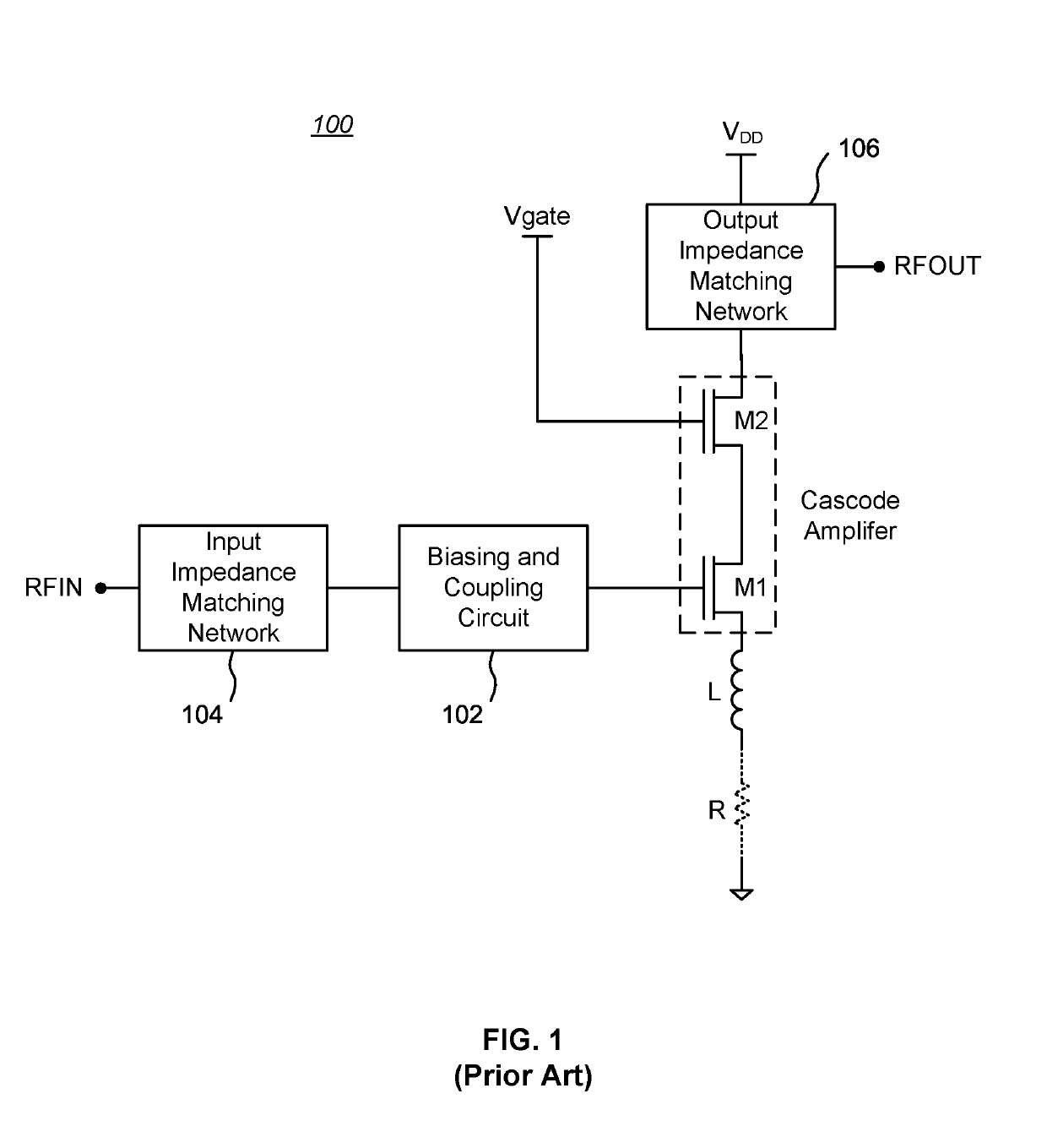
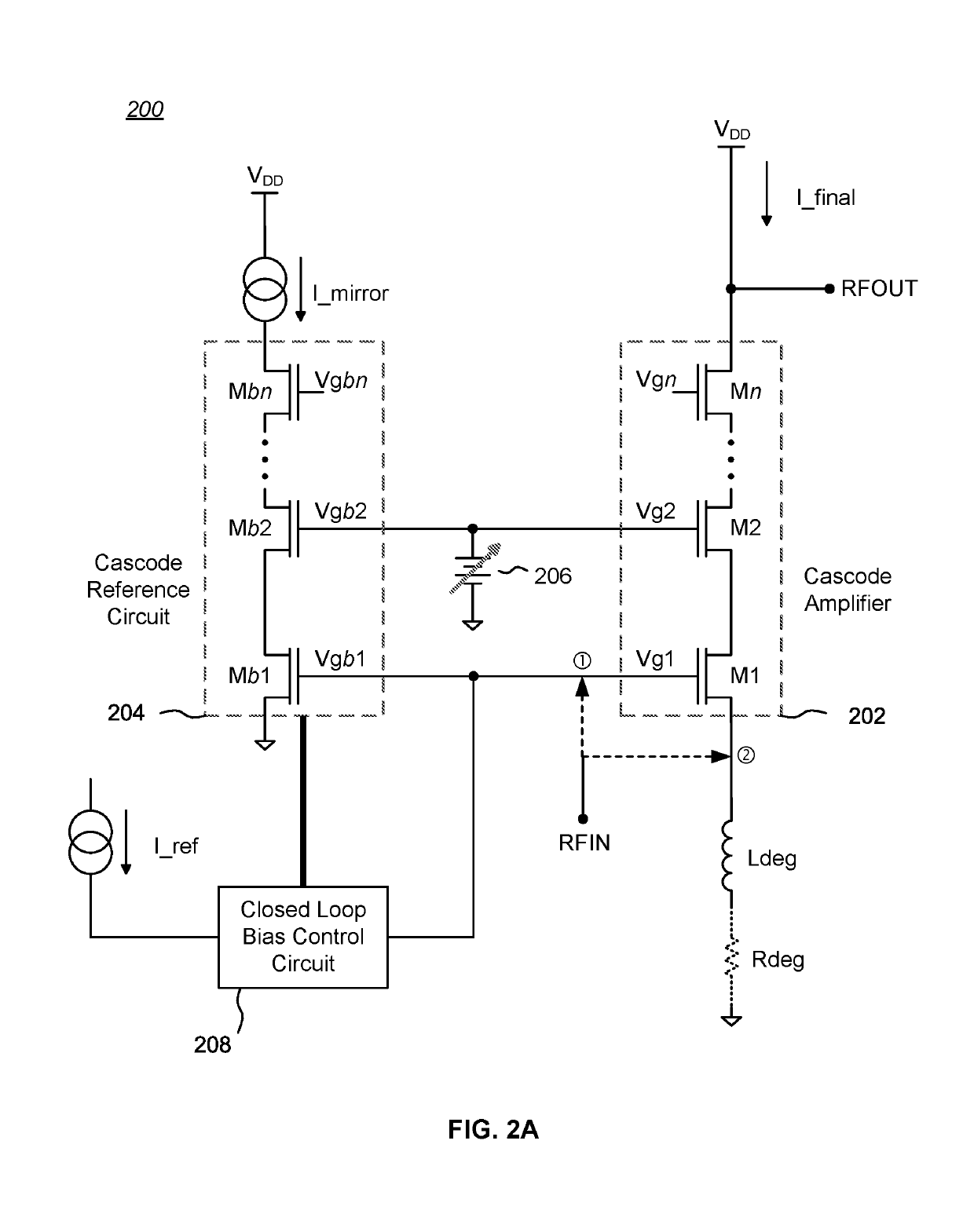
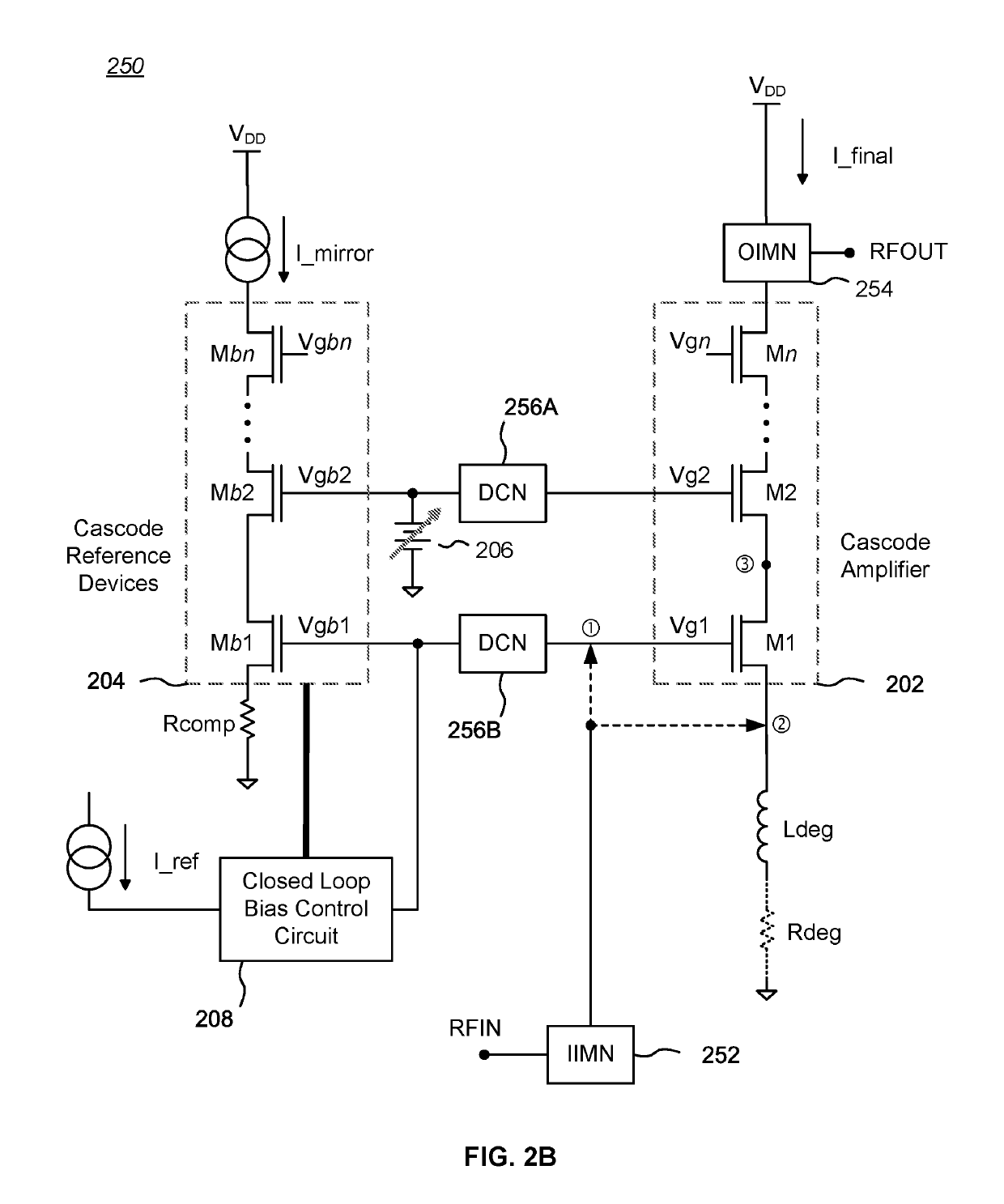
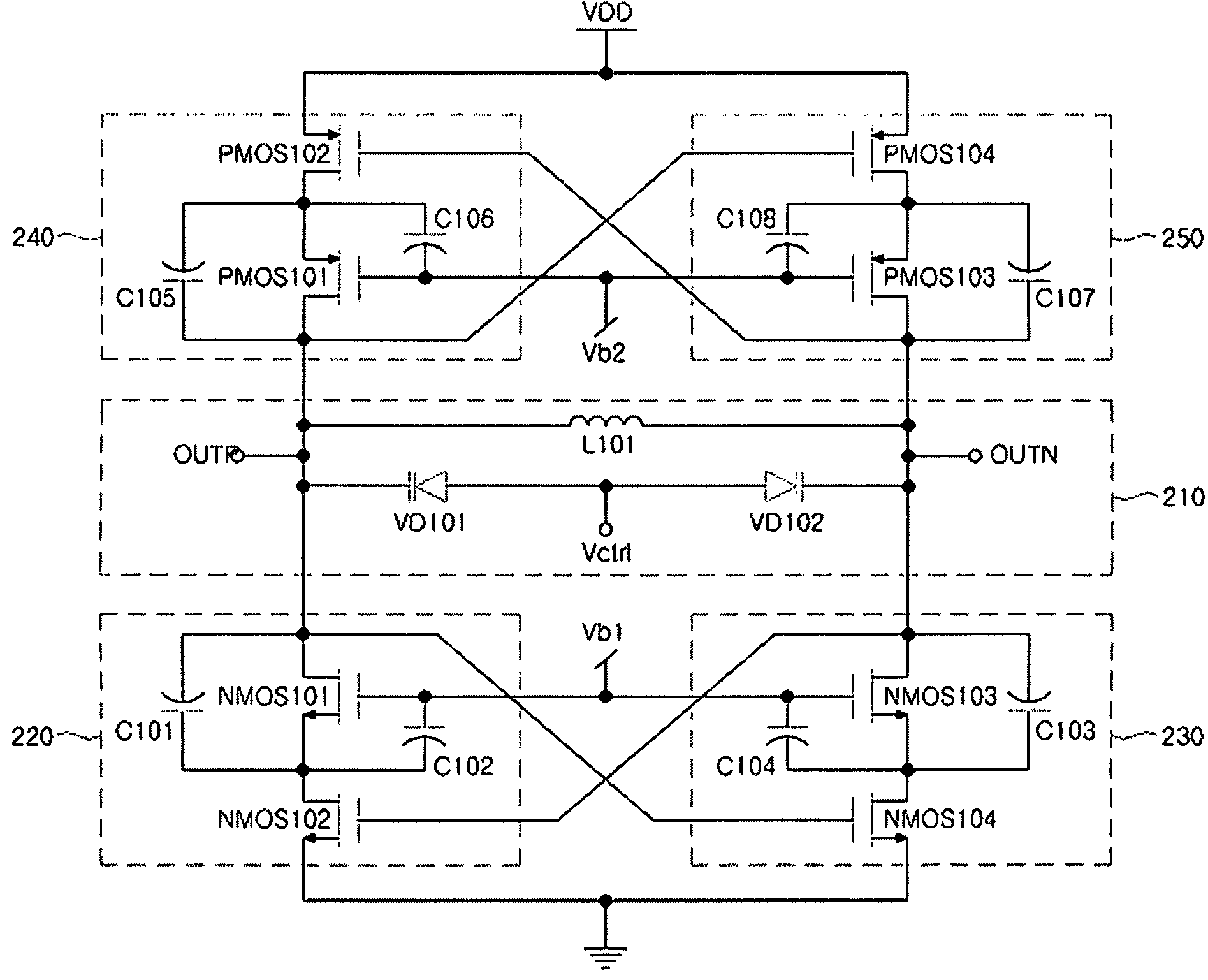
Patents
Literature
199 results about "Cascode amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
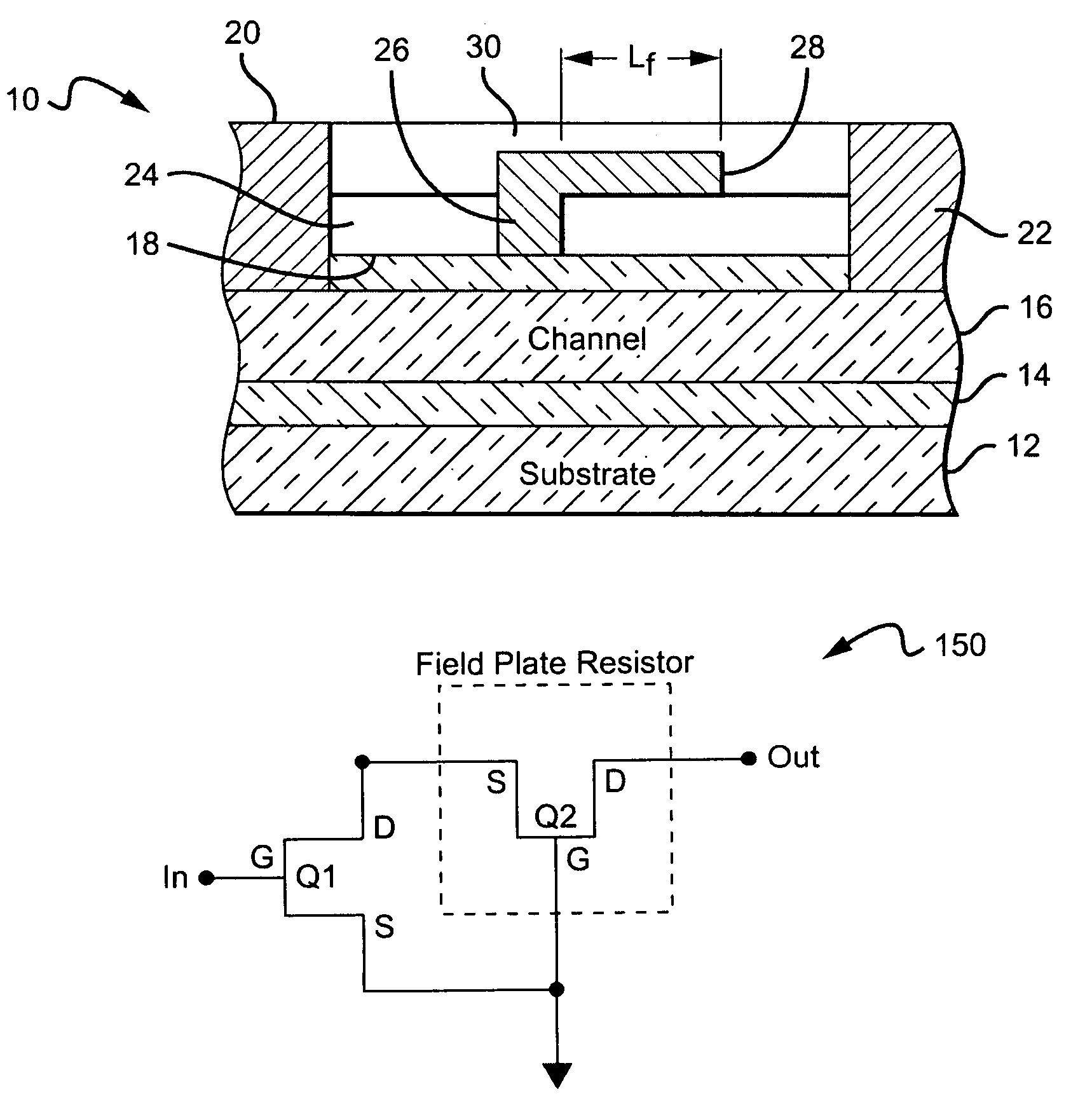
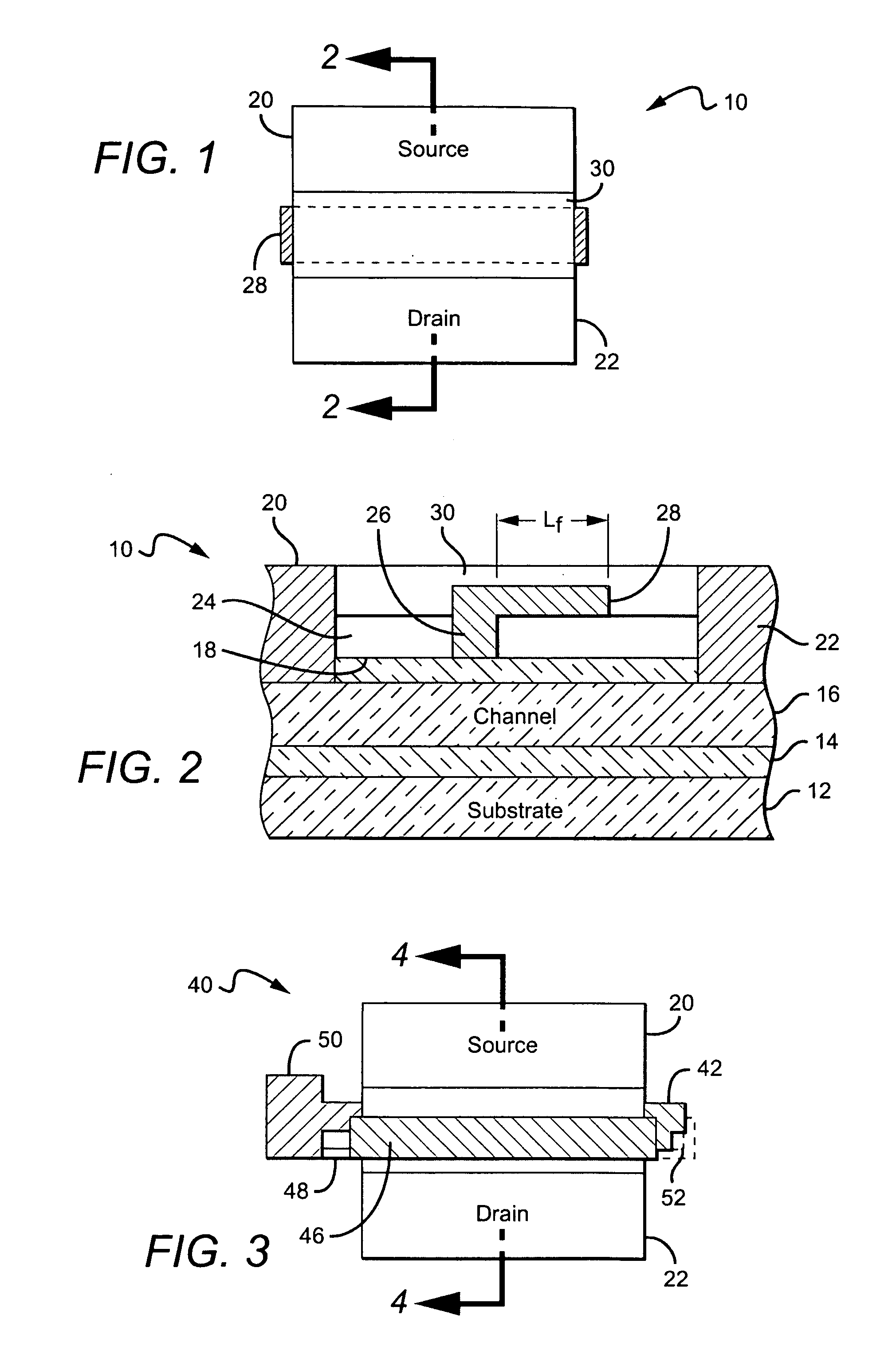
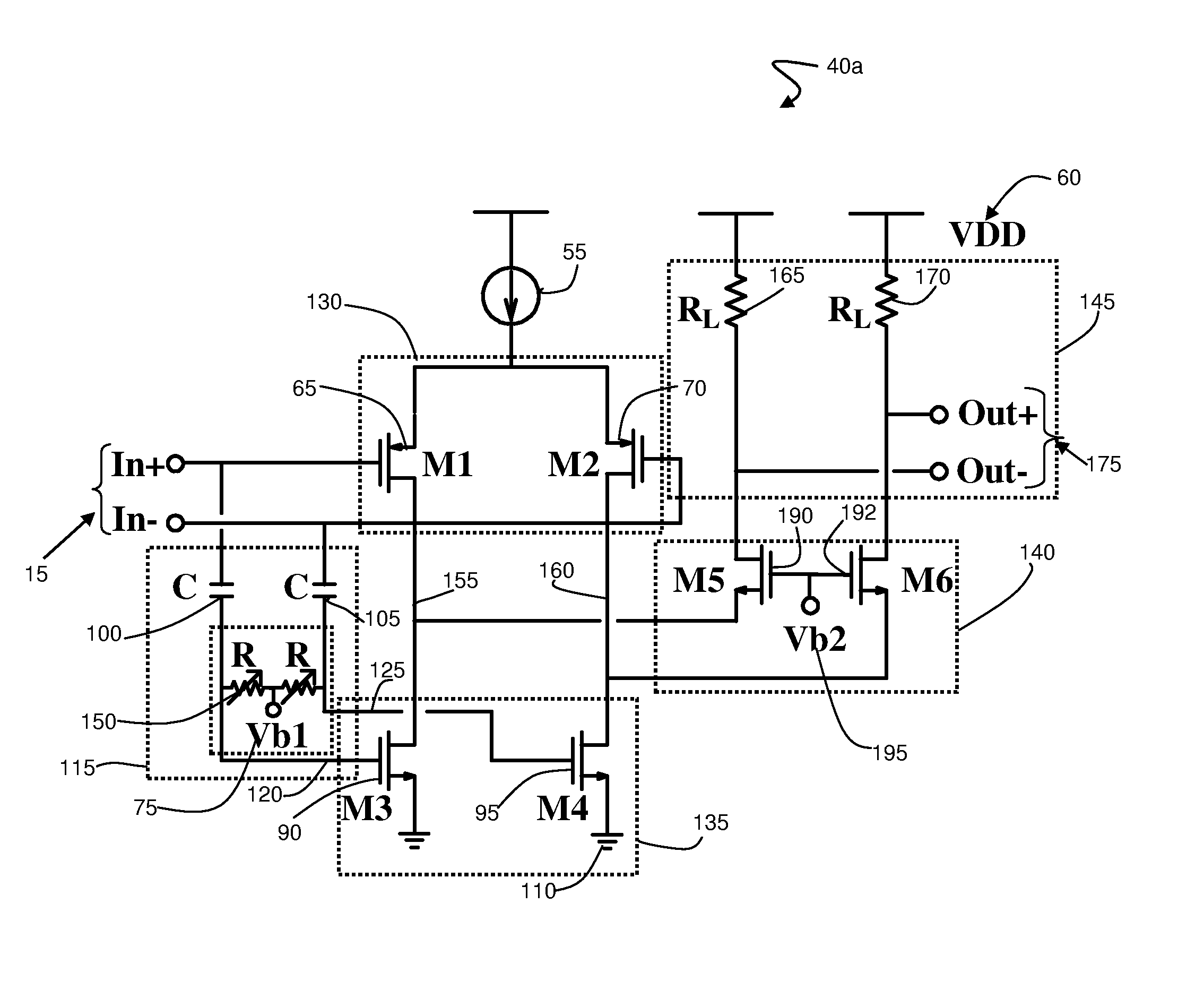
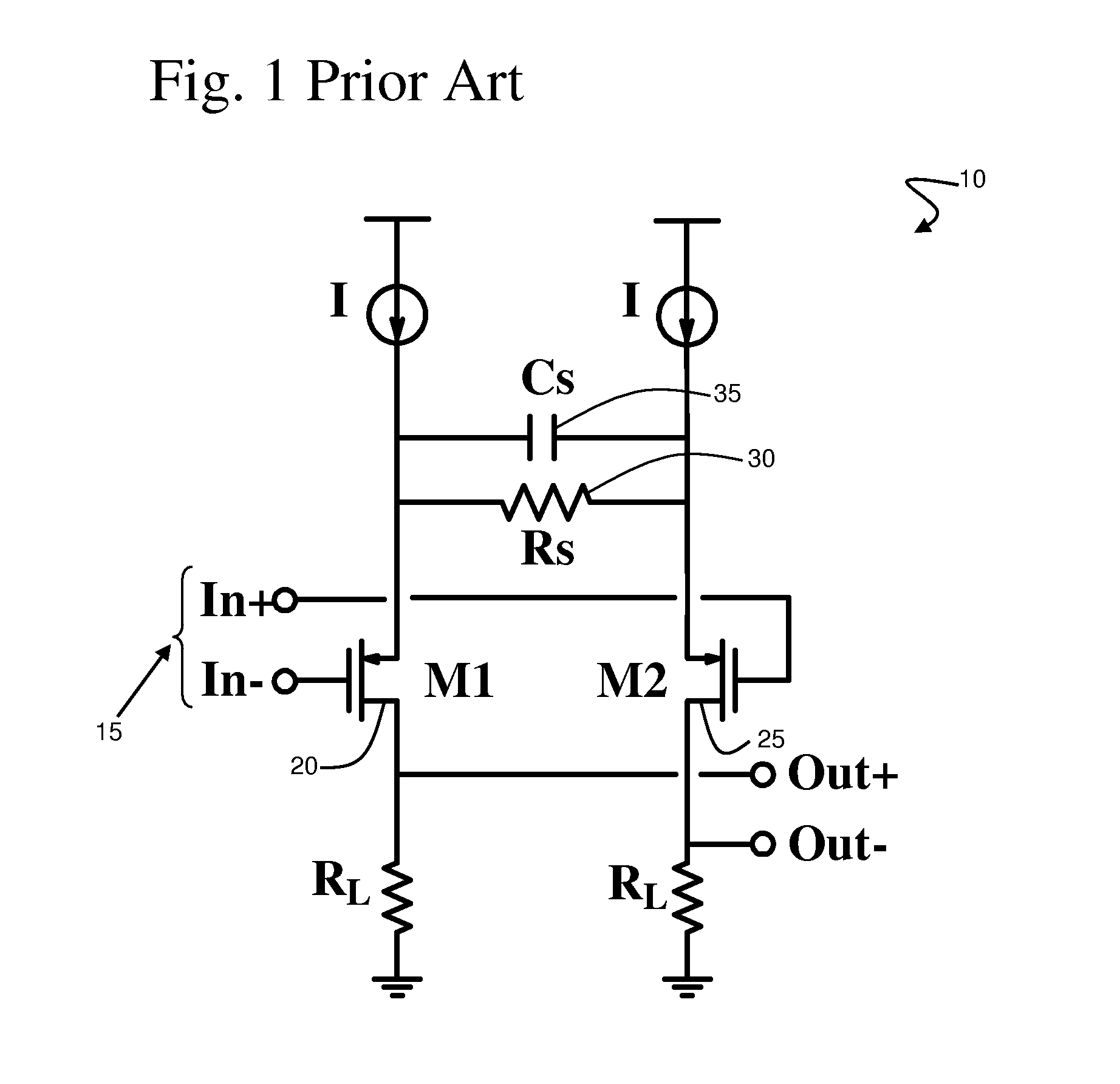
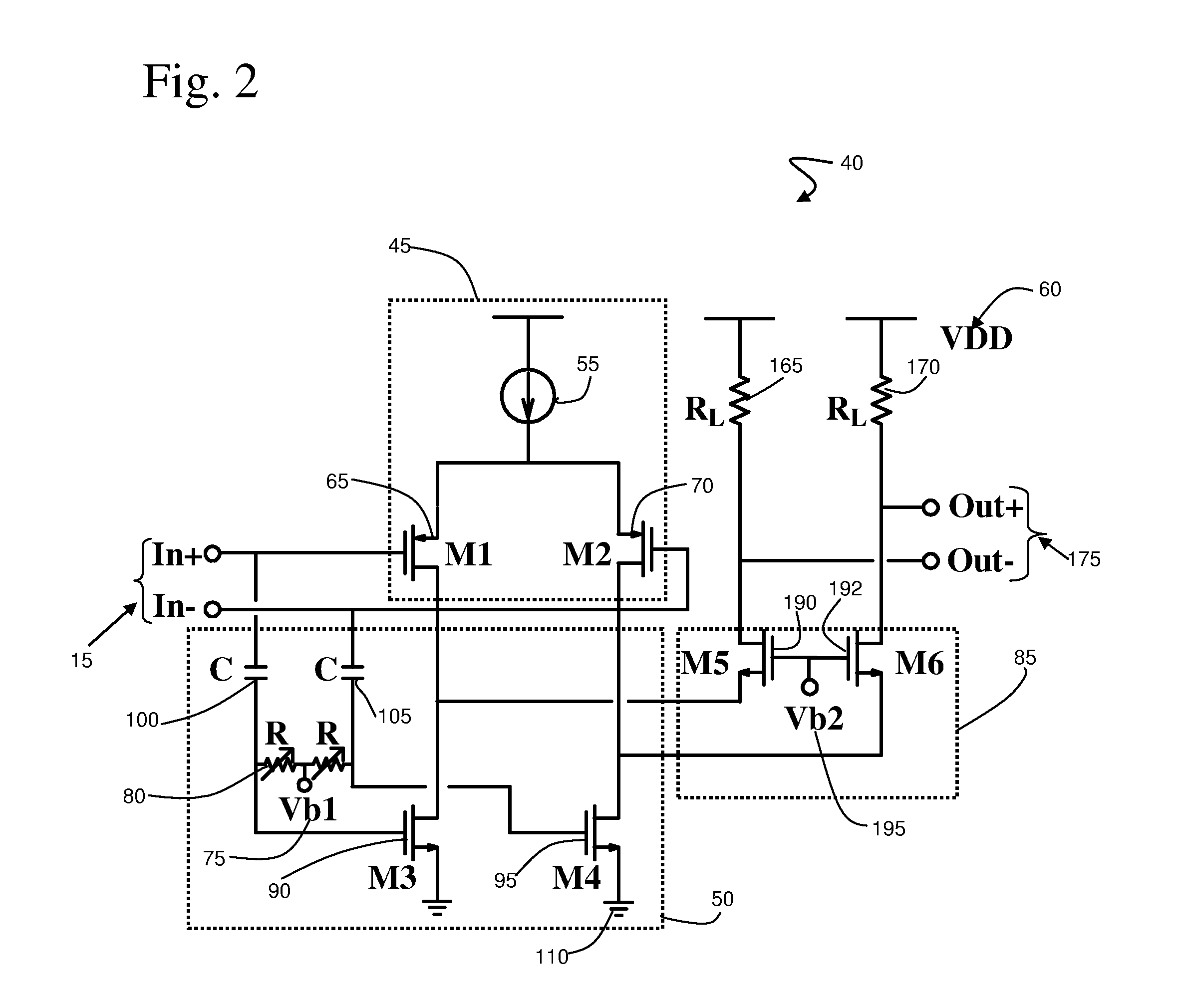
Cascode amplifier structures including wide bandgap field effect transistor with field plates
ActiveUS20050051800A1Efficient high powerEfficient high-frequency signal amplificationSolid-state devicesAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierHemt circuits
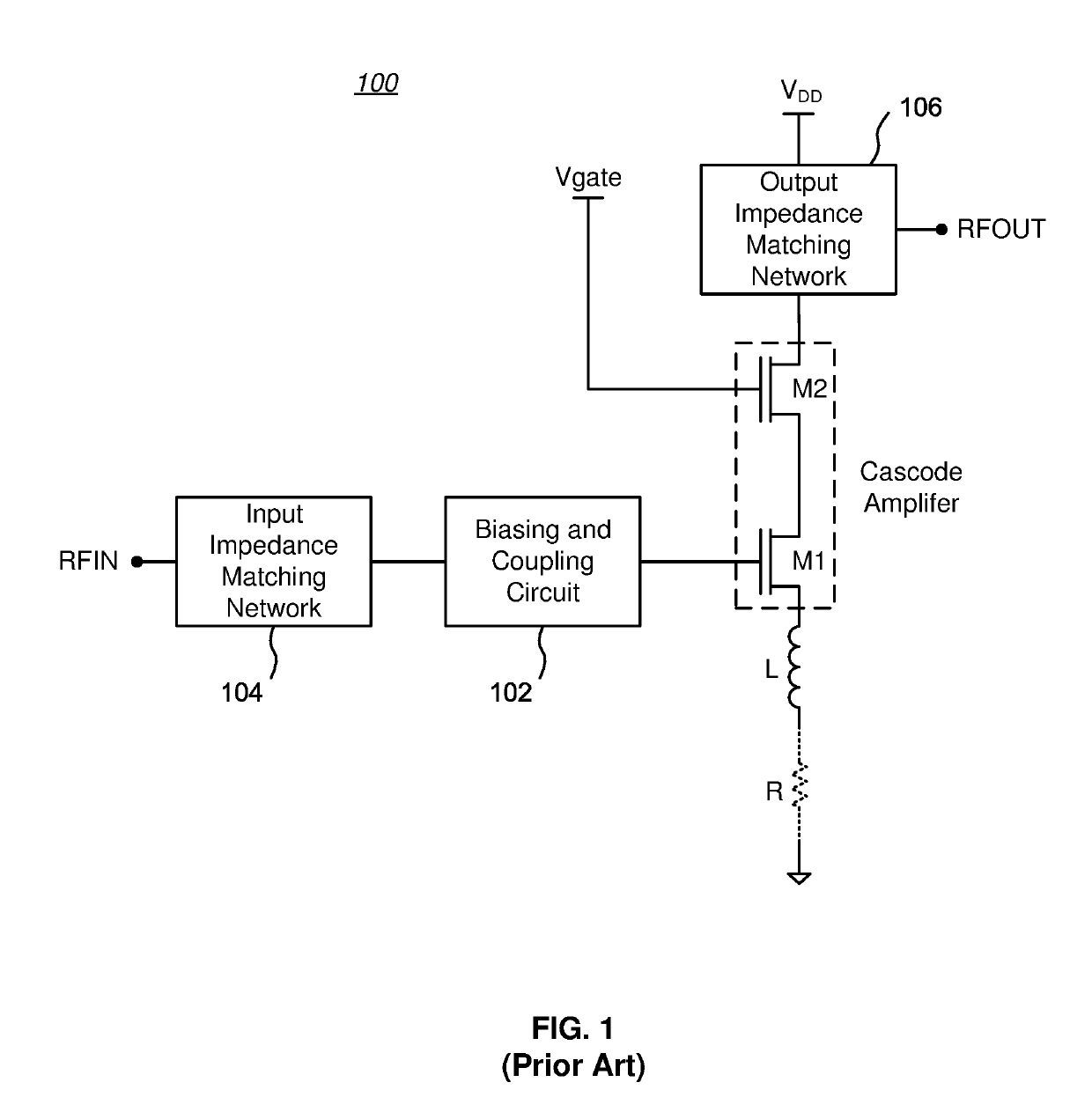
A multi-stage amplifier circuit arranged to take advantage of the desirable characteristics of non-field-plate and field plate transistors when amplifying a signal. One embodiment of a multi-stage amplifier according to the present invention comprises a non-field-plate transistor and a field-plate transistor. The field-plate transistor has at least one field plate arranged to reduce the electric field strength within the field plate transistor during operation. The non-field plate transistor is connected to the field plate transistor, with the non-field-plate providing current gain and the field plate transistor providing voltage gain. In one embodiment the non-field-plate and field plate transistors are coupled together in a cascode arrangement.
