Method and apparatus for network allocation vector resetting
A technology of network allocation vector and reset method, which is applied in the field of network allocation vector reset method and device, can solve the problems that various stations cannot compete for channels fairly, and achieve the effect of improving utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
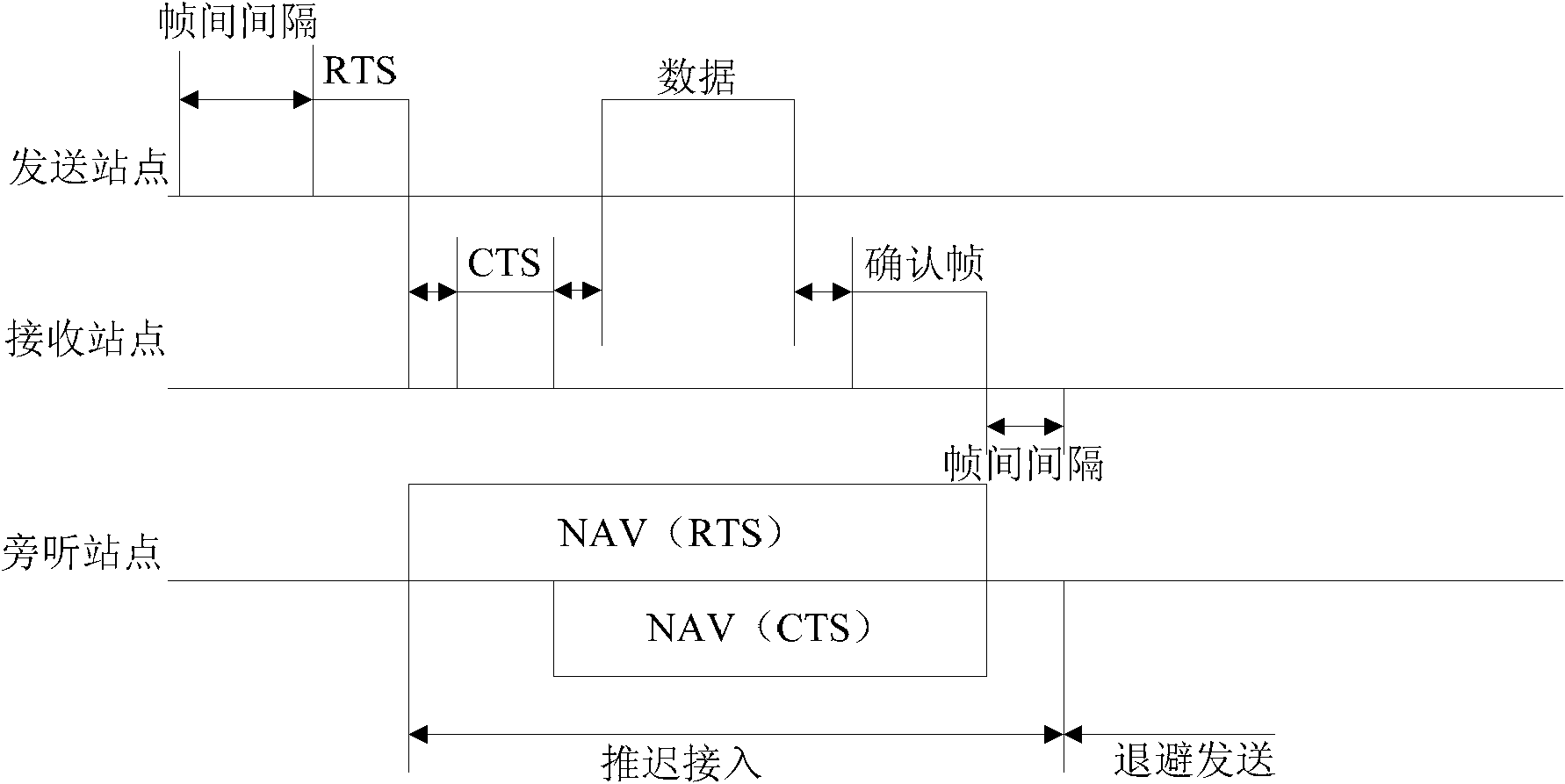
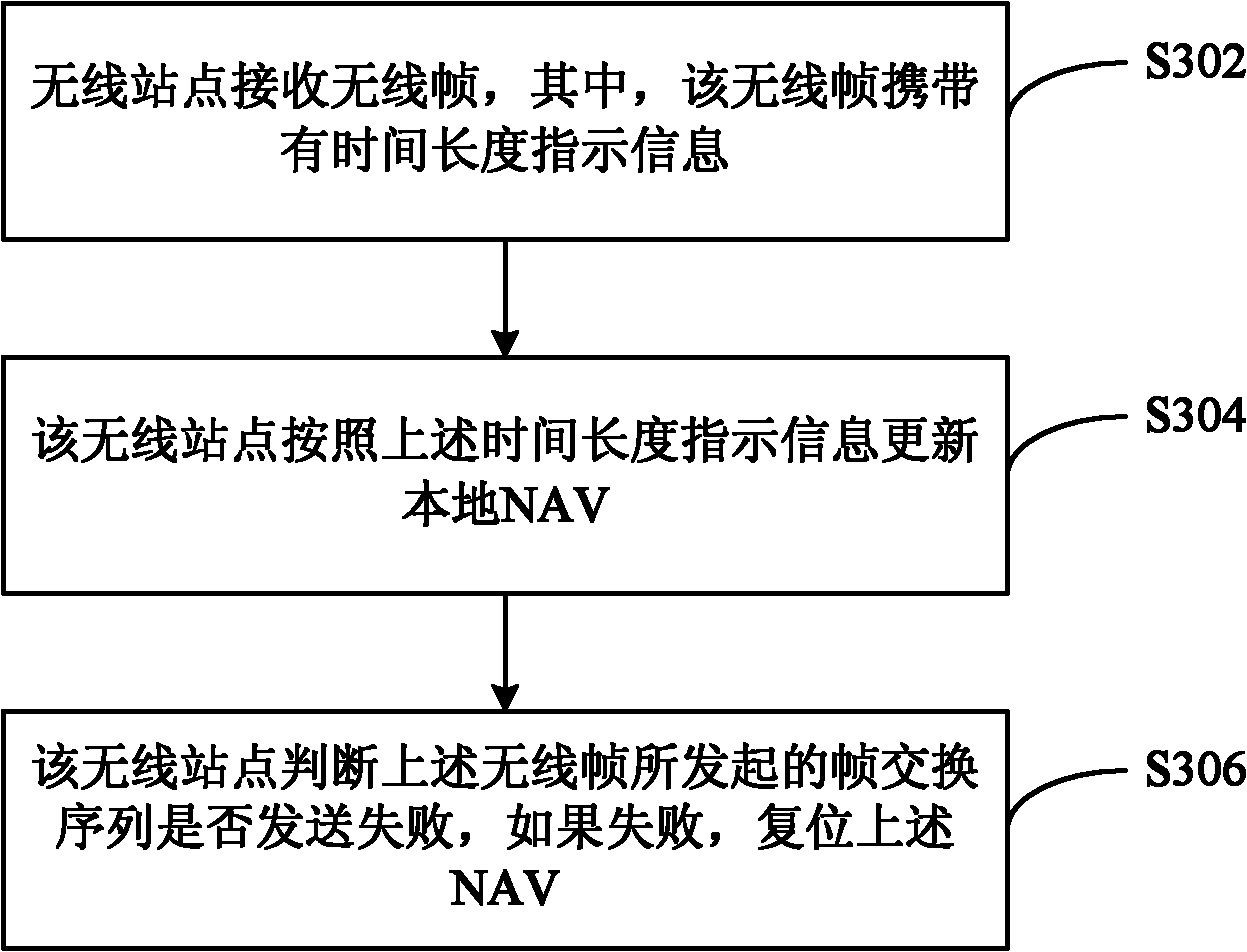
[0022] This embodiment provides a NAV reset method, see image 3 , the method includes the following steps:
[0023] Step S302, the wireless station receives the wireless frame, wherein the wireless frame carries time length indication information, which means that the wireless frame contains or indicates the time length;
[0024] The wireless frame is one or more wireless frames sent by the sender to obtain the current transmission opportunity, which can be an NDPA frame or a polling (Sounding Poll) frame; the wireless station refers to the information in the NDPA or Sounding Poll frame Stations that update the NAV, for example, listen stations for transceiver stations.
[0025] Step S304, the wireless station updates the local NAV according to the above time length indication information;
[0026] The specific update method of the NAV in this embodiment can be implemented with reference to related technologies, and will not be described in detail here;
[0027] Step S306,...
