Patents
Literature
407 results about "Grid bias" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Grid bias is a DC voltage applied to electron tubes with three electrodes or more, such as triodes. The control grid of these devices is used to control the electron flow from the heated cathode to the positively charged anode. Bias point in small-signal applications is set to minimize distortion and achieve sufficiently low power draw. In high-power applications, biasing is typically set for maximum available output power or voltage, with a secondary target of either low distortion or high efficiency. In a typical voltage amplifier, including power stages of most audio power amplifiers, DC bias voltage is negative relative to cathode potential. Instant grid voltage should never rise above cathode potential to prevent grid-to-cathode currents that overload preceding amplifier stages and may cause severe even-order distortion. High transconductance tubes develop significant grid currents even with small negative bias; in these cases, maximum instant voltage ceiling is lowered to -1.0..-0.5 Volt. High efficiency Class B+ push-pull amplifiers operate at higher bias points.
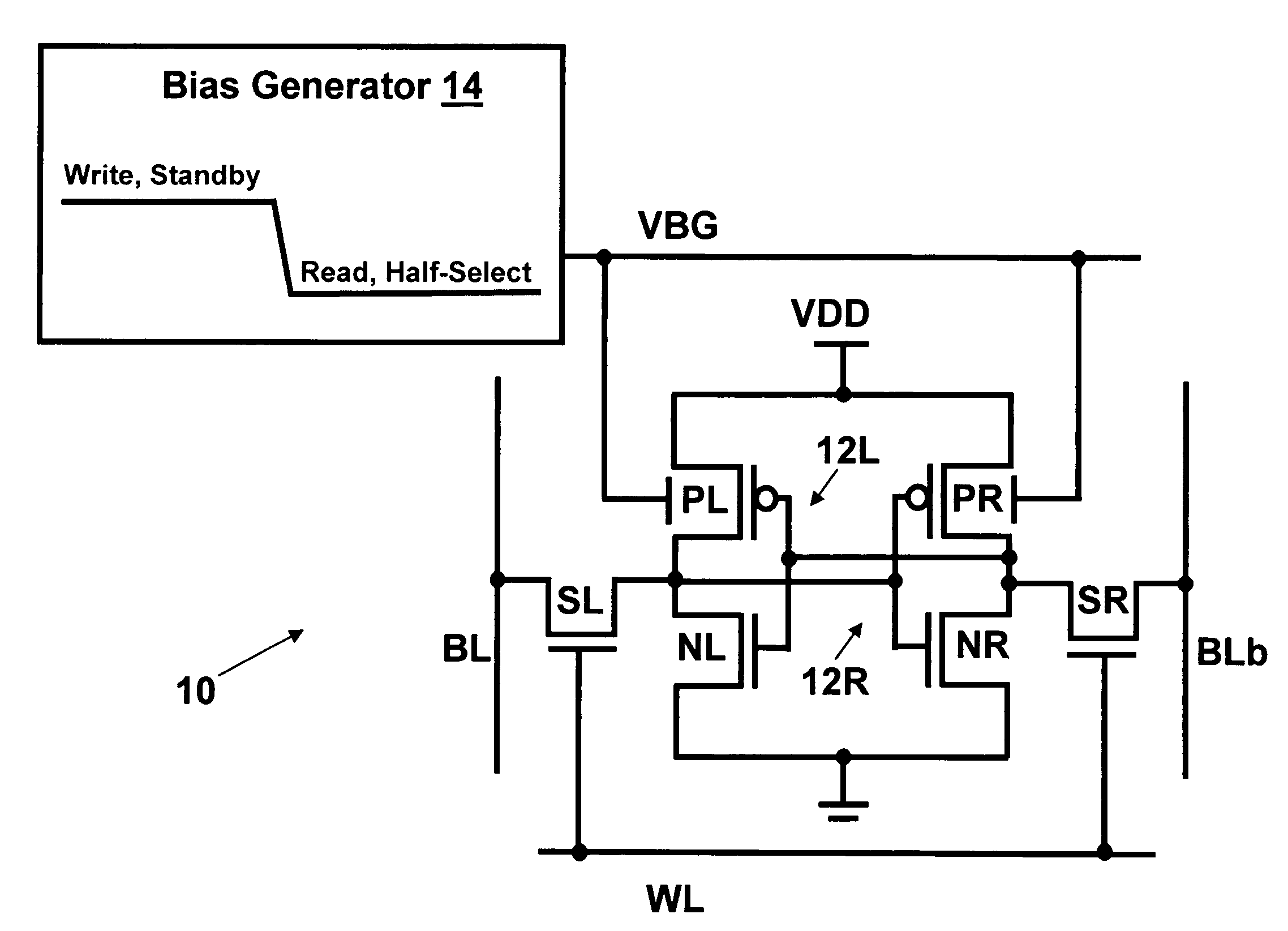
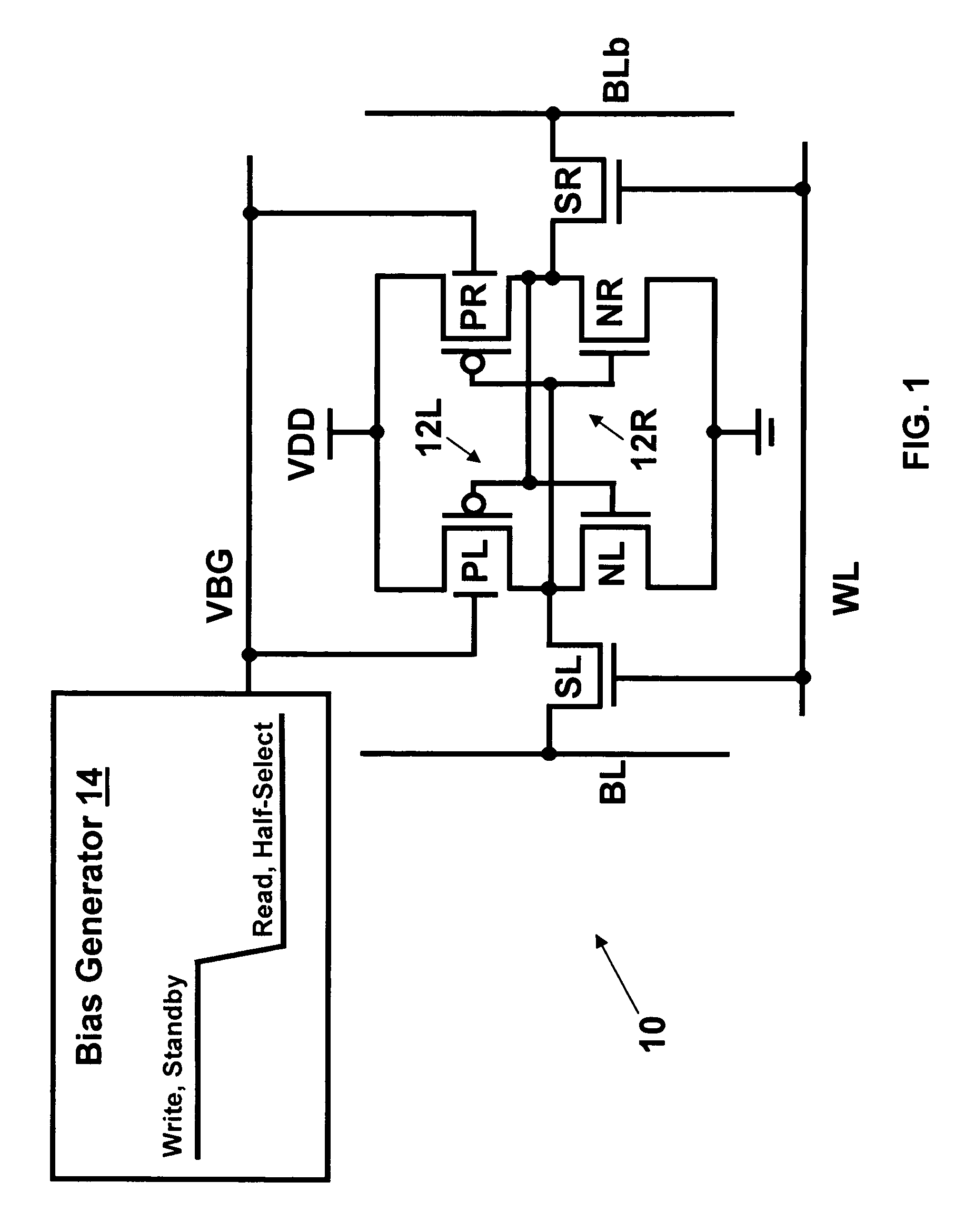
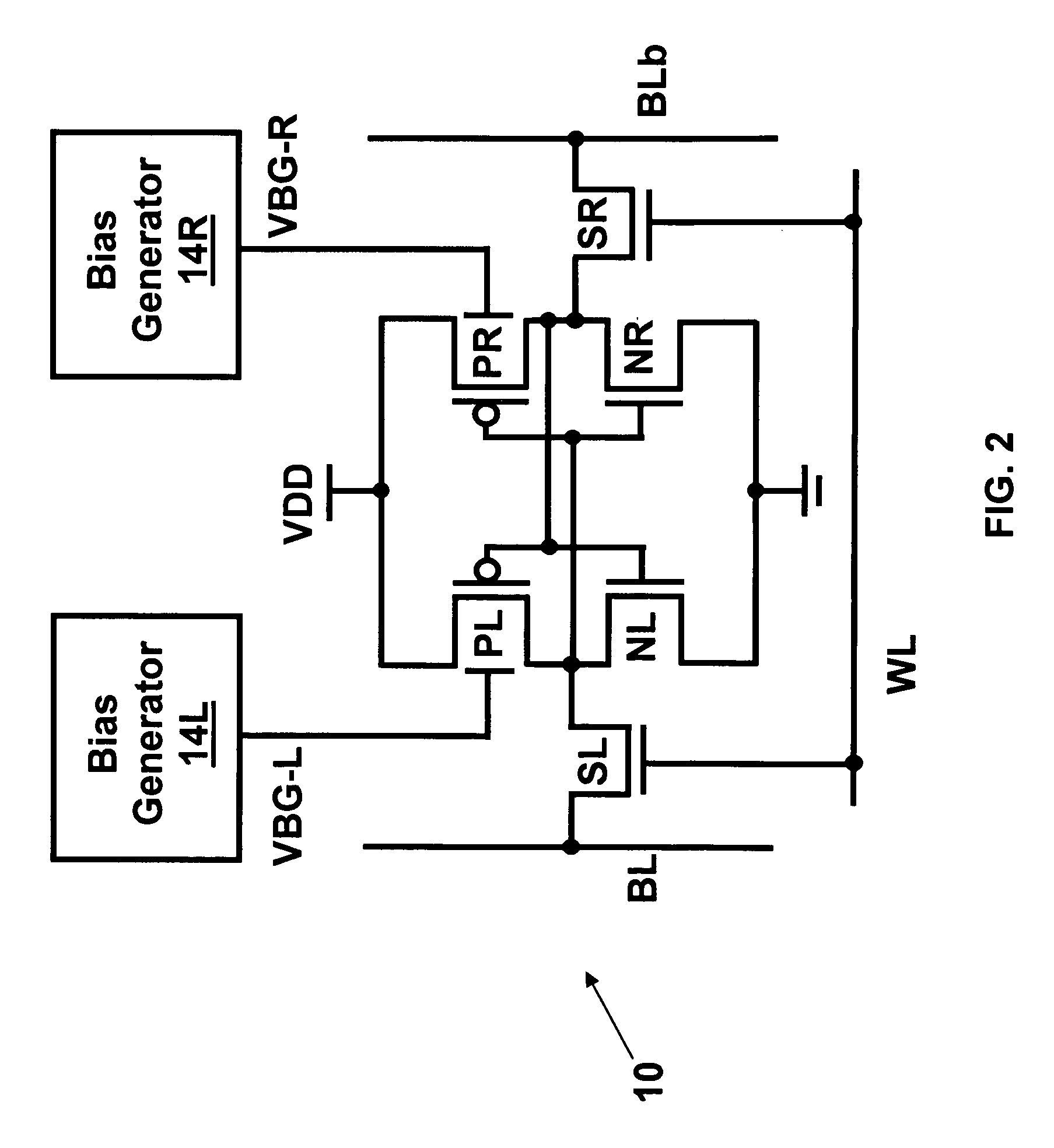
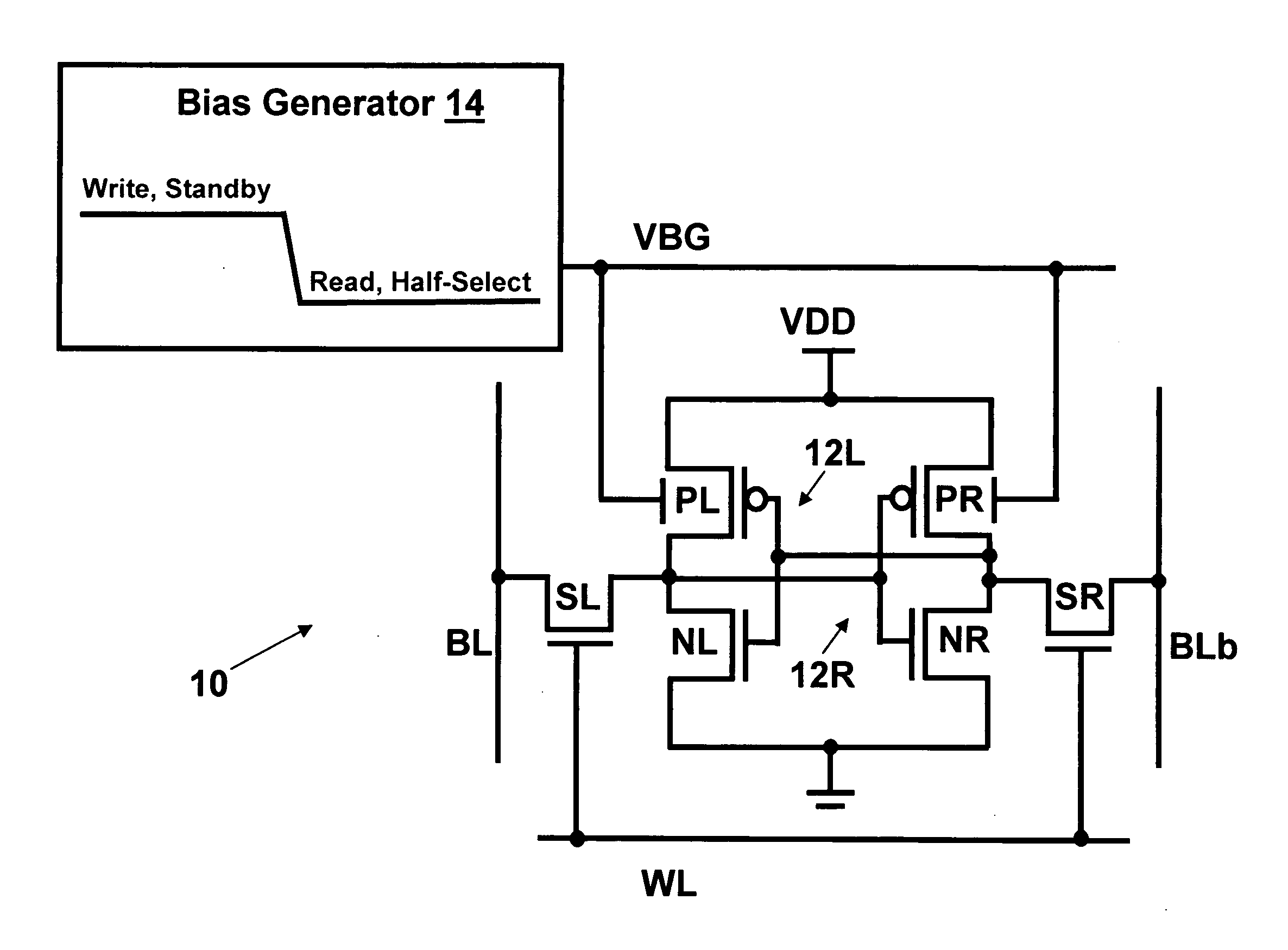
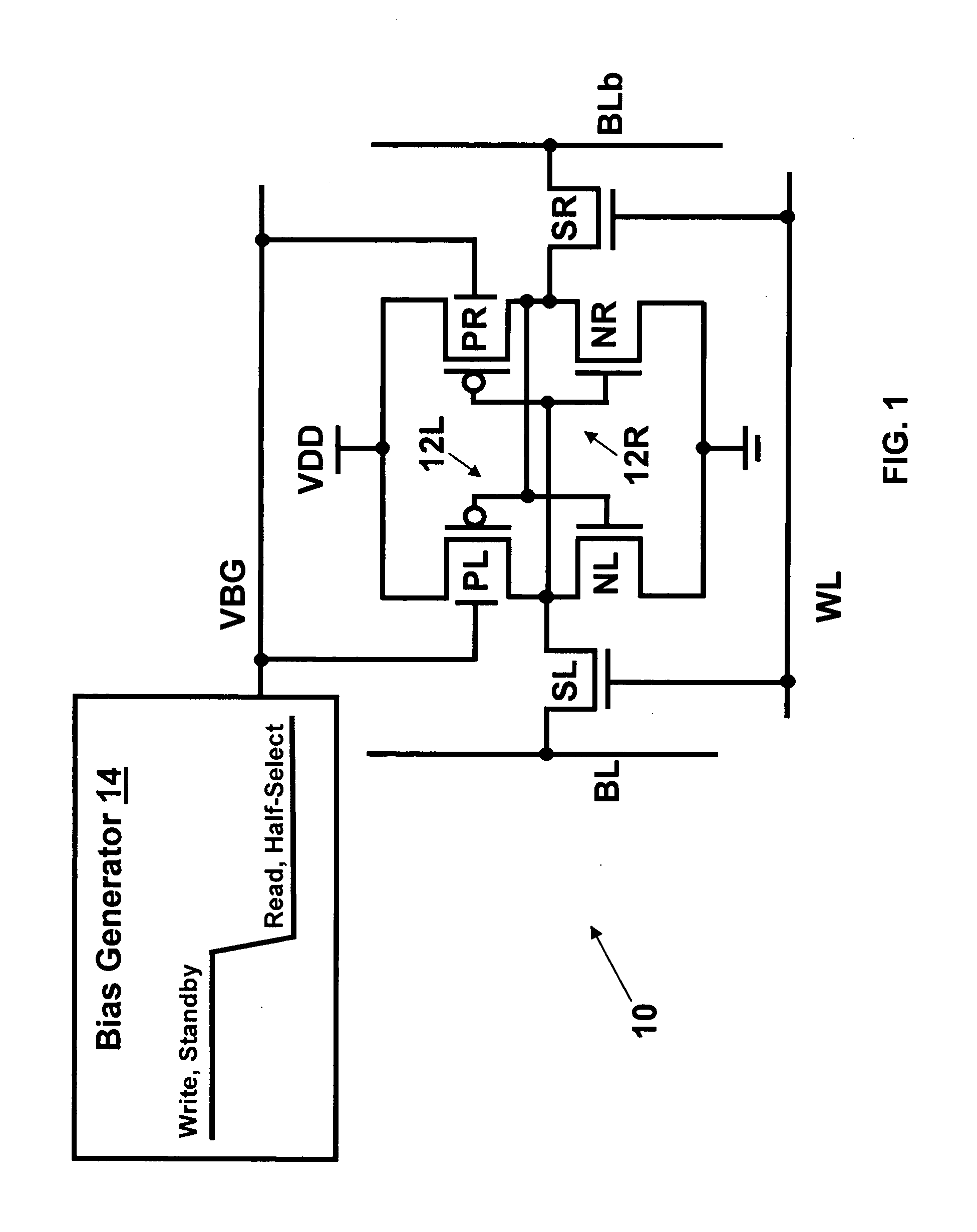
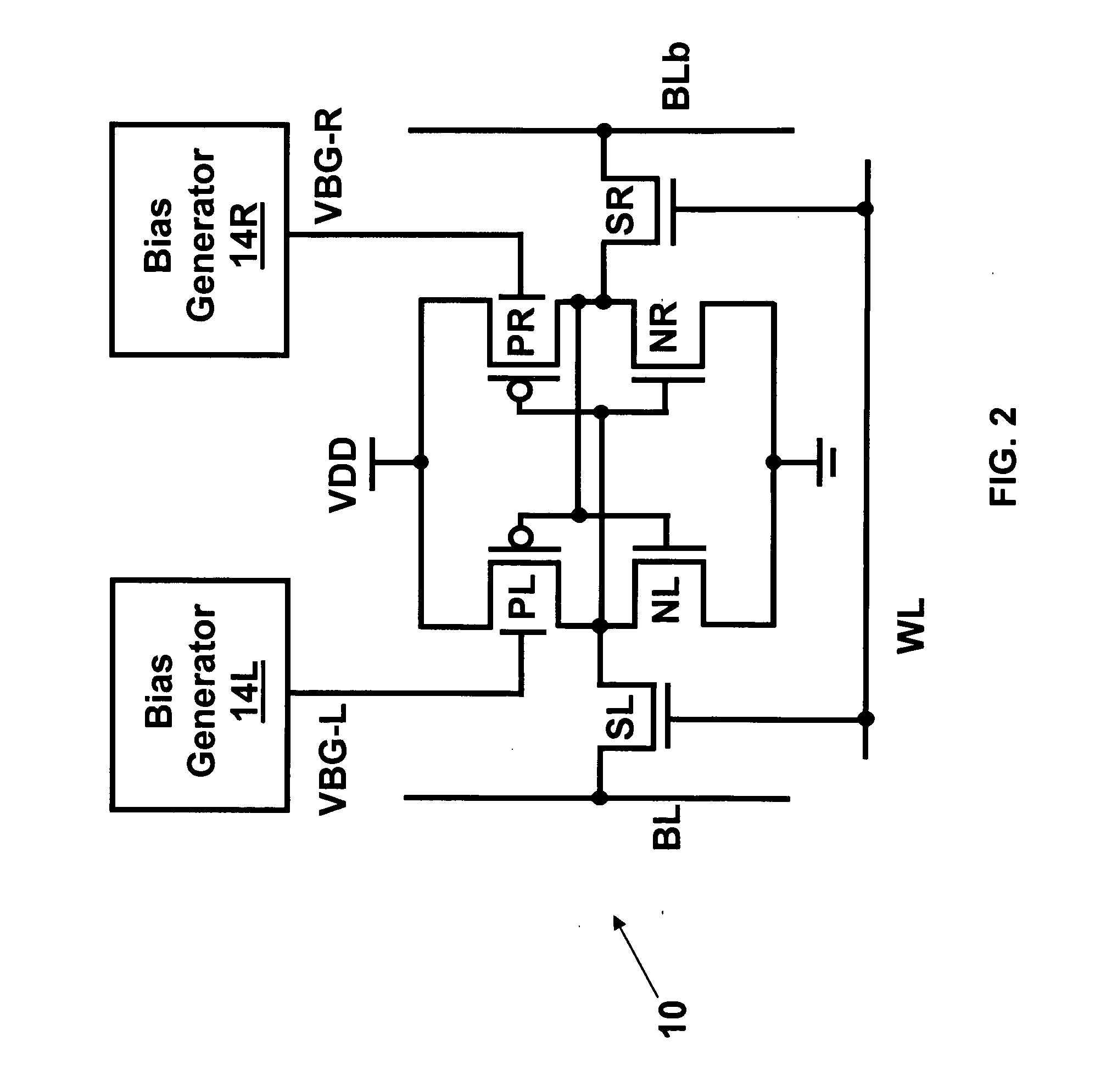
Dynamic control of back gate bias in a FinFET SRAM cell
The present invention provides dynamic control of back gate bias on pull-up pFETs in a FinFET SRAM cell. A method according to the present invention includes providing a bias voltage to a back gate of at least one transistor in the SRAM cell, and dynamically controlling the bias voltage based on an operational mode (e.g., Read, Half-Select, Write, Standby) of the SRAM cell.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
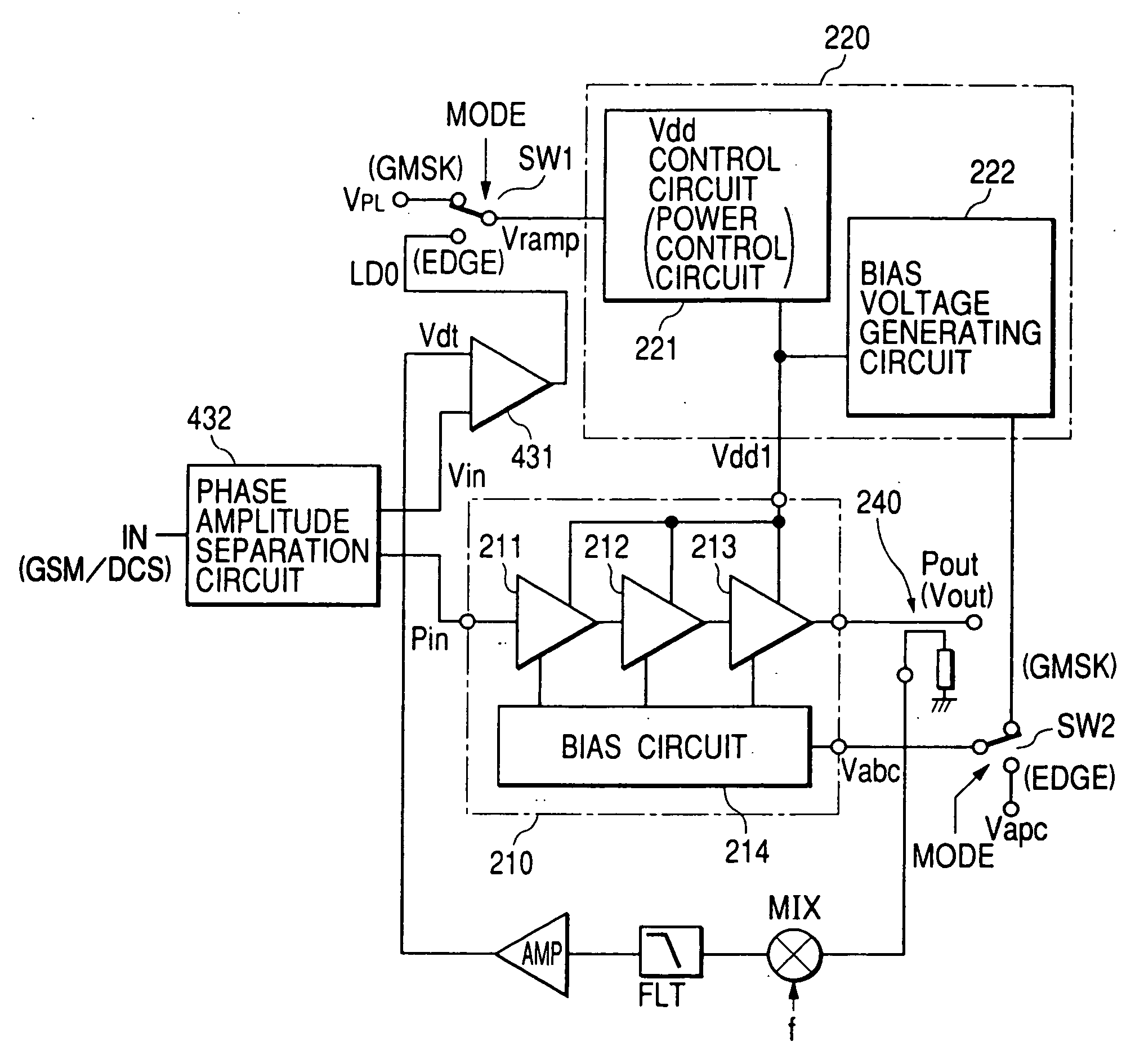
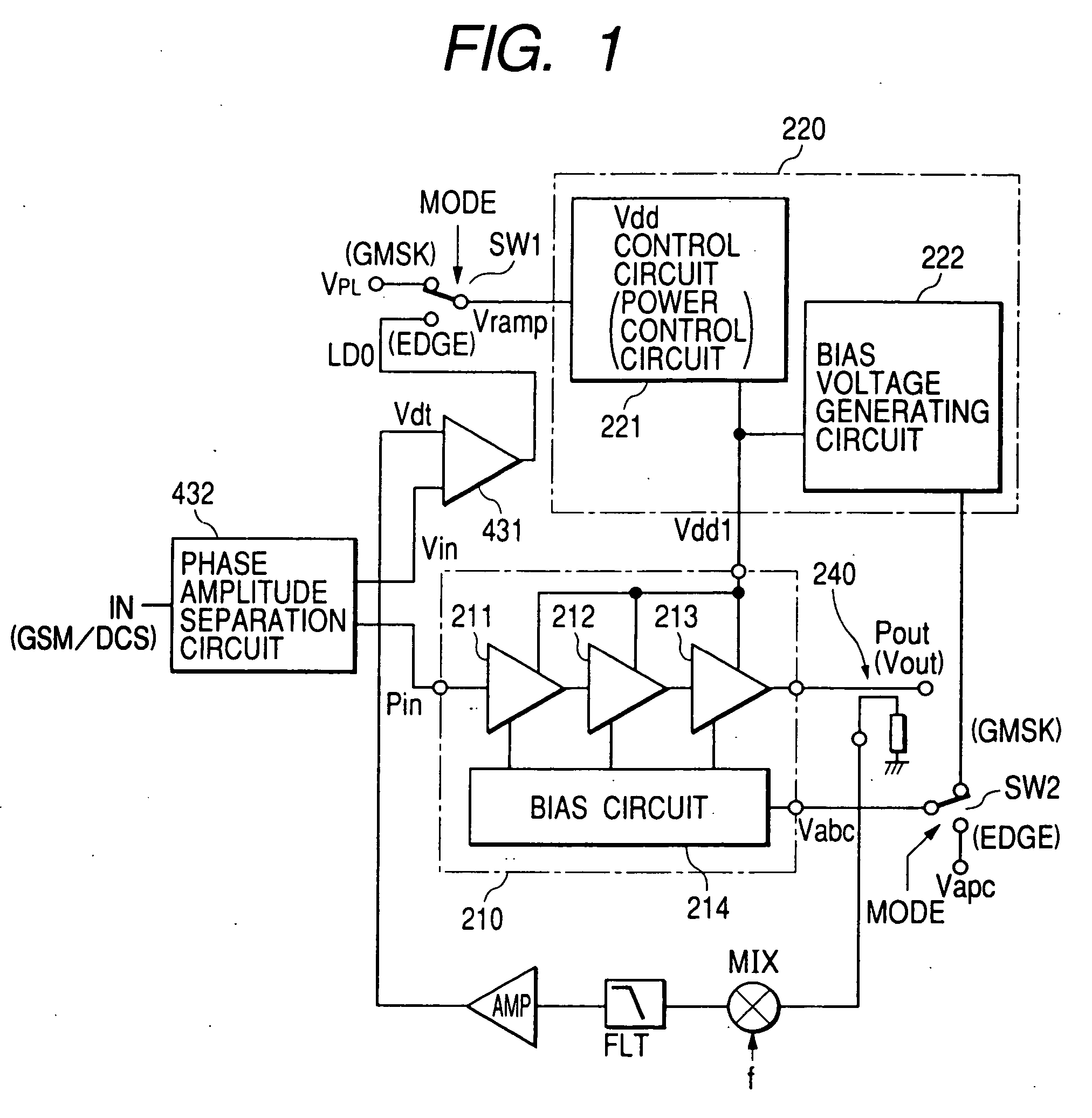
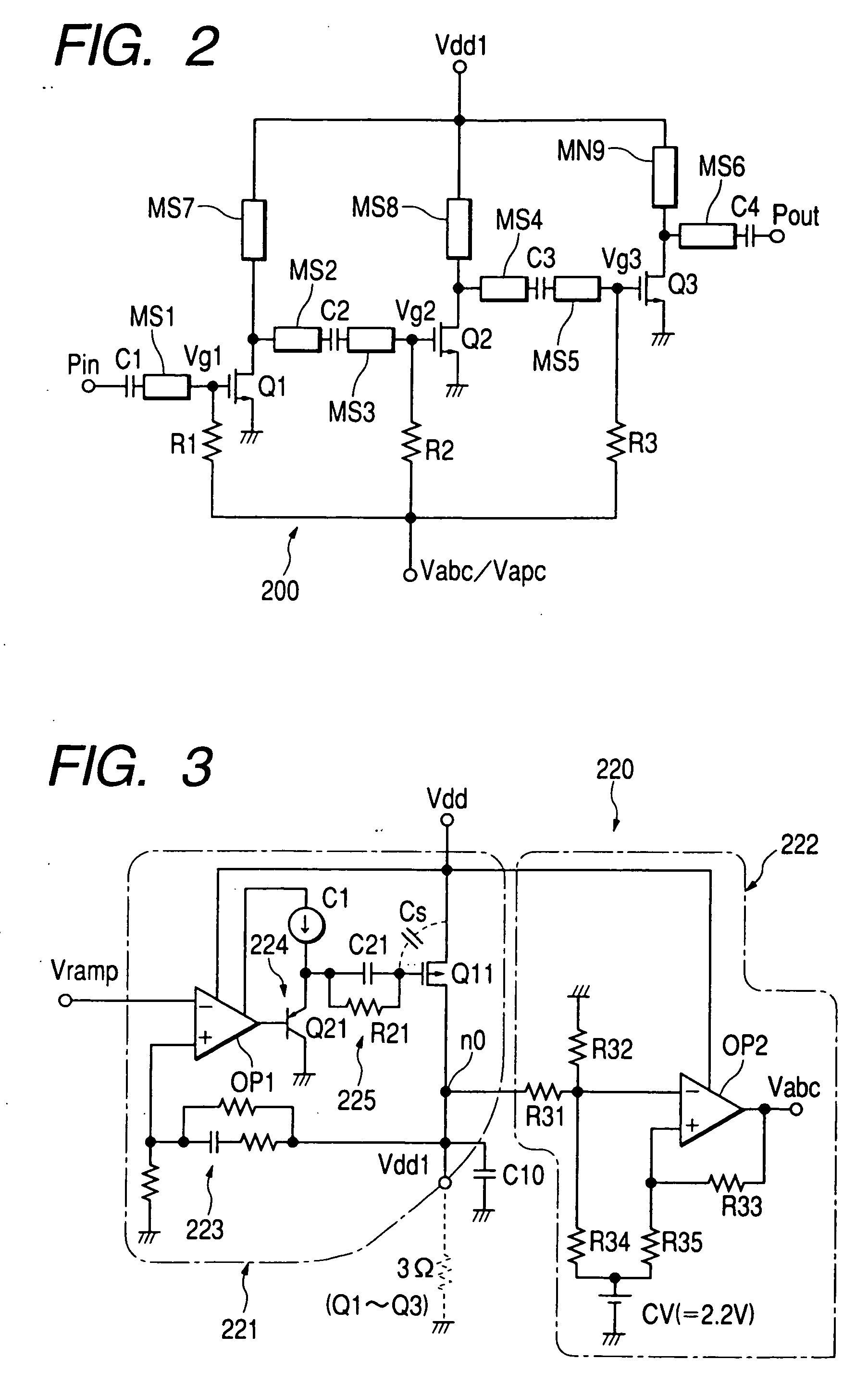
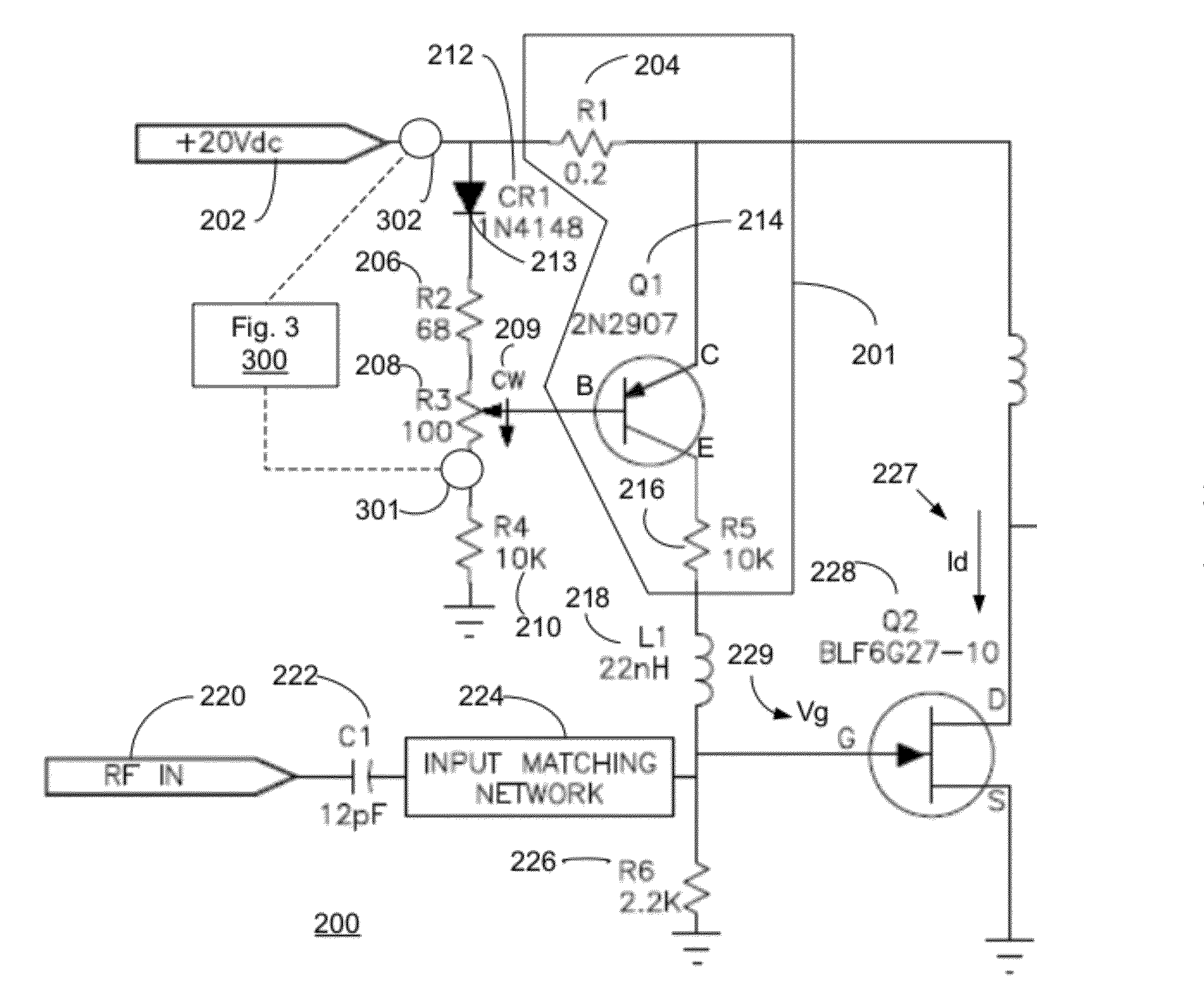
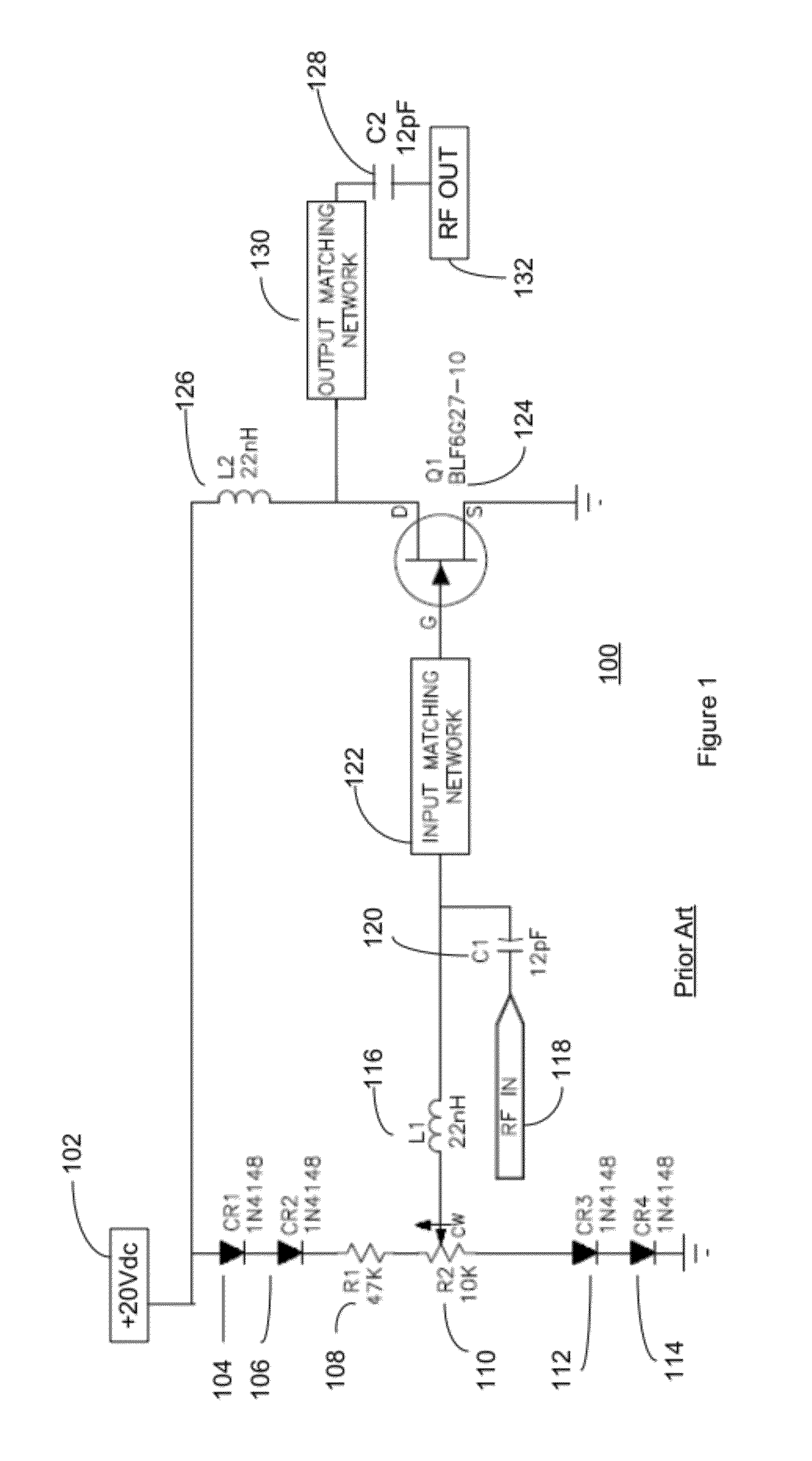
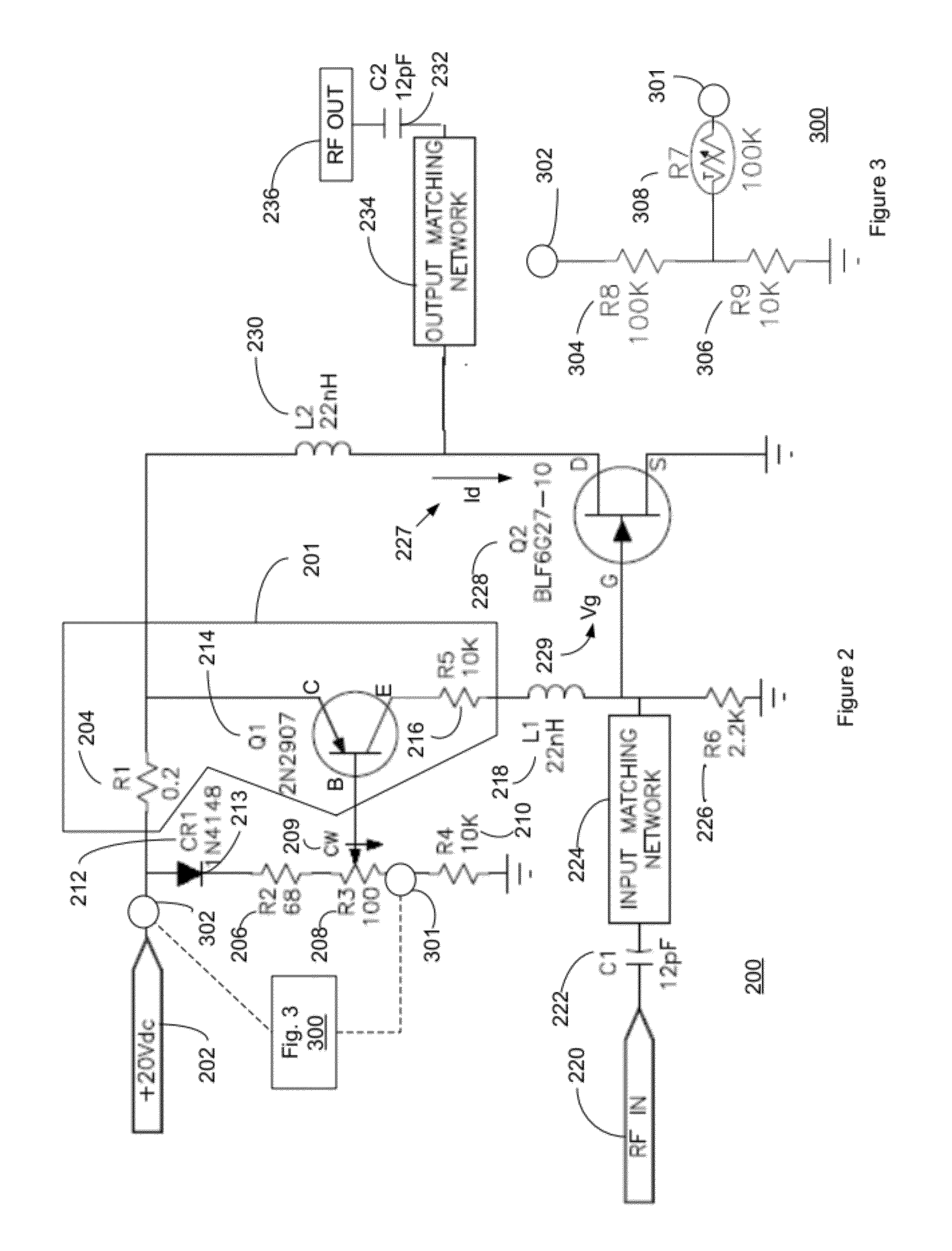
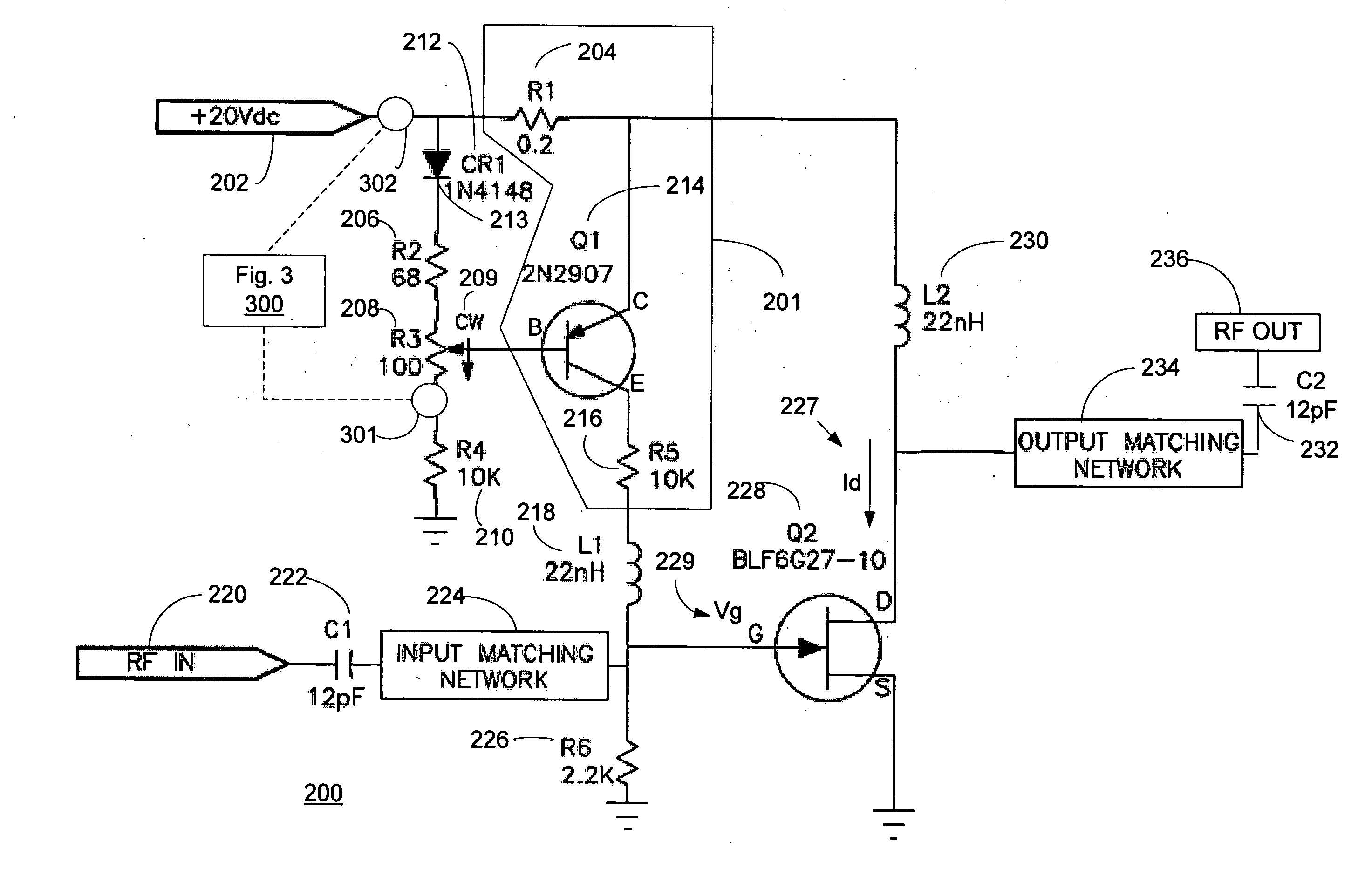
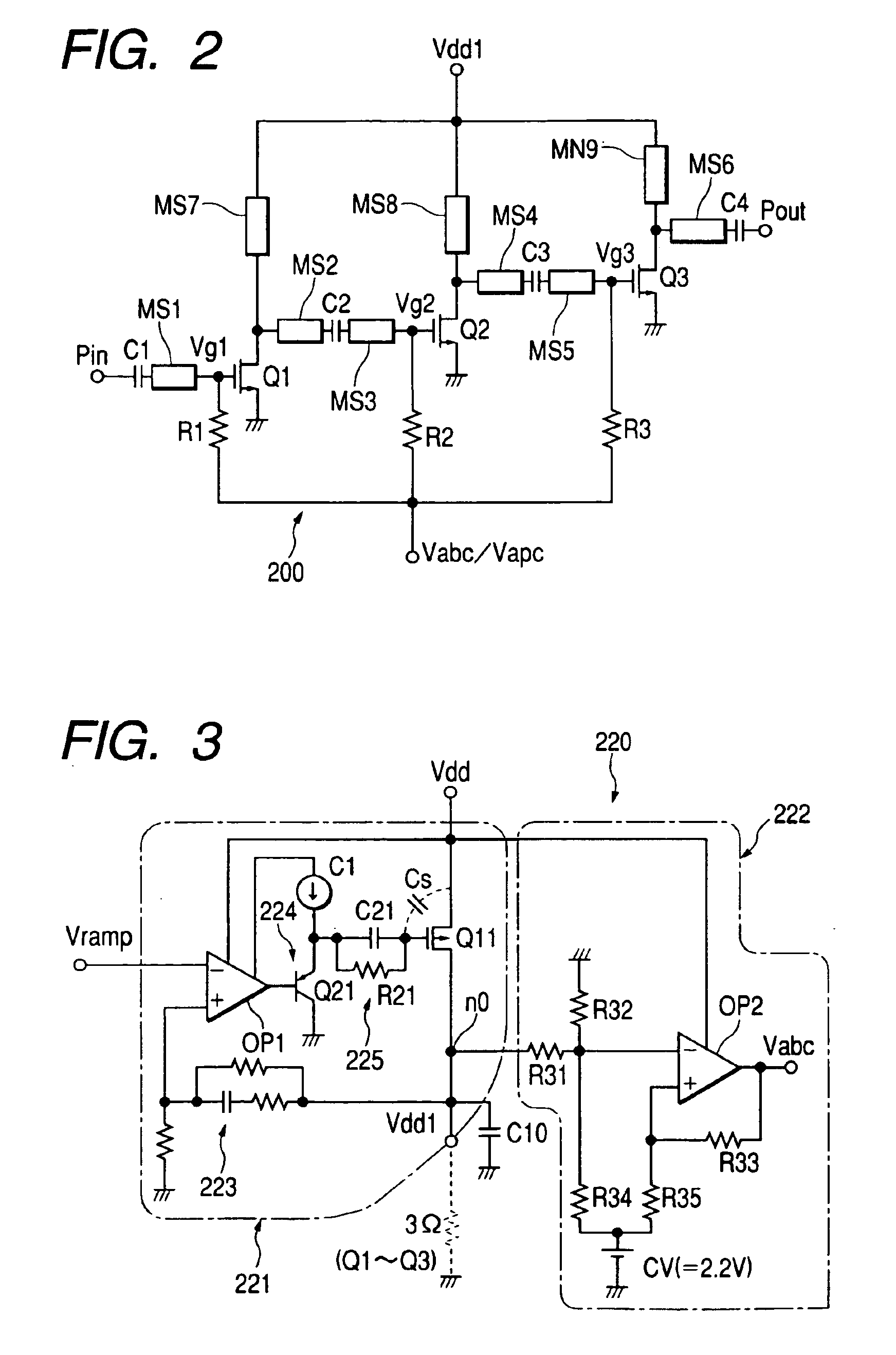
High frequency power amplifier and wireless communication module
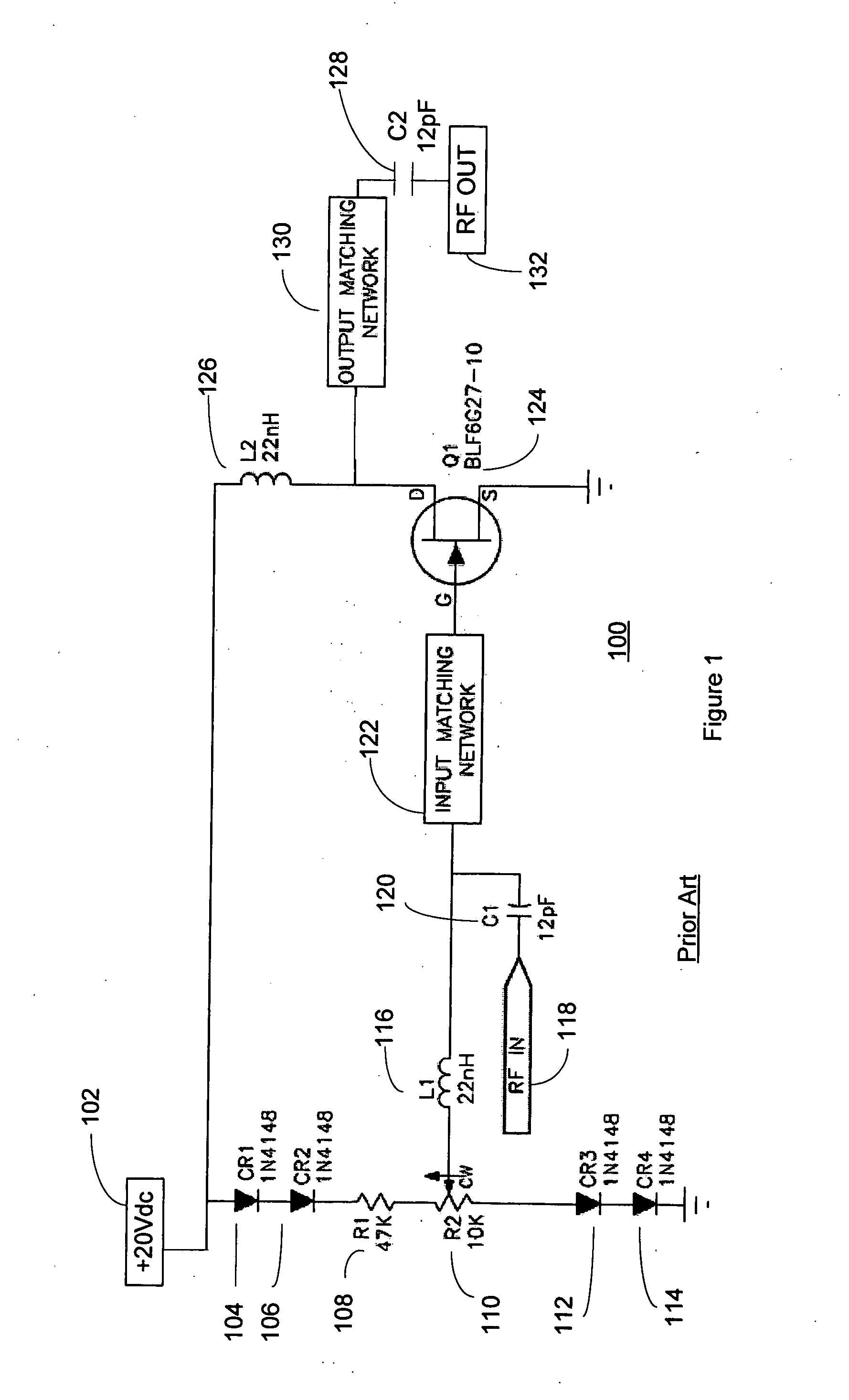
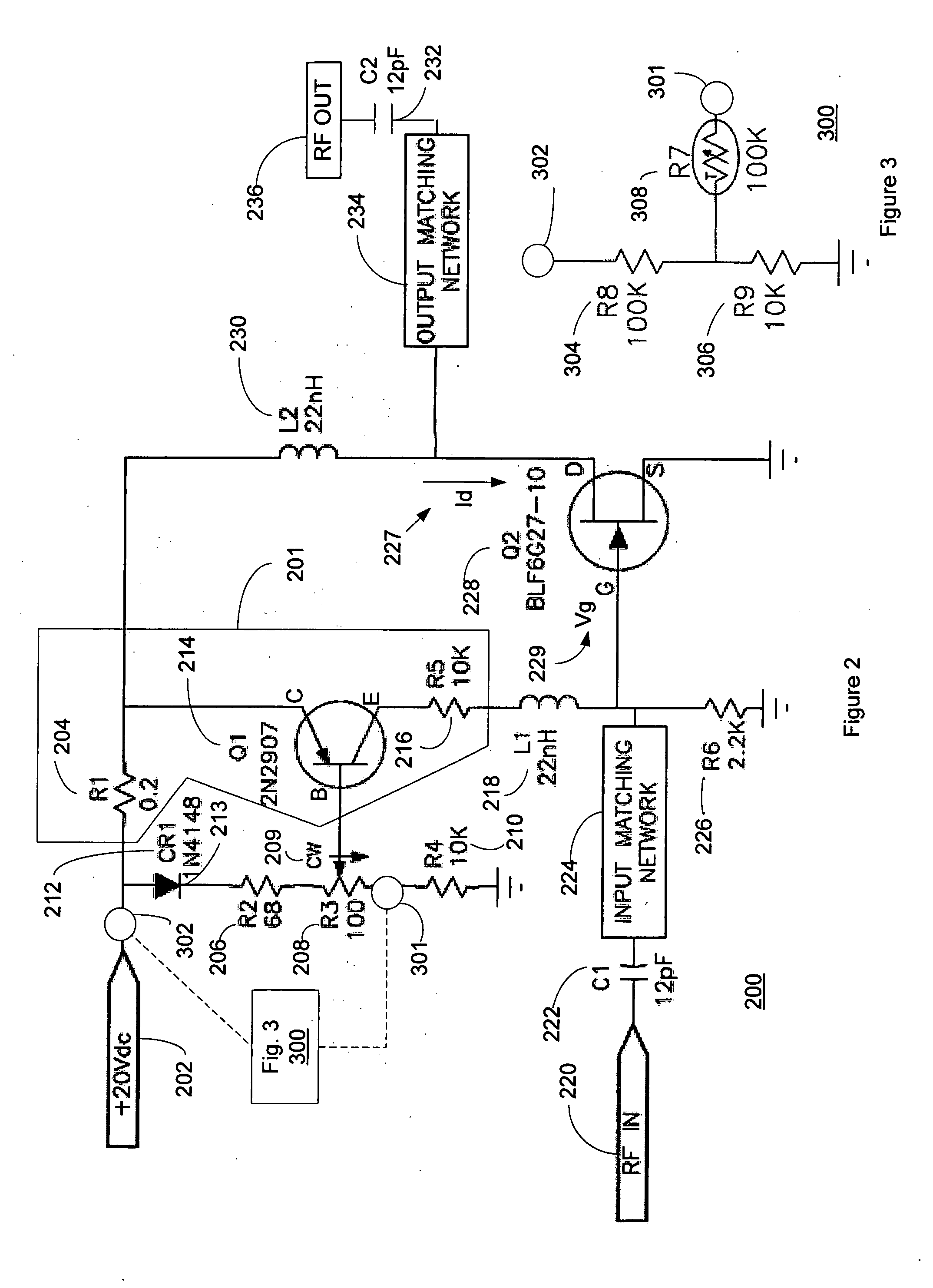
InactiveUS20050200407A1Reduce circuit sizeReduce the packing densityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierHigh frequency power
