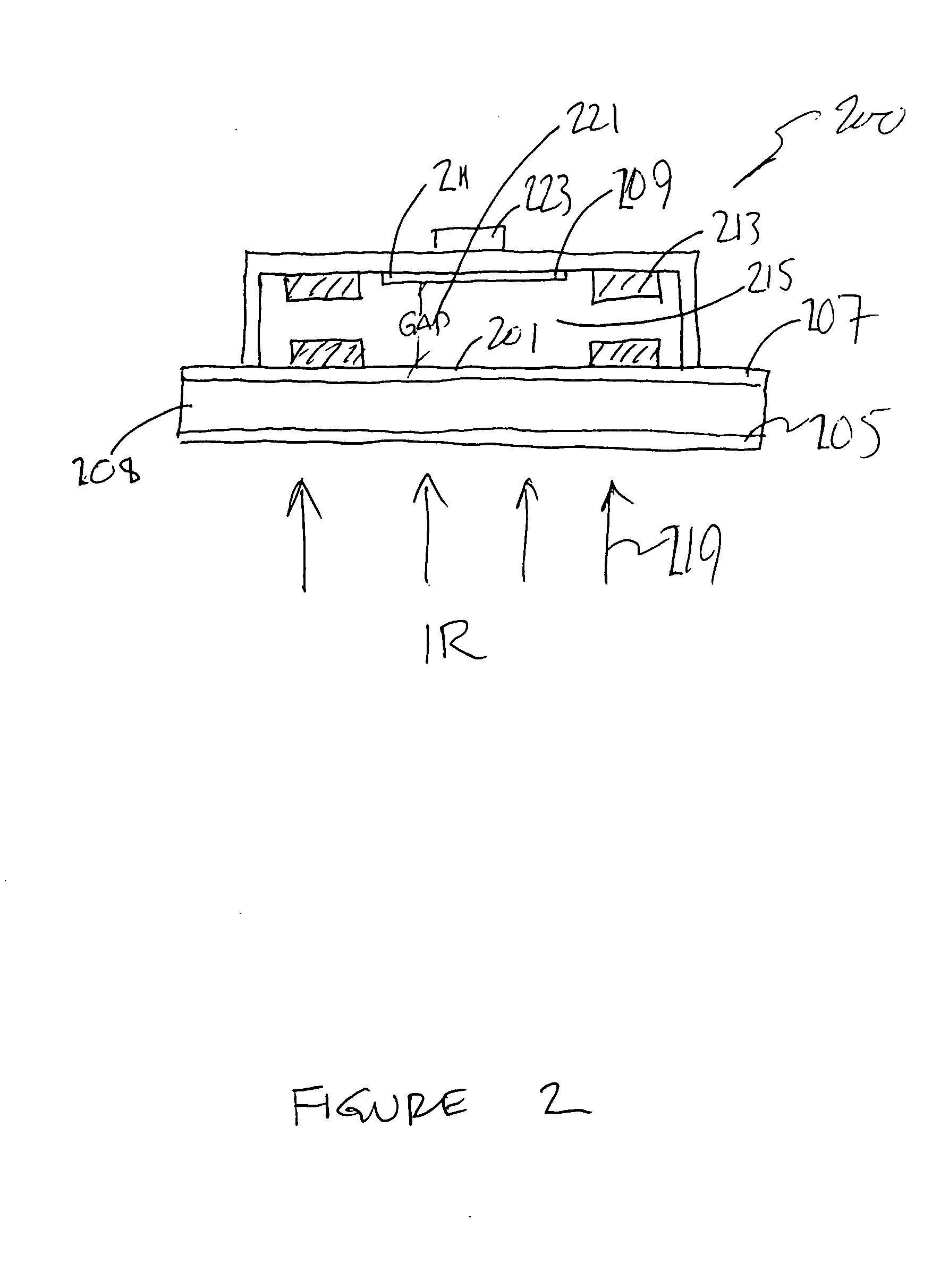
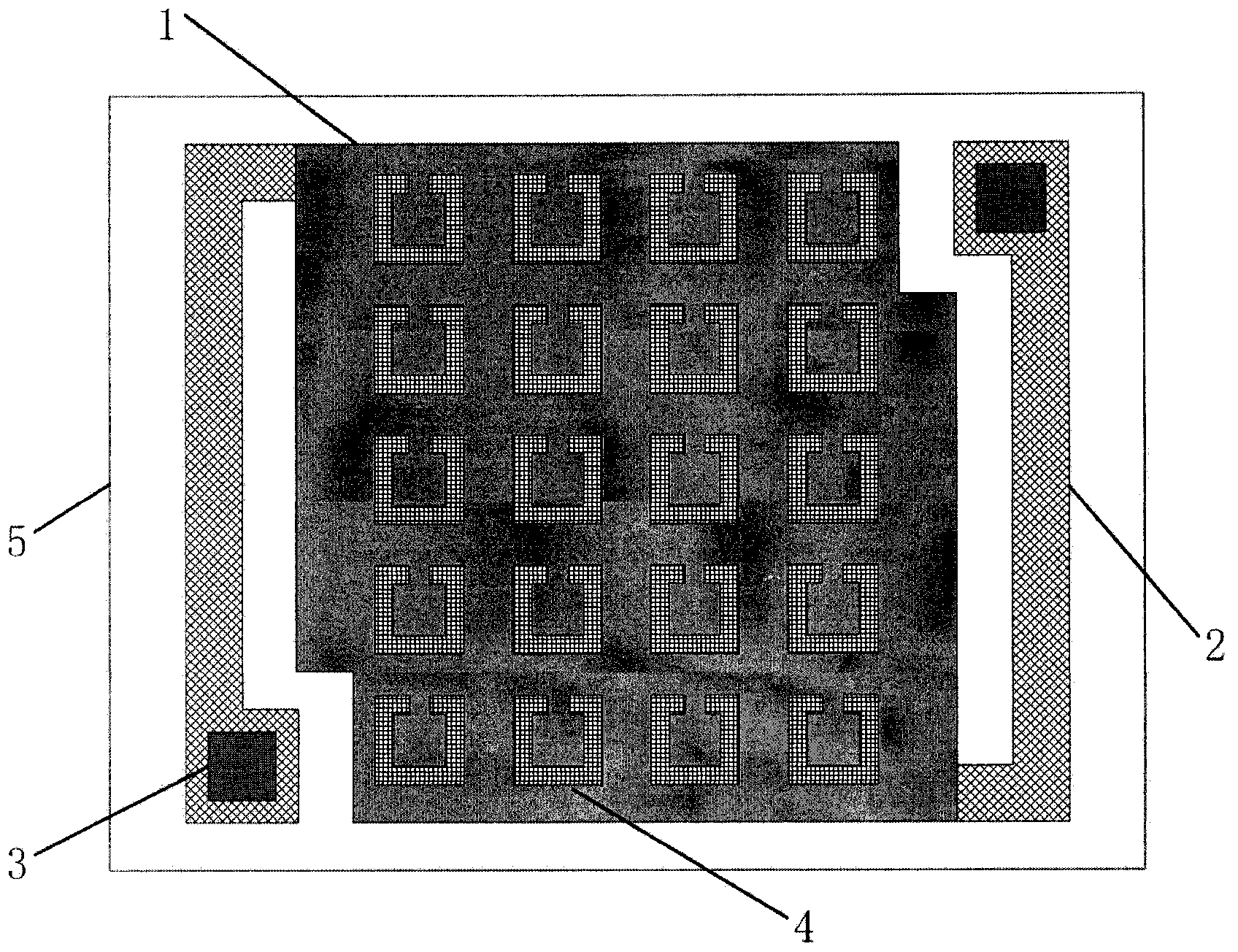
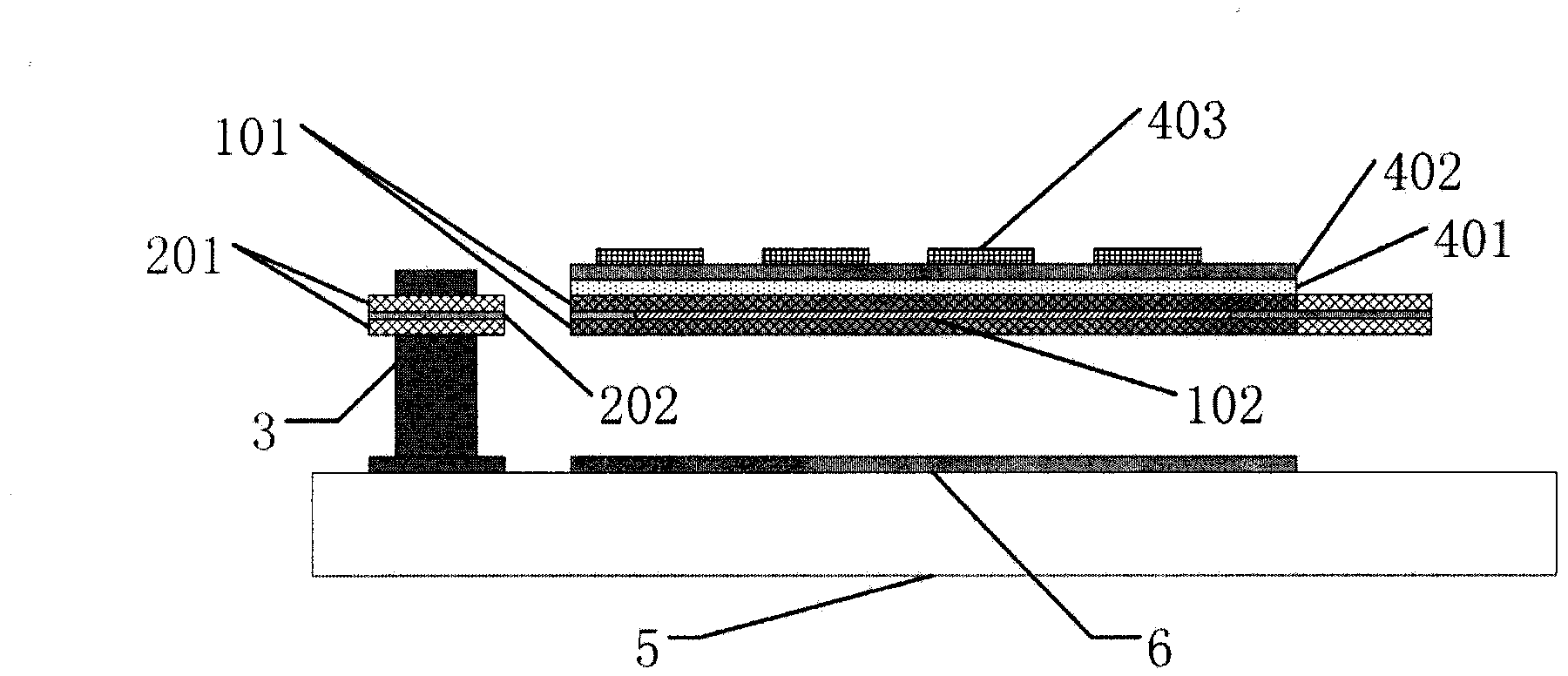
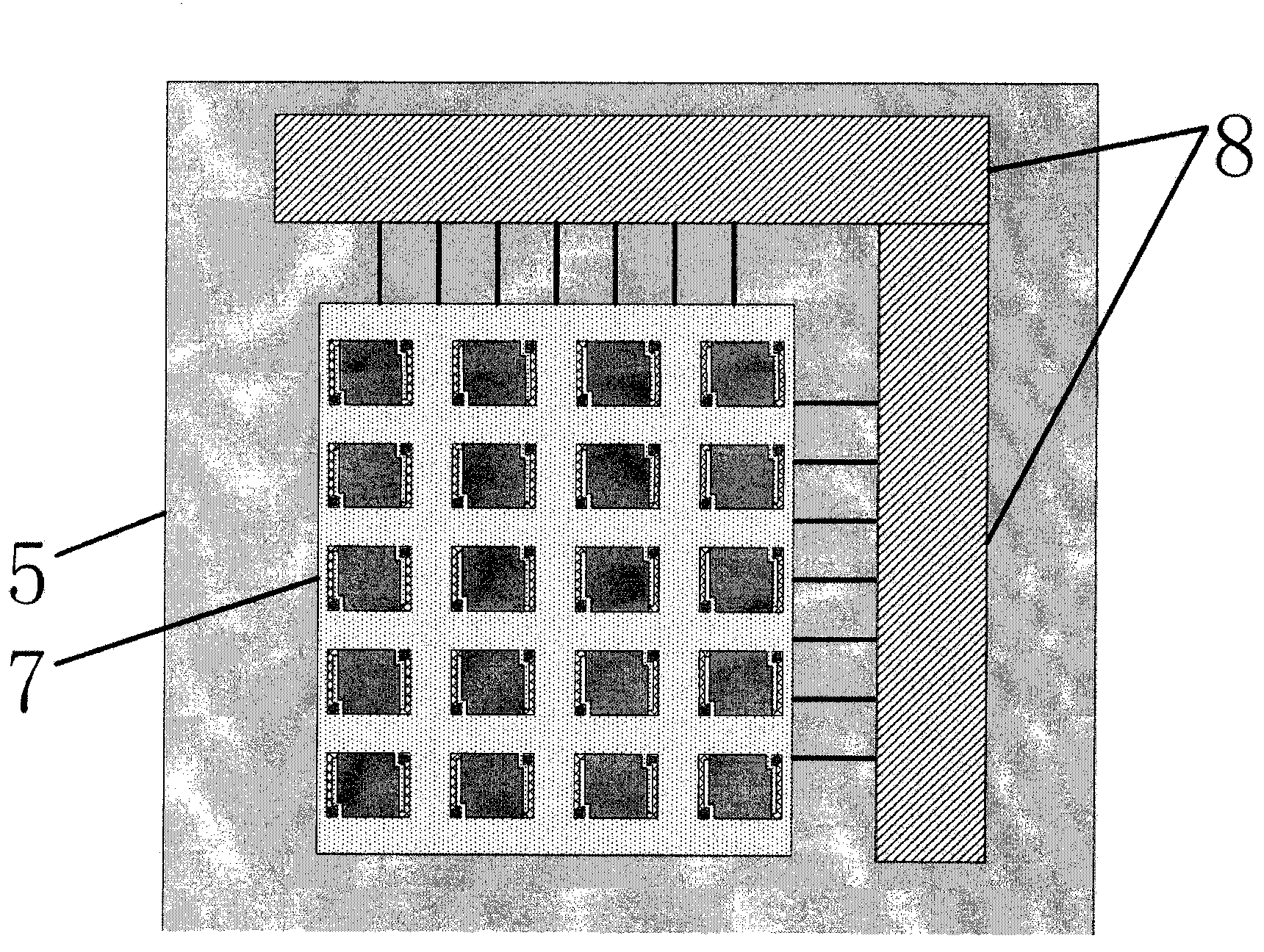
Patents
Literature
332 results about "Bolometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
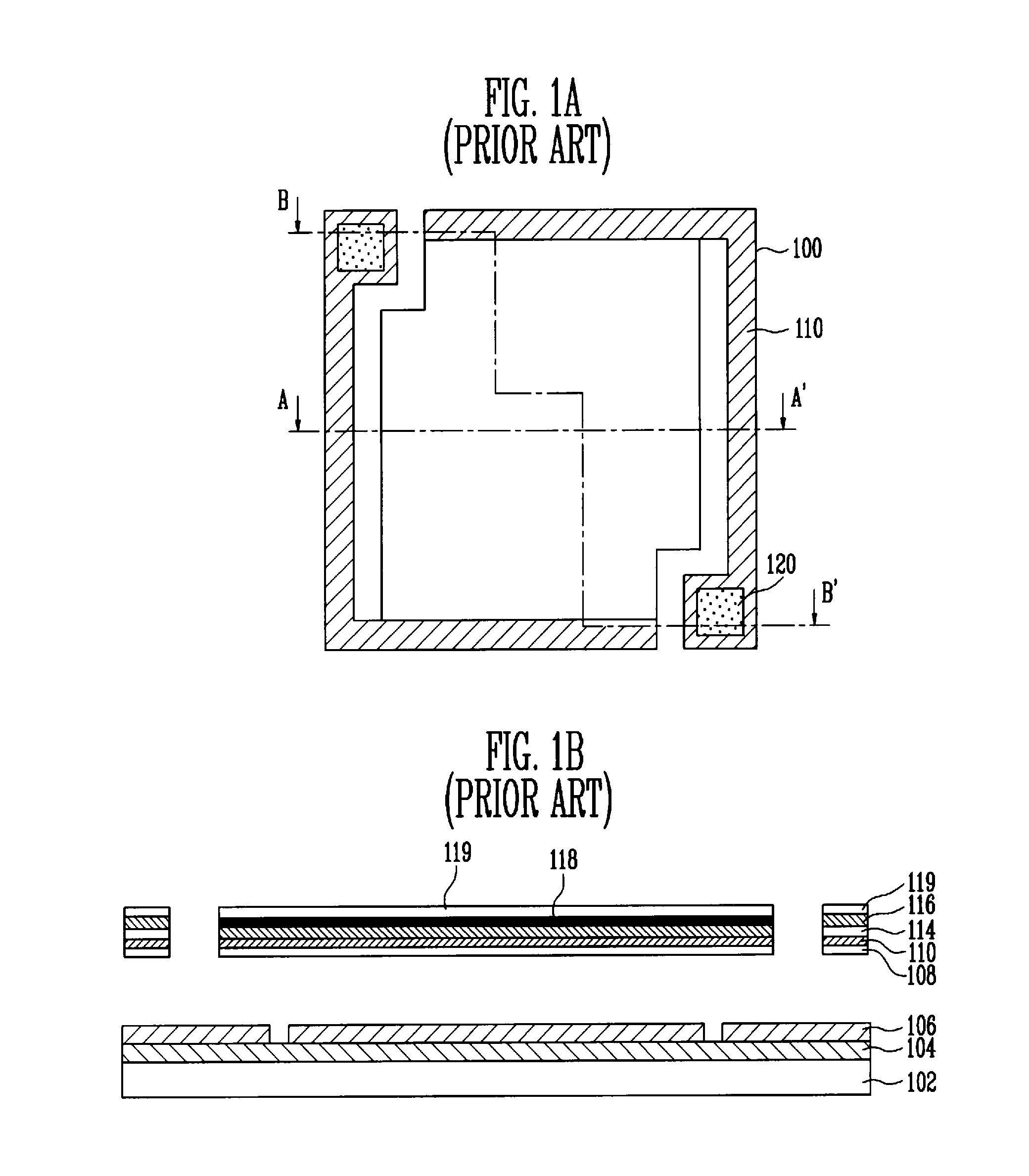
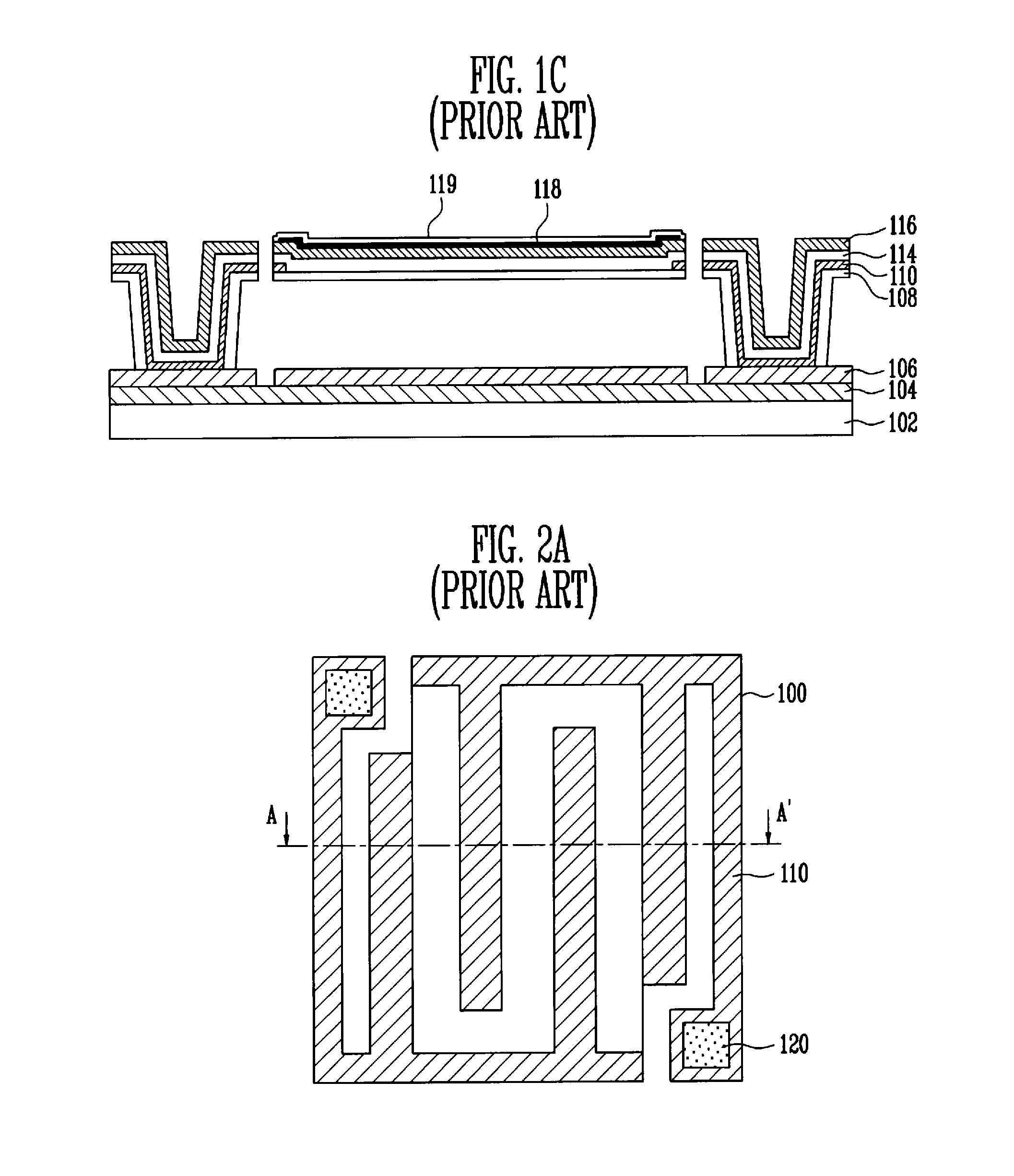
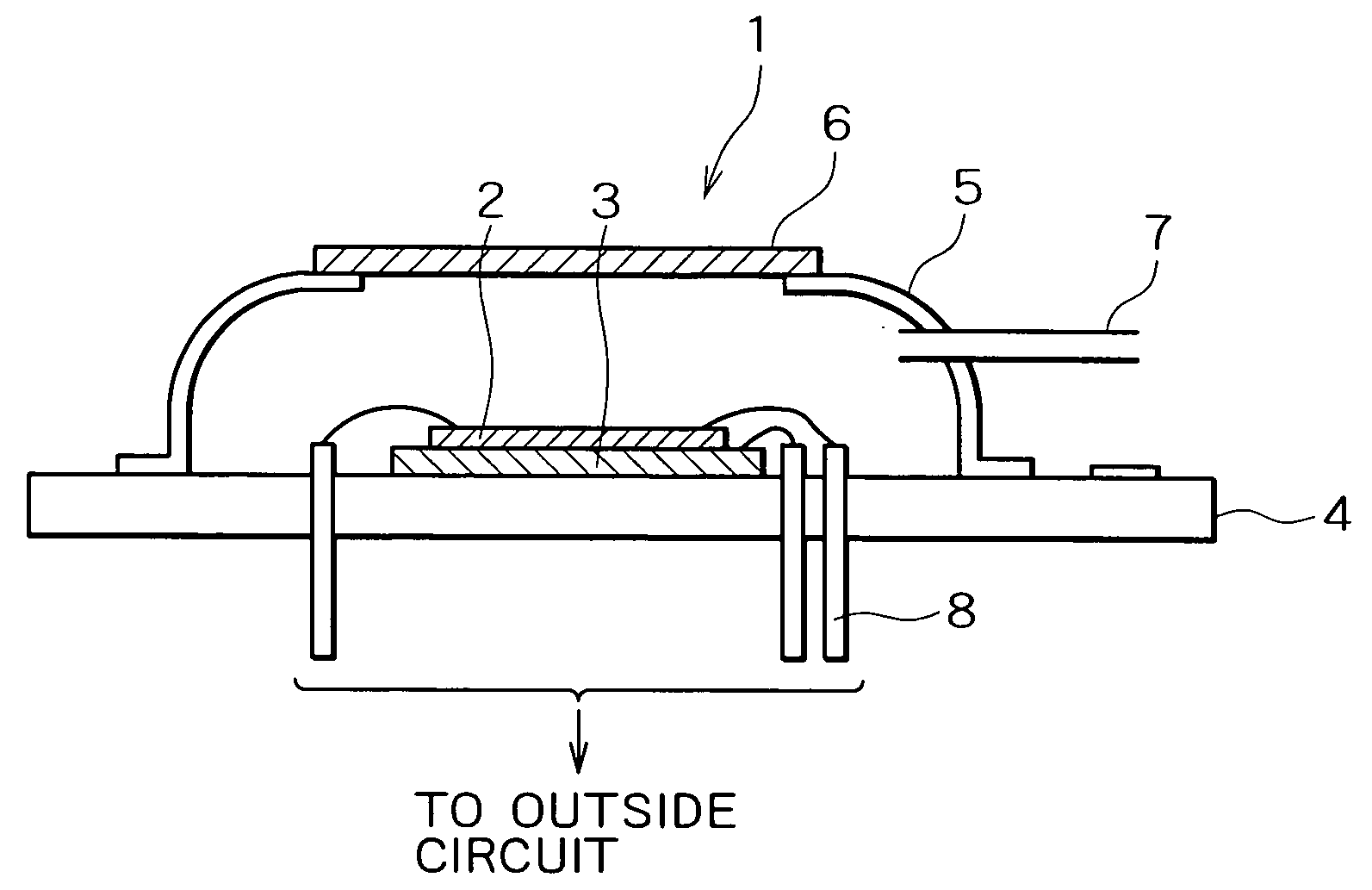
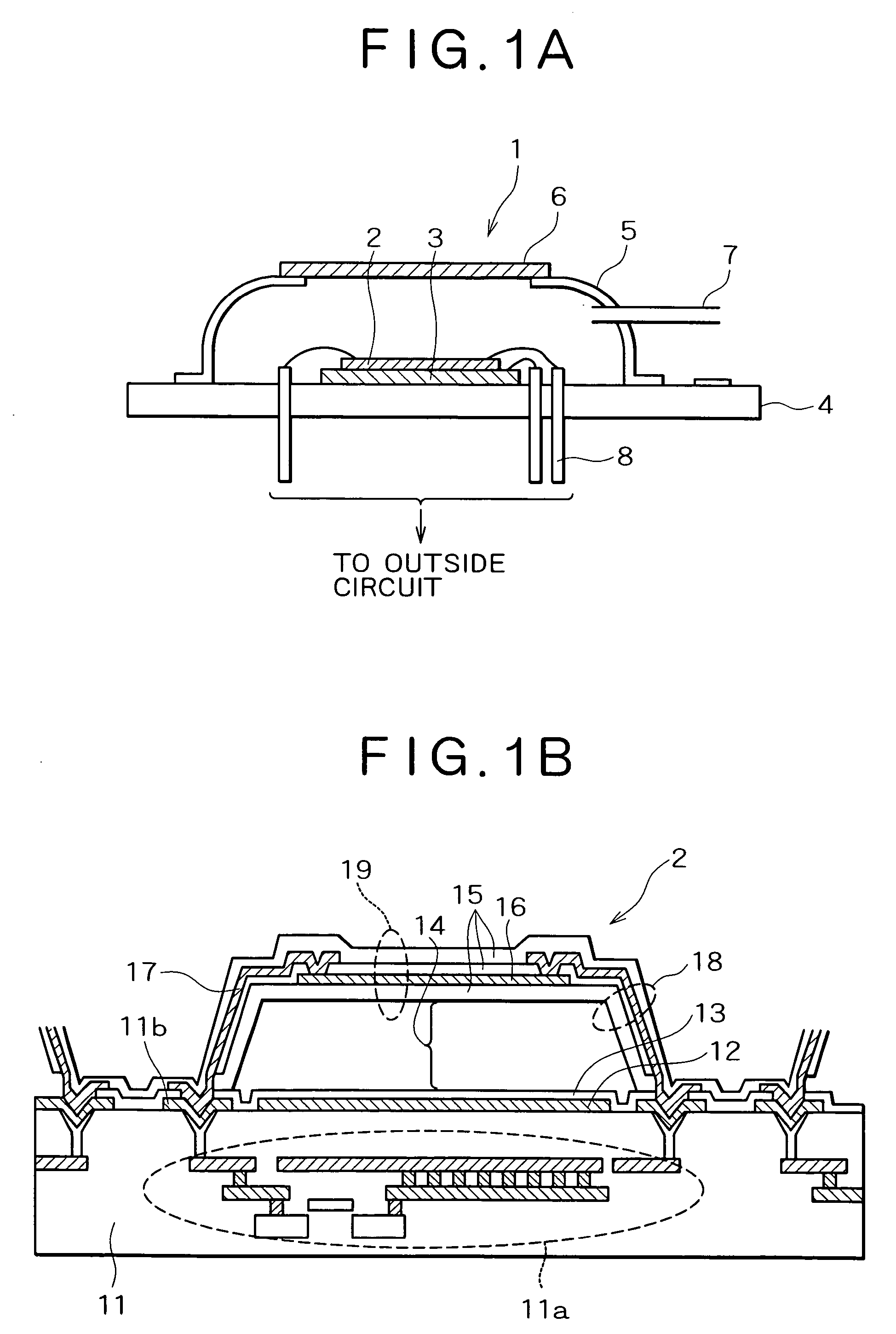
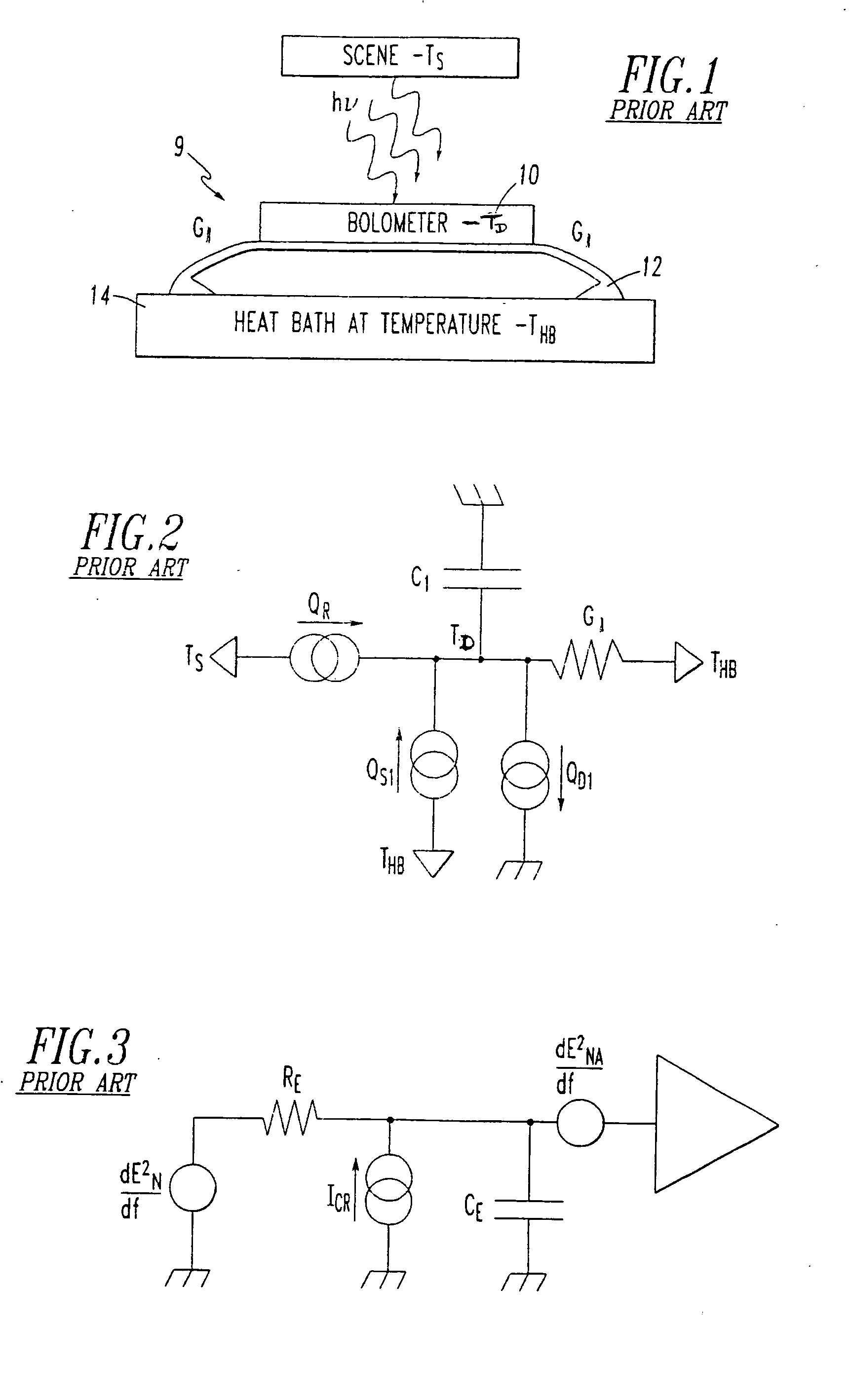
A bolometer is a device for measuring the power of incident electromagnetic radiation via the heating of a material with a temperature-dependent electrical resistance. It was invented in 1878 by the American astronomer Samuel Pierpont Langley.
