Patents
Literature
1833 results about "Enthalpy Unit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
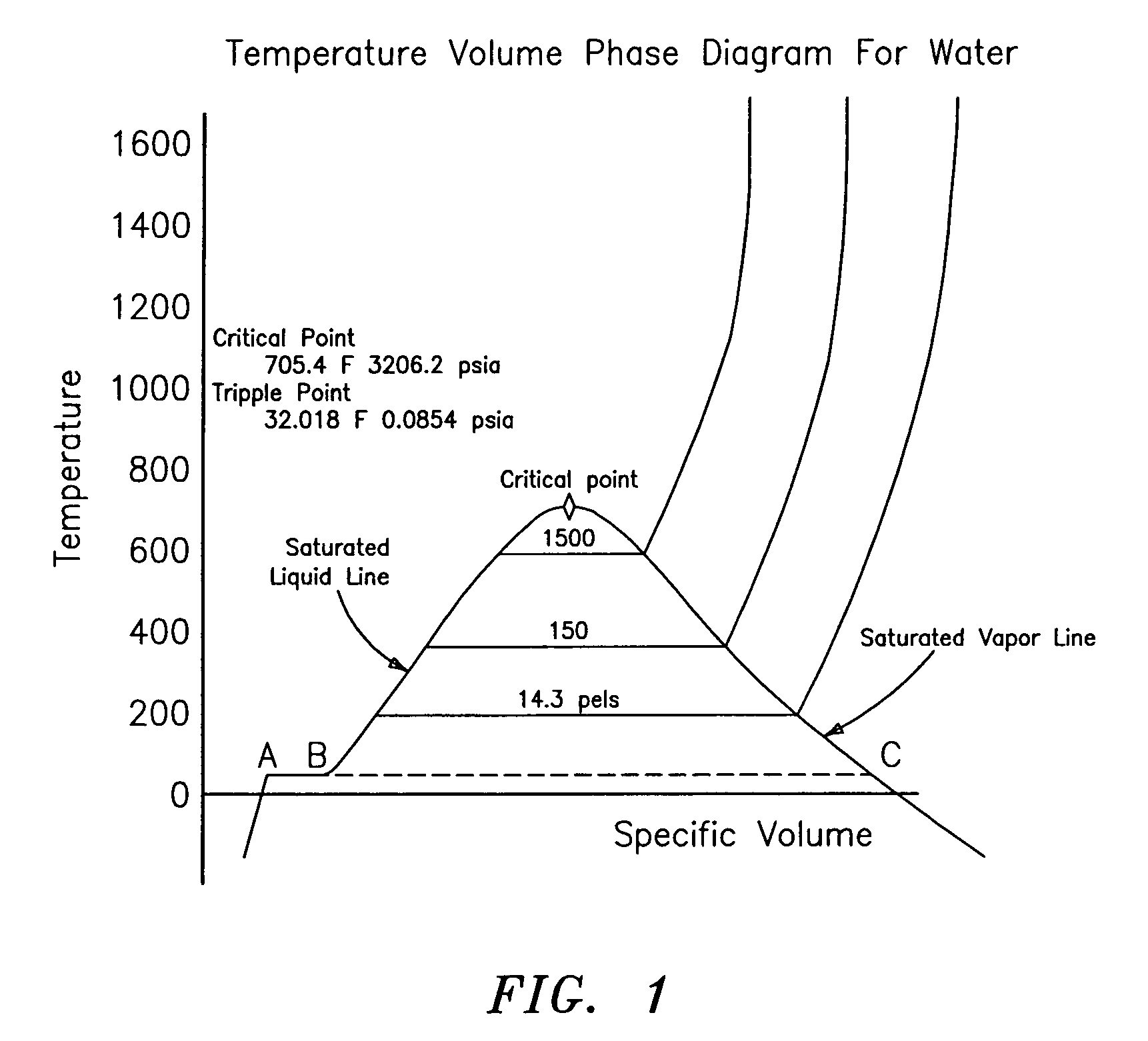
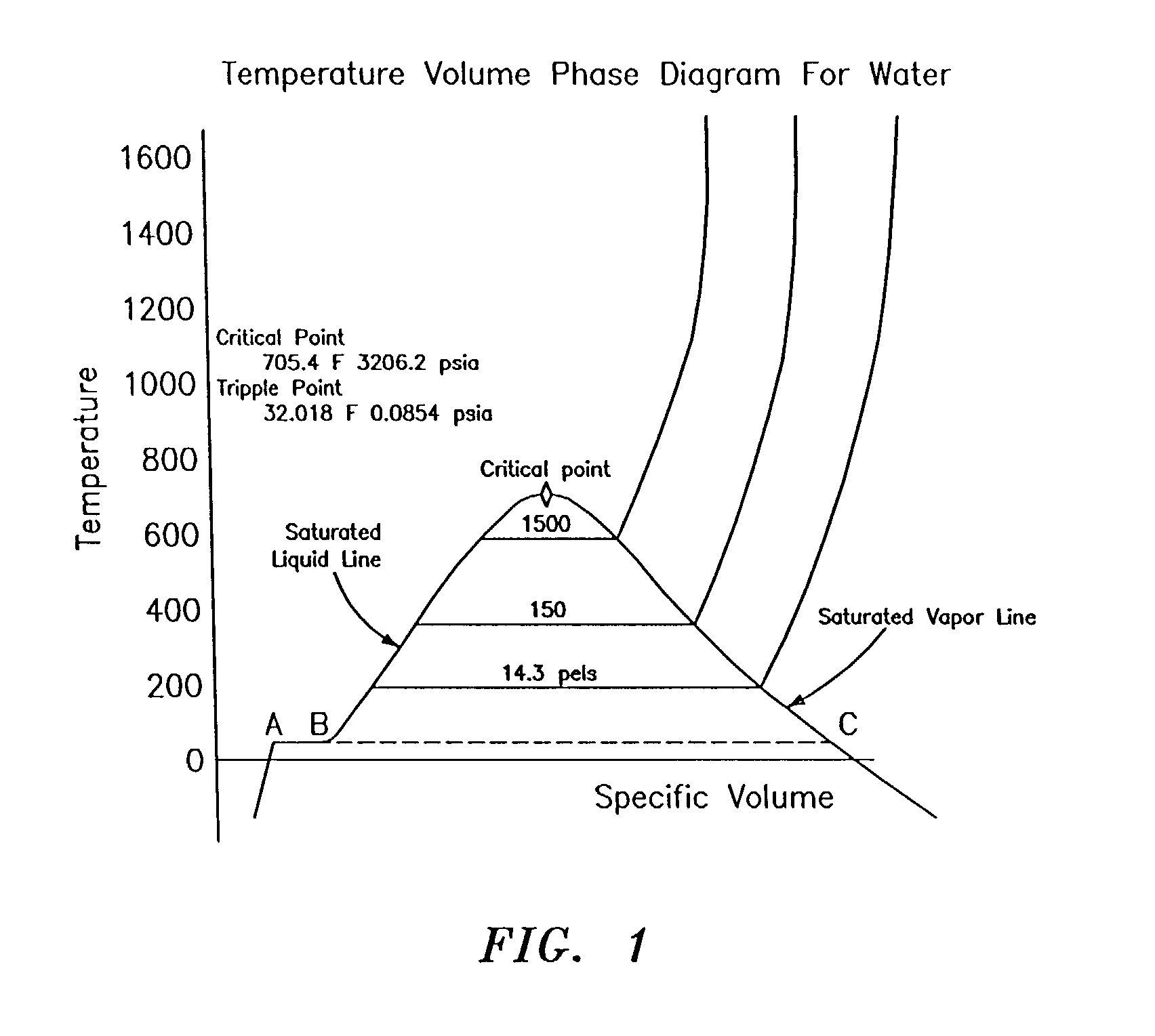
The SI unit for specific enthalpy is joule per kilogram. It can be expressed in other specific quantities by h = u + pv, where u is the specific internal energy, p is the pressure, and v is specific volume, which is equal to 1ρ, where ρ is the density.
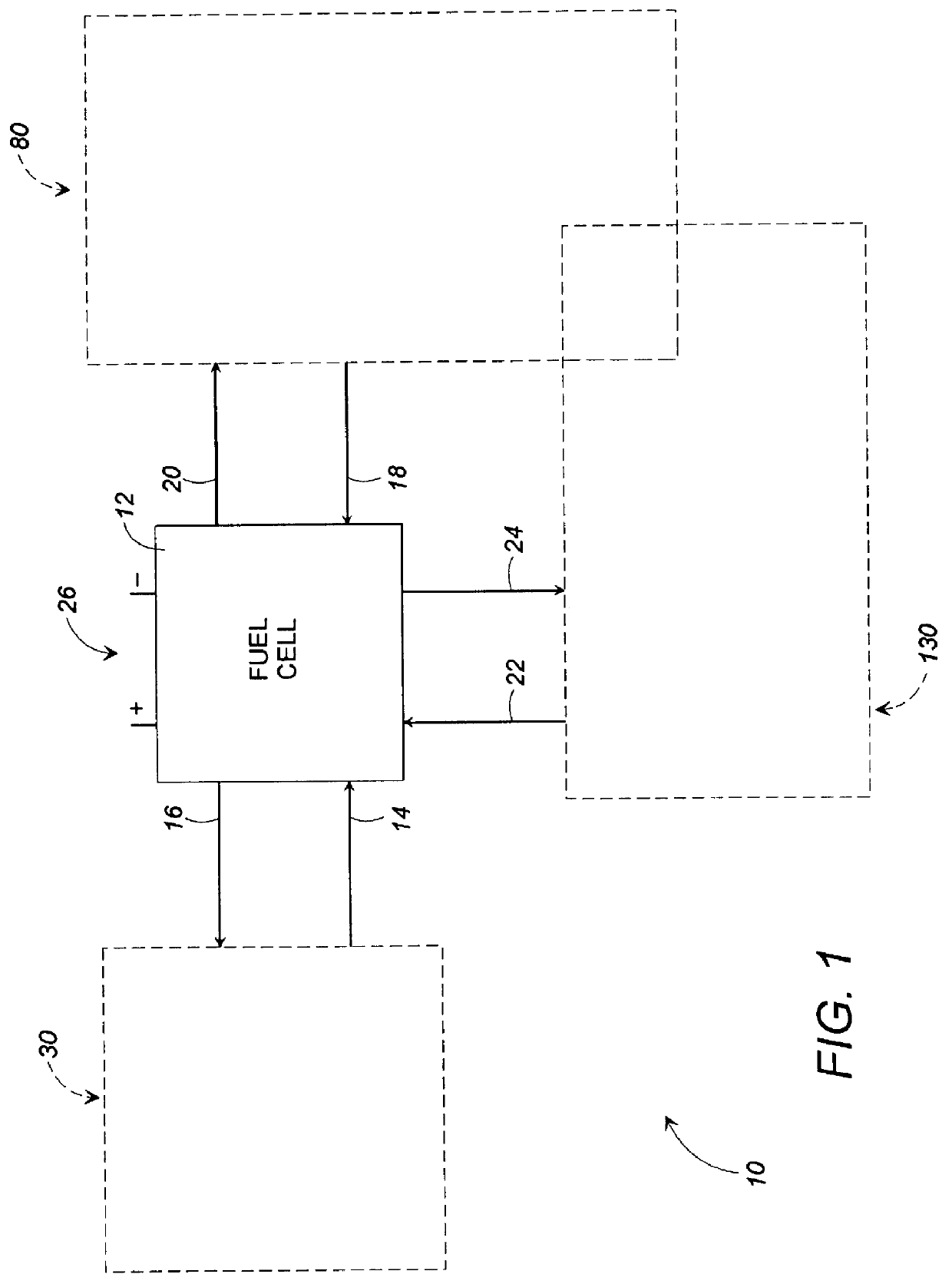
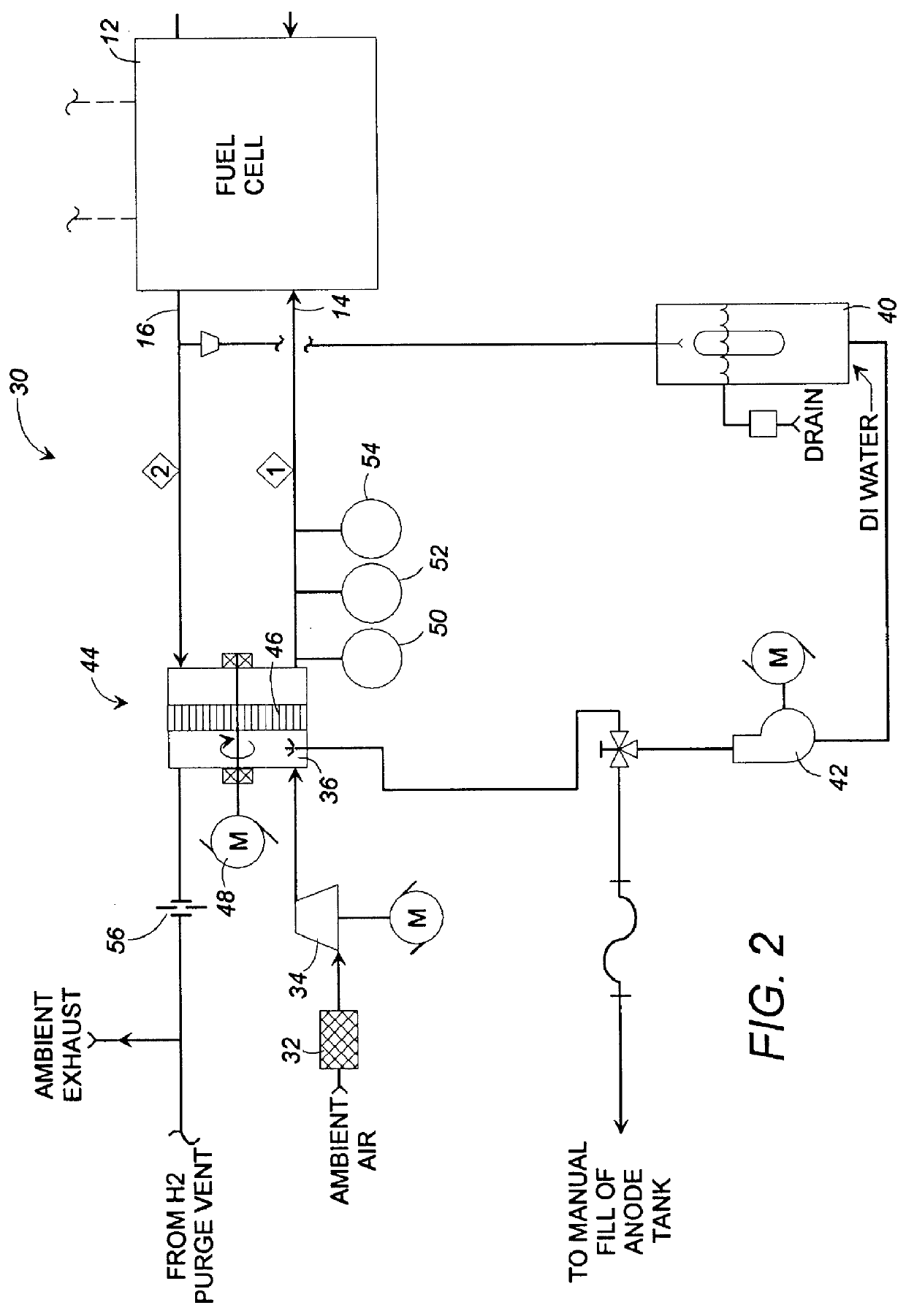
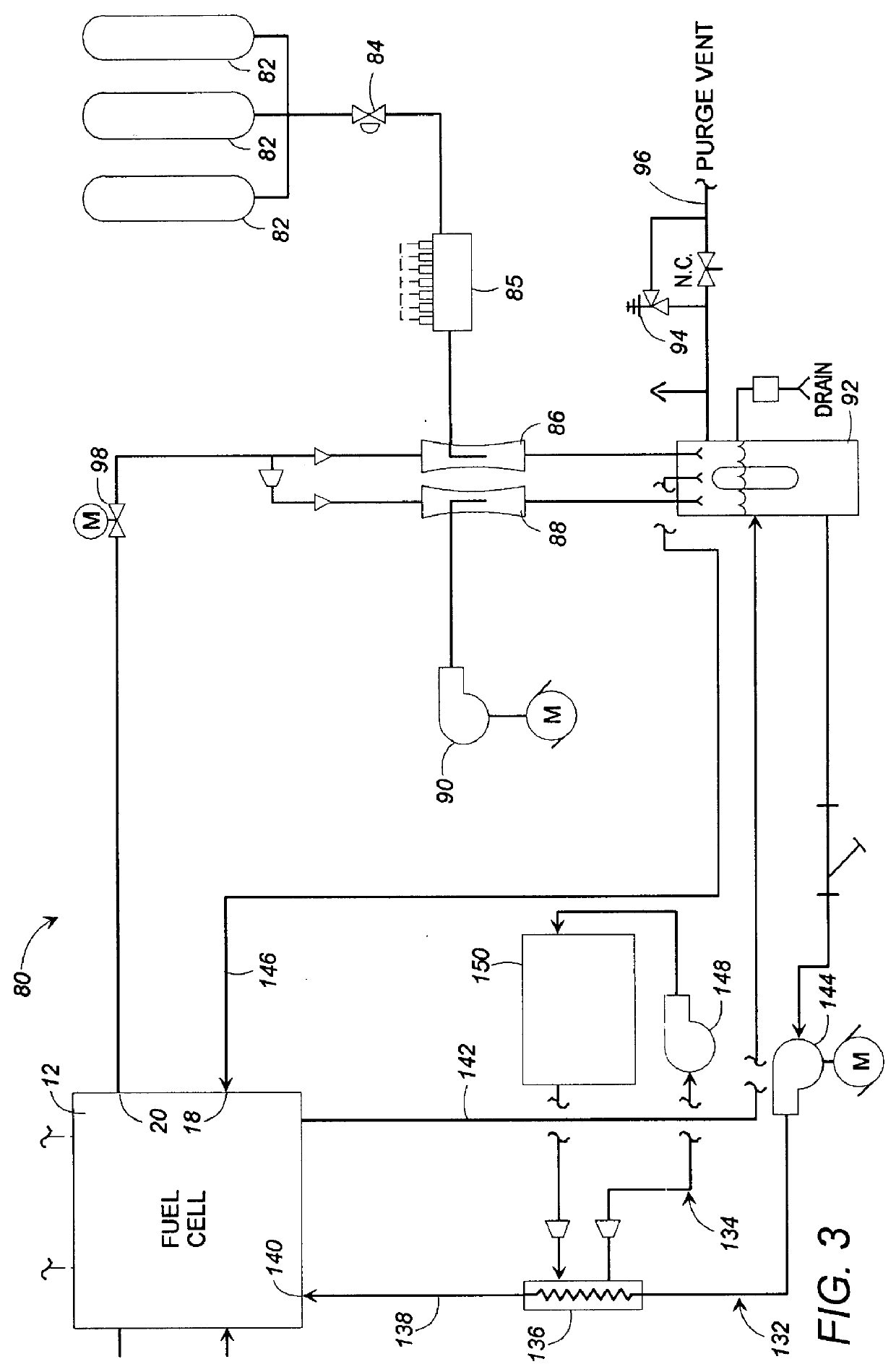
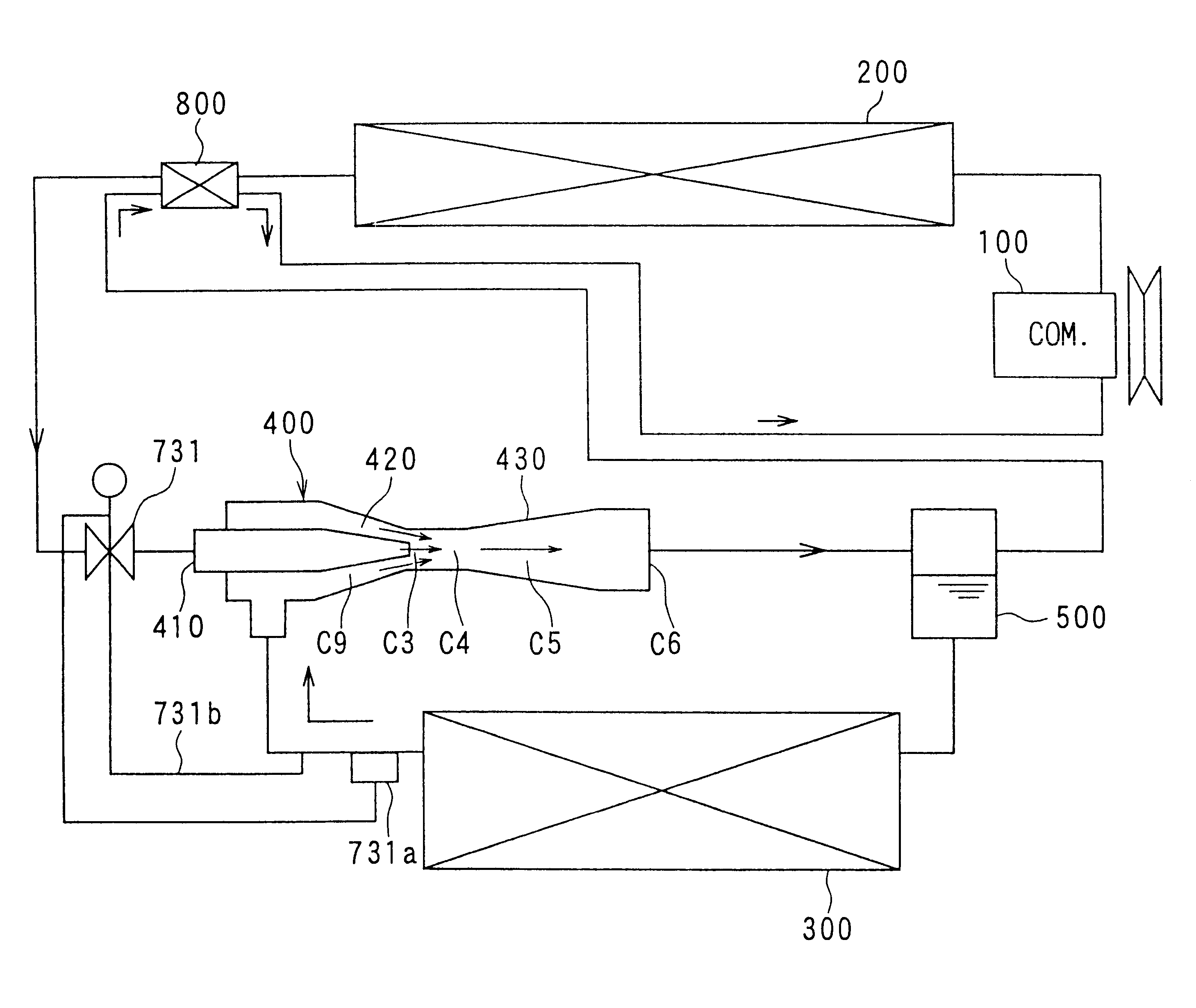
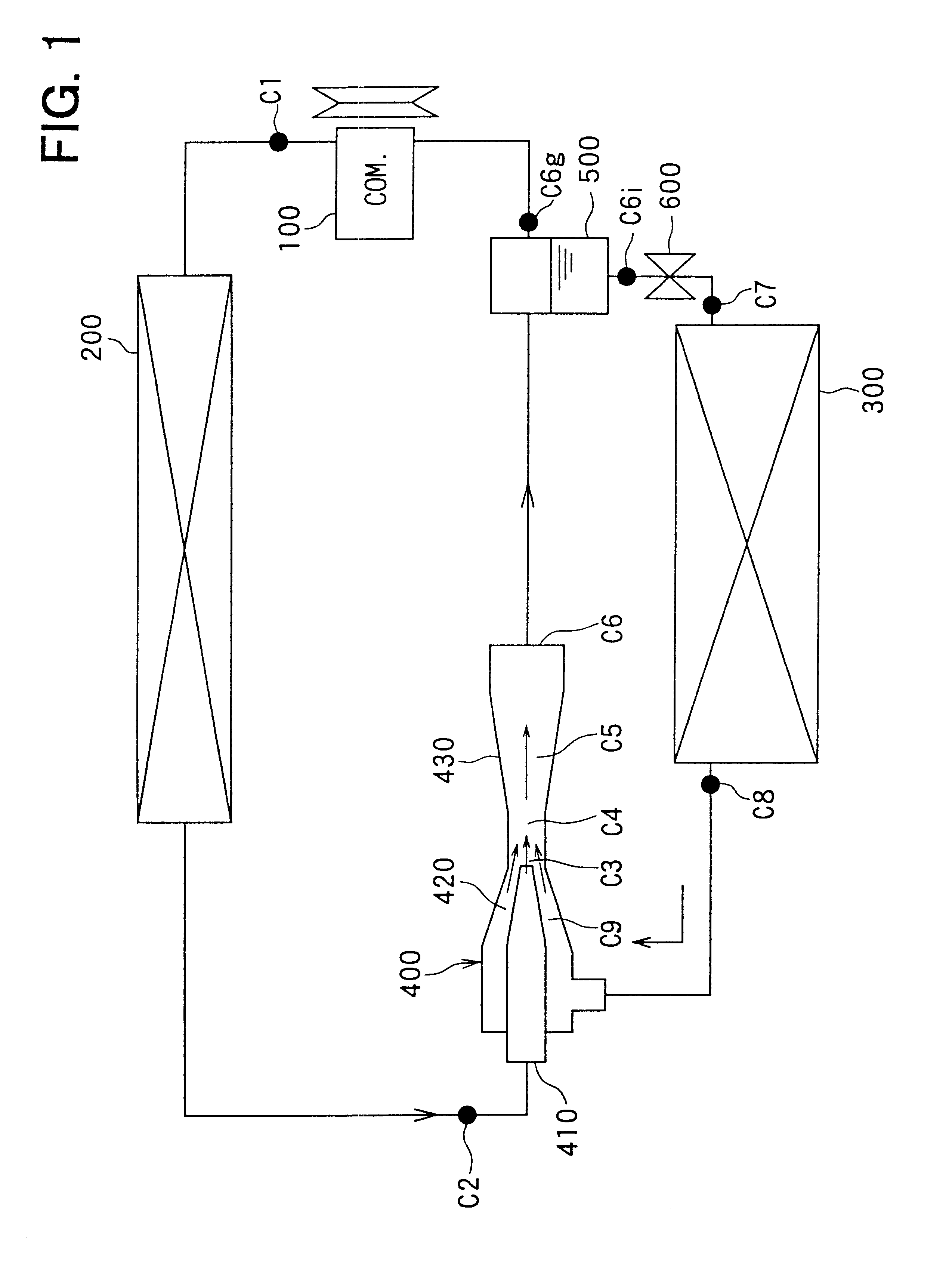
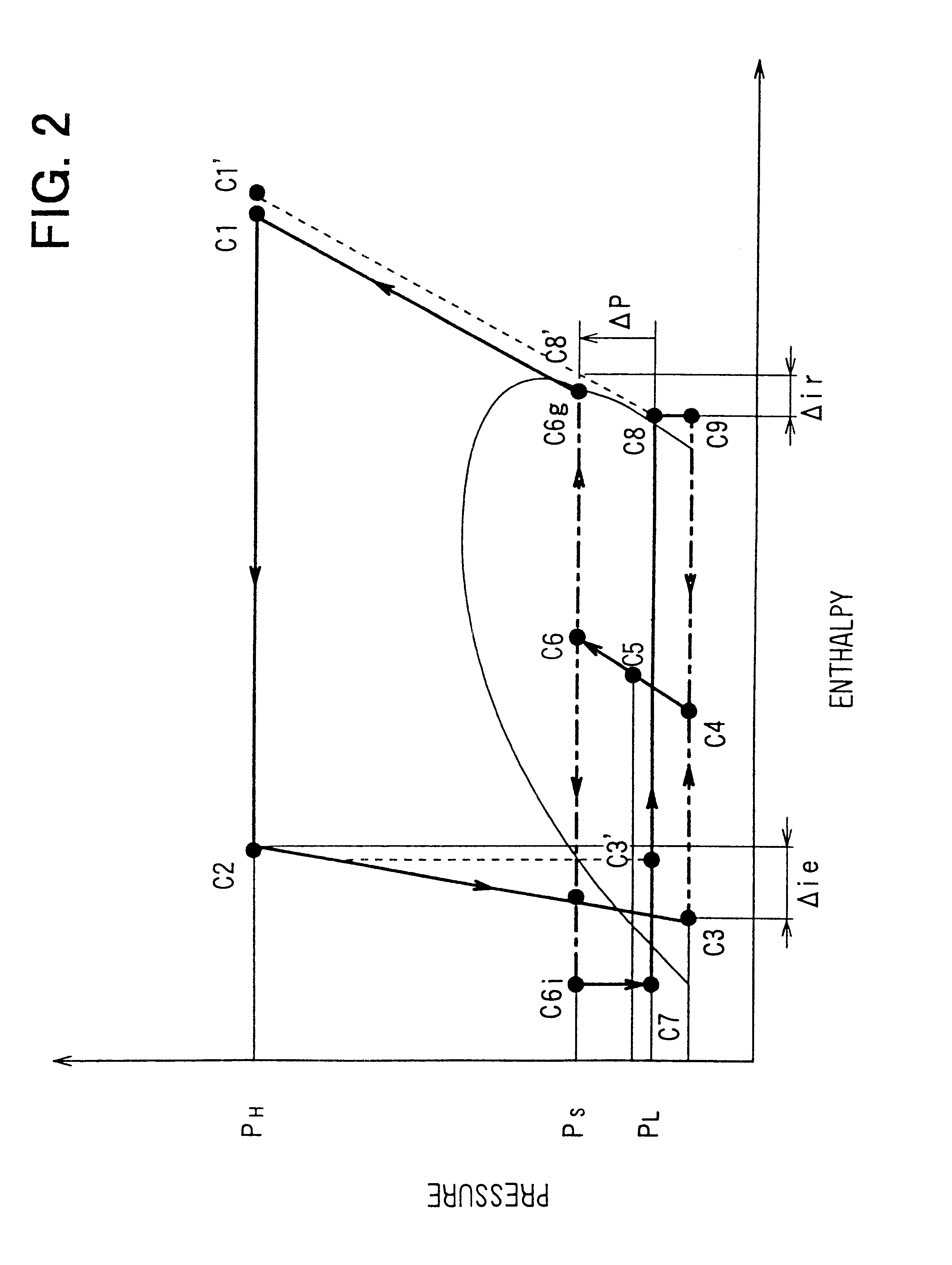
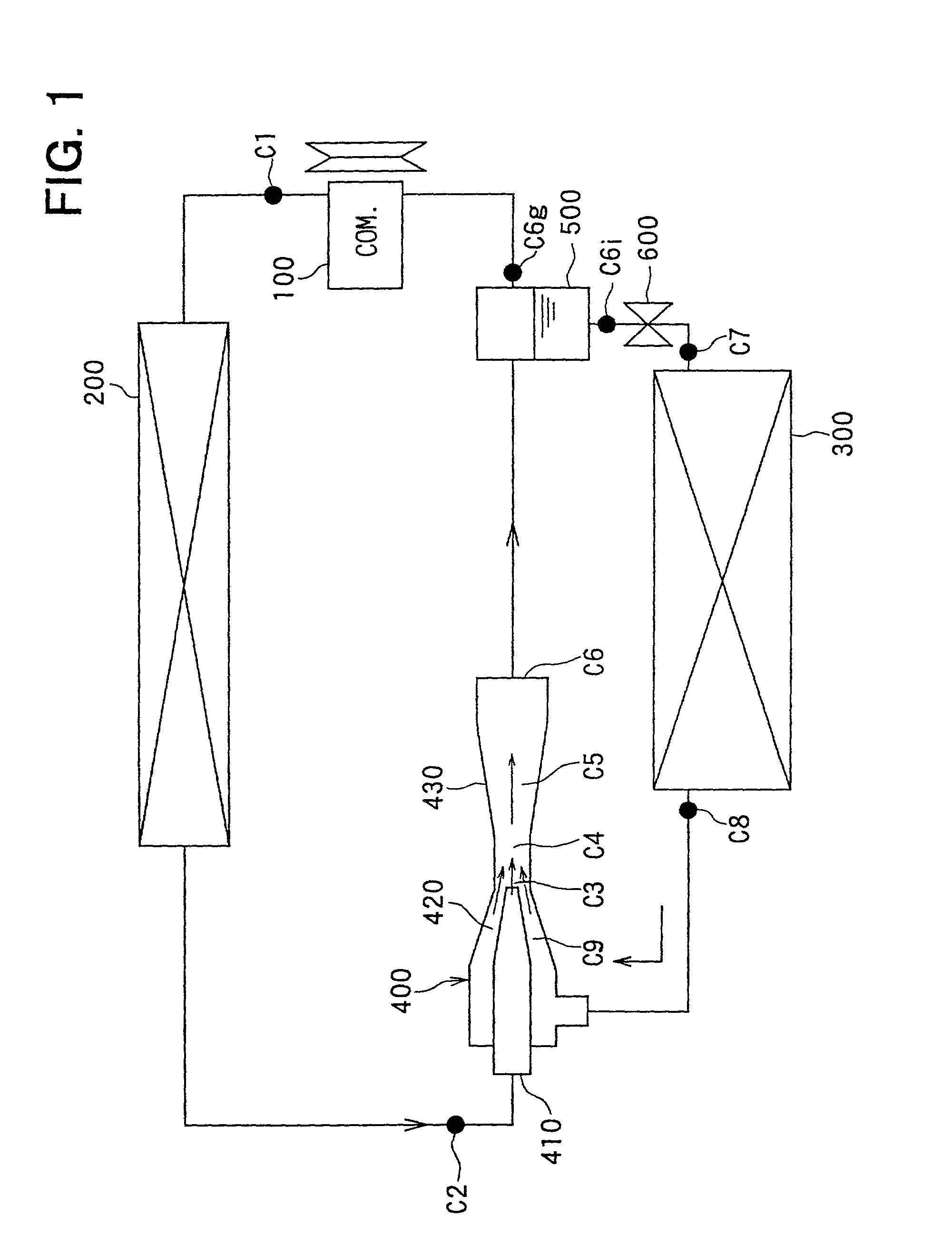
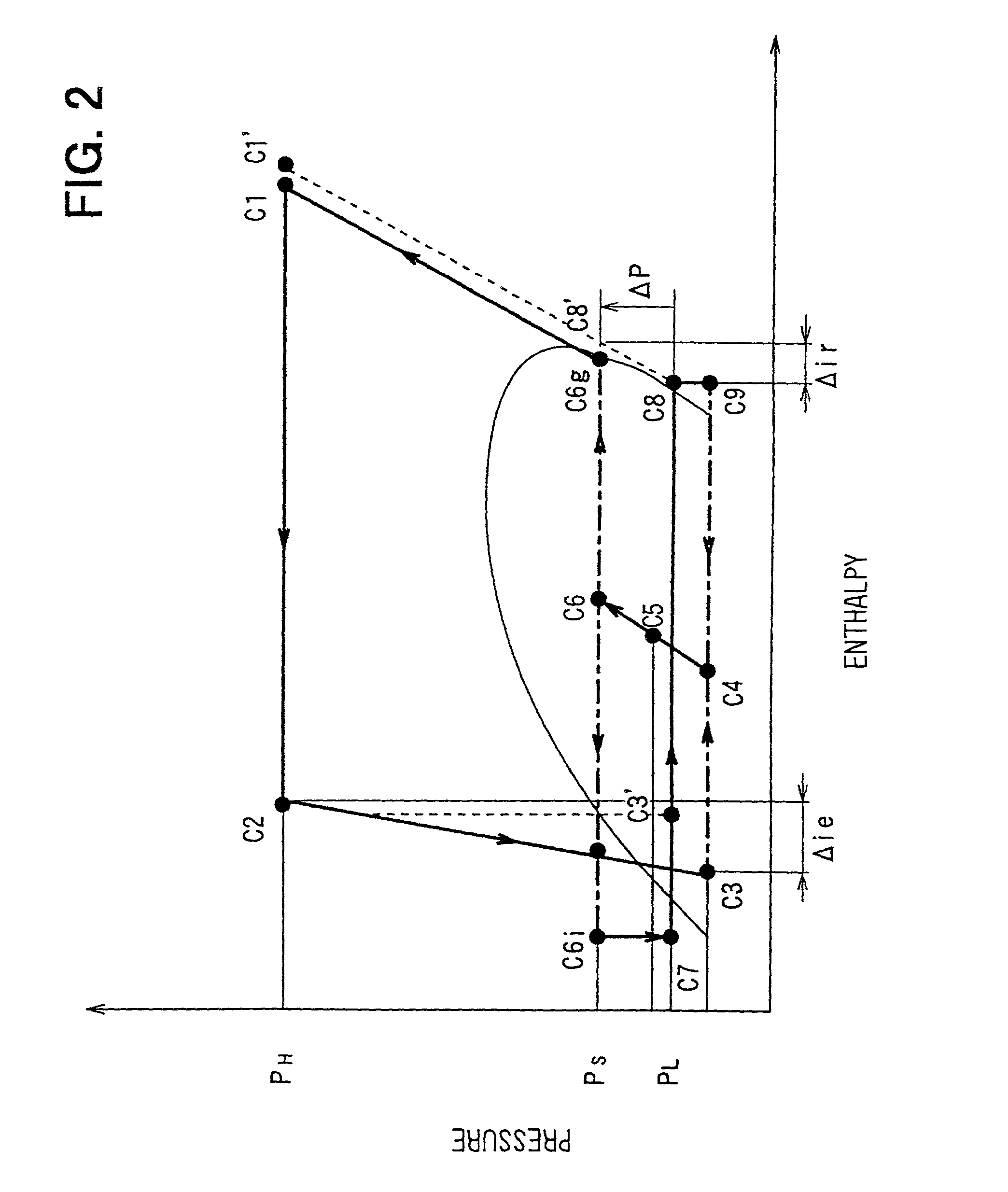
Fuel cell gas management system
InactiveUS6013385AImprove battery efficiencyMinimize the possibilityFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cell controlIonEnthalpy
A fuel cell gas management system including a cathode humidification system for transferring latent and sensible heat from an exhaust stream to the cathode inlet stream of the fuel cell; an anode humidity retention system for maintaining the total enthalpy of the anode stream exiting the fuel cell equal to the total enthalpy of the anode inlet stream; and a cooling water management system having segregated deionized water and cooling water loops interconnected by means of a brazed plate heat exchanger.
Owner:EMPRISE TECH ASSOC
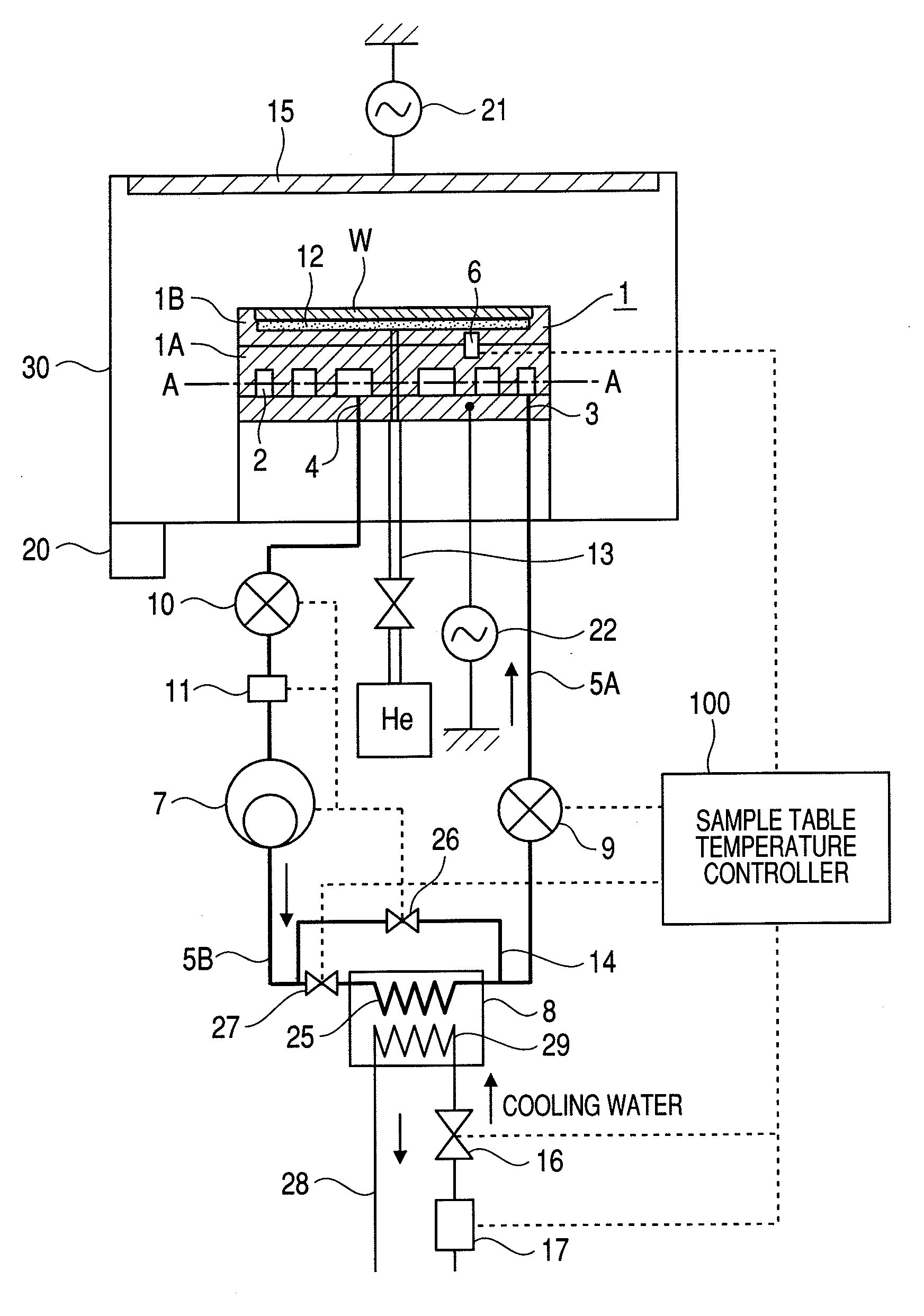
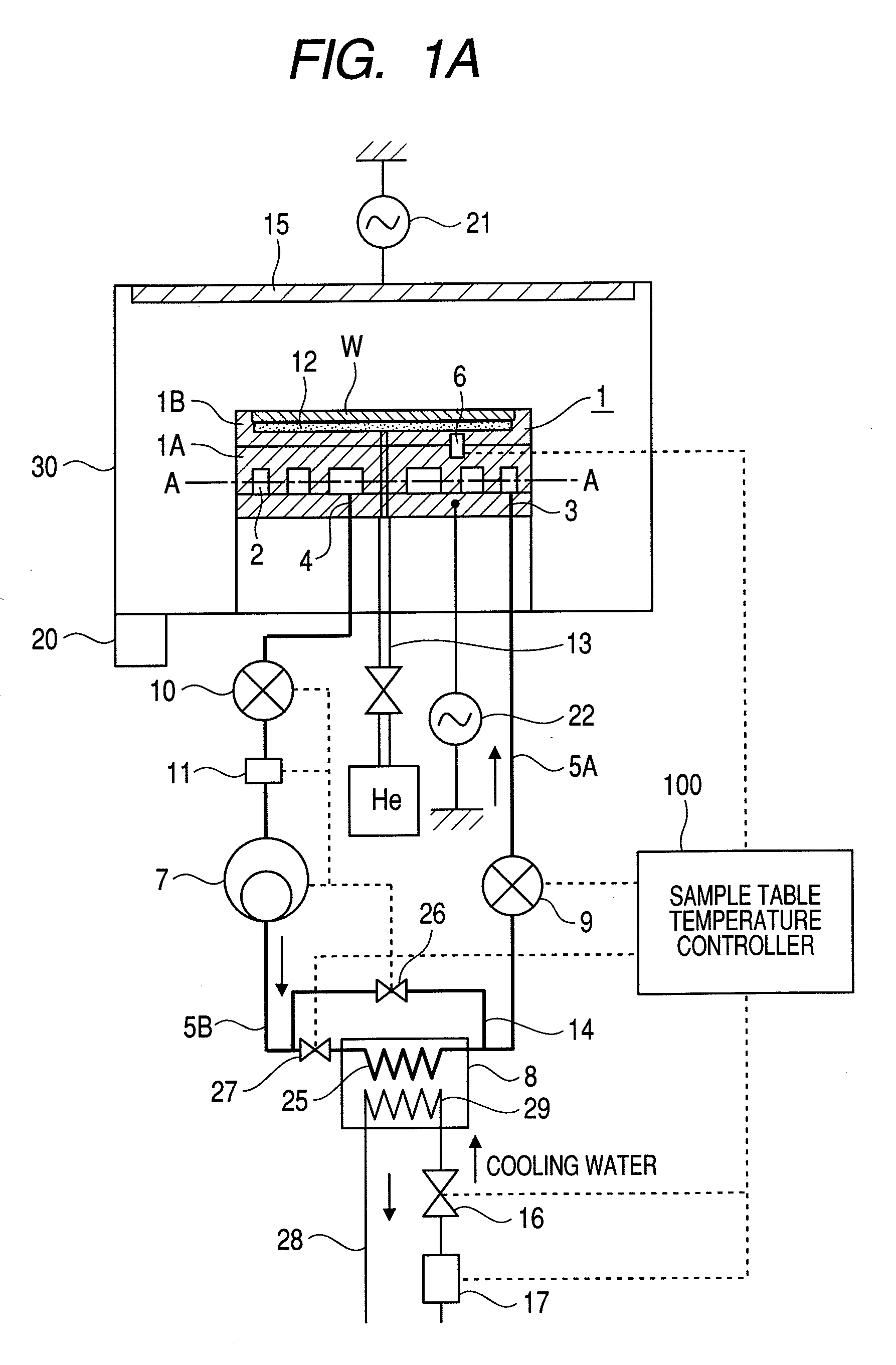
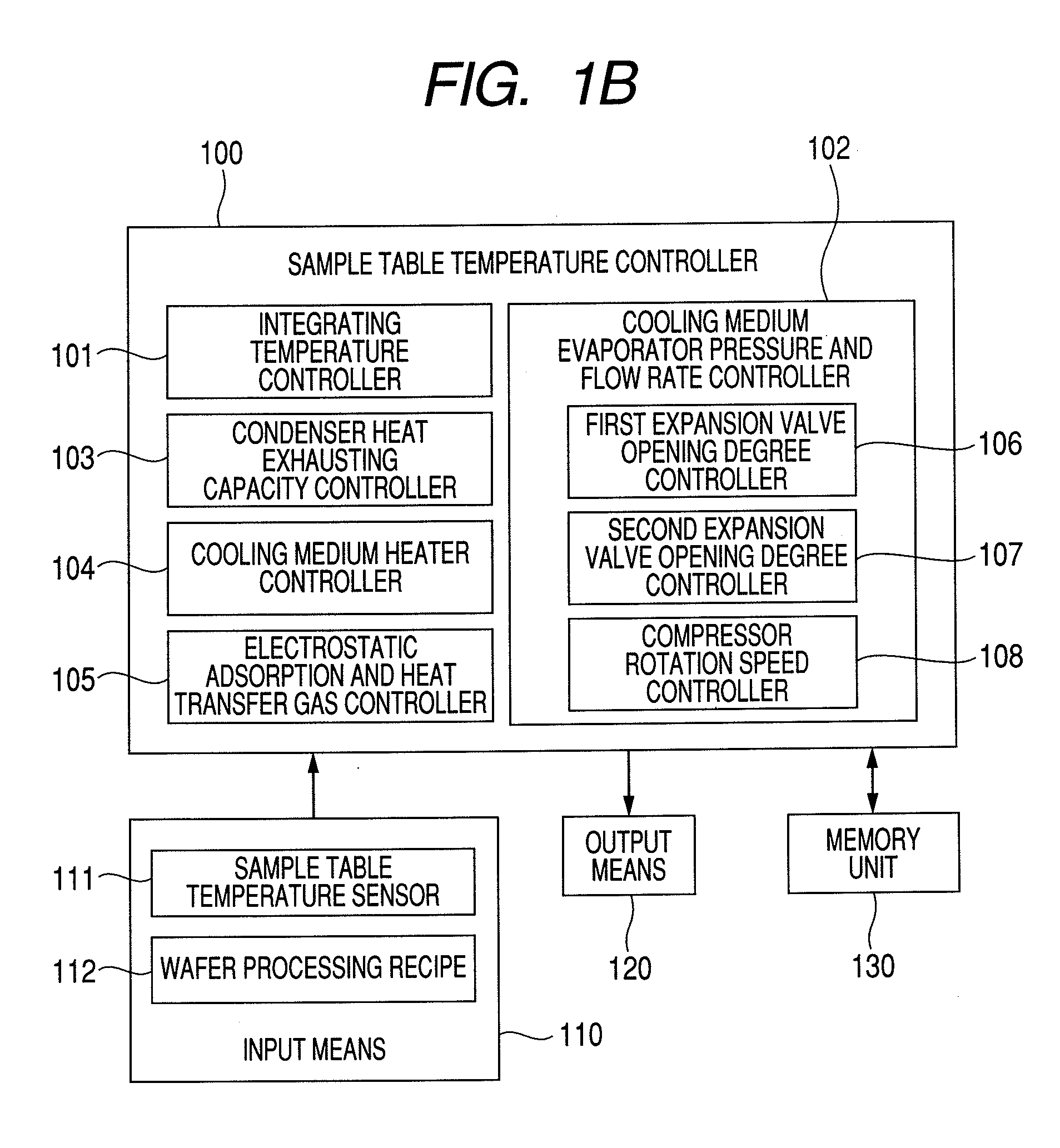
Plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS20100126666A1Uniform processingUnified controlElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIn planeEngineering
In a plasma processing apparatus; a refrigerant flow passage being formed in the sample table and constituting an evaporator of a cooling cycle and the in-plane temperature of the sample to be processed is controlled uniformly by controlling the enthalpy of the refrigerant supplied to the refrigerant flow passage and thereby keeping