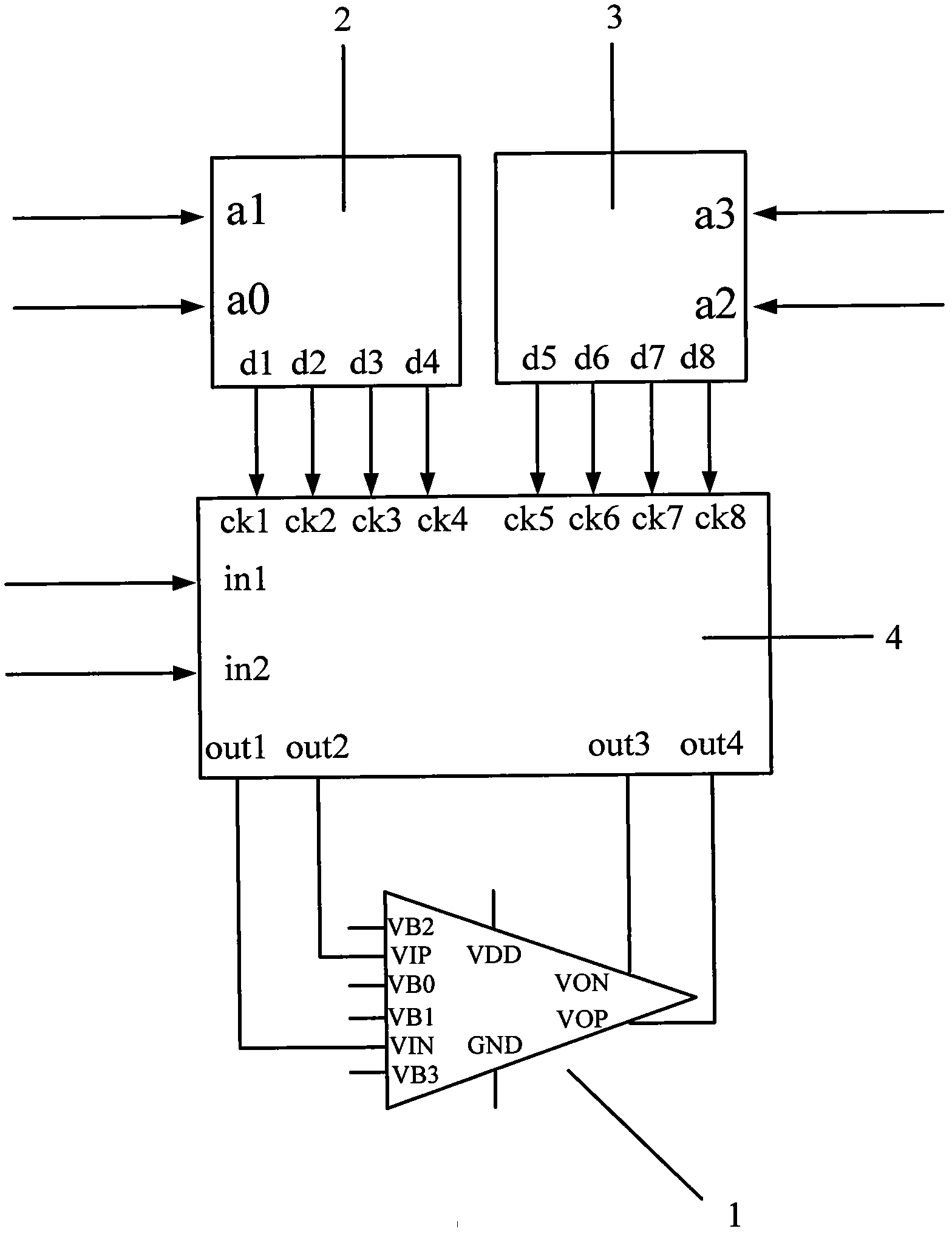
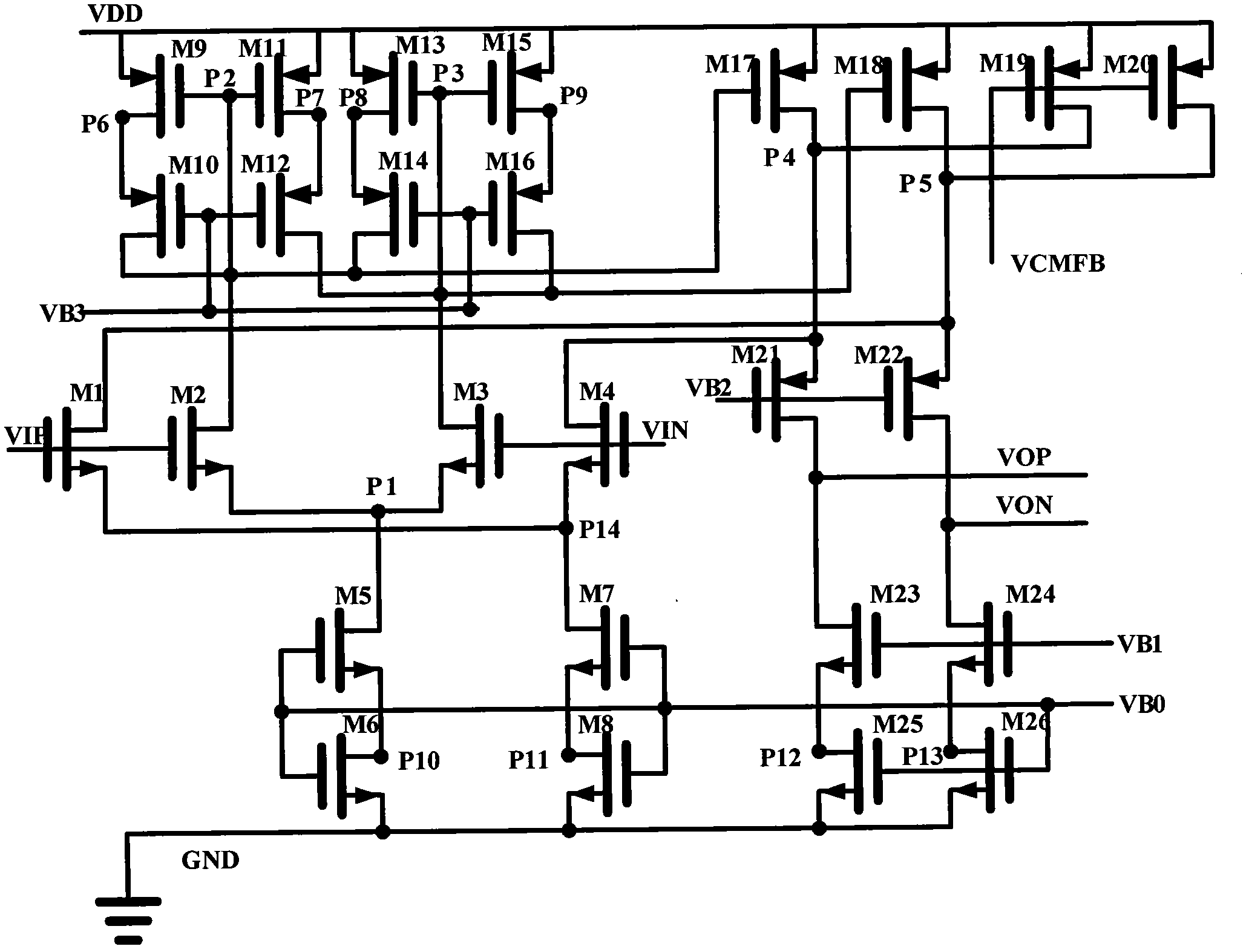
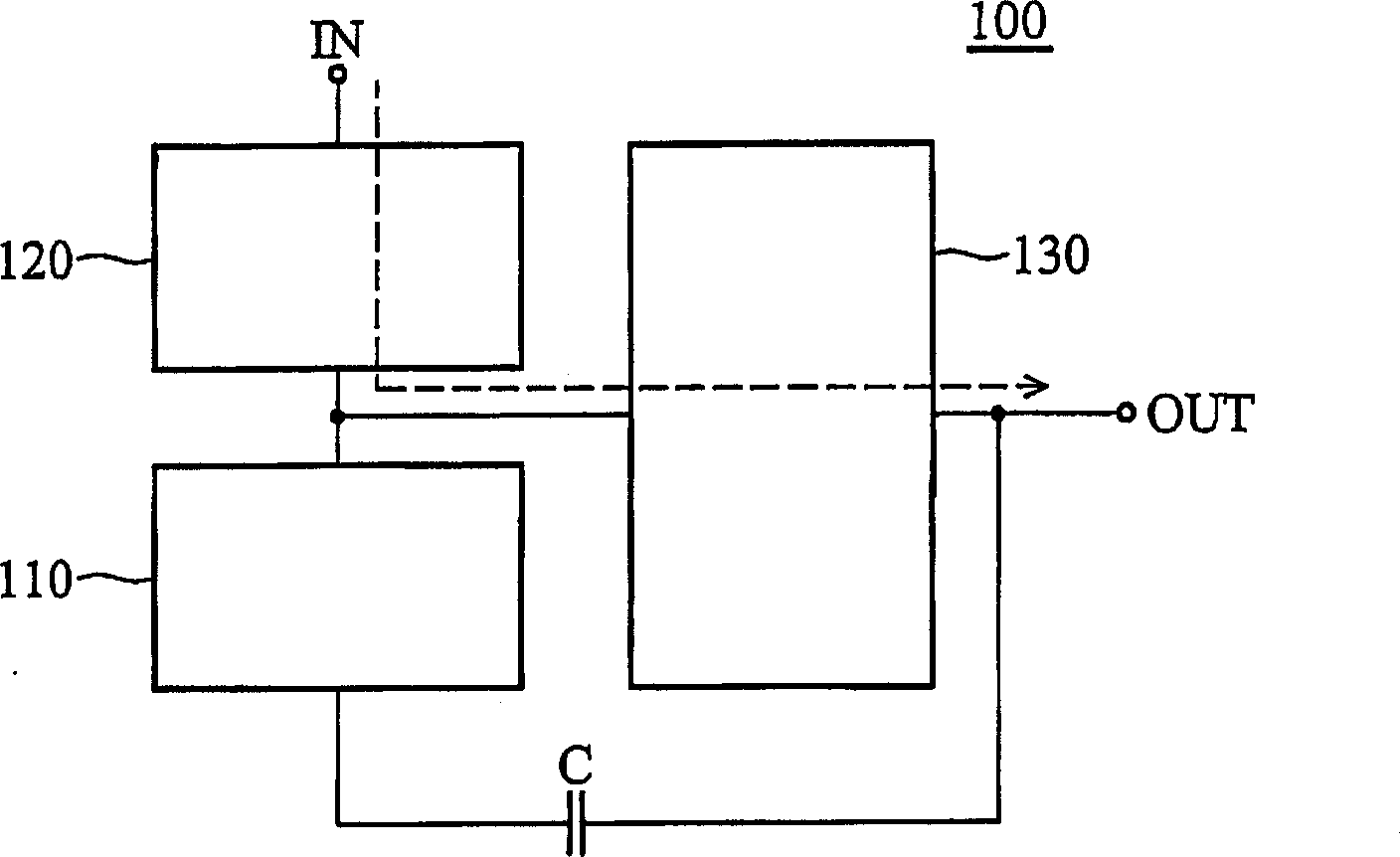
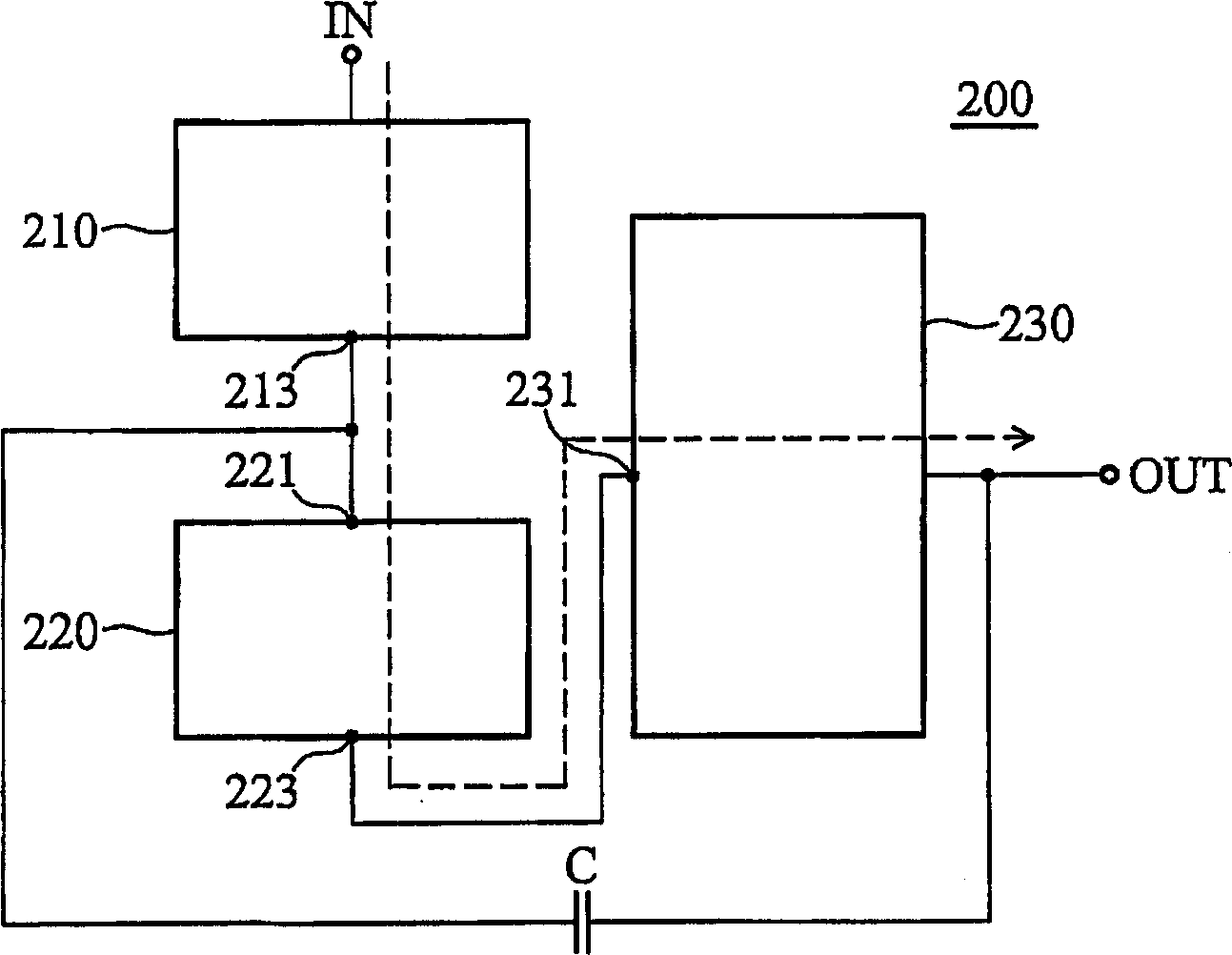
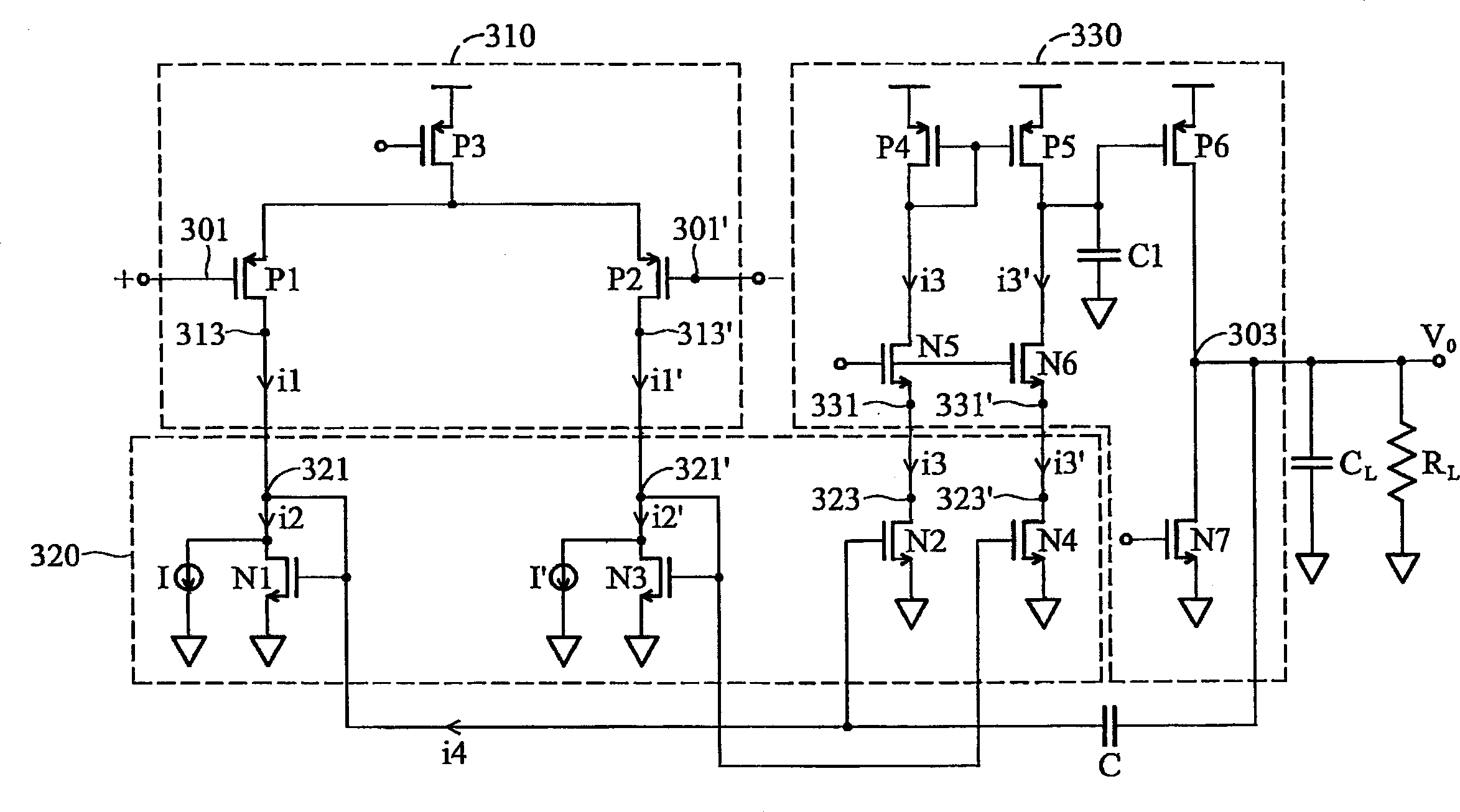
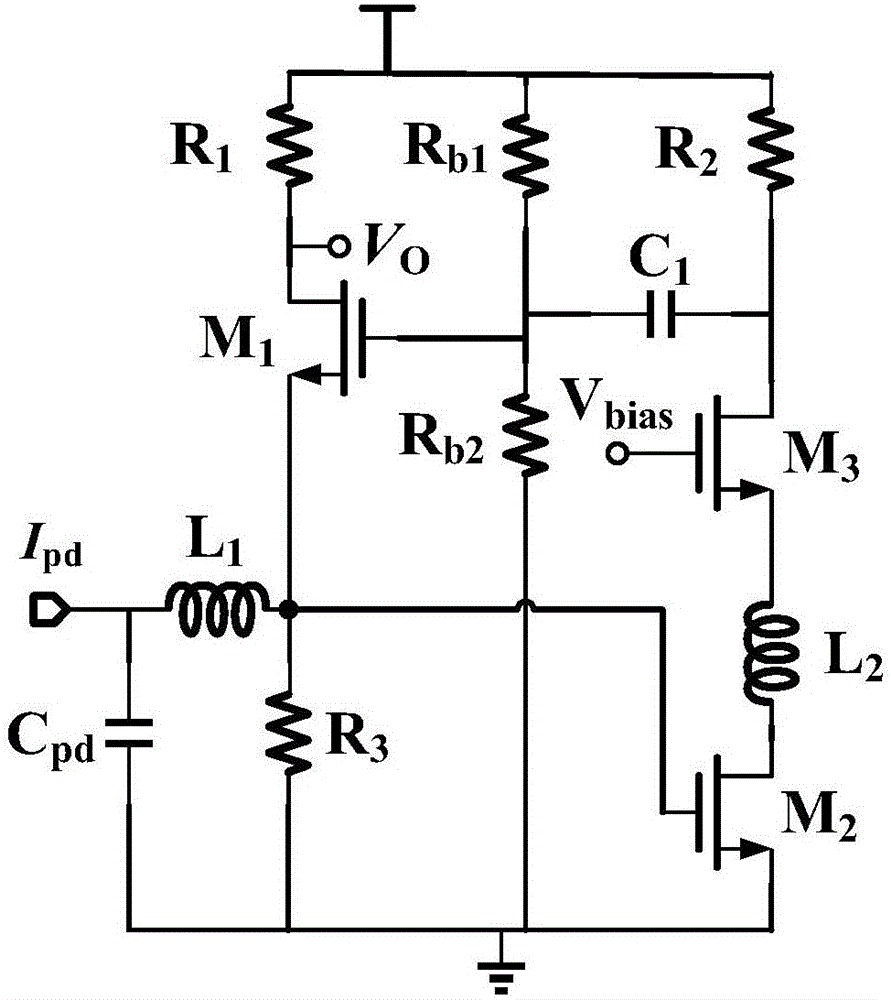
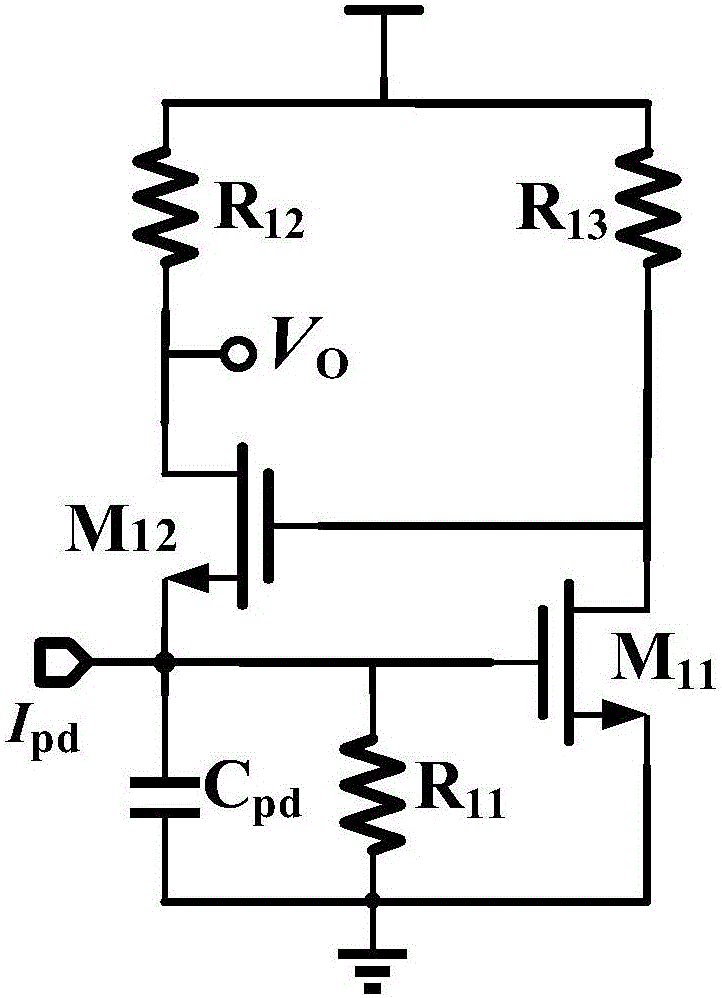
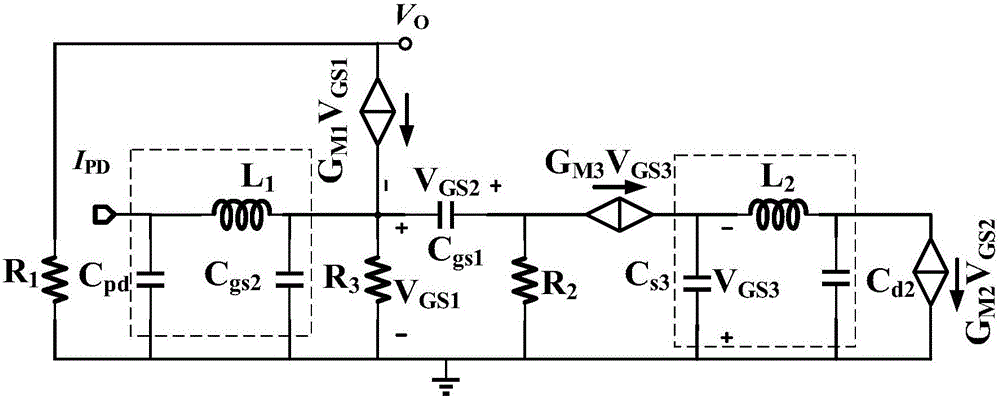
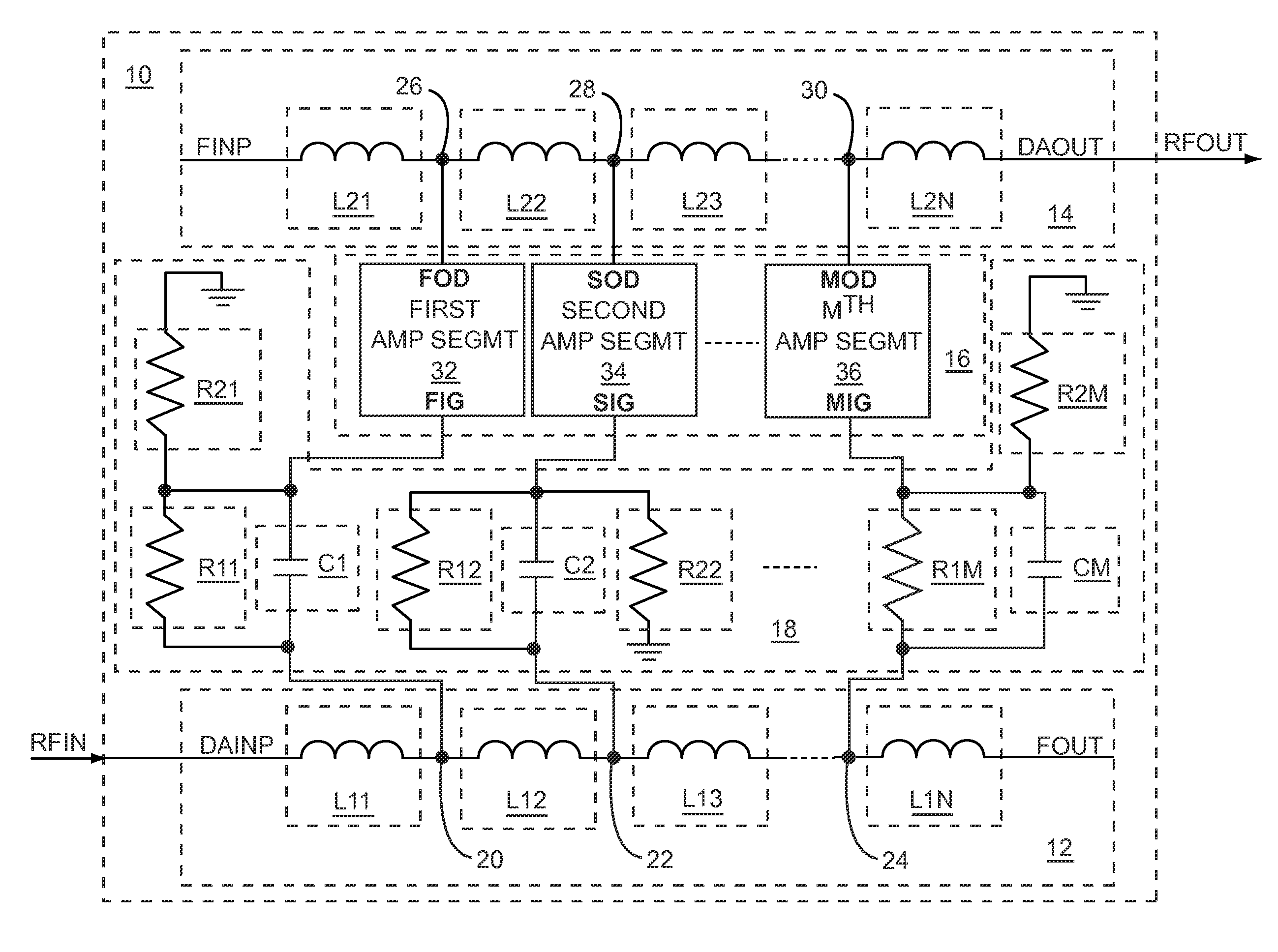
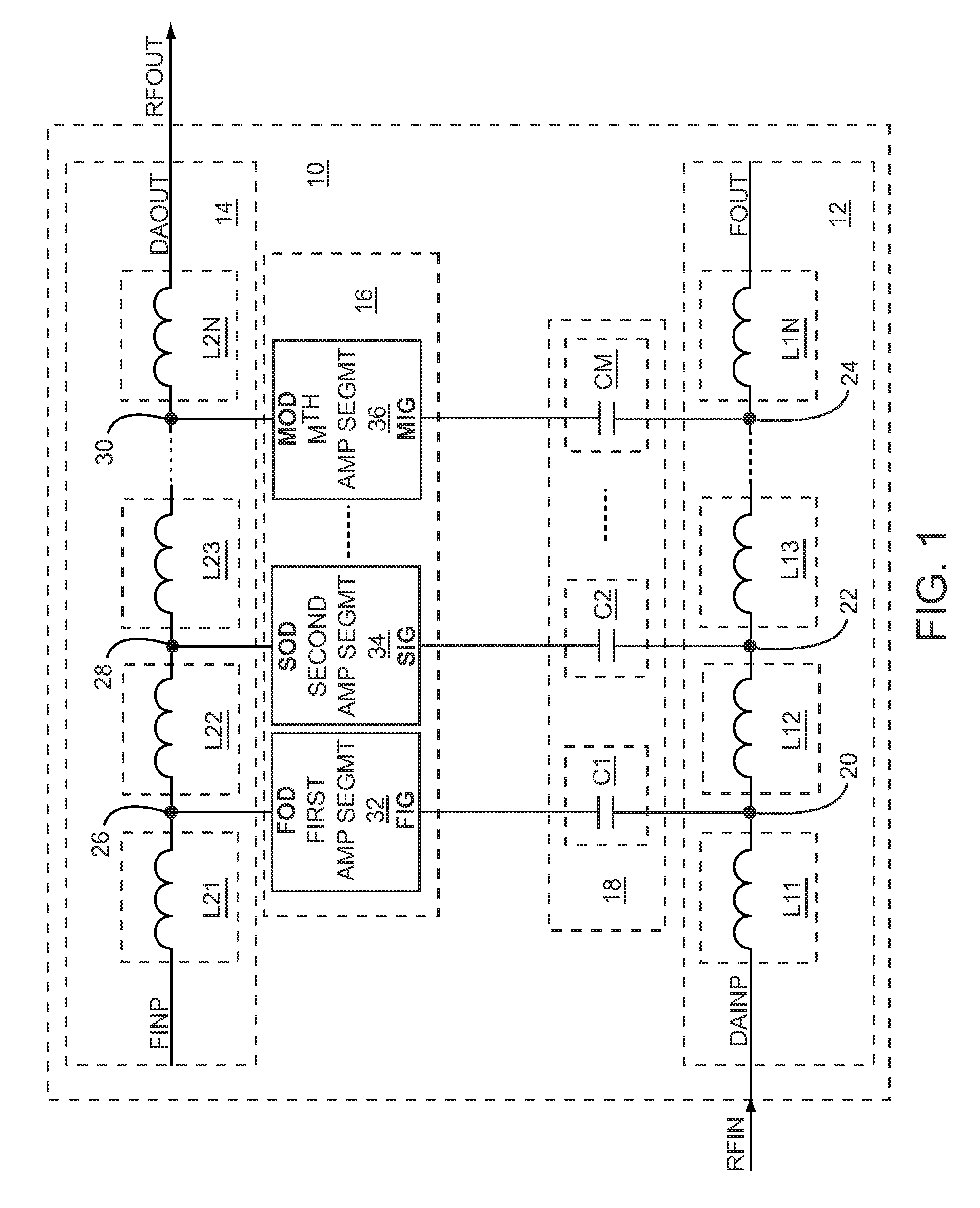
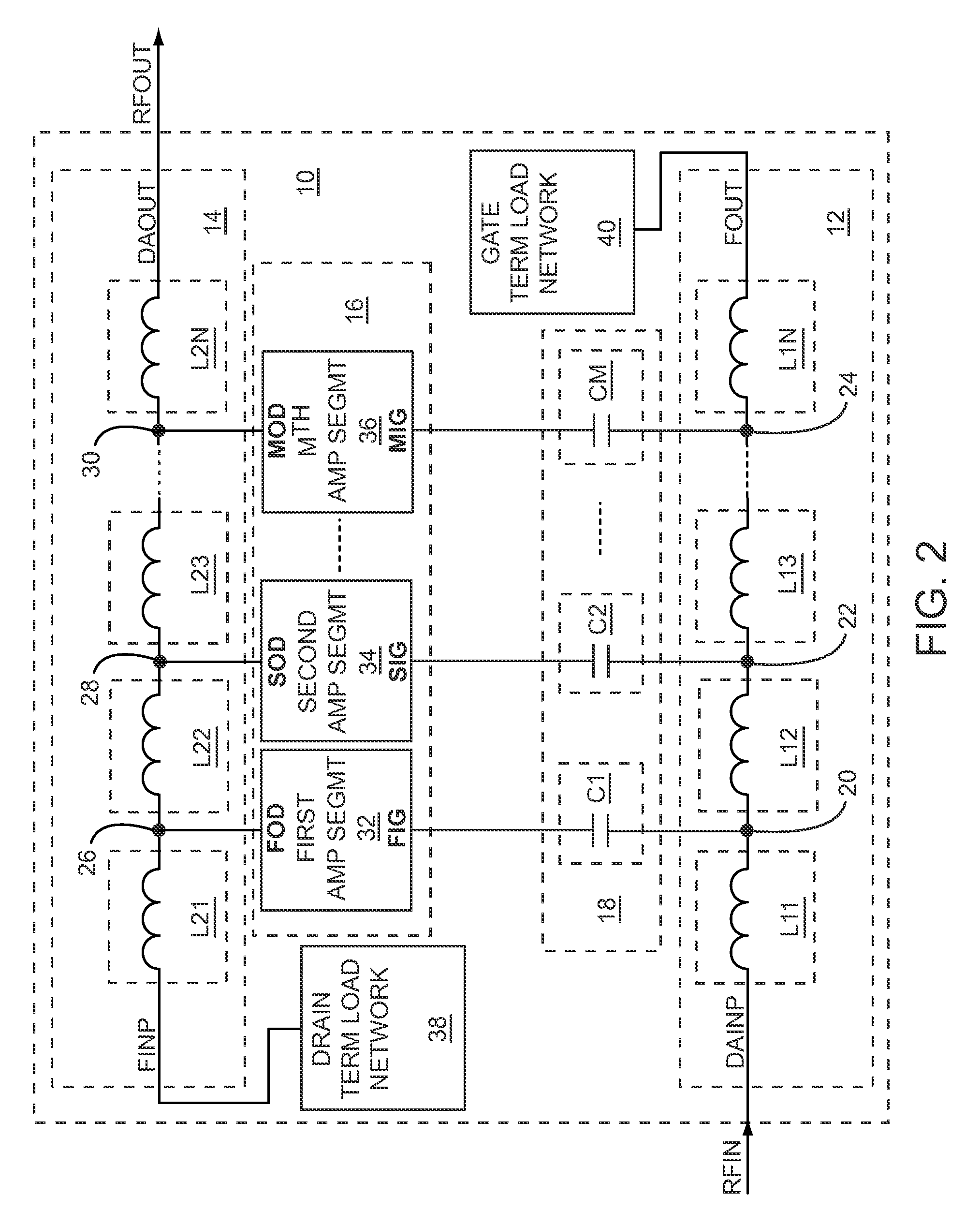
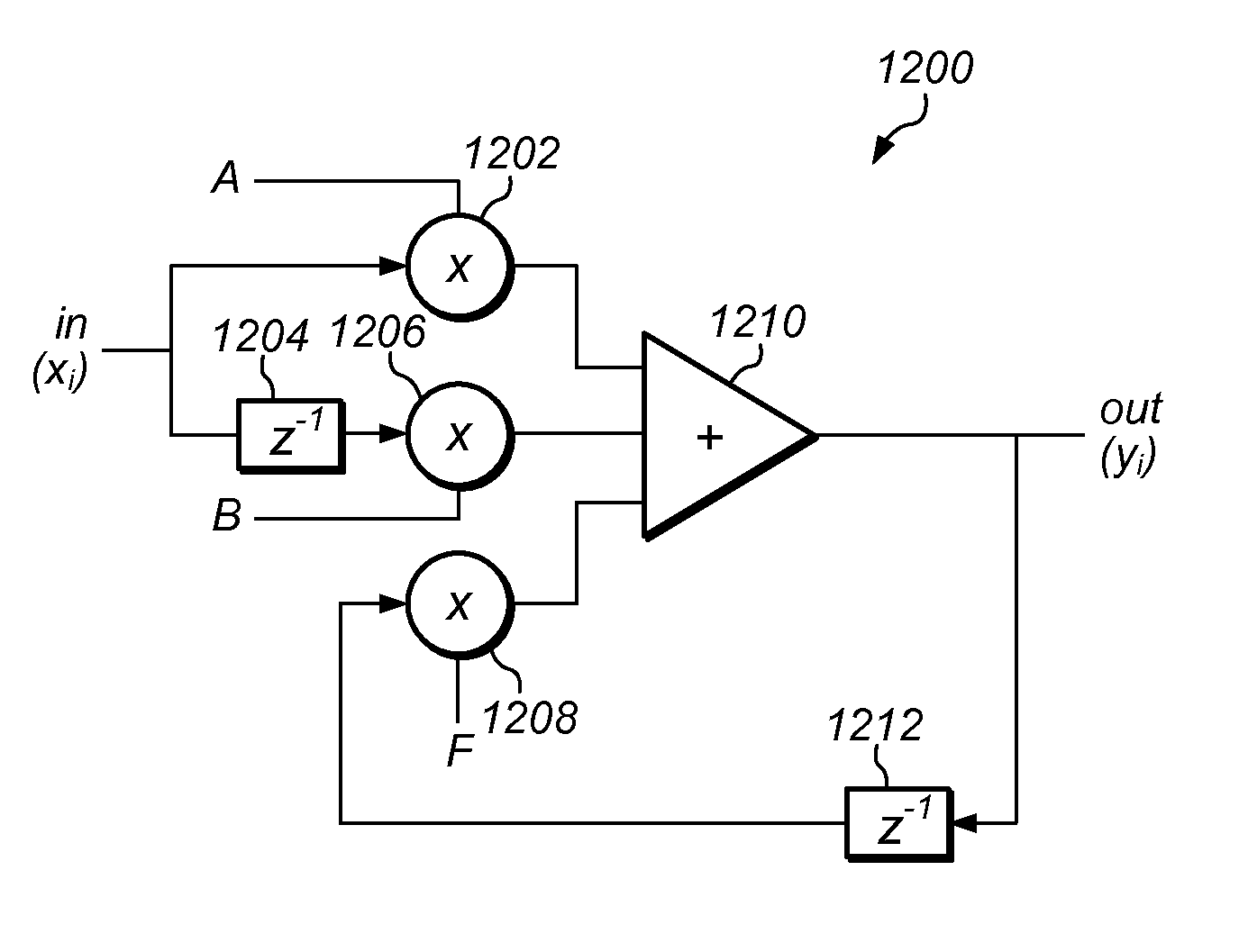
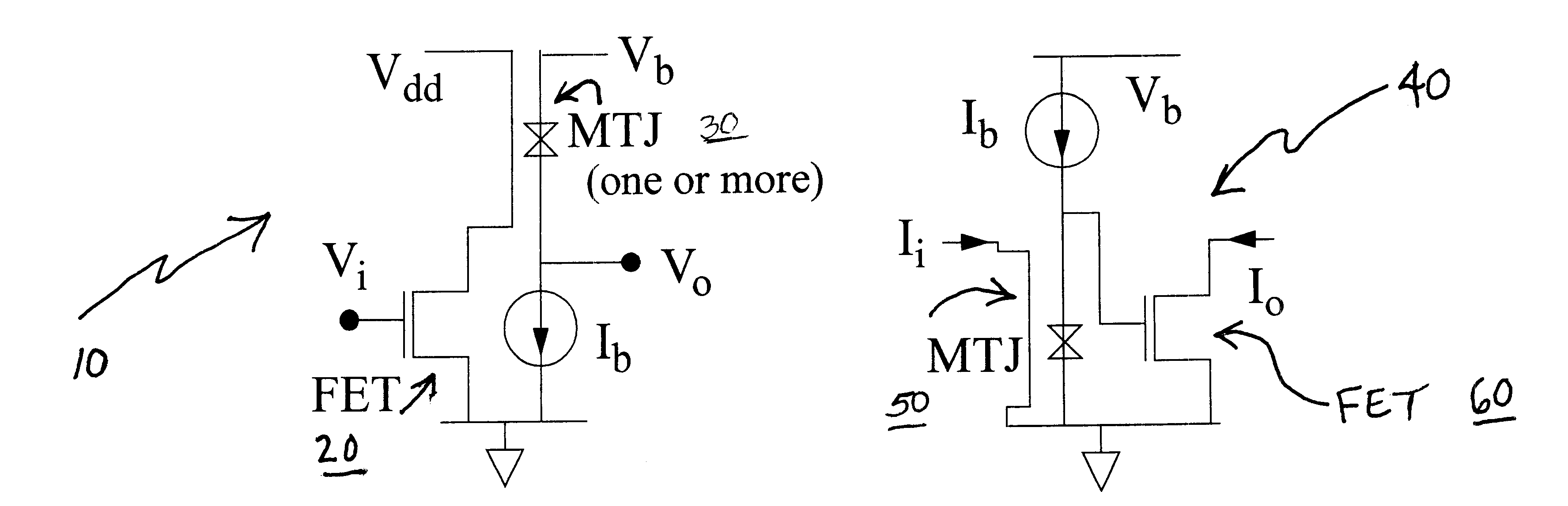Patents
Literature
79 results about "Gain–bandwidth product" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The gain–bandwidth product (designated as GBWP, GBW, GBP, or GB) for an amplifier is the product of the amplifier's bandwidth and the gain at which the bandwidth is measured. For devices such as operational amplifiers that are designed to have a simple one-pole frequency response, the gain–bandwidth product is nearly independent of the gain at which it is measured; in such devices the gain–bandwidth product will also be equal to the unity-gain bandwidth of the amplifier (the bandwidth within which the amplifier gain is at least 1). For an amplifier in which negative feedback reduces the gain to below the open-loop gain, the gain–bandwidth product of the closed-loop amplifier will be approximately equal to that of the open-loop amplifier. According to S. Srinivasan, "The parameter characterizing the frequency dependence of the operational amplifier gain is the finite gain–bandwidth product (GB)."
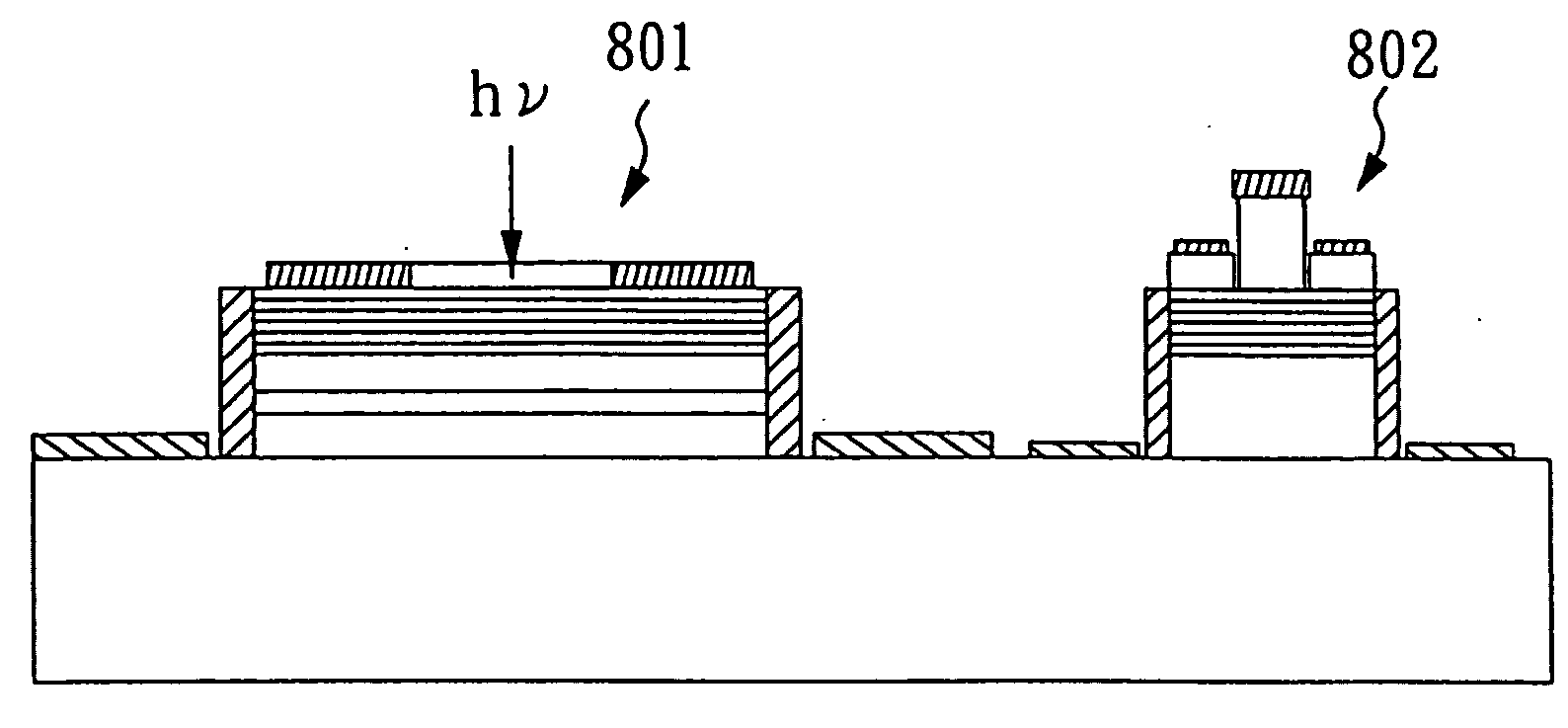
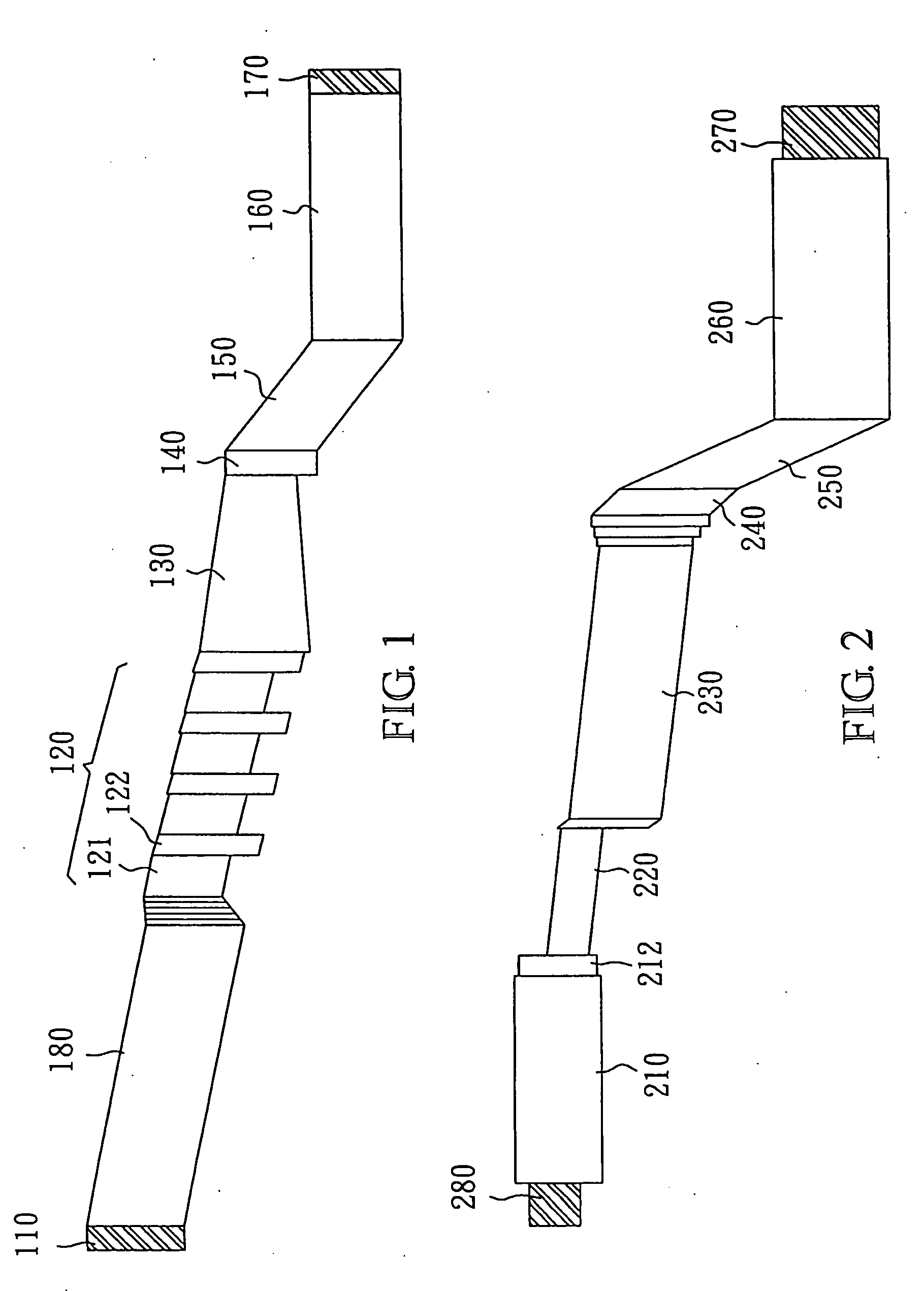
