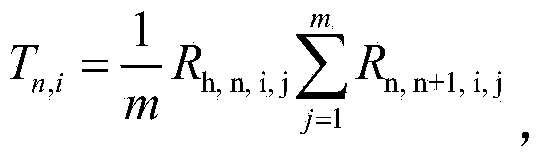Patents
Literature
60 results about "Dynamic Source Routing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dynamic Source Routing (DSR) is a routing protocol for wireless mesh networks. It is similar to AODV in that it forms a route on-demand when a transmitting node requests one. However, it uses source routing instead of relying on the routing table at each intermediate device.
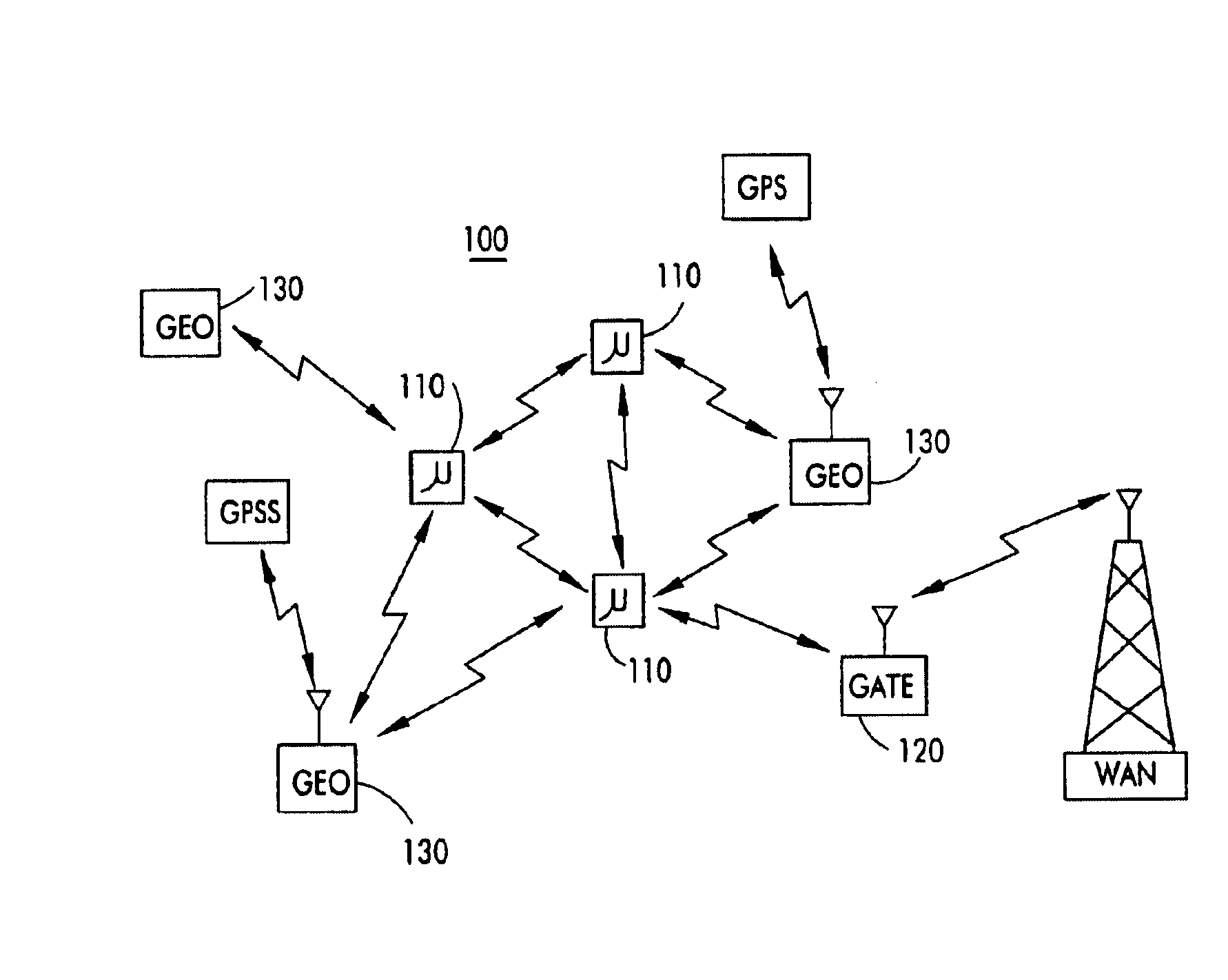
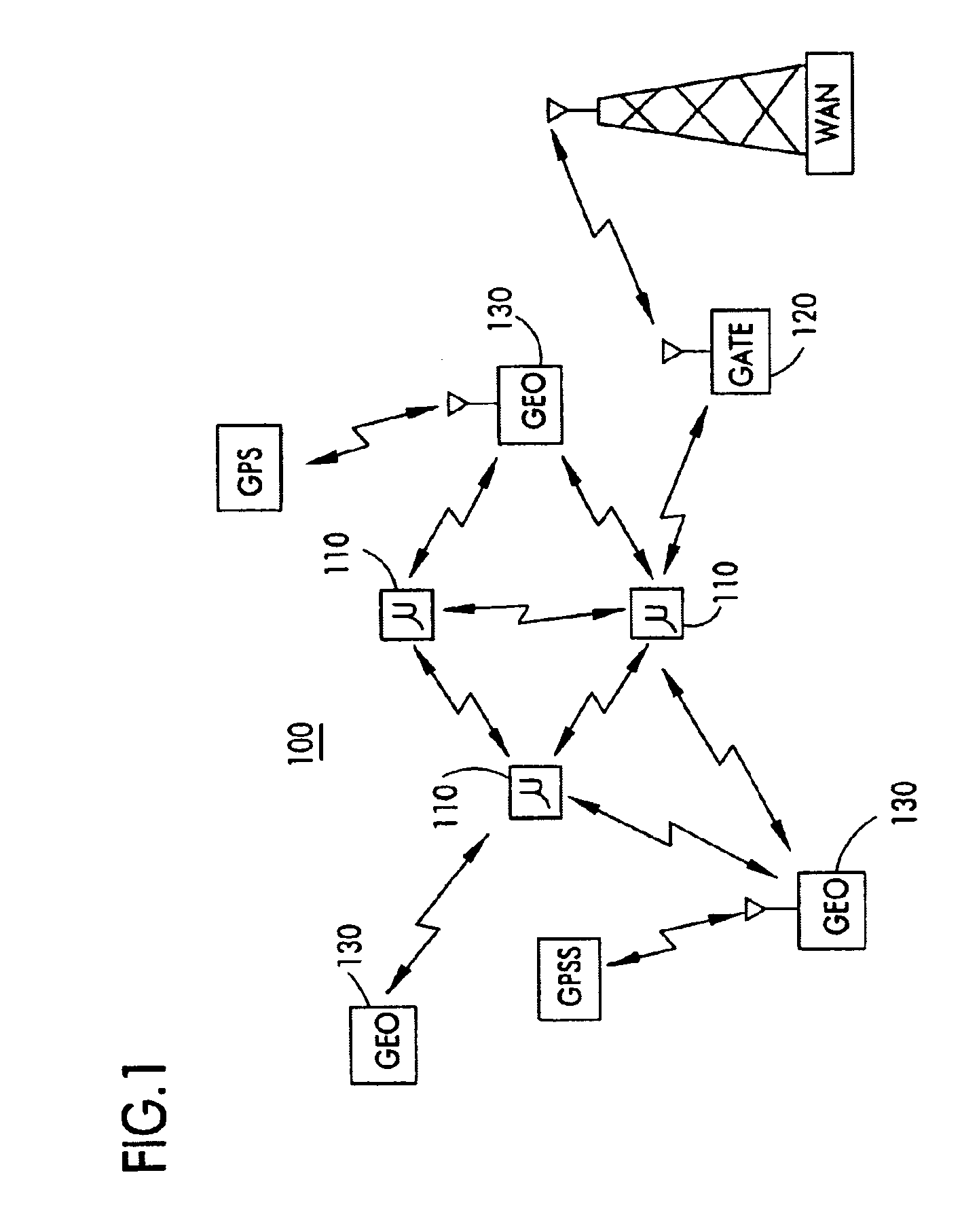
On/off keying node-to-node messaging transceiver network with dynamic routing and configuring
InactiveUS7027773B1Low costReduce trafficNear-field transmissionError preventionTransceiverAdaptive routing
The invention is a system operating on a reference frequency. The system comprises a plurality of at least three nodes. Each node hands off a message received from another node to a subsequent node. Each of the nodes comprises a transceiver receiving a message on the reference frequency from another node and transmitting the received message on the reference frequency to a subsequent node, and a controller controlling operation of the transceiver to receive the.. message transmitted by another node and to transmit the received message to a subsequent node.
Owner:AFX TECH GRP INT
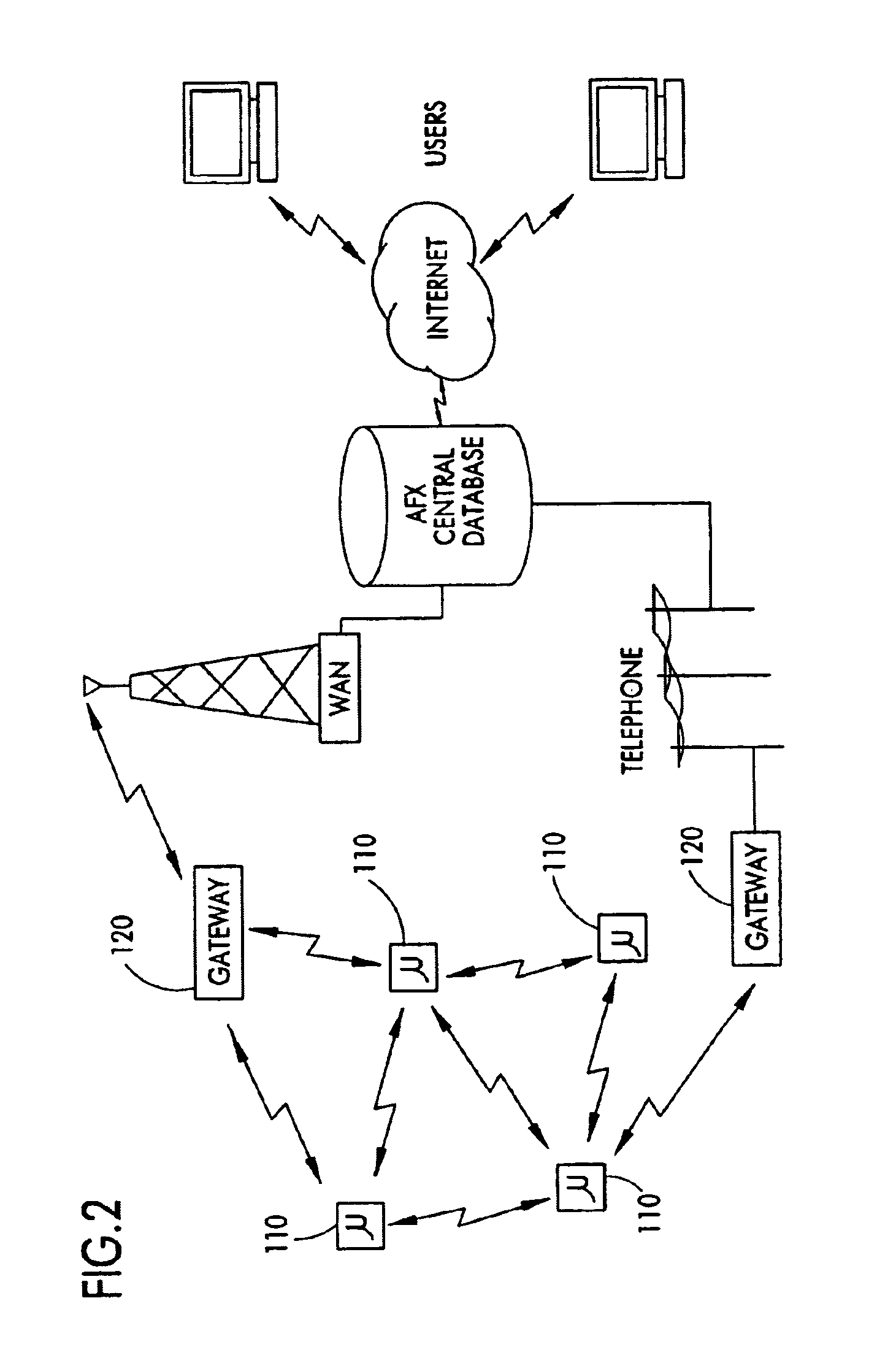
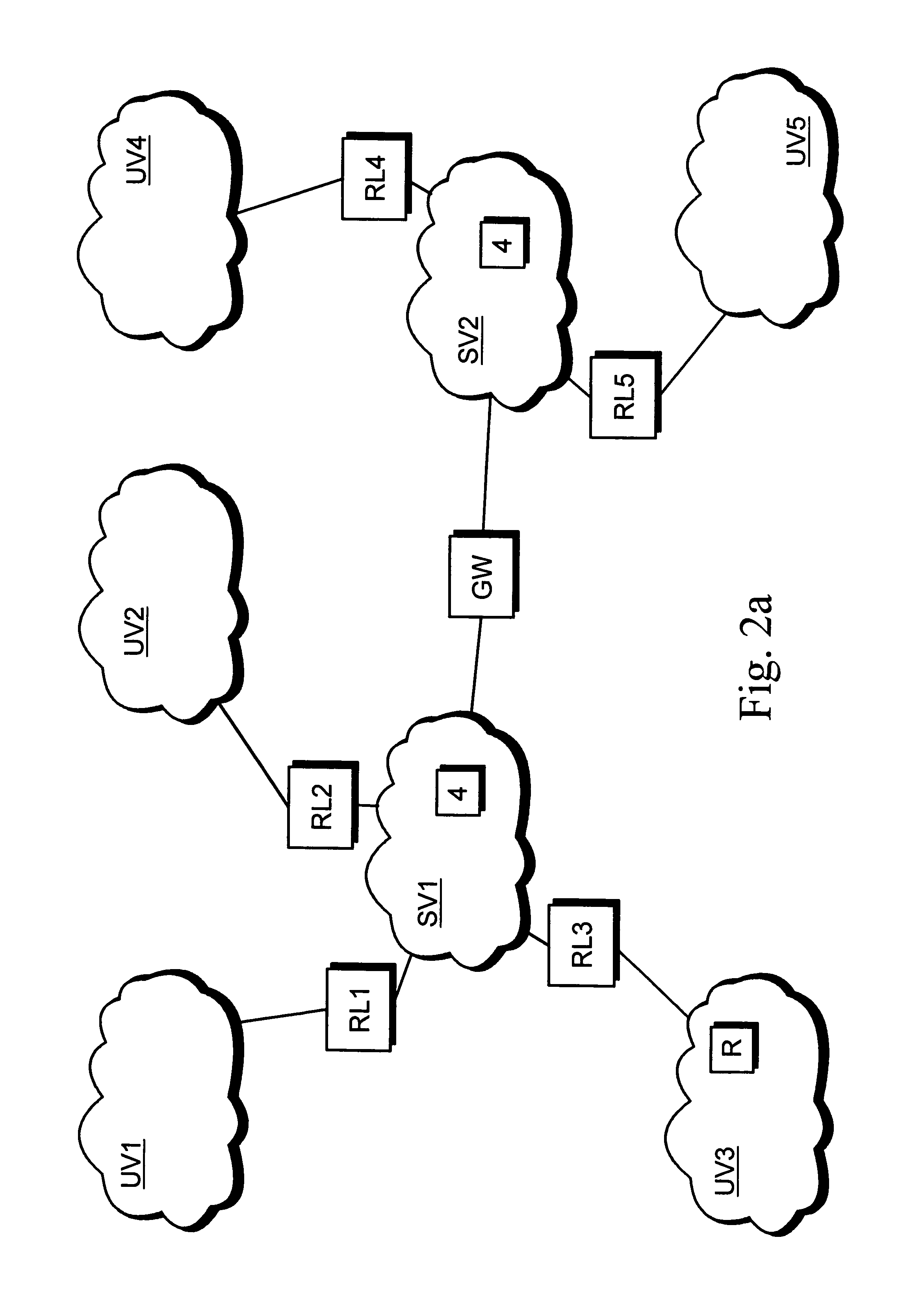
Hierarchical mobile ad-hoc network and methods for performing reactive routing therein using dynamic source routing (DSR)
InactiveUS6870846B2Use to determineError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsWireless ad hoc networkSelf-organizing network
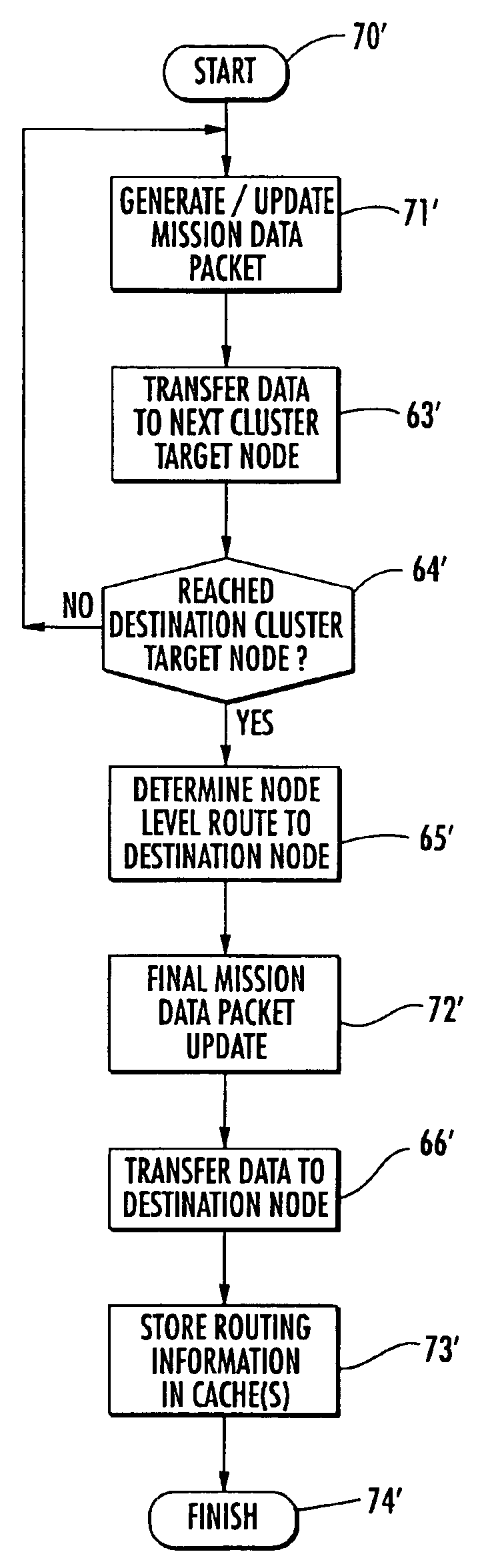
A method is provided for sending data in a wireless ad-hoc network including a plurality of nodes grouped into clusters of nodes and a plurality of wireless links connecting the plurality of nodes, where each cluster node has a designated cluster leader node. The method may include sending a cluster-level route request from a source node of a source cluster to a cluster leader node of the source cluster, and determining a cluster-level route between the source cluster and a destination cluster including a destination node responsive to the cluster-level route request and using a plurality of the cluster leader nodes. Furthermore, at least one cluster target node may be designated in a cluster along the cluster-level route, and a node-level route determined from the source node to the destination node including the at least one cluster target node. In addition, the method may also include generating a mission data packet for transferring the data.
Owner:STINGRAY IP SOLUTIONS LLC
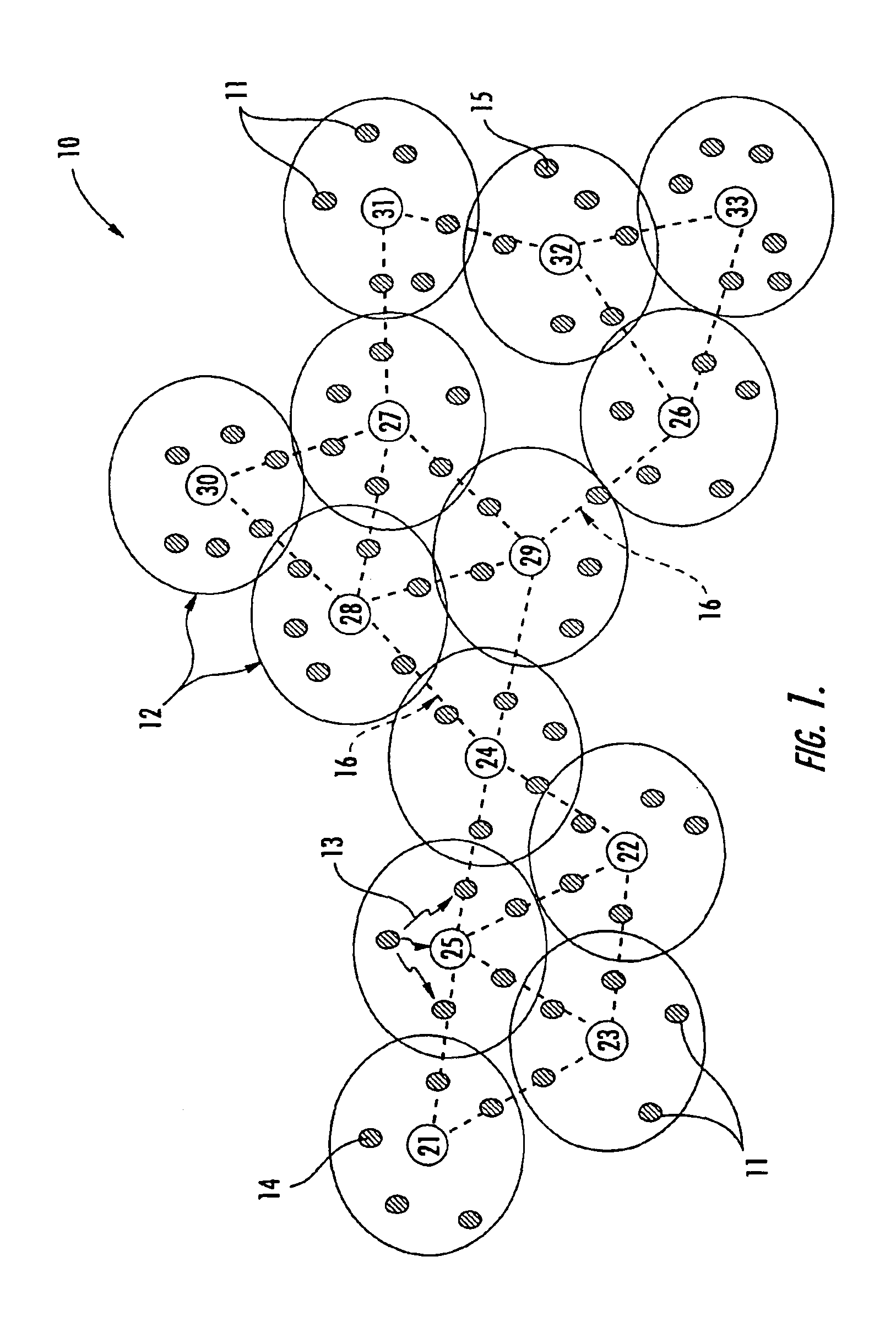
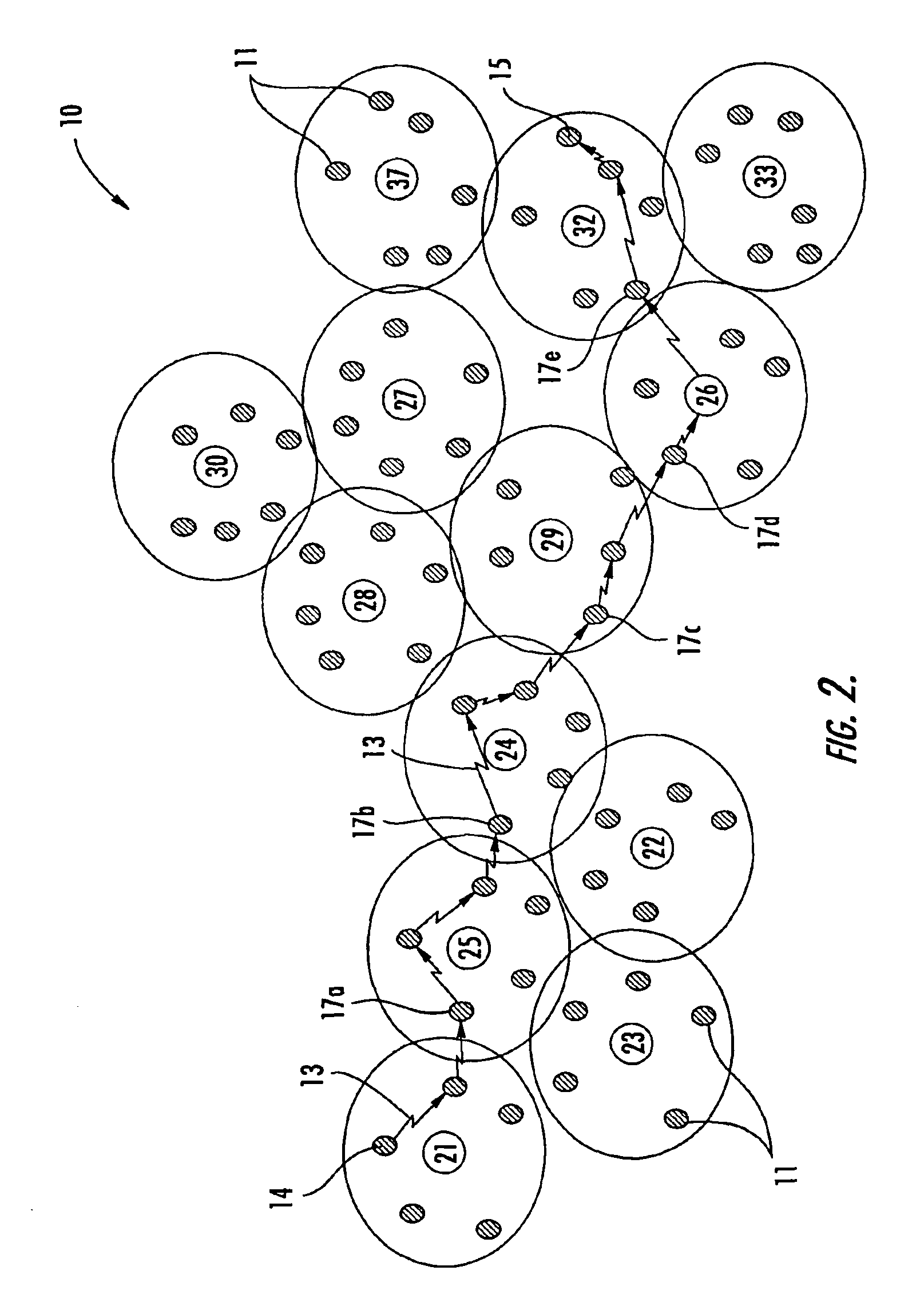
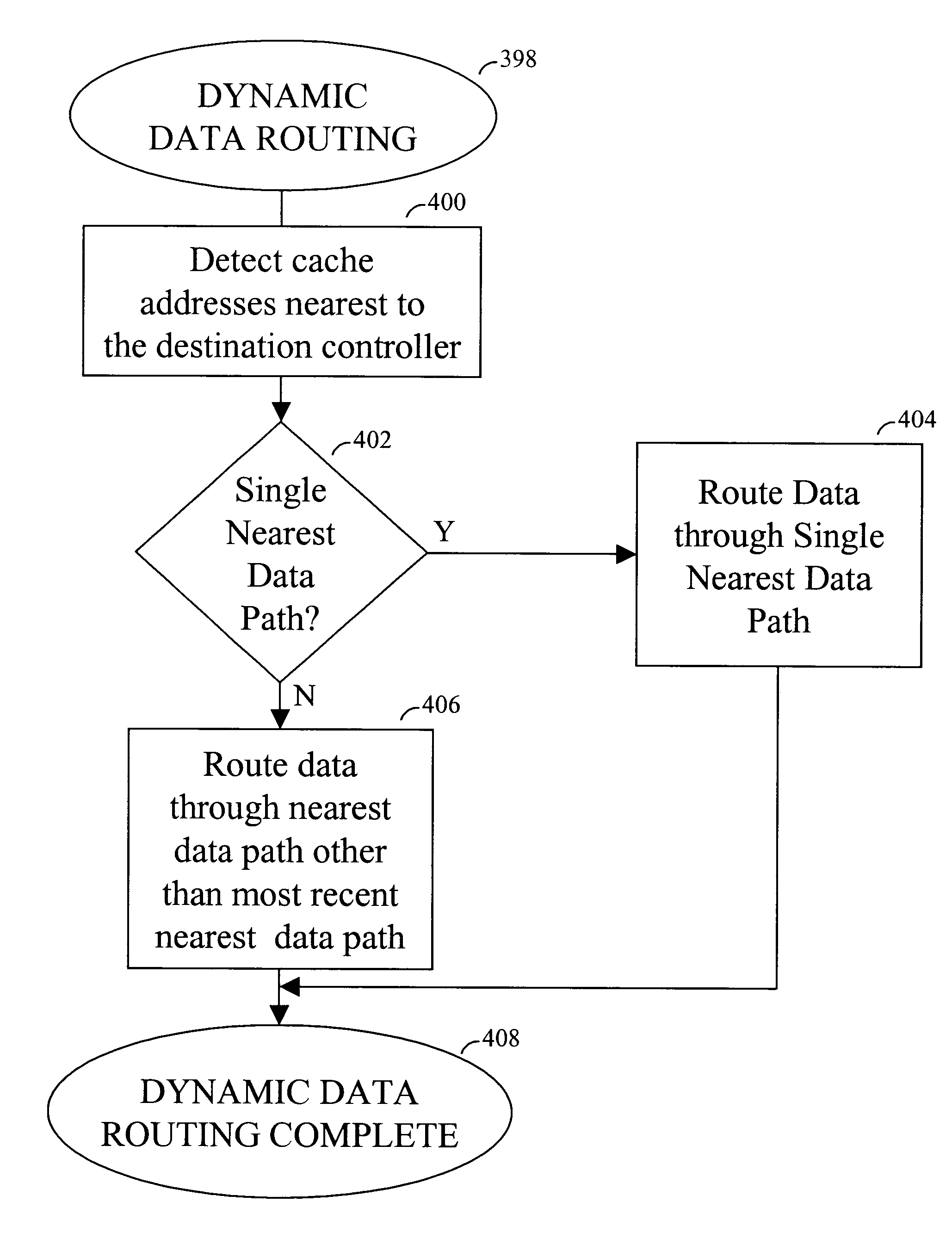
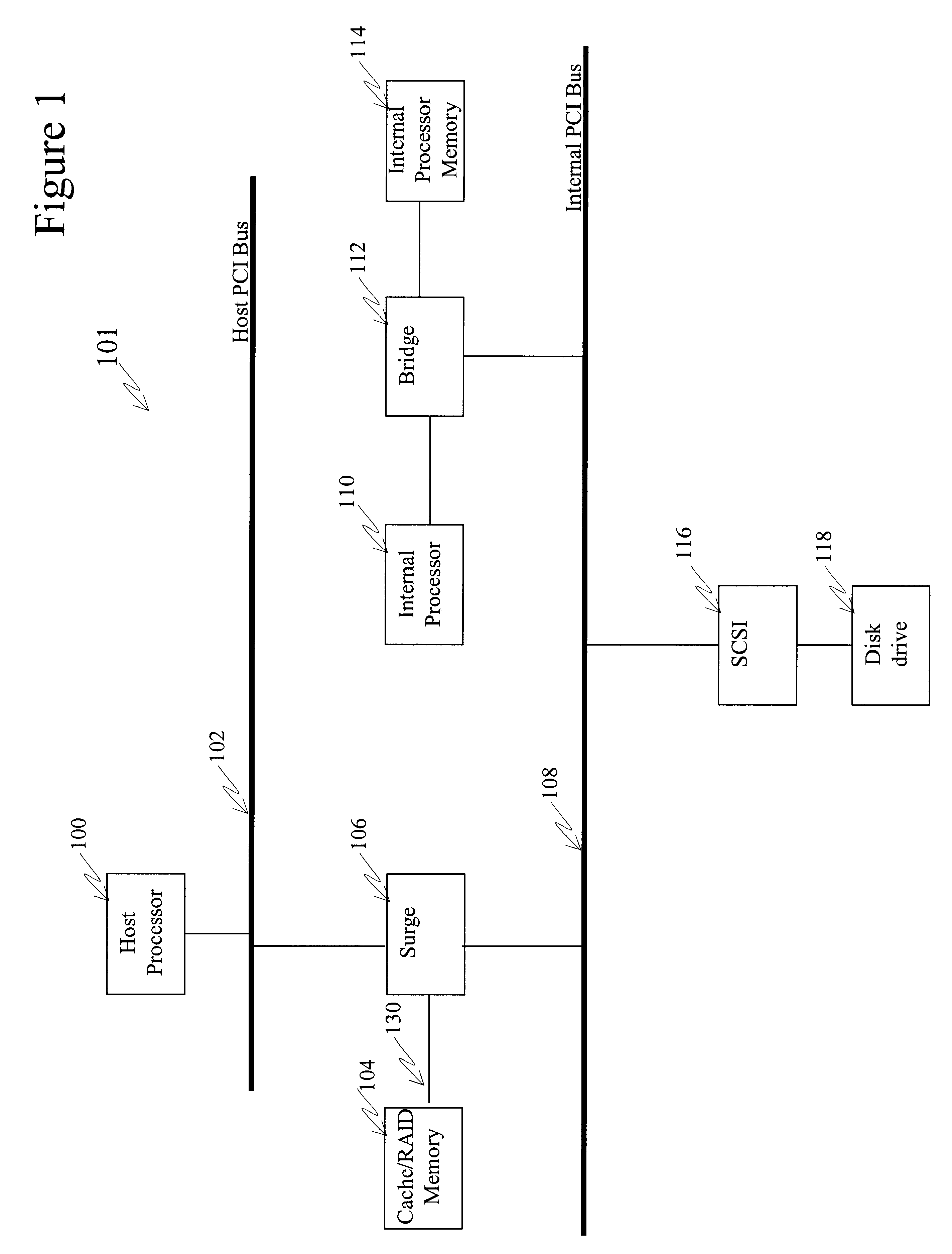
Dynamic routing of data across multiple data paths from a source controller to a destination controller
InactiveUS6675253B1Input/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory interfaceDatapath
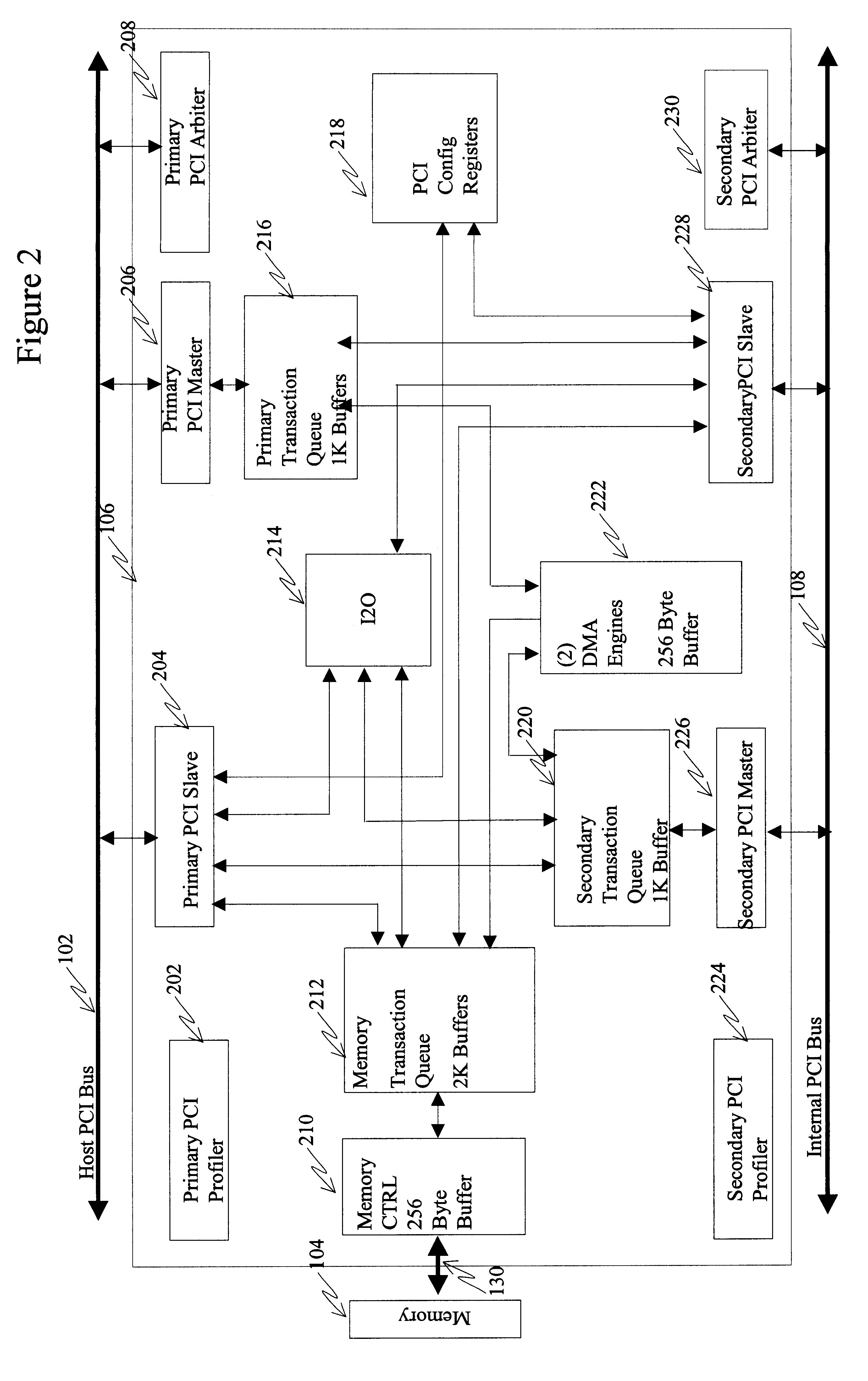
A drive array controller or other data handling system supports dynamic data routing across multiple data paths between a source controller and a destination controller. Each data path between the source controller and the data controller can include a cache memory. Based on detection of a cache address, the data path with the cache memory corresponding to the cache address is selected. Data transfer to a single destination controller can be alternated between different data paths based on detection of different cache addresses. Each data path can include a plurality of bus / memory interface devices and a peripheral bus such as a peripheral component interconnect (PCI) bus. As an alternative to dynamic data routing based on addressing, data routing can be based on command type.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
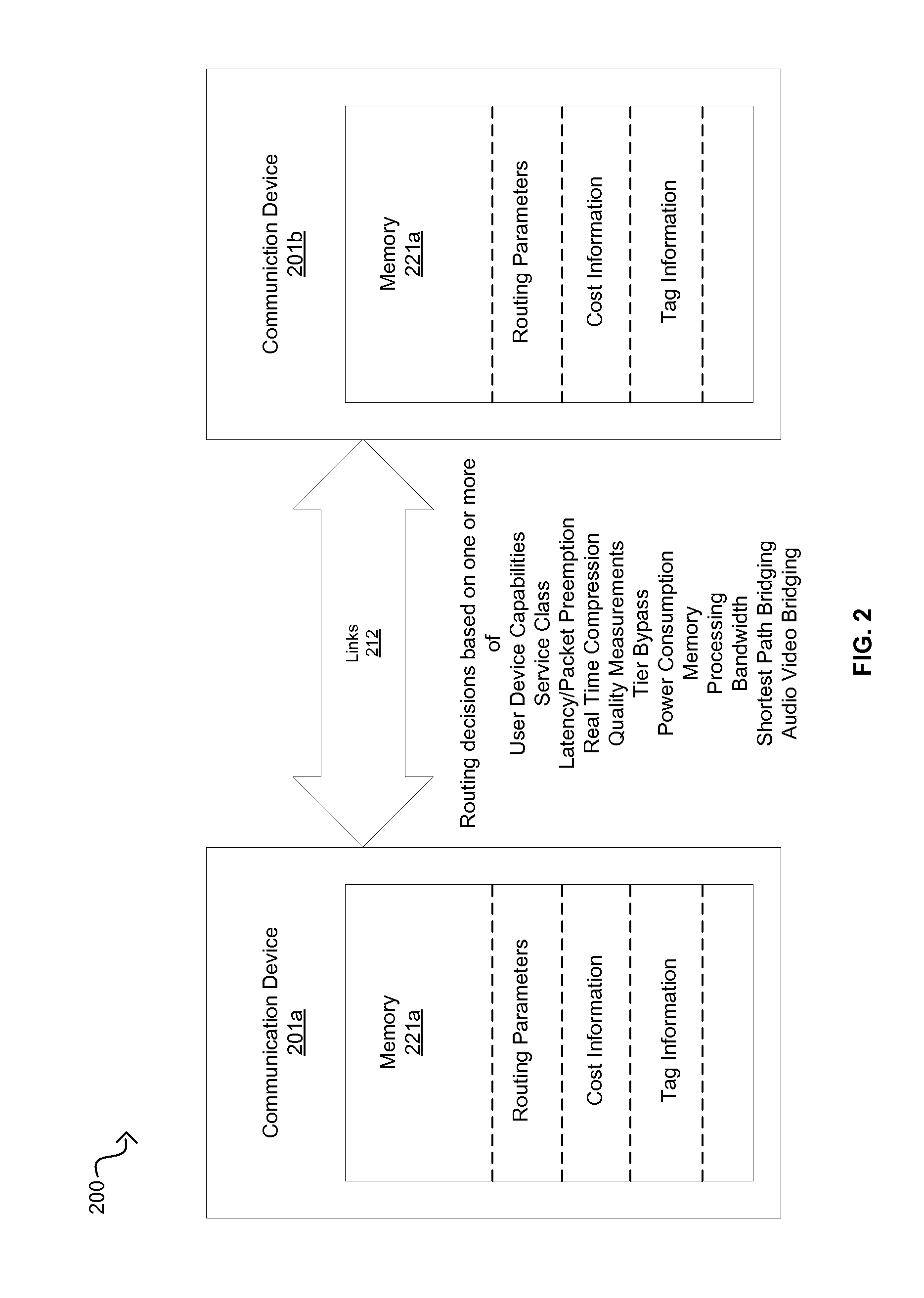
Method And System For Dynamic Routing And/Or Switching In A Network
Communication devices may determine routes for packets based on packet marking, routing parameters and / or costs associated with routes. A route may be selected and the packets may be communicated via the selected route. The parameters may comprise service class, real time compression, packet preemption, quality measurements, tier bypass and / or power usage information. The costs may comprise capacity, efficiency and / or performance information for power usage, bandwidth, memory and / or processing. The marking may comprise traffic type, user device capabilities, service class, quality measurements, latency requirements and / or power usage information. Endpoint devices, software applications and / or service providers may insert the marking into packets. Routes may be determined and / or selected based on shortest path bridging, audio video bridging, the marking, the routing parameters and / or the costs. Parameters and / or costs may be received and / or discovered from communication devices. Packets and / or the marking may be parsed and / or inspected. Costs may be based on routing parameters.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Dynamic routing