the flow mode in the refrigerant flow passage, namely in the sample table, in the state of a gas-liquid two-phase. If by any chance dry out of the refrigerant occurs in the refrigerant flow passage because the heat input of plasma increases with time or by another reason, it is possible to increase speed of a compressor and inhibit the dry out from occurring in the refrigerant flow passage. Further, if the refrigerant supplied to the refrigerant flow passage is liquefied, it is kept in the gas-liquid two-phase state.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
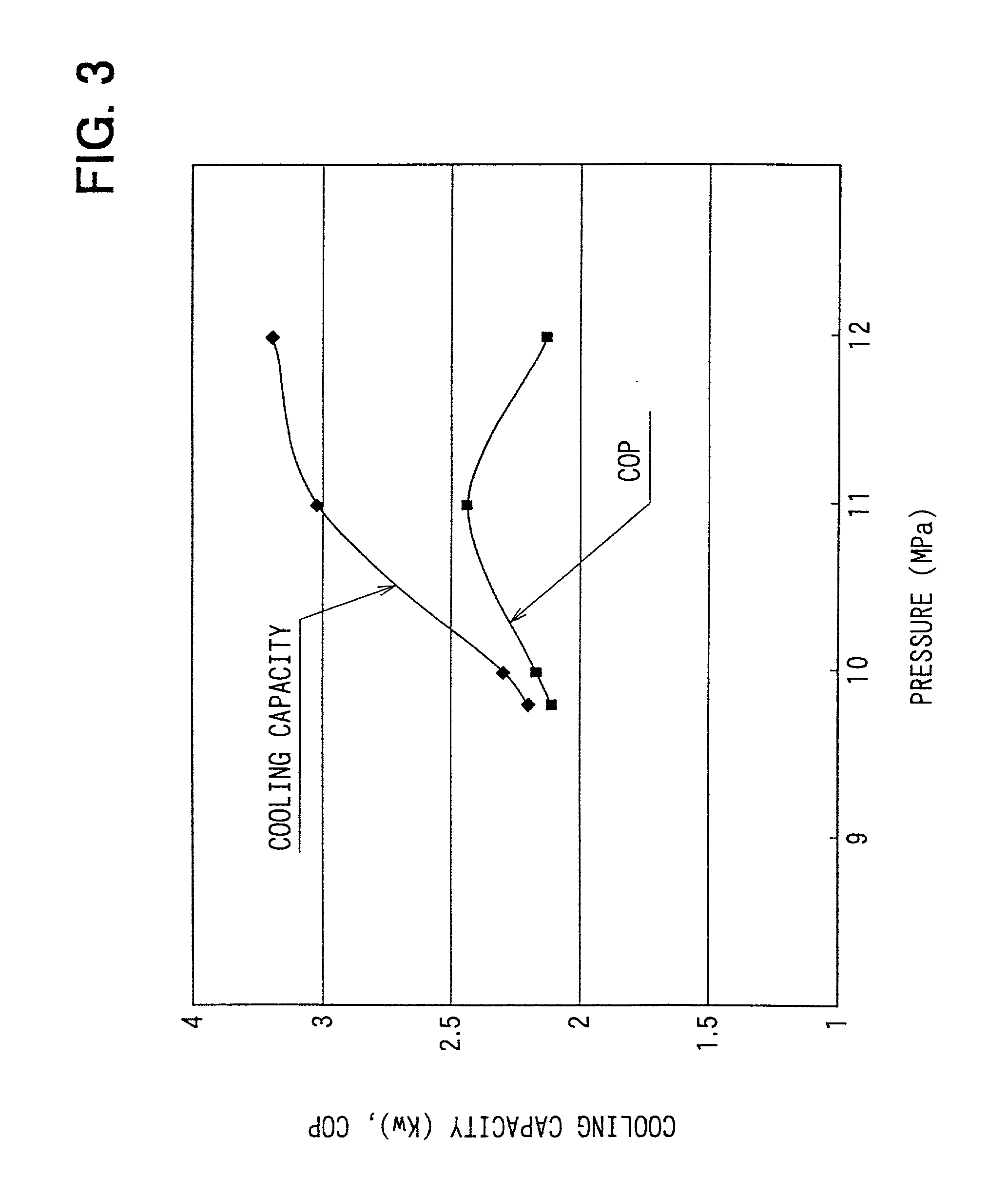
Method and apparatus for cooling
ActiveUS20080245083A1Increase loopHigh trafficMechanical apparatusTemperatue controlEngineeringCooling capacity
A method of calculating net sensible cooling capacity of a cooling unit includes measuring a discharge pressure from of fluid from a compressor and a suction pressure from an evaporator, calculating a condensing temperature of fluid flowing from the compressor and an evaporating temperature of fluid flowing from the evaporator, calculating a mass flow rate of fluid flowing from the compressor, calculating enthalpy of fluid flowing from the compressor, of fluid flowing from the thermal expansion valve, and of fluid flowing from the evaporator, calculating a mass flow rate of fluid flowing through the hot gas bypass valve, and calculating net sensible cooling capacity. Embodiments of cooling units and other methods are further disclosed.
Owner:AMERICA POWER CONVERSION CORP
Flame made metal oxides
ActiveUS7211236B2Add featureWell mixedMaterial nanotechnologyZirconium oxidesSpray pyrolysisCarboxylic acid
Described is a method for the production of metal oxides by flame spray pyrolysis, in particular mixed metal oxides such as ceria / zirconia, and metal oxides obtainable by said method. Due to high enthalpy solvents with a high carboxylic acid content said metal oxides have improved properties. For example ceria / zirconia has excellent oxygen storage capacity at high zirconium levels up to more than 80% of whole metal content.
