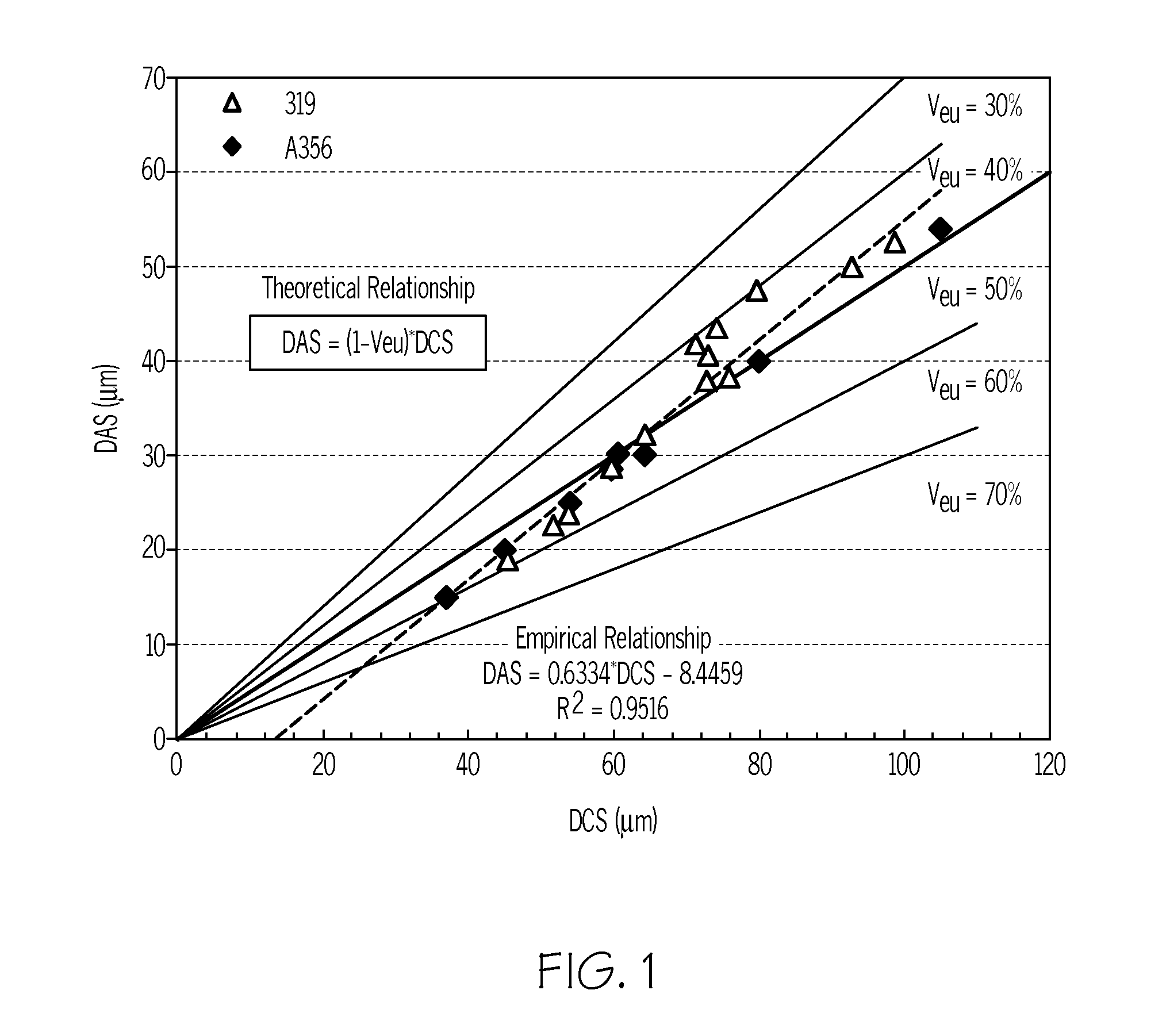
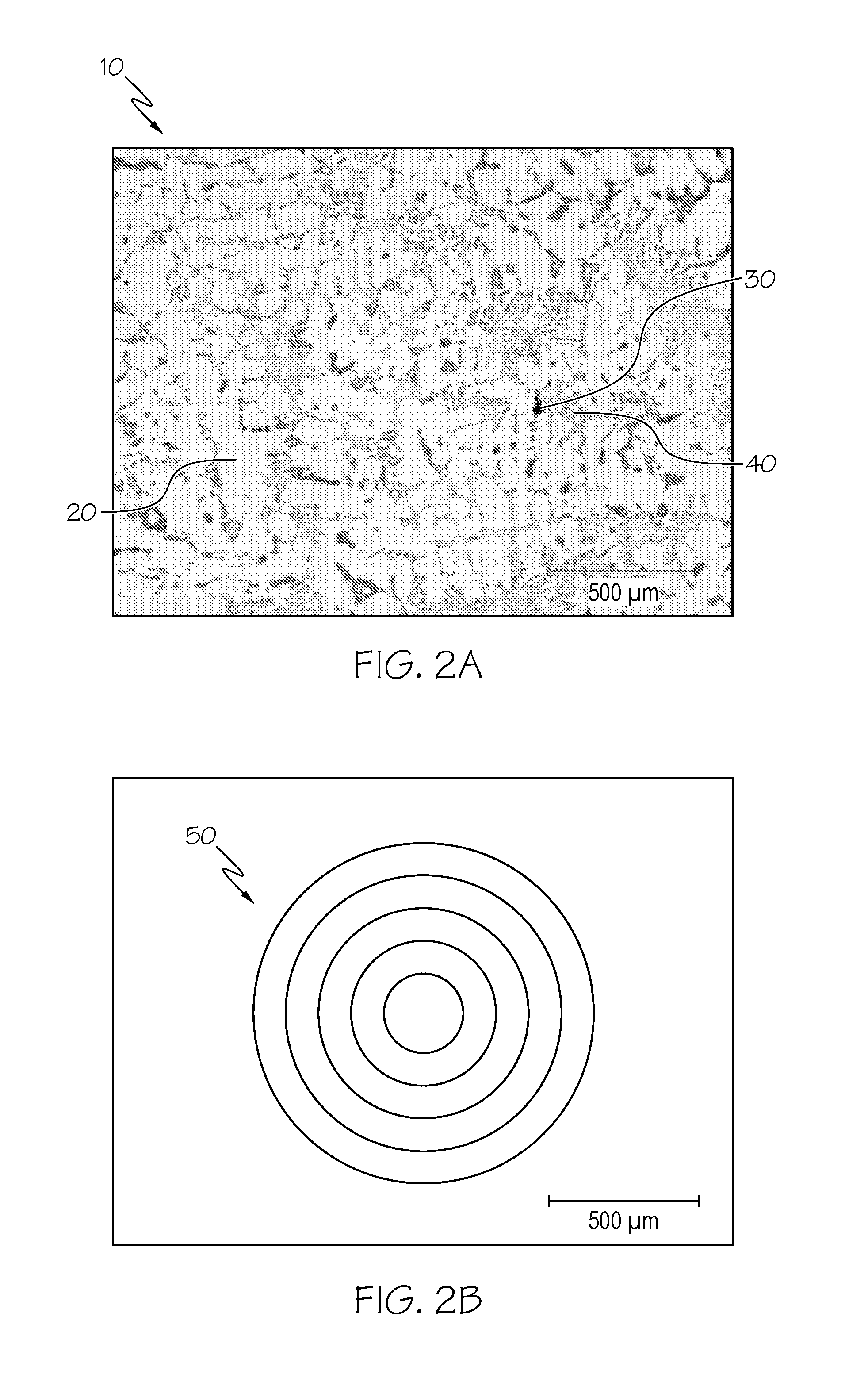
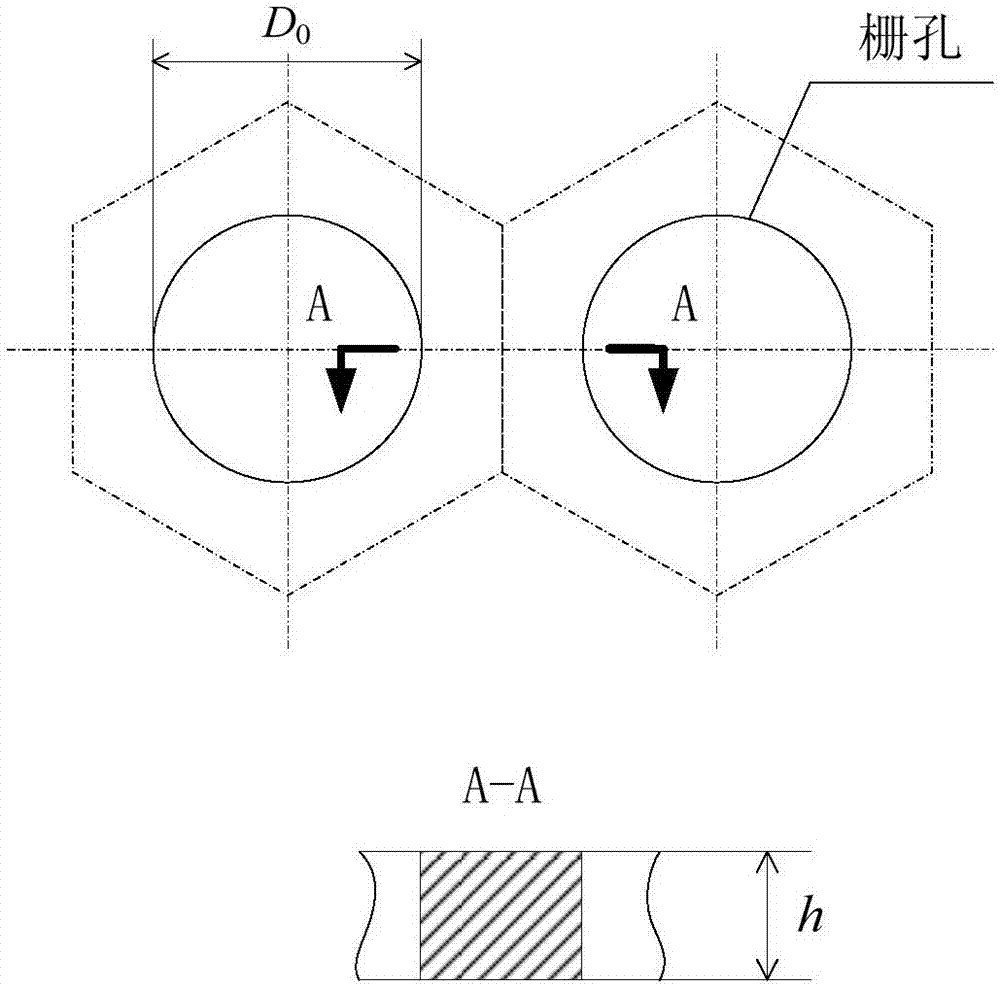
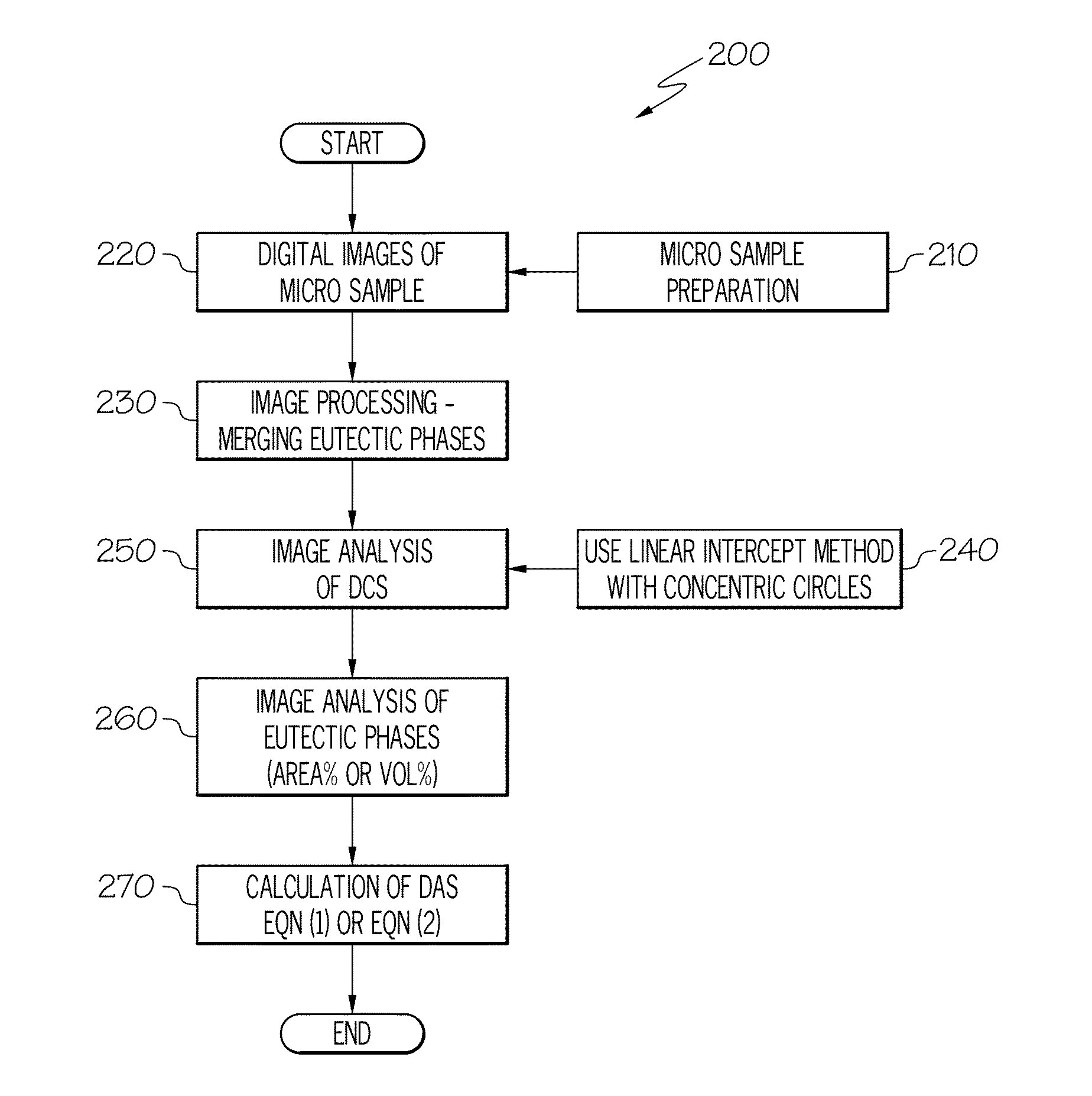
Method for automatic quantification of dendrite arm spacing in dendritic microstructures
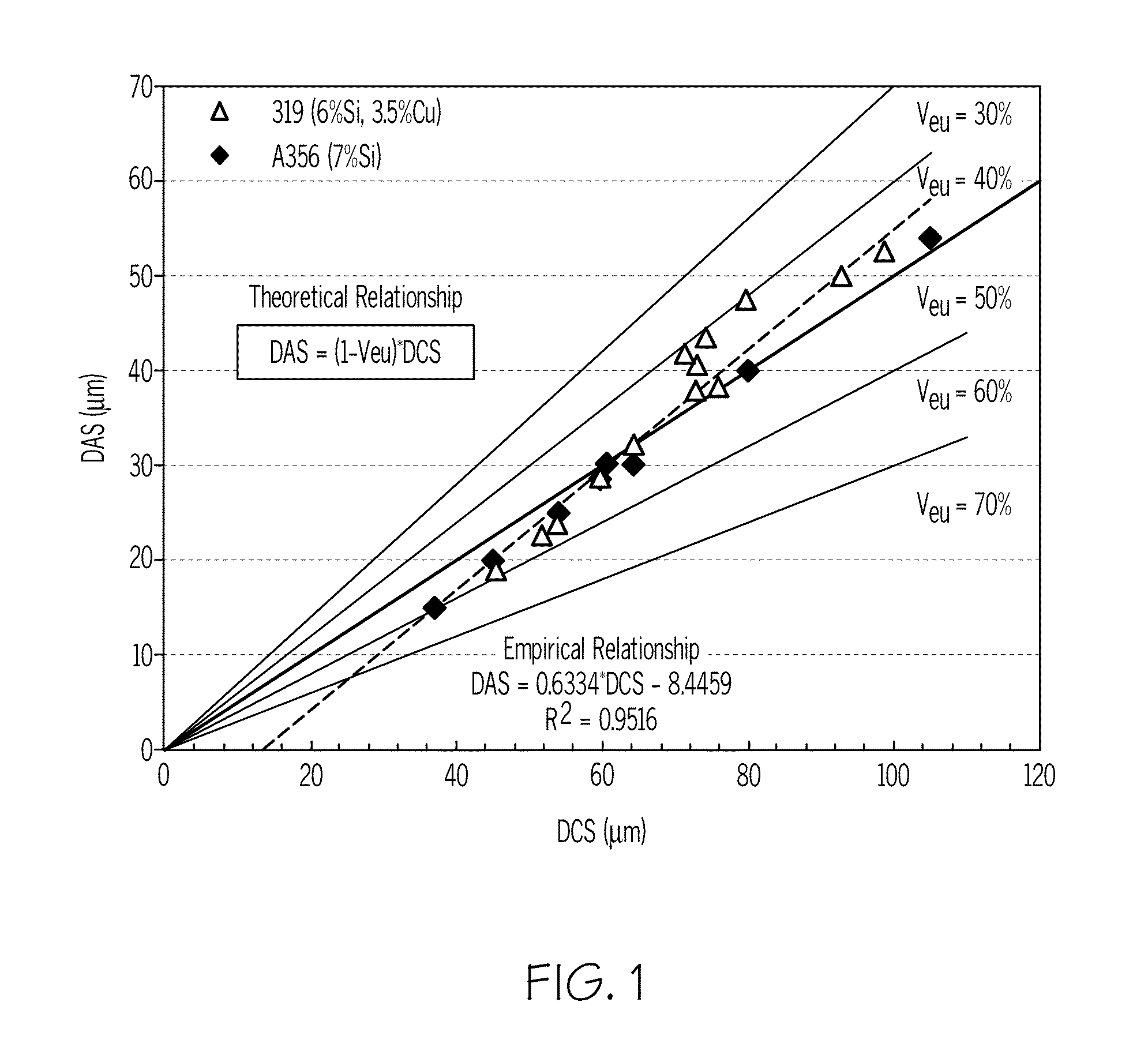
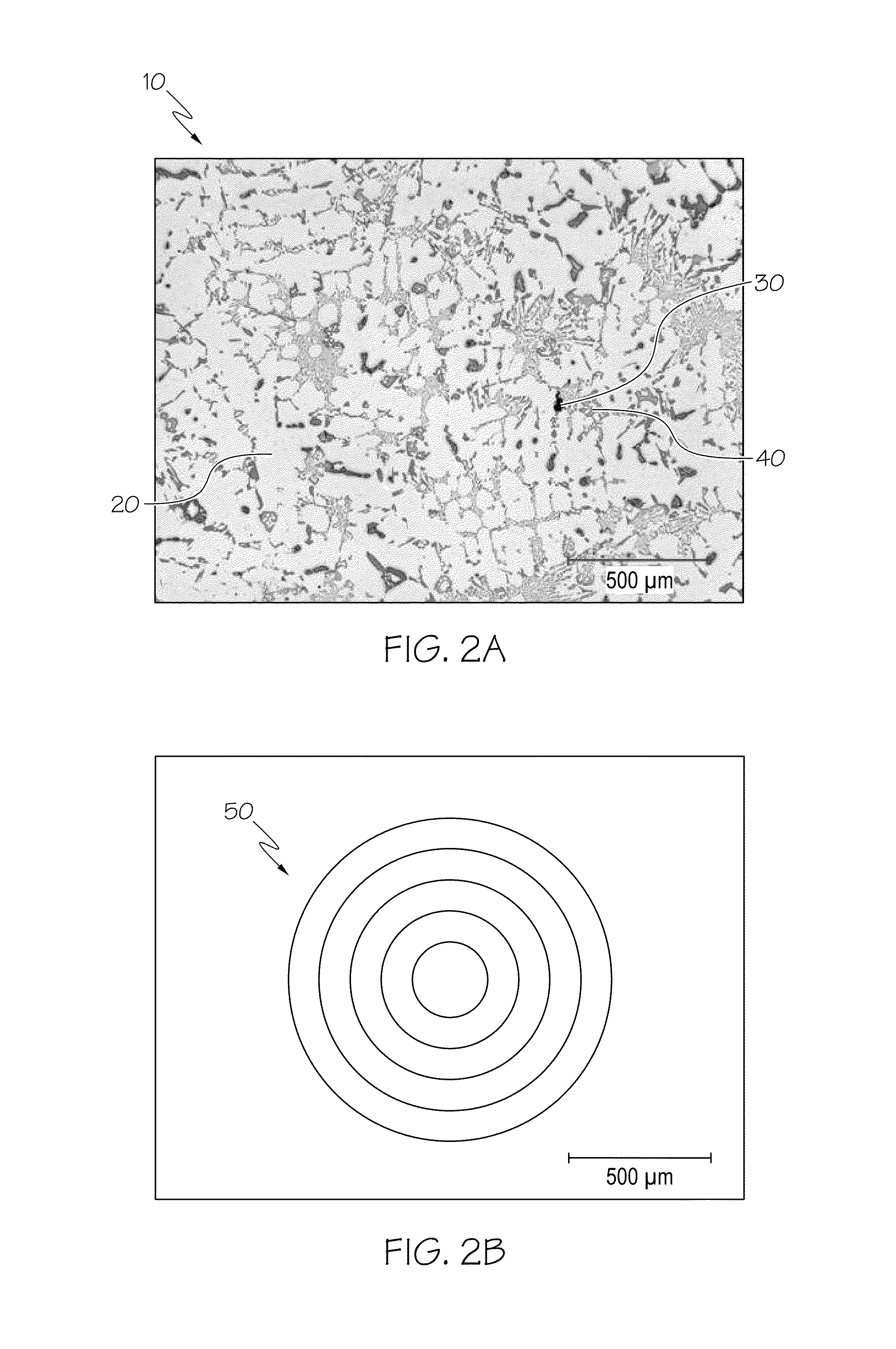
A method to automatically quantify dendrite arm spacing in dendritic microstructures. Once a location of interest in a cast material specimen has been identified, the information contained in it is automatically analyzed to quantify dendrite cell size information that is subsequently converted into a quantified dendrite arm spacing through an empirical relationship or a theoretical relationship. In one form, the relationship between DCS and DAS is such that the DAS in dendritic structure of cast aluminum alloys may be automatically determined from the measurement of one or more of dendrite cell size and the actual volume fraction of the eutectic phases in the local casting microstructure. Non-equilibrium conditions may be accounted for in situations where a theoretical volume fraction of a eutectic phase of the alloy in equilibrium condition is appropriately modified. Thus, in situations where equilibrium conditions—such as those where the casting is cooled very slowly during solidification—does not apply (such as during rapid cooling and consequent solidification), the eutectic measured in the non-equilibrium condition, which can be smaller than the theoretical value in equilibrium, can be accounted for.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
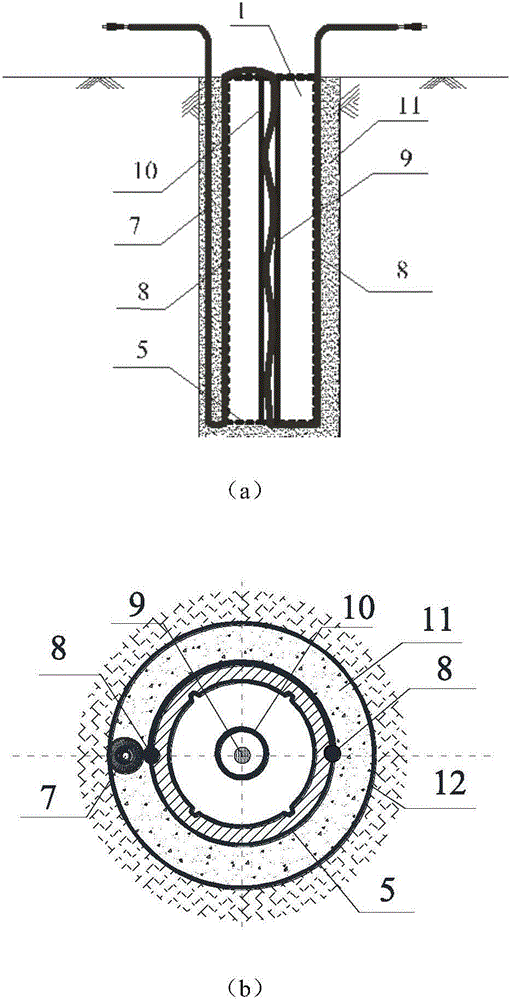
Slope stability monitoring and landslide warning and forecasting method based on all-fiber sensor network
ActiveCN106767476AHigh monitoring sensitivityAccurately identify critical safety statesMaterial heat developmentUsing optical meansFiberBedrock
The invention discloses a slope stability monitoring and landslide warning and forecasting method based on an all-optical fiber sensing network. A number of drill holes are drilled in a direction perpendicular to a potential sliding surface or a joint surface and a bedrock surface in the top and surface of a rocky soil slope. An all-optical fiber integrated gauging pipe is buried in each drill hole. All optical fibers are mutually welded to form the all-optical fiber sensing network which is connected with an optical fiber demodulator to measure the strain and temperature distribution of each optical fiber. On the basis of early