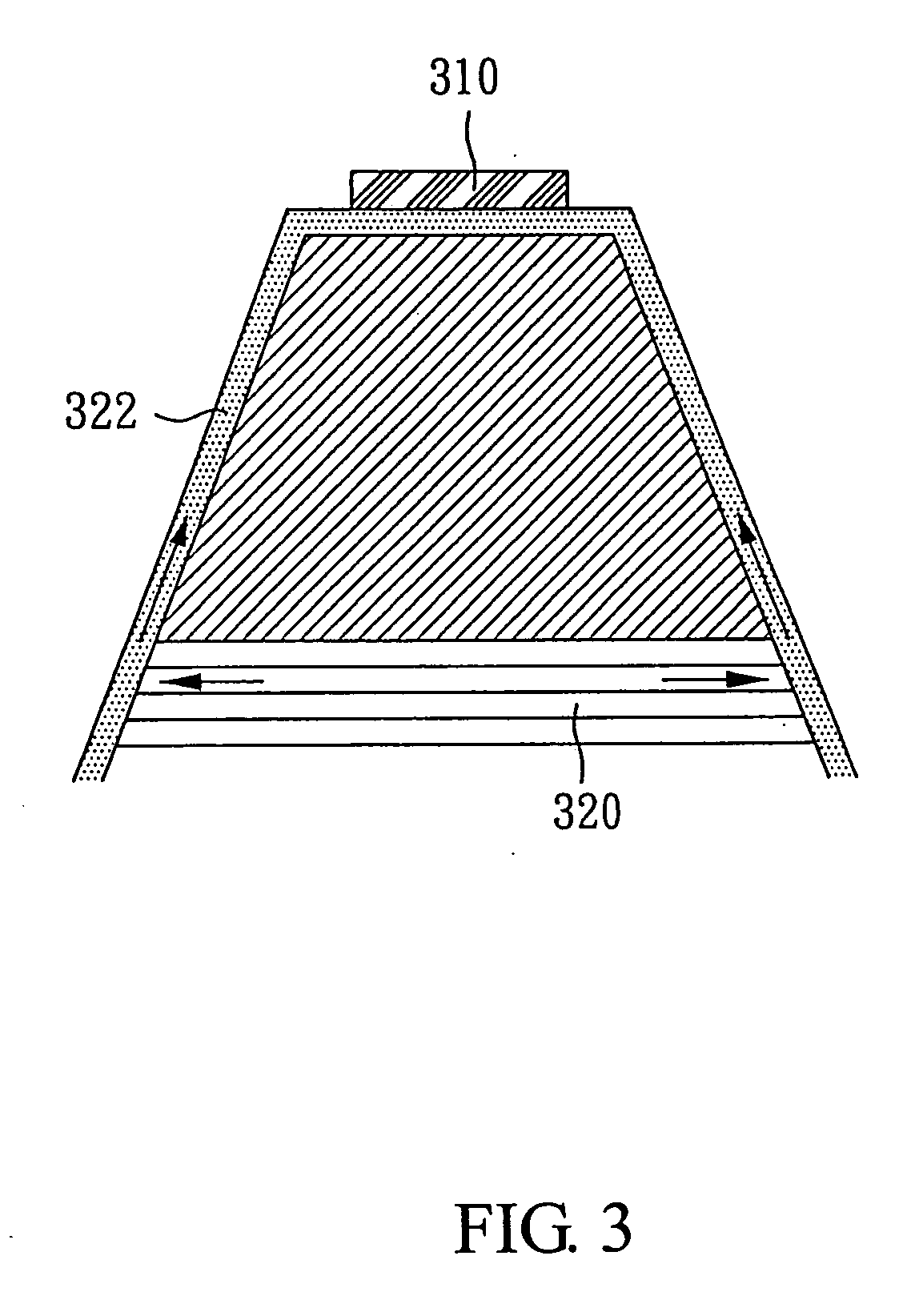
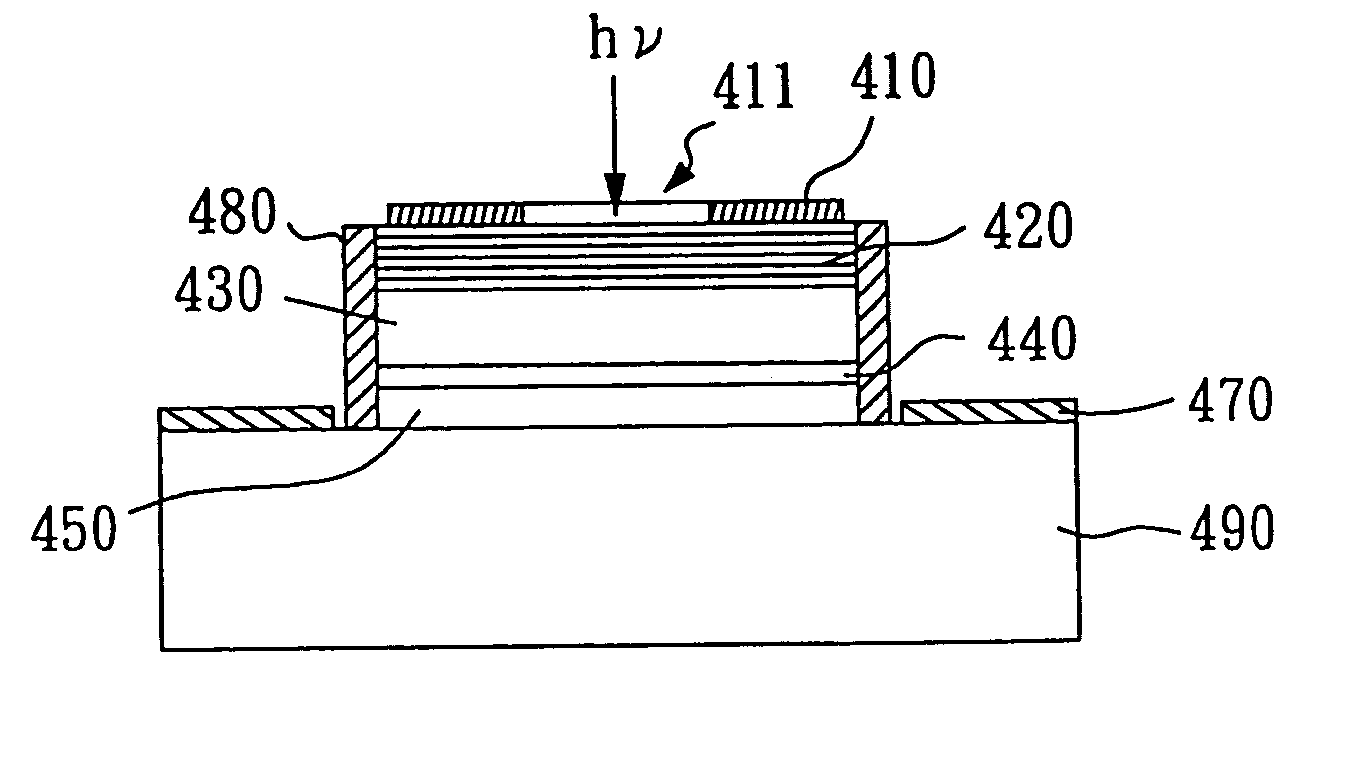
Avalanche photo-detector with high saturation power and high gain-bandwidth product
InactiveUS20050051861A1Reduce operating voltageReducing carrier transport timeNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesLow noiseCapacitance
An avalanche photo-detector (APD) is disclosed, which can reduce device capacitance, operating voltage, carrier transport time and dark current as well as increasing response speed and output power. Thus, an avalanche photo-detector (APD) with high saturation power, high gain-bandwidth product, low noise, fast response, low dark current is achieved. The APD includes an absorption layer with graded doping for converting an incident light into carriers, an undoped multiplication layer for multiplying current by means of receiving carriers, a doped field buffer layer sandwiched between the absorption layer and the multiplication layer for concentrating an electric field in the multiplication layer when a bias voltage is applied, and an undoped drift layer sandwiched between the absorption layer and the field buffer layer for capacitance reduction.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Avalanche photo-detector with high saturation power and high gain-bandwidth product
InactiveUS6963089B2Reduce capacitanceReduce voltageNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesLow noiseCapacitance
