Photon counting laser radar based on composite pseudo-random coding
A pseudo-random coding and photon counting technology, which is applied in the field of photon counting lidar, can solve the problems of low detection efficiency and the influence of dead time, and achieve the effects of reducing imaging time, reducing poor correlation, improving anti-noise ability and ranging performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
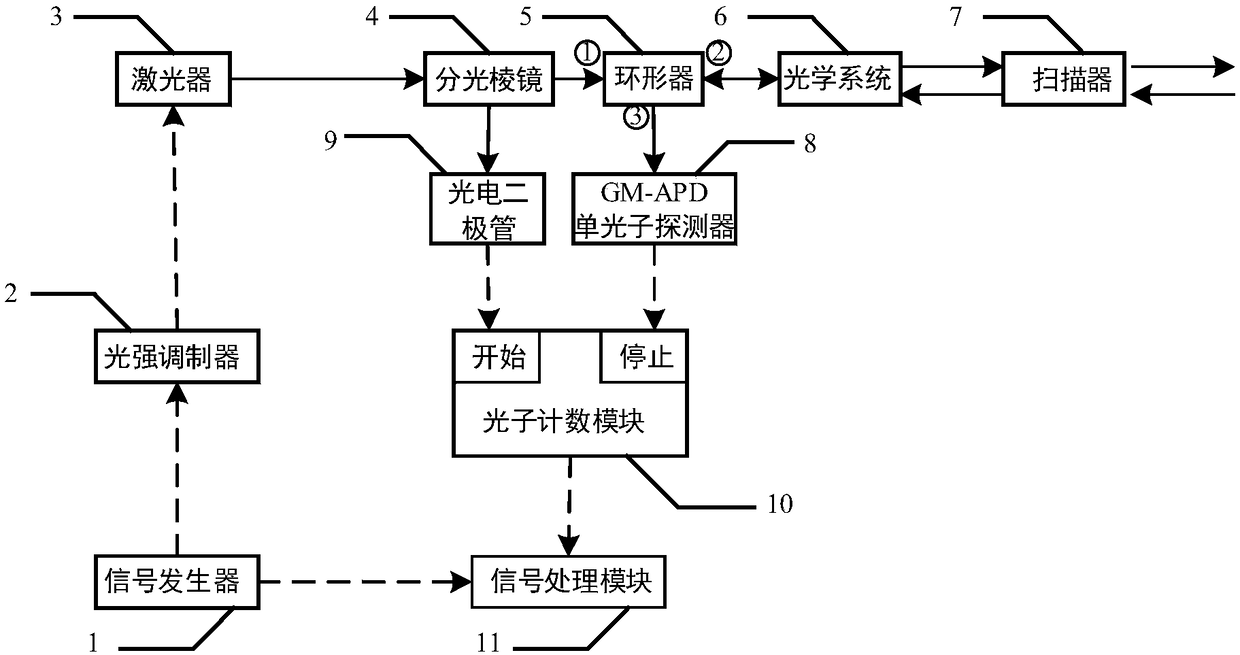
[0018] Specific implementation mode one: see figure 1 Describe this embodiment, a photon counting laser radar based on composite pseudo-random coding described in this embodiment, it includes a signal generator 1, a light intensity modulator 2, a laser 3, a beam splitting prism 4, a circulator 5, an optical system 6. Scanner 7, GM-APD single photon detector 8, photodiode 9, photon counting module 10, signal processing module 11;
[0019] Described signal generator 1 produces the pulse signal output end of composite pseudo-random code and is connected with the signal input end of light intensity modulator 2 and the signal input end of signal processing module 11 simultaneously, and the composite code output end of light intensity modulator 2 is connected with The input end of the laser 3 is connected, the pulse signal output end of the laser device 3 is connected with the input end of the beam splitting prism 4, an output end of the beam splitting prism 4 is connected with the ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0020] Specific implementation mode two: see figure 2 Describe this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and the composite pseudo-random code-based photon counting lidar described in the first embodiment is that the specific process of the signal generator module is as follows:
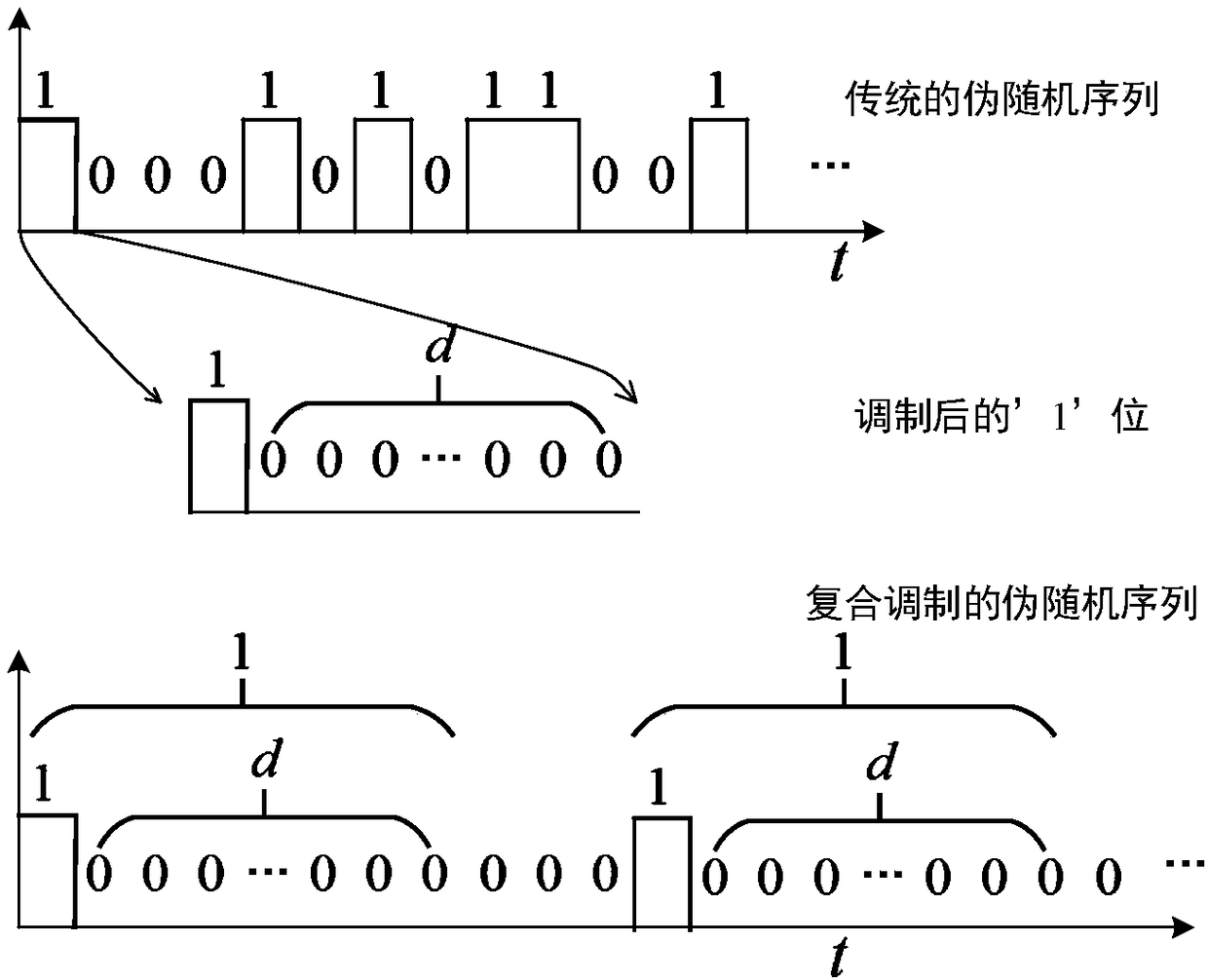
[0021] First, according to the principle of pseudo-random coding, a traditional pseudo-random sequence is generated. The traditional pseudo-random sequence contains two types of codes '0' and '1', and these two types of codes have the same symbol width, so The above-mentioned '0' code represents not emitting laser pulses, and the above-mentioned '1' represents emitting laser pulses;
[0022] Secondly, the '1' code in the traditional pseudo-random sequence is modulated, and the modulation method is to change all the '1' codes in the traditional pseudo-random sequence into one actual '1' code corresponding to the dead time length Composed of several '0' codes, no modulation is performed ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0024] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and the photon counting laser radar based on composite pseudo-random coding described in Embodiment 2 is that the modulated laser pulse described in Embodiment 2 realizes specific distance measurement through the radar system. The process is:
[0025] The composite pseudo-randomly modulated laser sequence generated by the second specific embodiment forms a transceiver with synchronous triggering of optical signals through the beam splitter, circulator, optical system, scanner, GM-APD single photon detector and photodiode. In the optical measurement system of the road, a part of the light is irradiated by the beam splitting prism to the photosensitive surface of the photodiode to get a synchronous trigger of an optical signal, and the other part of the light is emitted to the target through the ring, optical system, and scanner, and then reflected by the target and returned to the original path. The second port ② of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com