monitoring results, the vertical strain eigenvalue of the slope is selected, and the safety factor of the slope is acquired. The empirical relationship between the vertical strain eigenvalue and the safety factor is acquired. According to the measured result of the vertical strain eigenvalue, the safety factor of the slope is estimated, and warning and forecasting of slope instability are realized. Based on the optical fiber monitoring data, the process of birth, occurrence and development of the potential sliding surface of the slope and the position of a multi-level potential sliding surface can be accurately identified.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
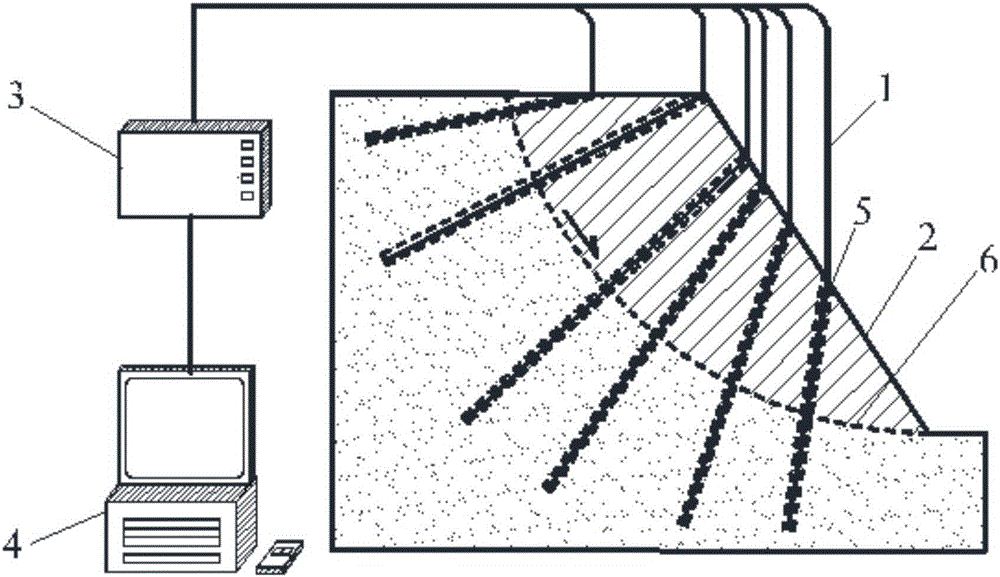
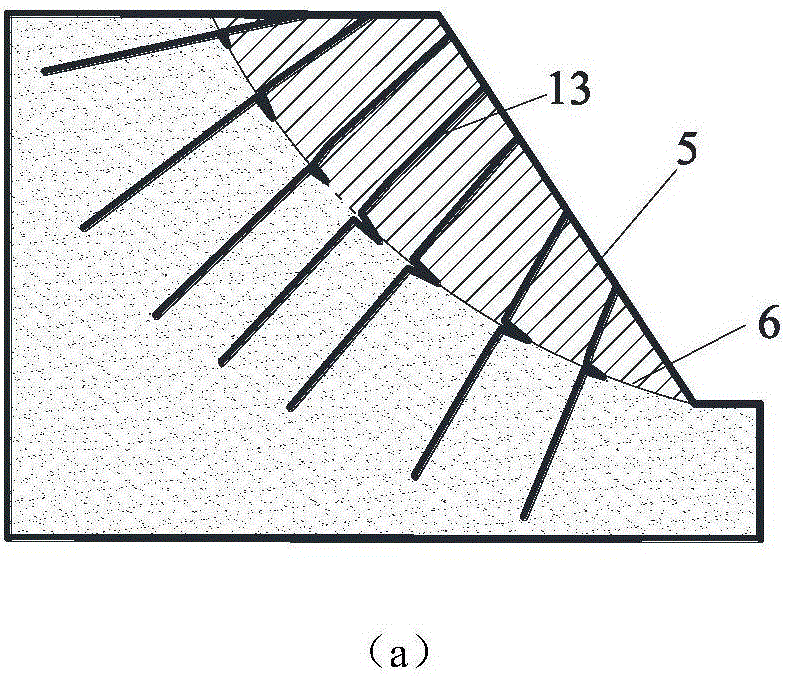
Quantitative method utilizing equivalent rock mass basic quality index to predict shield driving parameters
The invention relates to a quantitative method utilizing an equivalent rock mass basic quality index to predict shield driving parameters and relates to the geotechnical engineering and tunnel engineering investigation, design and construction technology field. According to the method, the equivalent rock mass basic quality index is taken as basis, geological segmentation of complex strata is carried out, and segmented statistics of the driving parameters is carried out; experience relationships among the driving rate, cutterhead torque and other driving parameters are calculated through gradual regression to acquire a general driving rate prediction model and a general cutterhead torque prediction model which adapt to uniform strata and the complex strata; through quantitative analysis on the corresponding relationships among a general driving rate prediction model coefficient, a general cutterhead torque prediction model coefficient and the equivalent rock mass basic quality index, the driving parameters are acquired through prediction. The method is advantaged in that the method has great theoretical meaning and engineering application values for construction scheme design, construction cost-construction period control and shield-surrounding rock interaction rule analysis.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
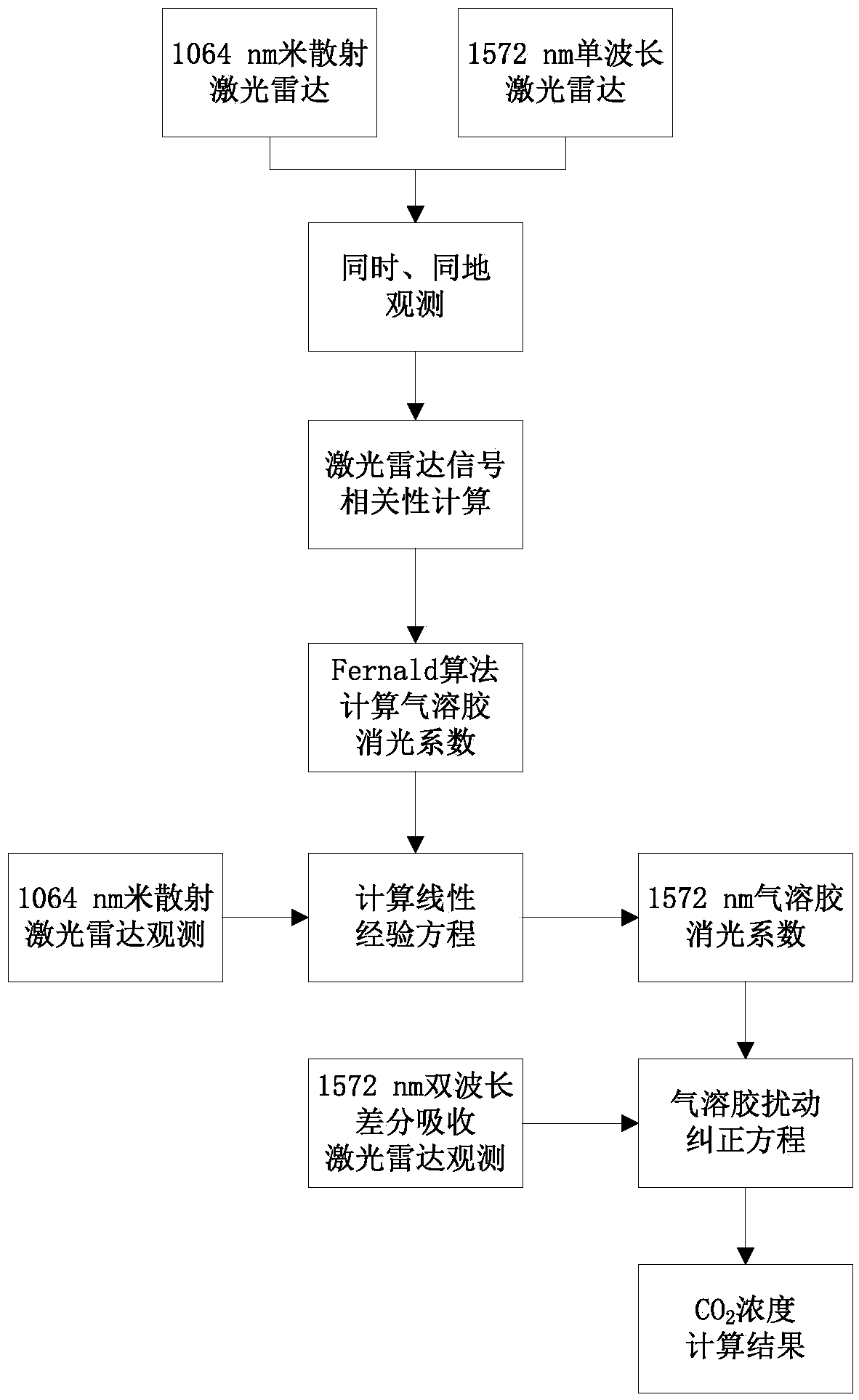
CO2 detection method through difference absorbing laser radar based on aerosol disturbance correcting
ActiveCN105510260AEasy to implementConcentration inversion results are accurateWave based measurement systemsColor/spectral properties measurementsExtinctionRadar