Owner:EIDGENOSSISCHE TECHN HOCHSCULE ZURICH
Ejector cycle system with critical refrigerant pressure
InactiveUS6477857B2Recover energyReduce power consumptionCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEvaporators/condensersEngineeringPressure difference
Owner:DENSO CORP
Air re-circulation index
InactiveUS7051946B2Reducing air re-circulationMechanical apparatusDomestic cooling apparatusData centerEngineering
An index of air re-circulation in a data center having one or more racks is determined to identify the level of heated air re-circulation into cooling fluid delivered to the one or more racks. The one or more racks comprise inlets and outlets and are positioned along a cool aisle and a hot aisle. The index is calculated by dividing the enthalpy rise due to infiltration of heated air into the cool aisle and the total enthalpy rise of the heated air from the outlets of the one or more racks.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
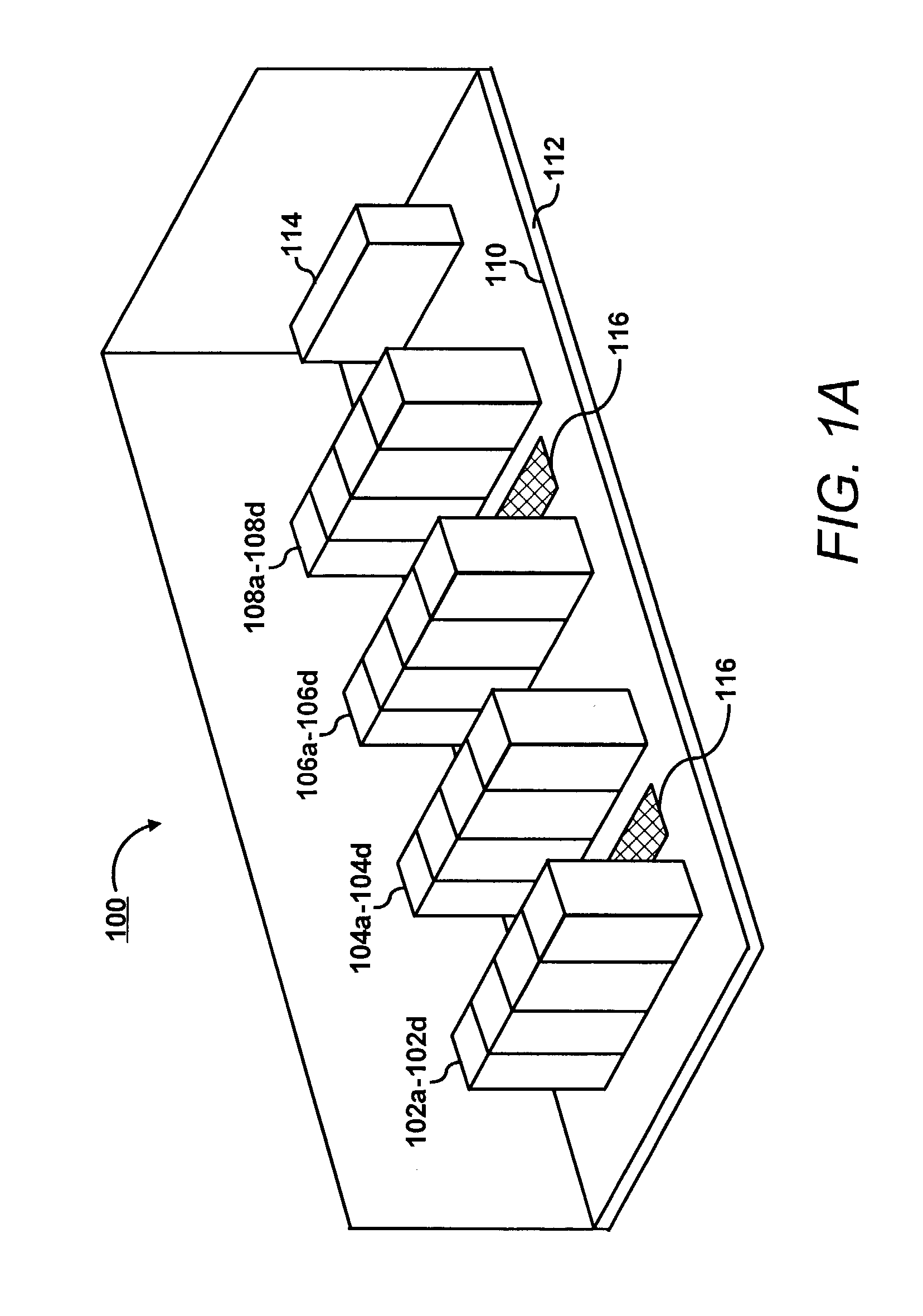
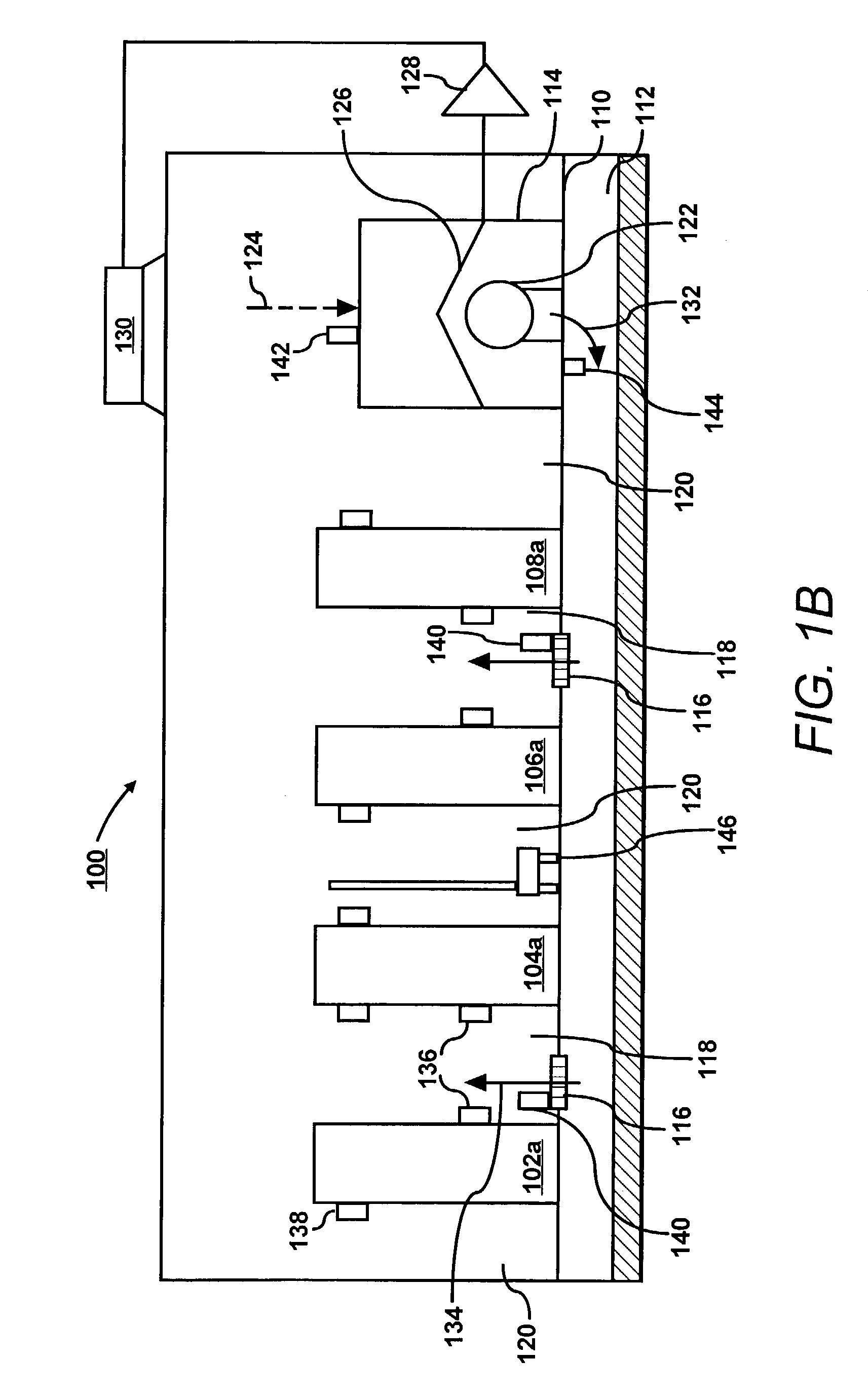
Apparatus for measuring parameters of a flowing multiphase mixture
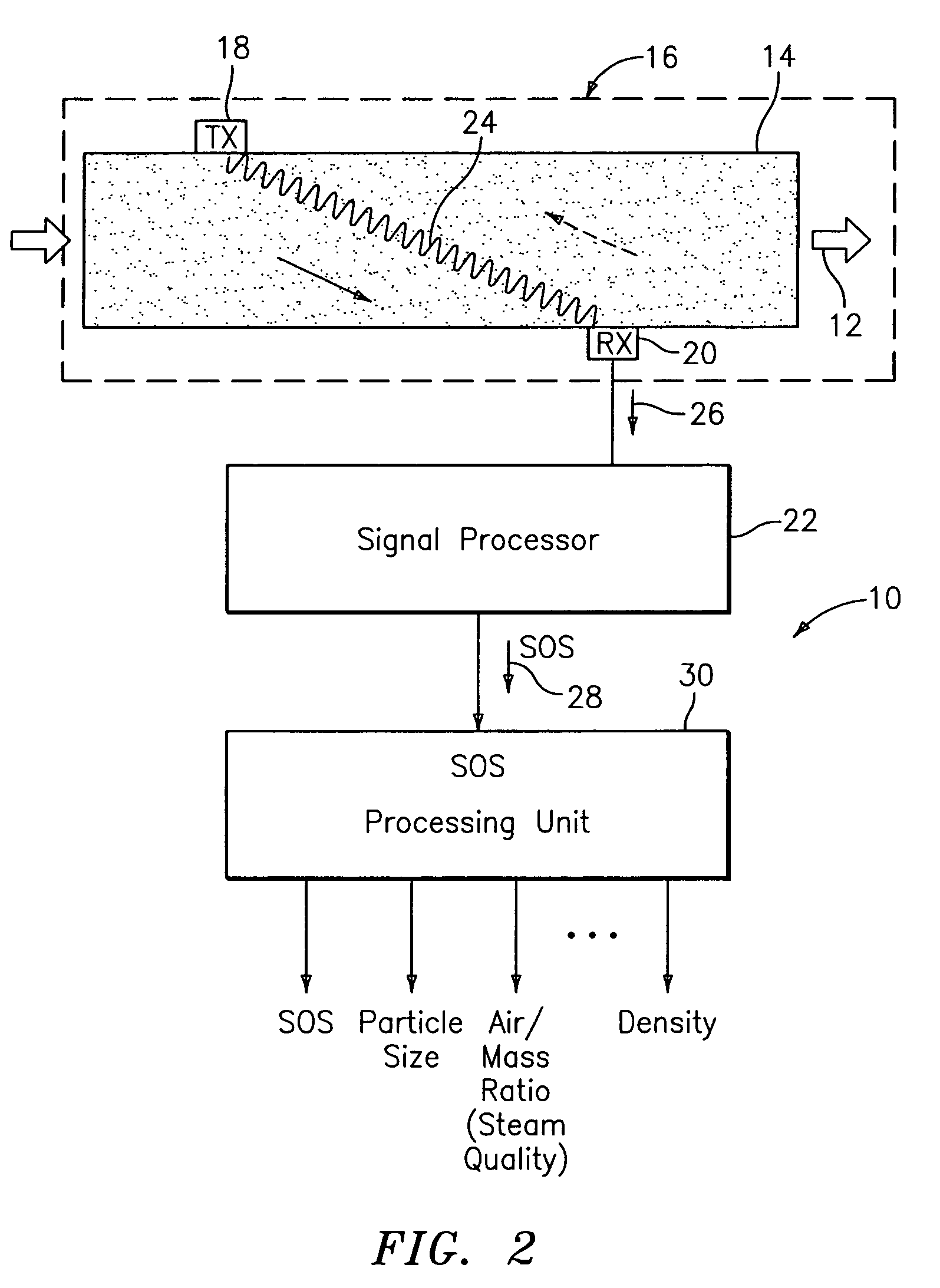
ActiveUS7096719B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic sensorMass ratio
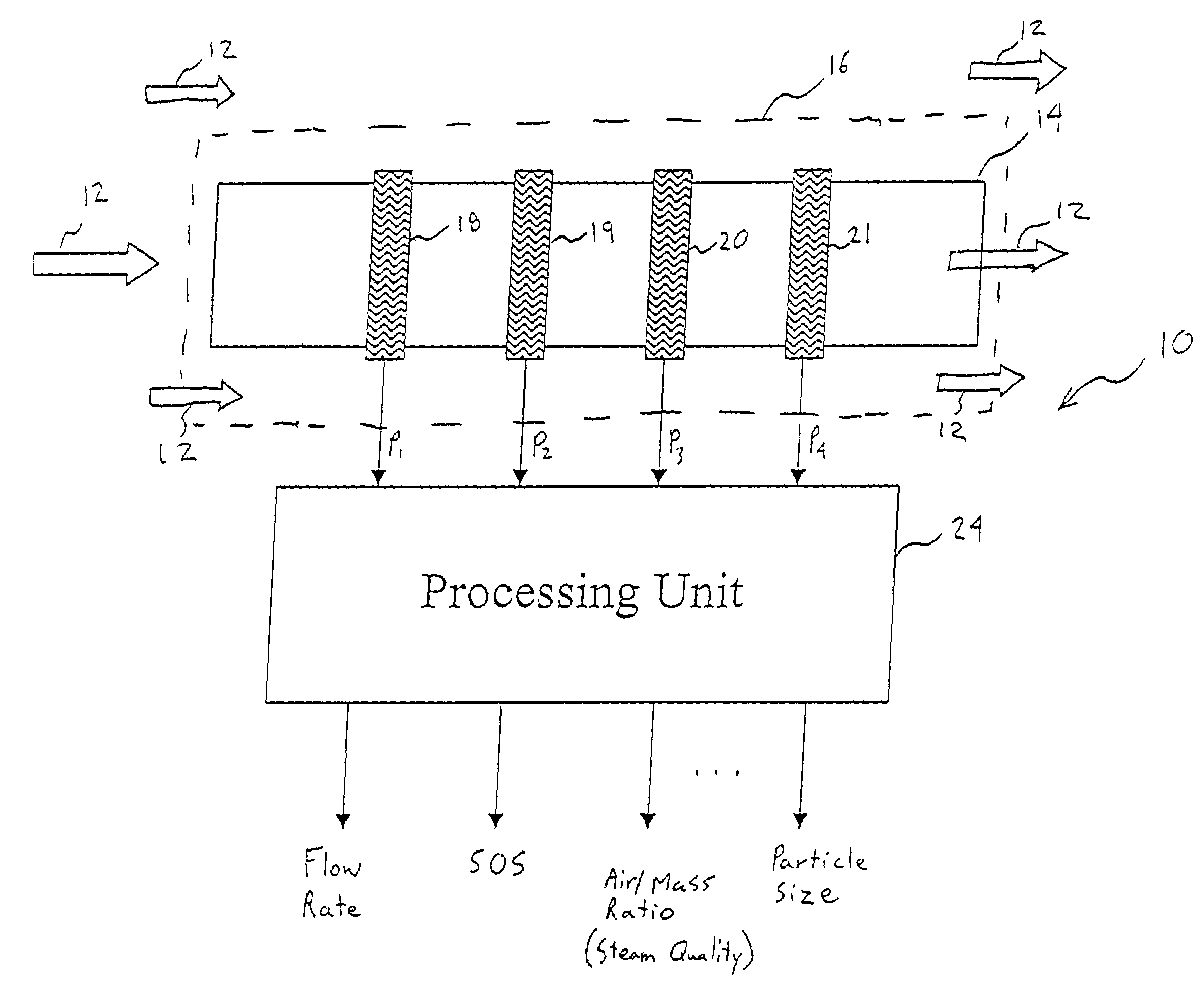
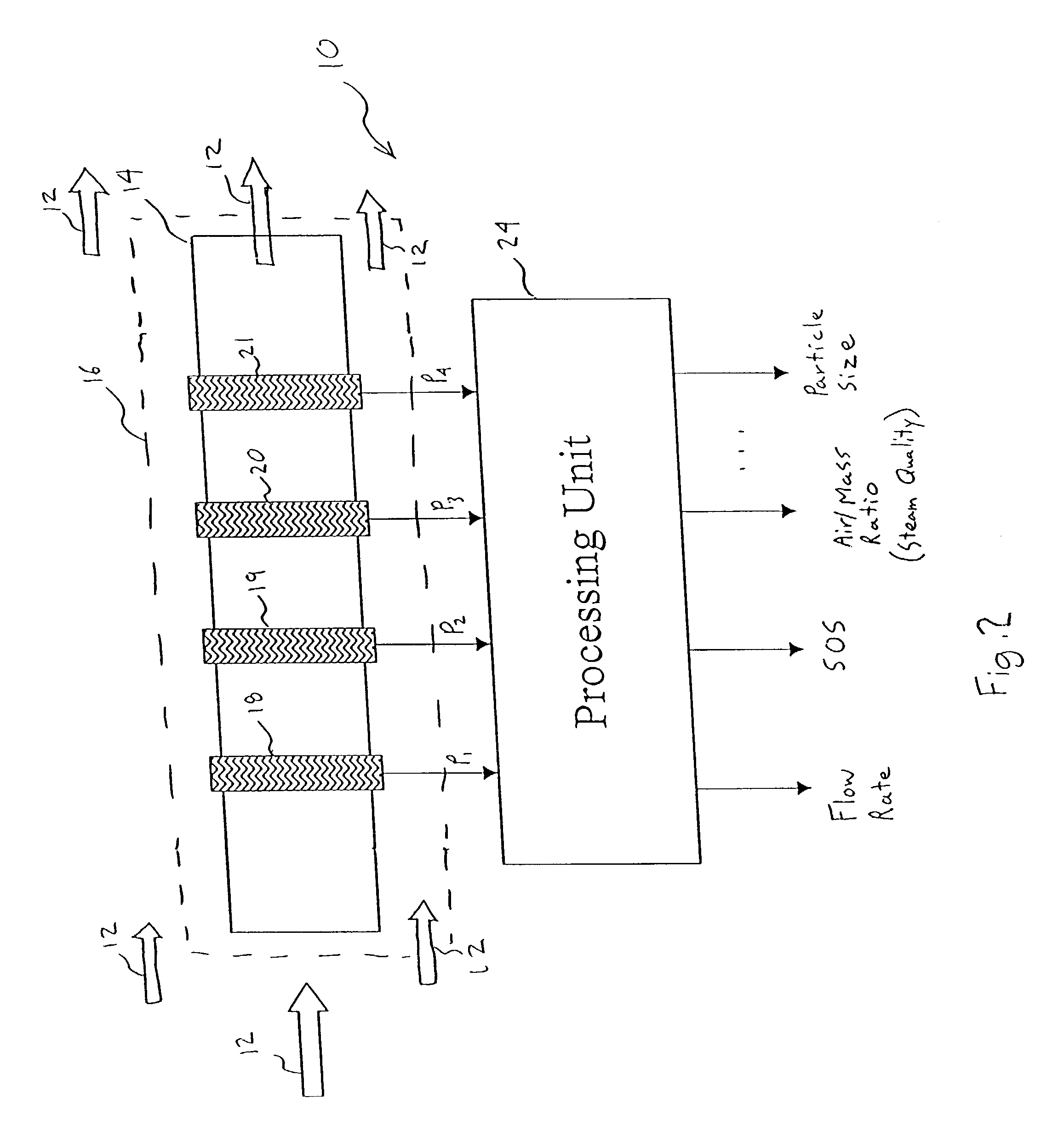
An apparatus 10 is provided that measures the speed of sound propagating in a multiphase mixture to determine parameters, such as mixture quality, particle size, vapor / mass ratio, liquid / vapor ratio, mass flow rate, enthalpy and volumetric flow rate of the flow in a pipe or unconfined space, for example, using acoustic and / or dynamic pressures. The apparatus includes a pair of ultrasonic transducers disposed axially along the pipe for measuring the transit time of an ultrasonic signal to propagate from one ultrasonic transducer to the other ultrasonic transducer. A signal process, responsive to said transit time signal, provides a signal representative of the speed of sound of the mixture. An SOS processing unit then provides an output signal indicative of at least one parameter of the mixture flowing through the pipe. The frequency of the ultrasonic signal is sufficiently low to minimize scatter from particle / liquid within the mixture. The frequency based sound speed is determined utilizing a dispersion model to determine the at least one parameter of the fluid flow and / or mixture.
Owner:CIDRA CORP SERVICES
High-temperature dual-source organic Rankine cycle with gas separations
InactiveUS20100300093A1Increase temperatureMinimize timeAuxillary drivesInternal combustion piston enginesWorking fluidOrganic Rankine cycle
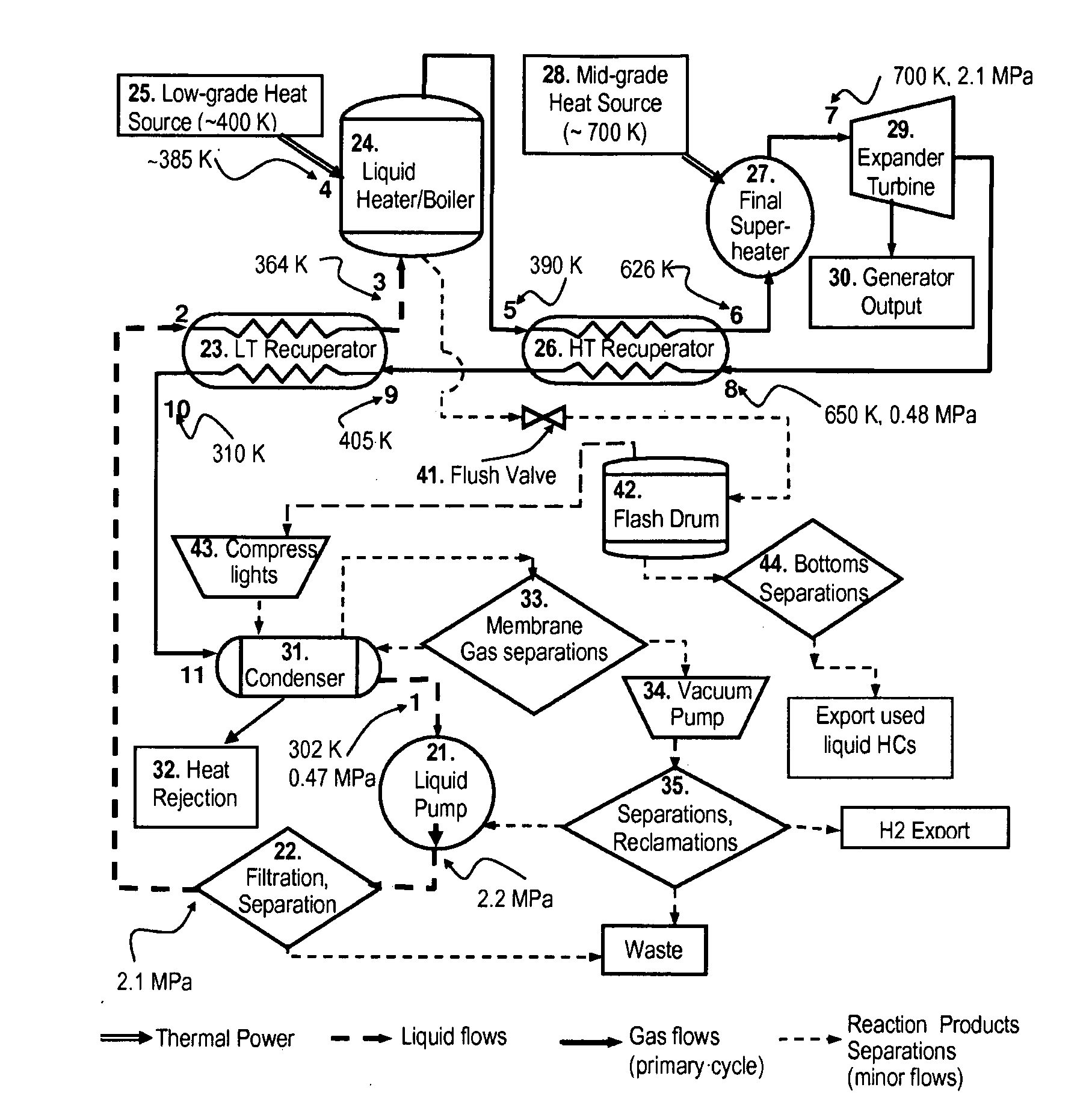
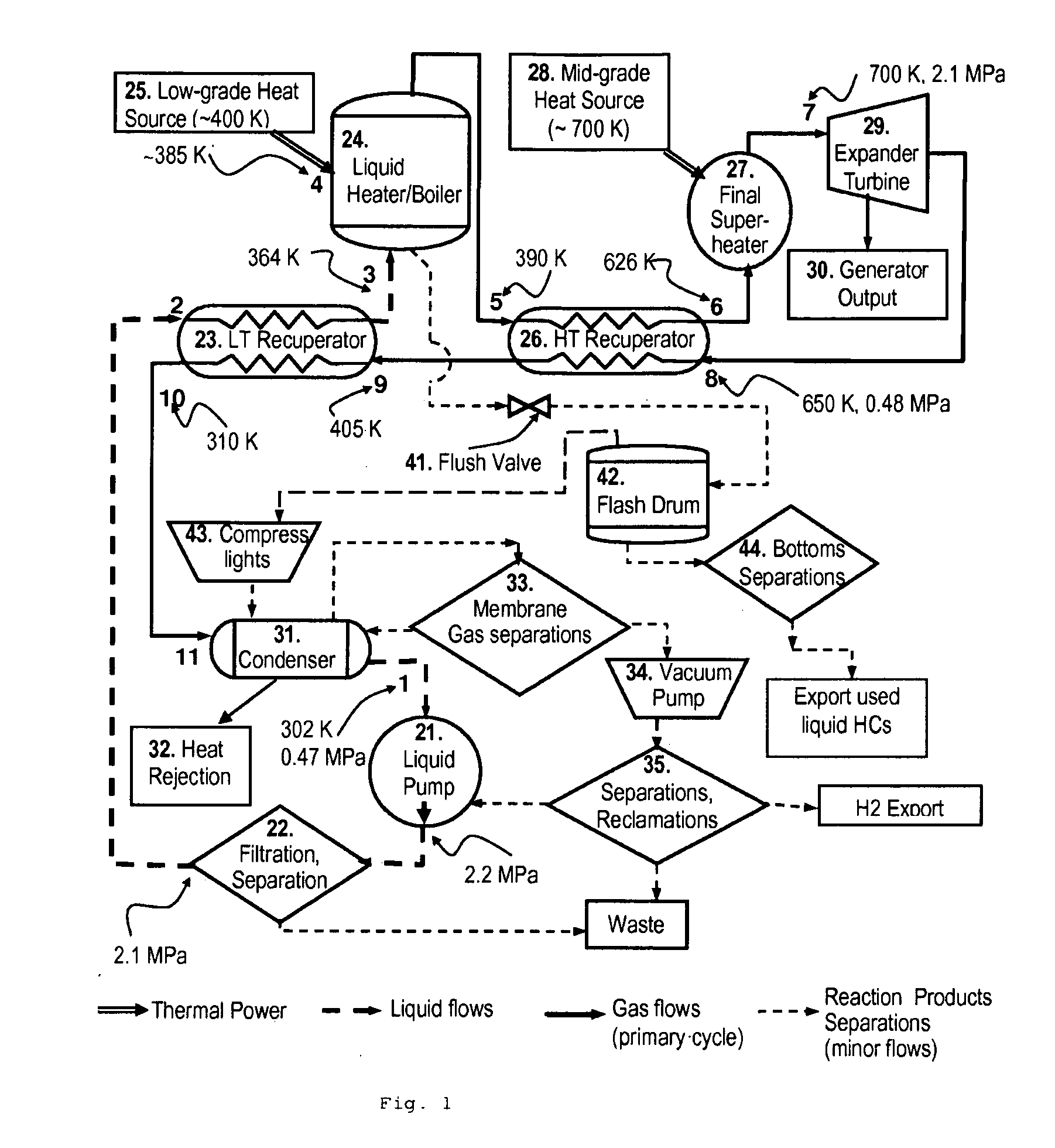
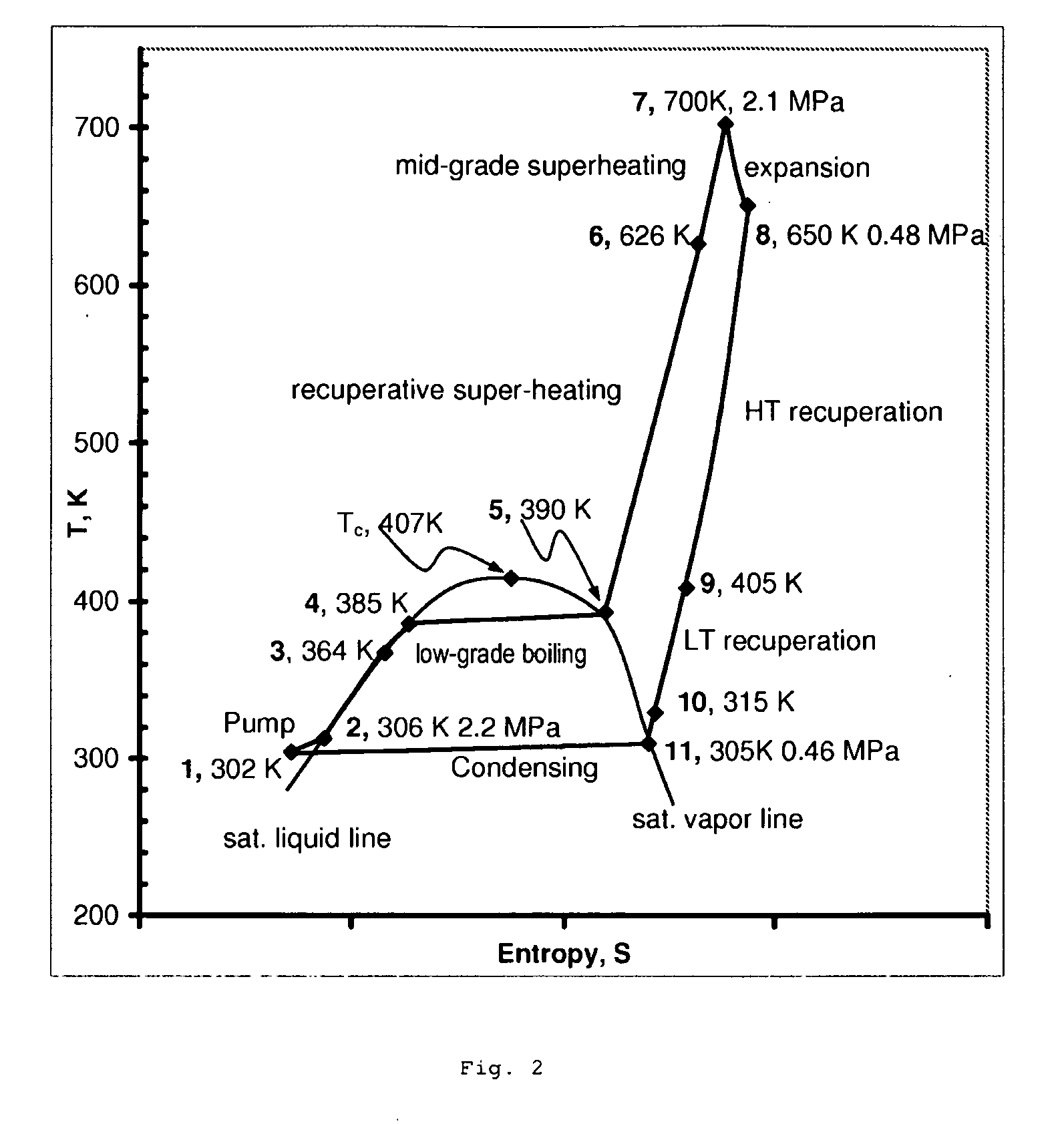