The present invention provides a high frequency power amplifier of an open-loop type, which outputs a signal having a level corresponding to an output level required under control of a power supply voltage for each output power FET, based on a control signal for the output level. The high frequency power amplifier is provided with a bias voltage generating circuit which generates a gate bias voltage of each output power FET according to an output voltage of a power control circuit for controlling the power supply voltage for the output power FET, based on the control signal for the output level.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
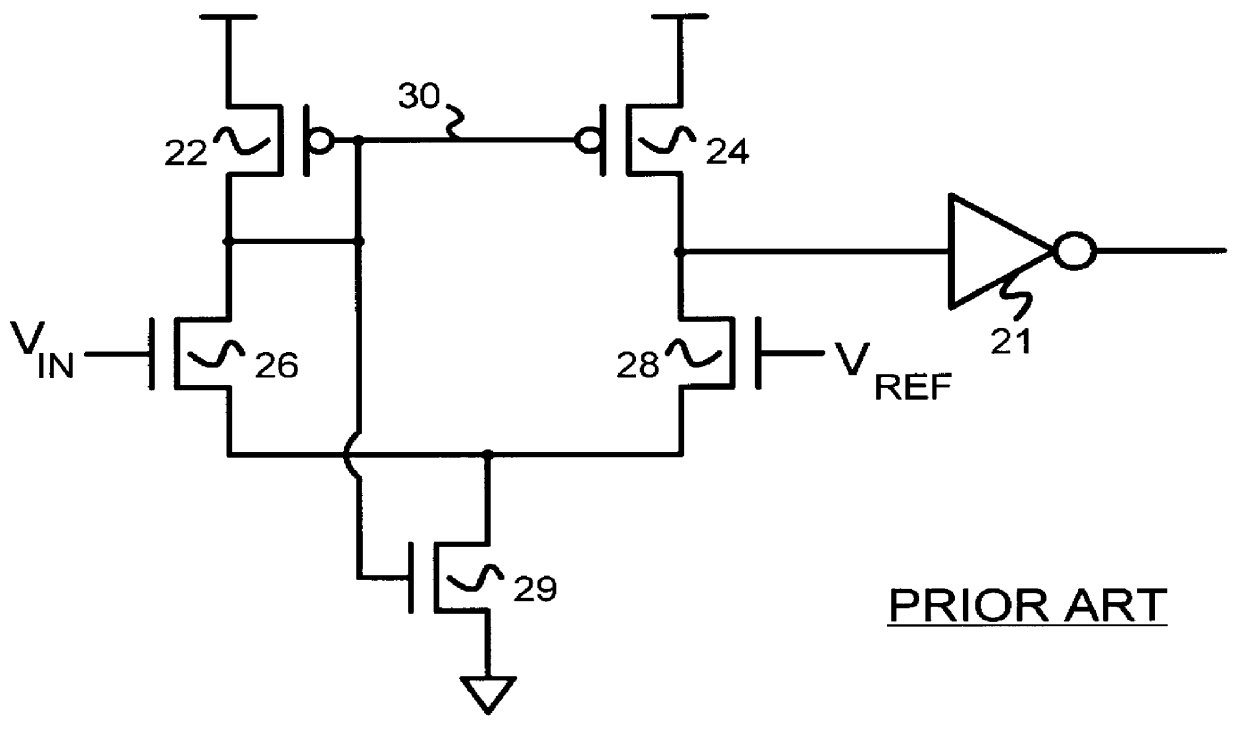
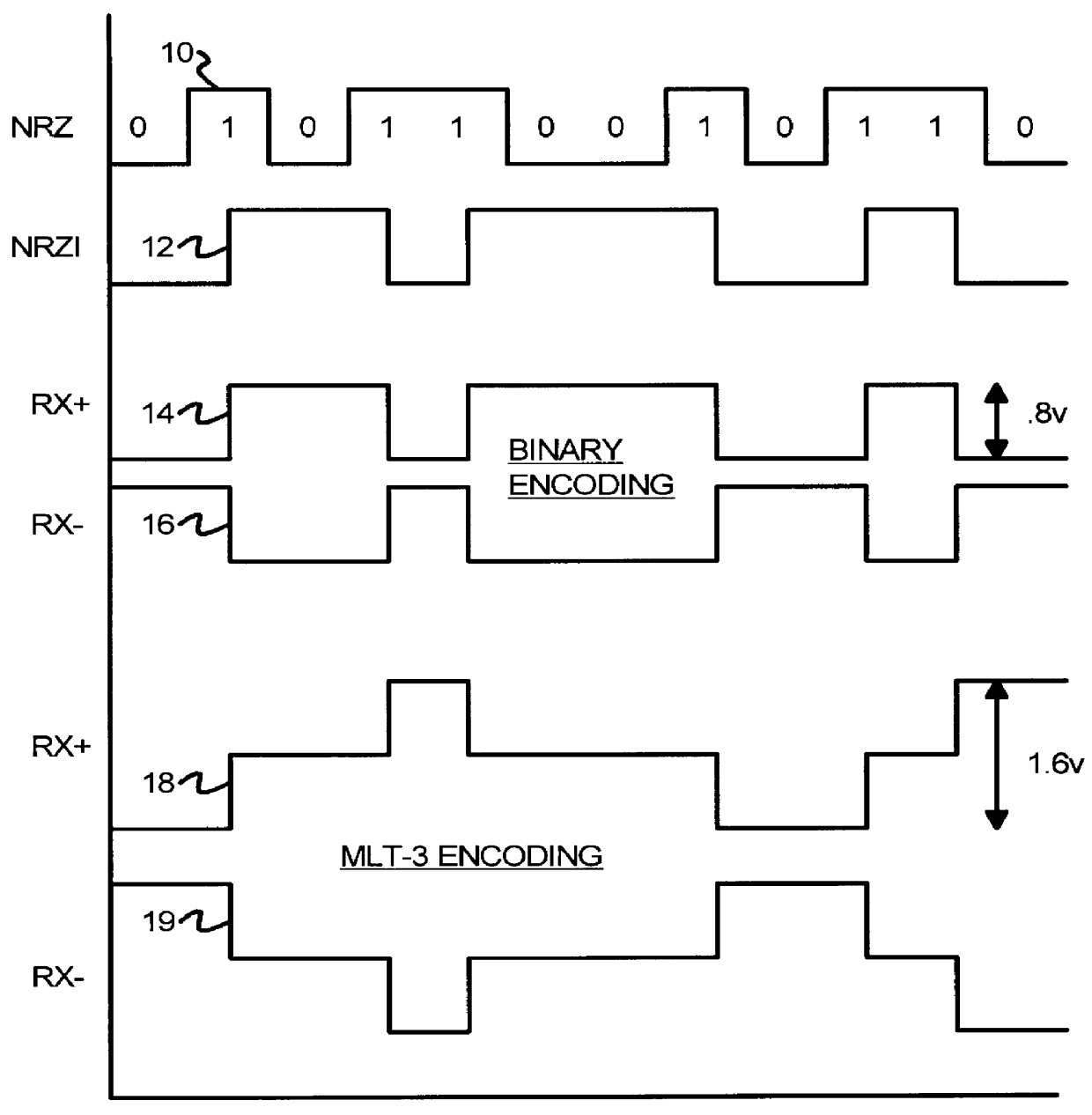
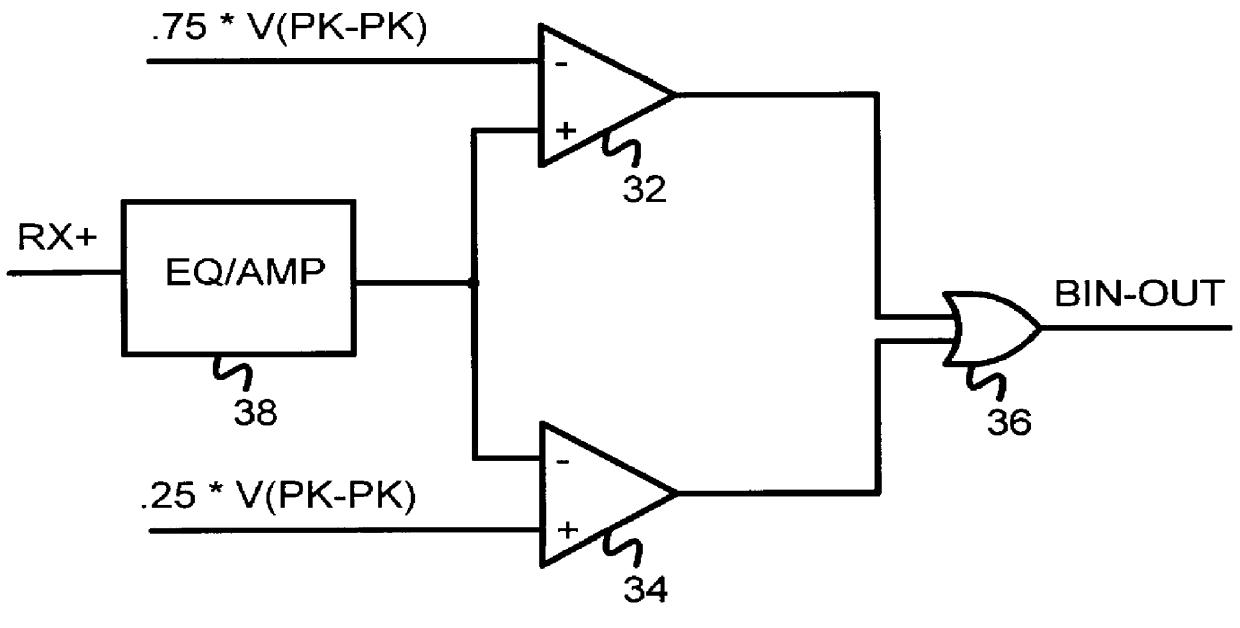
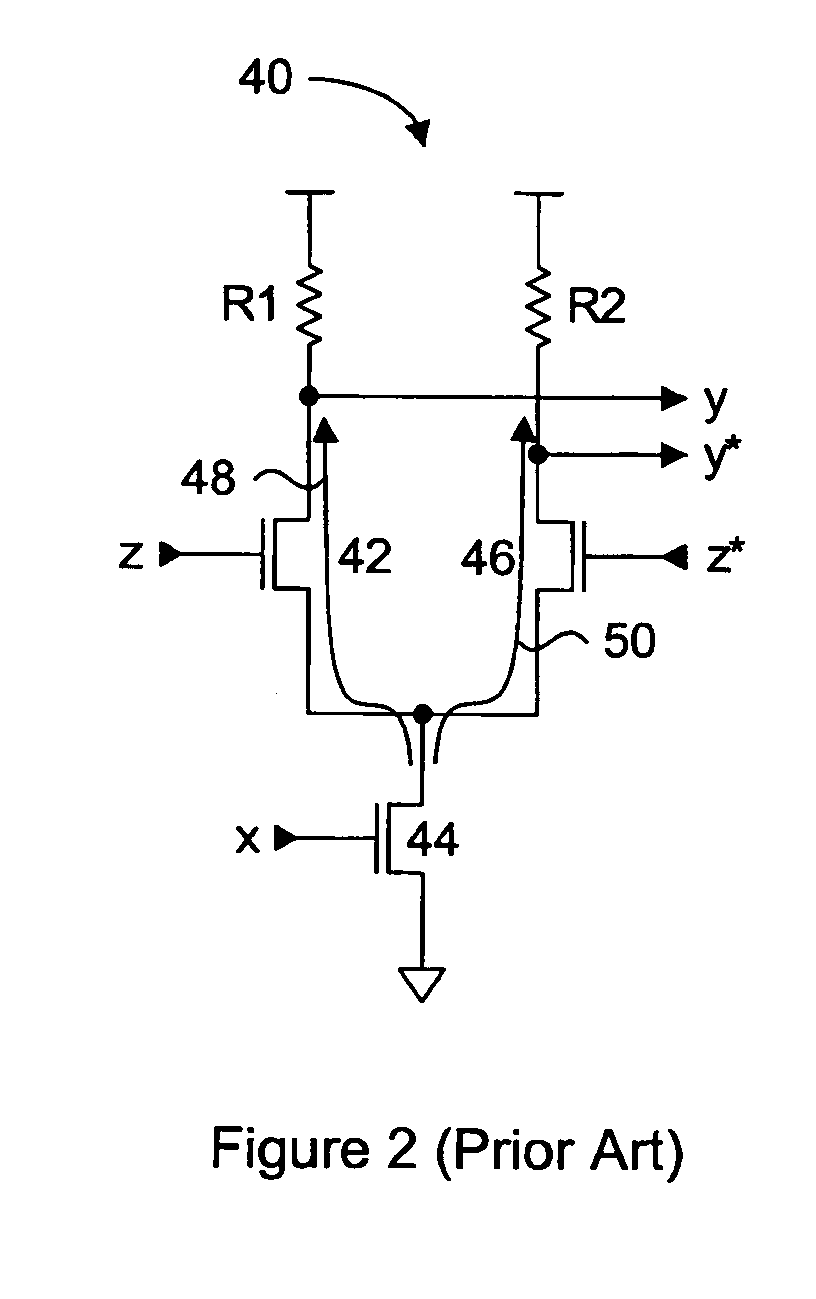
Self-biasing CMOS PECL receiver with wide common-mode range and multi-level-transmit to binary decoder
InactiveUS6049229AReduced Power RequirementsSimplify interconnect routingLogic circuits characterised by logic functionLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsThree levelEmitter-coupled logic
A pseudo-emitter-coupled-logic (PECL) receiver has a wide common-mode range. Two current-mirror CMOS differential amplifiers are used. One amplifier has n-channel differential transistors and a p-channel current mirror, while the second amplifier has p-channel differential transistors and an n-channel current mirror. When the input voltages approach power or ground, one type of differential transistor continues to operate even when the other type shuts off. The outputs of the two amplifiers are connected together and each amplifier receives the same differential input signals. The tail-current transistor is self-biased using the current-mirror's gate-bias. This self biasing of each amplifier eliminates the need for an additional voltage reference and allows each amplifier to adjust its biasing over a wide input-voltage range. Thus the common-mode input range is extended using self biasing and complementary amplifiers. The complementary self-biased comparators can be used for receiving binary or multi-level-transition (MLT) inputs by selecting different voltage references for threshold comparison. Using the same reference on both differential inputs eliminates a second reference for multi-level inputs having three levels. Thus binary and MLT inputs can be detected and decoded by the same decoder.