The invention discloses a CO2 detection method through difference absorbing laser radar based on aerosol disturbance correcting. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, considering the aerosol disturbance influence in a CO2 concentration inversion model; performing simultaneous observation of mie scattering laser radar in 1064nm and 1572nm wavelength, thereby acquiring a linear empirical relationship of an extinction coefficient and a backscatter coefficient of the aerosol in 1064nm and 1572nm wavelength; continuously detecting by using the mie scattering laser radar in 1064nm and 1572nm wavelength while performing conventional double-wavelength alternate emitting difference absorbing laser radar CO2 detection; acquiring the extinction coefficient and backscatter coefficient in on wavelength and off wavelength on the basis of the linear empirical relationship of the extinction coefficient and the backscatter coefficient; by combining with the CO2 concentration inversion model, acquiring a CO2 concentration inversion result. According to the method, the inversion result is more accurate. The method has wide application prospect in the field of detecting atmosphere trace gas through difference absorbing laser radar.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Walkaway vsp calibrated sonic logs
ActiveUS20110170372A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingAcoustic waveEmpirical relationship
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
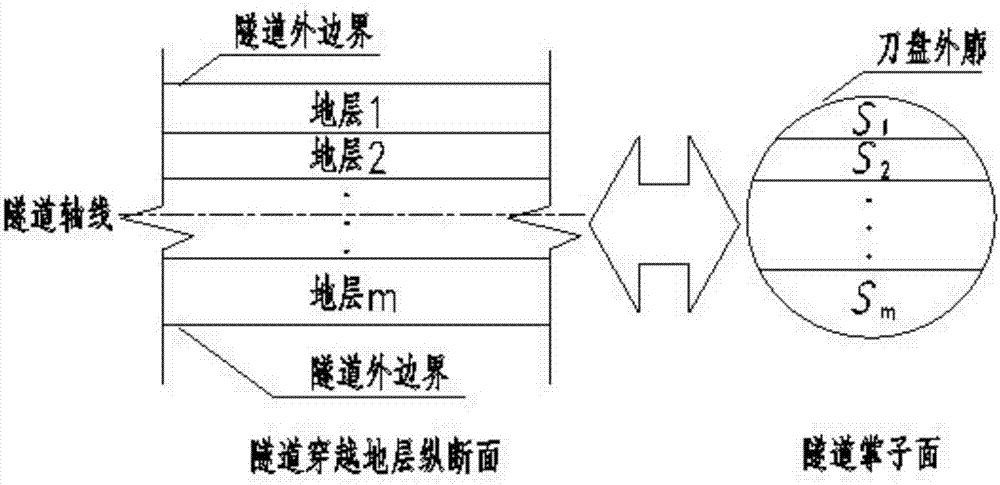
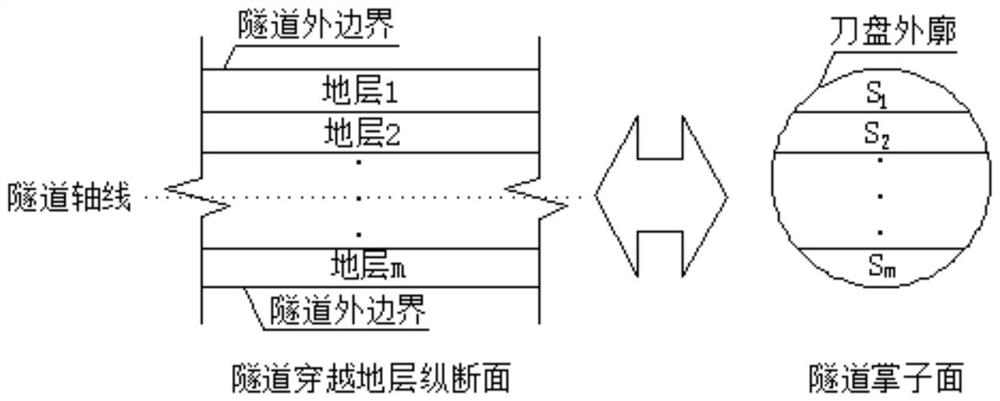
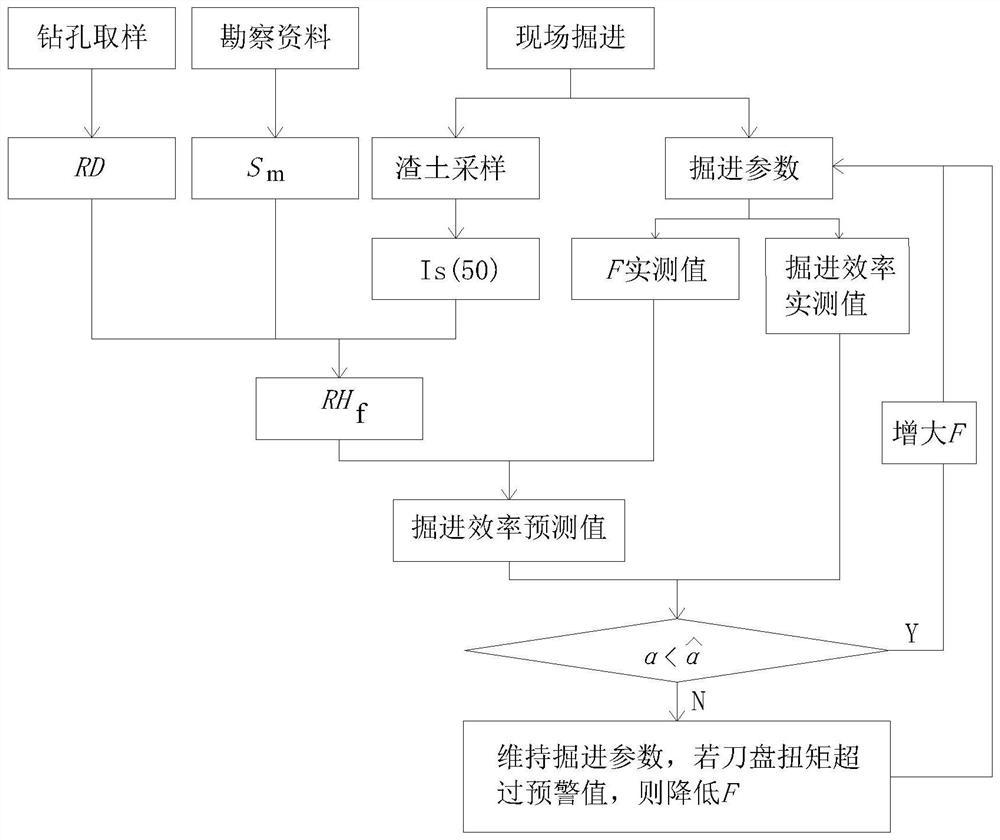
Composite stratum shield tunneling efficiency on-site prediction and calculation method
ActiveCN111946398AOut-of-the-box indicatorsReady-to-use calculation parametersMining devicesTunnelsEconomic benefitsShield tunneling
The invention discloses a composite stratum shield tunneling efficiency on-site prediction and calculation method. The method mainly comprises the steps that a rock crushing degree index of a drilledrock core is measured and calculated; the BQ value of each stratum is calculated according to engineering investigation data, and the rock slag point load intensity is obtained according to rock slagsof a construction site; and an empirical relationship formula between the crushing degree index and the point load intensity is obtained; and based on the result and the area ratio of each stratum ofa tunnel face, a composite stratum full-section on-site rock mass tunneling difficulty index RH<f> can