An avalanche photo-detector (APD) is disclosed, which can reduce device capacitance, operating voltage, carrier transport time and dark current as well as increasing response speed and output power. Thus, an avalanche photo-detector (APD) with high saturation power, high gain-bandwidth product, low noise, fast response, low dark current is achieved. The APD includes an absorption layer with graded doping for converting an incident light into carriers, an undoped multiplication layer for multiplying current by means of receiving carriers, a doped field buffer layer sandwiched between the absorption layer and the multiplication layer for concentrating an electric field in the multiplication layer when a bias voltage is applied, and an undoped drift layer sandwiched between the absorption layer and the field buffer layer for capacitance reduction.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
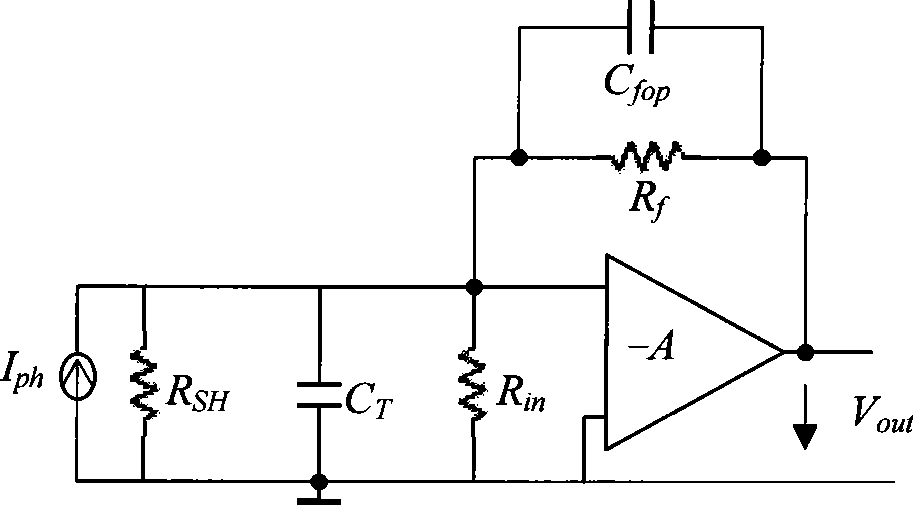
Trans-impedance amplifier with low noise and high gain-bandwidth product
ActiveCN101505140AWide signal bandwidthIncrease signal gainAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifiers controlled by lightCapacitanceLow noise
The invention provides an optical-receiver preamplifier for receiving analog or digital optical signals. The preamplifier comprises a high-gain amplifier A1, an input circuit, a negative-feedback impedor Zf, a low-gain amplifier A2 adjustable in gain and a feedback capacitor Cff, wherein the input circuit takes a photoelectric converter as a main component; the negative-feedback impedor Zf is connected with the reverse input end and the output end of the A1; the feedback capacitor Cff connects the output end of the A2 with the reverse input end of the A1; and the output end of the A1 can be directly connected with the input end of