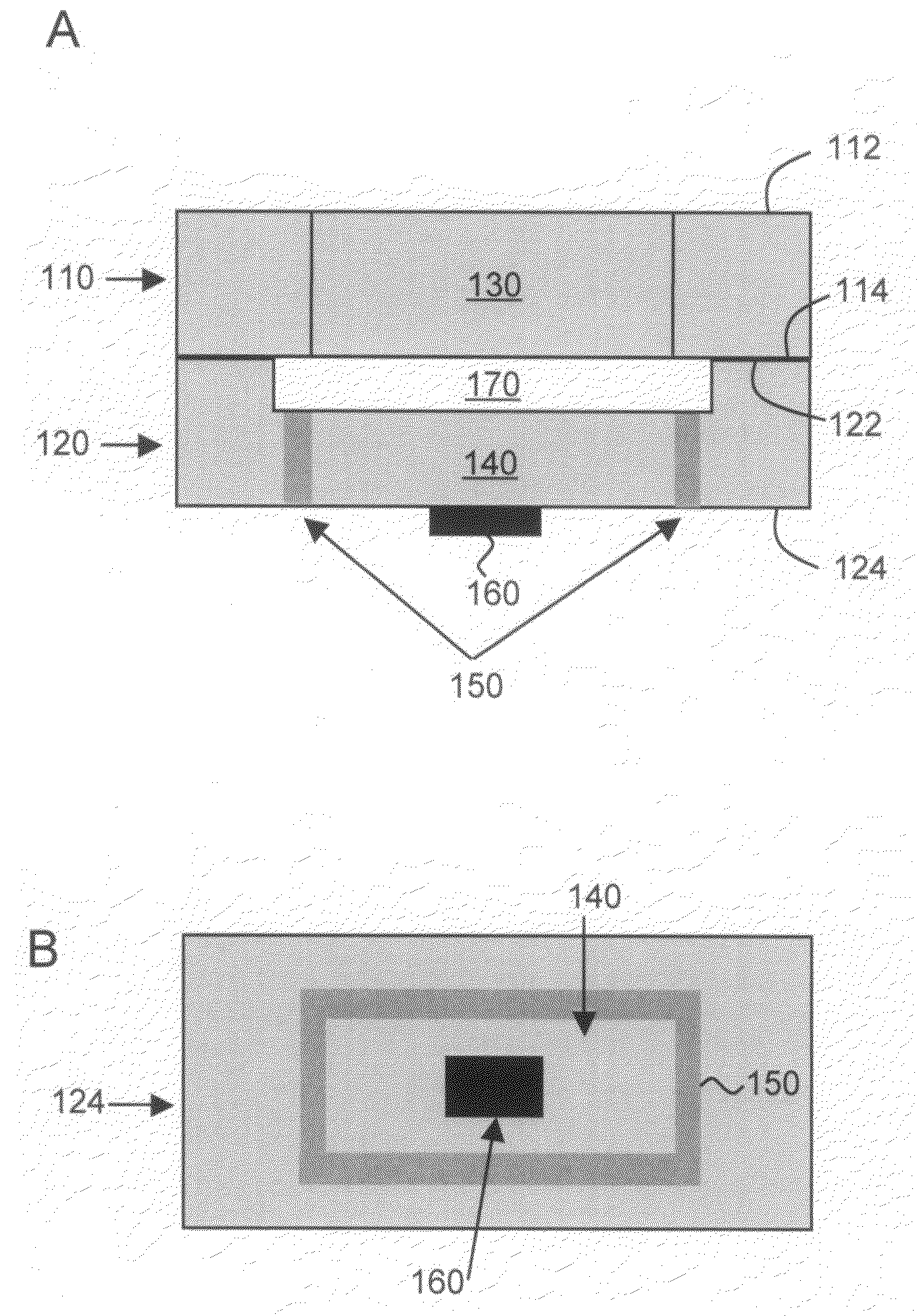
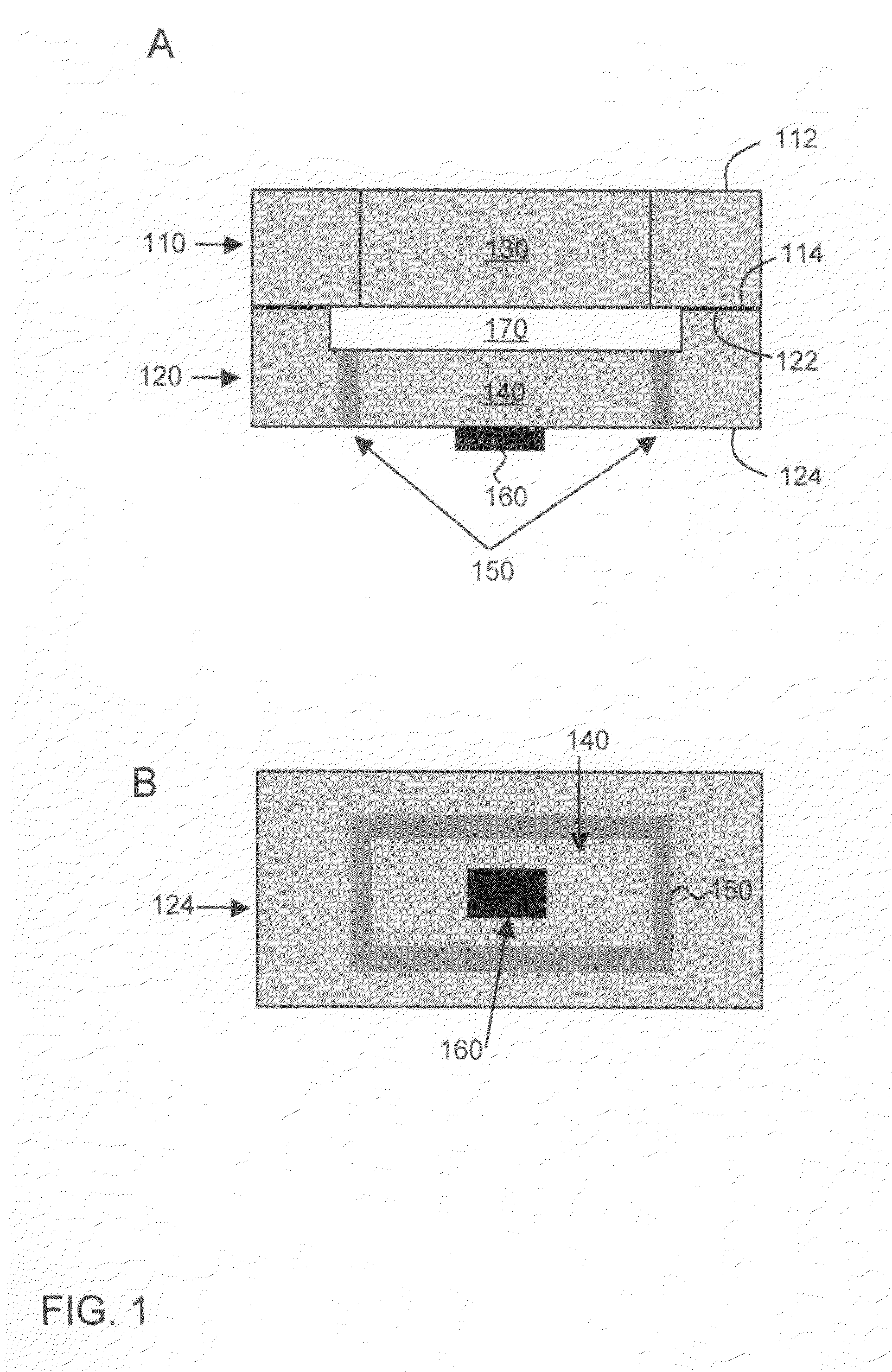
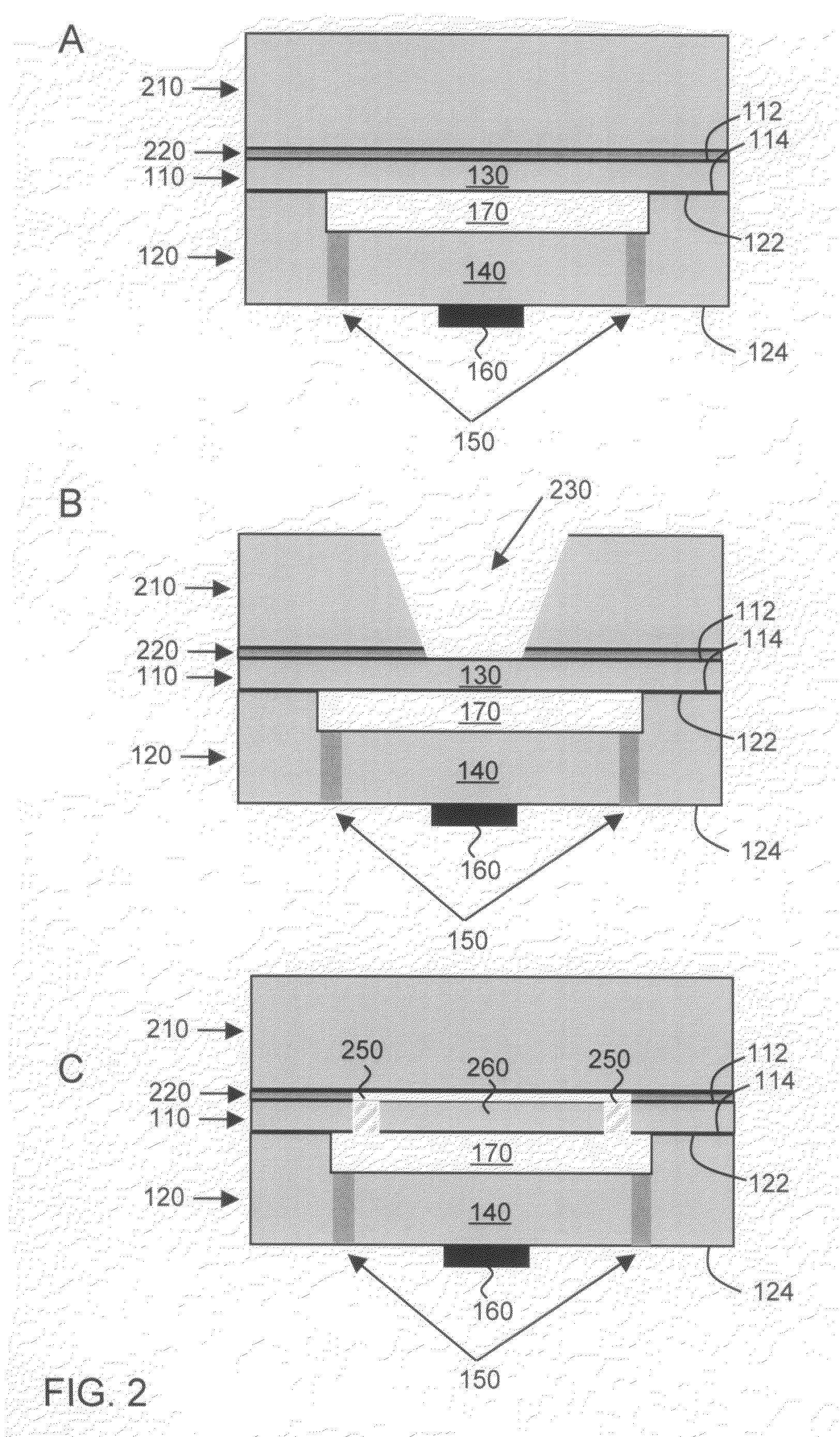
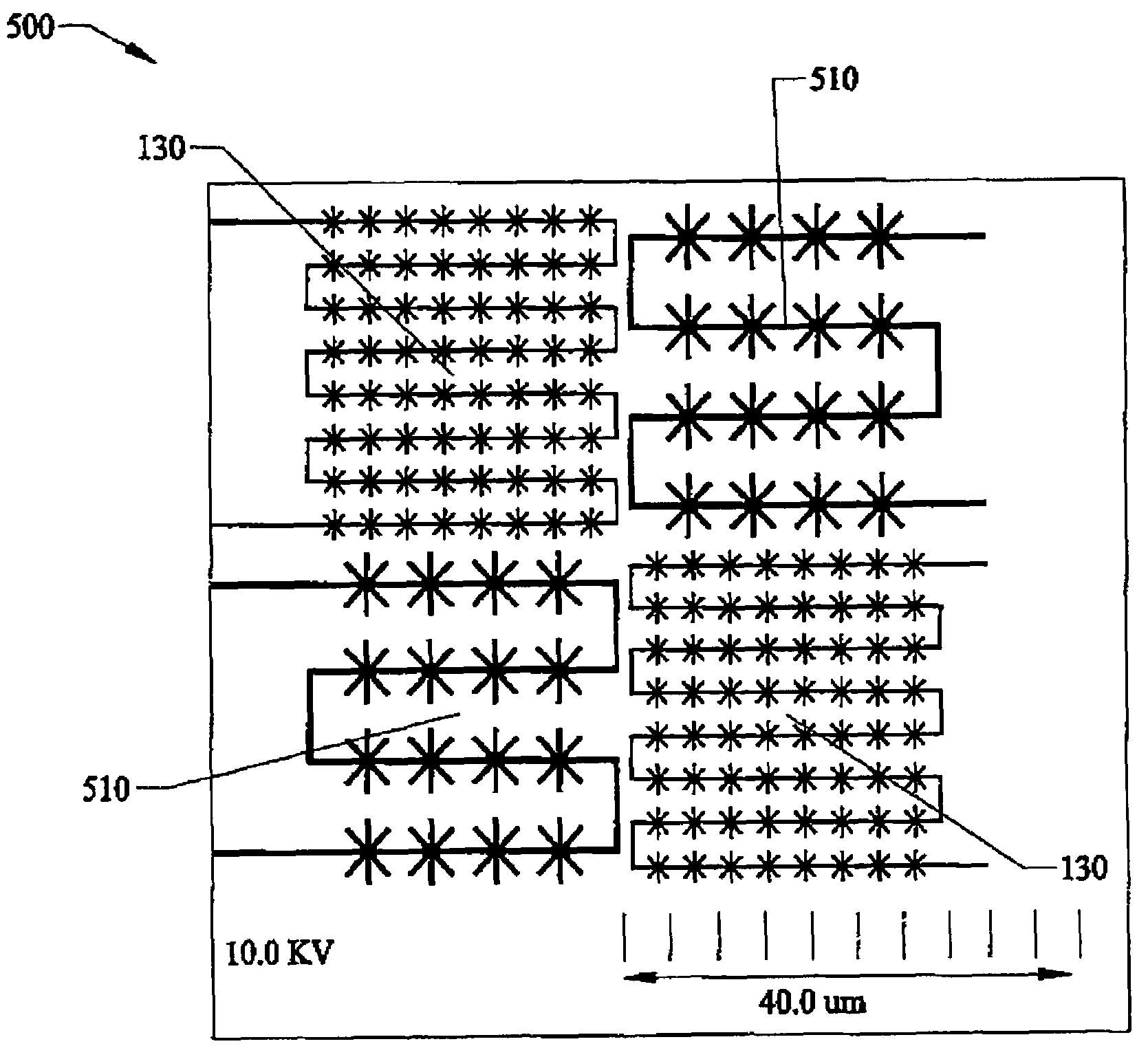
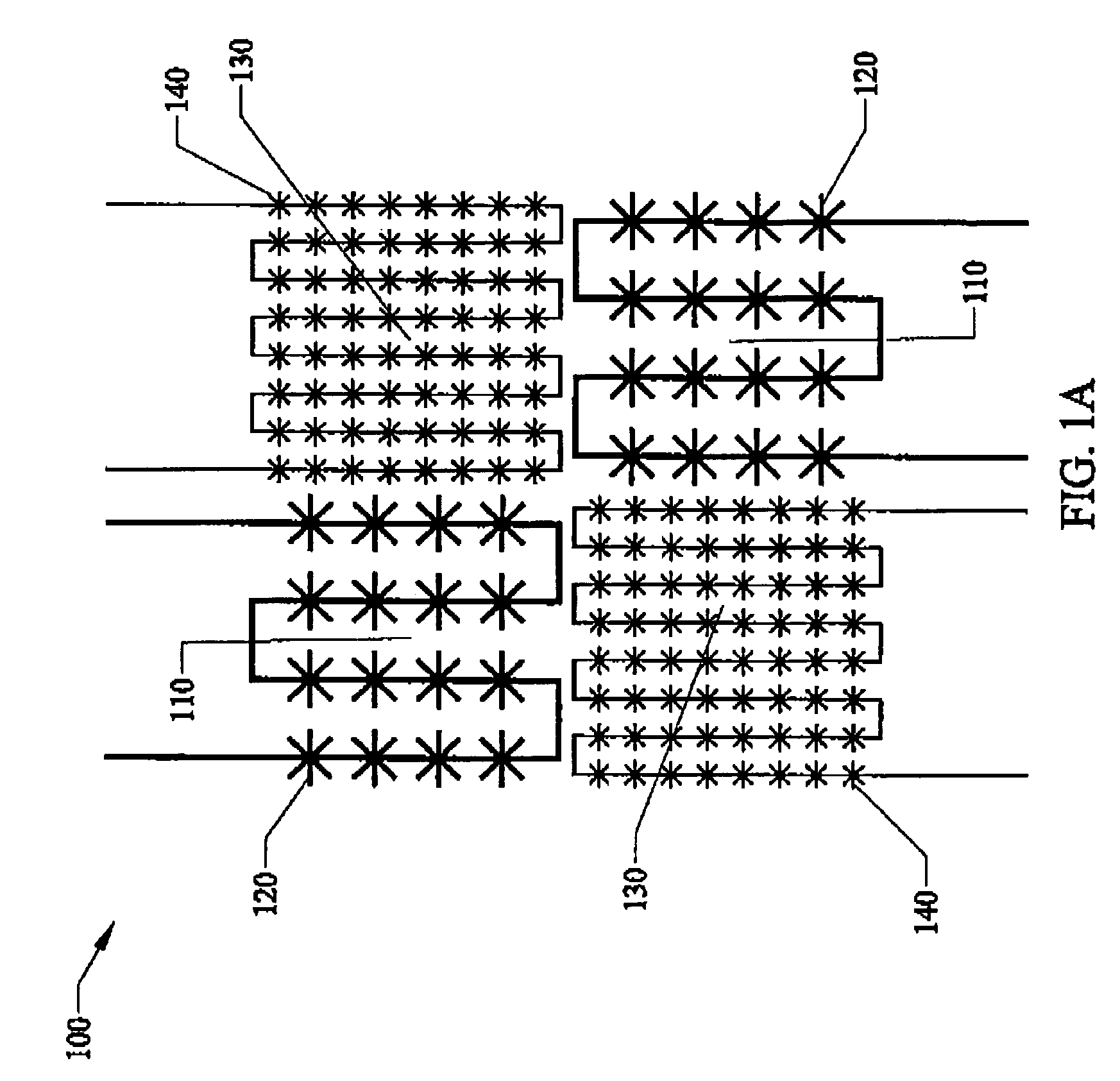
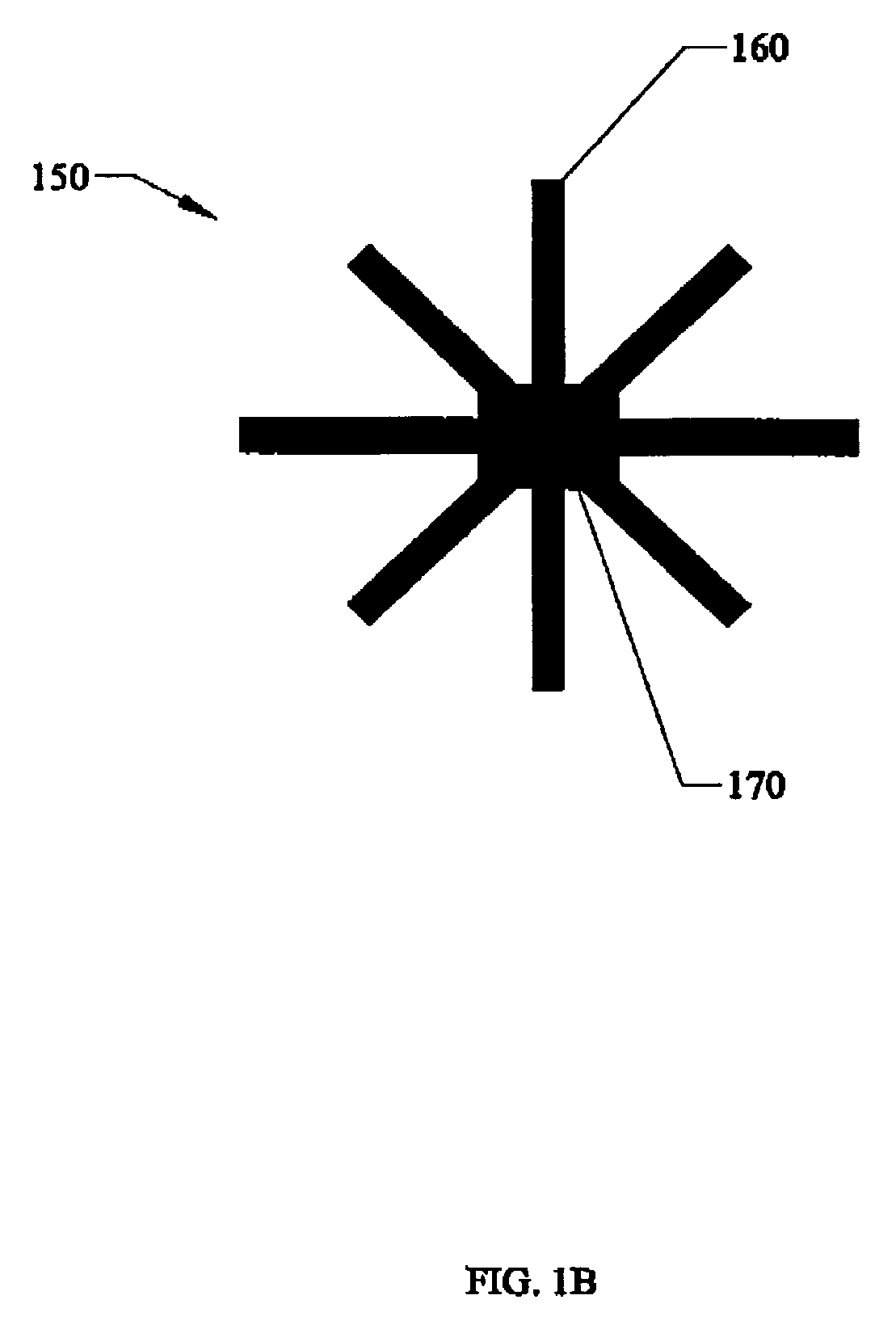
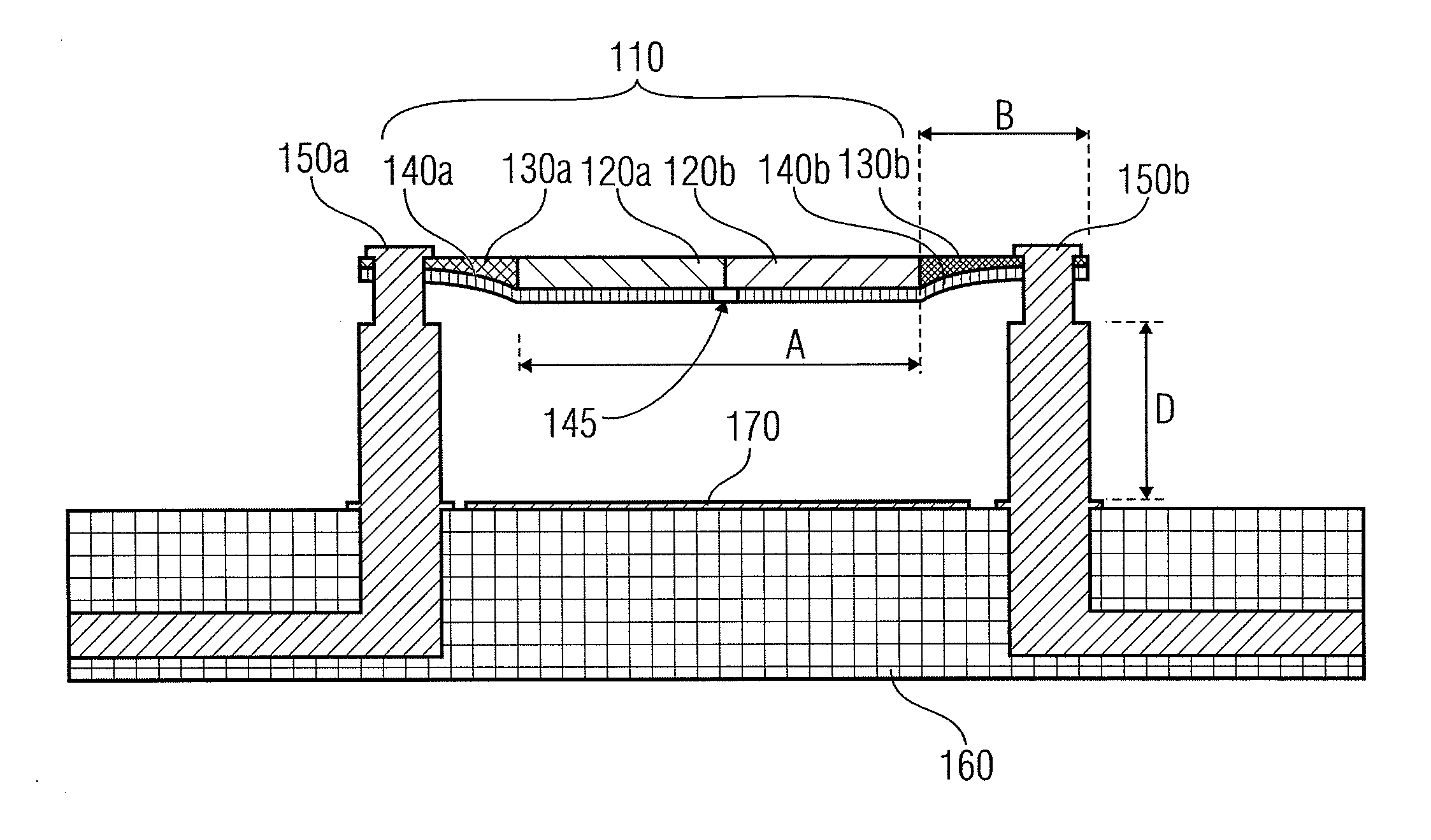
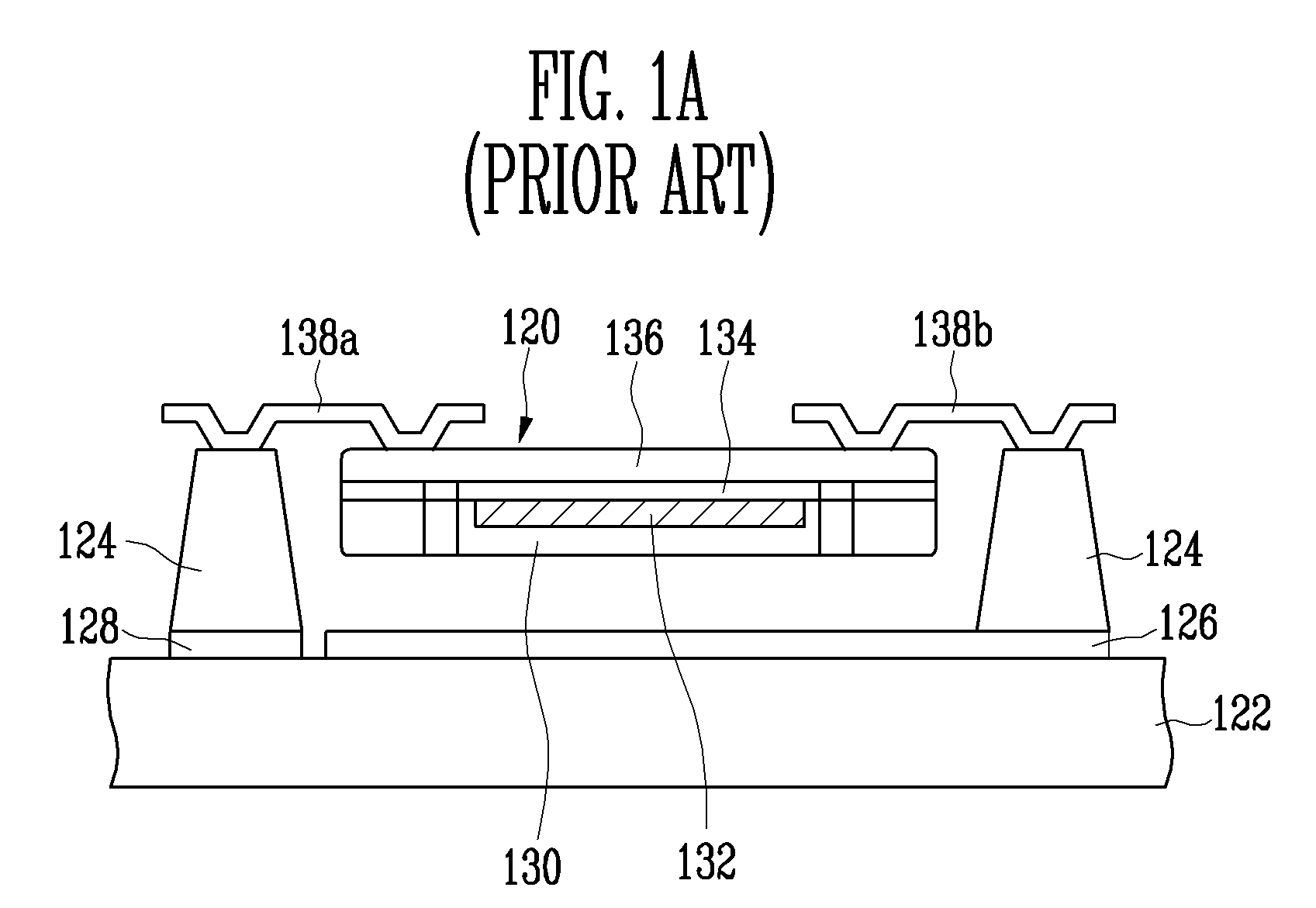
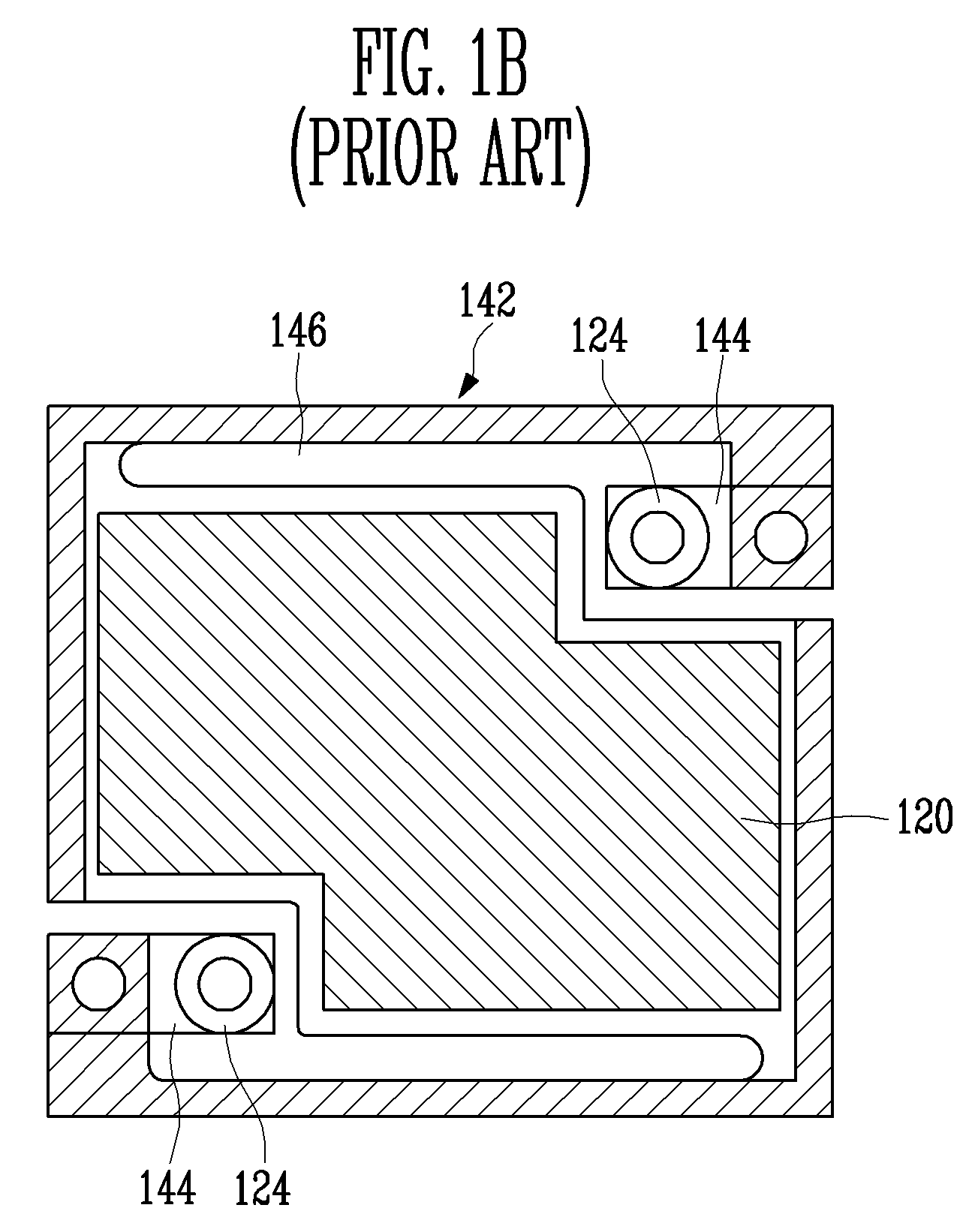
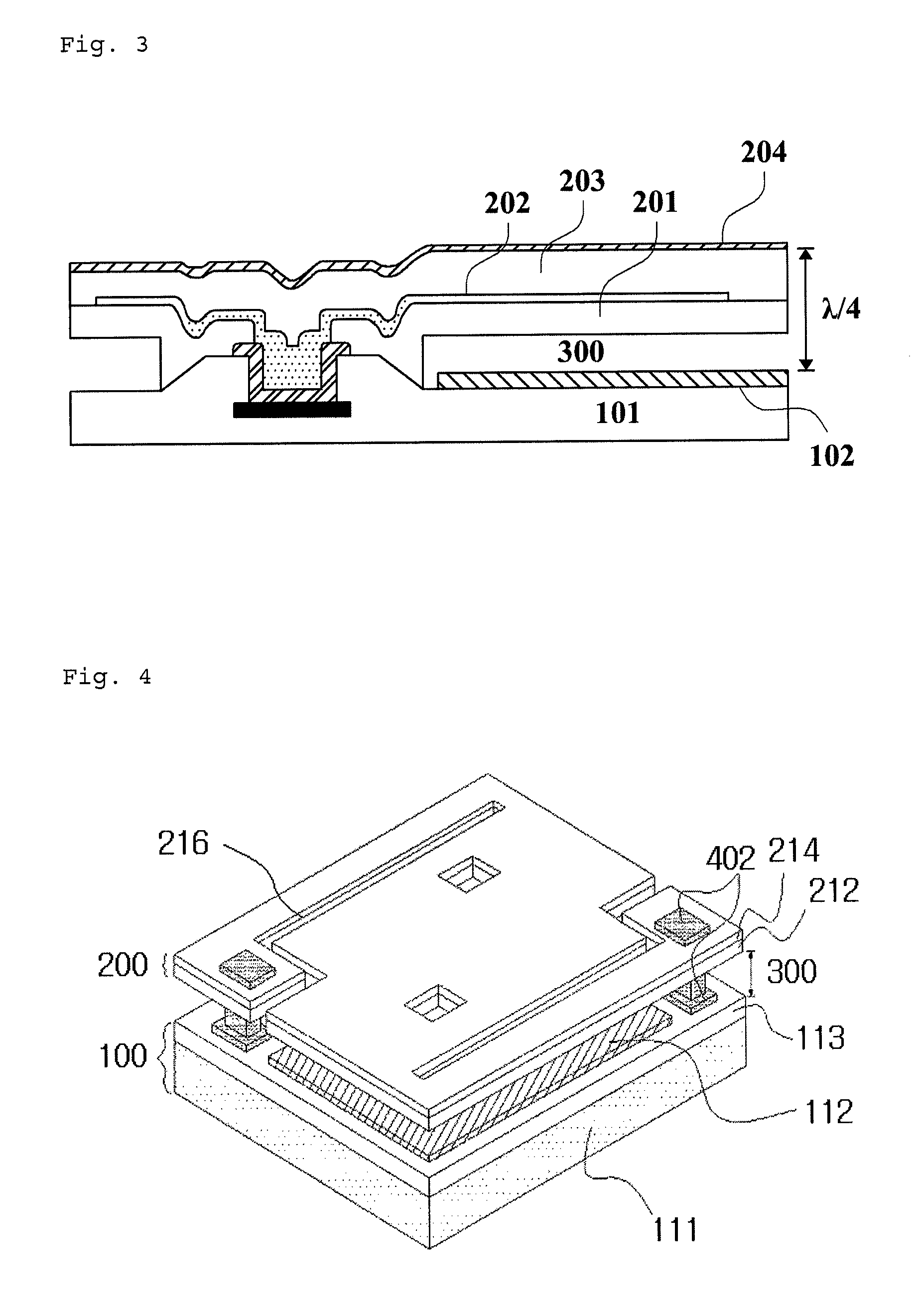
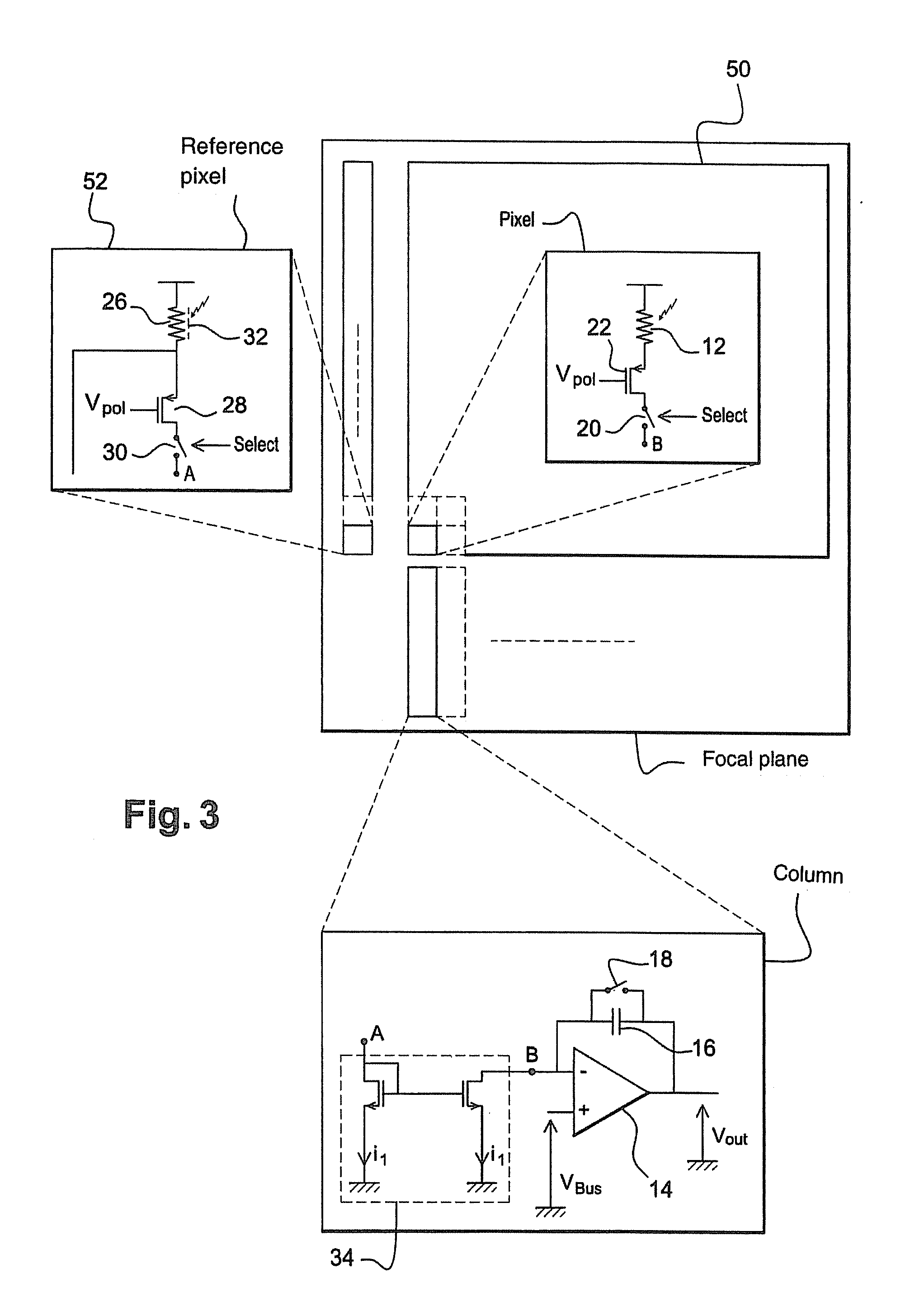
Capacitive micro-electro-mechanical sensors with single crystal silicon electrodes
ActiveUS7539003B2Mechanically variable capacitor detailsCapacitor with electrode area variationIn planeAccelerometer
The devices presented herein are capacitive sensors with single crystal silicon on all key stress points. Isolating trenches are formed by trench and refill forming dielectrically isolated conductive silicon electrodes for drive, sense and guards. For pressure sensing devices according to the invention, the pressure port is opposed to the electrical wire bond pads for ease of packaging. Dual-axis accelerometers measuring in plane acceleration and out of plane acceleration are also described. A third axis in plane is easy to achieve by duplicating and rotating the accelerometer 90 degrees about its out of plane axis Creating resonant structures, angular rate sensors, bolometers, and many other structures are possible with this process technology. Key advantages are hermeticity, vertical vias, vertical and horizontal gap capability, single crystal materials, wafer level packaging, small size, high performance and low cost.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
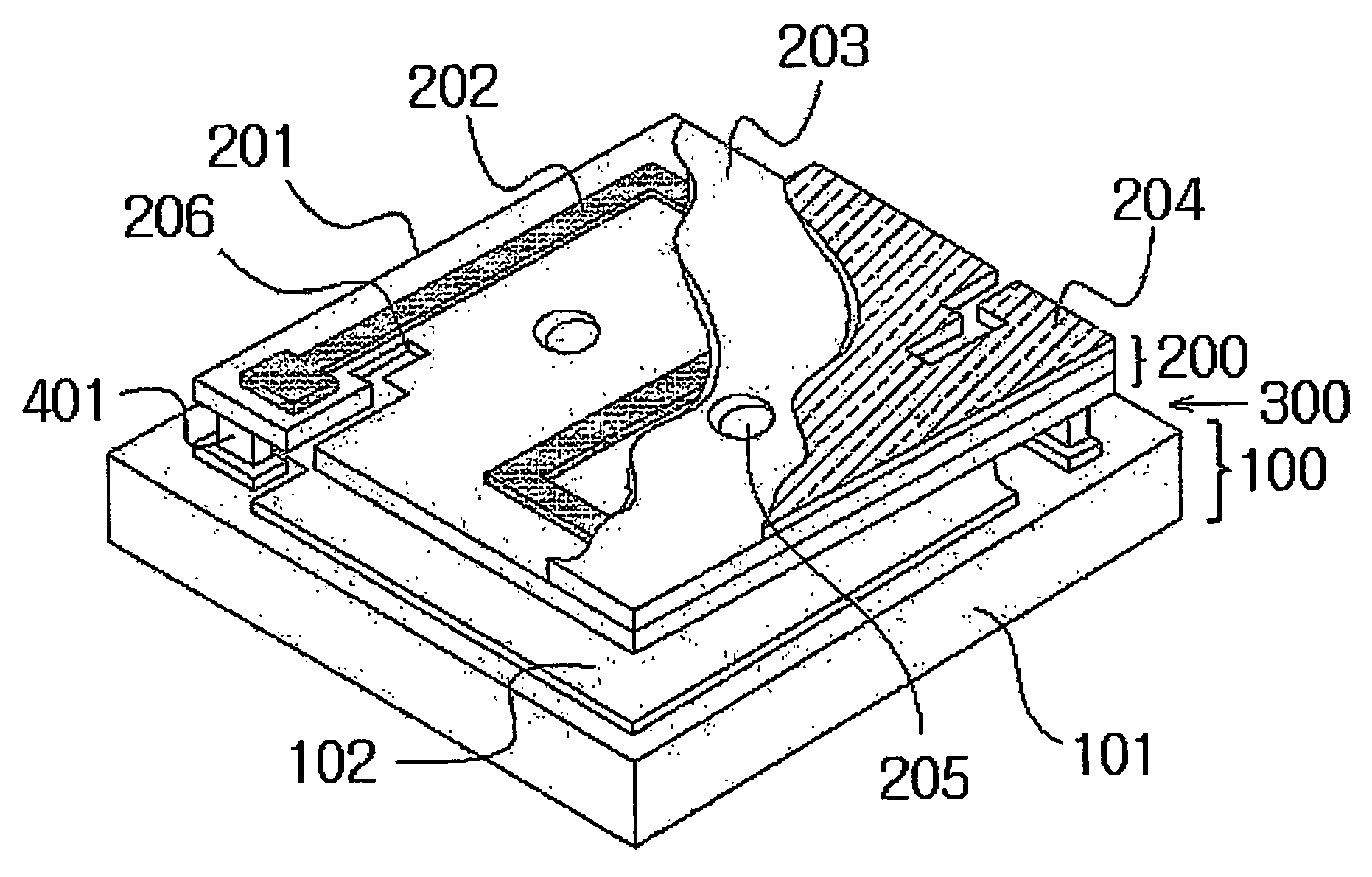
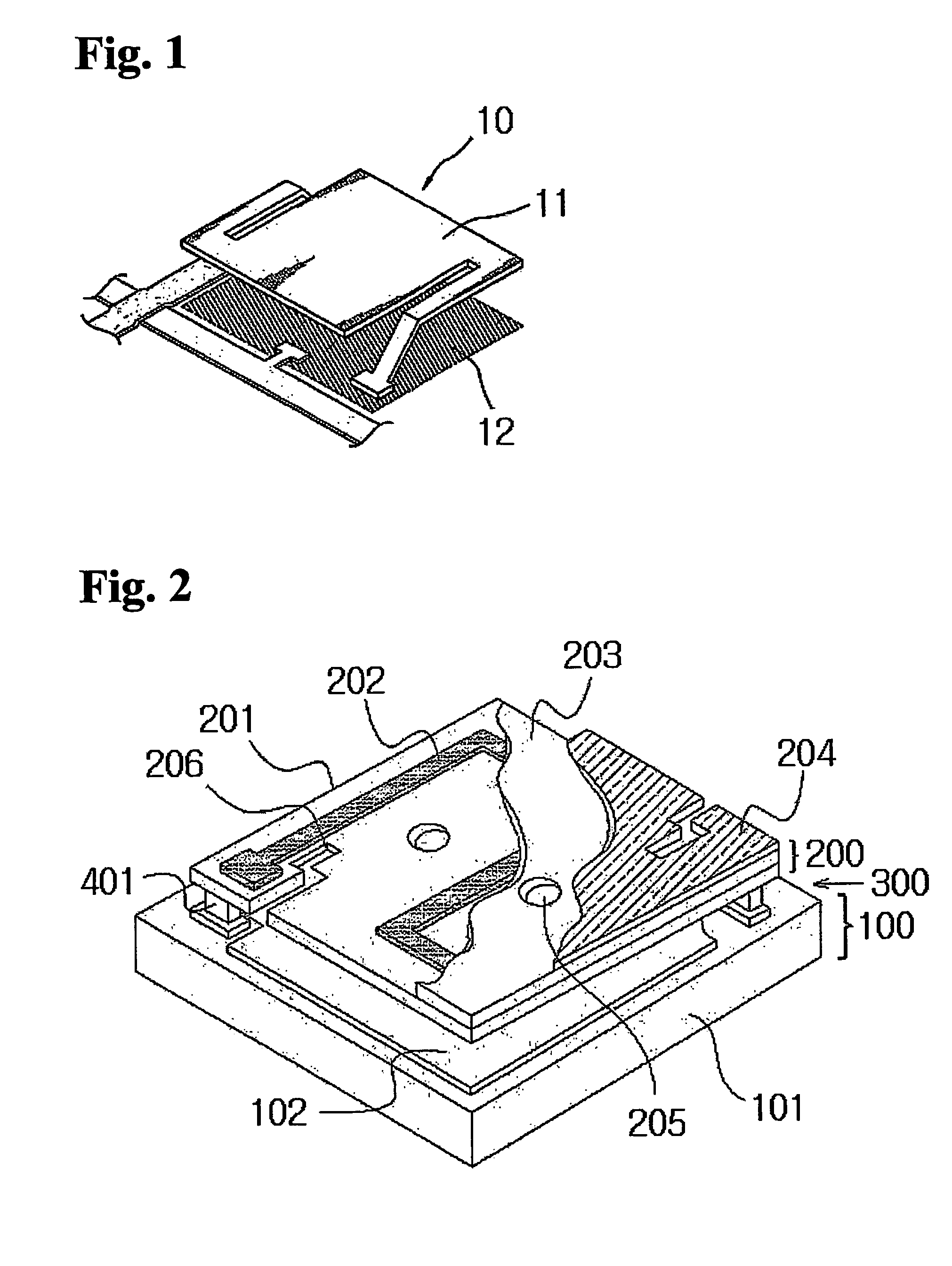
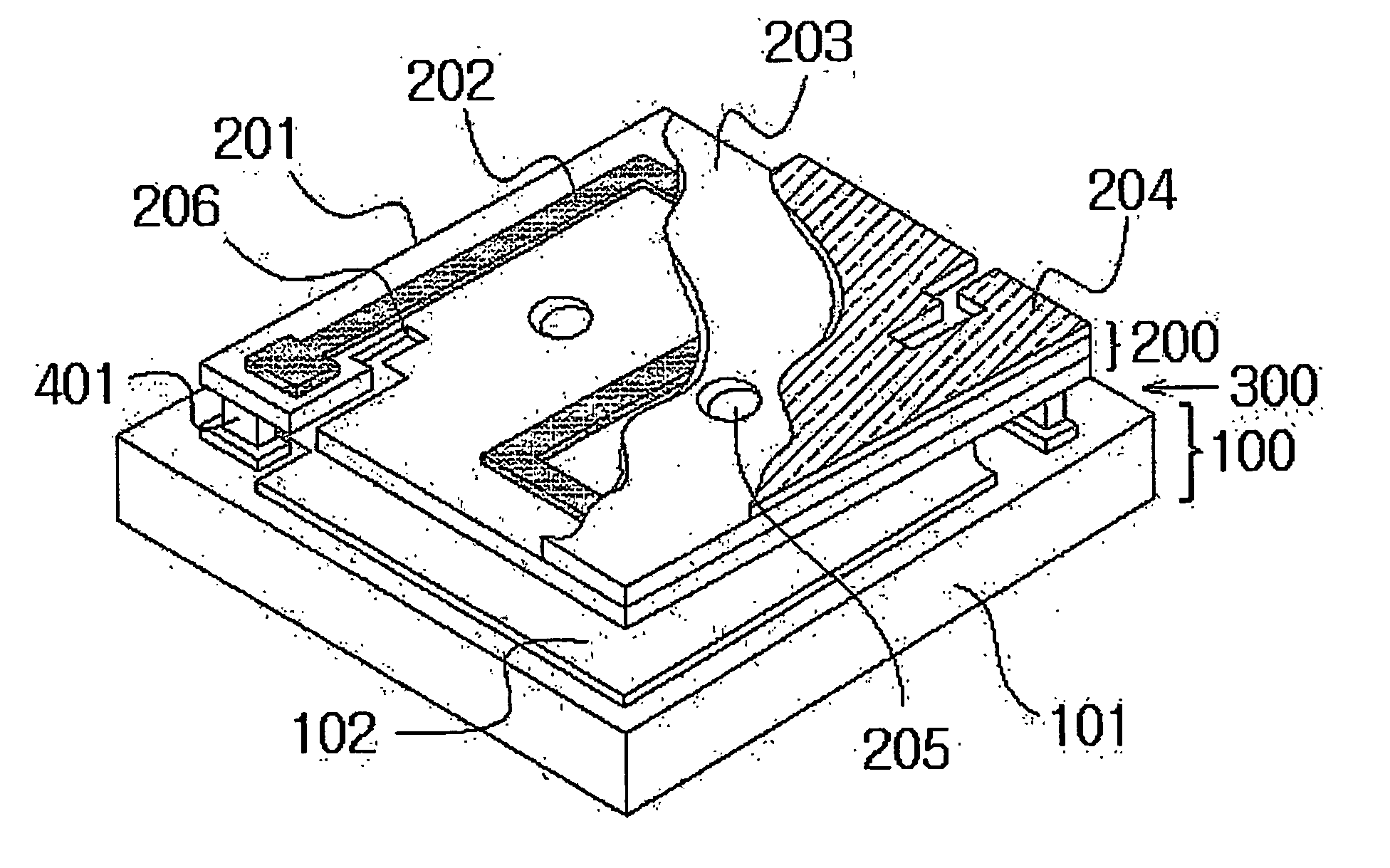
Electromagnetic radiation detection device with integrated housing comprising two superposed detectors
InactiveUS20060043297A1Improve performanceSmall dimensionSpectrum investigationSolid-state devicesElectricityElectrical connection
The invention concerns an electromagnetic radiation sensing device with integrated housing including two superimposed sensors. A first sensor detects one first wavelength range, and a second sensor detects a second wavelength range. The first sensor is arranged inside a protective housing, whereof at least the upper wall includes the second sensor. The wavelengths of the first range, for example included in the infrared domain are, preferably, greater than the wavelengths of the second range, which can be included in the visible or ultraviolet domain. The first sensor is, preferably, a bolometer comprising a sensitive elements and support element forming electrical connection elements between the first sensor and / or the second sensor and an electronic processing circuit.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
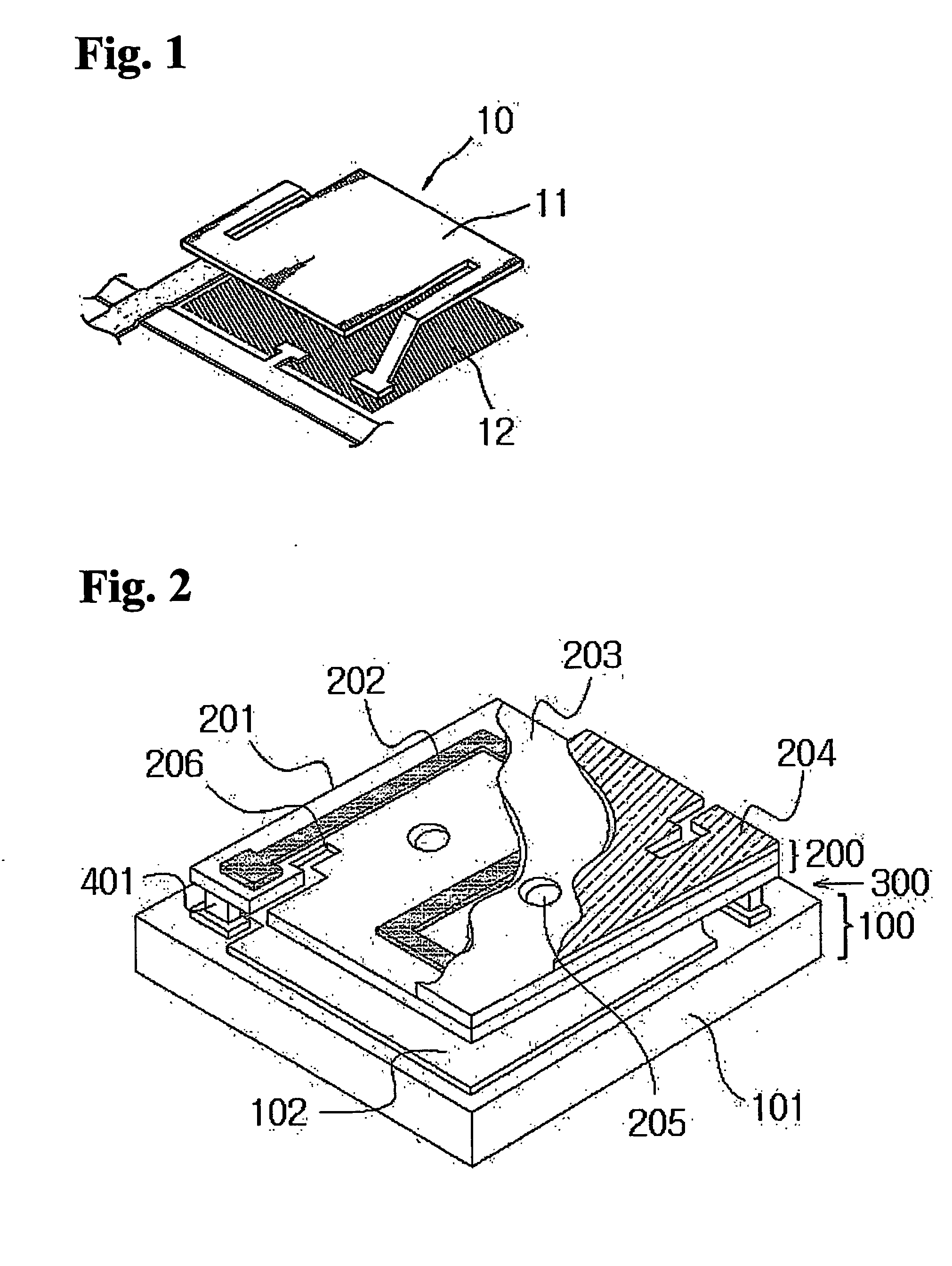
Apparatus and method for sensing electromagnetic radiation using a tunable device
InactiveUS20050017177A1Easy to useHigh device yieldSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectromagnetic radiationBolometer
A method for manufacturing a sensing device, such as a bolometer device or other devices. The method includes providing a substrate, e.g., silicon wafer. The method includes forming a first reflection layer overlying the substrate and forming a first electrode layer overlying the substrate. The method includes forming a sacrificial layer overlying a portion of the first reflection layer and a portion of the first electrode layer. The sacrificial layer is patterned using photolithography techniques. The patterned sacrificial layer corresponds to a cavity region. The method also forms a second electrode layer overlying the sacrificial layer and forms an elastic layer overlying the patterned sacrificial layer. The elastic layer encloses the cavity region corresponding to the patterned sacrificial layer. The method releases the sacrificial layer to form an opening in the cavity region.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
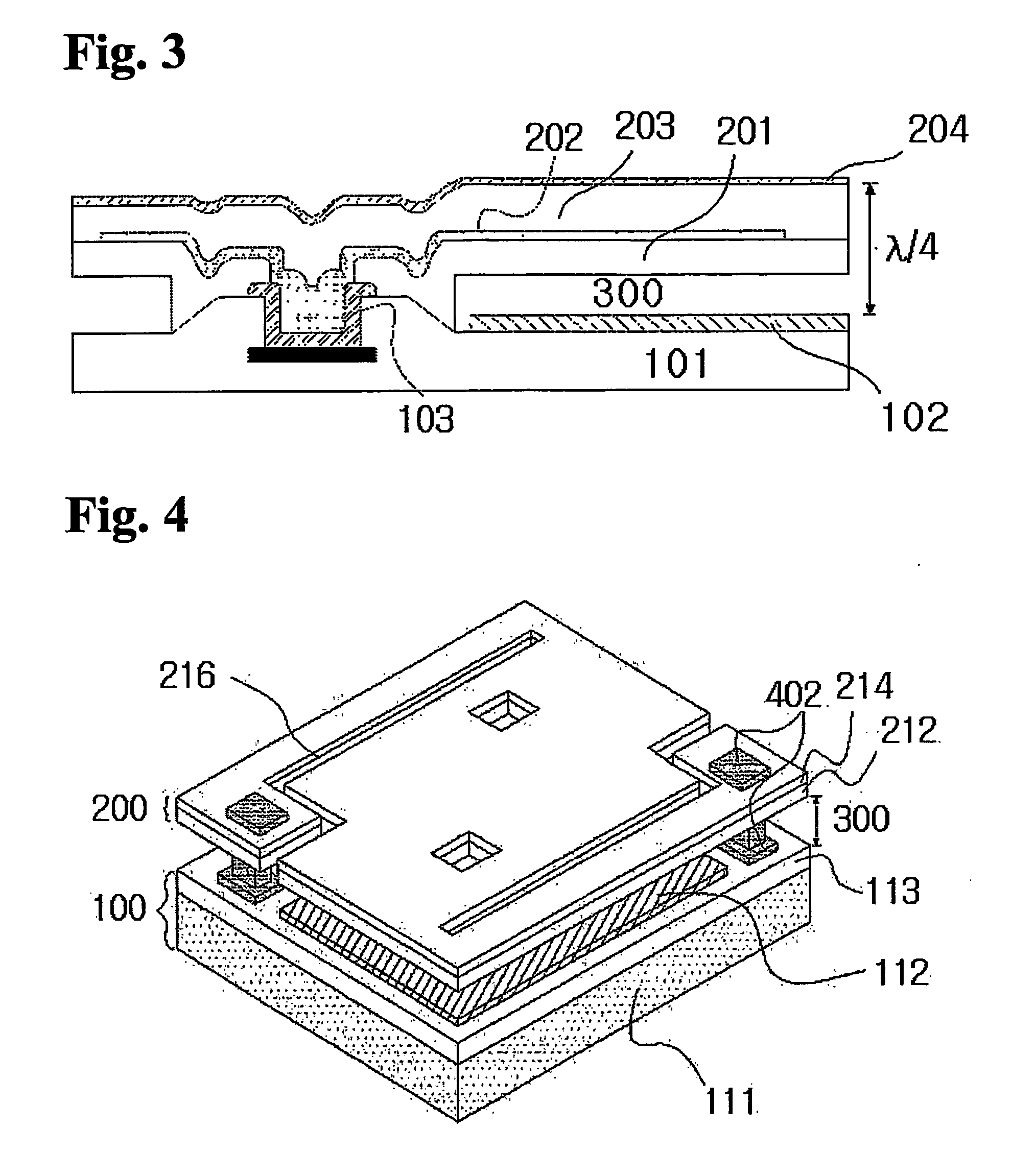
Terahertz radiation detector
InactiveCN103575407AThe implementation method is simpleLow costSolid-state devicesFluid speed measurementTerahertz radiationAbsorbed energy
The invention provides a terahertz radiation detector. The terahertz radiation detector comprises a terahertz sensitive structure and a substrate chip including a reading circuit, wherein the terahertz sensitive structure comprises a terahertz absorption structure, a heat conversion layer and a protection layer, when passive / active terahertz waves are focused on the terahertz sensitive structure through a terahertz object lens, absorbed energy is converted into heat energy through the terahertz absorption structure, the heat energy is converted into an electric signal through the heat conversion layer, and the electric signal is read through the reading circuit on the substrate chip. According to the terahertz radiation detector, a terahertz micro-bolometer micro-bolometer operates under a non-refrigeration environment, single point detection can be carried out, terahertz imaging can further be realized through a focal plane array.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Image sensor for detecting wide spectrum and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7723686B2Reduce light lossImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyTelevision system detailsSpectrum investigationInfraredOptical distortion