be obtained, and finally a composite stratum shield tunneling efficiency prediction model established based on the total shield thrust F and the RH<f> is obtained according to the tunneling efficiency, the total thrust, the cutterhead torque and the tunneling rate. The method can be directly applied to the shield construction site, indexes and calculation parameters have the advantages of measurement-and-use, convenience and high efficiency, the construction period cost is saved, the economic benefit is remarkable, the index calculation evaluation result conforms to the actual law, and the method has important engineering significance for guiding and perfecting intelligent construction of a roadheader.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +1
Noninvasive method and system for measuring pulmonary ventilation
ActiveUS20140323847A1Reduce and eliminate drawbackConvenient and accurateRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsIntensive care medicineEmpirical relationship
A pulmonary ventilation system comprising means for storing an empirical relationship that is designed and adapted to determine at least one pulmonary ventilation parameter as a function of a plurality of measured anatomical distances and volume-motion coefficients, means for acquiring the anatomical distances, means for determining the plurality of motion coefficients, and processing means for determining the ventilation parameter based on the acquired anatomical distances and determined plurality of volume-motion coefficients. In one embodiment, the system further includes means for acquiring base-line ventilation characteristics and means for correlating the base-line ventilation characteristics to the ventilation parameter determined with the empirical relationship.
Owner:ADIDAS
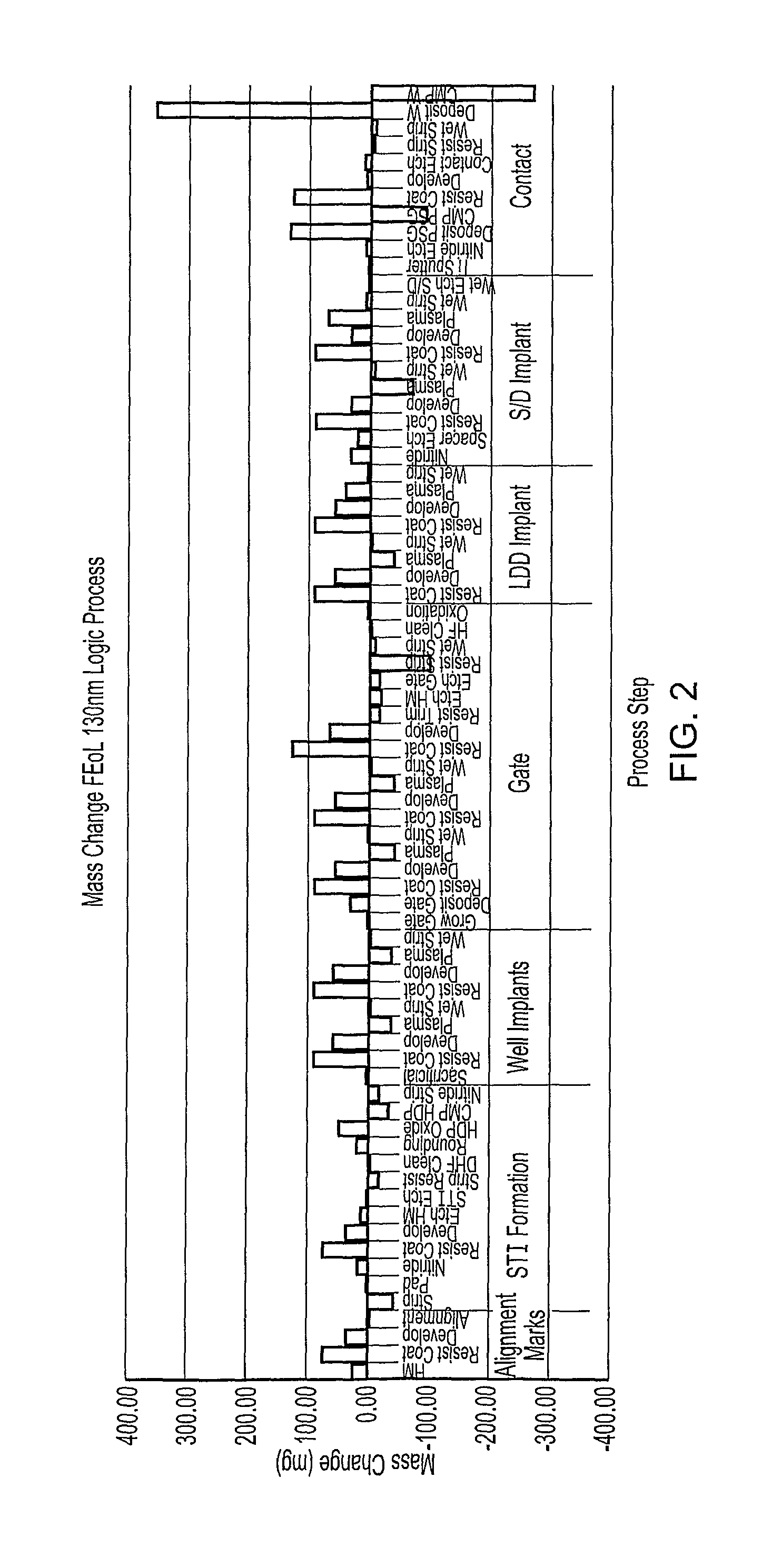
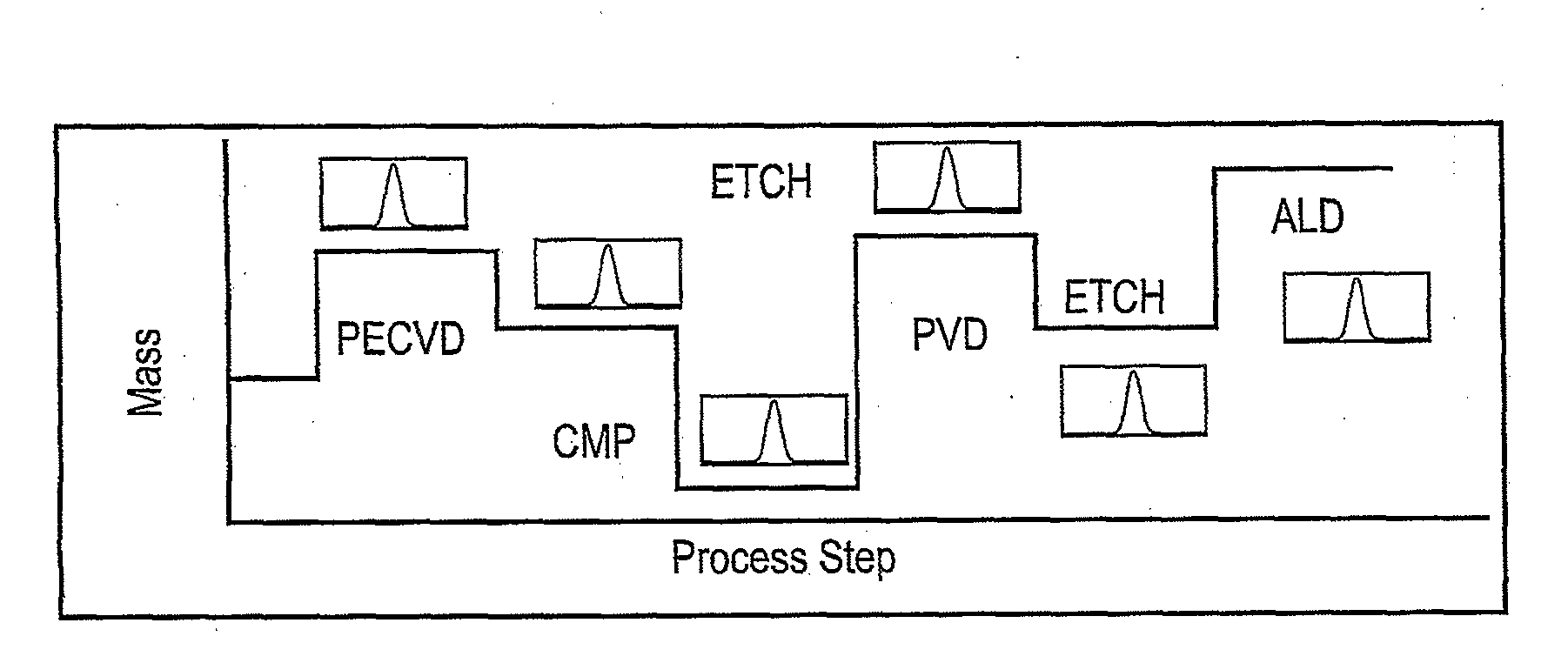
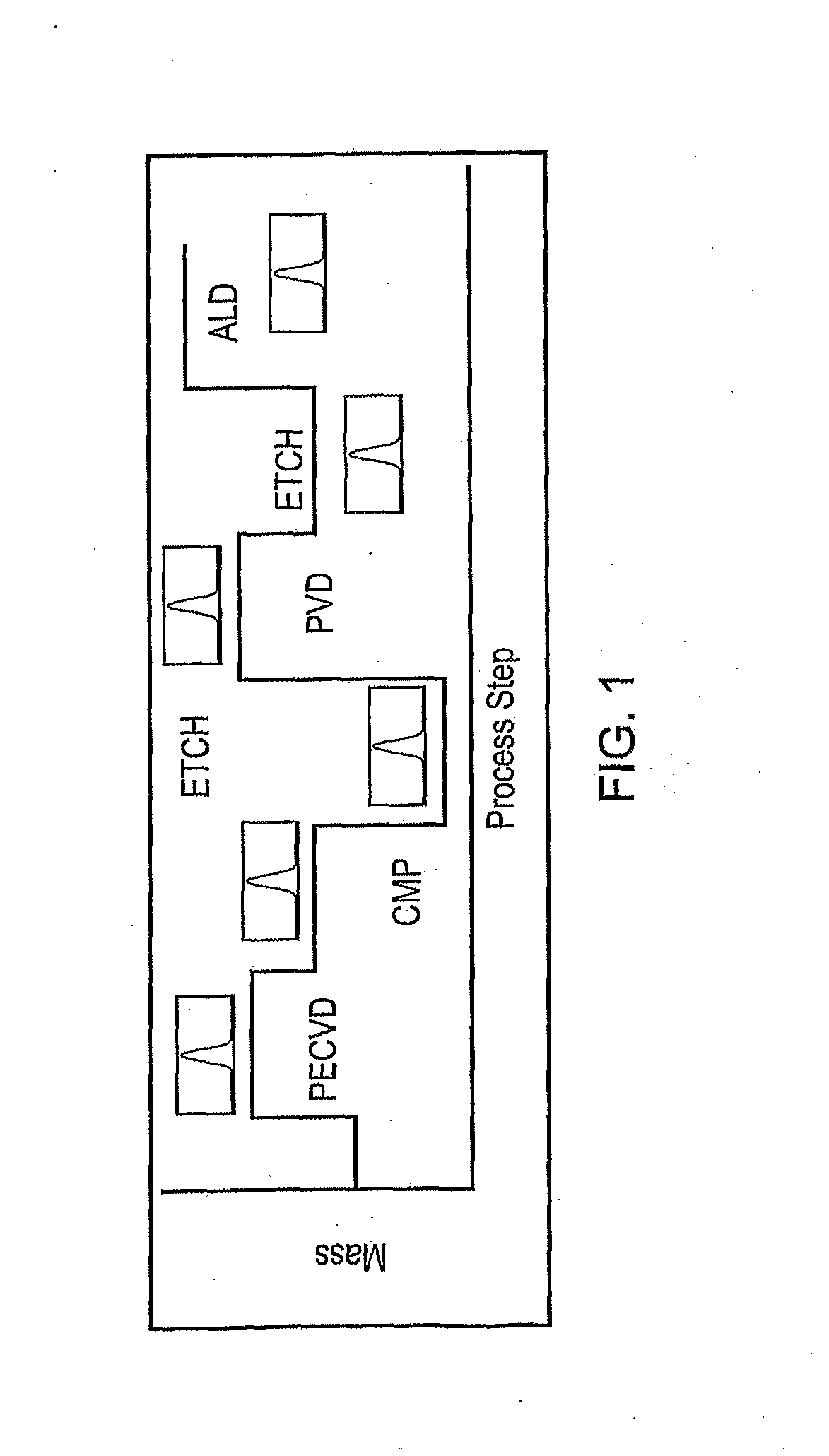
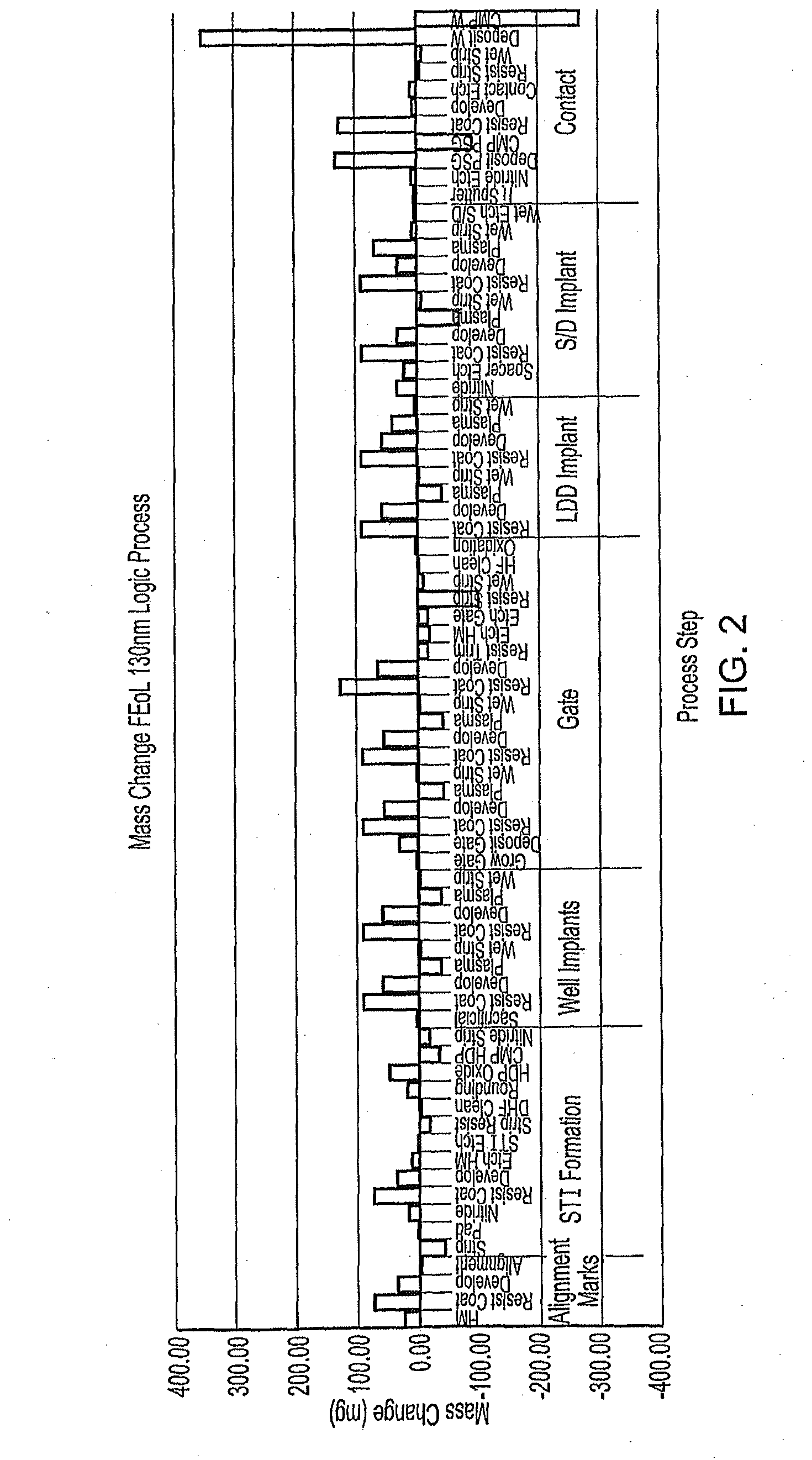
Method of Controlling Semiconductor Device Fabrication
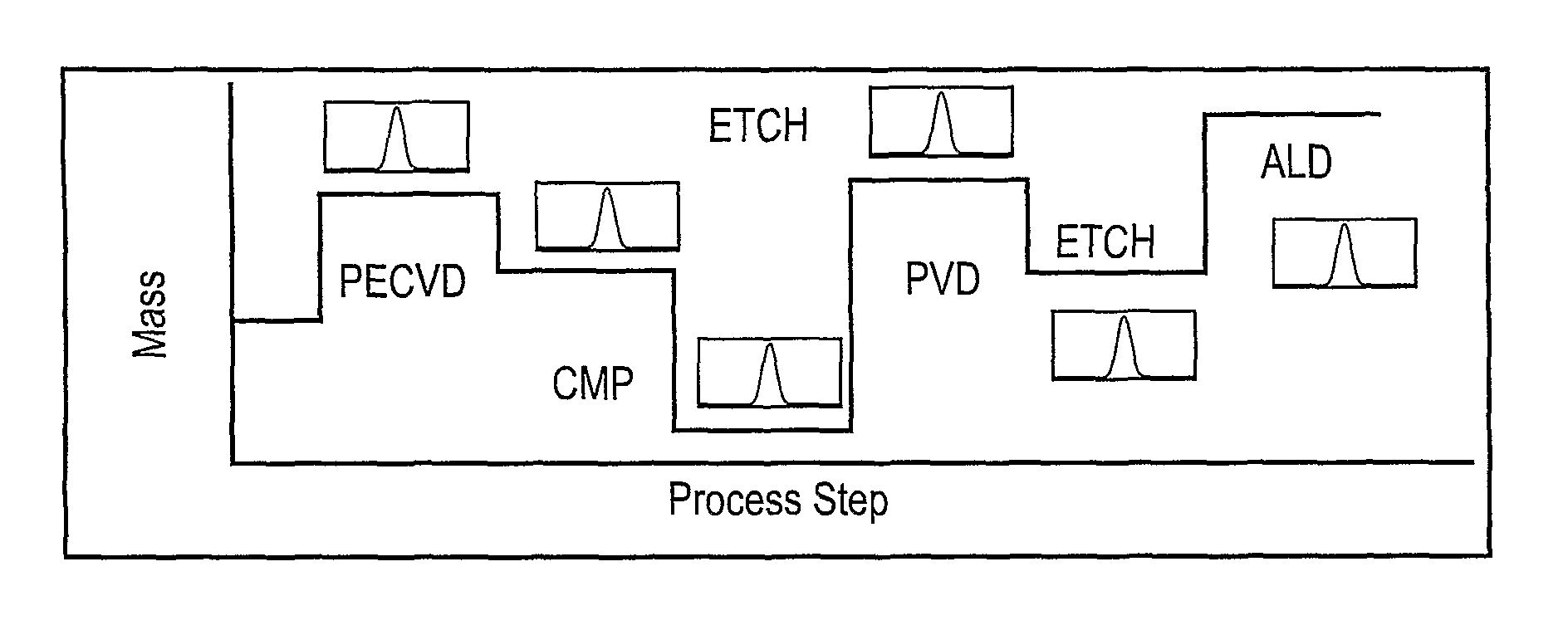
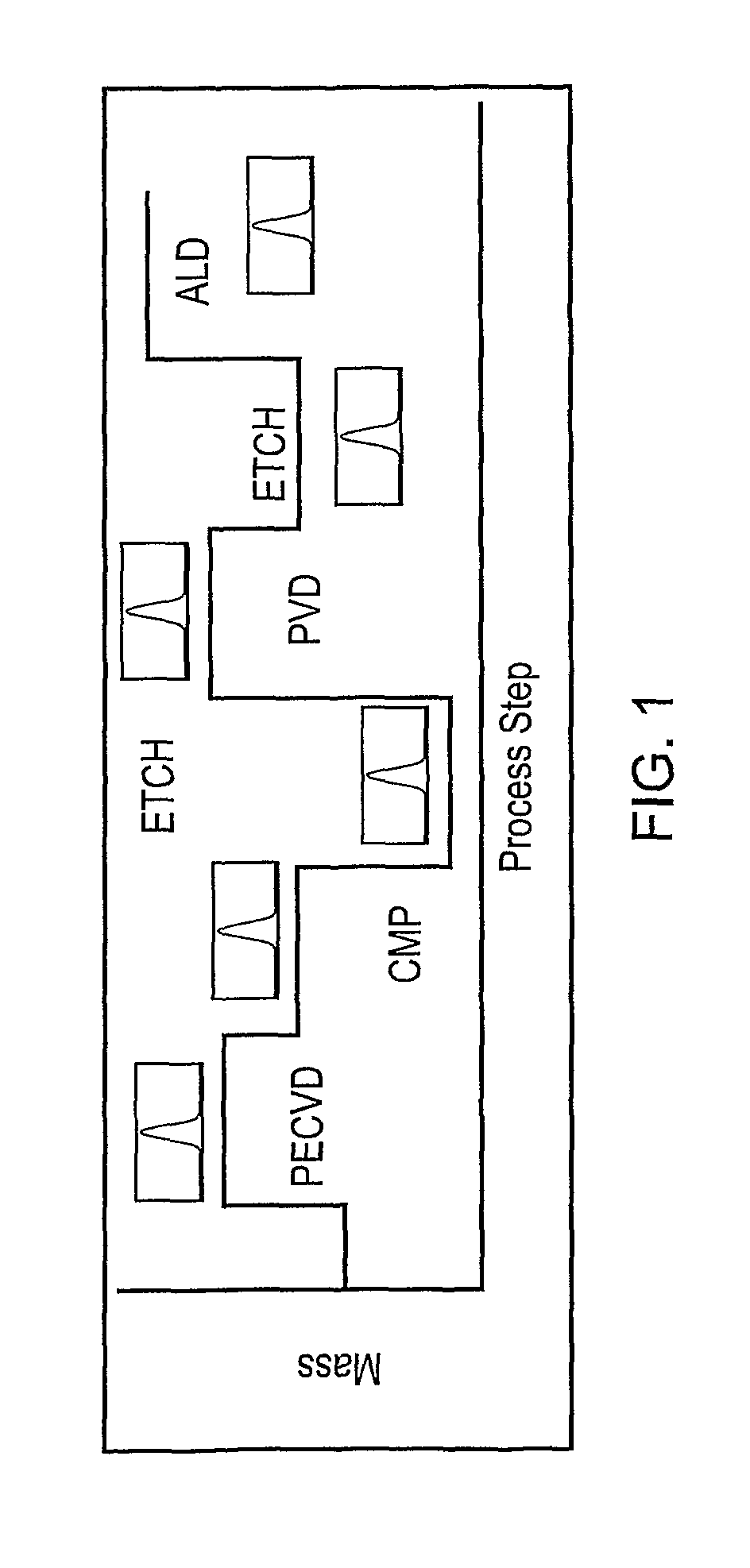
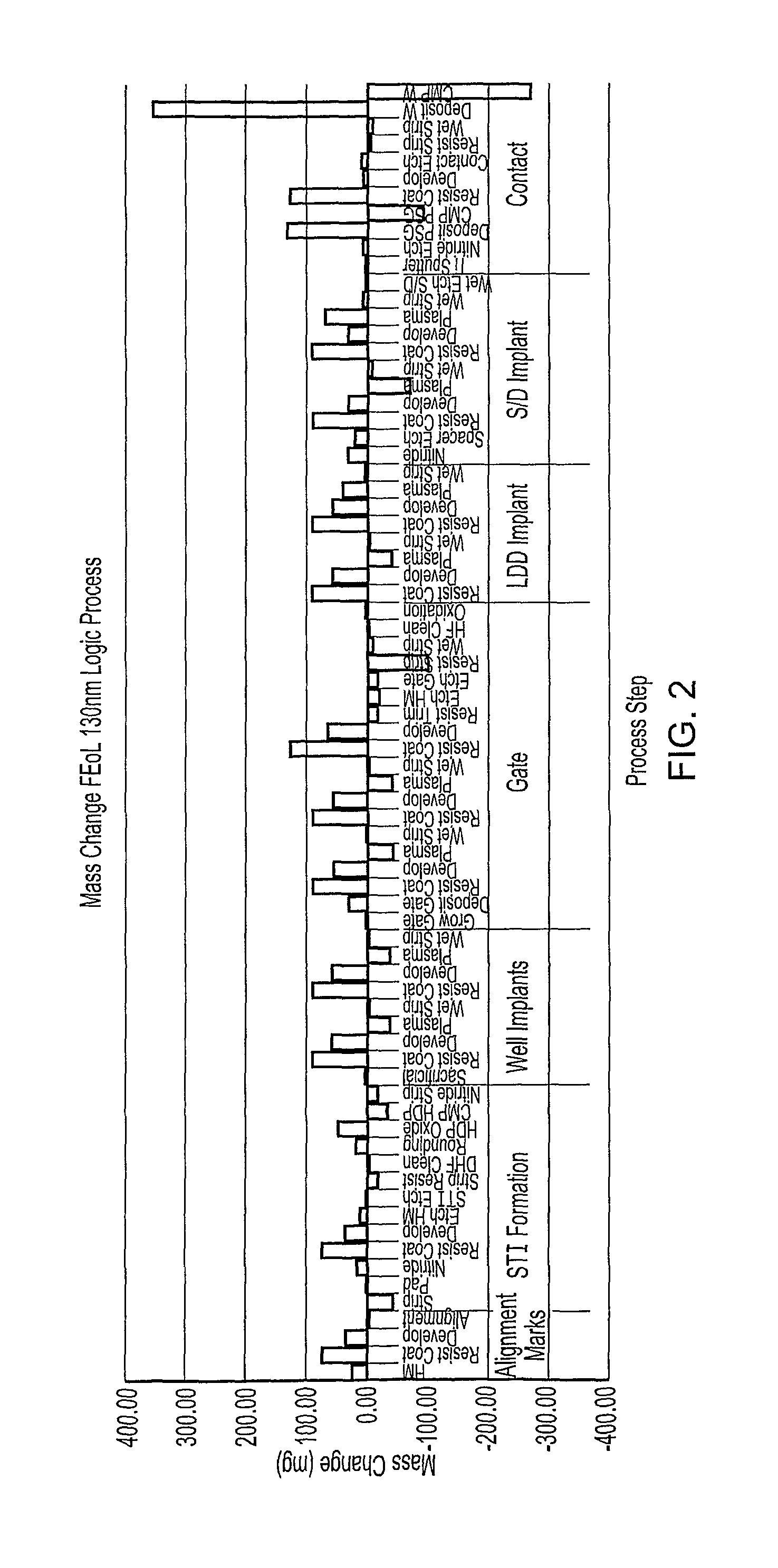
ActiveUS20110190919A1Efficiently takenInformation can be usedVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMetrologyCurrent distribution
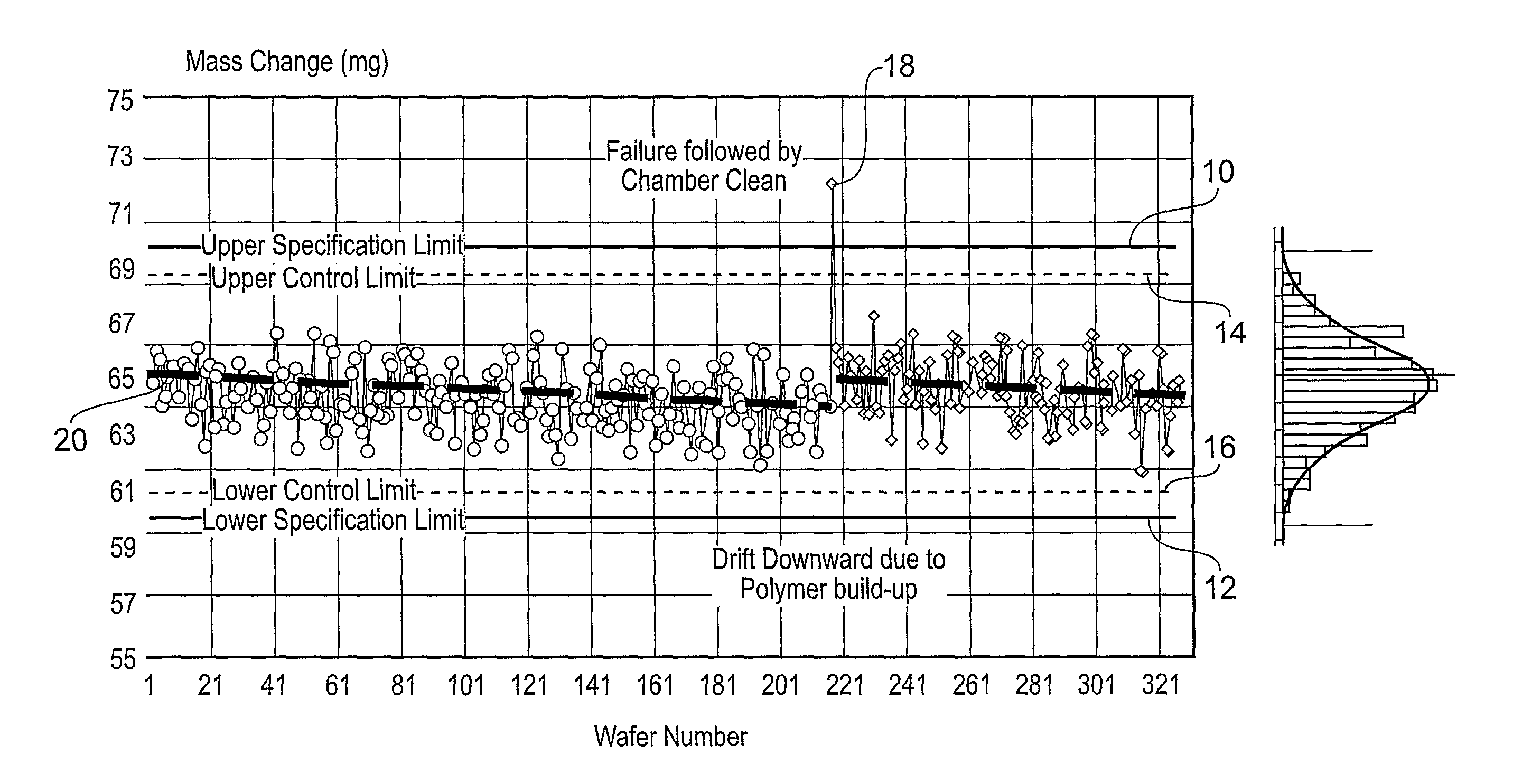
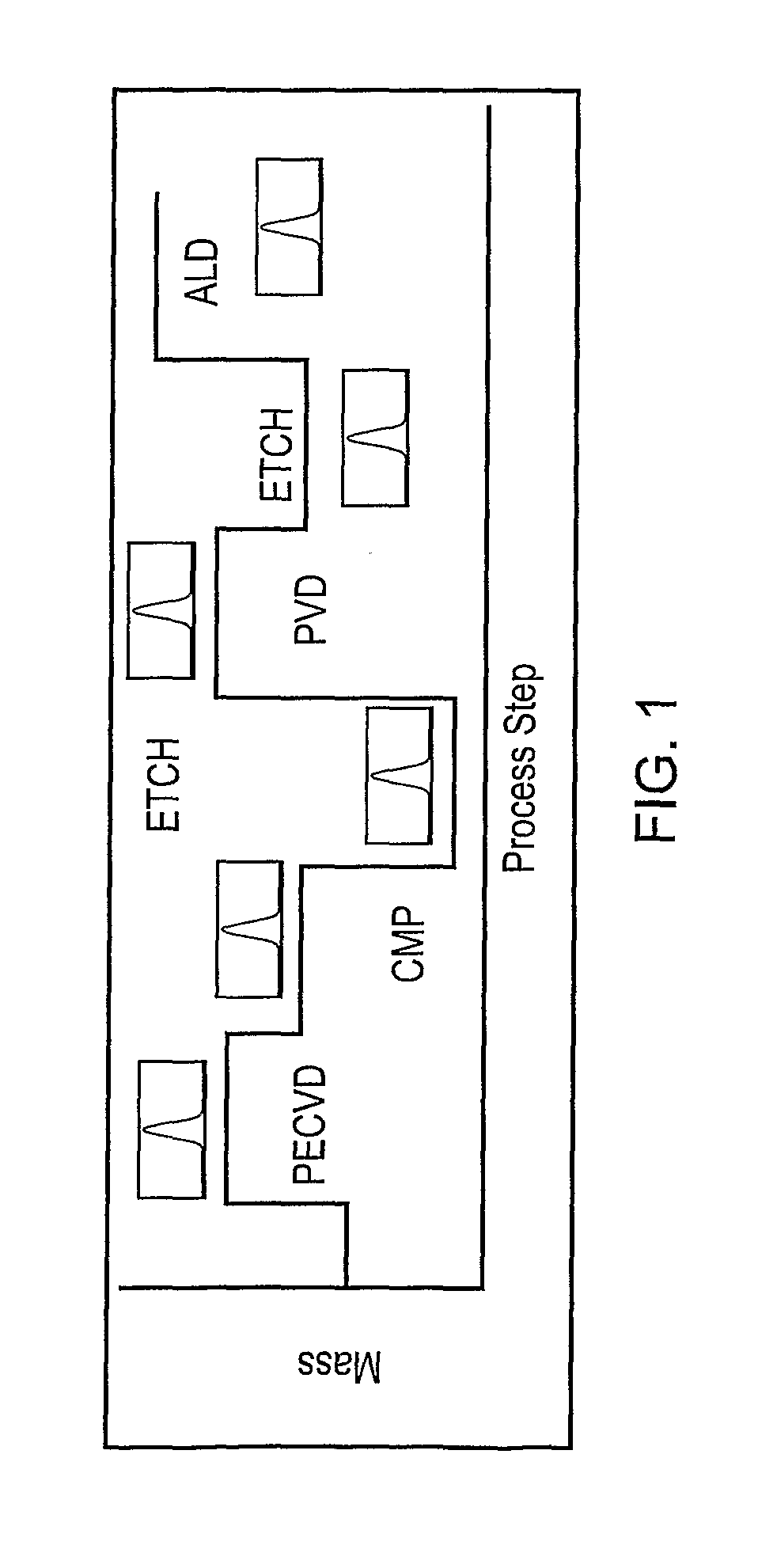