the A2 or can be connected with the input end of the A2 through a buffer. Output signals of the preamplifier are taken out from the output end of the A1 or the output end of the buffer, and can be directly subjected to subsequent signal processing or be further amplified and then subjected to subsequent signal processing.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
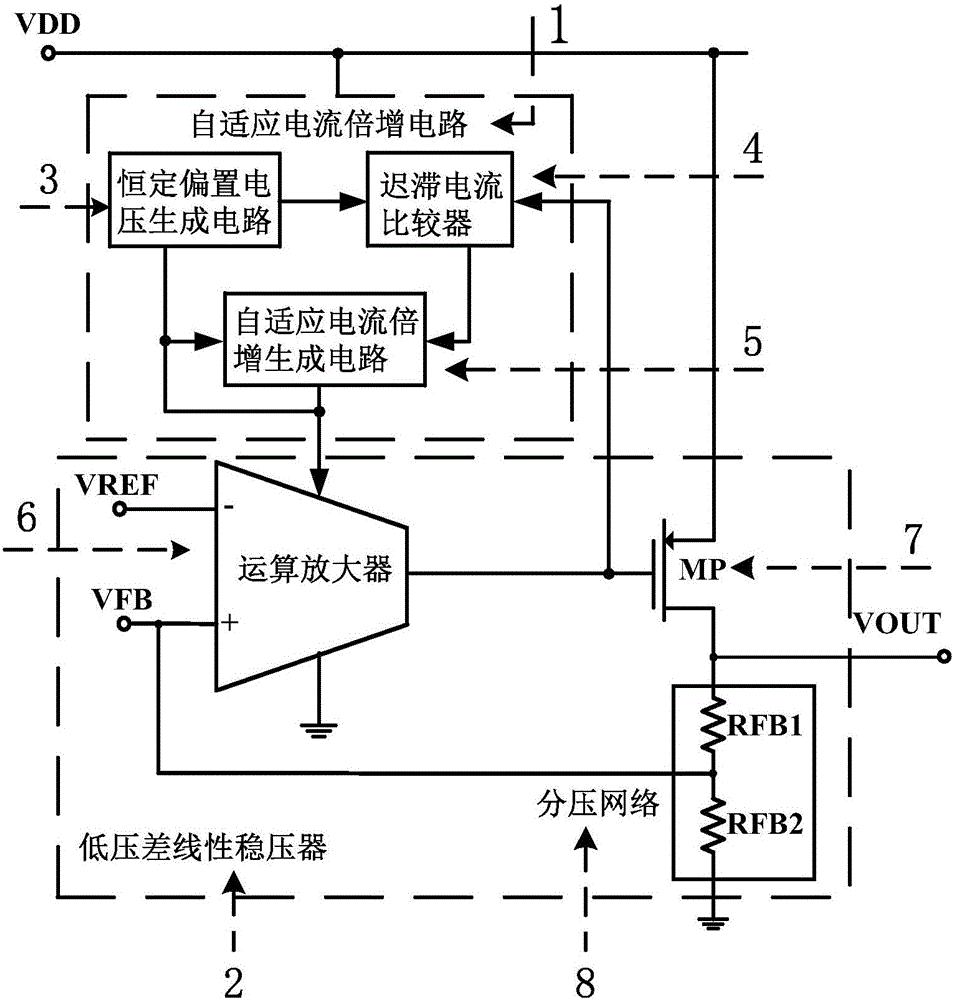
Self-adapting current multiplication circuit and low-dropout-voltage linear voltage regulator integrating same
ActiveCN104460802AExcellent stabilityExcellent robustnessElectric variable regulationDropout voltageEngineering
The invention discloses a self-adapting current multiplication circuit and a low-dropout-voltage linear voltage regulator integrating the circuit. Firstly, constant bias voltage of an NMOS transistor and constant bias voltage of a PMOS transistor are generated through a constant bias voltage generating circuit, and then a lagging current comparator collects small part of load current which is compared with constant current; when a load is in a light load, the lagging current comparator shuts off a self-adapting current multiplication generating circuit, self-adapting current multiplication voltage VBPA rises, the bias current of an operational amplifier of the low-dropout-voltage linear voltage regulator lowers, in this way, stability is guaranteed, and quiescent dissipation is reduced; when the load is in a heavy load from a moderate load, the lagging current comparator turns on the self-adapting current multiplication generating circuit, the self-adapting current multiplication