Patents
Literature
139 results about "Packet collision" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
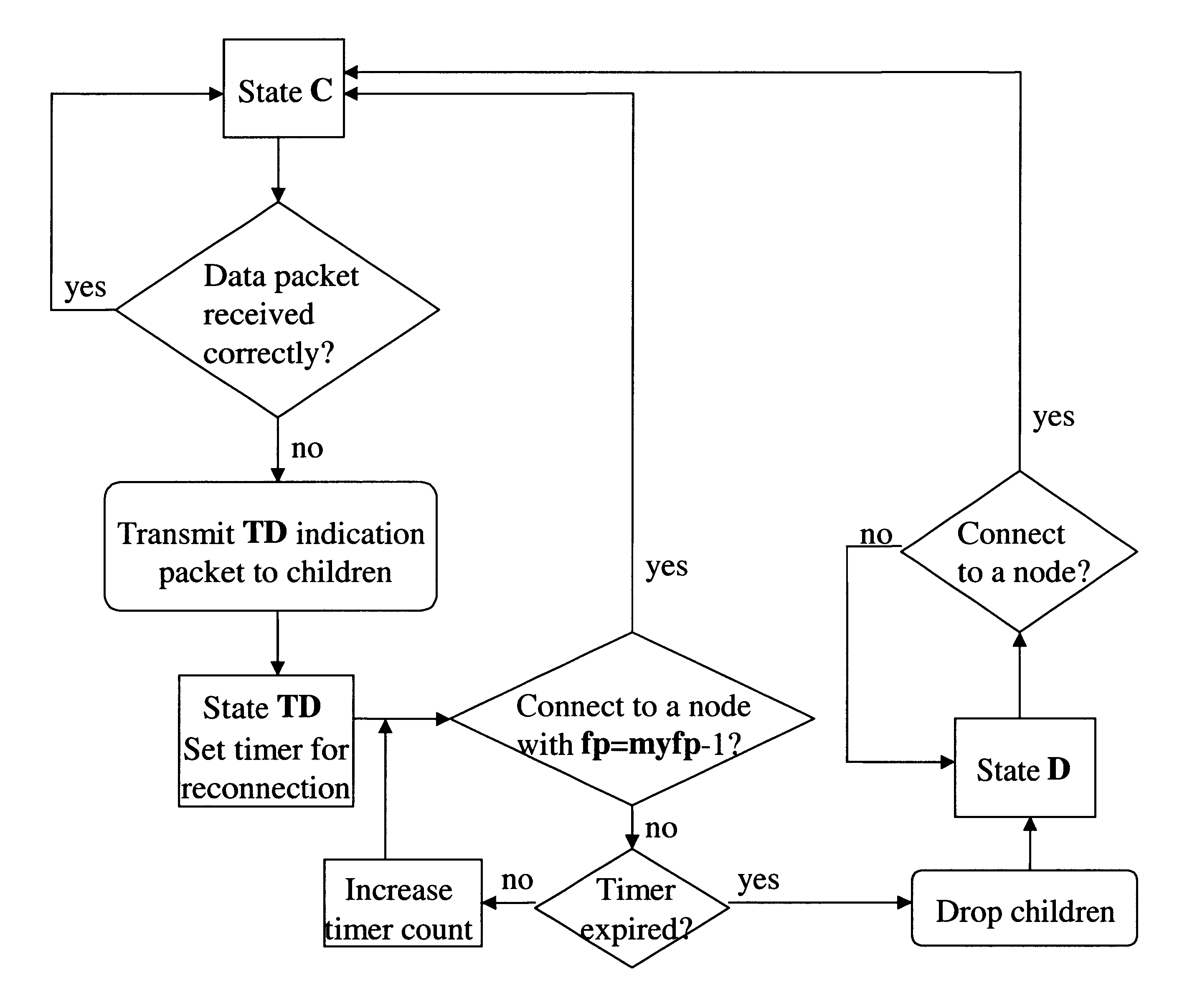
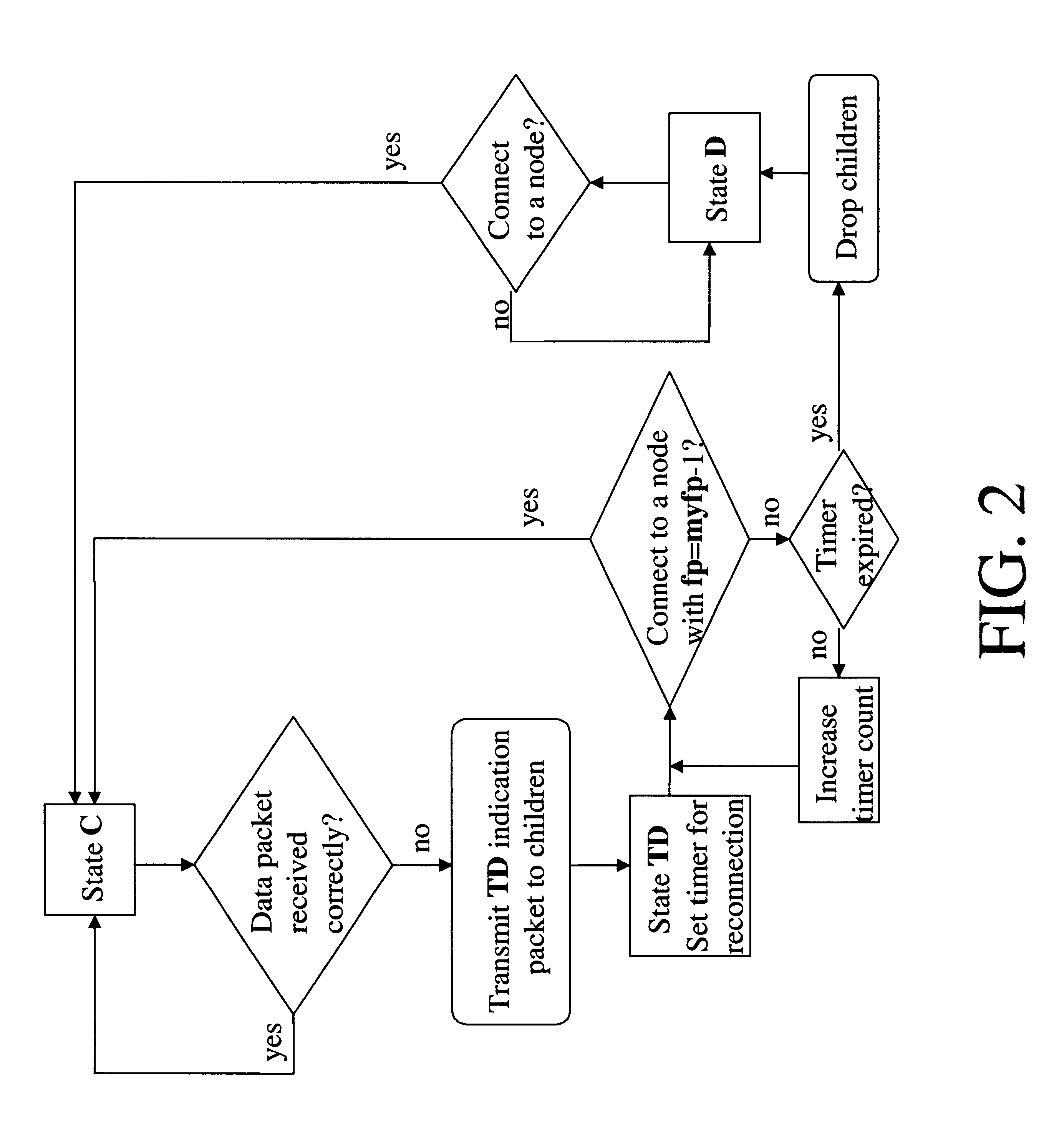
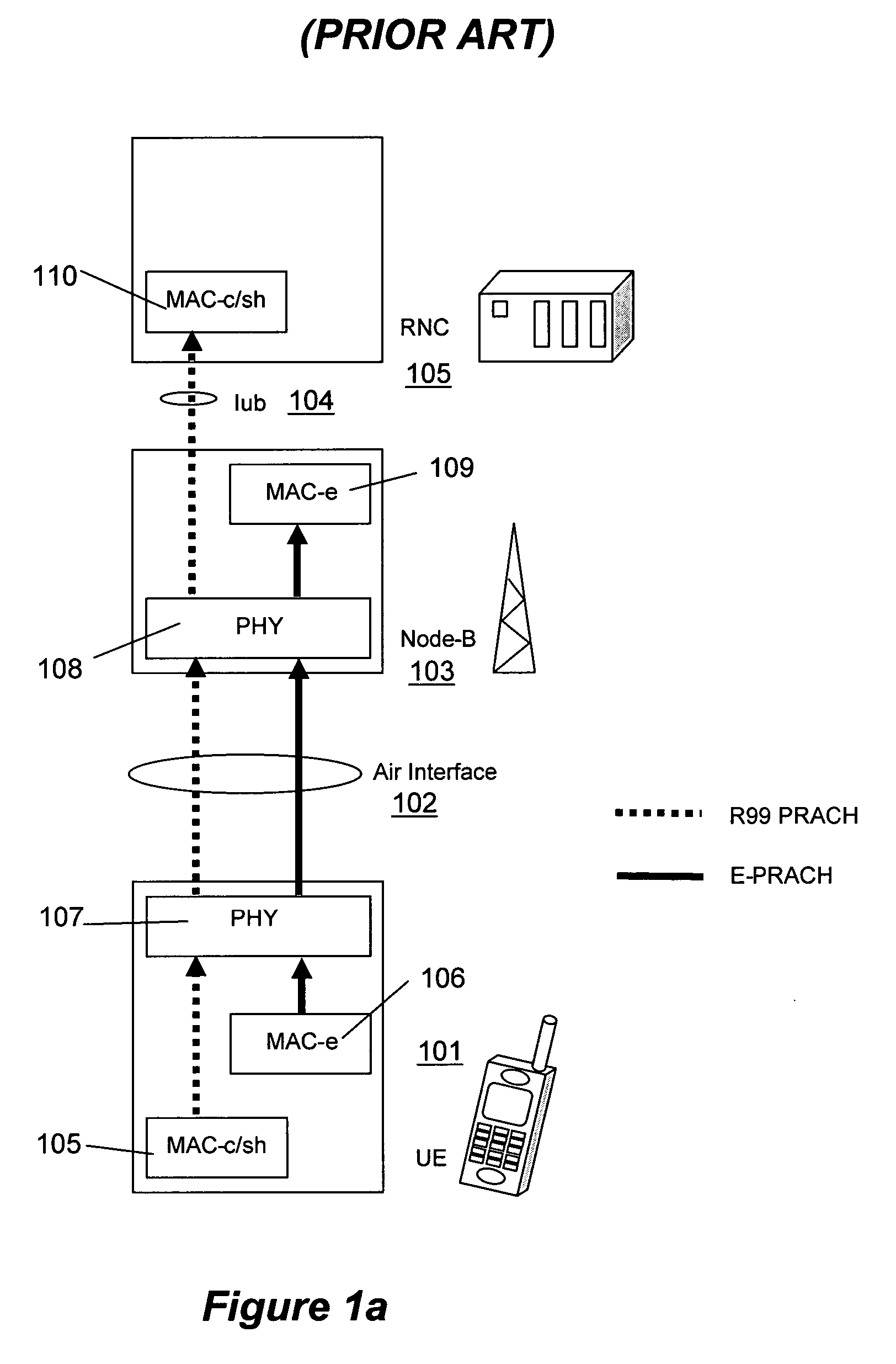
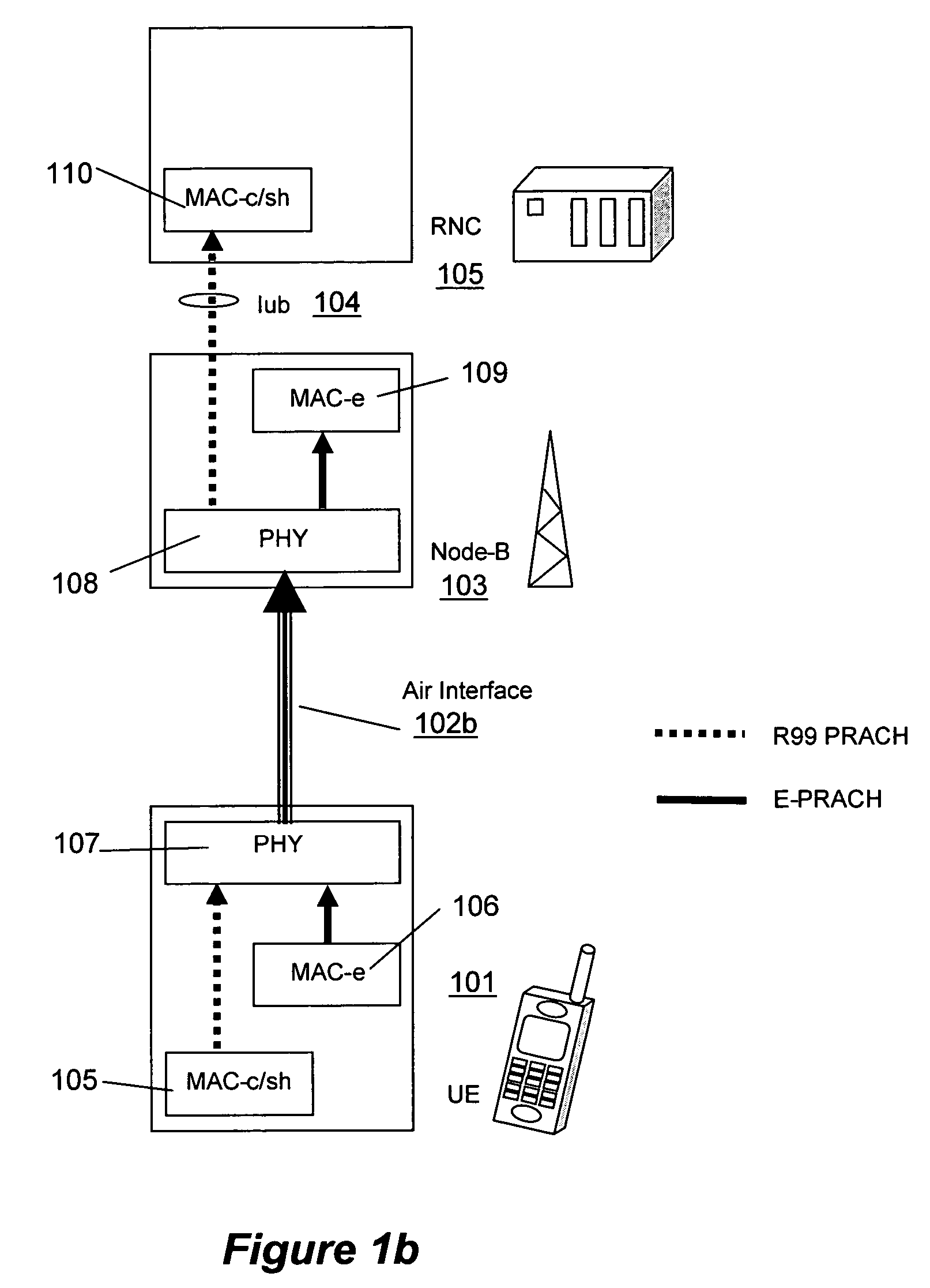
When a packet collision occurs, the packets are either discarded or sent back to their originating stations and then retransmitted in a timed sequence to avoid further collision. Packet collisions can result in the loss of packet integrity or can impede the performance of a network.
Method and apparatus for multicasting real time traffic in wireless ad-hoc networks
InactiveUS6721290B1Speed up decision making processSpecial service provision for substationNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of servicePacket loss
A real-time multicast scheduler method and apparatus is presented, to facilitate multicasting of real-time constant bit rate data in wireless ad-hoc networks. Constant bit rate traffic cannot tolerate delay jitter. However, a small amount of packet losses may be tolerable. In order to ensure the provisioning of a desired level of quality of service, bandwidth is reserved on the multicast structure. A goal of the real-time multicast scheduler is to avoid packet collisions and to facilitate color re-use, where "color" is defined as a channel selected as a combination of time-division multiple access, frequency-division multiple access, and code-division multiple access schemes. The real-time multicast scheduler provides a self-healing network which corrects for disconnections caused by node movement and nodes moving out of range of each other, while accounting for colors already assigned for data transmission in order to prevent packet collisions.
Owner:HRL LAB
Adaptive communication protocol for wireless networks
InactiveUS7184413B2Network topologiesTime-division multiplexWireless mesh networkNetwork Communication Protocols
A communication protocol that provides link-level and media access control (MAC) level functions for wireless (e.g., ad-hoc) networks and is robust to mobility or other dynamics, and for scaling to dense networks. In a mobile or otherwise dynamic network, any control-packet collisions will be only temporary and fair. In a dense network, the network performance degrades gracefully, ensuring that only a certain percentage of the common channel is consumed with control packets. The integrated protocol allows packets (e.g., data scheduling control packets) to be scheduled in a collision-free and predictable manner (known to all neighbors), multicast packets can be reliably scheduled, as well as streams of delay- or delay-jitter-sensitive traffic. Further, using an optional network code, the scheduling of control packets can appear to observers to be randomized.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Mobile ad-hoc network
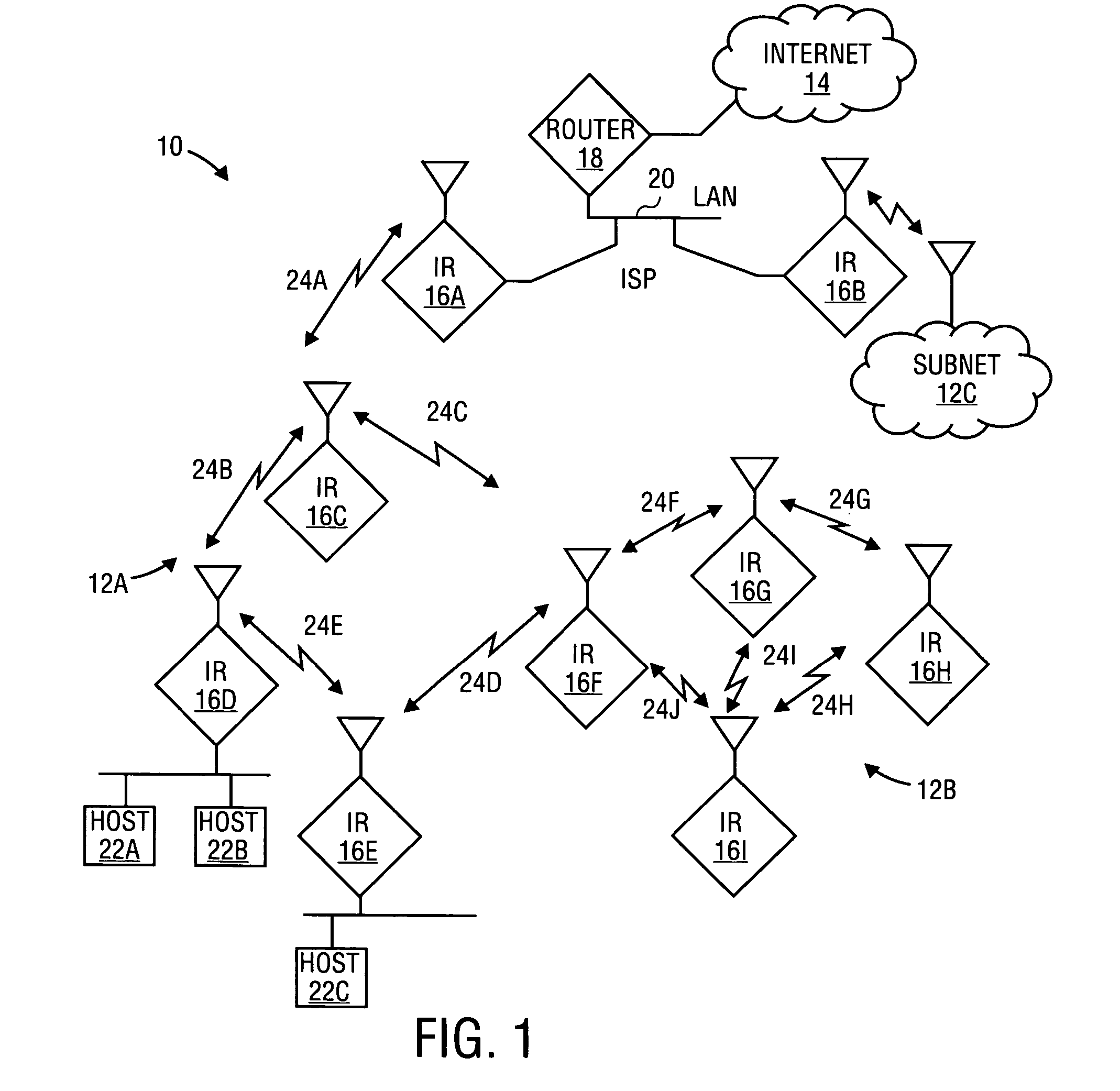
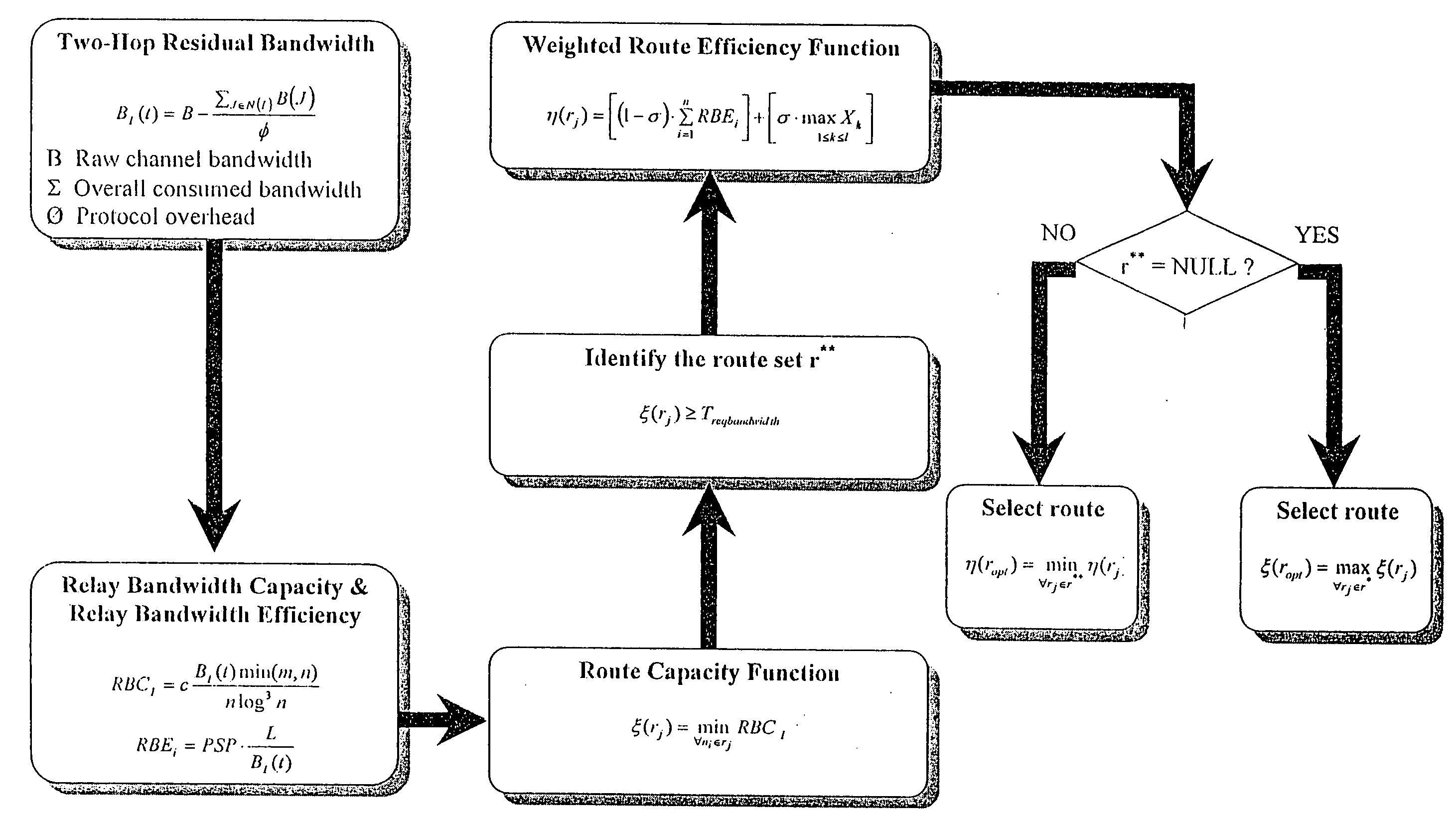
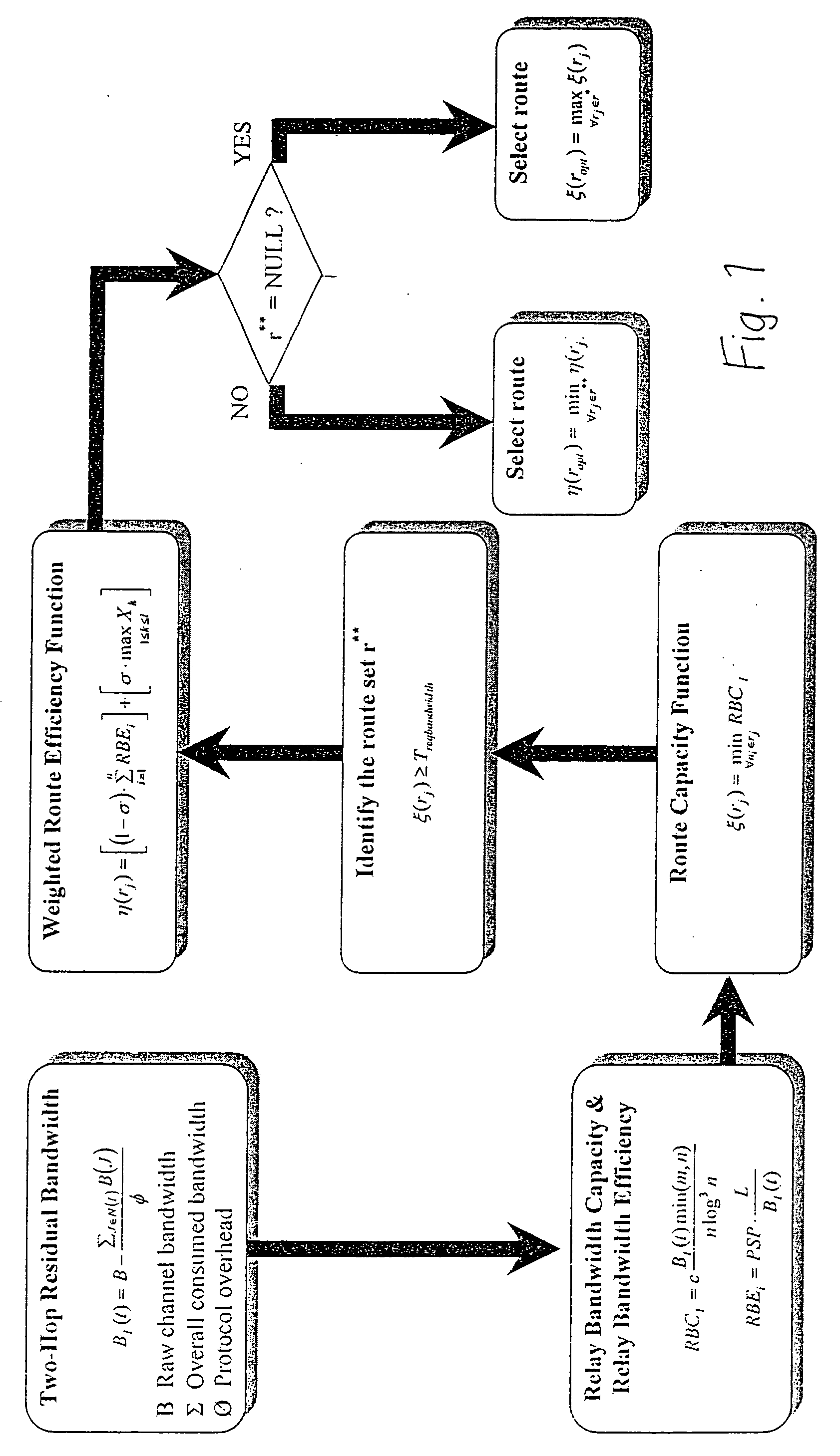
InactiveUS20060176829A1Lower Level RequirementsReduce disruptionError preventionTransmission systemsPacket collisionProtocol overhead