A semiconductor wafer fabrication metrology method in which process steps are characterised by a change in wafer mass, whereby during fabrication mass is used as a measurable parameter to implement statistical process control on the one or more of process steps. In one aspect, the shape of a measured mass distribution is compared with the shape of a predetermined characteristic mass distribution to monitor the process. An determined empirical relationship between a control variable of the process and the characteristic mass change may enable differences between the measured mass distribution and characteristic mass distribution to provide information about the control variable. In another aspect, the relative position of an individual measured wafer mass change in a current distribution provides information about individual wafer problems independently from general process problems.
Owner:METRYX
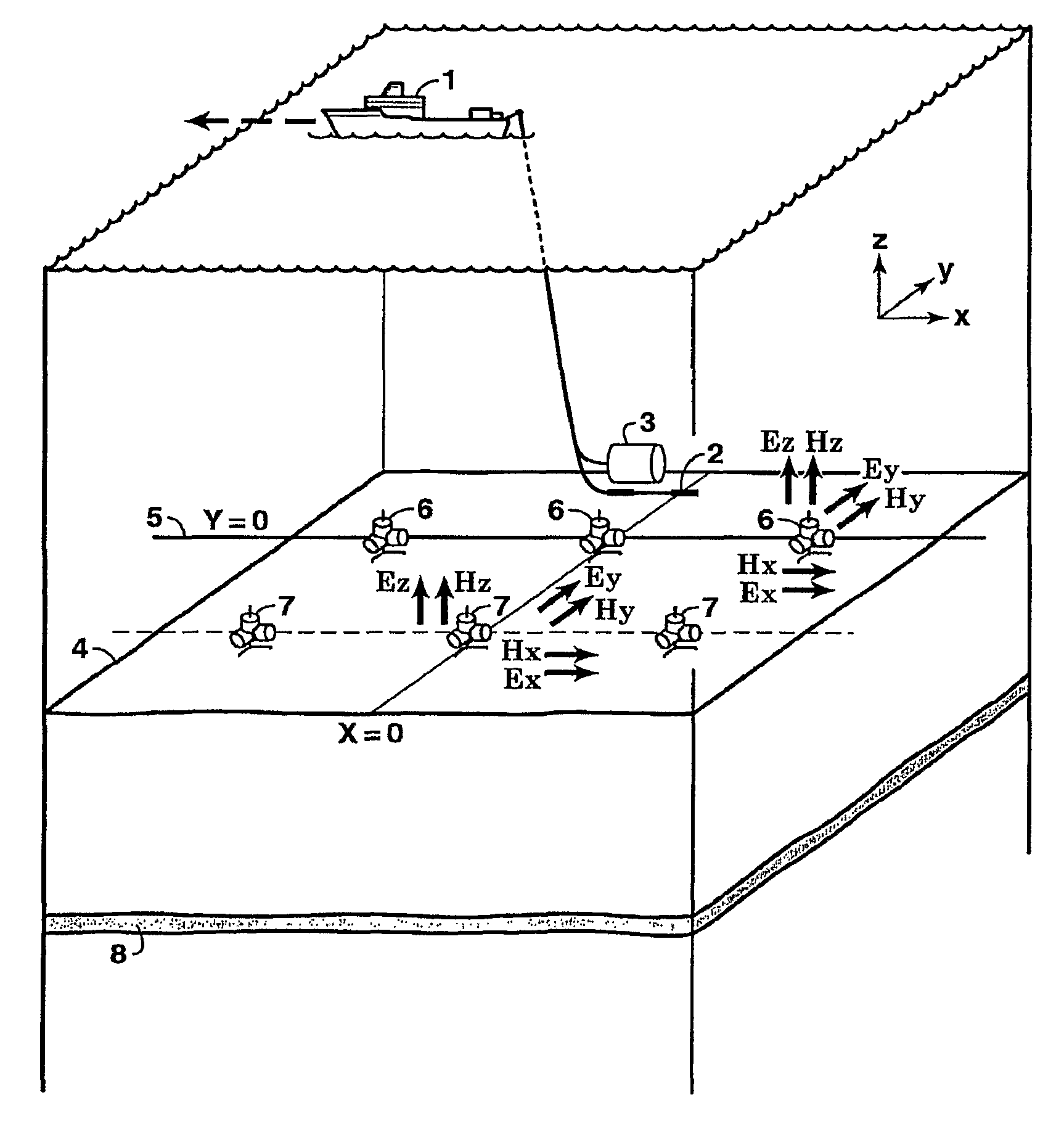
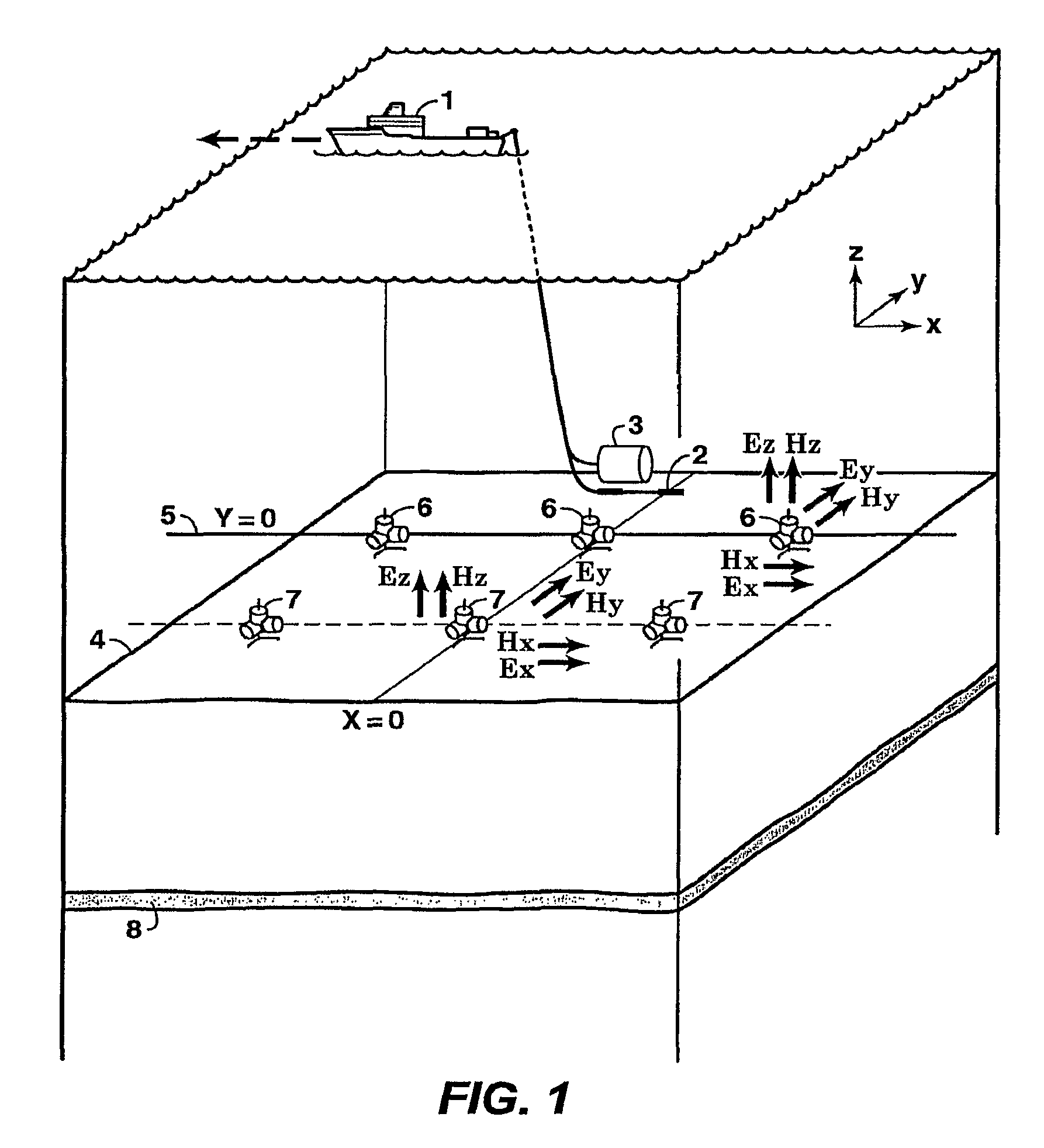
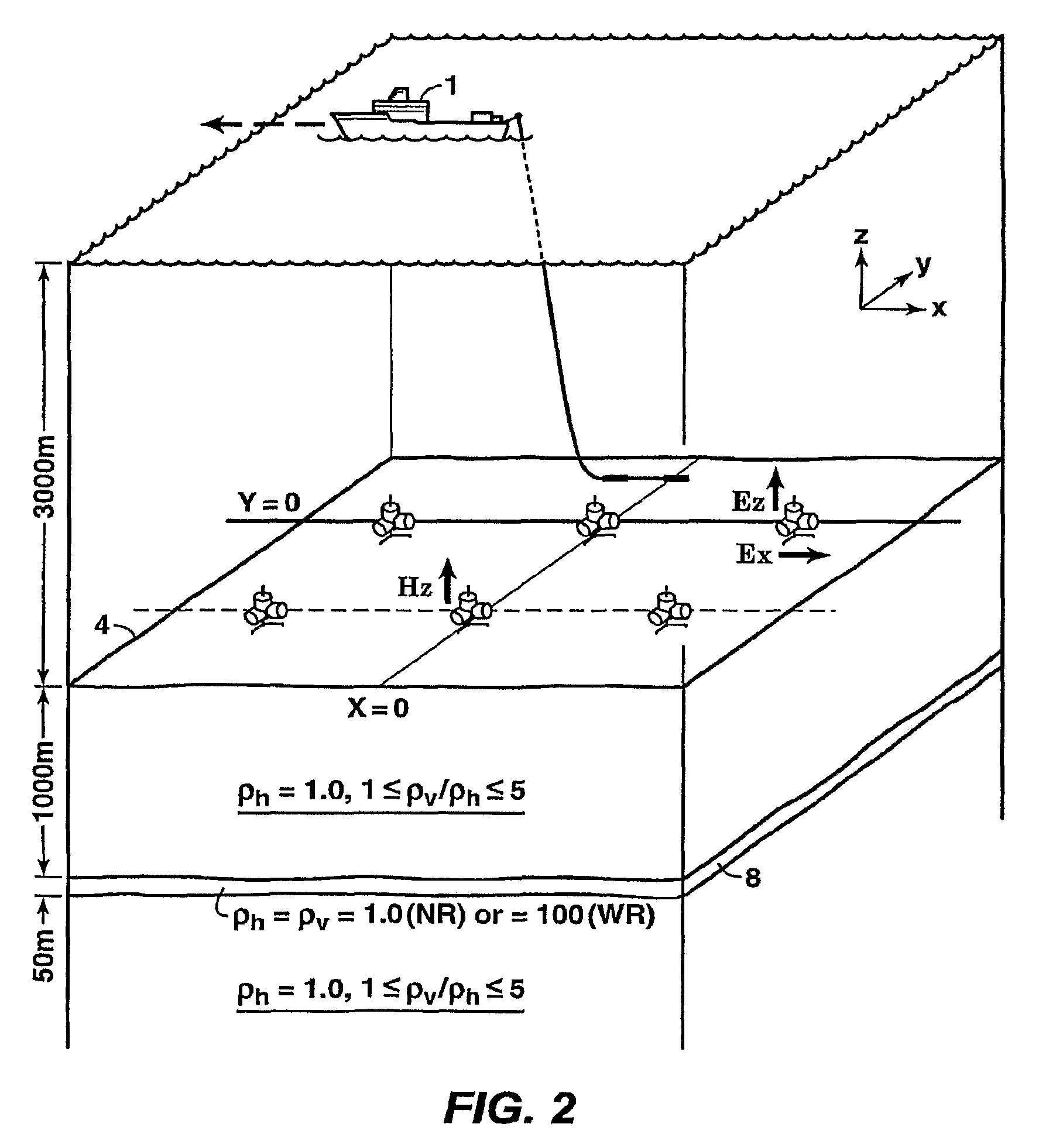
Time lapse analysis with electromagnetic data
ActiveUS8437961B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurement arrangements for variableComputational scienceFluid saturation
Method for determining time-dependent changes [73] in the earth vertical and horizontal electrical resistivity and fluid saturations from offshore electromagnetic survey measurements. The method requires both online and offline data, which should include at least one electromagnetic field component sensitive at least predominantly to vertical resistivity and another component sensitive at least predominately to horizontal resistivity [62]. Using a horizontal electric dipole source, online Ez and offline Hz measurements are preferred. For a horizontal magnetic dipole source, online H2 and offline E2 data are preferred. Magnetotelluric data may be substituted for controlled source data sensitive at least predominantly to horizontal resistivity. Maxwell's equations are solved by forward modeling [64,65] or by inversion [66,67], using resistivity models of the subsurface that are either isotropic contrast, and [64,66] or anisotropic [65,67]. Fluid saturation is determined from the vertical and horizontal resistivities using empirical relations or rock physics models [70].
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
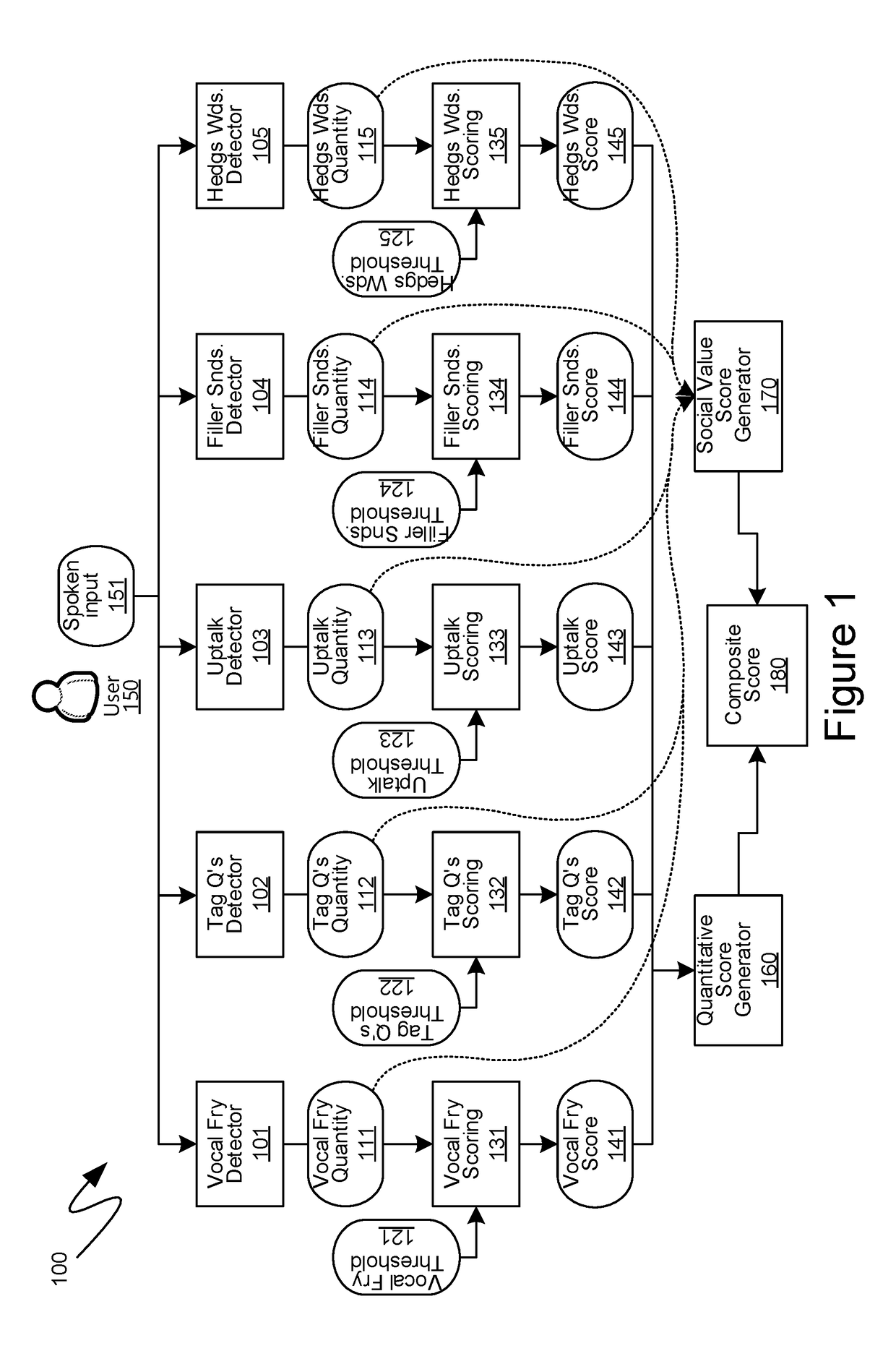
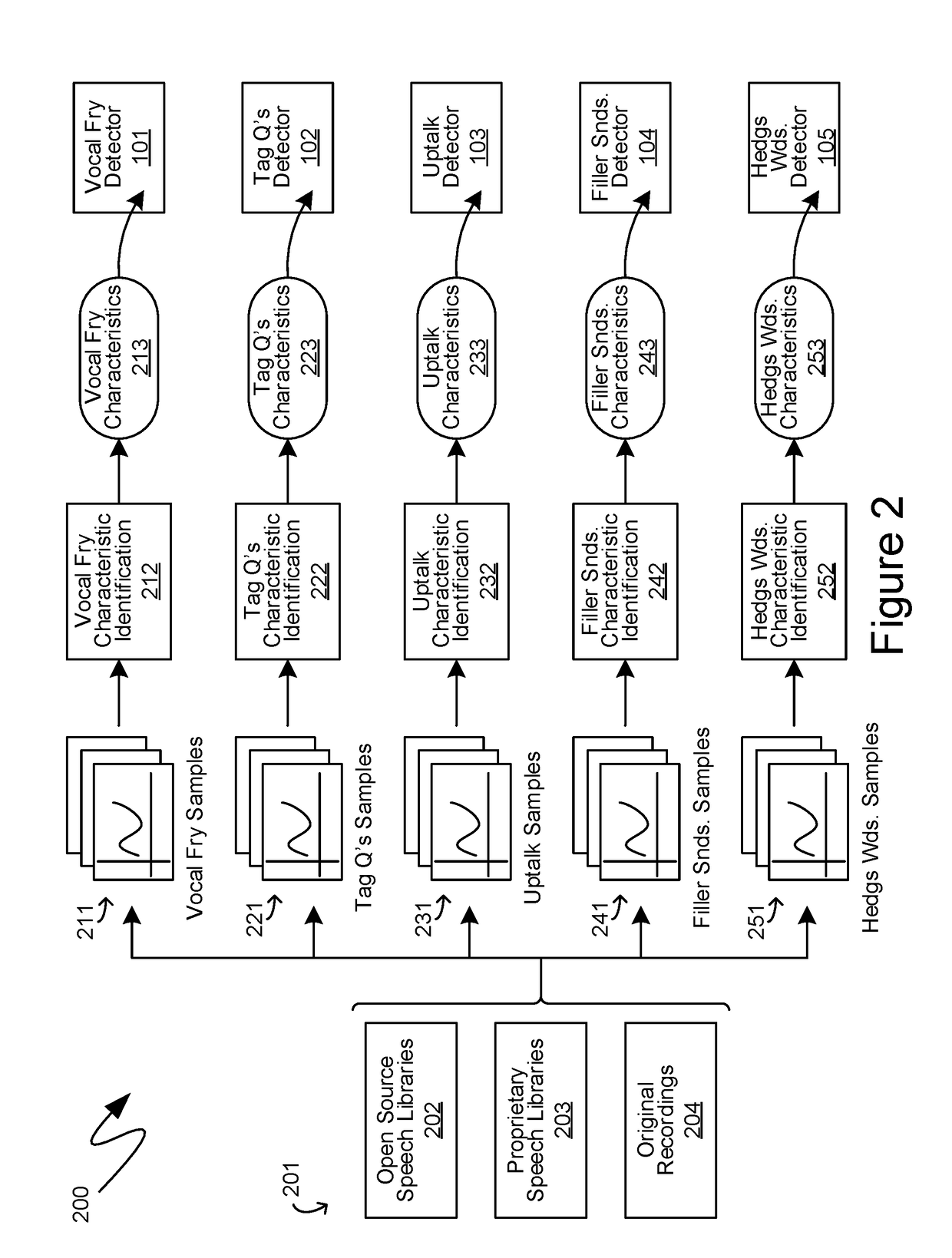
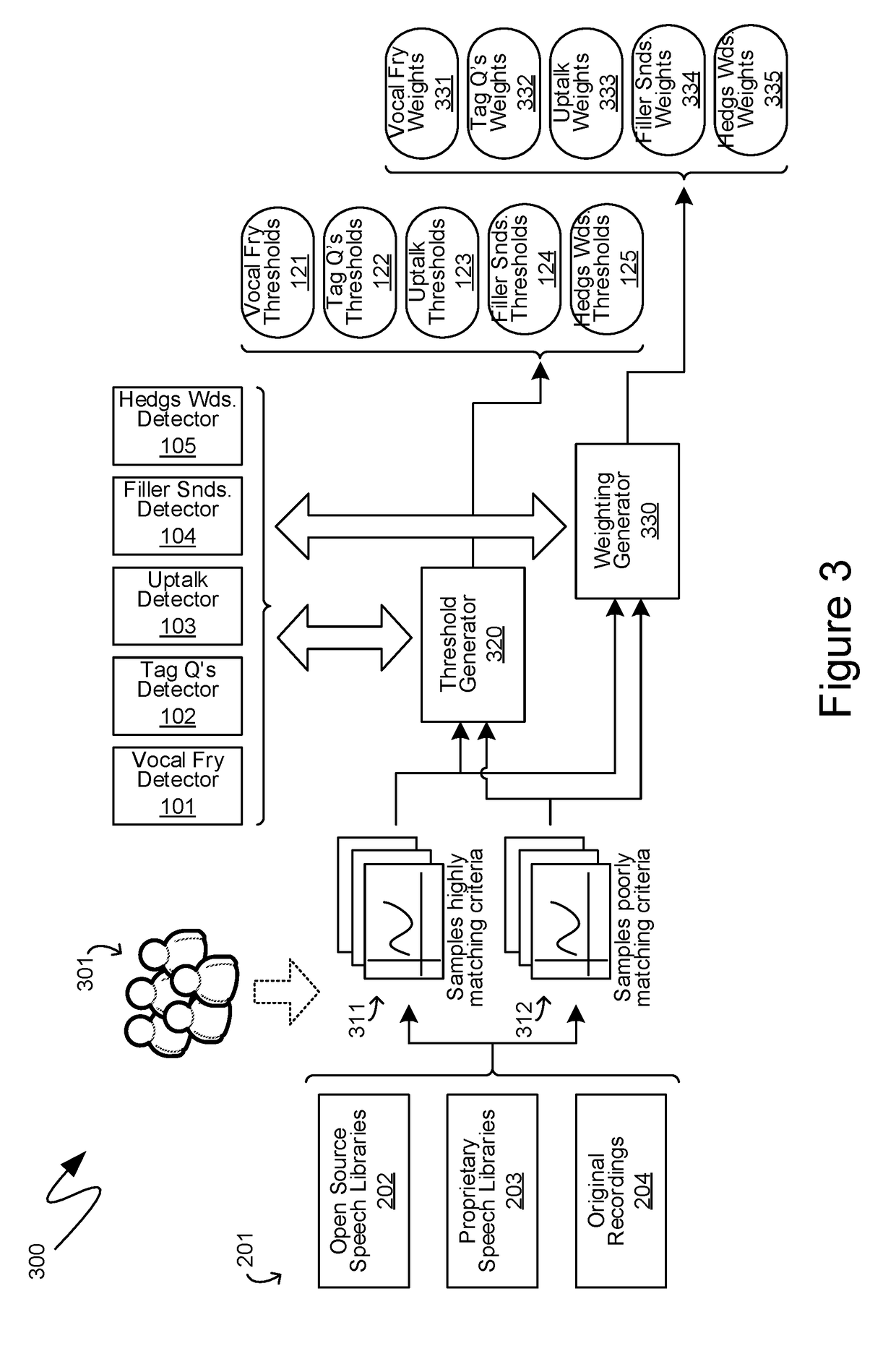
Computer-Generated Feedback Of User Speech Meeting Subjective Criteria