Embodiment 2
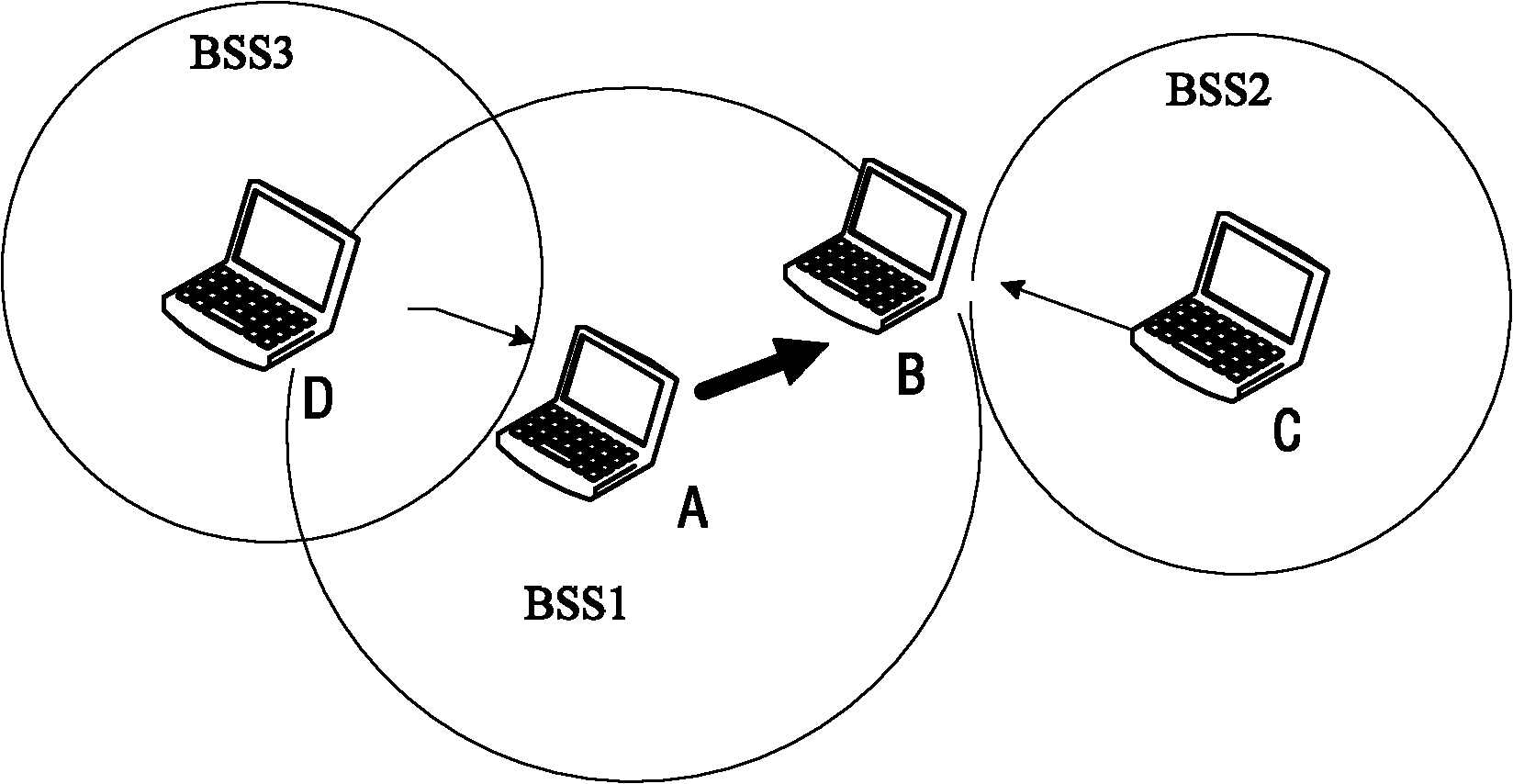
[0043] This embodiment provides a NAV reset method, and the frame exchange sequence of this embodiment is described by taking NDPA-NDP-1stSND FB as an example. see Figure 4 Schematic diagram of NAV reset. After the sending station wins the competition and tries to obtain the TXOP, it sends the NDPA frame as the first frame, and sends the NDP after the SIFS time after the NDPA frame. The first feedback station identified by the NDPA defaults after the SIFS after the NDP ends. Feedback, the sender and receiver obtain TXOP through NDPA-NDP-1stSND FB frame exchange. Here, the 1stSND FB may be a response frame Null FB frame without feedback information.
[0044] The listening station has correctly received the NDPA frame, and set its own NAV through the information of the NDPA frame. If the listening station does not receive the physical layer to start receiving the primitive PHY- RXSTART.indication (that is, the physical layer does not generate a report of receiving a radio fra...
Embodiment 3
[0047] This embodiment provides a NAV reset method, and the frame exchange sequence of this embodiment is described by taking the Poll-SND FB as an example. The sending station wins the competition. When trying to obtain TXOP, the sending (Sounding) Poll frame is used as the first frame. The feedback station identified in the Poll frame will give feedback after SIFS after the Poll frame ends, and the sending and receiving parties exchange Poll-SND FB frames to obtain TXOP. .
[0048] The observer station correctly receives the Poll frame, and sets its own NAV through the information of the Poll frame. If the observer station is (2×aSIFSTime)+(SND FB_Time)+(2×aSlotTime)+aPHY-RX - Within the START-Delay period (ie, the specified period of time in Embodiment 1), if the physical layer start receiving primitive PHY-RXSTART.indication is not received, then the listening station can reset its own NAV. Here, SND FB_Time refers to the feedback SND FB transmission time that the listeni...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com