A method of assessing a communication route comprising a plurality of links between nodes in a mobile ad-hoc network comprises calculating the two-hop residual bandwidth of each node I of the route as BI(t)=B-∑J∈N(I)B(J)ϕwhere B is the raw channel bandwidth, the summation is the overall consumed bandwidth from node I's two-hop neighborhood nodes, JεN(I) and φ is a factor to account for protocol overhead, which may include handshaking, packet collision, re-transmission and / or back-off scheme traffic. An estimated transmission time for each of a plurality of links between said nodes may be calculated taking said two-hop residual bandwidth into account. For each possible route, a route efficiency function is determined at least by summing the estimated transmission times for all the links in the route, and the route in which the value of the route efficiency function is smallest is selected.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF EDINBURGH
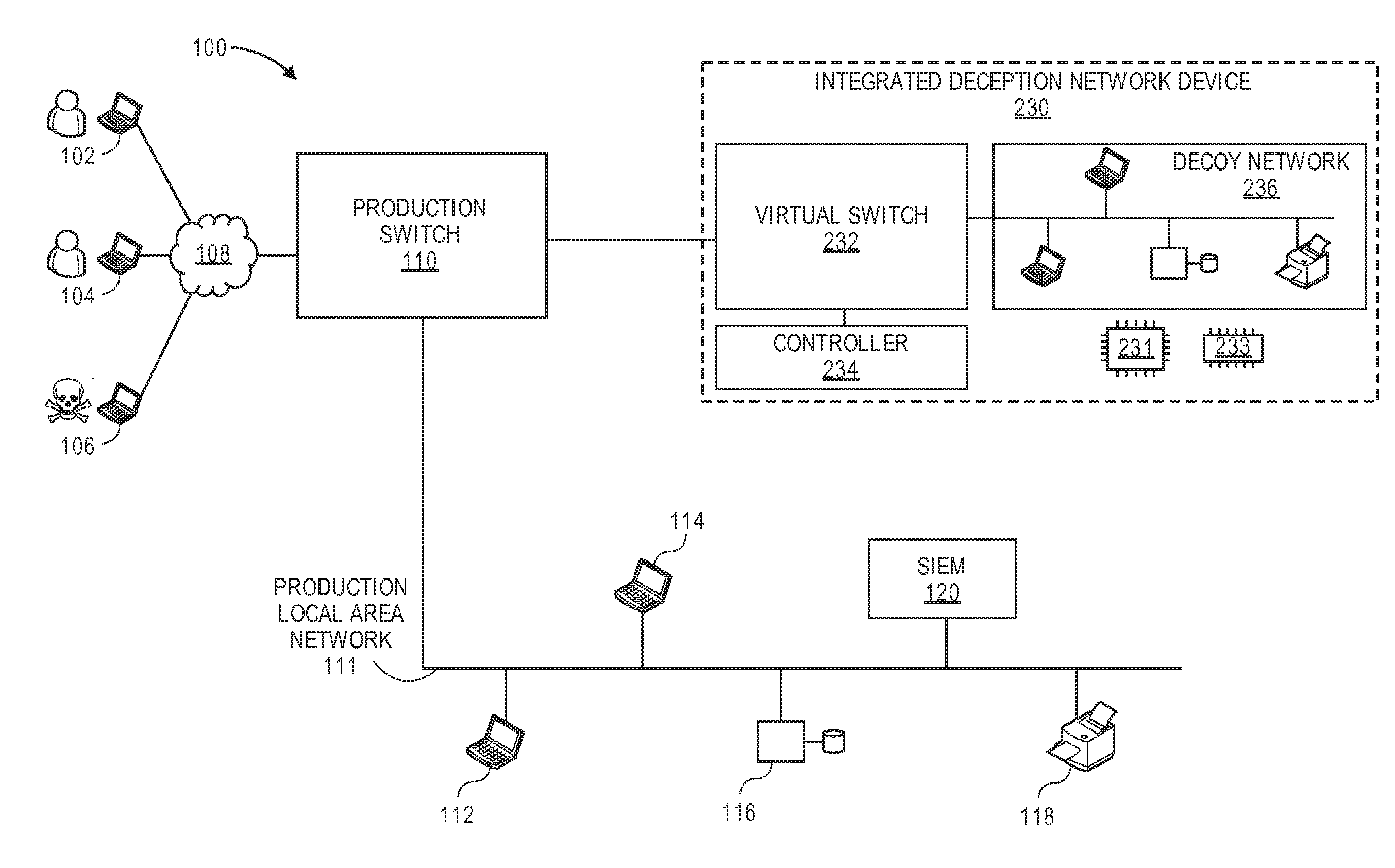
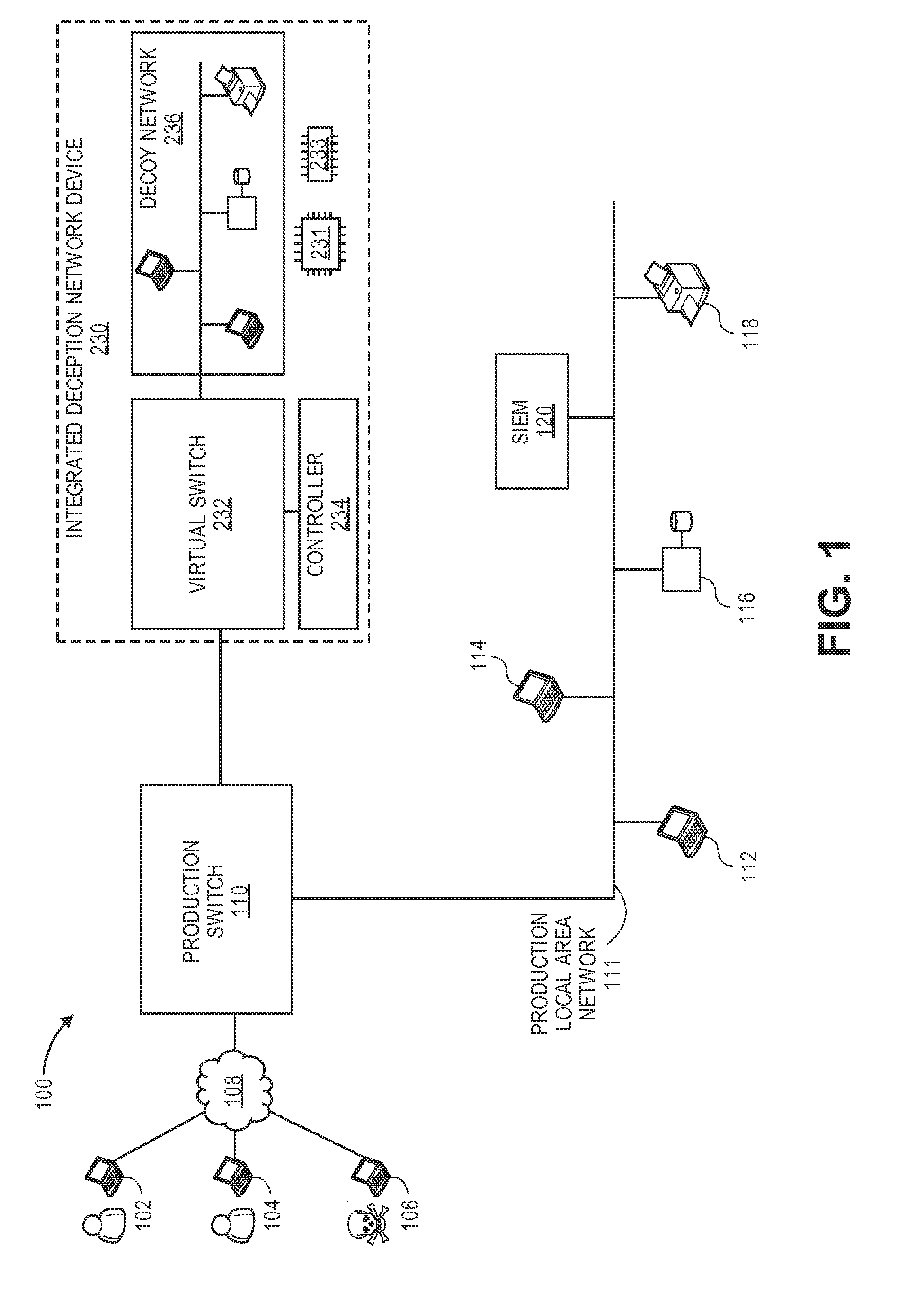
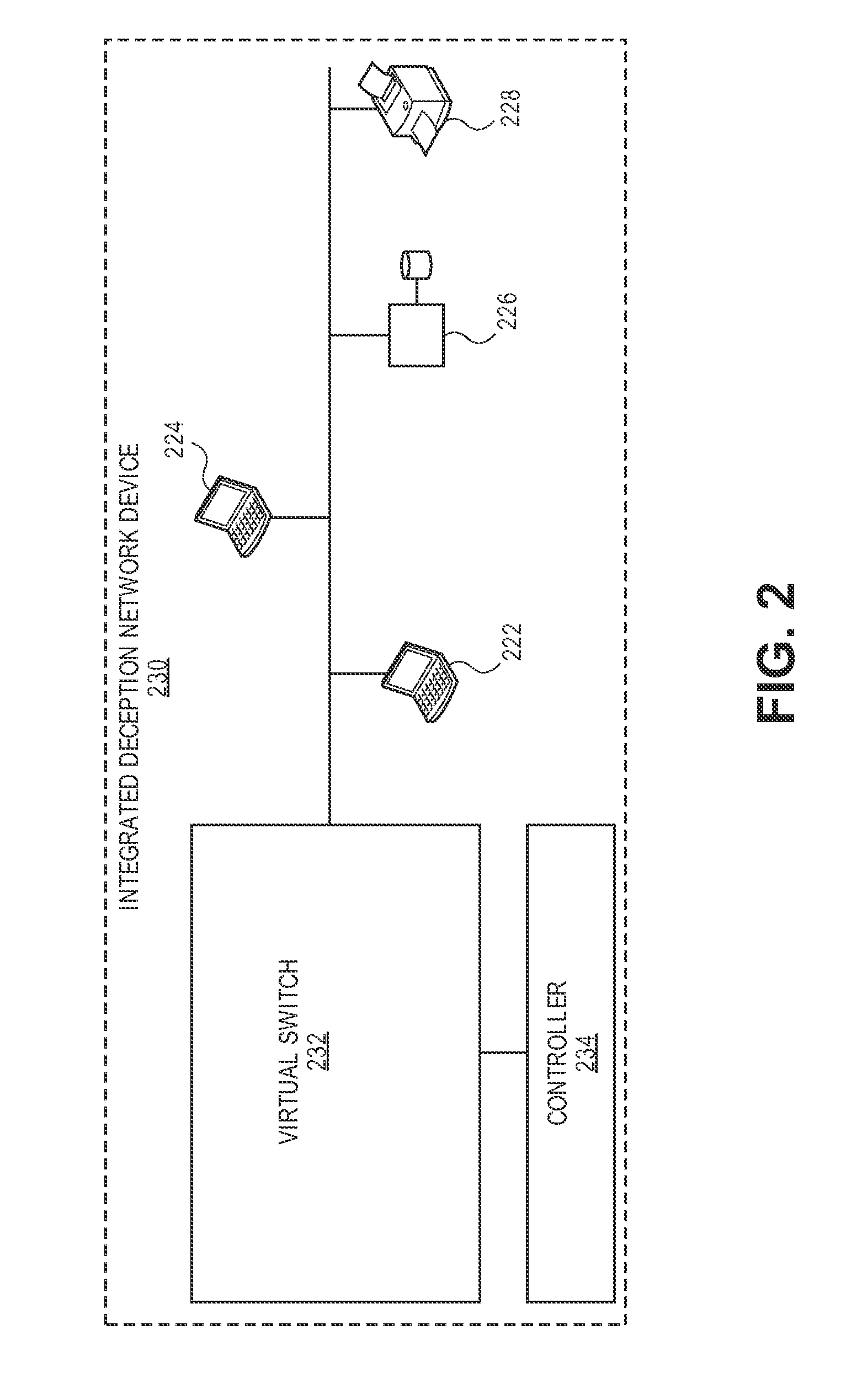
Network intrusion diversion using a software defined network
ActiveUS20160080415A1Avoid collisionMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionPacket collisionIp address
Methods, devices, and systems are described for diverting a computer hacker from a physical or other targeted production computer to a decoy software-based host emulator that emulates the physical computer. The decoy has the exact same IP address as the physical computer. In order to avoid packet collisions, a programmable physical switch and a virtual networking switch are employed, both of which can use software-defined networking (SDN). The virtual switch prevents packets from the decoy from flowing out of its virtual network until commanded. Upon a command, the physical switch redirects specific flows to the virtual switch, and the virtual switch opens specific flows from the decoy. The specific flows are those with packets containing the hacker's computer IP address, production computer IP address, and production computer port. The packets are associated with TCP connections or UDP sessions. The decoy host emulator can be a virtual machine (VM) running alongside many other VMs in a single computer. If the hacker performs a horizontal scan of the network, additional flows are diverted to other decoy host emulators.
Owner:ACALVIO TECH
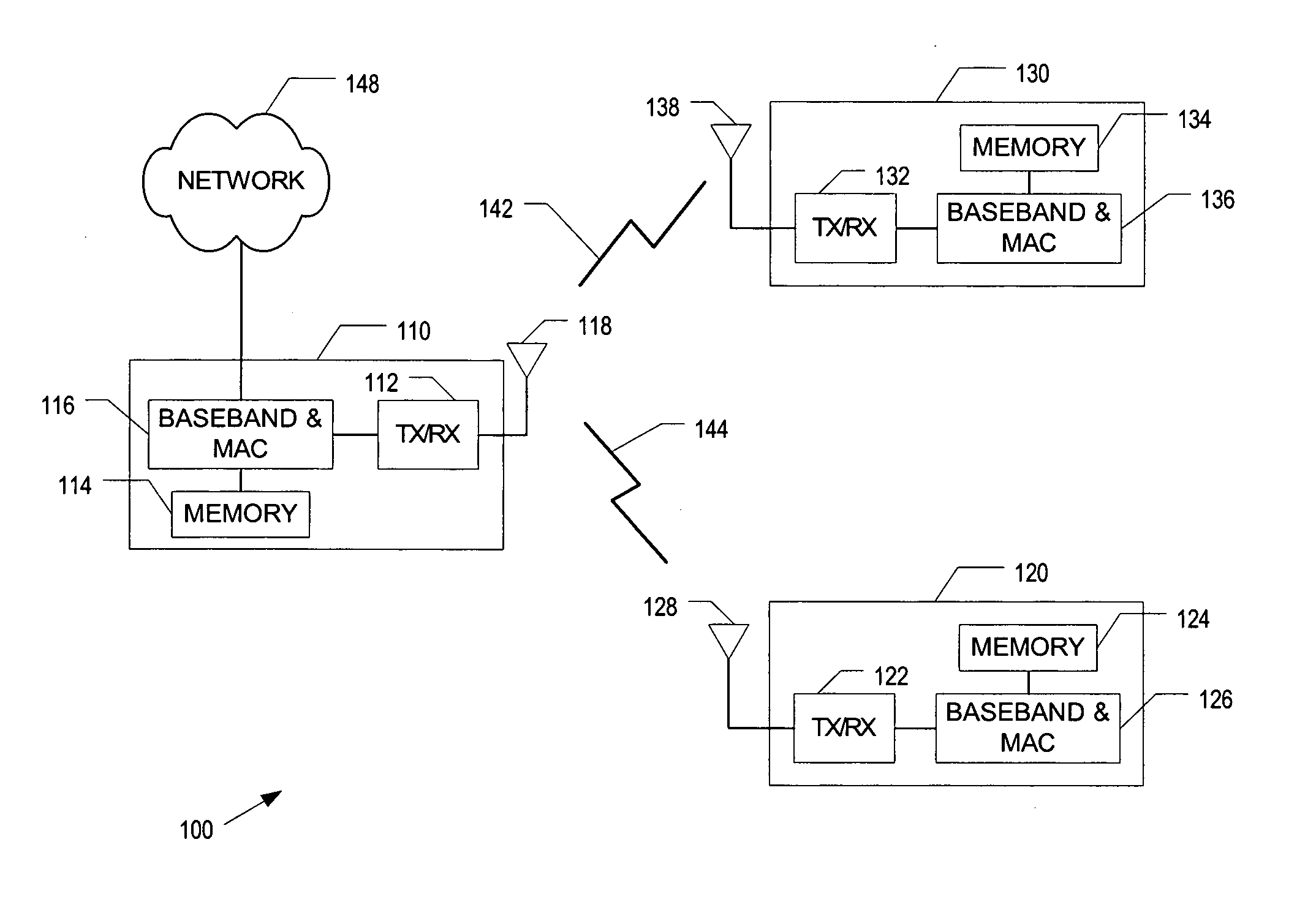
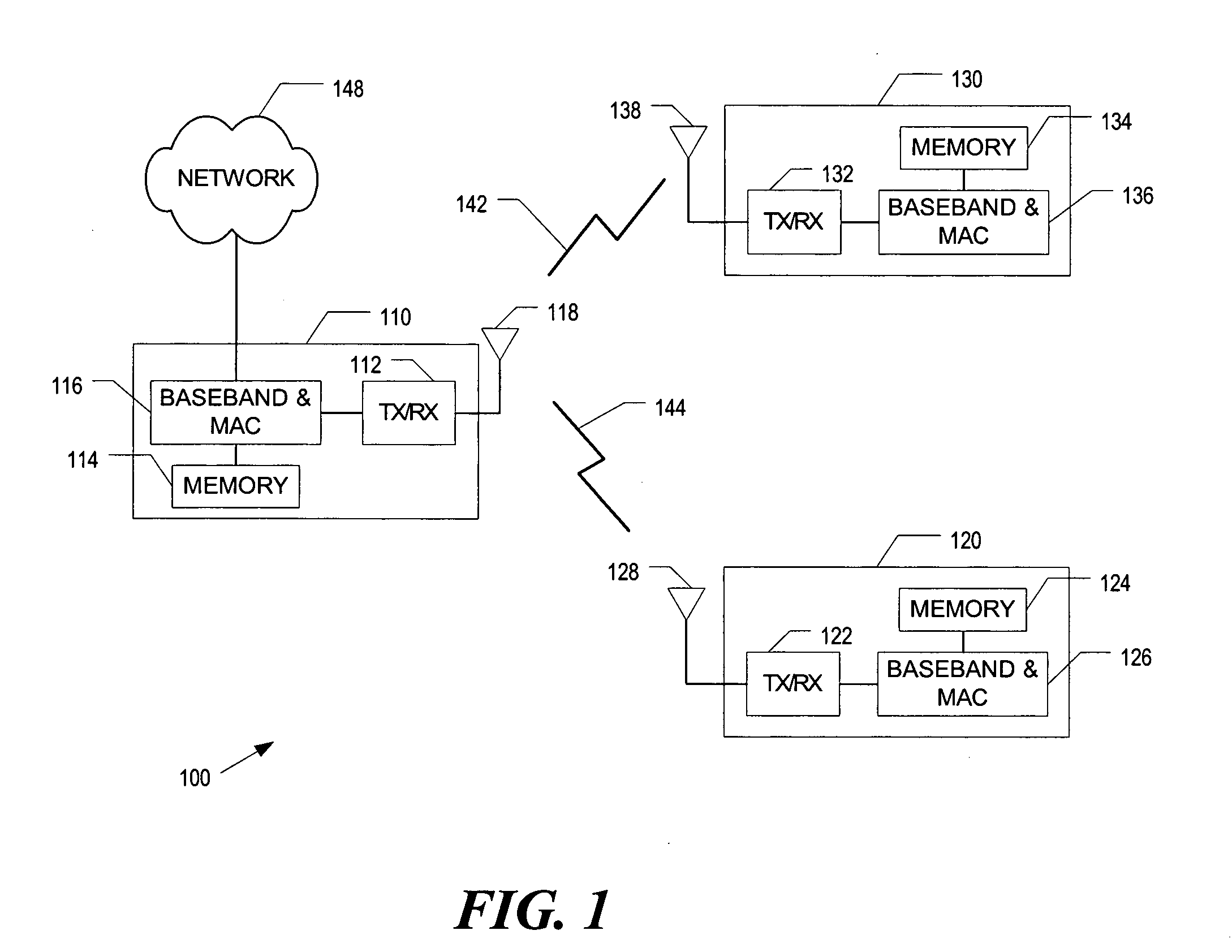
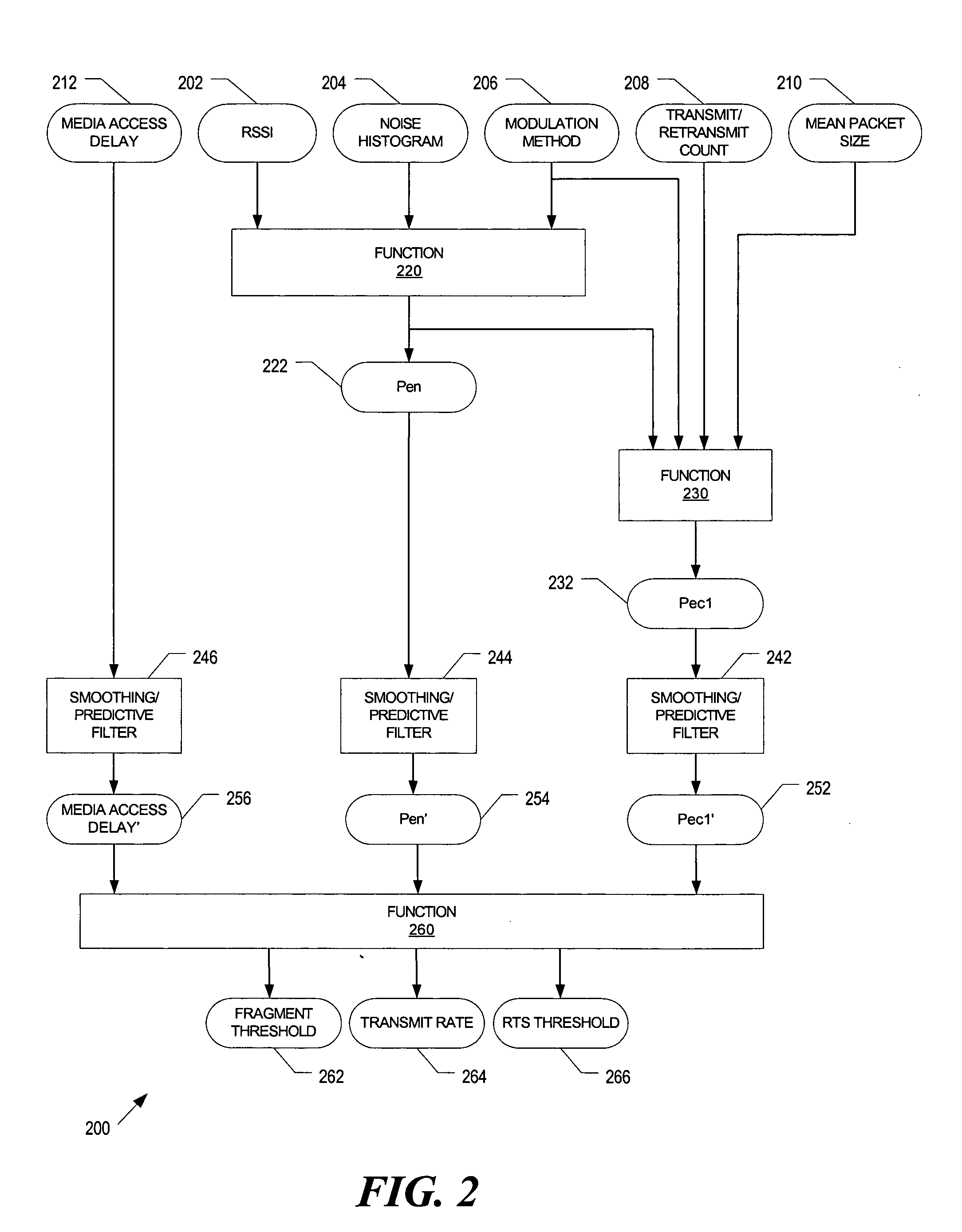
Method and apparatus to provide adaptive transmission parameters for wireless networks
InactiveUS20050268181A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsPacket collisionProtection mechanism
A method and apparatus that dynamically adjust transmission parameters based on channel conditions. Channel conditions include error rate due to packet collisions and an error rate due to noise. Transmission parameters include a fragmentation threshold, a transmit rate, and a transmission protection mechanism threshold.