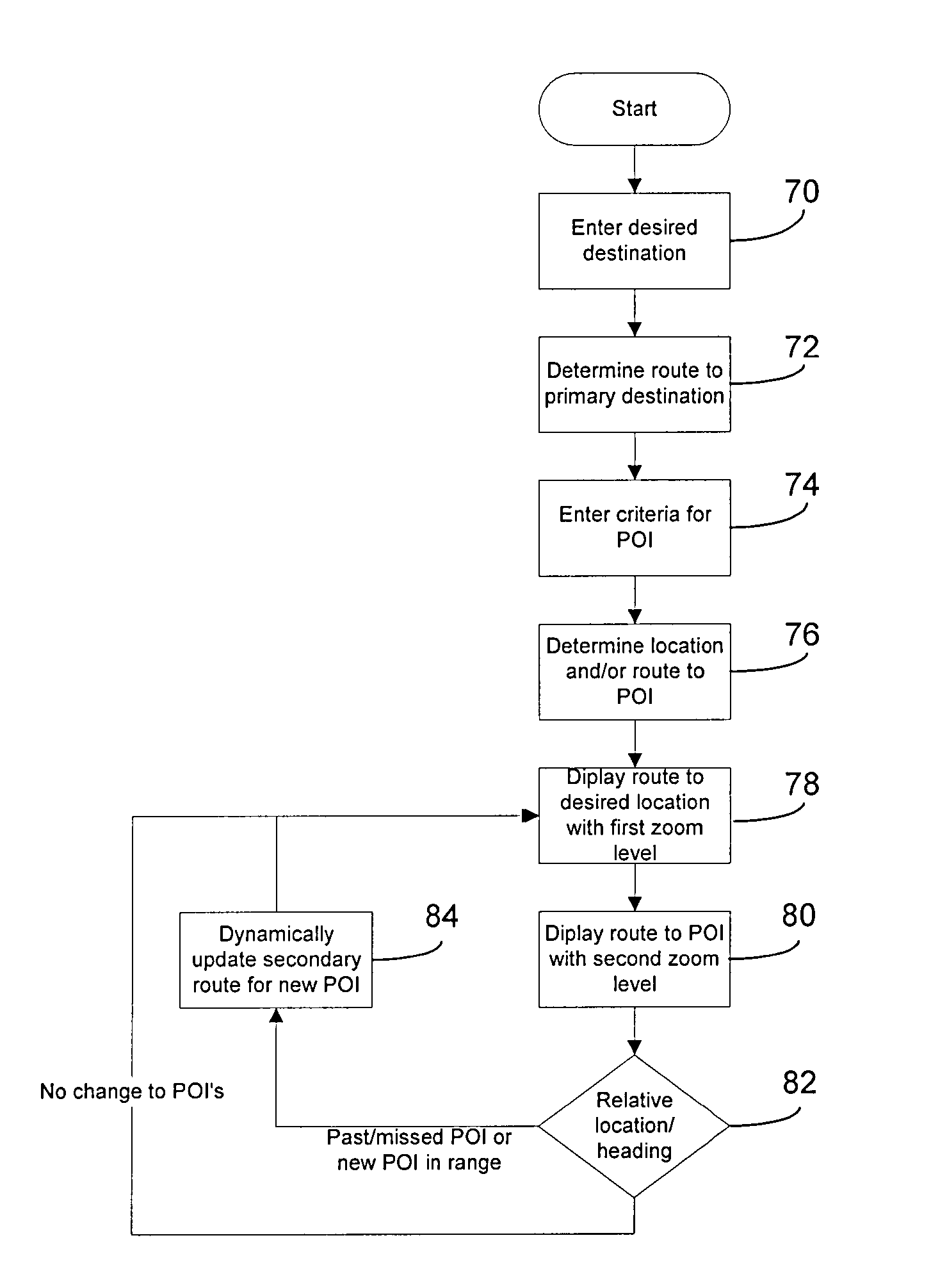
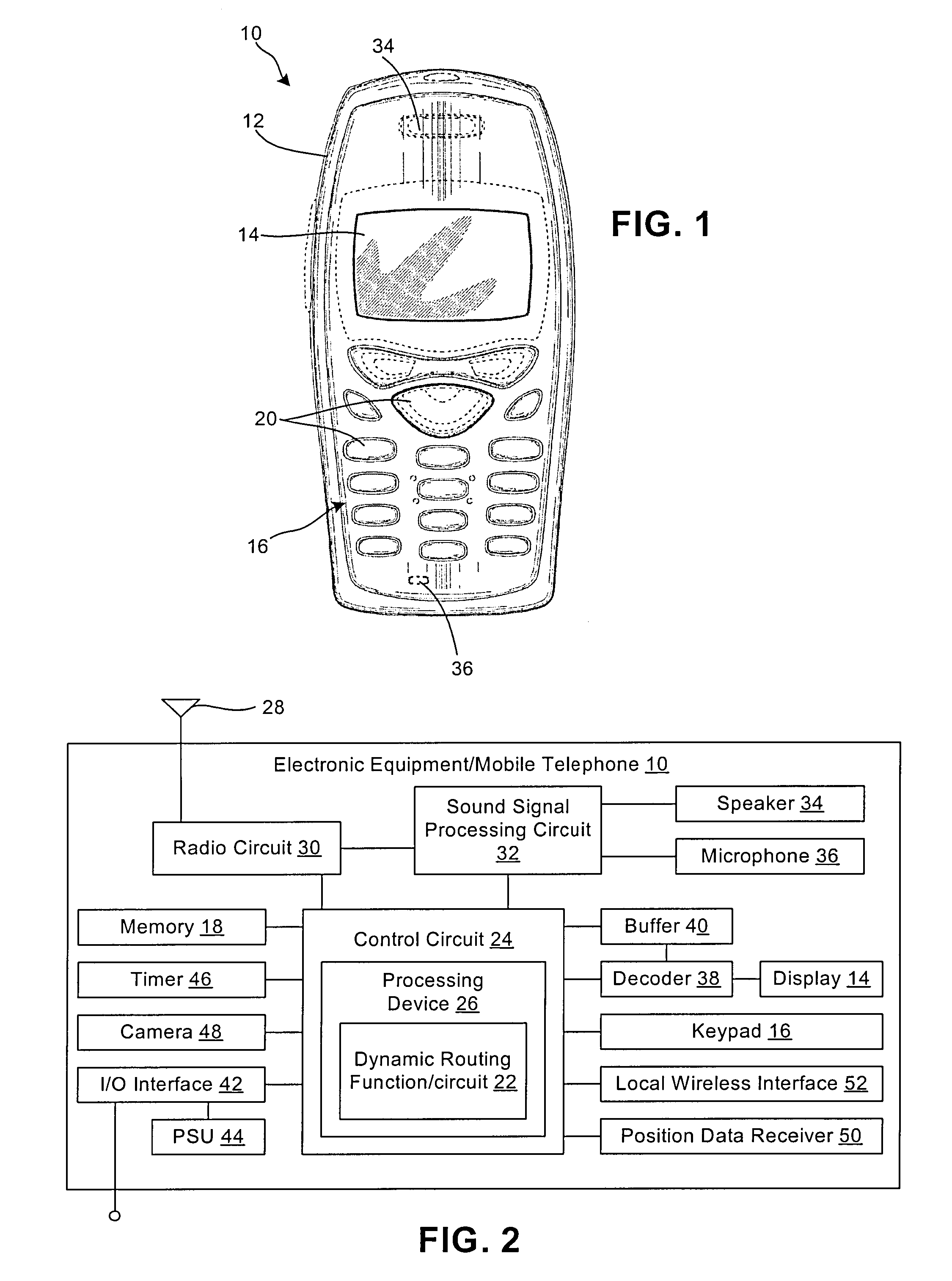
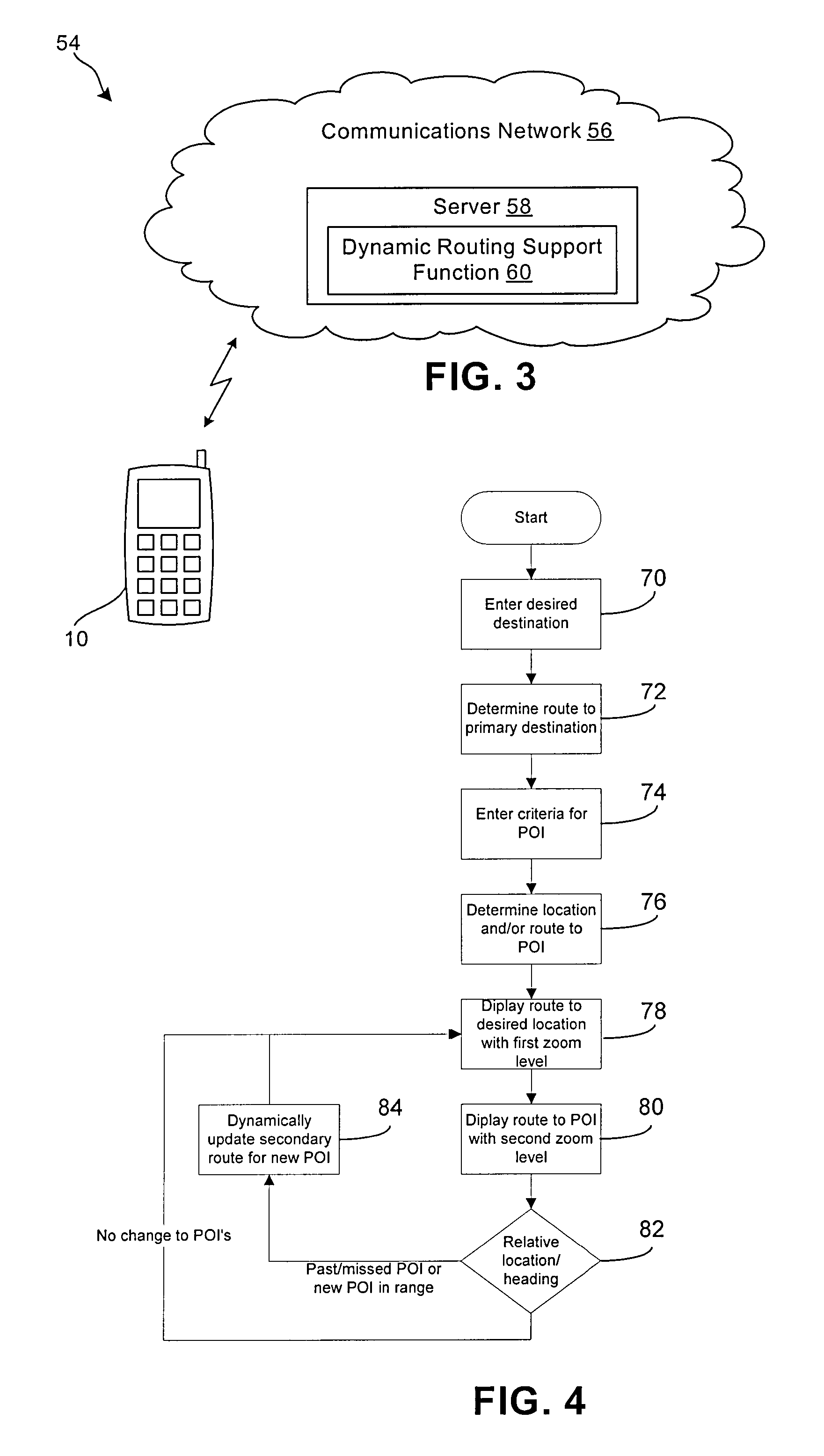
ActiveUS20080140309A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlAdaptive routingComputer science
An apparatus and method for providing navigation information via electronic equipment includes dynamically displaying a first route from a current location to a desired location; and dynamically displaying a second route to at least one point of interest. The first route is automatically displayed at a first zoom level, and the second route is automatically displayed at a second zoom level, wherein the first and second zoom levels are independent of one another. The apparatus and method can further use electronic equipment to identify at least one point of interest along a planned route, including comparing a user selected characteristic to at least one characteristic of a plurality of potential points of interest, said potential points of interest being within a predetermined range of the planned route; and identifying as a point of interest any of the plurality of potential points of interest that have at least one characteristic that satisfies the user selected characteristic.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for establishing layer-striding dynamic source route protocol based on load balance
InactiveCN101415248AReduce the scope of query floodingReduce the number of discoveriesNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesIdle timeNetwork allocation vector
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication and discloses a building method for a layer-spanning dynamic source routing protocol based on load balance. With a single-path routing mode adopted and based on the dynamic source routing protocol, the method comprises the following steps: based on IEEE802.11 MAC layer technology, a cycle T is determined, network distribution vectors in a request frame and an allowing frame sent by a neighbor node S are intercepted within the cycle T, and the idle time of the node is calculated to obtain the residual available bandwidth of the node; the residual available bandwidth, the load, the hop count and the data quantity in a buffer queue of the node S are transferred to the network layer to form routing metrics, and a path parameter with the biggest metric is selected; a plurality of gateways used for shifting flows are built for shunting the flows to separate gateway. The building method for the layer-spanning dynamic source routing protocol based on the load balance can maintain the load balance of the whole network, reduce the routing query flooding range, reduce the times of routing discovery and improve the throughput of WMN.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
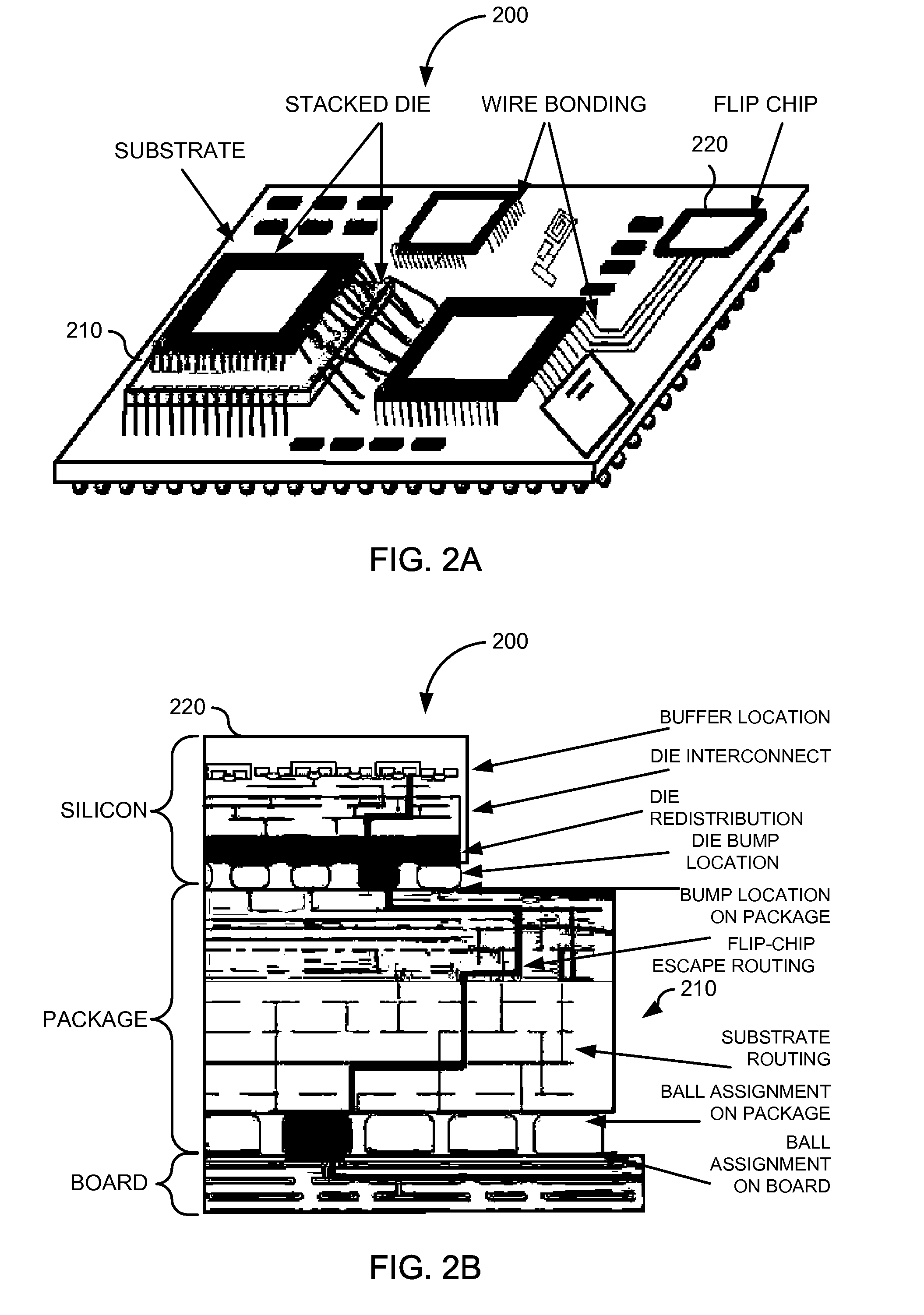
Dynamic push for topological routing of semiconductor packages
ActiveUS8006216B1Shorten the lengthLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNet orderingSemiconductor package
Techniques are disclosed for performing topologically planar routing of System in Packages (SiPs). A routing graph can be represented by a particle-insertion-based constraint Delaunay triangulation (PCDT) and its dual. A dynamic search routing may be performed using a DS* routing algorithm to determine the shortest path on the dual graph between a start point and an end point. Based on a dynamic pushing technique, net ordering problems may be solved. A first wire can be topologically routed. Dynamic search routing of a second wire may be performed. The first wire may be pushed or detoured in response to the dynamic searching routing of a second wire.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
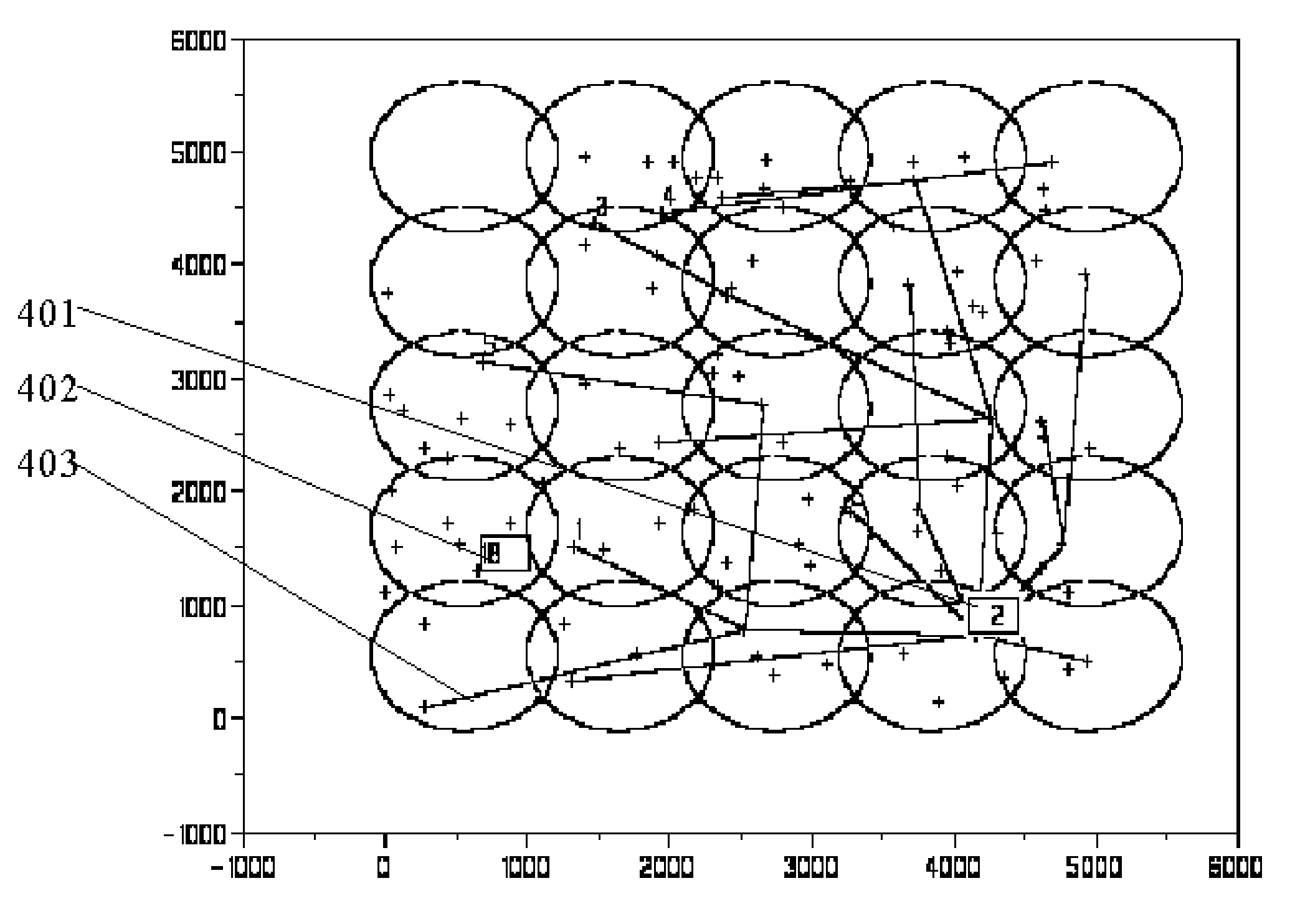
Small Geographical Area Cell-based Dynamic Source Routing for Mobil Ad-hoc Networks
InactiveUS20070280174A1Reduce routing overheadLess affectedData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork densityNetworked system
This invention is about creating a new routing protocol, called Small Geographical Area Cell-based Dynamic Source Routing (SGA-DSR), for the mobile ad-hoc network systems (MANET). The design of this SGA-DSR protocol has greatly reduced the routing overheads over the many other MANET protocols. Because of the routing overhead reduction and its insensitive to the network density, SGA-DSR scales very well to fairly large networks such as covering the whole area, having over thousands of nodes. In all geographical based protocols, the positions and the geographical area boundaries are used in their special ways. Here, in SGA-DSR, the SGA based cells are constructed in a special way. The routing routes are much less affected by the dynamics of the topology changes.