voltage VBPA lowers, the bias current of the operational amplifier increases to the specific times the bias current of the operational amplifier during the light load, the gain bandwidth product of the low-dropout-voltage linear voltage regulator increases, and transient response performance is enhanced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Low power consumption high slew rate high gain bandwidth product fully differential operational amplifier
ActiveCN104079246AIncrease slew rateLower effective resistanceAnalogue conversionDifferential amplifiersTransient stateAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a low power consumption high slew rate high gain bandwidth product fully differential operational amplifier. An operational amplifier circuit adopts an input stage current extraction structure and partially extracts currents inside a load pipe through an active current mirror to reduce the effective resistance of the operational amplifier; slew rate enhancing circuits are in parallel connection with bilateral sides of a main operational amplifier to enhance the slew rate of output signals; an output stage applies a Class-AB output structure. According to the low power consumption high slew rate high gain bandwidth product fully differential operational amplifier, the current mirror is connected to an input end load pipe in a parallel mode, the effect of transconductance reduction is achieved due to adjustment of the breadth length ratio of the current mirror, and accordingly the integral circuit keeps the gain bandwidth product and satisfies the integral modulator required level under the condition that the power consumption is reduced and a feedforward structure is connected to the operational amplifier in a parallel mode to inject compensating current for the load to increase the slew rate of the output signals when the operational amplifier is in a working state and transient state power consumption is not consumed excessively.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
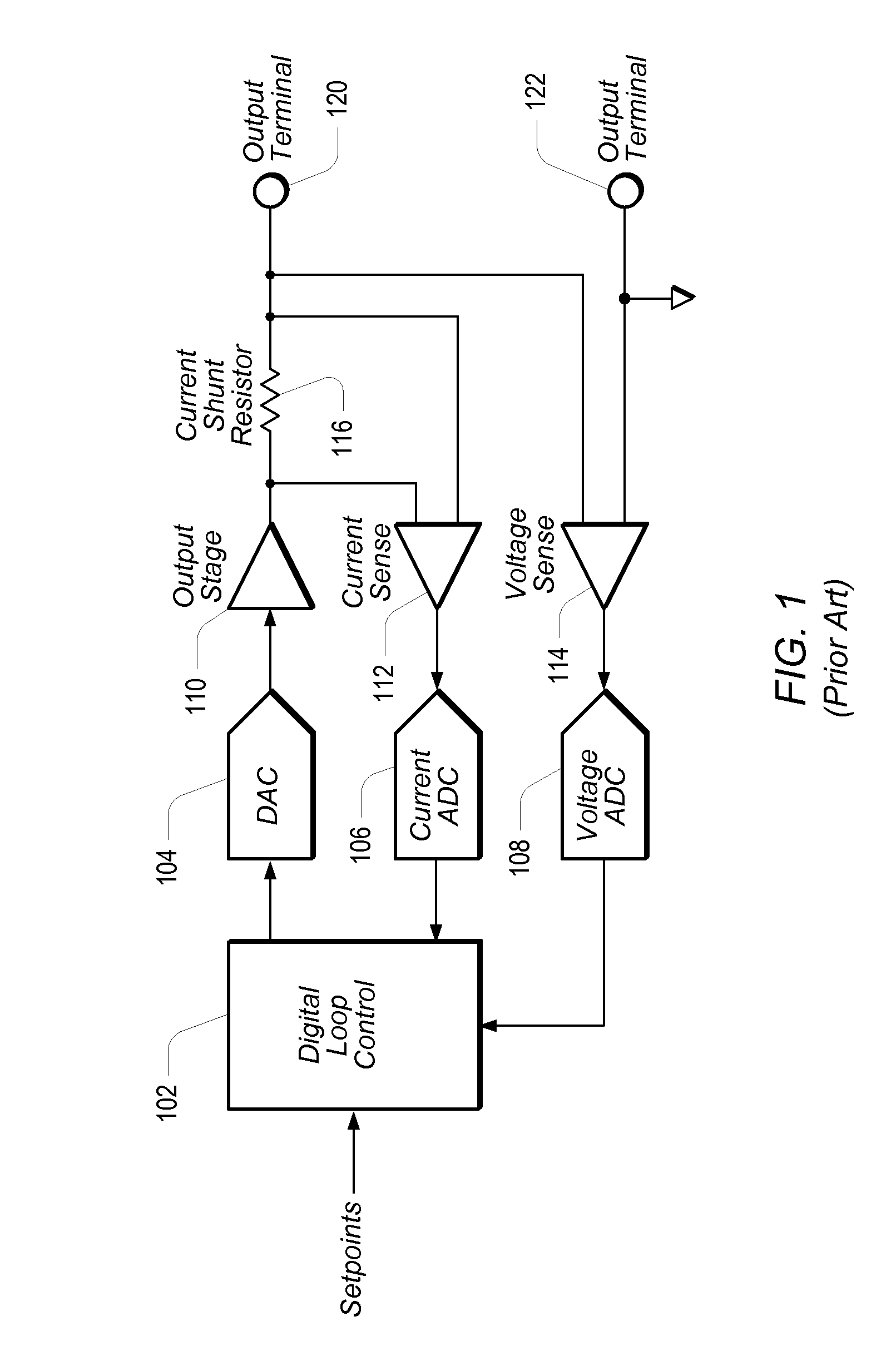
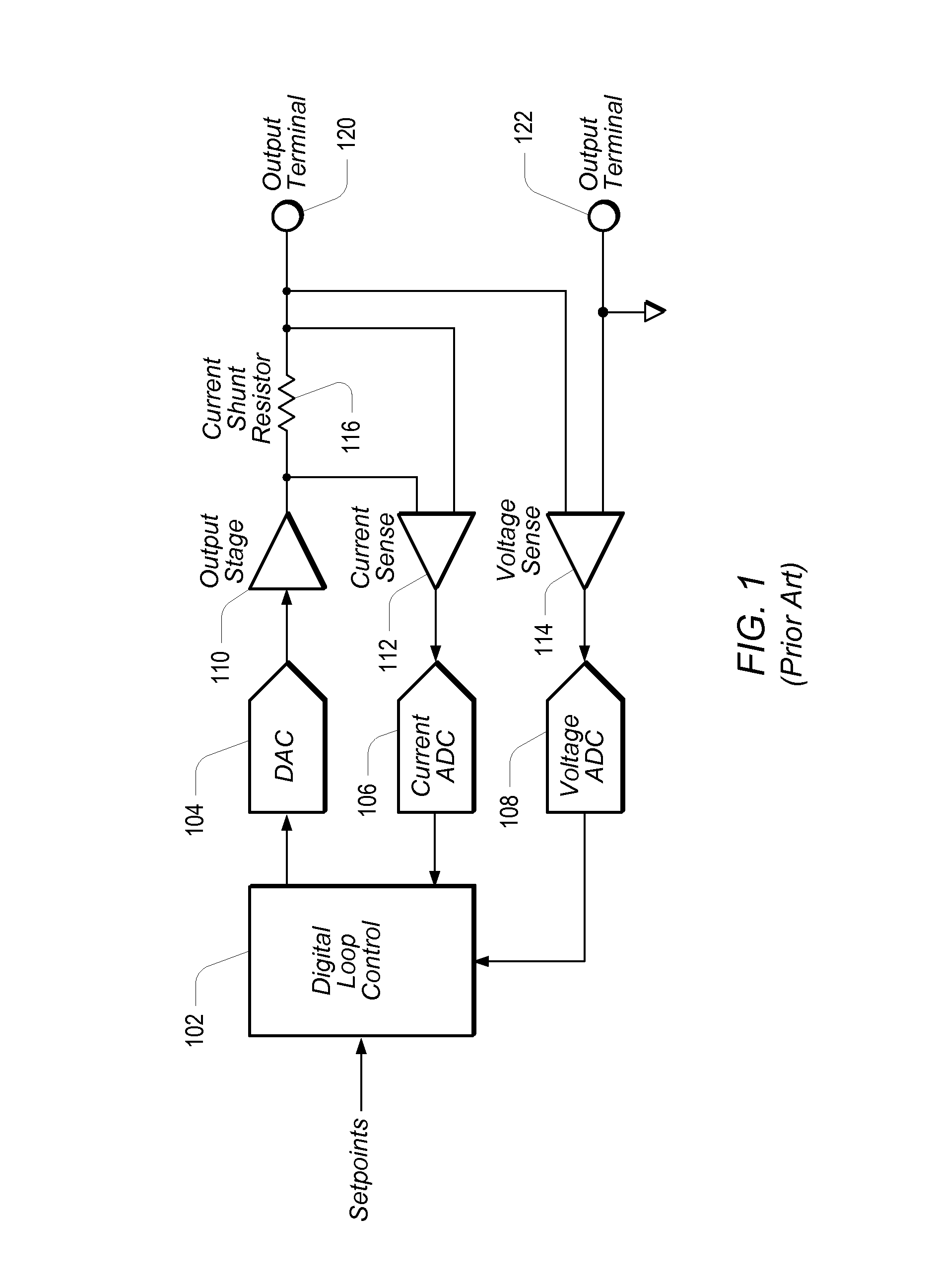
Compensation Methods for Digital Source-Measure-Units (SMUs)
ActiveUS20120306517A1Increase flexibilityConvenient and accurateFault location by increasing destruction at faultEngineeringZero frequency
A source-measure unit (SMU) may be implemented with respective digital control loops for output voltage and output current. The output voltage and output current may be measured with dedicated ADCs (analog-to-digital converters). The readings obtained by the ADCs may be compared to a setpoint, which may be set in a digital loop controller. The digital loop controller may be used to produce an output to drive a DAC (digital-to-analog converter) until the output voltage and / or output current and / or a function thereof reach the respective desired levels. The digital loop controller may implement respective integrating functions for the respective digital control loops, and may also implement a compensation function featuring pole-zero pairs to stabilize the respective current / voltage outputs. Coefficients of the compensation function may be calculated based on user programmable parameters corresponding to the gain bandwidth product, compensation frequency, and ratio of the added pole-zero frequencies.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