Owner:INTEL CORP
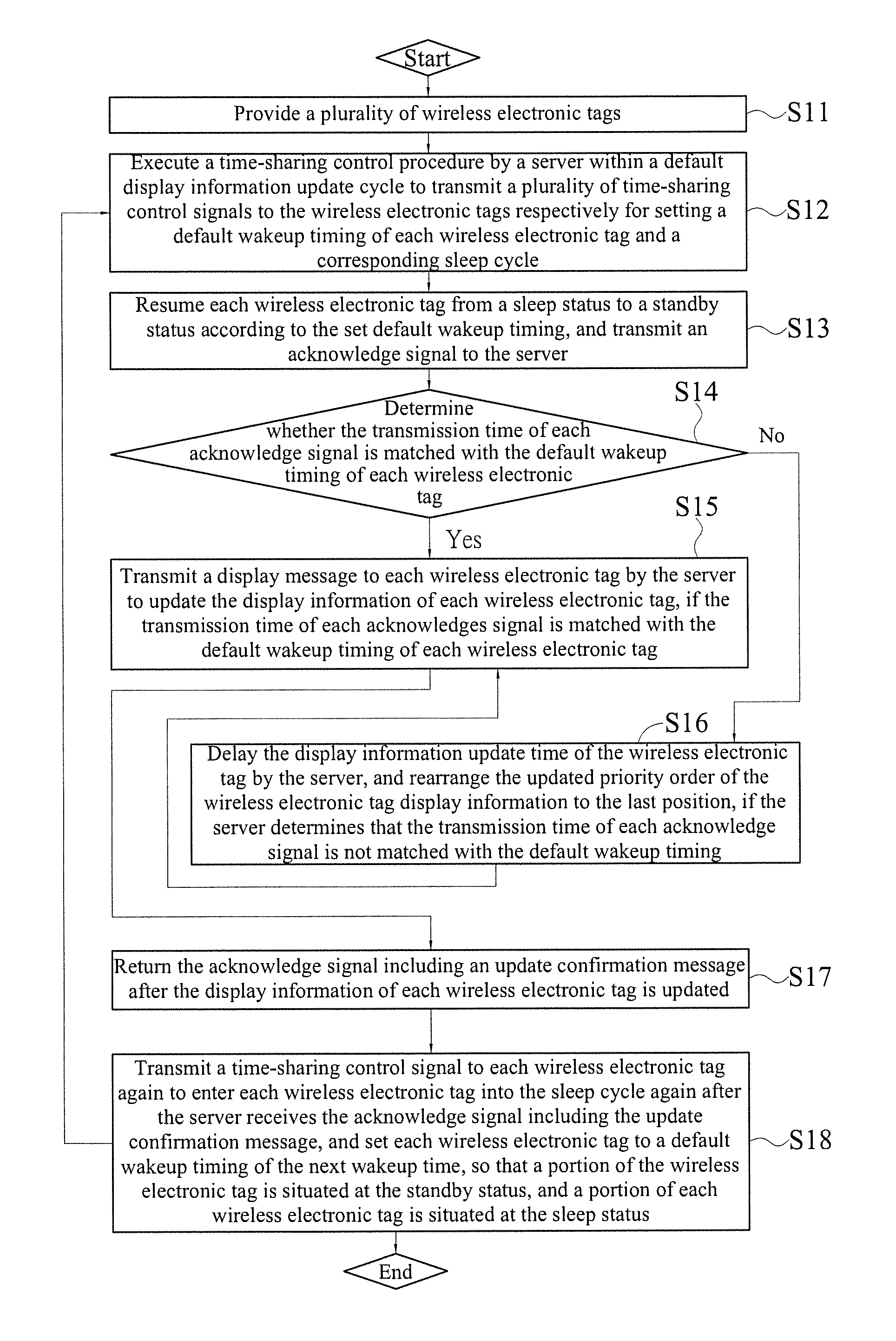
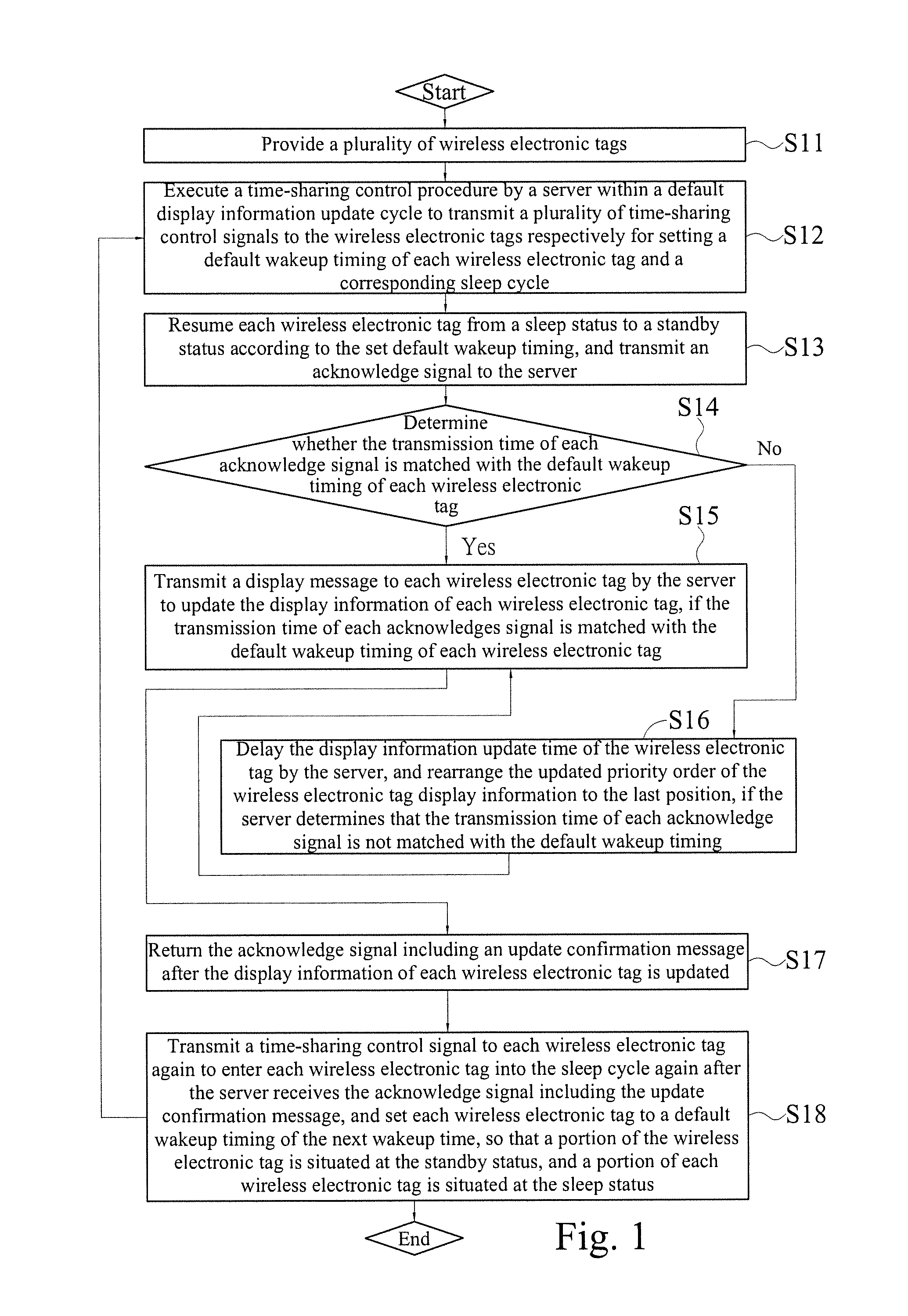
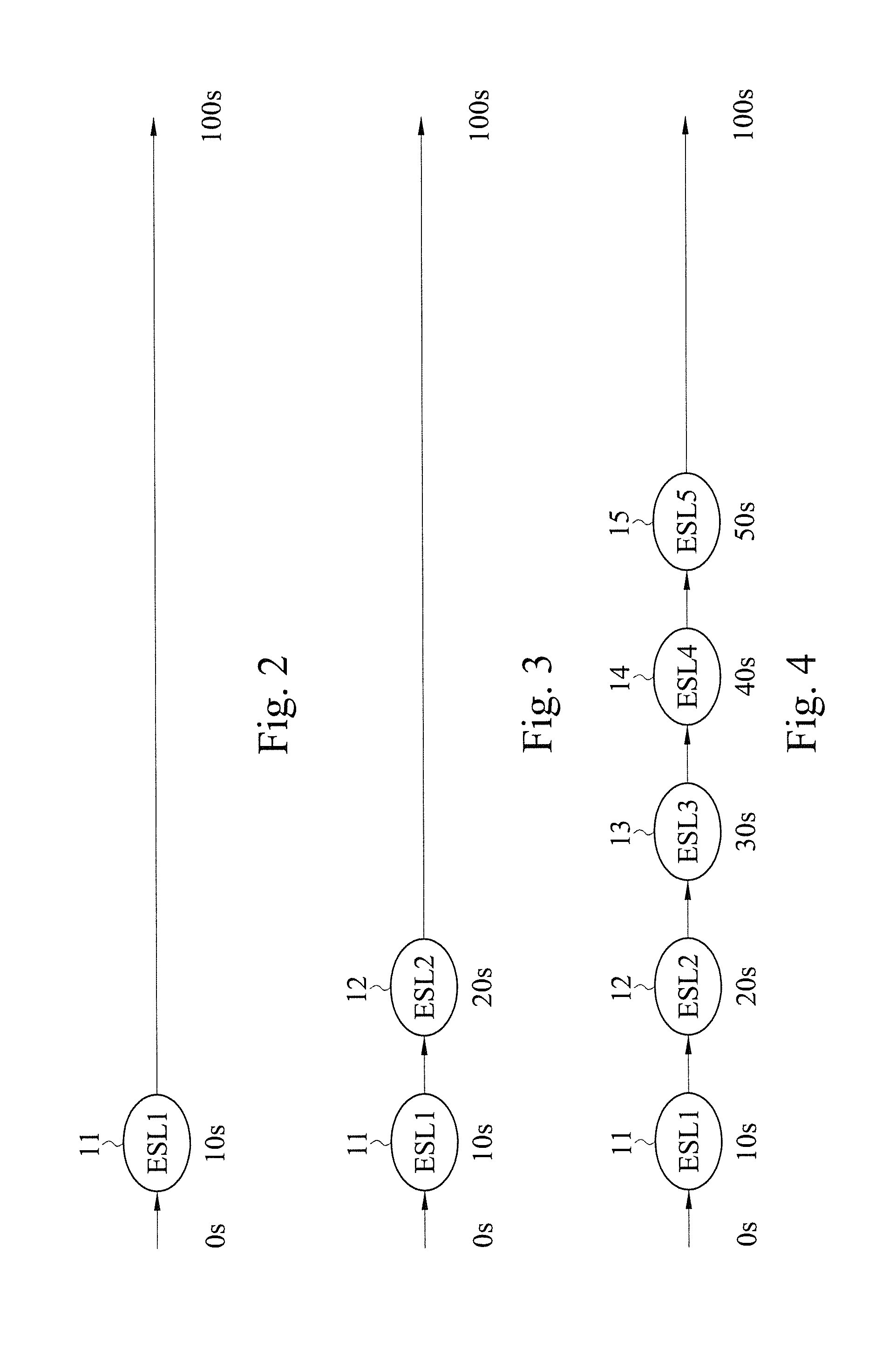
Electronic tag time-sharing control system and method thereof
InactiveUS20120326846A1Extended operating timeReduce network bandwidth requirementsSensing detailsCo-operative working arrangementsData packPacket collision
The present invention discloses an electronic tag time sharing control system and a method thereof, and the system comprises a server, at least one coordinator and a plurality of wireless electronic tags. The server transmits a time-sharing control signal. The coordinator and the server form a wireless connection for receiving and transmitting the time-sharing control signal. The wireless electronic tags and the coordinators form a wireless connection. After each wireless electronic tag receives the time-sharing control signal, different sleep cycle and wakeup timing are generated to update display information sequentially. A portion of the wireless electronic tag is situated at a sleep status and a portion of the wireless electronic tag is situated at a standby status to receive the update display information, so as to achieve the effects of saving bandwidth, reducing packet collisions and extending the service life of the wireless electronic tag.
Owner:CERAMICRO TECH
Packet Conflict Resolution
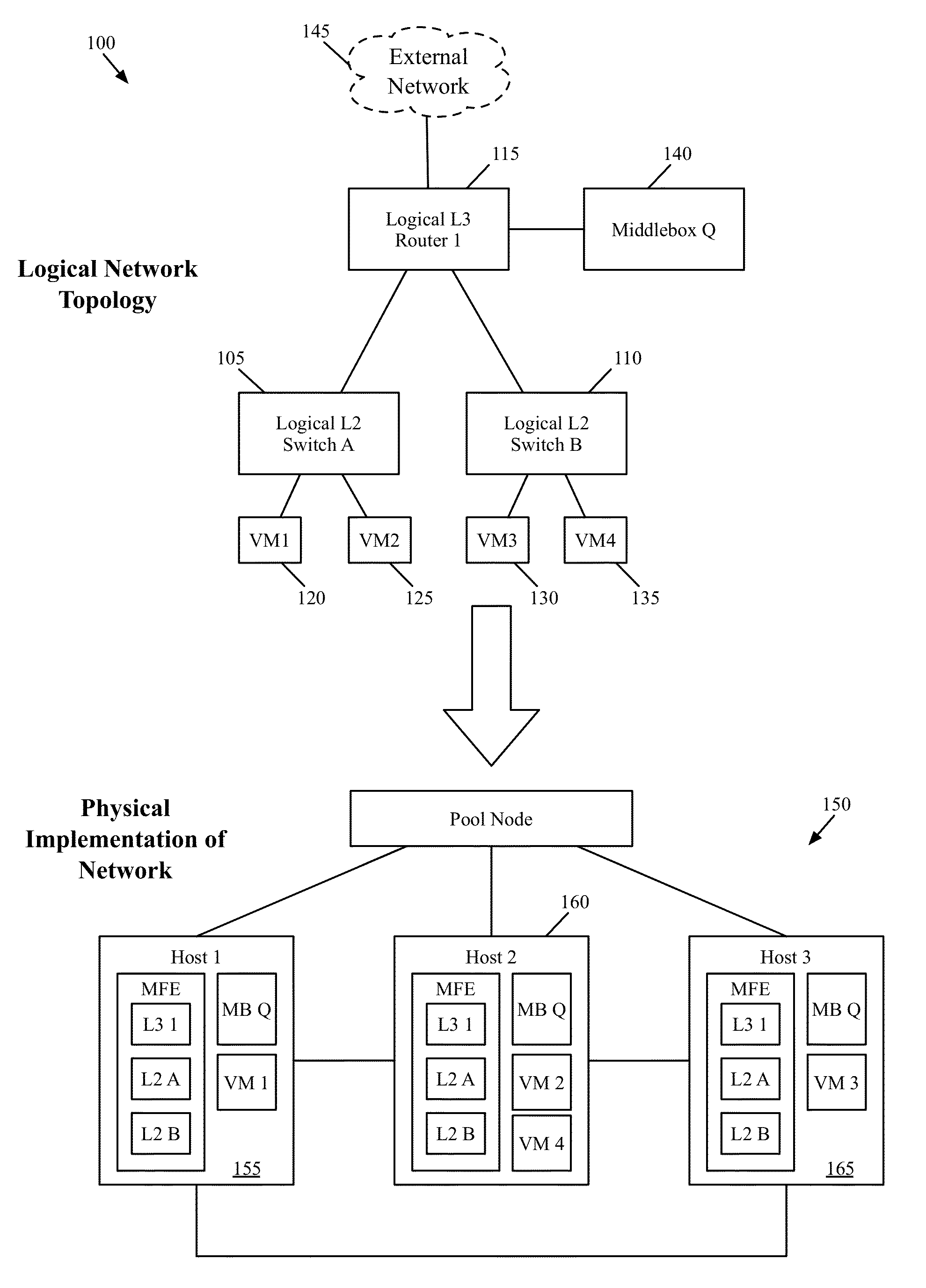
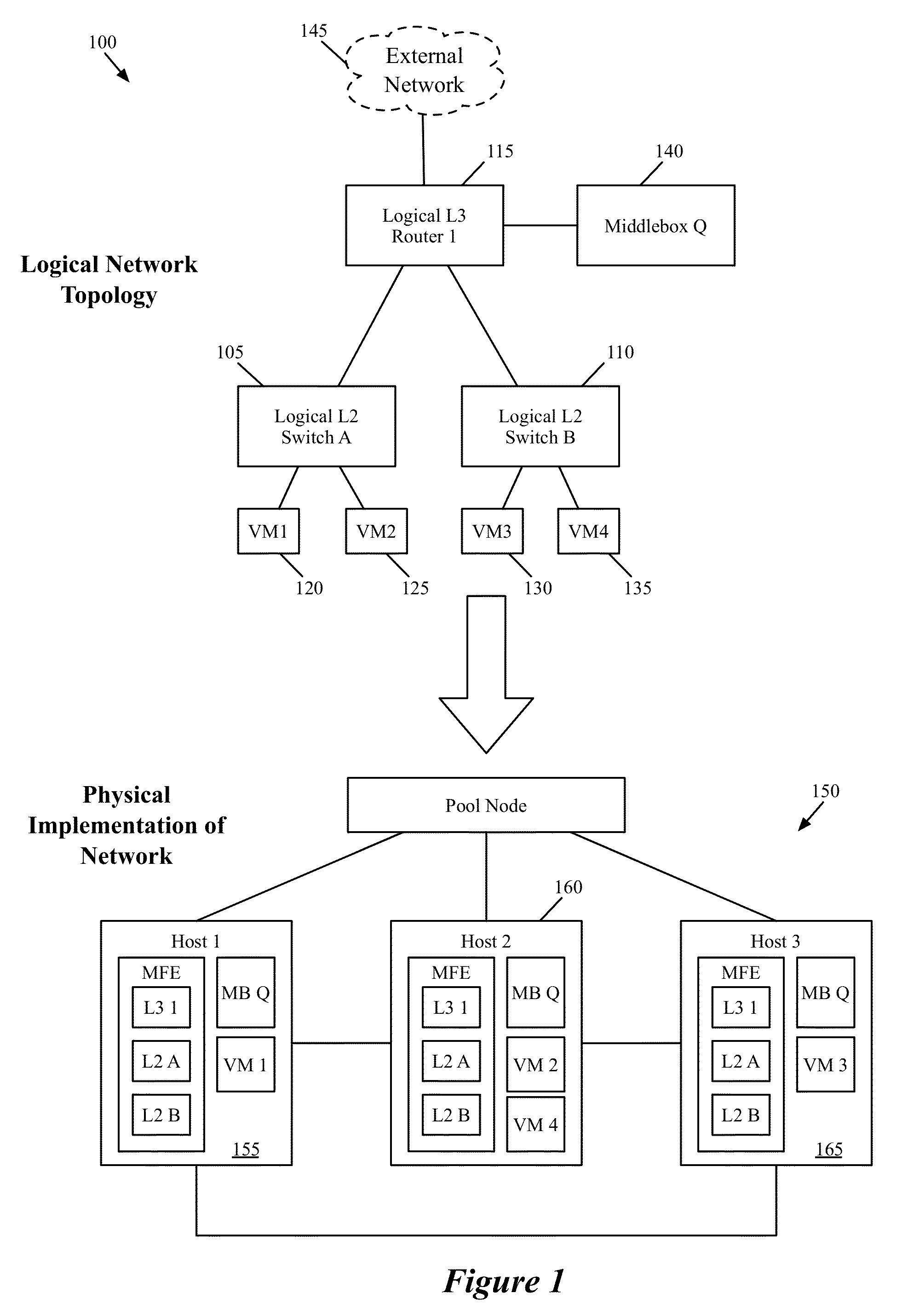
ActiveUS20150117445A1Fault responseData switching by path configurationPacket collisionLogical network
Some embodiments provide a method for a first managed forwarding element that implements a logical network. The method receives a packet from a second managed forwarding element. The first packet has an initial set of characteristics defining a first connection between a source machine connected to the second managed forwarding element and a destination machine connected to the first managed forwarding element. The method determines whether a second connection exists with the initial set of characteristics between a different machine connected to a third managed forwarding element and the destination machine. When a second connection exists with the initial set of characteristics, the method modifies at least one characteristic of the packet such that the modified packet does not have the same set of characteristics. The method delivers the modified packet to the destination machine.