Owner:CREE INC
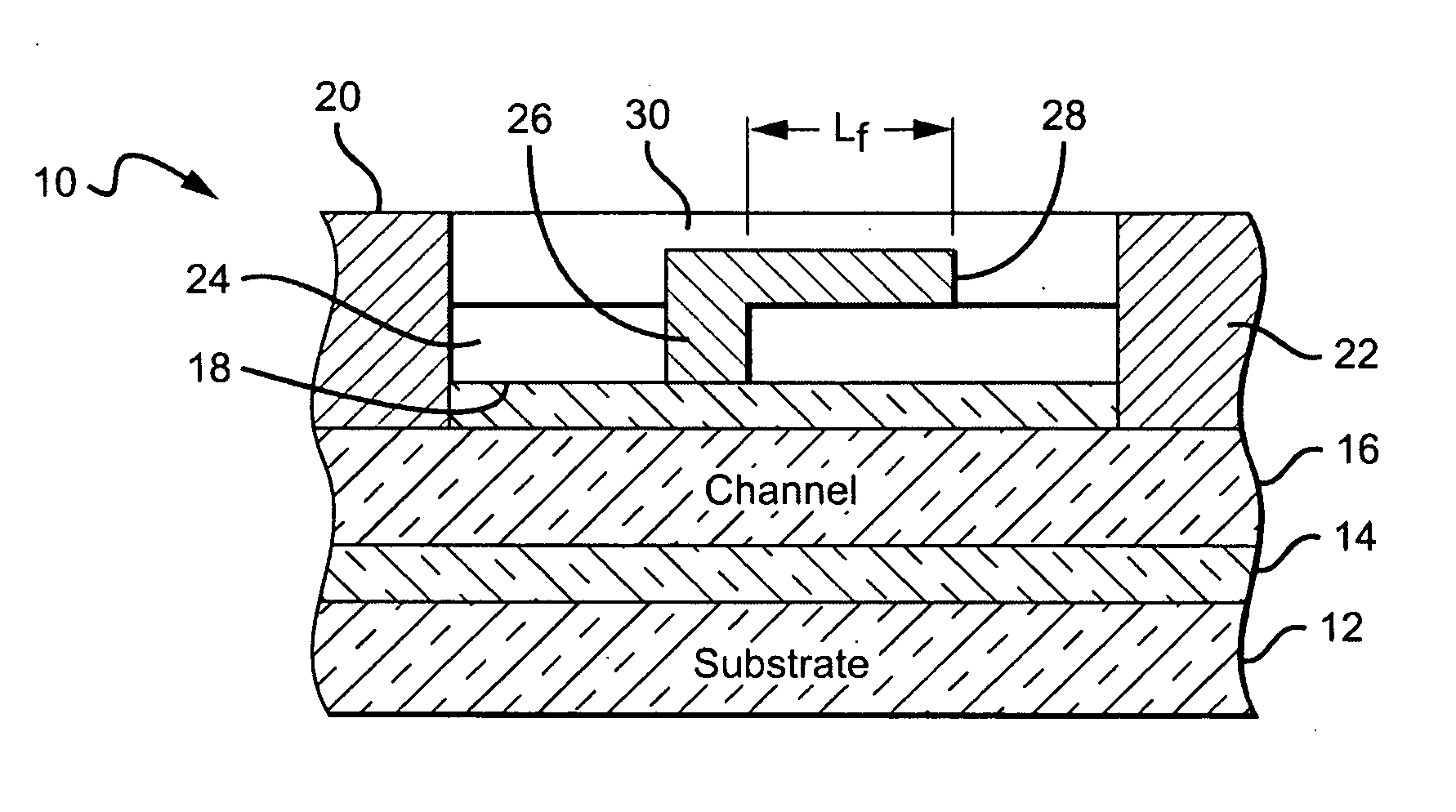
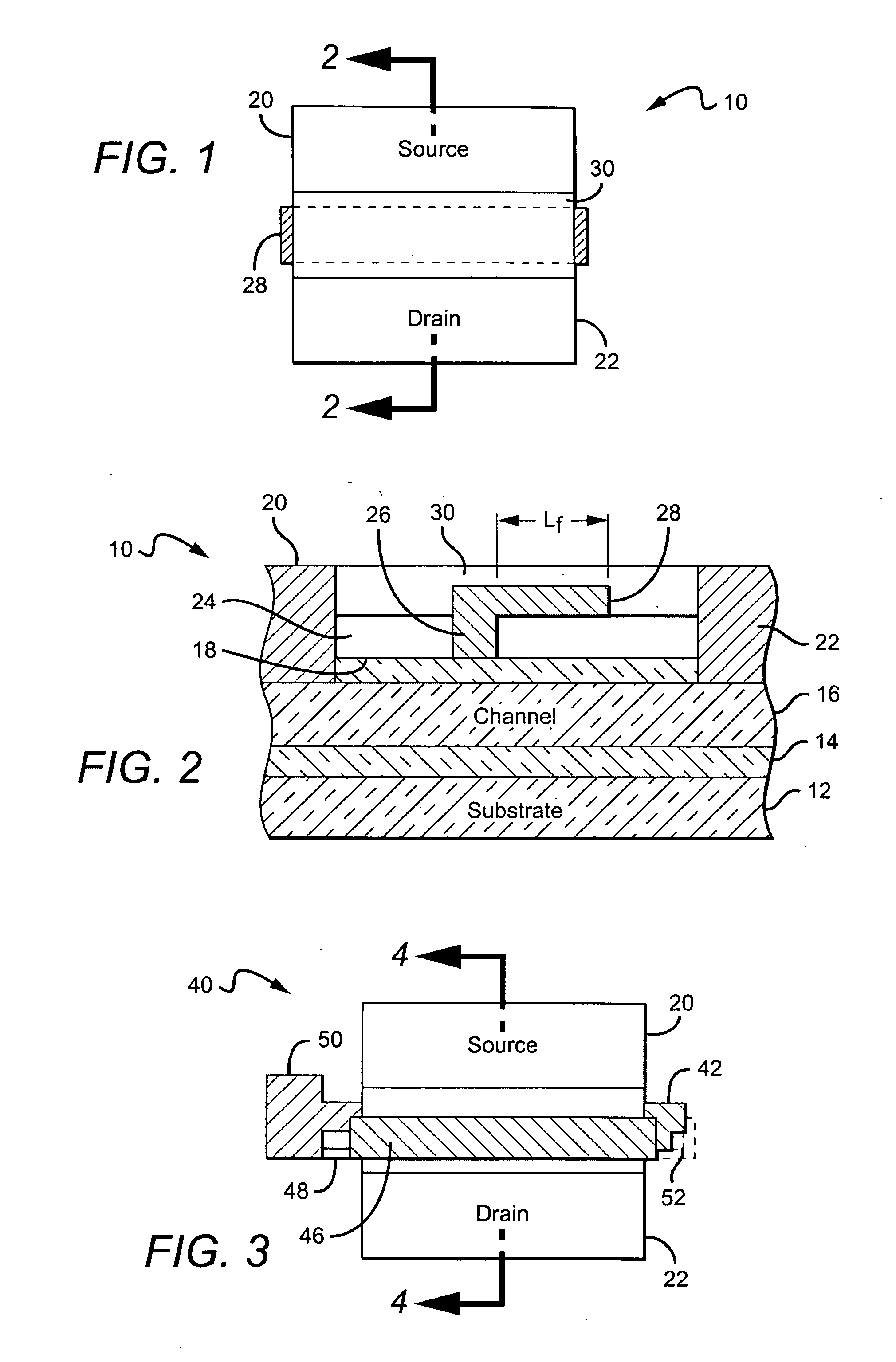
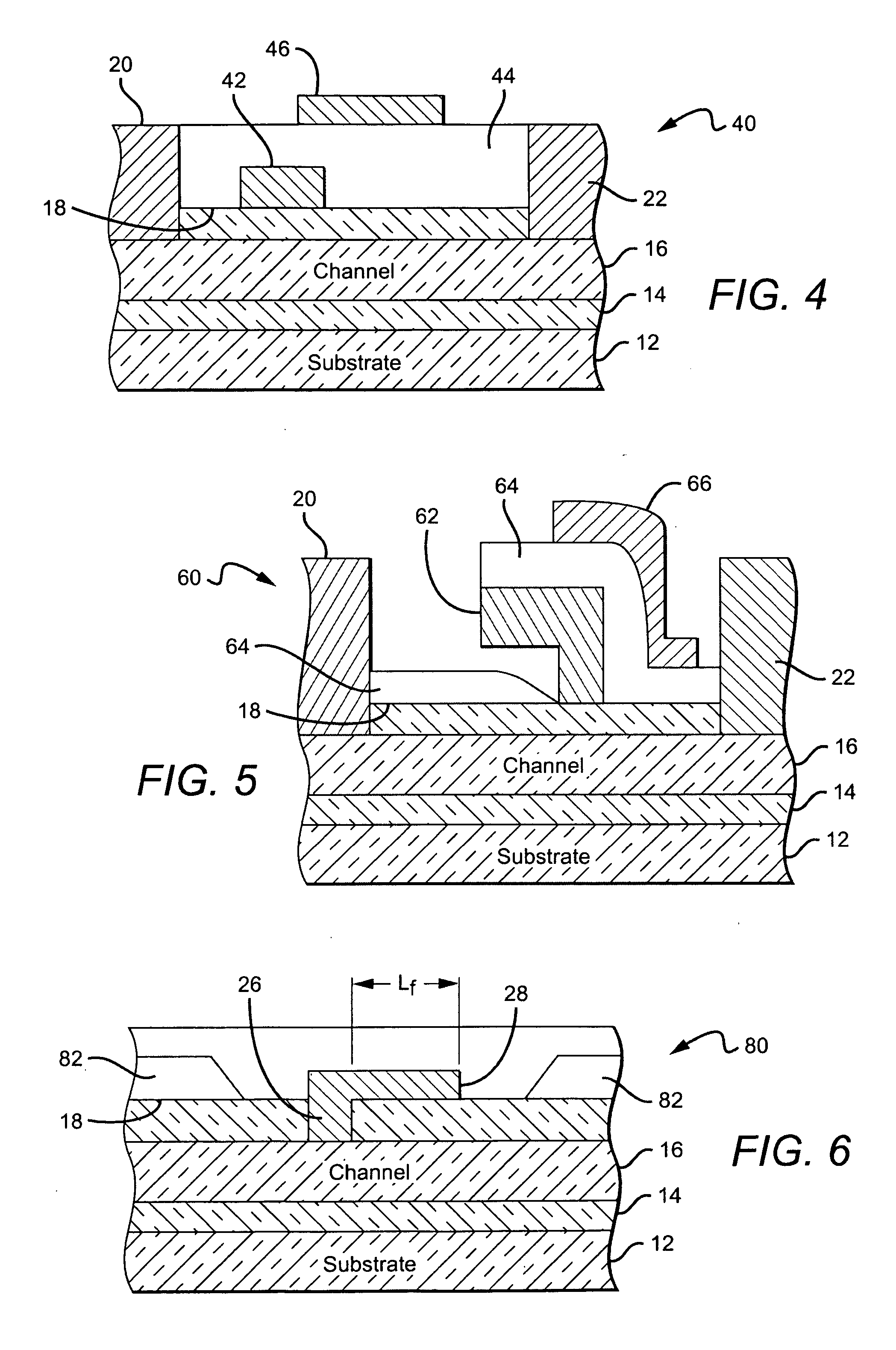
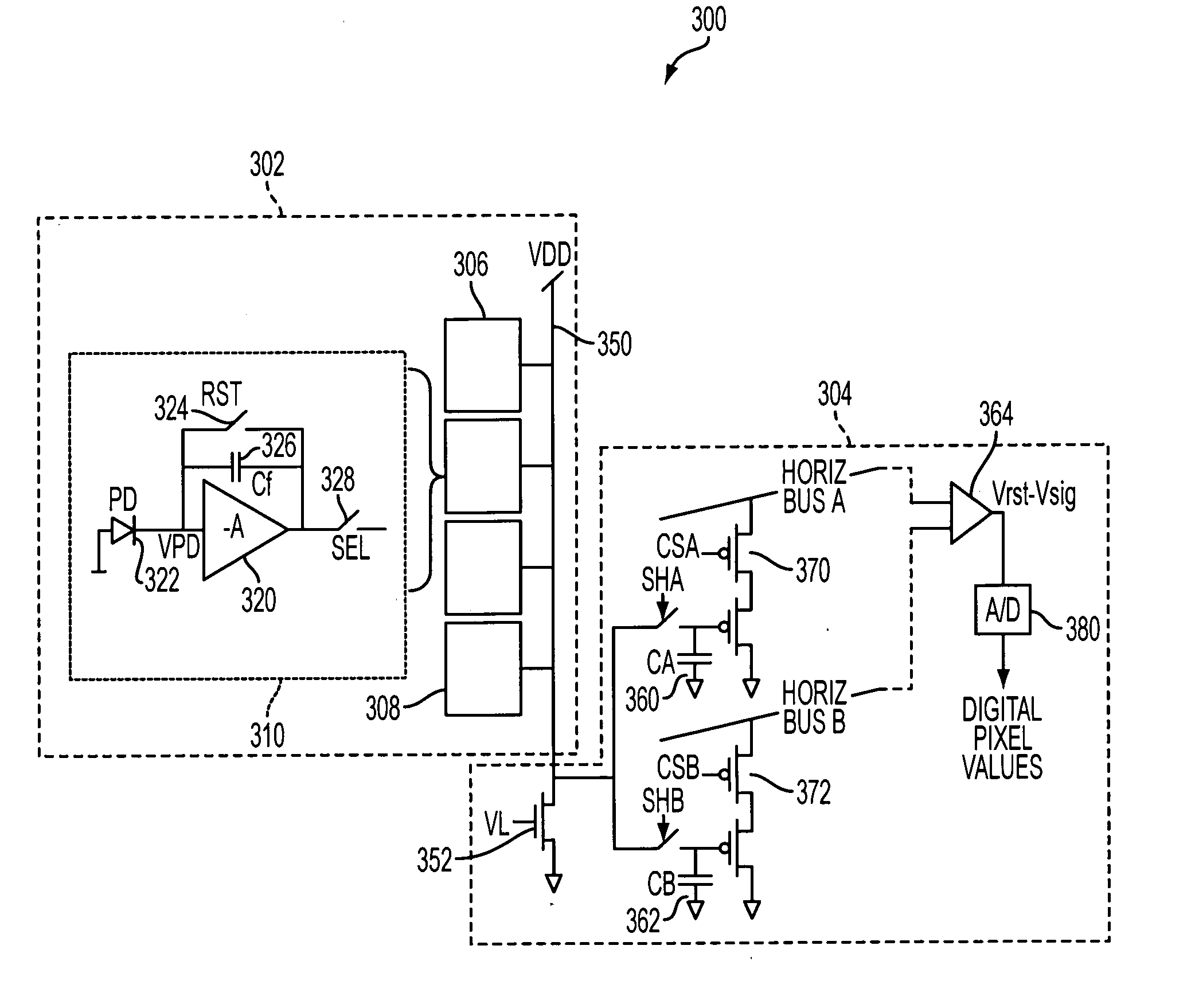
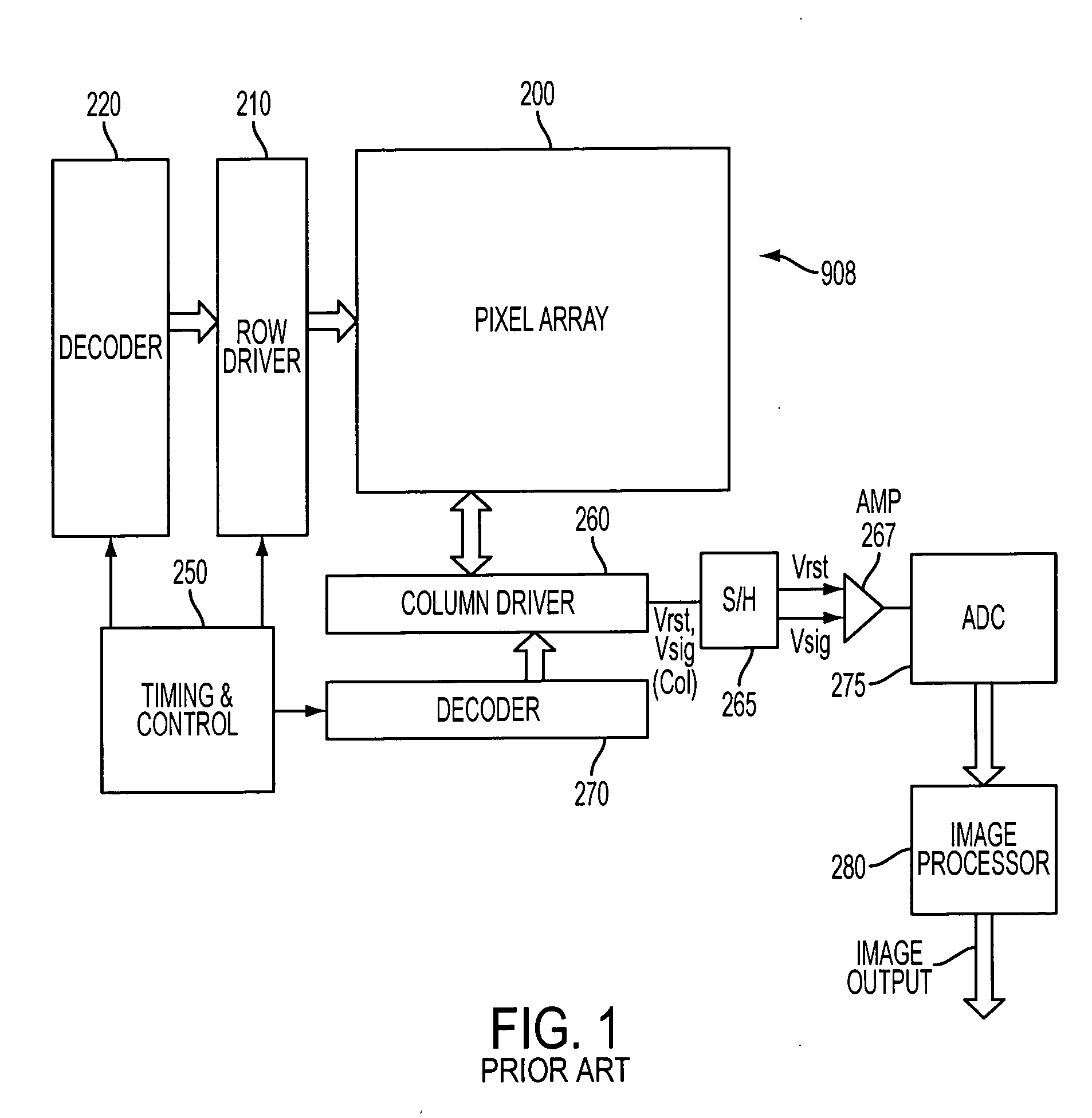
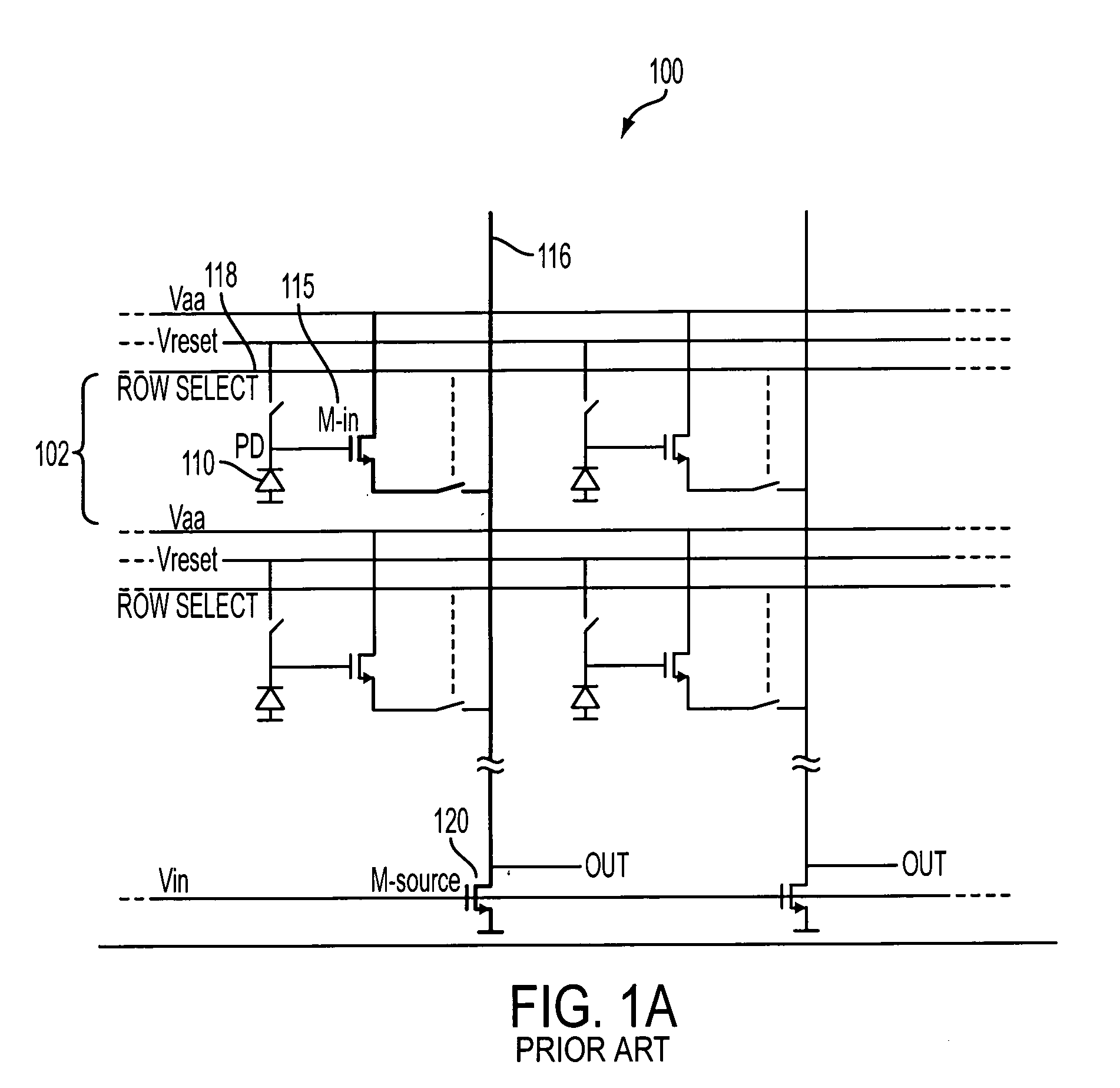
Amplification with feedback capacitance for photodetector signals
ActiveUS20050218299A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitancePhotodetector
Signals from an imager pixel photodetector are received by an amplifier having capacitive feedback, such as a capacitive transimpedance amplifier (CTIA). The amplifier can be operated at a low or no power level during an integration period of a photodetector to reduce power dissipation. The amplifier can be distributed, with an amplifier element within each pixel of an array and with amplifier output circuitry outside the pixel array. The amplifier can be a single ended cascode amplifier, a folded cascode amplifier, a differential input telescopic cascode amplifier, or other configuration. The amplifier can be used in pixel configurations where the amplifier is directly connected to the photodetector, or in configurations which use a transfer transistor to couple signal charges to a floating diffusion node with the amplifier being coupled to the floating diffusion node.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Cascode amplifier structures including wide bandgap field effect transistor with field plates
ActiveUS7126426B2Increase powerHigh frequency signal amplificationSolid-state devicesAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierEngineering
A multi-stage amplifier circuit arranged to take advantage of the desirable characteristics of non-field-plate and field plate transistors when amplifying a signal. One embodiment of a multi-stage amplifier according to the present invention comprises a non-field-plate transistor and a field-plate transistor. The field-plate transistor has at least one field plate arranged to reduce the electric field strength within the field plate transistor during operation. The non-field plate transistor is connected to the field plate transistor, with the non-field-plate providing current gain and the field plate transistor providing voltage gain. In one embodiment the non-field-plate and field plate transistors are coupled together in a cascode arrangement.