Owner:DIODES INC
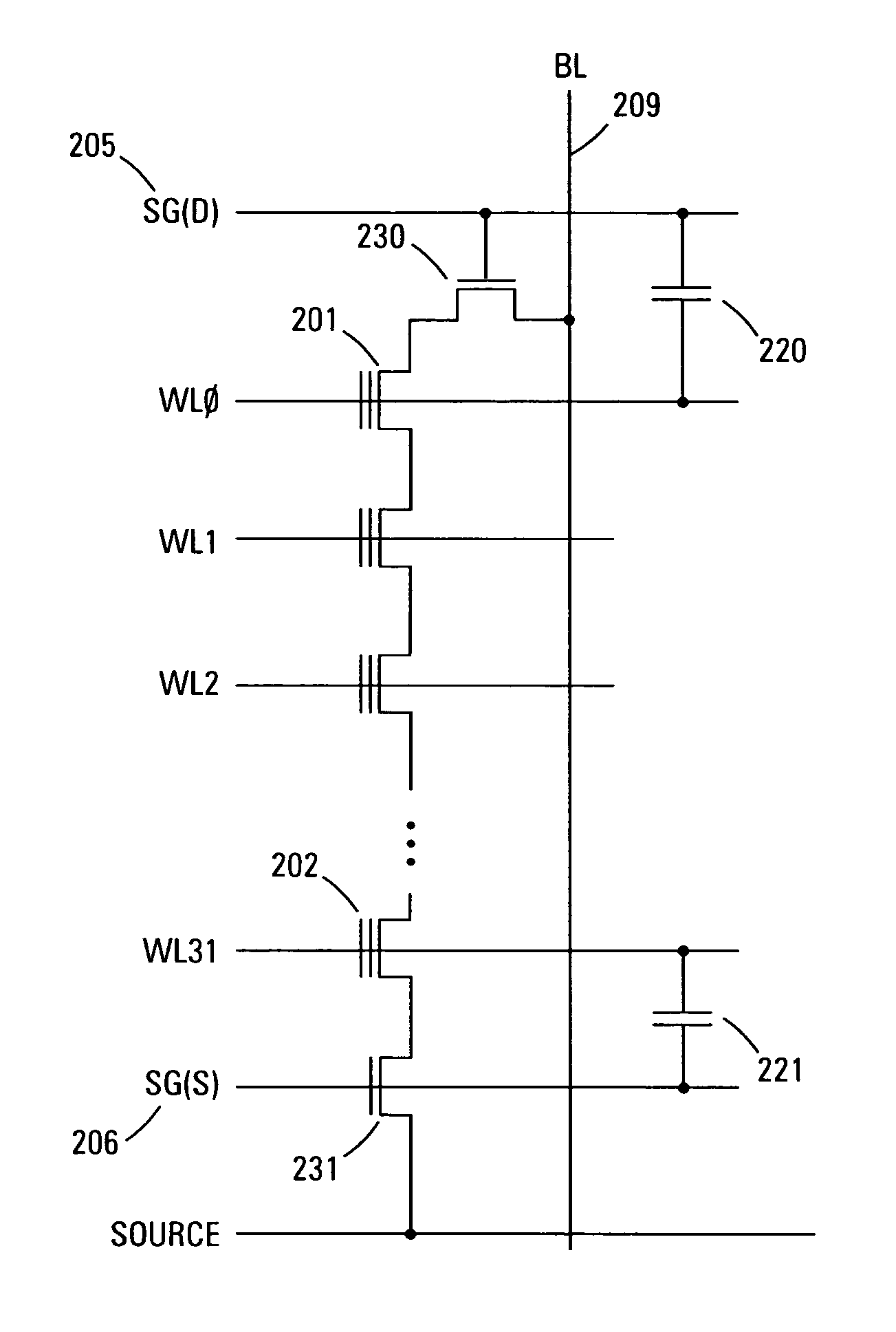
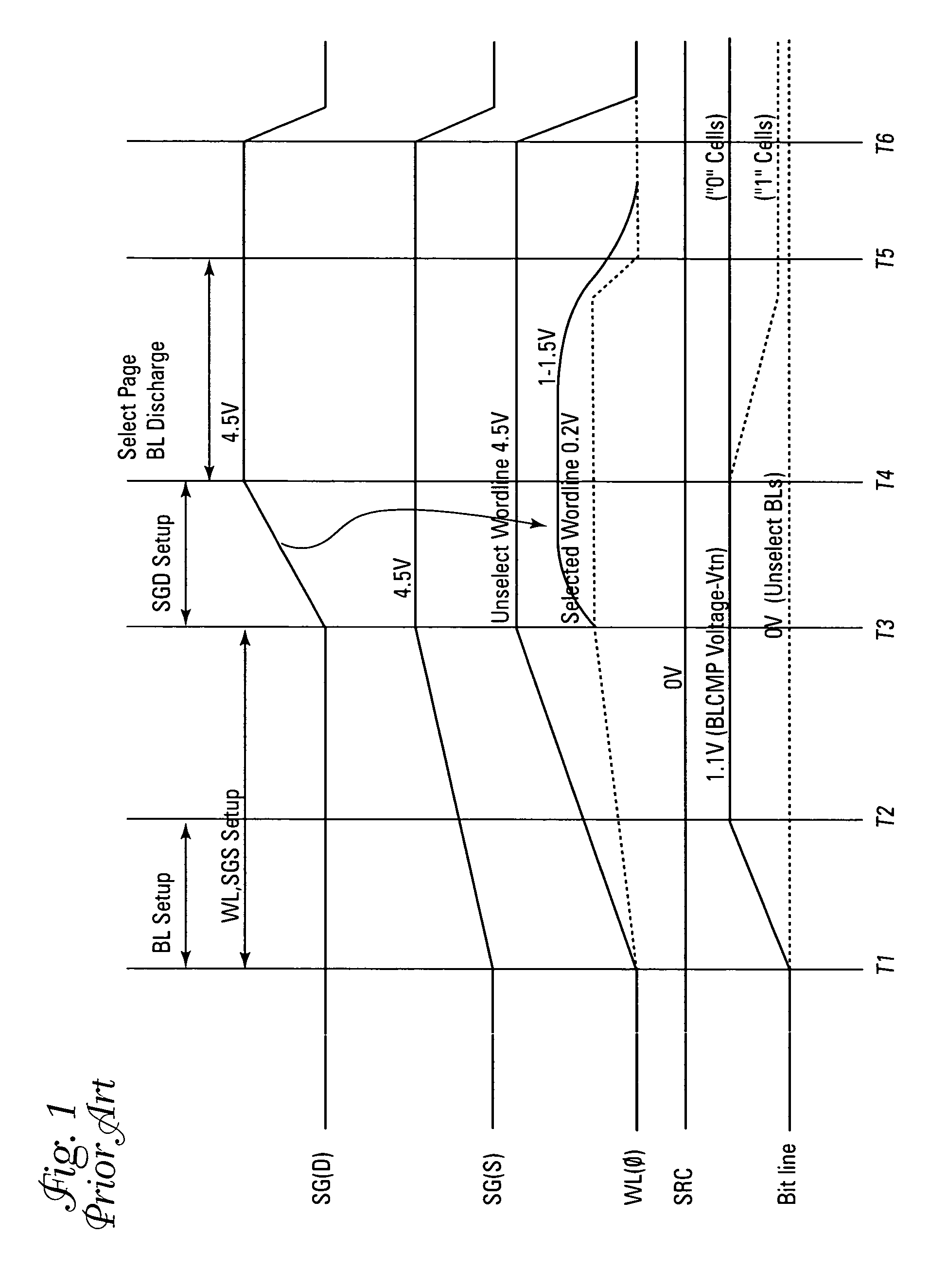
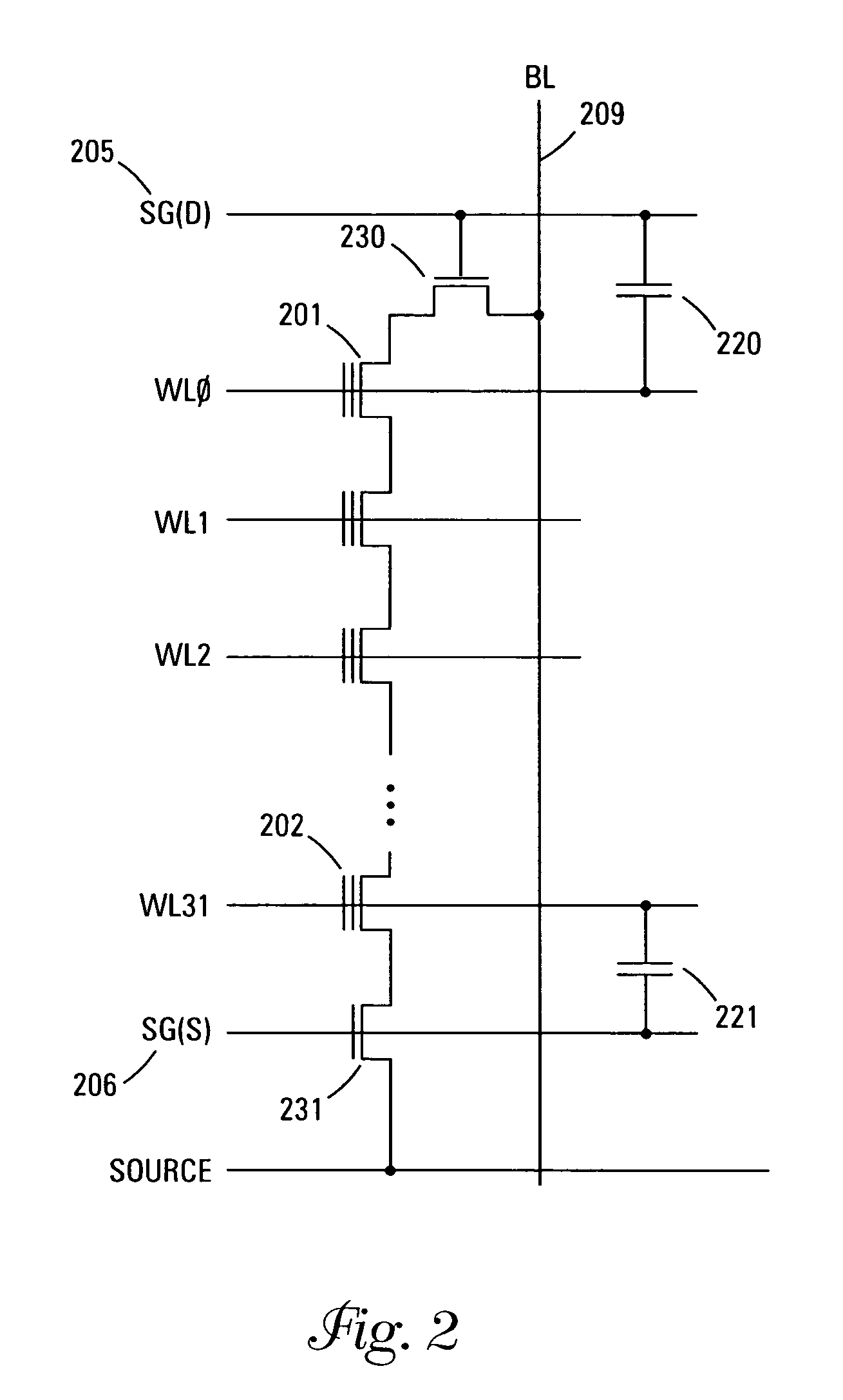
Method and apparatus for reading NAND flash memory array
The method for reading / verifying a NAND flash memory device alternates the select gate biasing in response to the position of the cell to be read. If the cell is closer to the top of the column, the SG(D) line is biased prior to the SG(S) line. If the cell is closer to the bottom of the column, the SG(S) line is biased prior to the SG(D) line.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
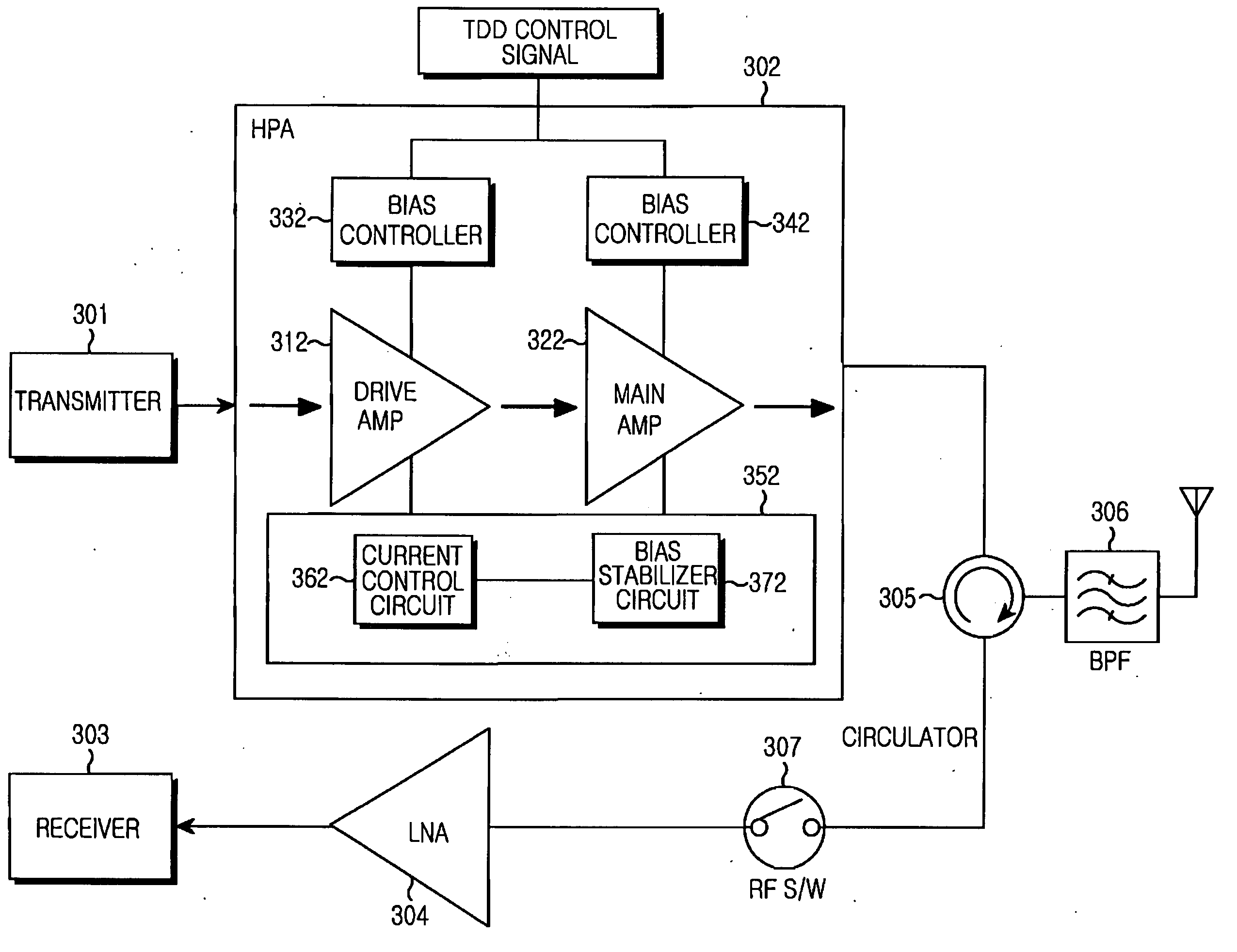
High-power amplifier apparatus for TDD wireless communication system
ActiveUS20070111686A1Avoid powerReduce leakage powerResonant long antennasHigh frequency amplifiersCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
Provided is an HPA apparatus for a TDD wireless communication system. In the HPA apparatus, a power amplifier amplifies the power of an input signal. A gate bias controller turns on / off a gate bias of the power amplifier in accordance with a TDD control signal. A constellation error optimizer circuit removes a current fluctuation and a power noise, which occur when the gate bias controller turns on / off the power amplifier in a TX mode, to stabilize a drain bias thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
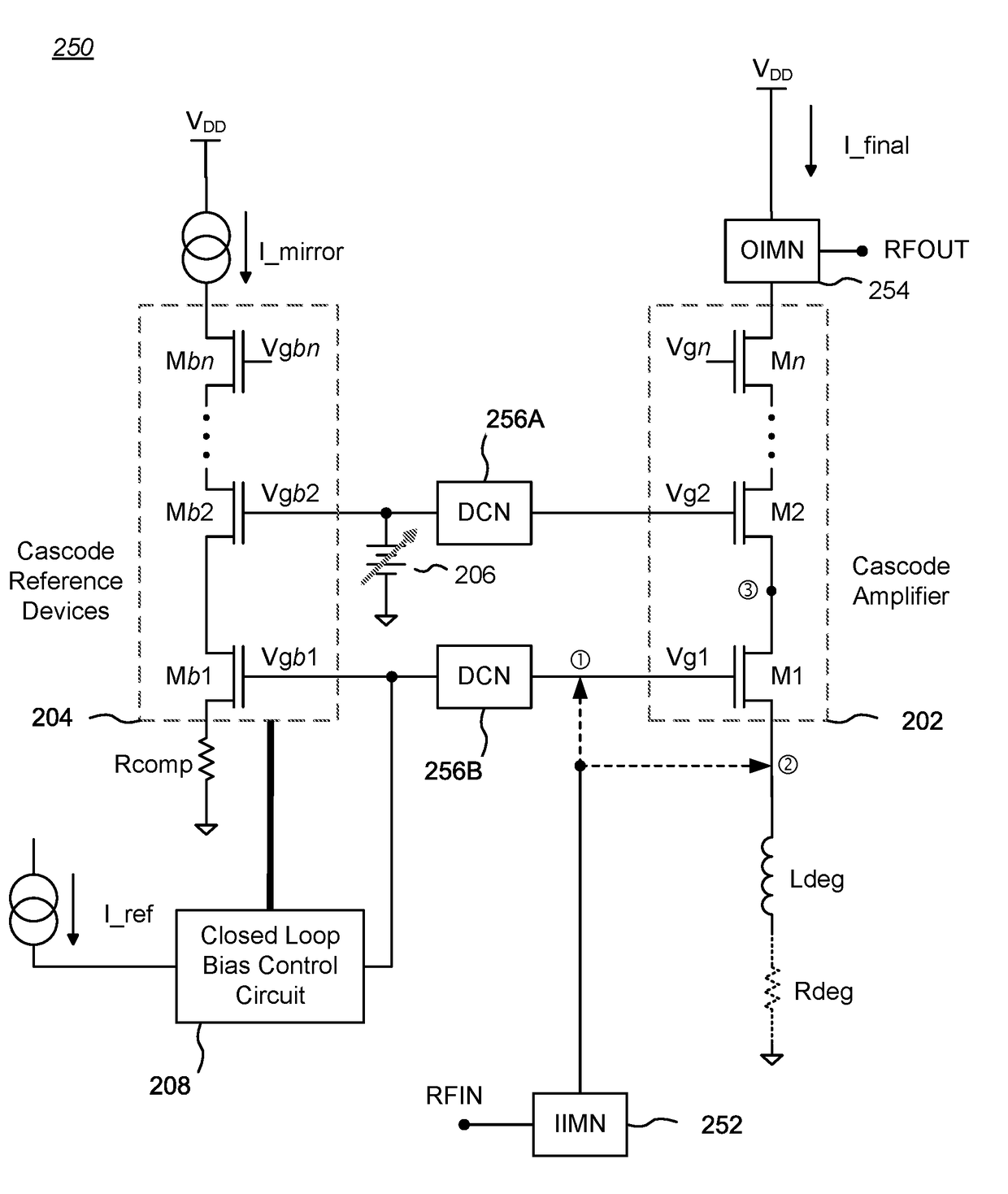
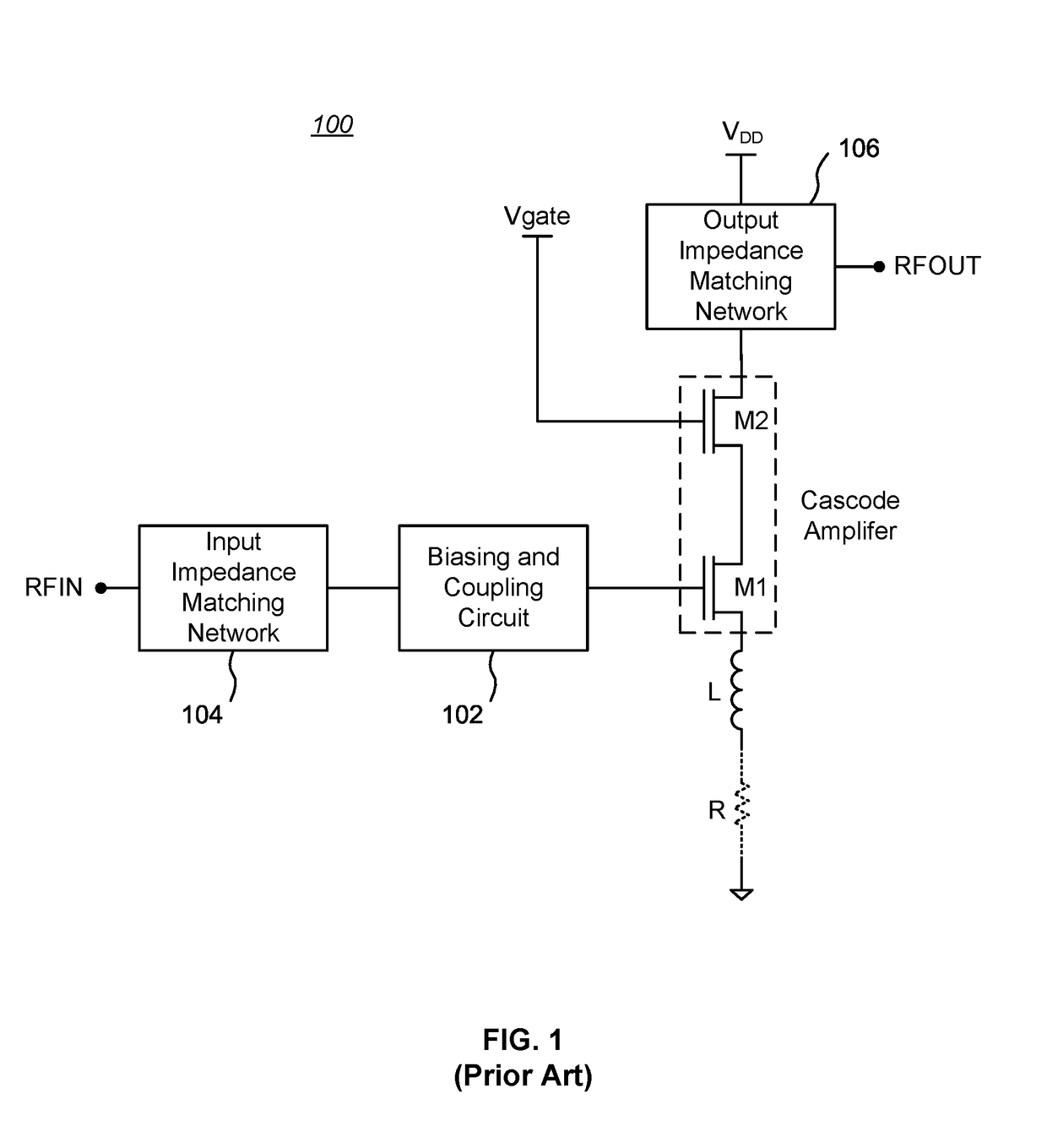
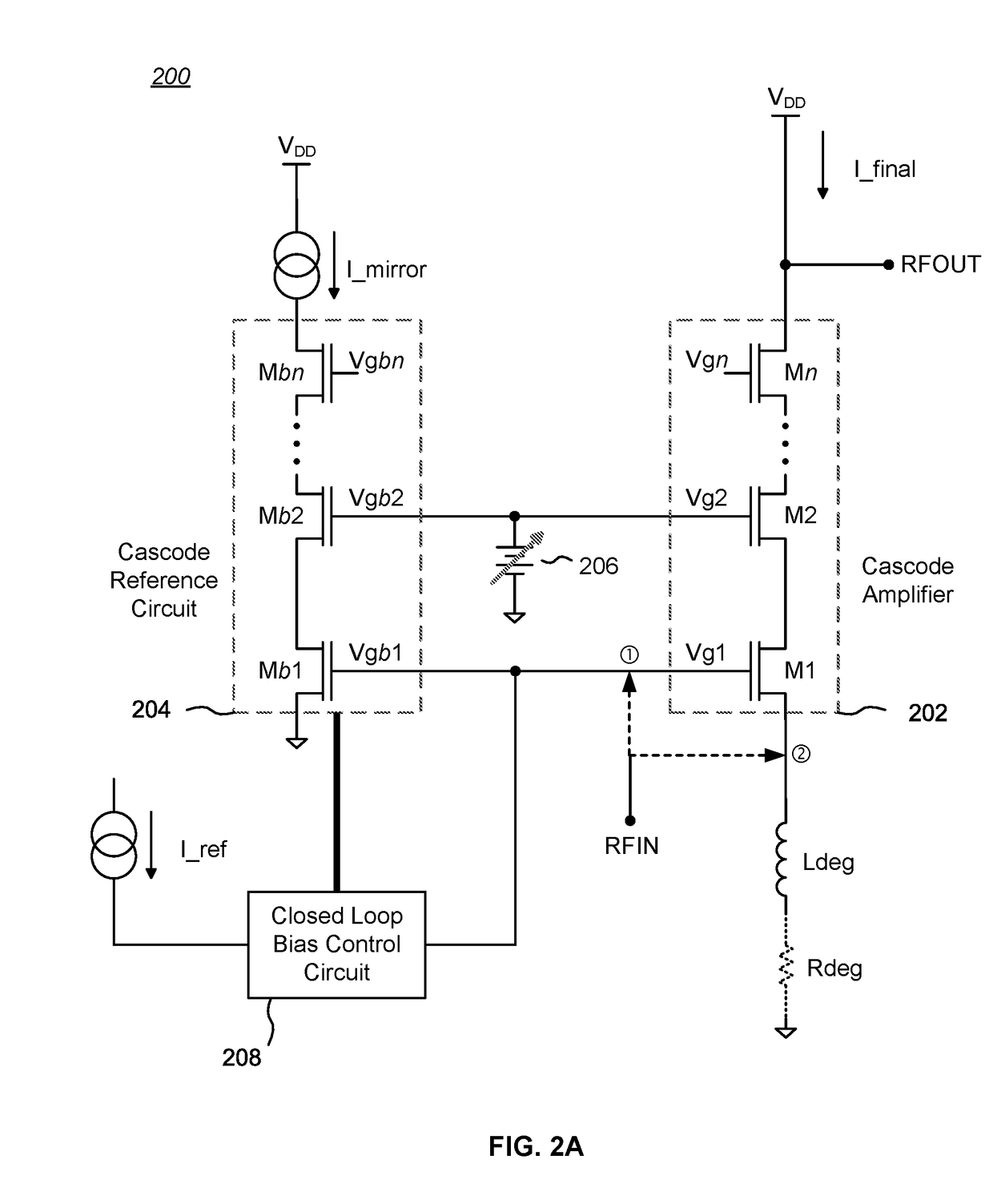
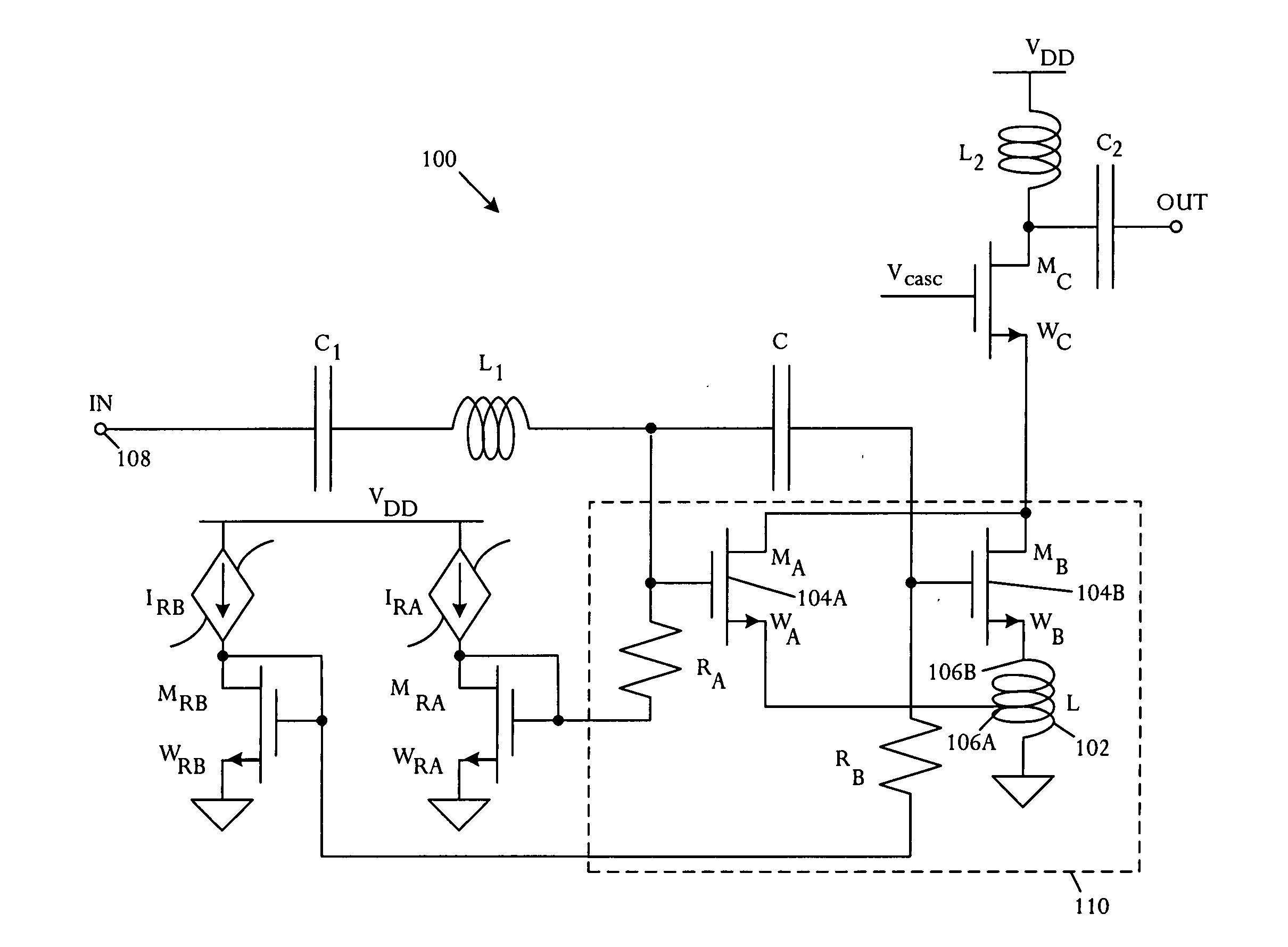
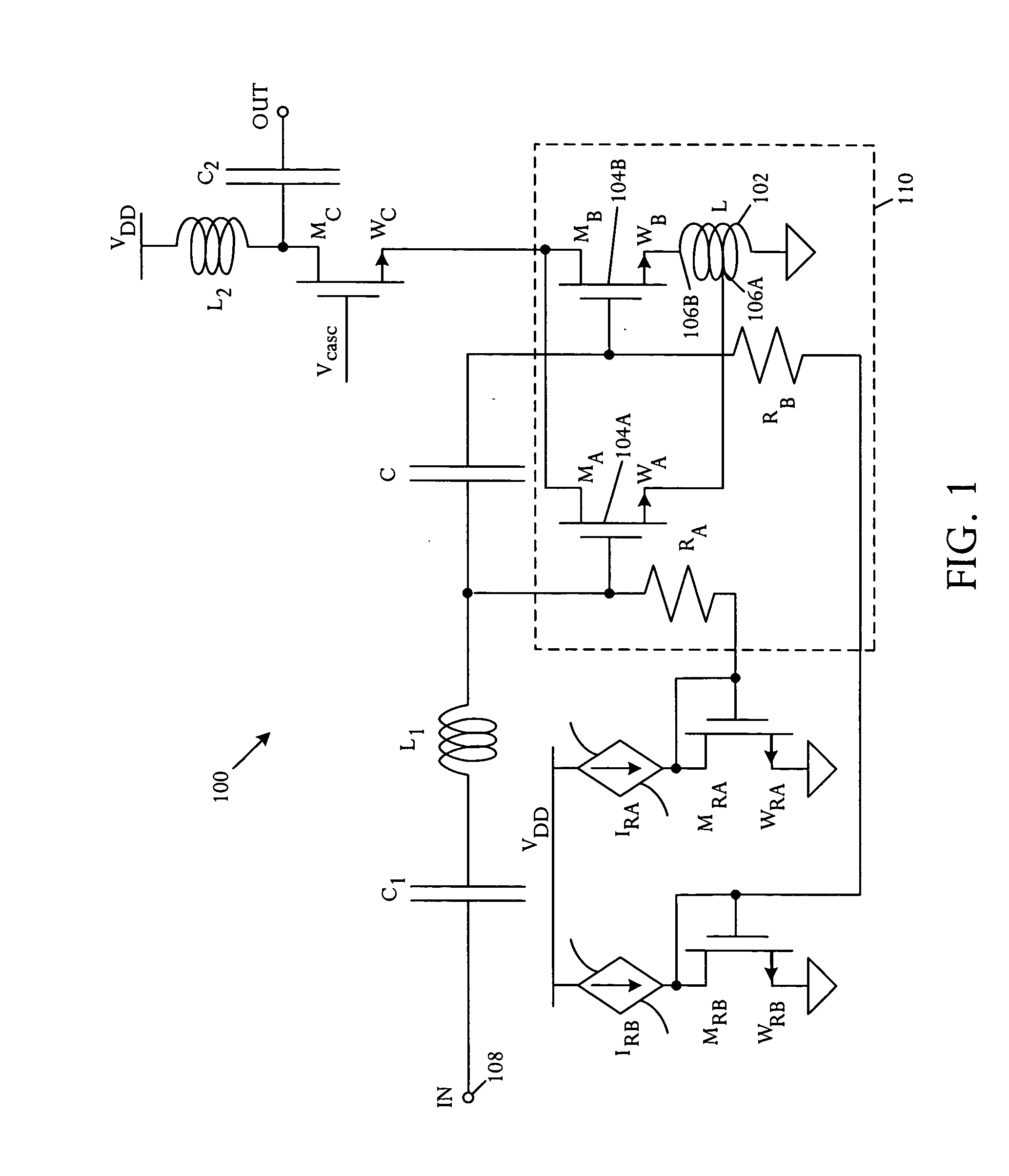
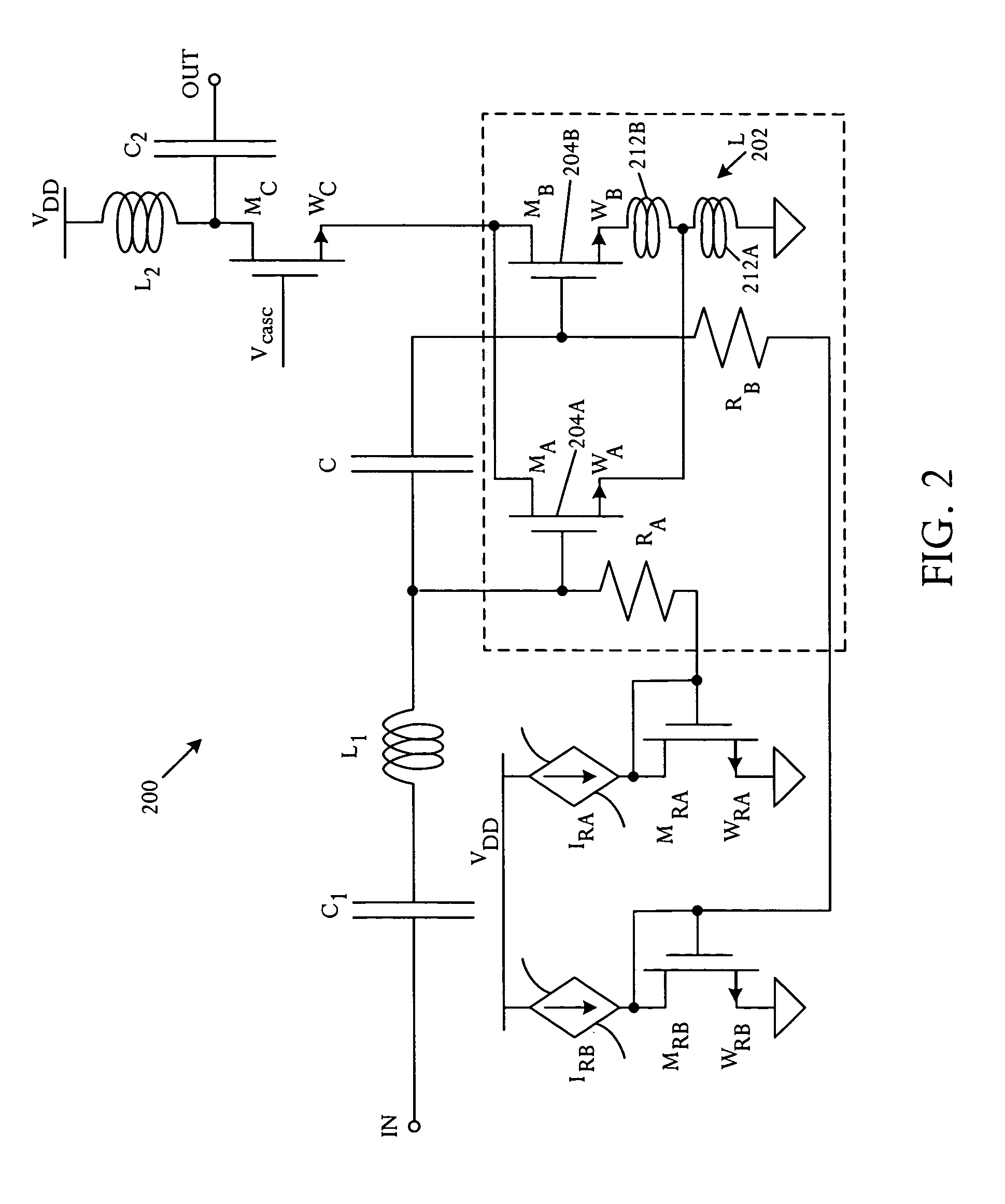
Cascode Amplifier Bias Circuits
ActiveUS20180083578A1Amplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesLow noiseAudio power amplifier
Bias circuits and methods for silicon-based amplifier architectures that are tolerant of supply and bias voltage variations, bias current variations, and transistor stack height, and compensate for poor output resistance characteristics. Embodiments include power amplifiers and low-noise amplifiers that utilize a cascode reference circuit to bias the final stages of a cascode amplifier under the control of a closed loop bias control circuit. The closed loop bias control circuit ensures that the current in the cascode reference circuit is approximately equal to a selected multiple of a known current value by adjusting the gate bias voltage to the final stage of the cascode amplifier. The final current through the cascode amplifier is a multiple of the current in the cascode reference circuit, based on a device scaling factor representing the relative sizes of the transistor devices in the cascode amplifier and in the cascode reference circuit.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
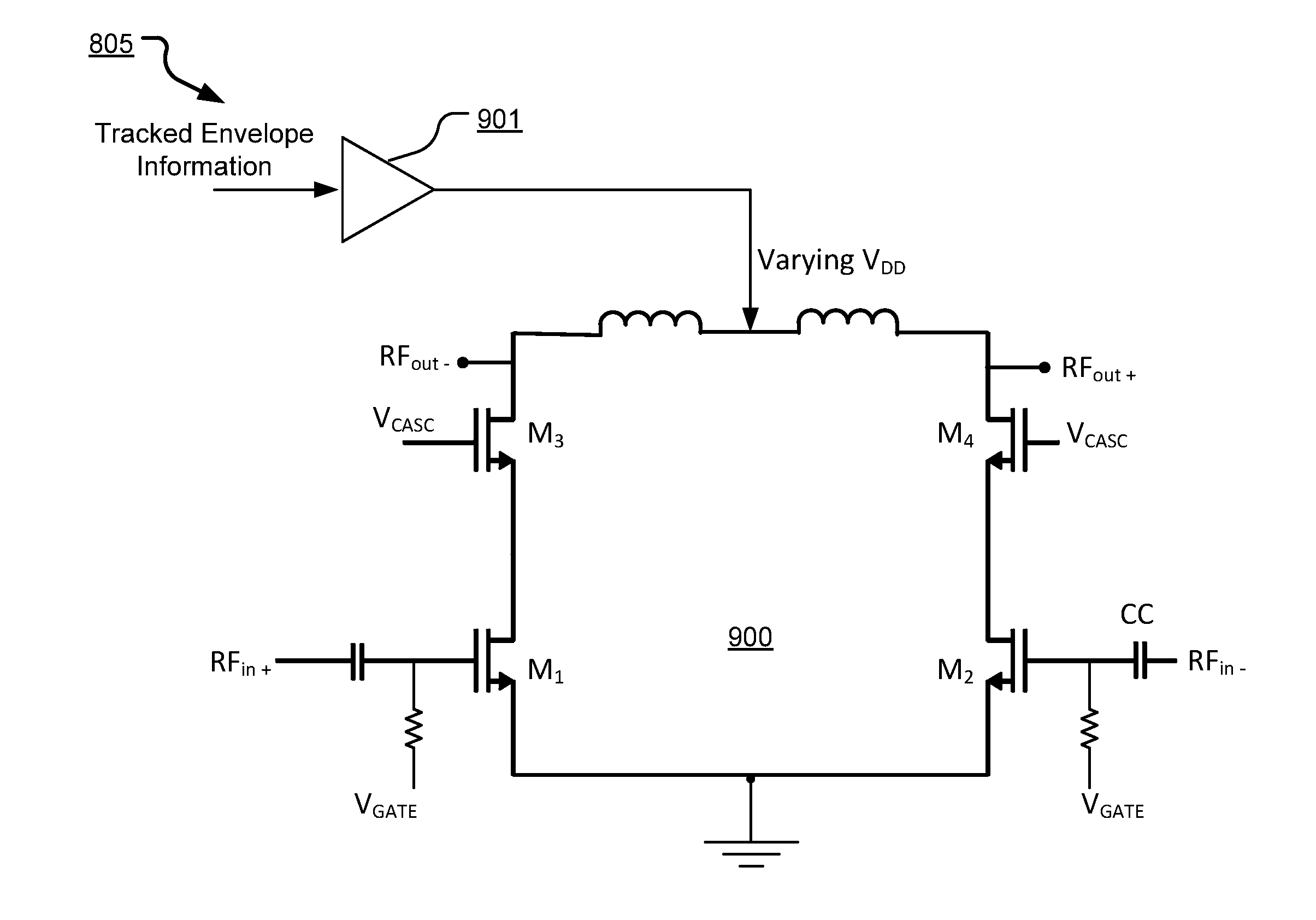
Supply tracking
ActiveUS20130285750A1Amplifier detailsAmplifiers with semiconductor devices onlyAudio power amplifierCascode
A power amplifier includes generation, tracking and usage of an envelope of an input RF signal. To improve upon the efficiency of the power amplifier, various configurations include using the tracked envelope, for example, an OFDM signal, to improve the average efficiency. Suitable hardware / software in the form of circuitry, logic gates, and / or code functions to generate and track an envelope of an input RF signal and modulate one or more of the input supply voltage, cascode gate bias or parallel PA branches using the tracked envelope.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Field effect transistor amplifier with linearization
ActiveUS20050176399A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAudio power amplifierField-effect transistor
An amplifier comprises a source degeneration inductance and at least two field effect transistors coupled in parallel and having mutually different gate biasing. Source connections of the field effect transistors are coupled along different positions of the source degeneration inductance.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Radio-frequency switch circuit and semiconductor device
InactiveUS7391282B2Improve performanceIncrease in sizeElectronic switchingTransmissionHigh resistanceEngineering
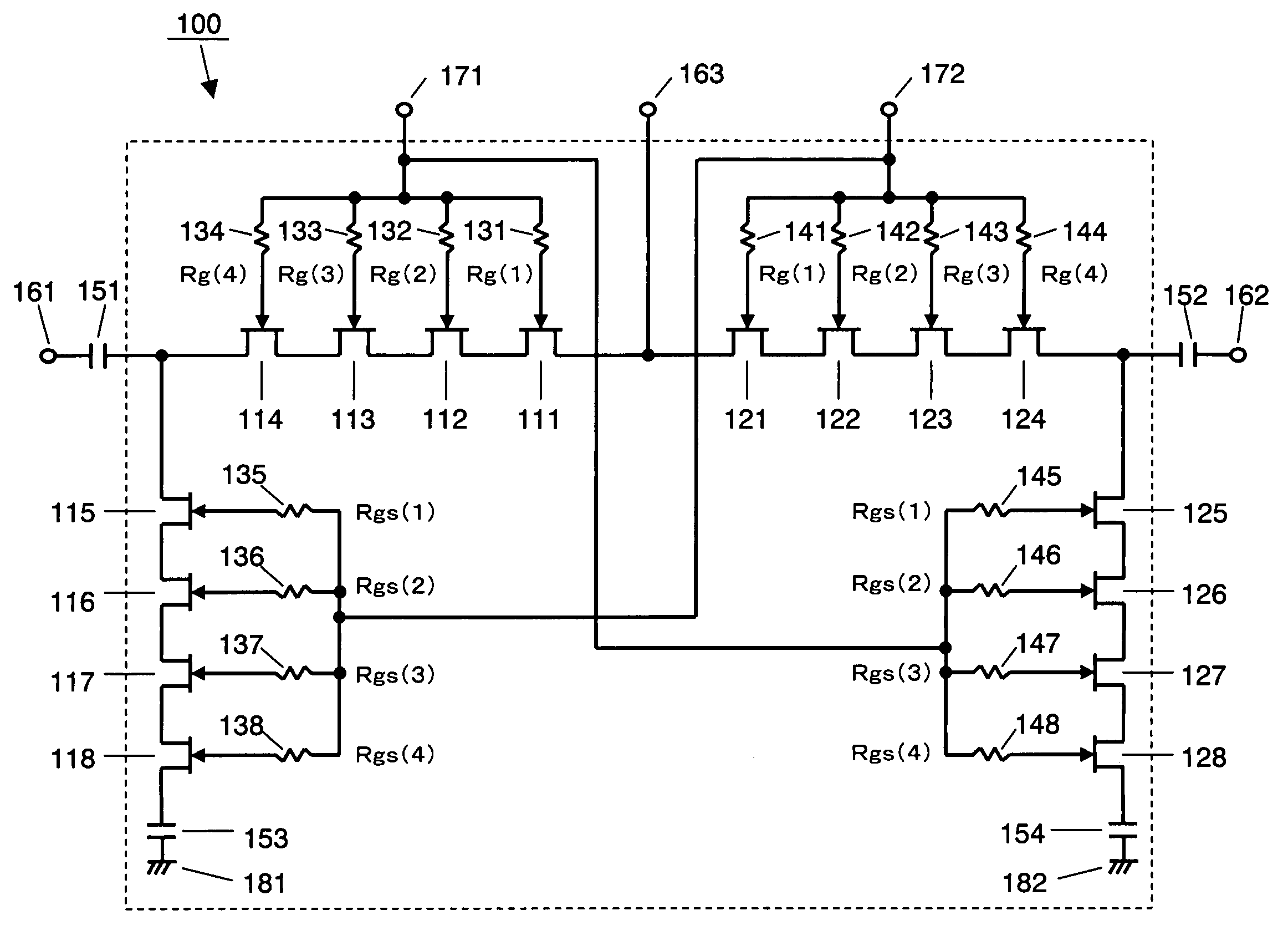
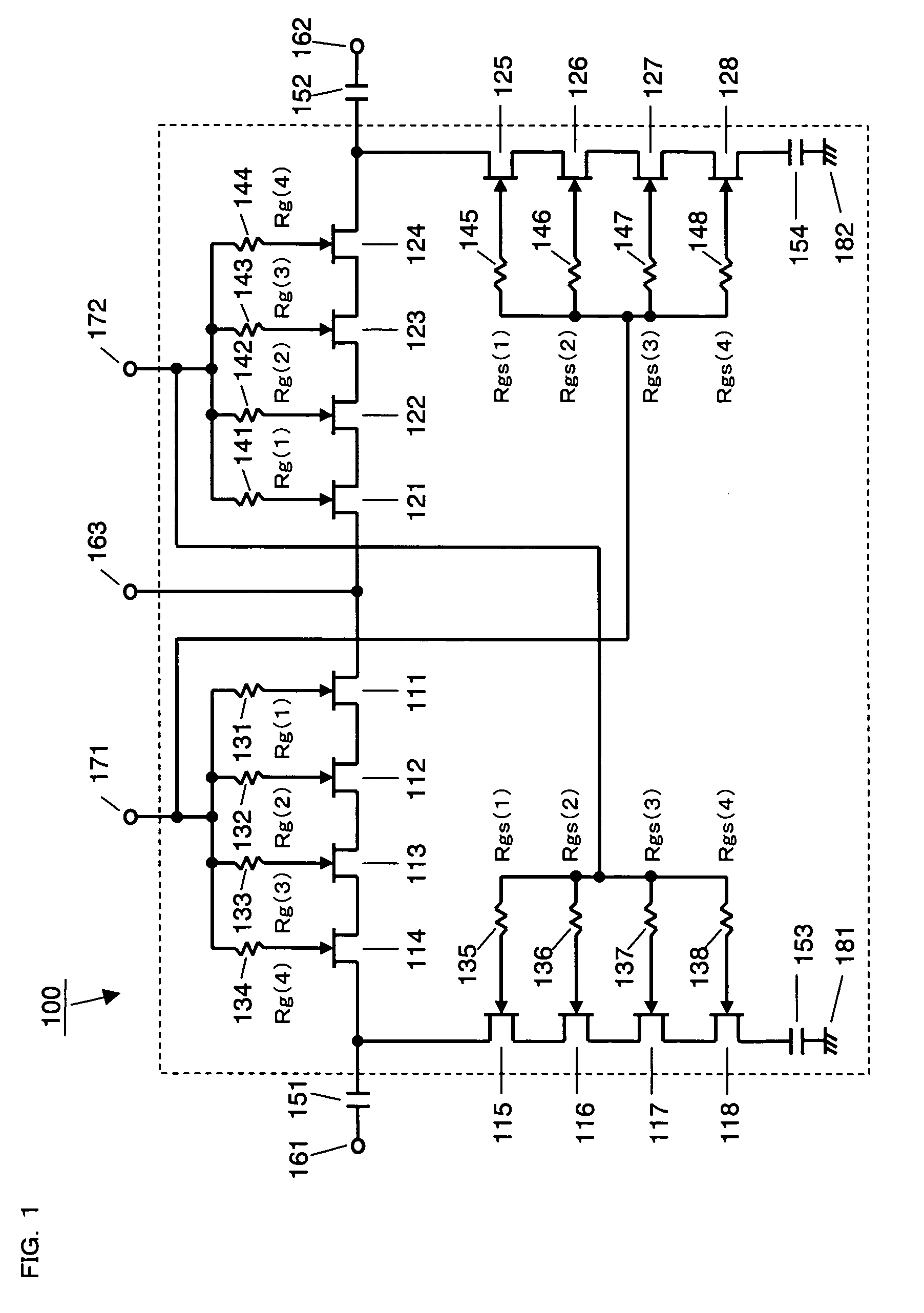
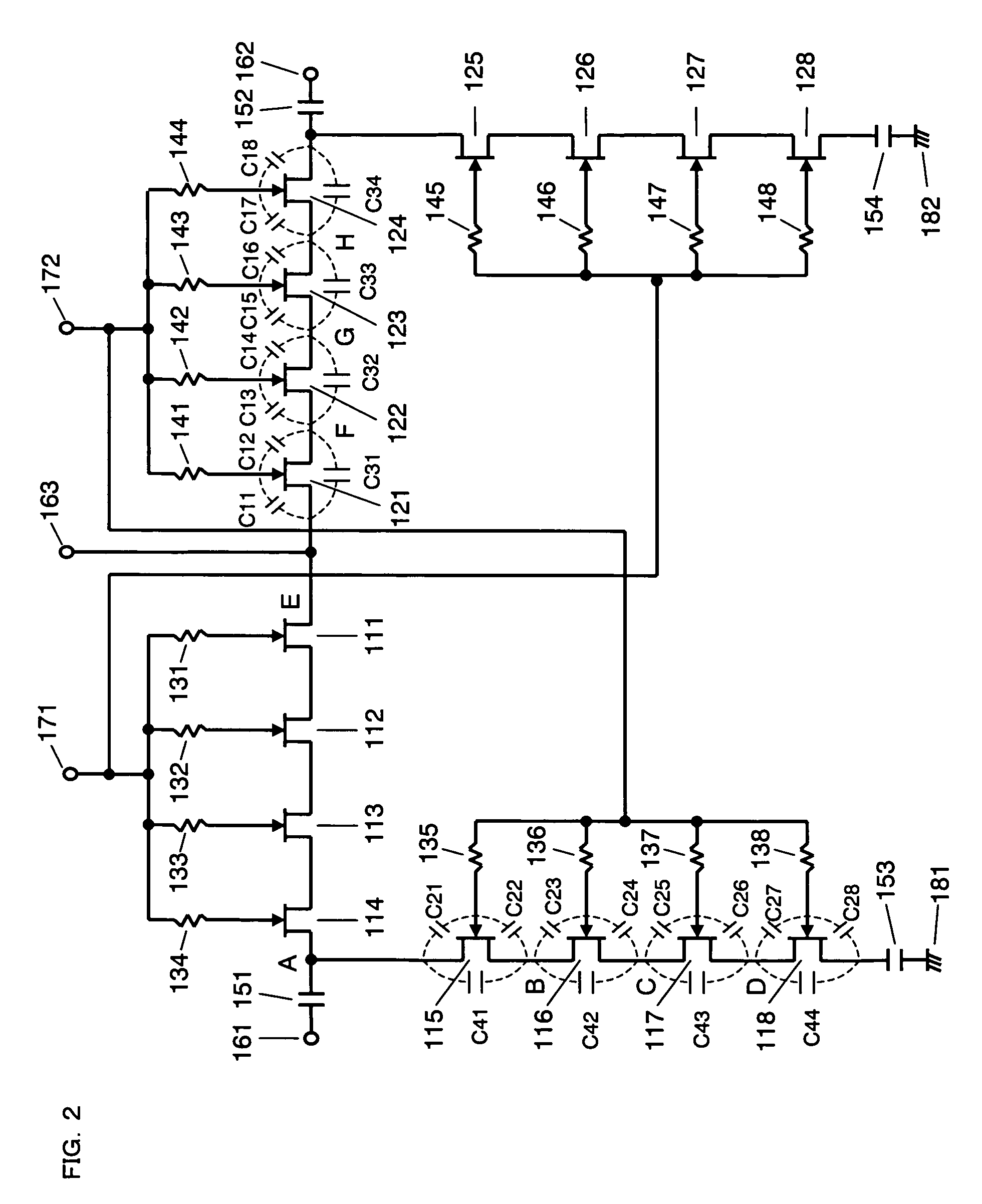