An image sensor for detecting a wide spectrum includes a plurality of infrared ray receiving layers which individually receive infrared rays having different wavelengths for each pixel, the plurality of infrared ray receiving layers stacked to each other. The image sensor, which is an integrated image sensor where at least two micro bolometers are stacked, acquires spectrum information about visible rays and near-infrared rays as well as two or more infrared rays applied on an object, without mechanical / thermal / optical distortion, and provides the spectrum information to a silicon-based semiconductor such as a photodiode, thereby improving photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Owner:HANVISION +1
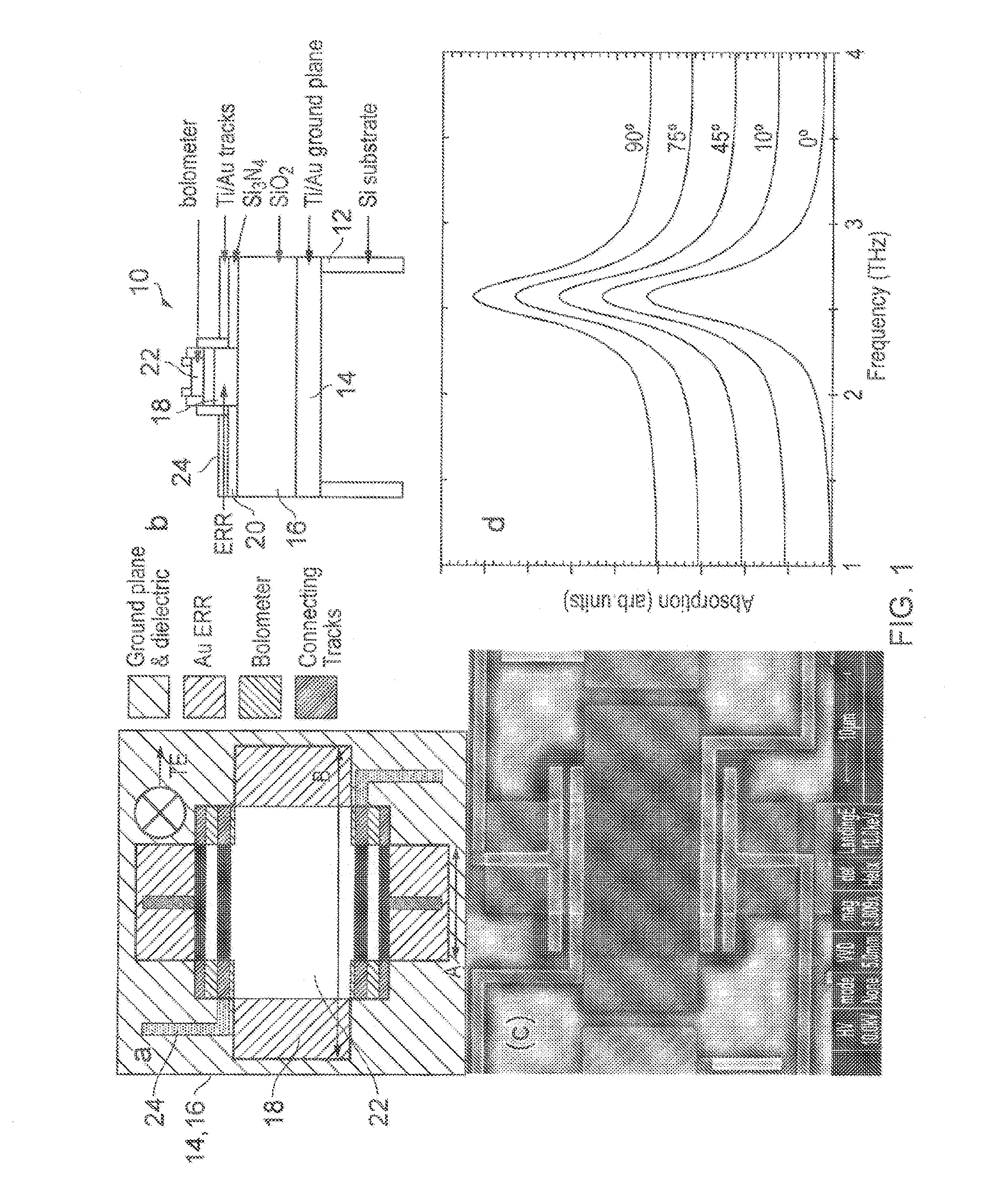
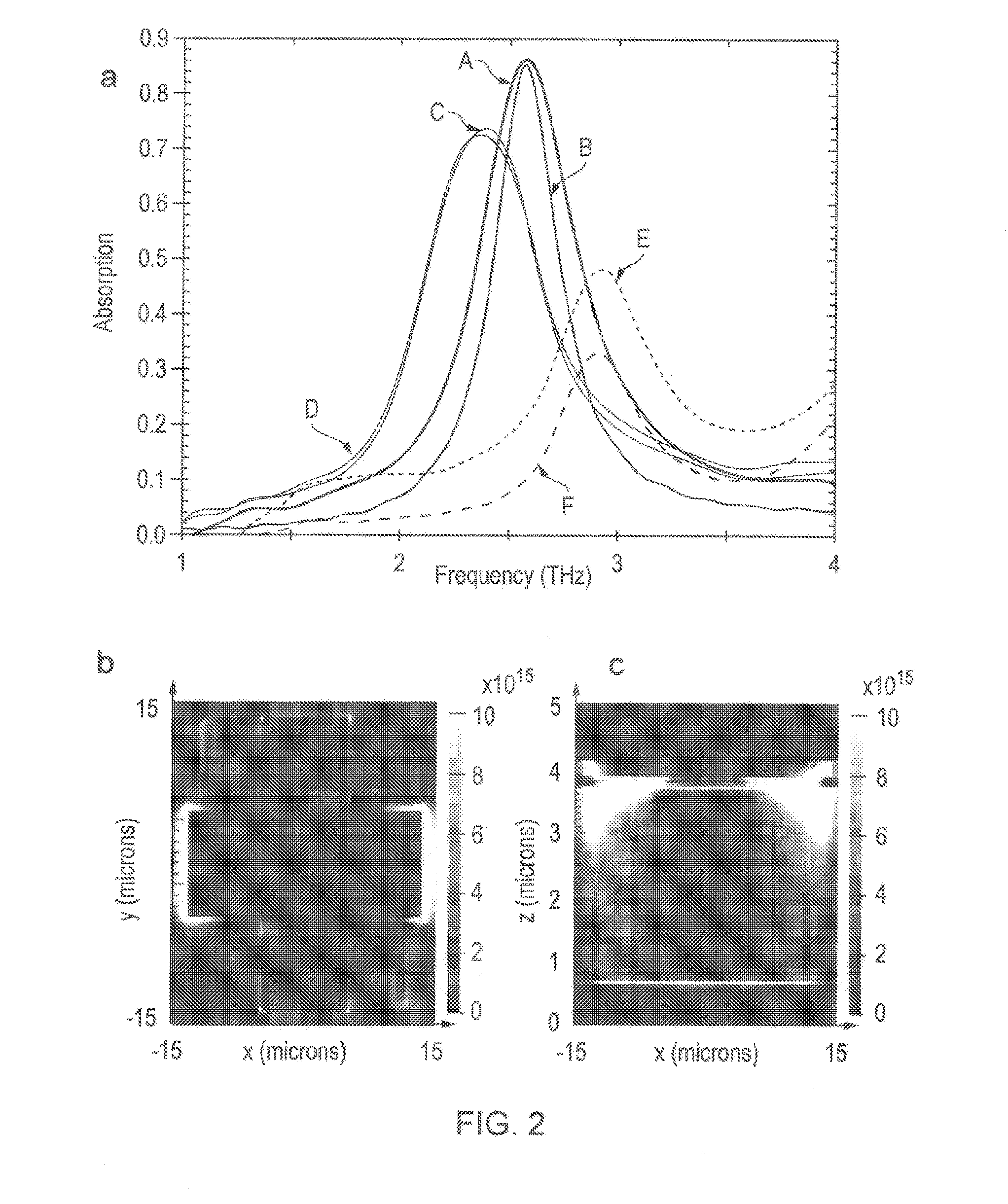
Terahertz radiation detector, focal plane array incorporating terahertz detector, multispectral metamaterial absorber, and combined optical filter and terahertz absorber
InactiveUS20150276489A1Partly effectiveMinimised and possibly eliminatedMaterial analysis by optical meansPyrometry using electric radation detectorsOptical radiationInformation density
The invention provides a detector comprising a metamaterial absorber and a micro-bolometer arranged to detect terahertz (THz) radiation. The metamaterial absorber can absorb multiple frequency bands, from the infrared and the THz regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The detector is scalable to be suitable for use in a focal plane array.The invention also provides a hybrid of a plasmonic filter, e.g. for optical radiation, and a metamaterial absorber for terahertz (and / or infrared) radiation, to create a single material capable of absorbing narrow band terahertz radiation and filtering radiation in another part of the spectrum, e.g. optical radiation. Such material has great potential in future imaging technology where hybridisation can maximise the spectral information density of an optical system.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
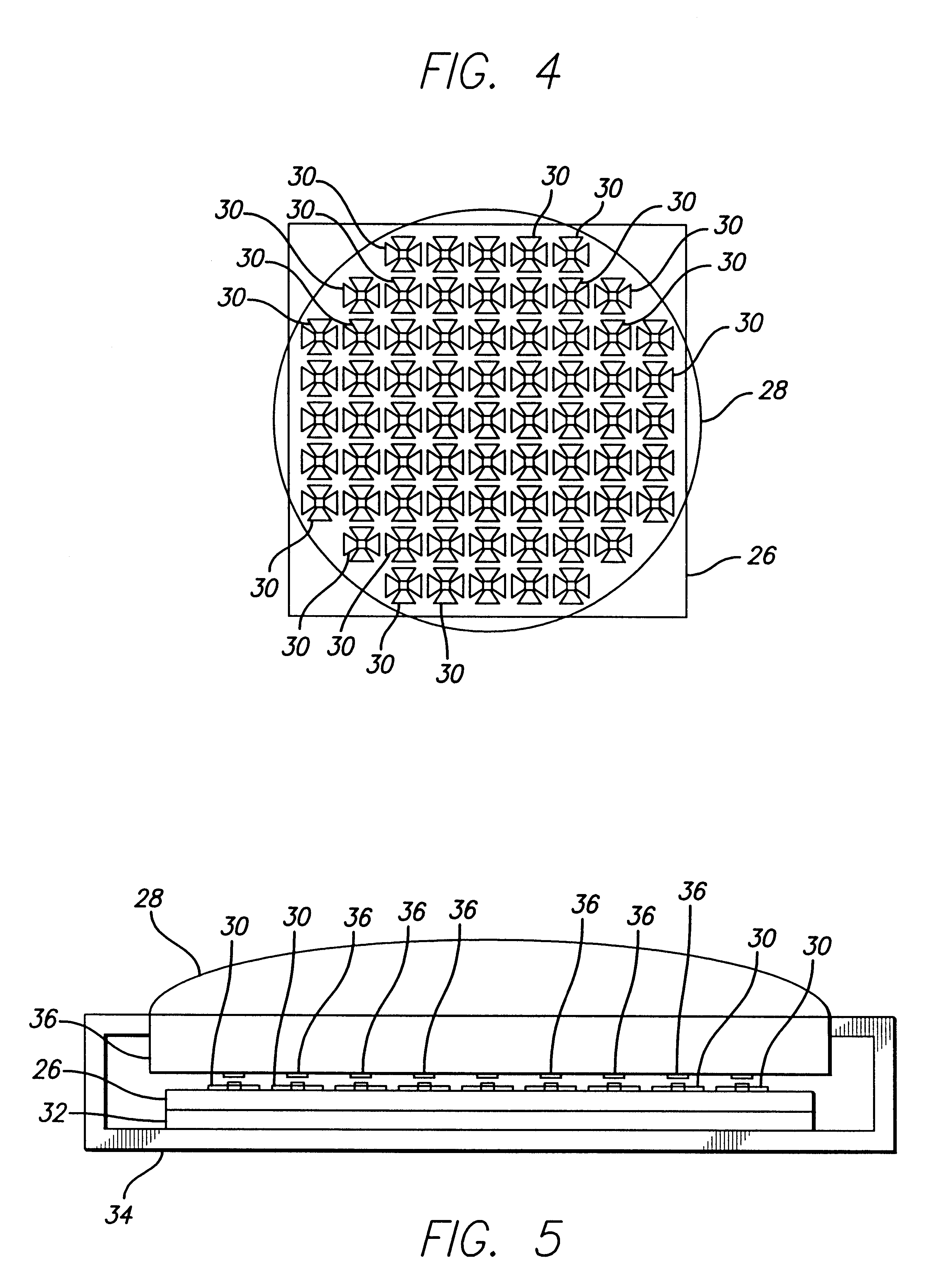
Infrared/visible energy protection for millimeter wave bolometer antenna method and apparatus
InactiveUS6441368B1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansInfraredBolometer
A method and apparatus for protecting a bolometer antenna imaging array from out of band electromagnetic energy is disclosed. Protective pads are disposed upon a window in an optical system forming a millimeter wave image on an array of bolometer antenna sensors. The protective pads are effectively opaque to infrared and visible emissions and are aligned to shade the bolometer portion of the bolometer antennas from infrared and visible emissions, while leaving the antenna portion of each sensor in the array exposed to intercept the millimeter wave energy incident upon them.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
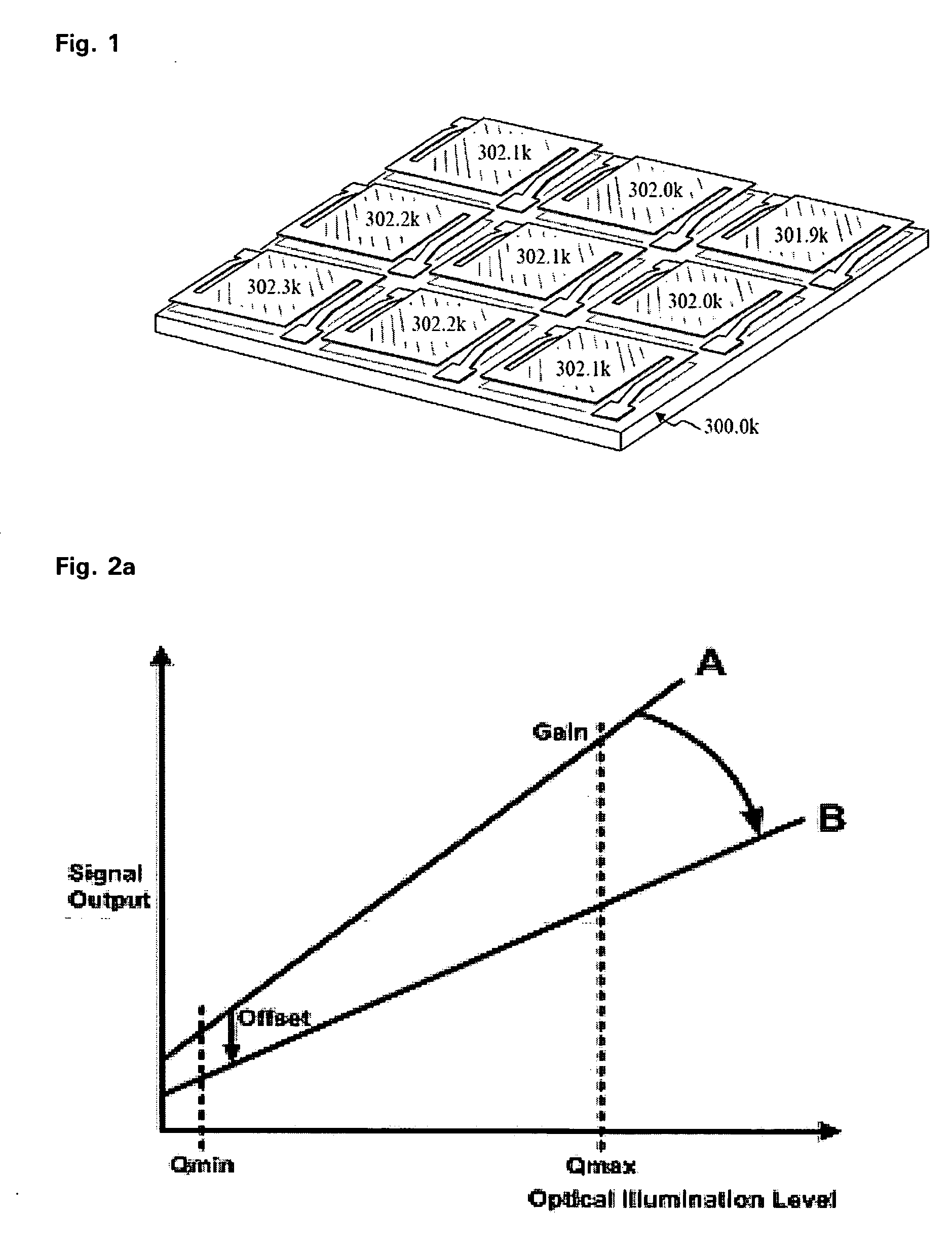
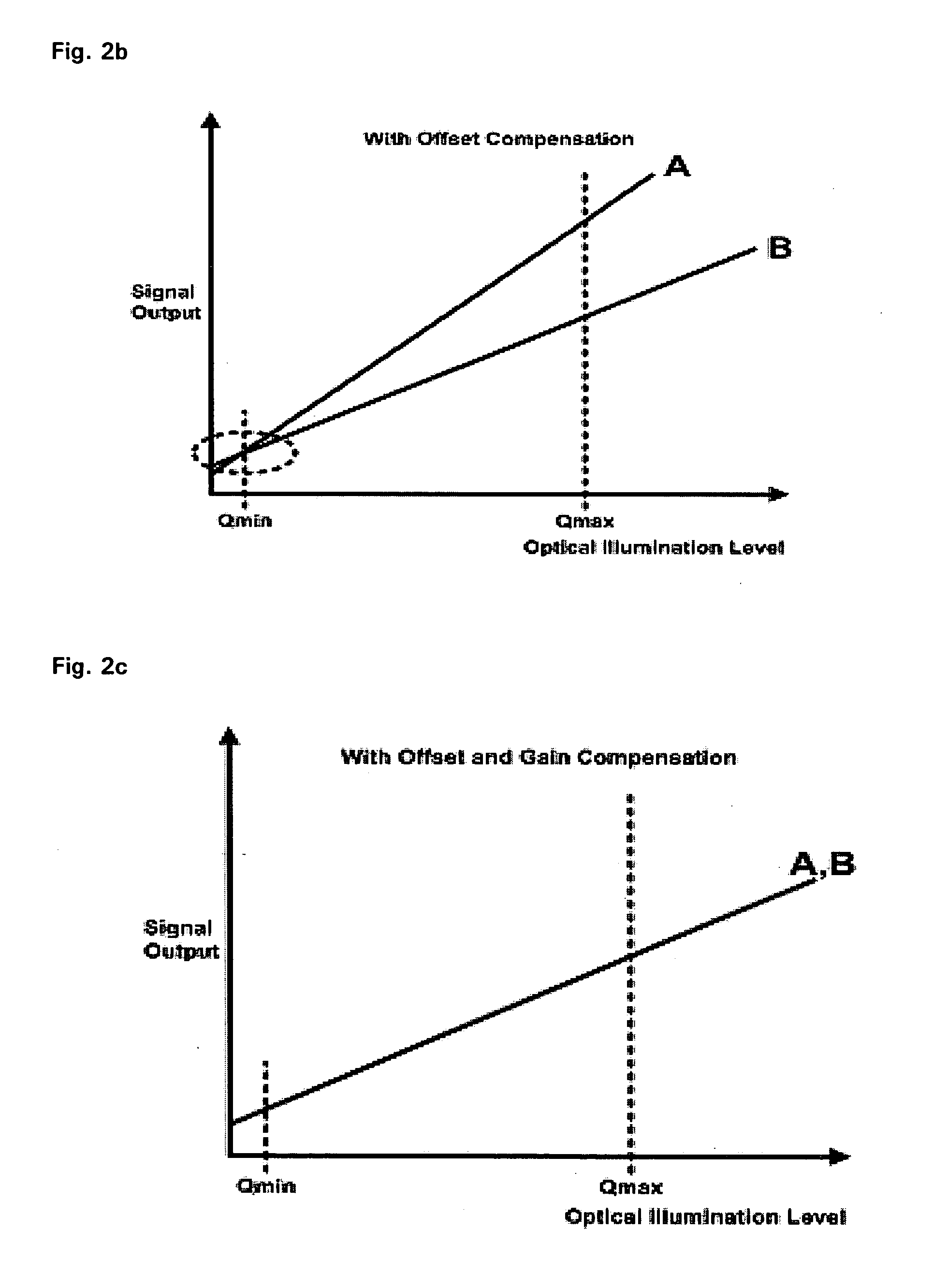
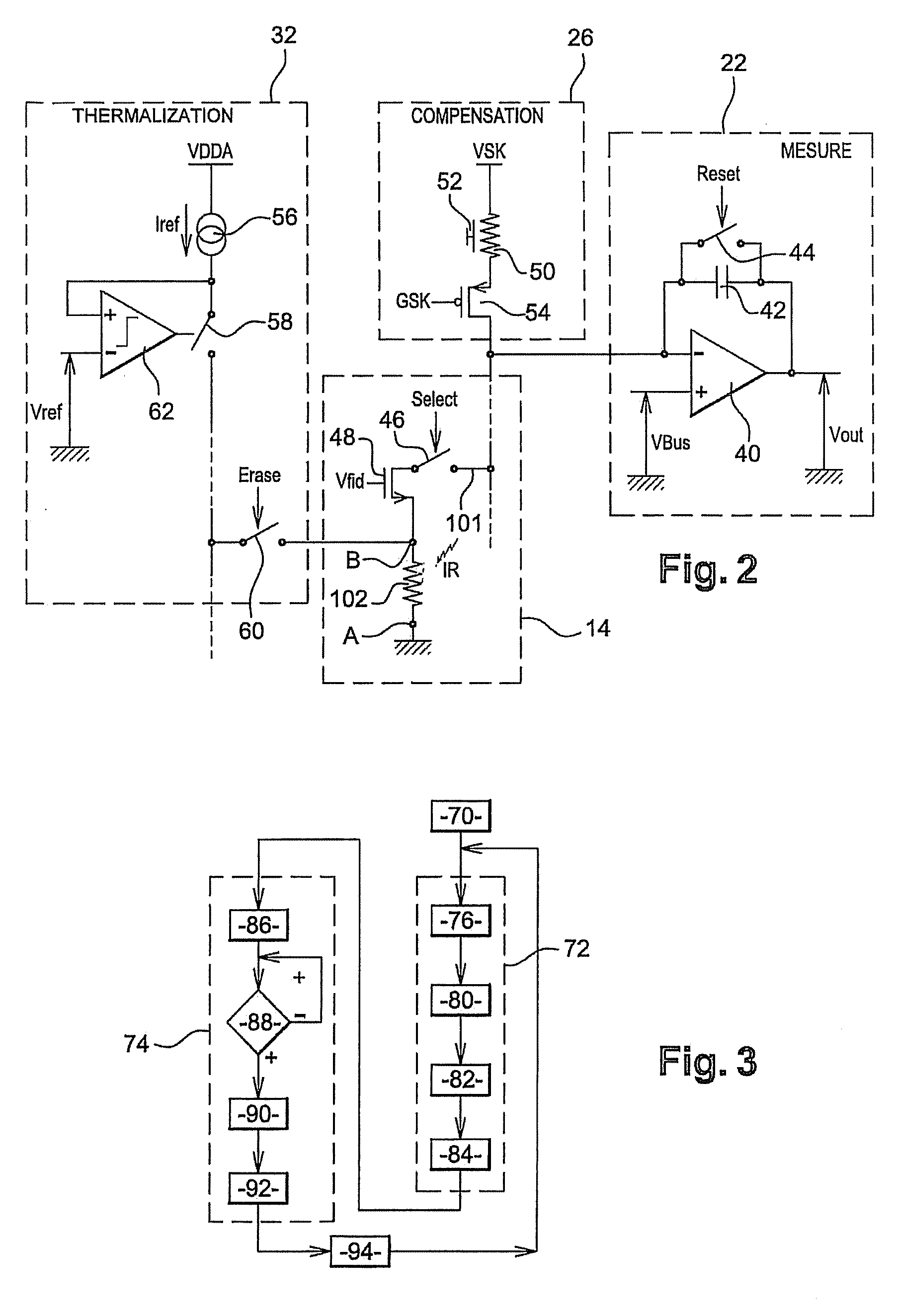
Compensation circuit for compensating non-uniformity according to change of operating temperature of bolometer
InactiveUS20060231760A1Eliminate needSimple processTelevision system detailsData processing applicationsSemiconductor materialsEngineering
The present invention relates to a bolometer, and more specifically to a compensation circuit for compensating non-uniformity due to the difference of operating temperature between bolometers which exist in bolometer array using semiconductor material. A compensation circuit according to the present invention comprises a biasing part including a first transistor generating bias current according to the change of operating temperature to have a dependency of exponential function for the operating temperature of circuit, and a second transistor turned on / off according to the column signal of a bolometer array; a bolometer part including a variable resistor for detecting IR in a pixel base, a third transistor turned on / off according to the column signal of a bolometer array coupled to one end of the variable resistor, and a fourth transistor turned on / off according to the row signal of a bolometer array coupled to the other end of the variable resistor; and an off-set compensation part for compensating the non-uniformity of the bolometer unit.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Multispectral multipolarization antenna-coupled infrared focal plane array
InactiveUS7095027B1Reduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansTunnel diodeOptical polarization
Adjacent pixels of an infrared focal plane array (IR FPA) can be configured to have different spectral or polarization responses by adjustment of the lengths or orientations of the antenna arms which couple radiation into the sensors. The manufacturing costs of such an antenna-coupled IR FPA would be much less than integration of spectral or polarization filters onto each pixel, or fabrication of adjacent pixels with materials of different bandgaps. The antenna-coupled pixels can be made smaller than usual pixels, allowing this diversity of spectral or polarization information on the FPA without losing spatial resolution. The infrared (IR) sensors can be tunnel diodes, schottky diodes, photovoltaics, photoconductors, bolometers, and pyroelectrics. Application areas can include military and civilian remote sensing, automotive driving aids, industrial sensing, medical imaging, and general surveillance.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Diode bolometer and method for producing a diode bolometer