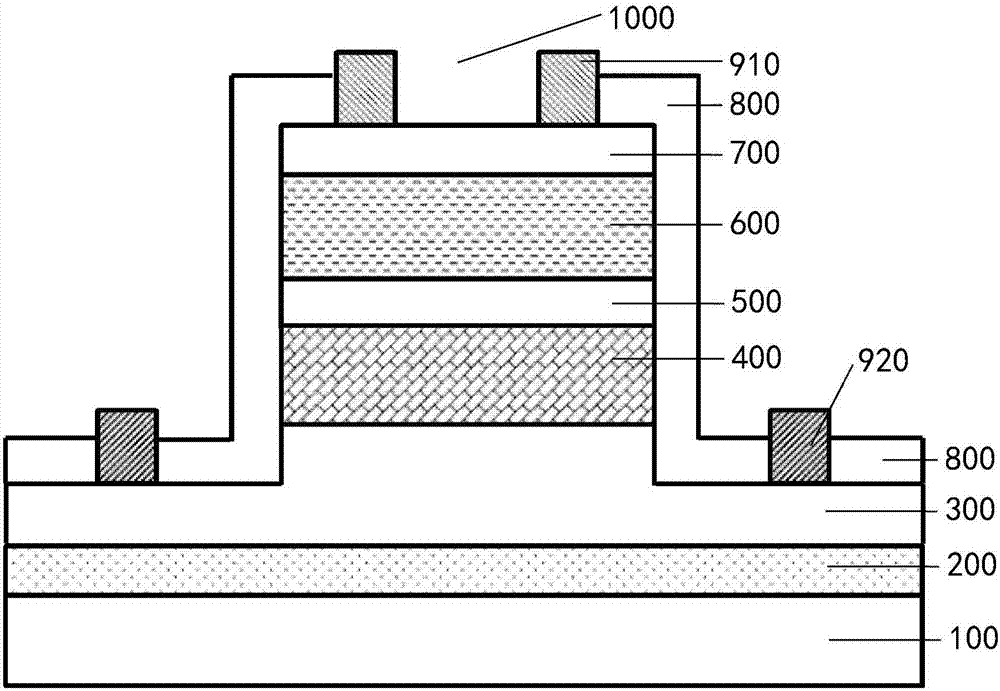
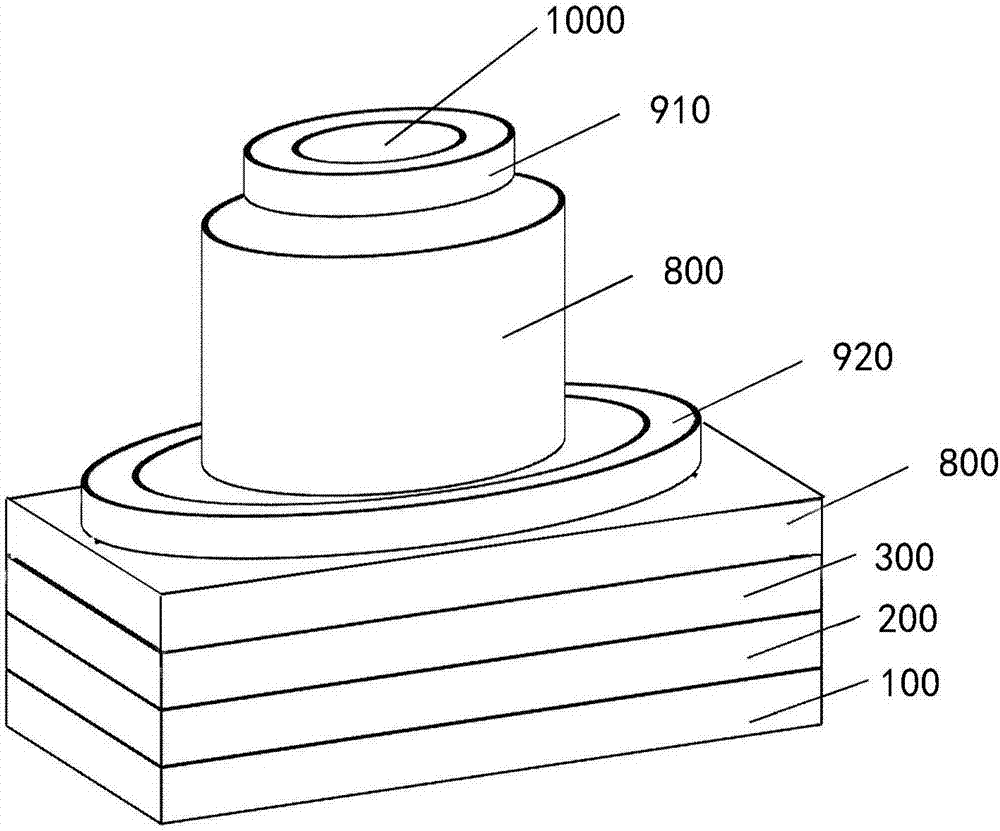
Avalanche photo-diode based on AlInAsSb body material as multiplication region and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN107170847AReduce noiseHigh Gain-Bandwidth ProductSemiconductor devicesHigh bandwidthOhmic contact
The invention provides an avalanche photodiode based on AlInAsSb body material as the multiplication region, comprising: a substrate; a buffer layer epitaxially on the substrate; an N-type ohmic contact layer epitaxially on the buffer layer and having a cross section of "" Convex" shape, its lower half is consistent with the shape of the substrate, and its upper half is cylindrical; the avalanche multiplication layer is epitaxial on the upper surface of the upper half of the N-type ohmic contact layer, composed of AlxIn1‑xAsySb1‑y Bulk material preparation, the doping concentration is less than 1016cm-3, the value range of x is: 0≤x≤1, the value range of y is: 0.08≤y≤1; the P-type charge layer is epitaxial on the avalanche multiplication layer ; The light absorbing layer is epitaxial on the P-type charge layer; and the P-type ohmic contact layer is epitaxially on the light absorbing layer. The avalanche photodiode has the advantages of low noise and high gain-bandwidth product, and at the same time effectively reduces the dark current, which not only meets the requirement of high sensitivity of the photodetector, but also realizes the design of energy band engineering and broadens its application range.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