Switch sections composed of a plurality of FETs 111 to 118 and 121 to 128 connected in series are provided between input / output terminals 161 and 162 and ground terminals 181 and 182, and between the input / output terminals 161 to 163. A plurality of gate bias resistors 131 to 138, 141 to 148 are also provided. One terminal of each gate bias resistor is connected to a gate electrode of a corresponding one of the FETs 111 to 118 and 121 to 128, while a control voltage 171 and 172 for switching an ON state and an OFF state of the switch section is applied to the other terminal. Among the FETs included in each switch section, concerning the FETs 114, 115, 124, and 125 to which signal power is applied when the switch section is in the OFF state, the gate bias resistors 134, 135, 144, and 145 connected to the gate electrodes are set to have a highest resistance value.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
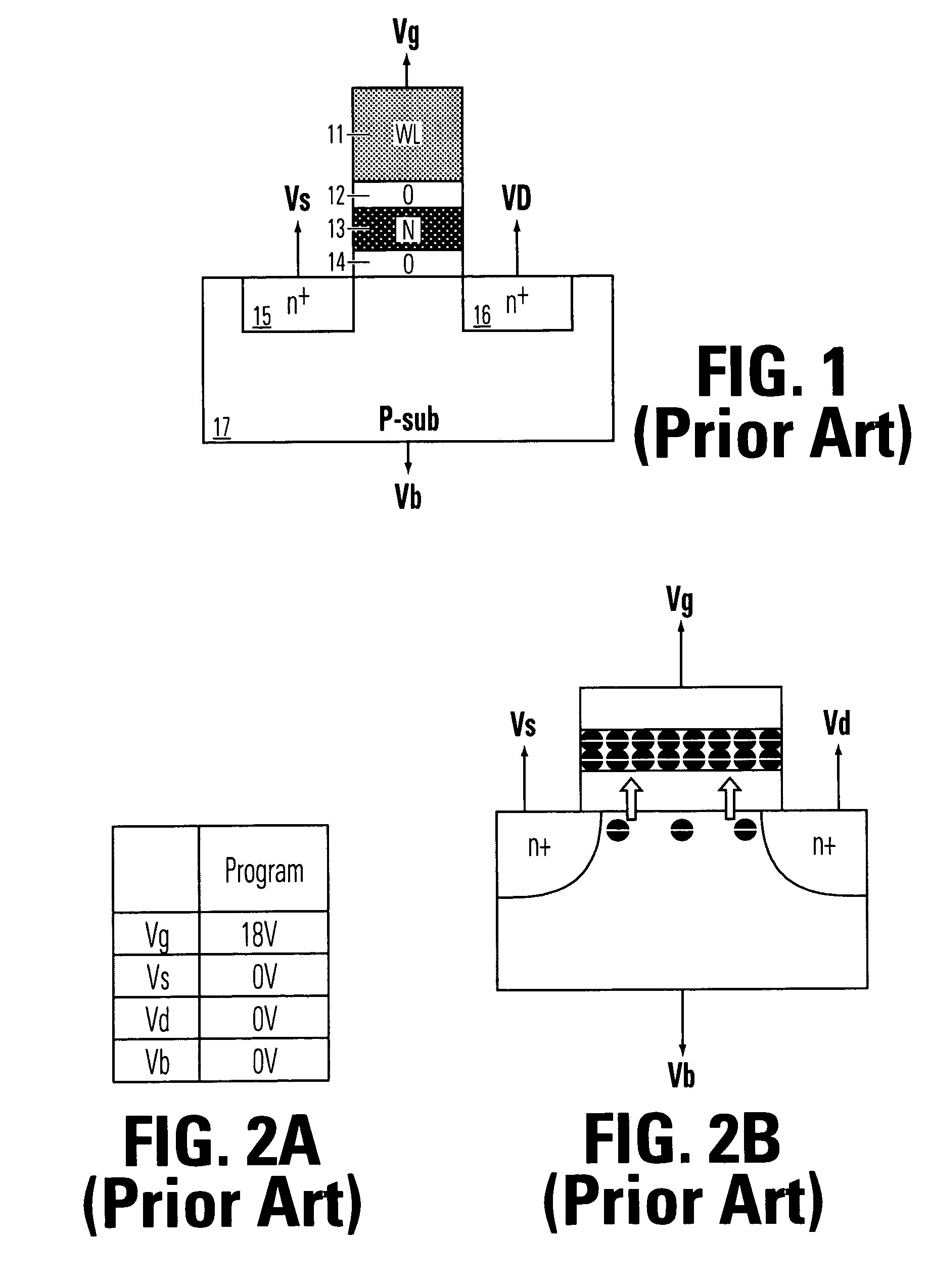
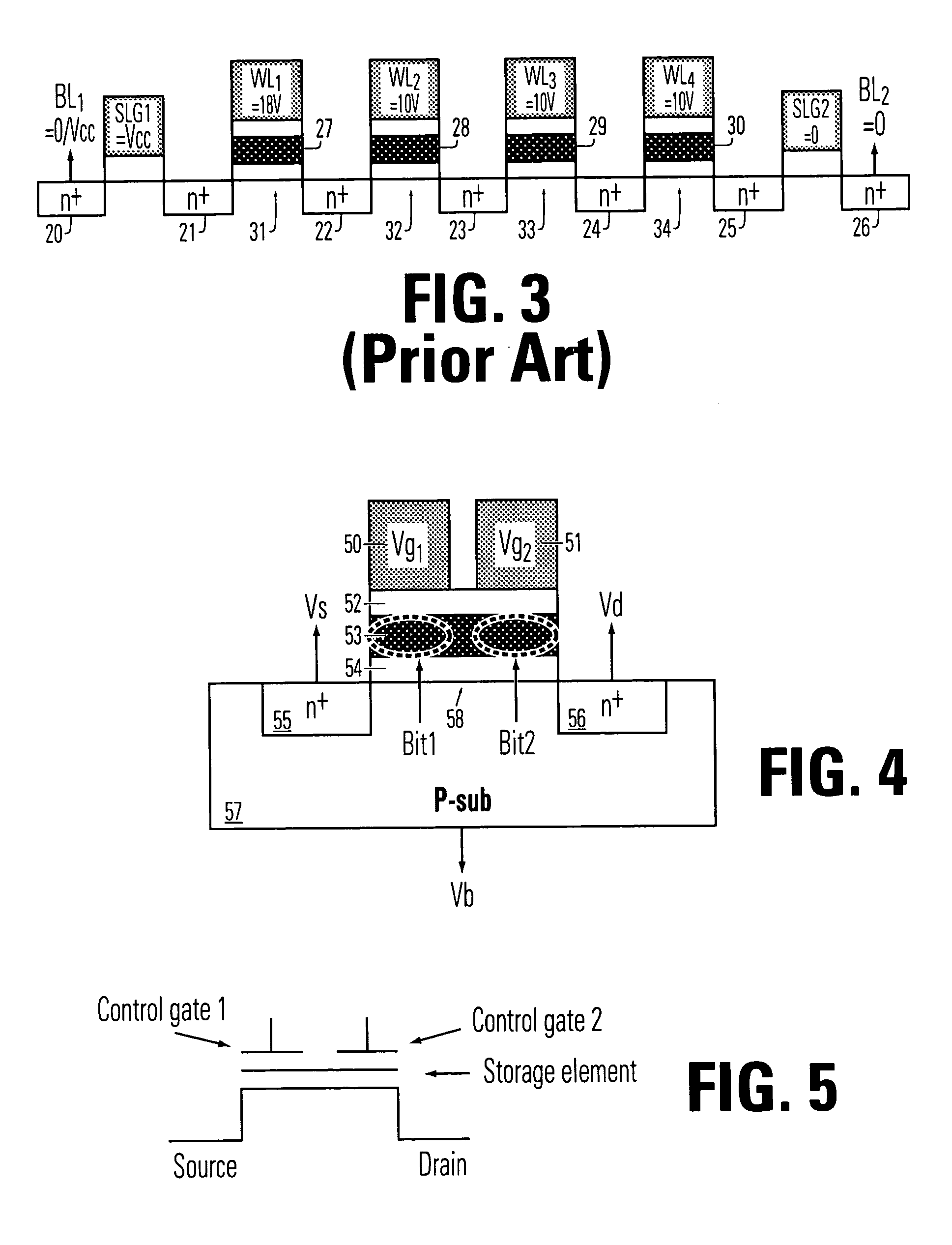
Charge trapping non-volatile memory with two trapping locations per gate, and method for operating same
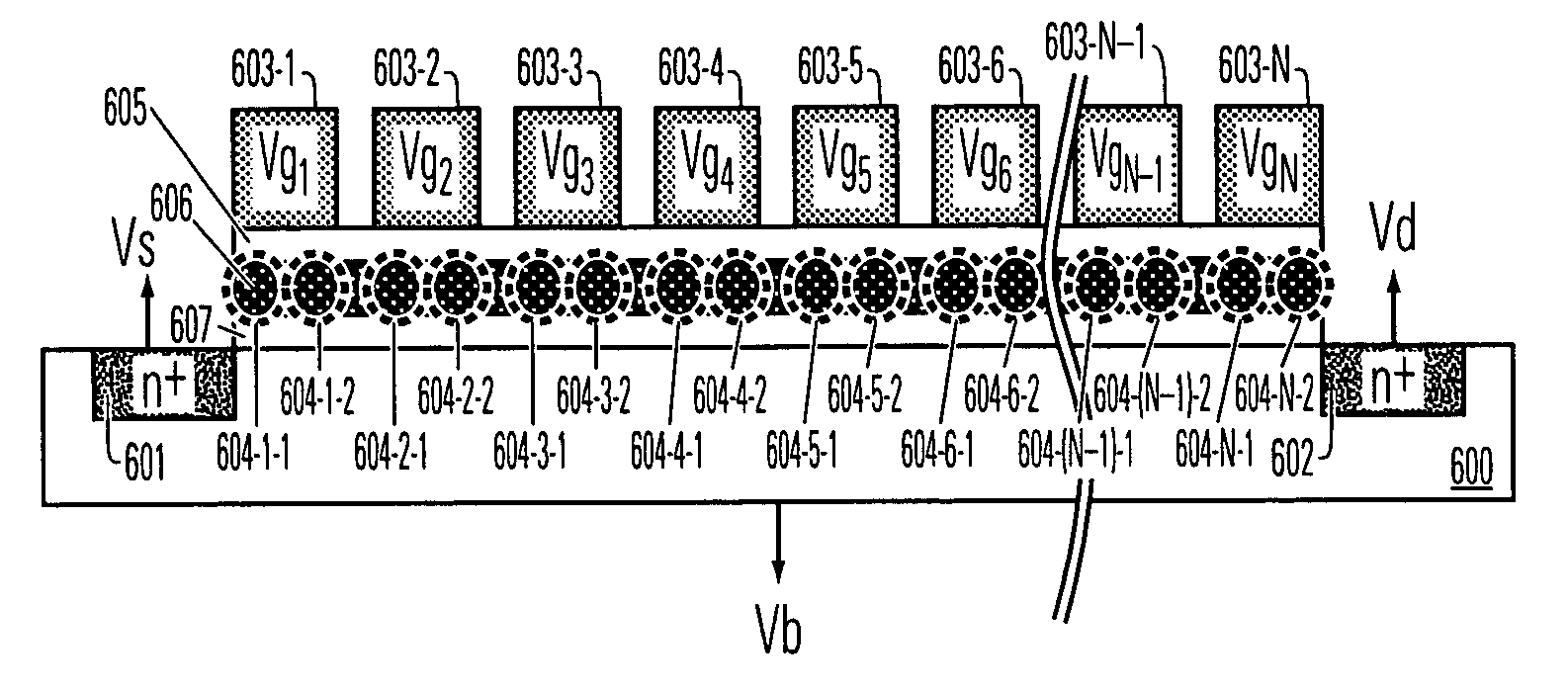
A multiple-gate memory cell comprises a semiconductor body and a plurality of gates arranged in series on the semiconductor body. A charge storage structure on the semiconductor body includes two charge trapping locations beneath each of all or some of the gates in the plurality of gates. Circuitry to conduct source and drain bias voltages to the semiconductor body near a first gate and a last gate in the series, and circuitry to conduct gate bias voltages to the plurality of gates are included. The multiple-gate memory cell includes a continuous, multiple-gate channel region beneath the plurality of gates in the series, with charge storage locations between some or all of the gates.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
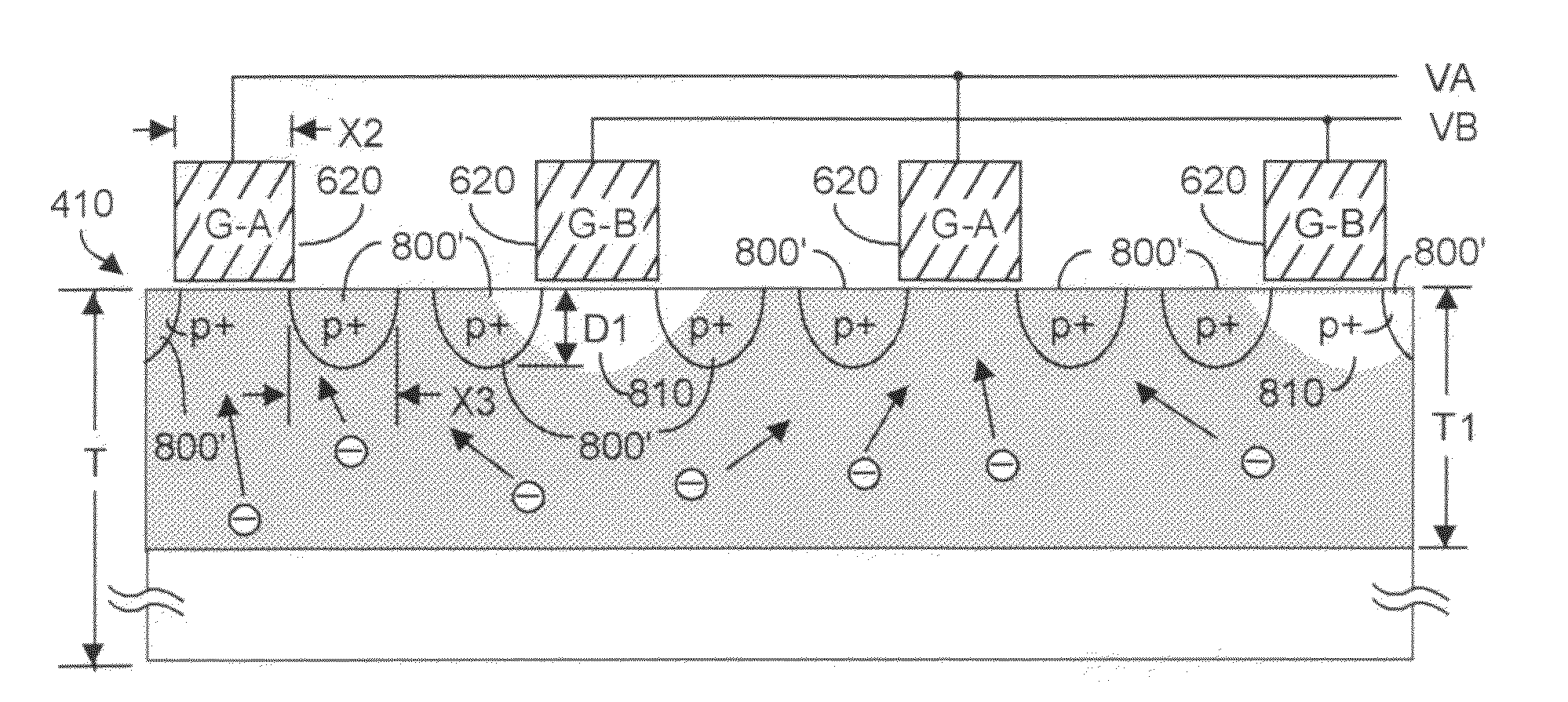
CMOS three-dimensional image sensor detectors having reduced inter-gate capacitance, and enhanced modulation contrast
A CMOS detector with pairs of interdigitated elongated finger-like collection gates includes p+ implanted regions that create charge barrier regions that can intentionally be overcome. These regions steer charge to a desired collection gate pair for collection. The p+ implanted regions may be formed before and / or after formation of the collection gates. These regions form charge barrier regions when an associated collection gate is biased low. The barriers are overcome when an associated collection gate is high. These barrier regions steer substantially all charge to collection gates that are biased high, enhancing modulation contrast. Advantageously, the resultant structure has reduced power requirements in that inter-gate capacitance is reduced in that inter-gate spacing can be increased over prior art gate spacing and lower swing voltages may be used. Also higher modulation contrast is achieved in that the charge collection area of the low gate(s) is significantly reduced.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
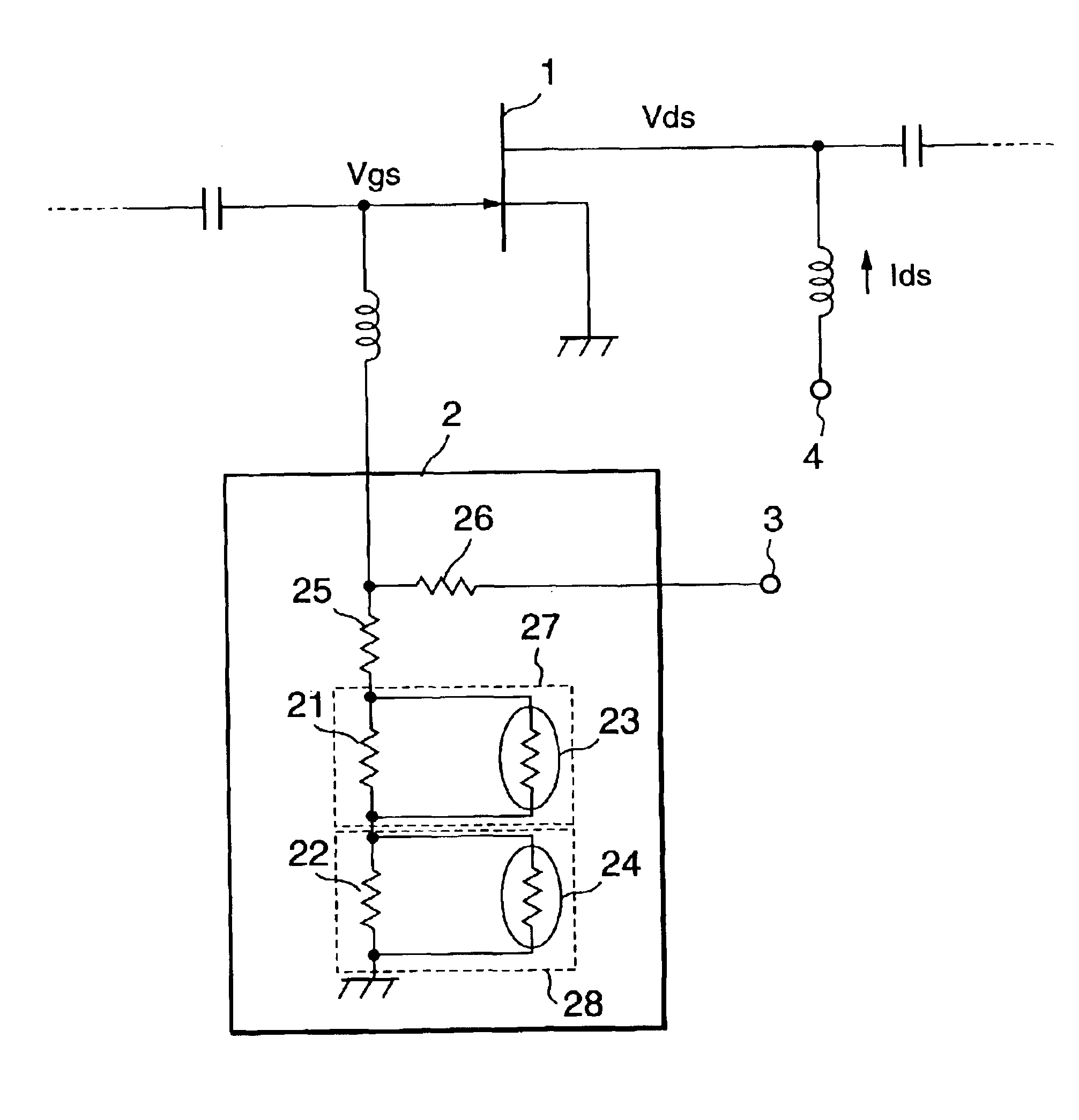
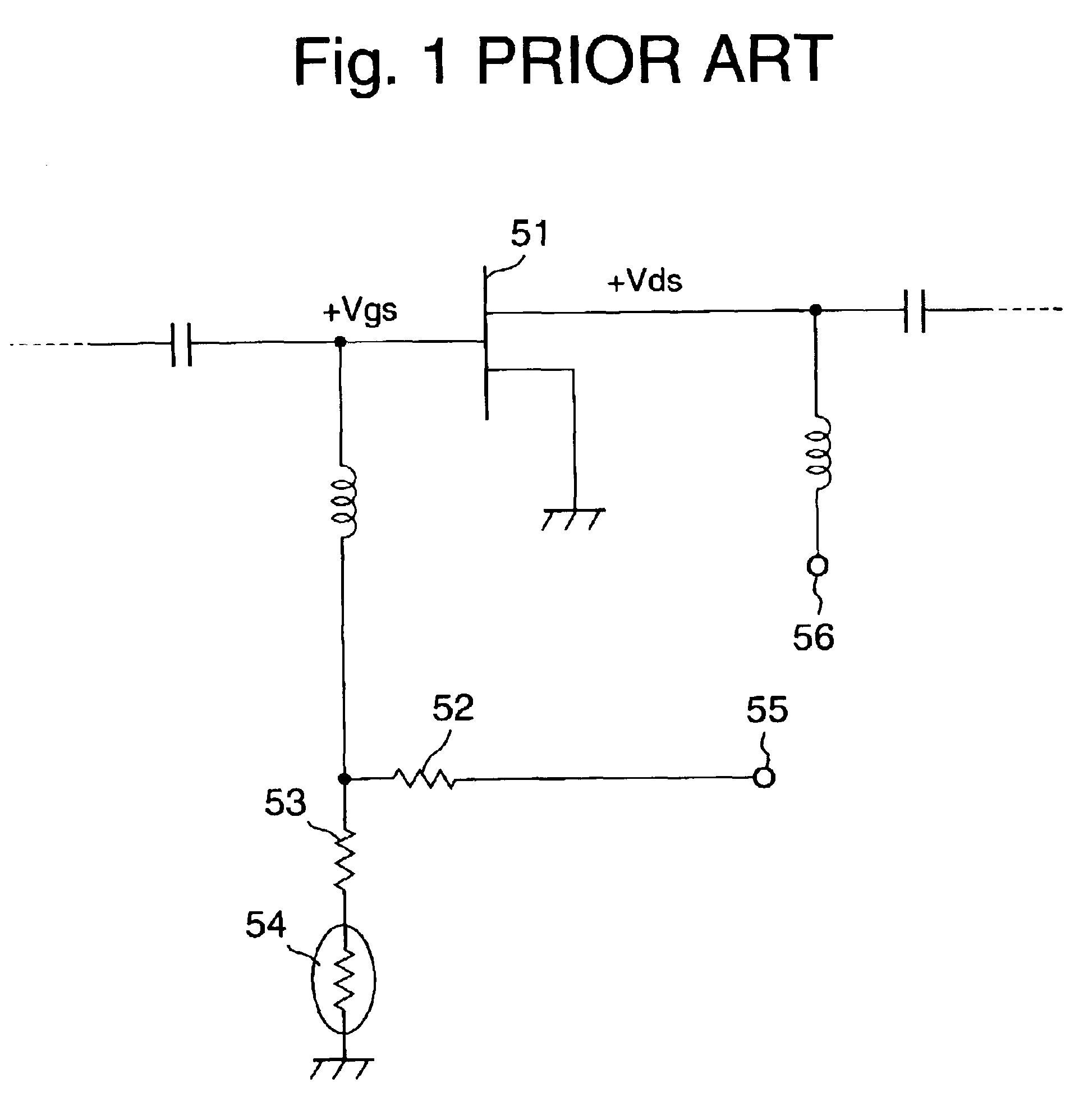
FET amplifier with temperature-compensating circuit
InactiveUS6906590B2Minimizing worseningMinimizing the worsening of the distortion-susceptibilityHigh frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationFET amplifierLDMOS
A FET amplifier which minimizes the worsening of the distortion-susceptibility due to variations in the ambient temperature of operation is to be provided. An LDMOS FET 1, whose source terminal is grounded and to which are applied a gate voltage Vgs from a gate bias terminal 3 via a temperature-compensating circuit 2 and a choke coil and a drain voltage Vds from a drain bias terminal 4 via a choke coil operates as a source-grounded type amplifier. In the temperature compensating circuit 2, the resistances of fixed resistance elements 21 and 22 connected in parallel are set to be the same or have the same number of digits, and those of thermosensitive resistance elements (thermistors) 23 and 24 are set to be a combination of a value greater by one digit and a value smaller by one digit than that of the fixed resistance element 21 or the fixed resistance element 22 at the standard level (+25° C.) in the ambient temperature range of operation.