Owner:CREE INC
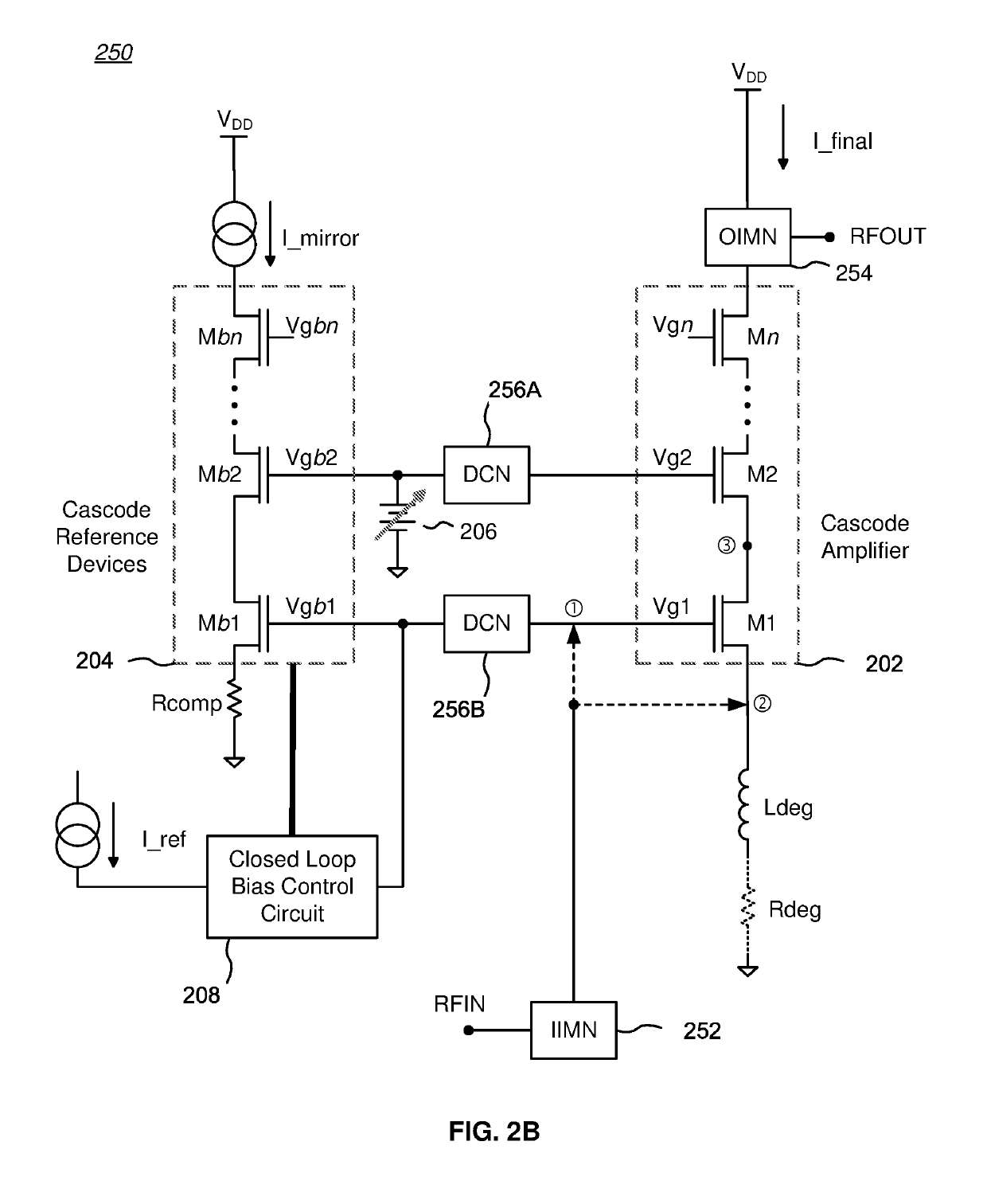
Cascode Amplifier Bias Circuits
ActiveUS20180083578A1Amplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesLow noiseAudio power amplifier
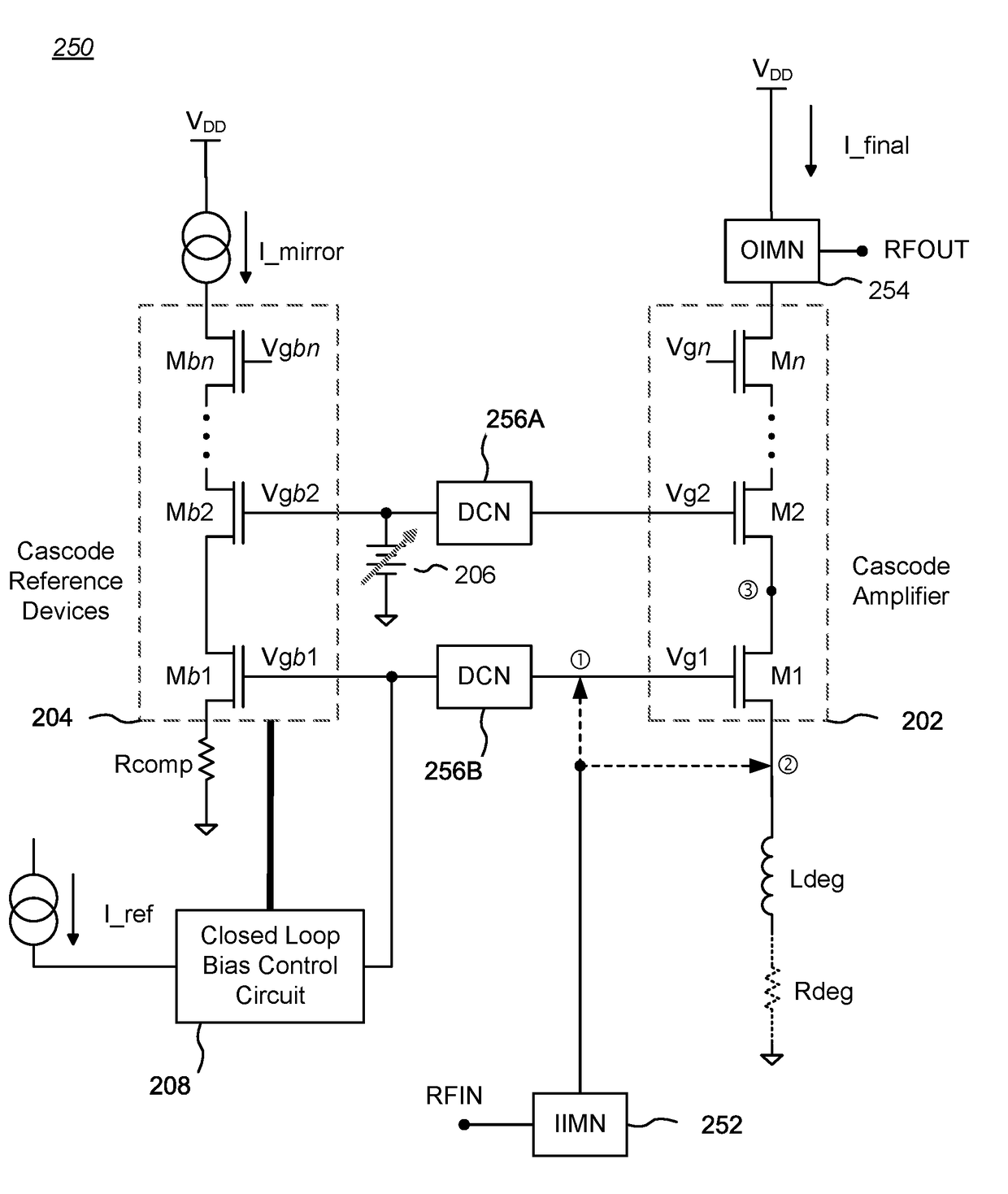
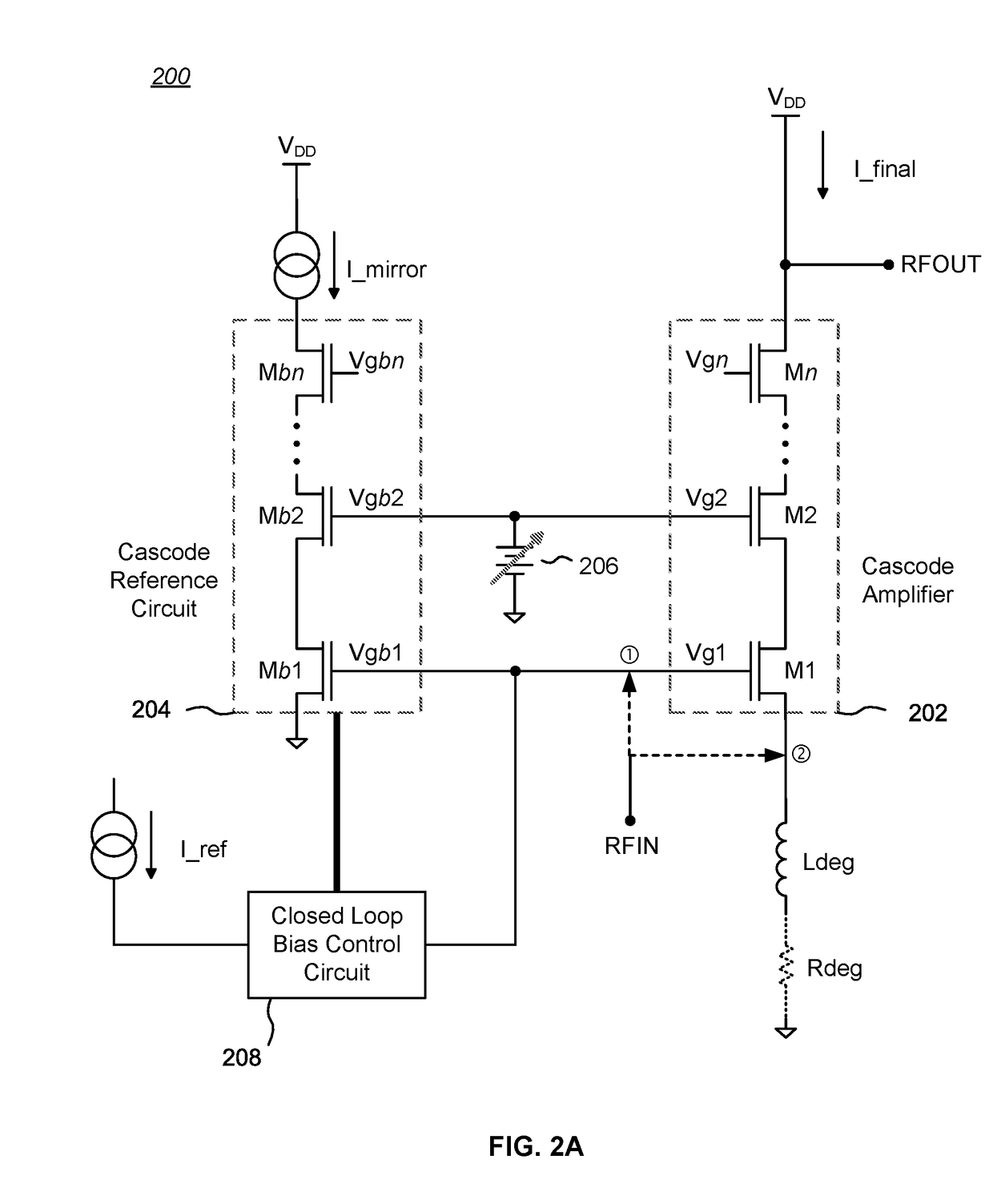
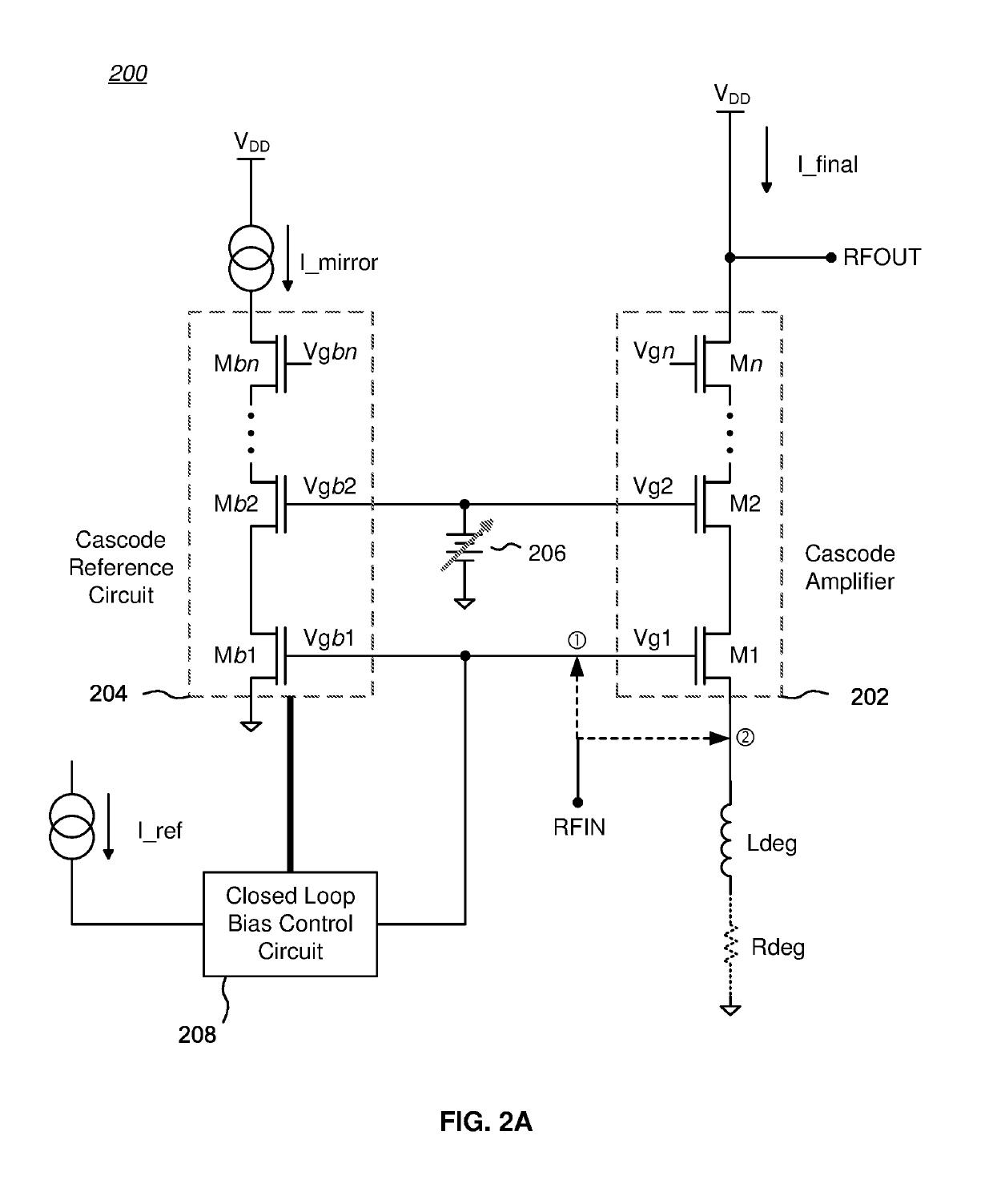
Bias circuits and methods for silicon-based amplifier architectures that are tolerant of supply and bias voltage variations, bias current variations, and transistor stack height, and compensate for poor output resistance characteristics. Embodiments include power amplifiers and low-noise amplifiers that utilize a cascode reference circuit to bias the final stages of a cascode amplifier under the control of a closed loop bias control circuit. The closed loop bias control circuit ensures that the current in the cascode reference circuit is approximately equal to a selected multiple of a known current value by adjusting the gate bias voltage to the final stage of the cascode amplifier. The final current through the cascode amplifier is a multiple of the current in the cascode reference circuit, based on a device scaling factor representing the relative sizes of the transistor devices in the cascode amplifier and in the cascode reference circuit.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Folded-cascode amplifier with adjustable continuous time equalizer
InactiveUS7683720B1High gainAmplifier combinationsMetal working apparatusAudio power amplifierEngineering
A system and method are provided for a folded cascode amplifier circuit that includes a first order high-pass filter coupled to a first bias voltage, a first input signal and a second input signal, the first input signal and the second input signal defining a differential input signal and the first order high-pass filter arranged to establish a first bias output and a second bias output. To amplify the full-spectrum content of the input signal, the amplifier circuit includes a full-spectrum content amplifier coupled between the first input signal, the second input signal and a current source. To amplify the high-frequency content of the input signal to achieve equalization, the amplifier circuit includes a high-frequency content amplifier coupled to the first bias output and the second bias output, the high-frequency content amplifier arranged to amplify the high-frequency content of the differential input signal to achieve equalization.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Variable-gain amplifier
ActiveUS7649418B2Reduce voltageImprove featuresGain controlAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Slew rate enhancement circuitry for folded cascode amplifier
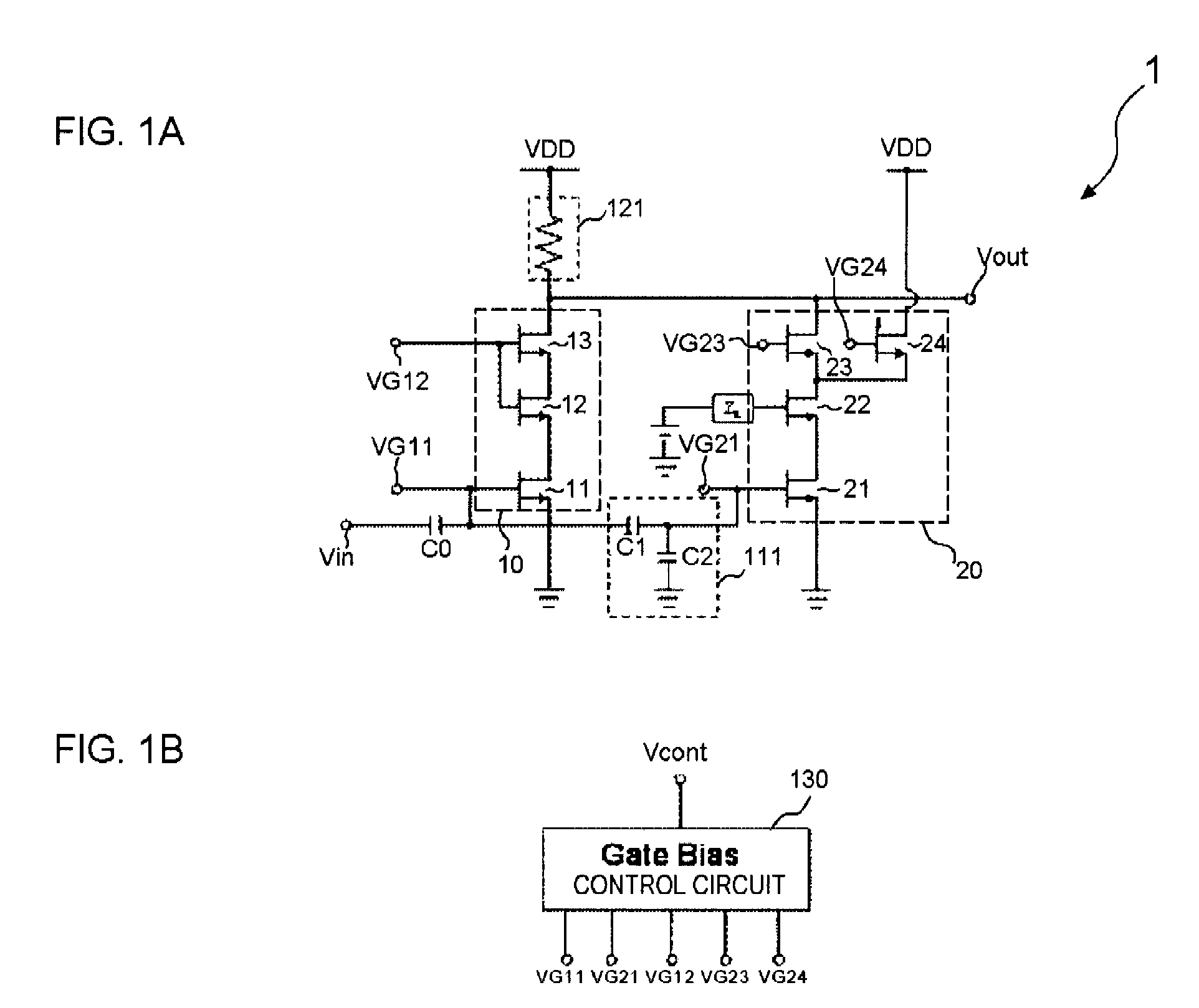
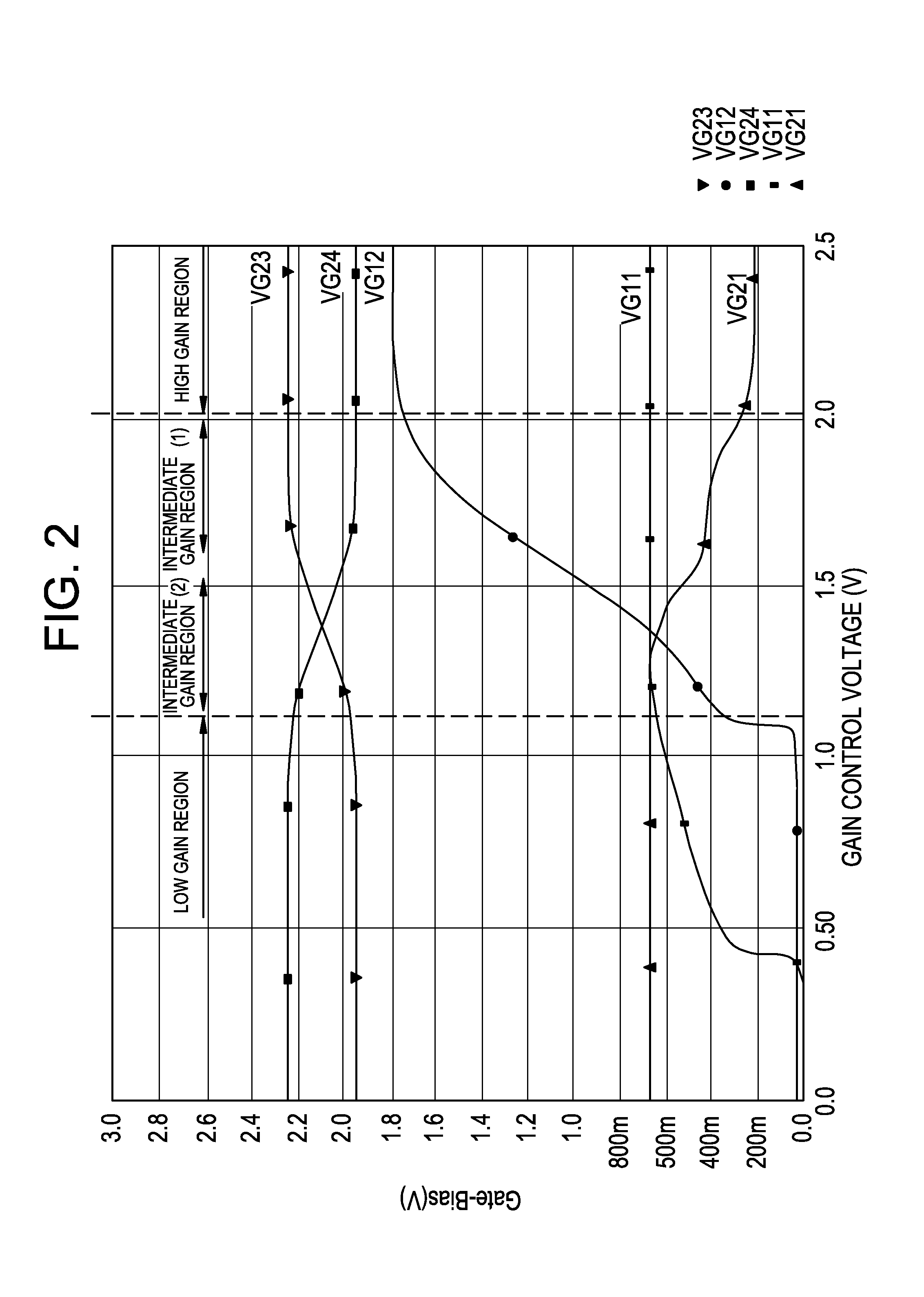
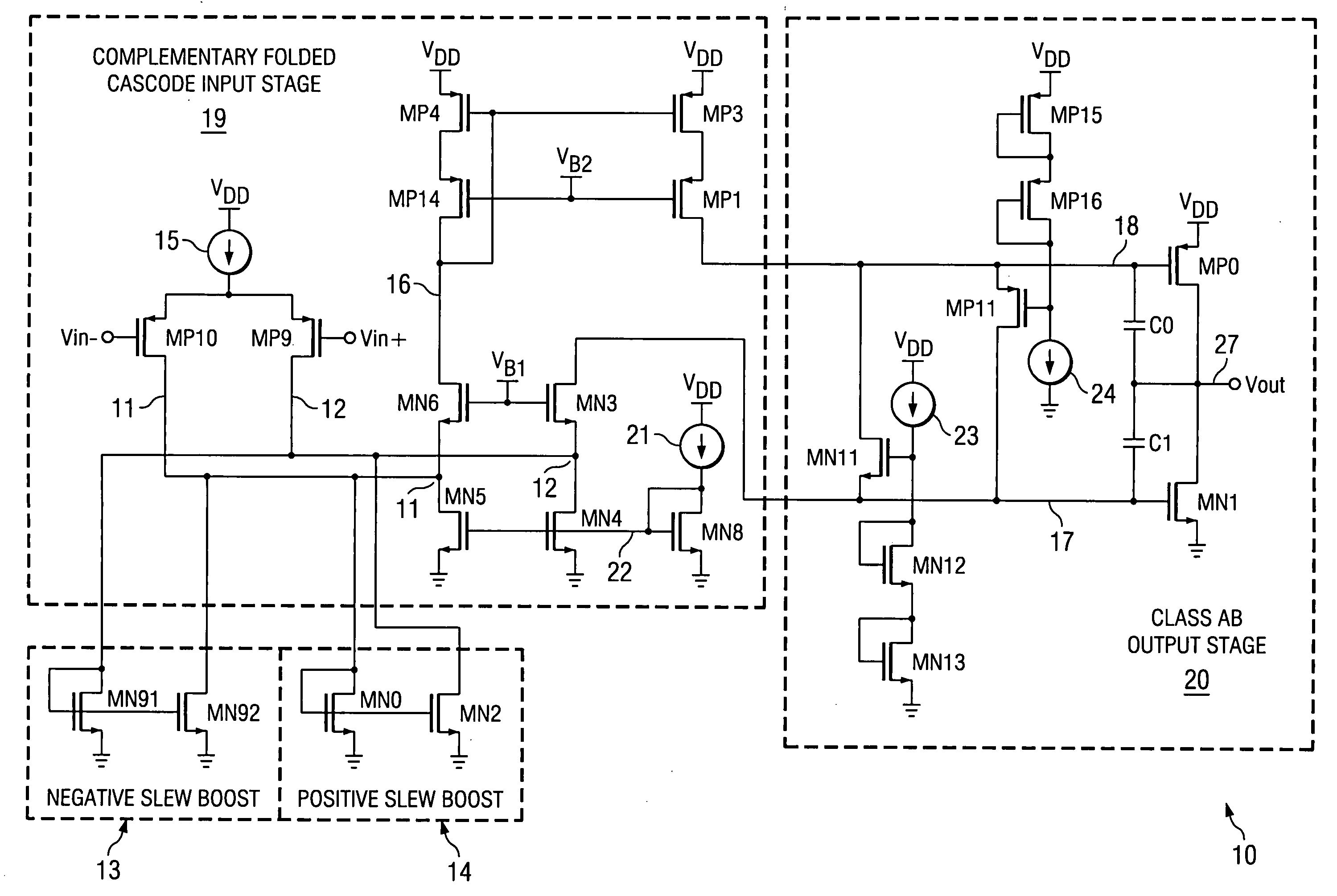
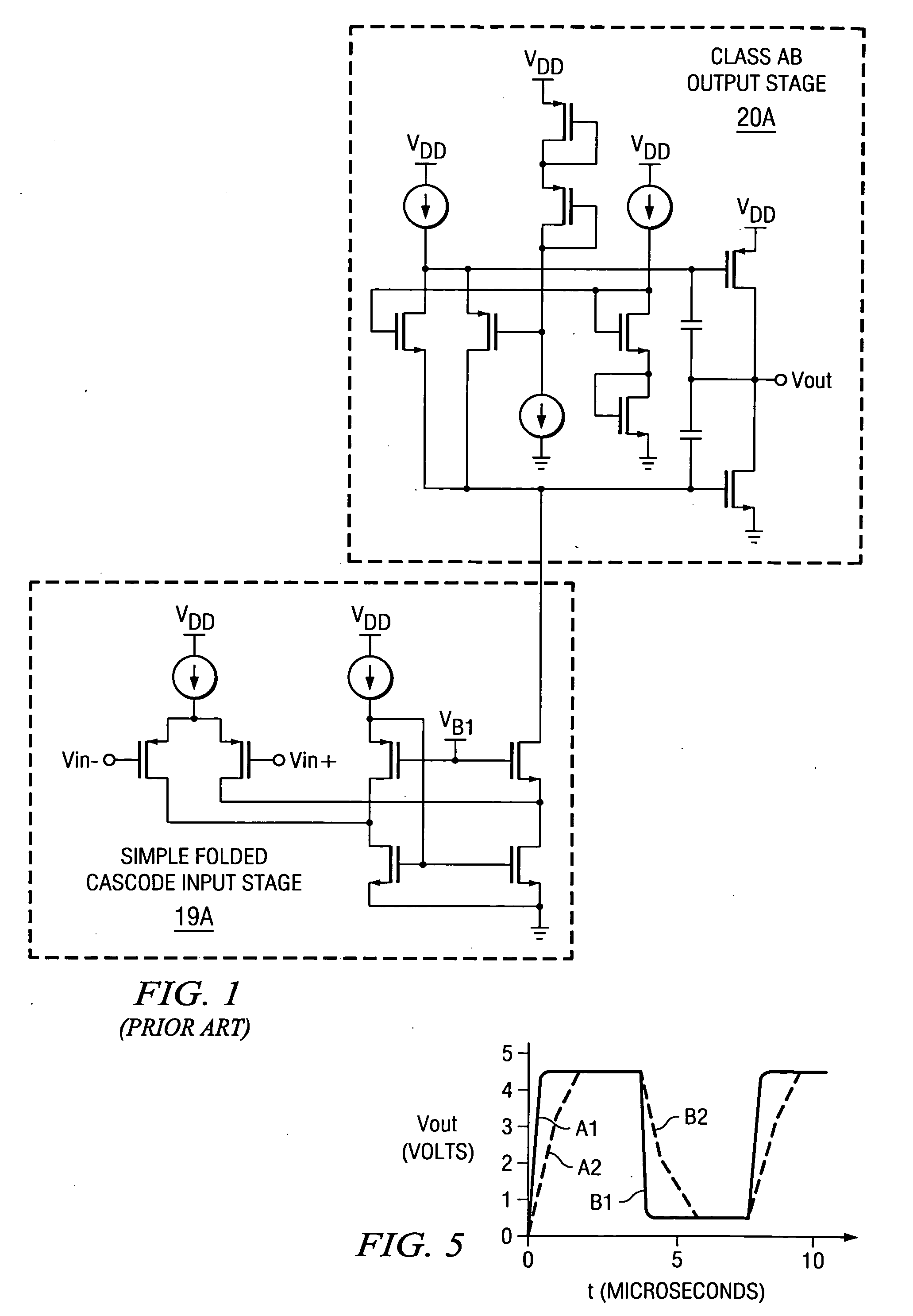
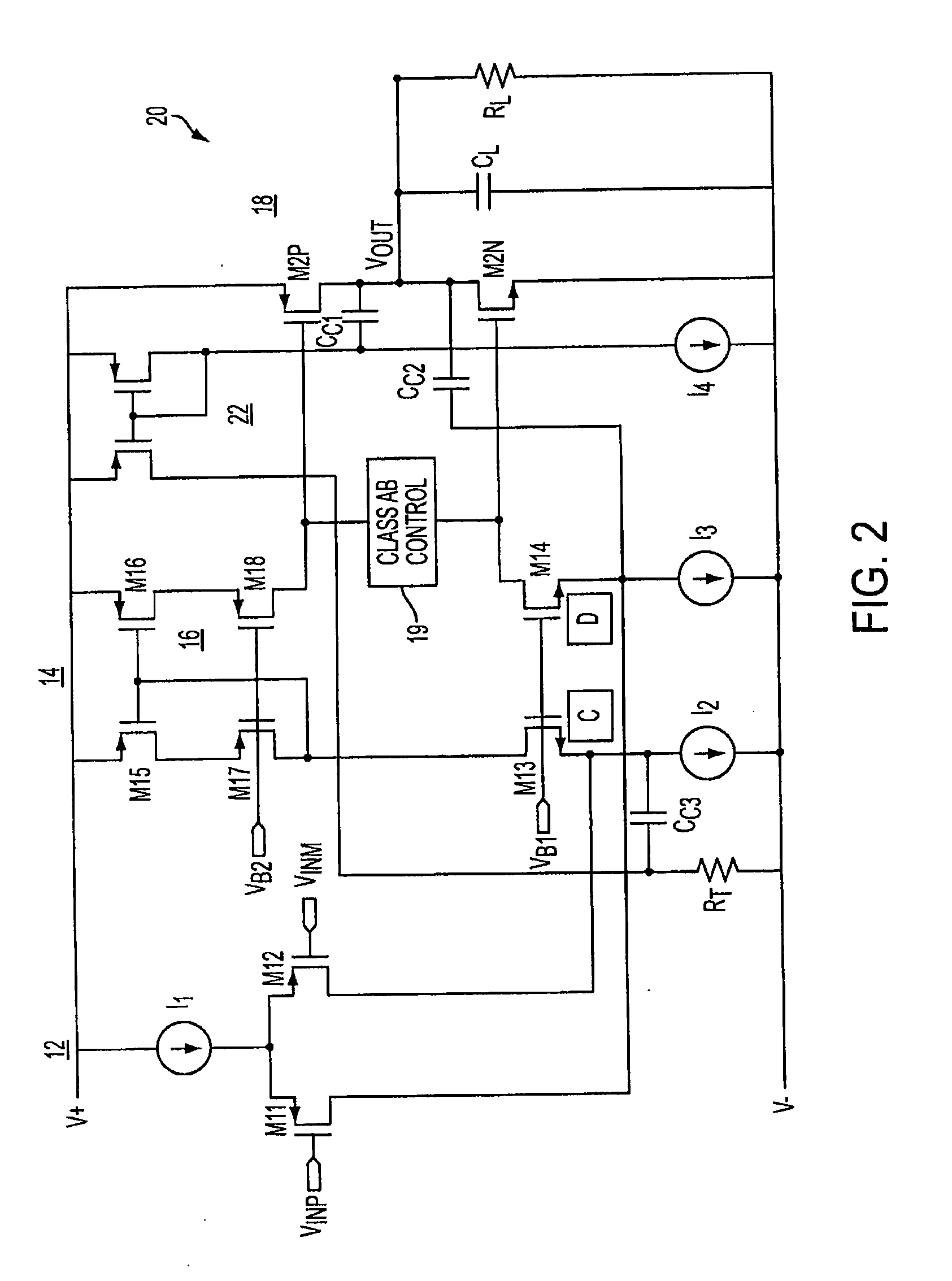
InactiveUS20050285676A1Low costIncrease conversion rateDifferential amplifiersSingle-ended push-pull amplifiersAudio power amplifierSlew rate
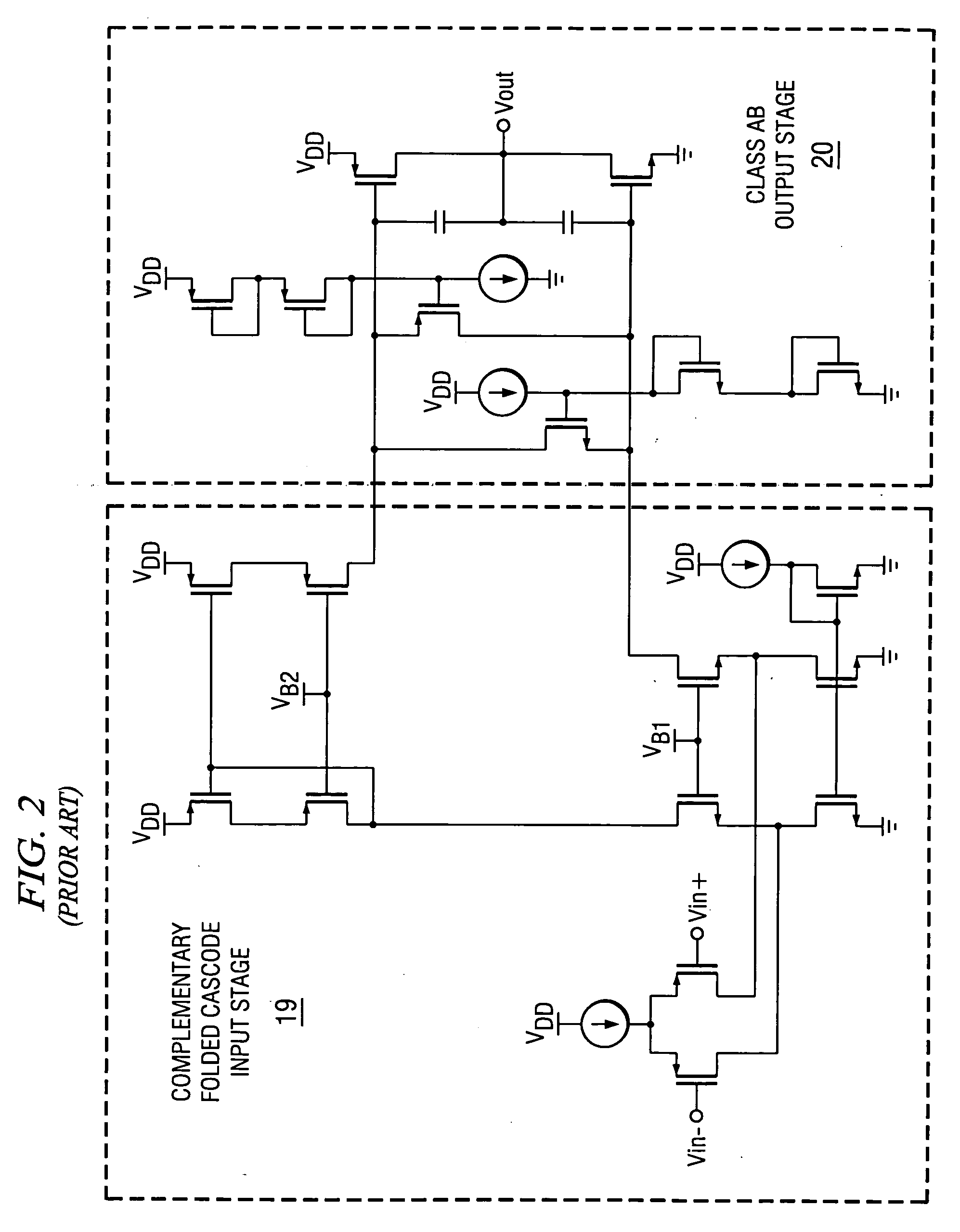
A folded-cascode operational amplifier including a differential input stage (19) and a class AB output stage (20) includes a first slew boost current mirror (13) and a second slew boost current mirror (14) having inputs connected to drains of the input transistors, respectively. Each current mirror amplifies excess tail current steered into it as a result of a large, rapid input signal transition. The amplified excess tail current is used to boost the slew rate of the class AB output stage. in accordance with a first polarity of the difference between the first (Vin+) and second (Vin−) input voltages. The drains of the input transistors are maintained at a voltage less than a transistor threshold voltage above the ground except during slewing operation of the operational amplifier to effectively isolate the current mirrors except during slewing operation.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Low-voltage difference voltage adjuster
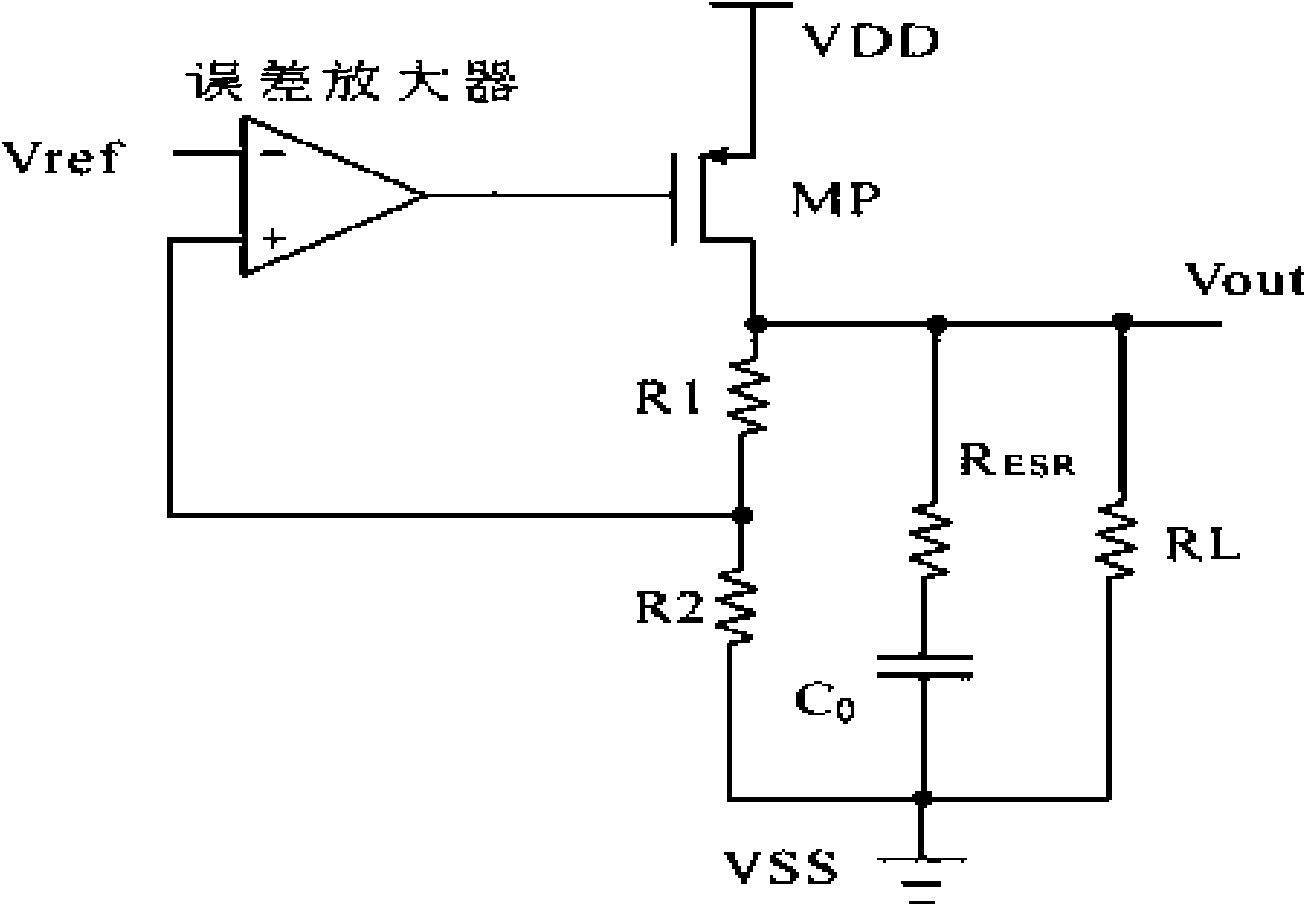
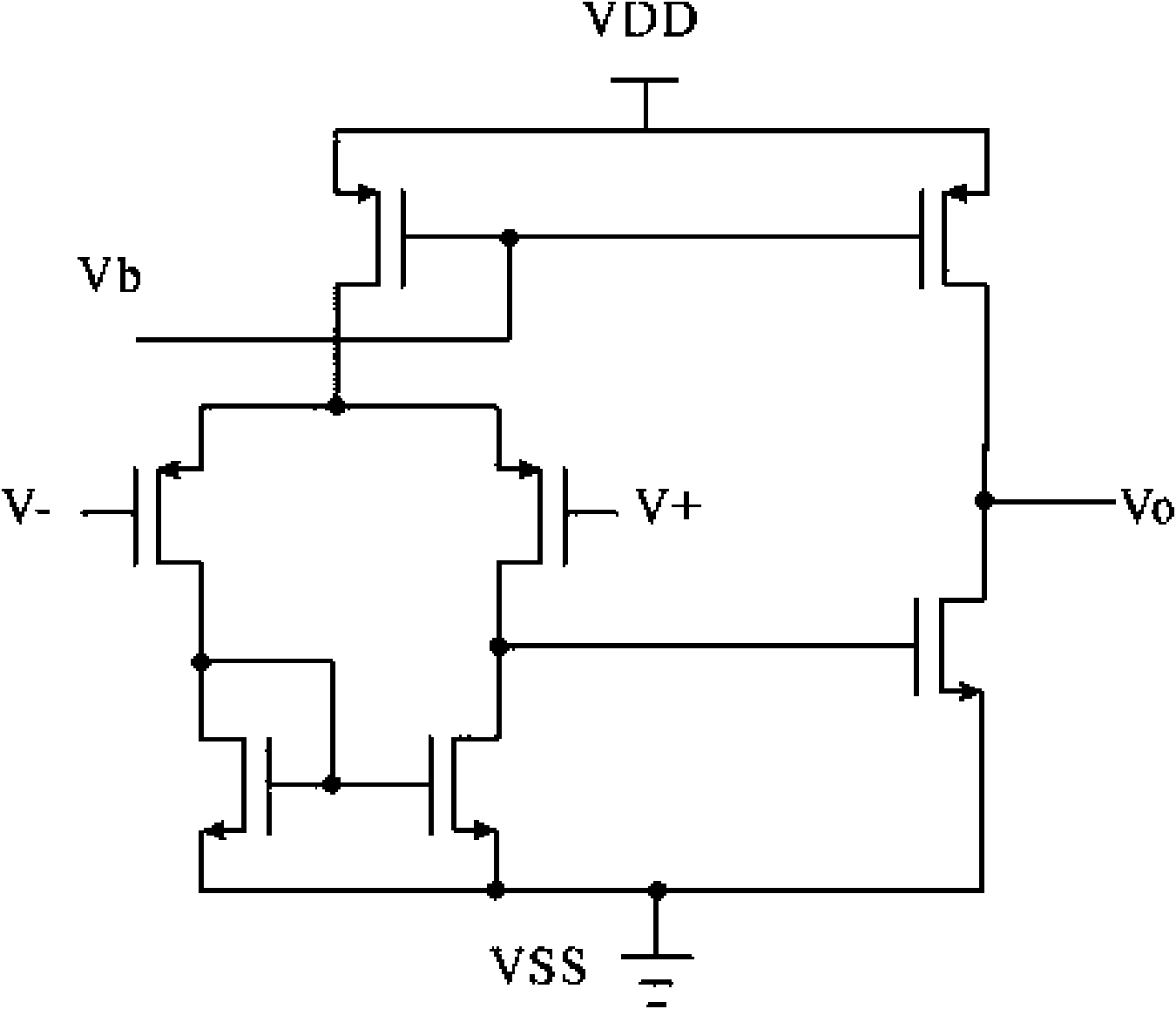
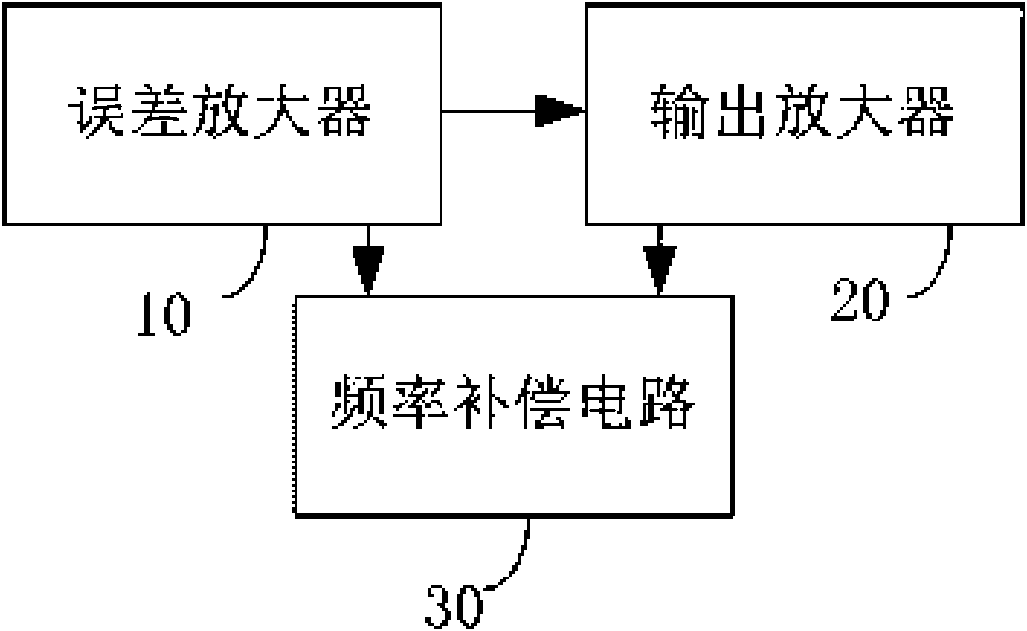
ActiveCN101667046AGood power supply rejection ratio performanceReduce the numberMultiple-port active networksAmplififers with field-effect devicesCapacitanceFrequency compensation
The invention discloses a low-voltage difference voltage adjuster, belonging to the technical field of an electronic circuit. The low-voltage difference voltage adjuster comprises an error amplifier,an output amplifier and a frequency compensating circuit, wherein the error amplifier is a first-class folding cascode amplifier, the output amplifier is coupled with the error amplifier, receives control voltage and comprises a transistor and two divider resistors which are connected in series; the frequency compensating circuit is respectively coupled with the error amplifier and the output amplifier; and the frequency compensating circuit comprises a voltage-controlling current source circuit consisting of at least one transistor and at least one compensating capacitor coupled with the voltage-controlling current source circuit. The low-voltage difference voltage adjuster can solves the problems that the current voltage adjuster has larger compensating capacitance and can not carry outon-chip integration, can provide complete chip integration, has good voltage-suppression specific characteristic, reduce the number of the compensating capacitance and simplify the compensating circuit.
Owner:灿芯创智微电子技术(北京)有限公司
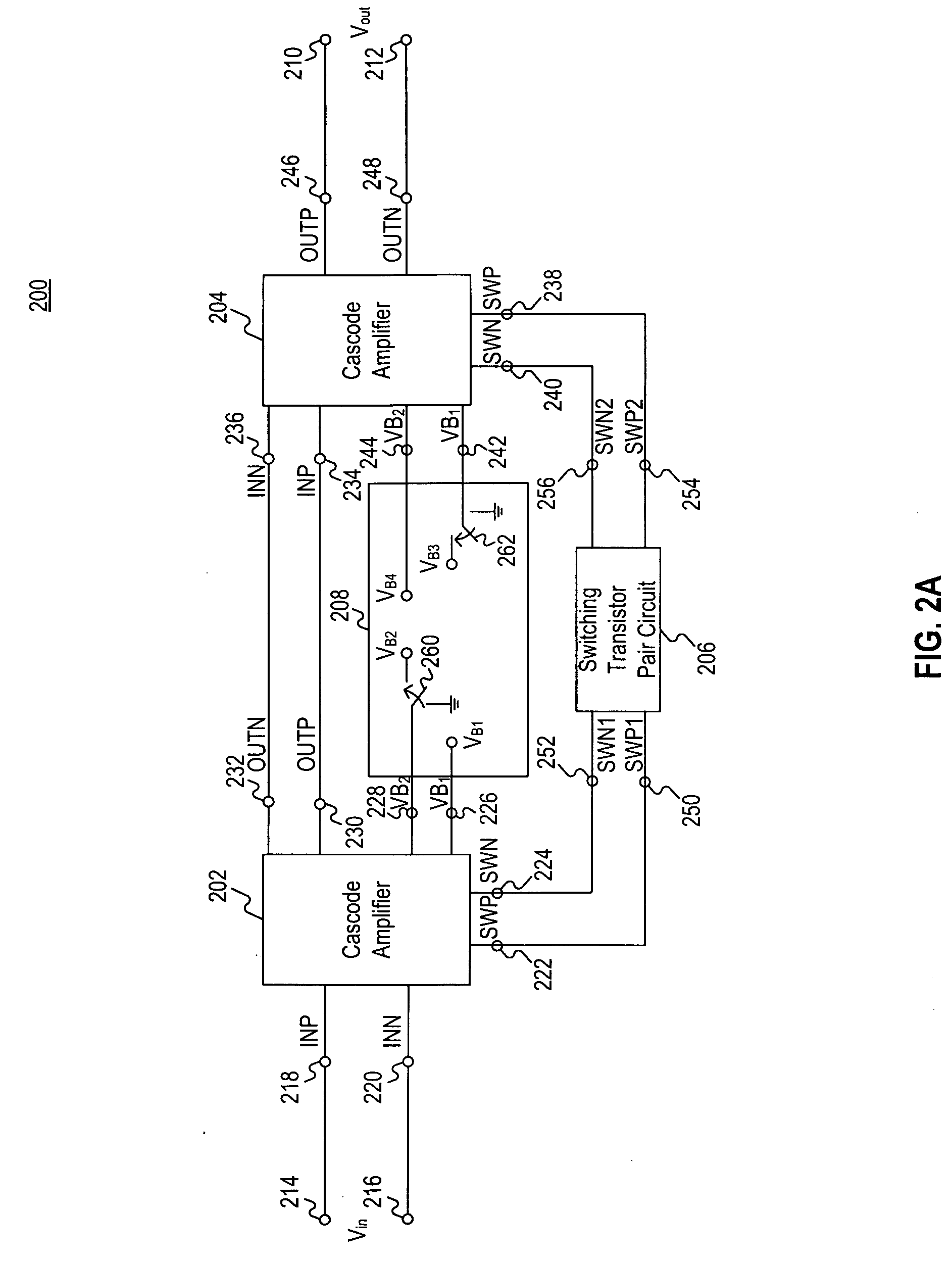
Variable gain amplifier and communication apparatus
InactiveUS20070222515A1Wide rangeSuppresses deterioration of linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
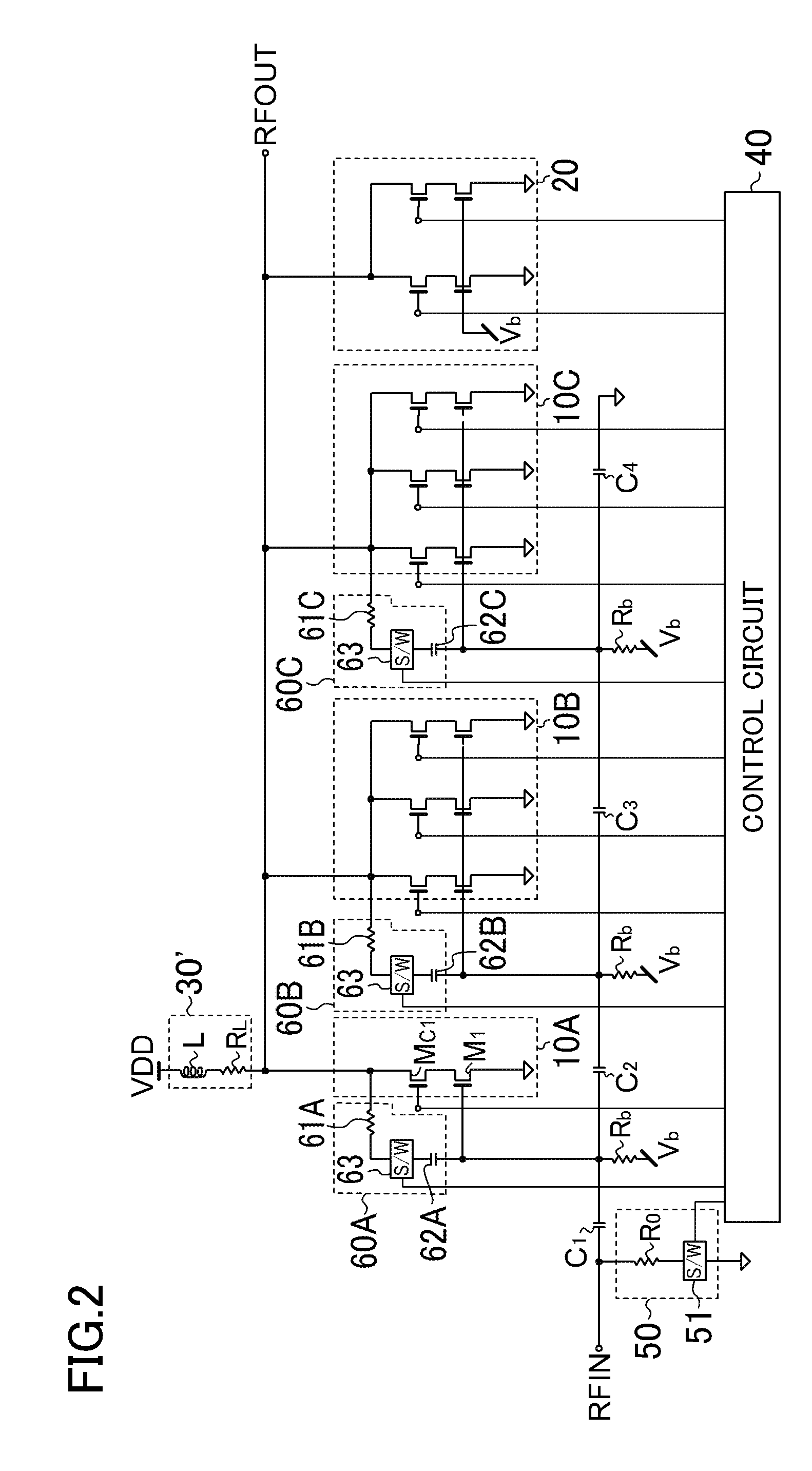
A variable gain amplifier is provided that can obtain a wide range of gain variation and suppress the deterioration of linearity when switching between amplifying transistors. The variable gain amplifier includes a plurality of cascode amplifiers each including an amplifying transistor and a plurality of cascode transistors connected in a cascode arrangement to an output terminal of the amplifying transistor. The plurality of cascode amplifiers are connected through attenuators. The variable gain amplifier further includes a first controller that controls ON / OFF operations of the plurality of cascode transistors included in each cascode amplifier; and a second controller that controls ON / OFF operations of a plurality of amplifying transistors, only one of which is included in each of the plurality of cascode amplifiers, such that only selected one of the plurality of amplifying transistors is turned on.
Owner:SHARP KK
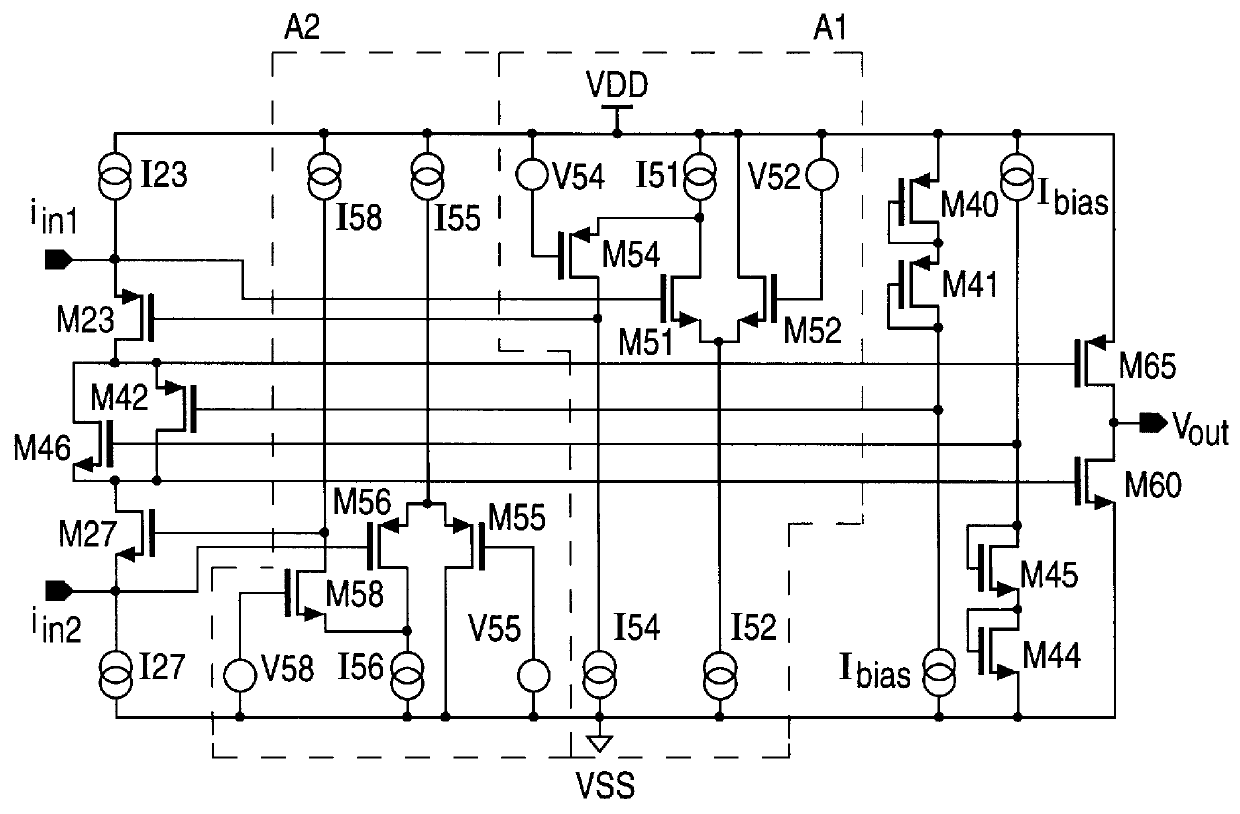
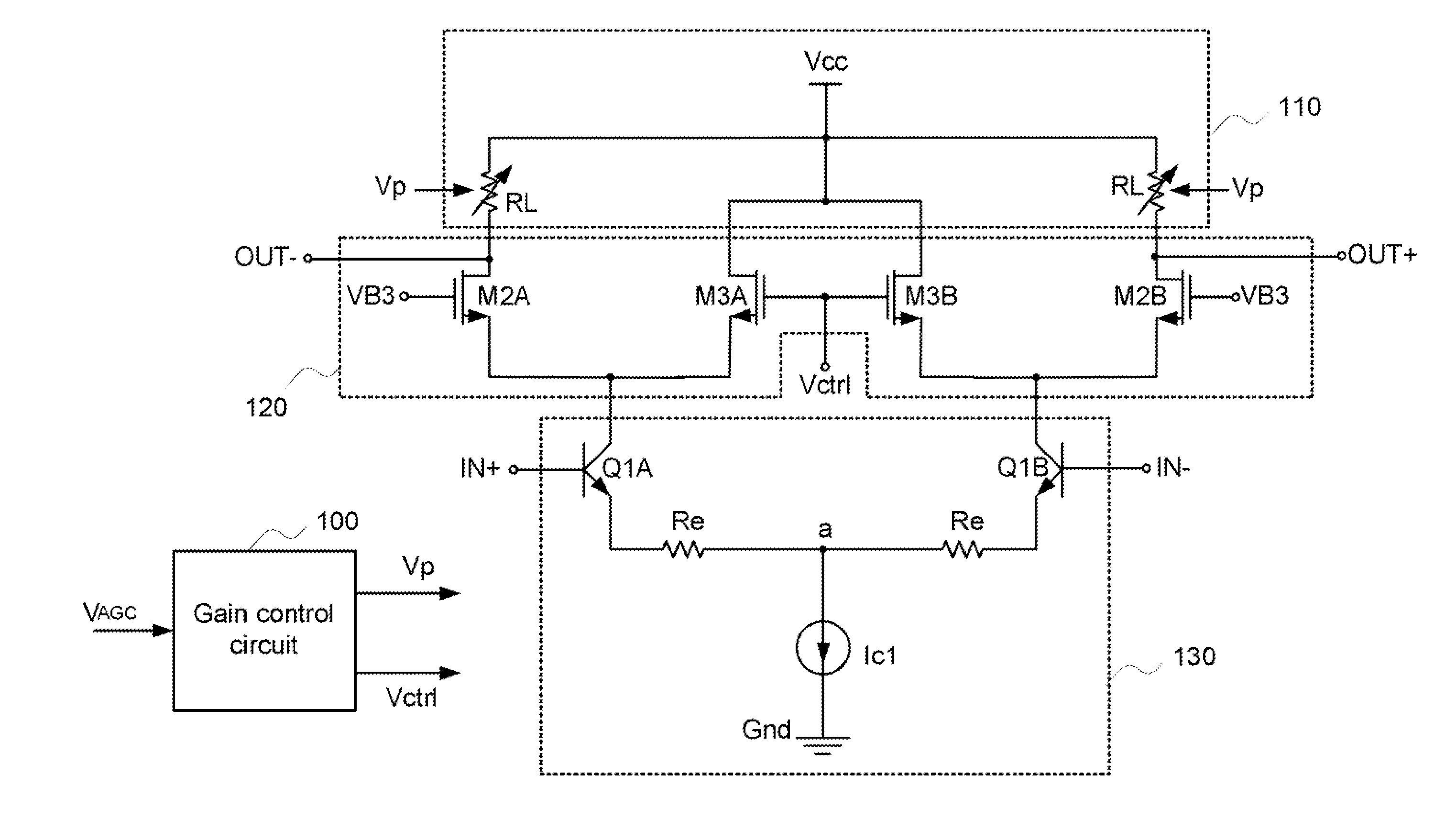
Low voltage class AB amplifier with gain boosting