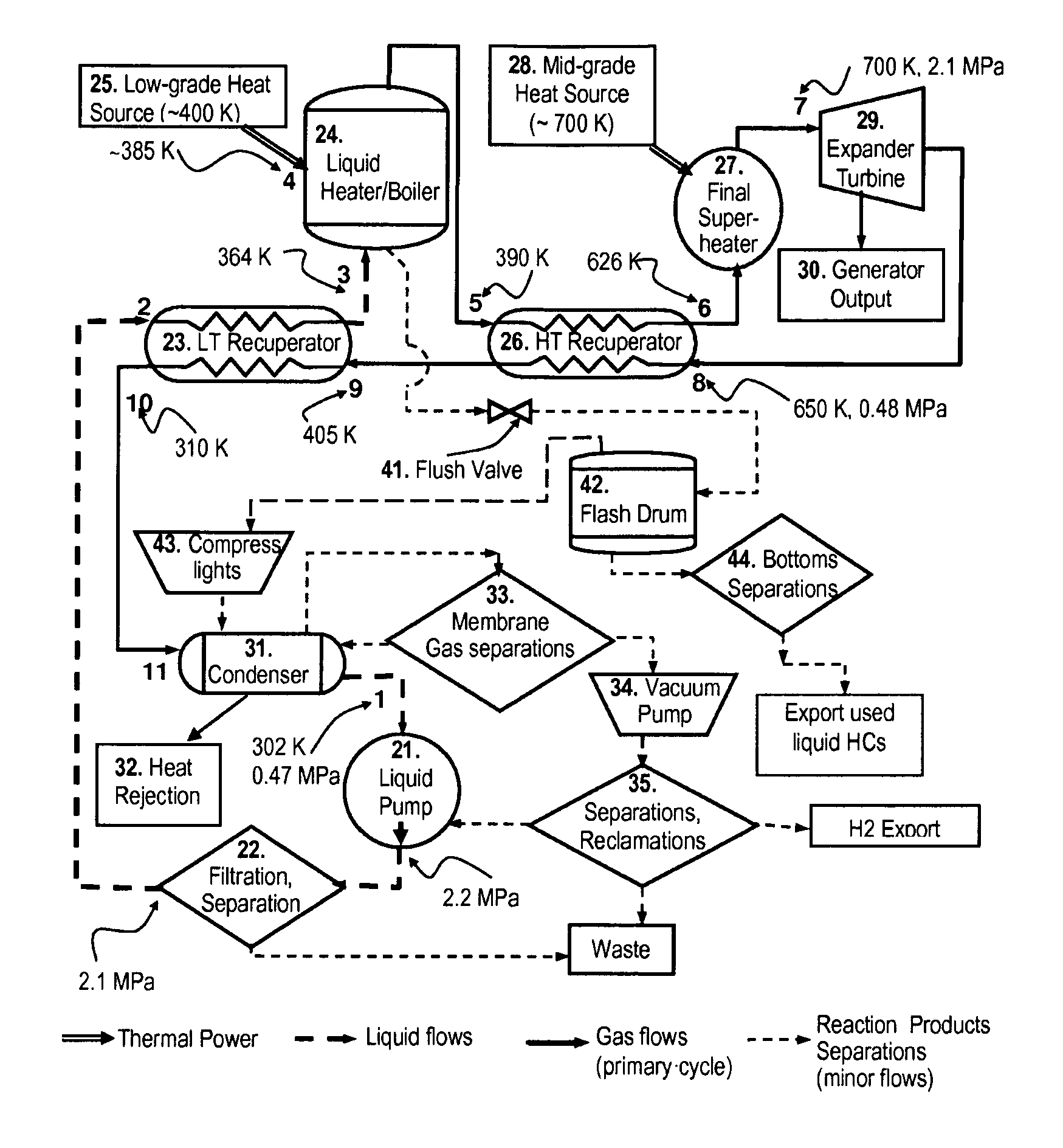
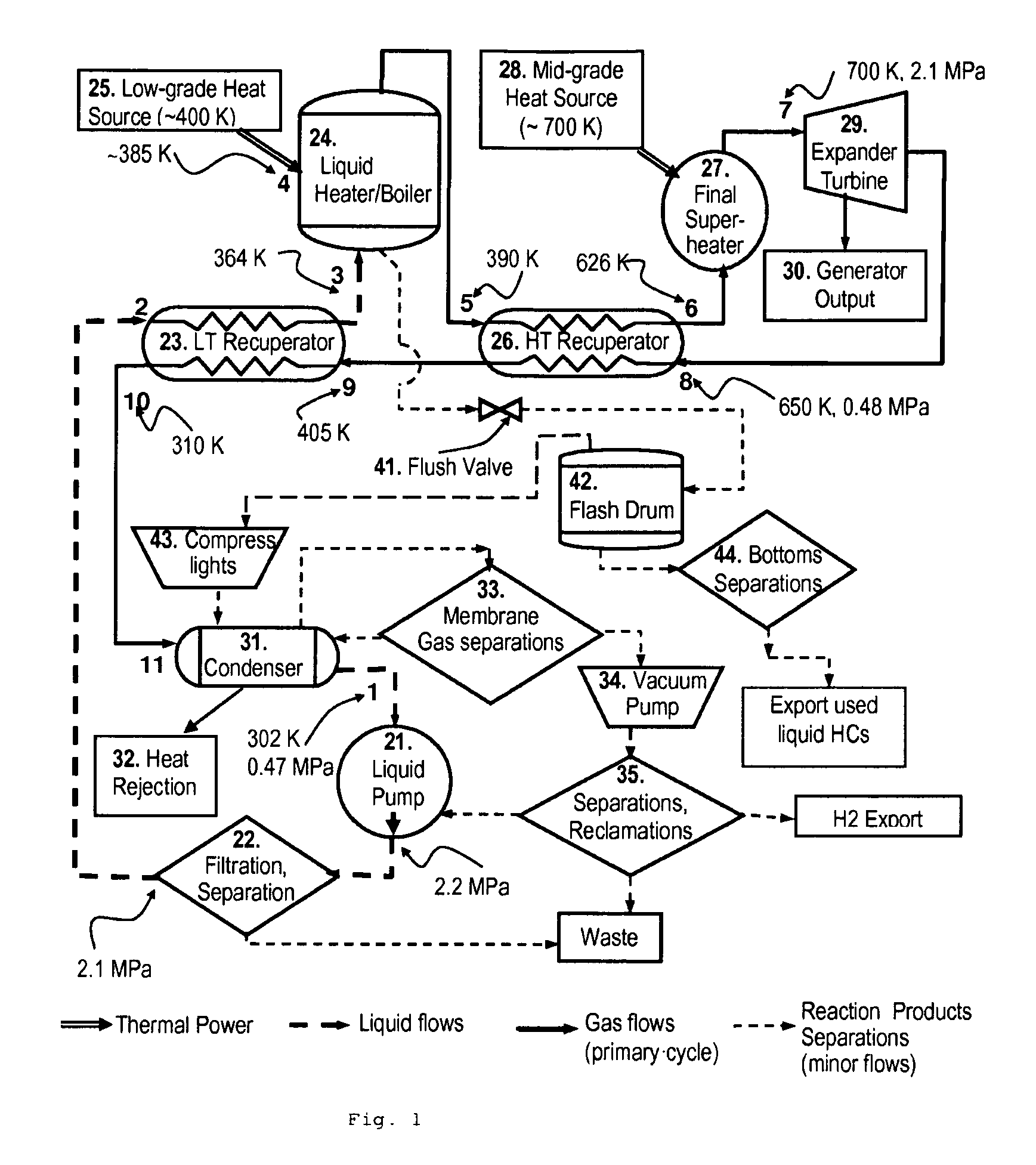
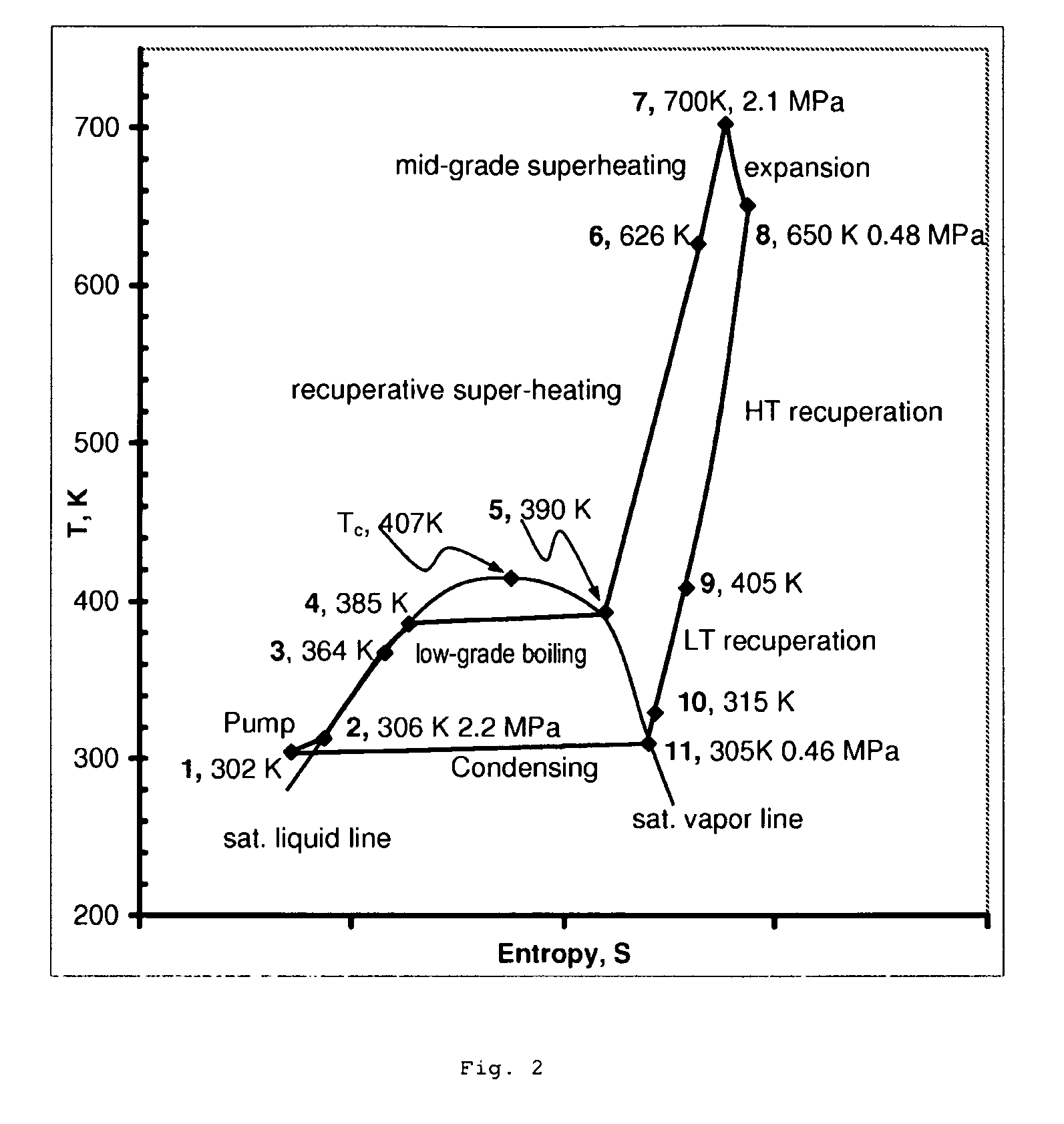
In a dual-source organic Rankine cycle (DORC), the condensed and slightly sub-cooled working fluid at near ambient temperature (˜300 K) and at low-side pressure (0.1 to 0.7 MPa) is (1) pumped to high-side pressure (0.5-5 MPa), (2) pre-heated in a low-temperature (LT) recuperator, (3) boiled using a low-grade heat source, (4) super-heated in a high-temperature (HT) recuperator to a temperature close to the expander turbine exhaust temperature using this exhaust vapor enthalpy, (5) further super-heated to the turbine inlet temperature (TIT) using a mid-grade heat source, (6) expanded through a turbine expander to the low-side pressure, (7) cooled through the HT recuperator, (8) cooled through the LT recuperator, (9) mostly liquefied and slightly subcooled in a condenser, and (10) the condensed portion is returned to the pump to repeat this cycle.
Owner:DOTY SCI
Plasma spray method and apparatus for applying a coating utilizing particle kinetics
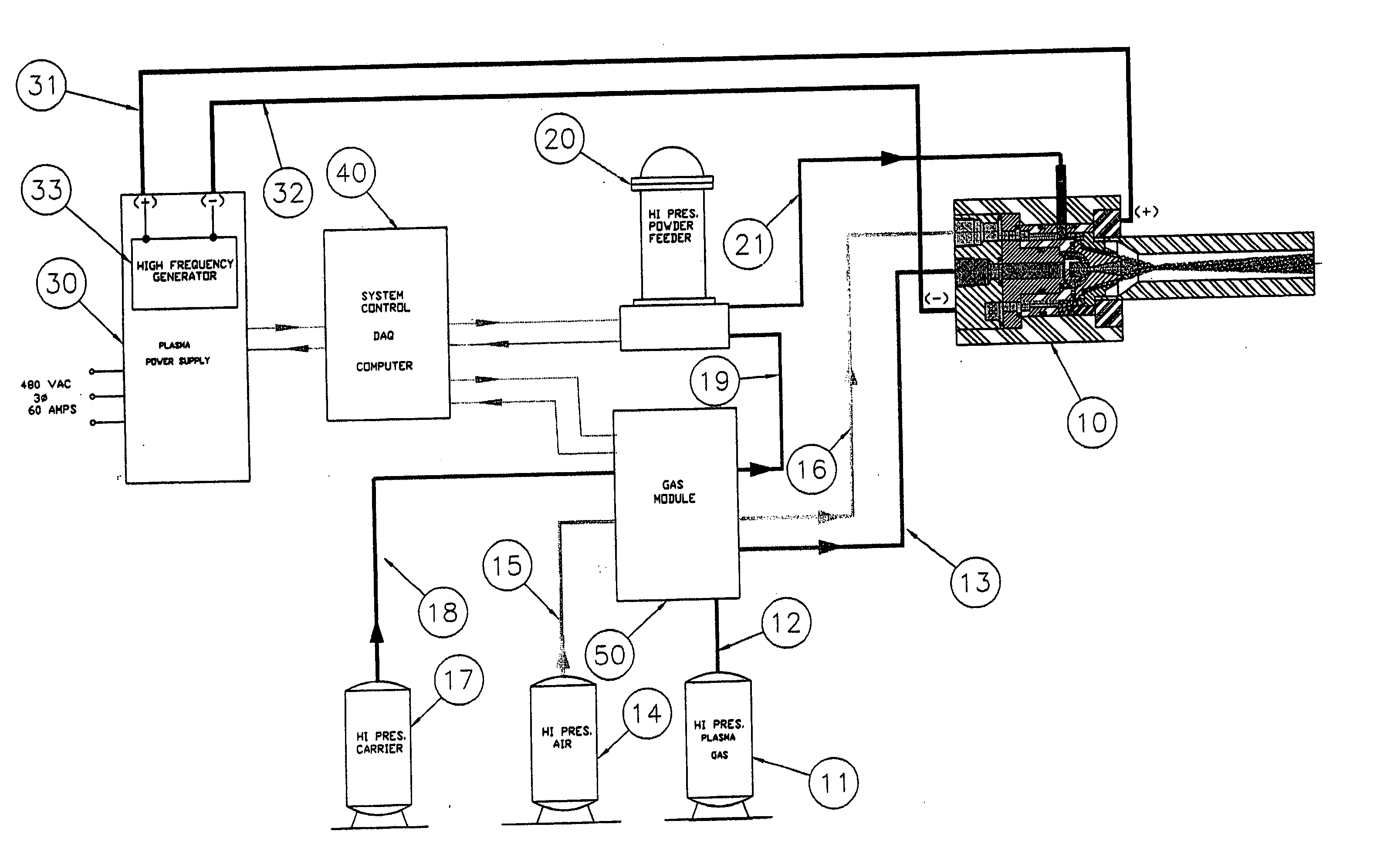
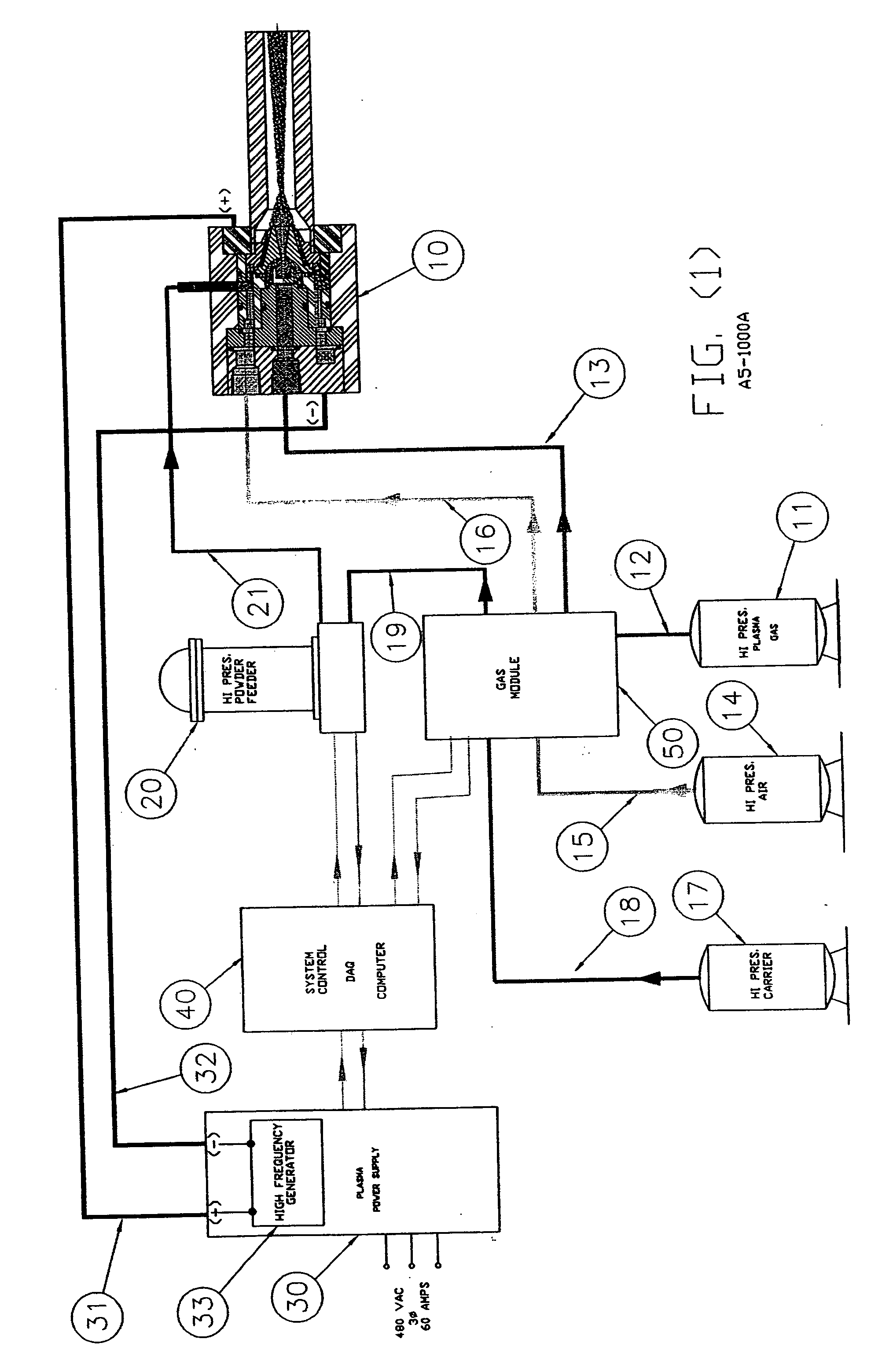
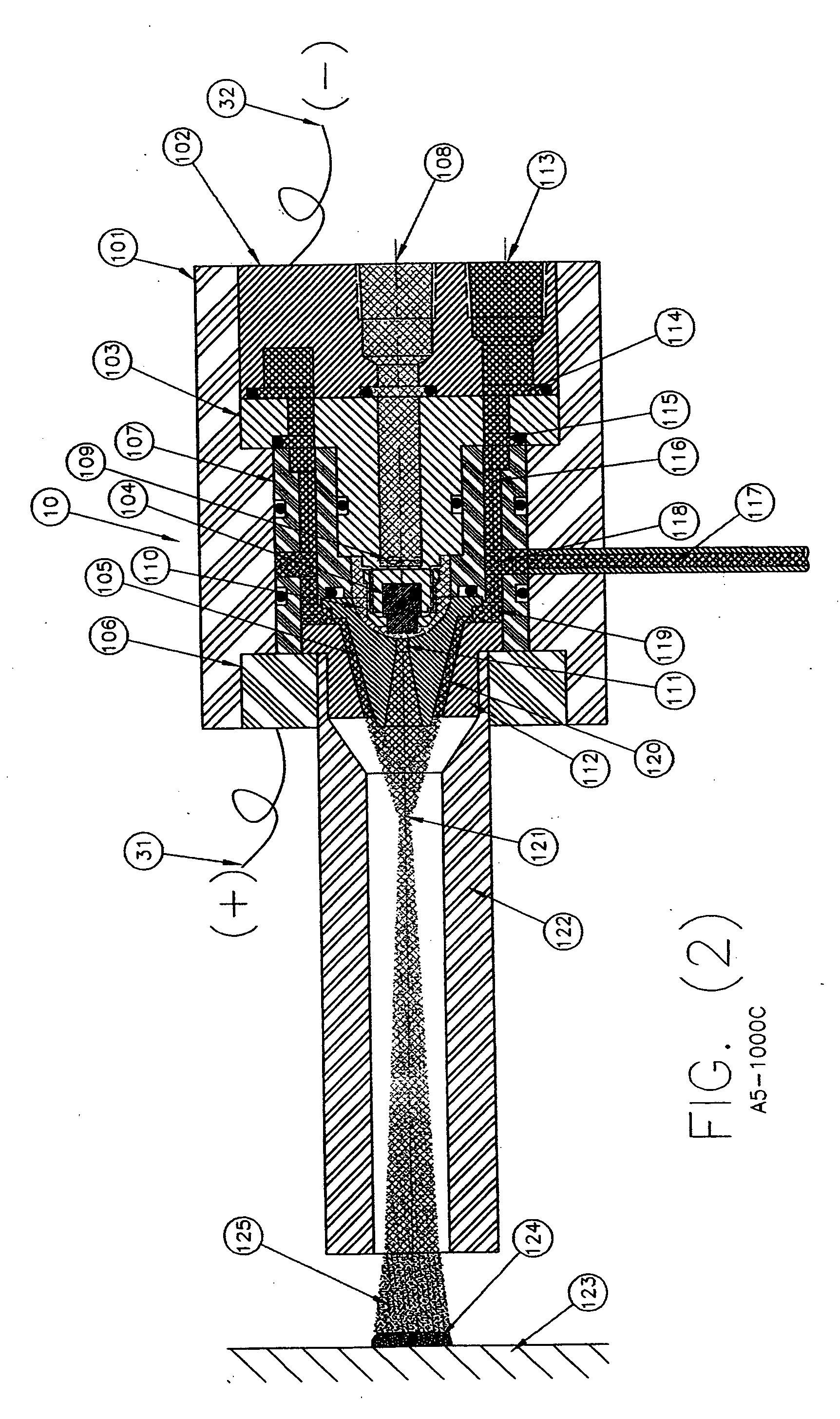
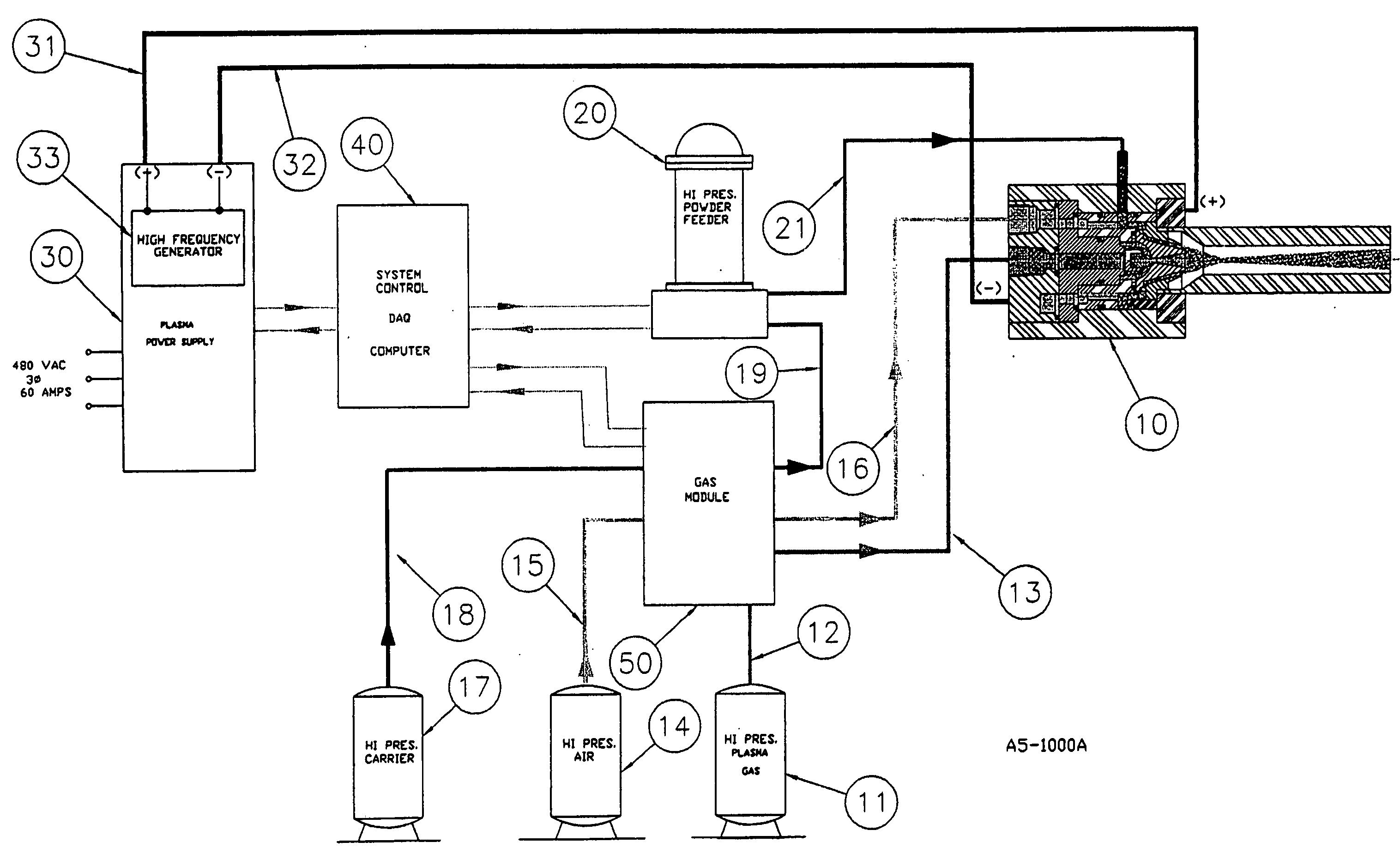
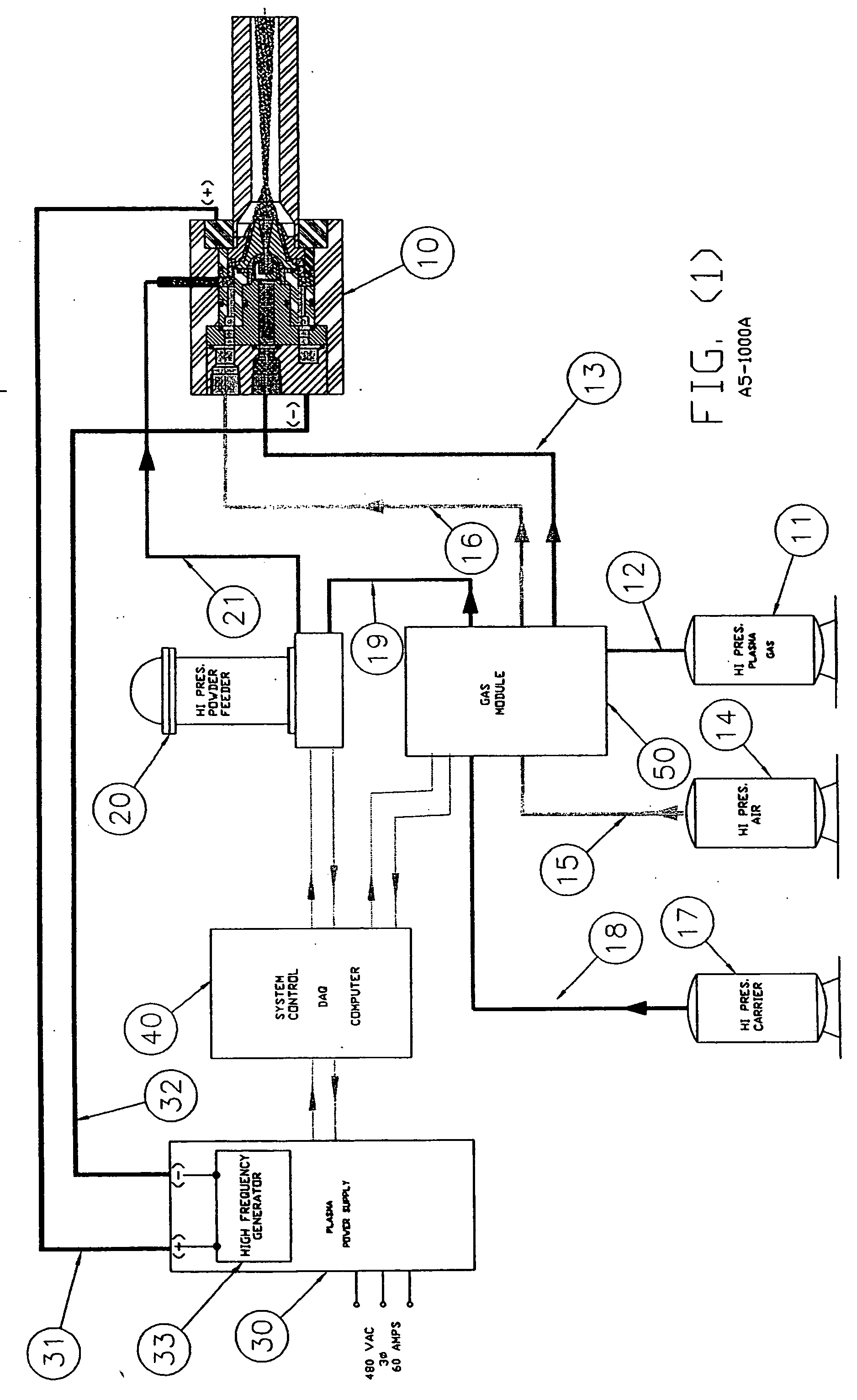
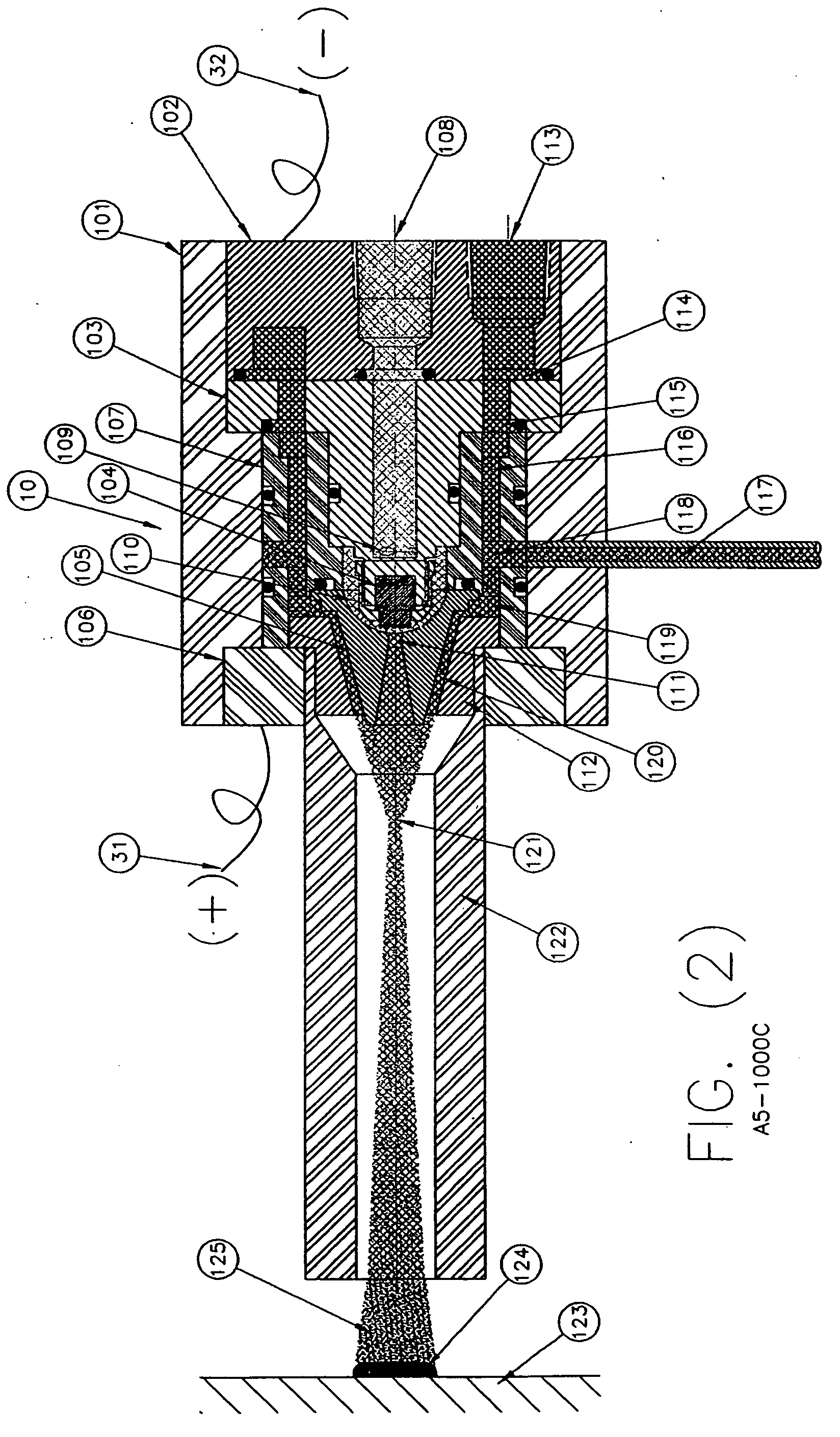
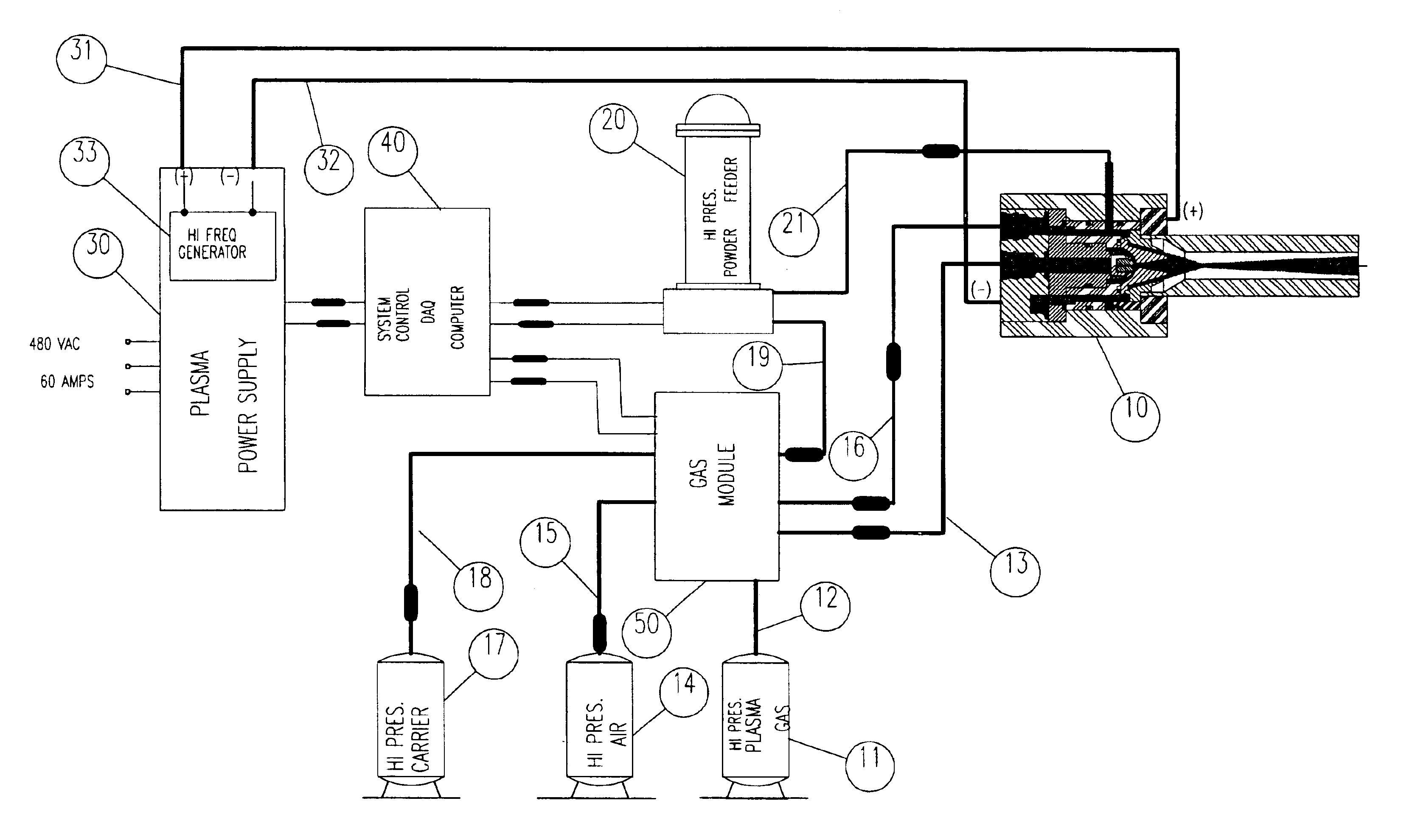
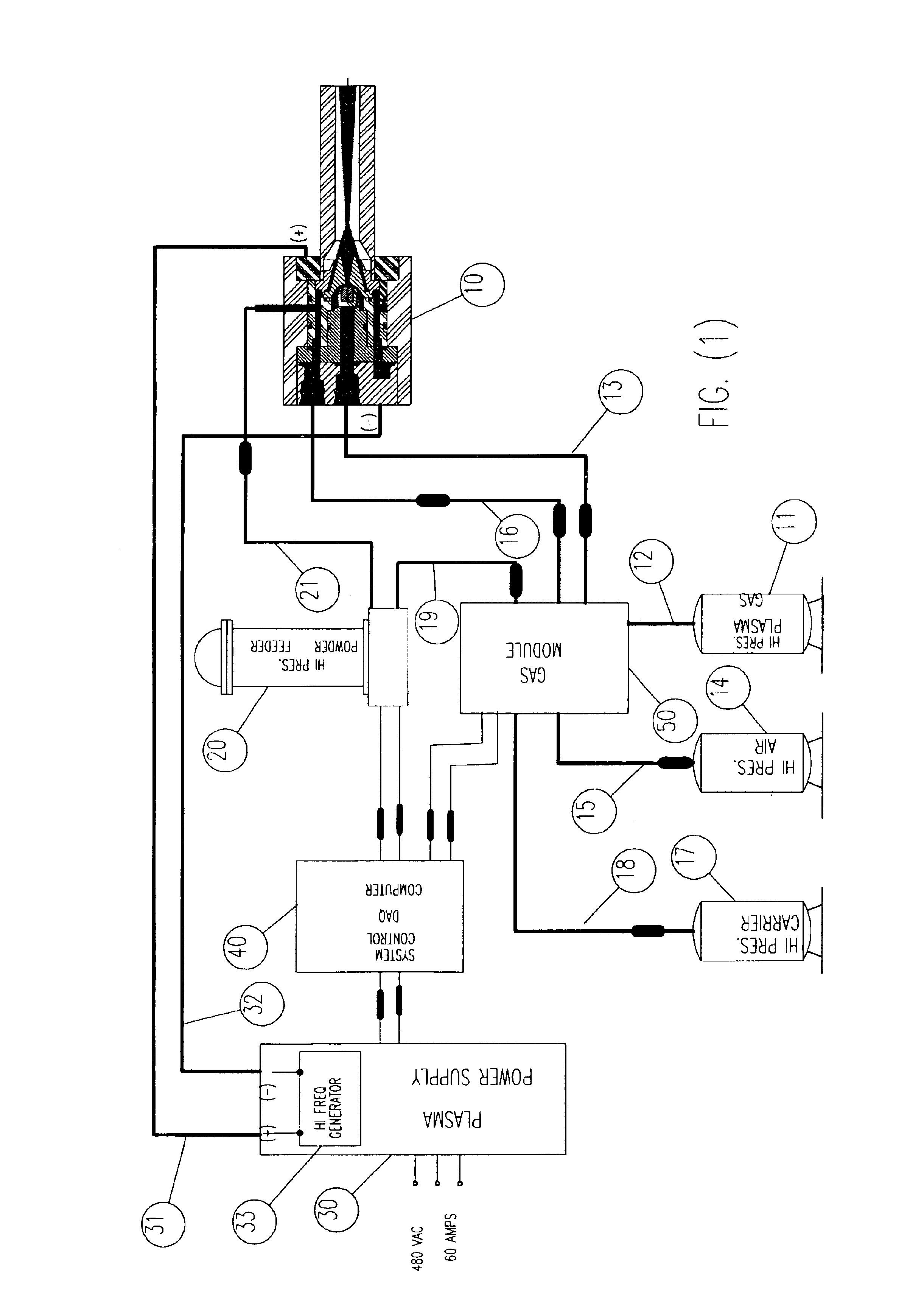
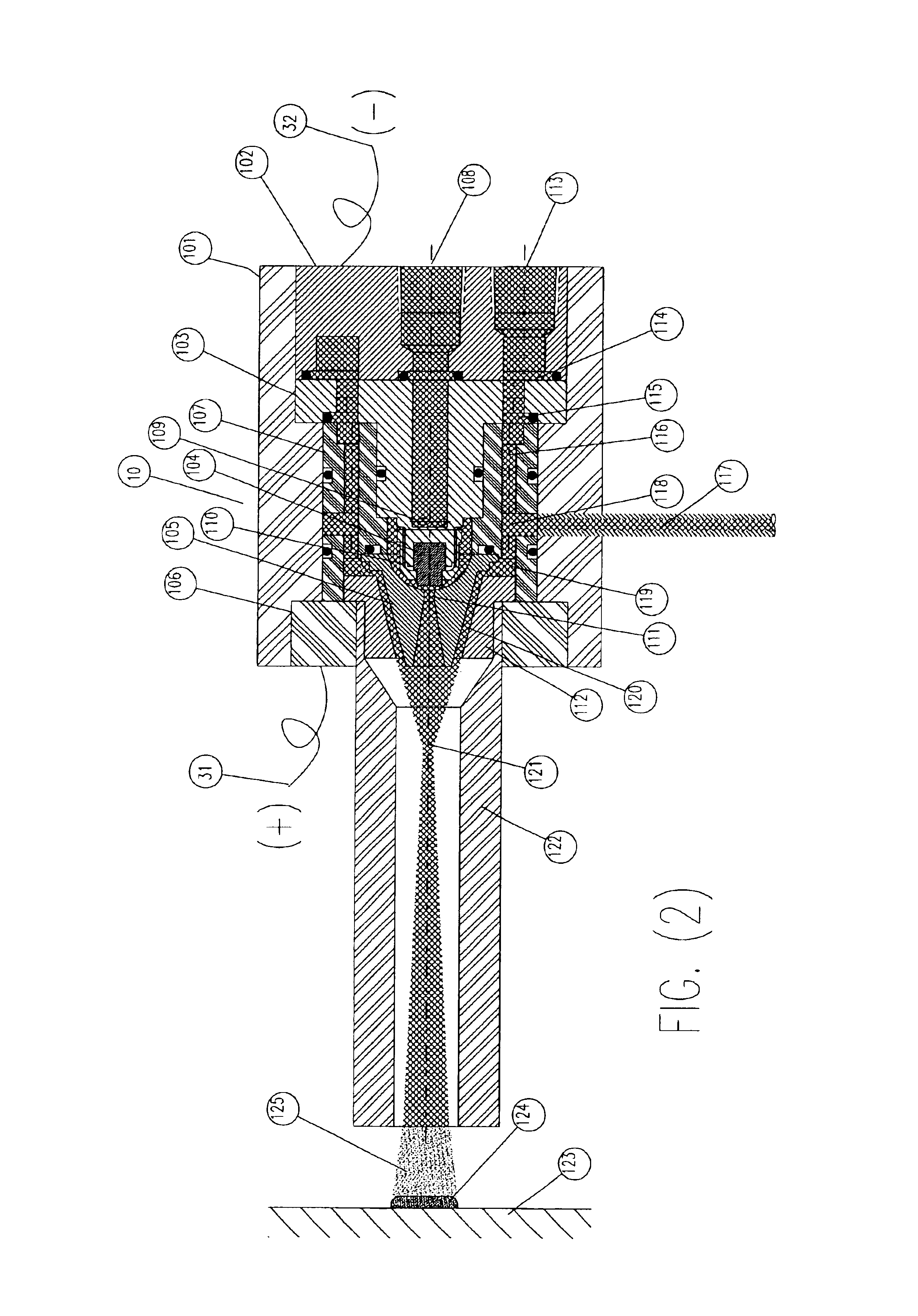
InactiveUS20050120957A1Efficient systemUniform compositionLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingPlasma generatorAlloy
A method of operation of a plasma torch and the plasma apparatus to produce a hot gas jet stream directed towards a workpiece to be coated by first injecting a cold high pressure carrier gas containing a powder material into a cold main high pressure gas flow and then directing this combined high pressure gas flow coaxially around a plasma exiting from an operating plasma generator and converging directly into the hot plasma effluent, thereby mixing with the hot plasma effluent to form a gas stream with a net temperature based on the enthalpy of the plasma stream and the temperature and volume of the cold high pressure converging gas, establishing a net temperature of the gas stream at a temperature such that the powdered material will not melt or soften, and projecting the powder particles at high velocity onto a workpiece surface. The improvement resides in mixing a cold high pressure carrier gas with powder material entrained in it, with a cold high pressure gas flow of gas prior to mixing this combined gas flow with the plasma effluent which is utilized to heat the combined gas flow to an elevated temperature limited to not exceeding the softening point or melting point of the powder material. The resulting hot high