InactiveUS20110140224A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPyrometry using electric radation detectorsSingle crystalBolometer
A bolometer has a semiconductor membrane having a single-crystalline portion, and spacers so as to keep the semiconductor membrane at a predetermined distance from an underlying substrate. The complementarily doped regions of the single-crystalline portion form a diode and the predetermined distance corresponds to a fourth of an infrared wavelength.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Bolometer-type thz-wave detector
ActiveUS20080237467A1High yieldImprove absorption ratePhotometryColor/spectral properties measurementsPhase detectorAbsorptance
In a micro-bridge structure in which a temperature detecting portion (diaphragm) including a bolometer thin film is supported by a supporting portion in a state floated from a circuit substrate, a reflective film reflecting a THz wave is formed on the circuit substrate, an absorbing film absorbing the THz wave is formed on the temperature detecting portion, and an optical resonance structure is formed by the reflective film and temperature detecting portion. A gap between the reflective film and temperature detecting portion measures approximately ¼ infrared wavelength (e.g., 1.5 to 2.5 μm). Sheet resistance of the temperature detecting portion is set in a range in which an absorptance of the THz wave becomes a predetermined value or above on the basis of the THz wave (approximately 10-100 Ω / sq.). The absorptance of the THz wave is drastically improved while using the structure and manufacturing technique of a bolometer-type infrared detector.
Owner:NEC CORP +2
Multispectral sensor
InactiveUS20110194100A1Lower unit production costAllow useSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansTerahertz radiationSpectroscopy
A multispectral sensor which includes a complementary metal oxide semiconductor substrate having a switching circuit, at least one antenna-receiving combination device for detecting terahertz radiation, at least one additional bolometer for detecting mid-range infrared radiation, and at least one diode for detecting radiation in the visible to near-infrared range. A multispectral imaging and / or spectroscopy system, a method for detecting and / or examining life forms, objects, and materials using such a system, and the use of such a sensor and system are also described.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH +1
Bolometer and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090140148A1Reduce noiseHigh temperature sensitivitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansAmorphous siliconOptoelectronics
A bolometer having decreased noise and increased temperature sensitivity and a method of manufacturing the same are provided. The bolometer has a resistive layer formed of single crystalline silicon (Si) or silicon germanium (Si1-xGex, x=0.2˜0.5) having high crystallinity, such that 1 / f noise can be reduced and temperature sensitivity can be significantly improved compared to a conventional amorphous silicon bolometer.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Bolometric infrared sensor having two-layer structure and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7554085B2Avoid deformationSimple structureSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansInfraredOptoelectronics
The present disclosure is related to bolometric infrared sensors having a two-layer structure and methods for manufacturing the same for improving an absorption rate by a spectroscopic design for resonantly absorbing infrared, and preventing the deformation of a sensor caused by stresses due to heat. The infrared sensor including an ROIC substrate and several pixels, comprises: a bottom layer including a reflective metal layer on the ROIC substrate; a cavity for resonantly absorbing infrared ray over the bottom layer; an upper layer of a sandwich shape including an absorption-transmission layer having a cutting area in the middle thereof and a bolometer layer placed both on and under the absorption-transmission layer; and anchors positioned at the edges of the pixel for supporting the upper layer and functioning as electrodes.
Owner:OCAS
Bolometric Infrared Sensor Having Two-Layer Structure and Method for Manufacturing the Same
InactiveUS20070262256A1Improve absorption rateAvoid deformationSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansInfraredOptoelectronics
The present disclosure is related to bolometric infrared sensors having a two-layer structure and methods for manufacturing the same for improving an absorption rate by a spectroscopic design for resonantly absorbing infrared, and preventing the deformation of a sensor caused by stresses due to heat. The infrared sensor including an ROIC substrate and several pixels, comprises: a bottom layer including a reflective metal layer on the ROIC substrate; a cavity for resonantly absorbing infrared ray over the bottom layer; an upper layer of a sandwich shape including an absorption-transmission layer having a cutting area in the middle thereof and a bolometer layer placed both on and under the absorption-transmission layer; and anchors positioned at the edges of the pixel for supporting the upper layer and functioning as electrodes.