A low voltage amplifier with gain boosting and a reduced power supply voltage requirement. A cascode amplifier circuit, biased with the power supply voltage, amplifies a pair of related, differential input signals based upon a pair of gain boost control signals and in accordance therewith provides a pair of gain boosted signals which correspond to the input signals. A gain boost control circuit, also biased with the power supply voltage, uses the differential input signals to generate the gain boost control signals. A class AB amplifier circuit, also biased with the power supply voltage, amplifies the gain boosted signals and in accordance therewith provides a class AB output signal which corresponds to the original input signals. The cascode amplifier circuit, gain boost control circuit and class AB amplifier circuit together operate with a minimum power supply voltage which equals a sum of one active transistor input bias potential and two active transistor output bias potentials
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Variable gain amplifier and high-frequency signal receiving apparatus comprising the same
ActiveUS20110221531A1Easy to implementReduce degradationGain controlGated amplifiersLoad circuitAudio power amplifier
A cascode amplification unit includes a plurality of cascode amplifiers connected in parallel. Each of the cascode amplifiers has two transistors. A cascode current source unit includes a plurality of cascode current sources connected in parallel. Each of the cascode current sources has two transistors. Both the output end of the cascode amplification unit and the output end of the cascode current source unit are connected to a load circuit. The control circuit turns on and off each cascode transistor of the cascode amplifier and each cascode transistor of the cascode current source so that an amount of current passing through the load circuit is constant.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Cascode amplifier with protection circuitry
InactiveCN102356542AReduce stressImprove reliabilityGated amplifiersPower amplifiersVoltage swingCascode amplifier
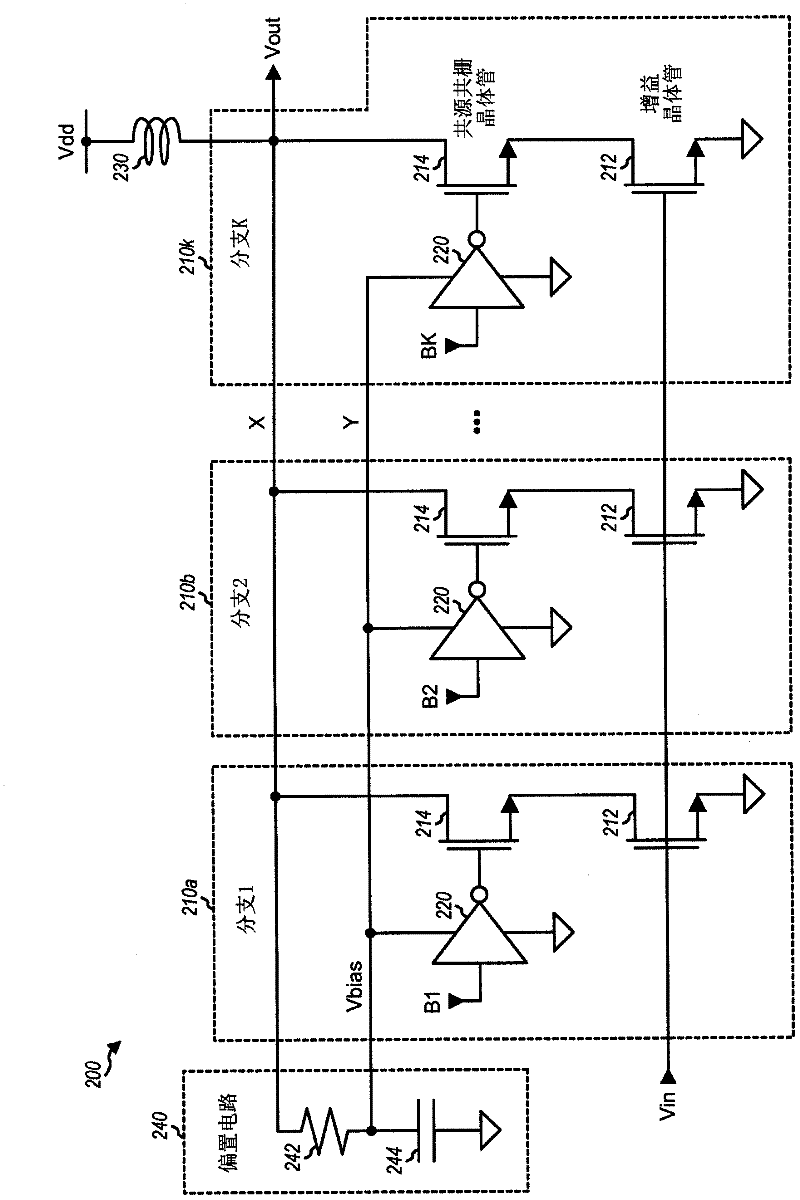
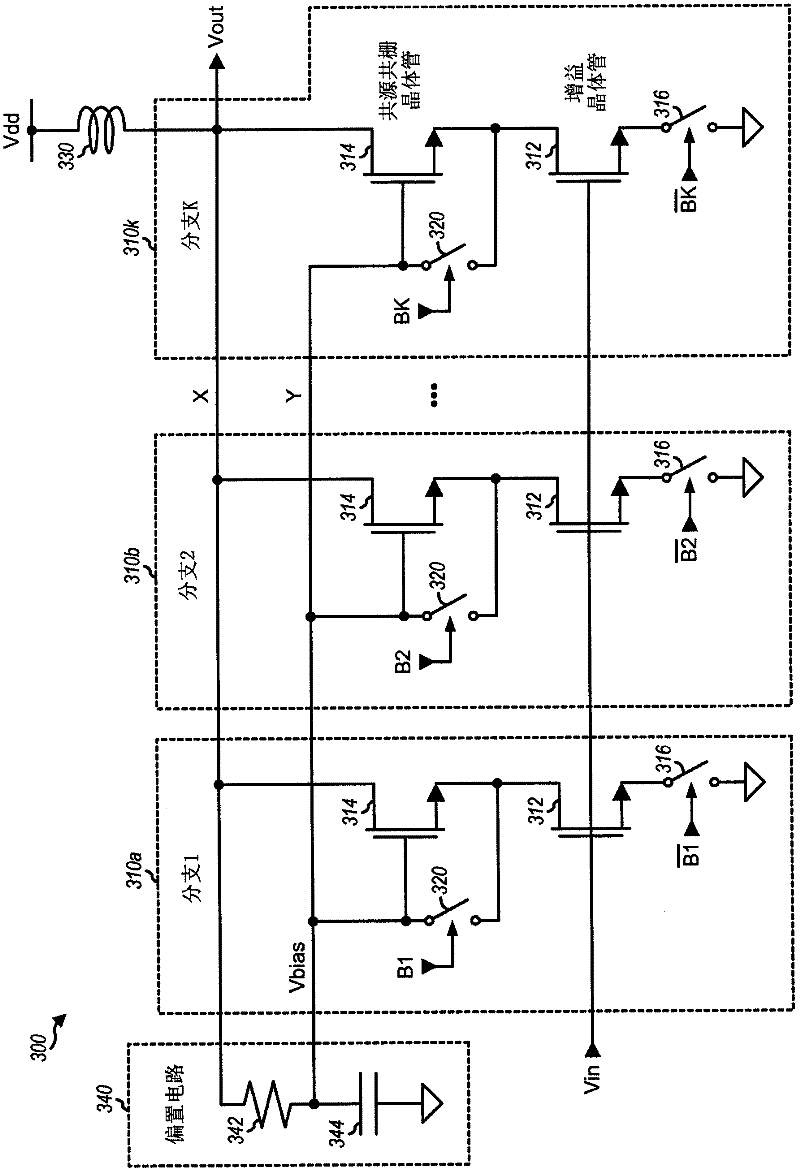
A cascode amplifier (300) with protection circuitry is described. In one exemplary design, the amplifier includes multiple branches coupled in parallel (310a, 310b, 310k), with at least one branch being switchable between "on" and "off states. Each switchable branch includes a gain transistor (312) coupled to a cascode transistor (314). The gain transistor (312) amplifies an input signal and provides an amplified signal in the on state and does not amplify the input signal in the off state. The cascode transistor (314) buffers the amplified signal and provides an output signal in the on state. The output signal swing may be split between the gain transistor (312) and the cascode transistor (314) in both the on and off states with the protection circuitry. Each transistor may then observe a fraction of the voltage swing.; The voltage splitting in the off state may be achieved by floating the gain transistor (312) and shorting the gate and source of the cascode transistor (314).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Cascode amplifier bias circuits
ActiveUS10250199B2Amplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationPower amplifiersLow noiseAudio power amplifier
Bias circuits and methods for silicon-based amplifier architectures that are tolerant of supply and bias voltage variations, bias current variations, and transistor stack height, and compensate for poor output resistance characteristics. Embodiments include power amplifiers and low-noise amplifiers that utilize a cascode reference circuit to bias the final stages of a cascode amplifier under the control of a closed loop bias control circuit. The closed loop bias control circuit ensures that the current in the cascode reference circuit is approximately equal to a selected multiple of a known current value by adjusting the gate bias voltage to the final stage of the cascode amplifier. The final current through the cascode amplifier is a multiple of the current in the cascode reference circuit, based on a device scaling factor representing the relative sizes of the transistor devices in the cascode amplifier and in the cascode reference circuit.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Cascode amplifier and differential cascode voltage-controlled oscillator using the same
InactiveUS7821349B2Reduce phase noiseReduce impactAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceHigh frequency amplifiersPhase noiseEngineering
Provided is a differential cascode voltage-controlled oscillator that can reduce a phase noise by the use of a quality factor enhancement technique with negative conductance and can mitigate a ground-caused noise effect by the use of a cascode connection technique. The differential cascode voltage-controlled oscillator includes an AC signal generator, and first through fourth cascode amplifiers. The AC signal generator generates an AC signal with a certain frequency according to a control voltage. The first cascode amplifier is connected in a cascode configuration, and amplifies the AC signal to output the resulting signal to a first output terminal. The second cascode amplifier is connected in a cascode configuration and connected to the first cascode amplifier in a cross-coupled configuration, to amplify the AC signal to output the resulting signal to a second output terminal. The third cascode amplifier is connected in a cascode configuration to amplify the AC signal to output the resulting signal to the first output terminal. The fourth cascode amplifier is connected in a cascode configuration and connected to the third cascode amplifier in a cross-coupled configuration, to amplify the AC signal to output the resulting signal to the second output terminal. Herein, the first and second cascode amplifiers and the third and fourth cascode amplifiers are symmetrically connected to differentially amplify the AC signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Multi-port cross-connected multi-level cascode differential amplifier
InactiveUS7161429B2Increasing current gain and input impedance and bandwidthReduce input currentAmplifier combinationsAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceCross connectionInput impedance
A differential cascode amplifier has first and second cascode circuits, driven by two differential signal sources including input resistances.The first cascode circuit includes a first input transistor having a first collector, a first emitter, and a first base, and a first output transistor having a second collector, a second base, and a second emitter coupled to the first collector. The second cascode circuit includes a second input transistor having a third collector, a third emitter, and a third base, and a second output transistor having a fourth collector, a fourth base, and a fourth emitter coupled to the third collector. The amplifier has a first connection connecting the first base to the fourth base, and a second connection connecting the second base to the third base.This cross-connected differential cascode architecture provides doubled output bandwidth and current gain (in dB), further increasing input impedance and output swing.