Owner:NEC CORP
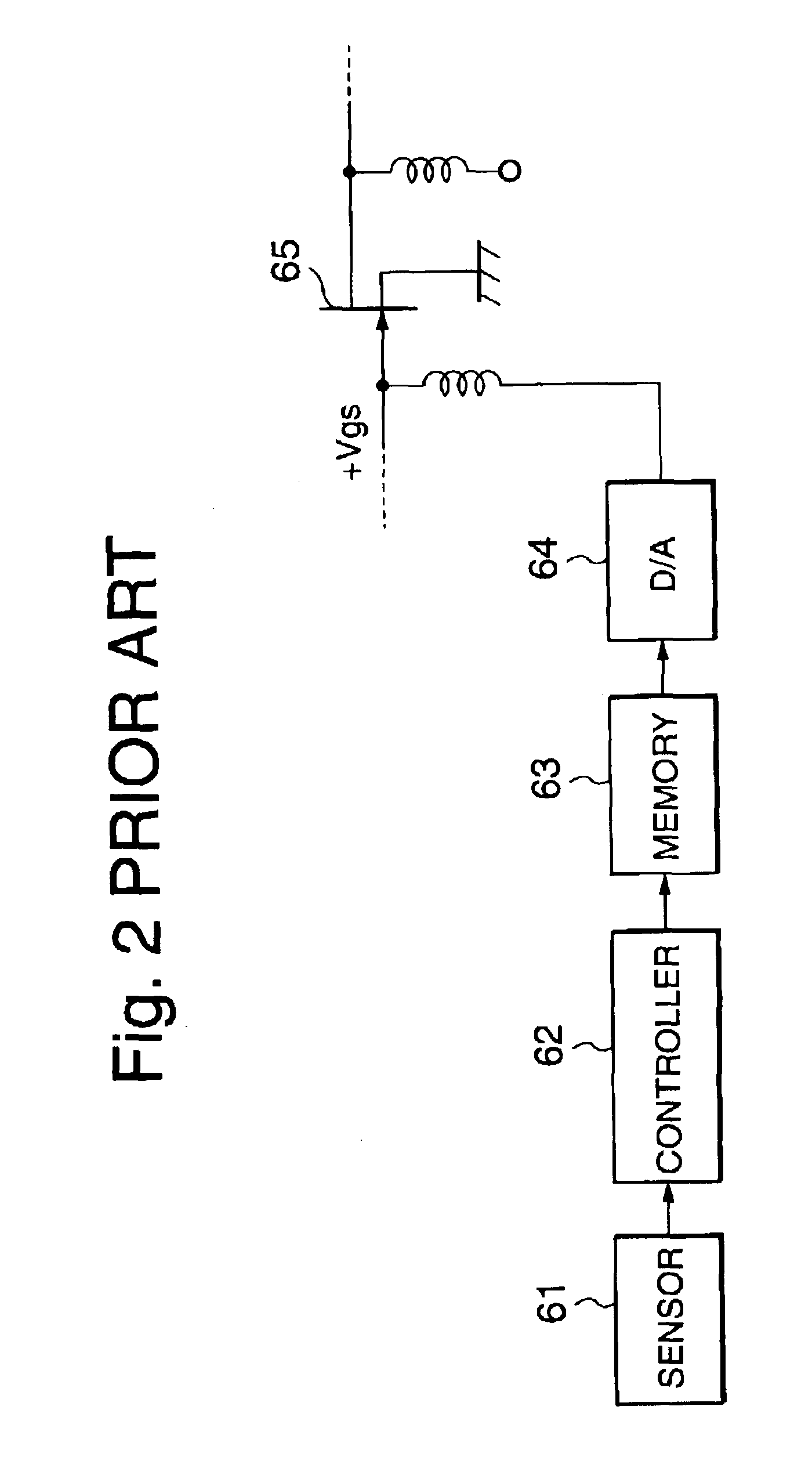
Automatic biasing and protection circuit for field effect transistor (FET) devices
ActiveUS7348854B1High power supply voltageHigh operating temperatureNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlNegative feedbackIntegrator
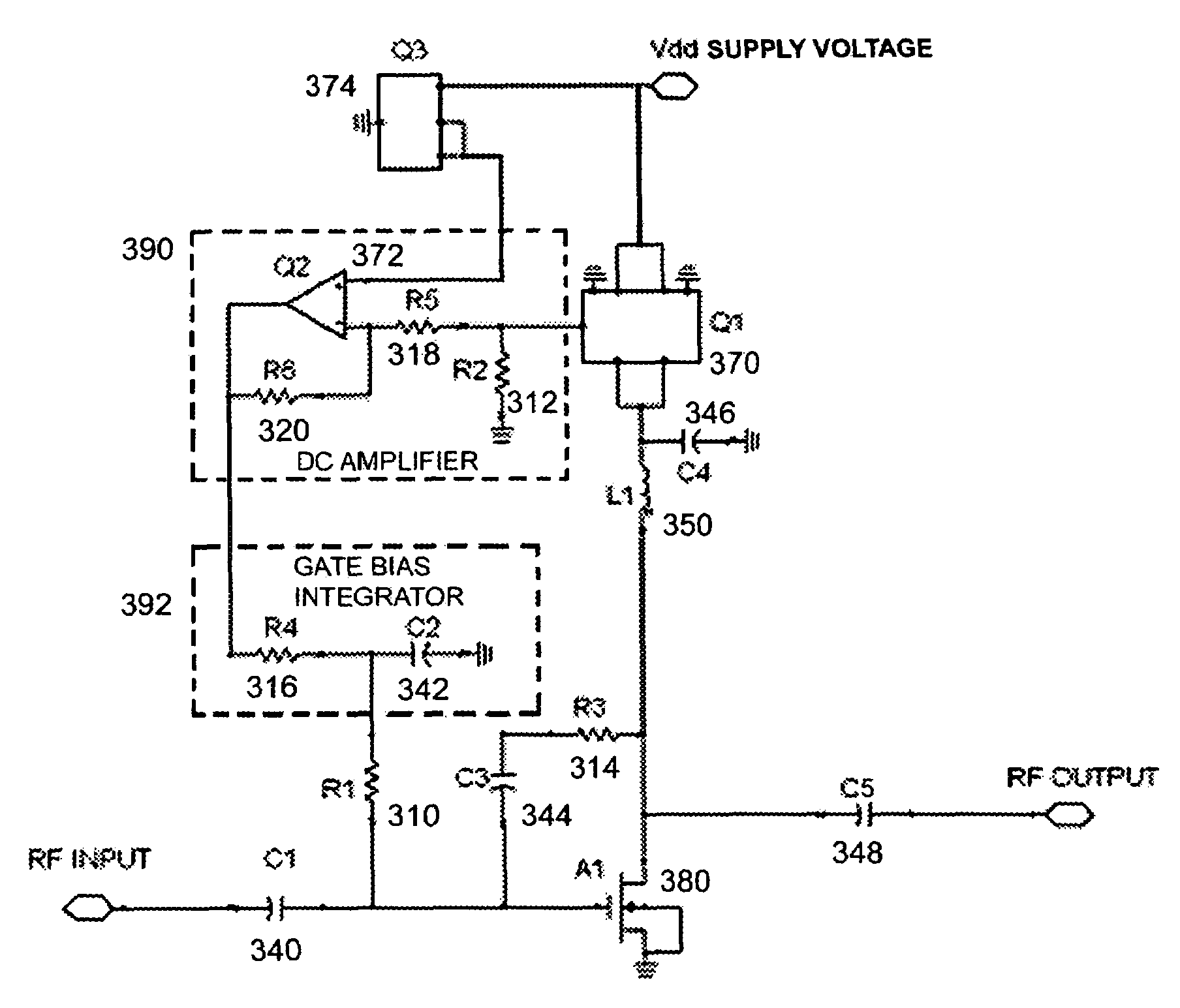
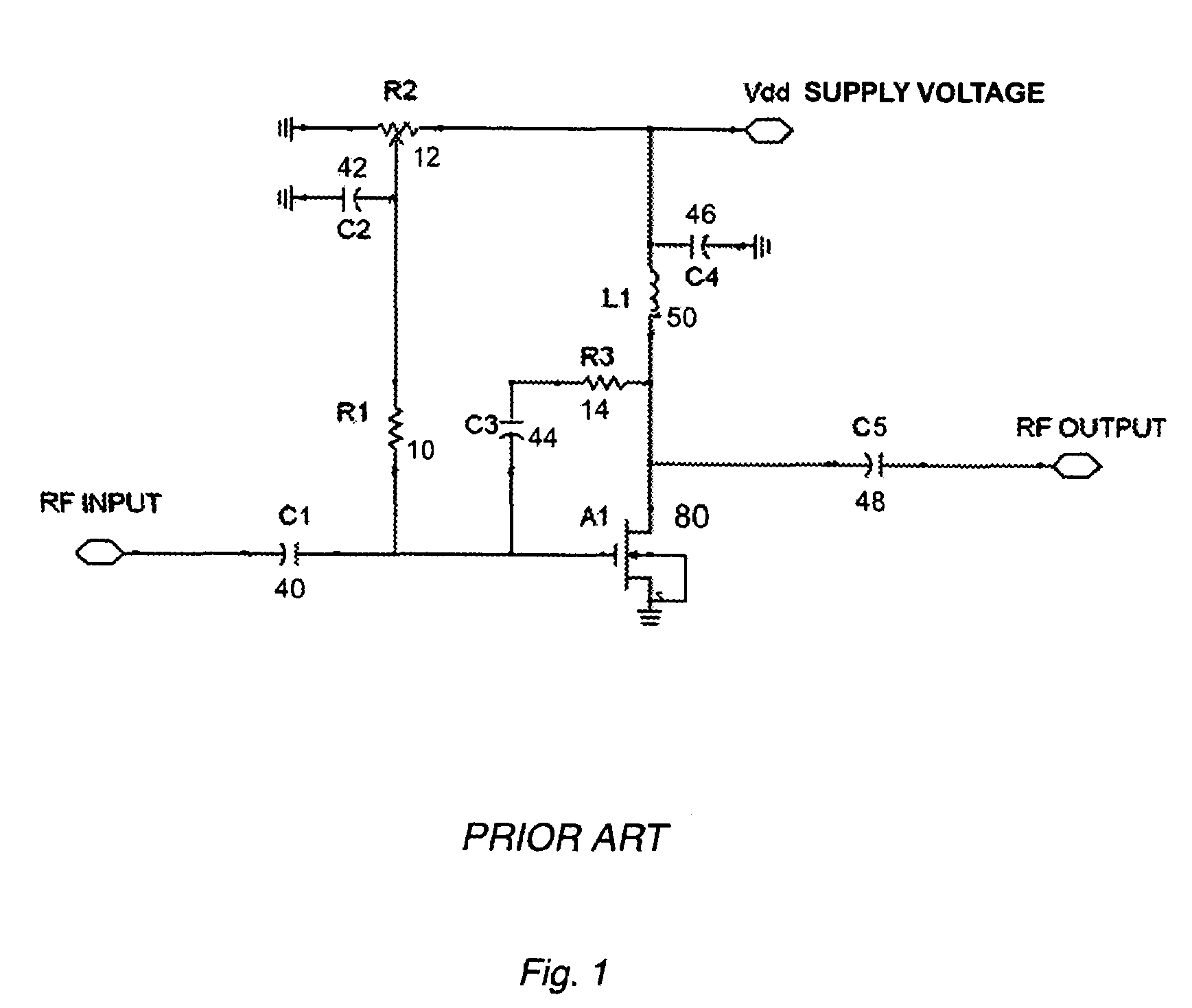
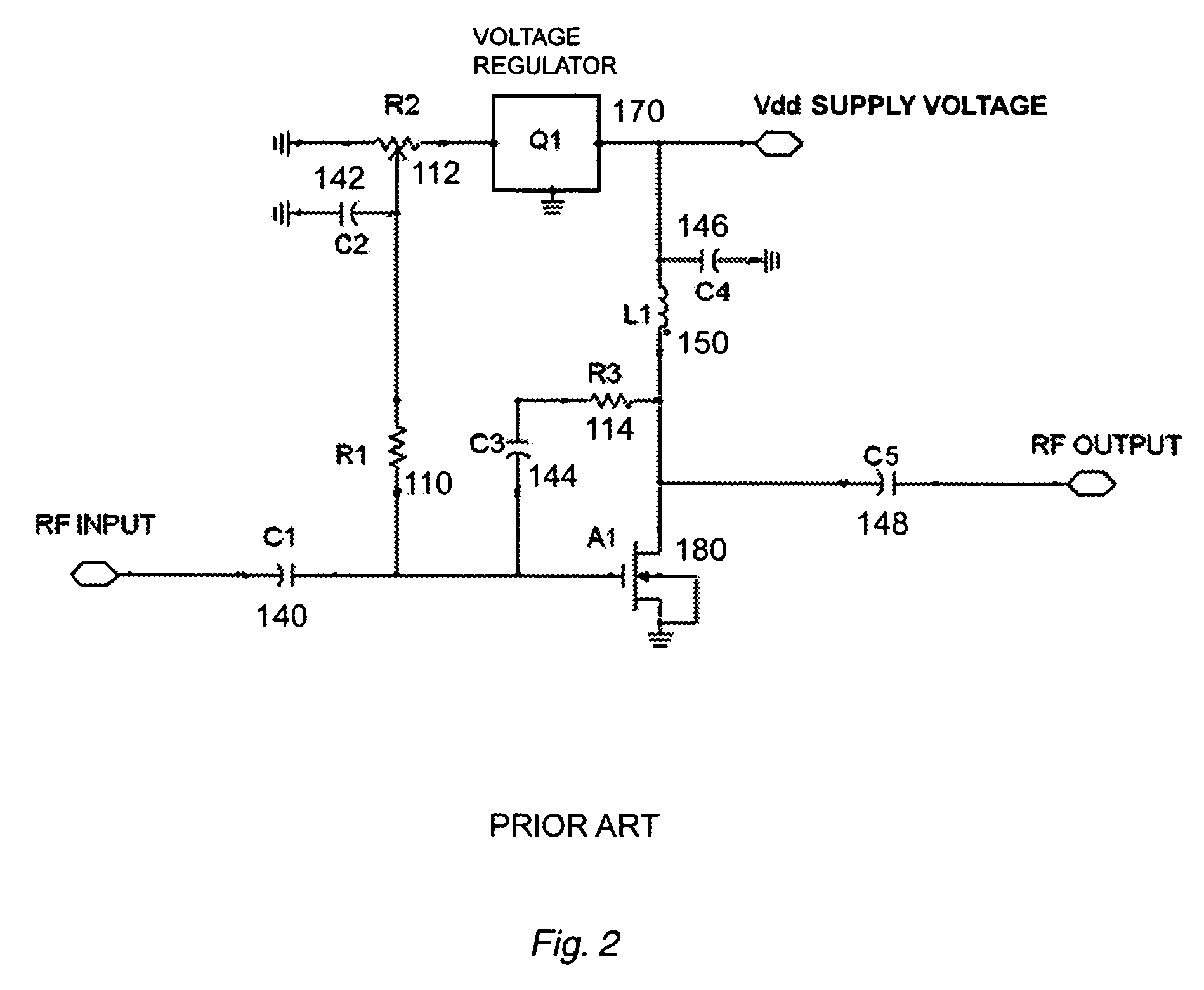
A transistor biasing circuit is shown that utilizes a negative feedback loop control circuit to set the gate bias voltage in the output transistors of a power amplifier. This control circuit has a current sensor in series with the drain of the transistor, the current sensor output in turn feeding a dc signal into a dc amplifier, and the output of the dc amplifier driving a gate bias integrator which forms a dc control loop for maintaining the bias point. The output transistor is protected from excessive temperature and / or excessive power dissipation.
Owner:SCI COMPONENTS
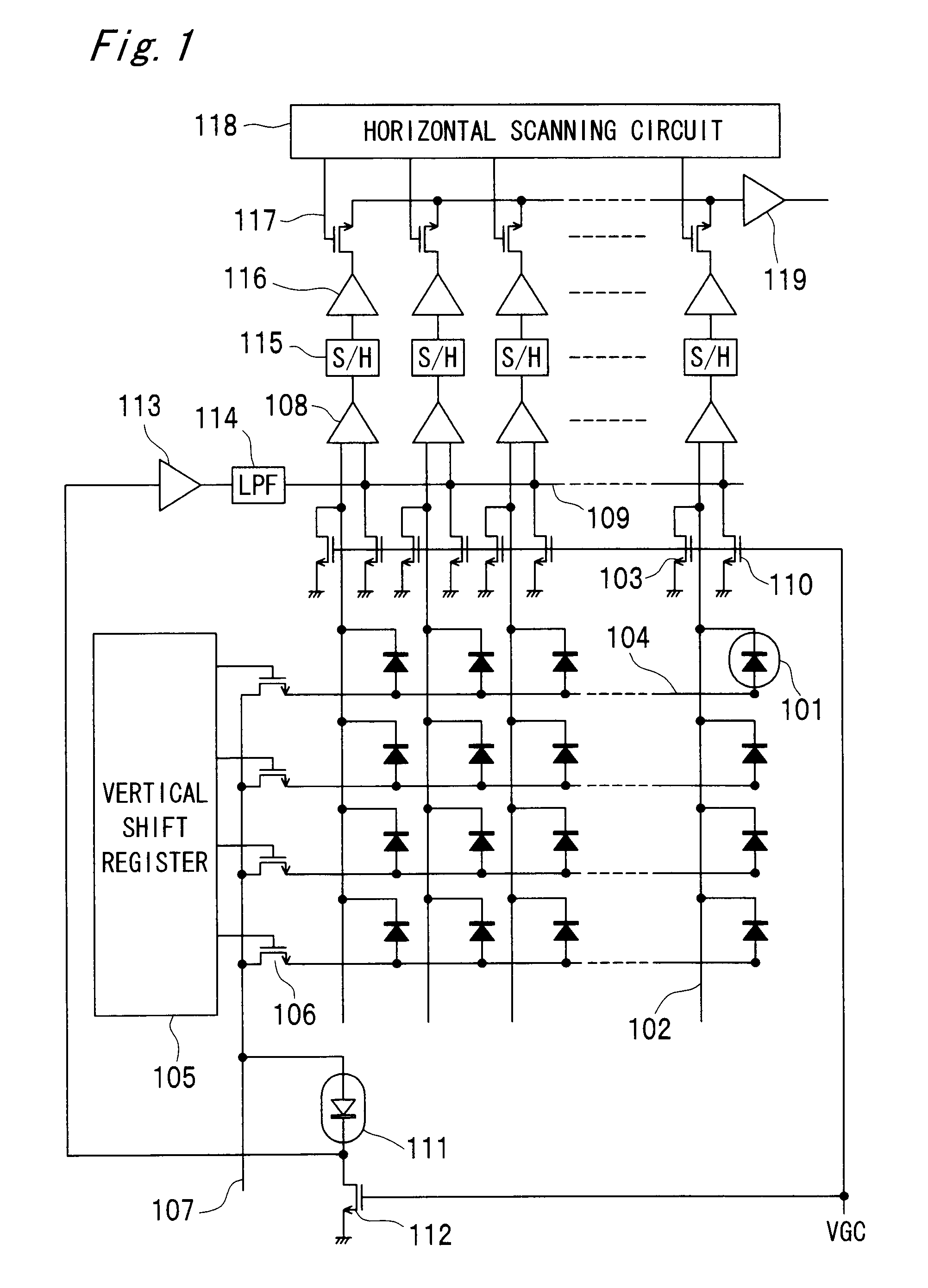
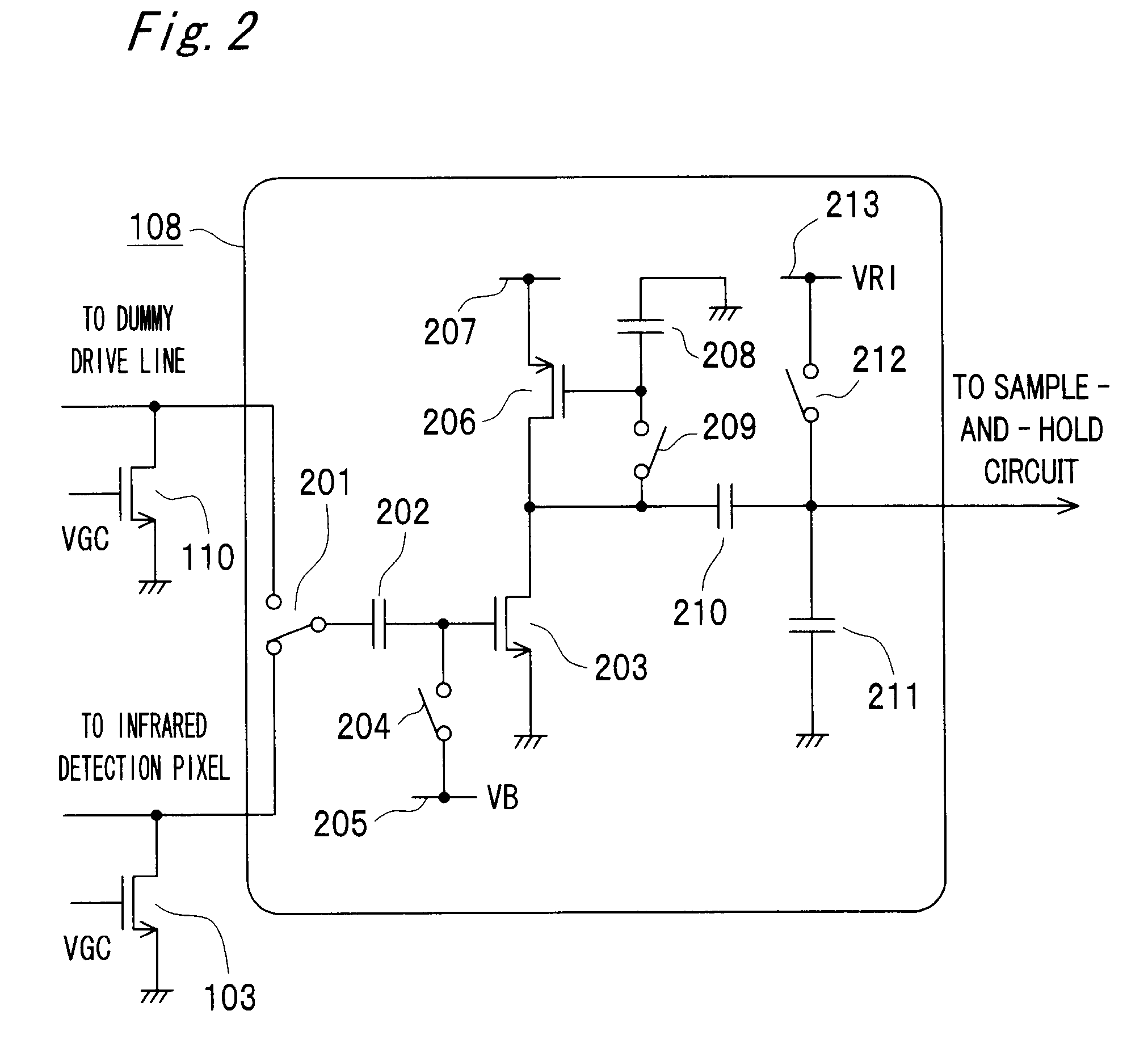
Thermal infrared solid state imaging device and infrared camera
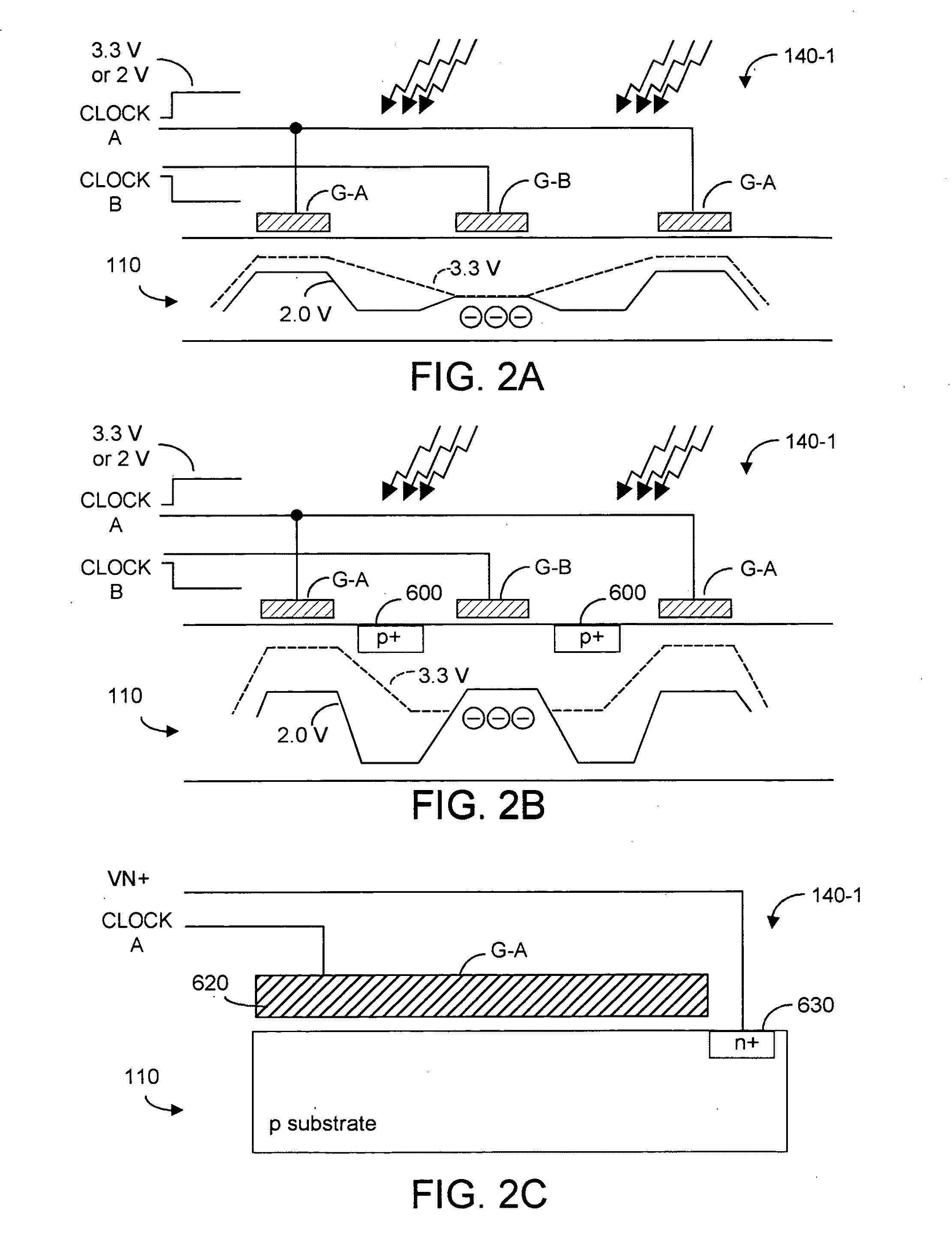
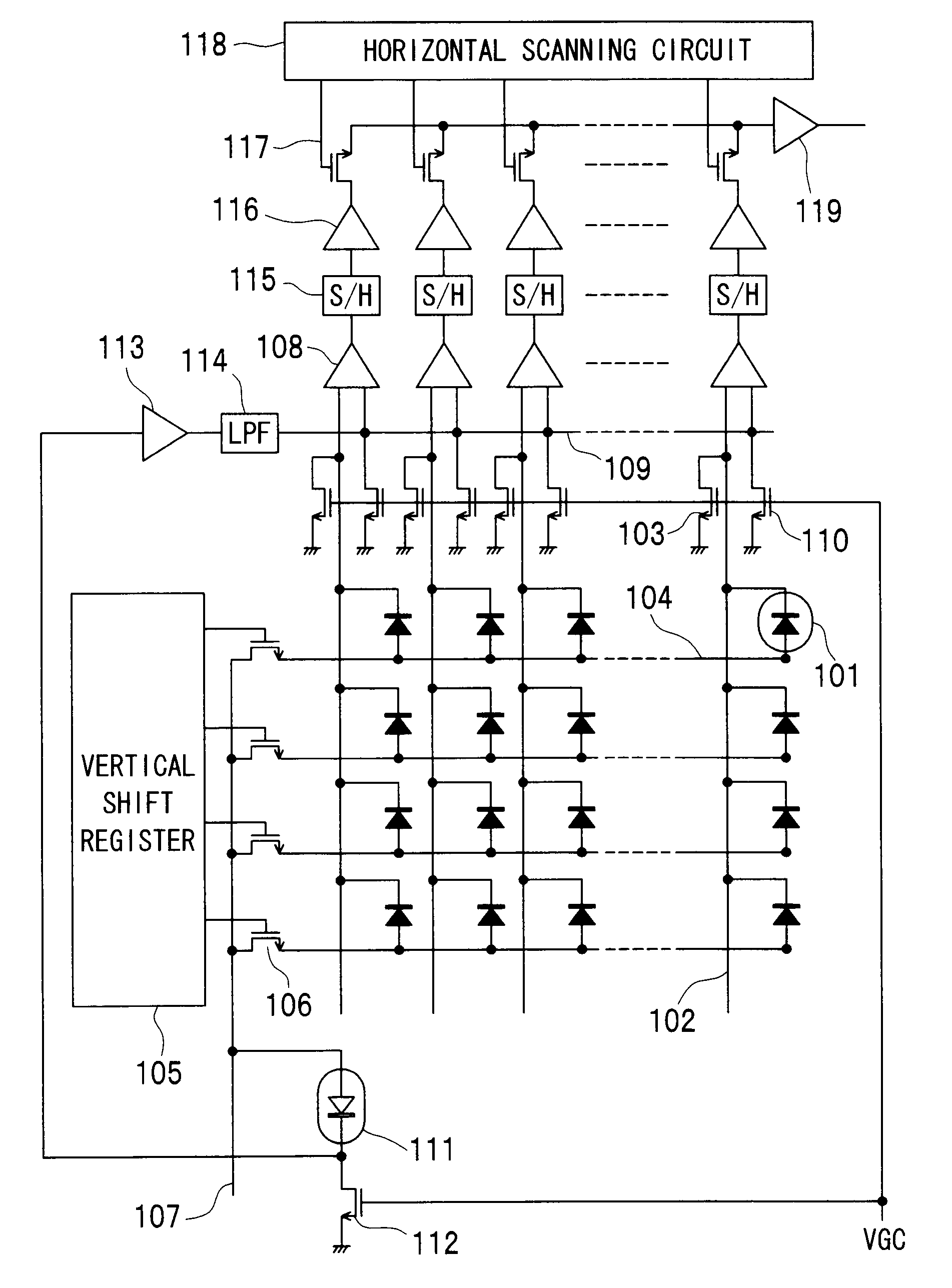
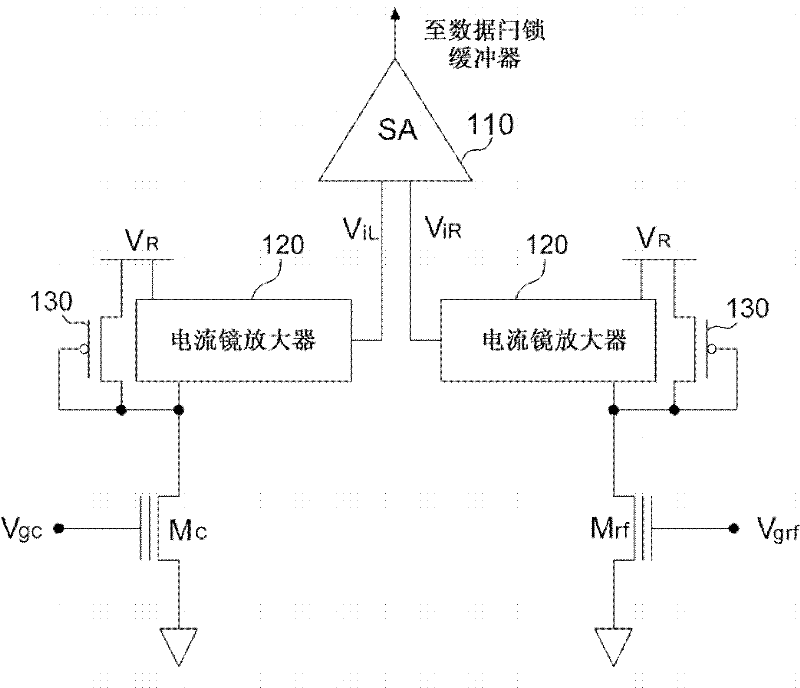
ActiveUS20080251721A1High gainReduce noiseTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringGrid bias
An infrared solid state imaging device includes a pixel area with arranged infrared detection pixels and a integration circuit for modulating output current based on the output of the pixel. The integration circuit contains an integrating transistor that modulates a current based on the difference in potential between first and second constant current devices, a integration capacitor for storing the modulated current and being reset periodically, a bias current supply transistor, a switch for connecting the drain with the gate of the bias current supply transistor, a capacitor providing AC coupling between the output of the integrating transistor and the integrating capacitor, a gate bias switch for providing the integrating transistor with a bias voltage, a switch for selecting, as input to the integrating transistor, either one of outputs from the first and second constant current devices, and a capacitor for providing AC coupling between the switch and the gate of the integrating transistor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
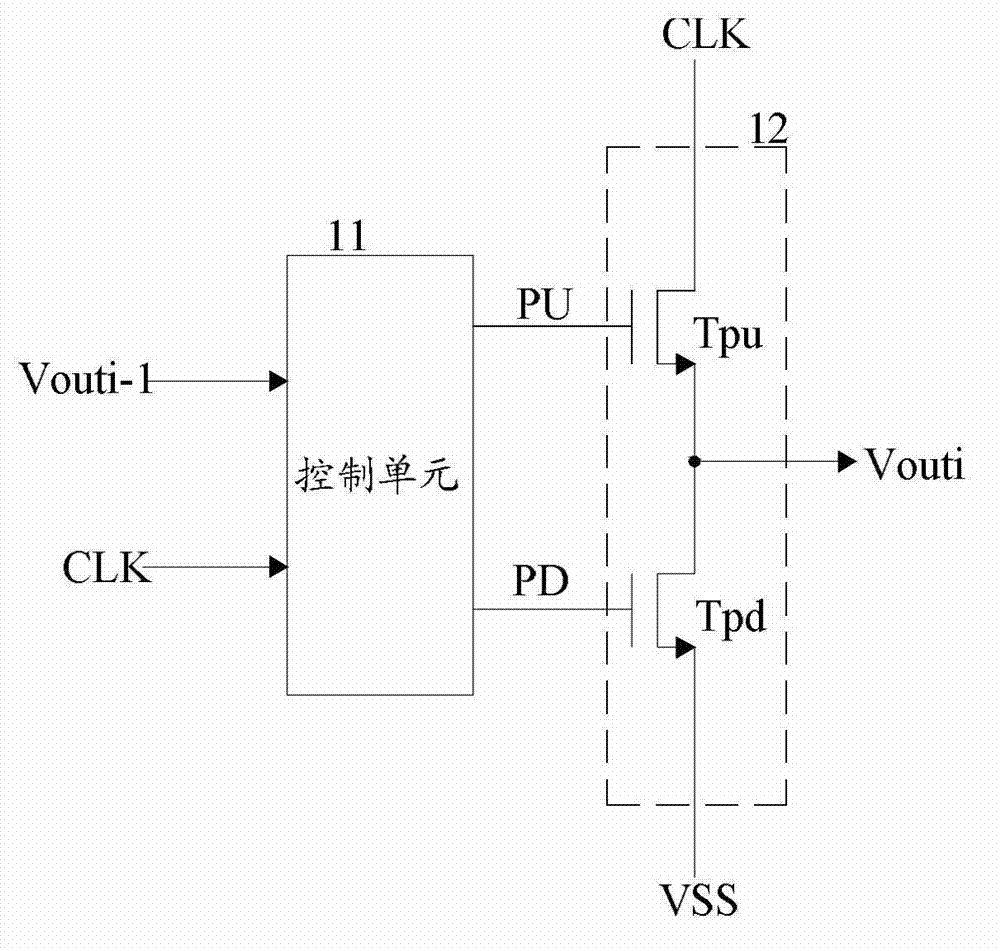
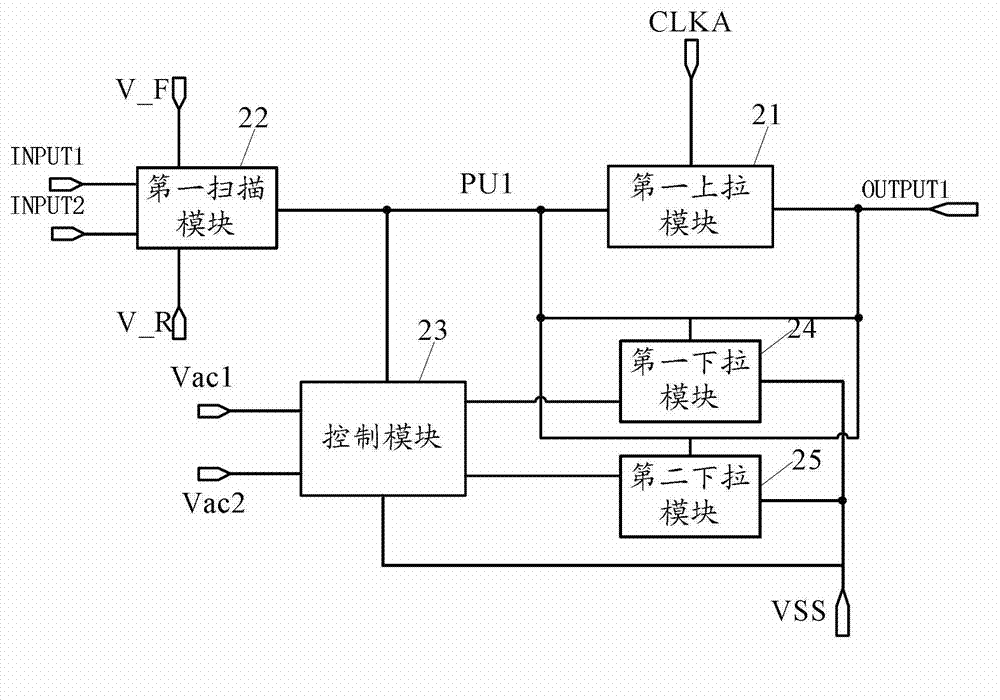
Shift register unit, grid driving circuit and display device
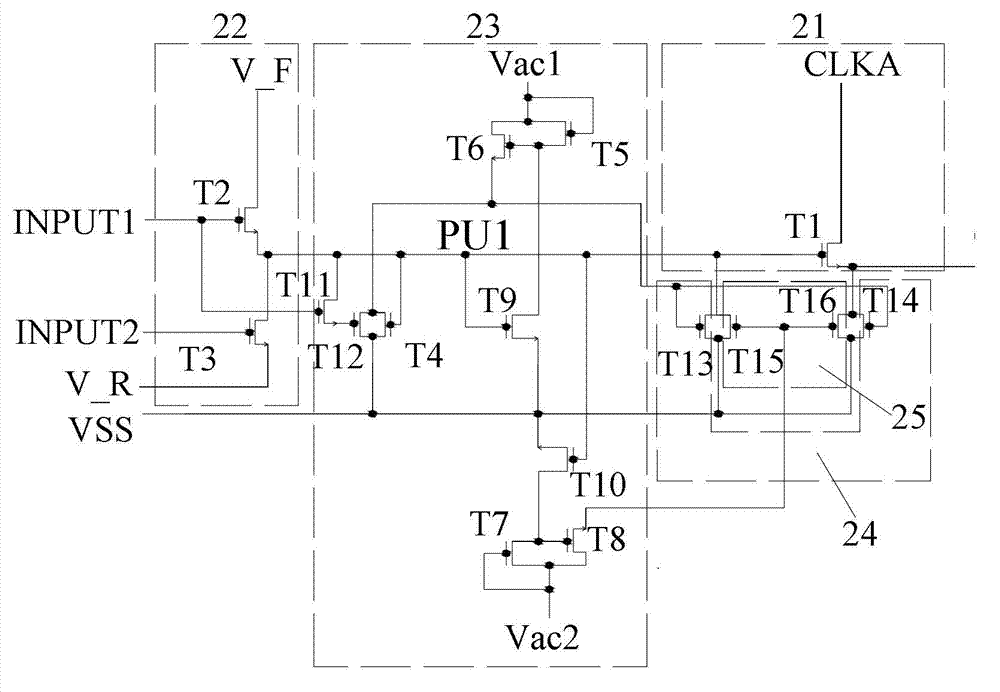
ActiveCN103035298AImprove stabilityReduce gate biasStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerComputer module
The embodiment of the invention provides a shift register unit, a grid driving circuit and a display device, belonging to the technical filed of displaying. The grid bias of a pull-down transistor can be improved, and the stability of the shift register unit can be increased. The shift register unit comprises a first pull-up module, a first scanning module, a control module, a first pull-down module and a second pull-down module. The embodiment of the invention is used for realizing grid driving scanning from top to bottom or from bottom to top.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Negative differential resistance pull up element for DRAM
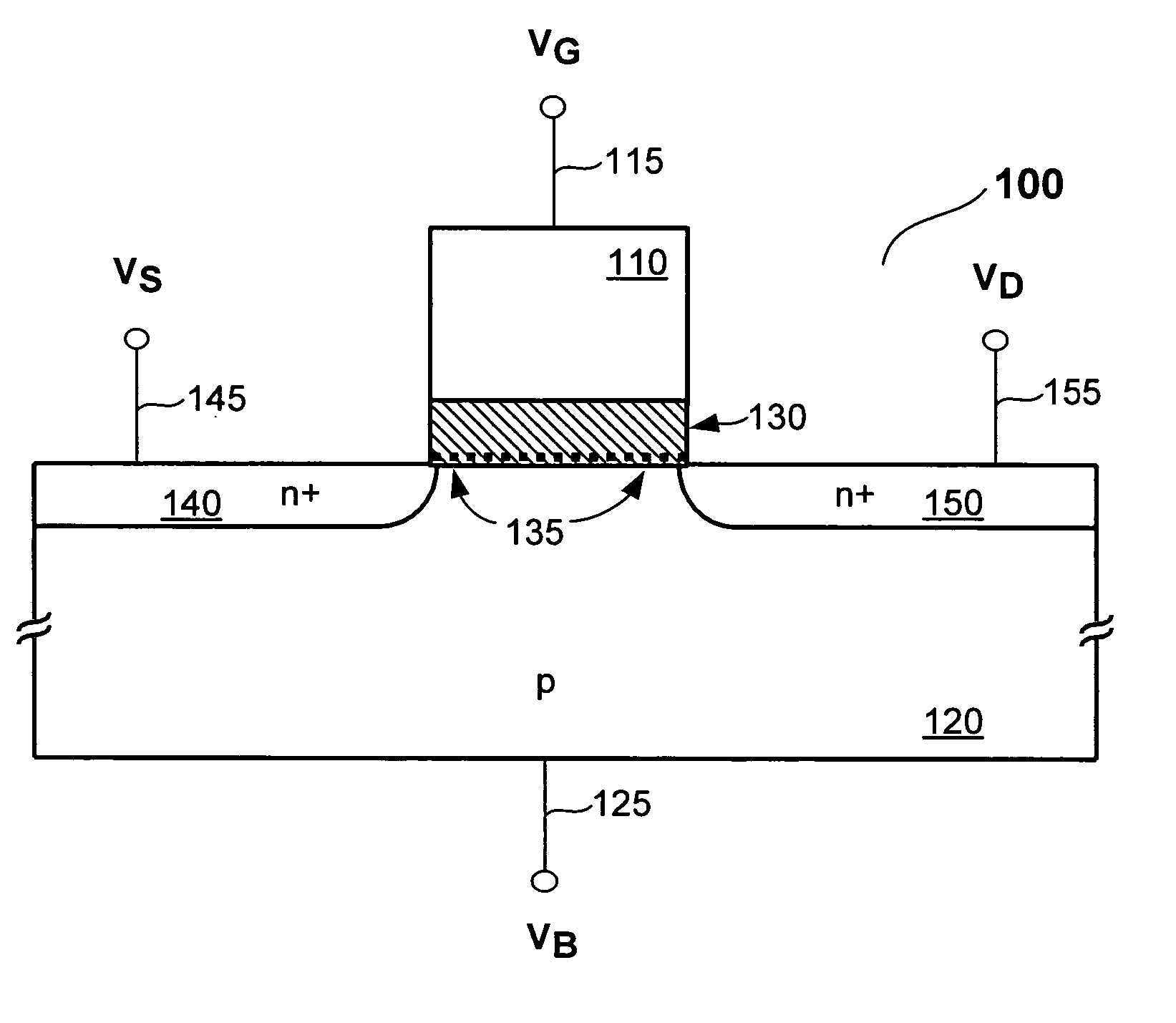
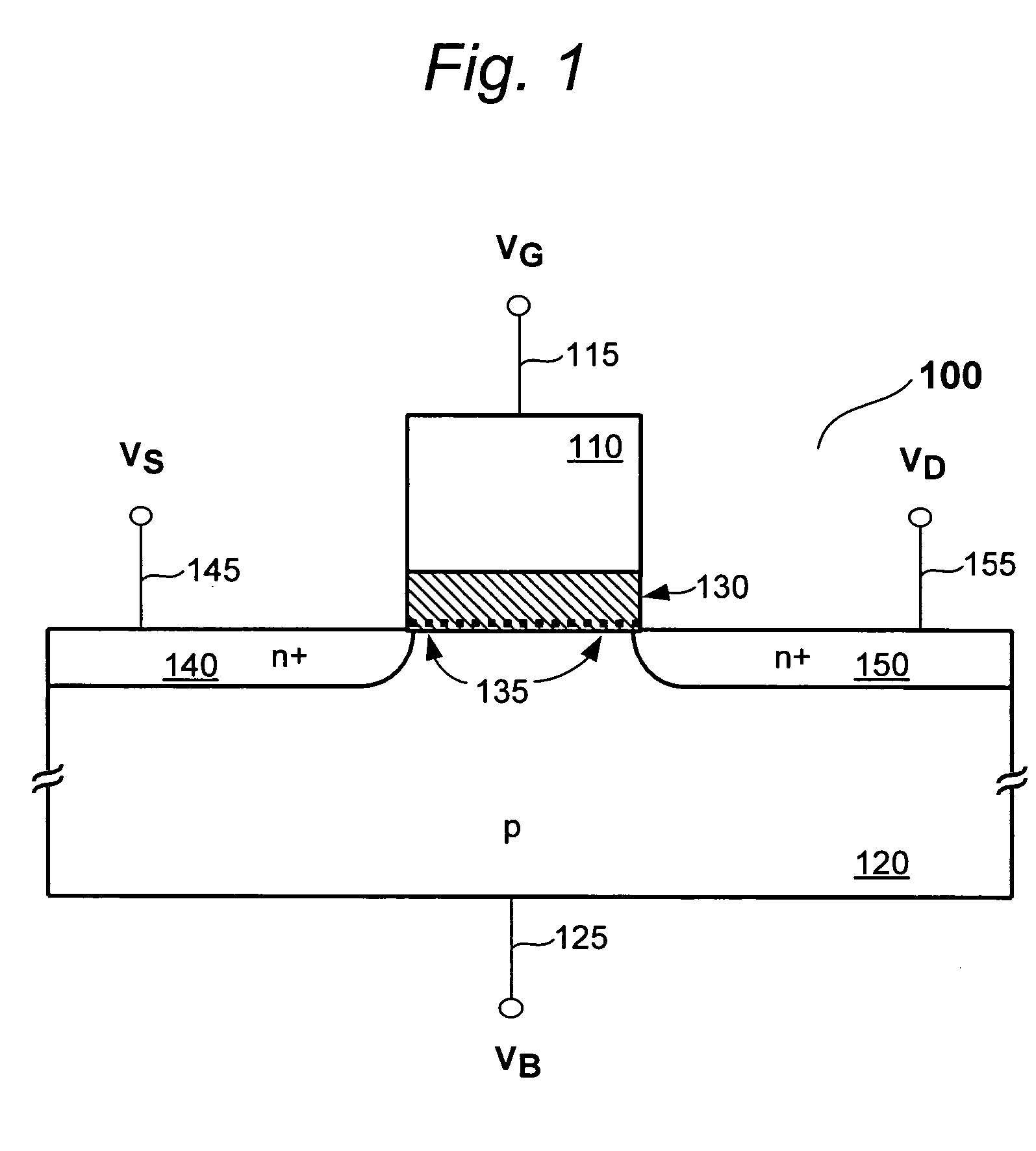
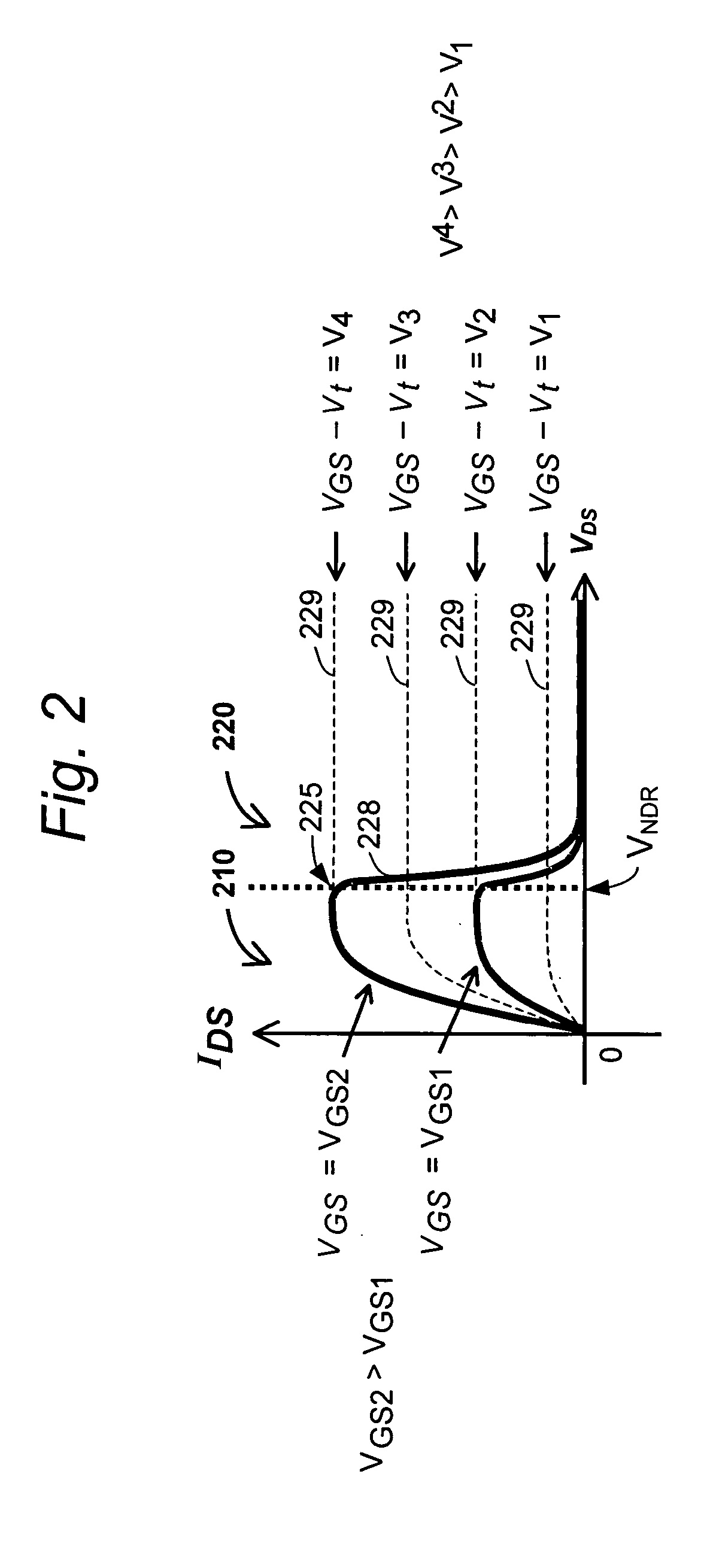
A memory cell includes a pull-up element that exhibits a refresh behavior that is dependent on the data value stored in the memory cell. The pull-up element is an NDR FET connected between a high voltage source and a storage node of the memory cell. The NDR FET receives a pulsed gate bias signal, wherein each pulse turns on the NDR FET when a logic HIGH value is stored at the storage node, and further wherein each pulse does not turn on the NDR FET when a logic LOW value is stored at the storage node. In this fashion a DRAM cell (and device) can be operated without a separate refresh cycle.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
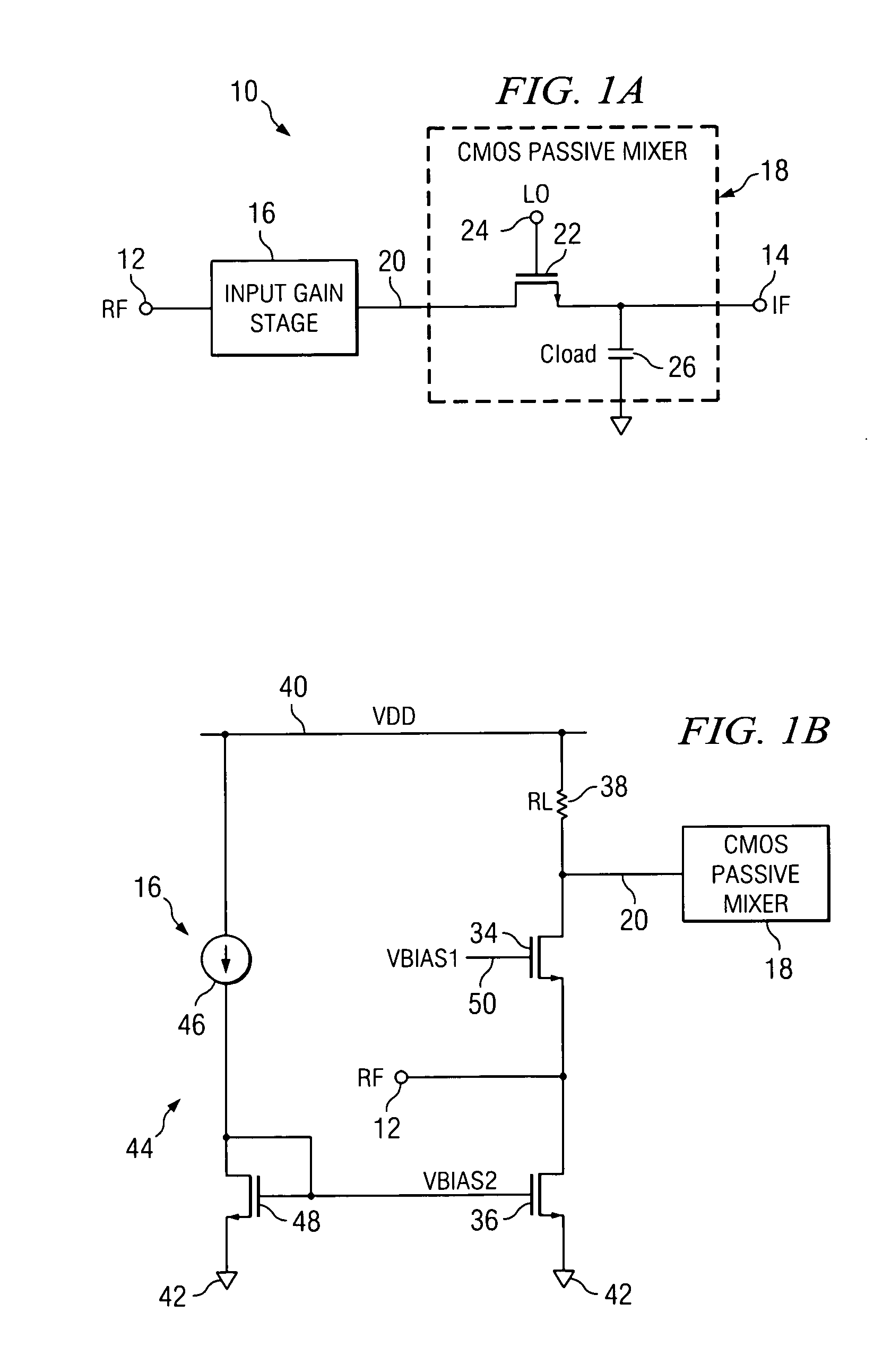
System for reducing second order intermodulation products from differential circuits
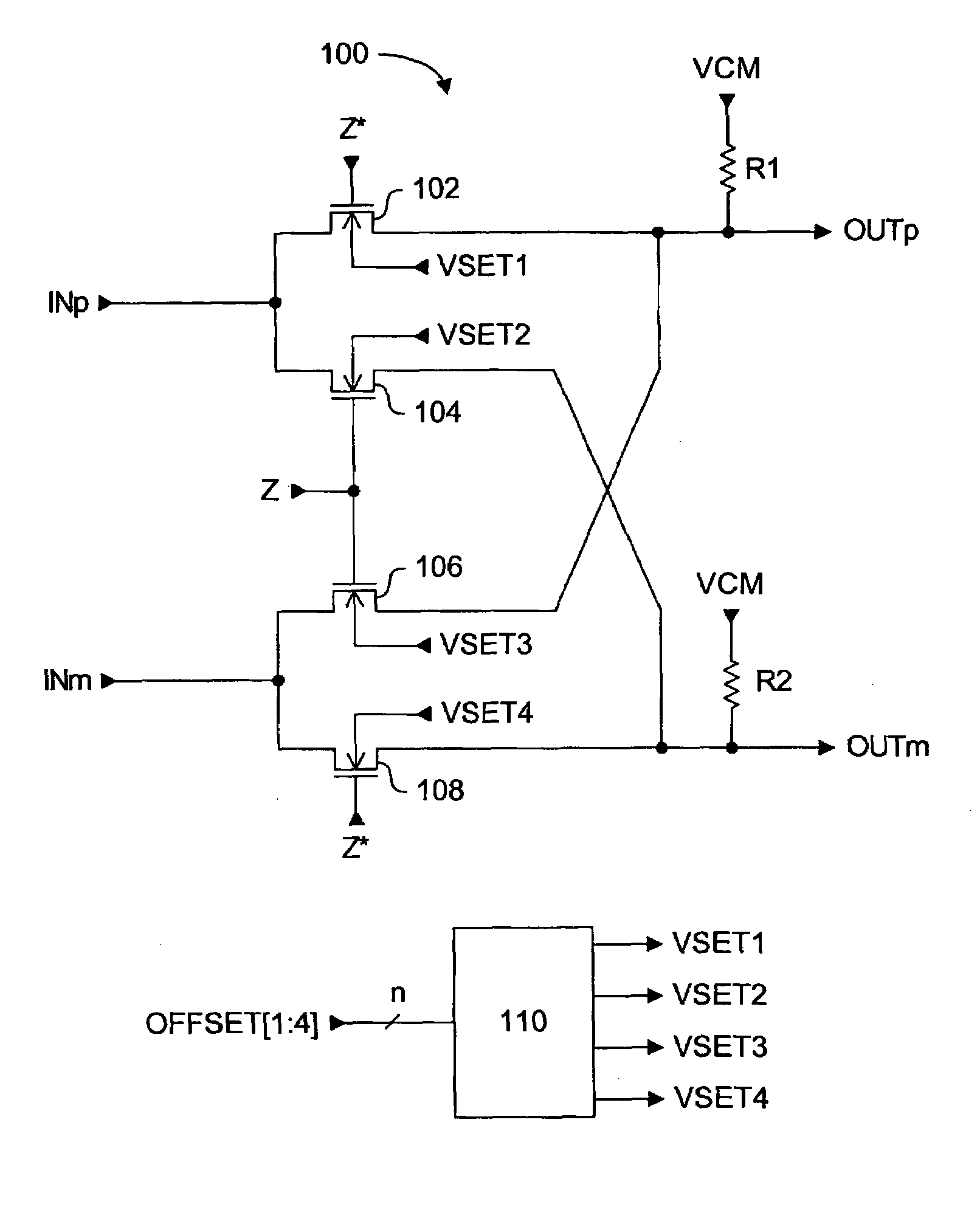
ActiveUS7554380B2Low intermodulationModulation transferenceComputations using contact-making devicesCMOSElectricity
A passive CMOS differential mixer circuit with a mismatch correction circuit for balancing the electrical characteristics of the two output paths. Once the output paths of the differential circuit are balanced, or matched as closely as possible, second order intermodulation product generation can be inhibited or at least reduced to acceptable levels. The mismatch correction circuit receives a digital offset signal, and generates one or more voltage signals to be selectively applied to the signal paths of the passive differential mixer circuit. The voltage signals can be adjusted back gate bias voltages applied to the bulk terminals of selected transistors to adjust their threshold voltages, or the voltage signals can be adjusted common mode voltages applied directly to a selected signal path. Since the differential mixer circuit is passive, no DC current contribution to noise is generated. The switching transistors of the mixer circuit can be maintained at minimal dimensions to reduce switching signal drive loading, resulting in lower power consumption and higher operating frequencies than if larger switching transistors were used.