Owner:PUN NGAN CHEUNG
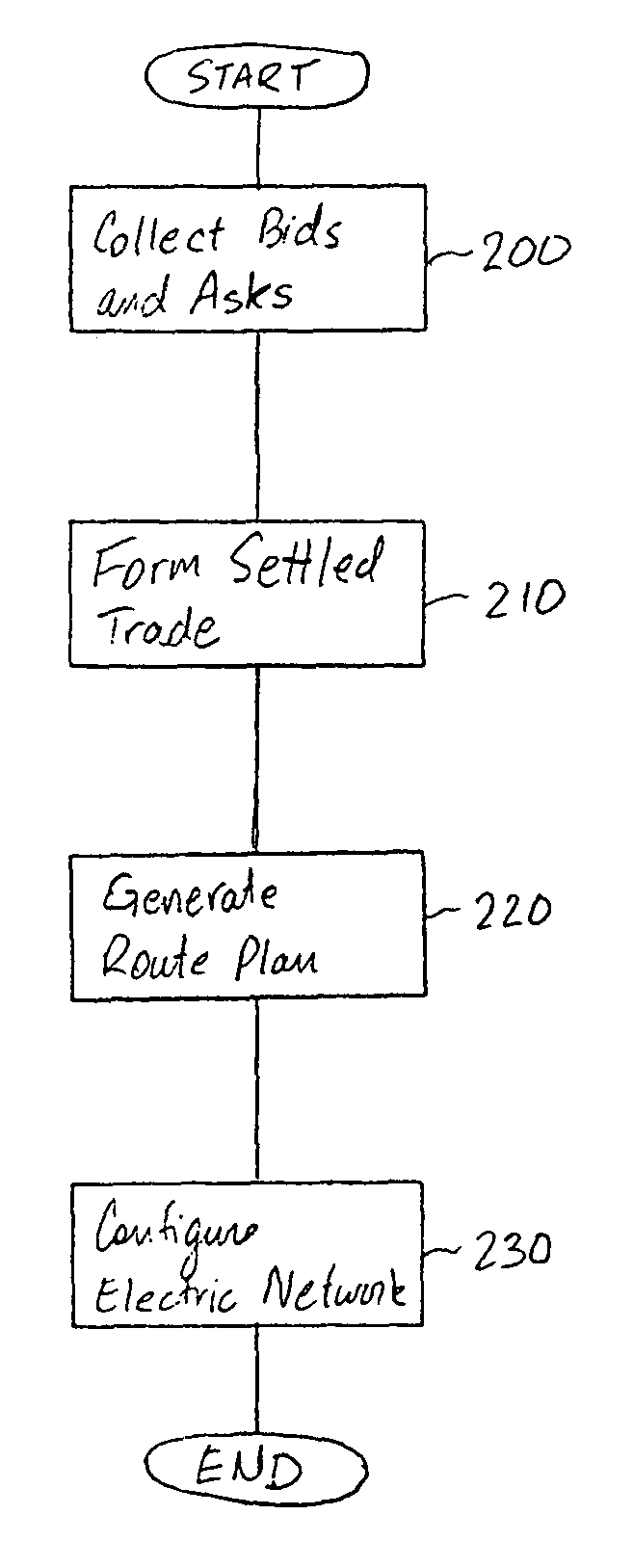
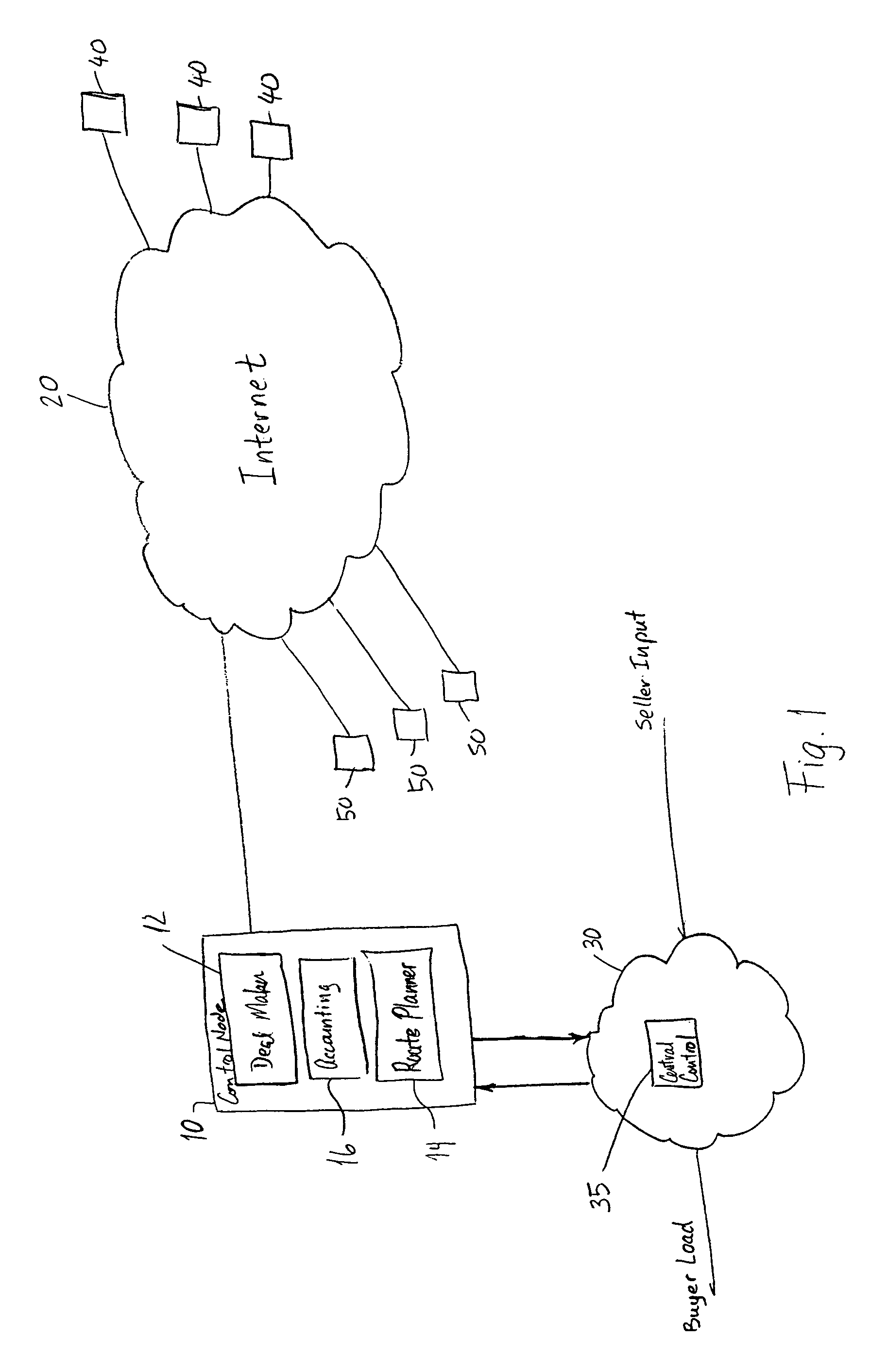
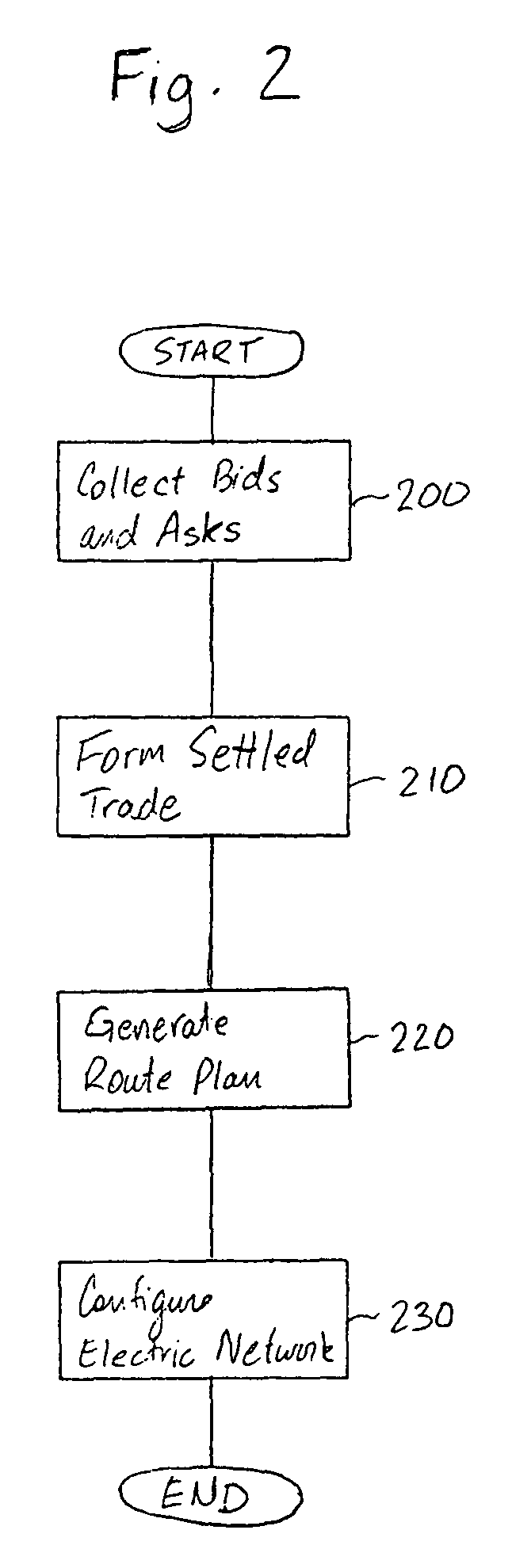
Online trading and dynamic routing of electric power among electric service providers
A method and system for trading electric power on a spot market and dynamically matches bids and asks and routes the electric power in accordance with the matches to effect the settled trades. A control node is arranged for receiving bids and asks via a wide area network. The control node is also connected to a transmission system and a central control of the transmission system to dynamically switch the transmission system to effect the matched bids and asks.
Owner:GRID INNOVATIONS LLC
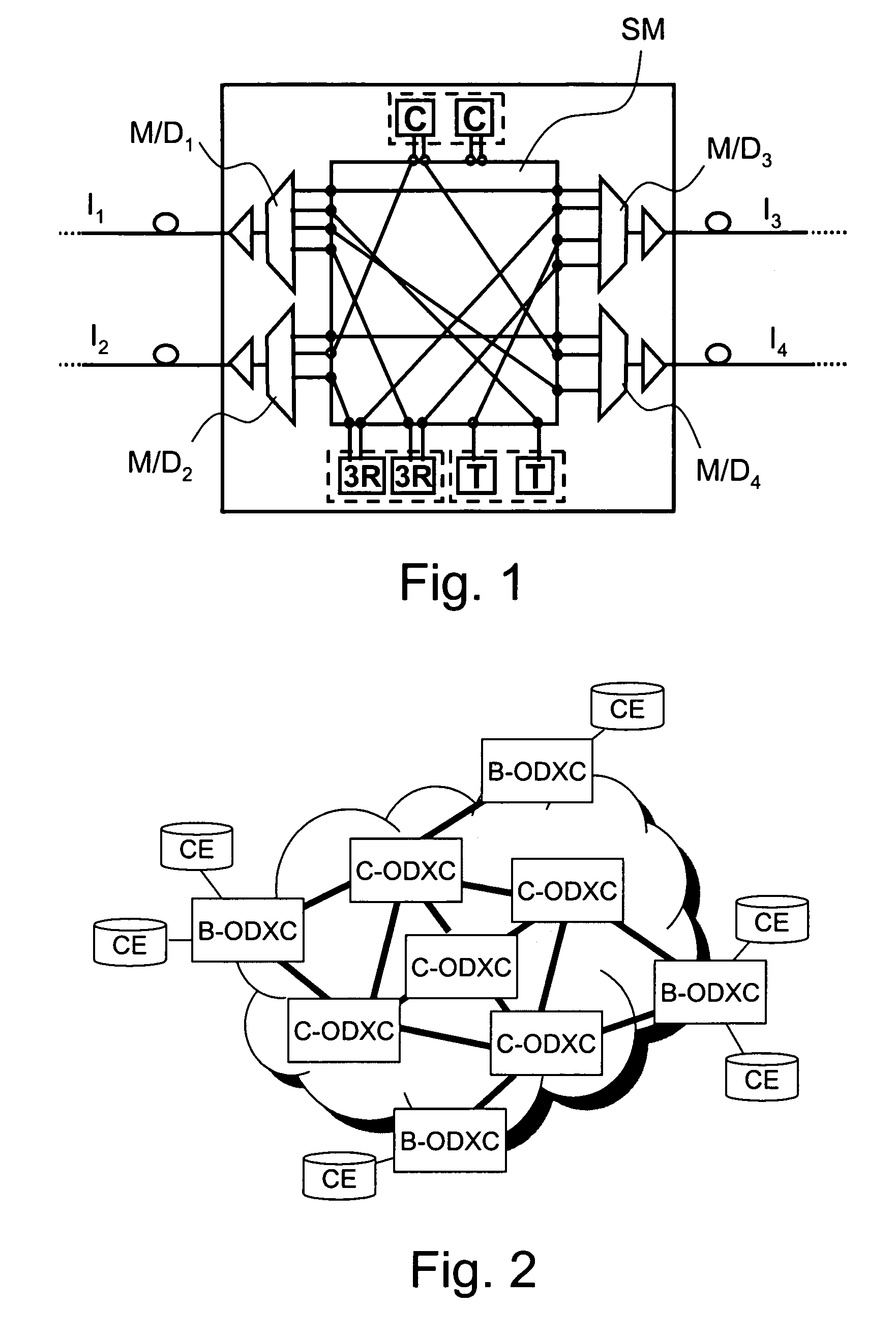
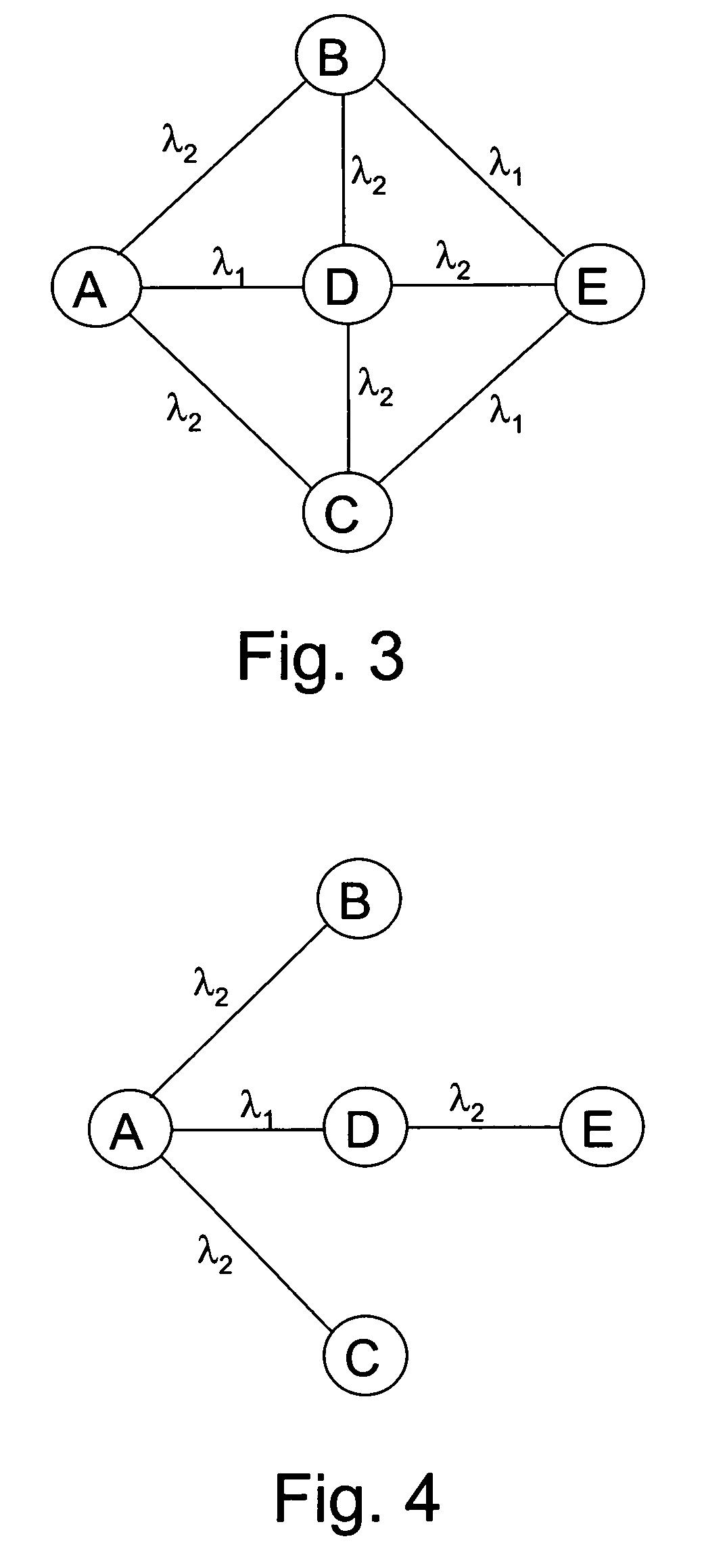
Dynamic routing of optical signals in optical networks
InactiveUS20100086306A1Risk minimizationReduced availabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsData switching by path configurationUltrasound attenuationShort path algorithm
A method for dynamic routing an optical signal in an optical network is provided, including: executing a shortest-path algorithm receiving input concerning a source node, a destination node and the topology of the network, providing a shortest-path tree comprising nodes and arcs connecting the nodes, the shortest-path tree comprising branches along which an effective attenuation is no greater than a predetermined limit, each branch comprising an end node and each end node being associated with a corresponding set of wavelengths; checking, for each end node having no wavelength conversion resources and for each wavelength, if the end node is connected to at least another node external to the branch through the wavelength; excluding, for any end node if the result of the checking is negative for at least one wavelength, the at least one wavelength from the corresponding set of wavelengths, thus updating the topology; and re-executing the shortest-path algorithm.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Distributed dynamic routing
ActiveUS7529239B2Efficient implementationNetworks interconnectionNetwork connectionsTelecommunications networkAdaptive routing
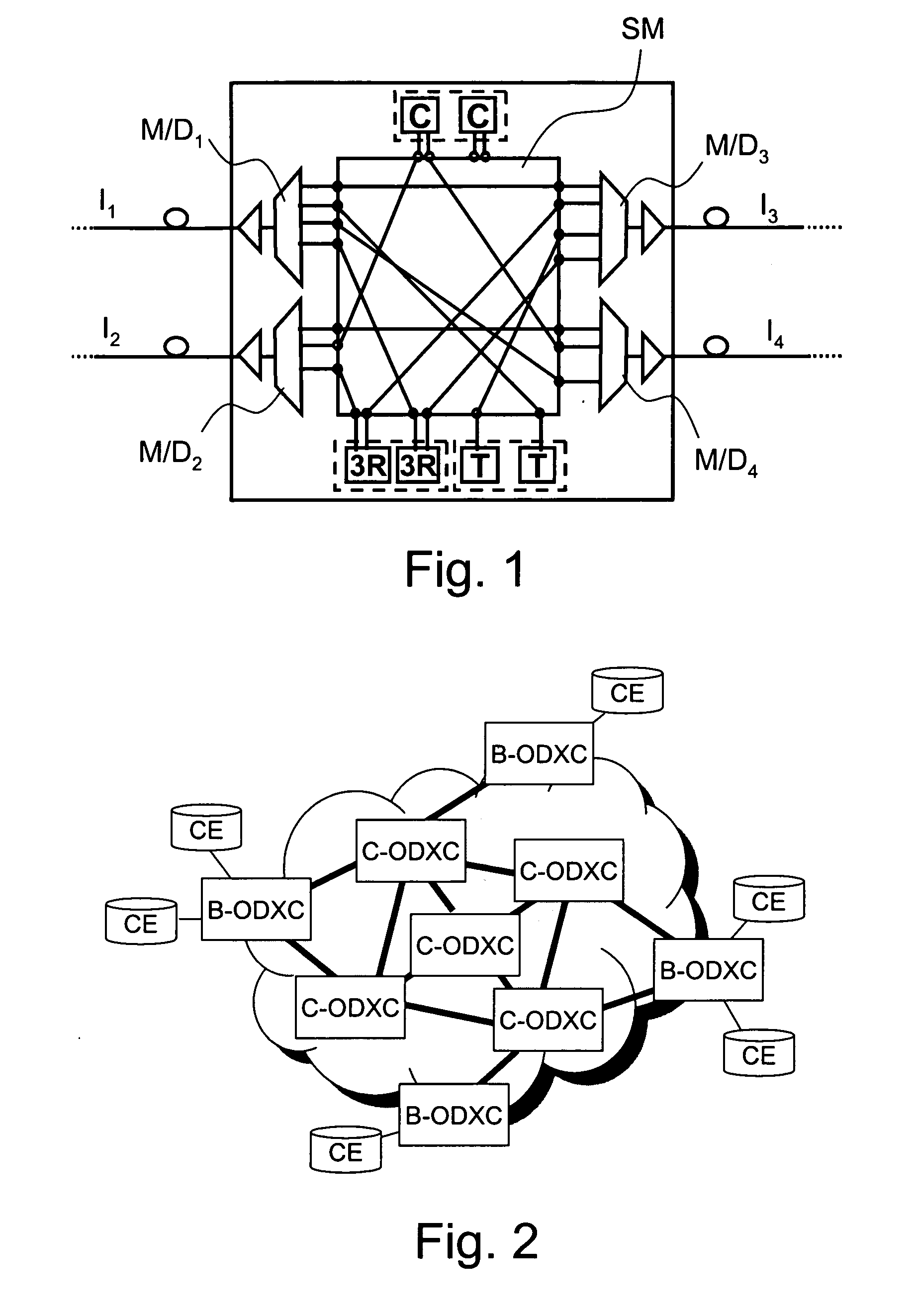
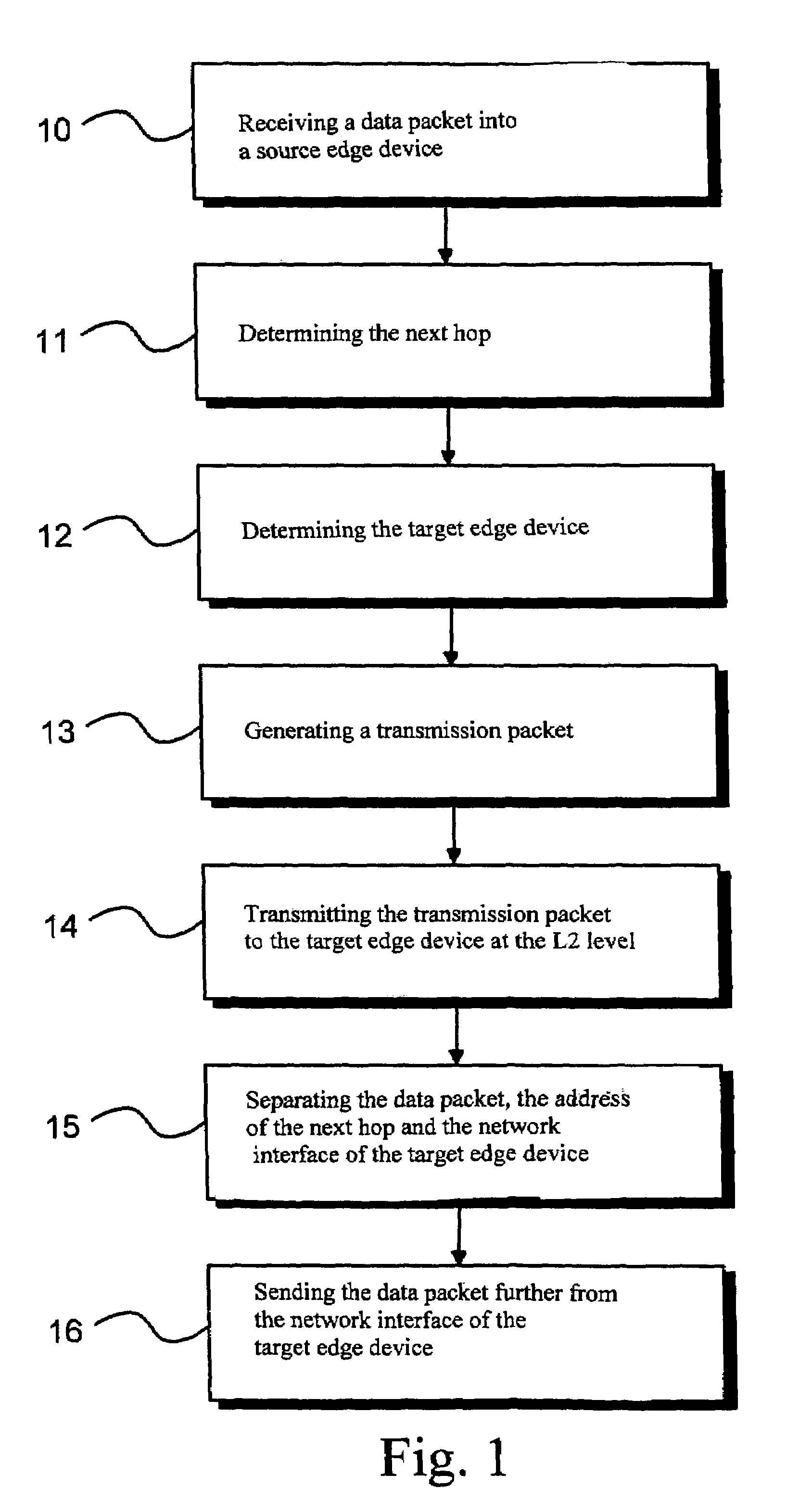
In the present invention, packets are routed in a distributed and dynamic manner via an internal packet-switched telecommunication network comprising edge devices. A data packet is received from an external telecommunication network to a source edge device, wherein there is determined the address of the next-hop corresponding to the destination address prefix of the received data packet. The address and network interface of the target edge device corresponding to the determined next hop are determined and there is generated a transmission packet addressed to the determined target edge device, the transmission packet comprising the received data packet and the determined address of the next hop and the determined network interface of the target edge device. The generated transmission packet is transmitted from the source edge device to the target edge device via one or more internal telecommunication networks at the data link layer level. The data packet is sent further via the network interface of the target edge device based on the next-hop address in question.