Owner:IBM CORP
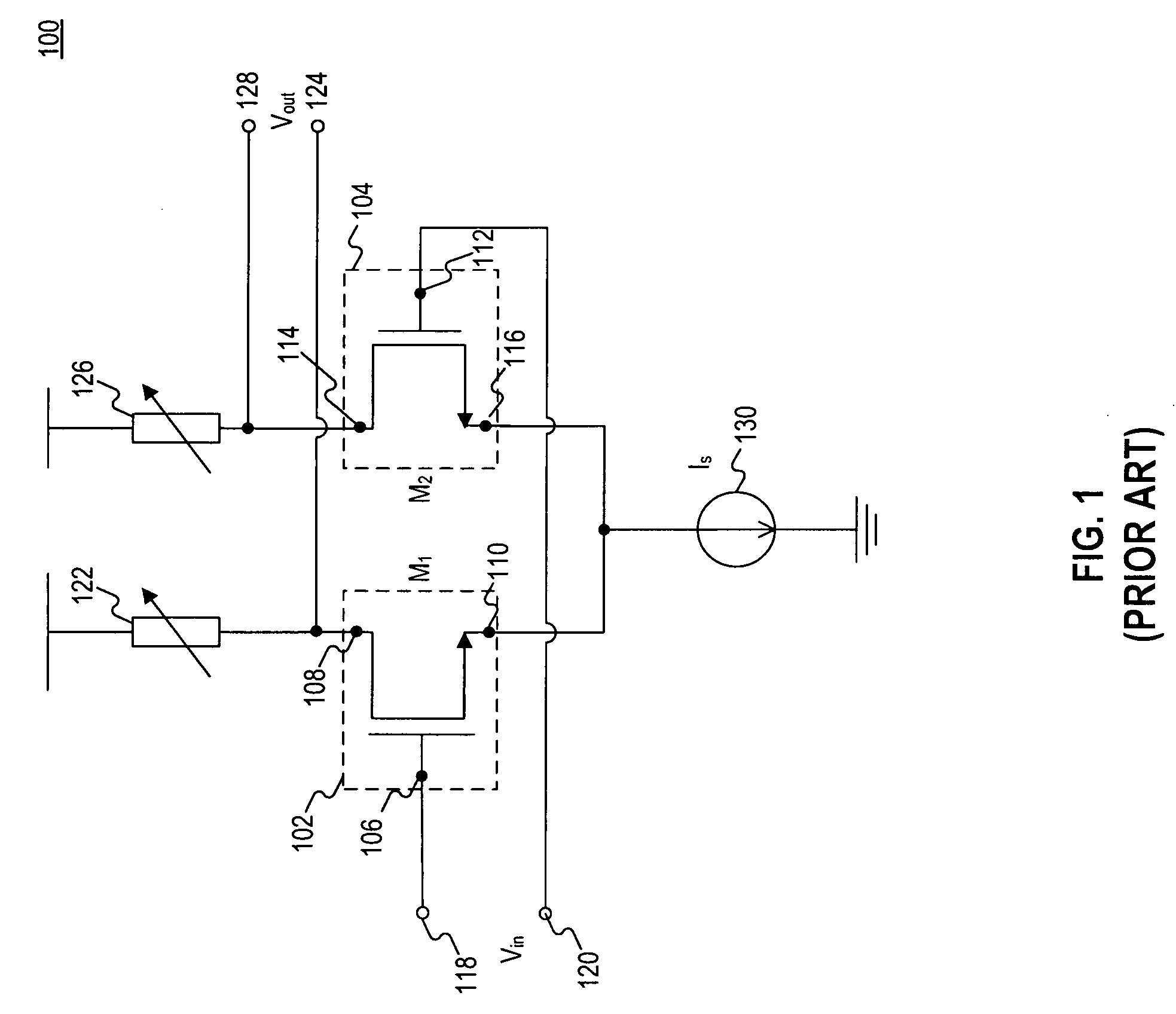
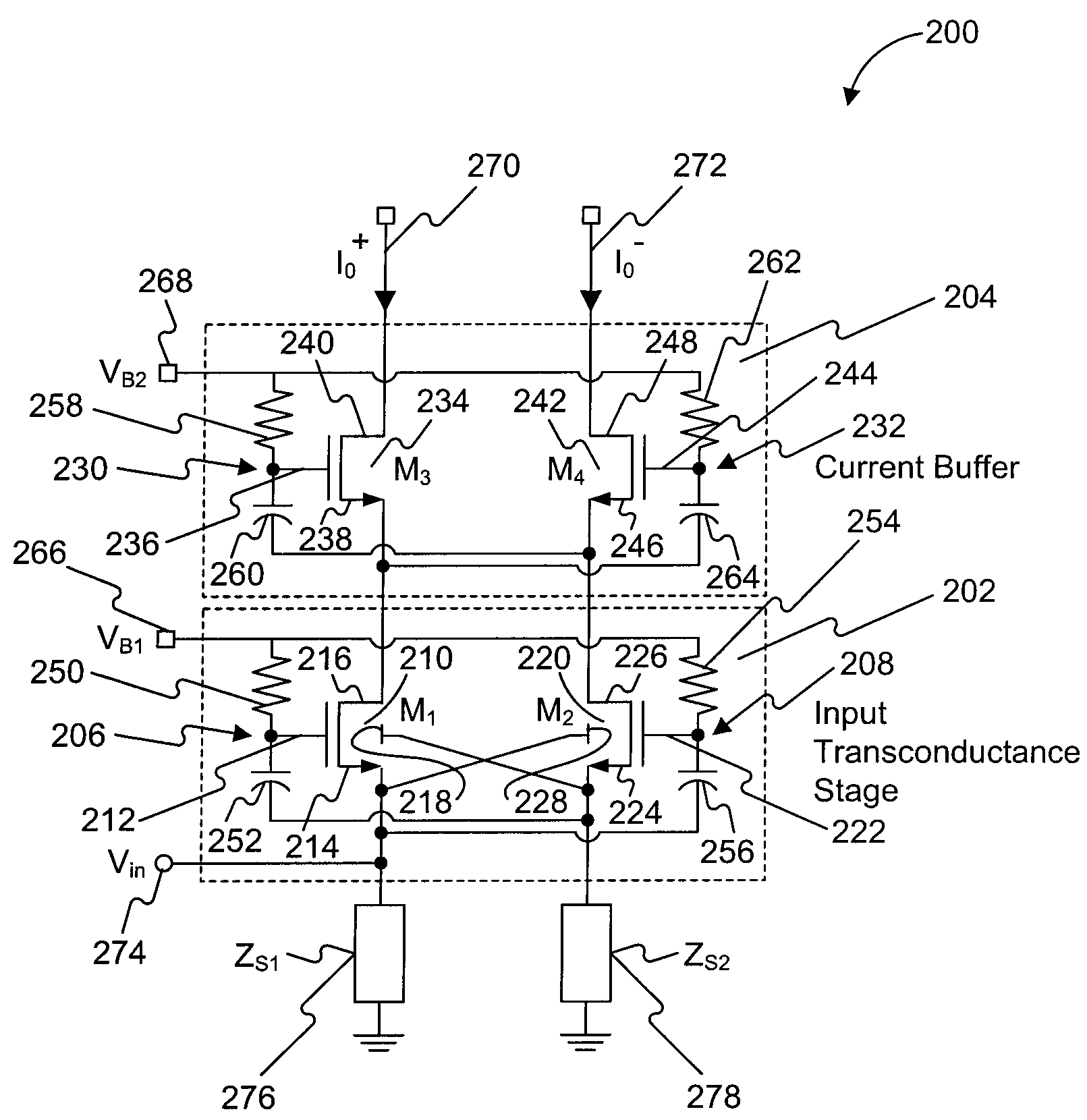
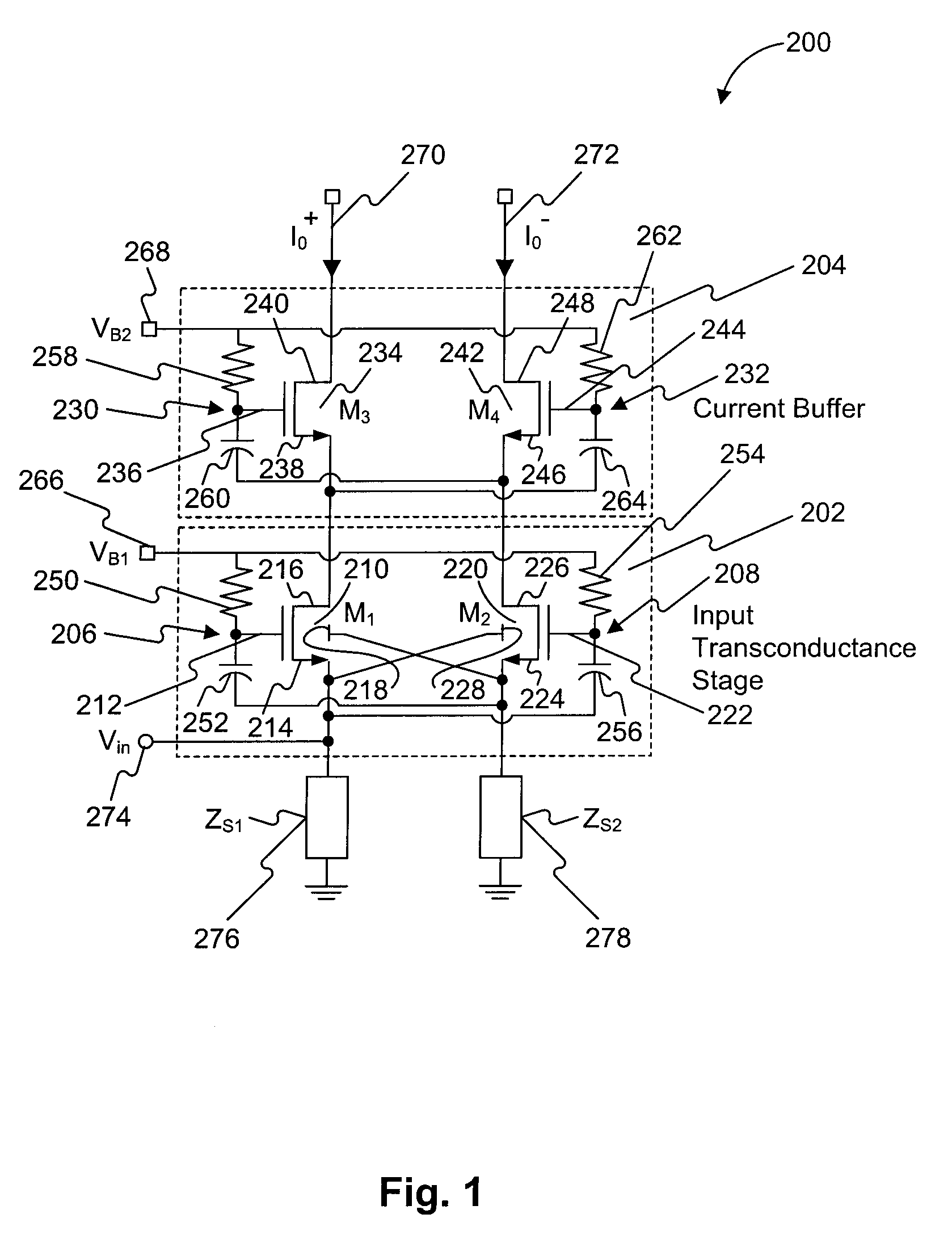
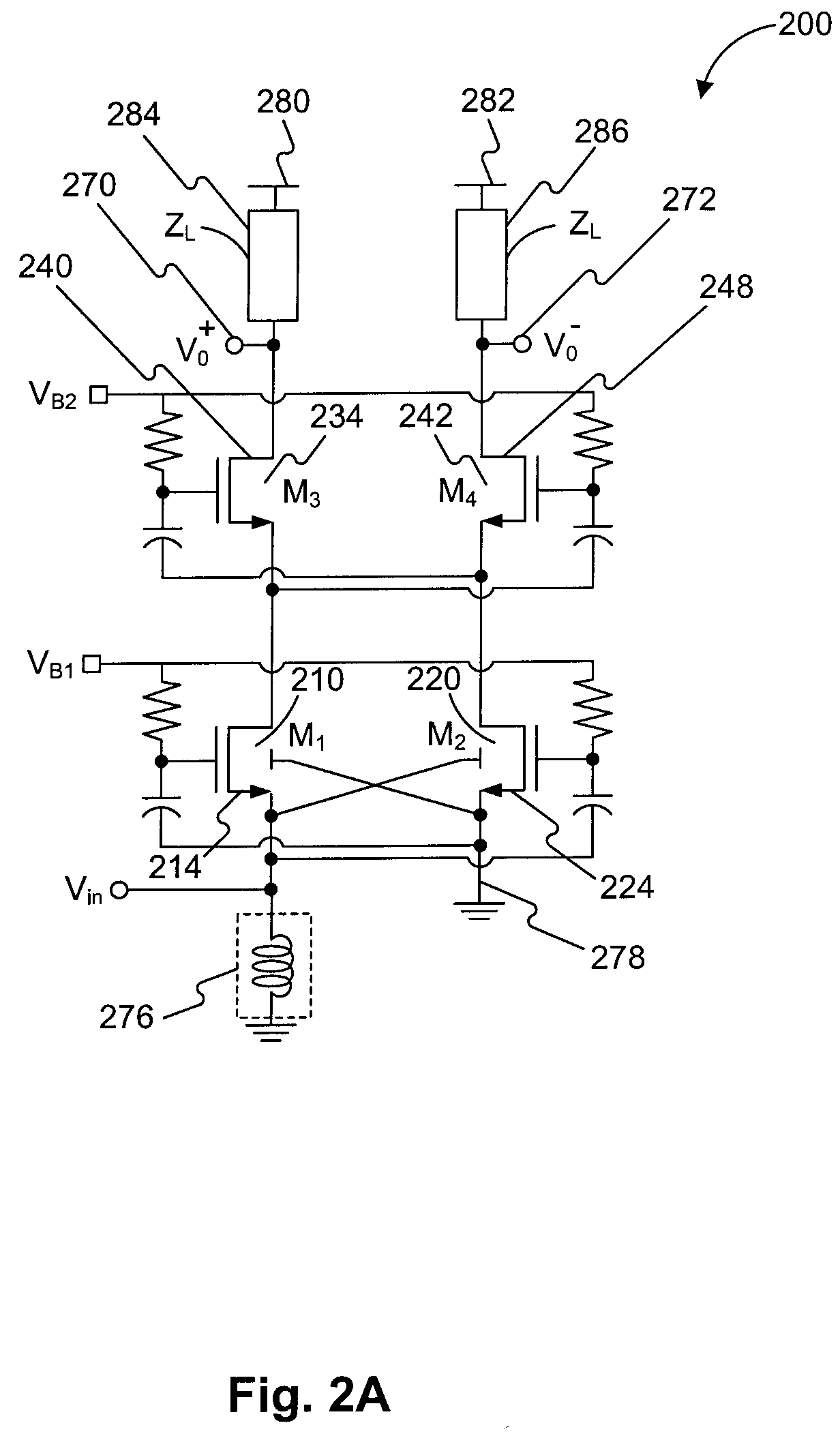
Low noise amplifier
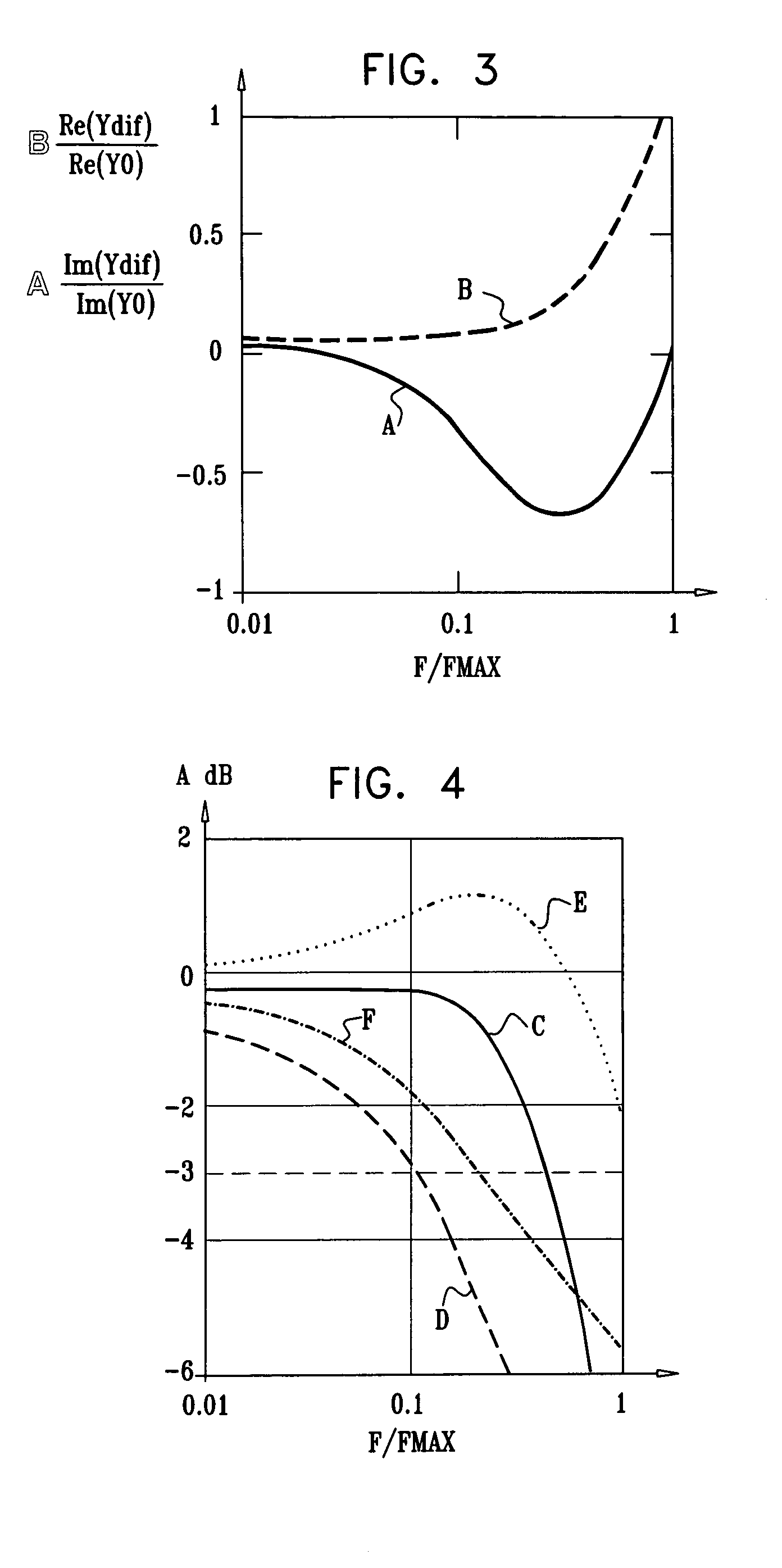
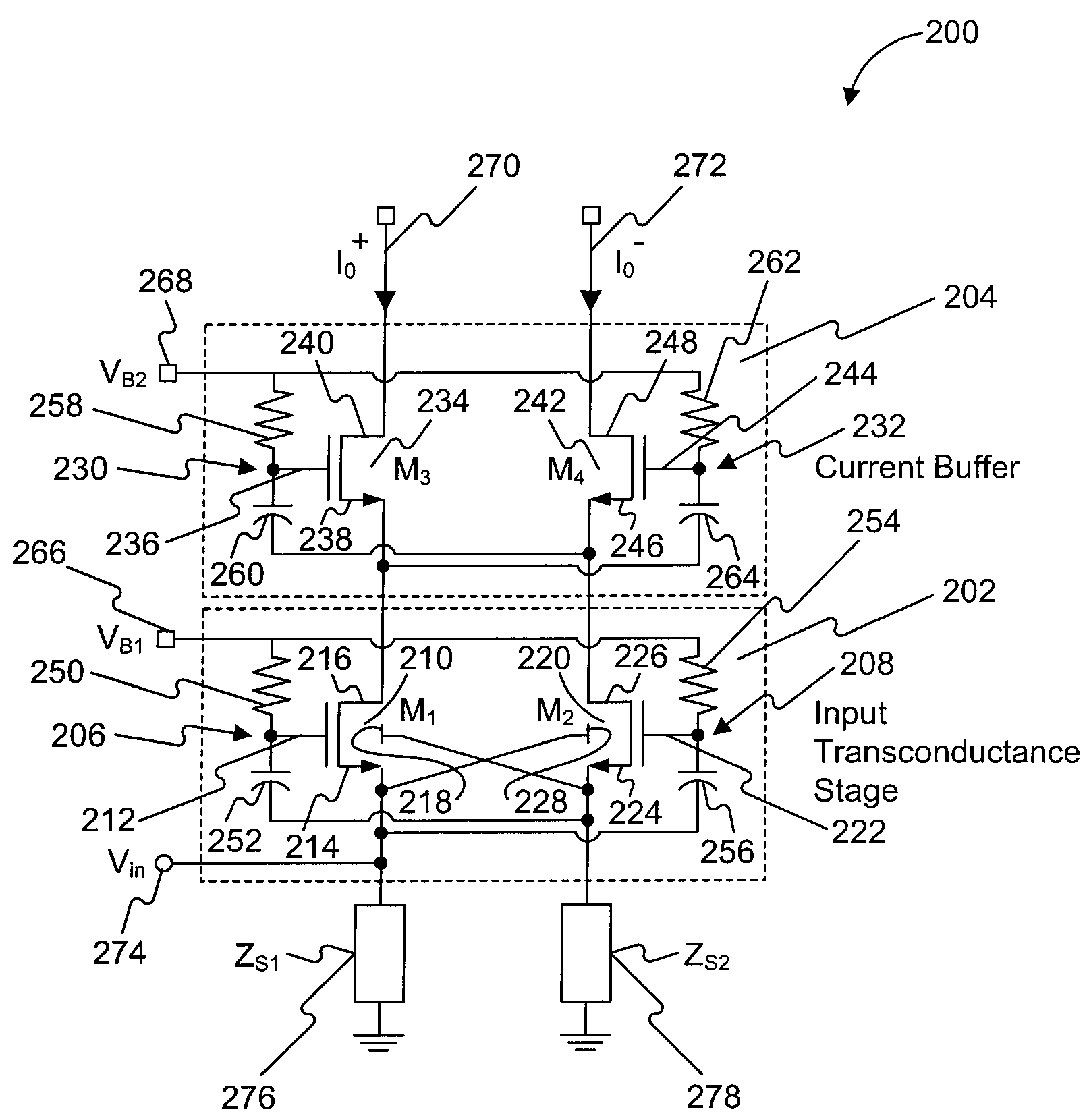
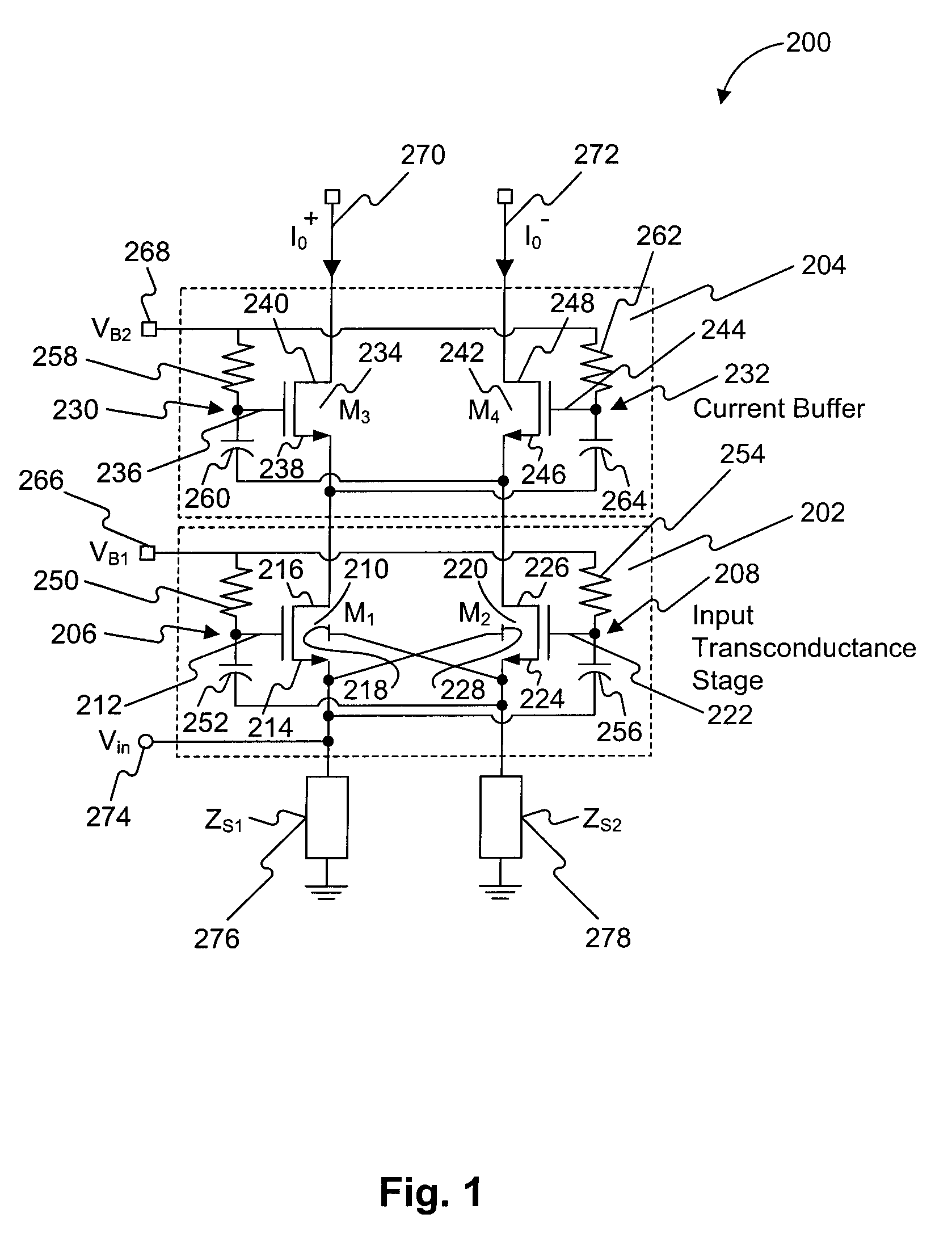
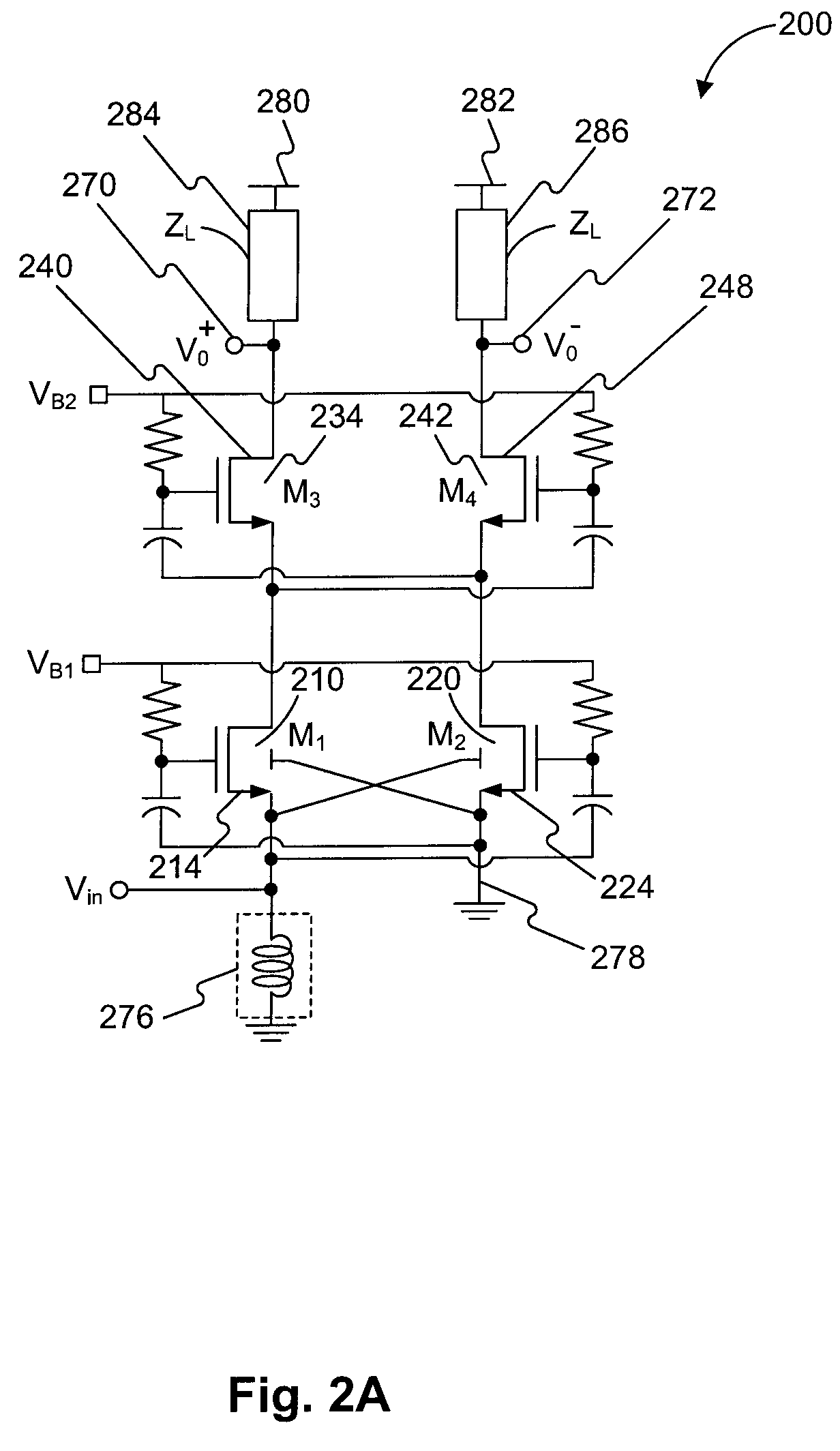
A low-noise amplifier circuit to convert a single-ended input into a dual-ended output includes an input transconductance stage circuit, including a first MOS transistor coupled in parallel with a second MOS transistor; a current buffer circuit, including a third MOS transistor coupled in parallel with a fourth MOS transistor; each of the first, second, third, and fourth transistors having a body, gate, source, and drain; the input transconductance stage circuit and the current buffer circuit being cascode coupled, forming a cascode amplifier configuration; the single-ended input being at the source of one of the first and second transistors in the input transconductance stage circuit; the dual-ended output being a differential output across the drain of the third transistor and the drain of the fourth transistor; the first and second transistors of the input transconductance stage circuit being cross-coupled, wherein the body of the first transistor is coupled to the source of the second transistor, and the body of the second transistor is coupled to the source of the first transistor; and the third and fourth transistors of the current buffer circuit being cross-coupled, wherein a first capacitance is coupled between the gate of the third transistor and the source of the fourth transistor, and a second capacitance is coupled between the gate of the fourth transistor and the source of the third transistor.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
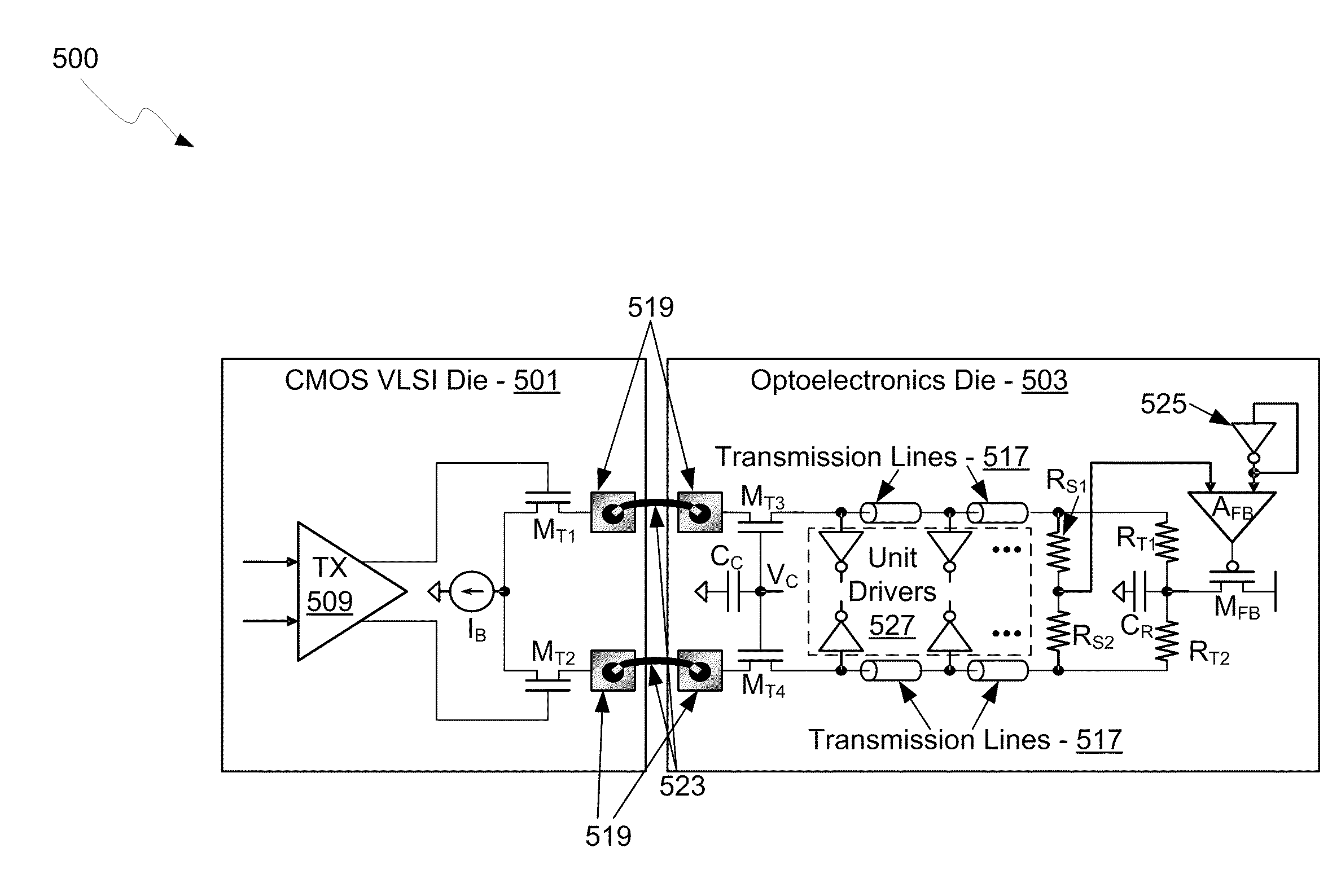
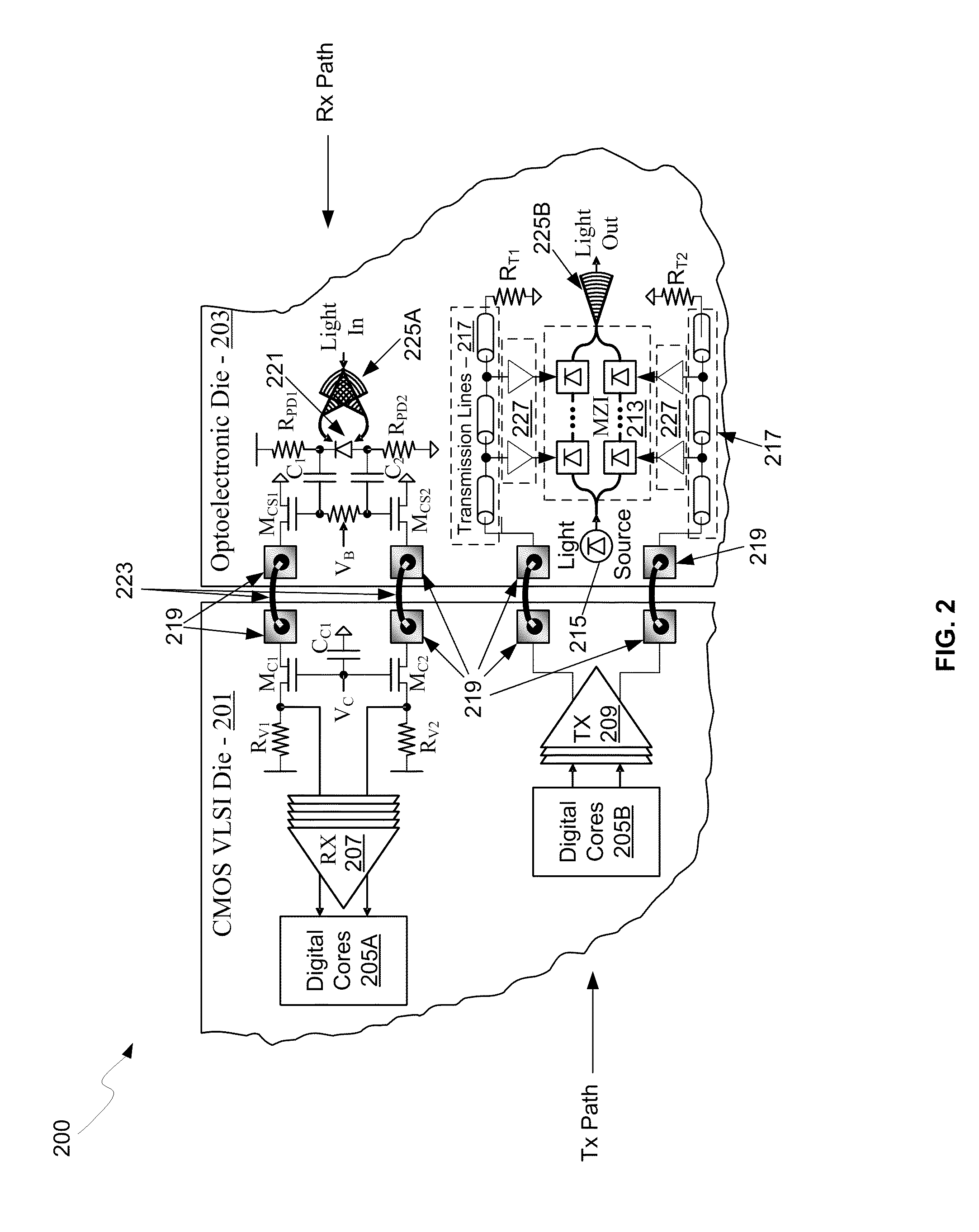
Method and System for Implementing High-Speed Interfaces Between Semiconductor Dies in Optical Communication Systems
A method and system for implementing high-speed electrical interfaces between semiconductor dies in optical communication systems are disclosed and may include communicating electrical signals between an electronics die and an optoelectronics die via coupling pads which may be located in low impedance points in Tx and Rx paths. The electrical signals may be communicated via one or more current-mode, controlled impedance, and / or capacitively-coupled interfaces. The current-mode interface may include a cascode amplifier stage split between source and drain terminals of transistors on the dies. The controlled-impedance interfaces may include transmission line drivers on a first die and transmission lines on a second die. The capacitively-coupled interfaces may include capacitors formed by contact pads on the dies. The coupling pads may be connected via one or more of: wire bonds, metal pillars, solder balls, or conductive resin. The dies may comprise CMOS and may be coupled in a flip-chip configuration.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Variable gain amplifier
InactiveUS20060071712A1Stable input/output matching characteristicGain controlDifferential amplifiersVariable-gain amplifierAudio power amplifier
A variable gain amplifier is provided. The variable gain amplifier includes a first cascode amplifier which includes a first common source transistor and a first common gate transistor, a second cascode amplifier which forms a differential pair with the first cascode amplifier and includes a second common source transistor and a second common gate transistor, and a gain adjustment unit having a side connected to the drain of the first common source transistor and the source of the first common gate transistor and another side connected to the drain of the second common source transistor and the source of the second common gate transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Cascode current mirror and method