Owner:OCAS
Image sensor for detecting wide spectrum and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100038540A1Reduce light lossImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyTelevision system detailsSpectrum investigationInfraredOptical distortion
Provided are an image sensor for detecting a wide spectrum, including a plurality of infrared ray receiving layers which individually receive infrared rays having different wavelengths for each pixel, the plurality of infrared ray receiving layers stacked to each other, and a manufacturing method thereof. The image sensor, which is an integrated image sensor where at least two micro bolometers are stacked, acquires spectrum information about visible rays and near-infrared rays as well as two or more infrared rays applied on an object, without mechanical / thermal / optical distortion, and provides the spectrum information to a silicon-based semiconductor such as a photodiode, thereby improving photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Owner:HANVISION +1
Bolometer structure, infrared detection pixel employing bolometer structure, and method of fabricating infrared detection pixel
InactiveUS20100148067A1Improve processing yieldImprove responsivityMaterial analysis by optical meansPyrometry using electric radation detectorsResponsivityReadout integrated circuit
Provided are a bolometer structure, an infrared detection pixel employing the bolometer structure, and a method of fabricating the infrared detection pixel.The infrared detection pixel includes a substrate including a read-out integrated circuit (ROIC) and on which a reflection layer for reflecting infrared light is stacked, a bolometer structure formed to be spaced apart from the substrate and including a temperature-sensitive resistive layer, a first metal layer formed in a pattern on one surface of the temperature-sensitive resistive layer, a second metal layer formed in a pattern complementary to the pattern of the first metal layer on the other surface of the temperature-sensitive resistive layer in order to complementarily absorb infrared light, and an insulating layer formed between the temperature-sensitive resistive layer and the first metal layer, and a metal pad receiving a change in resistance of the temperature-sensitive resistive layer according to infrared light absorbed by the first metal layer and the second metal layer from the second metal layer, and transferring the change in resistance to the ROIC.Thus, it is possible to improve responsivity, and implement a simple bolometer structure robust against stress. Consequently, process yield can be improved, and the volume, weight, price, etc., of application products can be reduced by reducing the volume of a bolometer structure.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Bolometer infrared detector and afterimage reduction method
InactiveUS20050274892A1Increase the pulse widthReduce afterimagePhotometrySolid-state devicesThermal isolationBolometer
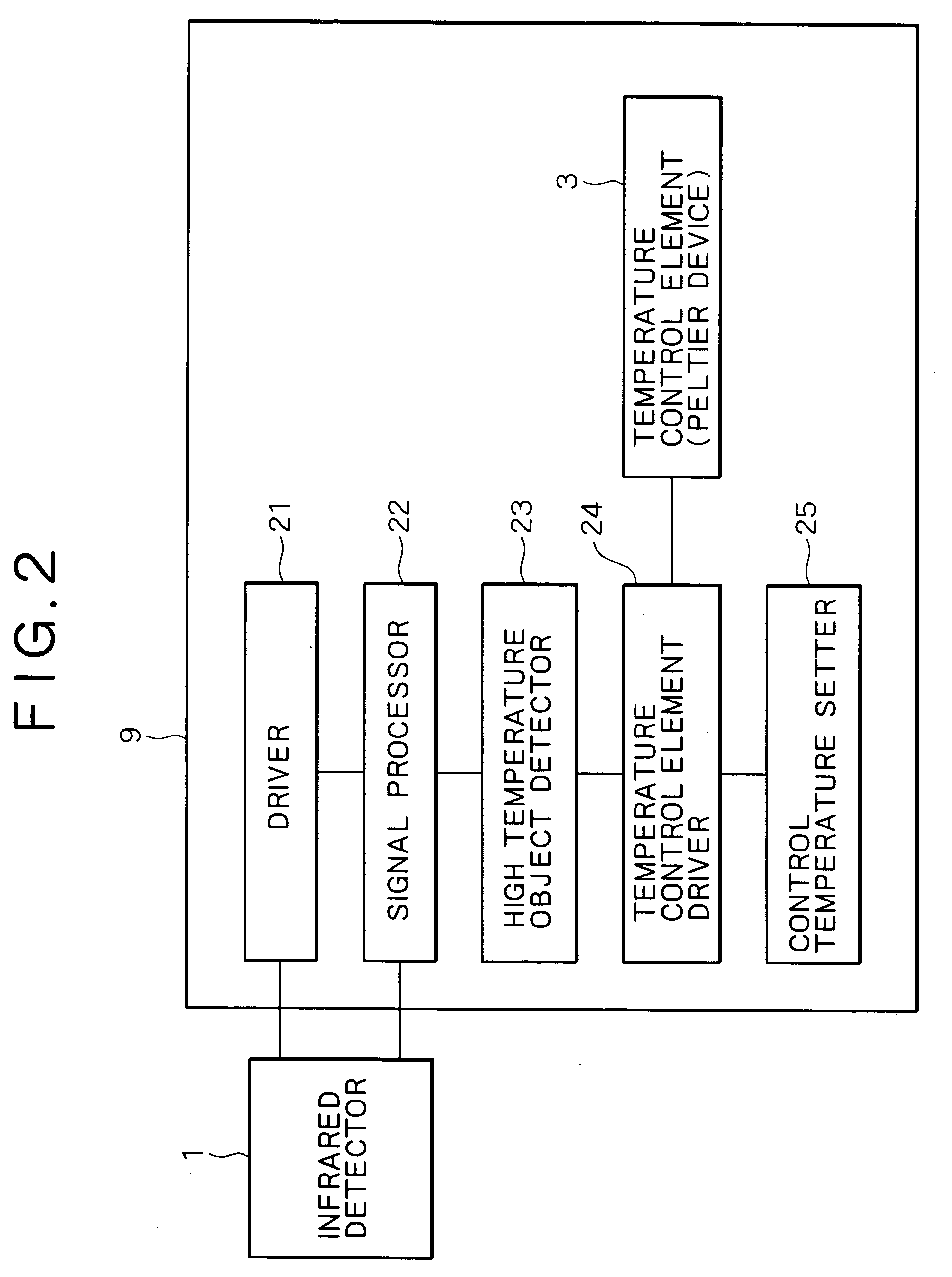
A bolometer infrared detecting element has a thermal isolation structure in which a temperature detector comprising a bolometer thin film is held floating from a circuit substrate by beams. As infrared rays incident on the temperature detector or reflected by an infrared reflector are absorbed by a protective film and the bolometer thin film, the temperature of the bolometer thin film rises, and the temperature rise is detected as a change in resistance. When a high temperature object whose temperature is equal to or higher than a predetermined temperature or whose output voltage is equal to or higher than a value corresponding to the predetermined temperature is detected, a control temperature setter or a pulse bias setter performs control in such a way as to raise the temperature of a Peltier device stepwise or in a pulse form, or to increase the width of a pulse of pulse bias, or to increase the voltage value of the pulse. This makes it possible to raise the temperature of the infrared detecting element, thereby reducing an afterimage.
Owner:NEC CORP
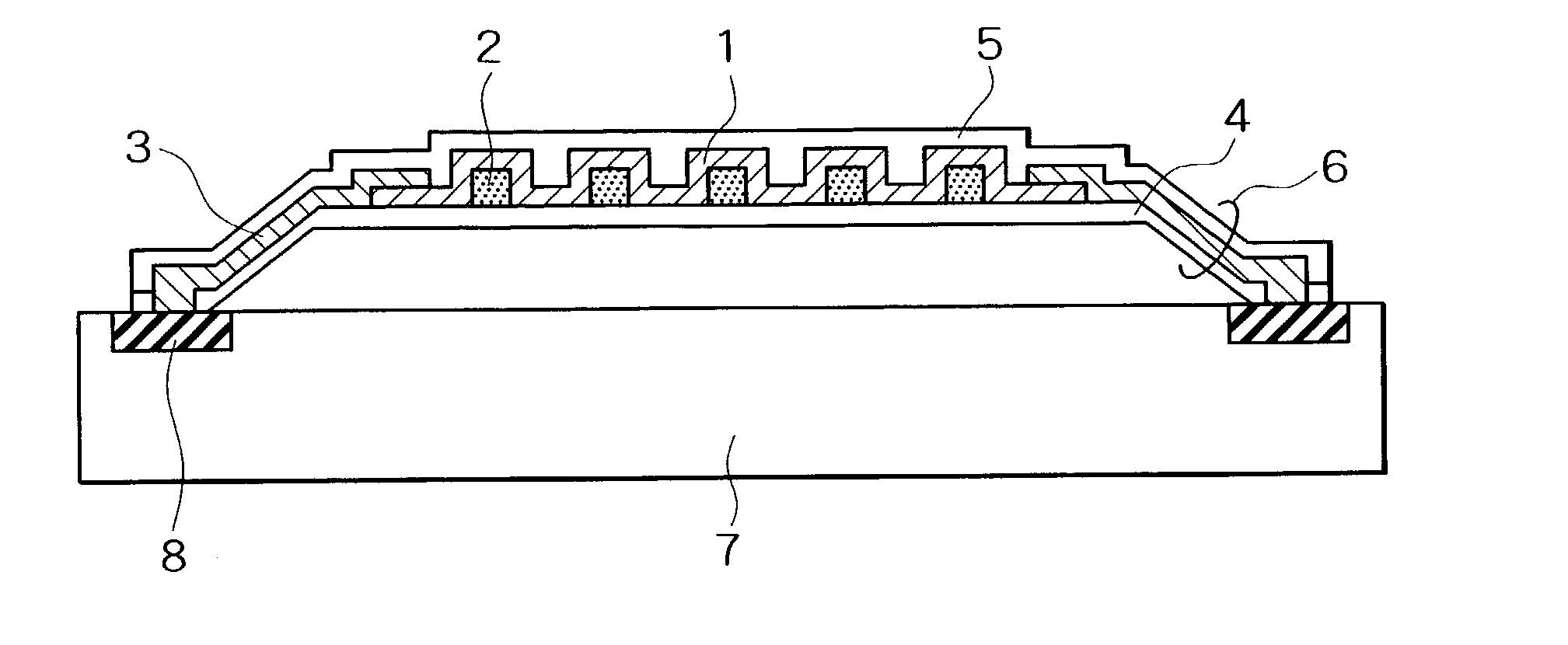
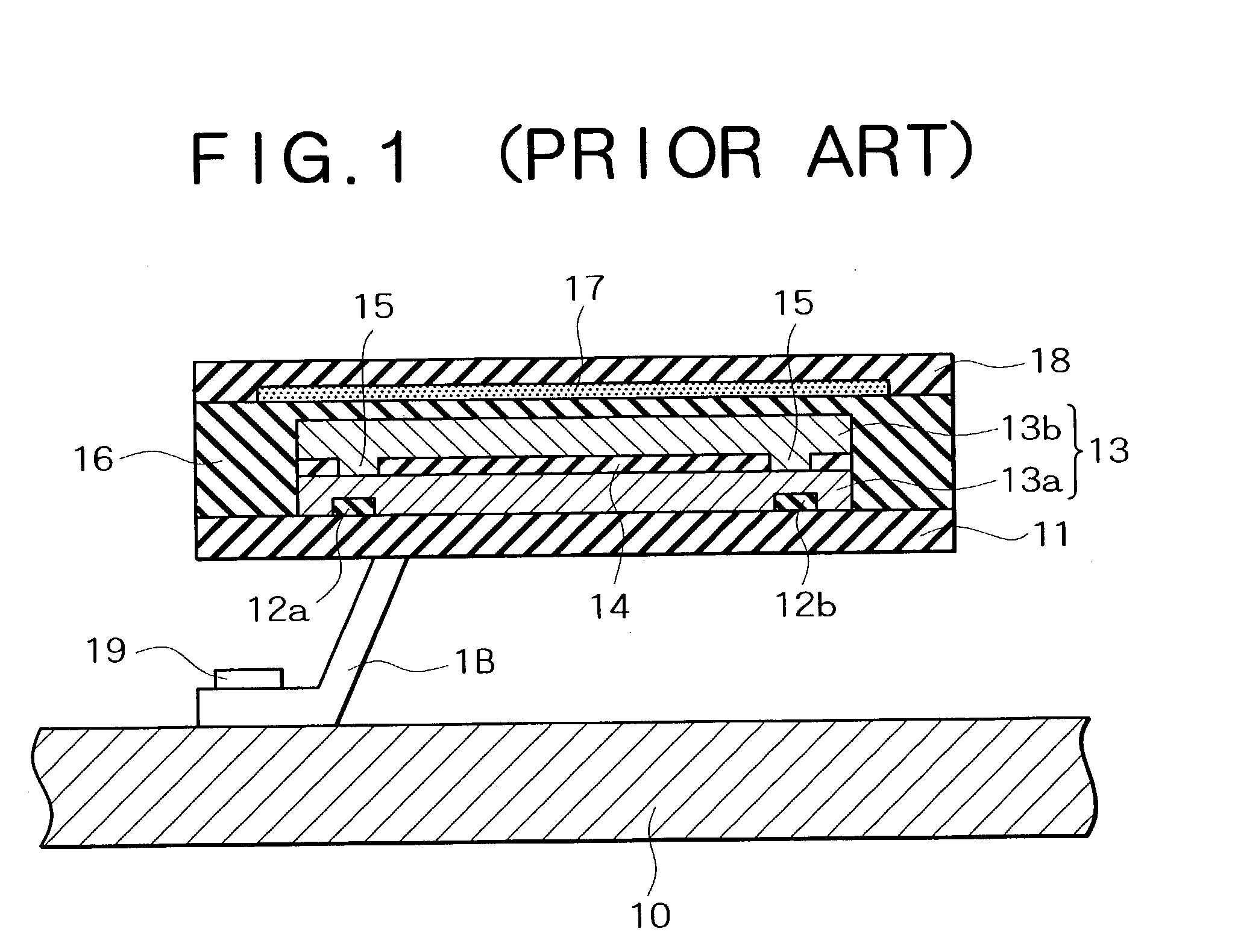
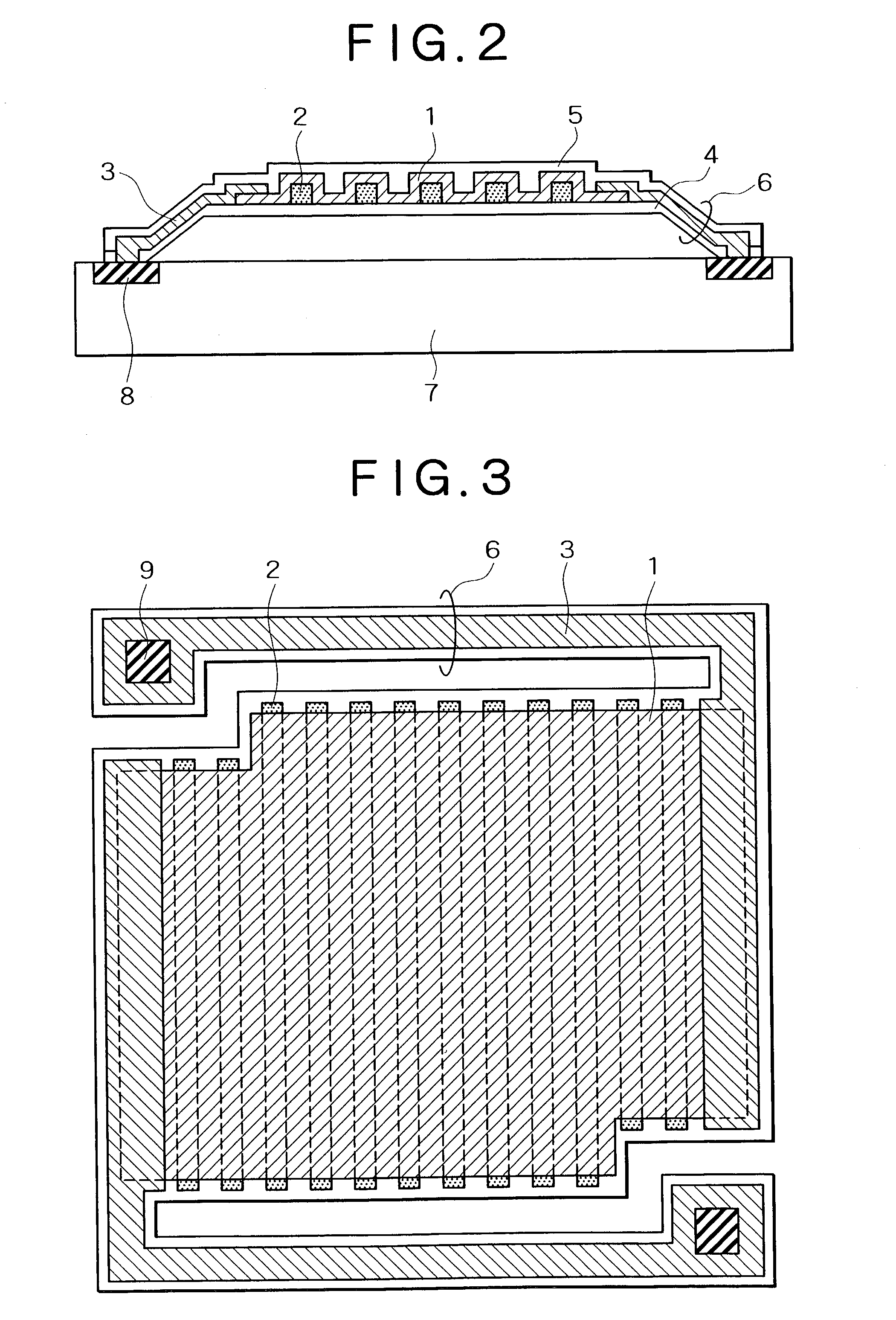
Bolometer-type infrared solid-state image sensor
A bolometer-type infrared solid-state image sensor has a plurality of infrared detecting elements provided above the substrate, which has diaphragm spacing from the substrate and supported by beams. The diaphragm has a bolometer thin film, electrodes arranged on the both end of the bolometer thin film, an upper layer protective film and a lower layer protective film, which are formed so as to sandwich and cover said bolometer thin film and the electrodes, and concave or convex sections formed on said lower layer protective film. The bolometer thin film is formed on the sides of the concave or convex sections. The beams includes wiring material and insulating protective films surrounding the wiring material.
