Positive activation converter
A forward converter, a technology of forward conversion, applied to instruments, conversion equipment with intermediate conversion to AC, conversion of DC power input to DC power output, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to directly apply the conversion circuit JFET drive circuit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
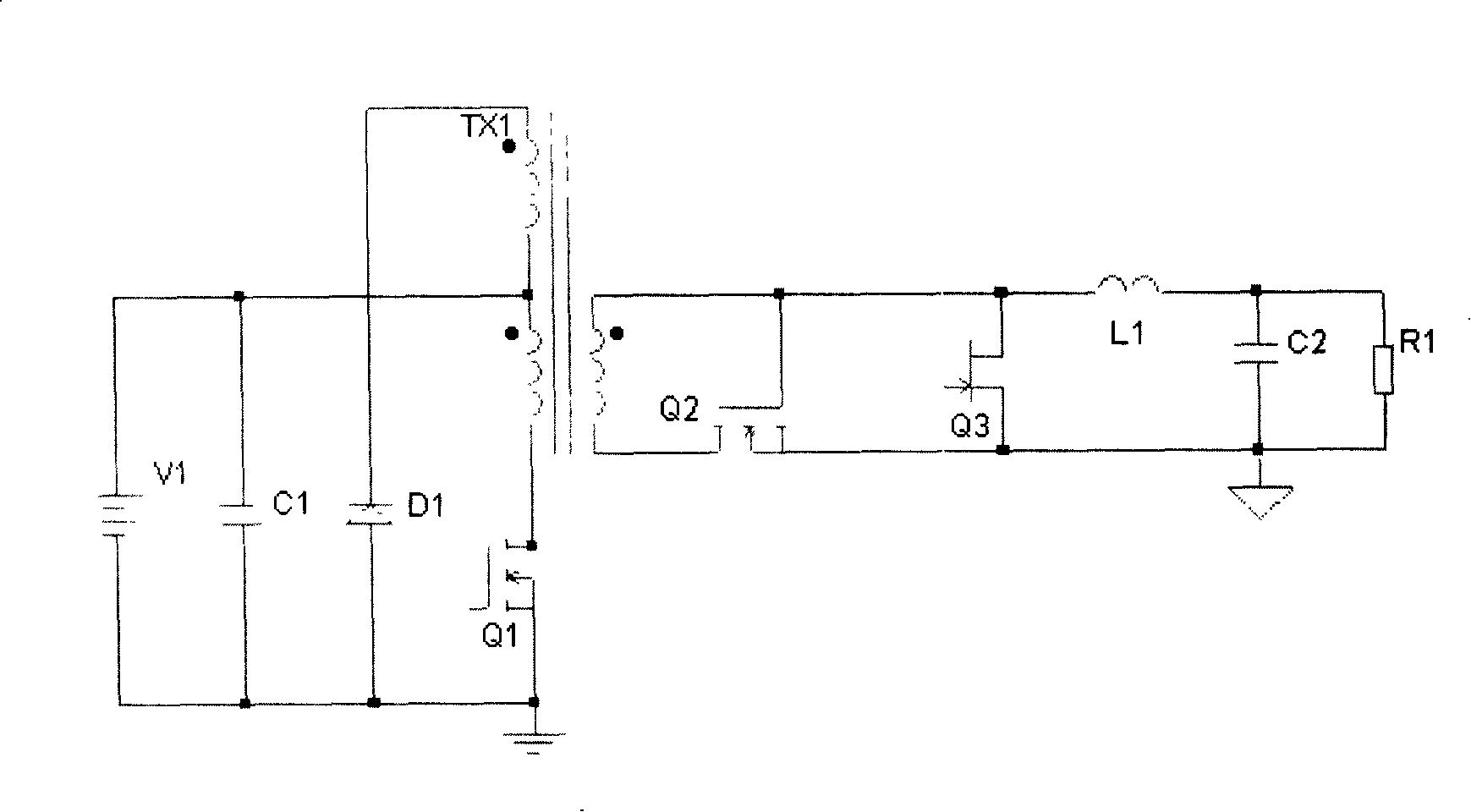
[0039] like Figure 2a As shown, the forward converter has the first basic form of drive circuit, and the input control loop uses the auxiliary winding to reset the forward circuit.
[0040] Among them, Q1 is an N-channel MOSFET main switching tube, Q2 is an N-channel MOSFET rectifier tube, and Q3 is an N-channel depletion type JEFET freewheeling tube. V1 is the input power supply, and the inductor C1 is used for input filtering, respectively connected to the positive and negative ends of the input power supply V1 with the same name. There are two windings on both sides of the primary and secondary sides of the transformer TX1 respectively. The two windings on the primary side are the primary winding and the demagnetizing winding respectively. The positive end of the main winding on the primary side (the end of the main winding on the primary side connected to the positive pole of the power supply is called the positive end, and the end with the same name is the positive end...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0047] like Image 6 As shown, the forward converter has the second basic form of drive circuit, and the input control loop uses the auxiliary winding to reset the forward circuit. Except for the driving circuit, the structure of the forward converter of this embodiment is the same as that of the forward converter of the first embodiment.