pressure gas flow is directed through a supersonic nozzle to accelerate this heated gas flow to supersonic velocities, thereby providing sufficient velocity to the particles striking the workpiece to achieve a kinetic energy transformation into elastic deformation of the particles as they impact the onto the workpiece surface and forming a dense, tightly adhering cohesive coating. Preferably the powder material is of metals, alloys, polymers and mixtures thereof or with semiconductors or ceramics and the powder material is preferably of a particle size range exceeding 50 microns.
Owner:FLAME SPRAY IND
Plasma spray method and apparatus for applying a coating utilizing particle kinetics
InactiveUS20050252450A1Efficient systemUniform compositionLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingPlasma generatorAlloy
A method of operation of a plasma torch and the plasma apparatus to produce a hot gas jet stream directed towards a workpiece to be coated by first injecting a cold high pressure carrier gas containing a powder material into a cold main high pressure gas flow and then directing this combined high pressure gas flow coaxially around a plasma exiting from an operating plasma generator and converging directly into the hot plasma effluent, thereby mixing with the hot plasma effluent to form a gas stream with a net temperature based on the enthalpy of the plasma stream and the temperature and volume of the cold high pressure converging gas, establishing a net temperature of the gas stream at a temperature such that the powdered material will not melt or soften, and projecting the powder particles at high velocity onto a workpiece surface. The improvement resides in mixing a cold high pressure carrier gas with powder material entrained in it, with a cold high pressure gas flow of gas prior to mixing this combined gas flow with the plasma effluent which is utilized to heat the combined gas flow to an elevated temperature limited to not exceeding the softening point or melting point of the powder material. The resulting hot high pressure gas flow is directed through a supersonic nozzle to accelerate this heated gas flow to supersonic velocities, thereby providing sufficient velocity to the particles striking the workpiece to achieve a kinetic energy transformation into elastic deformation of the particles as they impact the onto the workpiece surface and forming a dense, tightly adhering cohesive coating. Preferably the powder material is of metals, alloys, polymers and mixtures thereof or with semiconductors or ceramics and the powder material is preferably of a particle size range exceeding 50 microns. The system also includes a rotating member for coating concave surfaces and internal bores or other such devices which can be better coated using rotation.
