Method for deep brain stimulation targeting based on brain connectivity
a brain connectivity and deep brain stimulation technology, applied in the field of deep brain stimulation targeting based on brain connectivity, can solve the problems of insufficient evaluation of the utility or reliability of dbs targeting, the complexity of preoperative identification of precise anatomical or physiological targets, and the inability to achieve the implementation of the described methodologies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021]Reference will now be made in detail to various embodiments of the present invention(s), examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings and described below. While the invention(s) will be described in conjunction with exemplary embodiments, it will be understood that present description is not intended to limit the invention(s) to those exemplary embodiments. On the contrary, the invention(s) is / are intended to cover not only the exemplary embodiments, but also various alternatives, modifications, equivalents and other embodiments, which may be included within the spirit and scope of the invention as defined by the appended claims.
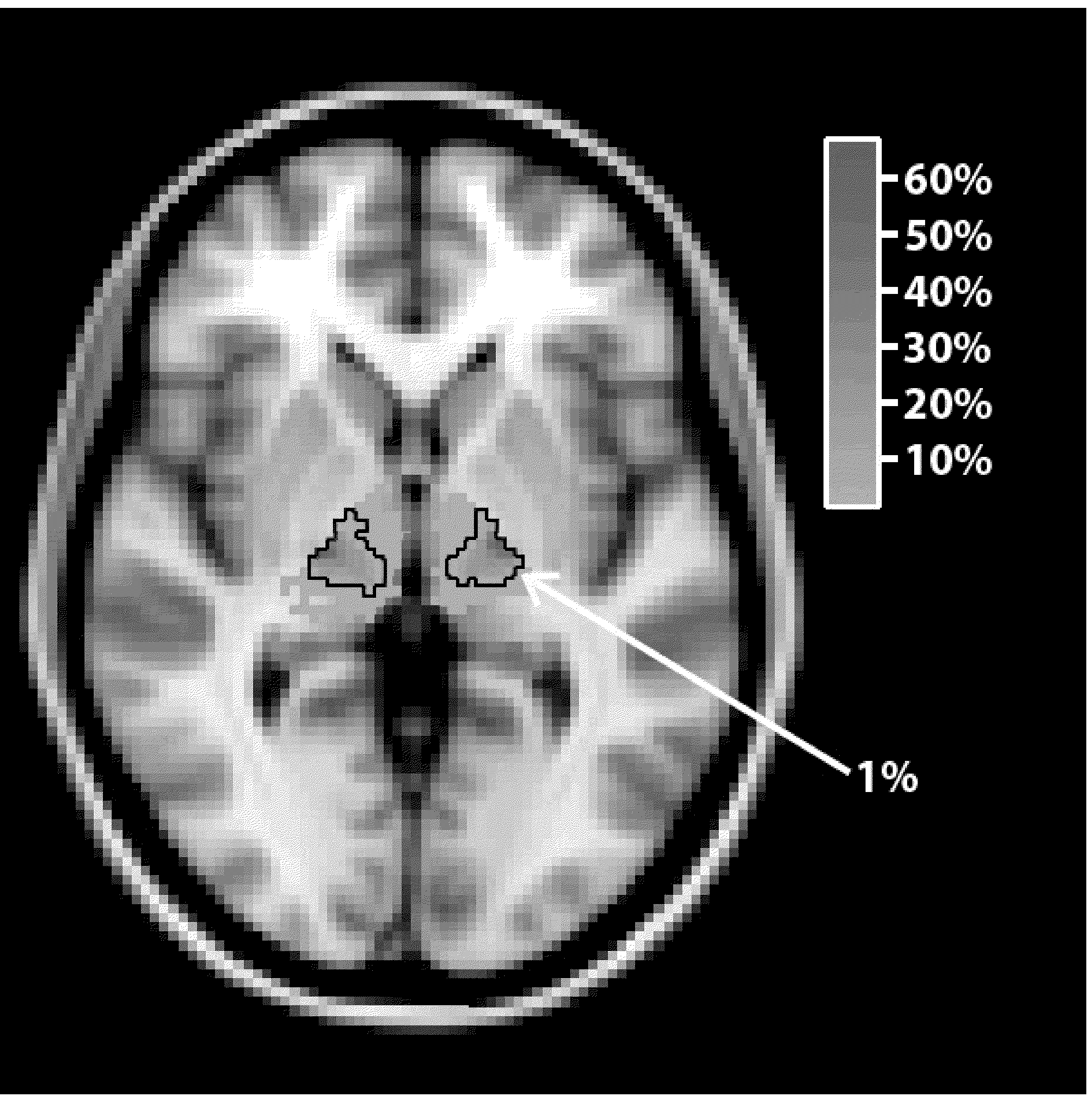
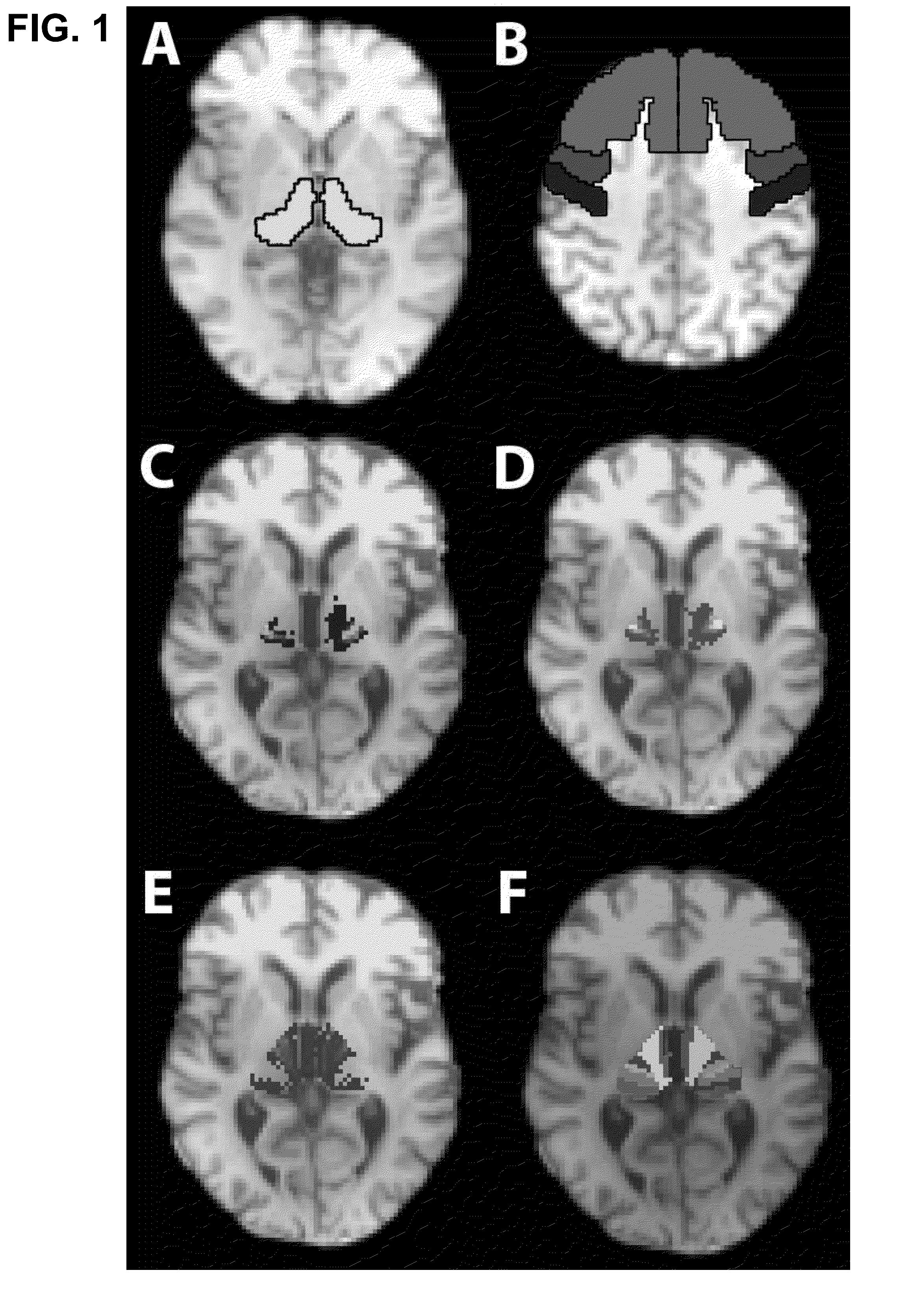
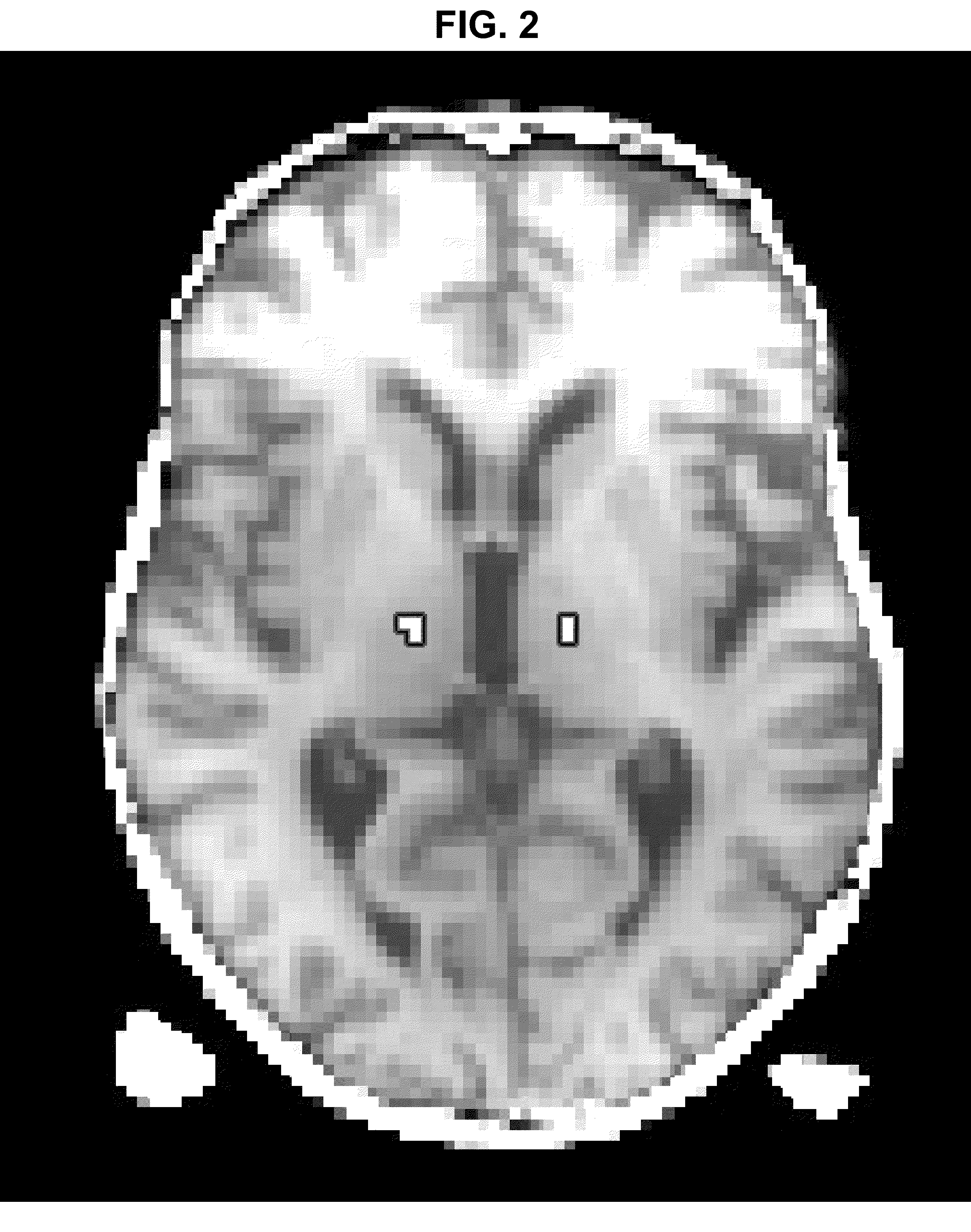
[0022]By way of background, due to the lack of internal anatomic detail with traditional magnetic resonance imaging, preoperative stereotactic planning for the treatment of tremor usually relies on indirect targeting based on atlas-derived coordinates. In accordance with the present invention, probabilistic tractography-based thalamic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com