[0048] The charging circuit part in the forward converter drive circuit includes a second diode D2, the discharging circuit includes a fourth diode D4 and a fifth diode D5, the positive terminal of the secondary auxiliary winding of the transformer is grounded, and its other One end is connected to the anode of the second diode D2 and the cathode of the fourth diode D4, the input end of the level coupling circuit is connected to the cathode of the second diode D2, the output end is connected to the gate of the freewheeling tube Q3, and simultaneously connected to the first Anode connection of five diodes D5.
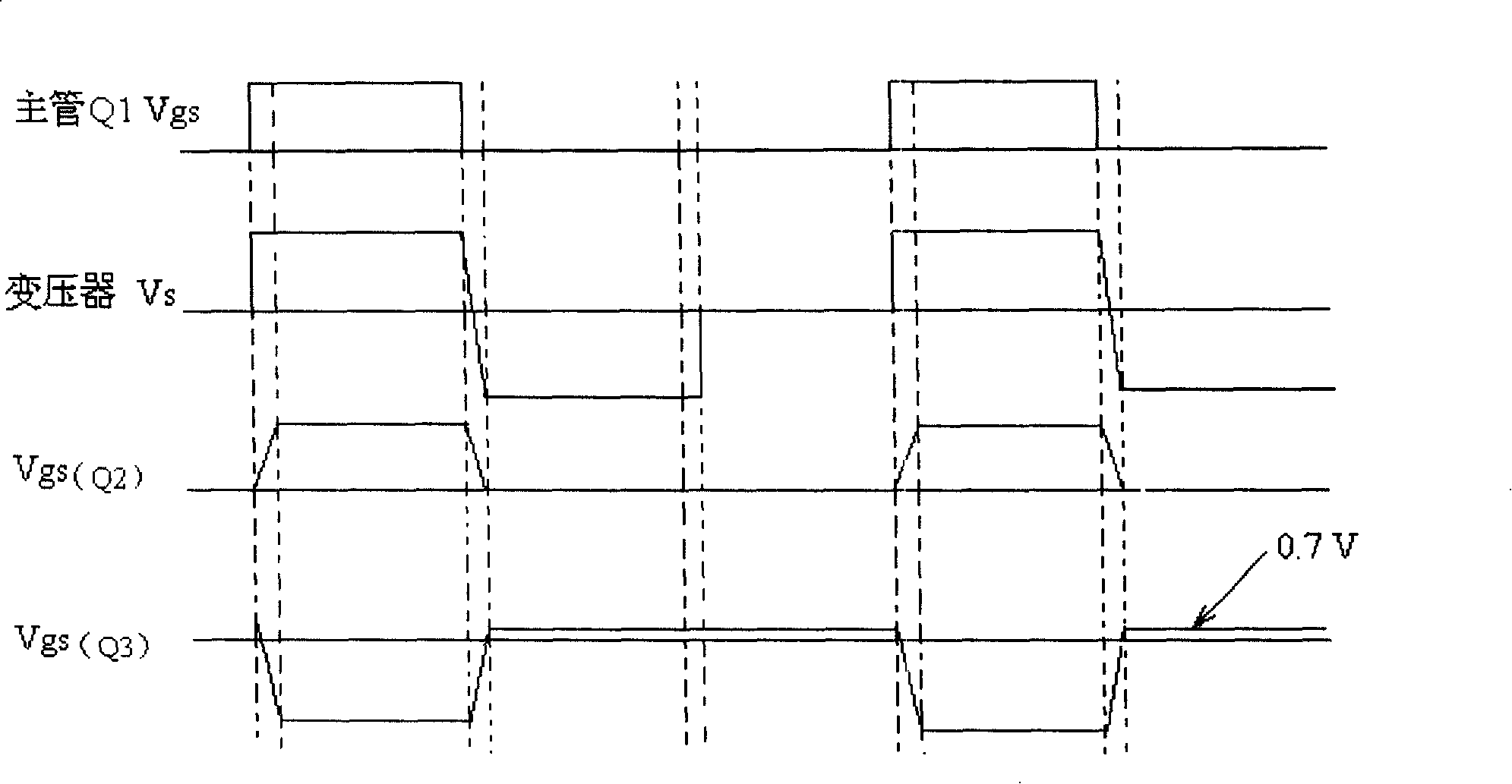
[0049] In this embodiment, t...