Owner:ICERA CANADA ULC
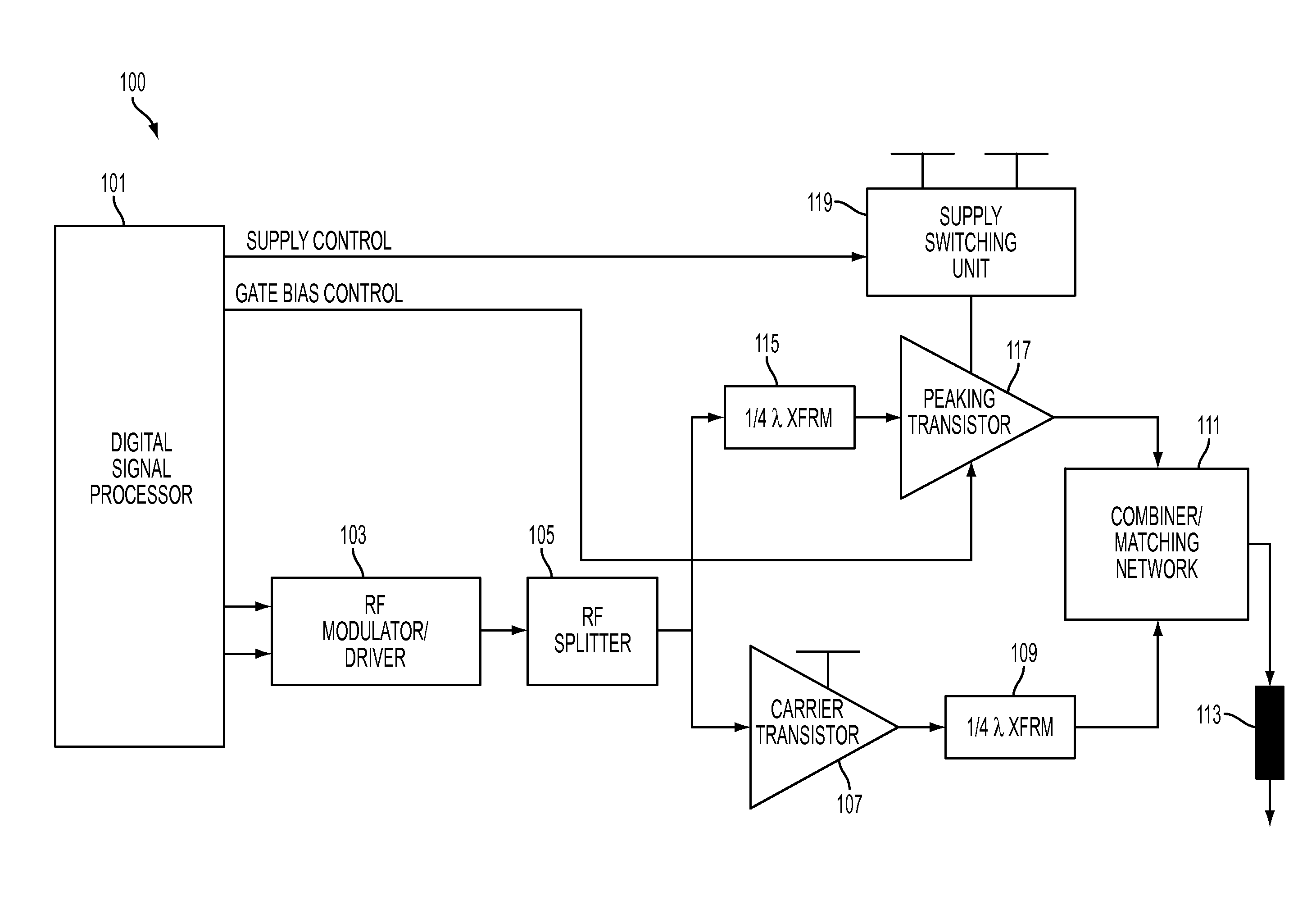
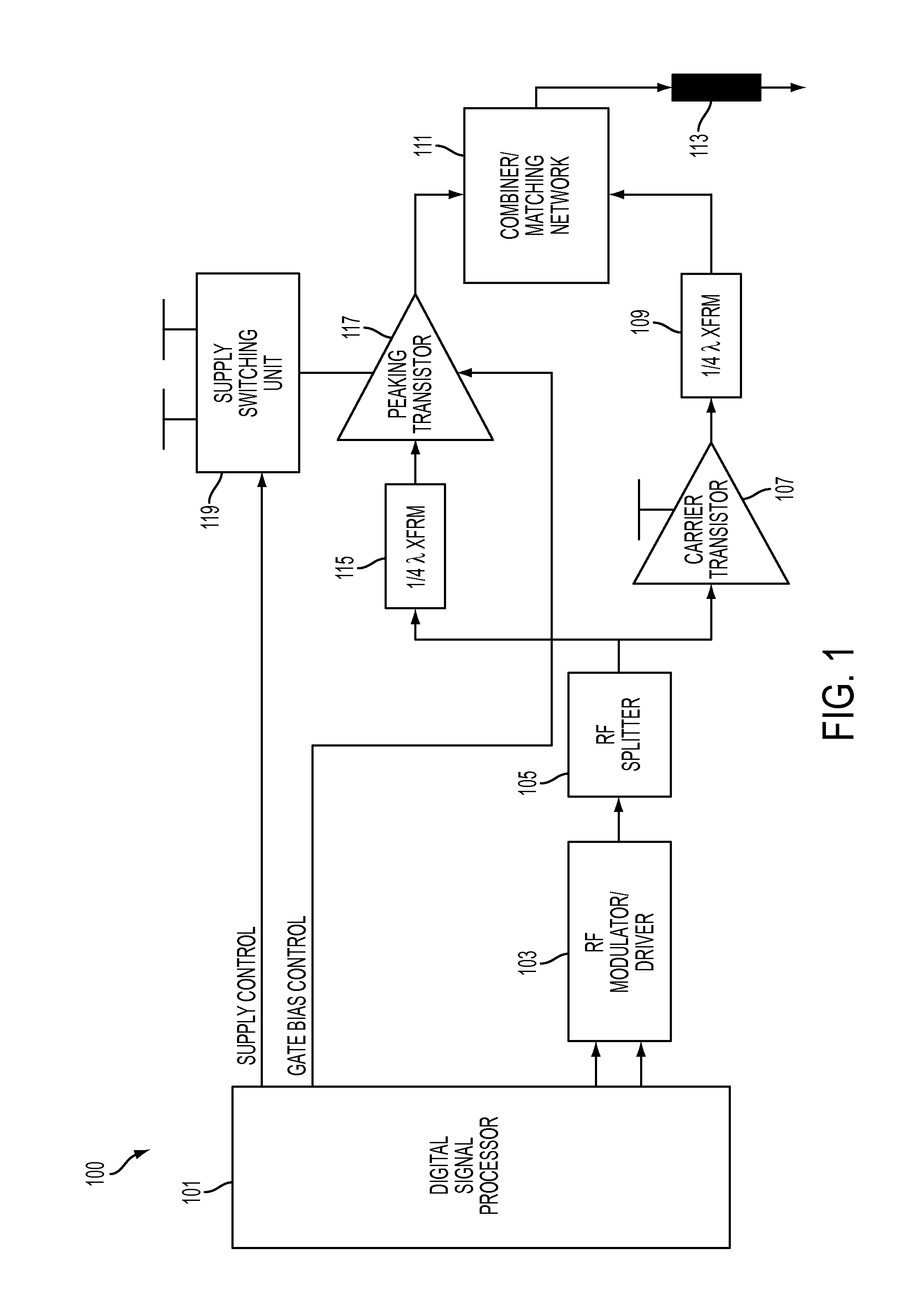
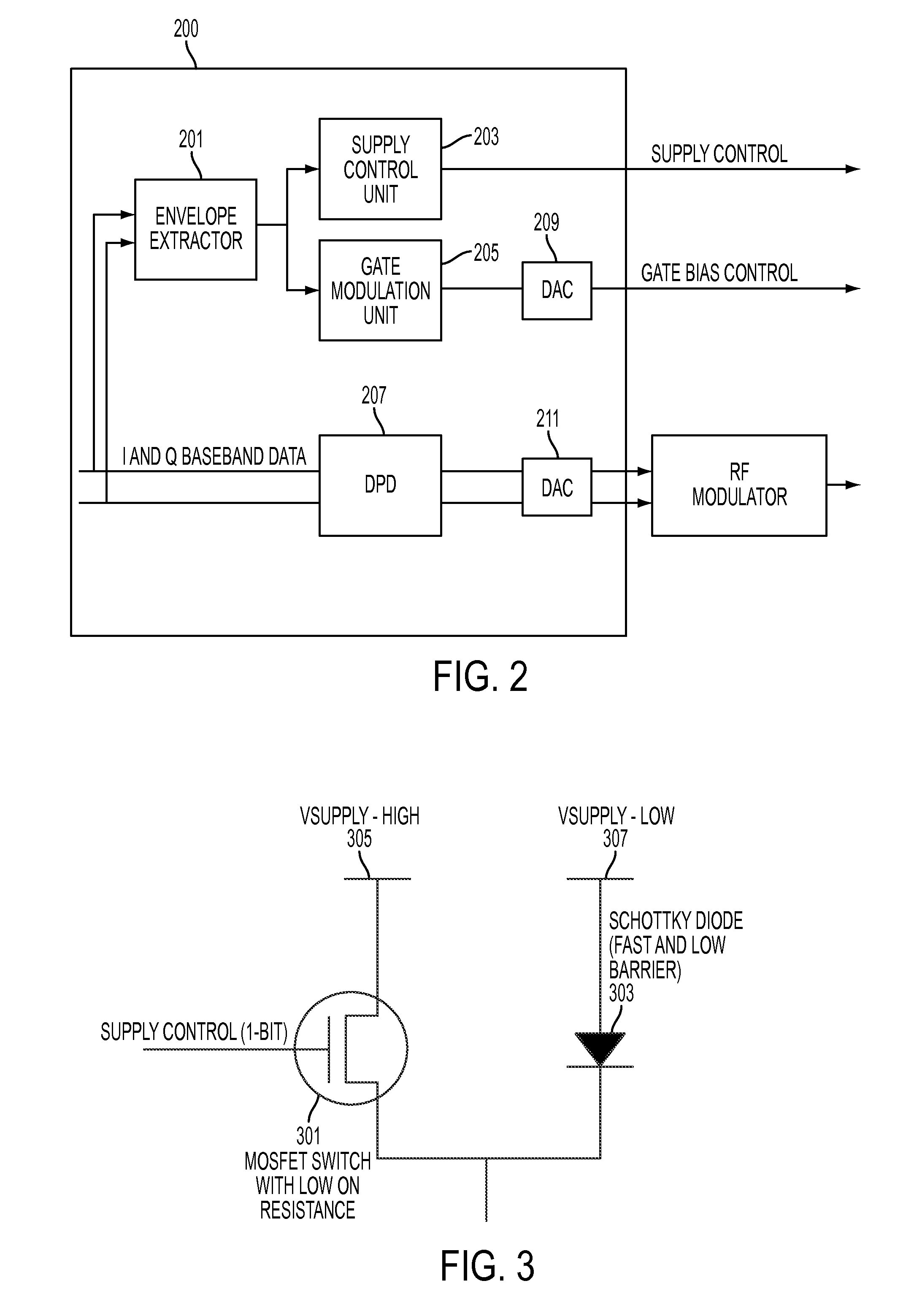
Efficiency improvement of doherty power amplifier using supply switching and digitally controlled gate bias modulation of peaking amplifier
InactiveUS20120299659A1Improve efficiencySimple designHigh frequency amplifiersPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
An apparatus for amplifying a signal is provided. The apparatus includes a carrier transistor, a peaking transistor, a controller, and a power supply switching unit, wherein the controller controls the power supply switching unit to switch between two or more power supplies and wherein the power supply switching unit provides power from one of the two or more power supplies to the peaking transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
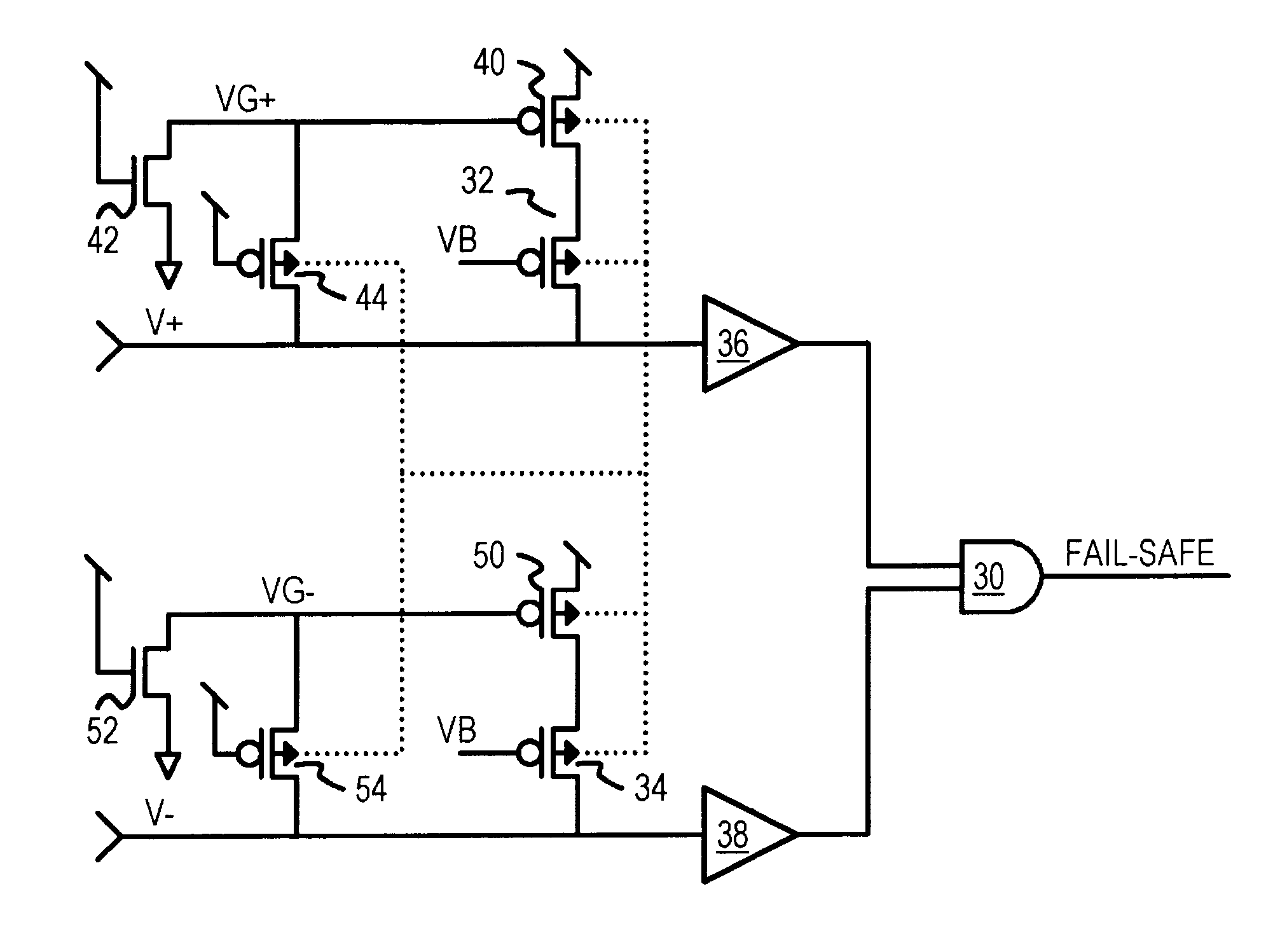
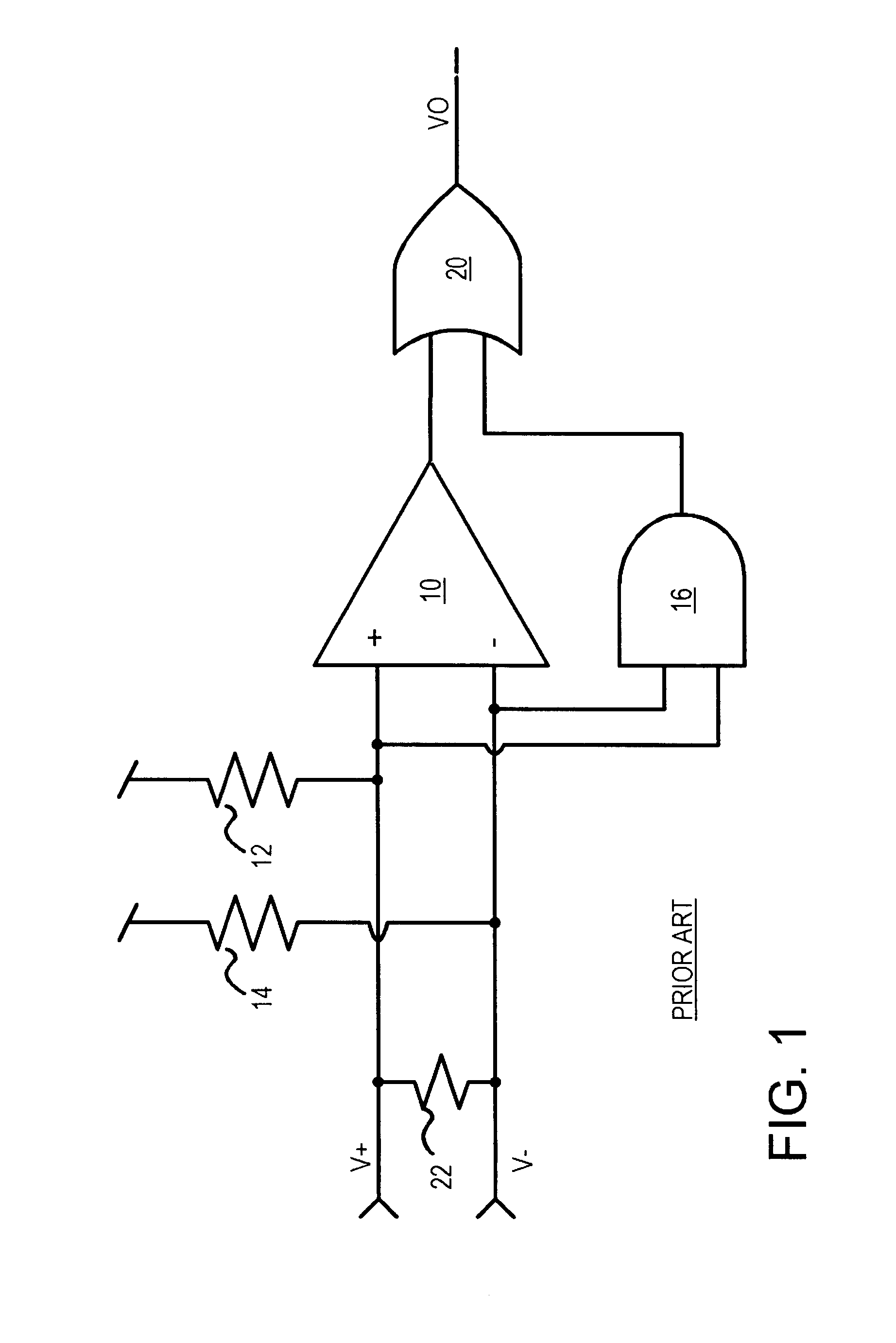
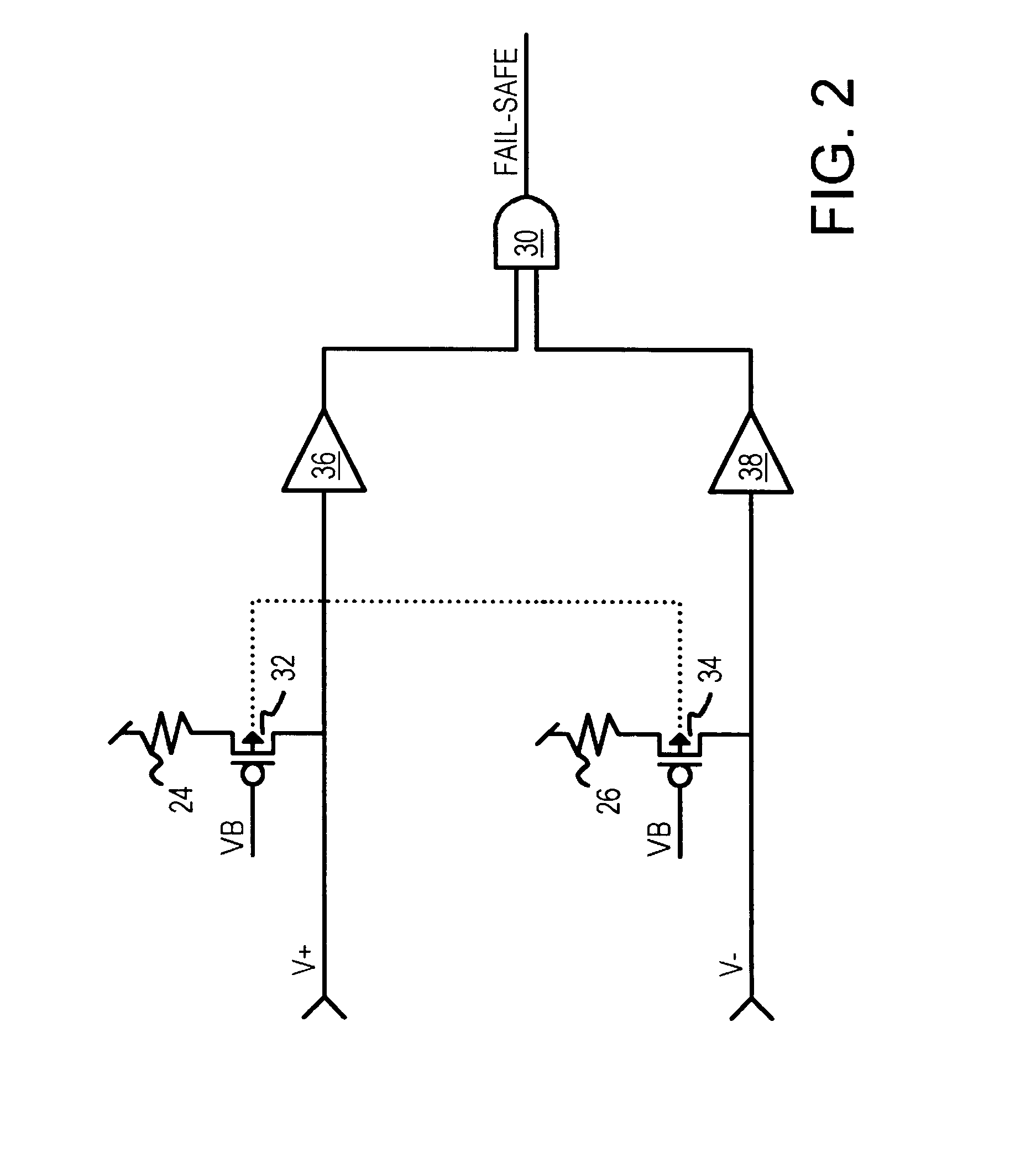
Fail-safe circuit with low input impedance using active-transistor differential-line terminators
InactiveUS6525559B1Reliability increasing modificationsFail-safe circuitsEngineeringPull-up resistor
A fail-safe circuit for a pair of differential input lines detects when one or both lines are open. Each line has a pull-up of a switched p-channel transistor in series with a resistor or another p-channel transistor that has its effective resistance controlled by a gate bias. The gate of the switched p-channel transistor is driven to ground when power is applied to the gate of a grounding n-channel transistor. When power is off, a p-channel connecting transistor charges the gate node from the differential input line when a positive voltage is applied to the input line, such as during a leakage test. Charging the gate node prevents the switched p-channel transistor from turning on, blocking a leakage current path through the pull-up. An N-well bias circuit can be added, which connects the N-well under p-channel transistors to power or the gate node or the input line.
Owner:DIODES INC
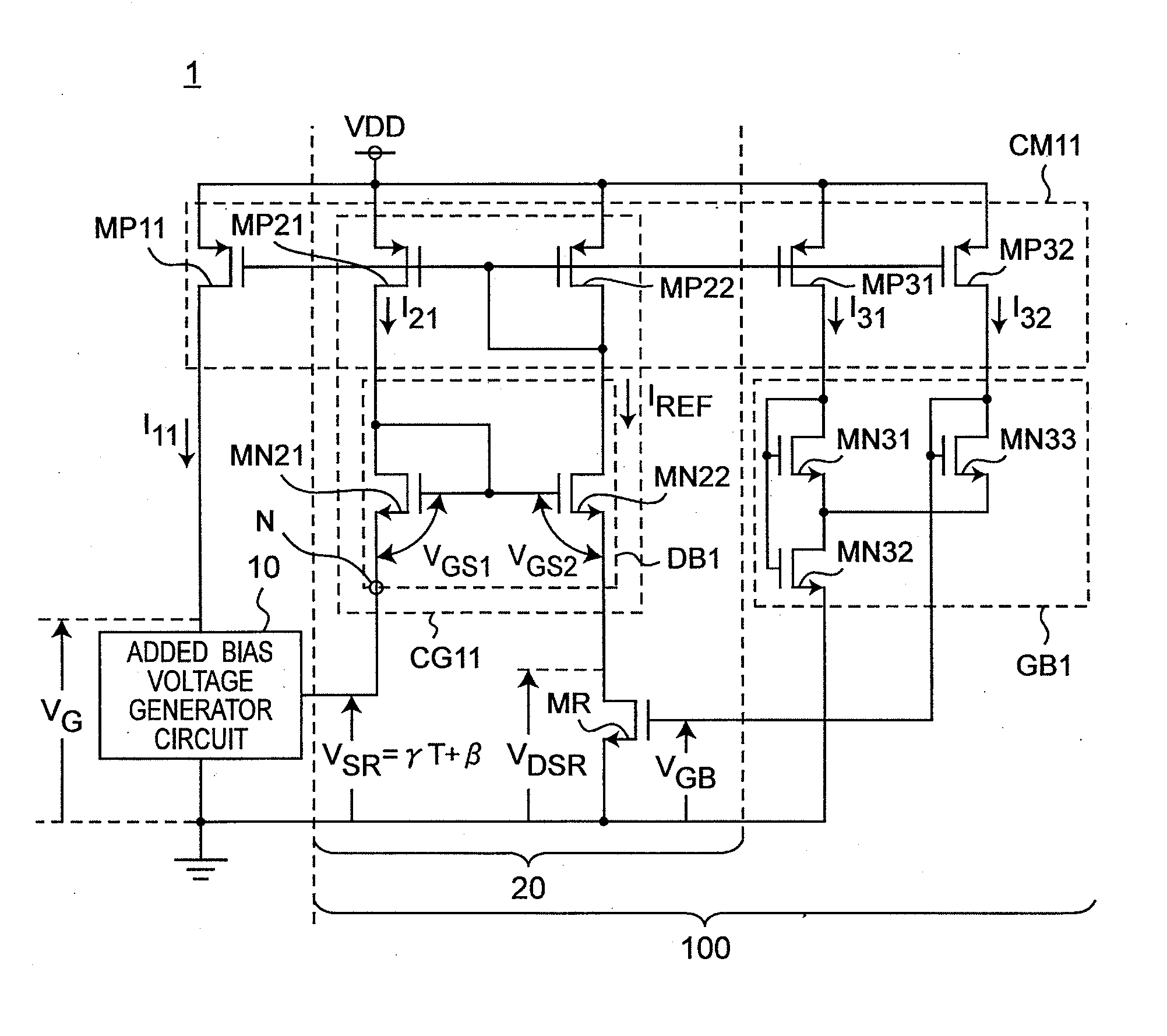
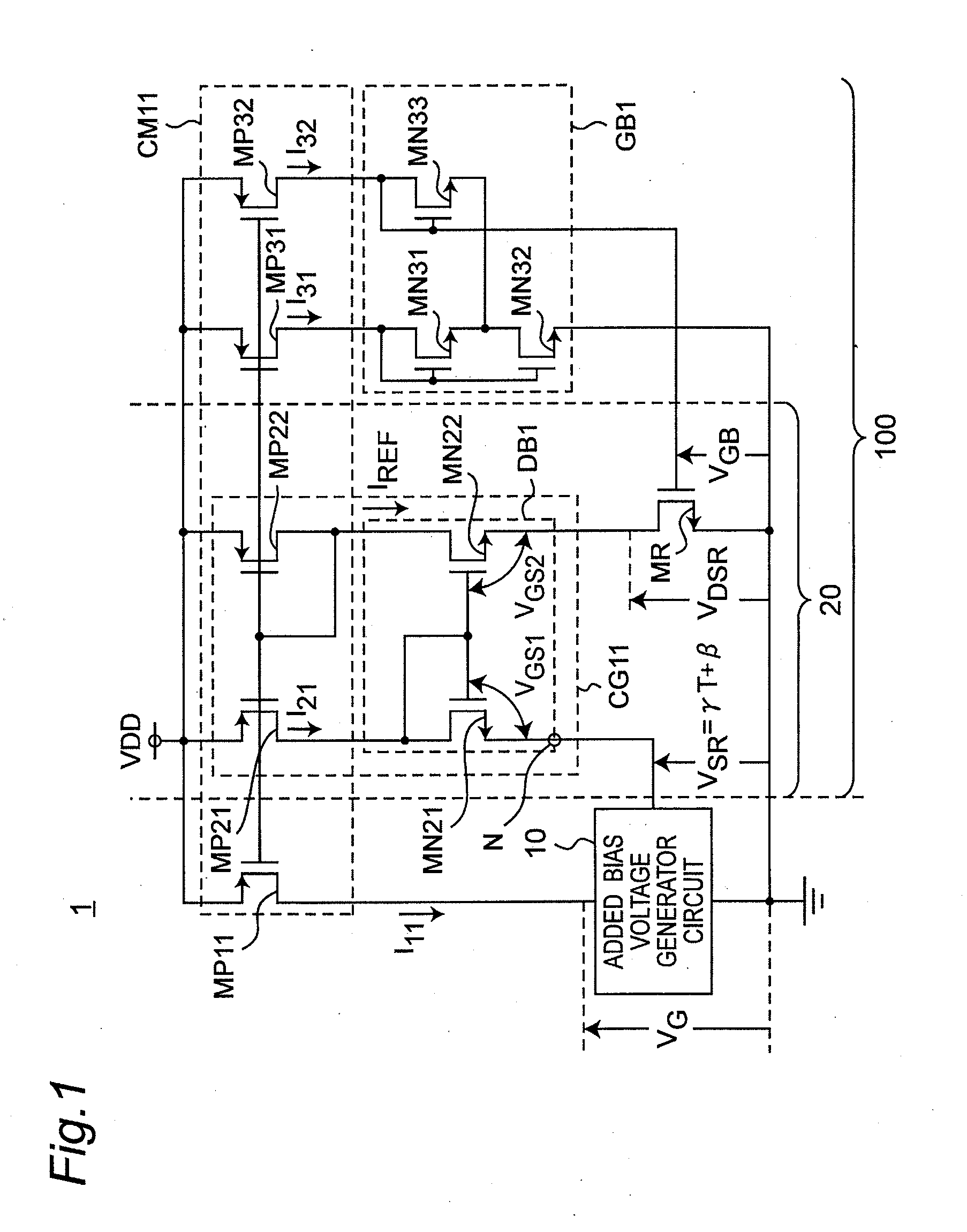
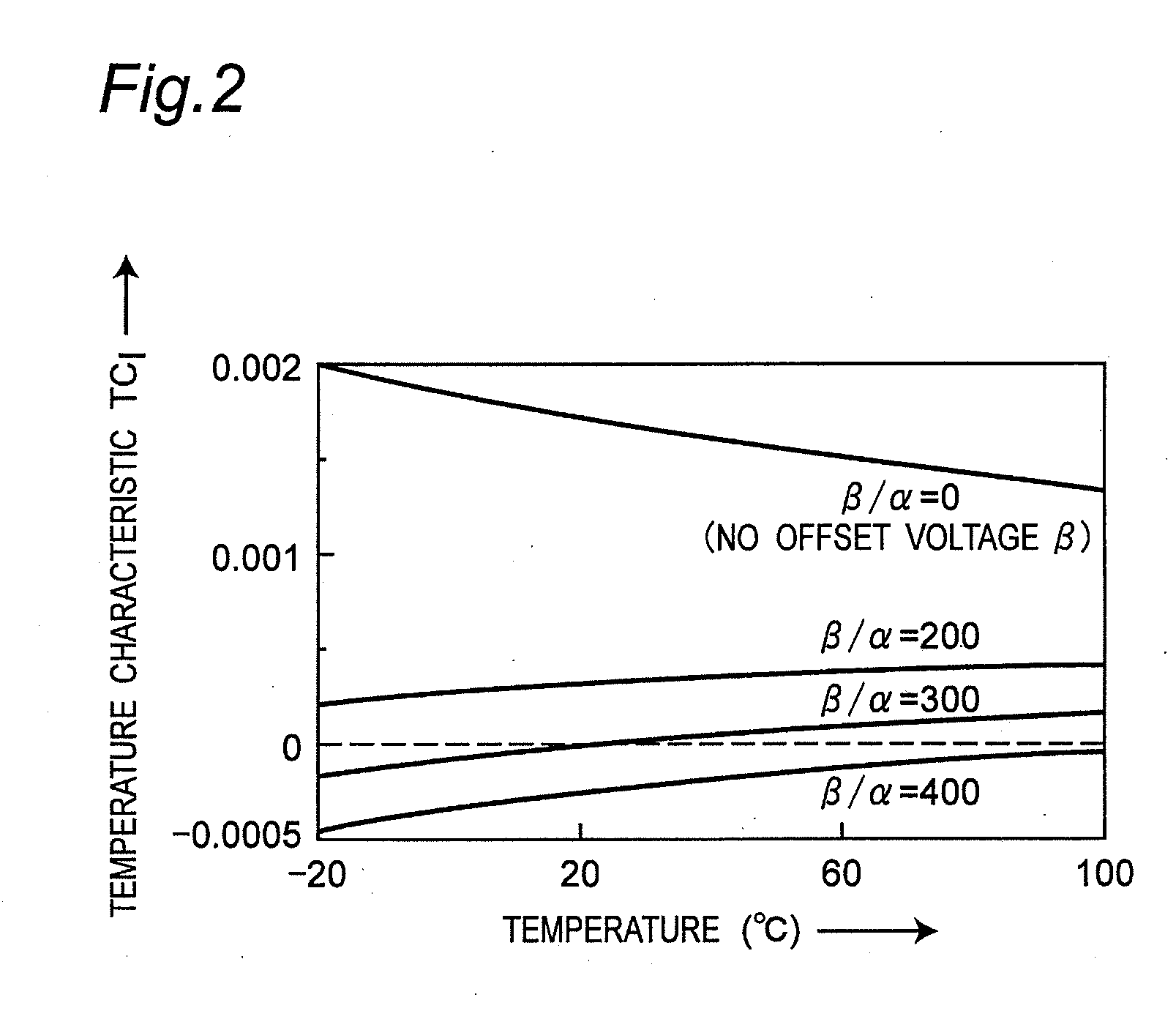
Reference current source circuit including added bias voltage generator circuit
InactiveUS20120025801A1Reduce circuit areaSuppress inclinationElectric variable regulationVoltage generatorLinear region
A MOS resistor generates an output current based on a voltage induced across a drain and a source thereof. A gate bias voltage generator circuit generates a gate bias voltage so as to operate the MOS resistor in a strong-inversion linear region, and applies the gate bias voltage to a gate of the MOS resistor. A drain bias voltage generator circuit generates a drain bias voltage, and applies the drain bias voltage to the drain of the MOS resistor. An added bias voltage generator circuit generates an added bias voltage, which has a predetermined temperature coefficient and includes a predetermined offset voltage, so that the output current becomes constant against temperature changes. The drain bias voltage generator circuit adds the added bias voltage to the drain bias voltage, and applies a voltage of adding results to the drain of the MOS resistor as the drain bias voltage.
Owner:SEMICON TECH ACADEMIC RES CENT
Method and system for providing automatic gate bias and bias sequencing for field effect transistors
ActiveUS20120313709A1Low costLight weightHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlEngineeringDrain current
A feedback gate bias circuit for use in radio frequency amplifiers to more effectively control operation of LDFET, GaNFET, GaAsFET, and JFET type transistors used in such circuits. A transistor gate bias circuit that senses drain current and automatically adjusts or biases the gate voltage to maintain drain current independently of temperature, time, input drive, frequency, as well as from device to device variations. Additional circuits to provide temperature compensation, RF power monitoring and drain current control, RF output power leveler, high power gain block, and optional digital control of various functions. A gate bias circuit including a bias sequencer and negative voltage deriver for operation of N-channel depletion mode devices.
Owner:EMHISER RES
Dynamic control of back gate bias in a FinFET SRAM cell
InactiveUS20070242497A1Digital storageStationary tubular conduit assembliesEngineeringOperation mode