Owner:FLAME SPRAY IND
Selective catalytic reduction of nox enabled by sidestream urea decomposition
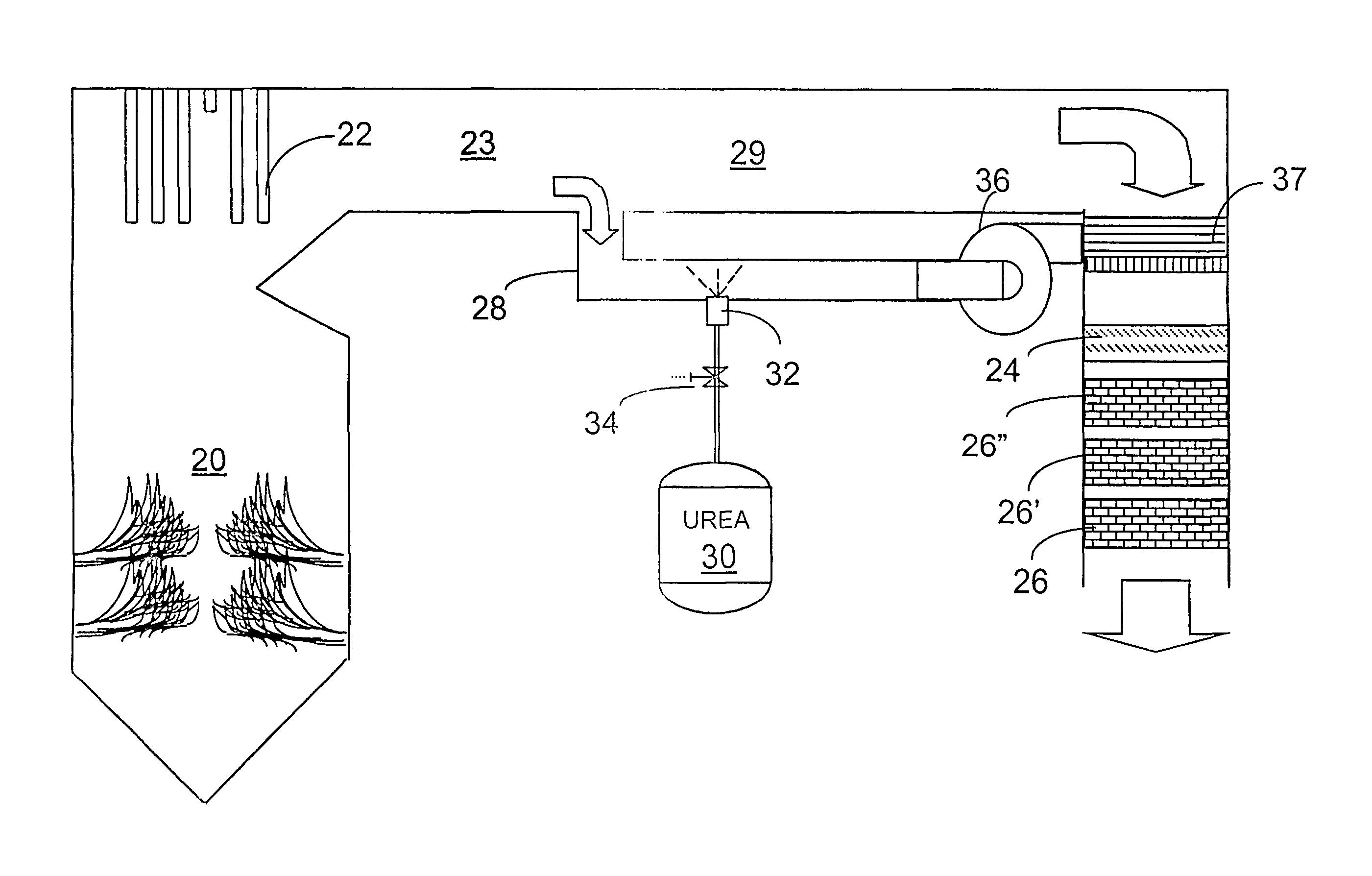
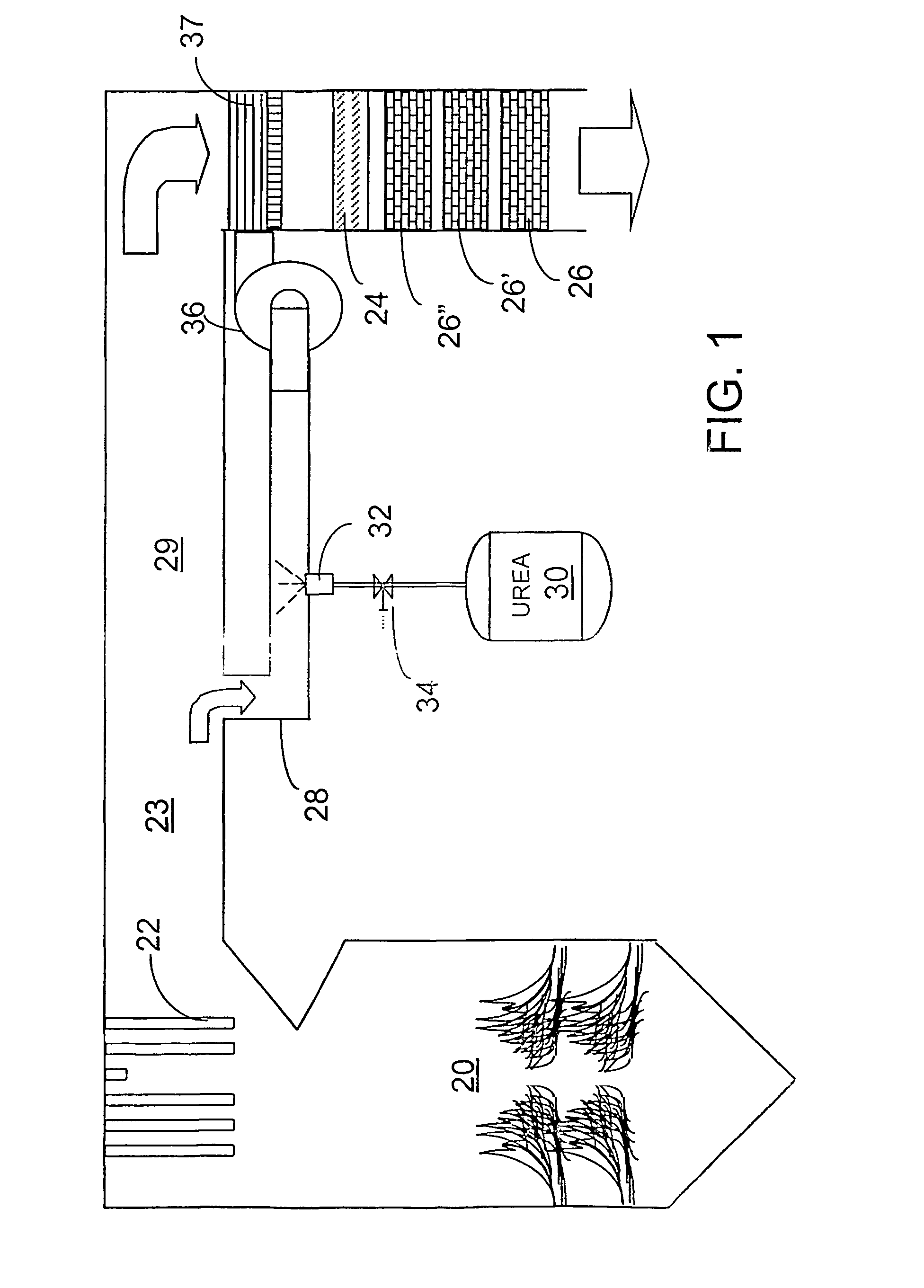
InactiveUS7090810B2Well mixedAccurate temperatureNitrogen compoundsInternal combustion piston enginesParticulatesSuperheater
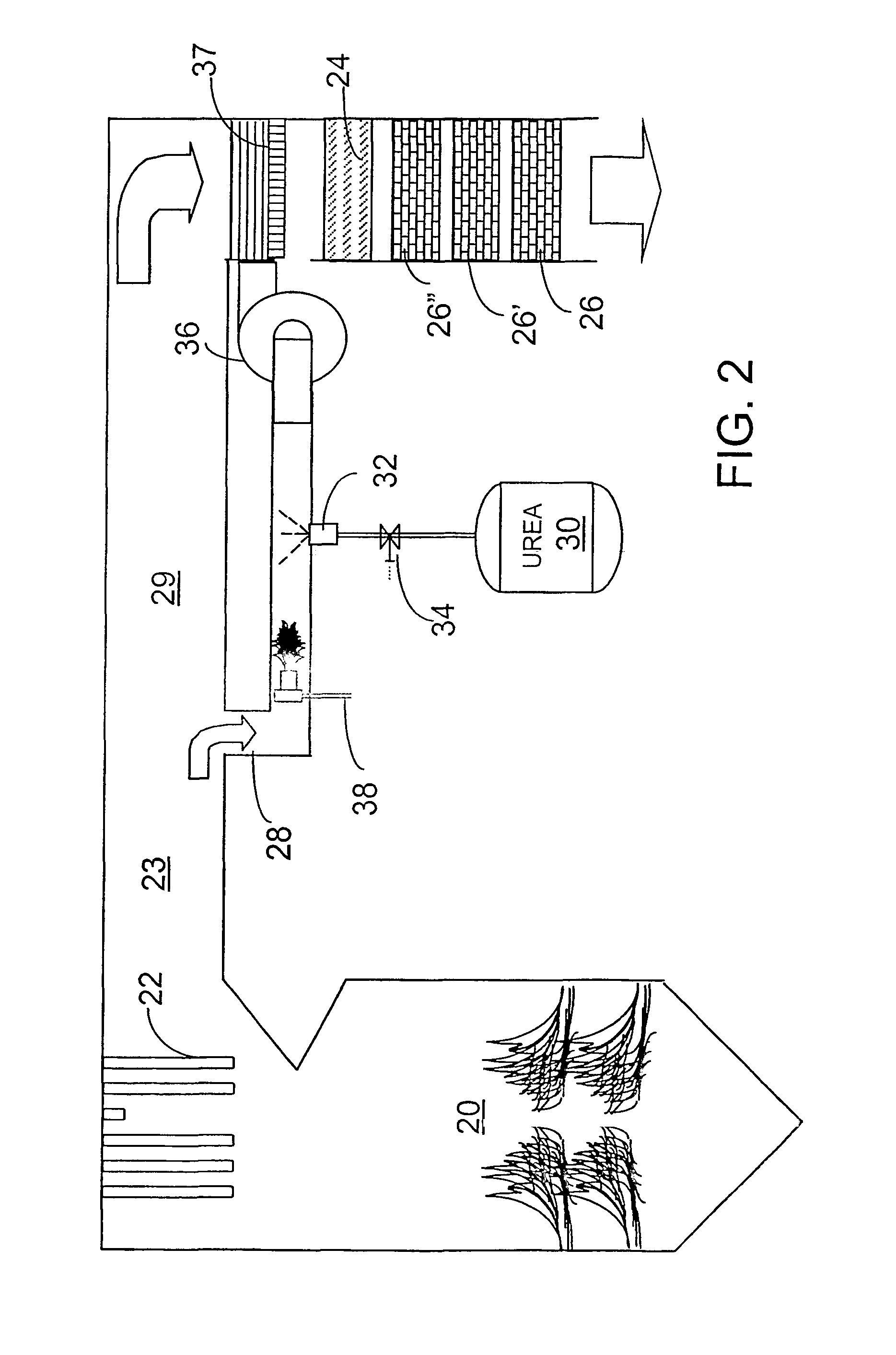
A preferred process arrangement utilizes the enthalpy of the flue gas, which can be supplemented if need be, to convert urea (30) into ammonia for SCR. Urea (30), which decomposes at temperatures above 140 ° C., is injected (32) into a flue gas stream split off (28) after a heat exchanger (22), such as a primary superheater or an economizer. Ideally, the side stream would gasify the urea without need for further heating; but, when heat is required it is far less than would be needed to heat either the entire effluent (23) or the urea (30). This side stream, typically less than 3% of the flue gas, provides the required temperature and residence time for complete decomposition of urea (30). A cyclonic separator can be used to remove particulates and completely mix the reagent and flue gas. This stream can then be directed to an injection grid (37) ahead of SCR using a blower (36). The mixing with the flue gas is facilitated due to an order of magnitude higher mass of side stream compared to that injected through the AIG in a traditional ammonia-SCR process.
Owner:FUEL TECH
High-temperature dual-source organic Rankine cycle with gas separations
InactiveUS8046999B2Increase temperatureMinimize timeAuxillary drivesFrom solar energyWorking fluidOrganic Rankine cycle
In a dual-source organic Rankine cycle (DORC), the condensed and slightly sub-cooled working fluid at near ambient temperature (˜300 K) and at low-side pressure (0.1 to 0.7 MPa) is (1) pumped to high-side pressure (0.5-5 MPa), (2) pre-heated in a low-temperature (LT) recuperator, (3) boiled using a low-grade heat source, (4) super-heated in a high-temperature (HT) recuperator to a temperature close to the expander turbine exhaust temperature using this exhaust vapor enthalpy, (5) further super-heated to the turbine inlet temperature (TIT) using a mid-grade heat source, (6) expanded through a turbine expander to the low-side pressure, (7) cooled through the HT recuperator, (8) cooled through the LT recuperator, (9) mostly liquefied and slightly subcooled in a condenser, and (10) the condensed portion is returned to the pump to repeat this cycle.
Owner:DOTY SCI
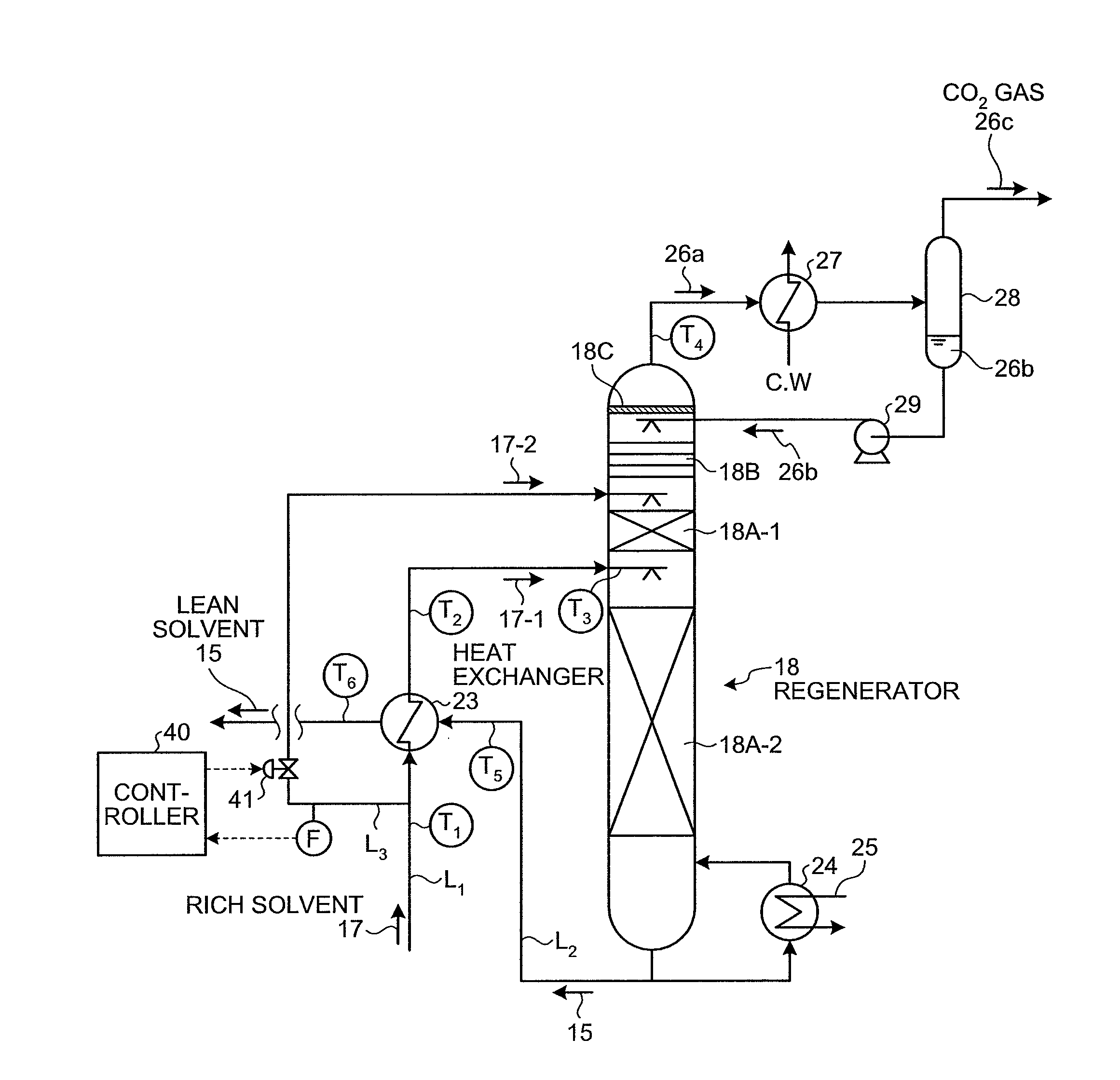
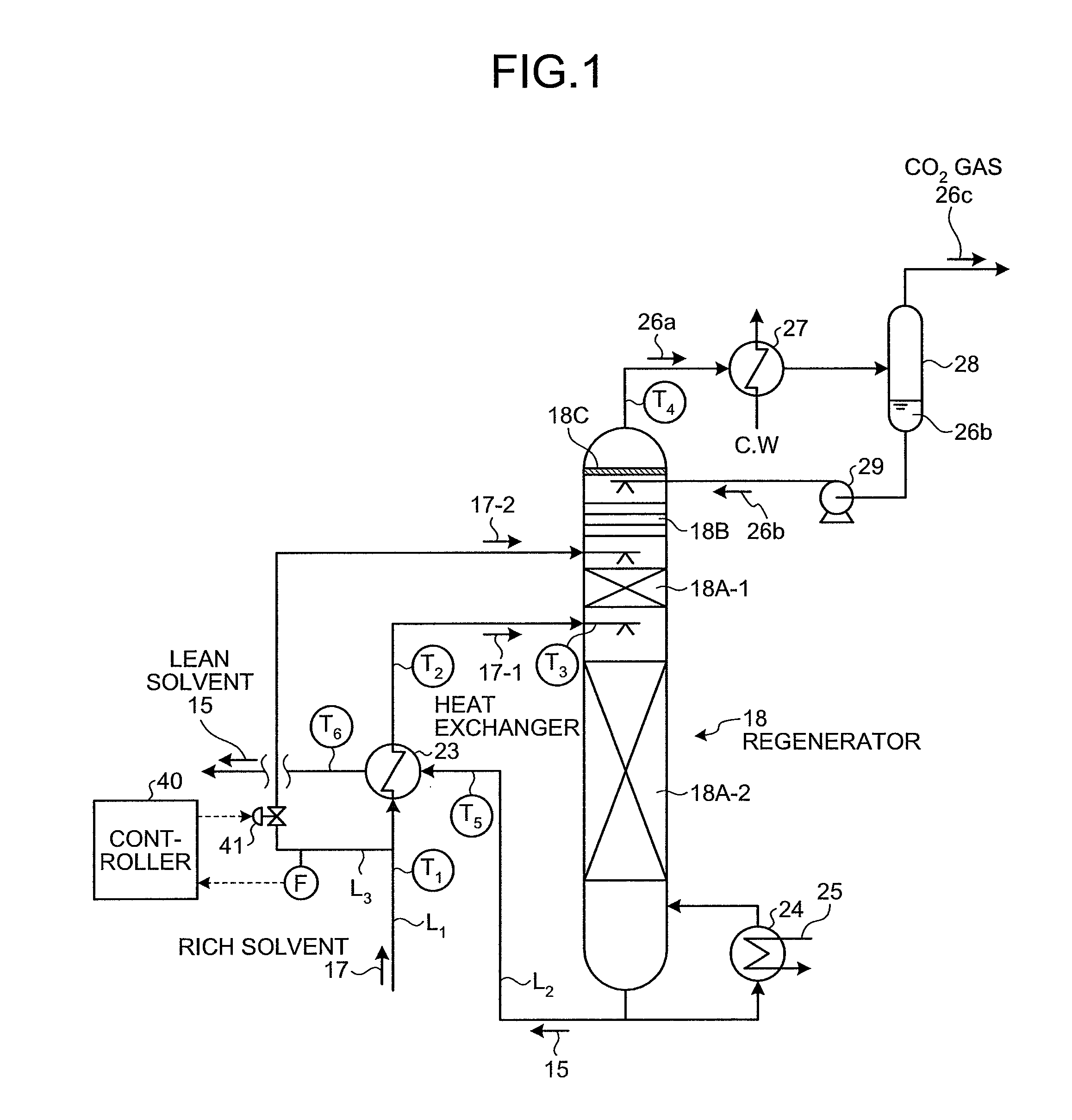
CO2 recovery apparatus and CO2 recovery method
ActiveUS8414694B2Reduce the amount requiredGas treatmentLiquid degasificationRecovery methodFlue gas
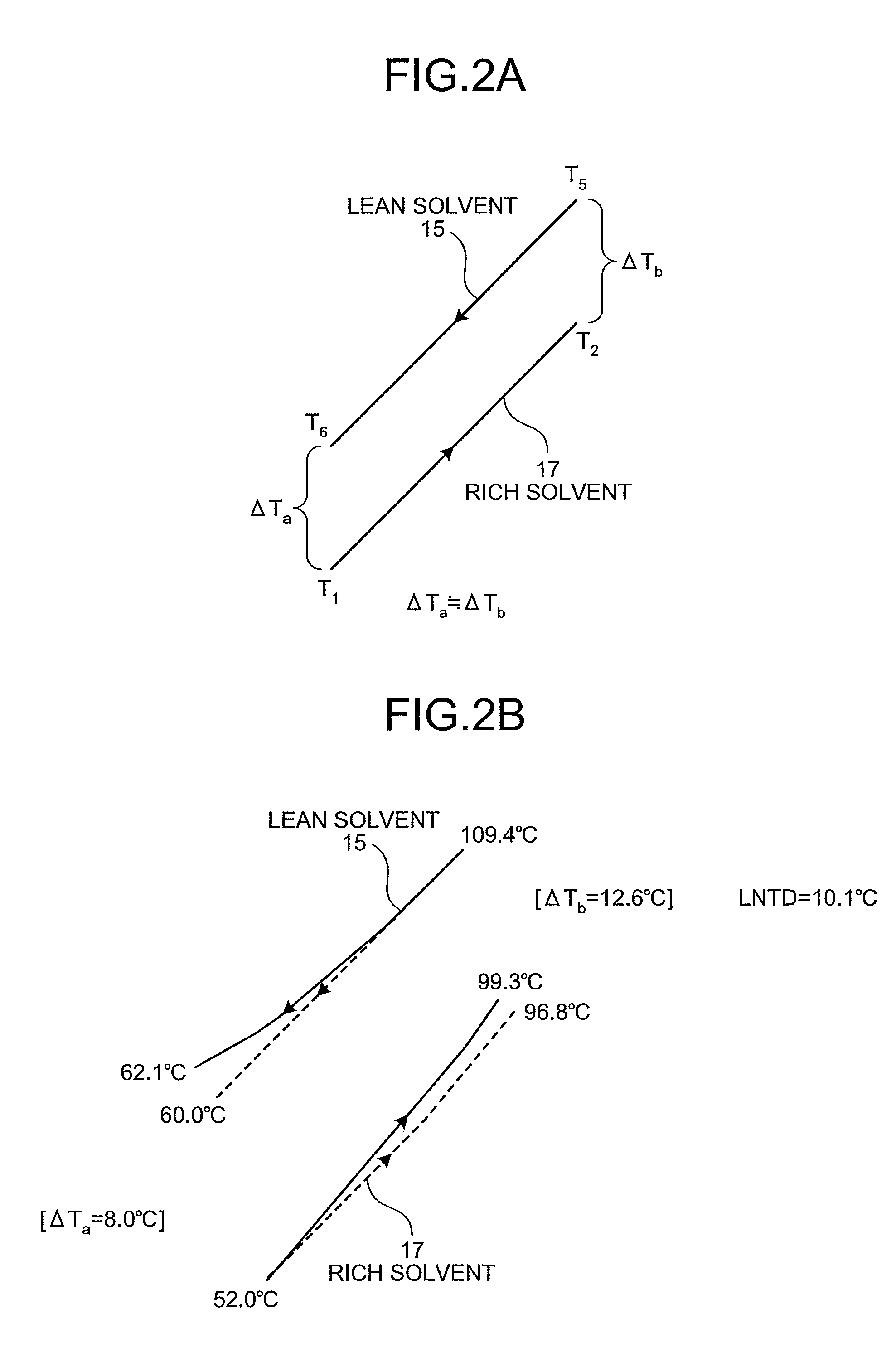
Provided are a CO2 absorber that reduces CO2 contained in flue gas; a regenerator that reduces CO2 contained in rich solvent absorbing CO2 to regenerate the rich solvent, so that lean solvent having the CO2 reduced in the regenerator is reused in the CO2 absorber; a heat exchanger that allows the rich solvent to exchange heat with the lean solvent; and a controller that controls to extract rich solvent portion that is part of the rich solvent, to allow the rich solvent portion to by pass the heat exchanger, and to be supplied into the top of the regenerator without exchanging heat so as to minimize a sum of an enthalpy that is taken out of the regenerator as CO2 gas accompanying steam and an enthalpy of the lean solvent after heat exchange with the rich solvent in the heat exchanger.