Owner:XYLON LLC
Wireless sensor network system based on dynamic routing and method thereof
InactiveCN103889020AImprove reliabilityCompliant with the process industryNetwork topologiesNode clusteringWireless mesh network
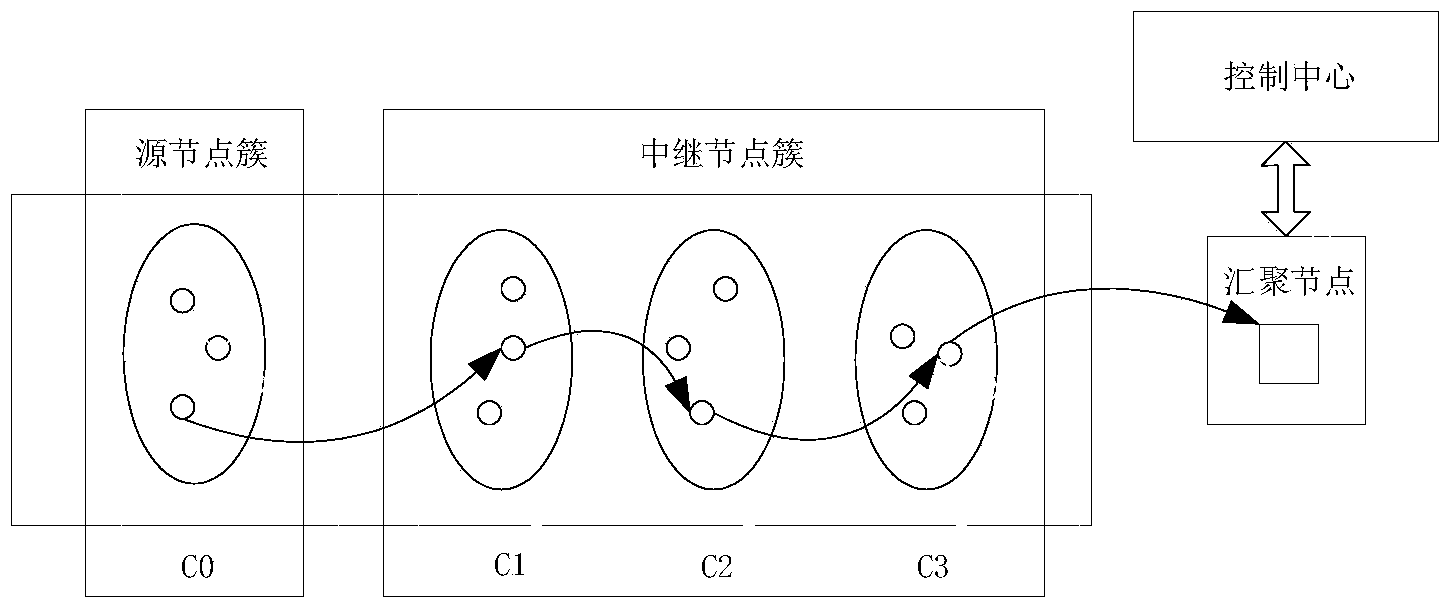
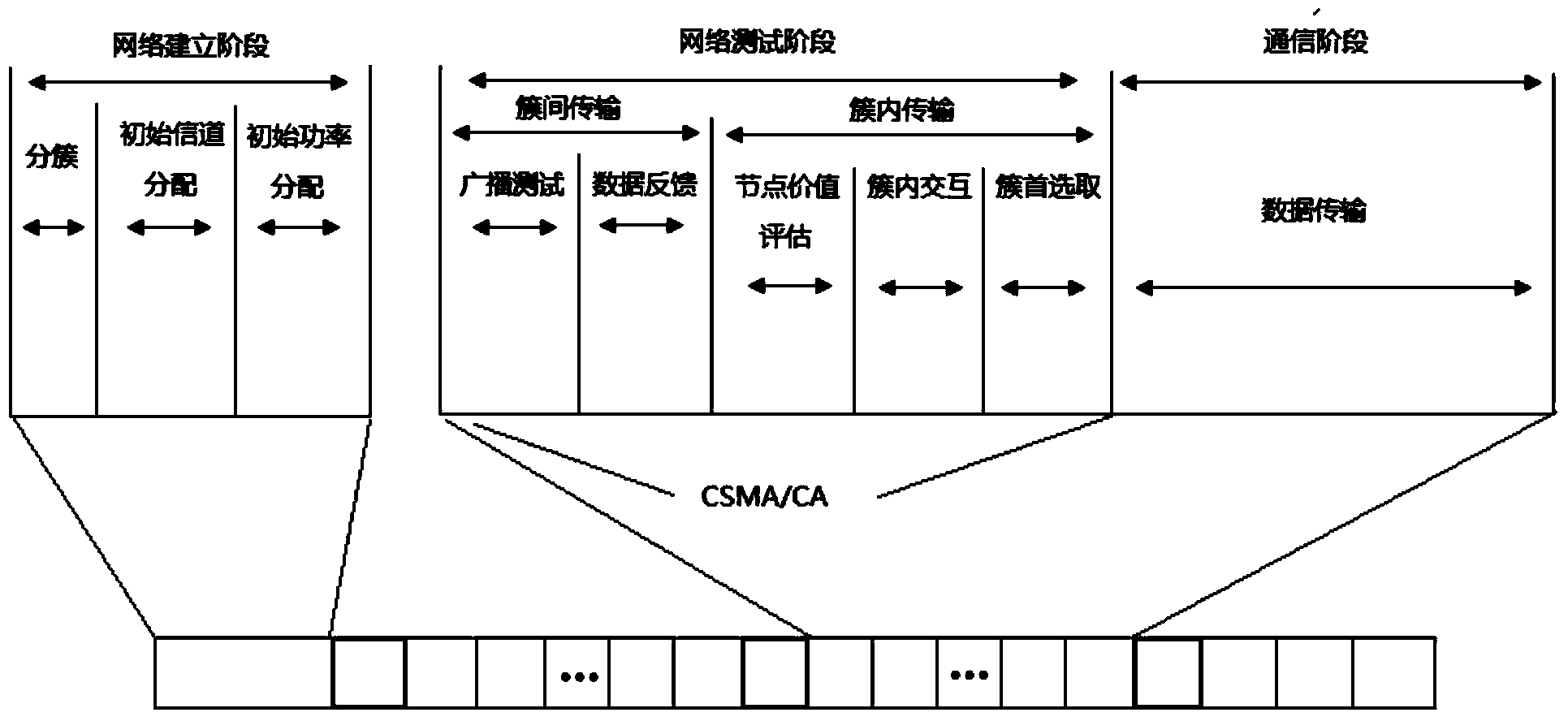
The invention provides a wireless sensor network system based on dynamic routing, wherein the system is used for the industry. The wireless sensor network system based on dynamic routing comprises a source node cluster, a relay node cluster, a sink node and a control center, and a routing link is composed of a cluster head node of the source node cluster, a cluster head node of the relay node cluster and the sink node. In the idle stage of an industrial network, a test is performed on the link to acquire link quality data, the cluster head nodes are selected according to the link quality data, and a routing link is dynamically selected. According to the wireless sensor network system based on dynamic routing and a dynamic routing selecting method of the system, a clustering structure is provided, a work node is divided into multiple modules, and thus the work node can be suitable for characteristics of the process industry. The periodization characteristic of the process industry is considered, the link test is completed in the idle time slot of the process industry, so that the routing link is dynamically selected, and the reliability of sensor network data transmission is improved. A data retransmission mechanism and an emergency mechanism are introduced, and thus sudden change of environment and other problems can be effectively handled.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Wireless network optimization method for intelligent meter reading system
InactiveCN104010343ASolve problems such as non-correlation cannot be guaranteedAvoid breakingNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission congestionData transmission
The invention discloses a wireless network optimization method for an intelligent meter reading system. The method is an improved dynamic routing allocation optimization algorithm. The method mainly solves the routing optimization problem of a wireless network layer, DSR is preliminarily optimized, the unrelated routing number in the DSR is increased, and the enhanced DSR optimization algorithm is provided. In order to solve the route selection problem in the enhanced DSR optimization algorithm, the minimum spanning tree thought is introduced into the DSR, a DSR optimization protocol based on a minimum spanning tree is provided, factors in multiple aspects of bandwidth, transmission congestion, network throughput and the like are comprehensively considered, simulation software NS-2 is used for simulation, and the result shows that the method can effectively shorten delay and improve data transmission efficiency and other indexes.
Owner:MICROCYBER CORP
Automatic routing to event endpoints
InactiveUS20180202819A1Well formedProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorPhysical spaceAutomatic routing
Automatically identifying a route for a physical entity to take within a physical space in order to go to an event endpoint where an event happened, is happening, or is predicted to happen. Thus, instead of static routing in which routing is made to a fixed endpoint, dynamic routing is achieved relating to event(s). The identified endpoint may be an activity, a mobile physical entity or a group of mobile physical entities, or the like. A route is formulated that moves a particular physical entity from a current location to a location of the identified event within the physical space. The route formulation may occur via reference to a physical graph representing physical entities that are monitored within the physical space over time. Furthermore, the route formulation may occur in coordination with a planning component that orchestrates movements of physical entities within the physical space.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Dynamic routing
InactiveUS20080102851A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmissionShort termsAdaptive routing
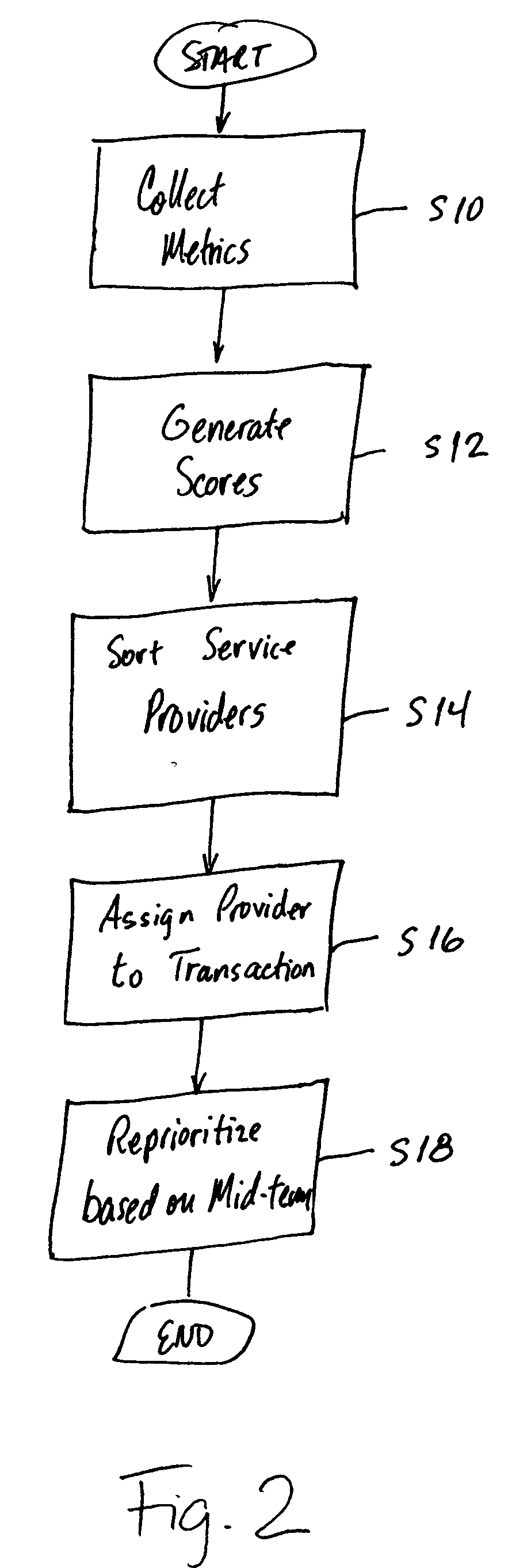
A method for managing transactions across a large number of service providers includes determining performance metrics associated with each of a plurality of service providers and generating a score for each service provider based on the performance metrics associated with each of the plurality of service providers taken over a short time period. The service providers are then sorted based on the scores to generate a list of service providers. Customer transactions are then assigned to one of the service providers based on the order of the list of service providers. The list of service providers is reprioritized based on mid-term metrics and accumulated costs taken over a mid-term period that is longer than the short term period.
Owner:AIP ACQUISITION
System and method for dynamic routing
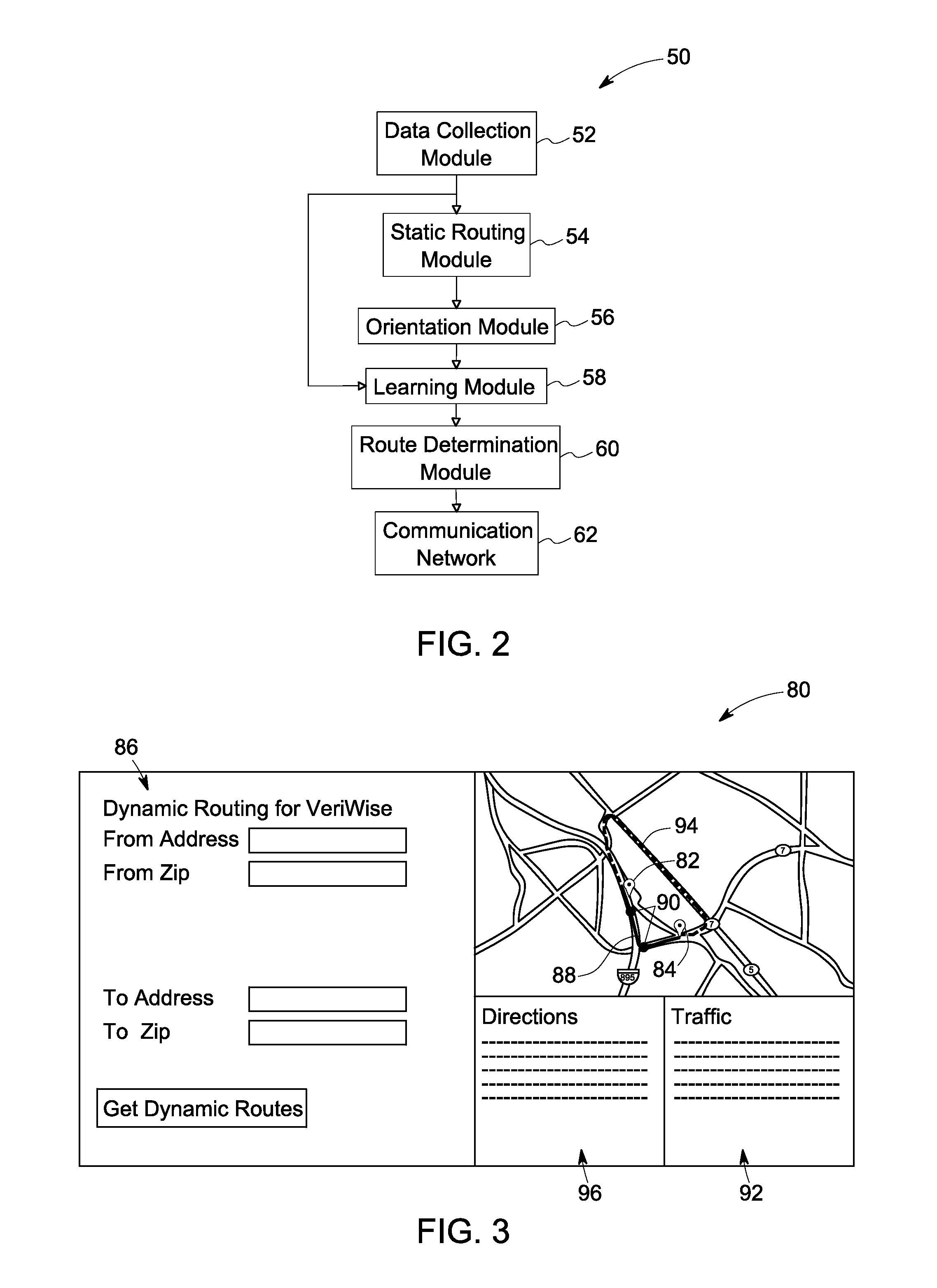
InactiveUS20110246067A1Improved and automatedInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlCommunication interfaceAdaptive routing
A dynamic routing system includes a data collection module, a static routing module, an orientation module, a learning module, and a route determination module. The data collection module receives real time trip data corresponding to a moving asset from a remote location, and the static routing module determines candidate routes from a source to a destination for the moving asset. The orientation module is configured to gather publically available information associated with candidate routes, and the learning module is configured to generate a learned route database based on the publically available information from the orientation module and the real time trip data from the data collection module. The route determination module determines an optimized route for the moving asset based on the learned route database. The system further includes a communication interface configured to transmit an optimized route signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
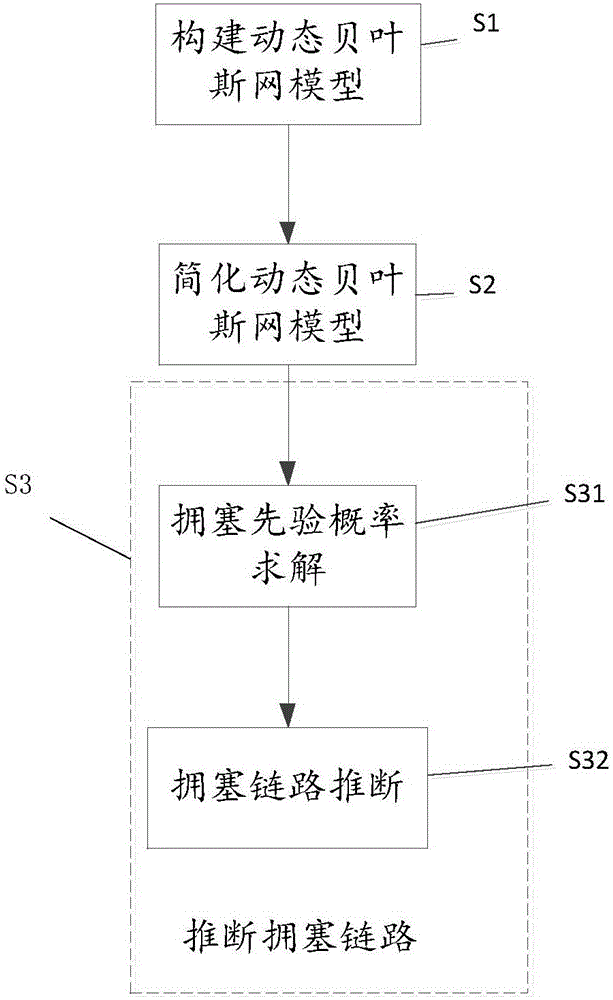
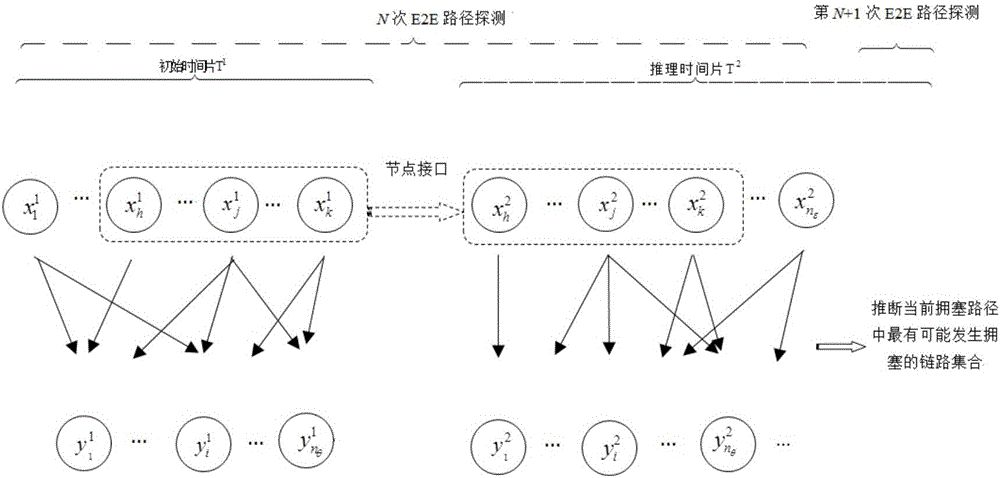
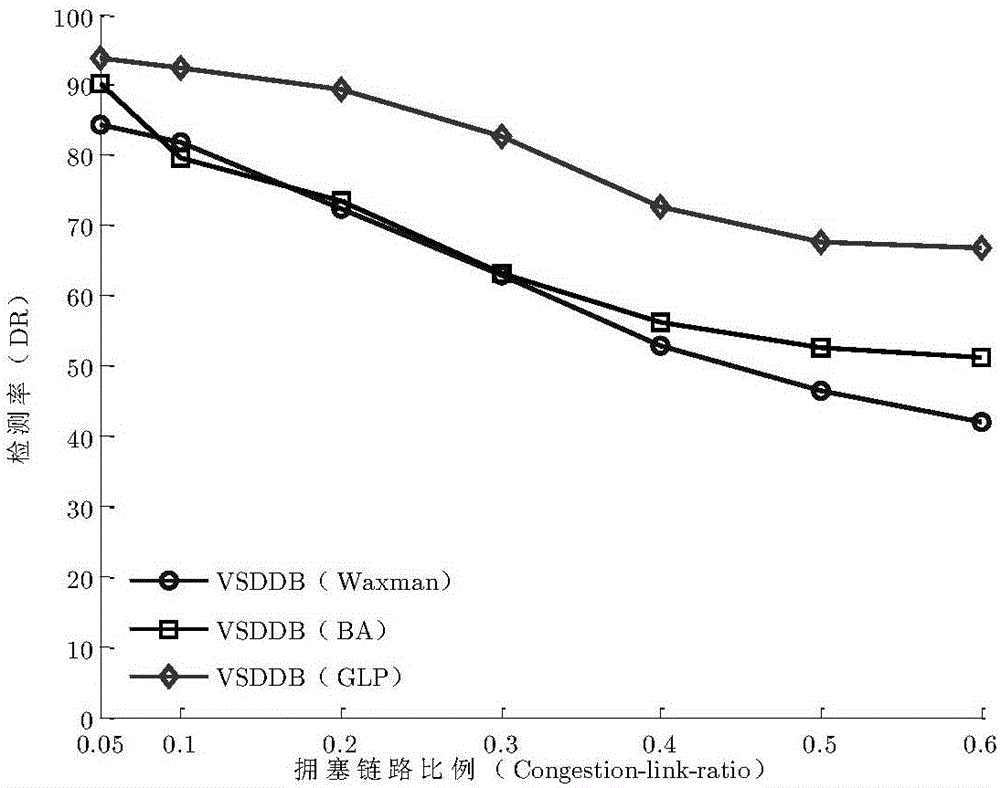
IP network congestion link positioning method
InactiveCN106453113AImprove accuracyImprove robustnessData switching networksReduced modelDynamic Bayesian network
The invention discloses an IP network congestion link positioning method. In the method, aiming at dynamic characteristics of IP network routing, a variable structure discrete dynamic Bayesian network model is established according to detection results of path performance and a topology structure obtained by multiple end-to-end detection, and is simplified according to first-order Markovian hypothesis and homogeneity hypothesis, and an IP network congestion link is deduced based on the simplified model, so that the deduction of the IP network congestion link under dynamic routing is realized. By performing imitation experiments and simulation experiments on different types and scales of IP networks and using a traditional CLINK algorithm and the method provided by the invention to deduce the congestion link in the same scene respectively, the experiment proves that compared with the CLINK algorithm, the method provided by the invention is higher in deduction accuracy and robustness.