Owner:NICIRA
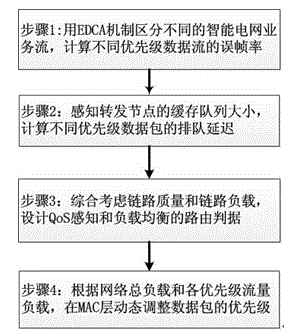
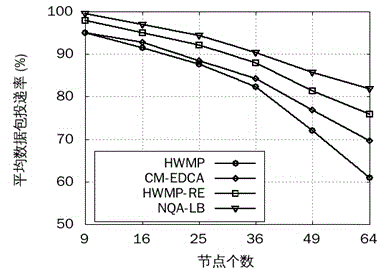
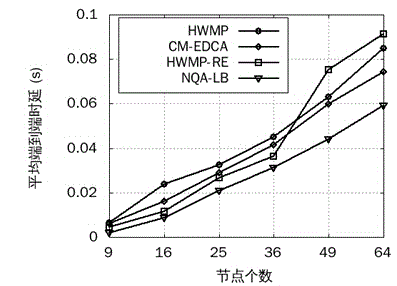
Wireless Mesh intelligent power grid routing mechanism with QoS perceiving and loading balancing
ActiveCN104661260AReduce end-to-end latencyImprove delivery rateNetwork traffic/resource managementHigh level techniquesService flowPacket collision
The invention provides a wireless Mesh intelligent power grid routing mechanism NQA-LB with QoS perceiving and loading balancing. The mechanism comprises four steps: firstly differentiating intelligent power grid service flows with different QoS requirements through an EDCA mechanism, and calculating the frame error rate of different service flows according to the data packet collision rate of the EDCA mechanism; secondly, calculating data packet queuing delay with different priorities of the queue length of forwarding node cache and the successful transmission probability of data packets; then designing the routing metric of QoS perceiving and loading balancing by comprehensively considering the data frame error rate and queuing delay of different service flows, and selecting an optimal path with less load for the service flow with different QoS demands; finally dynamically adjusting the data packet priority on an MAC layer according to network total loading and loading conditions of all priority service flows. The mechanism can more accurately perceive the link quality of the MAC layer, guarantees the QoS demands of different service flows of a power grid, further increases the data packet delivery rate and average throughput capacity, and reduces the end-to-end delay of all service flows.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
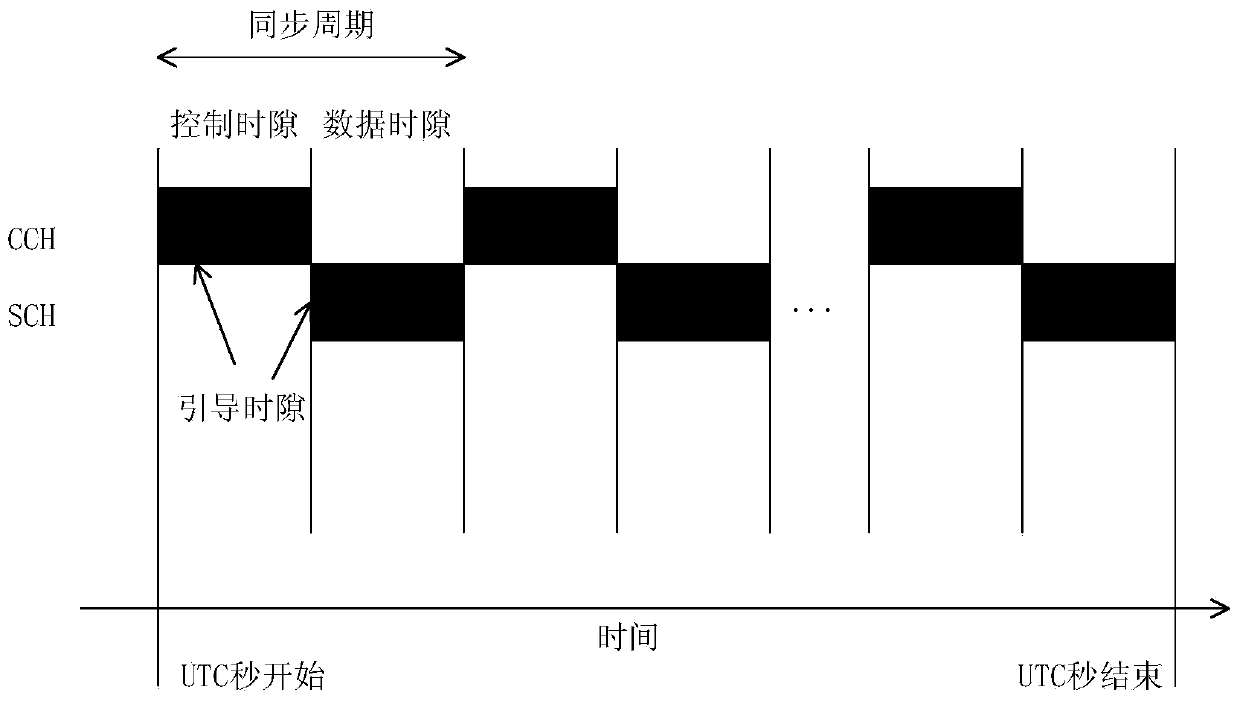
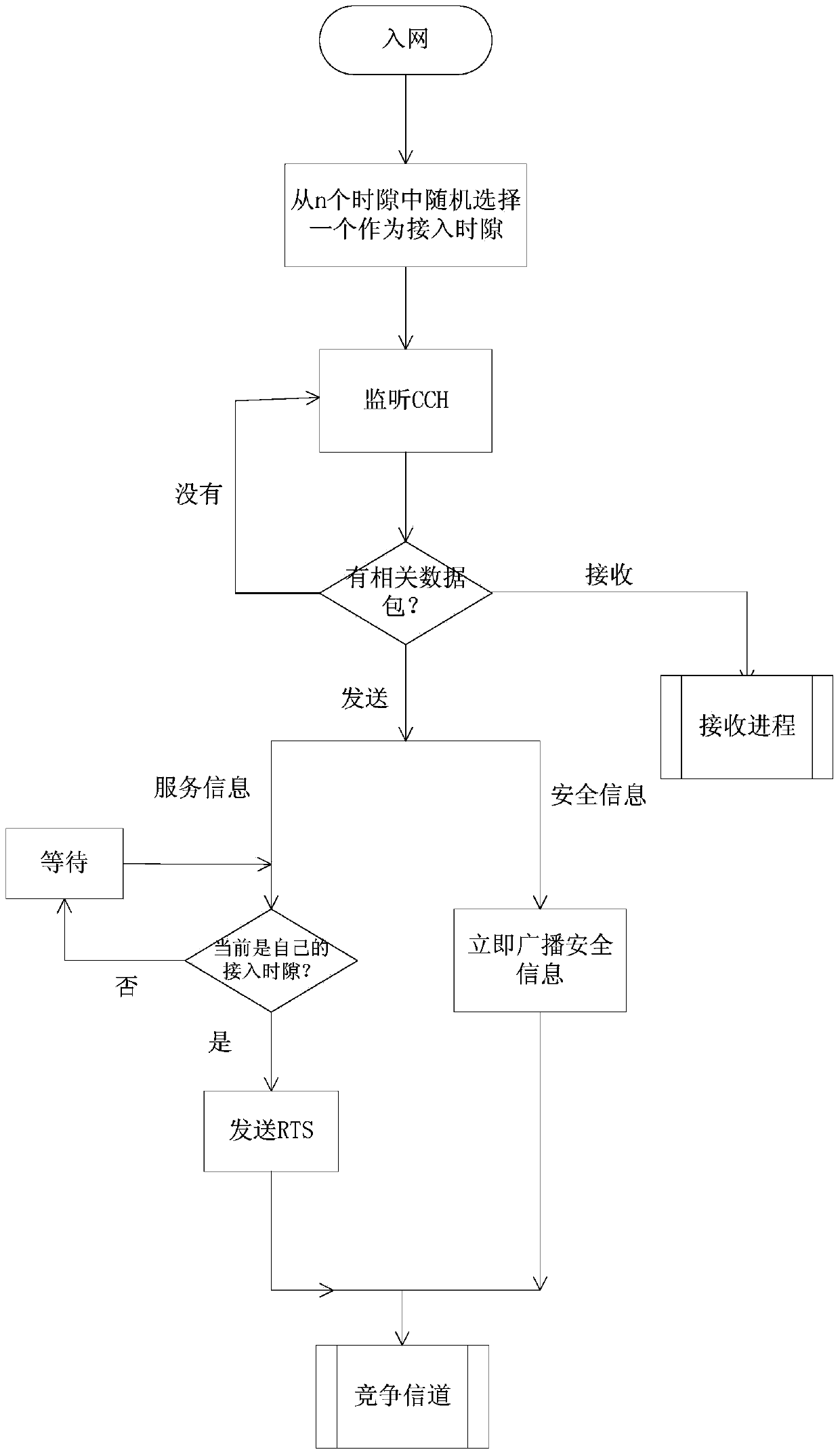
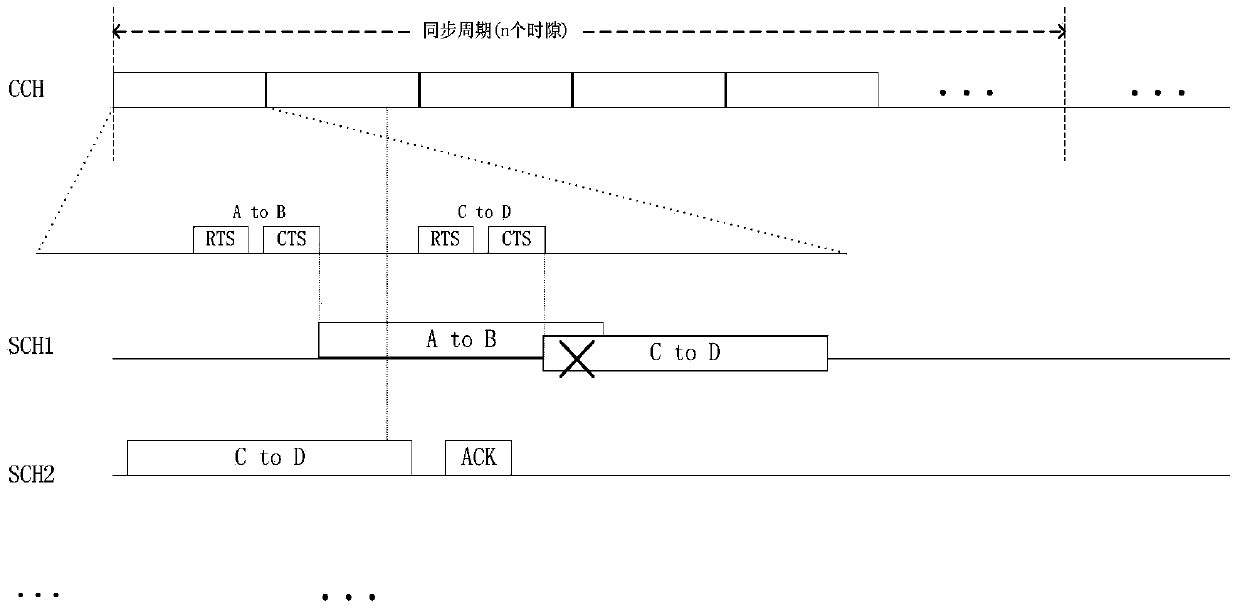
Vehicle-mounted ad-hoc network asynchronous multichannel MAC (media access control) access method based on time division multiplexing
InactiveCN103517445AIncrease profitReduce the probability of conflictNetwork topologiesPacket collisionCommunications system
The invention provides a vehicle-mounted ad-hoc network asynchronous multichannel MAC access method based on time division multiplexing, and relates to a mobile communication system. According to the invention, a node which is not required to transmit and receive service information is used to continuously monitor a control channel in an audio way to obtain security information and channel synergic information. The access method comprises the following steps: when a node is to send service information, transmitting channel reserving information, after reserving the channel, immediately transferring to the corresponding service channel to transmit the service information, after transmitting the service information, immediately returning to the control channel to perform audio monitoring, and solving the problems of low channel utilization and the bottleneck of the control channel. Compared to the mechanism that according to the IEEE 1609.4 standard, the channels of all nodes are synchronously switched, the vehicle-mounted ad-hoc network asynchronous multichannel MAC access method can avoid idle channel; in addition, the time division multiplexing method can solve the bottleneck problem of the control channel and reduce conflict possibility of the control channel; the node synergic method is used to reduce the influence caused by data packet collision on the service channel.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Data packet type recognition system
InactiveUS20070047513A1Reduces data packet collision probabilityError preventionTime-division multiplexPacket collisionCommunications system
Owner:SONY CORP
System and method for detection/interception of IP collision
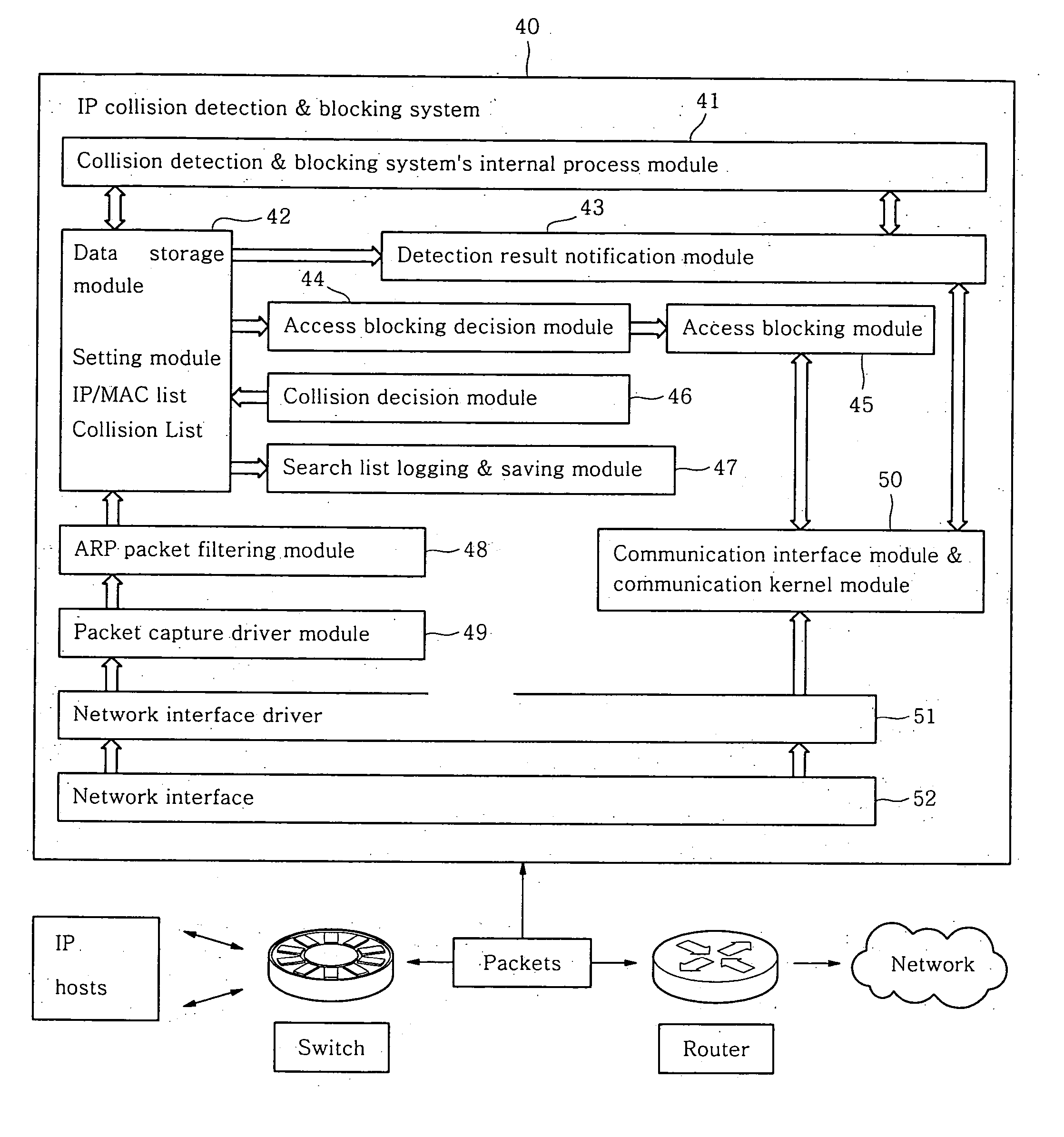
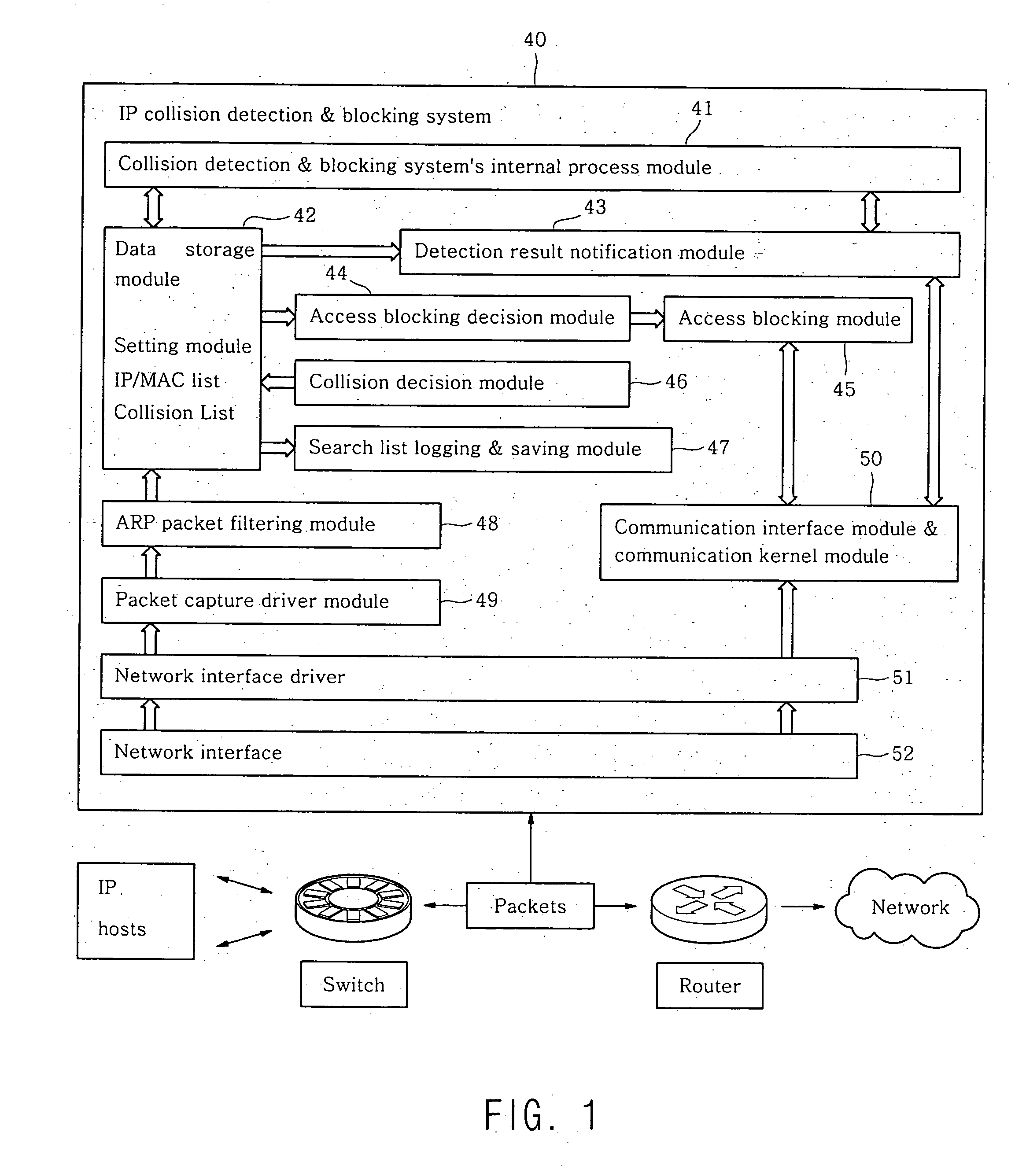
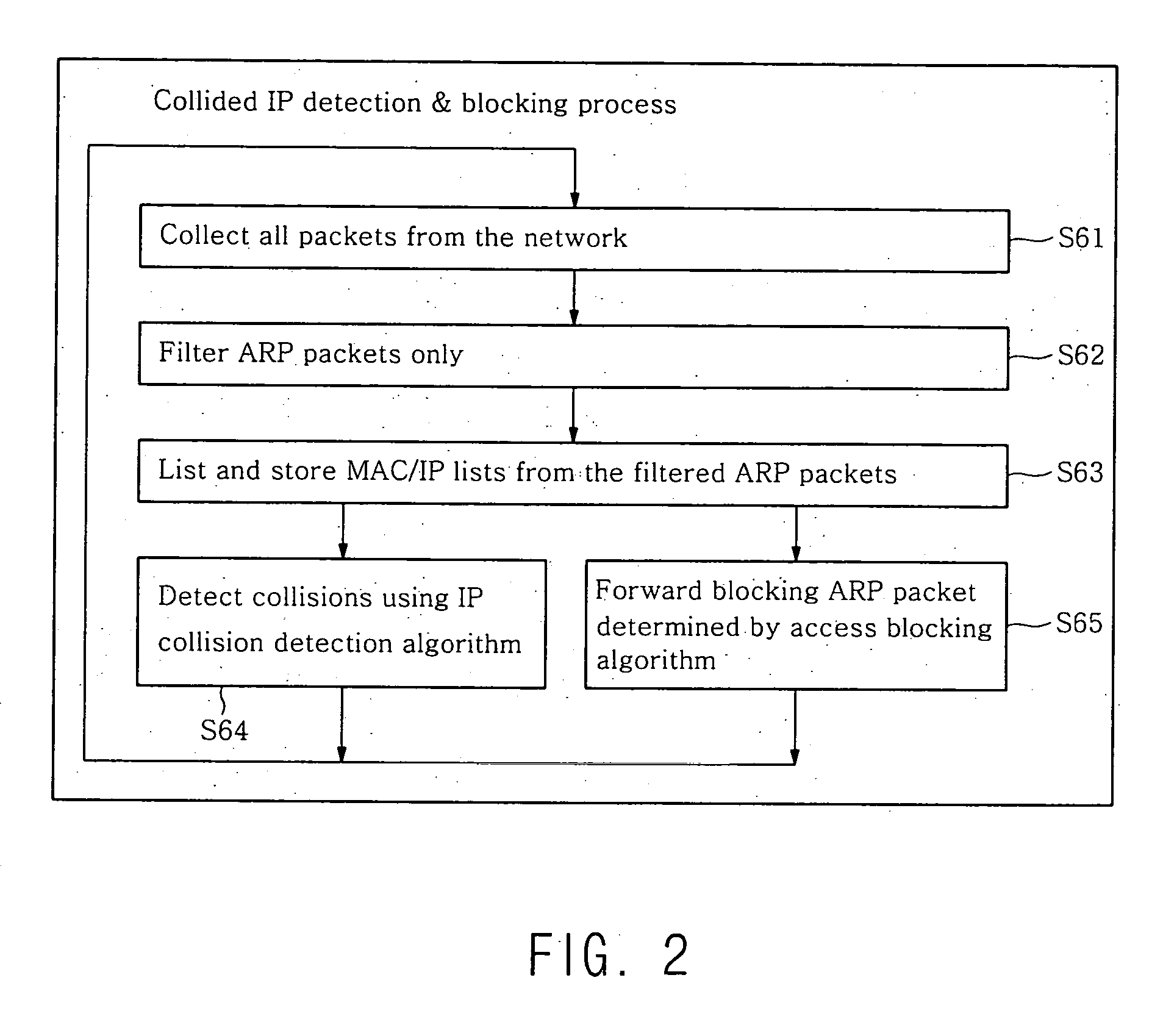
InactiveUS20050198242A1Low costMinimizes deployment riskDigital computer detailsTransmissionData packPacket collision
The present invention relates to detecting and analyzing interrupted ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) packets occurring when an IP communication is established in a network. The invention refers to IP collision detection and access blocking methods using ARP. The present invention monitors network traffic packets, detects packet collisions and notifies administrators on the status, and depending on network policies, blocks IP users' network access using ARP centered on MAC.