Computer-generated feedback directed to whether user speech input meets subjective criteria is provided through the evaluation of multiple speaking traits. Initially, discrete instances of various multiple speaking traits are detected within the user speech input provided. Such multiple speaking traits include vocal fry, tag questions, uptalk, filler sounds and hedge words. Audio constructs indicative of individual instances of speaking traits are isolated and identified from appropriate samples. Speaking trait detectors then utilize such audio constructs to identify individual instances of speaking traits within the spoken input. The resulting quantities are scored based on reference to predetermined threshold quantities. The individual speaking trait scores are then amalgamated utilizing a weighting that is derived based on empirical relationships between those speaking traits and the criteria for which the user's speech input is being evaluated. Further adjustments thereof can be made by separately, manually weighting the previously determined quantities.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
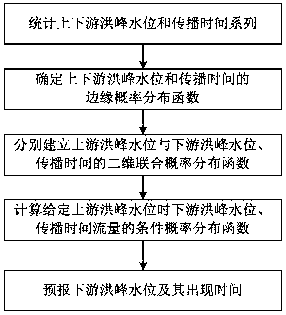
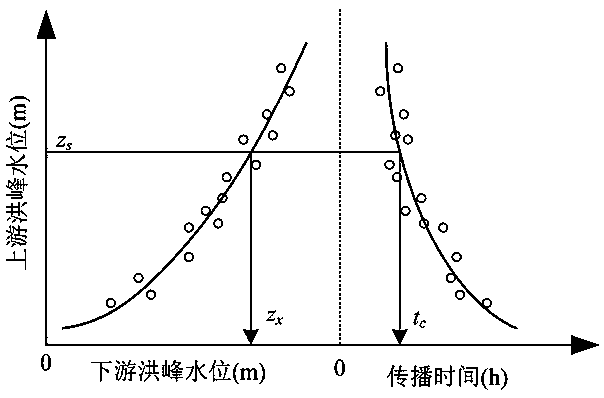
A river flood peak water level prediction method based on conditional probability distribution
ActiveCN109344993AStrong theoretical foundationReduce arbitrarinessWeather condition predictionClimate change adaptationPropagation timeWater level
The invention discloses a river flood peak water level prediction method based on conditional probability distribution. According to the statistics of the flood peak water level and the propagation time series of upstream and downstream, on the basis of determining the marginal probability distribution function, the two-dimensional joint probability distribution function of upstream peak water level and downstream peak water level and propagation time is constructed by using a Copula function, and then the conditional probability distribution function of downstream peak water level and propagation time is solved when the upstream peak water level is given, and then the downstream peak water level and its occurrence time are predicted. The method of the present invention quantitatively gives regression curves of flood peak level of upstream section and flood peak level of downstream section, flood propagation time based on probability theory and mathematical statistics method. Comparedwith the conventional method of drawing empirical relationship curve by hand, the method of the present invention has stronger theoretical foundation, effectively reduces arbitrariness brought by handdrawing, and is more objective and reasonable.