Owner:中国人民解放军防空兵学院 +1
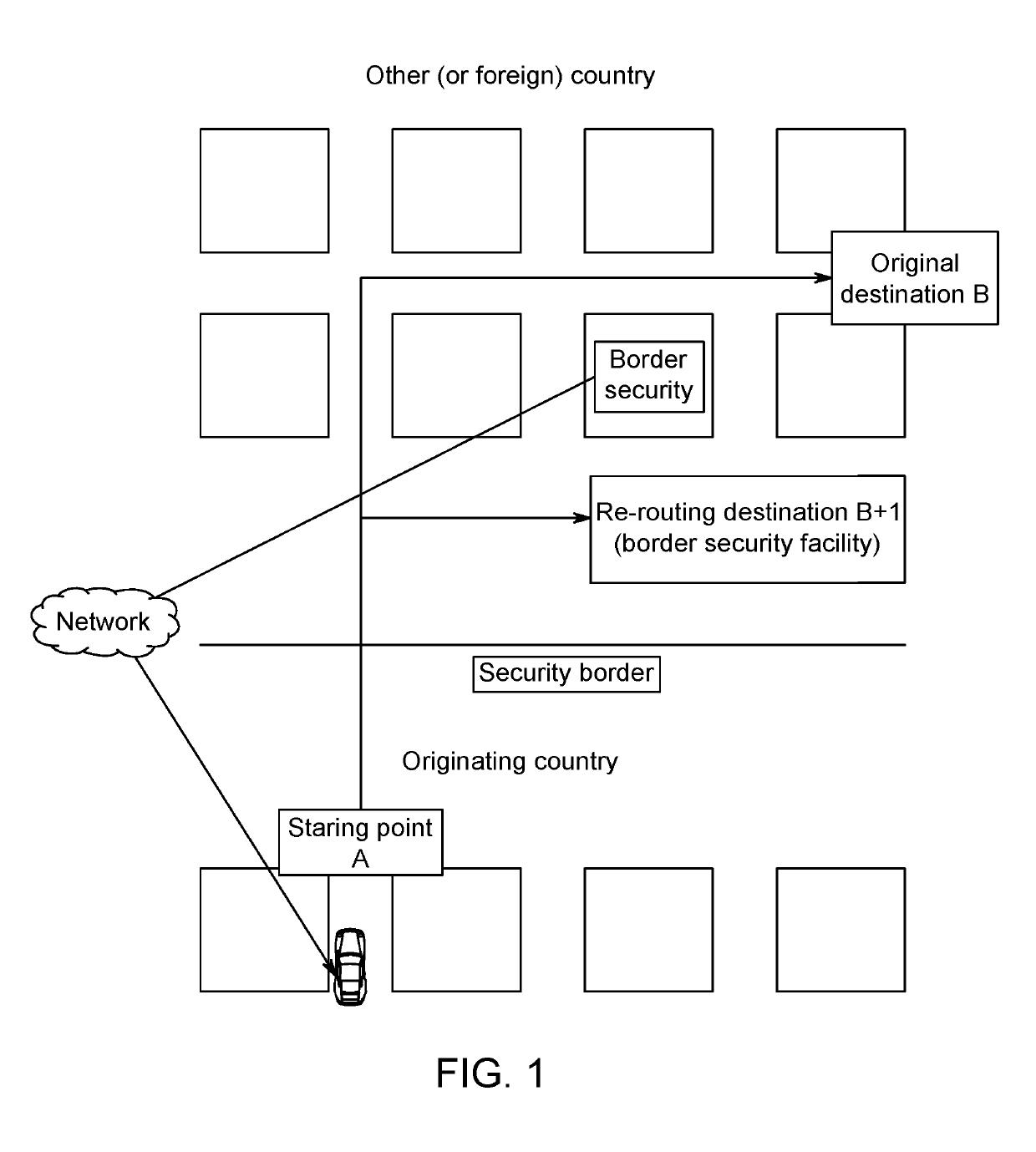
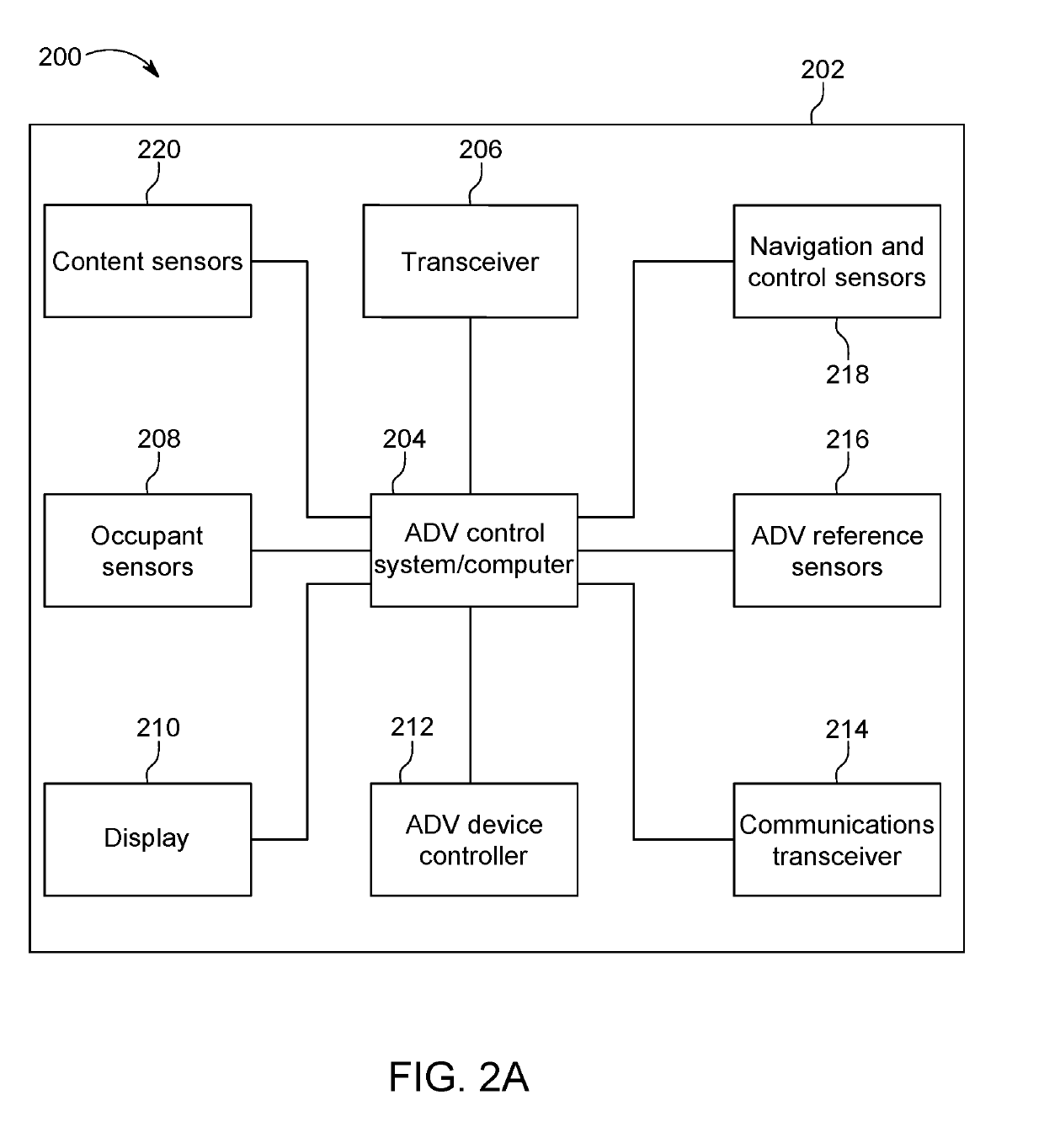
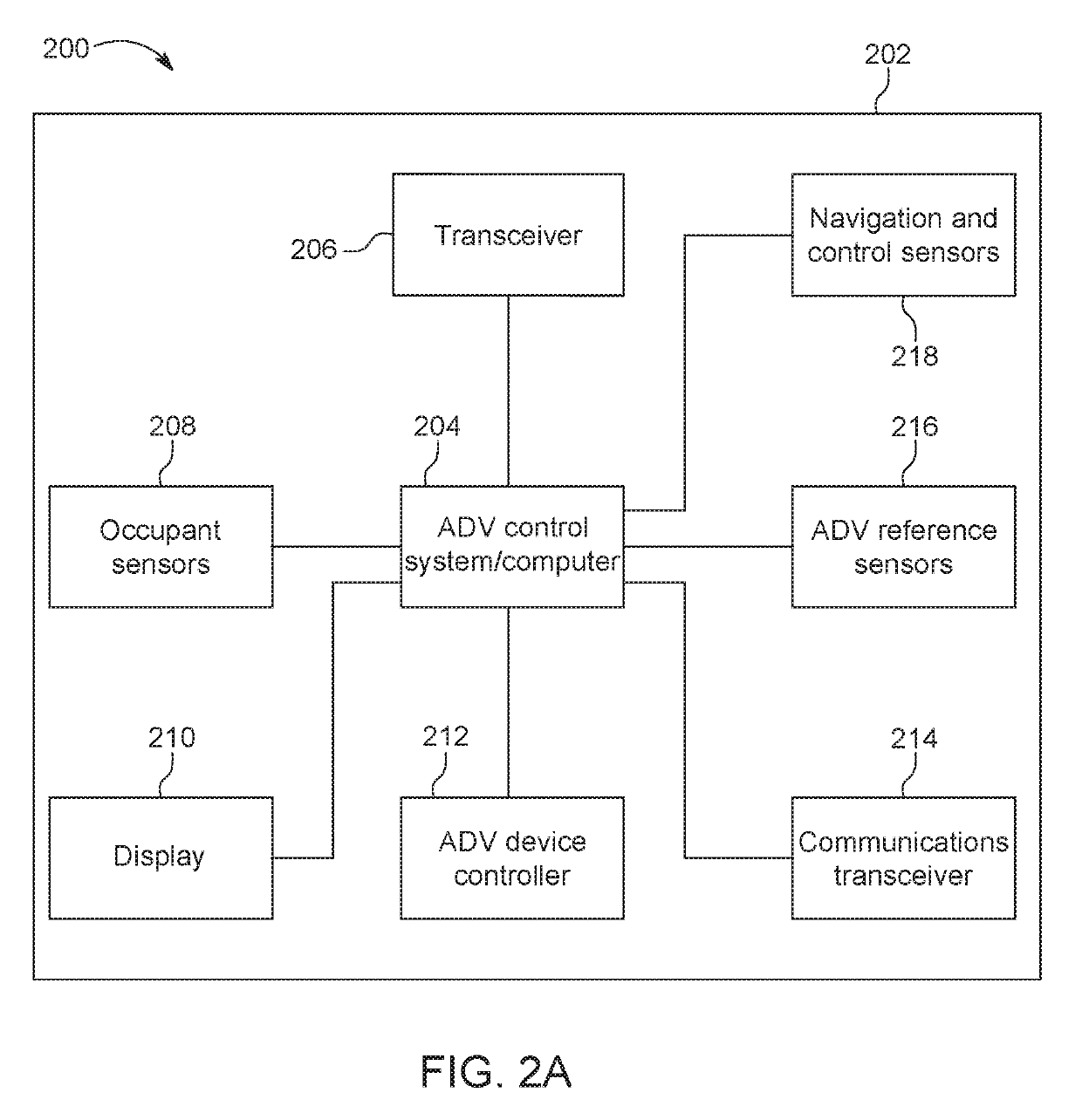
Re-routing autonomous vehicles using dynamic routing and memory management for border security purposes
ActiveUS20190293437A1Assisted identificationInstruments for road network navigationData processing applicationsOn boardControl system
The invention relates to a system and method for navigating an autonomous driving vehicle (ADV) that utilizes an-onboard computer and / or one or more ADV control system nodes in an ADV network platform. The on-board computer receives physiological and ADV occupant identification sensor data concerning one or more occupants occupying an ADV, sensor data concerning the items being transported within the ADV, and information concerning the ADV itself to aid border security agencies in protecting their respective borders and territories (e.g., international borders, security zone borders, geographical borders, etc.). The relevant border agency can receive certain information over a network concerning one or more ADVs and make a determination if a heightened security screening should be requested. In response to a request, the on-board computer automatically initiates a dynamic routing algorithm that utilizes artificial intelligence to re-route the ADV to a predetermined destination, for example a border security facility.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
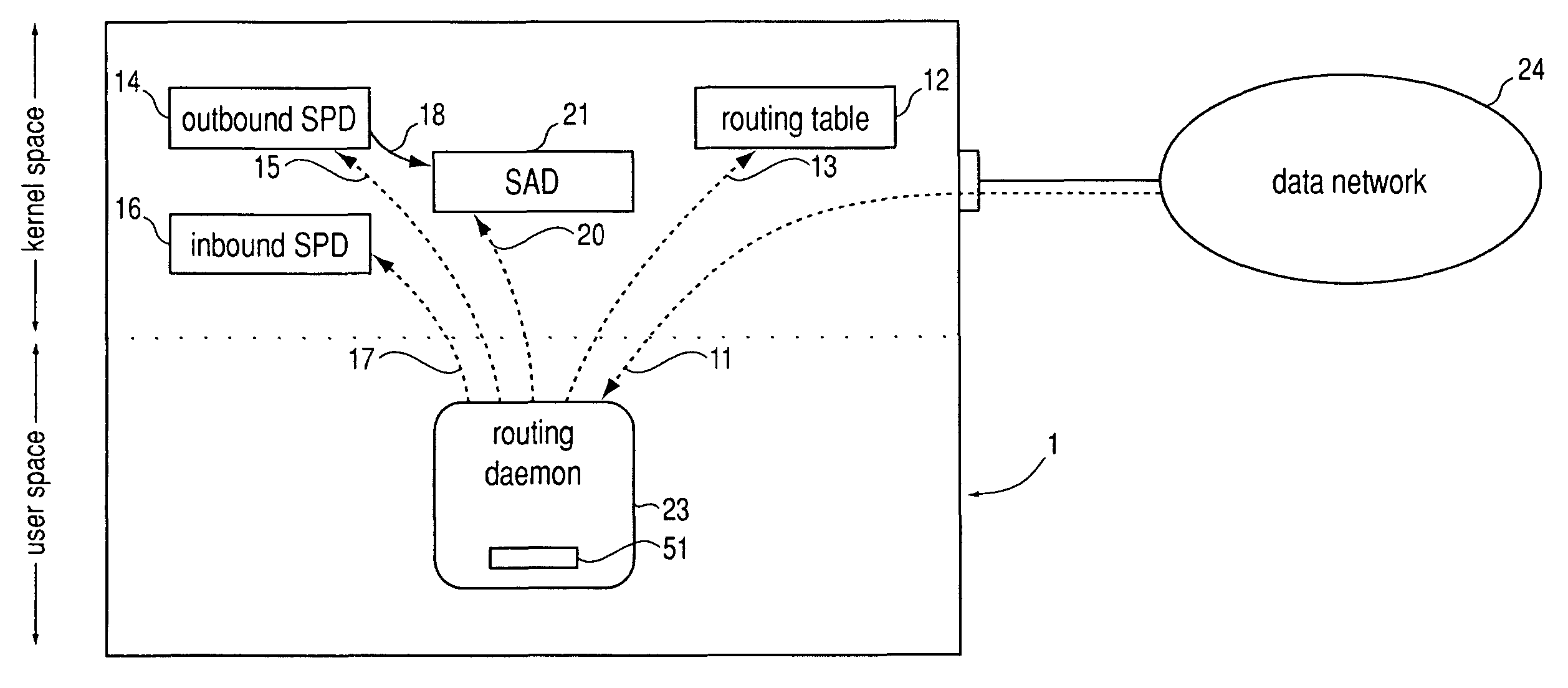
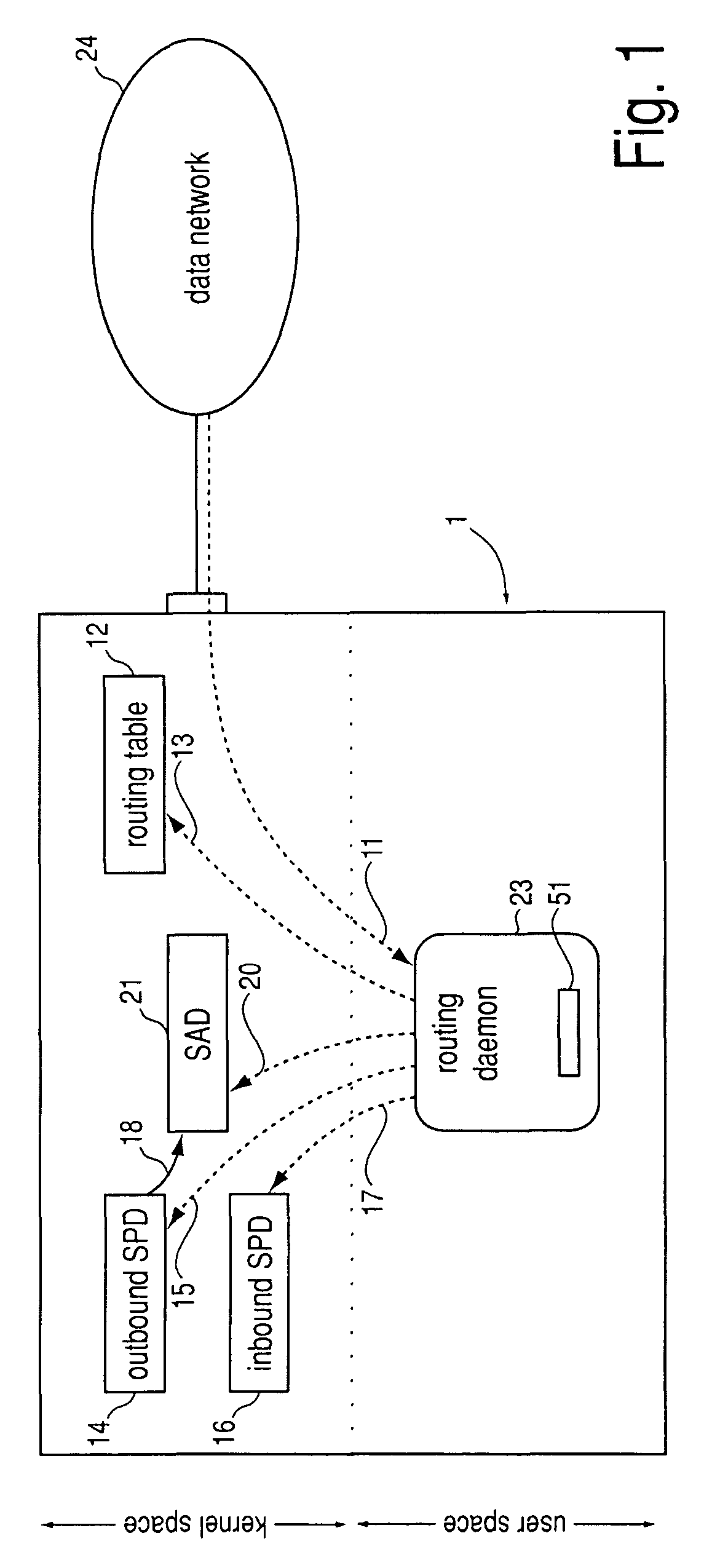
Method, system and storage medium for establishing compatibility between IPsec and dynamic routing
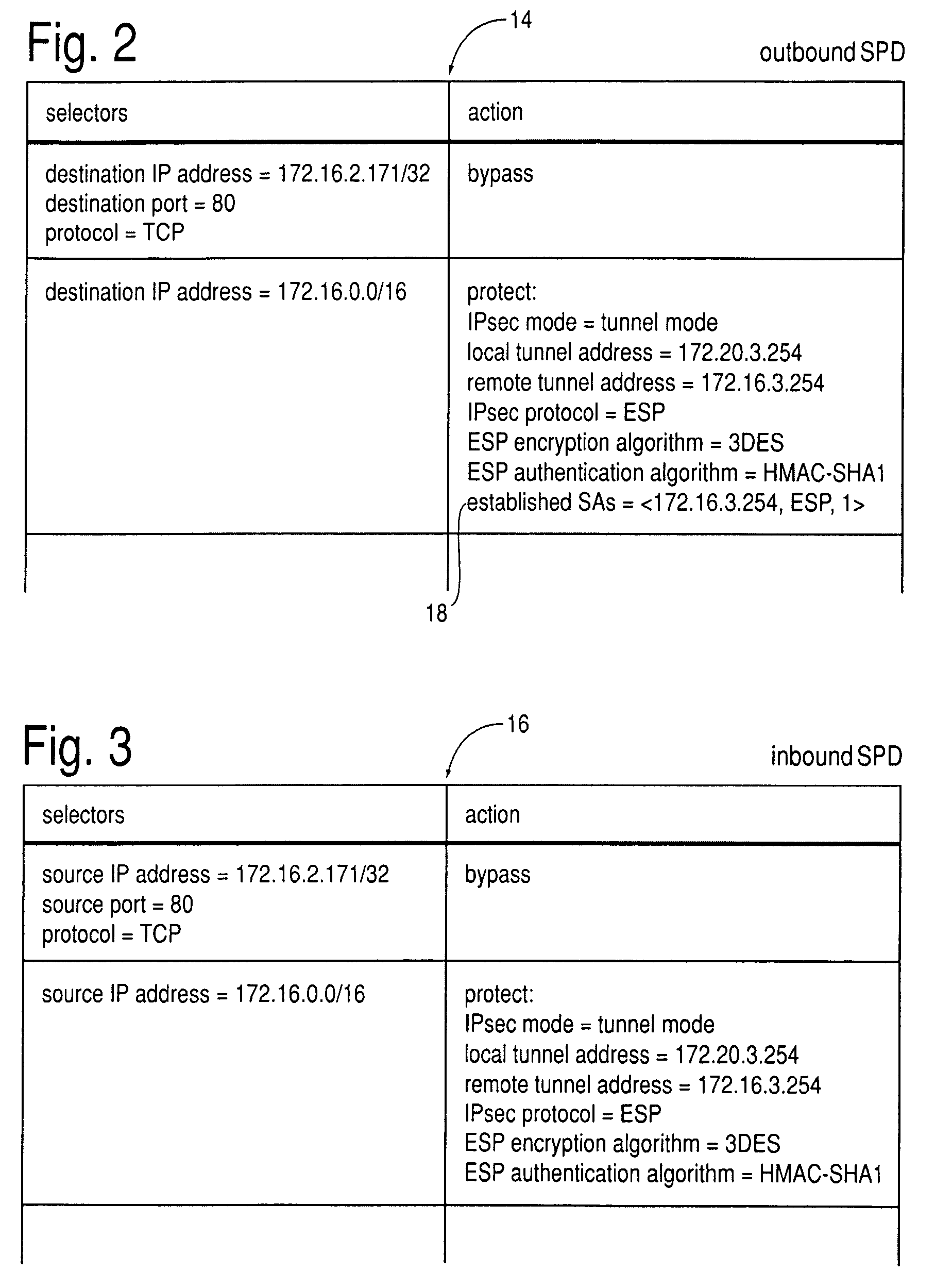
ActiveUS7945666B2Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsRouting tableIPsec
A method, system and storage medium wherein reachability information is exchanged over IPsec tunnels by means of a dynamic routing protocol, but instead of incorporating it into the normal routing table, it is incorporated into the IPsec data structures SPD and SAD by performing a set of steps.1 Thereby, disadvantages of prior art efforts to establish compatibility between IPsec and dynamic routing, for instance IIPtran (RFC 3884), are overcome in that compatibility is established without modifying the processing of datagrams by IPsec.2 This may be implemented by extending the routing daemon so that it supports inserting or removing entries in the SPD and SAD using the PF KEY API.3 Further embodiments feature cryptographically signing and filtering advertised reachability information, redistribution of reachability information between the dynamic routing in the base network and the overlay network, a new routing protocol tailored specifically to IPsec and load sharing over multiple IPsec tunnels.41 [0043-0054]2 [0009-0023]3 [0064-0068]4 [0055-0059], [0061-0063], [0069-0079] and [0080-0081]
Owner:WUNNER LUKAS
Ant-colony-system-based dynamic routing and wavelength assignment method for optical network
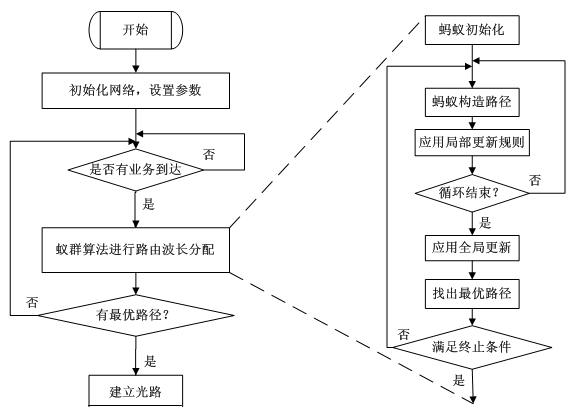
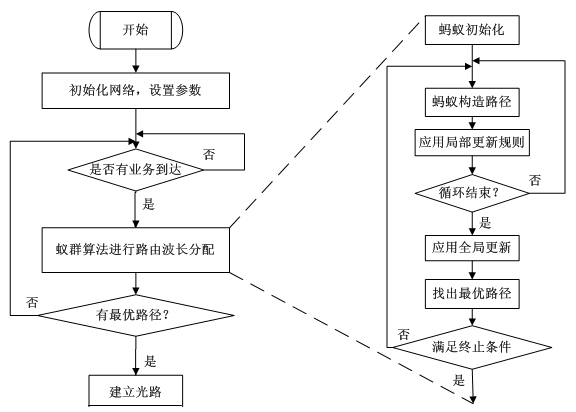
InactiveCN102196325AReduce search timeAvoid congestionMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLocal optimumEqualization
The invention discloses an ant-colony-system-based dynamic routing and wavelength assignment method for an optical network. In the method, an ant colony system is introduced into the dynamic routing and wavelength assignment of the optical network, the problems of wavelength assignment and network equalization are fully taken into account, and vacancy rates of links are introduced into the transition probability of an ant colony algorithm as constraint conditions to avoid overmany services selecting the same link, thereby effectively reducing the average blocking rate of the whole optical network; and non-intelligent ants are further introduced to meet the requirement of the routing and the wavelength assignment on real-time performance and prevent searching from being convergent in a locally optimal path too early.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Dynamic routing of optical signals in optical networks
InactiveUS8369707B2Improve availabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsData switching by path configurationUltrasound attenuationShort path algorithm
A method for dynamic routing an optical signal in an optical network is provided, including: executing a shortest-path algorithm receiving input concerning a source node, a destination node and the topology of the network, providing a shortest-path tree comprising nodes and arcs connecting the nodes, the shortest-path tree comprising branches along which an effective attenuation is no greater than a predetermined limit, each branch comprising an end node and each end node being associated with a corresponding set of wavelengths; checking, for each end node having no wavelength conversion resources and for each wavelength, if the end node is connected to at least another node external to the branch through the wavelength; excluding, for any end node if the result of the checking is negative for at least one wavelength, the at least one wavelength from the corresponding set of wavelengths, thus updating the topology; and re-executing the shortest-path algorithm.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Re-Routing Autonomous Vehicles Using Dynamic Routing and Memory Management
