Scheme for operating a wireless station having directional antennas
a wireless station and directional antenna technology, applied in the field of wireless networking, can solve the problems of deafness, interference between transmissions, and original 802.11 protocol not designed for directional antennas, and achieve the effects of enhancing hidden station problems and deafness problems, and solving the problem of enhanced deafness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
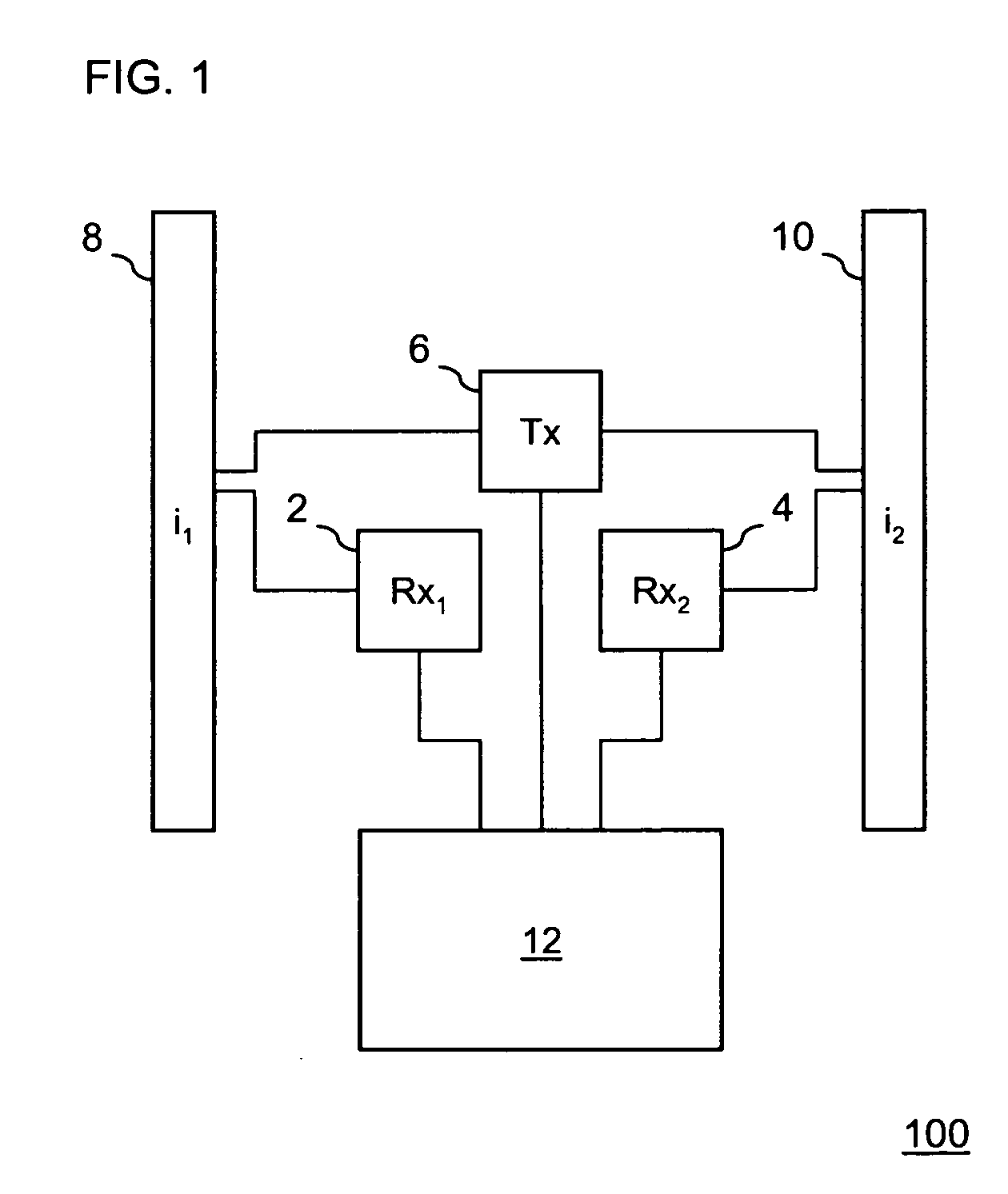
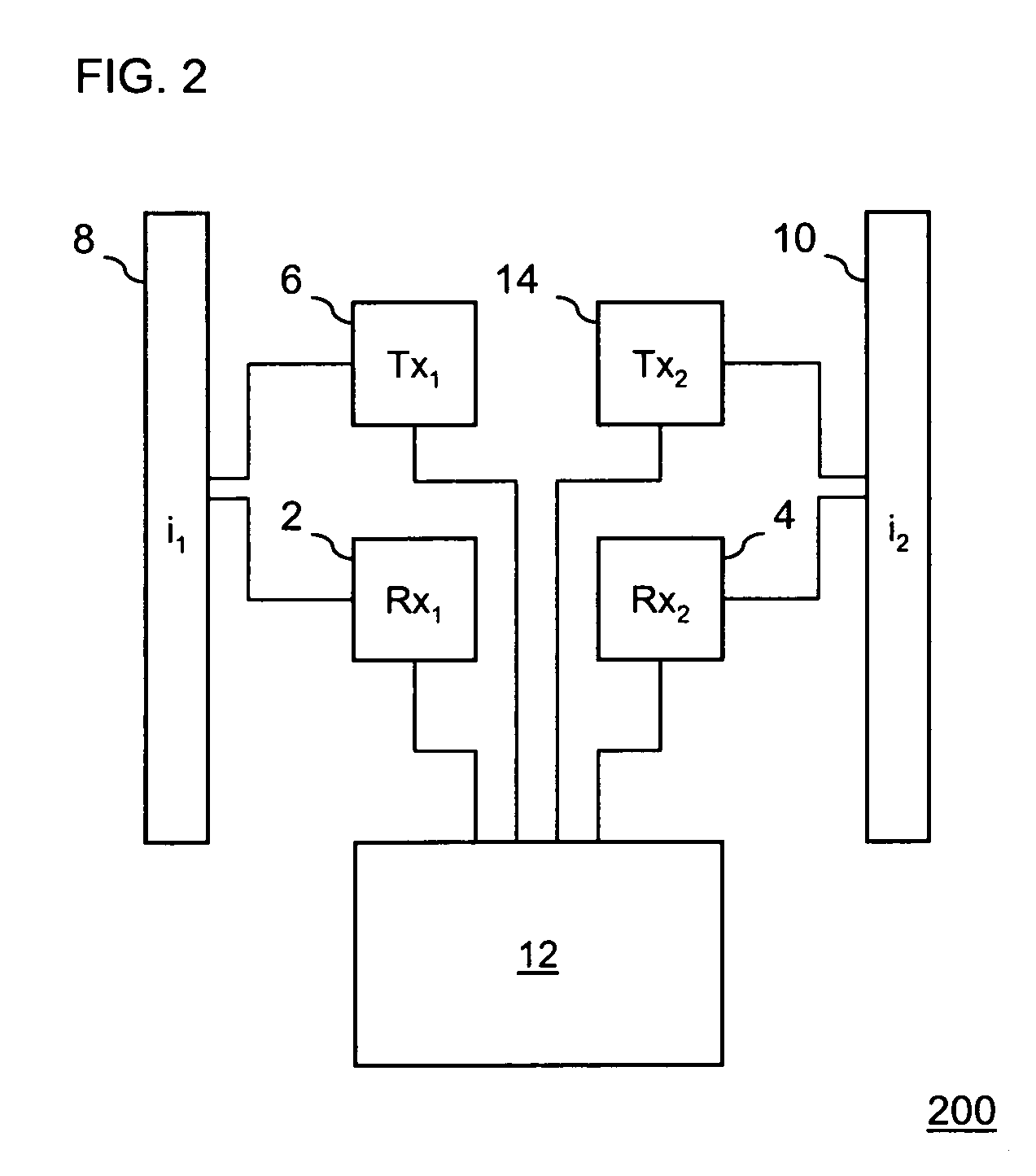
[0022] The present invention is a new scheme called sectorized MAC (“S-MAC”), which uses multiple directional antennas and multiple receivers to provide 360 degree coverage around a station. The scheme allows a station transmitting in some sectors to receive in others. It addresses the hidden station problem and the deafness problem by continuously monitoring the channel in all directions at all time for remote stations. The S-MAC protocol lends itself to both ad hoc mode and infrastructure mode, and can readily inter-operate with stations using an omni antenna. In fact, the sectorized operation of S-MAC is transparent to a regular omni station. A regular station can operate with the belief that all stations are omni and operate with the standard 802.11 MAC.