Owner:NEC CORP
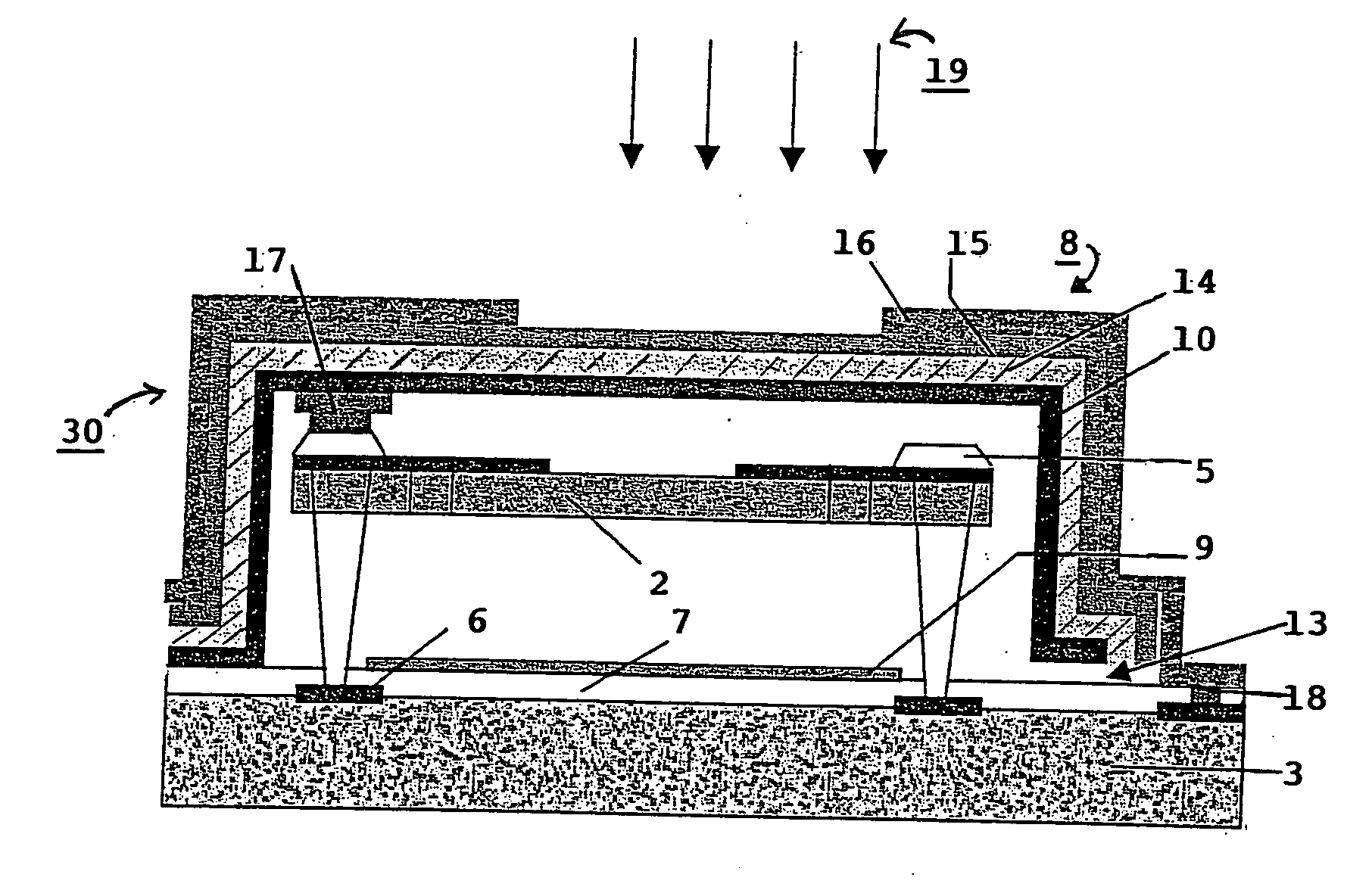
Compact all-weather electromagnetic imaging system
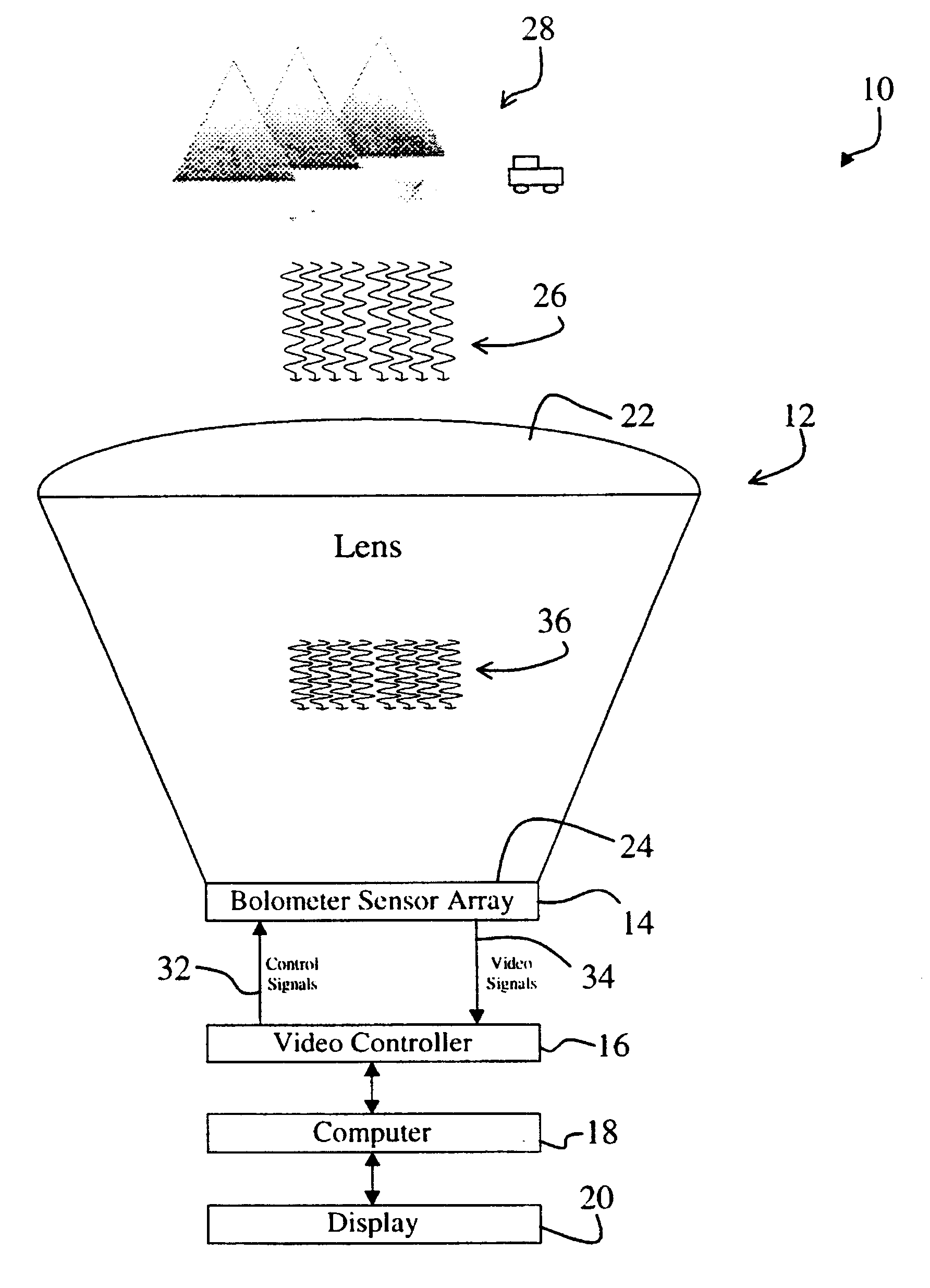
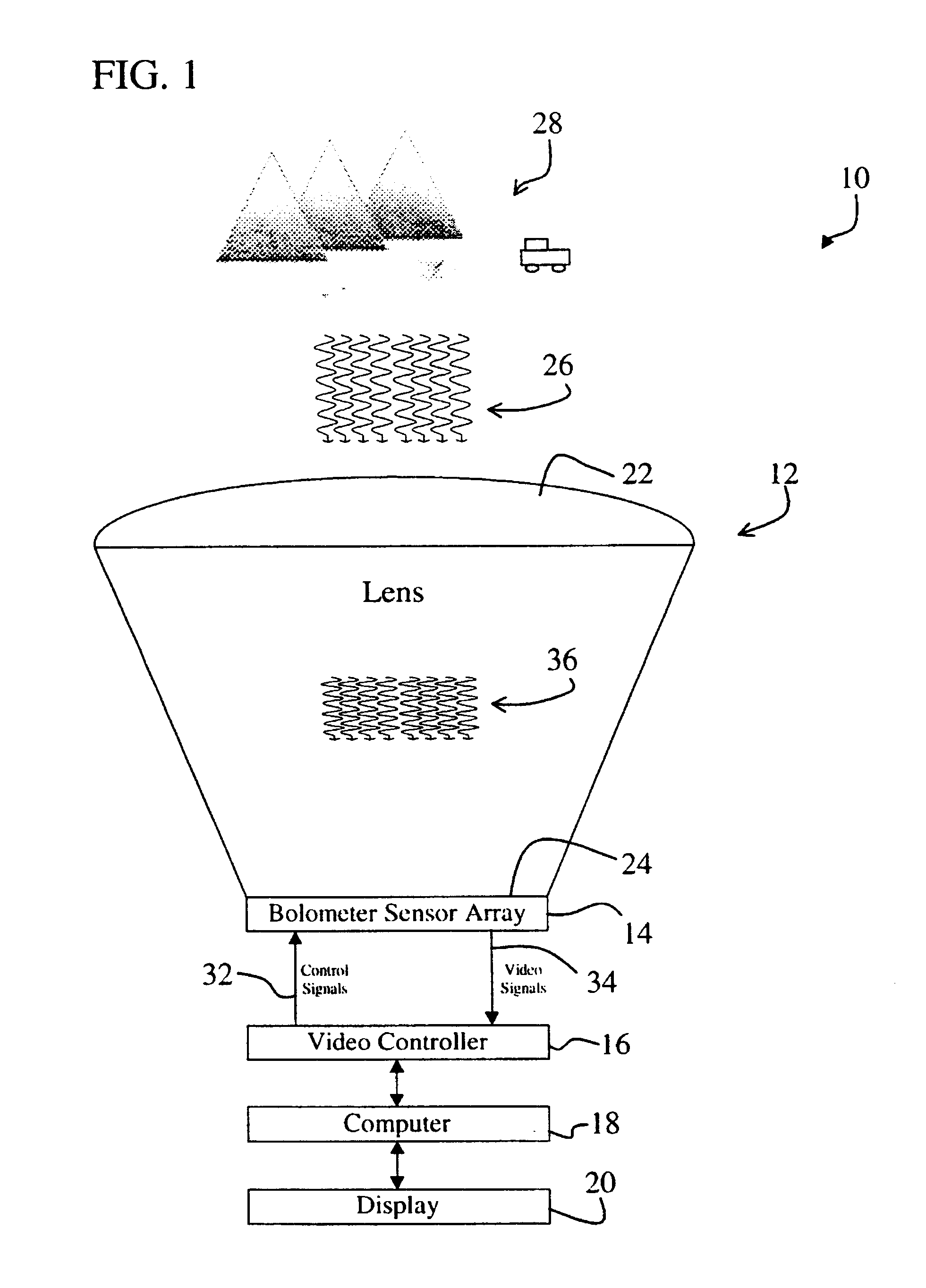
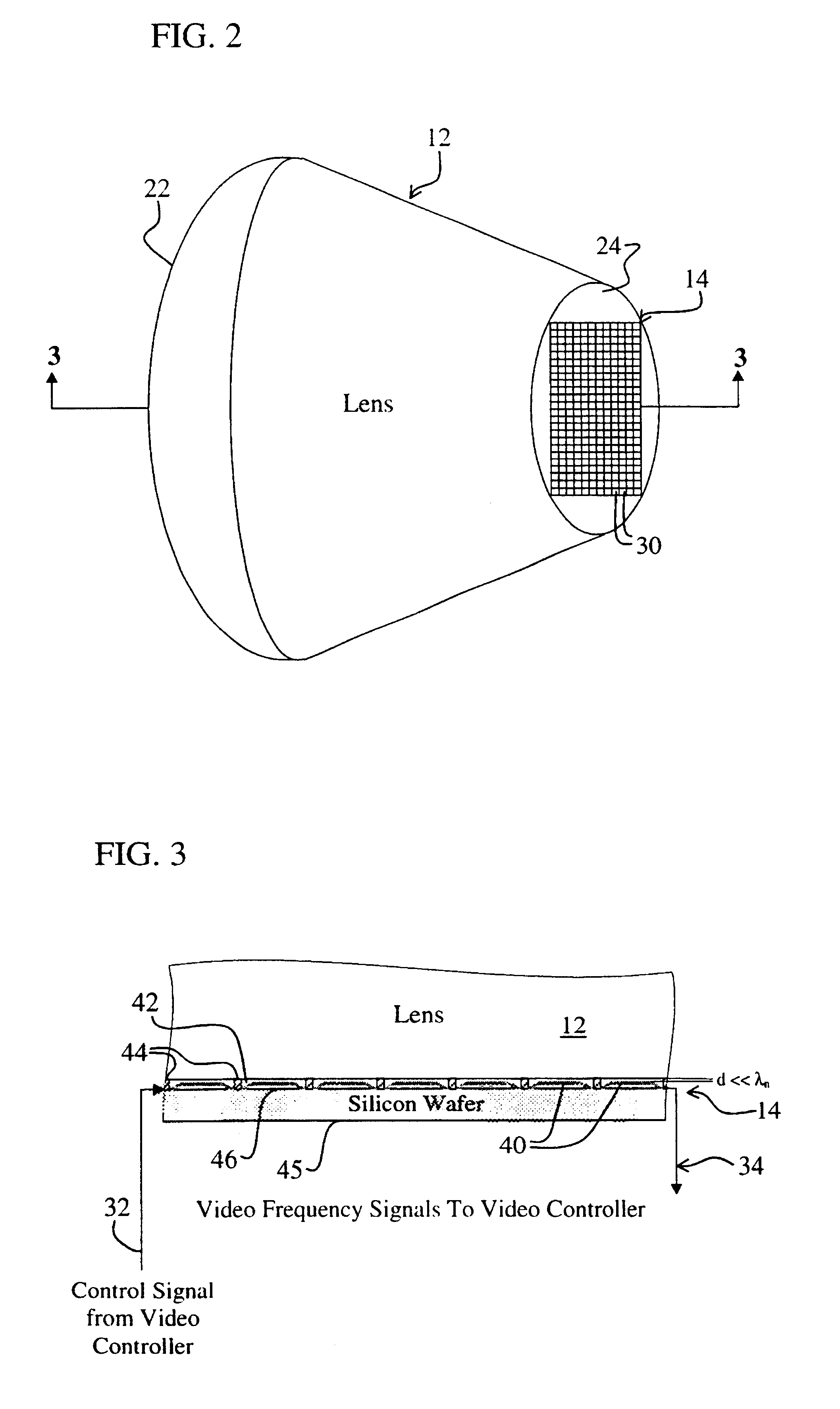
InactiveUS6404397B1Simultaneous aerial operationsGeological detection using milimetre wavesRefractive indexDisplay device
The system (10) includes a first mechanism (12) for receiving electromagnetic energy of a first wavelength from the scene (28) and providing electromagnetic energy of a second wavelength shorter than the first wavelength. A second mechanism (14) measures variations of the electromagnetic energy of the second wavelength over a predetermined area. The system is a millimeter wave imaging system (10). The first mechanism (12) includes a lens (12) having an index of refraction substantially greater than 1. The lens (12) is opaque to infrared electromagnetic energy and made of alumina, plastic, or other material having a relatively high index of refraction. The second mechanism (24) includes and array of bolometers (24) positioned parallel to an output aperture (24) of the lens and within a distance of the output aperture (24) that is much smaller than the second wavelength. A video controller (16), a computer (18), process video signals output from the array of bolometers (14) to yield an image, which is displayed on a display (20).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Focal plane antenna to sensor interface for an ultra-sensitive silicon sensor
ActiveUS20060076493A1Improve efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansPyrometry using electric radation detectorsThermal energyElectricity
An electrical interface between a scene to be imaged and a bolometer type sensor is disclosed. Efficiency is improved by means of a thermal energy concentrator including a lens and an antenna. Where a plurality of bolometer pixels are located in an array, a microantenna is provided for each pixel in the array with a common lens being provided to focus and channel incoming radiation to each microantenna. Radiation from a scene is further coupled by means of a lens and microantenna to the absorbing element of each bolometer through an AC coupling circuit including an electronic chopper implemented by means of a PIN diode, the conductivity of which is varied so as to affect the reflection coefficient of the input signal supplied through the microantenna.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Device for the detection of an electromagnetic radiation and electromagnetic radiation detector comprising such devices
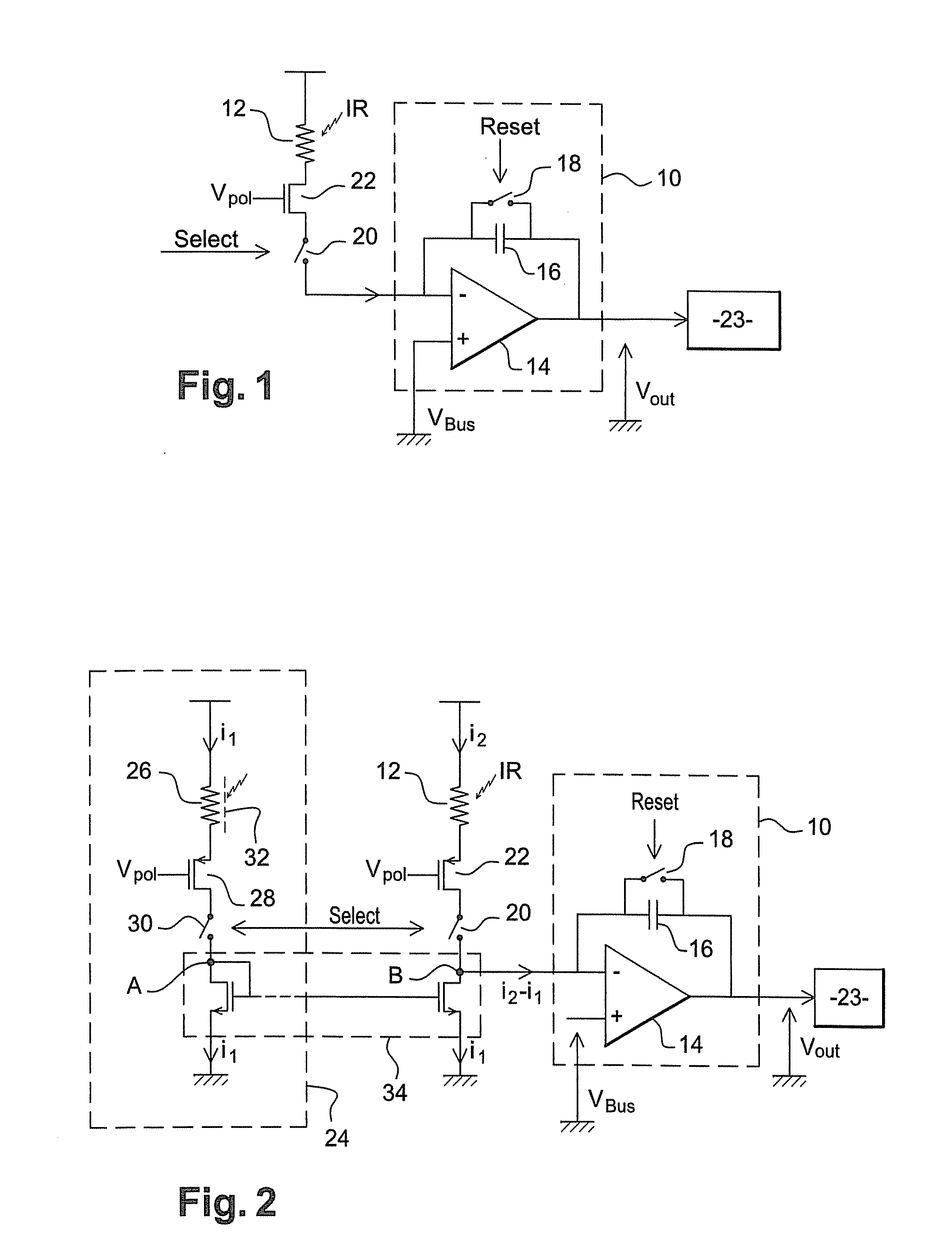
ActiveUS20100181485A1Simple preparation processSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectrical resistance and conductanceBolometer
The invention relates to a device for the detection of an electromagnetic radiation including: a substrate; a resistive imaging bolometer; a circuit for polarizing the bolometer at a predetermined voltage; a rejection circuit generating a common mode current, comprising a compensation bolometer thermalized in the substrate and a polarization circuit thereof; and a measuring circuit for measuring the difference between the current flowing in the imaging bolometer when it is polarized and the common mode current generated by the rejection circuit. According to the invention, the rejection circuit further comprises a current generator capable of producing a current that simulates the current induced by the self-heating of the imaging bolometer under the effect of its polarization, the sum of the current passing through the compensation bolometer and the current generated by the current generator forming the common mode current.