ActiveUS20190277643A1Insufficient improvementInstruments for road network navigationAutonomous decision making processControl systemOn board
The invention relates to a system and method for navigating an autonomous driving vehicle (ADV) that utilizes ADV an-onboard computer and / or one or more ADV control system nodes in an ADV network platform. The on-board computer receives sensor data concerning one or more occupants occupying an ADV and / or the ADV itself and, upon a detection of an event, automatically initiates a dynamic routing algorithm that utilizes artificial intelligence to re-route the ADV to another destination, for example a healthcare facility. One or more embodiment of the system and method include an ADV on-board computer and / or one or more ADV network platform nodes that utilize in-memory processing to aid in the generation of routing, health and navigational information to advantageously navigate an ADV.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
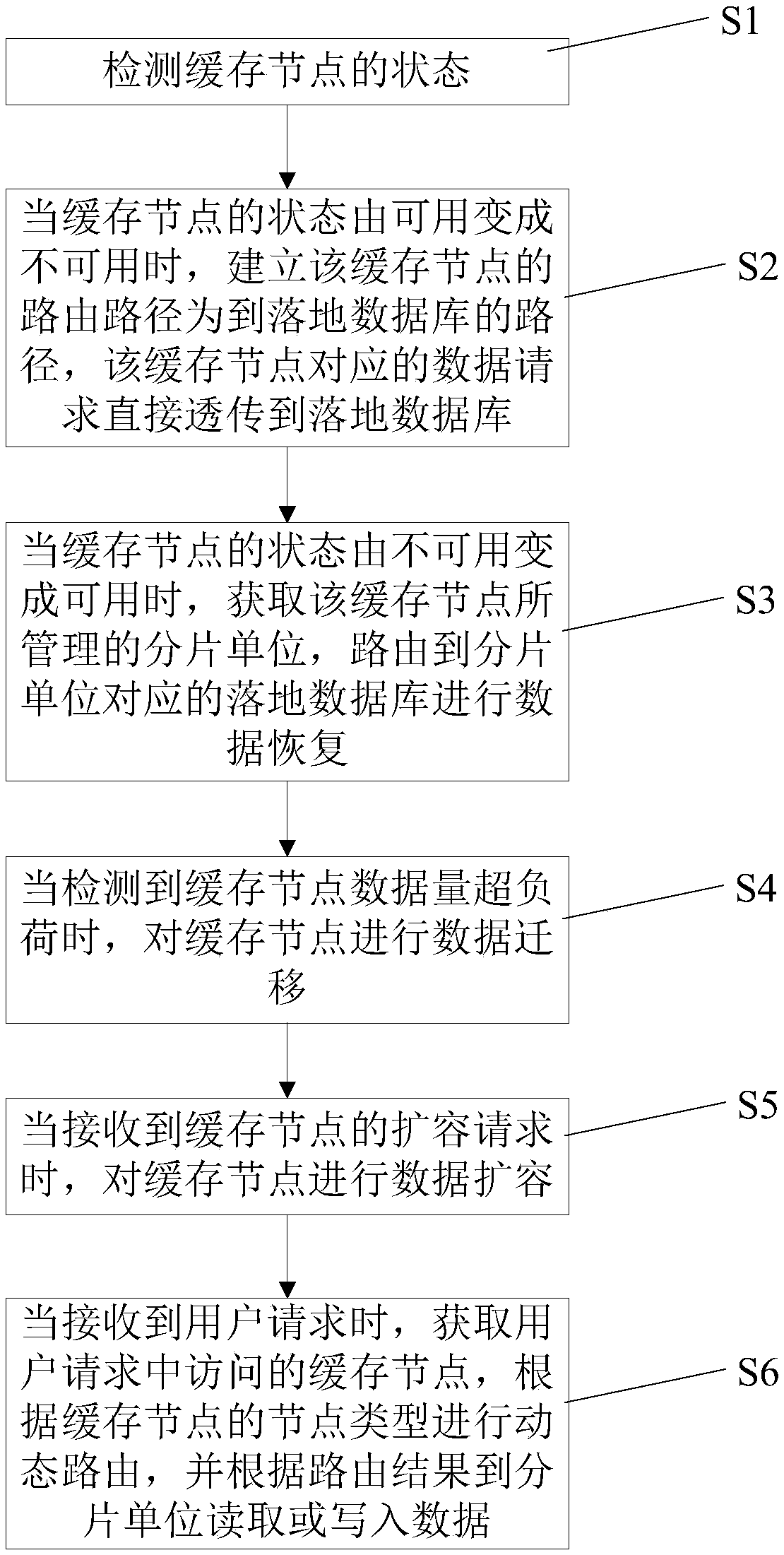
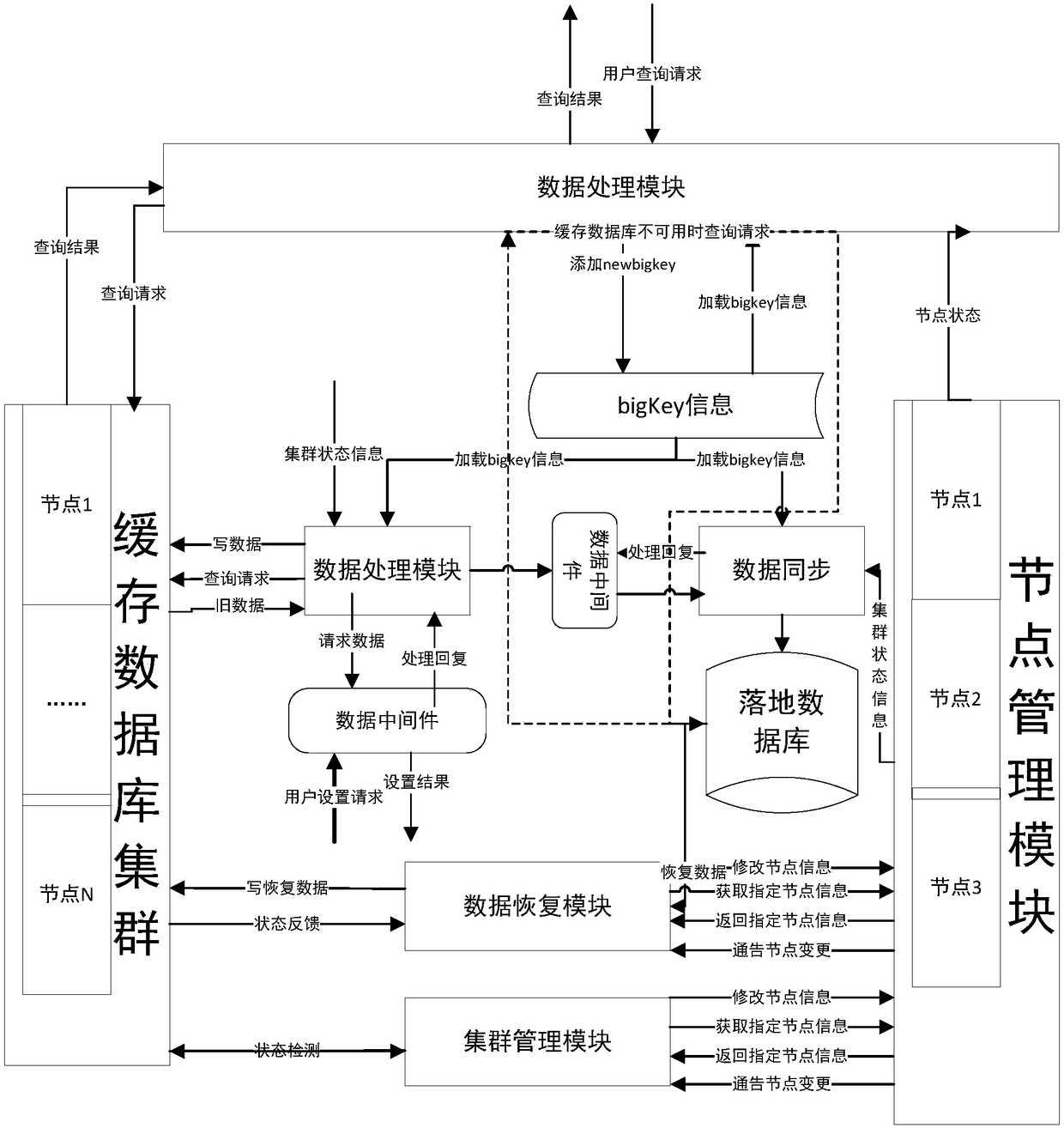
Data storage access method and system based on dynamic routing
The invention provides a data storage access method and system based on dynamic routing. The method comprises the following steps of directly transmitting a data request corresponding to a cache nodeto a landing database when a state of the cache node is changed from an available state to an unavailable state; when the state of the cache node is changed from the unavailable state to the availablestate, carrying out data recovery on fragment units managed by the cache nodes; when the data size of the cache node is detected to be overloaded, carrying out data migration on the cache node; whena capacity expansion request of the cache node is received, carrying out data expansion on the cache node; and when a user request is received, acquiring the cache node accessed by the user request, carrying out dynamic routing according to the node type of the cache node, and reading or writing the data into the fragment units according to a routing result. According to the method and the system,the state of the cache node is monitored in real time, and data recovery, data read-write, data migration and data expansion are carried out according to the state of the cache node, the dynamic routing can be carried out, and the quick response of an access end and an inquiry end is realized.
Owner:吉浦斯信息咨询(深圳)有限公司
Routing scheduling method, routing scheduling device and network equipment
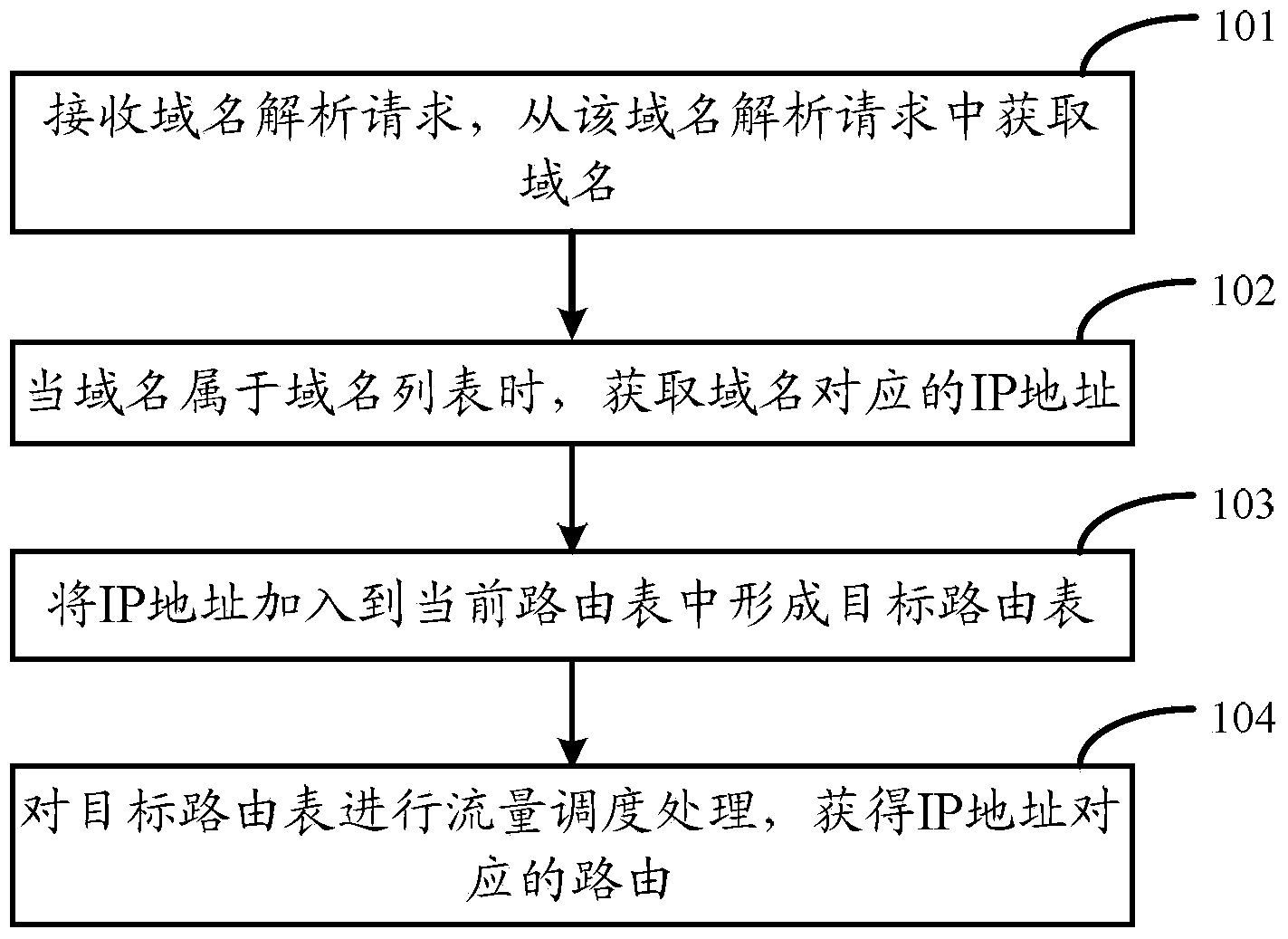
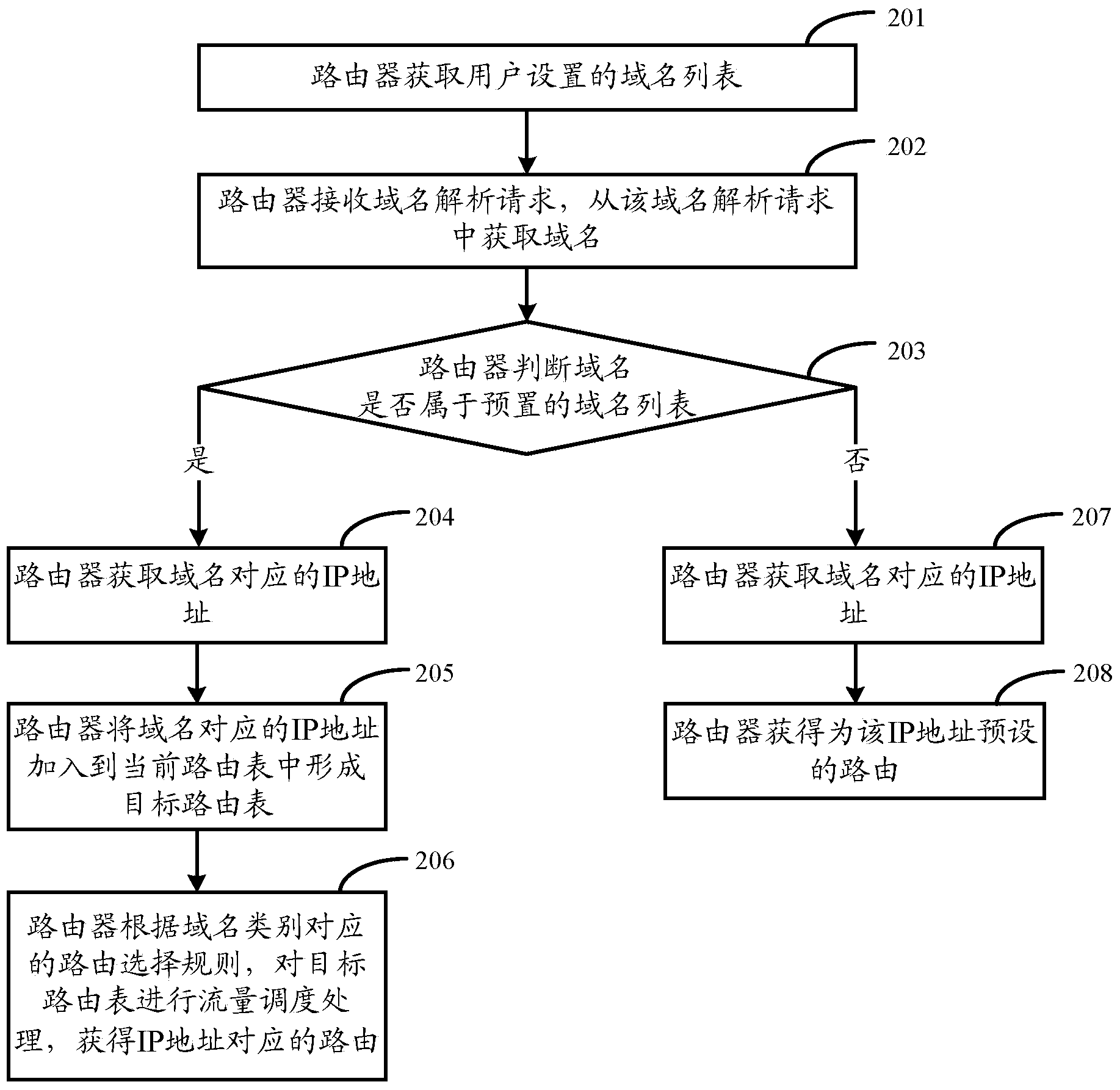
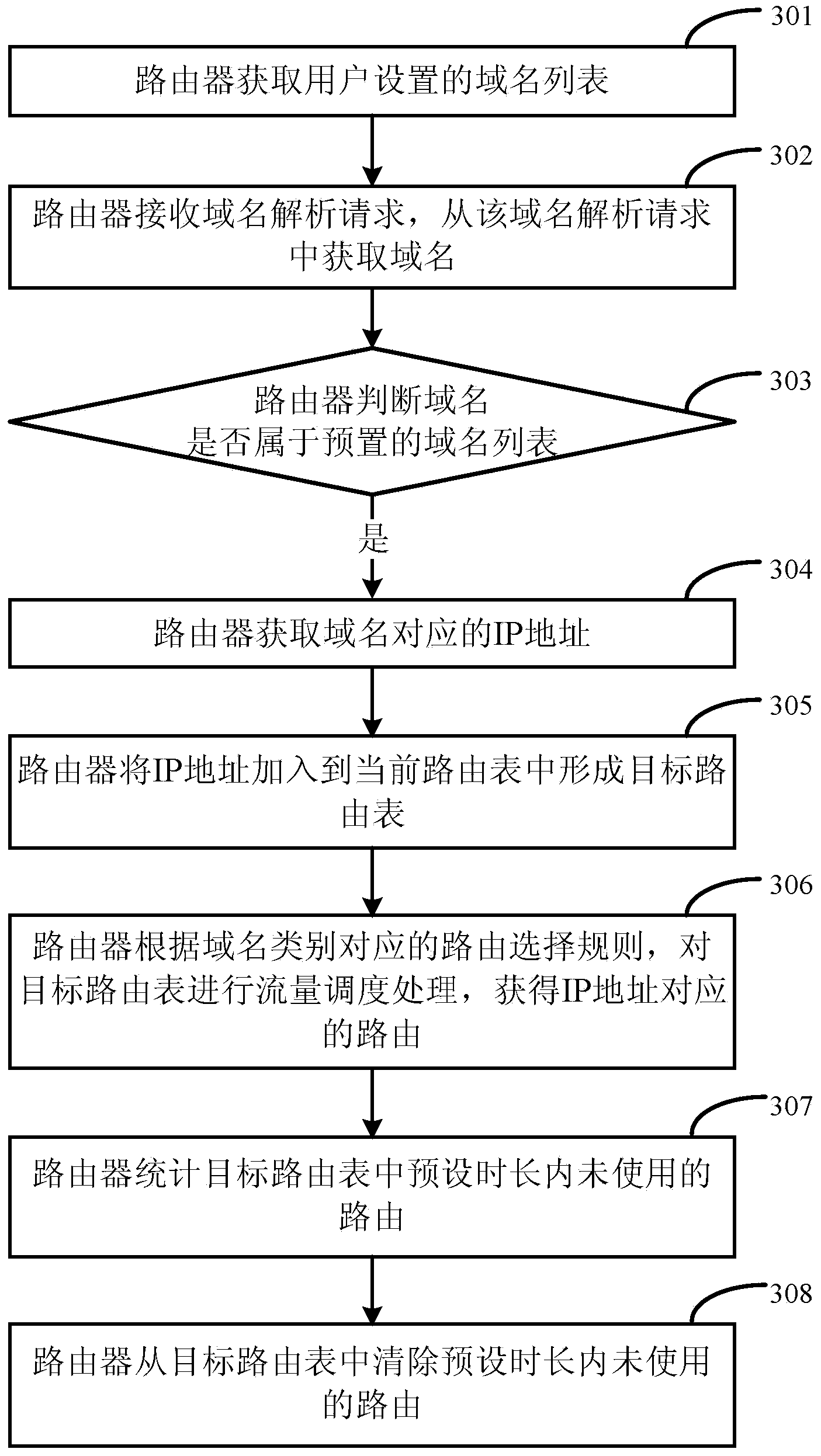
ActiveCN103532852ARouting is accurate and fastImprove scheduling efficiencyData switching networksDomain nameTraffic capacity
The invention relates to a routing scheduling method, a routing scheduling device and network equipment. Dynamic adjustment is added on the basis of static routing, and the dynamic adjustment added on the basis of static routing is not completely equivalent to dynamic routing. The routing scheduling method, the routing scheduling device and the network equipment are especially suitable for home routing systems, and are capable of improving the efficiency of traffic scheduling and convenient to manage. The routing scheduling method comprises the following steps of receiving a domain name resolution request, and acquiring a domain name from the domain name resolution request; acquiring an IP (Internet protocol) address which corresponds to the domain name when the domain name belongs to a domain name list; adding the IP address to a current routing table to form a target routing table; performing traffic scheduling processing on the target routing table to obtain routing which corresponds to the IP address.
Owner:XIAOMI INC
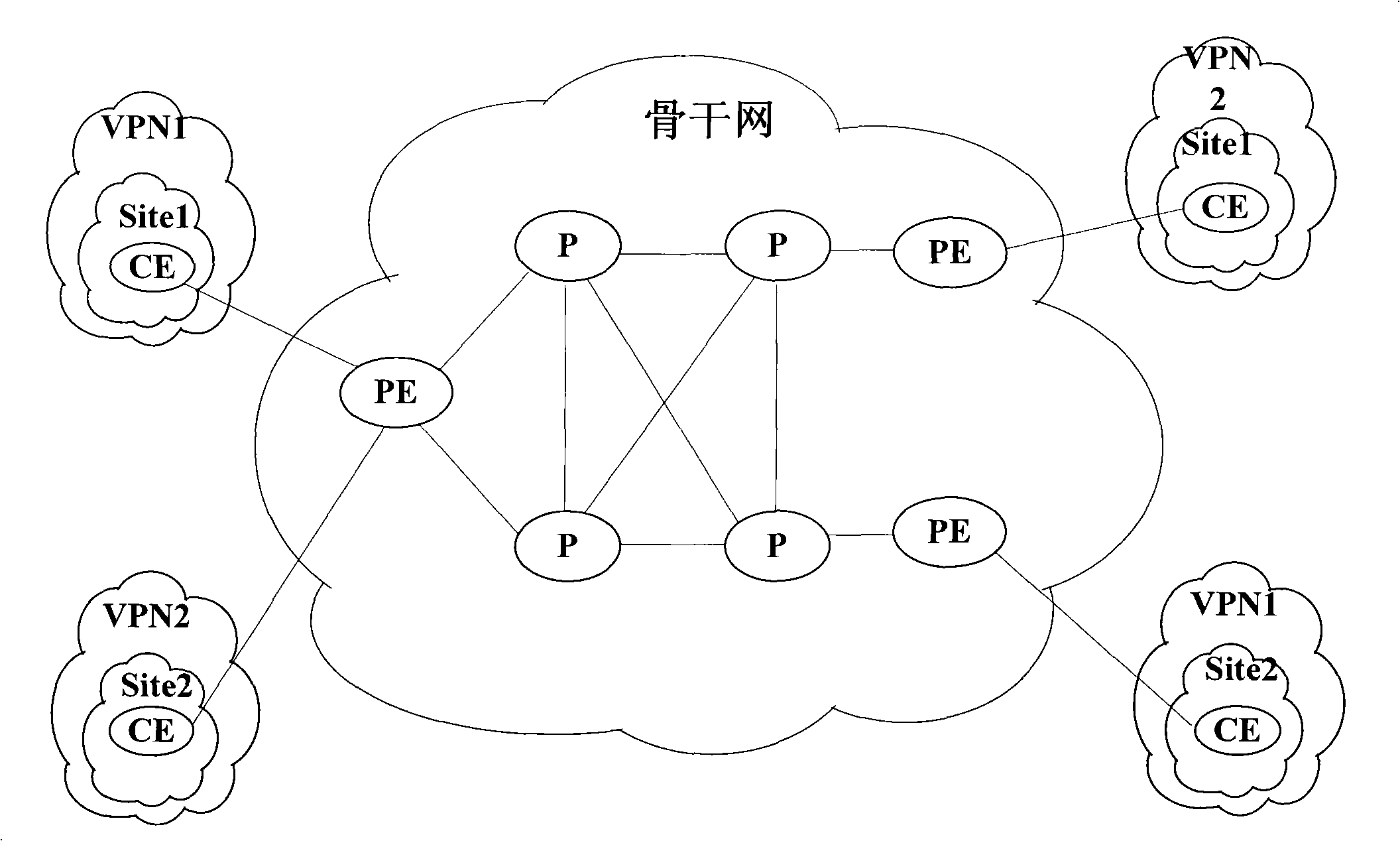
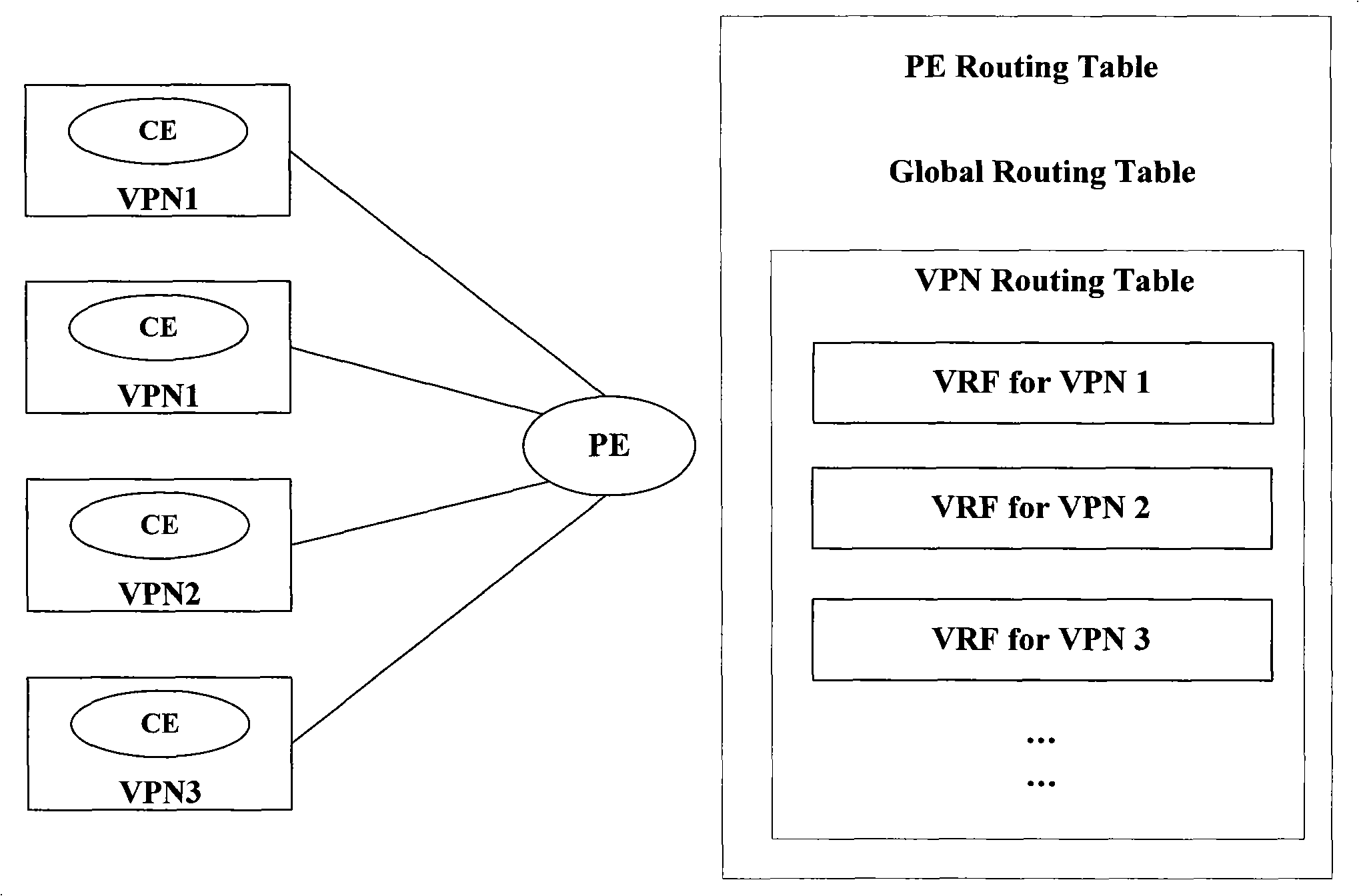
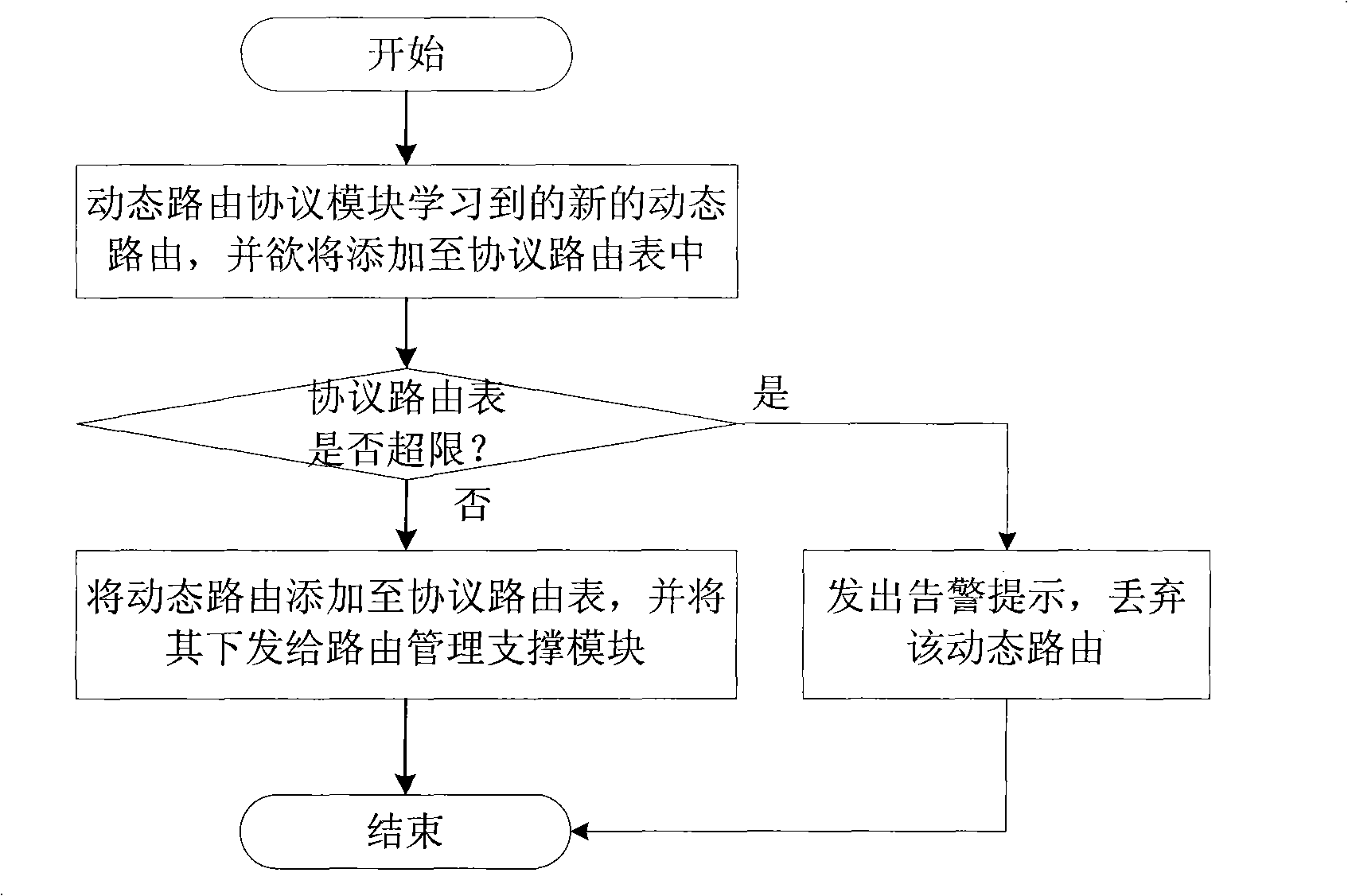
VRF route restriction management method of MPLS VPN network
InactiveCN101494612AImprove performanceImprove securityNetworks interconnectionRouting tableNetwork attack
The invention discloses a VRF routing restriction and management method under a MPLS VPN network, which comprises the following steps: a maximum VRF routing item number is set; when a user wants to configure new routing, a routing management supporting module notifies a dynamic routing protocol module to judge whether a protocol routing table can contain the routing to be configured according to item number of the routing to be configured and the maximum VRF routing item number, if so, the user is notified to continue normal configuration, otherwise, the user configuration is forbidden; and when the dynamic routing protocol module learns new dynamic routing and wants to add the new dynamic routing into the protocol routing table, whether the protocol routing table can contain the routing to be added is judged according to item number of the routing to be added and the maximum VRF routing item number, if so, the dynamic routing is added into the protocol routing table and assigned to the routing management supporting module, otherwise, the dynamic routing is discarded. The VRF routing restriction and management method under the MPLS VPN network can improve the PE performance and the network security and prevent network attacking activities realized by large numbers of poured routings.