The present invention provides dynamic control of back gate bias on pull-up pFETs in a FinFET SRAM cell. A method according to the present invention includes providing a bias voltage to a back gate of at least one transistor in the SRAM cell, and dynamically controlling the bias voltage based on an operational mode (e.g., Read, Half-Select, Write, Standby) of the SRAM cell.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
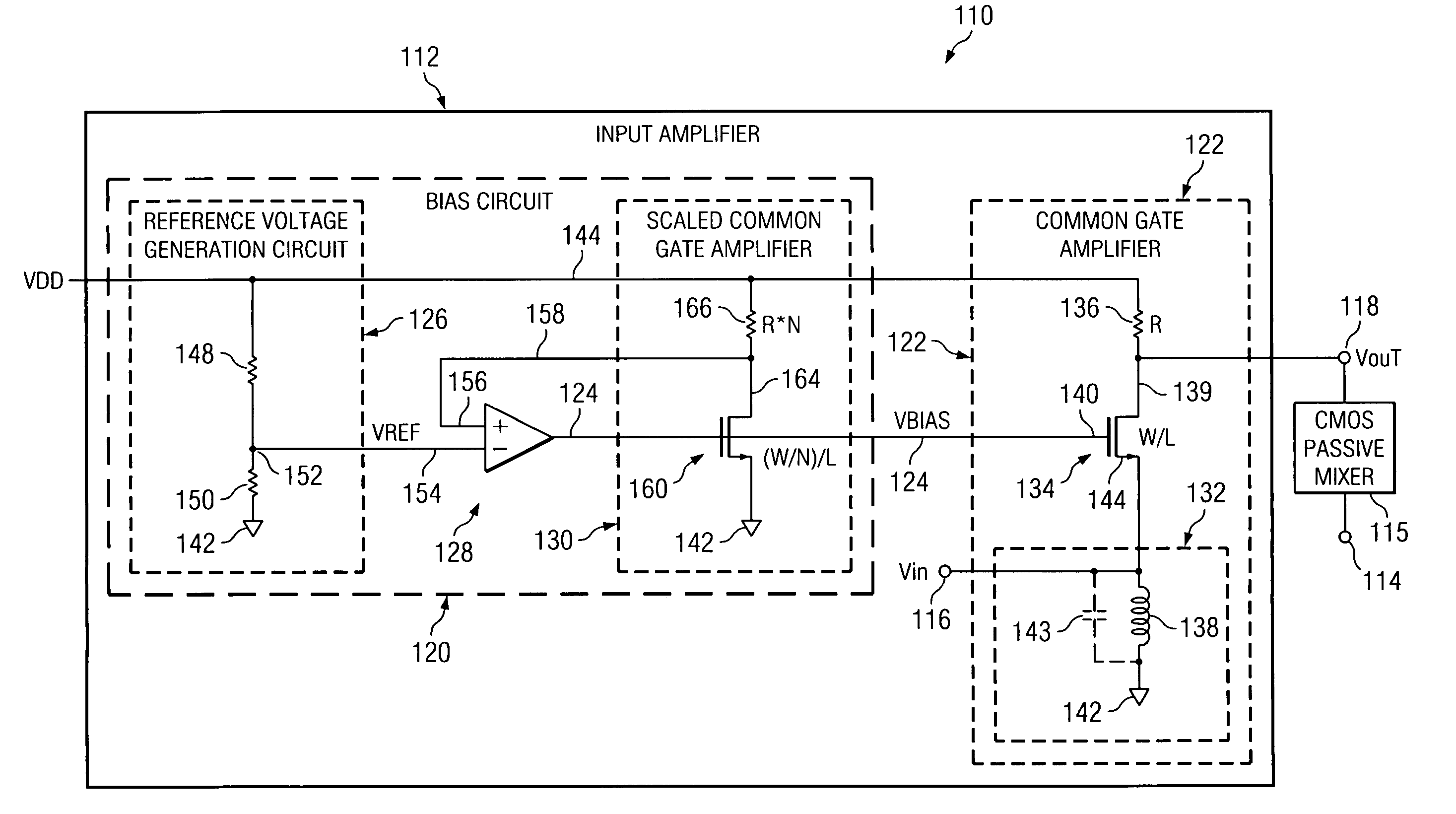
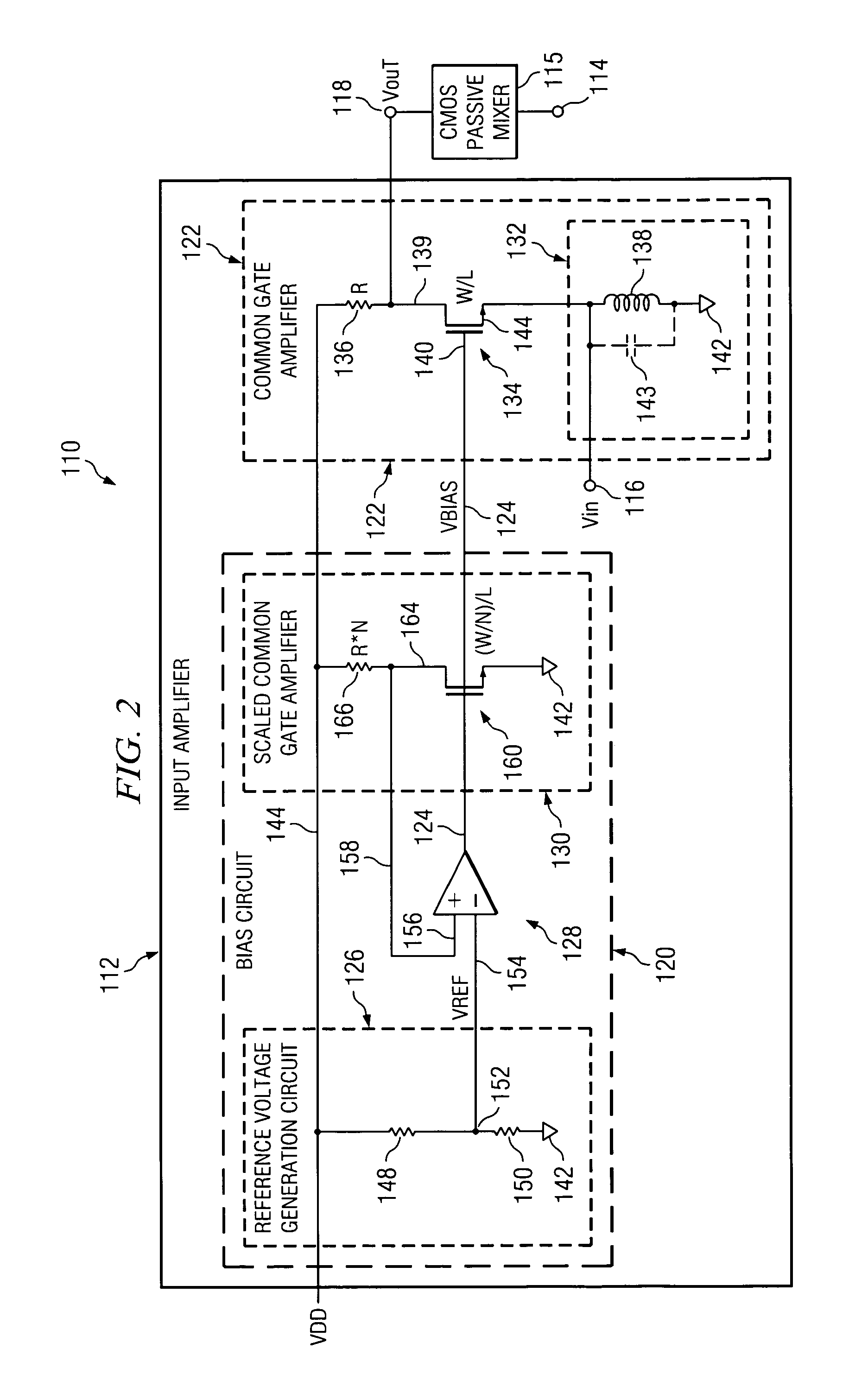
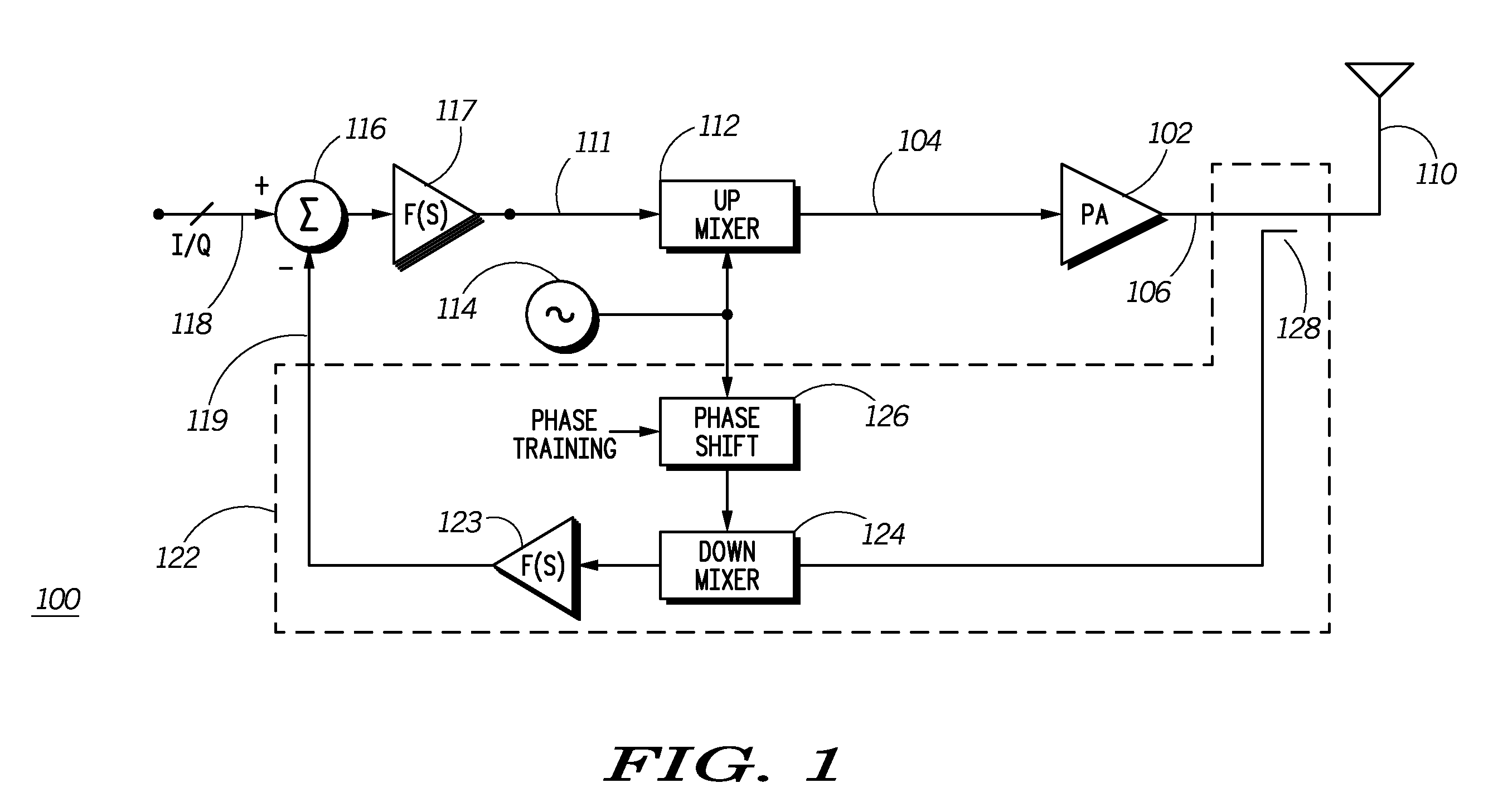
Method and system for amplifying a signal
ActiveUS20060152288A1Improve linearityHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierDc current
According to one embodiment of the invention, an amplifier includes a gate bias circuit operable to generate a gate bias voltage and a common gate amplifier that includes a transistor having a gate biased by an output of the gate bias circuit and also having a source connected to an inductor for providing a path to ground for direct current flowing through the transistor. According to another embodiment of the invention, a method for amplifying a signal by an amplifier includes generating a gate bias voltage indicative of a difference between a reference voltage and an output voltage of the amplifier, biasing the gate of the common-gate amplifier with the gate bias voltage, and blocking, by a passive device, alternating current signals from flowing from the source of the transistor to ground.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
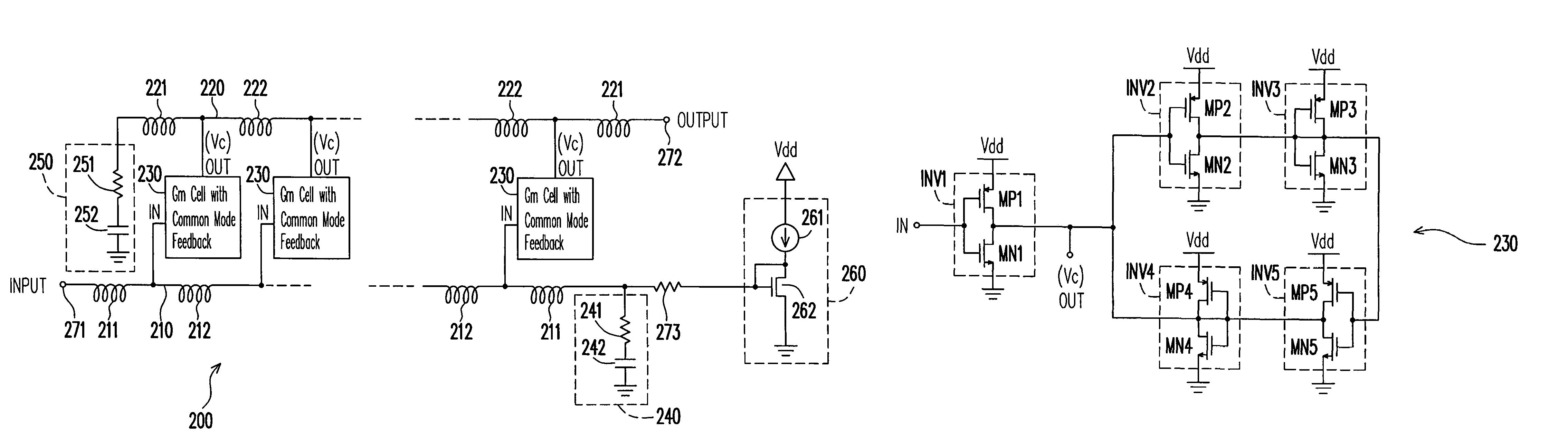
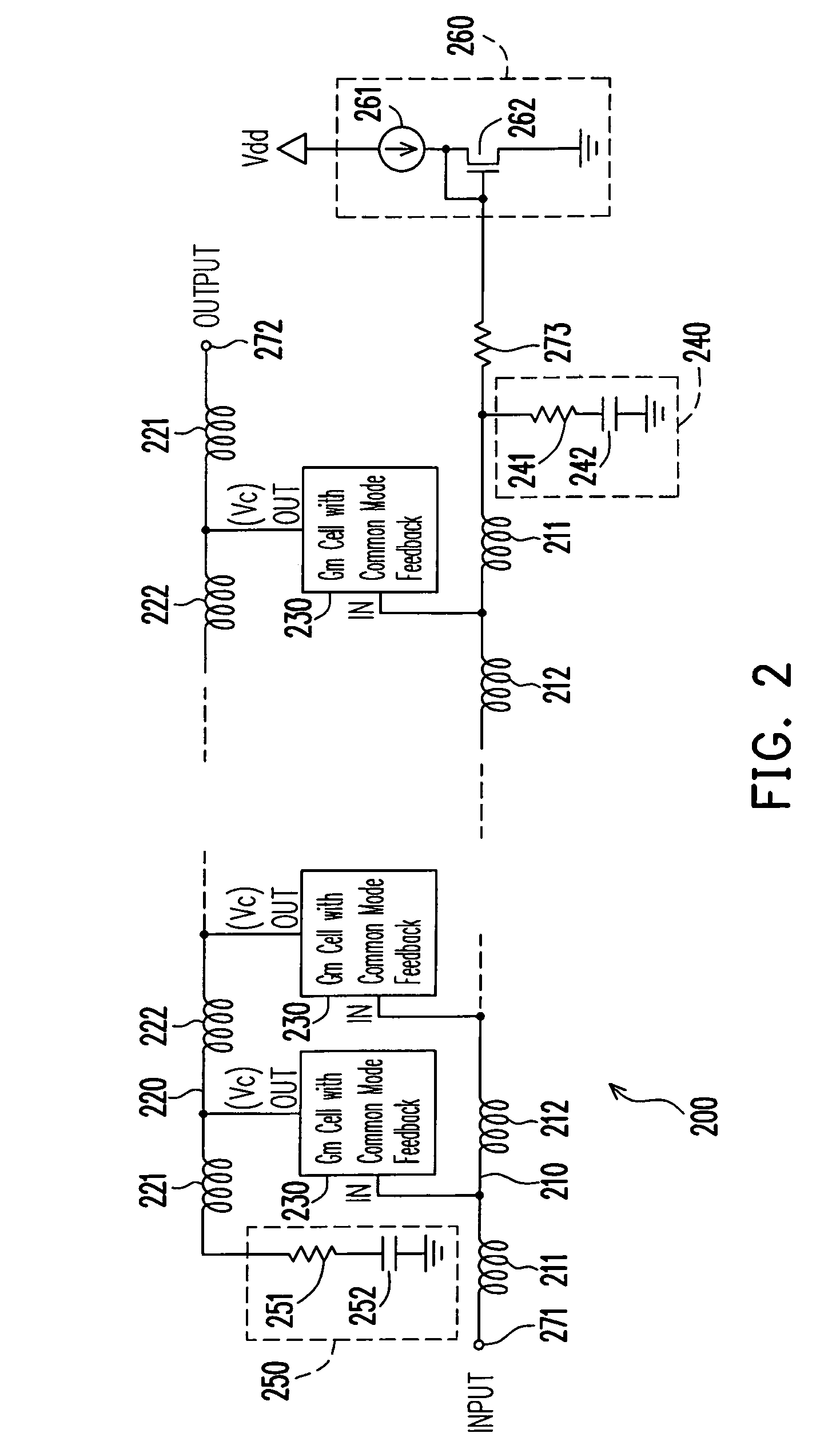
Low power comsumption, low noise and high power gain distributed amplifiers for communication systems
ActiveUS7579913B1Reduce power consumptionIncrease power gainAmplifier combinationsAmplifiers wit coupling networksLow noiseDistributed amplifier
Provided is a distributed amplifier in communication systems, including: an input transmission line; an output transmission line; an input impedance match and an output impedance match, for providing termination of the input transmission line and the output transmission line, respectively and for preventing signal reflection in the input transmission line and the output transmission line, respectively; multi-stage Gm cells with common mode feedback, the input transmission line being coupled to the output transmission line by the transconductance of the Gm cells; and an input gate bias circuit, for providing bias for the multi-stage Gm cells. In at least one of the Gm cells, one inverter performs V / I conversion while other inverters provide negative resistance to control common mode of output voltage and to enhance DC gain of the Gm cell. Due to common mode feedback, no output gate bias is needed.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
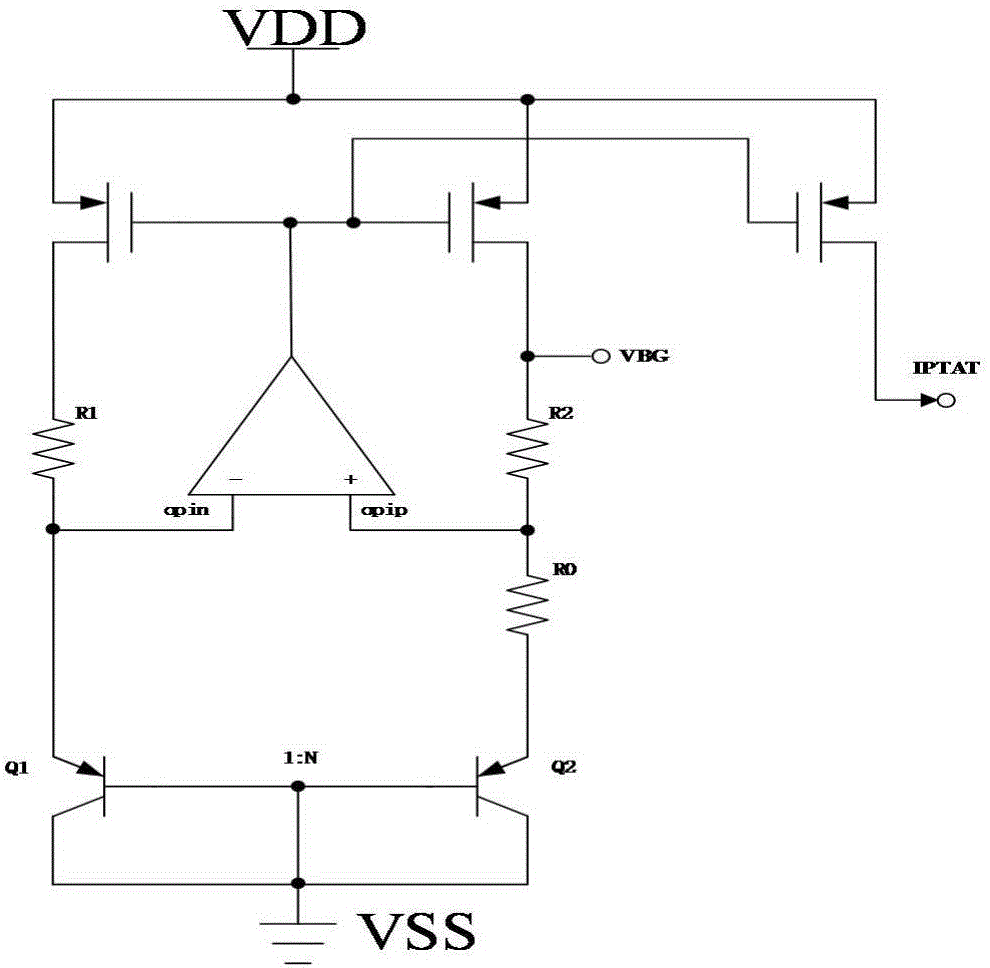
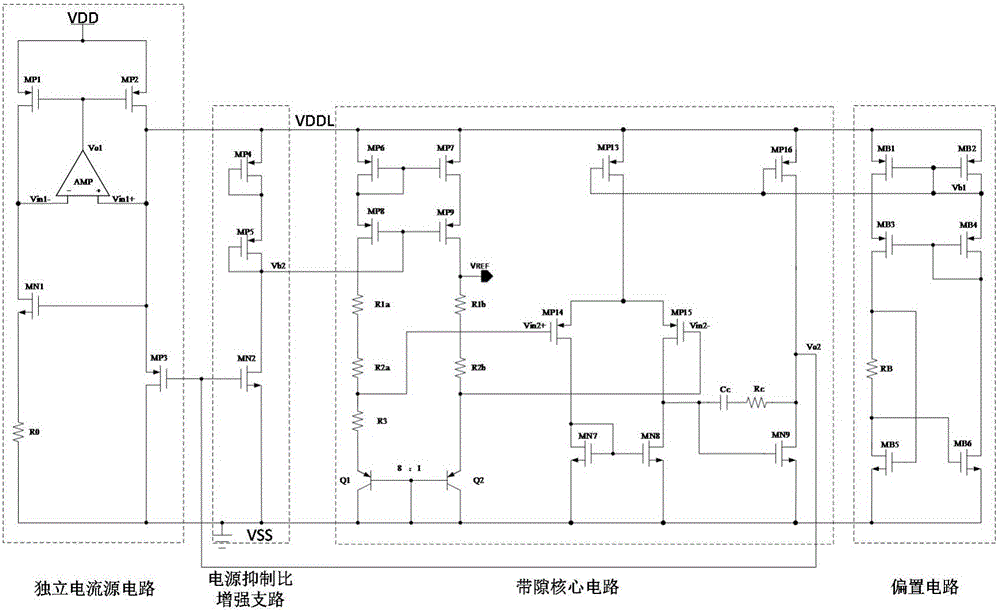
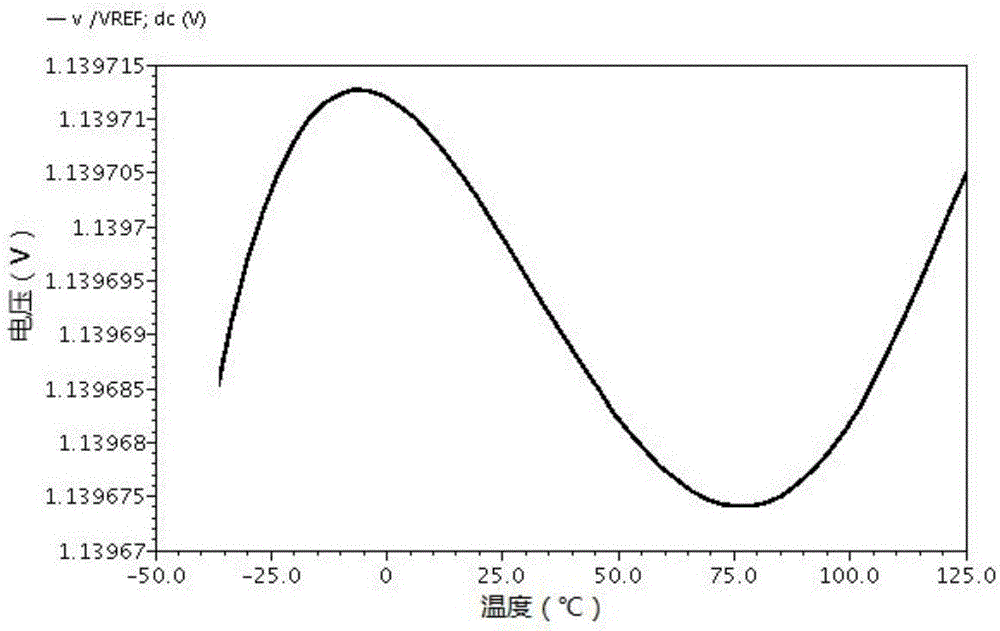
Ultralow temperature drift high power supply rejection ratio band-gap reference voltage source
InactiveCN106125811ASmall temperature coefficientHigh inhibition ratioElectric variable regulationEngineeringVoltage source
The invention provides an ultralow temperature drift high power supply rejection ratio band-gap reference voltage source, and relates to the field of analog integrated circuit design. Mainly aimed at problems of temperature drift and power supply rejection ratio of an existing reference source, a comprehensive solution is provided. The band-gap reference voltage source comprises an independent current source circuit, a biasing circuit, a band-gap core circuit, and a PSRR enhancing circuit. The independent current source circuit is used to generate current which is basically independent of supply voltage to supply power. The bias circuit generates bias voltage used for operational amplification of the band-gap core circuit. The band-gap core circuit uses temperature compensation to obtain reference voltage. The power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) enhancing circuit provides grid bias voltage of the band-gap core circuit and improves power supply rejection ratio. Beneficial effects of the band-gap reference voltage source are that temperature coefficient of band-gap reference is greatly reduced, and power supply rejection ratio is improved. The band-gap reference voltage source is suitable to be used for a radio frequency identification power management module.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method and system for providing automatic gate bias for field effect transistors
ActiveUS20110279185A1Low costLight weightHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAuto regulationEngineering
The present invention provides a feedback gate bias circuit for use in radio frequency amplifiers to more effectively control operation of LDFET, GaNFET, GaAsFET, and JFET type transistors used in such circuits. The invention provides a transistor gate bias circuit that senses drain current and automatically adjusts or biases the gate voltage to maintain drain current independently of temperature, time, input drive, frequency, as well as from device to device variations. The invention provides additional circuits to provide temperature compensation, RF power monitoring and drain current control, RF output power leveler, high power gain block, and optional digital control of various functions.