Owner:THE KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Molded article produced from aliphatic polyester resin composition
ActiveUS20050154148A1DistanceDeterioration of mechanical propertiesPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsDyeing processShell moldingPolyester resin
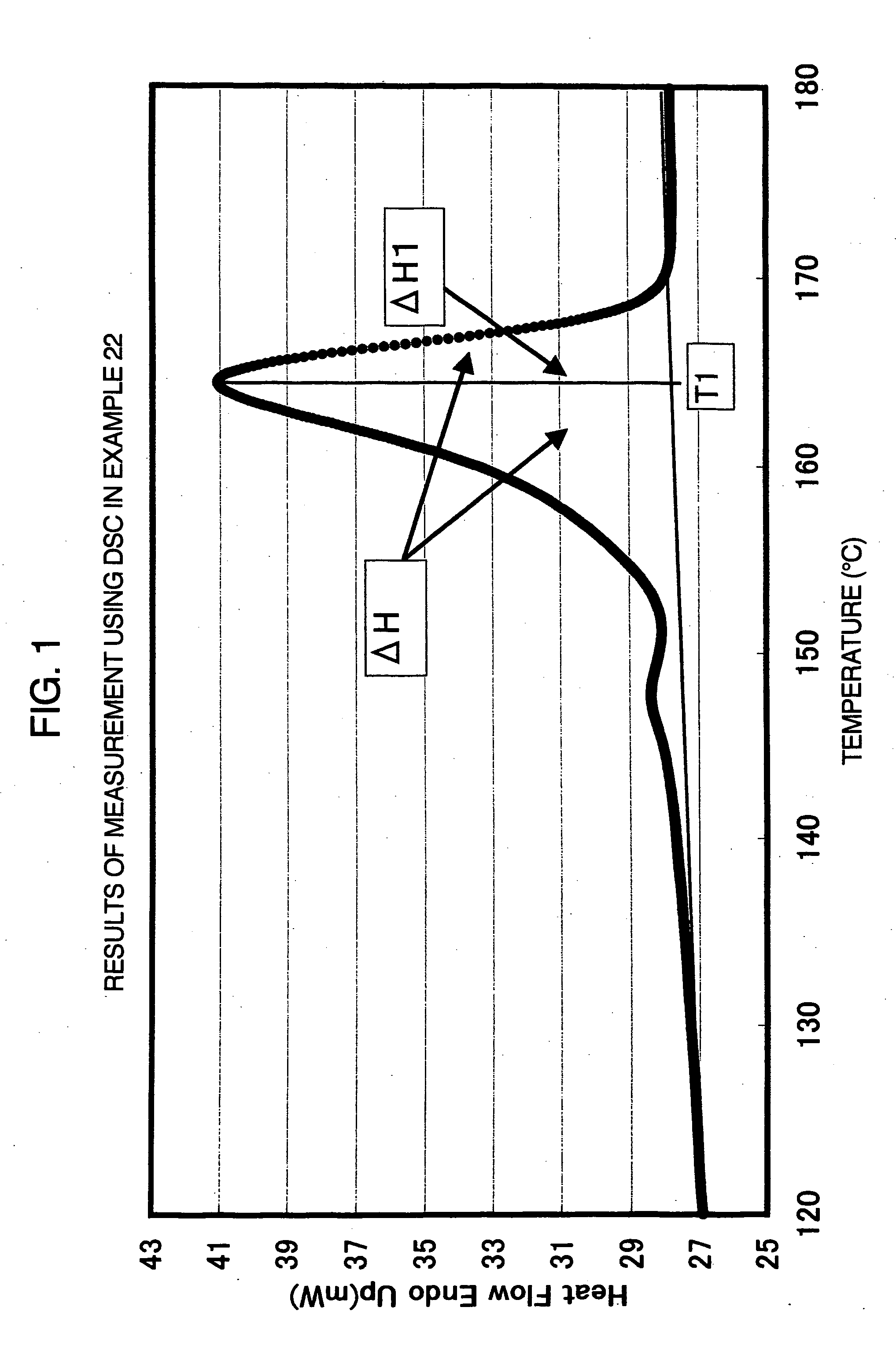
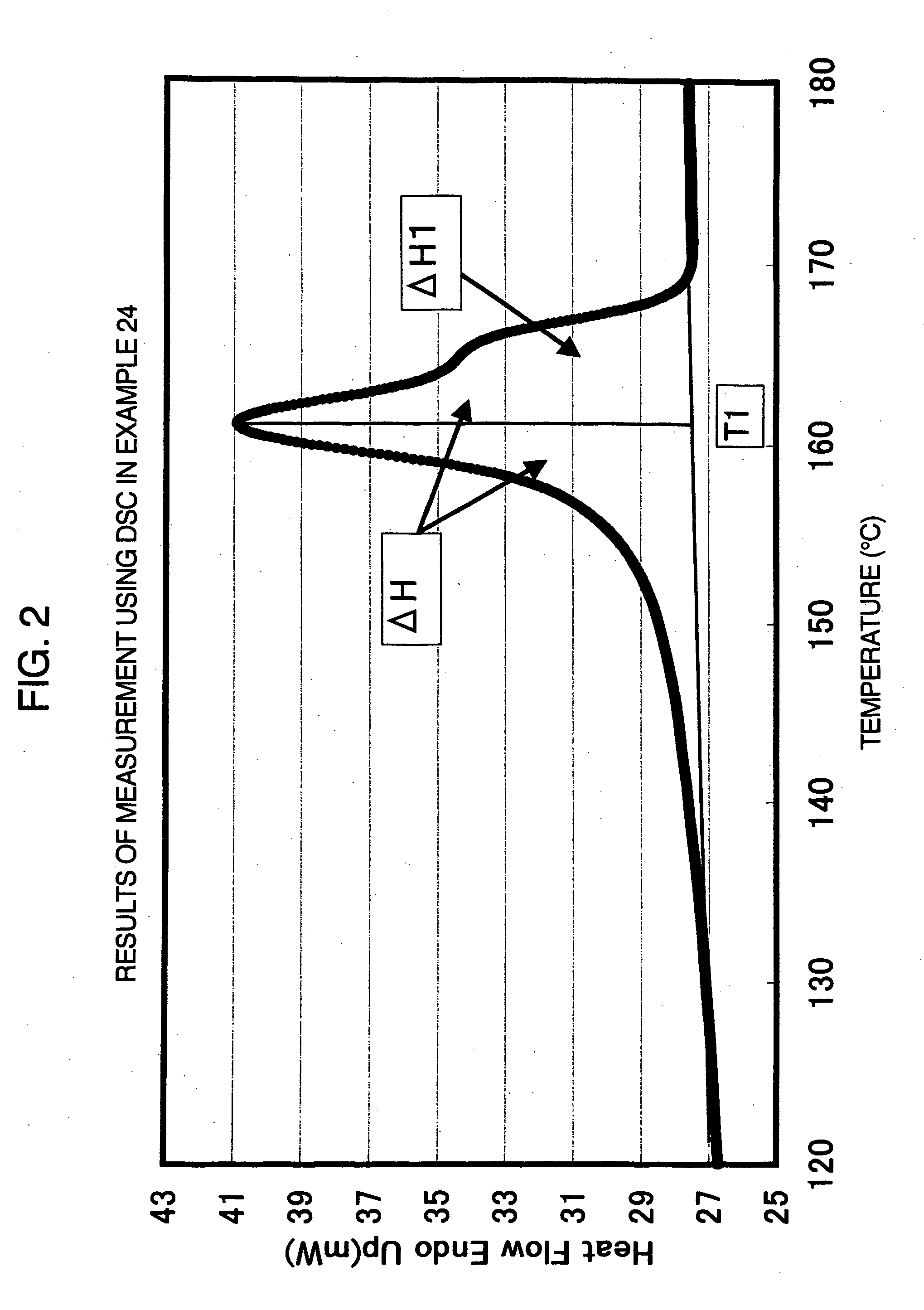
The present invention provides a molded article obtained from an aliphatic polyester resin composition comprising 60 to 99.9 parts by weight of at least one aliphatic polyester (A) and 0.1 to 40 parts by weight of at least one elastic polymer (B), provided that the total amount of the components (A) and (B) is 100 parts by weight, wherein the aliphatic polyester component in the molded article has an enthalpy of crystal fusion ΔH determined using a differential scanning calorimeter of 5 J / g or more, the molded article has a continuous phase composed of the aliphatic polyester (A) and dispersed phases composed of the elastic polymer (B), and the distance T between the walls of the dispersed phases is less than 5.0 μm.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Data center and methods for cooling thereof
InactiveUS20100136895A1Improve cooling efficiencyImprove performance efficiencyCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsIndirect heat exchangersData centerClosed loop
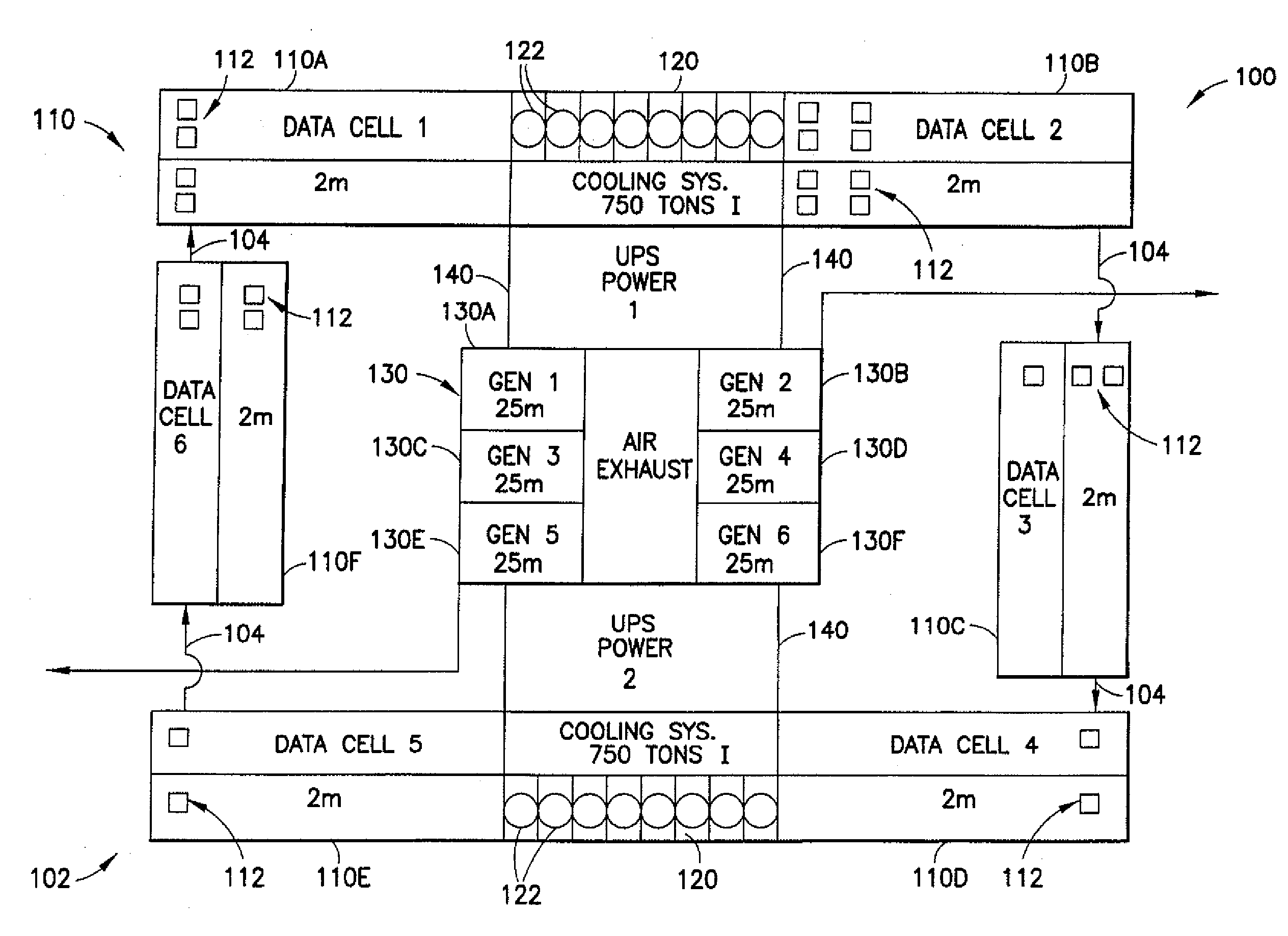
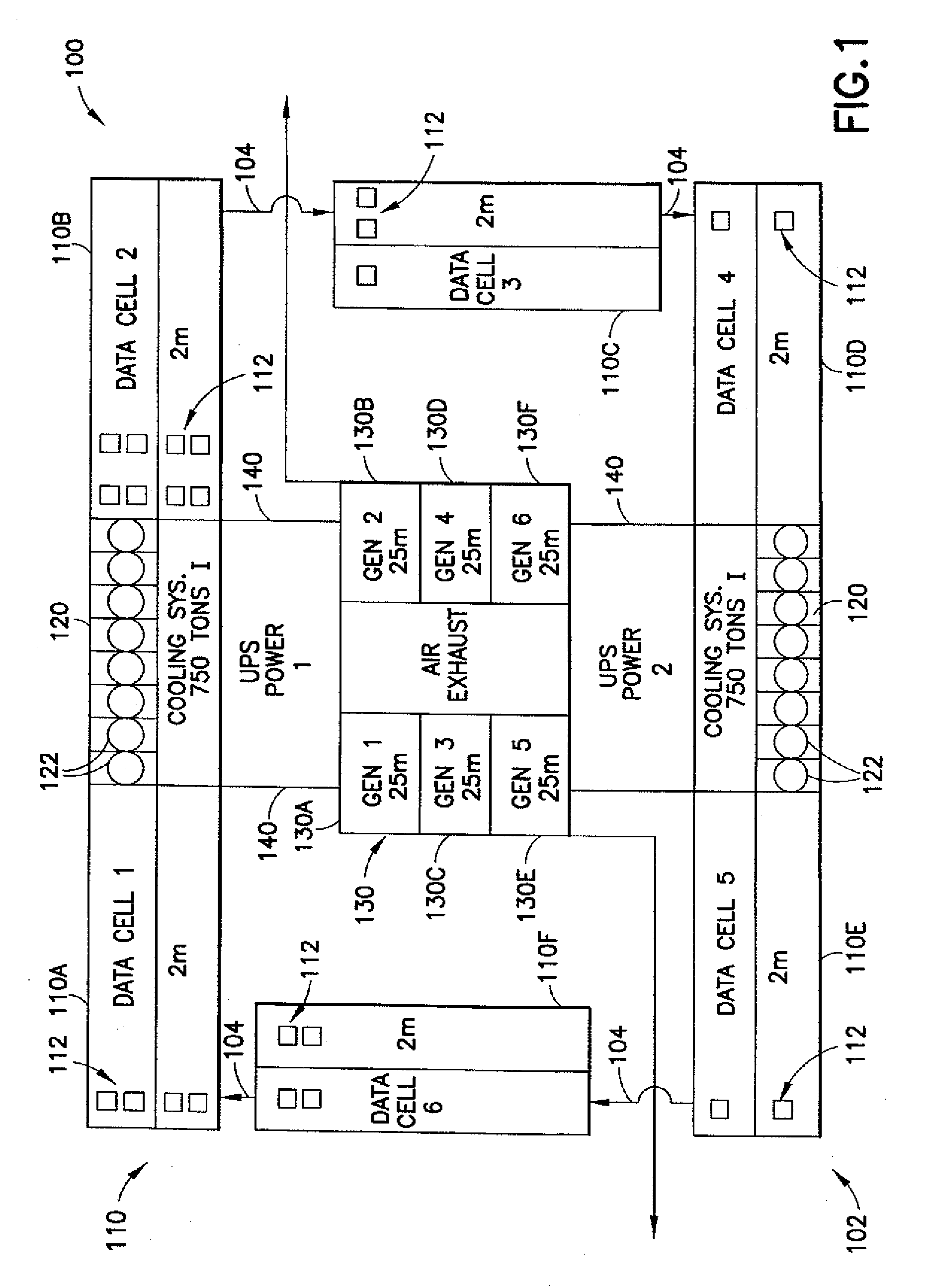
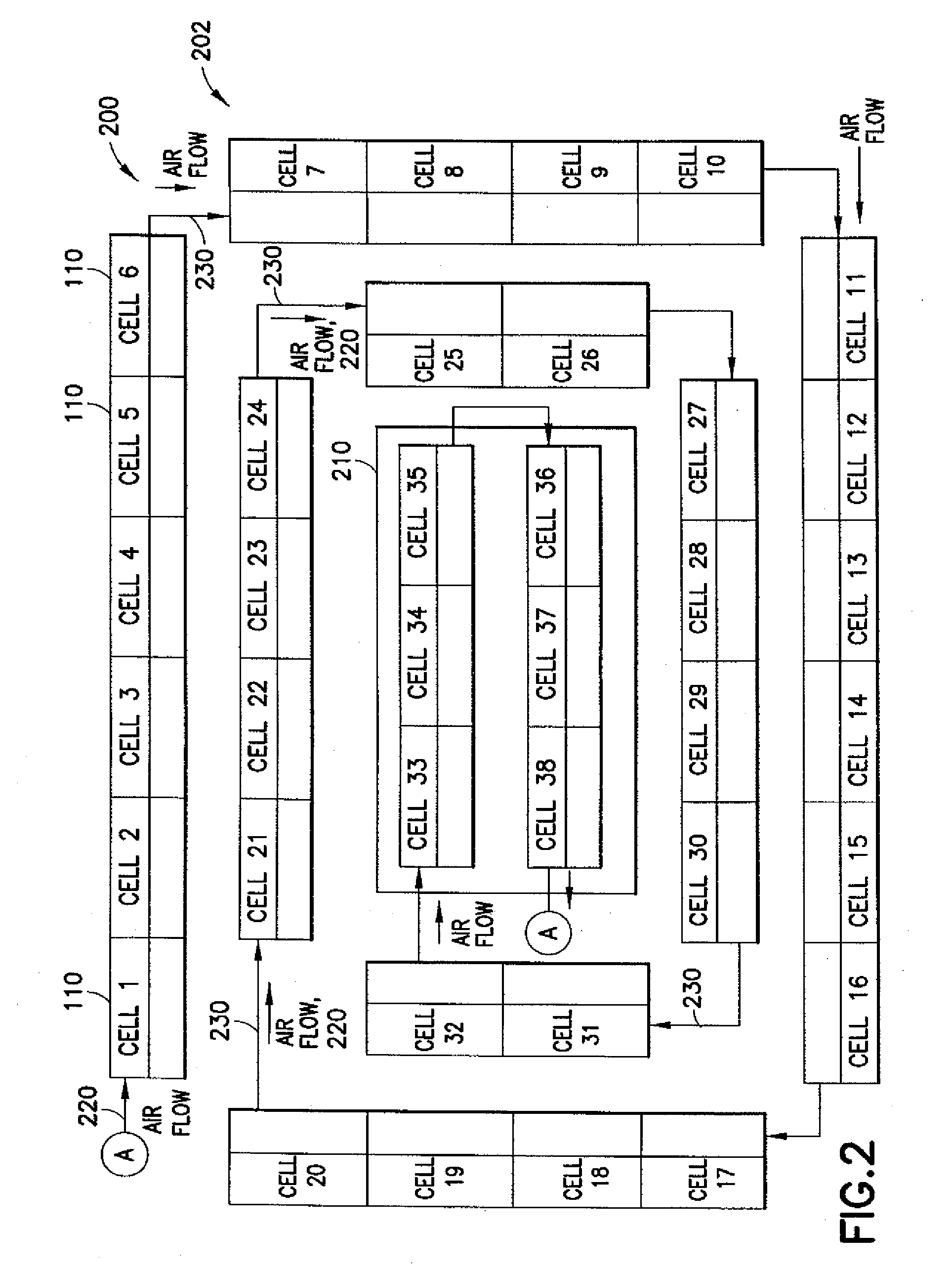
Disclosed is a data center and methods for cooling thereof. The data center includes a plurality of data cells. Each data cell included a first heat exchanger, a first set of equipment racks, a second heat exchanger, a second set of equipment racks, and a plurality of fans operable to establish a substantially horizontal and vertical air flow through the heat exchangers and the equipment racks. The data center includes a plurality of mixed air chambers. One air chamber is located between two data cells to form a substantially continuous, closed-loop air flow through the cells and chambers. The air chambers include an outside air intake for drawing ambient air into the closed loop air flow based on a comparison of enthalpy of the closed loop air and the ambient air.
Owner:TURNER LOGISTICS
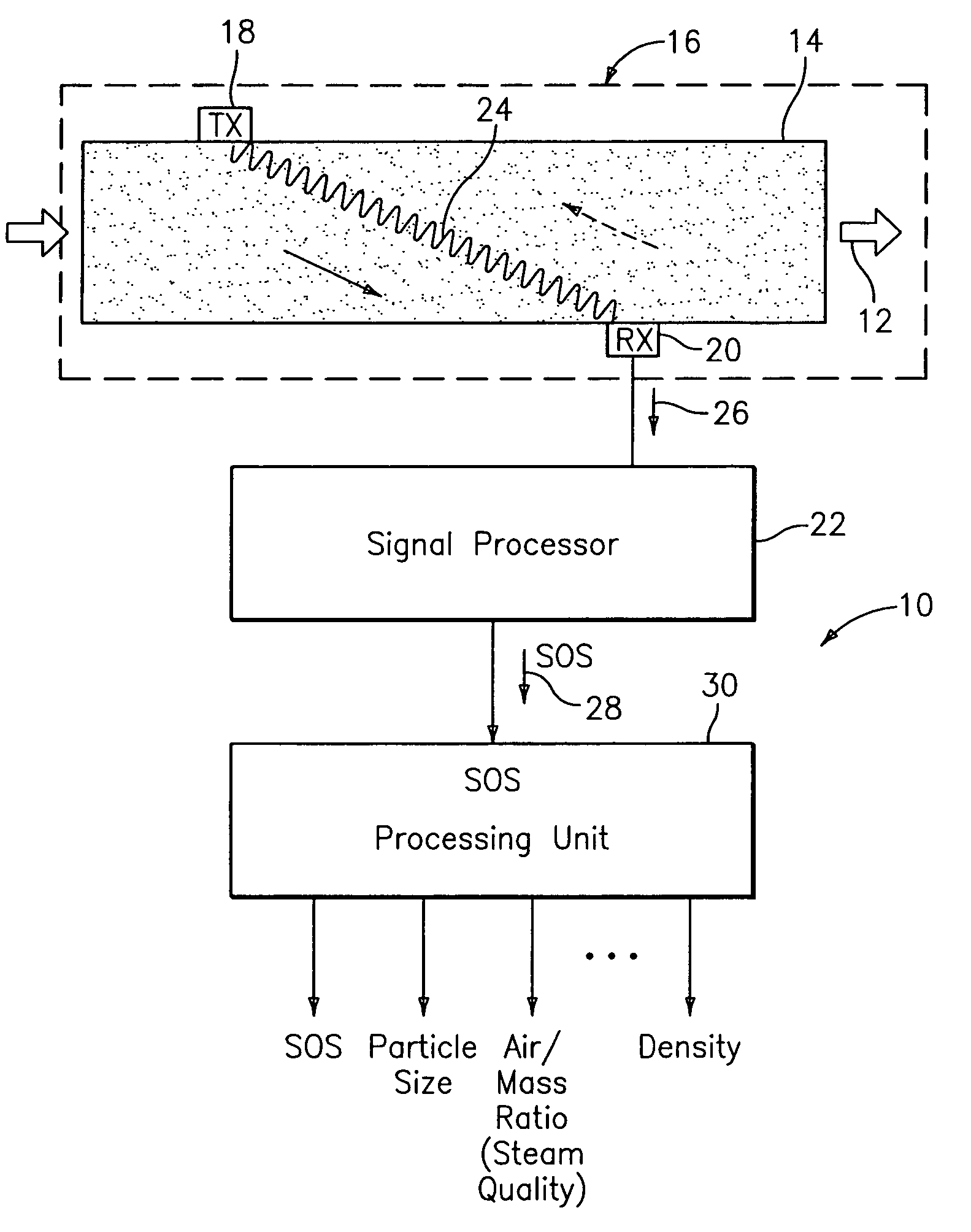
Probe for measuring parameters of a flowing fluid and/or multiphase mixture
A probe 10,170 is provided that measures the speed of sound and / or vortical disturbances propagating in a single phase fluid flow and / or multiphase mixture to determine parameters, such as mixture quality, particle size, vapor / mass ratio, liquid / vapor ratio, mass flow rate, enthalpy and volumetric flow rate of the flow in a pipe or unconfined space, for example, using acoustic and / or dynamic pressures. The probe includes a spatial array of unsteady pressure sensors 15-18 placed at predetermined axial locations x1-xN disposed axially along a tube 14. For measuring at least one parameter of a saturated vapor / liquid mixture 12, such as steam, flowing in the tube 14. The pressure sensors 15-18 provide acoustic pressure signals P1(t)-PN(t) to a signal processing unit 30 which determines the speed of sound amix propagating through of the saturated vapor / liquid mixture 12 in the tube 14 using acoustic spatial array signal processing techniques. Frequency based sound speed is determined utilizing a dispersion model to determine the parameters of interest.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Nano cellulose solid-solid phase transition material and its preparing method
InactiveCN1710012ASimple manufacturing processNo phase separationHeat-exchange elementsPolyethylene glycolFunction group
The invention relates to a kind of nano cellulose solid - solid phrase change material and its producing method. Its characteristics are: in non-homogeneous phase system, according to the reactants proportions as polyethylene glycol containing active group at one end or both ends 19.8% - 82.0%, crosslinking agent 0% - 55.1% and nanometer cellulose or its ramification 4.0% - 69.5%, ingraft the polyethylene glycol containing active group at one end or both ends as energy storing function group onto nanometer cellulose or its ramification framework material. The biggest enthalpy of phase change of the nanometer cellulose solid - solid phrase change material of the invention can get to over 110 J / g, the phrase change temperature is 0 - 60 Deg. C, and can keep good solid state before and after the phrase change. It won't occur phrase separation, besides it is non-toxic and harmless, low cost, simple producing technics.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Plasma spray method for applying a coating utilizing particle kinetics
InactiveUS6861101B1Efficient systemUniform compositionLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingPlasma generatorHigh pressure
A method of operation of a plasma torch. A cold high pressure carrier gas containing a powder material is injected into a cold main high pressure gas flow and then this combined flow is directed coaxially around a plasma exiting from an operating plasma generator and converging into the hot plasma effluent, mixing with the effluent to form a gas stream with a net temperature, based on the enthalpy of the plasma stream and the temperature and volume of the cold high pressure converging gas, such that the powdered material will not melt. The combined flow with entrained is directed through a supersonic nozzle accelerating the flow to supersonic velocites sufficient that the particles striking the workpiece achieve kinetic energy transformation into elastic deformation of the particles as they impact the workpiece forming a cohesive coating.
Owner:FLAME SPRAY IND
Chemical etching, cleaning and drying method of single-crystal silicon solar battery and integrated processing machine
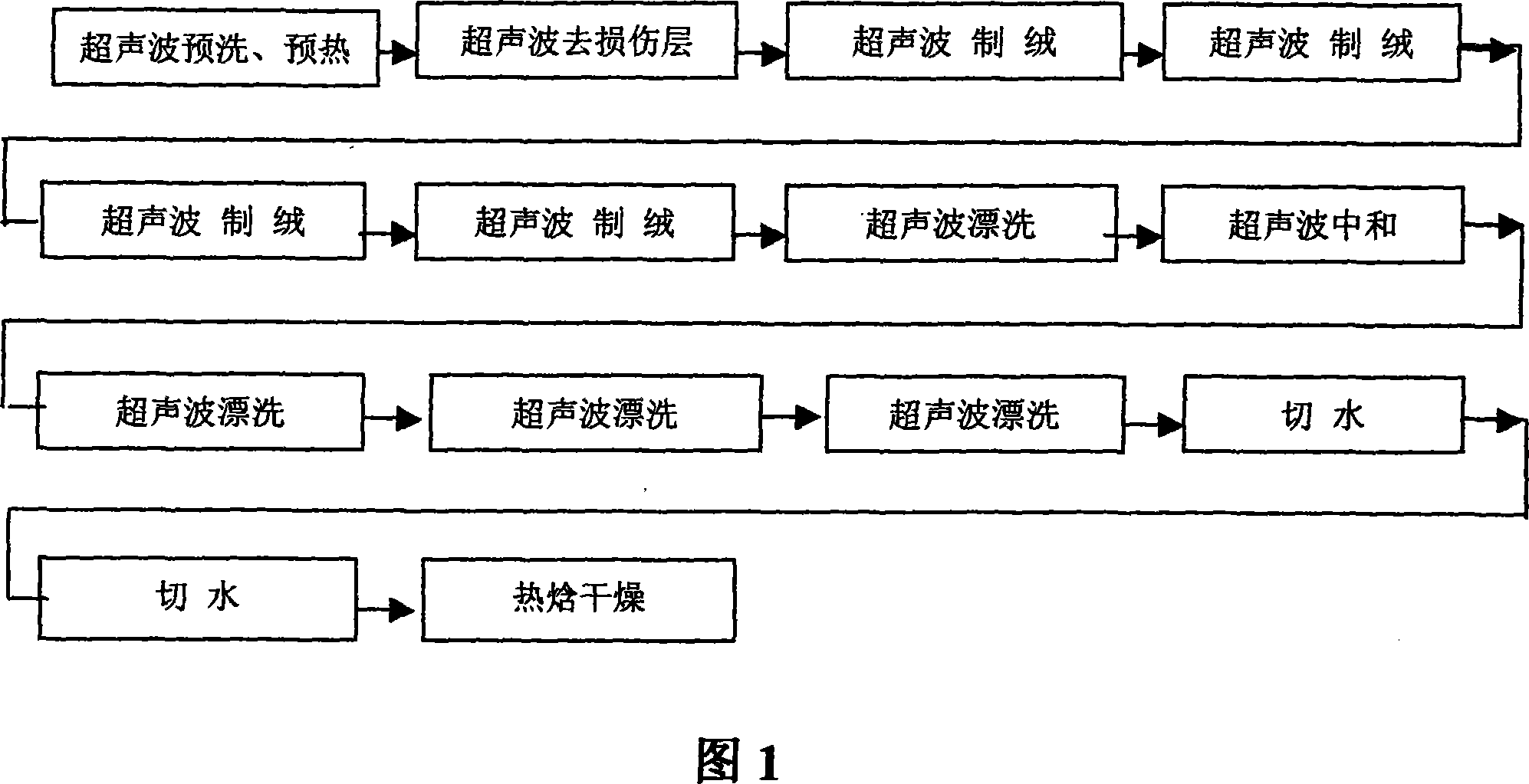
InactiveCN101087007AImprove reflective effectAvoid secondary pollutionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesEtchingWater source
Monocrystalline silicon solaode chemical etching, washing, drying method and integral processor belong to technique field of chemical etching technique and washing. It characterized in that it not only includes water, acid, alkali, but also ultrasonic participates in etching and washing course: it includes following steps: (1) ultrasonic washes and heats in advance, (2) ultrasonic removes damnification layer, (3) ultrasonic makes herbs into wool, (4) ultrasonic rinses, (5) washing with acid to counteract, (6) ultrasonic rinses, (7) cutting water, (8) hot enthalpy to dry. Positive effects of the invention are: adopting ultrasonic to etch and wash, liquid of making wool can be acted with silicon piece, similar coarseness degree can be generated on surface, perfect pyramid pattern can be obtained; it also eliminates kalium, natrium ion from alkalescent solution, and extends service life of silicon piece; pollution can be decreased, energy consumption and water source can be saved greatly, it is a practical invention.