Owner:SCOPE
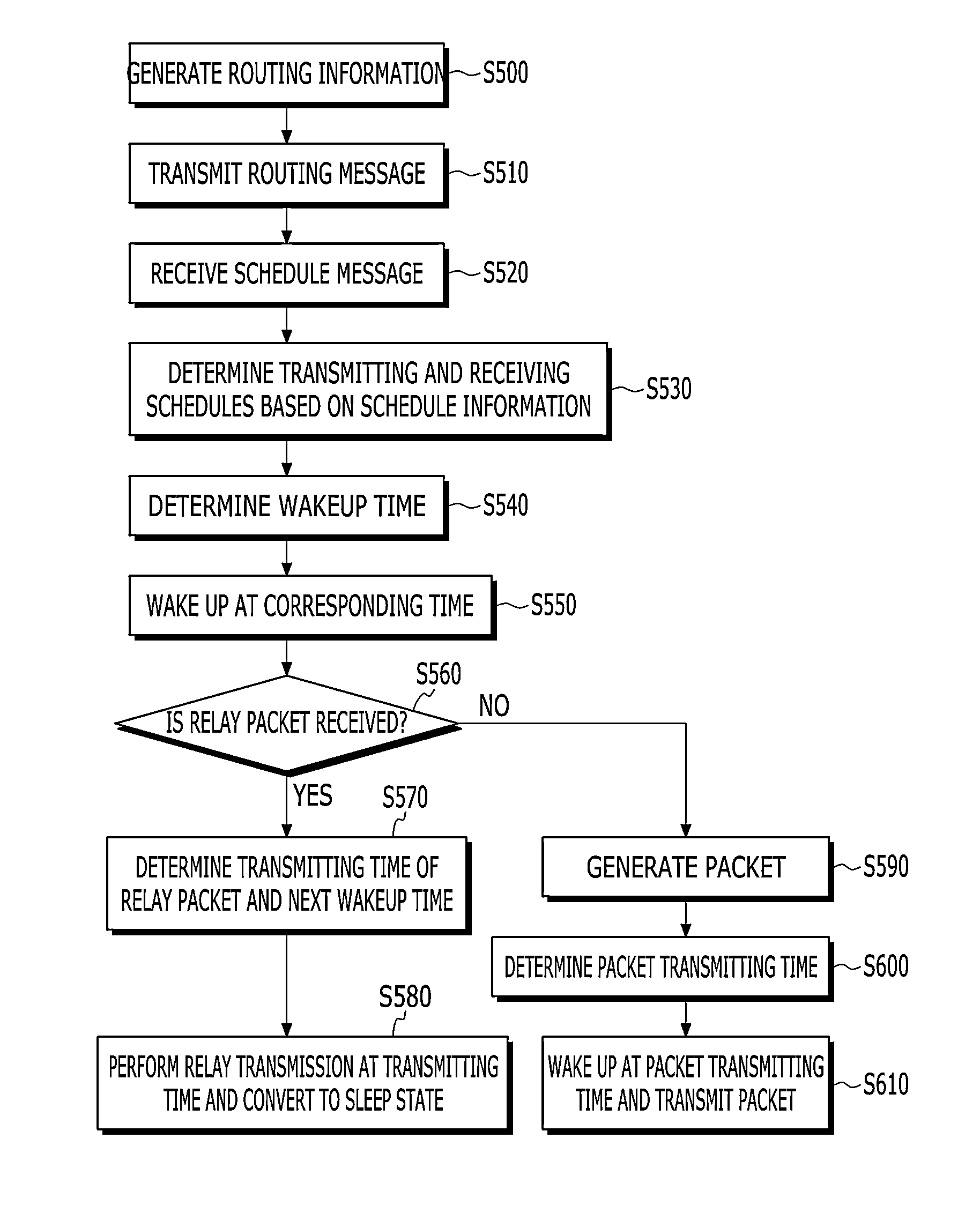
Method and apparatus for transmission scheduling in wireless sensor network
InactiveUS20150036570A1Minimizing delivery latencyDelay minimizationPower managementTransmission systemsWireless mesh networkStructure of Management Information
In a sensor network including a sink node and a plurality of sensor nodes, the sink node receives a routing message including routing information from the sensor nodes, analyzes a structure of the sensor network based on routing information, and calculates a transmission schedule of each sensor node based on the analyzed network structure. Schedule information according to the calculated transmission schedule includes a wakeup time of the sensor node, a time interval that is consumed for packet transmission, and a standby time for preventing a packet collision based on the time interval.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
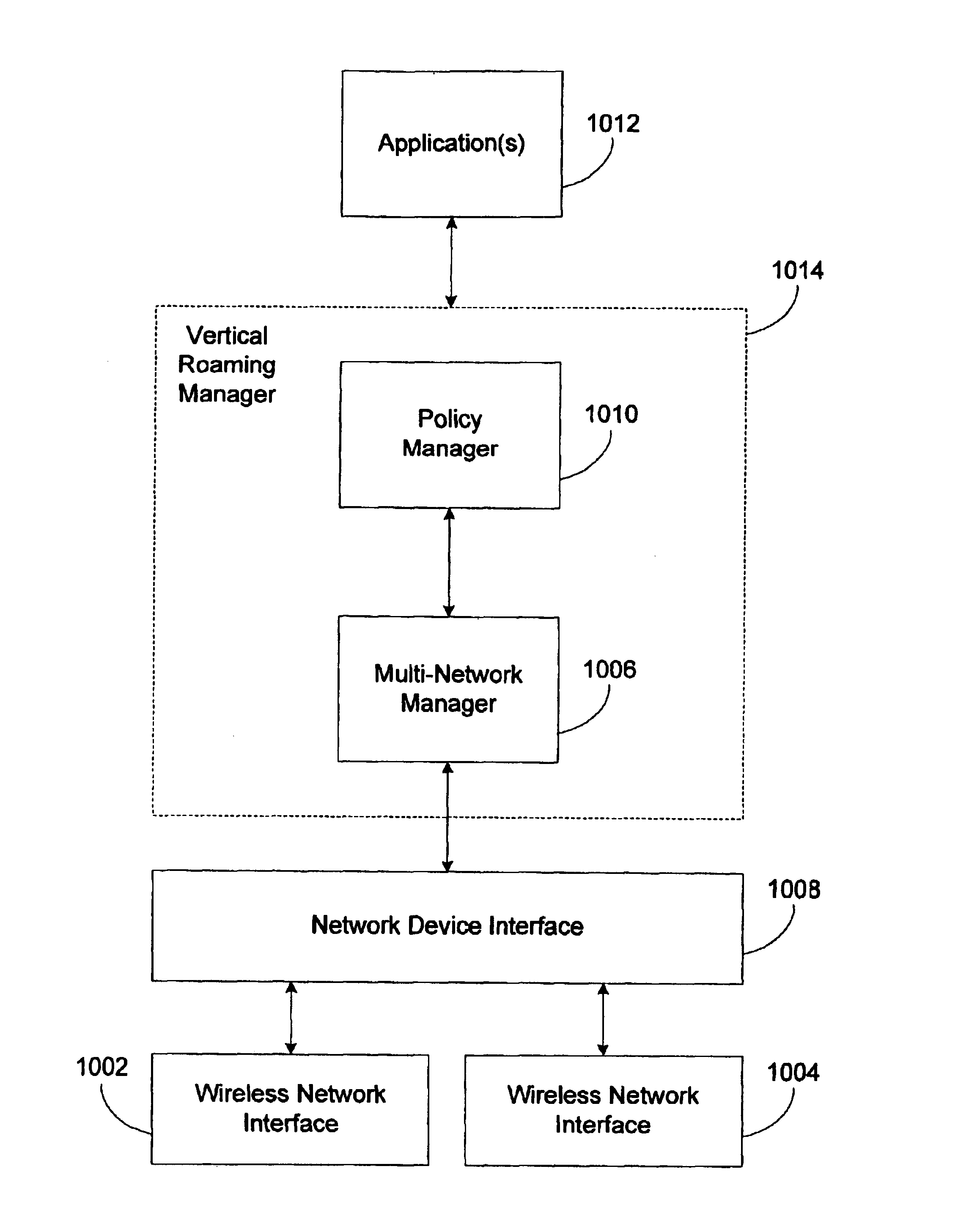
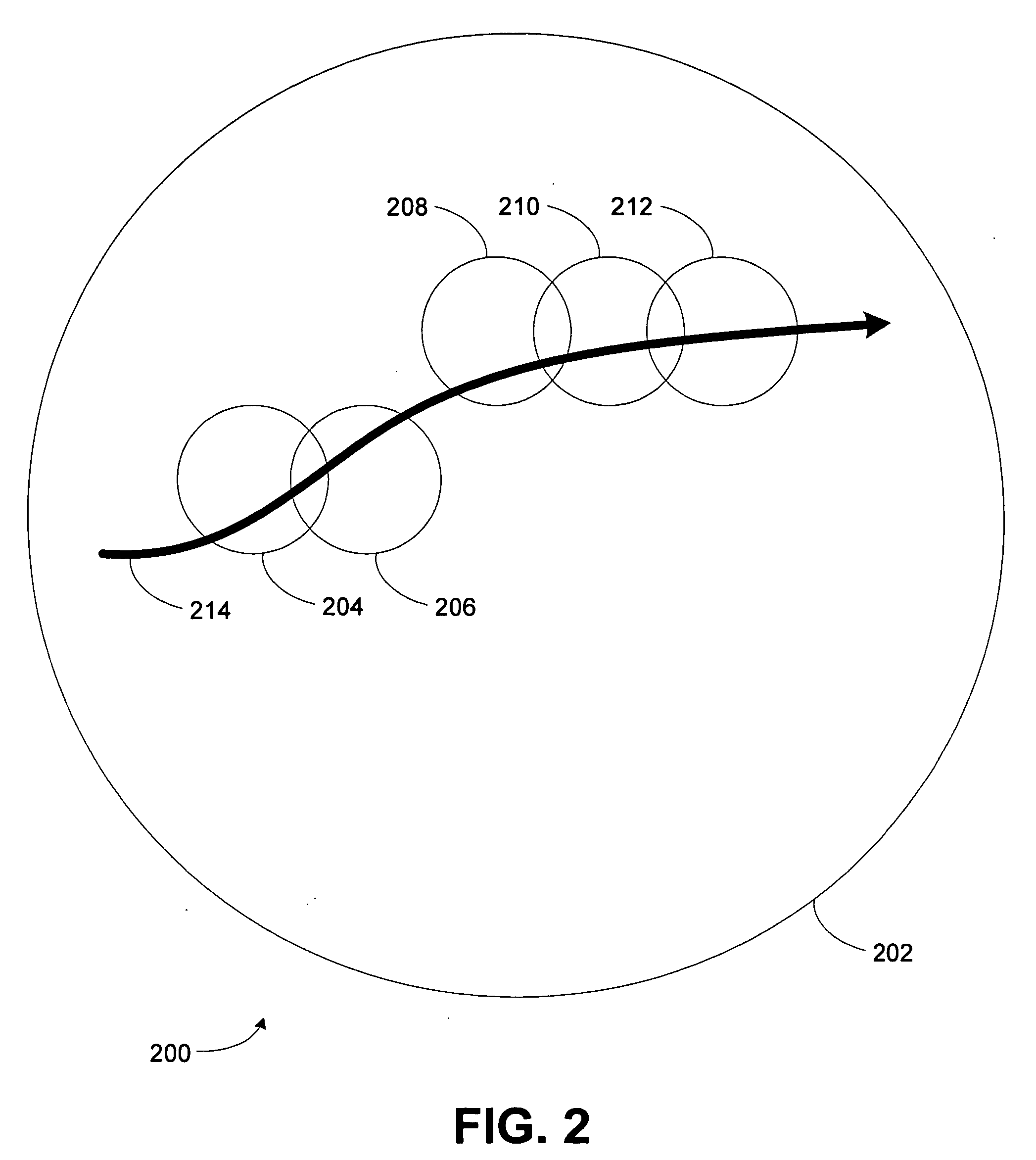
Vertical roaming in wireless networks through improved wireless network cell boundary detection
InactiveUS6982949B2Improved vertical handoffReliable detectionTime-division multiplexRadio transmission for post communicationQuality of servicePacket collision
A system and method for improved vertical handoff between different types of wireless network. Network allocation vector occupation and packet collision probability are used as quality of service measures, enabling vertical handoffs to be delayed until actually beneficial to quality of service. Improved wireless network cell boundary detection in vertical handoff scenarios is achieved with a Fourier-based technique in conjunction with an adaptively determined minimum operating signal strength threshold. Improved wireless network cell boundary detection enables vertical handoffs from high quality of service networks to be delayed as long as possible. Together, practical wireless network quality of service measures and improved detection of wireless network cell boundaries in vertical handoff scenarios reduce the rate of unnecessary vertical handoff resulting in higher overall quality of service experienced by a mobile computing device roaming between wireless network types.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
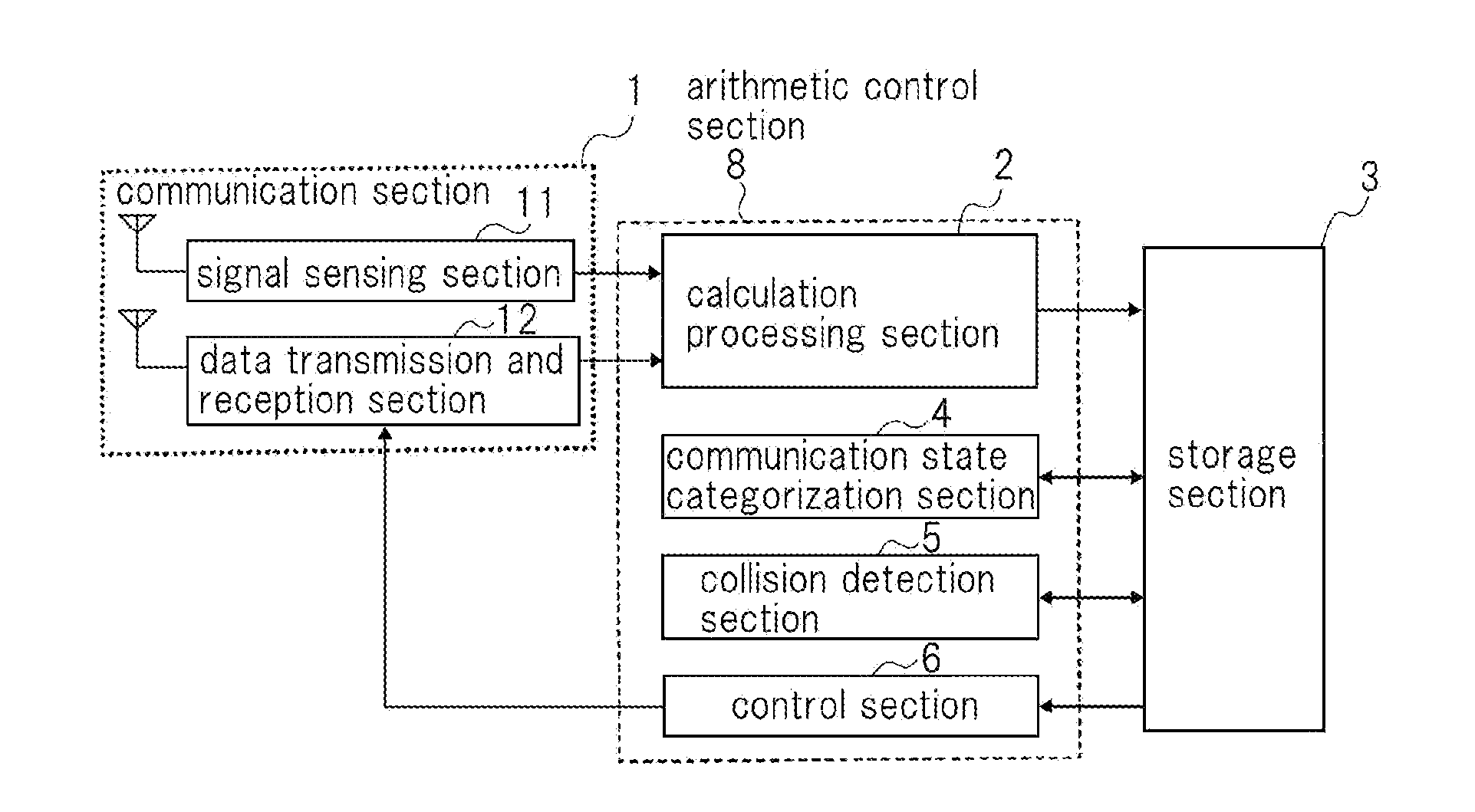
Wireless communication device that is capable of improving data transmission efficiency
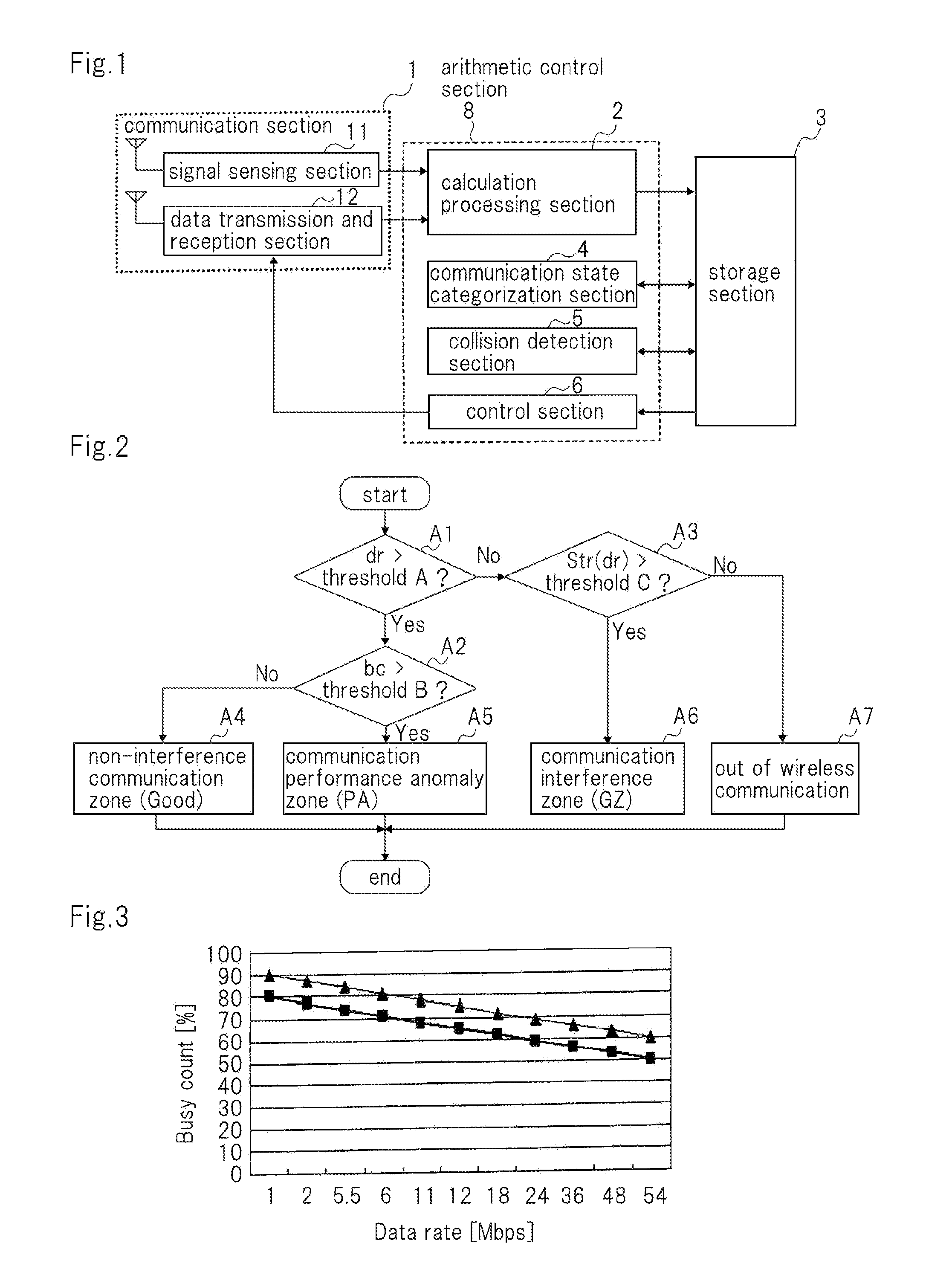
InactiveUS20120320759A1Suppress interferenceData augmentationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket collisionCollision detection
A wireless communication device includes a data transmission and reception section that wirelessly transmits a plurality of test packets; a signal sensing section that senses a power of a spatial radio wave signal on a frequency channel that is the same as the plurality of test packets and outputs sample data of the sensed spatial radio wave signal; a calculation processing section that converts the sample data into time series sample data; a collision detection section that calculates a packet collision rate based on the number of packet collisions and the number of the plurality of test packets if there is a packet collision due to interference of the plurality of test packets with another communication; and a control section that adjusts a parameter that the data transmission and reception section uses based on a calculation result of the collision detection section.
Owner:NEC COMM SYST
Methods and devices for scheduling the transmission of packets in configurable access wireless networks that provide Quality-of-Service guarantees
InactiveUS20060002341A1Save energyAvoid collisionEnergy efficient ICTTime-division multiplexQuality of servicePacket collision
A more energy efficient, medium access control (MAC) layer of a multi-hop wireless network is provided using scheduling techniques which reduce packet collisions, and therefore the need for packet re-transmissions, while ensuring both bandwidth and delay, Quality-of-Service (QoS) guarantees. The techniques are used in conjunction with the formation of a multi-hop, configurable access wireless network (CAN).