Owner:EMHISER RES
High frequency power amplifier and wireless communication module
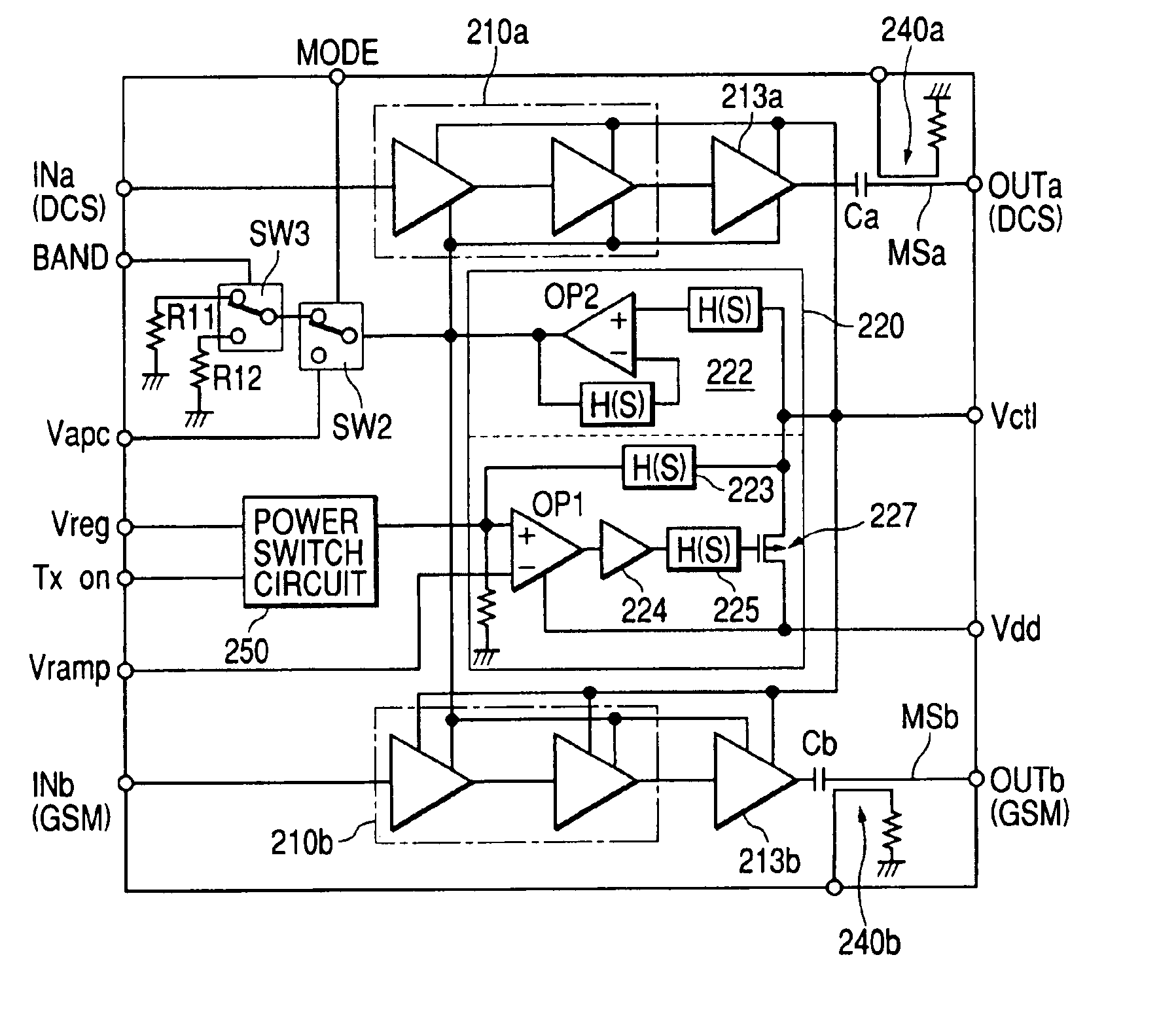
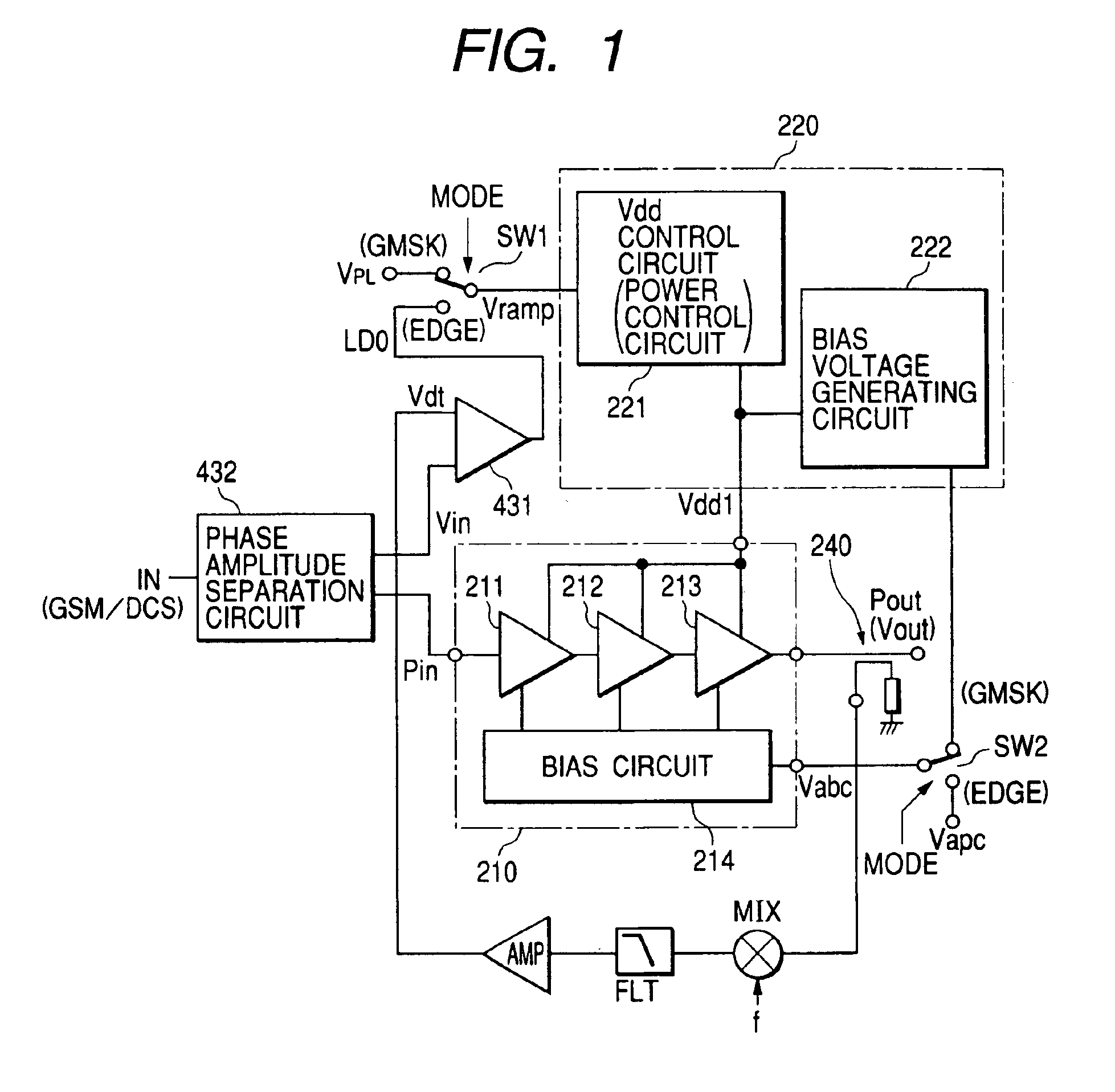
InactiveUS6914480B2Improve efficiencyExtend talk timeAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionSolid-state devicesHigh frequency powerAudio power amplifier
The present invention provides a high frequency power amplifier of an open-loop type, which outputs a signal having a level corresponding to an output level required under control of a power supply voltage for each output power FET, based on a control signal for the output level. The high frequency power amplifier is provided with a bias voltage generating circuit which generates a gate bias voltage of each output power FET according to an output voltage of a power control circuit for controlling the power supply voltage for the output power FET, based on the control signal for the output level.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
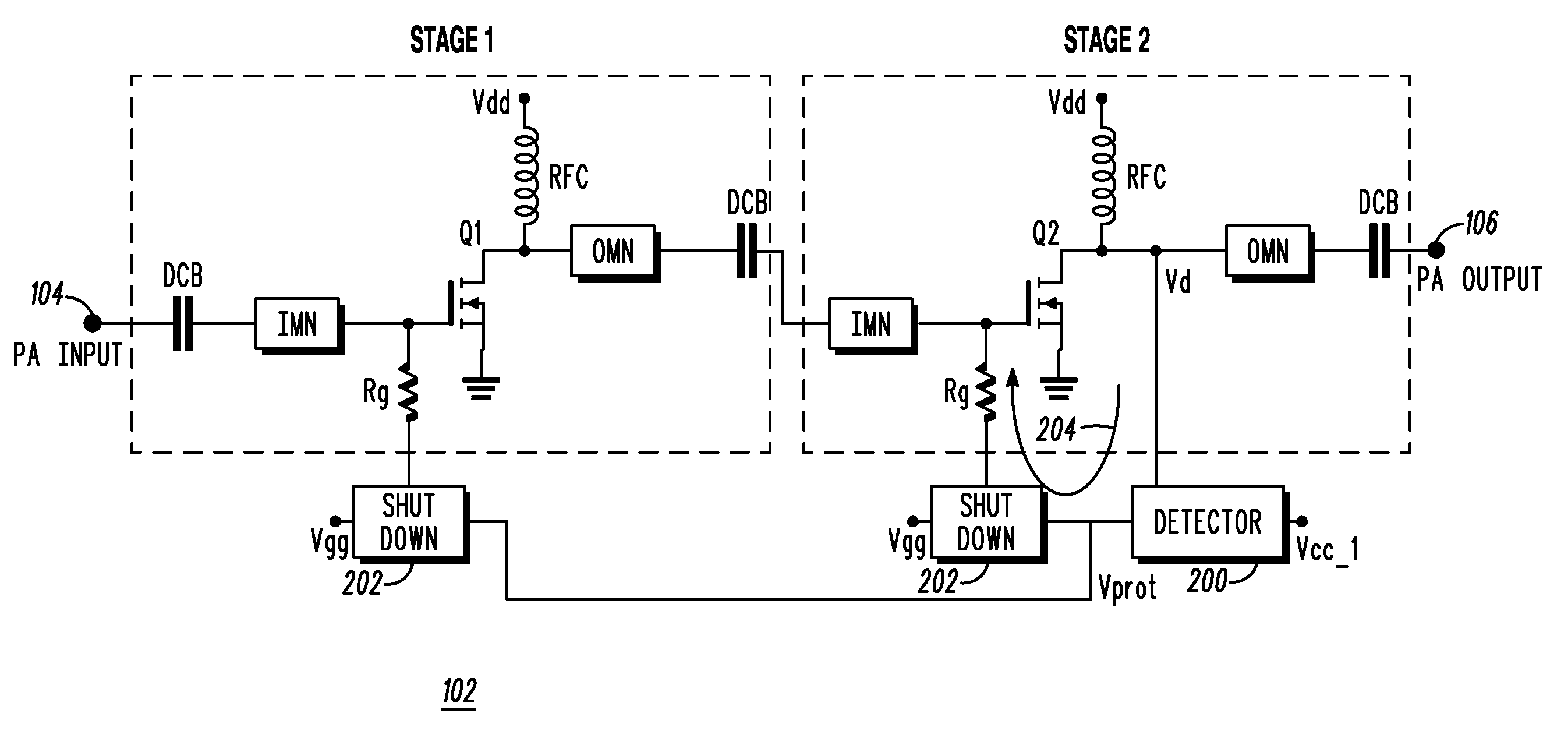
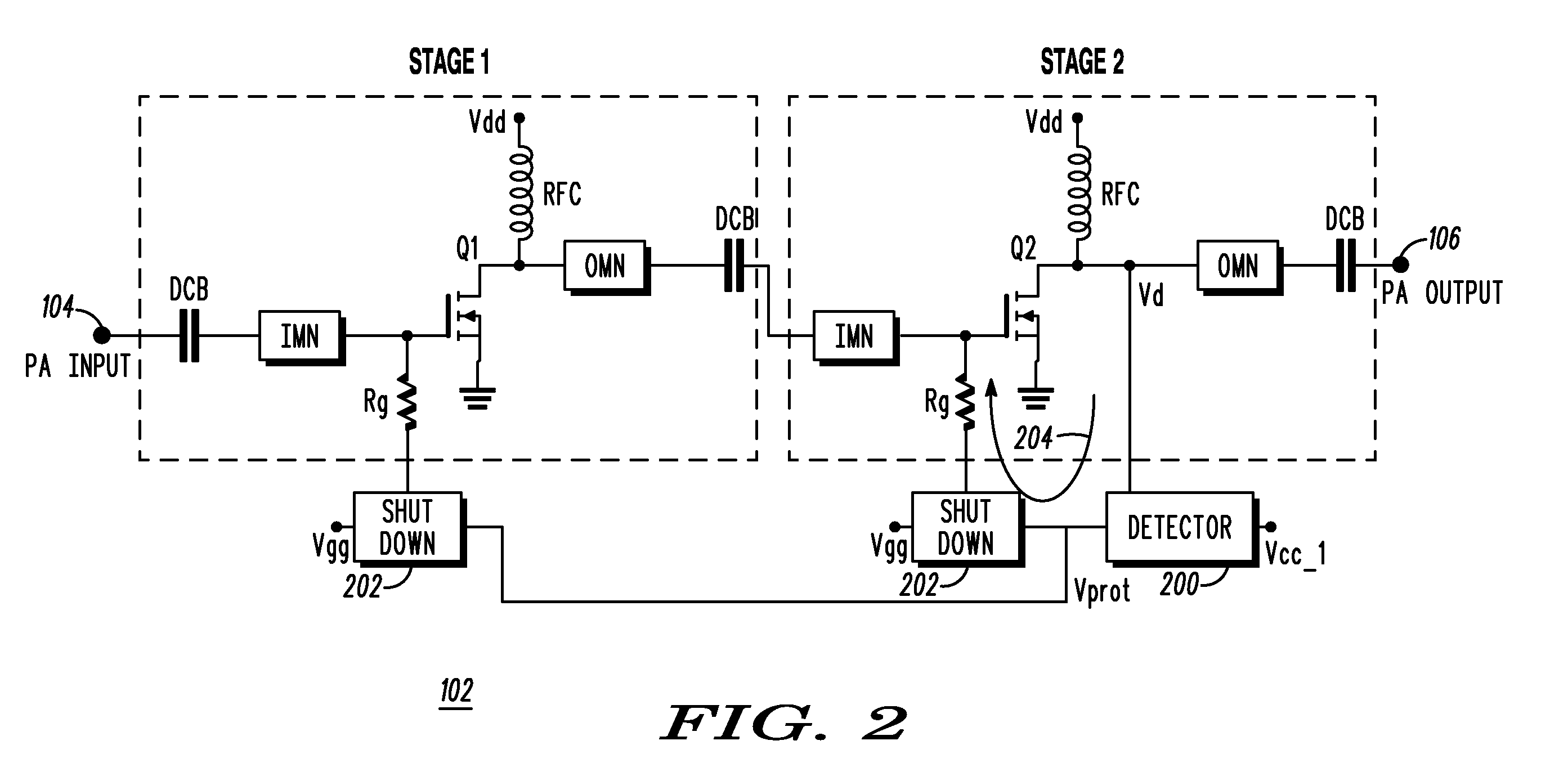
RF power amplifier protection
InactiveUS20080218271A1Emergency protective circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsDetector circuitsAudio power amplifier
A circuit and method for protecting a radio frequency power amplifier against peak drain voltage. A detector circuit has an input connected to a drain of a power transistor of an amplification stage of the power amplifier to detect a peak drain voltage therefrom. The detector circuit outputs a protection signal when the detected peak drain voltage exceeds a predetermined reference level. A shutdown circuit is coupled to the detector circuit and inputs the protection signal therefrom. The protection signal is used to remove a gate bias of at least one amplification stage of the power amplifier. High frequency components are used in the detector and protection circuits to immediately reduce the drain voltage from one or more of the amplification stages.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Structures and methods for data reading apparatus and reading out non-volatile memory using referencing cells
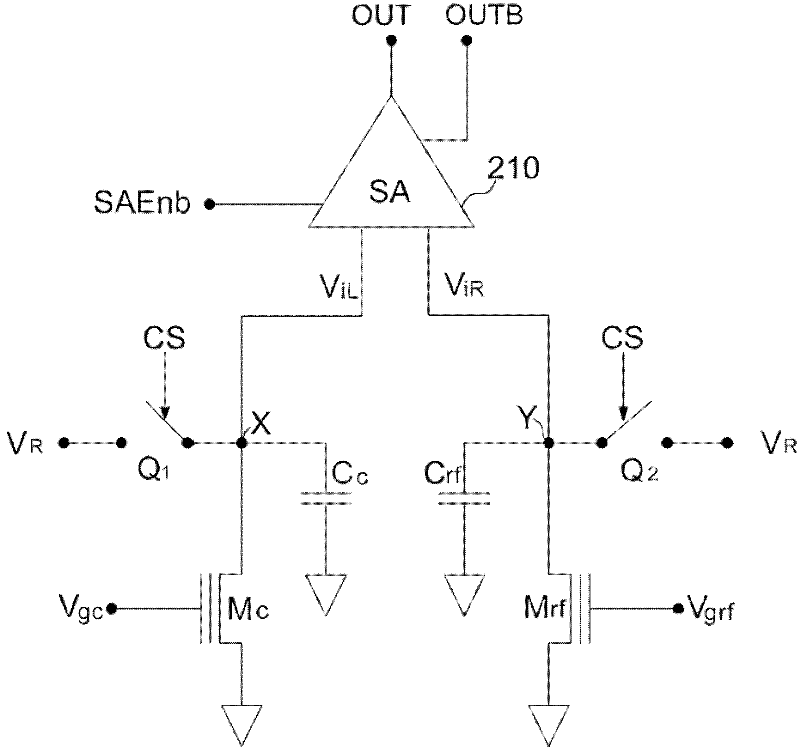
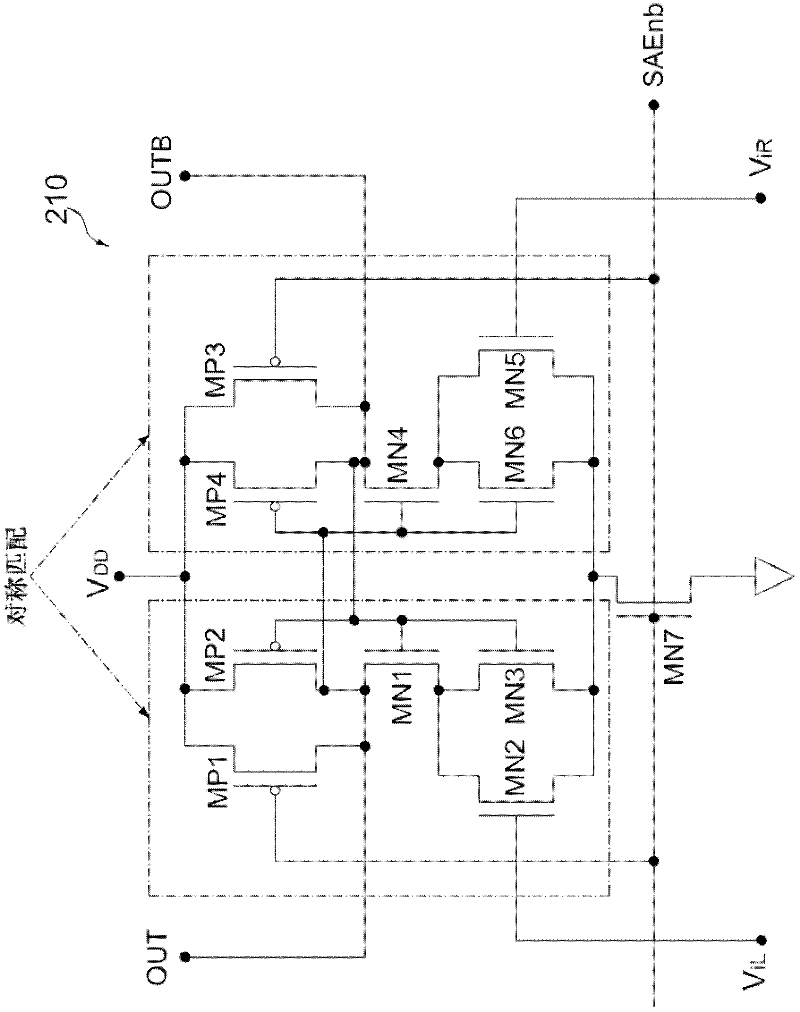
The structures and methods of a data reading apparatus and reading out semiconductor Non-Volatile Memory (NVM) using referencing cells are disclosed. The data reading apparatus comprises: -a sensing amplifier, which is used for sensing the sensing amplifier. -a first carry-in terminal and -a second carry-in terminal. The voltage difference between the first and second carry-in terminal. -a first capacitor and a second capacitor, connected with the first and second carry-in terminal respectively. The first capacitor and the second capacitor make an electrical discharge by reading a NVM unit and referencing a NVM unit when a grid bias is inflicted across control grids of a reading NVM unit and a referencing NVM unit simultaneously. And capacitance value of the first capacitor and the second capacitor is same materially. The new invented scheme can reduce large current consumption from the direct current biasing in the conventional scheme.
Owner:PEGASUS SEMICON SHANGHAI CO LTD
Thin film field effect transistor type gas sensor and preparation method thereof
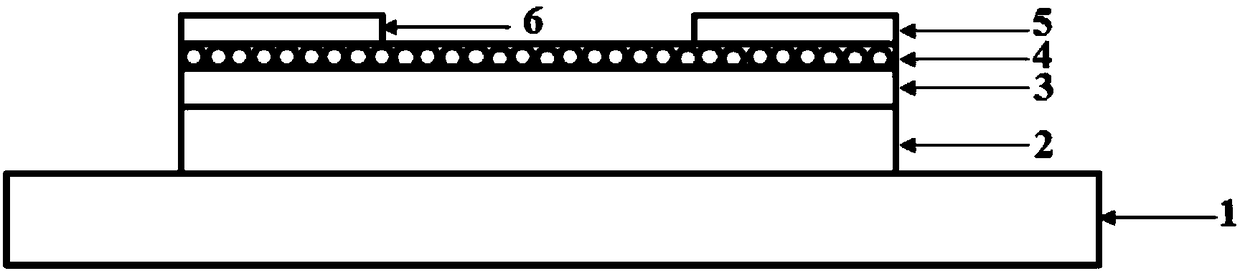
ActiveCN108447915AEnhanced room temperature gas-sensing effectImprove adsorption capacityTransistorMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBottom gate bottom contactQuantum dot
The invention discloses a thin film field effect transistor type gas sensor and a preparation method thereof. The sensor is a thin film field effect transistor with a bottom gate top contact type structure or a bottom gate bottom contact type structure. A thin film field effect transistor with a bottom grid top contact structure is taken as an example. The transistor comprises a substrate, a gateinsulating layer and a channel active layer from bottom to top. The channel active layer is a quantum dot thin film. A source electrode and a drain electrode are deposited above the substrate. A gateelectrode is further led out of the substrate. The internal composition, the structure, the overall process of the corresponding preparation method and the parameters during all steps of the preparation method of the thin film field effect transistor type gas sensor are improved. The quantum dot thin film serves as a channel active layer and a gas sensitive layer at the same time, and the gas response of multiple parameters is comprehensively regulated by utilizing the grid bias voltage. As a result, the prepared gas sensor is high in sensitivity, low in power consumption and high in selectivity. The effect of detecting low-concentration target gases, such as NO2 and H2S, is achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com