ActiveUS20080224221A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricReference current
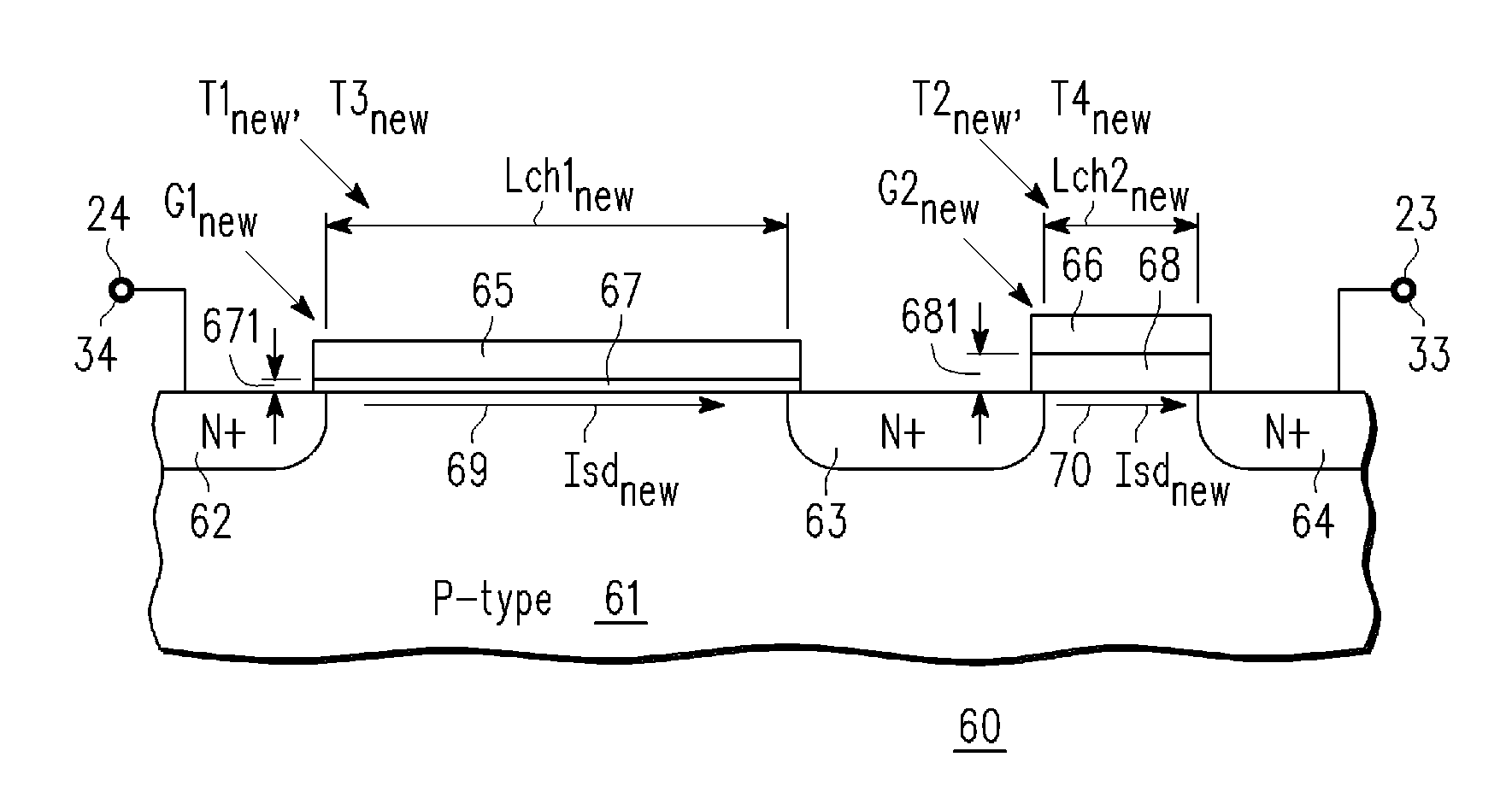
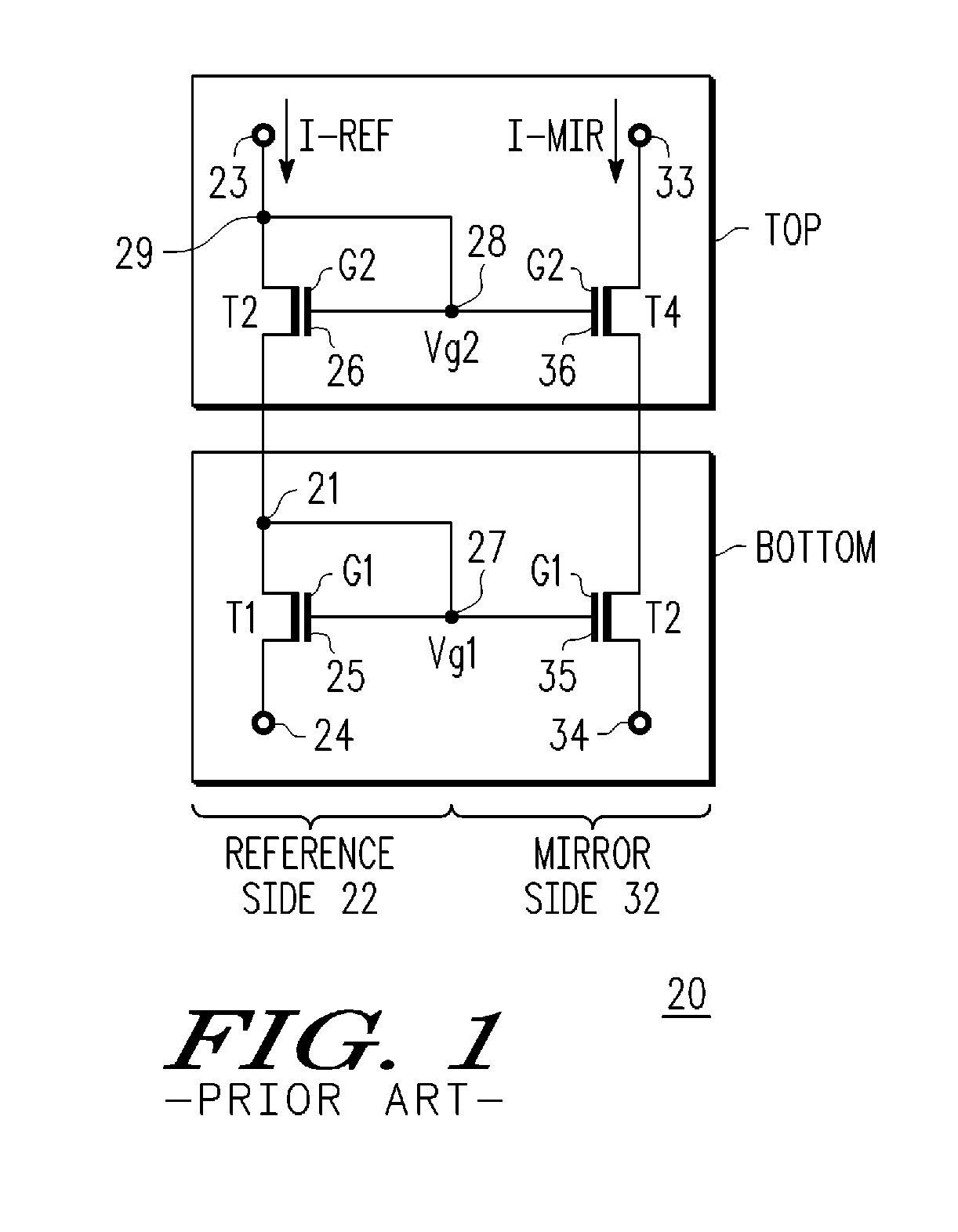
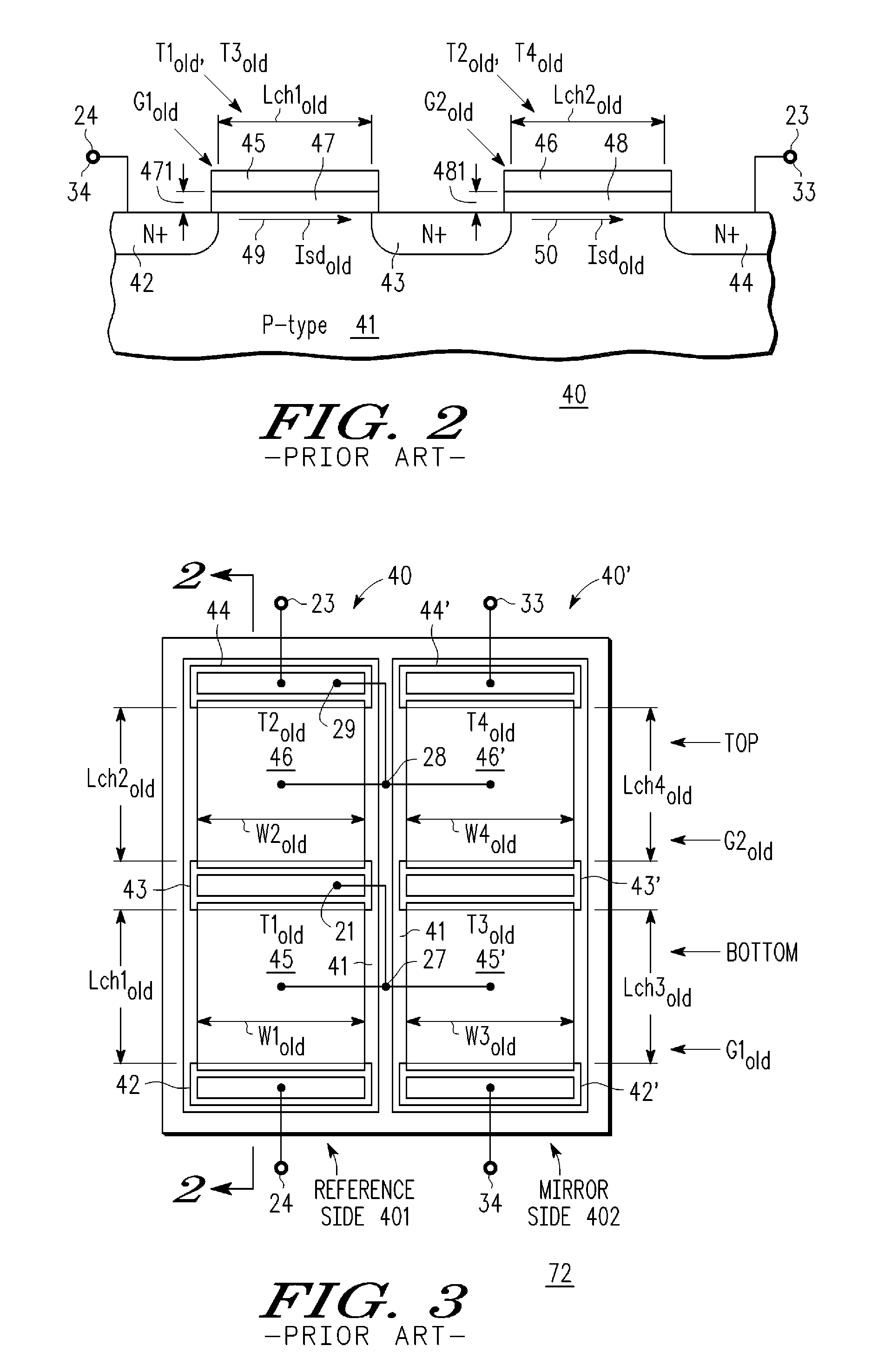
A cascode amplifier (CA) (60) is described having a bottom transistor (T1new) with a relatively thin gate dielectric (67) and higher ratio (RB) of channel length (Lch1new) to width (W1new) and a series coupled top transistor (T2new) with a relatively thick gate dielectric (68) and a lower ratio (RT) of channel length (Lch2new) to width (W2new). An improved cascode current mirror (CCM) (74) is formed using a coupled pair of CAs (60, 60′), one (60) forming the reference current (RC) side (601) and the other (60′) forming the mirror current side (602) of the CCM (74). The gates (65, 65′) of the bottom transistors (T1new, T3new) are tied together and to the common node (21) between the series coupled bottom (T1new) and top (T2new) transistors of the RC side (601), and the gates (66′, 66′) of the top transistors (T2new, T4new) are coupled together and to the top drain node (64) of the RC side (601). The area of the CCM (74) can be substantially shrunk without adverse affect on the matching, noise performance and maximum allowable operating voltage.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Amplifying circuit
InactiveUS7391269B2Reduce power consumptionSimple circuit structureGated amplifiersAmplifier combinationsControl signalEngineering
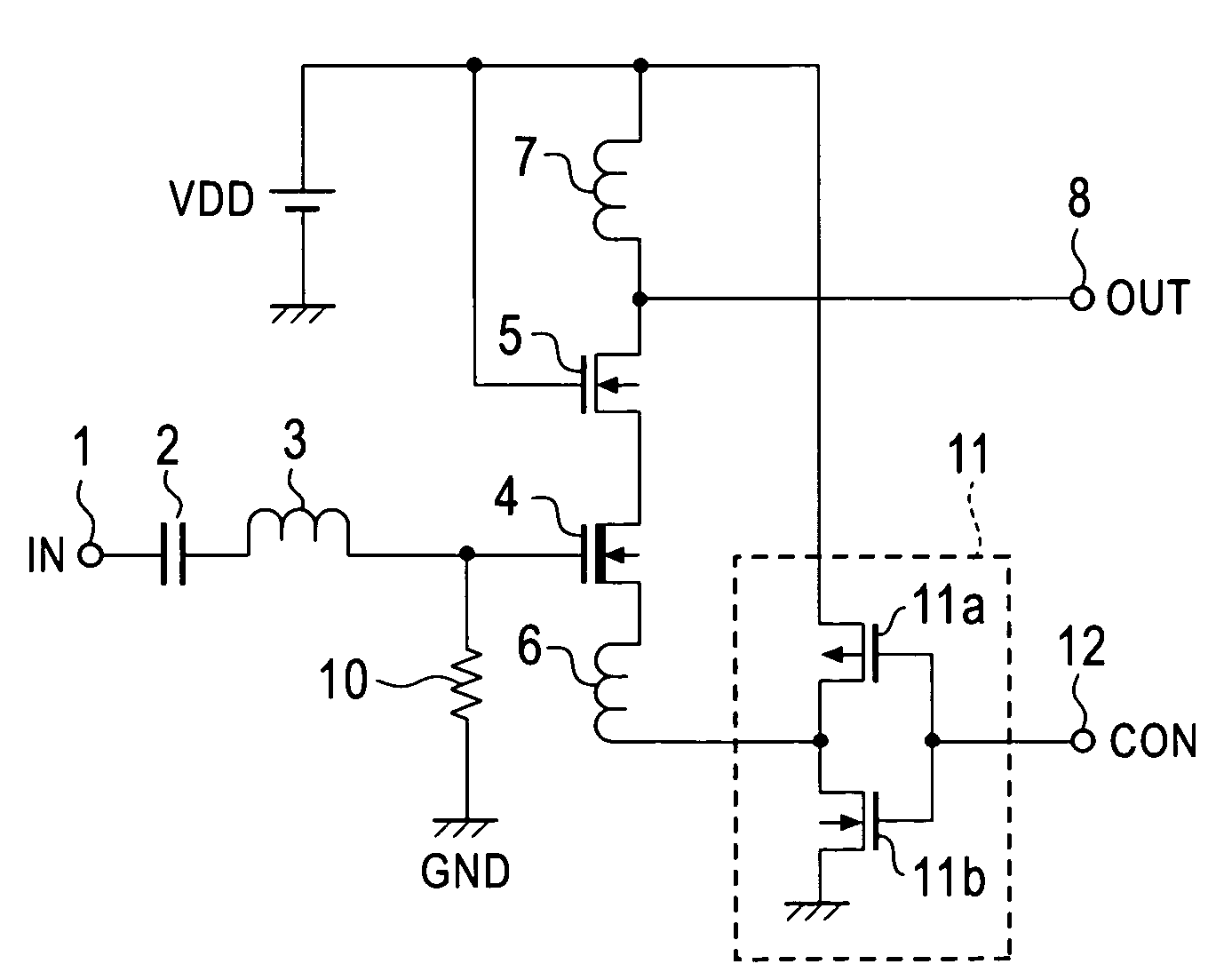
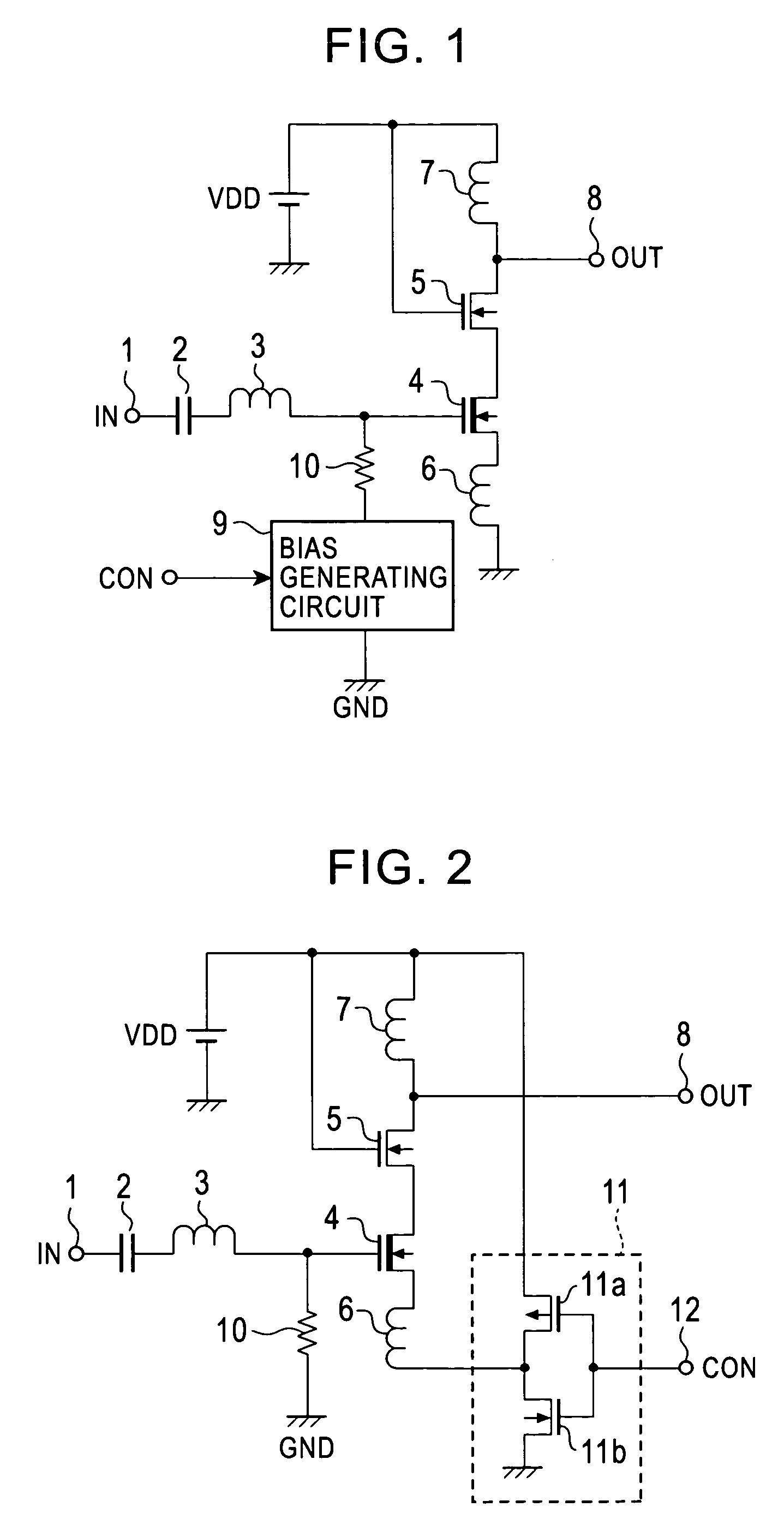
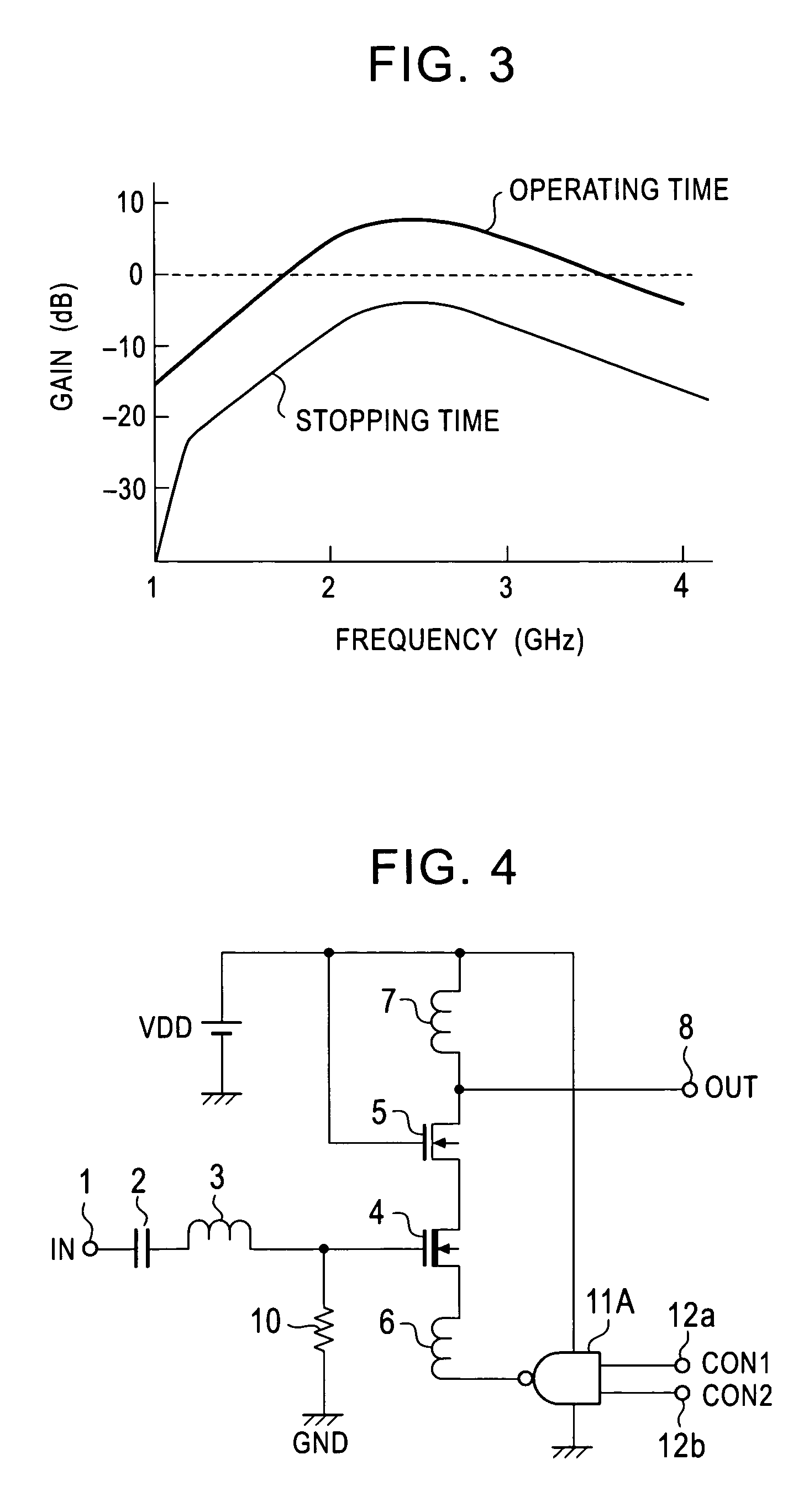
The invention provides an amplifying circuit for reducing electric power consumption at a standby mode time. Therefore, in DMOS and NMOS transistors constituting a cascode amplifier, the gate of the DMOS transistor of an initial stage is biased to a grounding voltage through a resistor, and the source of the DMOS transistor is connected to the output side of an inverter through an inductor. When a control signal is set to a level “H”, the output of the inverter becomes a level “L”, and the DMOS transistor attains a turning-on state and a sufficient operating electric current is flowed to the cascode amplifier. Thus, an input signal is amplified and is outputted as an output signal. In contrast to this, when the control signal is set to the level “L”, the output of the inverter becomes the level “H”, and the DMOS transistor attains a turning-off state and the operating electric current of the cascode amplifier is stopped.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Variable gain amplifier and communication apparatus
InactiveUS7482879B2Inhibit deteriorationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
A variable gain amplifier is provided that can obtain a wide range of gain variation and suppress the deterioration of linearity when switching between amplifying transistors. The variable gain amplifier includes a plurality of cascode amplifiers each including an amplifying transistor and a plurality of cascode transistors connected in a cascode arrangement to an output terminal of the amplifying transistor. The plurality of cascode amplifiers are connected through attenuators. The variable gain amplifier further includes a first controller that controls ON / OFF operations of the plurality of cascode transistors included in each cascode amplifier; and a second controller that controls ON / OFF operations of a plurality of amplifying transistors, only one of which is included in each of the plurality of cascode amplifiers, such that only selected one of the plurality of amplifying transistors is turned on.