Owner:SHANGHAI MINGXING KAICHENG ULTRASONIC TECH +2
Heat engine and heat to electricity systems and methods
ActiveUS20100156112A1Efficiently and effectively produce powerFluid heatersInternal combustion piston enginesThermal energyWorking fluid
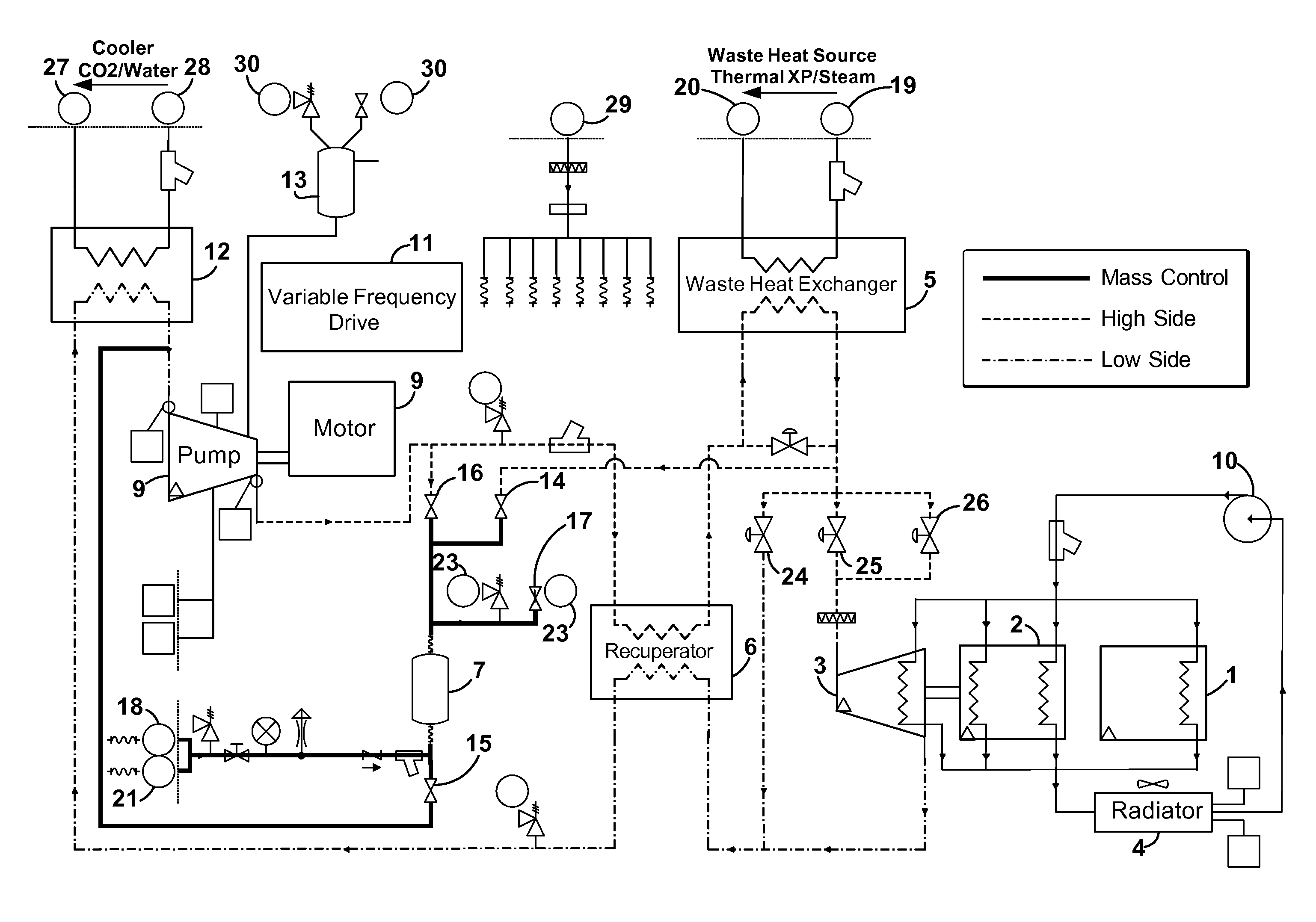
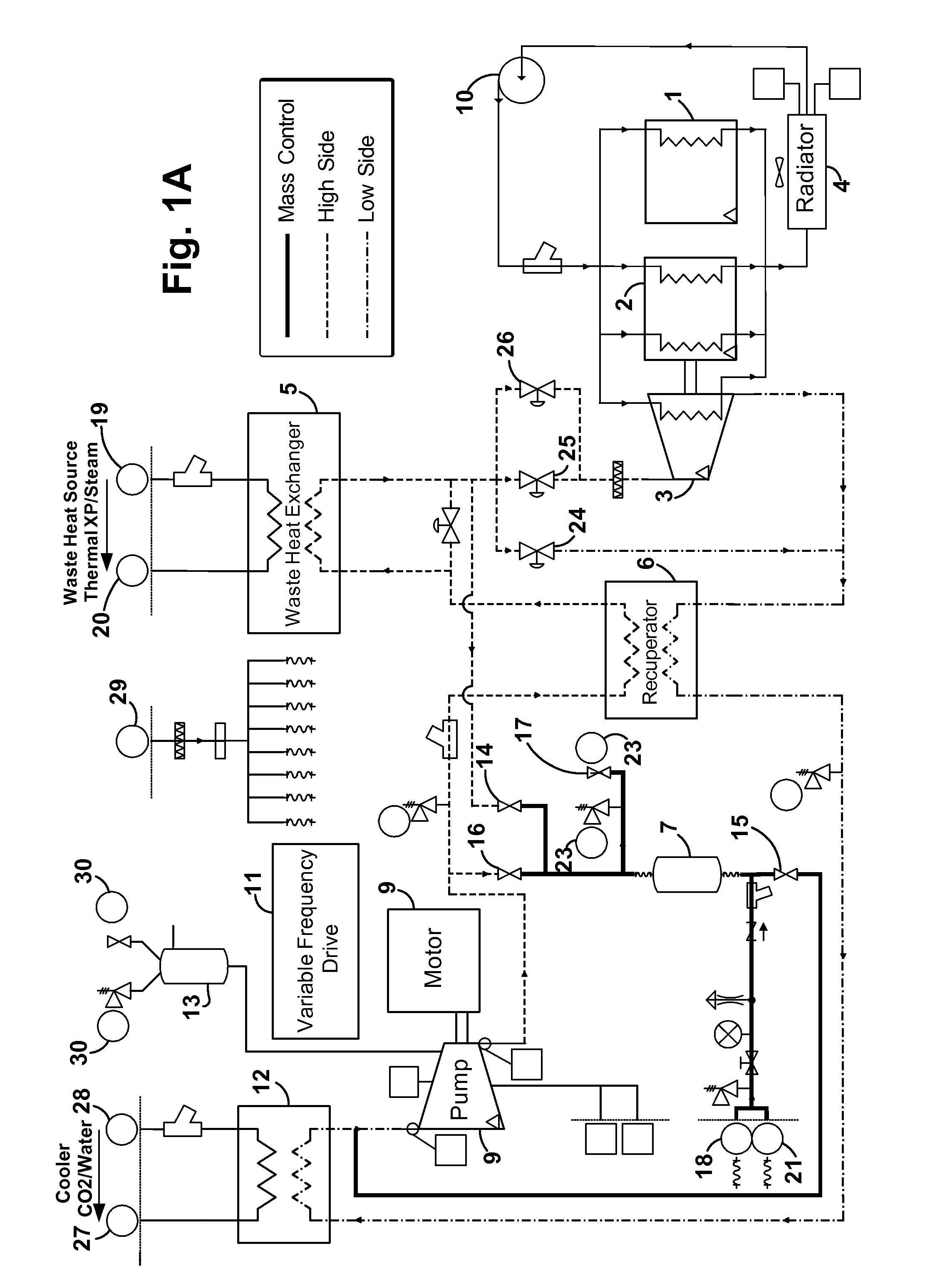
A waste heat recovery system, method and device executes a thermodynamic cycle using a working fluid in a working fluid circuit which has a high pressure side and a low pressure side. Components of the system in the working fluid circuit include a waste heat exchanger in thermal communication with a waste heat source also connected to the working fluid circuit, whereby thermal energy is transferred from the waste heat source to the working fluid in the working fluid circuit, an expander located between the high pressure side and the low pressure side of the working fluid circuit, the expander operative to convert a pressure / enthalpy drop in the working fluid to mechanical energy, a recuperator in the working fluid circuit operative to transfer thermal energy between the high pressure side and the low pressure side of the working fluid circuit, a cooler in thermal communication with the low pressure side of the working fluid circuit operative to control temperature of the working fluid in the low side of the working fluid circuit, a pump in the working fluid circuit and connected to the low pressure side and to the high pressure side of the working fluid circuit and operative to move the working fluid through the working fluid circuit, and a mass management system connected to the working fluid circuit, the mass management system, method and device having a working fluid vessel connected to the low pressure side of the working fluid circuit and configured to passively control an amount of working fluid mass in the working fluid circuit.
Owner:REXORCE THERMIONICS INC +1
Method for detecting changes in a first flux of a heat or cold transport medium in a refrigeration system
InactiveUS20050172647A1Ease of evaluationEasy to monitorSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsSpace heating and ventilation control systemsTransport mediumEngineering
The invention concerns a method for detecting changes in a first flow of a heating or cooling medium in a refrigeration system whereby the first flow is conveyed through a heat exchanger wherein occurs heat transfer from the first flow to a second flow of a heating or cooling medium. The earliest possible detection of the changes is desired. For this it is provided that for the supervision of the first media flow moving through the heat exchanger a change in the enthalpy of the second media stream or a value derived therefrom is determined.
Owner:DANFOSS AS
Stretch blow molded container and production process thereof
InactiveUS6159416AImprove barrier propertiesHigh mechanical strengthBottlesRefuse receptaclesShear rateVolumetric Mass Density
The invention provides a stretch blow molded container formed from a thermoplastic resin material which comprises polyglycolic acid having (a) a repeating unit represented by the following formula (1): (b) a melt viscosity, eta * [as measured at a temperature of (the melting point, Tm of the polymer+20 DEG C.) and a shear rate of 100 / sec] of 500-100,000 Pa.s; (c) a melting point, Tm of at least 180 DEG C.; (d) a melt enthalpy, DELTA Hm of at least 20 J / g; and (e) a density of at least 1.50 g / cm3 as measured in an unoriented, crystallized form, wherein the stretch blow molded container has tensile strength (in a circumferential direction) of at least 100 MPa and a carbon dioxide permeability (as measured at a temperature of 23 DEG C. and 80% relative humidity; in terms of the thickness of 50 mu m) of 300 cc / m2.day.atm or smaller at the body sidewall thereof, and a production process thereof.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Ejector cycle system with critical refrigerant pressure
InactiveUS20010025499A1Recover energyReduce power consumptionCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEvaporators/condensersEngineeringPressure difference
In an ejector cycle system using carbon dioxide as refrigerant, an ejector decompresses and expands refrigerant from a radiator to suck gas refrigerant evaporated in an evaporator, and converts an expansion energy to a pressure energy to increase a refrigerant pressure to be sucked into a compressor. Because refrigerant is decompressed and expanded in a super-critical area, a pressure difference during the decompression operation becomes larger, and a specific enthalpy difference becomes larger. Accordingly, energy converting efficiency in the ejector becomes higher, and efficiency of the ejector cycle system is improved.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Laminates comprising ionomer interlayers with low haze and high moisture resistance
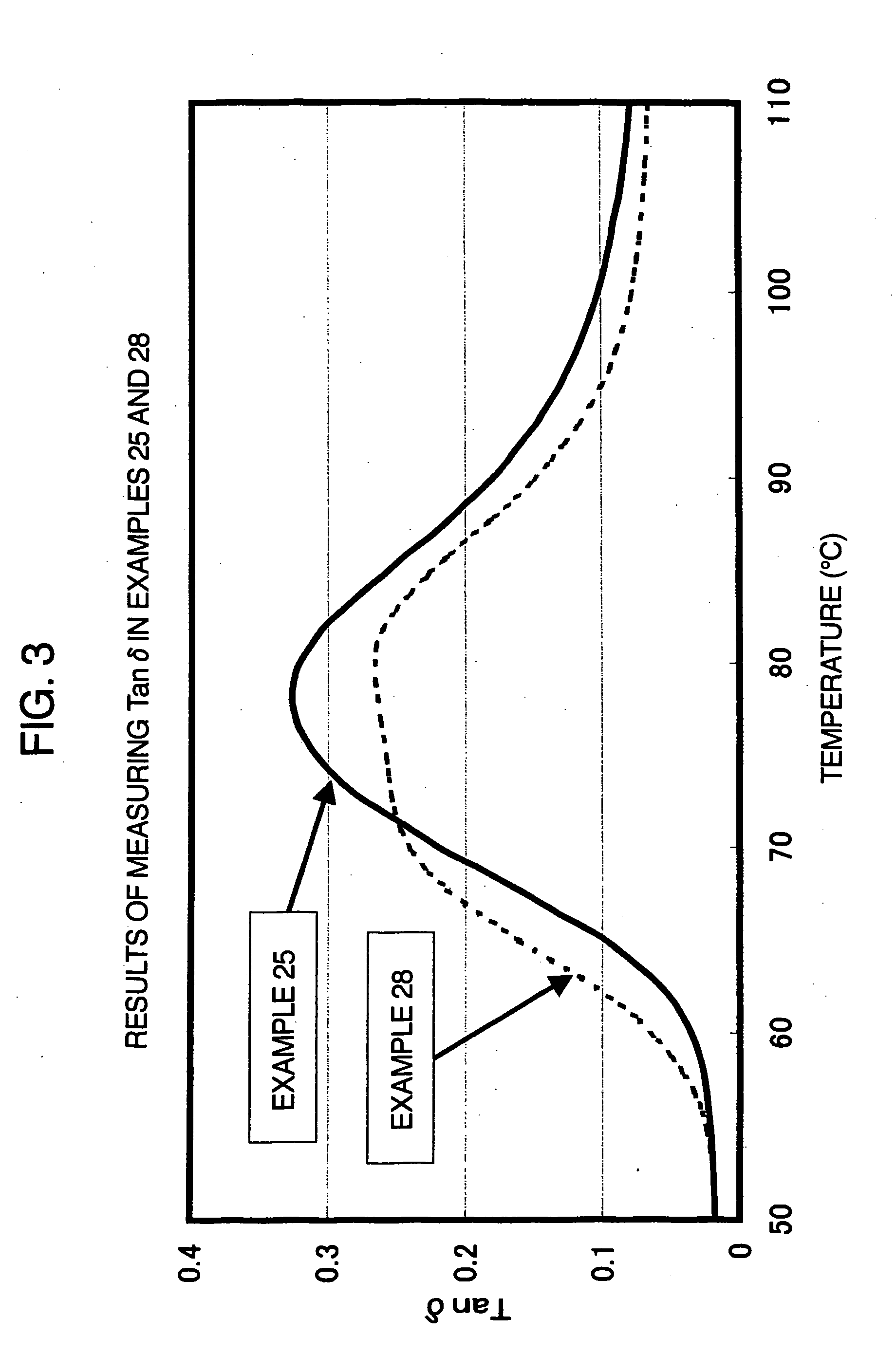
A laminate comprises an ionomeric interlayer sheet which, in turn, comprises or is prepared from a sodium / zinc mixed ionomer that comprises carboxylate groups and a combination of counterions that consists essentially of sodium cations and zinc cations. The sodium / zinc mixed ionomer is the neutralization product of a precursor acid copolymer. The precursor acid copolymer comprises copolymerized units of an α-olefin and an α,β-ethylenically unsaturated carboxylic acid, and it has a melt flow rate of about 70 to about 1000 g / 10 min. In addition, the precursor acid copolymer, when neutralized to a level of about 40% to about 90%, and when comprising counterions that consist essentially of sodium ions, produces a sodium ionomer that has a freeze enthalpy that is not detectable or that is less than about 3.0 j / g, when determined by differential scanning calorimetry.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Transparent polyamide molding materials having improved transparency, resistance to chemicals and high permanent fatigue strength
ActiveUS6943231B2High transparencyHigh permanent fatigue strengthNon-fibrous pulp additionFramesPolyamideCarboxylic acid
Transparent polyamide molding materials are provided which are characterized in that they have a melting enthalpy between 0 and 12 J / g and the polyamides are constituted of100 mole-% of a diamine mixture having 10-70 mole-% of PACM [bis-(4-amino-cyclohexyl)-methane] with less than 50 wt.-% of trans,trans-isomer and 90-30 mole-% of MACM [bis-(4-amino-3-methyl-cyclohexyl)-methane], wherein, optionally, 0-10 mole-% can be replaced by other aliphatic diamines having 6 to 12 C atoms, cycloaliphatic, alkyl-substituted cycloaliphatic, branched aliphatic diamines or multiamines having 3 to 12 amino groups or mixtures thereof, and100 mole-% of long-chain aliphatic dicarboxylic acids having 8 to 14 C atoms or mixtures of these dicarboxylic acids, wherein 0-10 mole-% can be replaced by other aromatic or cycloaliphatic dicarboxylic acids having 8 to 16 C atoms, which are especially selected from the group consisting of isophthalic acid, terephthalic acid, naphthalenedicarboxylic acid, cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid or mixtures thereof, andwherein, optionally, 0-10 mole-% of the other long-chain aliphatic diamines and 0-10 mole-% of the other long-chain aliphatic dicarboxylic acids can be added as 0-20 mole-% of ω-aminocarboxylic acids having 6 to 12 C atoms or lactams having 6 to 12 C atoms.Further, methods for producing the polyamide moulding materials and methods for producing and further treating moulded articles from the polyamide moulding materials are provided. Especially, the present invention relates to glasses and lenses which are obtainable from the polyamide moulding materials.
Owner:EMS CHEM AG
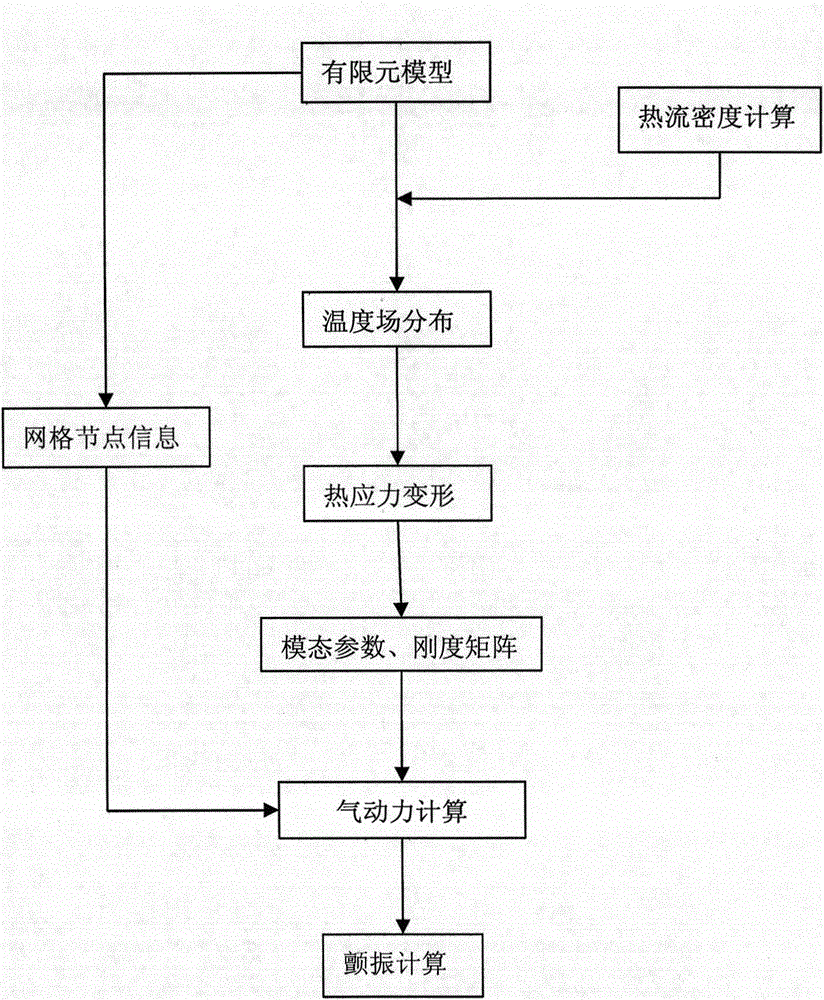
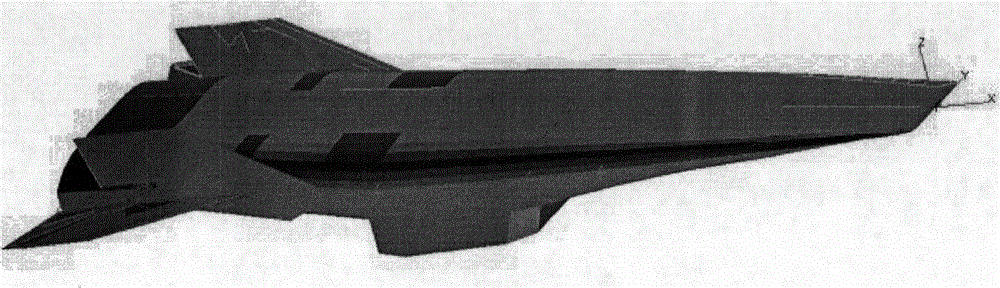
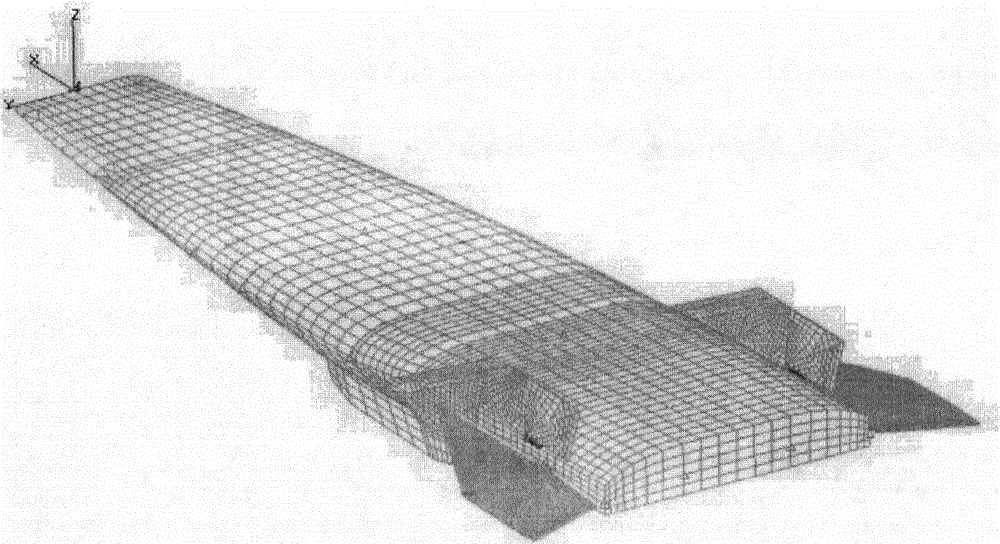
Pneumatic elastic mechanical characteristic analytical method of hypersonic speed aircraft in thermal environment
ActiveCN104133933AGuaranteed continuitySustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelEngineering
The invention relates to a pneumatic elastic analytical method, and provides a pneumatic elastic mechanical characteristic analytical method of a hypersonic speed aircraft in thermal environment. According to the method, the piston theory is used for carrying out frequency domain nonsteady aerodynamic calculation on a full-aircraft finite element model of the hypersonic speed aircraft; on the basis, the pneumatic thermal effect on the model in the hypersonic speed thermal environment is considered; the weak coupling effect of pneumatic thermal input in aerodynamic input and elastic force input is ignored; only the structure temperature steady-state characteristics under the pneumatic thermal load effect are considered; after the steady aerodynamic calculation, the thermal flux density on the surface of the aircraft is obtained by adopting a reference enthalpy method; further, the steady temperature distribution on the surface of the aircraft is calculated; the practical equivalent rigidity matrix of the structure at the moment is obtained; and the critical flutter speed is calculated by an engineering method. The pneumatic elastic mechanical characteristic analytical method has the advantages that the pneumatic elastic analytical problem of the hypersonic speed aircraft in the pneumatic thermal environment is solved, and the pneumatic elastic performance of the hypersonic speed aircraft is improved through flutter speed analysis.
Owner:ANHUI JINSANHUAN METAL SCI & TECH
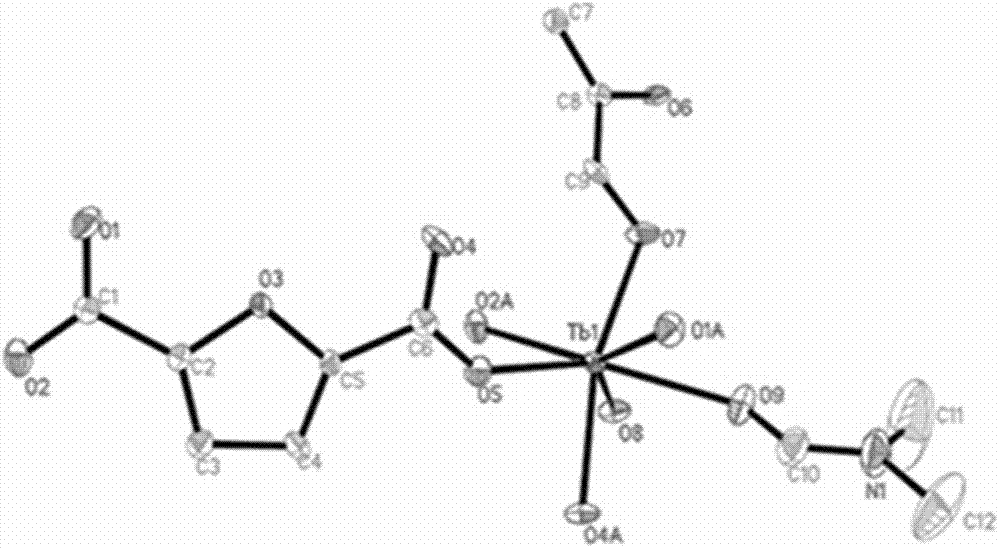
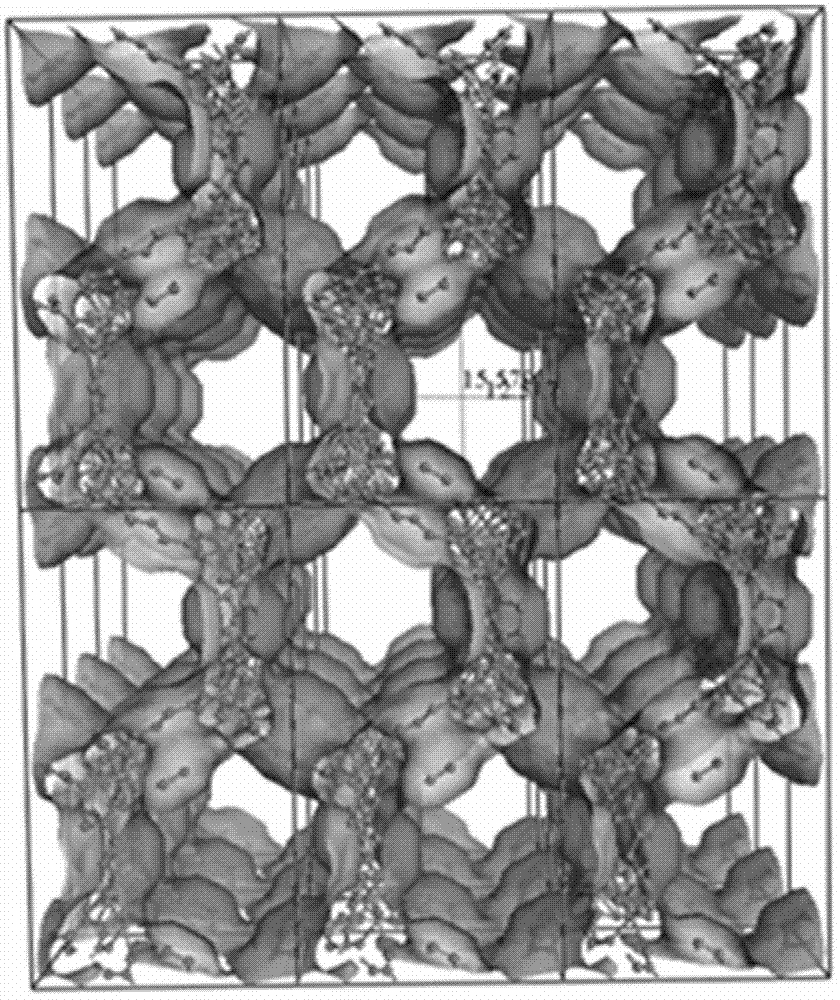
Multifunctional rare earth metal-organic framework and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102757453ANovel structureSensitive recognitionCarbon compoundsOther chemical processesCooking & bakingN dimethylformamide
The invention relates to a multifunctional rare earth metal-organic framework of which the chemical formula is {[Ln(FDA)1.5(DMF)].DMF}n, wherein Ln is Eu or Tb, the FDA is furyl-2,5-dicarboxylic acid, and the DMF is N,N-dimethylformamide; and the rare earth metal framework structure has an Eu<3+> / Tb<3+> ion in a coordination environment, and forms a three-dimensional framework structure containing one-dimensional honeycomb channels. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by using europium nitrate hexahydrate or terbium nitrate hexahydrate as a metal salt, H2FDA as a ligand and DMF as a solvent, stirring the mixed solution, baking, separating and washing the solid to obtain the multifunctional rare earth metal-organic framework. The multifunctional rare earth metal-organic framework provided by the invention has an fluorescent identification function on cancerigenic organic solvents, such as methylbenzene, benzene and acetone, has excellent selective adsorptivity for gas and high acting force with H2, contains high adsorptive enthalpy, and thus, is a multifunctional novel-structure microporous MOF (metal-organic framework) material.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Phase change cold storage material with double phase change points and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106675525AHigh latent enthalpy of phase changeThe role of proper thawingHeat-exchange elementsDouble phaseCold storage
The invention discloses a phase change cold storage material with double phase change points and a preparation method thereof. The phase change cold storage material with double phase change points is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 0 to 60 percent of inorganic salts, 5 to 60 percent of organic phase change materials, 20 to 95 percent of de-ionized water, 0.1 to 2 percent of surfactants, 1 to 5 percent of thickening agents and 1 to 5 percent of nucleating agents. The phase change cold storage material provided by the invention has double phase change points; the temperature can be controlled between the double phase change point temperatures in the material distribution process; the freezing and cold storage effect is achieved; the proper unfreezing effect can also be achieved; in addition, the material has high phrase change latent heat enthalpy value (greater than 220kJ / kg); the more efficient and faster temperature reduction effect is achieved; in addition, the temperature can be permanently maintained in a specific temperature range.
Owner:贺迈新能源科技(上海)有限公司
Method and apparatus for generating electricity
A method of converting energy into electricity using a gaseous working fluid and an evaporative fluid comprises pressuring the working fluid (20) in a compressor (1), heating the high-pressure working fluid (22) in a recuperator (8) using thermal energy in low-pressure working fluid (34) emerging from a turbine (2), adding energy from an energy source (5, 6) to increase the temperature and enthalpy of the working fluid (32), expanding the working fluid (32) through the turbine (2), using the turbine to generate electricity, and cooling the low-pressure working fluid (34) emerging from the turbine in the recuperator. The method further comprises lowering the temperature and increasing the mass of the high-pressure working fluid (22) after leaving the compressor (1), and / or after leaving the recuperator (8), by introducing the evaporative fluid (48, 49) to produce evaporative cooling.
Owner:SMITH DOUGLAS W P
Composite phase-change heat-storing material using gel as carrier and method for making same
InactiveCN101117572AImprove stabilityPromote recombinationHeat-exchange elementsTemperature controlThermal stability
The present invention provides composite phase transition heat accumulation material used gel as carrier, and the preparation method and the application of the material. The material of the present invention is formed by compositing the phase transition heat accumulation material accounted for 60 percent to 80 percent of the total mass into a macromolecule gel carrier accounted for 20 percent to 40 percent of the total mass, the material has thermo-plasticity and better thermo stability, compared with the same kind of macromolecule heat accumulation material, the material has higher phase transition enthalpy. The material can be used in temperature control and energy saving for buildings, and can also be used in heat preservation and energy saving fields for daily articles, thereby the present invention has wide application prospect.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com