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Wireless LAN system
ActiveUS20050243843A1Deterioration of throughput can be preventedAvoid collisionNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationPacket collisionData pack
A high-speed wireless LAN system capable of avoiding a collision of packets and maintaining the original transmission speed is provided. A transmitter is applied to an HT terminal using a second frequency band wider than a first frequency band used by a legacy terminal, in which an HT sequence is started after a legacy beacon as an occupation signal and a legacy CTS are transmitted using every frequency in the second frequency band. Due to this, an NAV is set at the legacy terminal and packets are no longer transmitted from the legacy terminal. As a result, a collision of packets is avoided and it becomes possible to perform communication between HT terminals at the original transmission speed.
Owner:SHARP KK
Packet conflict resolution
Some embodiments provide a method for a first managed forwarding element that implements a logical network. The method receives a packet from a second managed forwarding element. The first packet has an initial set of characteristics defining a first connection between a source machine connected to the second managed forwarding element and a destination machine connected to the first managed forwarding element. The method determines whether a second connection exists with the initial set of characteristics between a different machine connected to a third managed forwarding element and the destination machine. When a second connection exists with the initial set of characteristics, the method modifies at least one characteristic of the packet such that the modified packet does not have the same set of characteristics. The method delivers the modified packet to the destination machine.
Owner:NICIRA
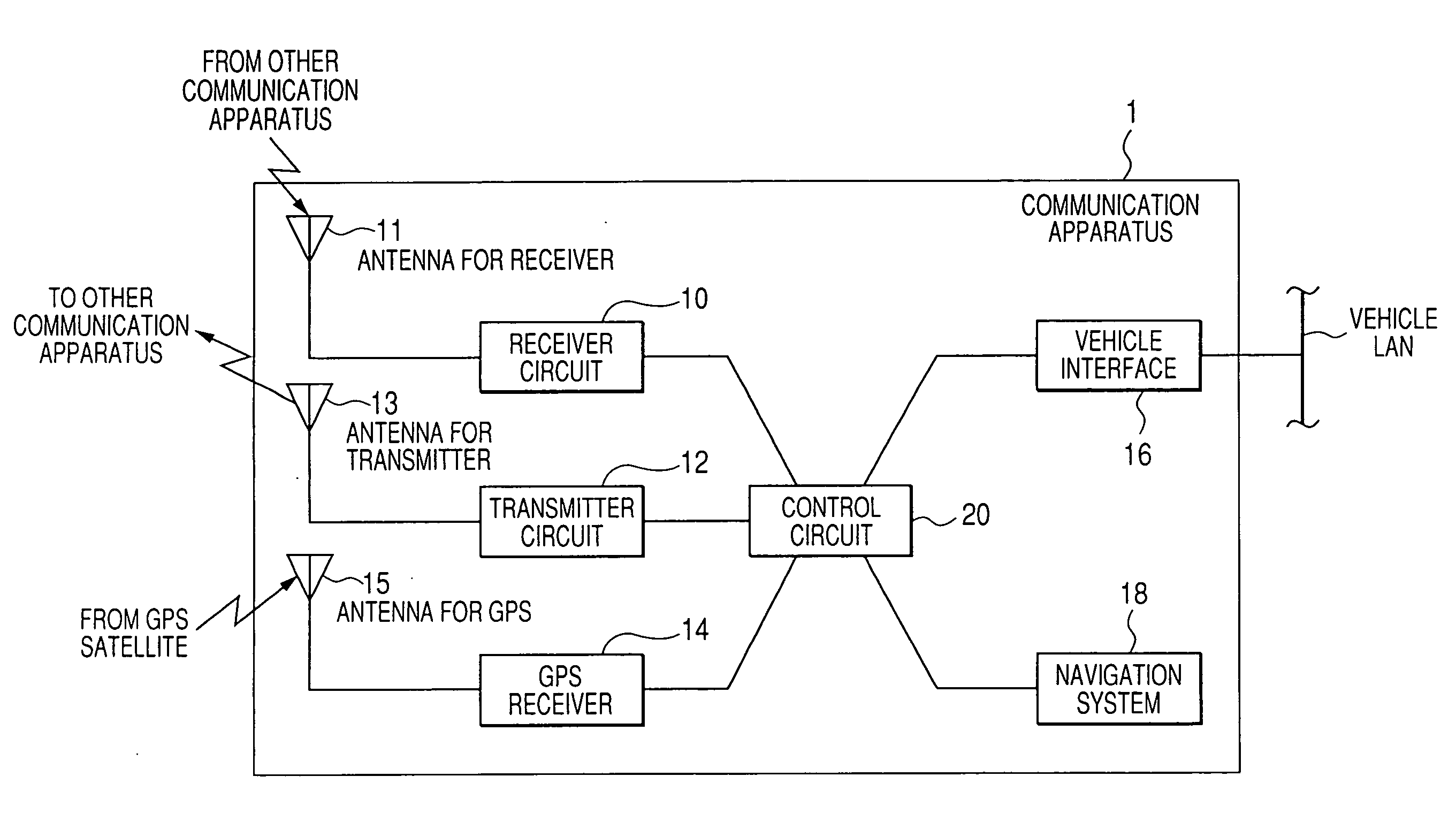
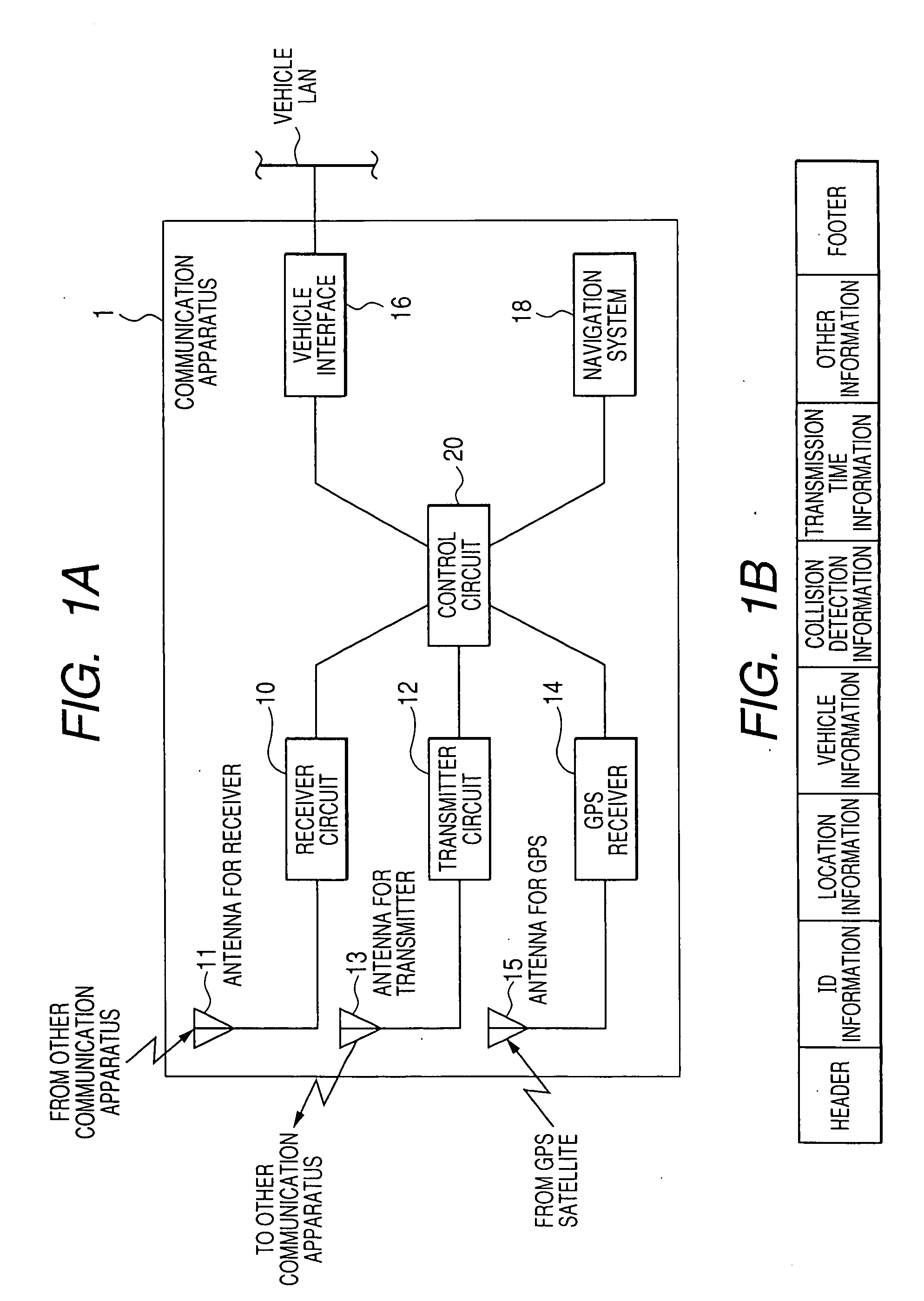
Inter-vehicle communication apparatus and method capable of detecting packet collision
InactiveUS20080037577A1Sure easyEasy to produceArrangements for variable traffic instructionsError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorPacket collisionControl circuit
In inter-vehicle communication, a communication apparatus may not normally receive a packet having a sufficient reception power level. Under such circumstances, a control circuit in the apparatus determines that the received packet has collided with other packet if a condition is met that a time period for a receiver circuit to receive a packet having a reception power level of equal to or more than a set value is longer than a time period required for the receiver circuit to receive a packet having a predetermined packet length.
Owner:DENSO CORP
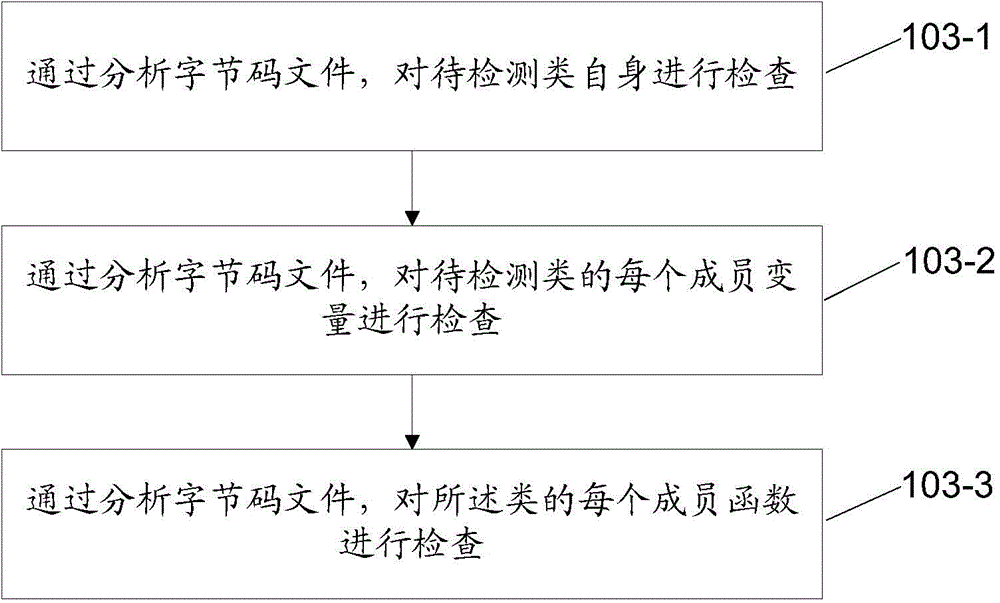
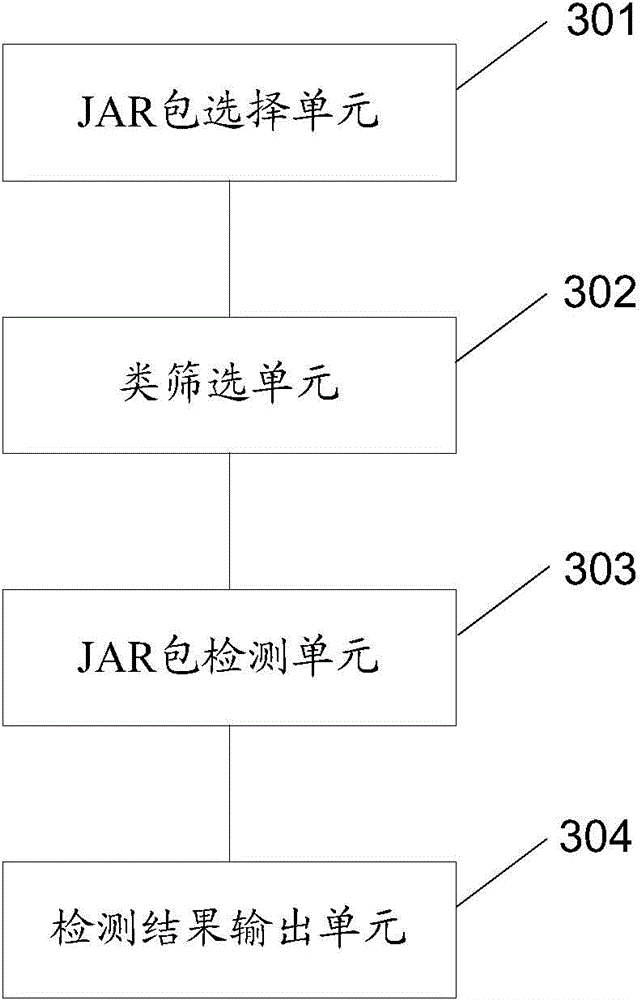
Method and device for detecting JAR packet collision
ActiveCN105630463AAutomatic conflict detectionAvoid failureSoftware testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsPacket collisionCollision detection
The invention discloses a method for detecting JAR packet collision. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a JAR packet which is about to undergo collision detection; in allusion to each class in the JAR packet, analyzing a bytecode file corresponding to the class, checking whether a bytecode file corresponding to a class depending on the class exists in a pre-assigned JAR packet list and checking whether elements accessed by the class exist in the bytecode file related to the depended class; and if any check result is negative, considering that the current JAR packet has collision. The invention furthermore provides a device for detecting JAR packet collision. By adopting the method provided by the invention, the collision of the JAR packet in the aspect of dependency completeness can be automatically detected, so that a foundation is provided for eliminating the collision through previously adopting a JAR packet updating manner and the like, and the fault caused by the deficiency of dependency completeness in the running stage can be effectively avoided.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
Communication method, radio terminal and base station
ActiveUS20070025288A1Avoid collisionNetwork topologiesConnection managementPacket collisionTelecommunications
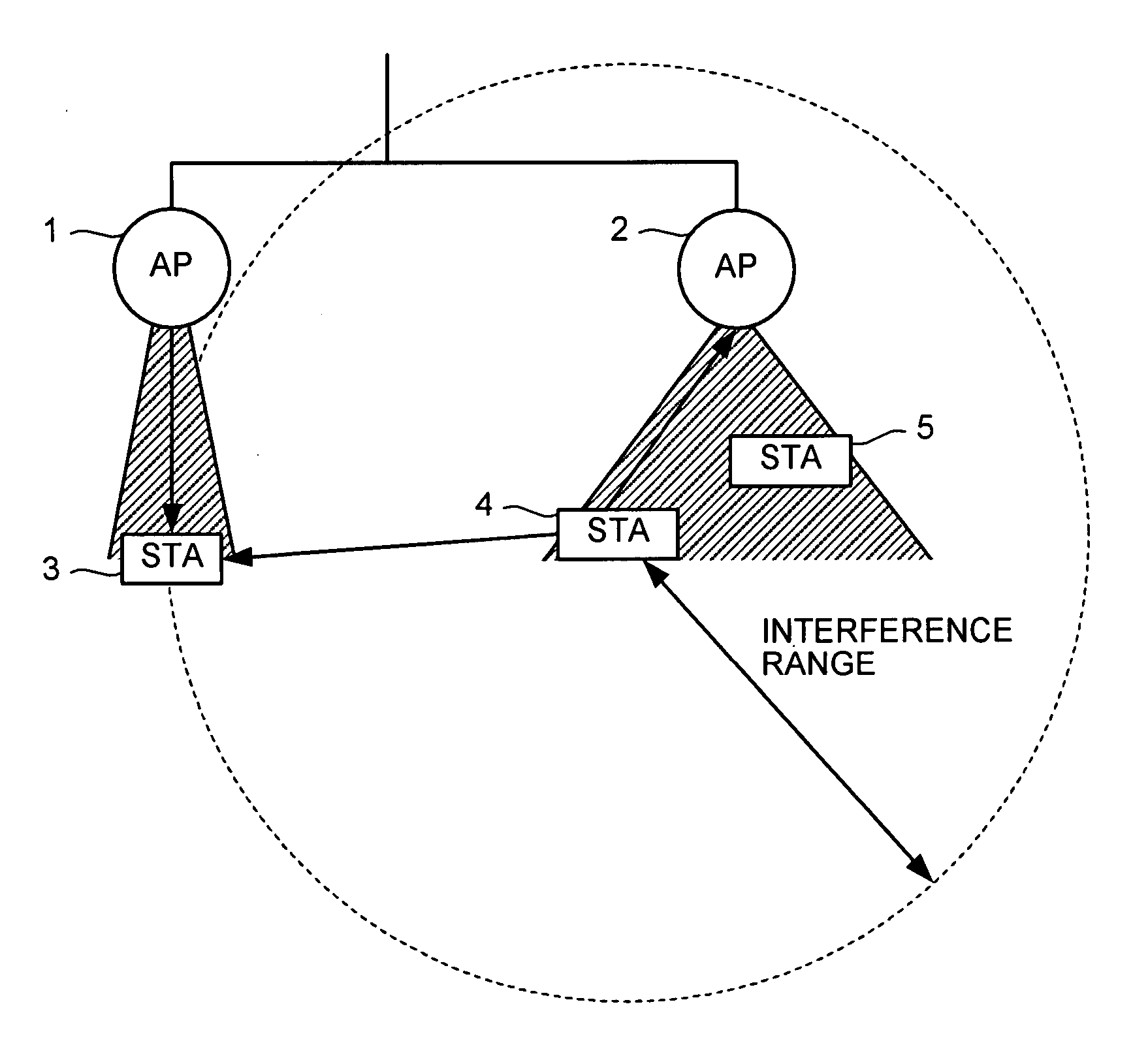
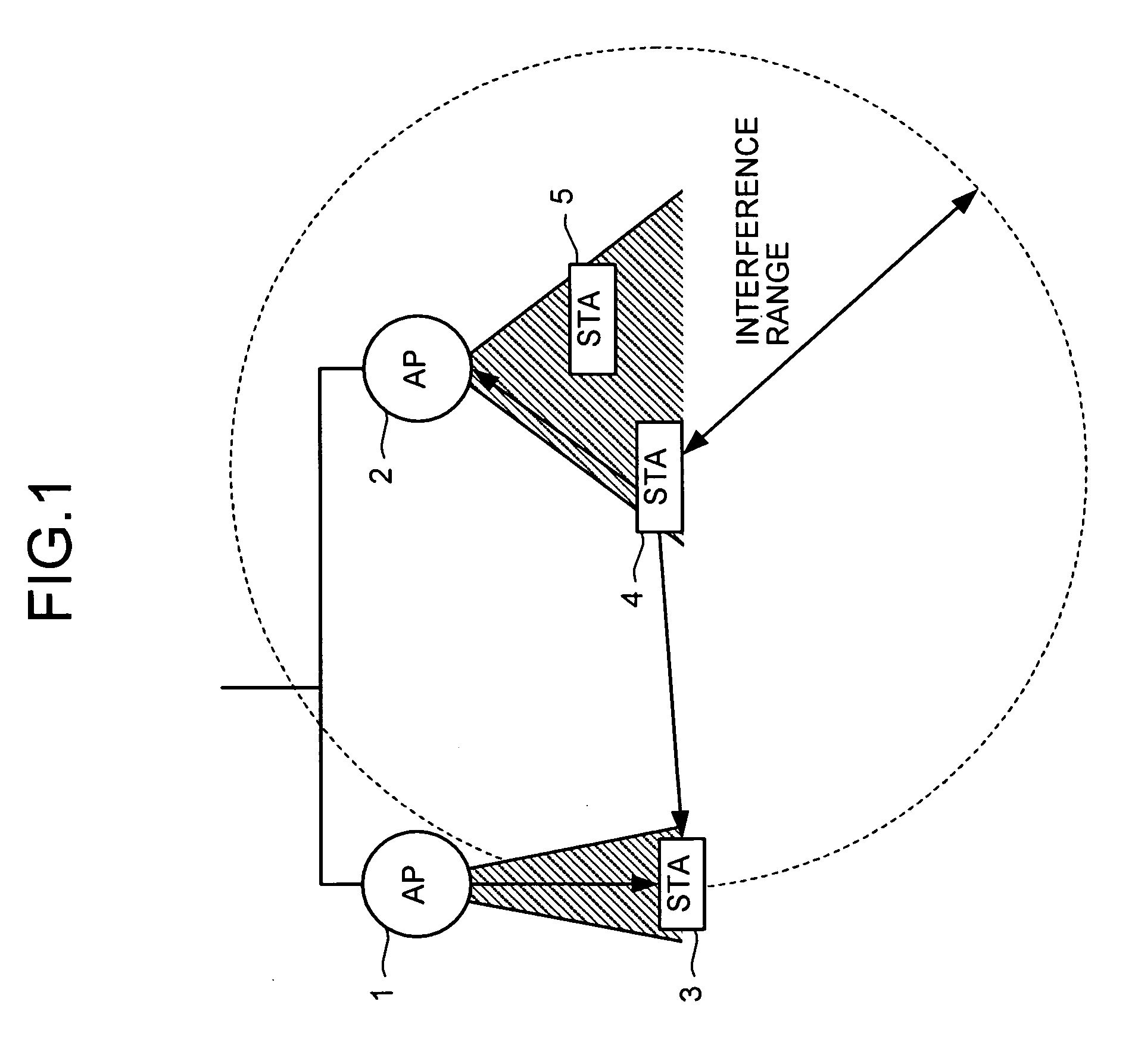
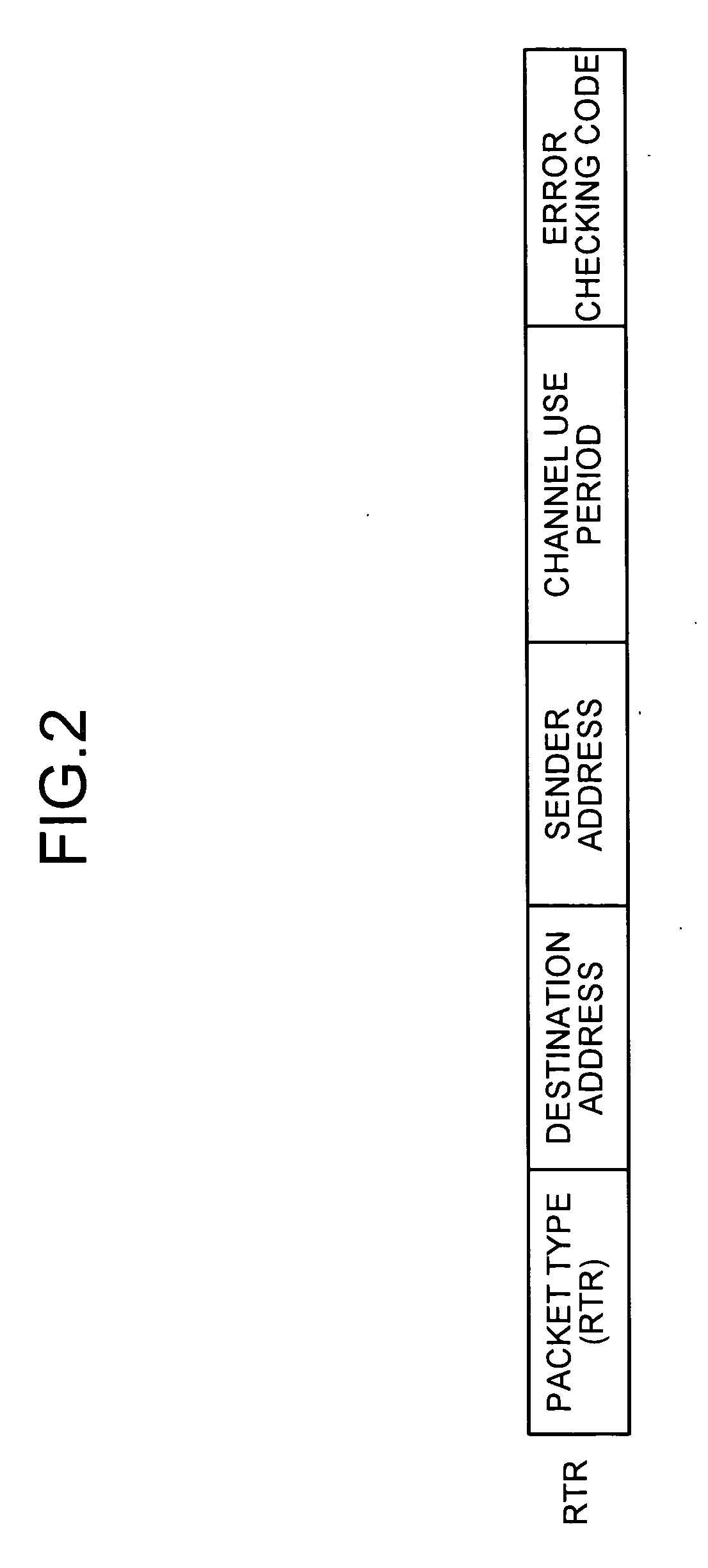
A communication method for a CSMA network including a radio terminal and a base station supporting RTS / CTS, includes: the base station transmitting and RTS frame to the radio terminal during a transmission-suspend-period in which the radio terminal suspends transmission to prevent a collision of packets; the radio terminal transmitting an RTR frame to the base station after the transmission-suspend-period has elapsed; and the base station transmitting a date frame to the radio terminal in response to the RTR frame.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
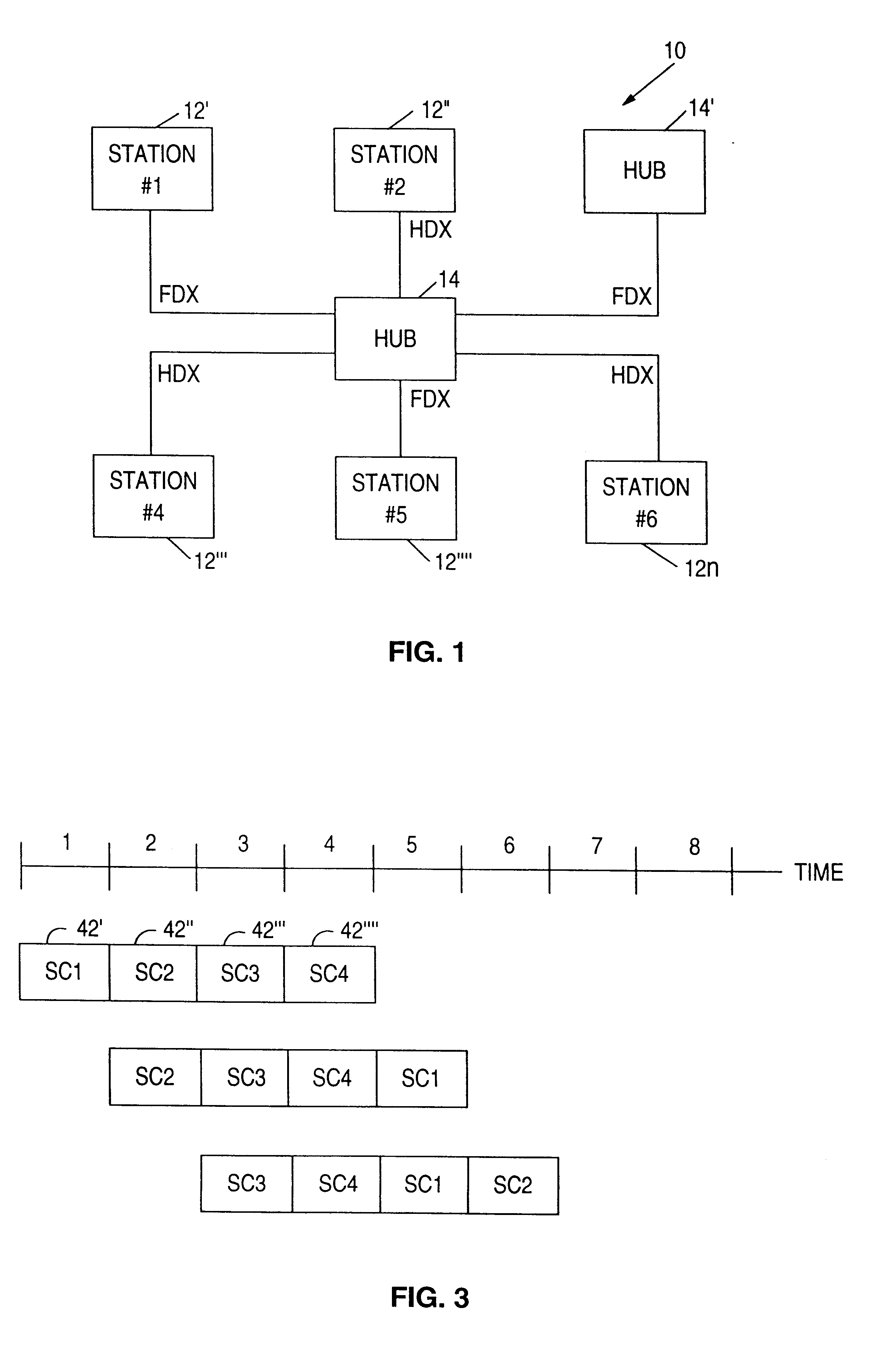
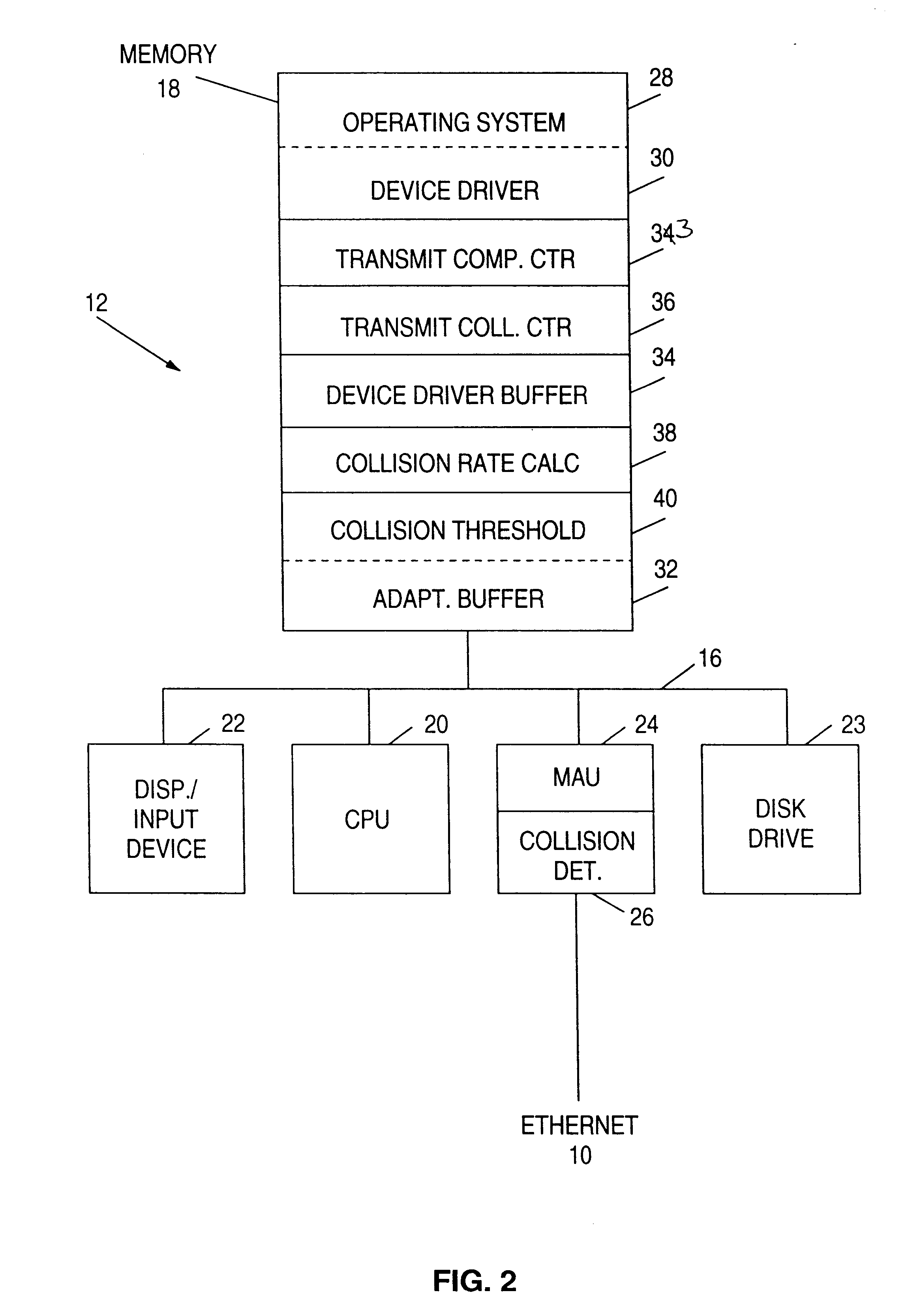
Dynamic transmit tuning for ethernet device drivers
InactiveUS6222850B1Improve latencyImprove throughputData switching networksData processing systemPacket collision
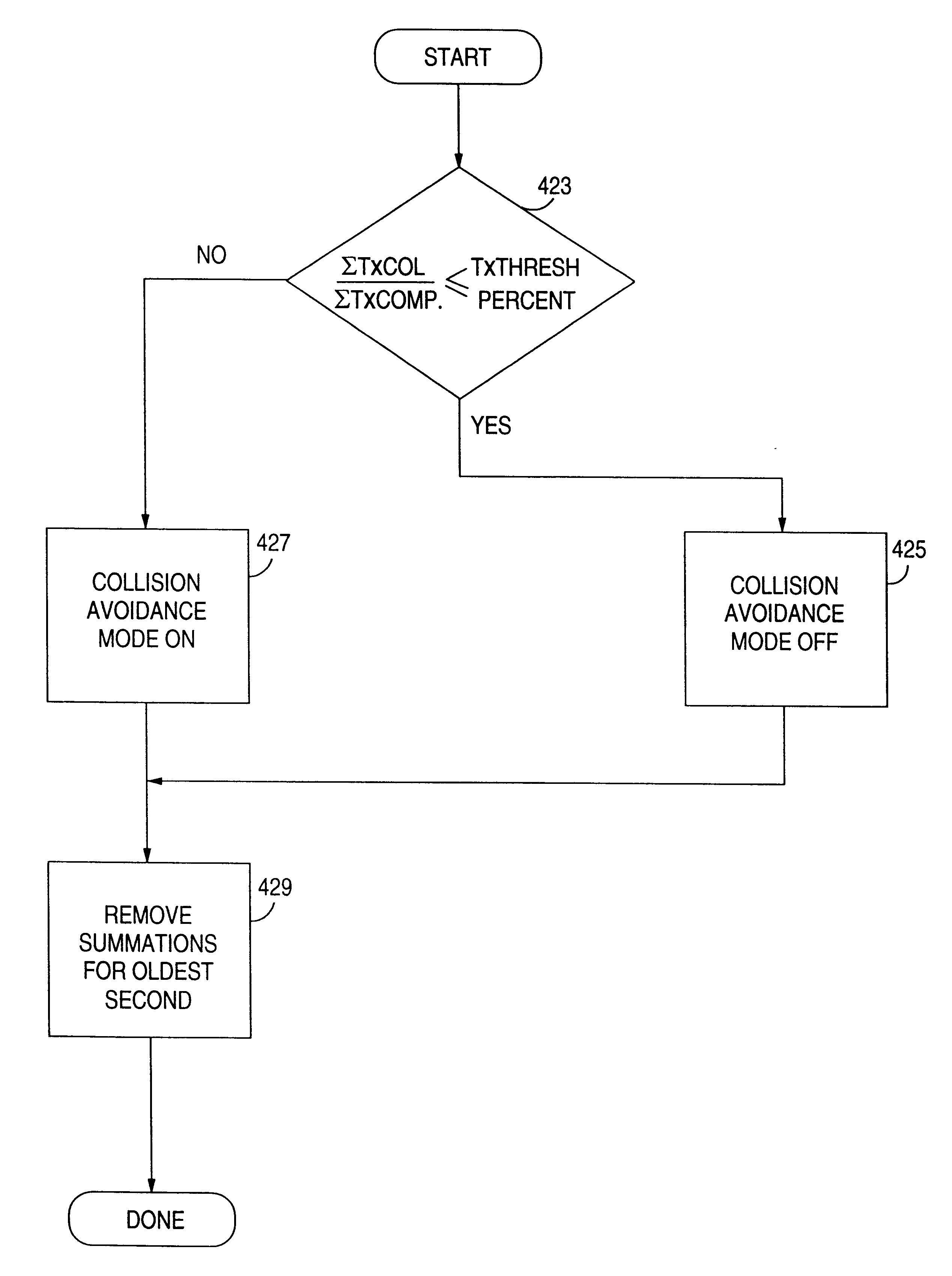
A LAN of the ethernet type employs CSMA / CD protocol for channel access by a plurality of network nodes. Each node includes a data processing system having a device driver and an adapter and transmits data packets to the LAN in accordance with the IEEE 802.3 standard. The adapter coupled is at one side to the network in either a half or full-duplex mode. The other side of the adapter is bound to the device driver which is dynamically tuned for reduced latency and increased network throughput, regardless of the transmitting mode of the node and the capture effect of the ethernet. Each device driver operates in a transmit chaining mode when the network is in a lightly loaded half-duplex, or full-duplex mode. The driver includes means for monitoring data packet collisions on a channel of the network. A "collision rate" or the percentage of data packets which were transmitted on the channel with collisions in a pre-selected time interval is calculated by the device driver. A "collision threshold" is assigned or calculated by the device driver. Data packets transmitted by each device driver are chained to increase network throughput when the "collision rate" is below the "collision threshold". Transmit chaining of data packets is disabled for the device driver when the "collision threshold" is exceeded on the channel.