specific Embodiment approach 3
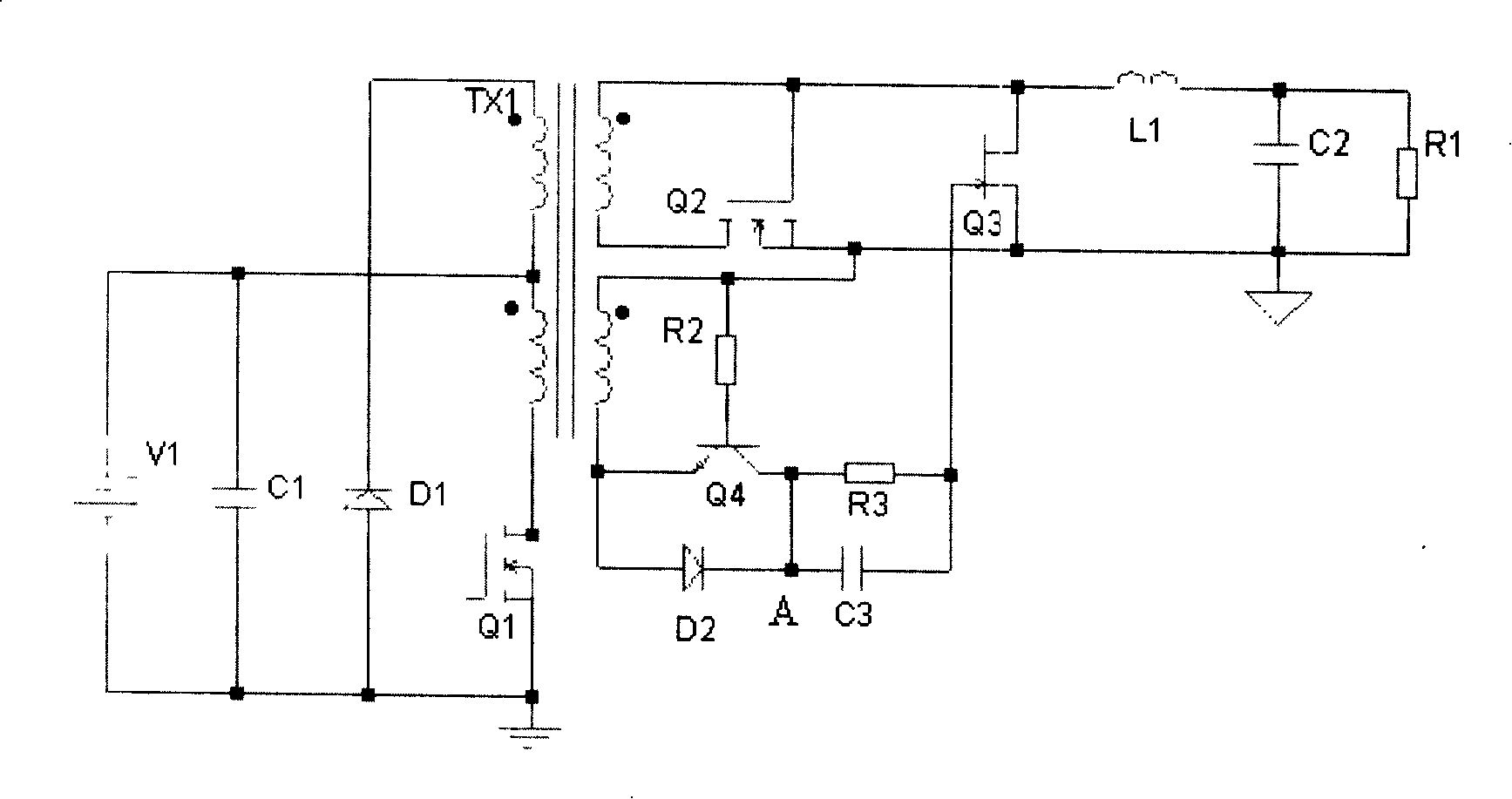
[0053] like Figure 9 As shown, the forward converter has the third basic form of drive circuit, and the input control loop uses the auxiliary winding to reset the forward circuit. Except for the driving circuit, the structure of the forward converter of this embodiment is the same as that of the forward converters of the first and second embodiments.
[0054] Different from the drive control signal in Embodiments 1 and 2 from the auxiliary winding on the secondary side of the transformer, the drive control signal in this implementation comes from the main winding on the secondary side of the transformer. In the drive circuit, the charging circuit includes a charging diode D2a, the discharging circuit includes a switching transistor Q4a, the emitter of the switching transistor Q4a is grounded, and its base is connected to the positive terminal of the secondary main winding of the transformer through a resistor R2a, and the anode of the charging diode D2a Connect the drain of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com