Owner:江西省水利科学研究院
Method of Controlling Semiconductor Device Fabrication
ActiveUS20130149800A1Information can be usedEasy to detectSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementComputer controlMetrologyCurrent distribution
A semiconductor wafer fabrication metrology method in which process steps are characterised by a change in wafer mass, whereby during fabrication mass is used as a measurable parameter to implement statistical process control on the one or more of process steps. In one aspect, the shape of a measured mass distribution is compared with the shape of a predetermined characteristic mass distribution to monitor the process. An determined empirical relationship between a control variable of the process and the characteristic mass change may enable differences between the measured mass distribution and characteristic mass distribution to provide information about the control variable. In another aspect, the relative position of an individual measured wafer mass change in a current distribution provides information about individual wafer problems independently from general process problems.
Owner:METRYX
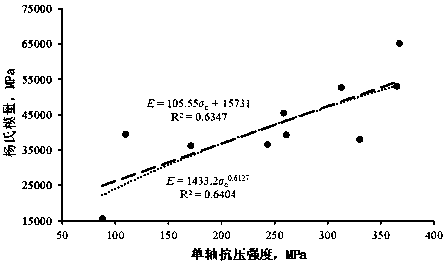
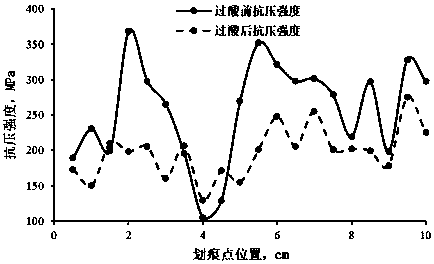
Method for determining influence of acid liquor on Young modulus of compact carbonate through experiments
ActiveCN108106938AAccurate assessmentOvercoming the limitation of not being able to accurately evaluate the Young's modulus change of tight carbonate rocks during acid fracturingEarth material testingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesAcid fracturingYoung's modulus
The invention discloses a method for determining influence of acid liquor on Young modulus of compact carbonate through experiments. The method comprises steps as follows: (1), a compact carbonate standard core is selected for use, a uniaxial compressive strength experiment is carried out, and an empirical relationship between uniaxial compressive strength of compact carbonate and the Young modulus is established; (2), a full-diameter core in a target work area is selected for use, a rock indentation instrument is adopted for implement a rock scratching experiment, compressive strength of thecore is tested, and the Young modulus of the core before acid treatment is acquired; (2), the acid liquor and the core are soaked in a high-temperature and high-pressure reactor for a reaction; (4), the core soaked with the acid liquor is subjected to the scratching experiment again in the original scratching experiment position, the compressive strength of the core is tested, the Young modulus ofthe core after acid treatment is acquired, and the influence of the acid liquor on the Young modulus of compact carbonate is determined. The principle is reliable, the operation is simple and convenient, the influence of the acid liquor on the Young modulus of compact carbonate under the reservoir condition is authentically evaluated, and acid fracturing reformation effect of compact carbonate isfurther improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Method of controlling semiconductor device fabrication
ActiveUS8364302B2Information can be usedEasy to detectSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementComputer controlMetrologyPower flow
A semiconductor wafer fabrication metrology method in which process steps are characterized by a change in wafer mass, whereby during fabrication mass is used as a measurable parameter to implement statistical process control on the one or more of process steps. In one aspect, the shape of a measured mass distribution is compared with the shape of a predetermined characteristic mass distribution to monitor the process. An determined empirical relationship between a control variable of the process and the characteristic mass change may enable differences between the measured mass distribution and characteristic mass distribution to provide information about the control variable. In another aspect, the relative position of an individual measured wafer mass change in a current distribution provides information about individual wafer problems independently from general process problems.
Owner:METRYX
Method and device for gravity-earthquake joint inversion
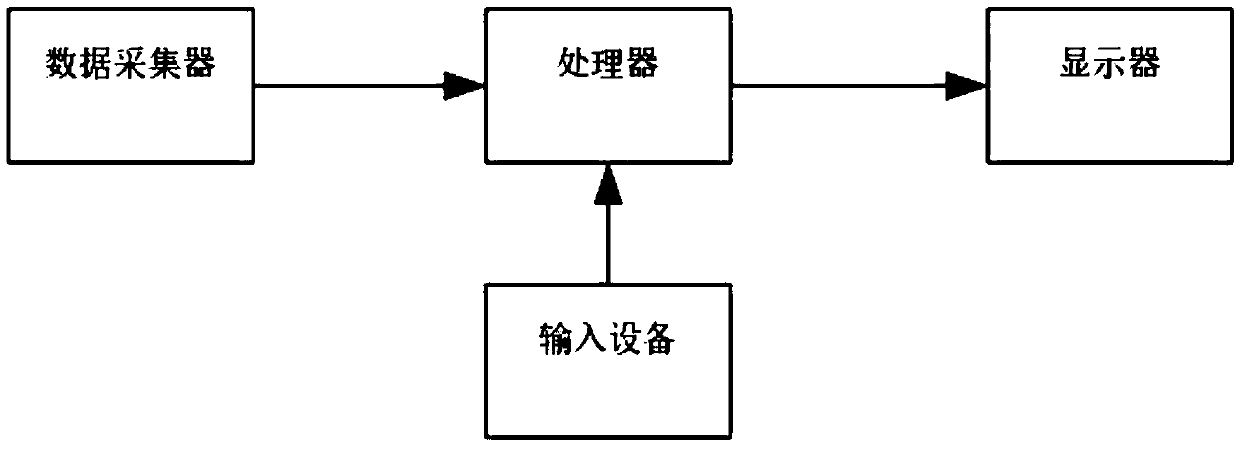
InactiveCN108845353AJoint Inversion RealizationImprove applicabilitySeismic signal processingData acquisitionDisplay device
The invention discloses a method and device for gravity-earthquake joint inversion. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining gravity data, seismic observation data and physical property statistical data of a study area; establish an initial model of density and velocity of the study area; establishing a new structure coupling method and constructing an objective function of gravity-earthquake joint inversion; optimizing and solving the objective function so as to obtain the density and velocity distribution in the study area; and performing image drawing. The device comprises a datacollector, a processor, a display and an input device. A data acquisition module is arranged in the data collector. The processor is therein provided with a data calculation module and a data analysis module. The display is therein provided with a data interpretation module and a data mapping module. Input devices are used to enter data and parameters. The invention overcomes the influence of human factors such as the empirical relationship between density and speed, and is reliable in data acquisition, strong in applicability, high in speed, high in efficiency and good in economical performance.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Noninvasive method and system for measuring pulmonary ventilation
ActiveUS8790273B2Reduce and eliminate drawbackConvenient and accuratePerson identificationUsing electrical meansIntensive care medicineEmpirical relationship
A pulmonary ventilation system comprising a method to determine at least one pulmonary ventilation parameter as a function of a plurality of measured anatomical distances and volume-motion coefficients, sensors for acquiring the anatomical distances, a device for determining the plurality of motion coefficients, and a device for determining the ventilation parameter based on the acquired anatomical distances and determined plurality of volume-motion coefficients. In one embodiment, the system further includes a method for acquiring base-line ventilation characteristics and a method for correlating the base-line ventilation characteristics to the ventilation parameter determined with the empirical relationship.
Owner:ADIDAS
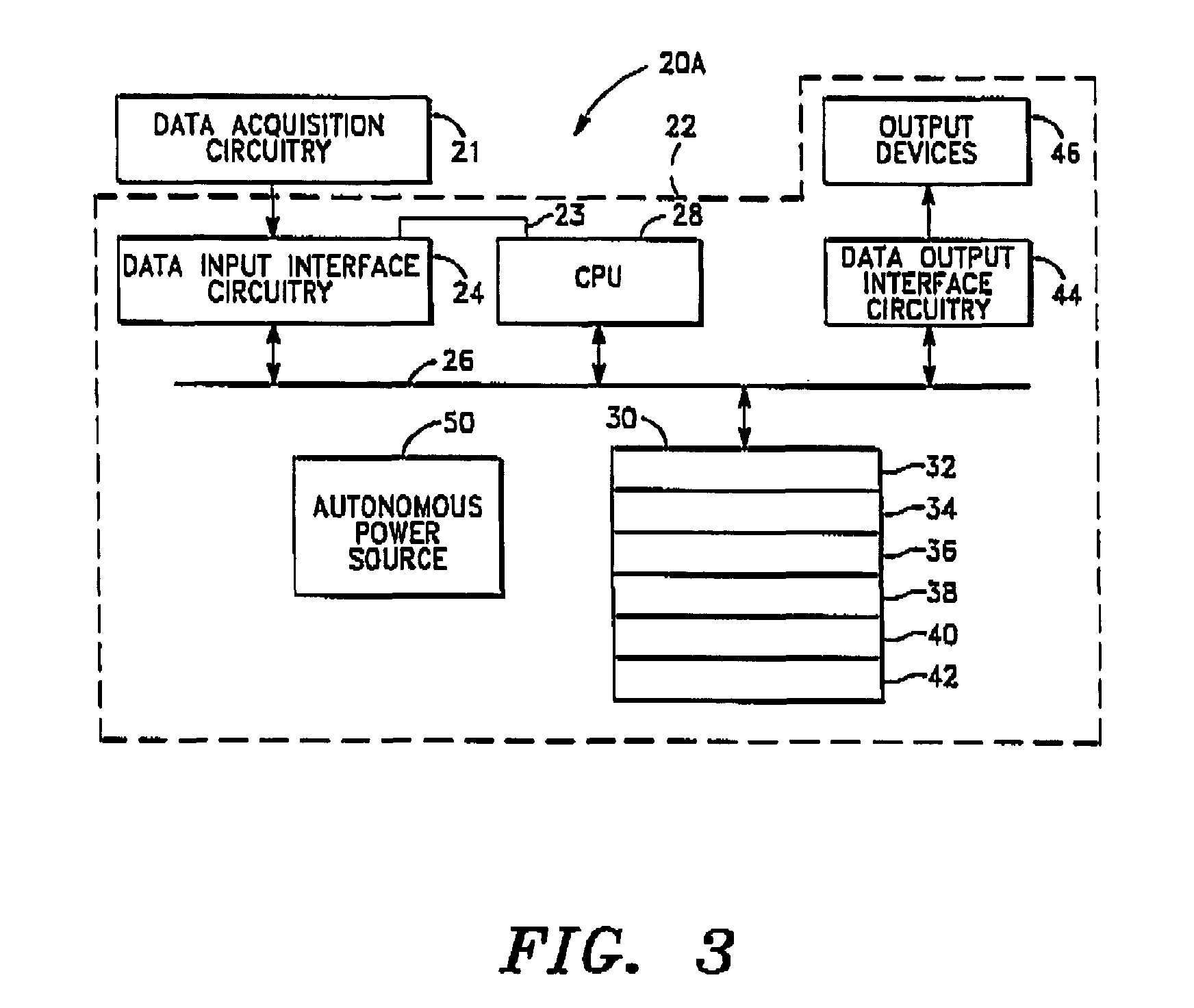
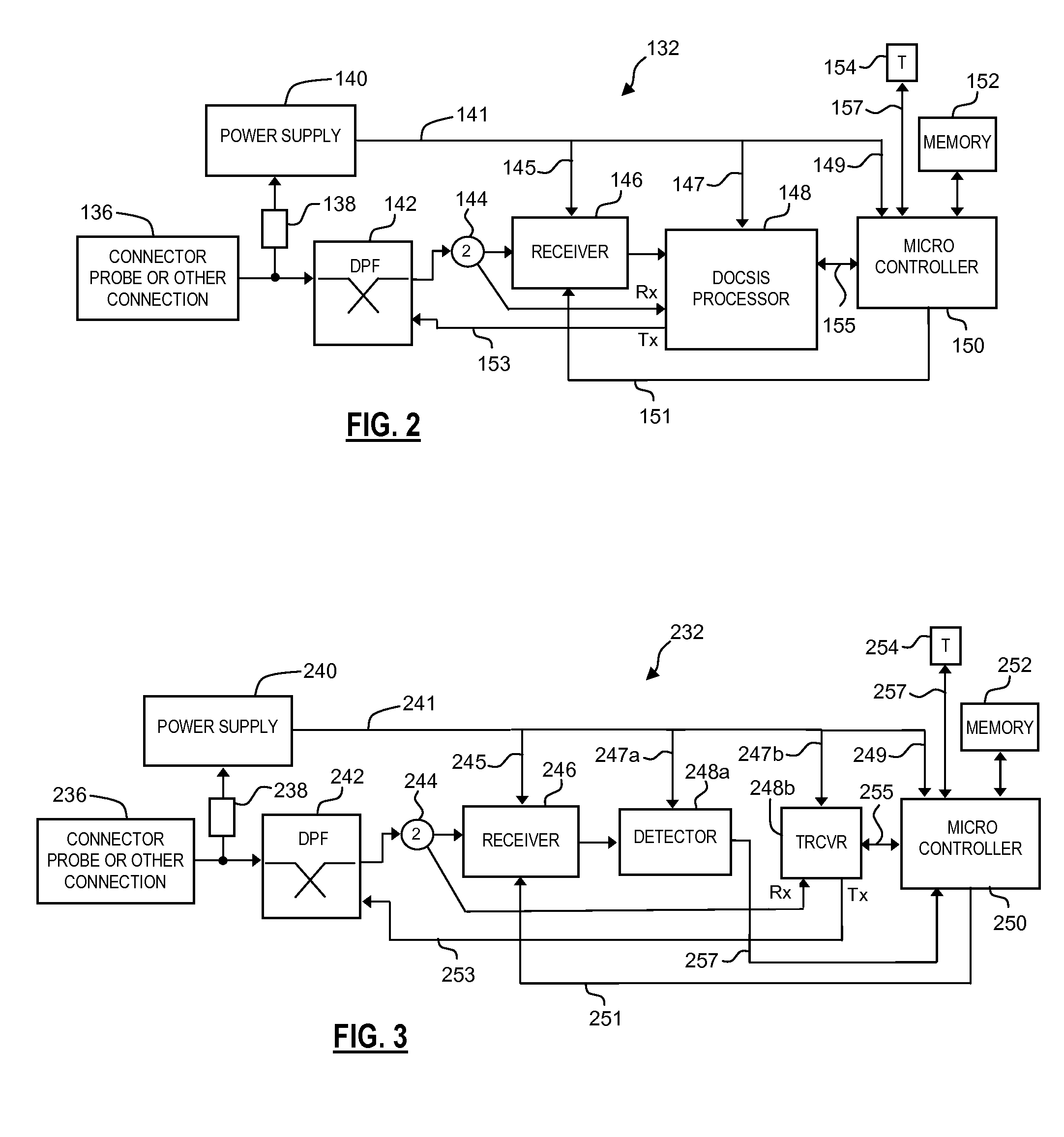
Signal level monitoring system that minimizes false alarms
InactiveUS20150091721A1Minimizes false alarmMinimizes false alarmsFire alarm electric actuationTransmissionMonitoring systemEngineering
A system for monitoring signal level of a signal in a communications network, comprising a monitor that includes (i) a receiver to receive the signal from the network, (ii) a detector for detecting signal level values of the signal, and (iii) a sensor for sensing temperatures at the monitoring point in association with the signal level values. The system further comprises (i) means for evaluating the signal level values relative to an alarm reference, (ii) means for issuing alarms based on an alarm criterion defined in terms of the signal level values and the alarm reference, (iii) means for deriving an empirical relationship between signal level and temperature from the signal level values and temperatures, and (iv) means for adjusting the alarm criterion in accordance with the empirical relationship, such that temperature-dependent variations of signal level are substantially accounted for in issuing alarms.