Owner:IBM CORP
Vertical roaming in wireless networks through improved wireless network cell boundary detection
InactiveUS20050213542A1Improved vertical handoffReliable detectionTime-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsQuality of servicePacket collision
A system and method for improved vertical handoff between different types of wireless network. Network allocation vector occupation and packet collision probability are used as quality of service measures, enabling vertical handoffs to be delayed until actually beneficial to quality of service. Improved wireless network cell boundary detection in vertical handoff scenarios is achieved with a Fourier-based technique in conjunction with an adaptively determined minimum operating signal strength threshold. Improved wireless network cell boundary detection enables vertical handoffs from high quality of service networks to be delayed as long as possible. Together, practical wireless network quality of service measures and improved detection of wireless network cell boundaries in vertical handoff scenarios reduce the rate of unnecessary vertical handoff resulting in higher overall quality of service experienced by a mobile computing device roaming between wireless network types.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
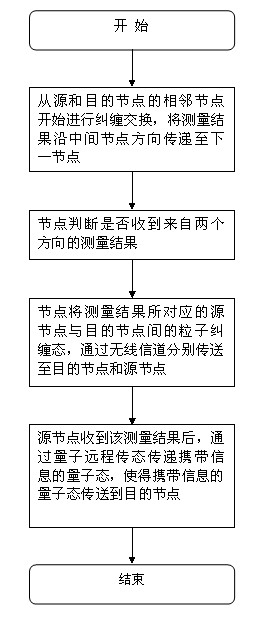
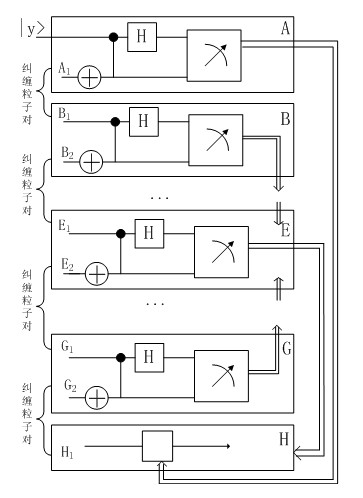
Method for building quantum channels and transmitting quantum information in wireless self-organizing quantum communication network
ActiveCN102694605AReduced settling timeReduce the probability of conflictPhotonic quantum communicationPacket collisionWireless transmission
The invention discloses a method for building quantum channels and transmitting quantum information in a wireless self-organizing quantum communication network, comprising the following steps of: (1) performing entanglement exchange from the adjacent nodes of a source node and a destination node, and transmitting the measurement results to the next node along the direction of the middle node; (2) judging whether receiving the measurement results coming from two directions by the node; (3) respectively transmitting the particle entanglement states of the source node and the destination node corresponding to the measurement to the destination node and the source node by the node through wireless channels; and (4) after receiving the measurement results, transmitting the quantum states of the carried information through quantum remote teleportation by the source node so that the quantum states of the carried information can be transmitted to the destination node. The method provided by the invention can obviously save the cost of wireless transmission for building the quantum channels and transmitting the quantum information, can reduce the data packets to be transmitted by the wireless channels, and can reduce the collision probability of the data packets in the wireless channels.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Delivery method of security information in vehicle wireless ad hoc network based on information correlation
InactiveCN102291687AReduce deliveryReduce collisionNetwork topologiesBroadcast service distributionPacket collisionRelevant information
The present invention relates to a method for delivering security information of a wireless ad hoc network for vehicles based on information correlation, which includes the following steps: Step 1: Source node generates and sends WSM message process: source node s discovers an abnormal event, and sends the message according to the correlation of information Determine the influence time, influence distance and influence lane set of the safety information; the source node s initializes the remaining influence time of the message, and selects the backward direction as the direction to be sent of the message. Step 2: The relay node relays and forwards the WSM message. The beneficial effects of the present invention are: taking into account the three correlation parameters of the safety information, the influence time, the influence distance and the influence lane, in the delivery process of the safety information, and adopting a designated relay in the relay process, insisting on relaying The idea is to reduce redundant message sending and message collision.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Vertical roaming in wireless networks through improved quality of service measures
InactiveUS20050068982A1Improved vertical handoffEnabling measurementTime-division multiplexWireless communicationQuality of servicePacket collision
A system and method for improved vertical handoff between different types of wireless network. Network allocation vector occupation and packet collision probability are used as quality of service measures, enabling vertical handoffs to be delayed until actually beneficial to quality of service. Improved wireless network cell boundary detection in vertical handoff scenarios is achieved with a Fourier-based technique in conjunction with an adaptively determined minimum operating signal strength threshold. Improved wireless network cell boundary detection enables vertical handoffs from high quality of service networks to be delayed as long as possible. Together, practical wireless network quality of service measures and improved detection of wireless network cell boundaries in vertical handoff scenarios reduce the rate of unnecessary vertical handoff resulting in higher overall quality of service experienced by a mobile computing device roaming between wireless network types.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Vertical roaming in wireless networks through improved quality of service measures