Owner:SHARP KK
Variable-gain low noise amplifier
InactiveUS20110095822A1Gain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceLoad circuitElectrical resistance and conductance
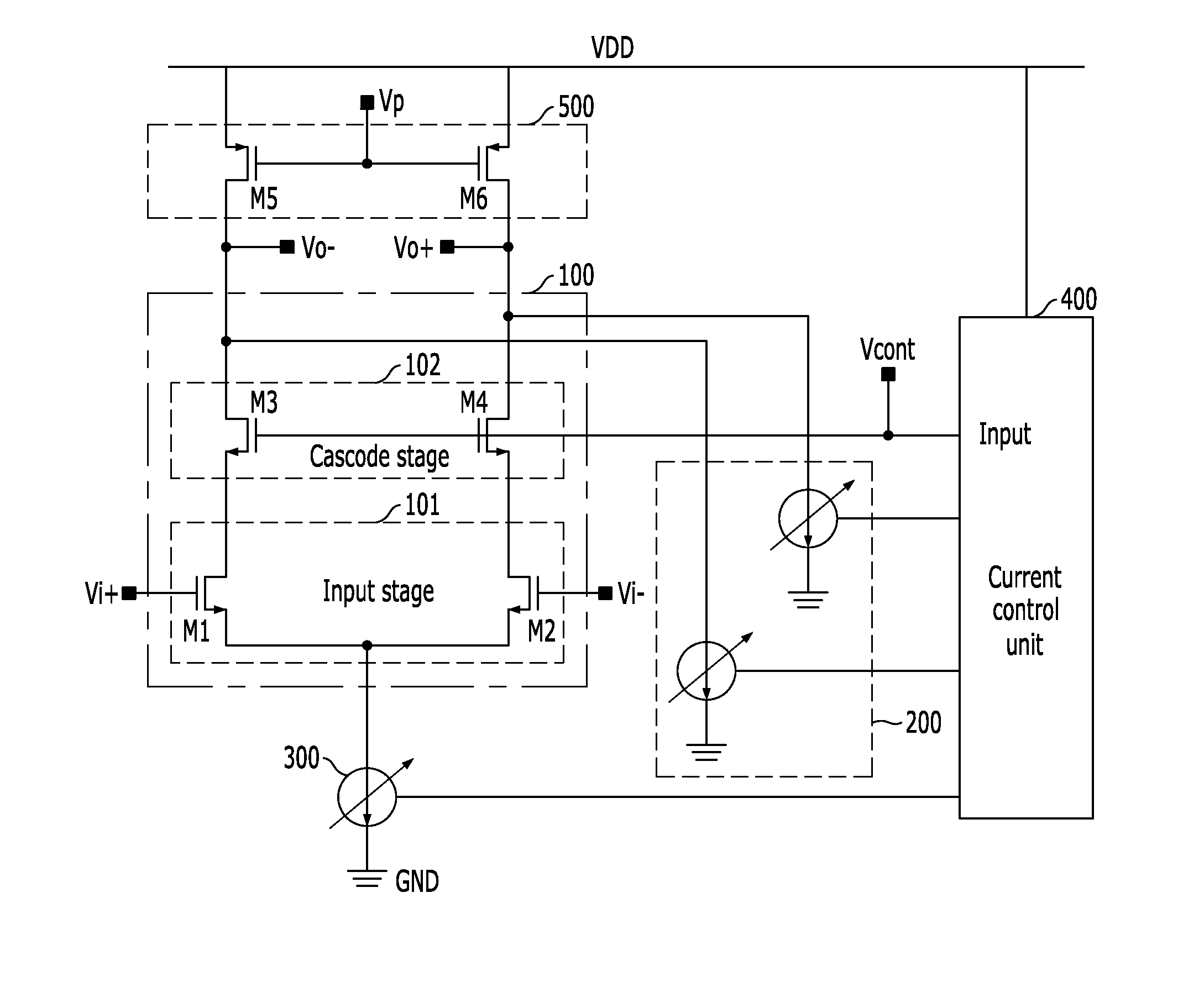
A highly linear variable-gain low noise amplifier is a cascode amplifier. The cascode amplifier includes a gain control circuit, a load circuit, a current steering circuit and an input circuit. The gain control circuit is used for receiving a gain adjusting voltage, thereby generating a resistance adjusting signal and a current steering control signal. The load circuit includes plural variable resistors. The resistances of the variable resistors are adjusted according to the resistance adjusting signal. The current steering circuit is connected to the load circuit through plural current paths for adjusting a current ratio between the plural current paths according to the current steering control signal. The current steering circuit has differential signal output terminals. The input circuit is connected to the current steering circuit. The input circuit has differential signal input terminals.
Owner:SUNPLUS TECH CO LTD
Class ab folded-cascode amplifier having cascode compensation
ActiveUS20080272844A1Improved gain-bandwidth productDifferential amplifiersAmplifier detailsEngineeringGain–bandwidth product
A class AB folded-cascode amplifier having improved gain-bandwidth product, comprises a differential input circuit including a differential transistor pair coupled to a source of tail current and responsive to a differential input signal for conducting a first current, a cascode circuit coupled to the differential input circuit for supplying a second current thereto, and a class AB output stage. A compensation circuit is configured for feeding back mutually complementary compensation signals from an output node to the differential input circuit. Another compensation circuit is configured for feeding back a signal from the output of the output stage to the input of the output stage.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
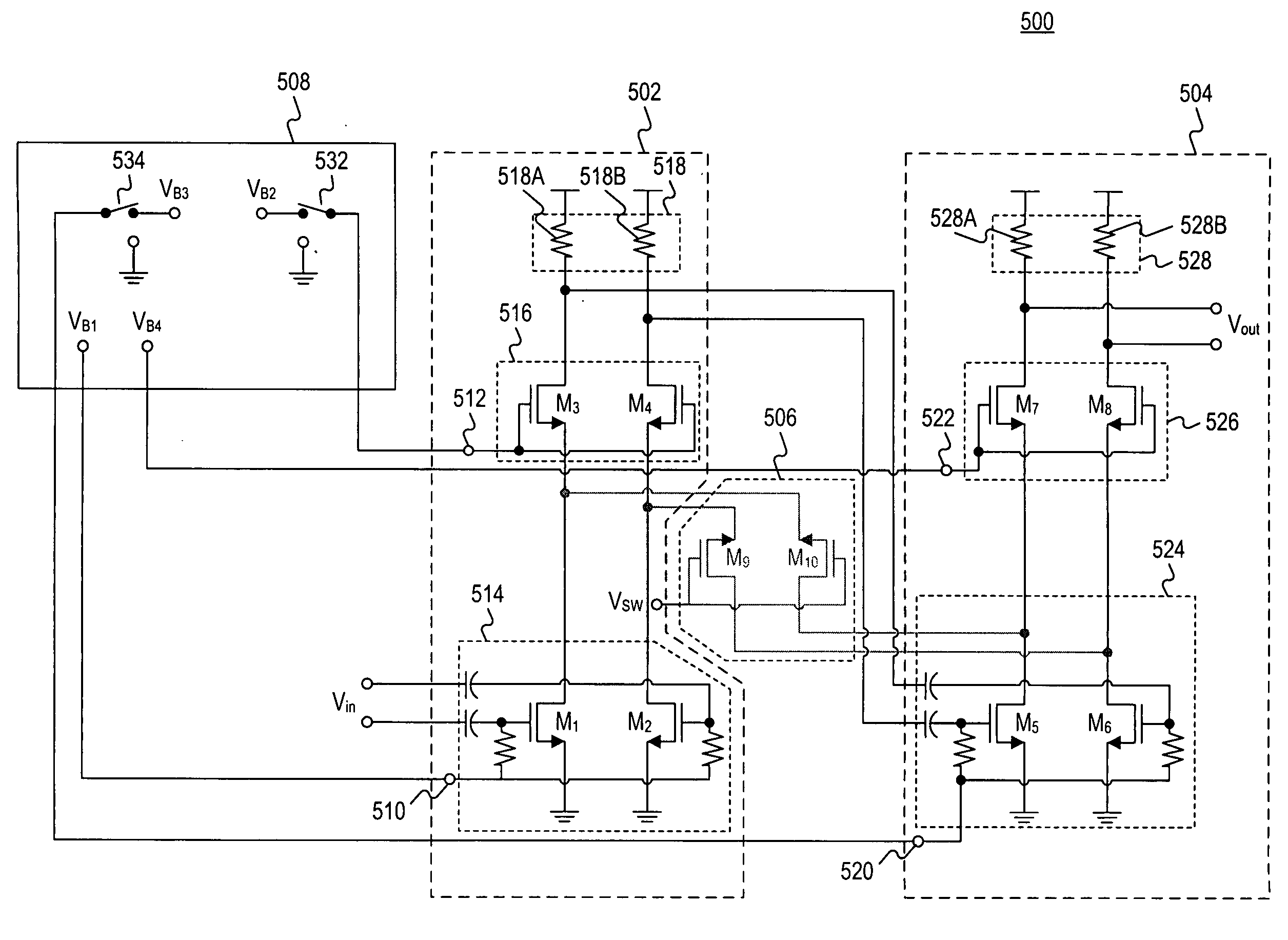
Variable gain amplifier including series-coupled cascode amplifiers
ActiveUS20090108935A1Gated amplifiersAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
A variable gain amplifier to convert an amplifier input voltage to an amplifier output voltage, the variable gain amplifier includes: a plurality of cascode amplifiers coupled in series; a plurality of switching transistor pair circuits coupled in series; and a bias circuit coupled to provide bias voltages to each of the plurality of cascode amplifiers; wherein each of the switching transistor pair circuits is further coupled between two consecutive ones of the cascode amplifiers; a first one of the cascode amplifiers is configured to receive the amplifier input voltage; and a last one of the cascode amplifiers is configured to provide the amplifier output voltage.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
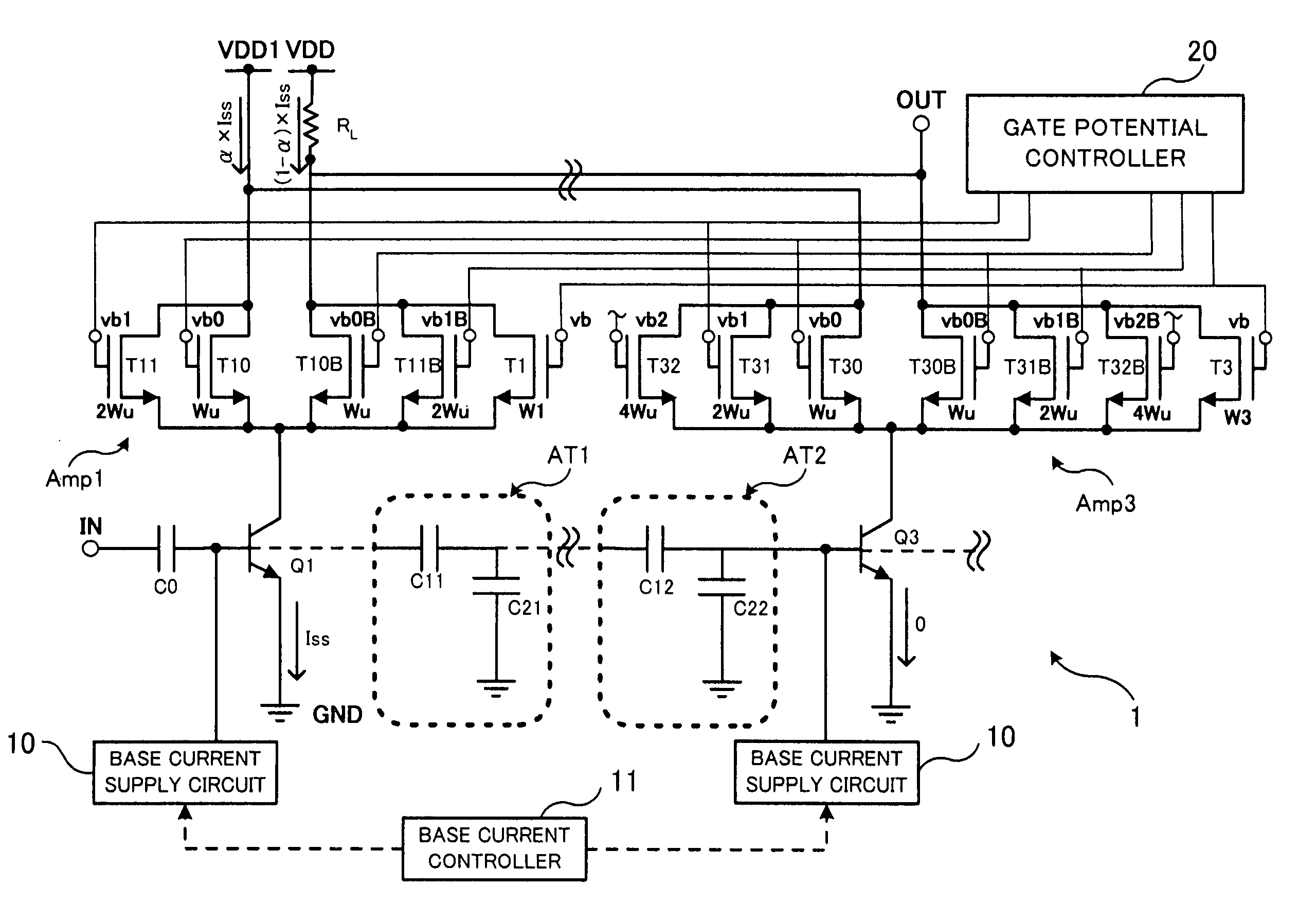
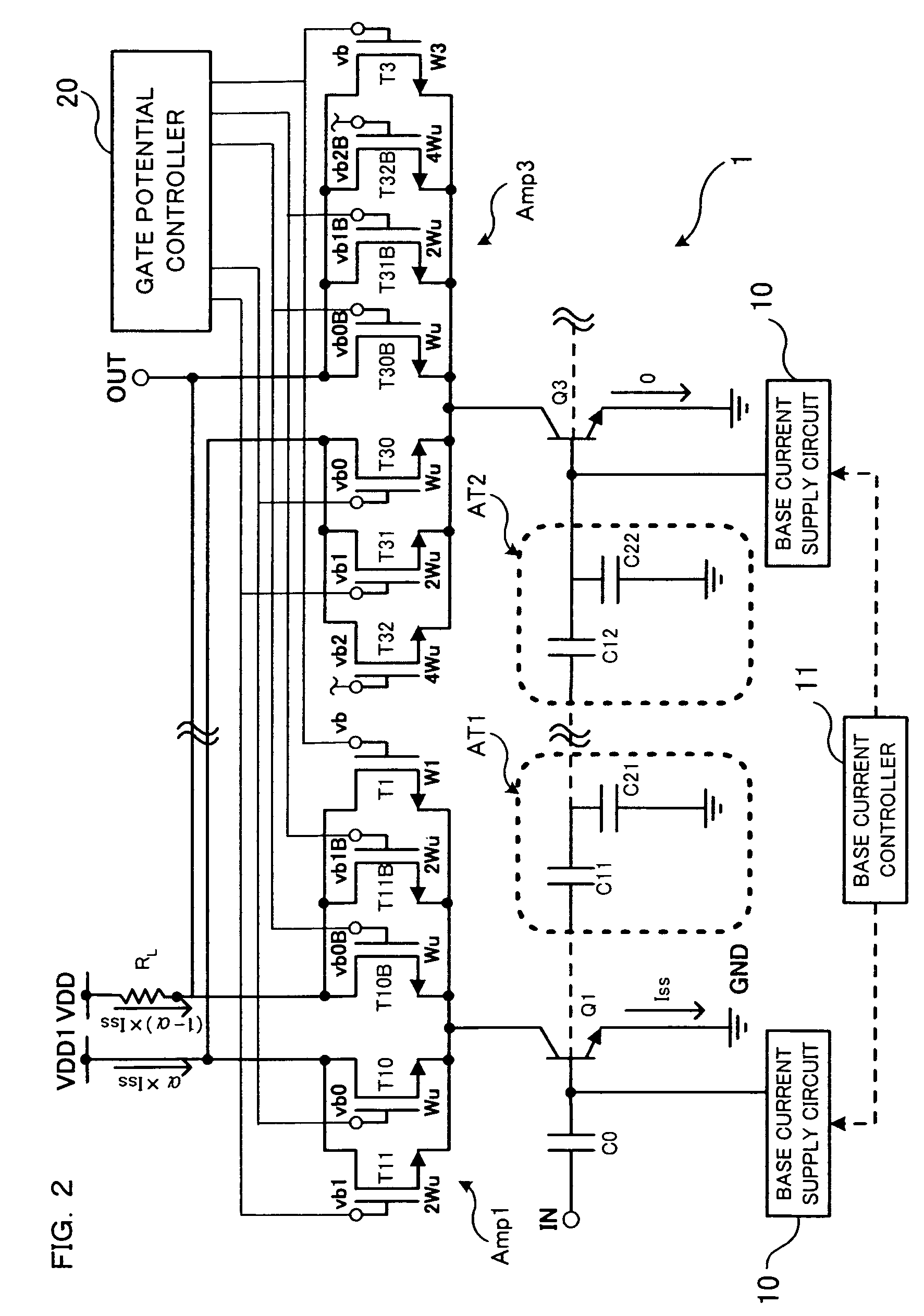
Electronic circuit with cascode amplifier
ActiveUS8228125B2Improve circuit efficiencyMaximize power efficiencyAmplifier combinationsAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
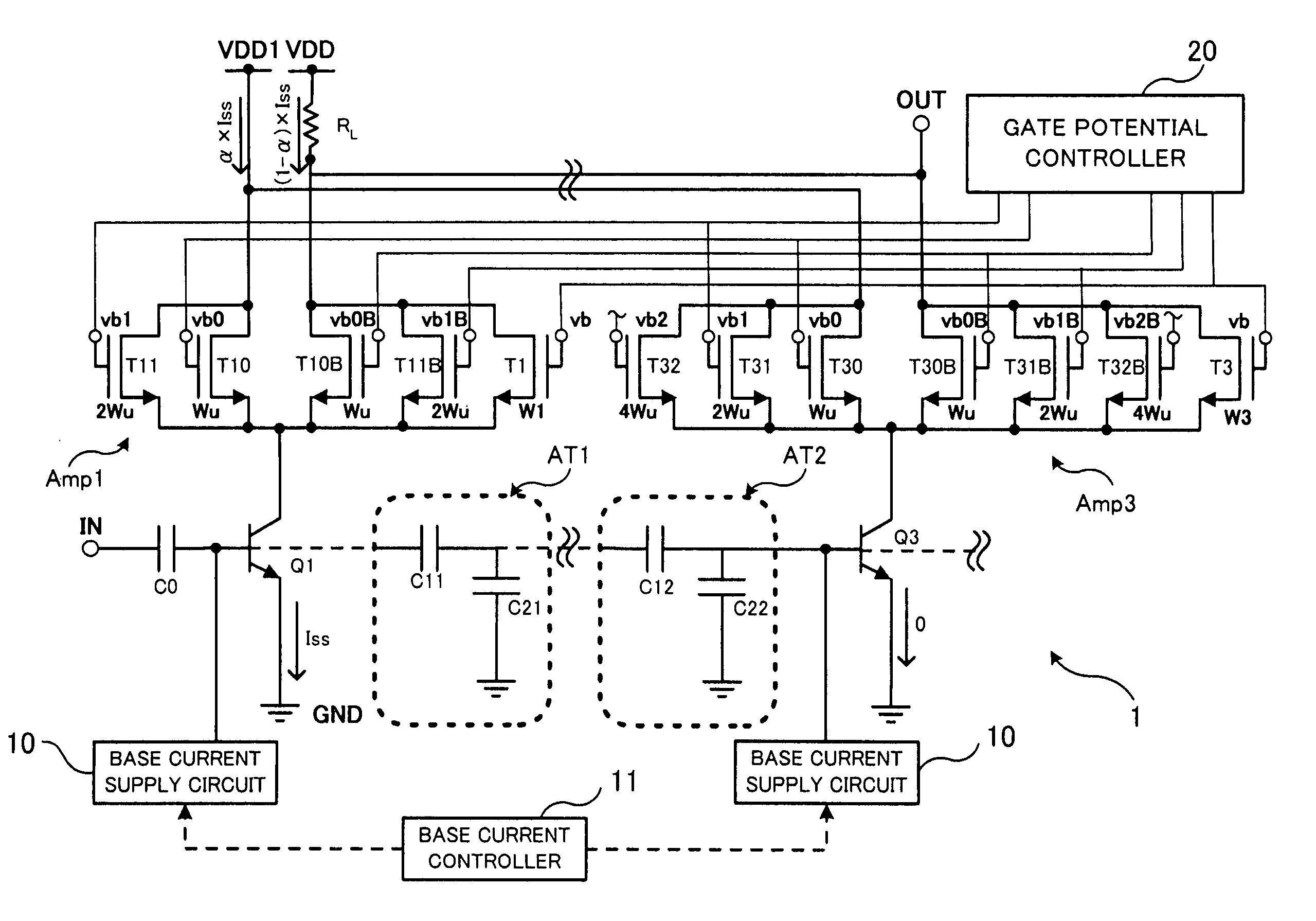
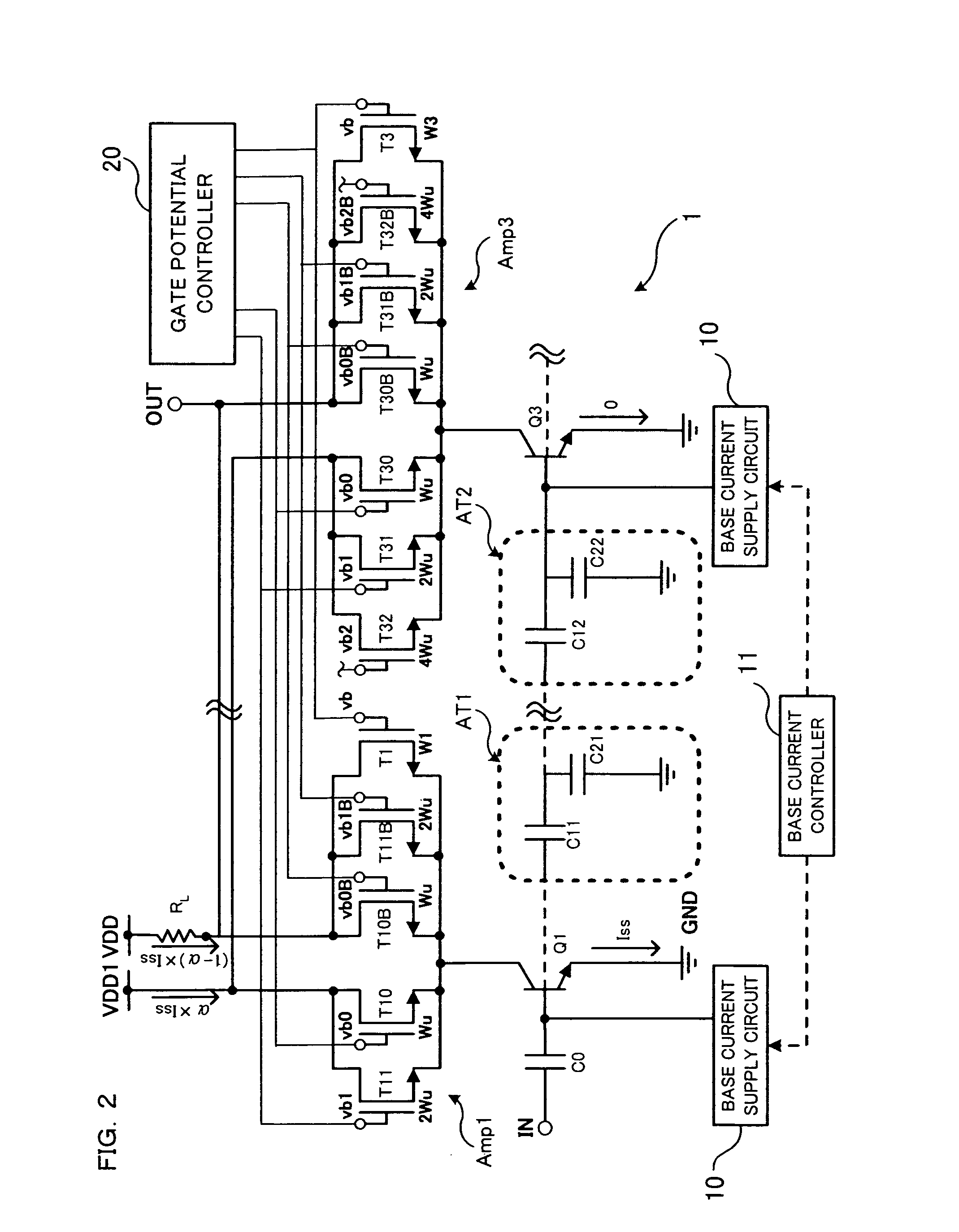
An electronic circuit has an amplifier with an amplifying transistor and a cascode transistor. A capacitive voltage divider applies a fraction of an RF signal swing from the drain of the cascode transistor to the gate of the cascode transistor, the fraction being determined by a ratio between capacitance values. In addition a bias voltage supply circuit is provided. The bias voltage supply circuit is configured to define a relation between an average gate voltage of the cascode transistor and an average drain supply voltage at the drain of the cascode transistor. This relation increases the average gate voltage with increasing average drain voltage, and the relation provides a non zero average gate voltage when extrapolated to zero average drain supply voltage.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
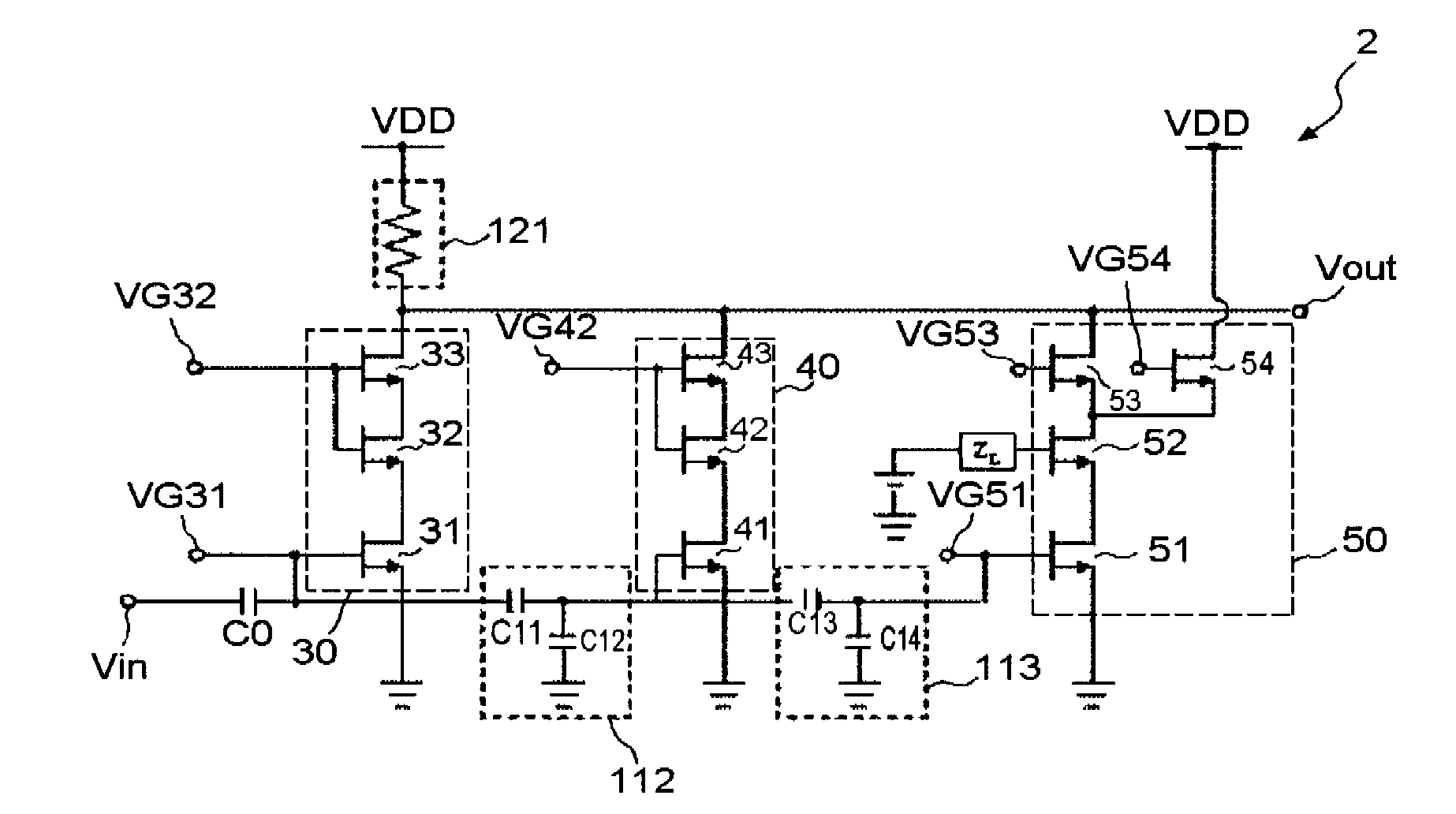
Electronic circuit
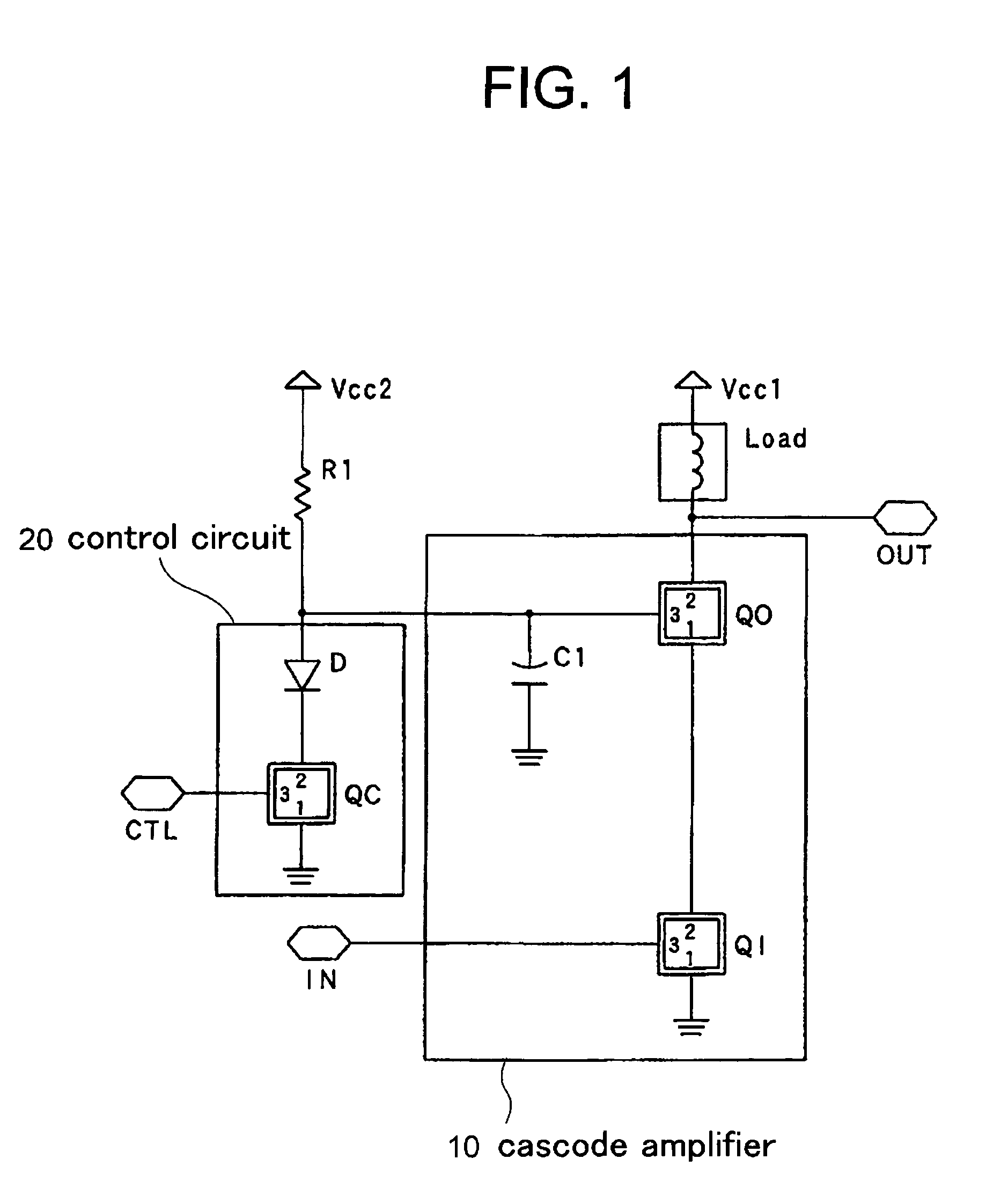
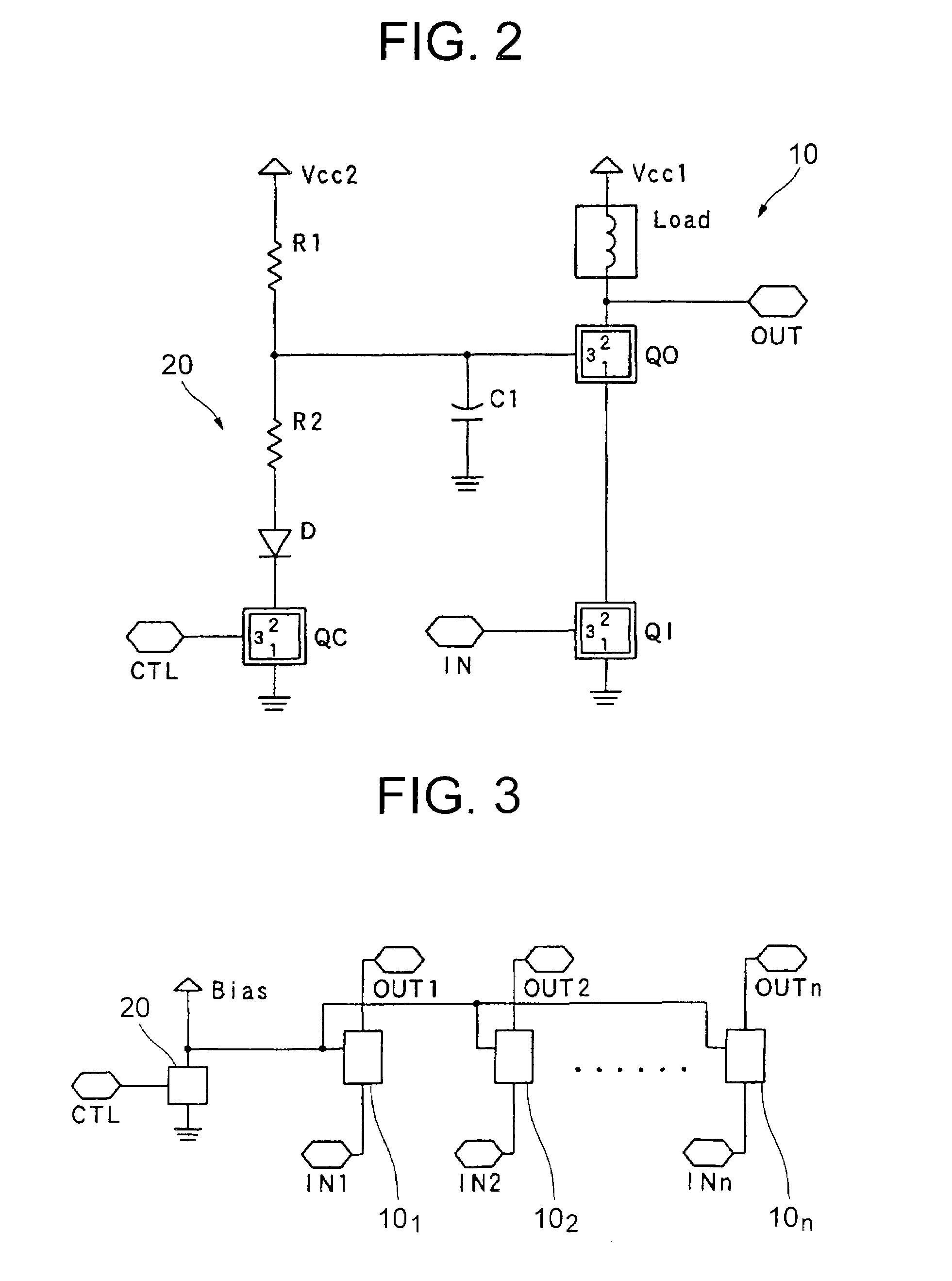
InactiveUS7126427B2Easy dischargeShorten charging timeTransistorAmplifier combinationsControl signalEngineering
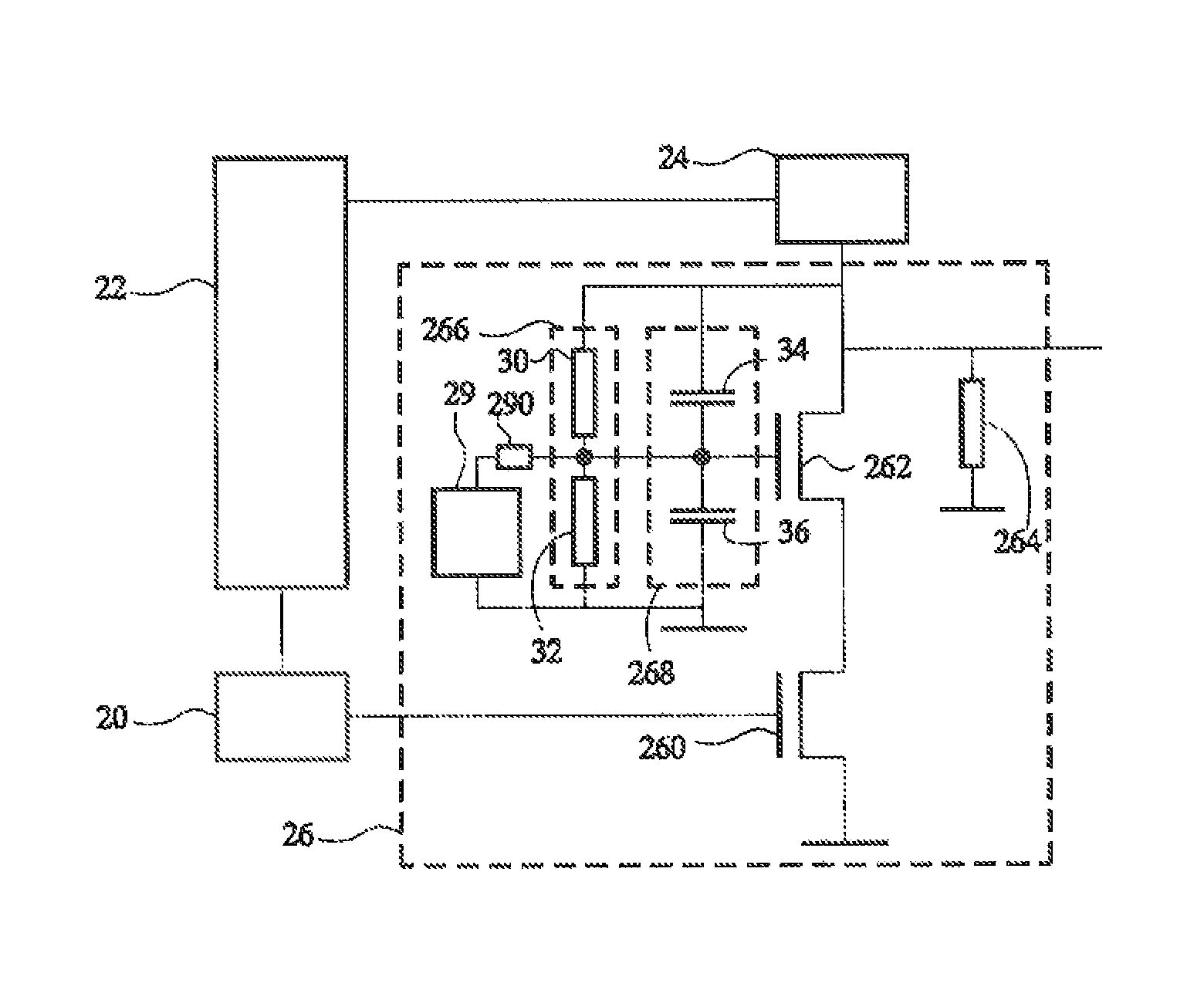
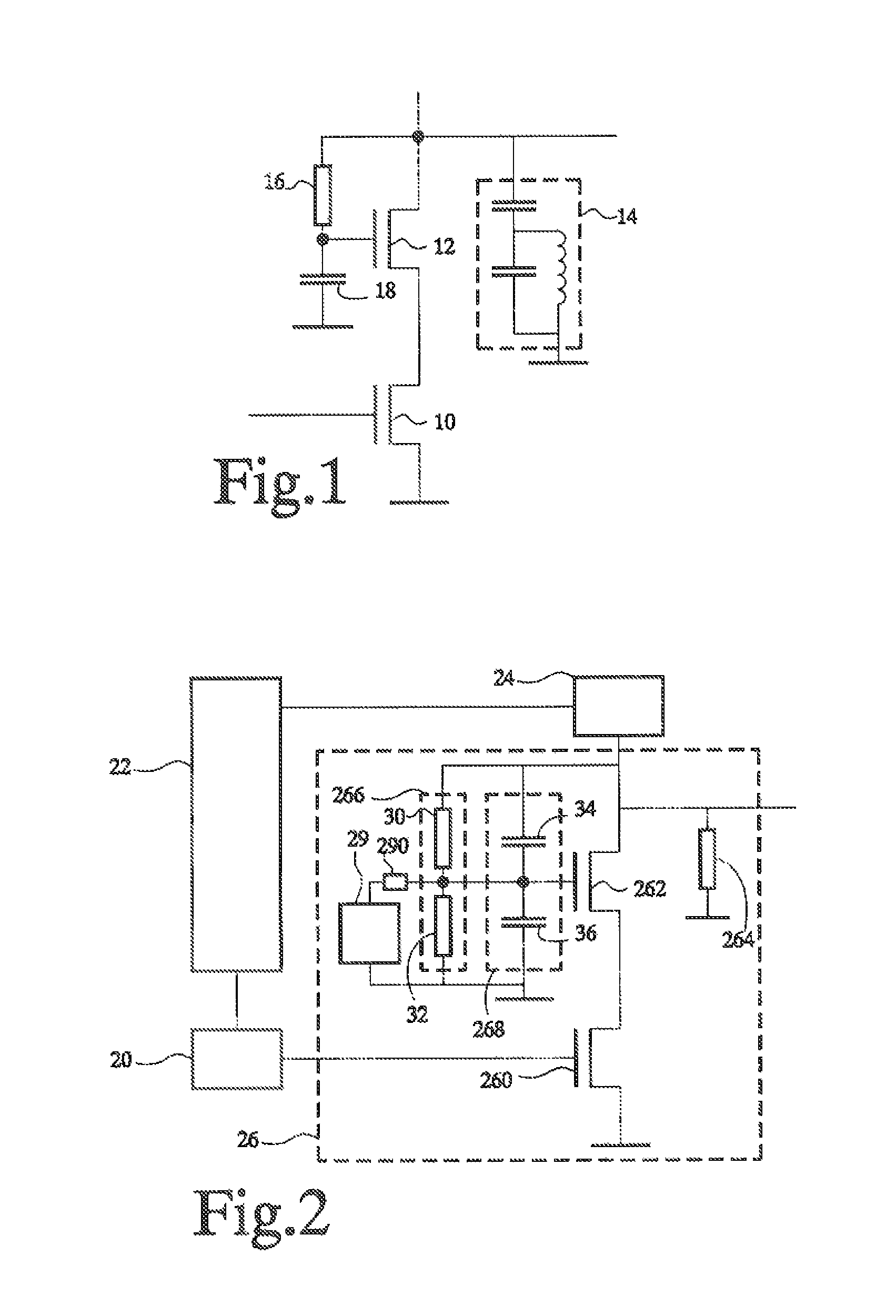
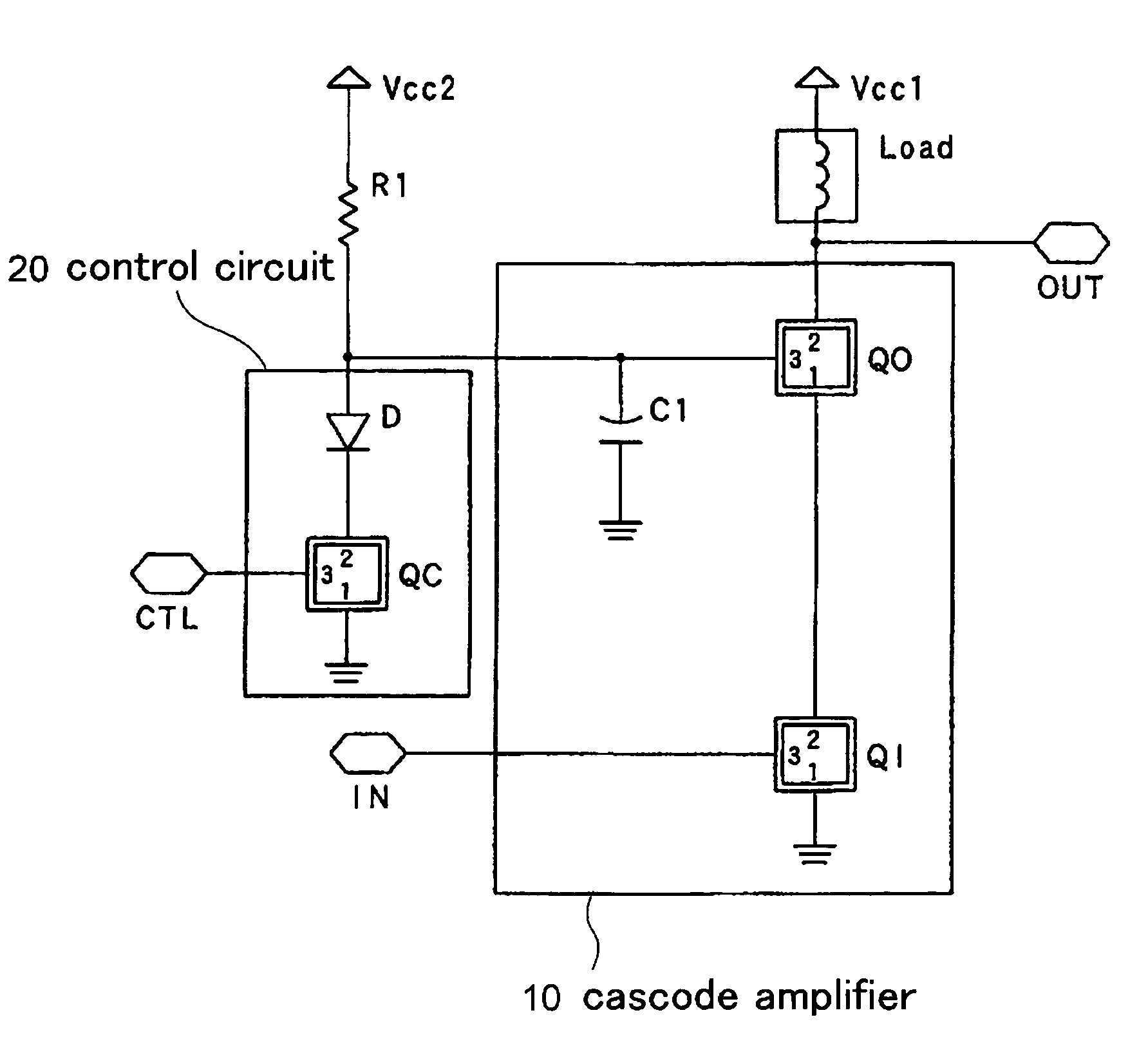
An electronic circuit includes transistors having first to third terminals, the third terminal controlling the current between the first terminal and the third terminal. The electronic circuit includes: a cascode amplifier (10) including an input transistor (Q1) receiving an input signal (IN) through the third terminal, and an output transistor (QO) having the first terminal connected to the second terminal of the input transistor (QI), the third terminal connected to the ground potential via a capacitor (C1) and the second terminal outputting therethrough an output signal; and a control circuit (20) including a control transistor receiving a control signal through the third terminal, and a diode connected to the first and second terminals of the control transistor (QC) in series. The third terminal of the output transistor (QO) of the cascode amplifier (10) is connected to the ground potential through the control transistor (QC) and the diode (D). The electronic circuit has a reduced signal switching time.