Owner:ZTE CORP
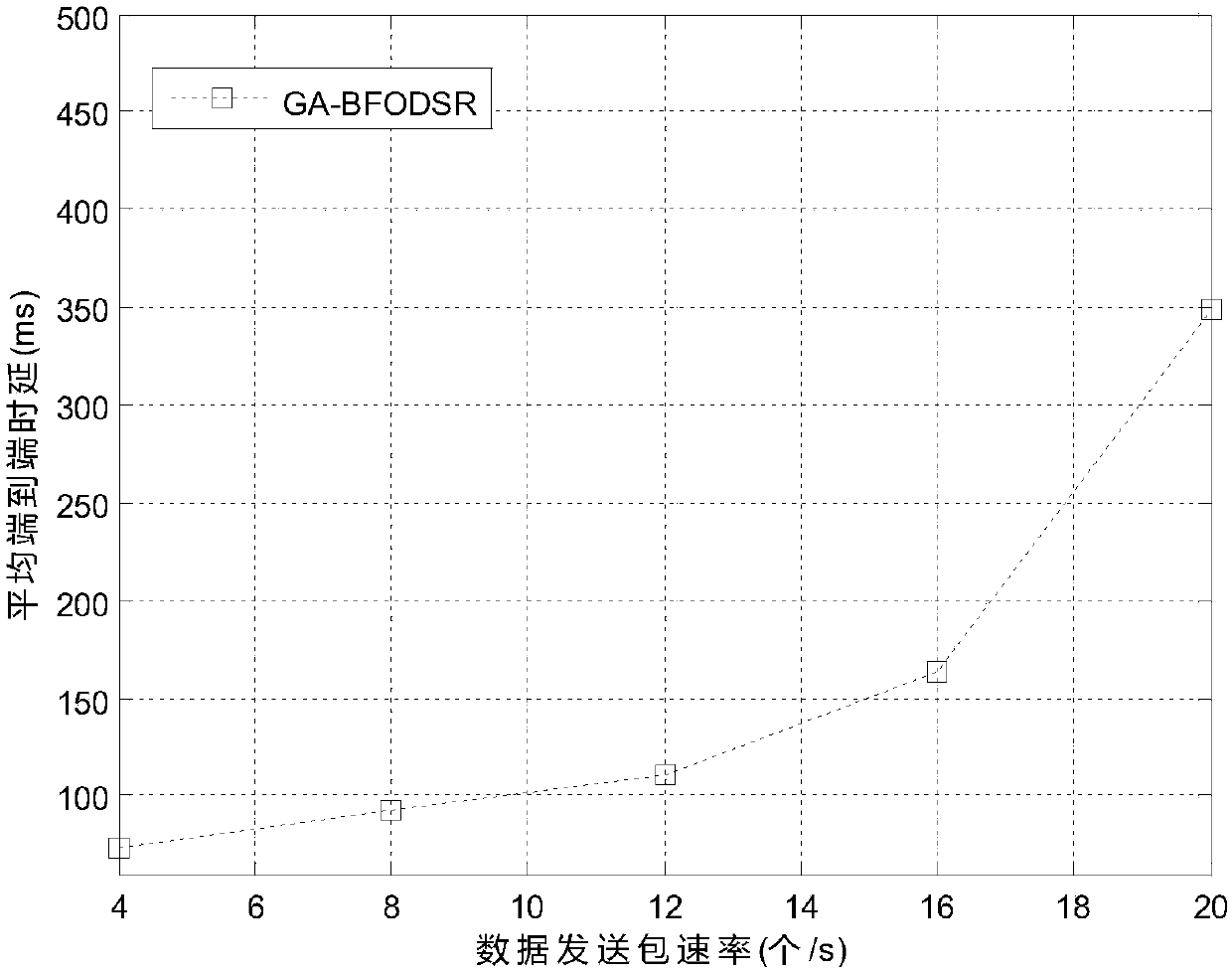
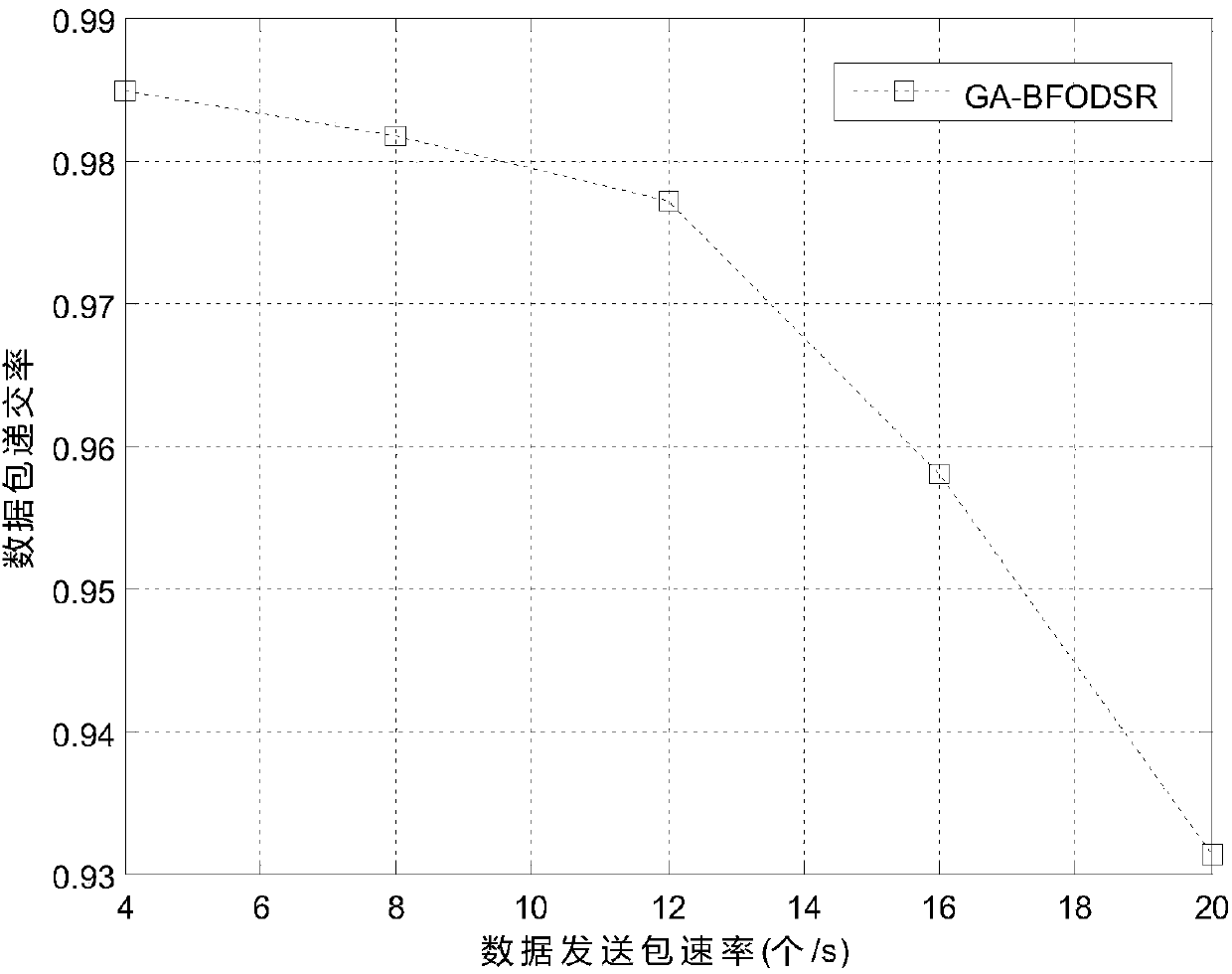
Dynamic source routing method based on genetic-bacterial foraging optimization strategy
InactiveCN107707472AImprove selection efficiencyReduce latencyData switching networksWireless communicationBacteria foragingEnergy information
The invention provides a dynamic source routing method based on a genetic-bacterial foraging optimization strategy. The method proposes a genetic-bacterial foraging optimization algorithm to perform route selection aiming at a DSR (Dynamic Source Routing) protocol and comprehensively considering node energy information, that is, after searching out multiple routes to a destination node, coding initialization is carried out on a path, a GA algorithm is firstly started, and the solving speed is fast by using the GA algorithm, and multiple groups of optimized paths are quickly searched out, thatis the location of the maximum probability of an optimal path, and the location is used as the initial position distribution of the flora of a BFO (Bacterial Foraging Optimization) algorithm; and in order to make up for the shortcoming of the low solving precision of the GA algorithm, the optimal path is searched out by using the characteristic that the BFO algorithm can search out an extreme value very easily. The optimization strategy proposed by the method improves the route selection efficiency and precision without changing the complexity of the DSR, and the characteristic that the convergence of the algorithm achieves the global optimal solution is proved. A simulation experiment shows that the method is feasible and applicable, and also has good experiment results.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
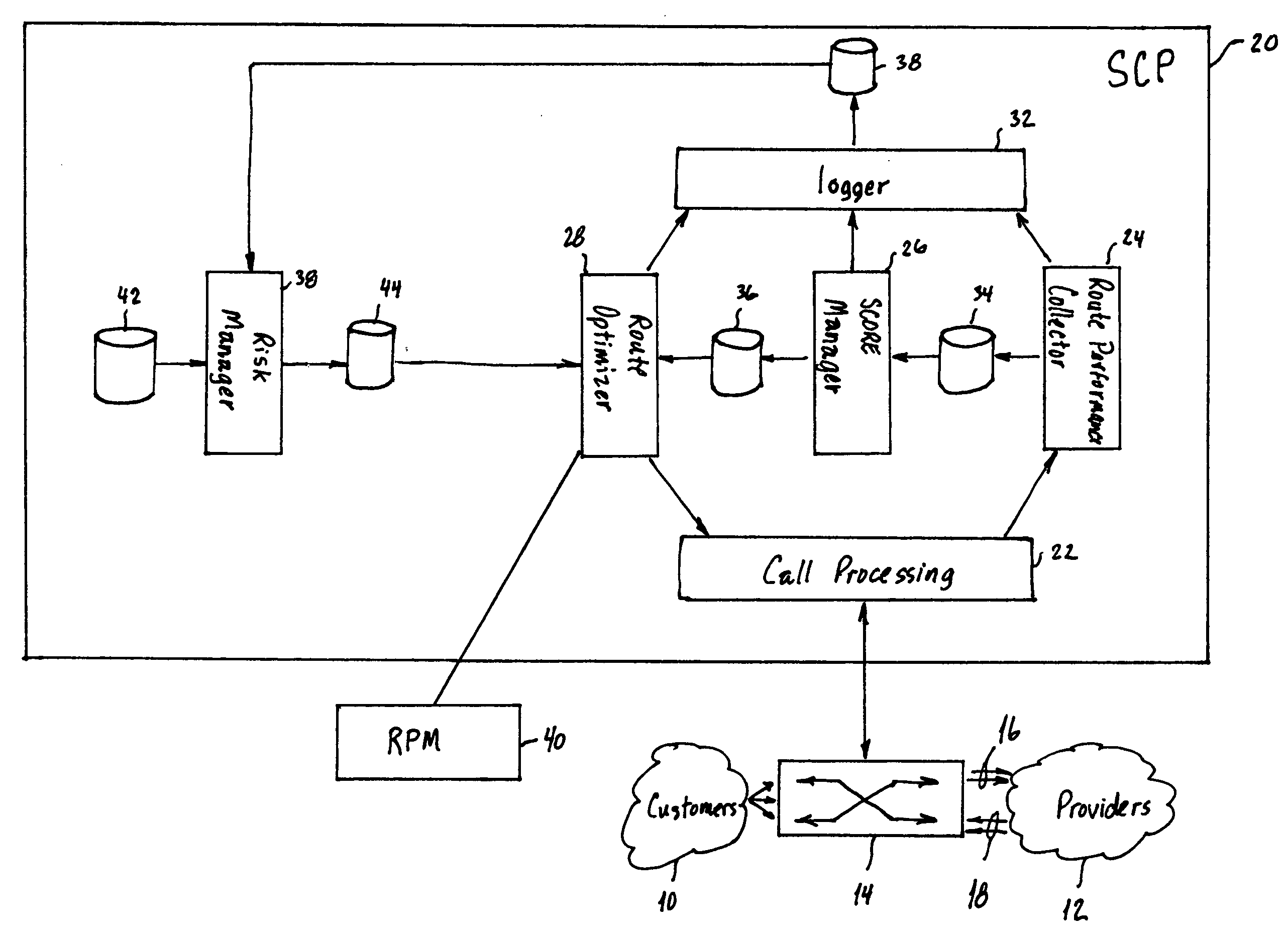
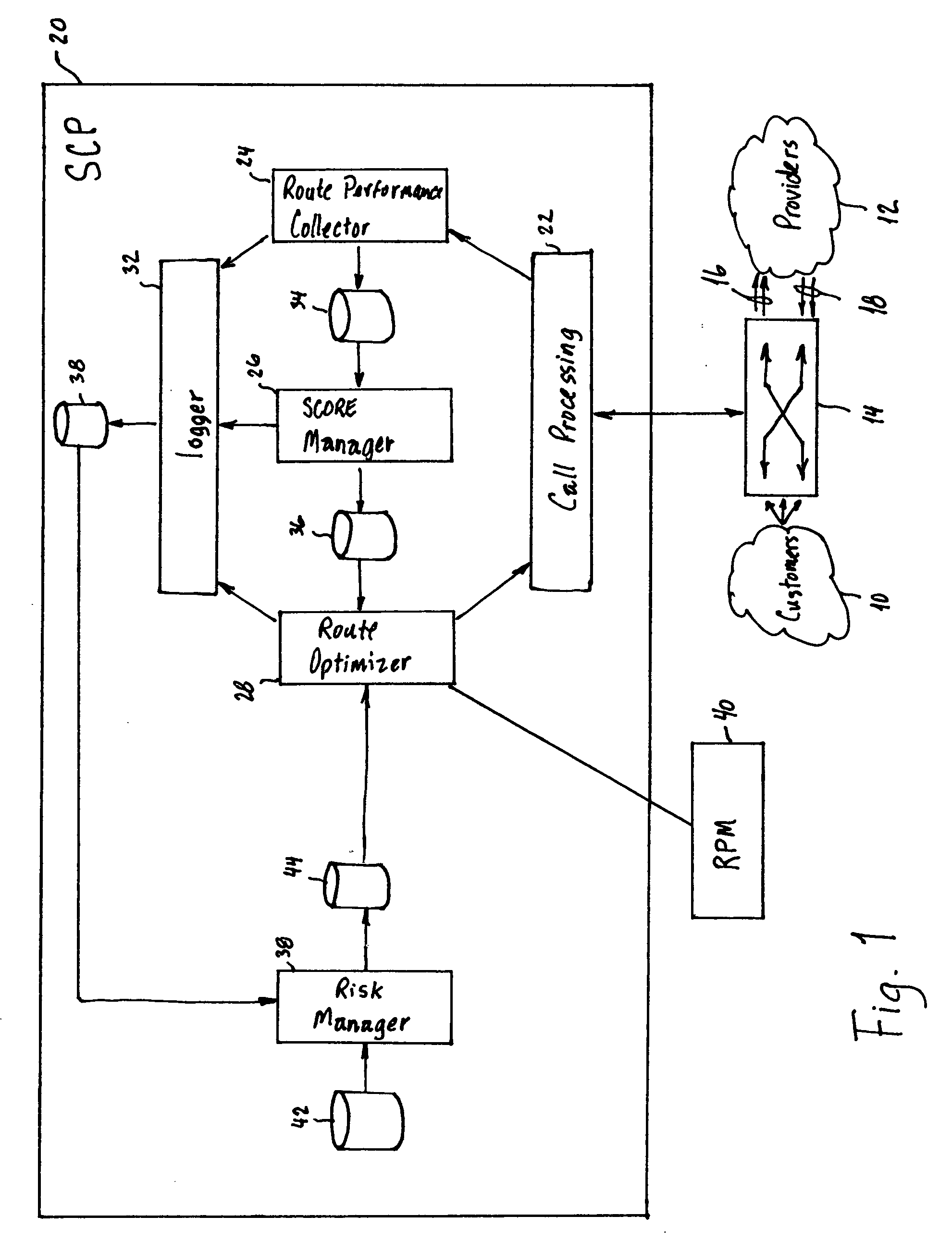
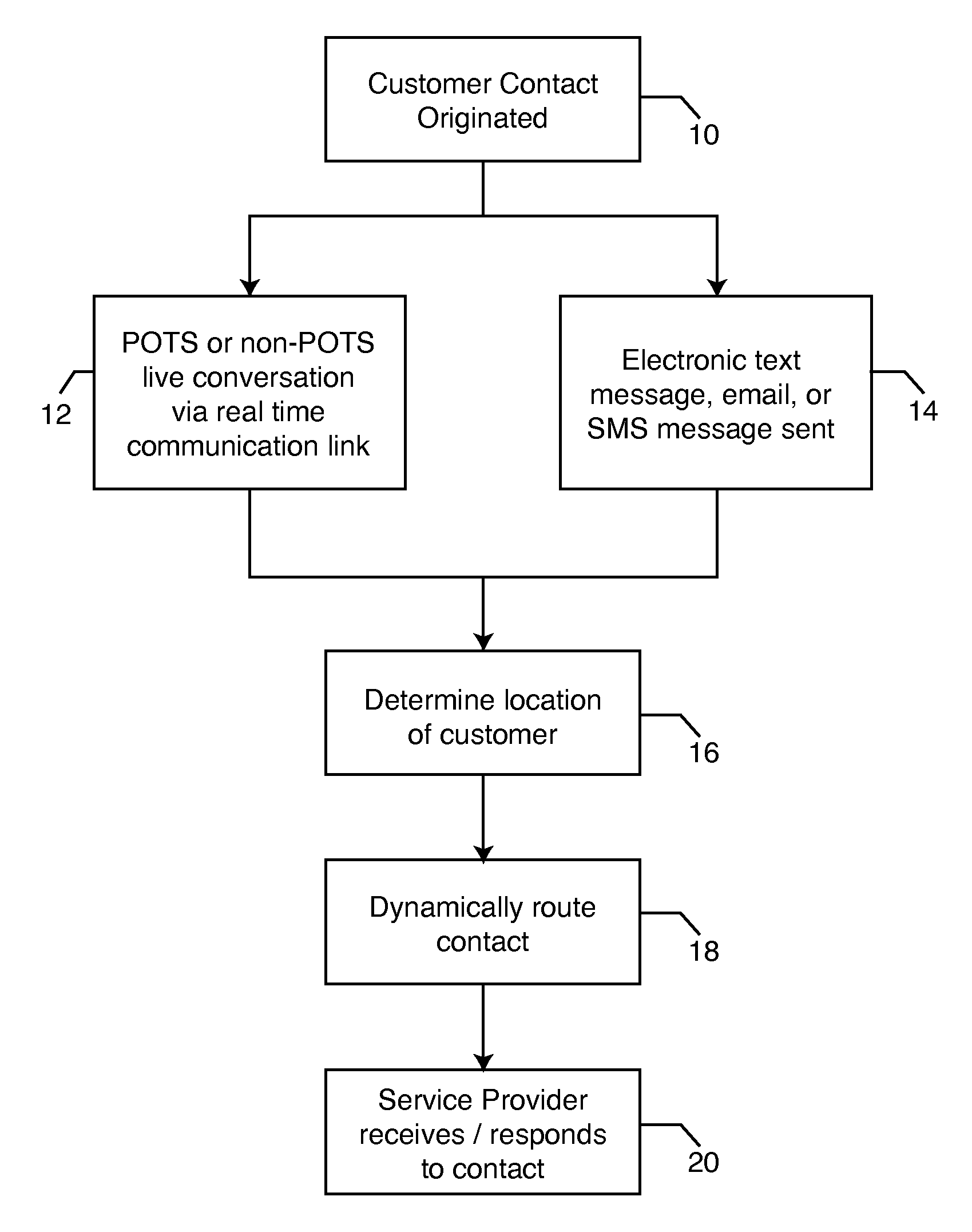
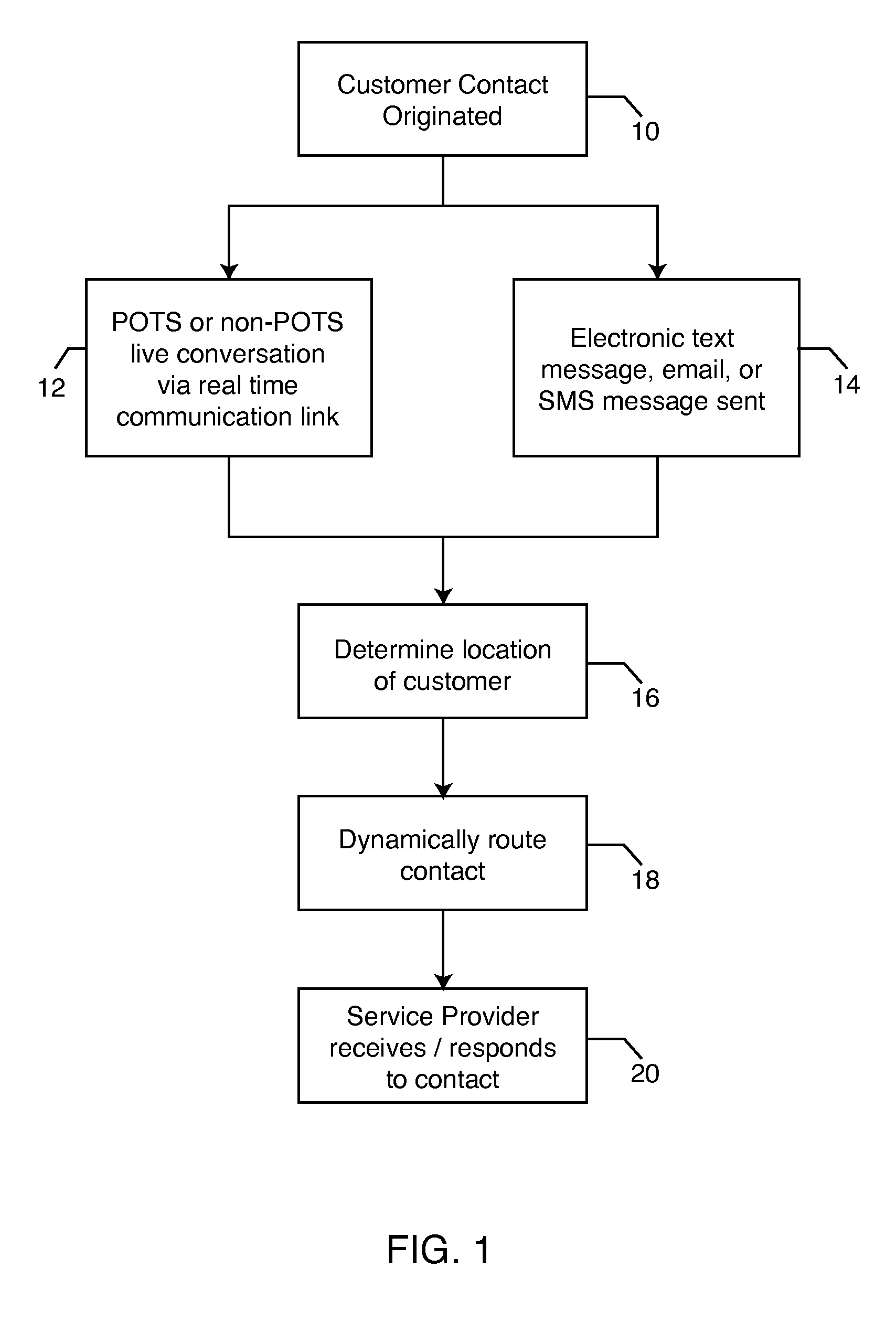
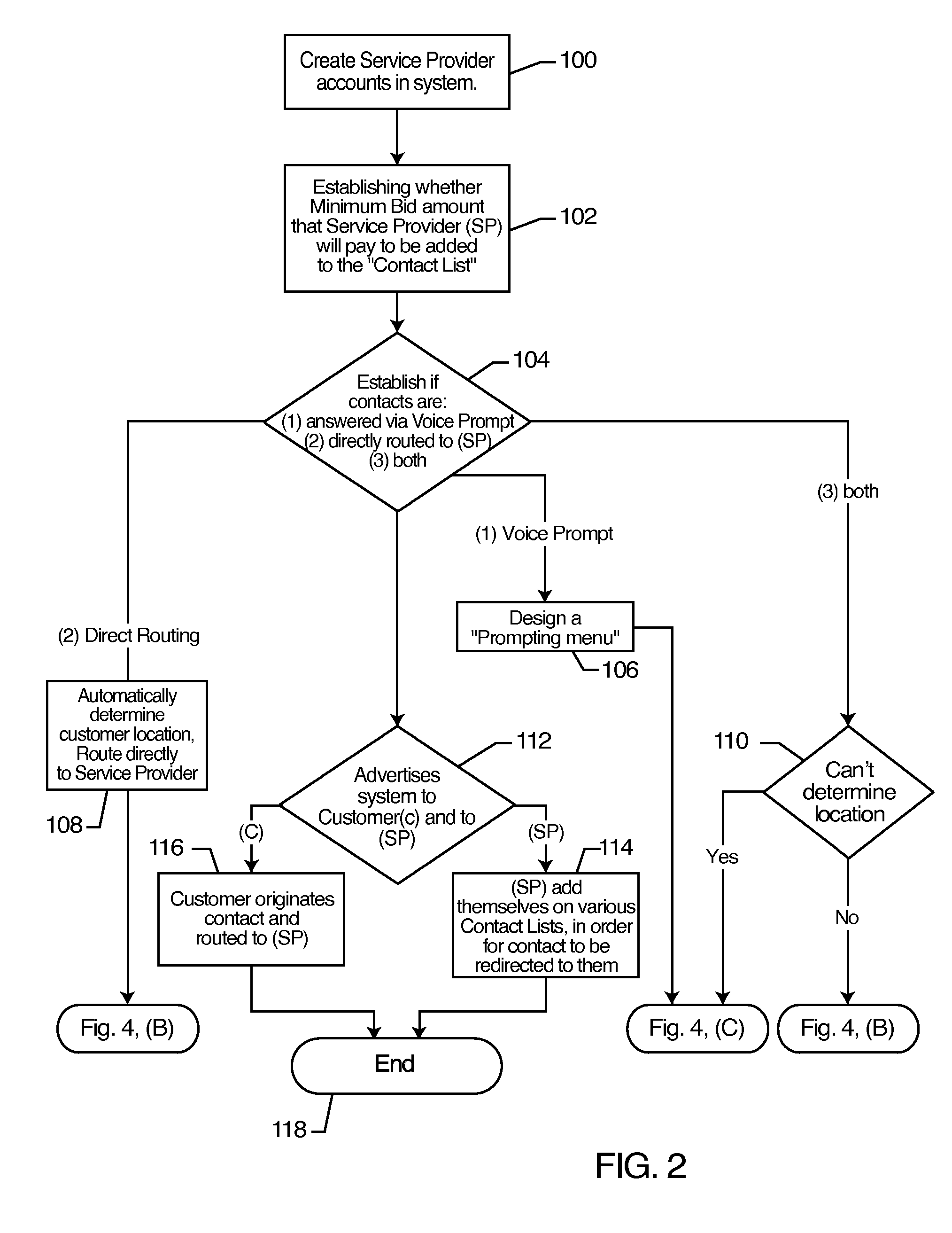
Process for dynamic routing of customer contacts to service providers in real time
A process for dynamic routing of customer contacts to service providers includes establishing accounts in a service provider contact system for a plurality of service providers. The plurality of service providers are permitted to bid against one another for providing goods and / or services to a customer. A contact list is created of service providers ranked from a lowest bidder service provider to a highest bidder service provider. A contact is received from a customer and routed from the customer to the lowest bidder service provider on the contact list. The service provider account receiving the contact and fulfilling the transaction is credited the amount bid by the service provider.