InactiveUS20050083874A1Improved vertical handoffEnabling measurementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesQuality of servicePacket collision
A system and method for improved vertical handoff between different types of wireless network. Network allocation vector occupation and packet collision probability are used as quality of service measures, enabling vertical handoffs to be delayed until actually beneficial to quality of service. Improved wireless network cell boundary detection in vertical handoff scenarios is achieved with a Fourier-based technique in conjunction with an adaptively determined minimum operating signal strength threshold. Improved wireless network cell boundary detection enables vertical handoffs from high quality of service networks to be delayed as long as possible. Together, practical wireless network quality of service measures and improved detection of wireless network cell boundaries in vertical handoff scenarios reduce the rate of unnecessary vertical handoff resulting in higher overall quality of service experienced by a mobile computing device roaming between wireless network types.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Multi-hop warn broadcasting method for urban VANETs
ActiveCN104394007AReduce overheadAvoid collisionSpecial service provision for substationBroadcast specific applicationsPacket collisionBroadcast radiation
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Multi-channel multi-address access method
InactiveCN101119590AAppointment flexibleIncreased utilization of bandwidthAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPacket collisionAccess method
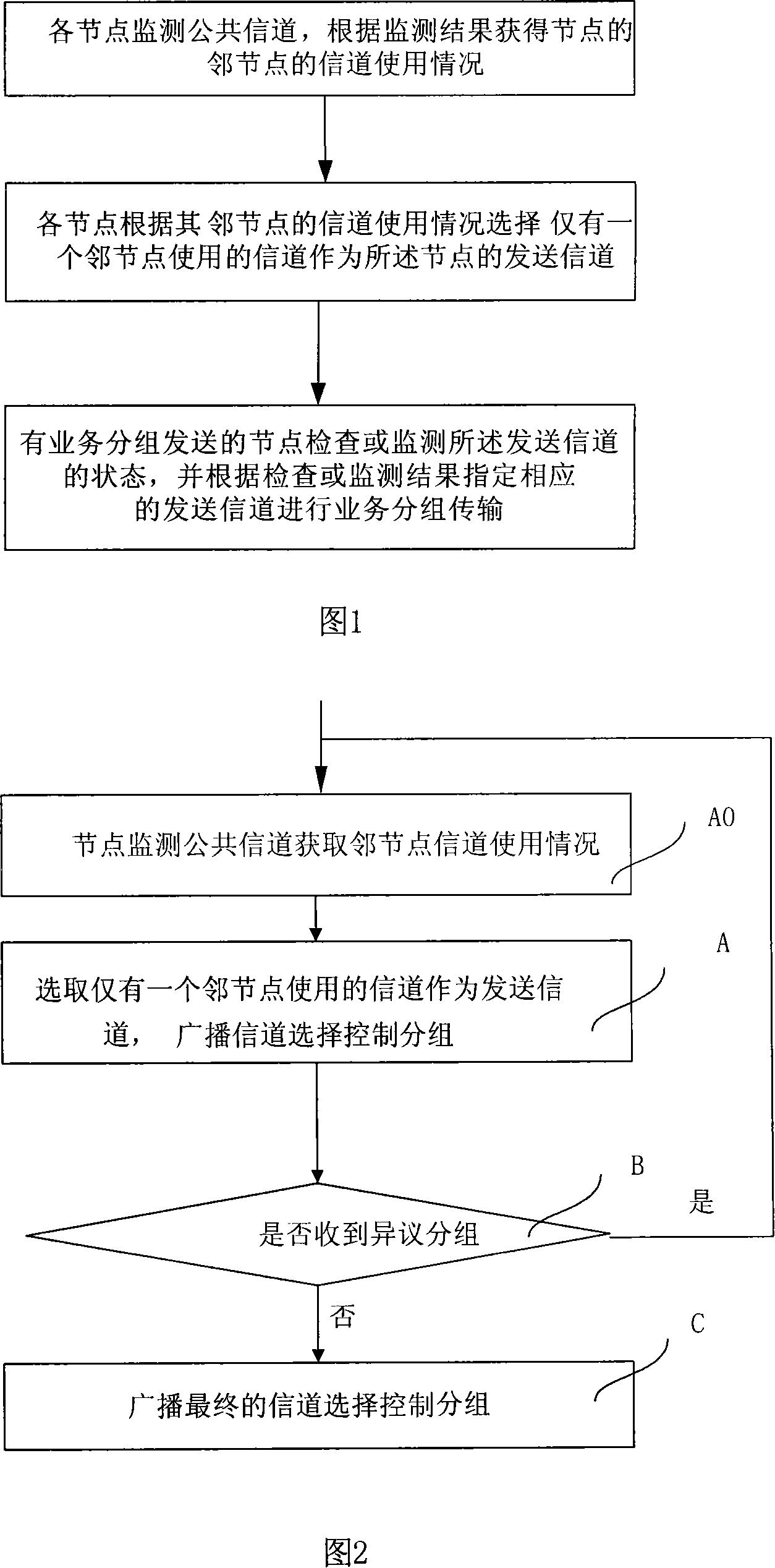
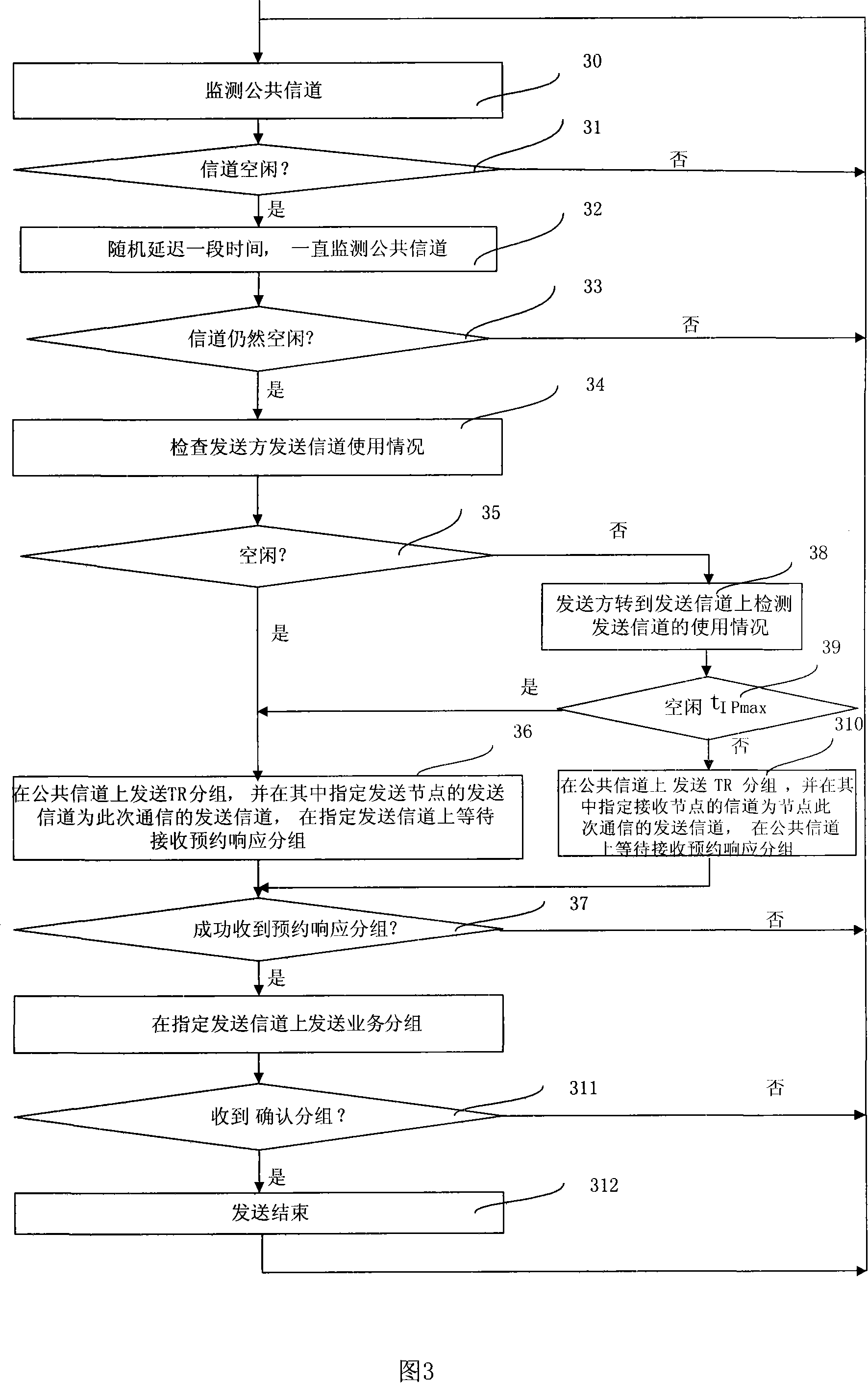
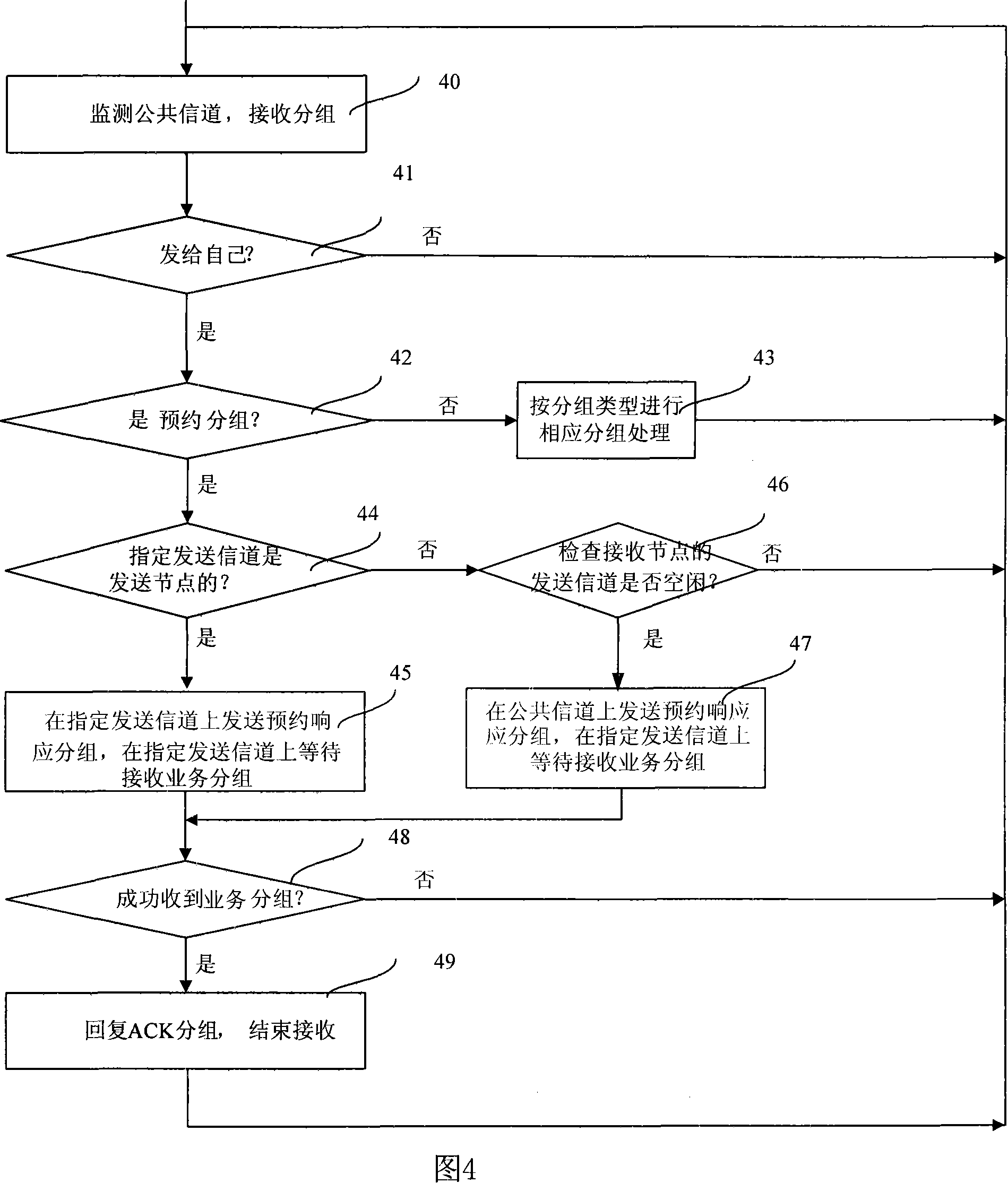
The present invention discloses a multi-channel and multi-address access method through a plurality of embodiments, including: a node monitoring public channel, obtaining the channel occupation mode of the neighboring node according to the monitoring result; according to the channel occupation node of the neighboring node, selecting a channel which is occupied by one neighboring node as the send channel of the aforesaid node; checking or monitoring the state of the aforesaid send channel, and appointing a corresponding send channel to conduct the service packet transmission according to the check or monitor result. The multi-channel and multi-address access method provided by the embodiments in the present invention can effectively solve the problems that the prior multi-address access method can not completely solve the channel waste caused by exposing the terminal and the packet collision caused by hiding the terminal and intruding the terminal, effectively improving the channel utilization rate in the network.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Radio transmission device and retransmission control method
InactiveUS20110119548A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce the probability of collisionError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsPacket collisionWireless transmission
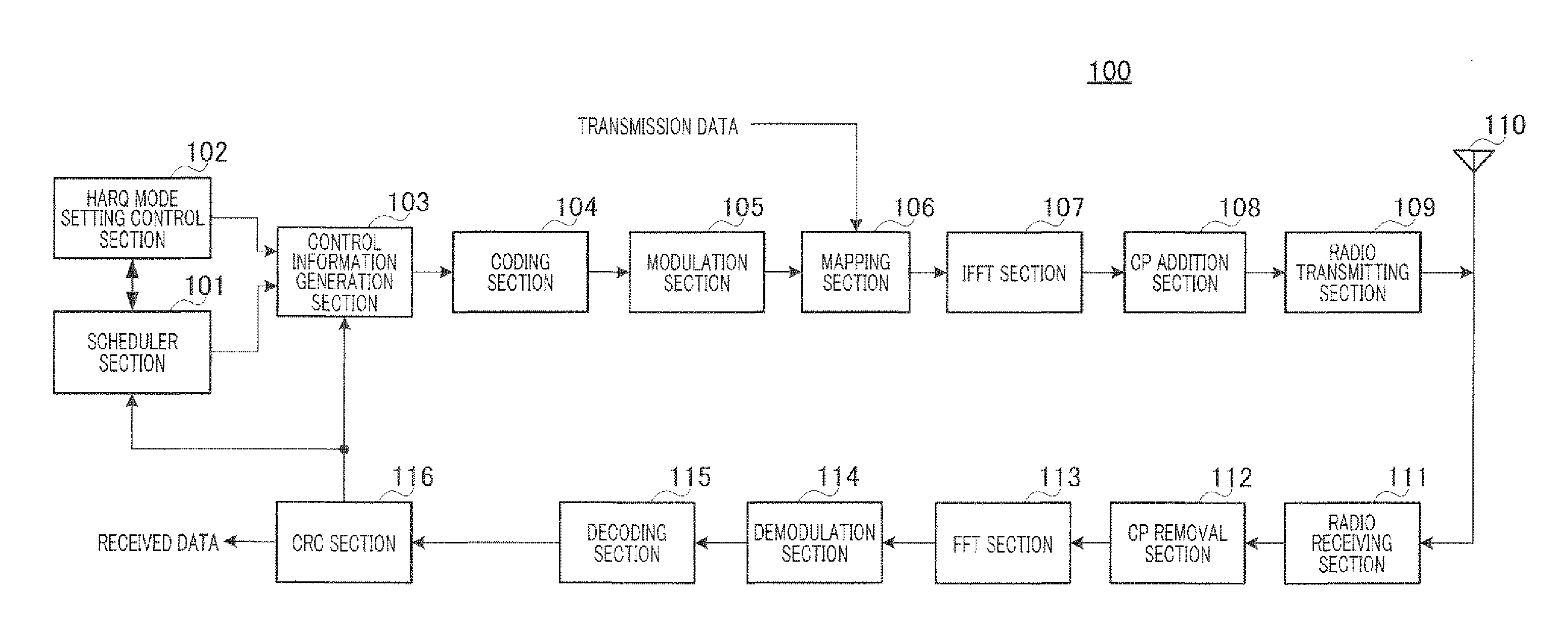
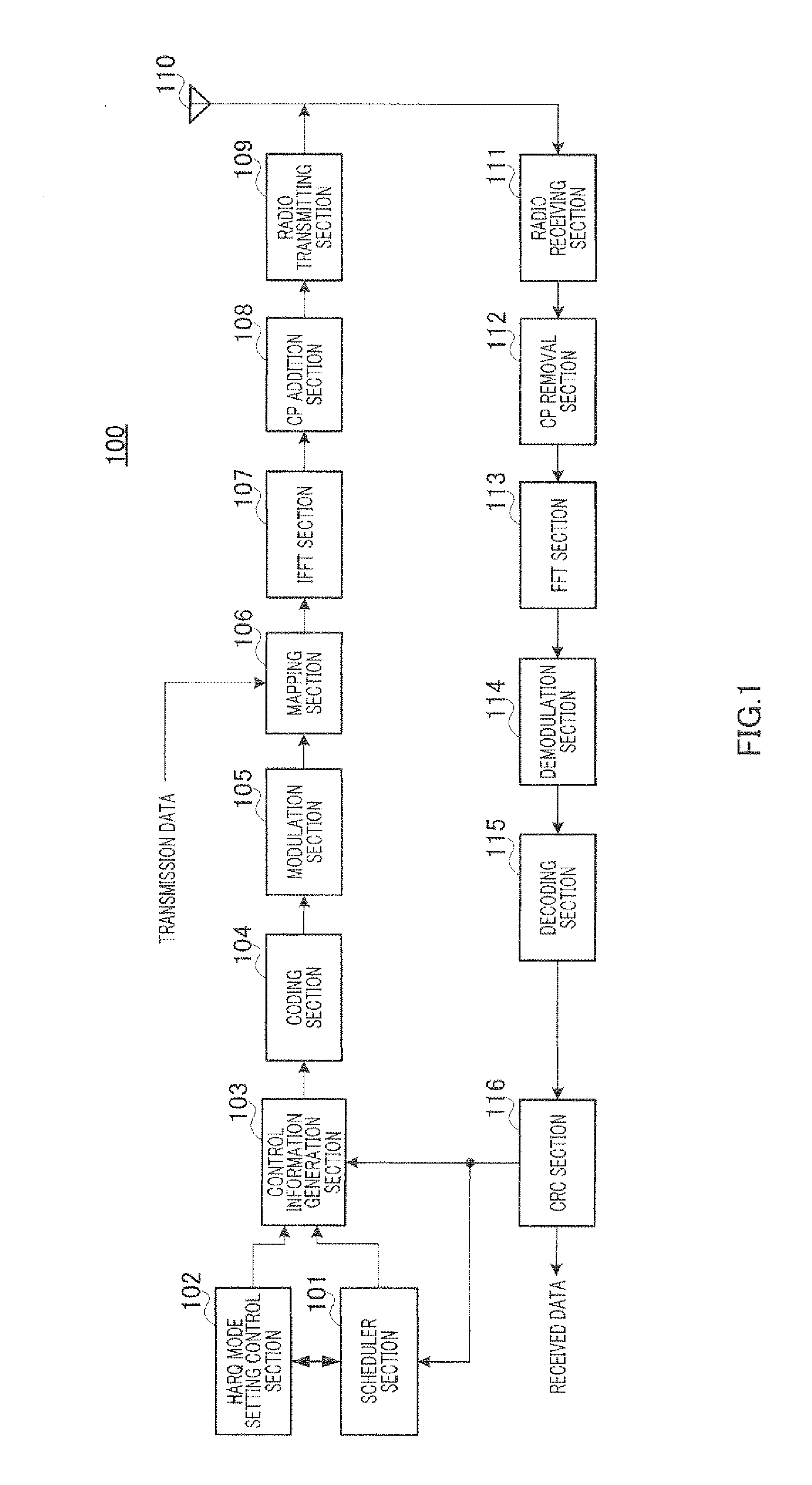
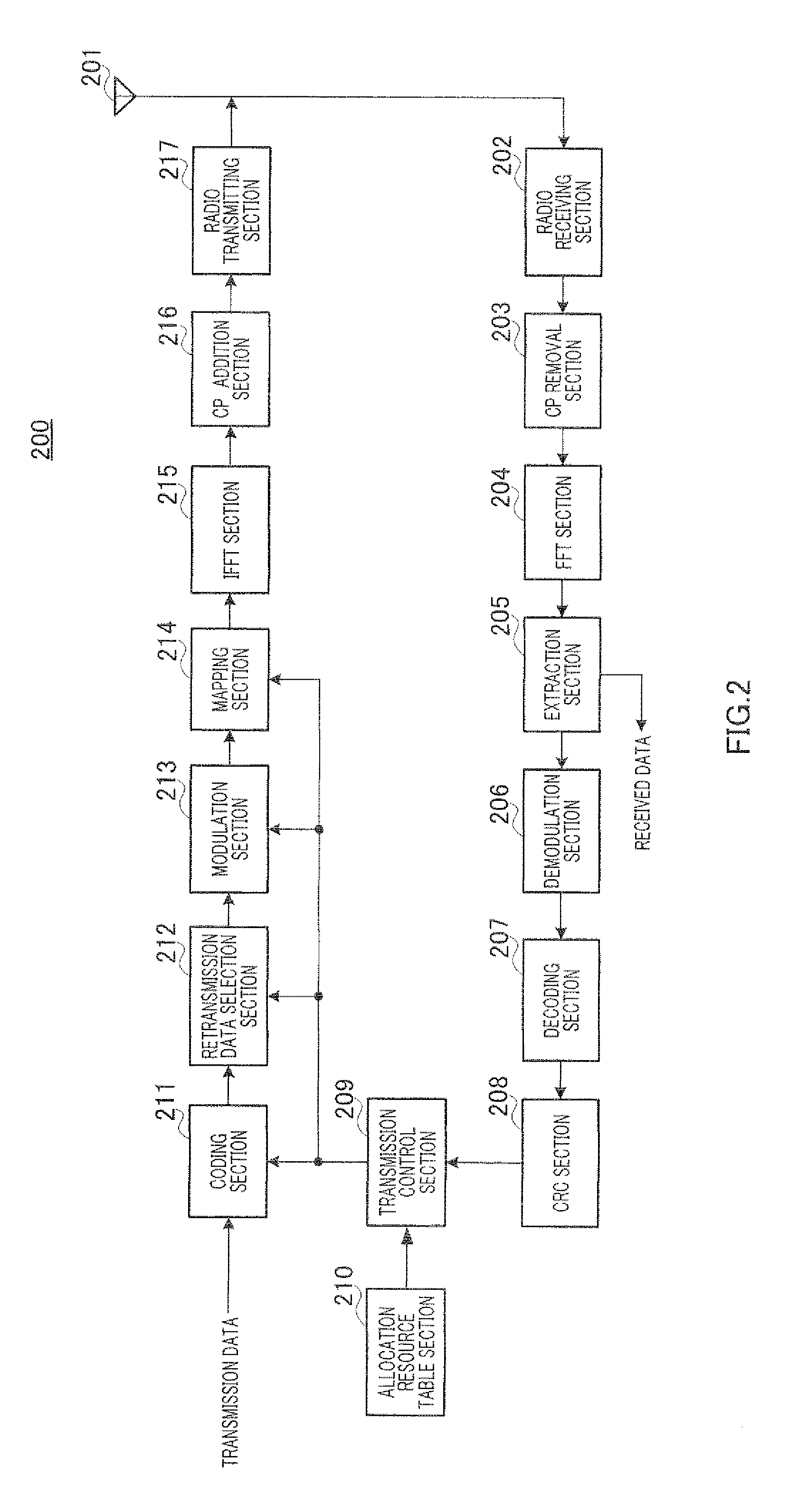
Provided is a radio transmission device which can simultaneously reduce: a radio resource consumption amount required for signaling to report band allocation information and a HARQ operation mode, and a transmission packet collision ratio accompanying a reception error of the band allocation information. The radio transmission device includes a transmission control unit (209) which inputs an encoding ratio, an initial transmission data range, a modulation method, a physical resource-to-be-transmitted position information to an encoding unit (211), a retransmission data selection unit (212), a modulation unit (213), and a mapping unit (214), respectively according the allocated radio resource and transmission parameter reported in the allocation information, if any allocation information is present. On the other hand, if no allocation information is present, the transmission control unit (209) judges whether to perform retransmission using a predetermined transmission parameter or terminate the retransmission according to the HARQ mode information and predetermined allocation radio resource information obtained from an allocation resource table unit (210).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Underwater sensor network routing method based on multiple underwater autonomous vehicles
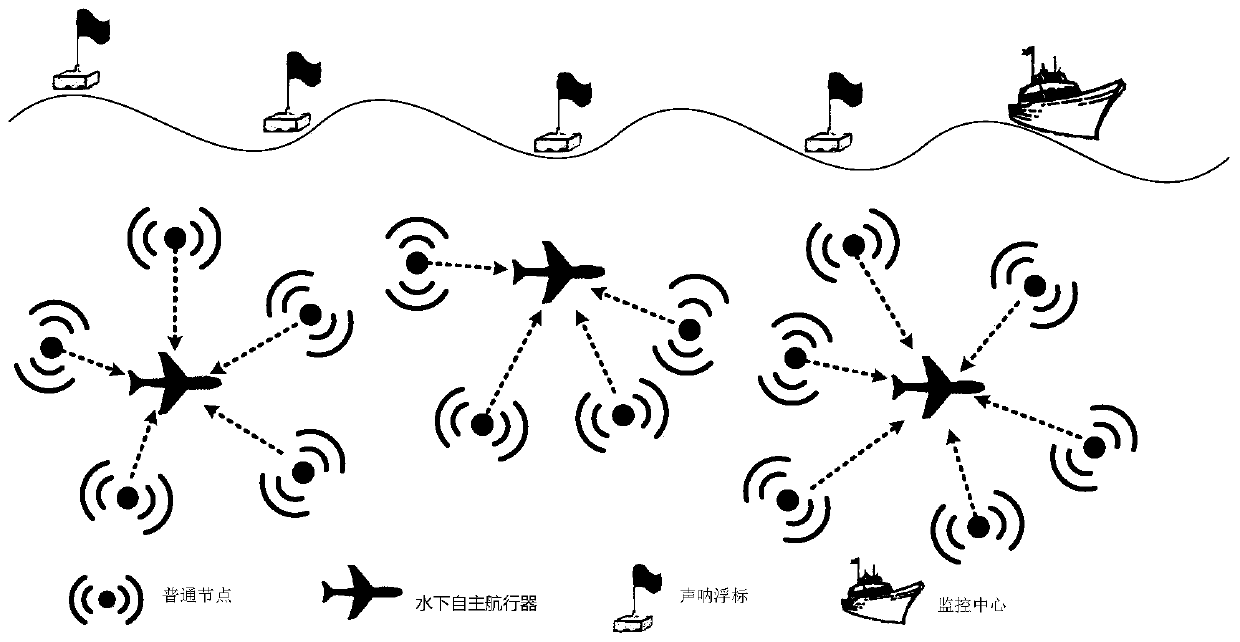
ActiveCN109769222AReduce latencyImprove transmission performanceParticular environment based servicesData switching networksPacket collisionUnderwater sensor networks
The invention discloses an underwater sensor network routing method based on multiple underwater autonomous vehicles. The method comprises the steps of network initialization, data transmission, network restoration and the like. In the network initialization stage, a dynamic network hierarchical structure is constructed; the underwater common sensor nodes in the underwater sensor network are layered, so that a progressive gradient is formed, and a data packet can be transmitted to a corresponding underwater autonomous vehicle according to the hierarchical relationship of the underwater commonsensor nodes in a subsequent data transmission stage. In the data transmission stage, the underwater common sensor node sorts the transmission priorities of the candidate nodes according to the composite forwarding factors of the candidate nodes, and transmission coordination of the candidate node set is carried out based on the transmission priorities of the candidate nodes, so that data packet conflicts are avoided, and the network delay is reduced; in the network restoration stage, the network restoration model is utilized to carry out periodic restoration when the initial dynamic network hierarchical structure changes, so that the transmission performance of the underwater sensor network is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN CHENGJIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com