Owner:ULIS SAS
Two-layer micrometering bolometer and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102393251AImprove temperature uniformityImprove mechanical stabilityDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingBridge deckThermistor
The invention discloses a two-layer micrometering bolometer and a manufacturing method thereof. The two-layer micrometering bolometer comprises a microbridge structure for a micrometering bolometer of an uncooled infrared detector or an uncooled terahertz detector, and is characterized in that: the microbridge consists of two independent bridge decks, namely an upper bridge deck and a lower bridge deck; a light absorbing material is positioned on the upper bridge deck; a thermistor material is positioned on the lower bridge deck; and four upper and lower bridge deck connecting posts on the upper bridge deck of the microbridge are connected with a metal heat transfer layer of the lower bridge deck of the microbridge. The upper bridge deck of the microbridge comprises one or more layers of light absorbing materials. The two-layer microbridge has higher light absorption rate and filling factor, and also has higher temperature uniformity and mechanical stability. The two-layer micrometering bolometer and the manufacturing method thereof can overcome the defects in the prior art, the working performance of a device is improved, and the two-layer micrometering bolometer is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Tera-hertz wave transmitting optical component, tera-hertz wave optical system, tera-hertz band wave processing device and method
InactiveUS20060268945A1Improve transmission characteristicsLaser using scattering effectsMirrorsOptical axisLight beam
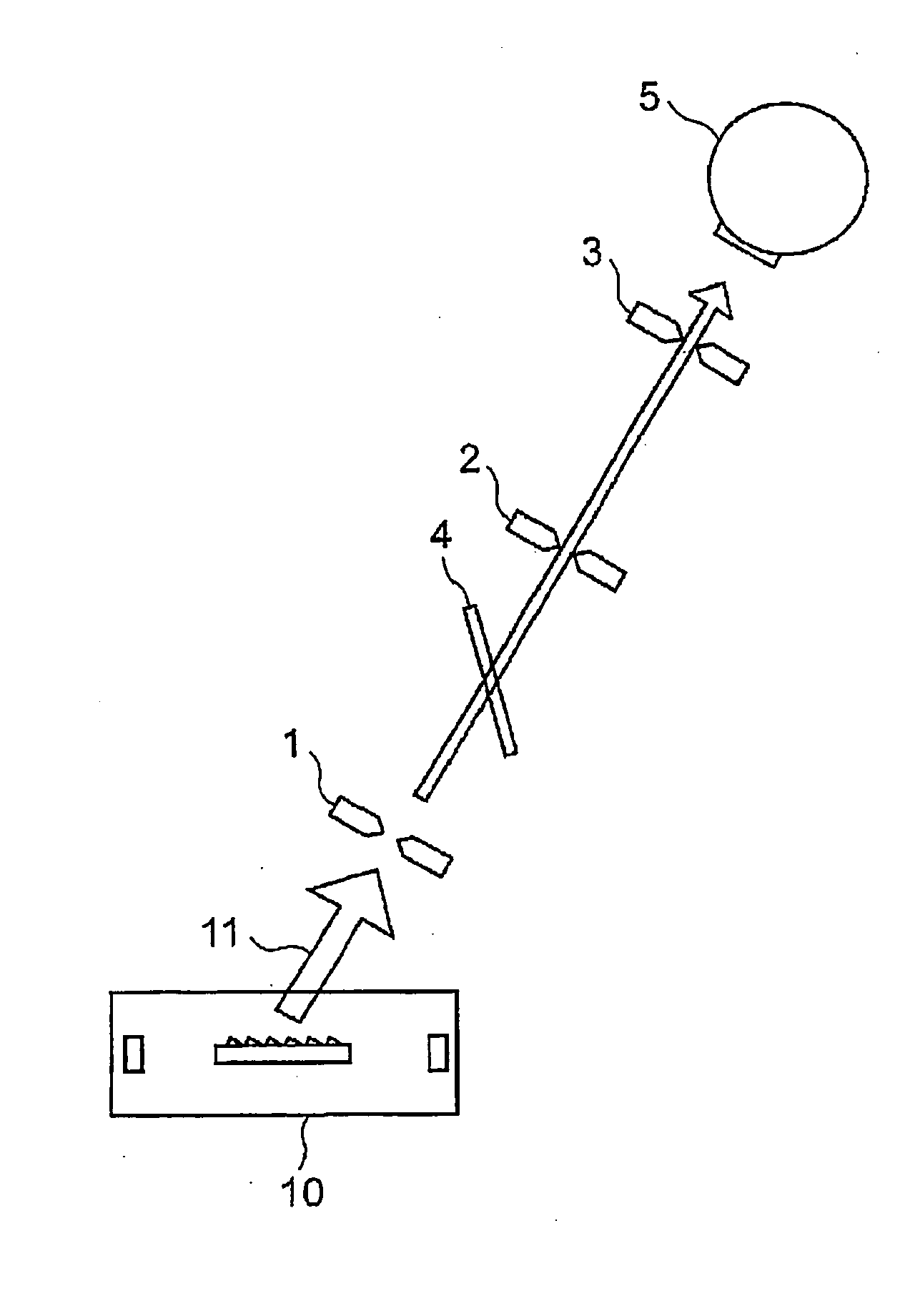
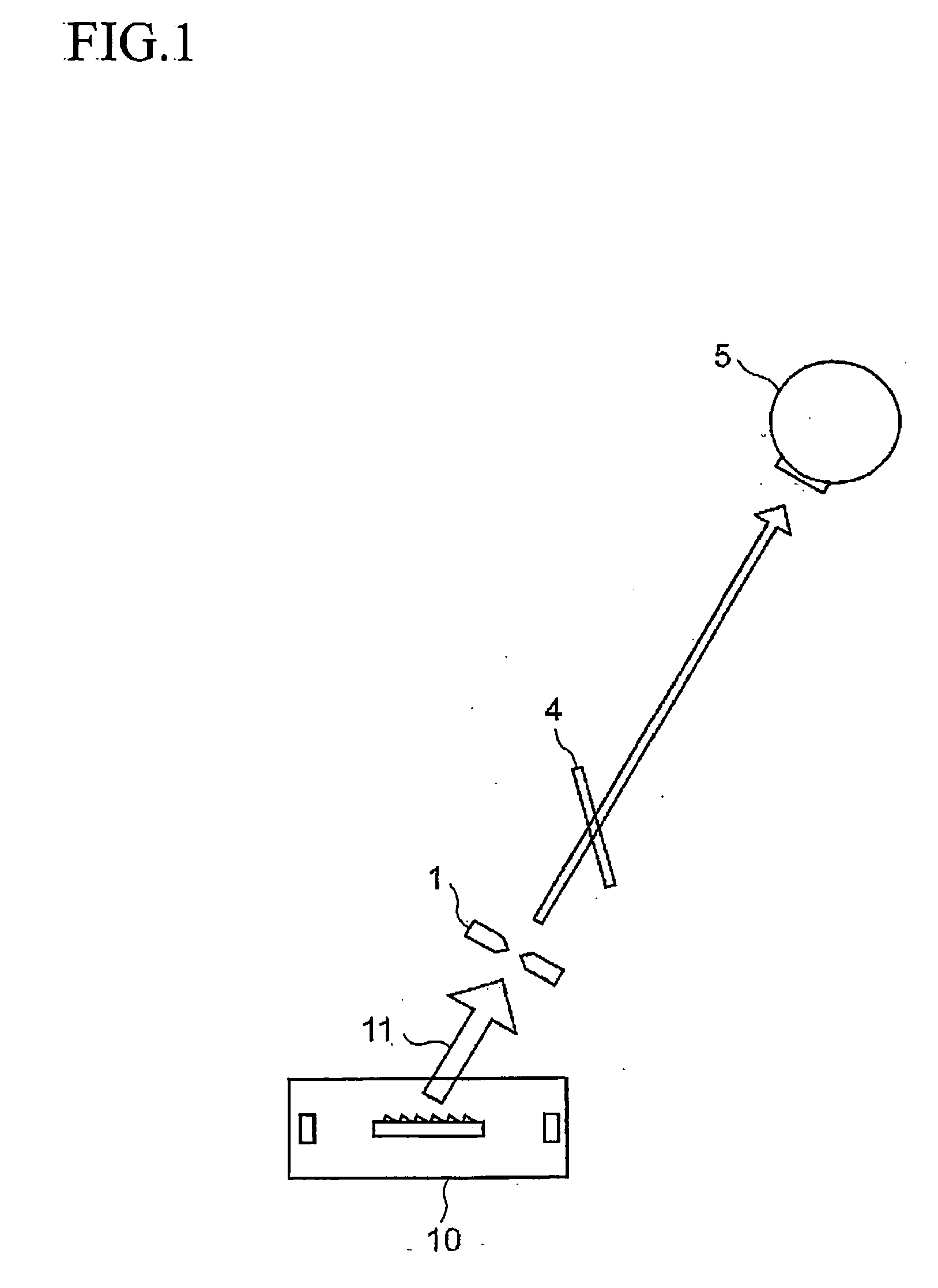
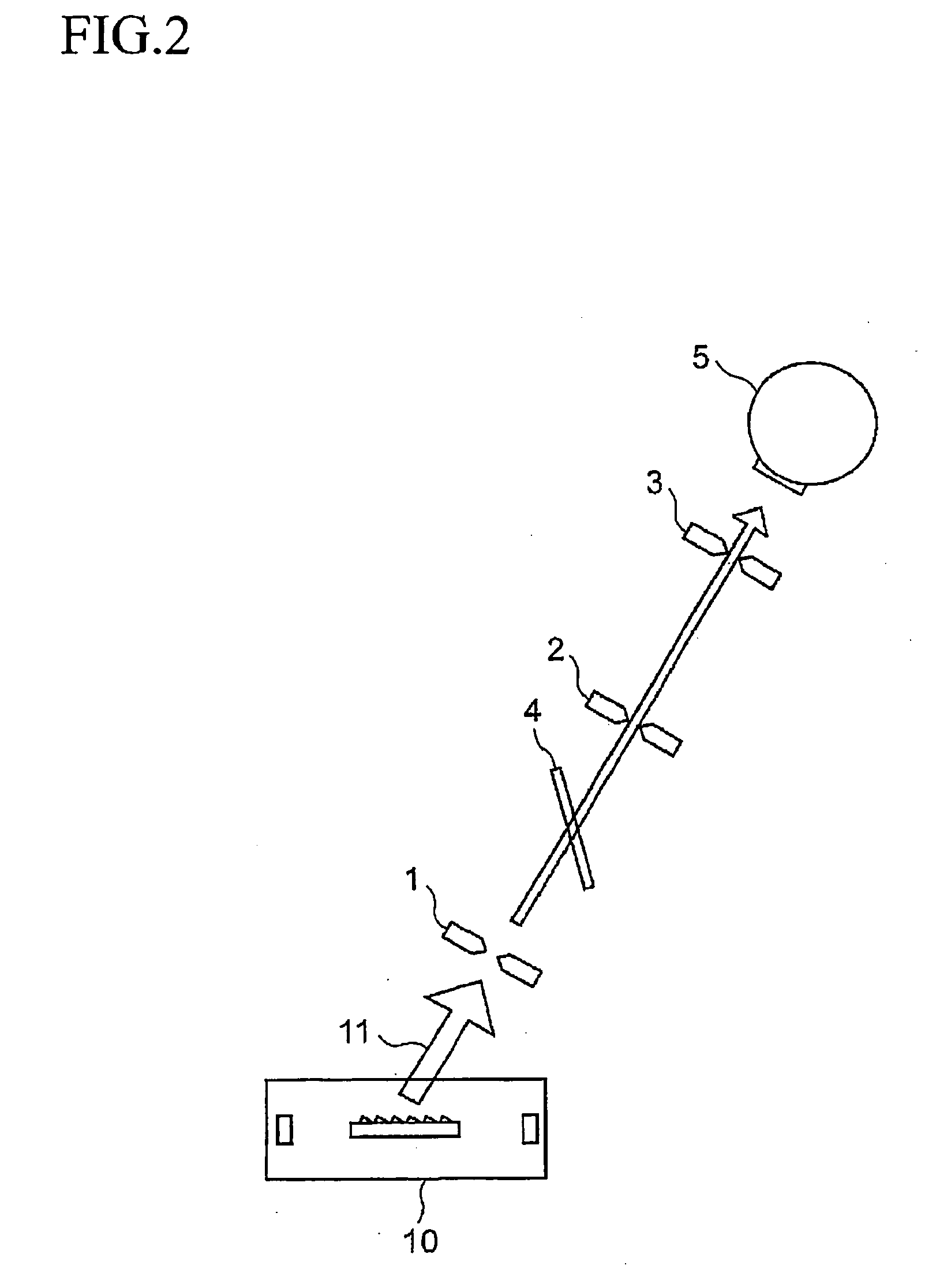
A tera-hertz band wave processing device includes a tera-hertz wave generator for generating a specified tera-hertz wave, and an optics optical plane composed of a high-function resin and provided ahead of the advancing direction of a generated tera-hertz wave. A translucent plate is formed as the optics optical plane. The optical axis between the plate and the generator is regulated by a first translucence regulator to transmit a tera-hertz wave on the optical axis and reflect a light beamed at a specified incident angle off the plate. Second translucence regulators are provided on the optical axis between the plate and on Si bolometer. A specified visible light is shone to the plate as a pilot light and is allowed to reflect off the plate to superimpose the optical axis of the reflected visible light on the optical axis of a tera-hertz wave.
Owner:RIKEN +1
Terahertz or infrared micro-bolometer and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102426060AMeet special needsImprove performanceLayered productsDecorative surface effectsCarbon nanotubeThermistor
The invention discloses a terahertz or infrared micro-bolometer, which comprises a micro-bridge structure of a micro-bolometer for an uncooled terahertz detector or an uncooled infrared detector, wherein a thermistor material and a light absorbing material in the micro-bridge structure are one of a vanadium oxide-fullerene binary composite thin film or a vanadium oxide-fullerene-carbon nanotube ternary composite thin film. The vanadium oxide composite film is formed by compounding two-dimensional vanadium oxide and zero-dimension fullerene components or two-dimensional vanadium oxide, zero-dimension fullerene and one-dimensional carbon nanotube components. The micro-bolometer and a manufacturing method thereof can overcome the defects existing in the prior art and are suitable for large-scale industrial production; and the working performance of the device is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
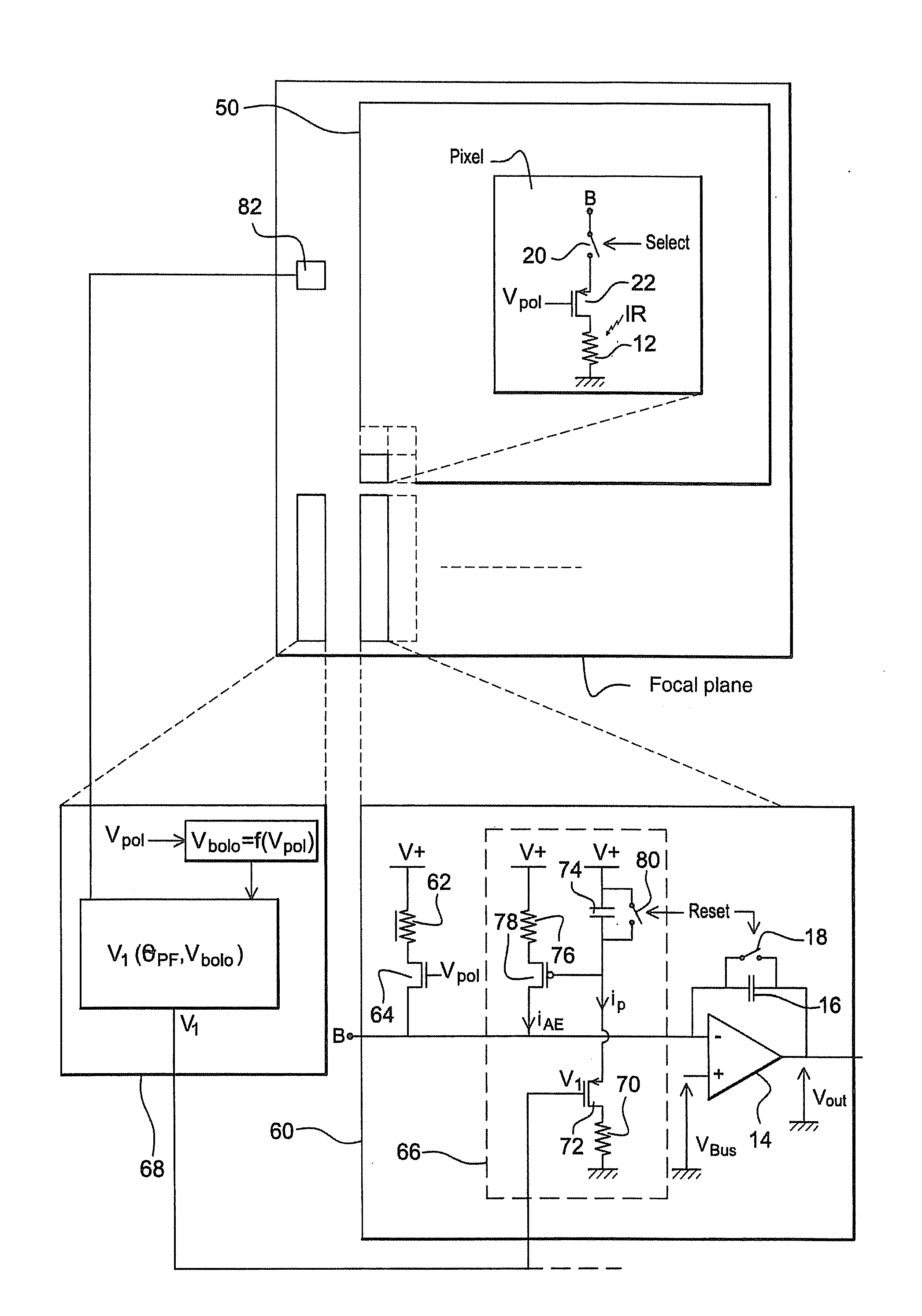
Device for detecting infrared radiation comprising a resistive imaging bolometer, a system comprising an array of such bolometers and a method for reading an imaging bolometer integrated into such a system
ActiveUS20090152465A1Remove background noiseEliminate the effects ofTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansElectrical resistance and conductanceBolometer
Owner:ULIS SAS
Oxide thin film for bolometer and infrared detector using the oxide thin film
ActiveUS20050167592A1Improve performanceLow device resistanceMaterial analysis by optical meansNegative temperature coefficient thermistorsIon beamBolometer
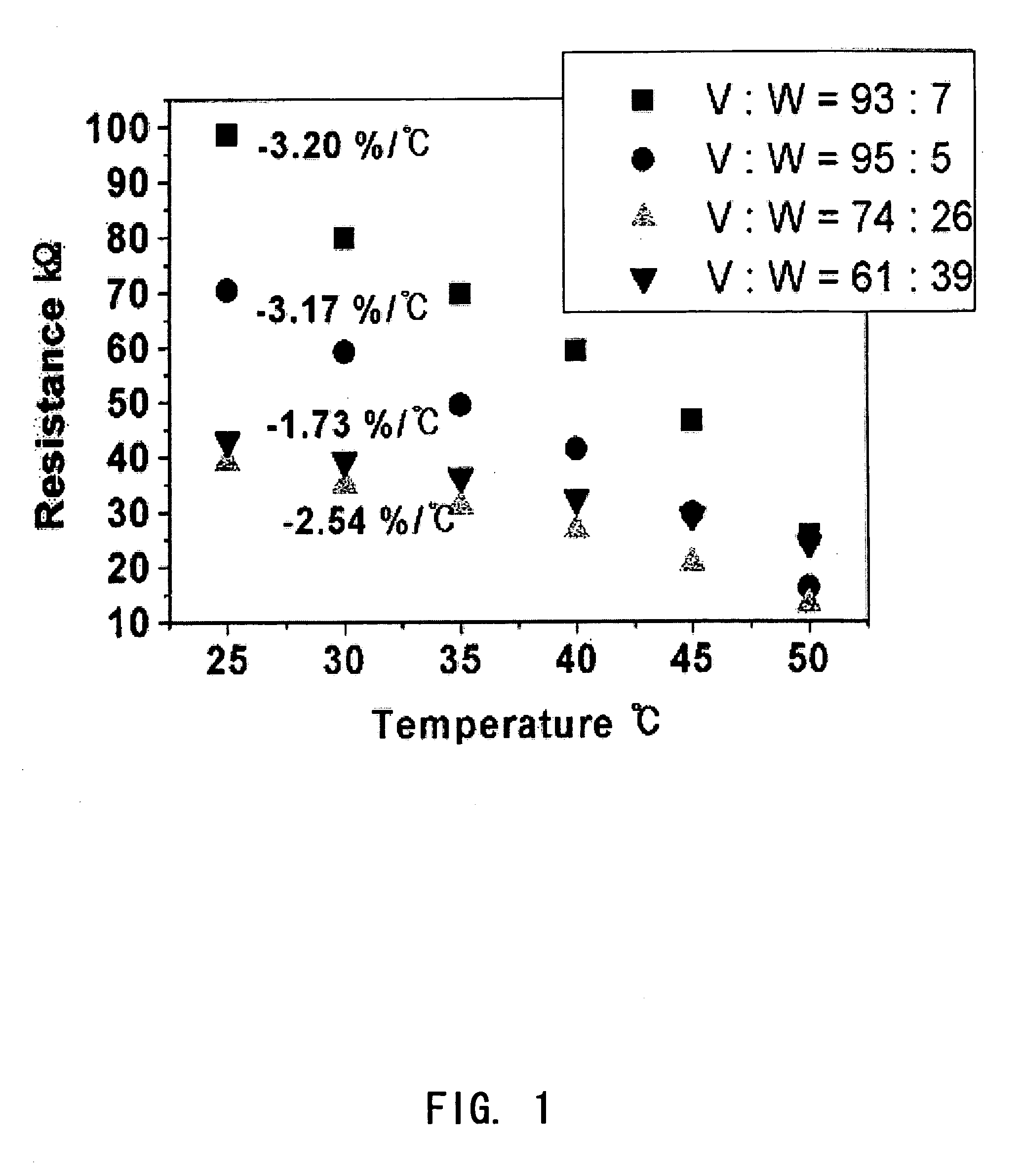
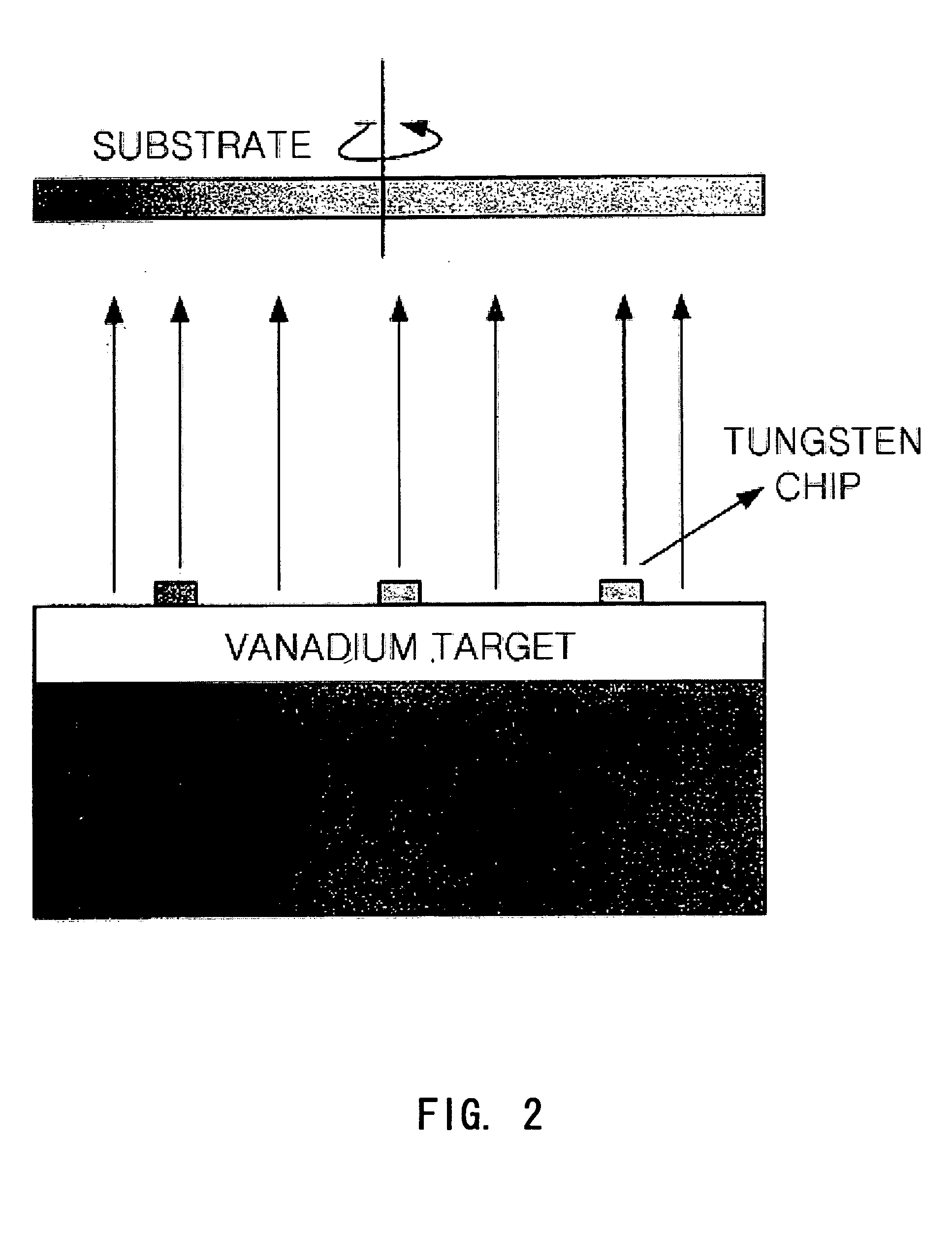
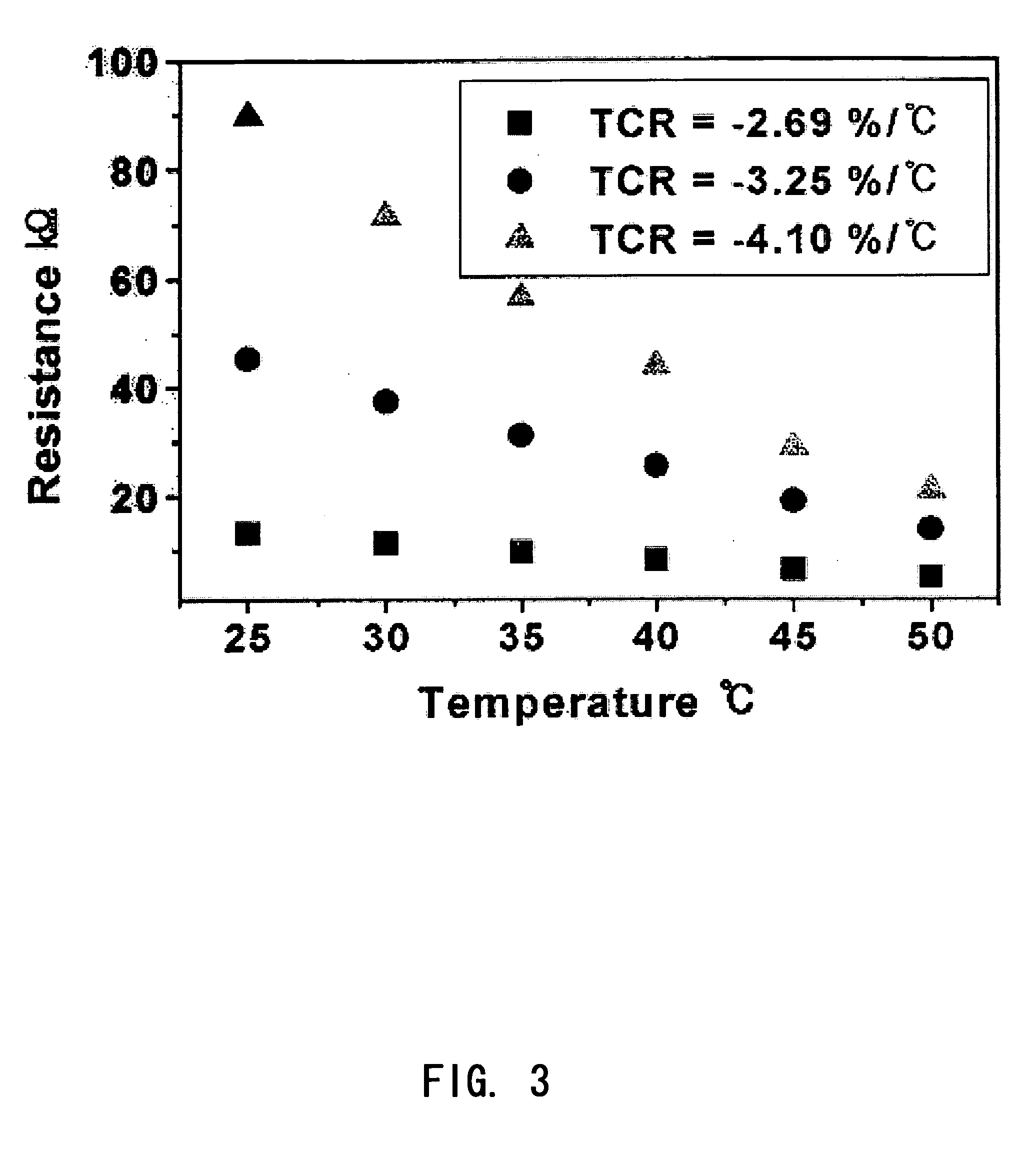
The present invention relates to an oxide thin film for a bolometer-type uncooled infrared detector having high sensitivity. A vanadium tungsten oxide (V—W—Ox), i.e. a tungsten-doped vanadium oxide, is provided as an oxide film for a bolometer. An oxide for bolometer having characteristics of low resistance of 5 to 200 kΩ and variable TCR between −1.5 and −4.1% / ° C. can be obtained by an oxidation of vanadium-tungsten metal film at a low temperature around 300° C., with changing a tungsten content and oxidation time. And a reproducible thin film can be fabricated by low price equipment for thin film deposition, without expensive ion beam or laser apparatus. Accordingly, an oxide for bolometer having characteristics of resistance lower than 100 kΩ and TCR higher than −3% / ° C. can be obtained with reproducibility, whereby an uncooled-type infrared detector having high sensitivity can be fabricated.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Large temperature coefficient of resistance material
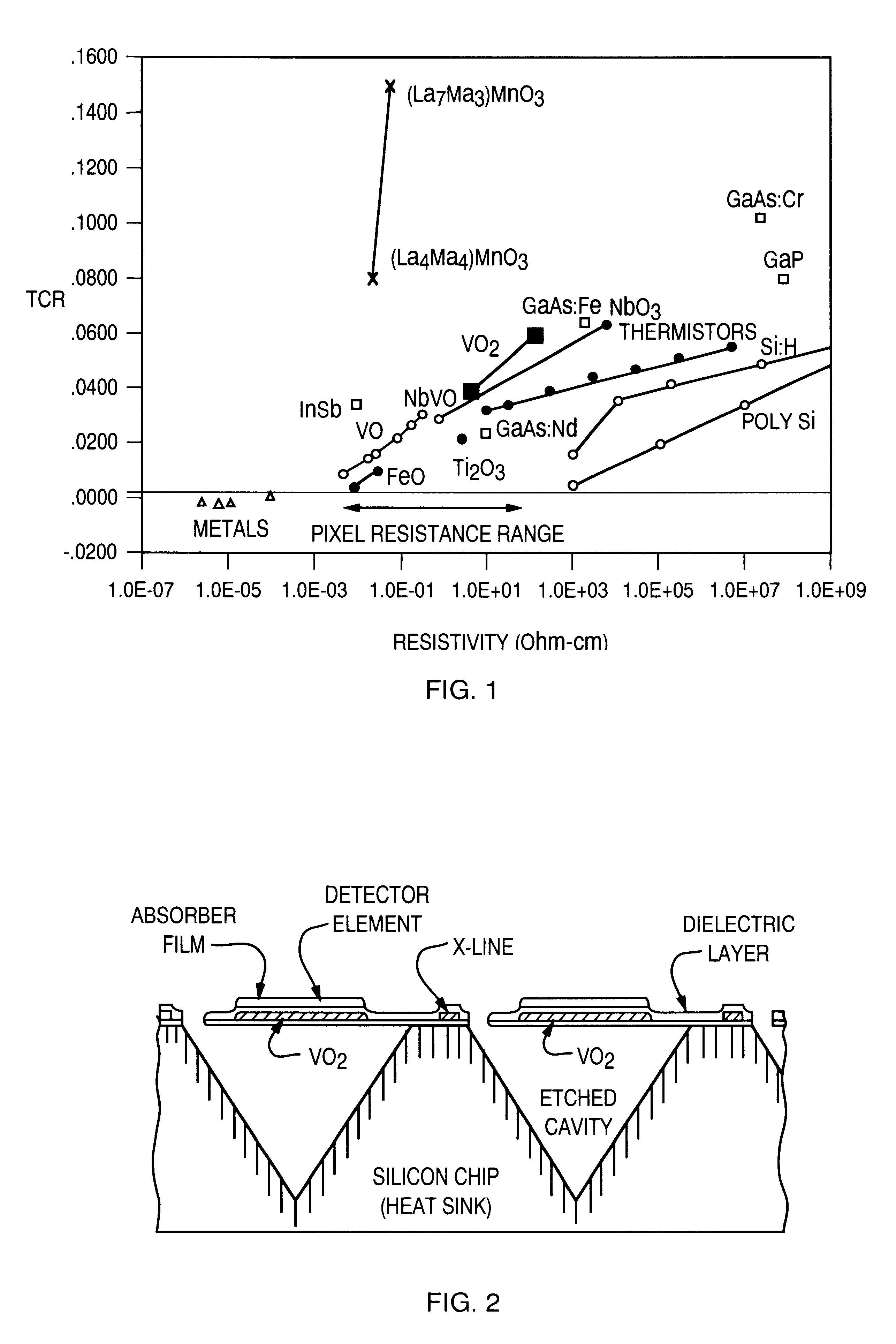
InactiveUS6337991B1Polycrystalline material growthSuperconductors/hyperconductorsHeat sensitiveThermistor
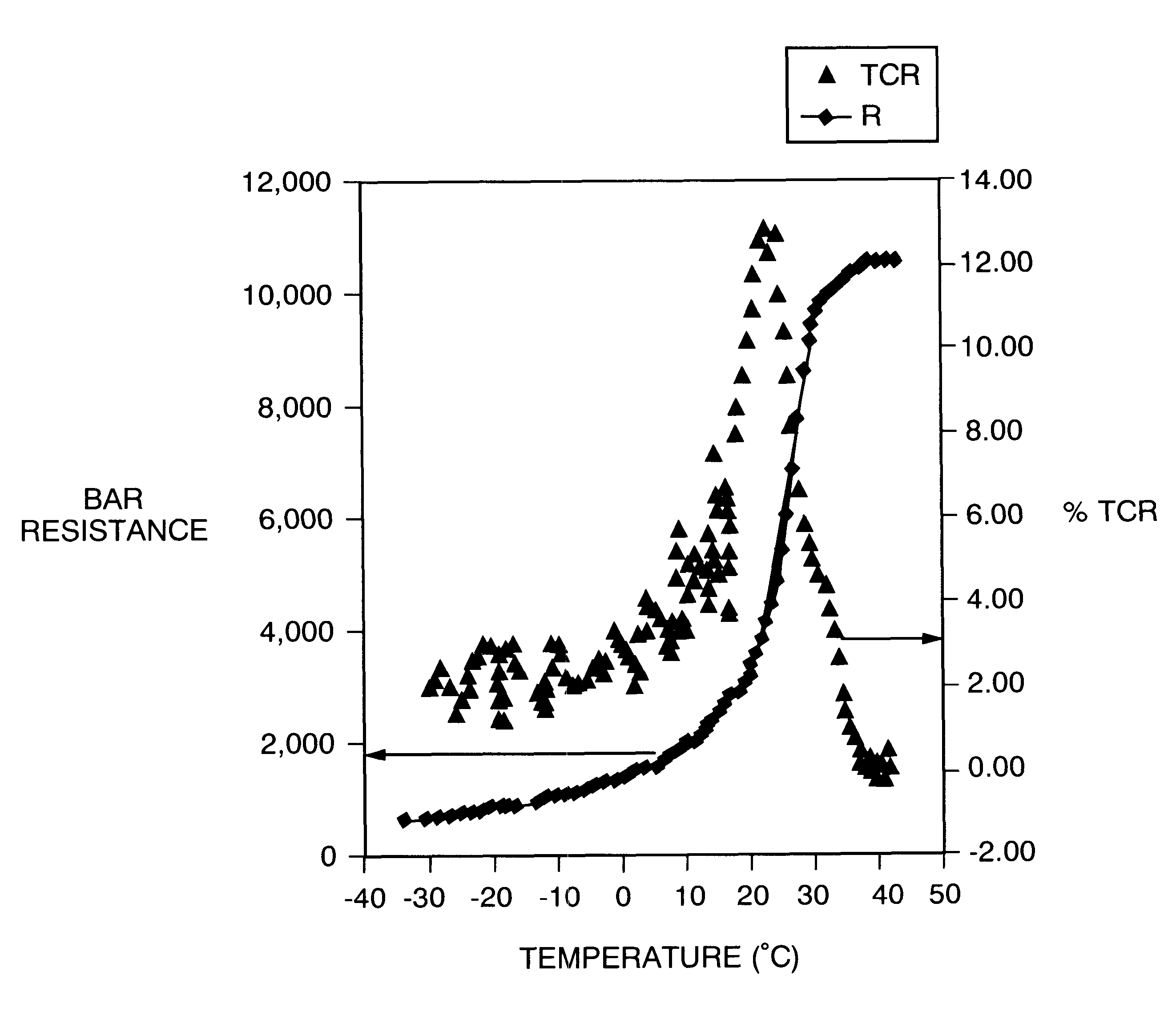
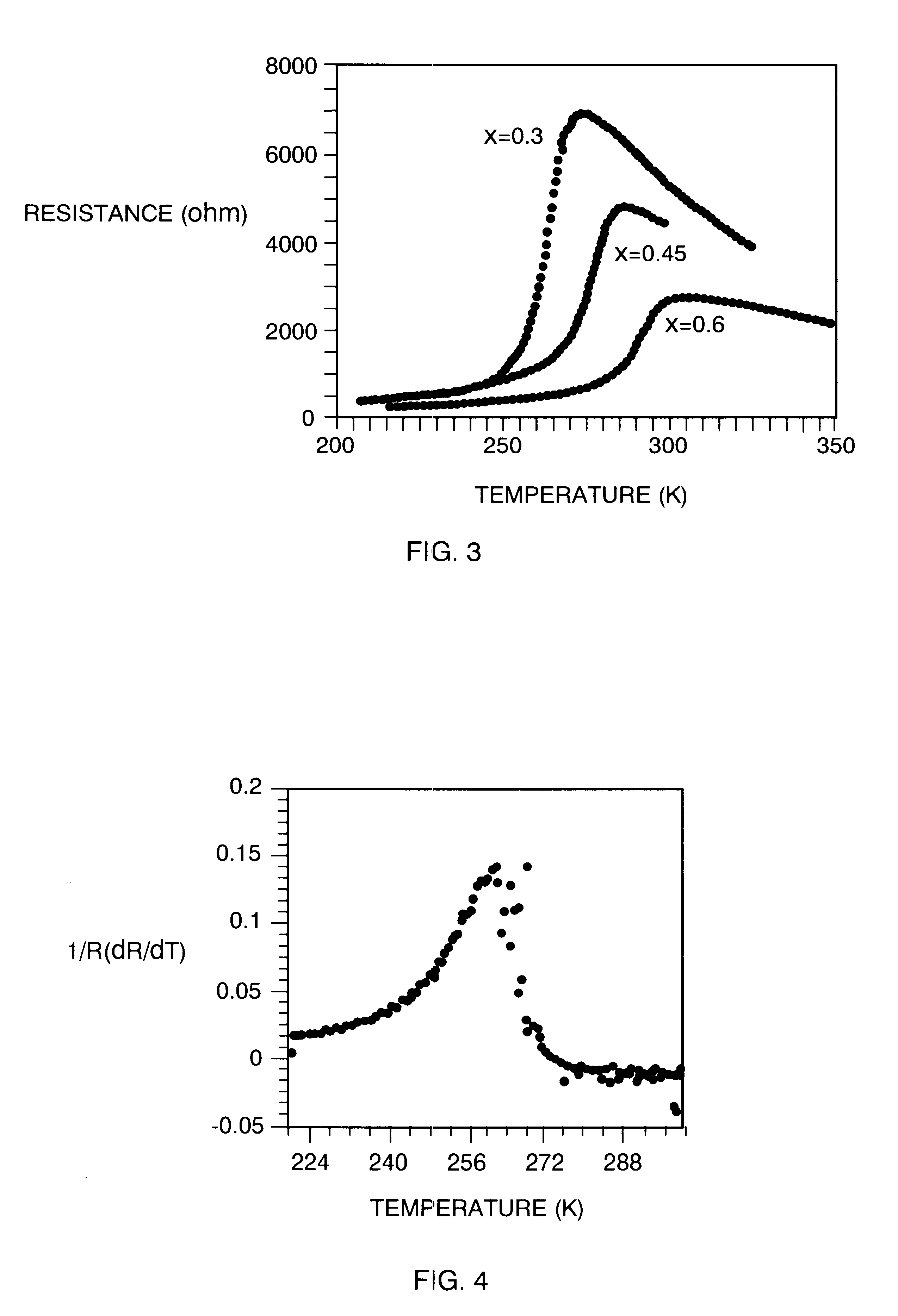
Oxide thin films having a perovskite-like structure and undergoing a ferromagnetic phase transition with large temperature coefficients of resistance (TCRs) are disclosed. These can be useful materials for making thermistors, bolometers, infrared detectors and the like. These can be fabricated with a number of methods, preferably including metal oxide chemical vapor deposition, laser ablation and sputtering. In one embodiment, the oxides are based on a LaMnO3 with substitutions of Ca, Sr, Ba, Mn, and Pb for some of the La. The amounts can be varied to maximize the TCR or shift the temperature at which the maximum occurs. Methods of making such thin films are disclosed. In one embodiment, the high sensitivity films can be used in an array of micro-bolometers in an infrared camera.