Owner:METRO ENTERPRISES INC
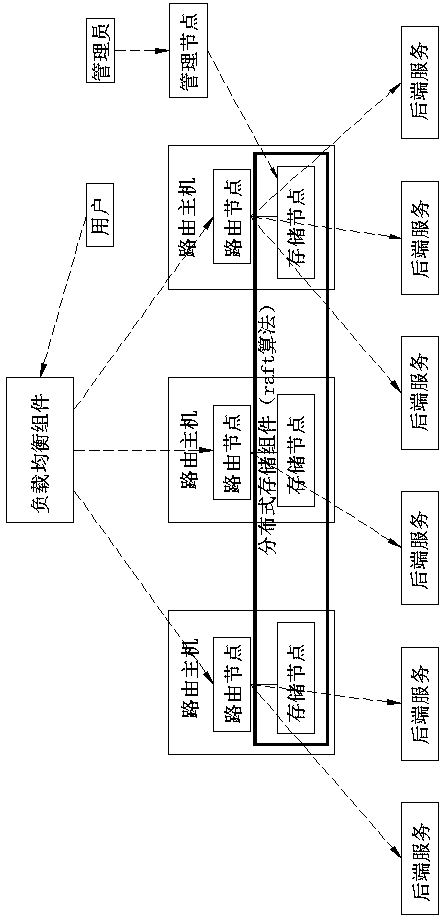
Implementation method for distributed dynamic routing based on Raft algorithm, and distributed dynamic routing system based on Raft algorithm
ActiveCN108494835ASolve the dynamic call problemRealize distributed featuresData switching networksDomain nameTraffic capacity
The invention belongs to the technical field of cloud computing data centers, and discloses an implementation method for distributed dynamic routing based on the Raft algorithm, and a distributed dynamic routing system based on the Raft algorithm, which are used to achieve dynamic calling of flexible resources in cloud computing that is unavailable in the conventional distributed dynamic routing.The method adopts the technical scheme that on a routing host upper layer, a load balancing assembly is used for evenly distributing an access traffic to all routing nodes; external services carry outaccesses through domain names provided by a platform; the routing nodes are used for forwarding an external access request for a cloud platform system and distributing the access traffic to back-endservice instances; storage nodes are arranged on a routing host bottom layer to form a distributed storage assembly, which is used for storing a mapping relationship between each domain name and the corresponding back-end service instance; data consistency between the storage nodes is maintained through the Raft algorithm, and each routing node only needs to read mapping data from the local storage node; and an administrator carries out addition, deletion and change operations on the mapping data in the storage nodes through a management node.
Owner:SHANDONG LANGCHAO YUNTOU INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Moving source routing method of dynamic transport network
ActiveCN103888357AShort switching timeIncrease switching rateData switching networksGrade of serviceComputer terminal
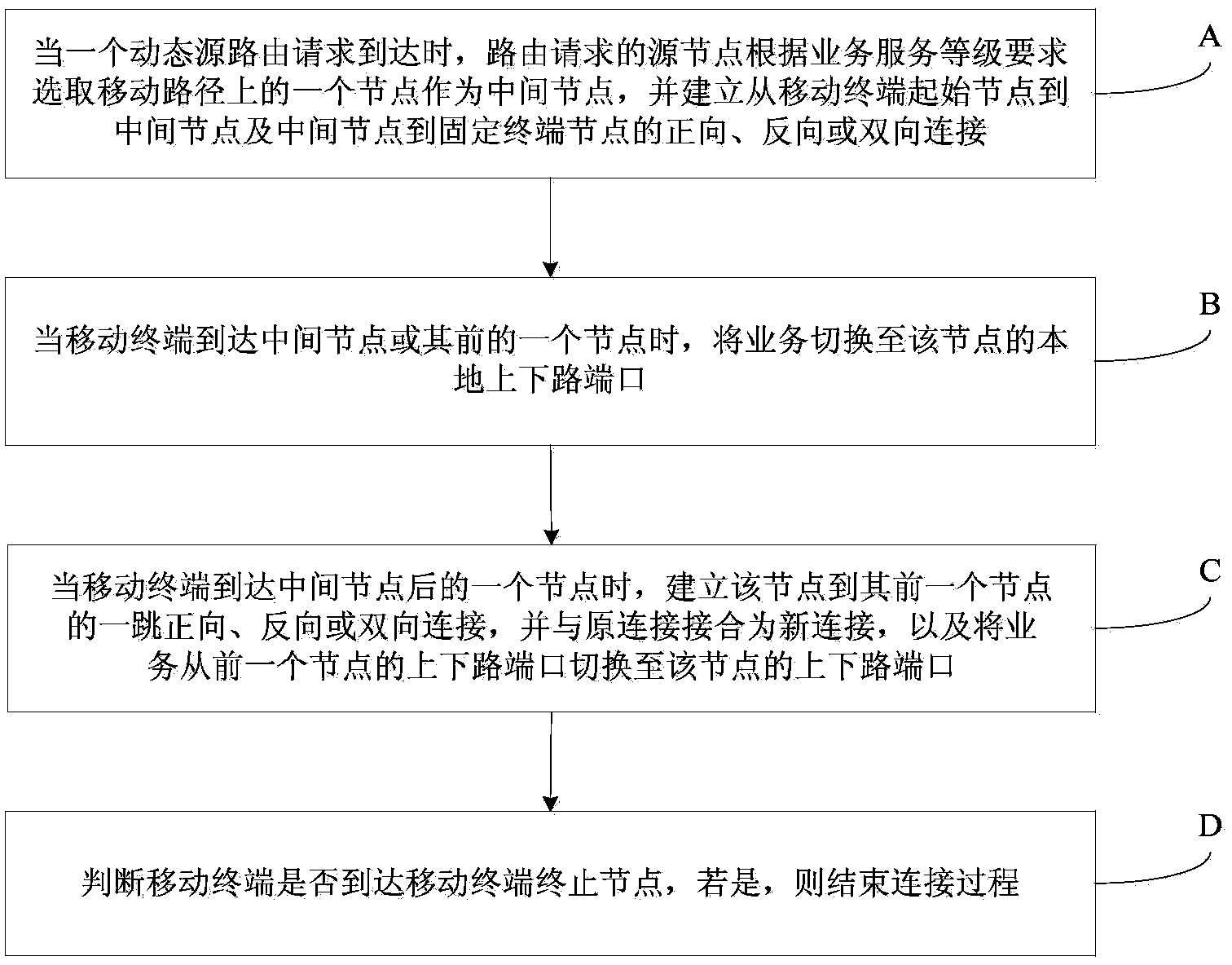
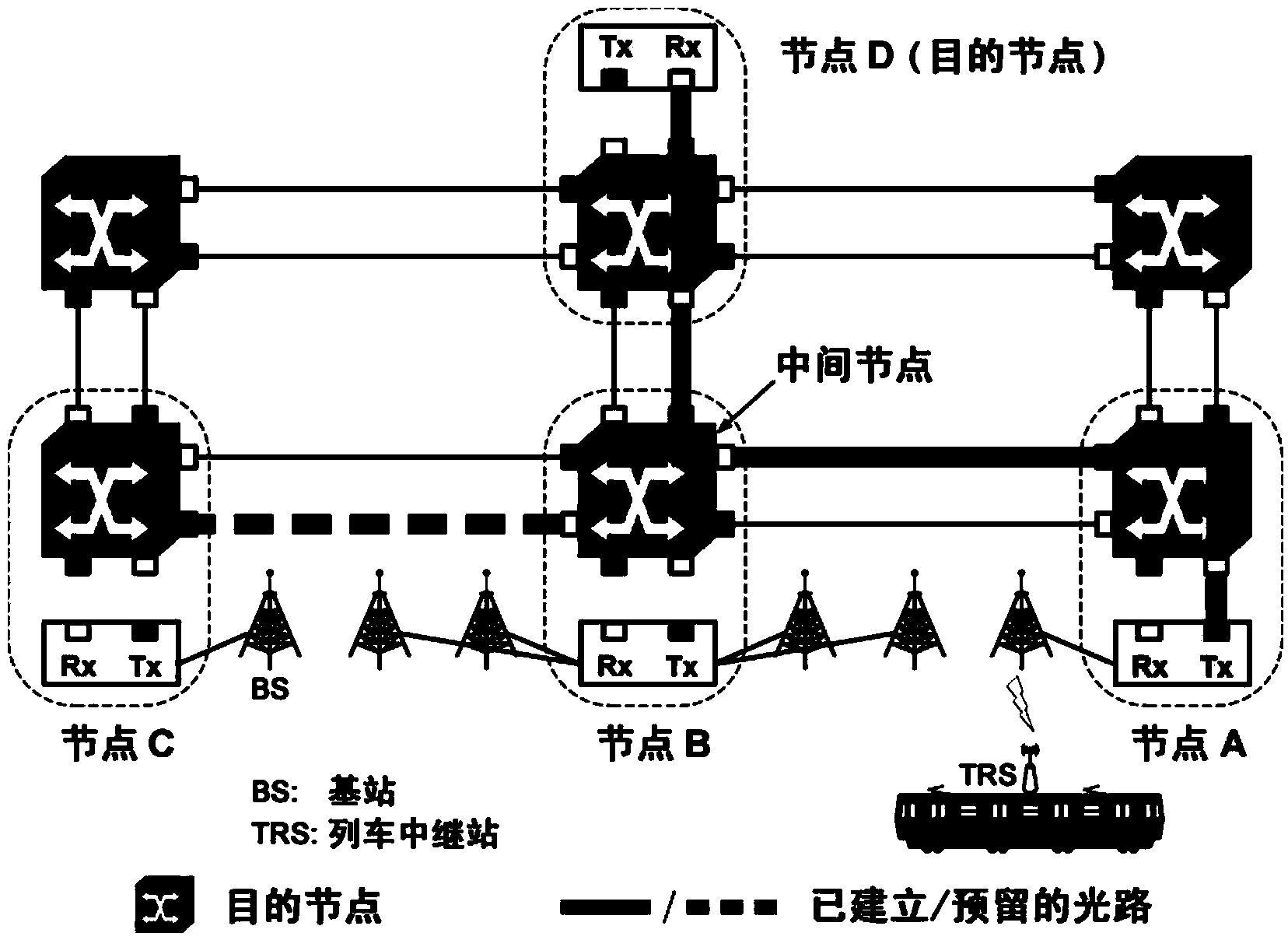
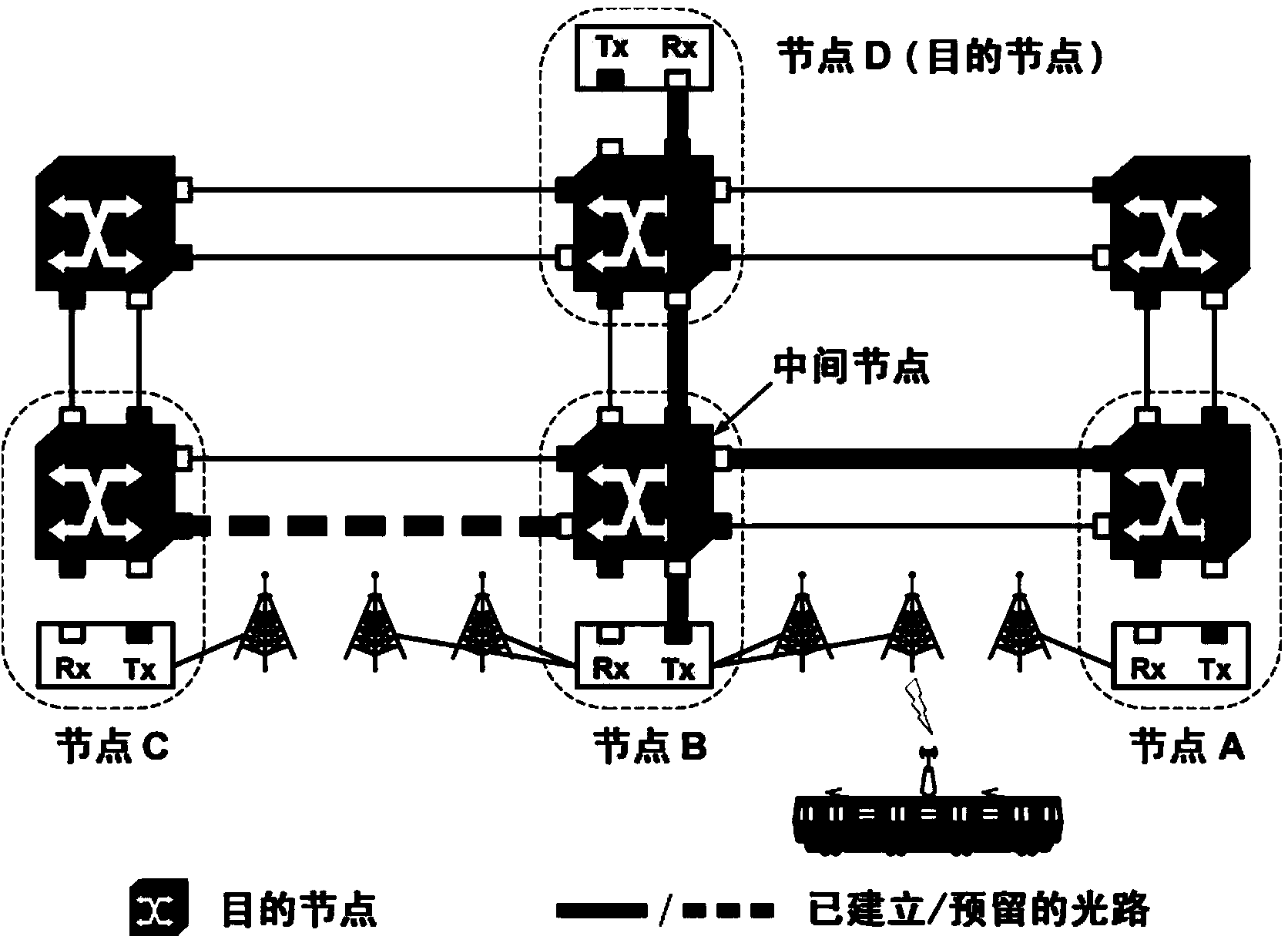
The invention provides a moving source routing method of a dynamic transport network. The method includes the following steps that when a dynamic source routing request arrives, a source node of the routing request selects a node on a moving path to be used as an intermediate node according to the service grade requirement, and forward connection or reverse connection or two-way connection from a mobile terminal start node to the intermediate node and from the intermediate node to a fixed terminal node is established; when a mobile terminal arrives at the intermediate node or a previous node, service is switched to a local up-down port of the node; when the mobile terminal arrives at the next node of the intermediate node, one hop of forward connection or reverse connection or two-way connection from the node to the previous node is established, the connection and original connection form new connection, and the service is switched to the up-down port of the node from the up-down port of the previous node; whether the mobile terminal arrives at a mobile terminal final node or not is judged, and if yes, the connecting process is over. By means of the moving source routing method of the dynamic transport network, handover time is shortened, and the handover success rate and the utilization rate of resources are improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for realizing upgraded dynamic source routing (DSR)
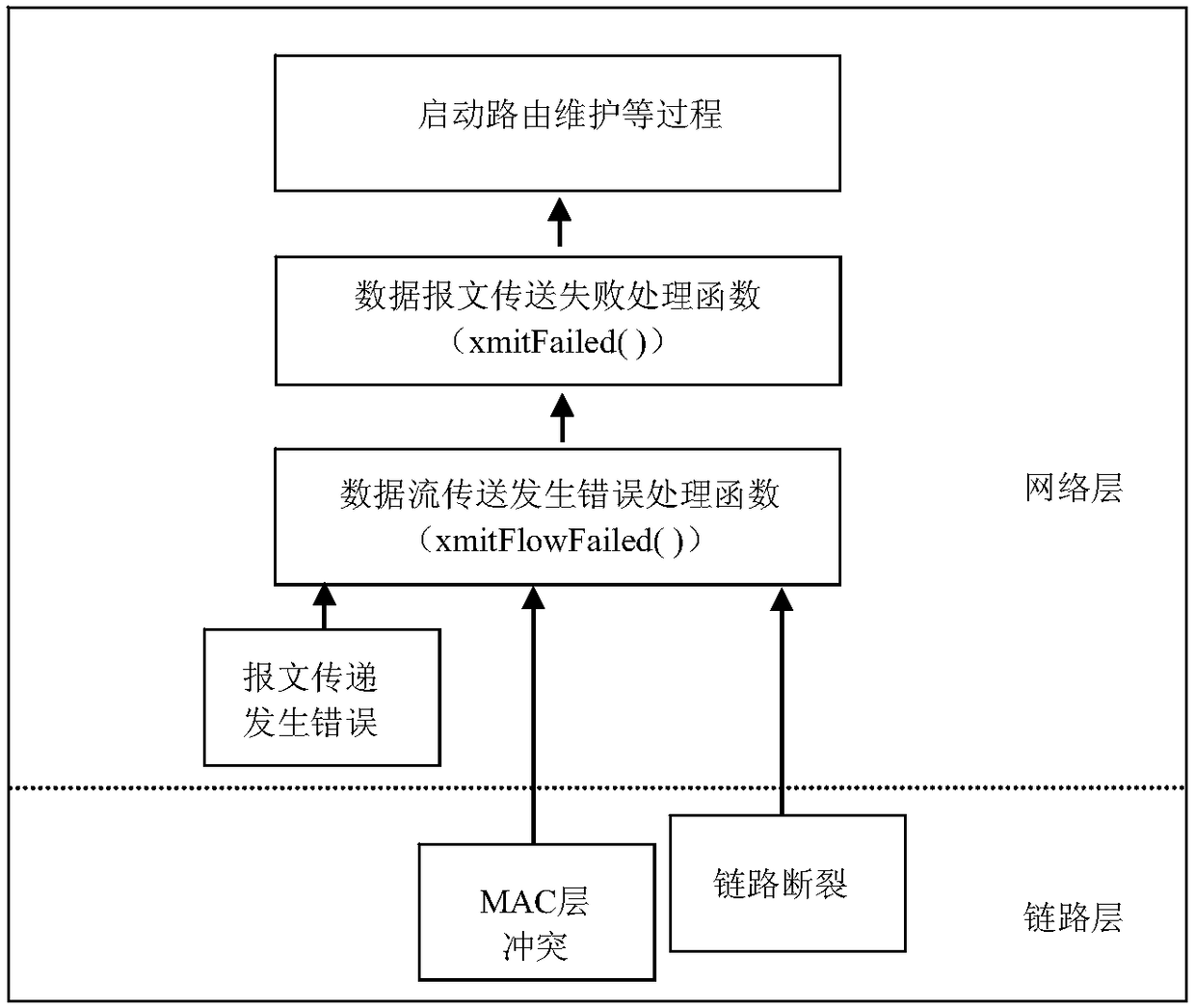
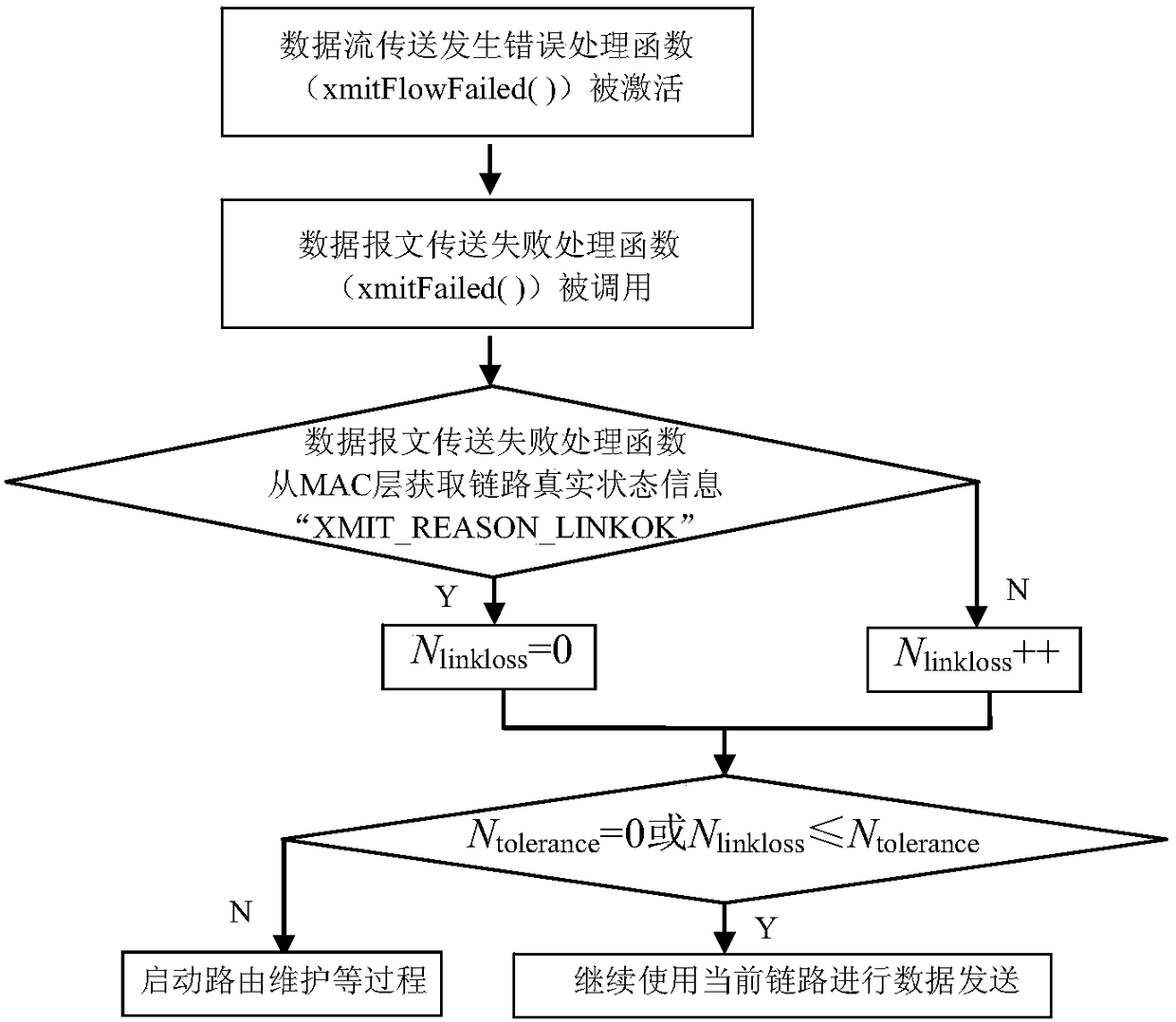
InactiveCN108092887AReduce the number of misjudged link failuresImprove throughputError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching networksLink layerDynamic Source Routing
The invention provides a method for realizing upgraded dynamic source routing (DSR). The method comprises the steps of sensing whether a current link fails when a current data frame is sent unsuccessfully, and if it is sensed that the link does not fails, generating corresponding indication information on a link layer and transmitting the indication information to a network layer; if the network layer receives the indication information, returning link failure times to zero, or, accumulating the link failure times and adding 1; and if it is sensed that the link failure times is not greater than a preset link failure sense tolerance times, continuing to send the data frame through the current link, or, starting a route maintenance mechanism. The method for realizing the upgraded SDR enhances information interaction and sharing between the link layer and the network layer and can find the true cause why the bottom layer link fails, so that the network layer can sense the bottom layer true link state effectively, the network layer determines link failure wrongly for fewer times, the negative effect of route maintenance on network performance is lowered, and the network performance indicator is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com