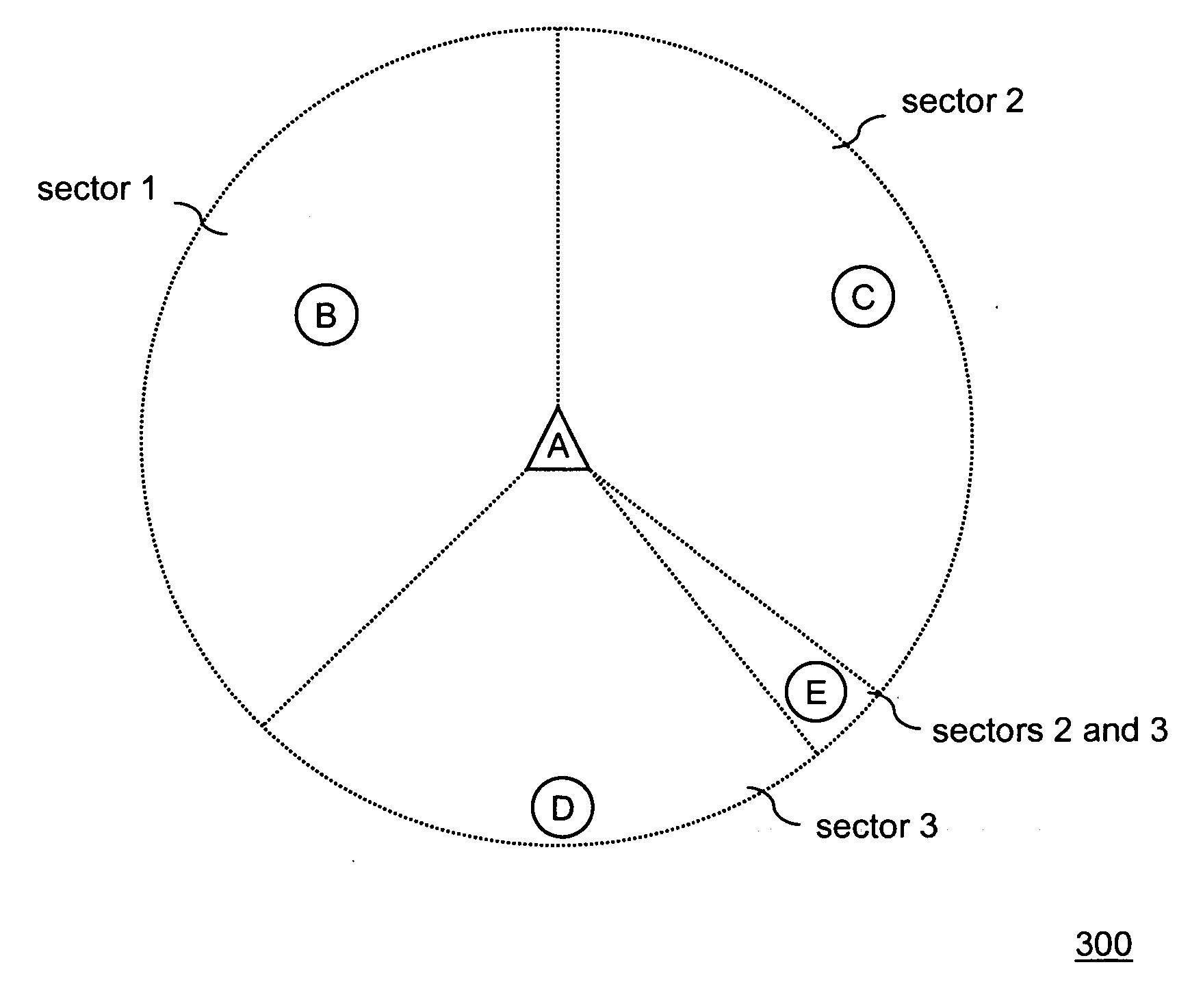
[0023] The coverage area of an S-MAC station is divided into M antennas, with directional antennas i1 through iM corresponding to each sector. The sectors could overlap due to antenna side lobes and back lobes. The station is eq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com