Owner:CORNING APPLIED TECH
Ultra sensitive silicon sensor millimeter wave passive imager
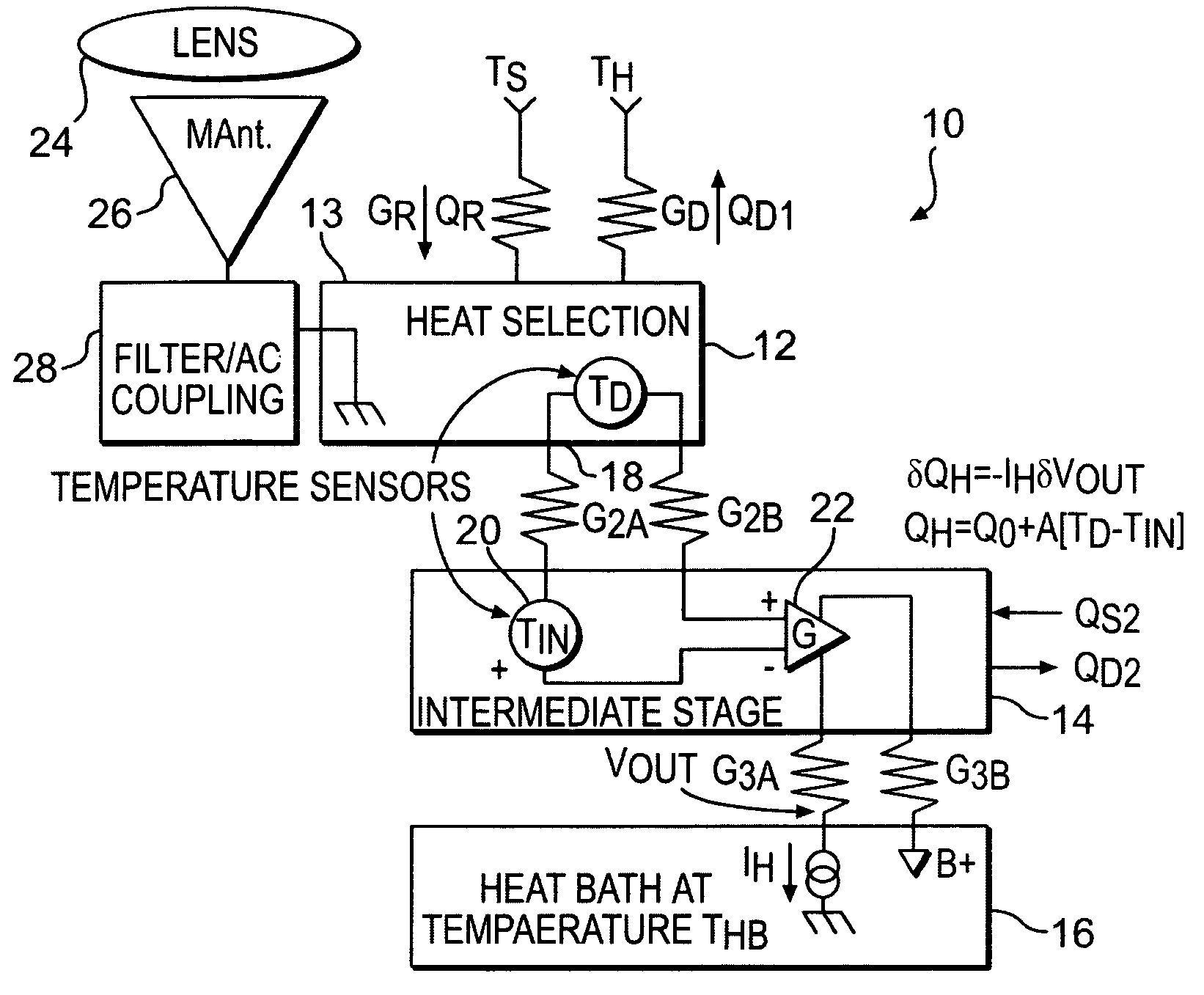
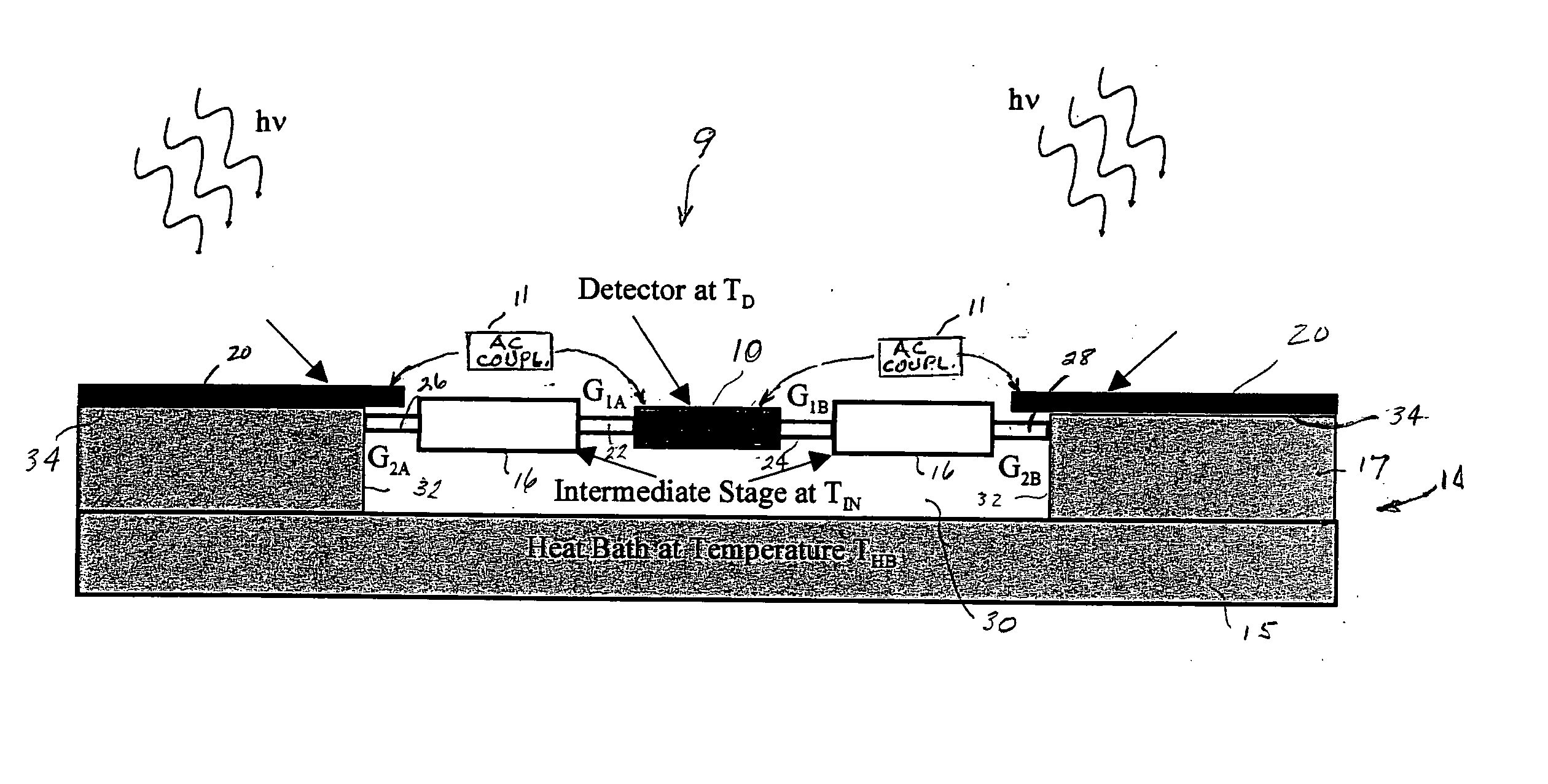
ActiveUS20050087687A1Low thermal conductivityMaximize sensitivitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansThermal isolationEngineering
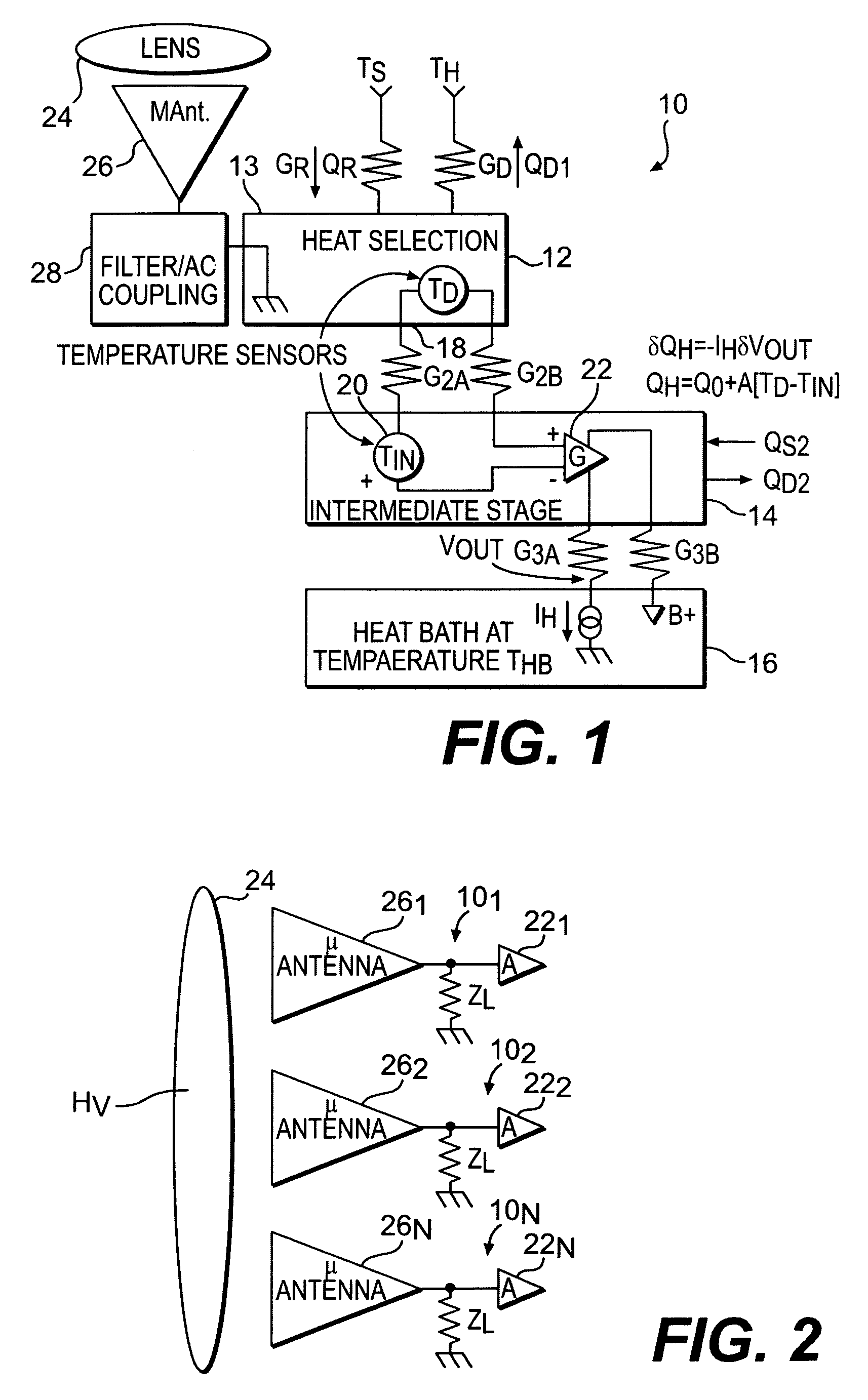
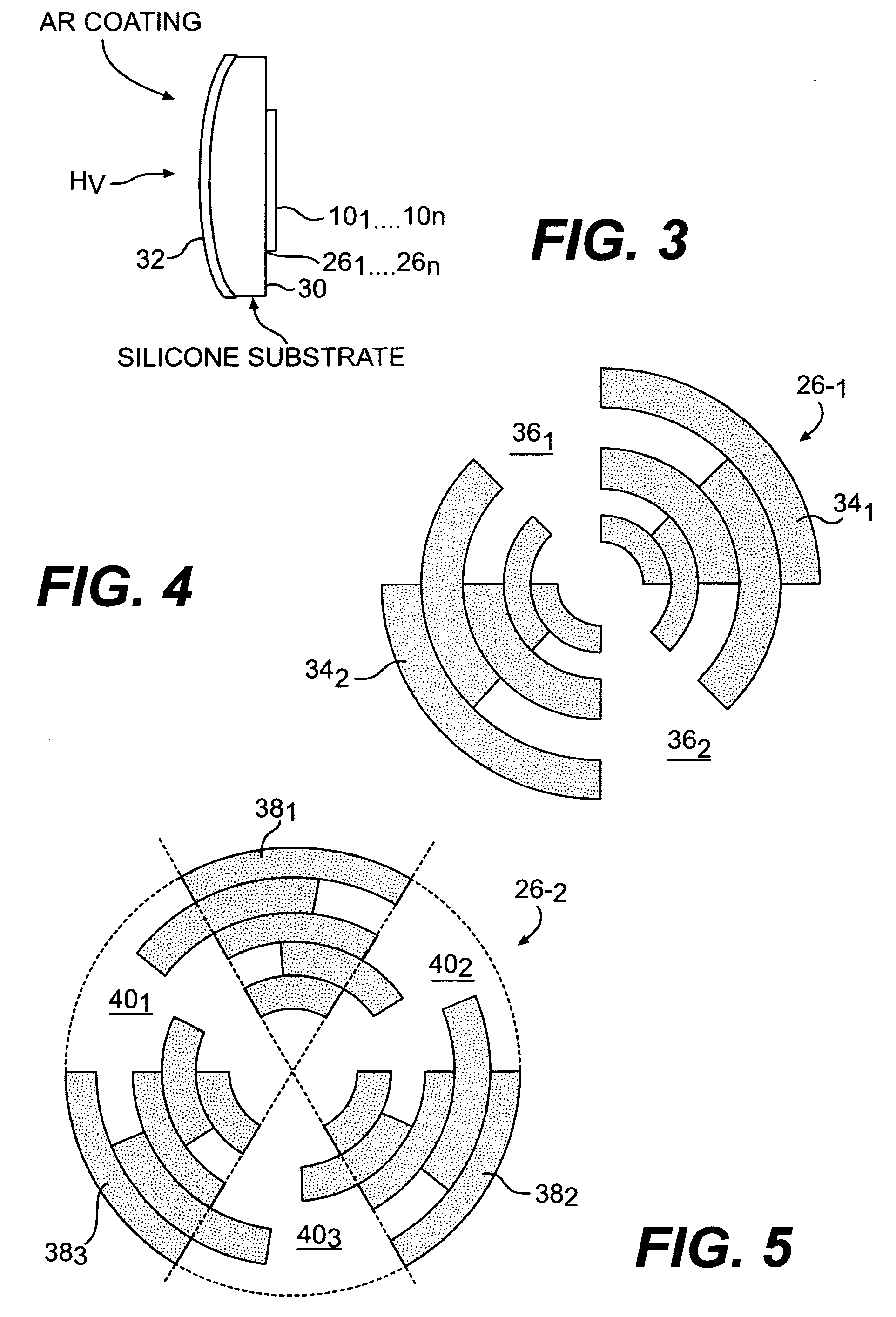
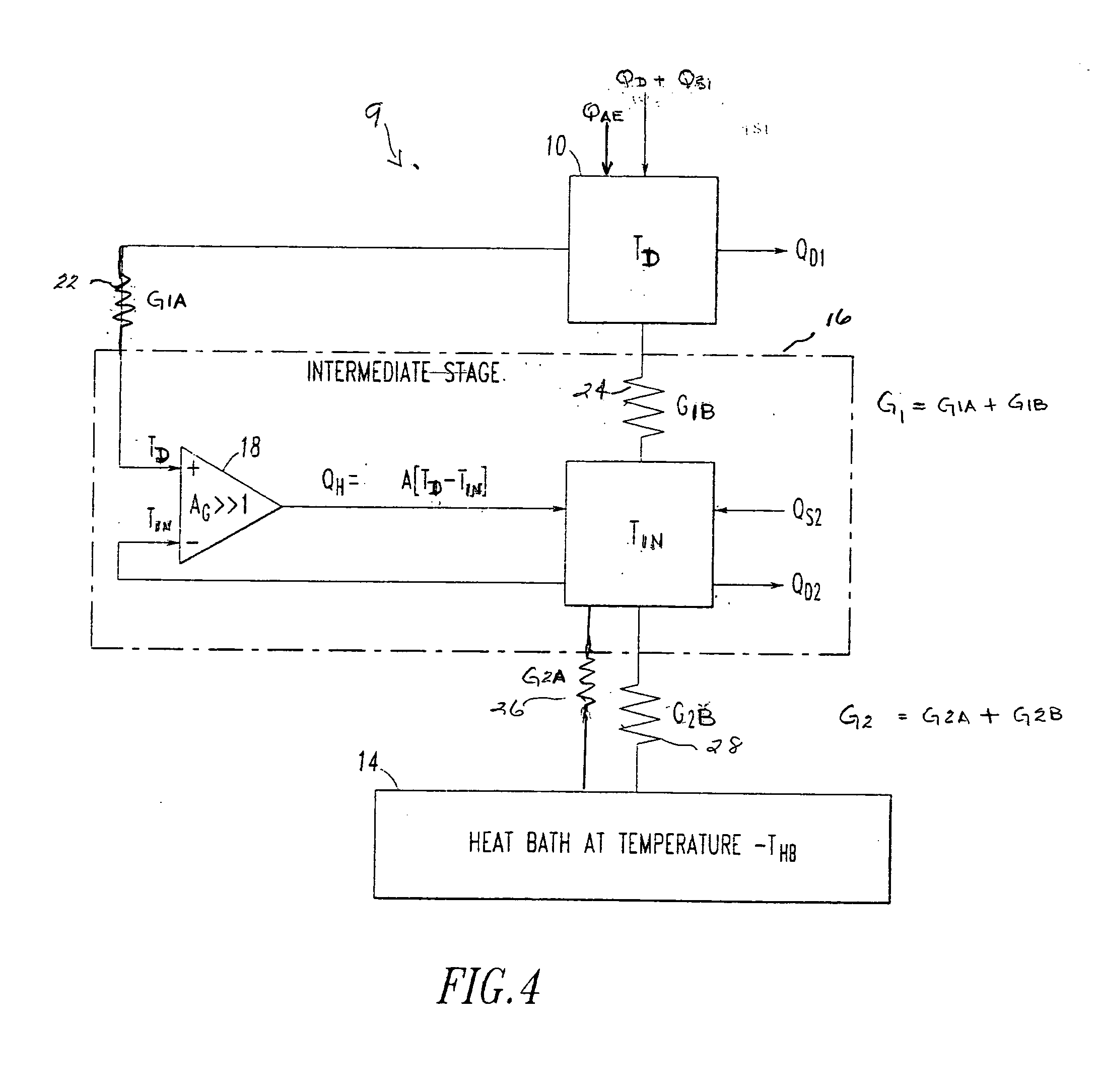
Electro-thermal feedback is utilized for zeroing the thermal conductance between a bolometer type detector element of a pixel in a thermal radiation sensor assembly and the environments through its mechanical support structure and electrical interconnects, thereby limiting the thermal conductance primarily through photon radiation. Zeroing of the thermal conductance associated with the mechanical support and electrical readout interconnect structures is achieved by electro-thermal feedback that adjust the temperature of an intermediate stage by the heating effect of a bipolar transistor amplifier circuit so that the temperature across the mechanical support and electrical interconnects structures are zeroed thereby greatly improving the thermal isolation, the responsivity and sensitivity of the electromagnetic radiation sensor.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Resistive material for bolometer, bolometer for infrared detector using the material, and method of manufacturing the bolometer
A resistive material for a bolometer, a bolometer for an infrared detector using the material, and a method of manufacturing the bolometer are provided. In the resistive material, at least one element selected from the group consisting of nitrogen (N), oxygen (O) and germanium (Ge) is included in antimony (Sb). The resistive material has superior properties such as high temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR), low resistivity, a low noise constant, and is easily formed in a thin film structure by sputtering typically used in a complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) process, so that it can be used as a resistor for the bolometer for an uncooled infrared detector, and thus provide the infrared detector with superior temperature precision.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com