Owner:NEC CORP
Cascode Amplifier Bias Circuits
ActiveUS20190158031A1Amplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationPower amplifiersLow noiseAudio power amplifier
Bias circuits and methods for silicon-based amplifier architectures that are tolerant of supply and bias voltage variations, bias current variations, and transistor stack height, and compensate for poor output resistance characteristics. Embodiments include power amplifiers and low-noise amplifiers that utilize a cascode reference circuit to bias the final stages of a cascode amplifier under the control of a closed loop bias control circuit. The closed loop bias control circuit ensures that the current in the cascode reference circuit is approximately equal to a selected multiple of a known current value by adjusting the gate bias voltage to the final stage of the cascode amplifier. The final current through the cascode amplifier is a multiple of the current in the cascode reference circuit, based on a device scaling factor representing the relative sizes of the transistor devices in the cascode amplifier and in the cascode reference circuit.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Low noise amplifier
A low-noise amplifier circuit to convert a single-ended input into a dual-ended output includes an input transconductance stage circuit, including a first MOS transistor coupled in parallel with a second MOS transistor; a current buffer circuit, including a third MOS transistor coupled in parallel with a fourth MOS transistor; each of the first, second, third, and fourth transistors having a body, gate, source, and drain; the input transconductance stage circuit and the current buffer circuit being cascode coupled, forming a cascode amplifier configuration; the single-ended input being at the source of one of the first and second transistors in the input transconductance stage circuit; the dual-ended output being a differential output across the drain of the third transistor and the drain of the fourth transistor; the first and second transistors of the input transconductance stage circuit being cross-coupled, wherein the body of the first transistor is coupled to the source of the second transistor, and the body of the second transistor is coupled to the source of the first transistor; and the third and fourth transistors of the current buffer circuit being cross-coupled, wherein a first capacitance is coupled between the gate of the third transistor and the source of the fourth transistor, and a second capacitance is coupled between the gate of the fourth transistor and the source of the third transistor.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Variable gain amplifier
A variable gain amplifier is provided. The variable gain amplifier includes a first cascode amplifier which includes a first common source transistor and a first common gate transistor, a second cascode amplifier which forms a differential pair with the first cascode amplifier and includes a second common source transistor and a second common gate transistor, and a gain adjustment unit having a side connected to the drain of the first common source transistor and the source of the first common gate transistor and another side connected to the drain of the second common source transistor and the source of the second common gate transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
CMOS variable gain amplifier
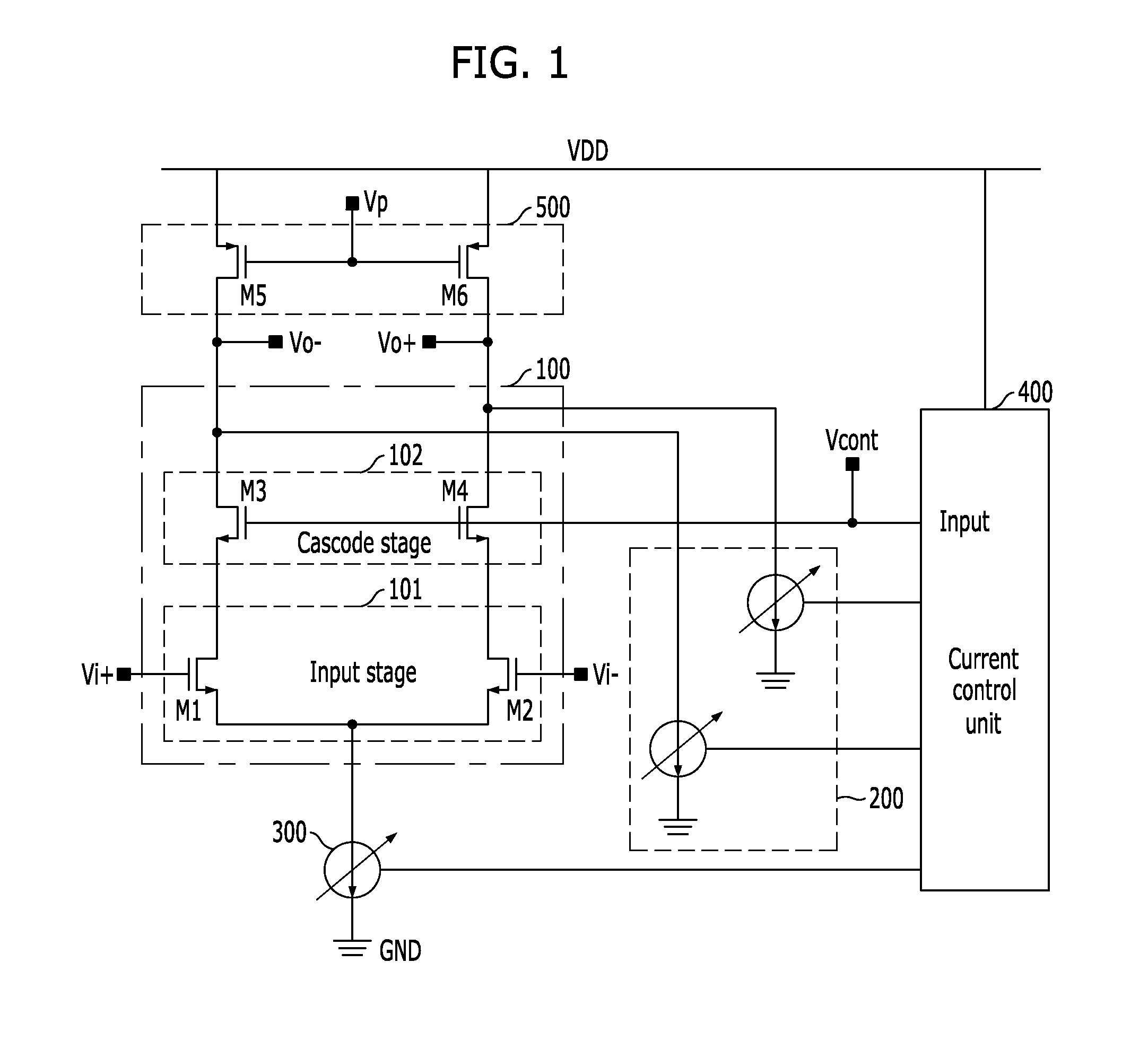
ActiveUS20110063030A1Gain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceControl signalEngineering
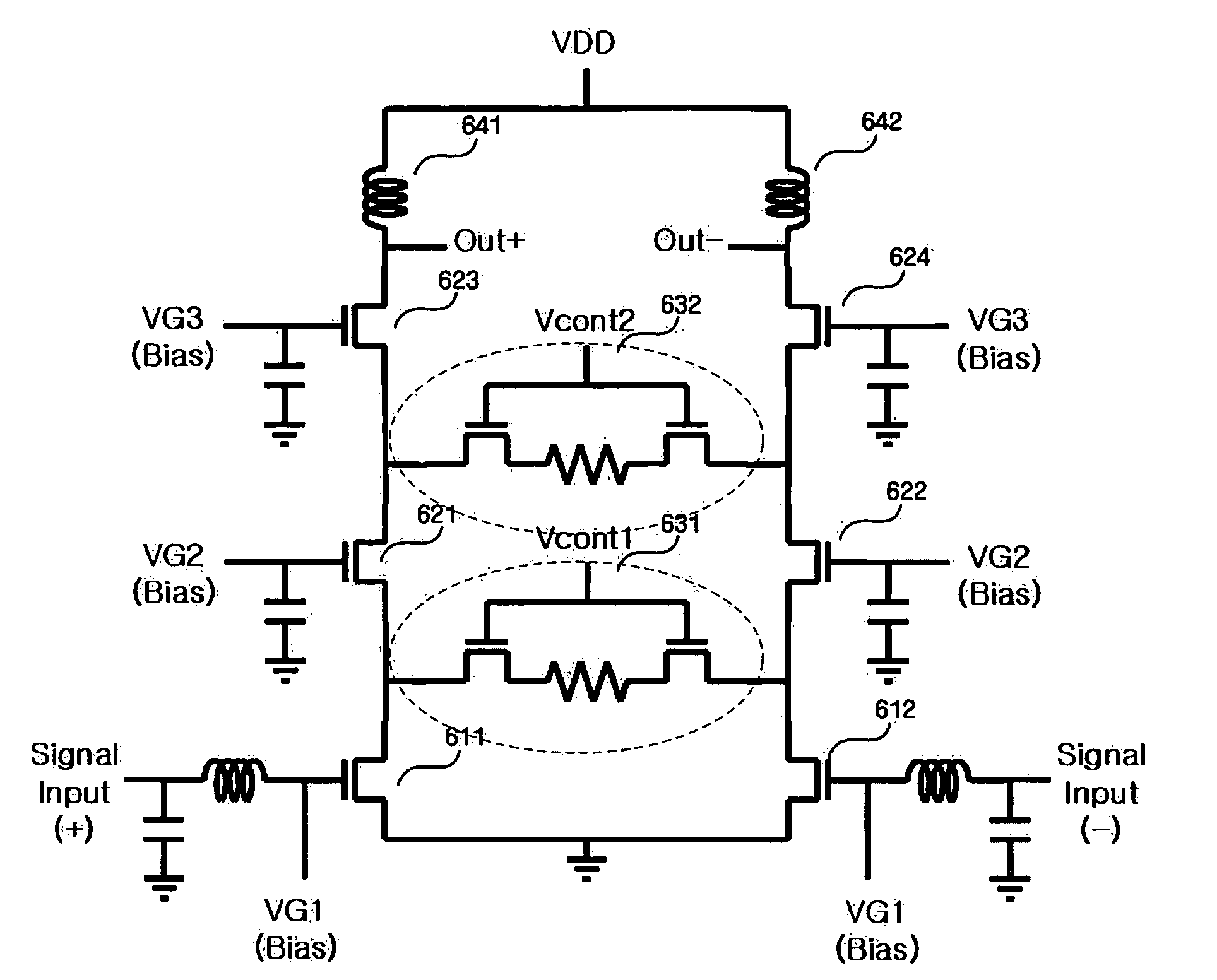
A complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) variable gain amplifier includes: a cascode amplifier including a common source field effect transistor and a common gate field effect transistor in a cascode structure; a first current generation unit connected in parallel to a drain of the common gate field effect transistor and configured to vary transconductance of the cascode amplifier; a second current generation unit connected to a common source of the cascode amplifier and configured to control a bias current of the cascode amplifier; a current control unit configured to generate a current control signal for the first and second current generation units; and a load stage connected in series to a drain of the cascode amplifier and configured to output an output current, which is varied by the overall transconductance of the cascode amplifier, as a differential output voltage.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com