Owner:ARCOM DIGITAL
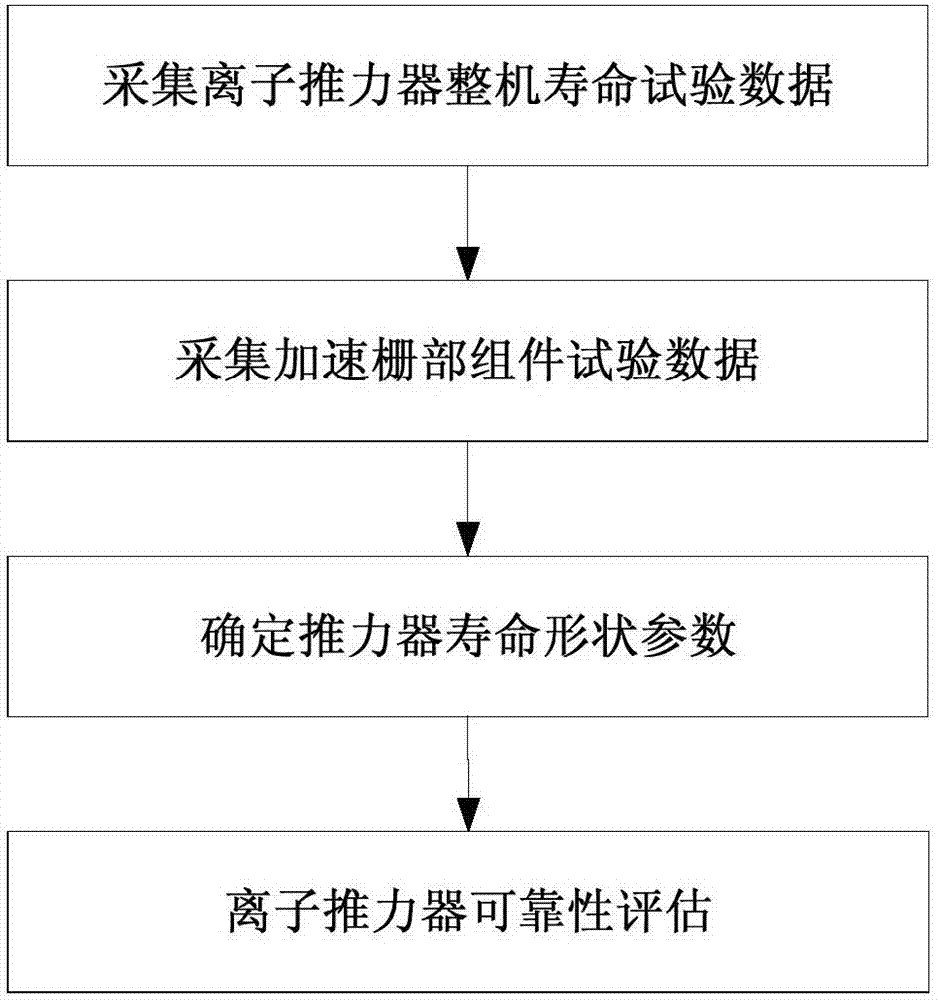
Method for determining reliability degree of minimum subsample ion thruster based on acceleration gate data
ActiveCN107966311AEasy accessSolve the problem of povertyStructural/machines measurementDependabilityEmpirical relationship
The invention discloses a method for determining a reliability degree of a minimum subsample ion thruster based on acceleration gate data. The method comprises the steps of: 1) acquiring whole machinelife test data of the ion thruster; 2) acquiring test data of an acceleration gate component; 3) determining shape parameters of thruster life; 4) and evaluating the reliability of the ion thruster,so as to obtain the reliability degree. According to the method, a model of an empirical relationship between acceleration gate life in an acceleration gate component test and the thruster life in a whole machine life test is established, the shape parameters of the thruster life are obtained by utilizing the test data of the acceleration gate component, further the reliability of the ion thrusteris evaluated, and the problem of ion thruster reliability evaluation under the condition that the whole machine life data is very few (only 1 or 2 pieces) is solved.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Method For Automatic Quantification Of Dendrite Arm Spacing In Dendritic Microstructures
A method to automatically quantify dendrite arm spacing in dendritic microstructures. Once a location of interest in a cast material specimen has been identified, the information contained in it is automatically analyzed to quantify dendrite cell size information that is subsequently converted into a quantified dendrite arm spacing through an empirical relationship or a theoretical relationship. In one form, the relationship between DCS and DAS is such that the DAS in dendritic structure of cast aluminum alloys may be automatically determined from the measurement of one or more of dendrite cell size and the actual volume fraction of the eutectic phases in the local casting microstructure. Non-equilibrium conditions may be accounted for in situations where a theoretical volume fraction of a eutectic phase of the alloy in equilibrium condition is appropriately modified. Thus, in situations where equilibrium conditions—such as those where the casting is cooled very slowly during solidification—does not apply (such as during rapid cooling and consequent solidification), the eutectic measured in the non-equilibrium condition, which can be smaller than the theoretical value in equilibrium, can be accounted for.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for realizing atmospheric correction of MODIS (moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer) image in turbid water body area
InactiveCN102508226AImprove Atmospheric Correction AccuracyOvercome the Difficult Problem of Atmospheric CorrectionWave based measurement systemsRayleigh scatteringBody area
The invention relates to a method for realizing atmospheric correction of an MODIS (moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer) image in a turbid water body area. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) reading an empirical relationship of actually measured standard water-leaving reflectivity of wave bands of 531, 551, 667 and 978 nm, a Rayleigh scattering look-up table, an MODIS image of the wave bands related by the model, synchronous atmospheric pressure, wind speed and ozone thickness data; (2) calculating the reflectivity contributed by each wave band Rayleigh scattering of the MODIS by using a Rayleigh scattering look-up table algorithm on the basis of meteorological data related in the step (1) and correcting the reflectivity; (3) building empirical relationships of thereflectivity of the wave bands of 531, 551, 667 and 978 nm by using the MODIS image data corrected by the Rayleigh scattering, (4) calculating the reflectivity contributed by aerosol scattering of each wave band of the MODIS by using an Angstrom aerosol exponential model on the basis of the step (4), and (5) calculating the reflectivity contributed by path radiance of the atmosphere based on the steps (2) and (4) and carrying out atmospheric correction on the MODIS image.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF MARINE GEOLOGY
Apparatus and method for real time measurement of a constituent of blood to monitor blood volume
ActiveUS9283315B2Reliable and accurate measurementEasy to useMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOther blood circulation devicesBlood componentMedicine
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
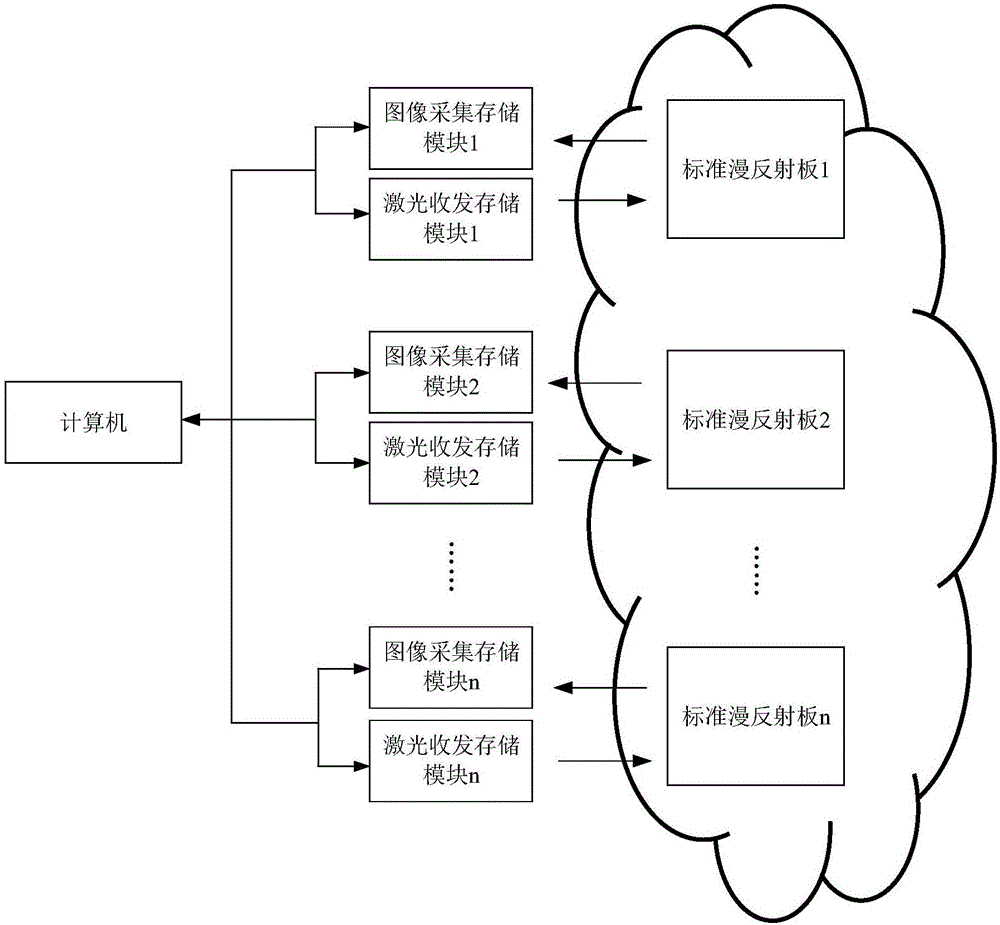
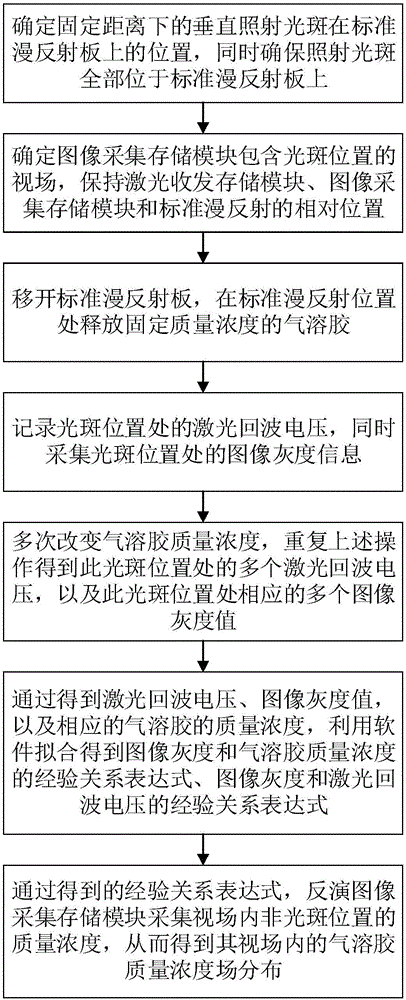
Non-contact measuring device and method for aerosol mass concentration field
The invention relates to a non-contact measuring device and method for an aerosol mass concentration field and belongs to the fields of laser technologies and image processing technologies. In order to measure mass concentration distribution of aerosol in space, the non-contact measuring device and method enable a laser detecting technology and an image processing technology to be combined. The non-contact measuring method comprises the steps: firstly, utilizing corresponding relation between laser echo voltage of aerosol at the laser radiation position and a gray level image of the laser radiation position to establish empirical relationship expression between image gray level and the laser echo voltage and empirical relationship expression between the image gray level and mass concentration; inverting image gray level of the aerosol at the non-laser-radiation position according to image gray level of the non-laser-radiation position of the aerosol; accordingly obtaining aerosol mass concentration field distribution in a collecting view field of an image collecting and storing module.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
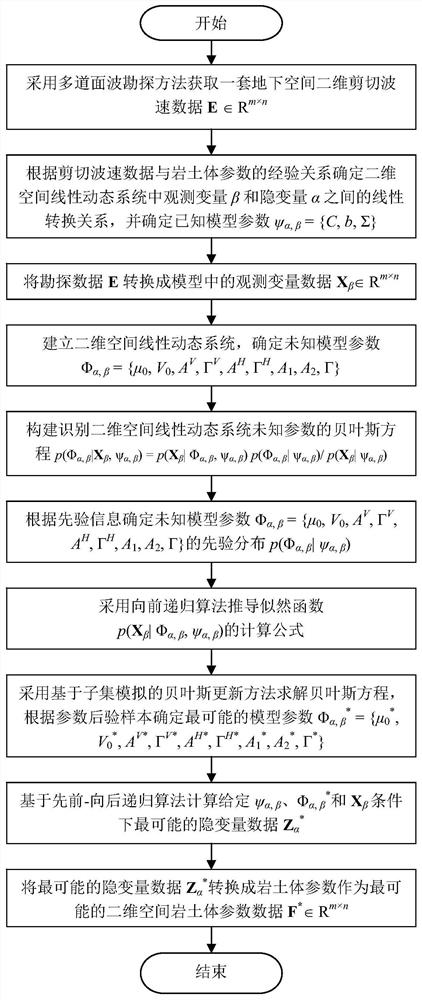
Rock-soil mass parameter two-dimensional space variability characterization method based on multi-surface wave exploration
ActiveCN113435022AOvercome limitationsImprove accuracyMathematical modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionSoil massClassical mechanics
The invention relates to a rock-soil mass parameter two-dimensional space variability characterization method based on multi-surface wave exploration, and belongs to the field of geotechnical engineering investigation. The method includes establishing a two-dimensional space linear dynamic system for representing the spatial variability of the rock and earth mass parameters; constructing a Bayesian equation for identifying parameters of a two-dimensional space linear dynamic system according to a Bayesian theory under the condition that two-dimensional shear wave velocity data of multi-surface wave exploration and an empirical relationship between exploration data in literatures and rock-soil body parameters are given; solving optimal model parameters by adopting a Bayesian updating method based on subset simulation; and obtaining the most possible two-dimensional spatial distribution of the rock-soil body parameters by adopting a forward recursive algorithm and a backward recursive algorithm. According to the invention, the influence of the two-dimensional spatial correlation of the shear wave velocity data on the spatial variability characterization recognition of the rock-soil body parameters is reasonably considered, the two-dimensional spatial exploration data are fully utilized to characterize the unstable spatial variability of the rock-soil body parameters, the limitation of a traditional steady-state random field model is overcome, and an effective way is provided for improving the exploration accuracy of a geotechnical engineering site.
Owner:POWERCHINA HUADONG ENG COPORATION LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com