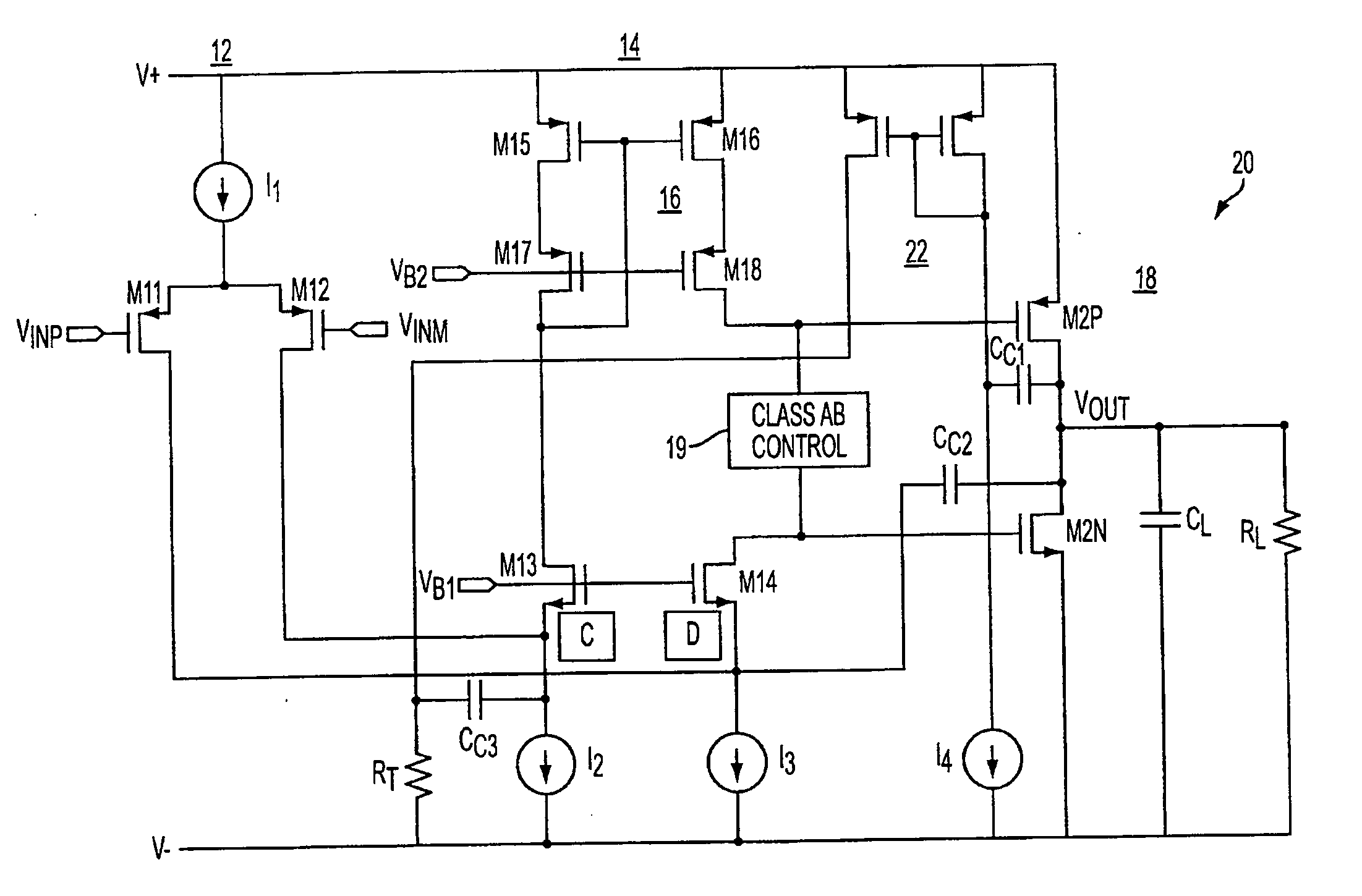
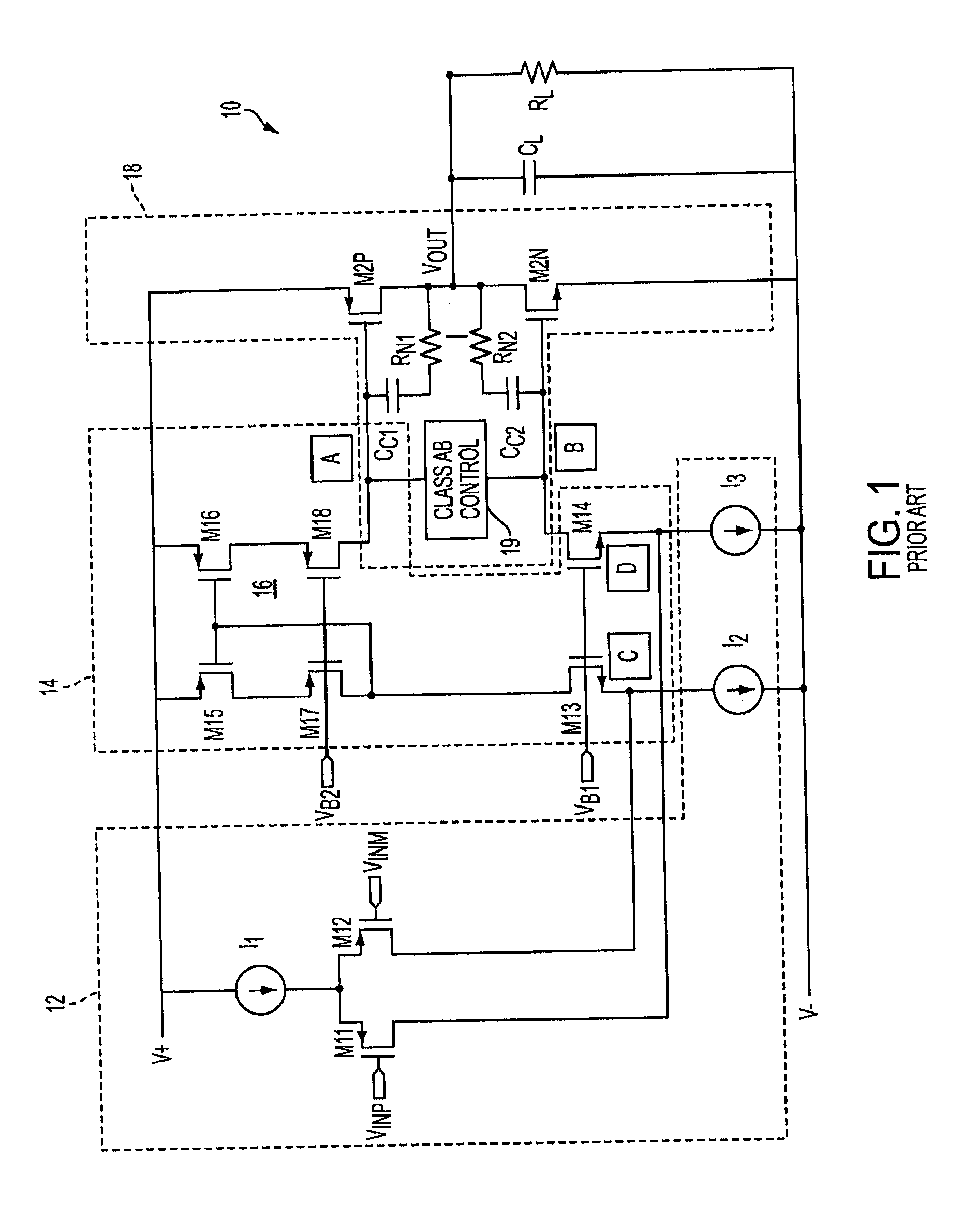
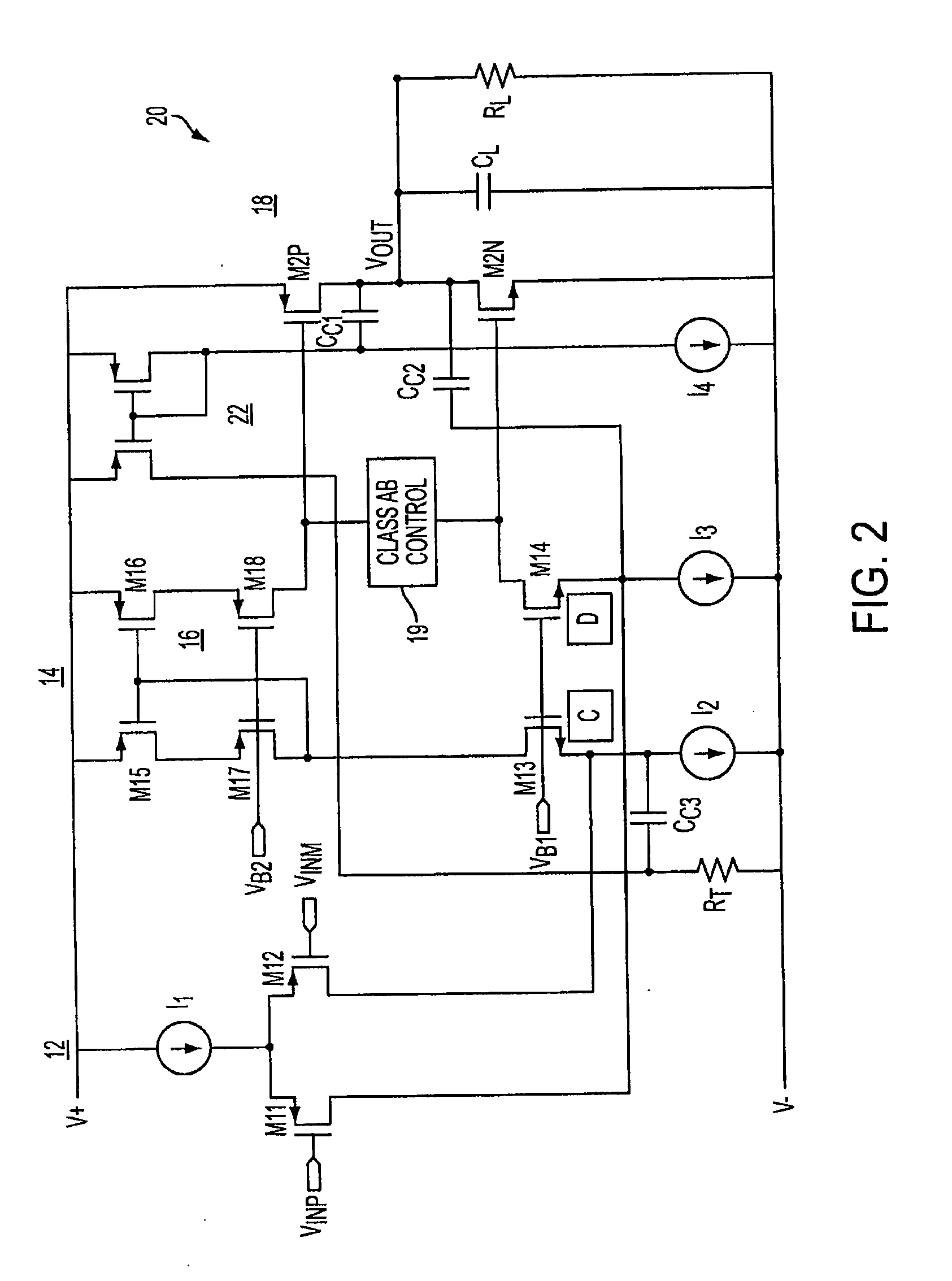
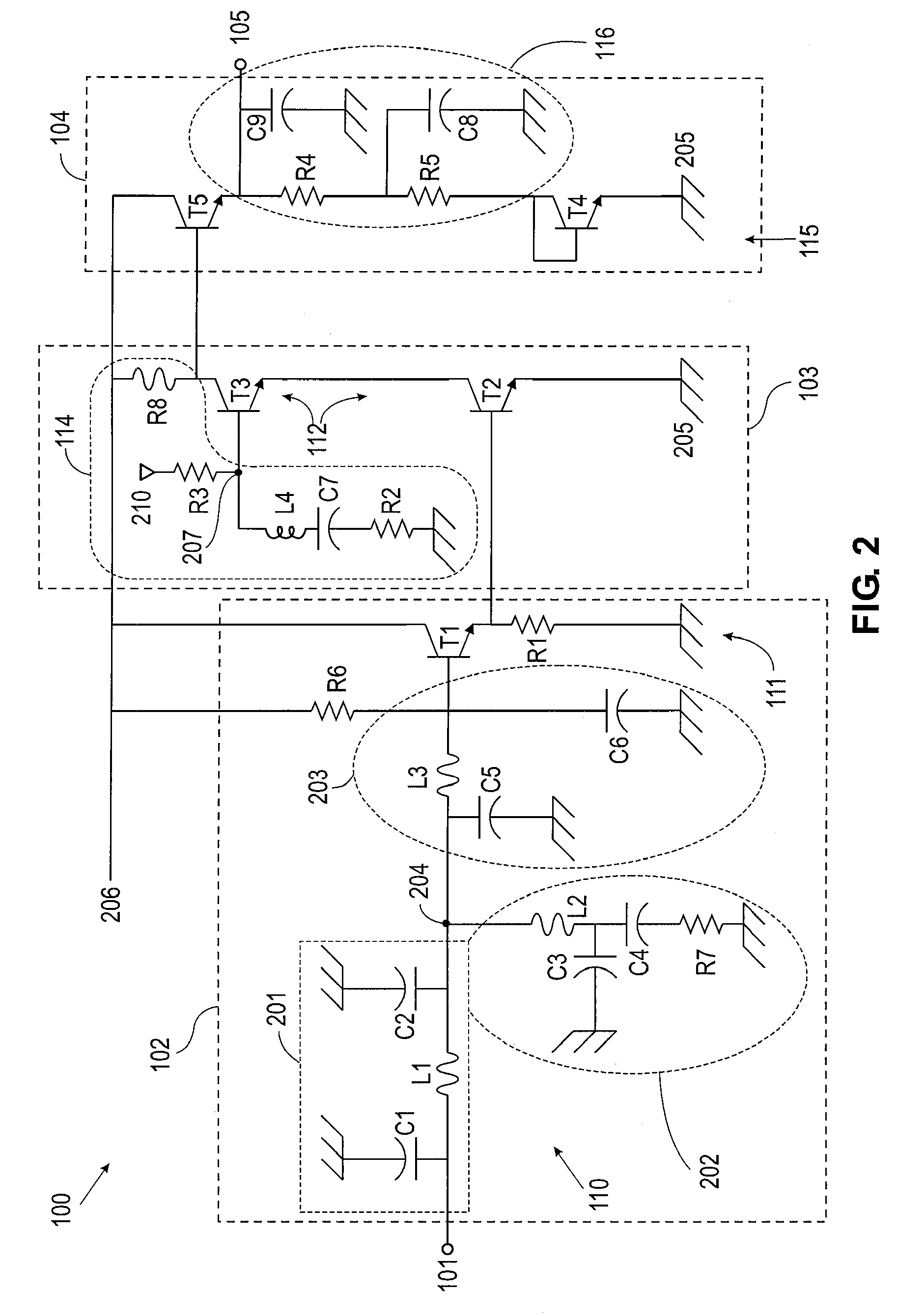
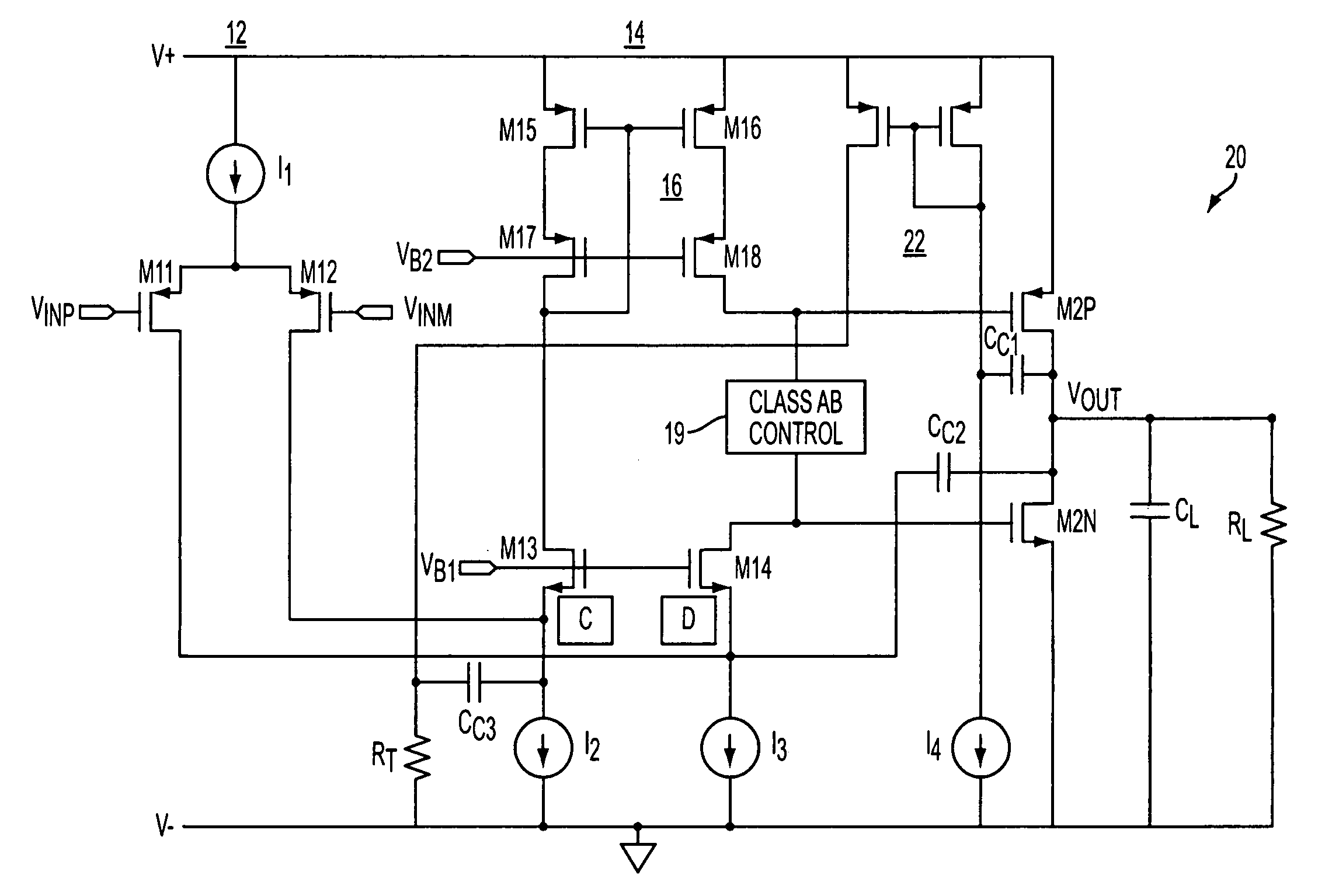
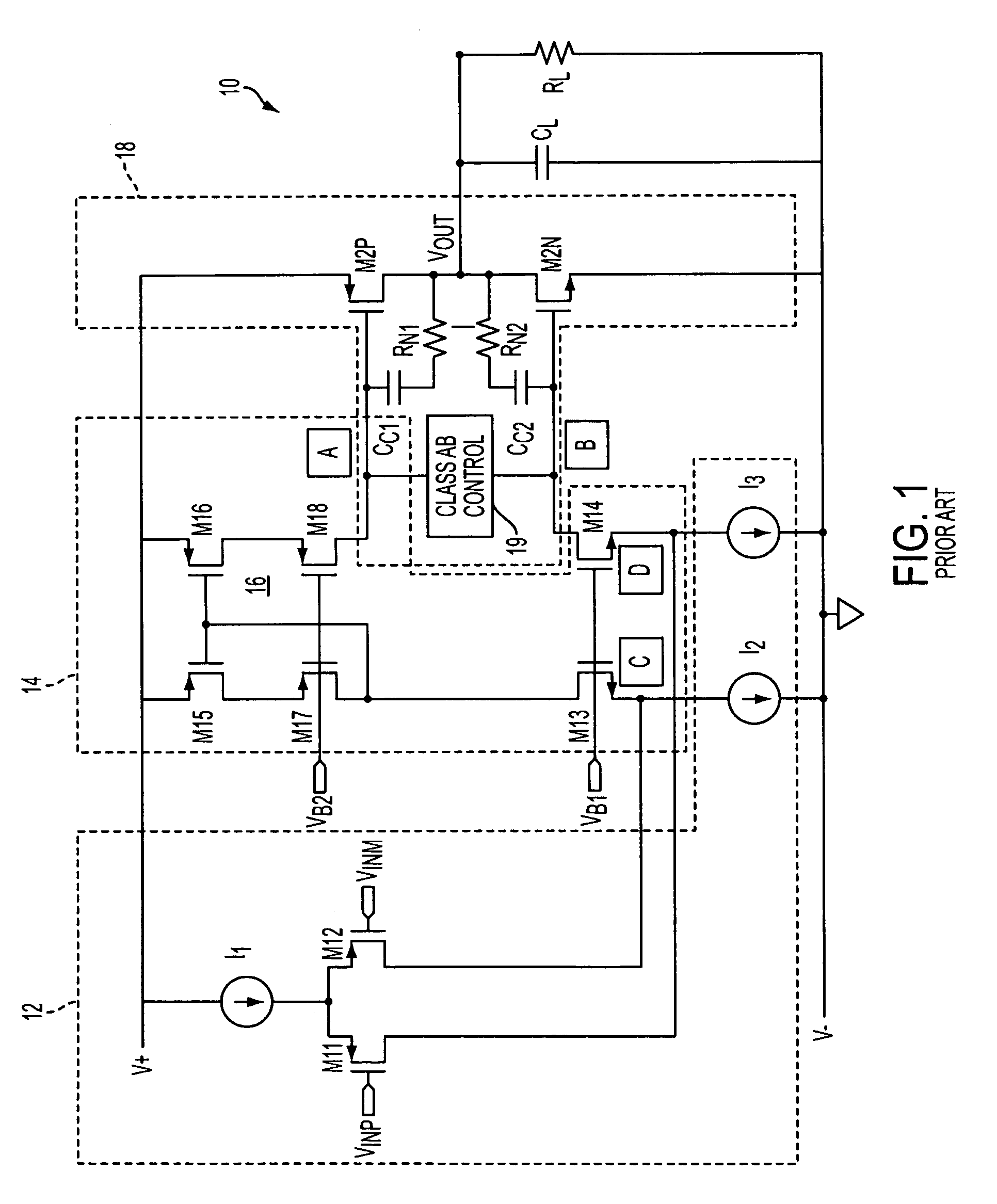
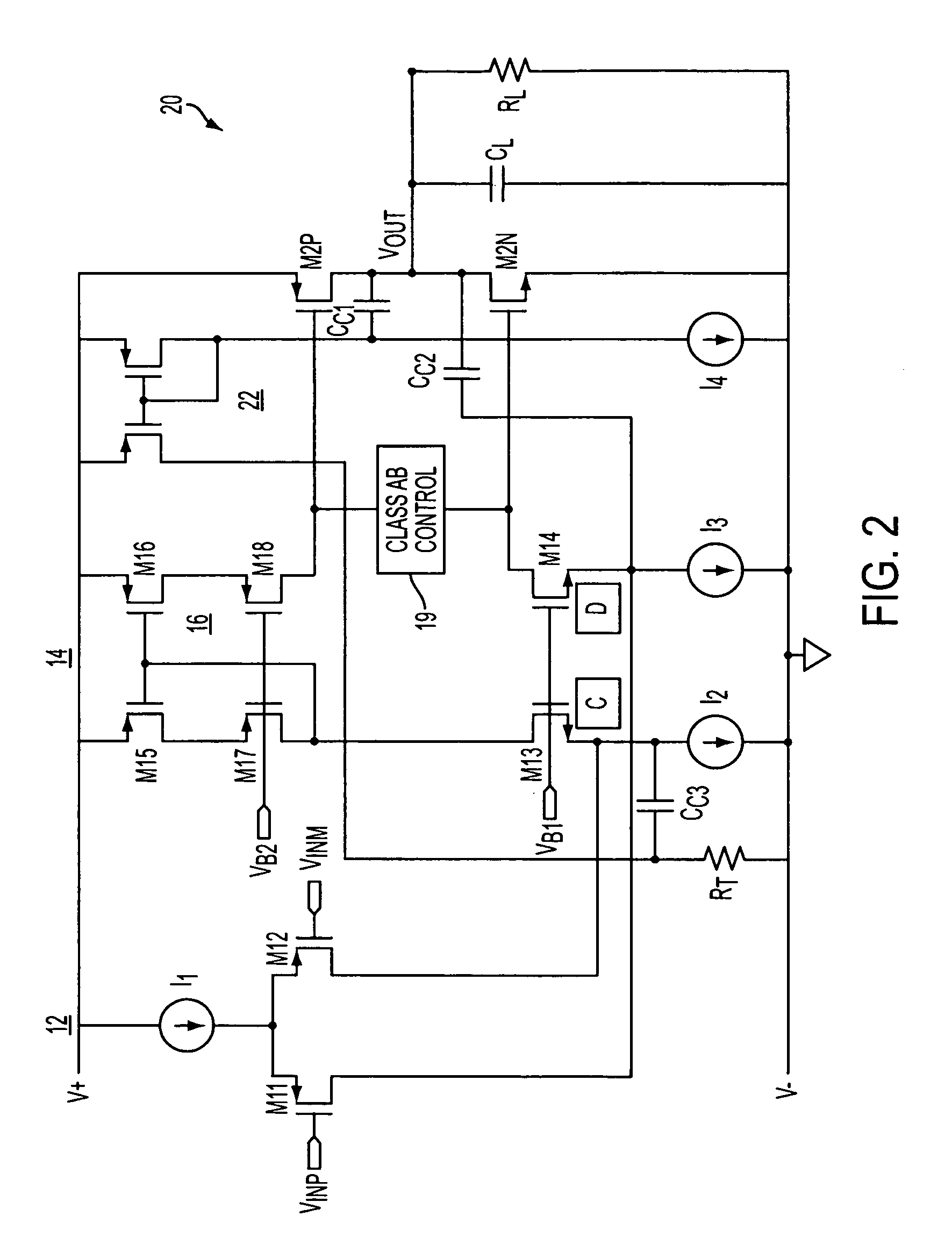
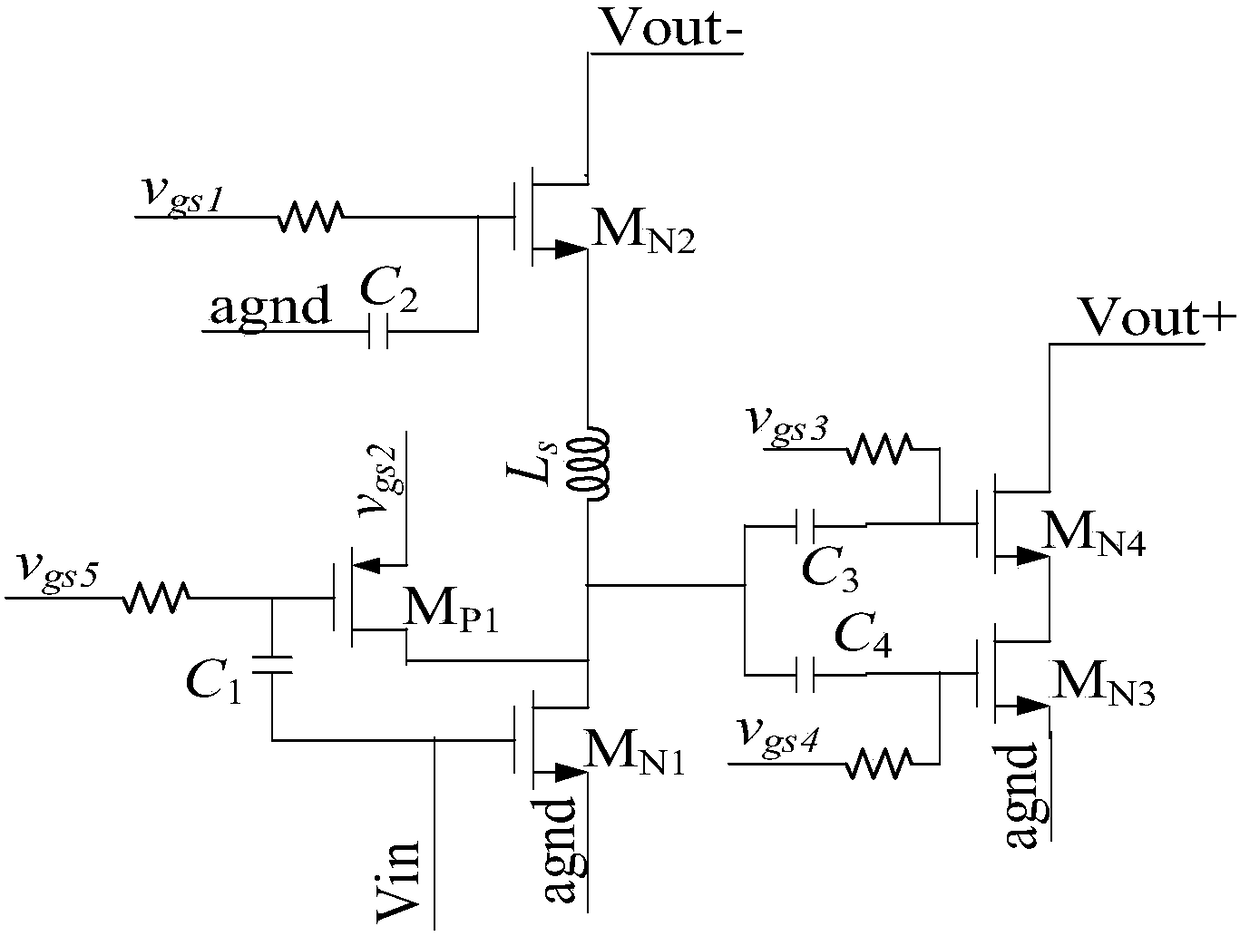
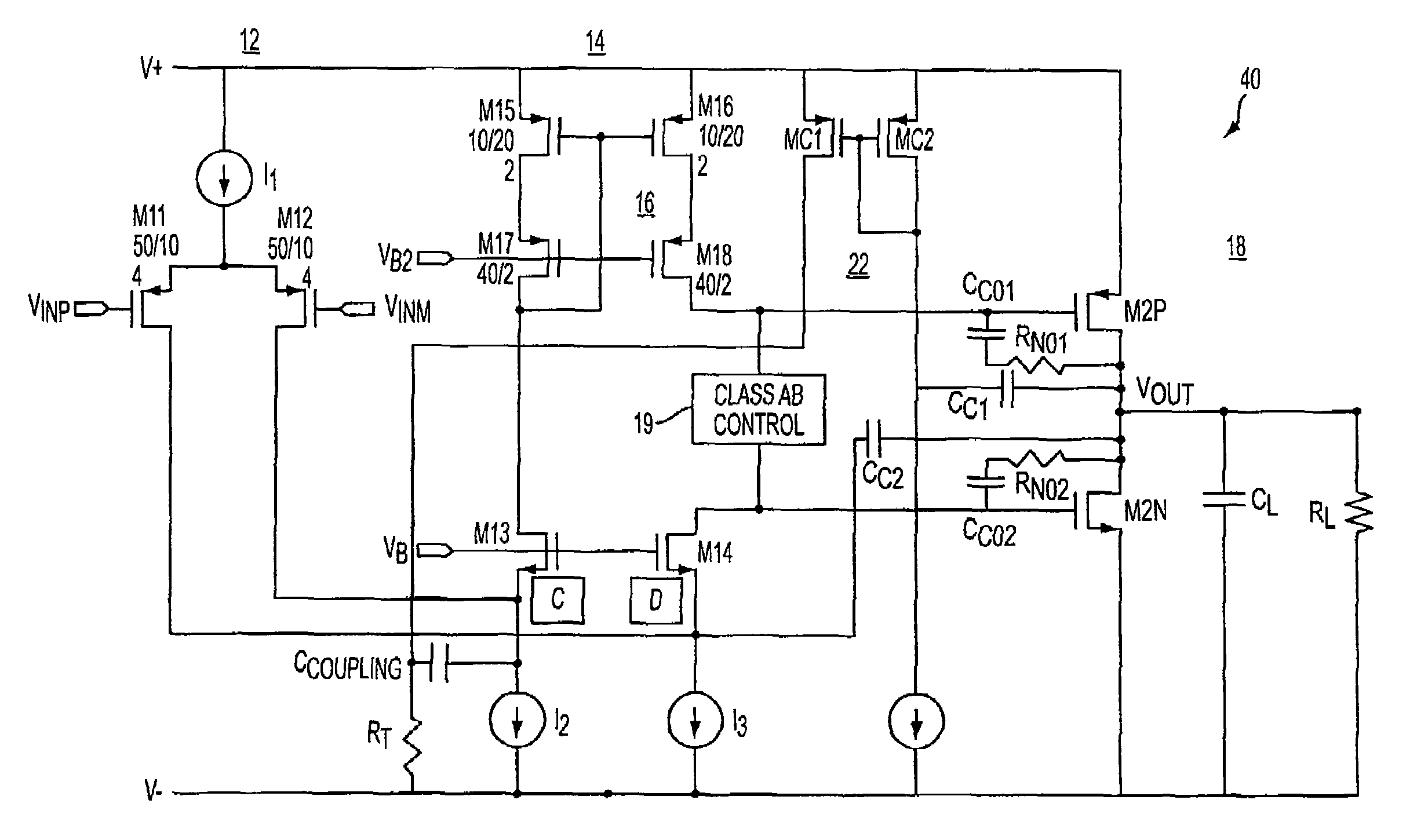
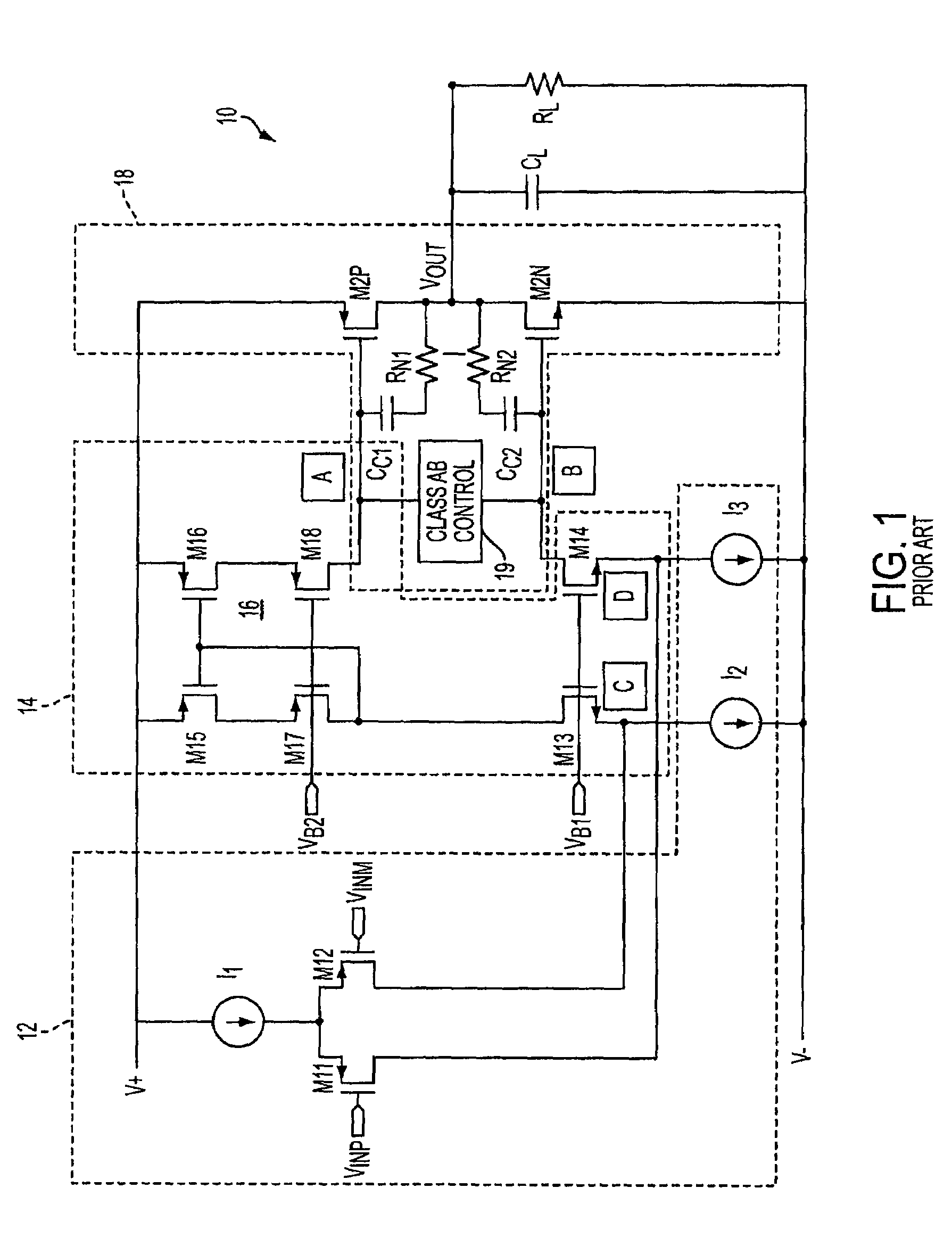
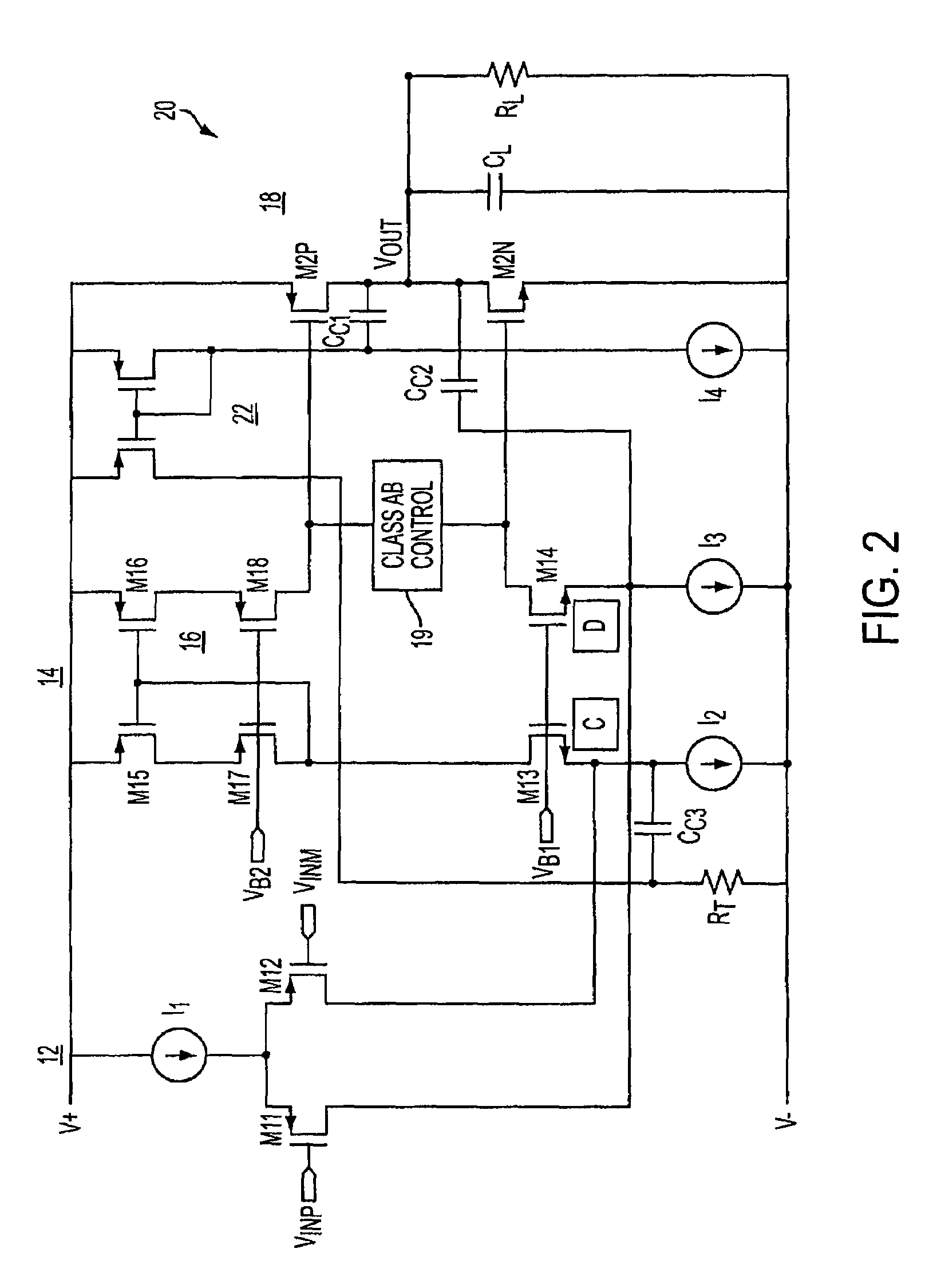
Class ab folded-cascode amplifier having cascode compensation
ActiveUS20080272844A1Improved gain-bandwidth productDifferential amplifiersAmplifier detailsEngineeringGain–bandwidth product
A class AB folded-cascode amplifier having improved gain-bandwidth product, comprises a differential input circuit including a differential transistor pair coupled to a source of tail current and responsive to a differential input signal for conducting a first current, a cascode circuit coupled to the differential input circuit for supplying a second current thereto, and a class AB output stage. A compensation circuit is configured for feeding back mutually complementary compensation signals from an output node to the differential input circuit. Another compensation circuit is configured for feeding back a signal from the output of the output stage to the input of the output stage.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
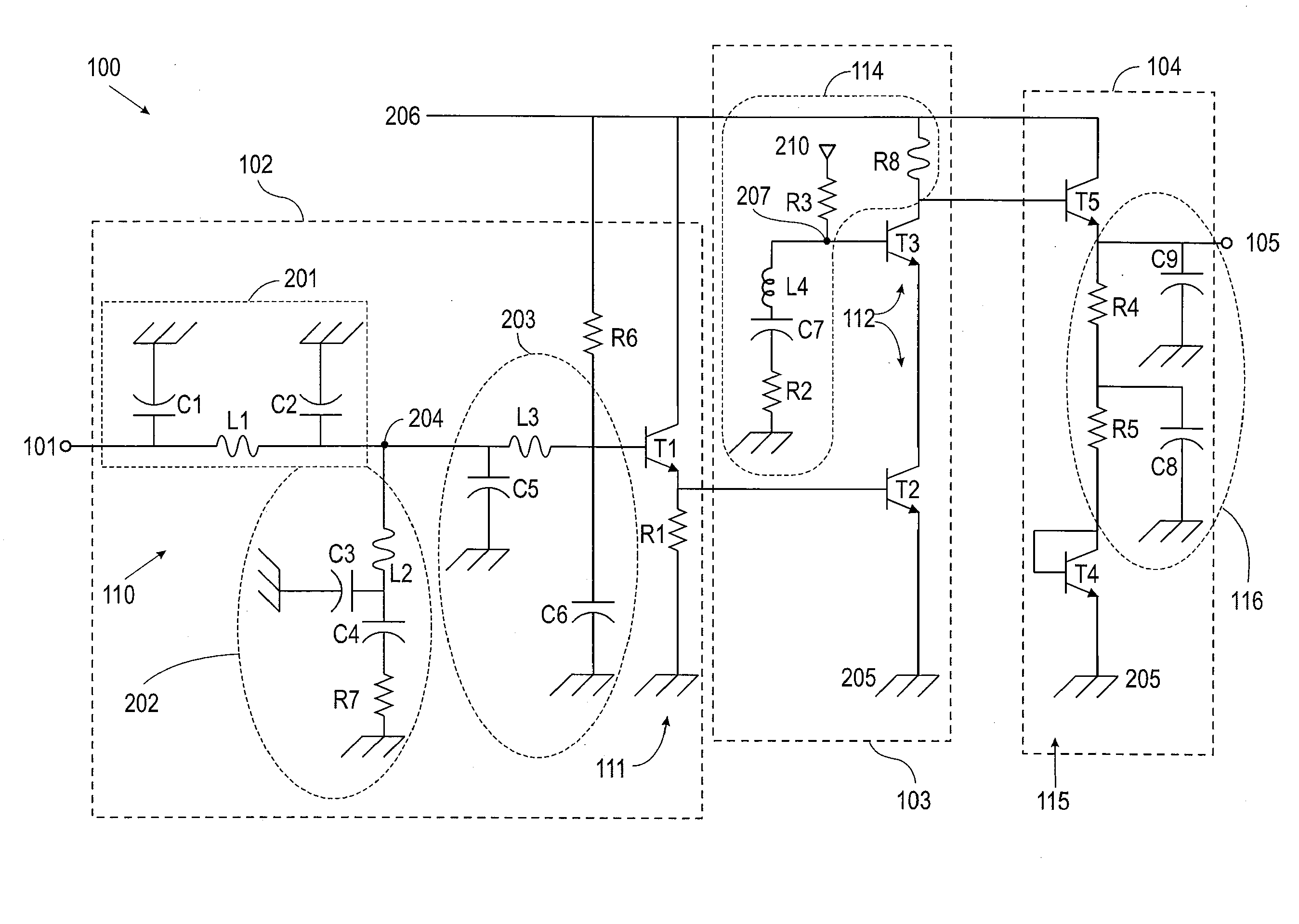
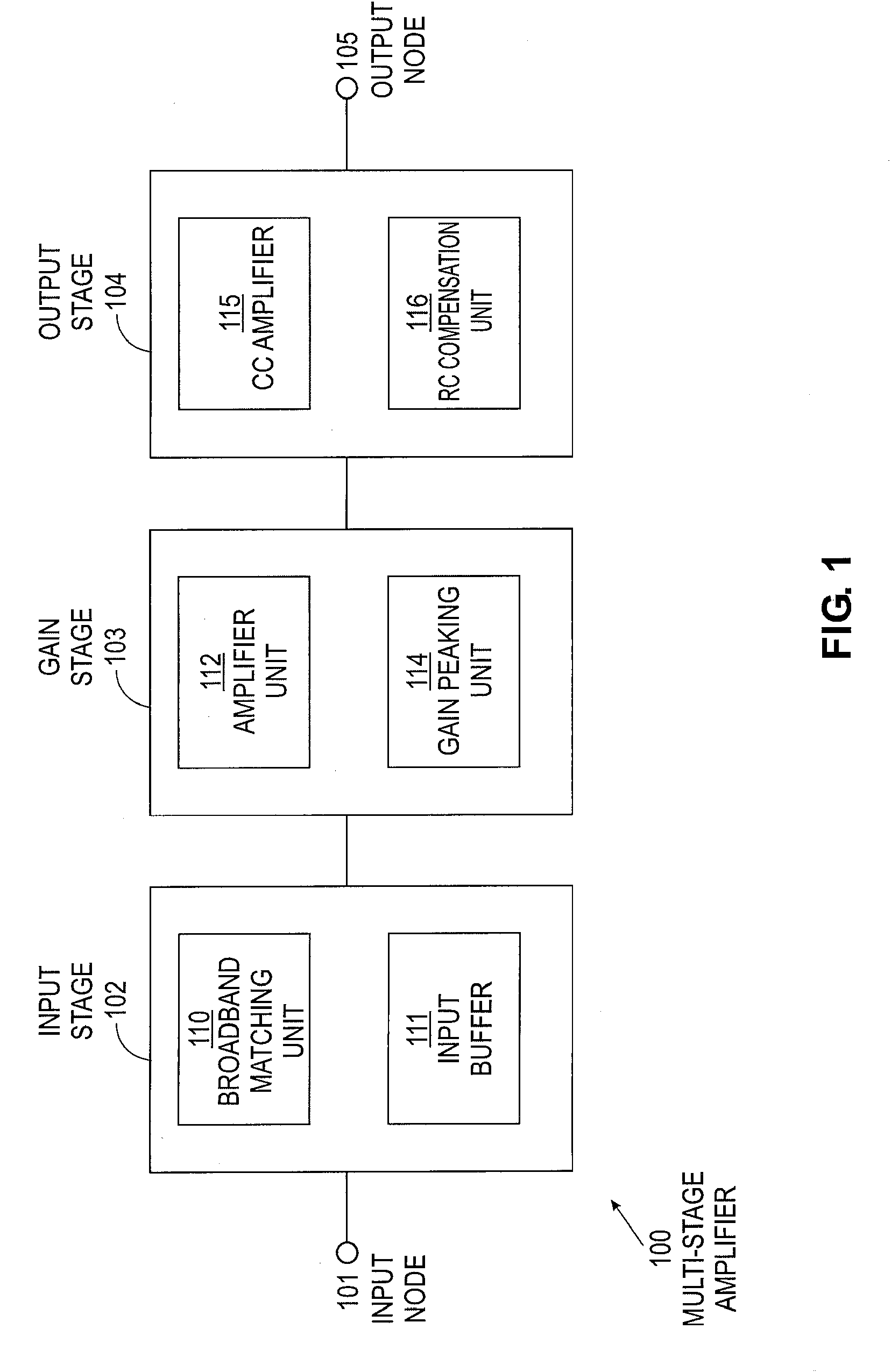
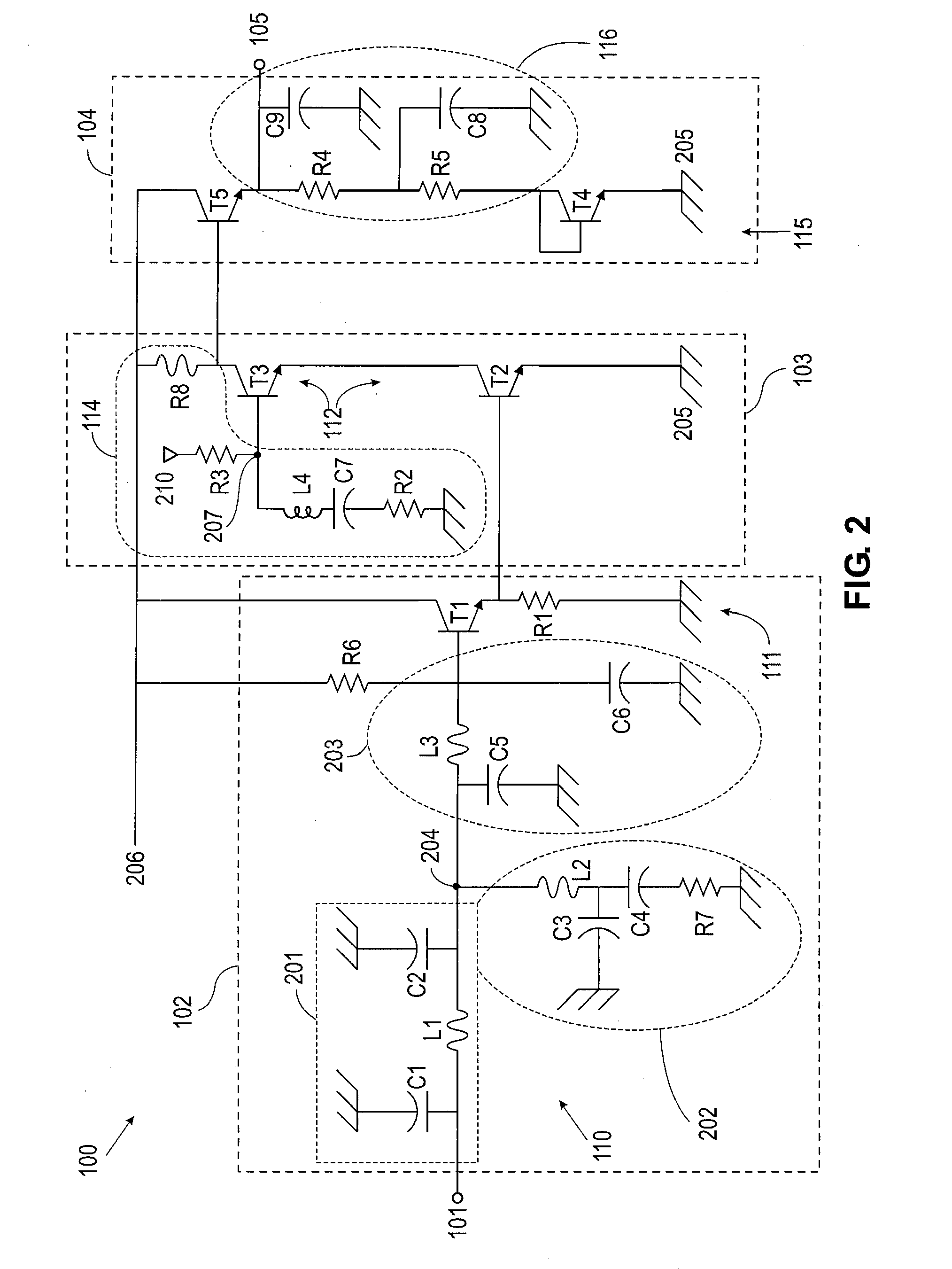
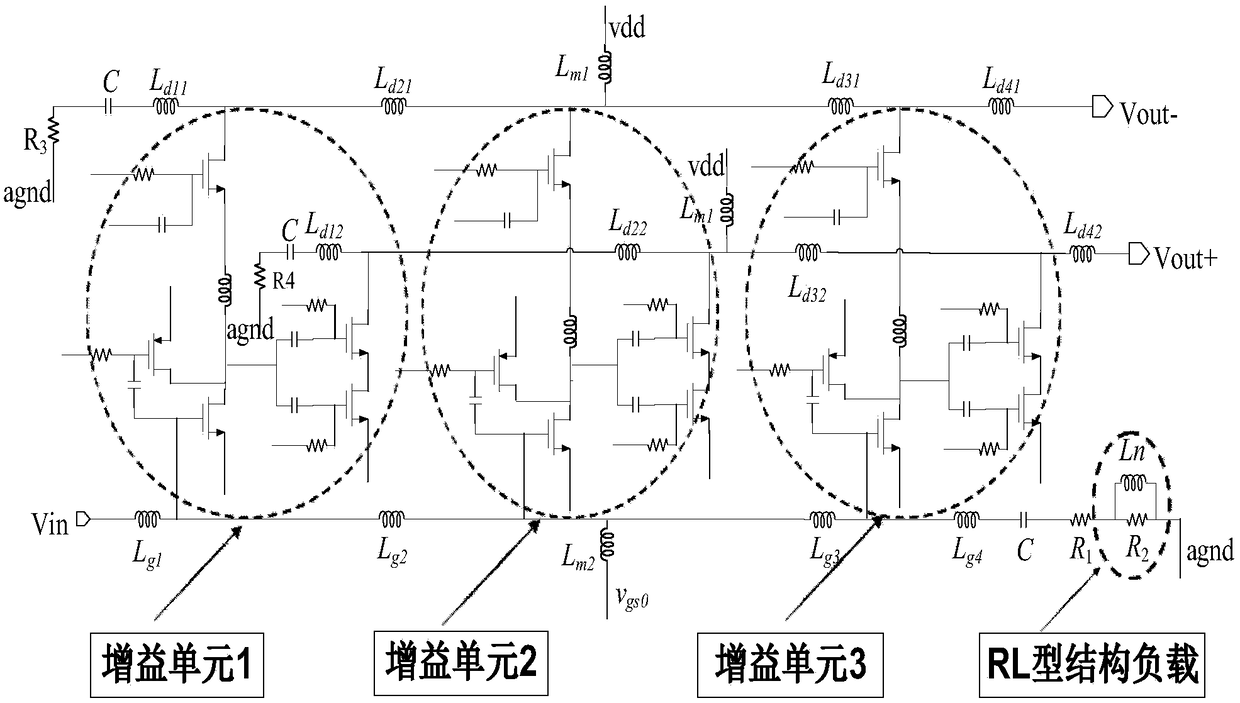
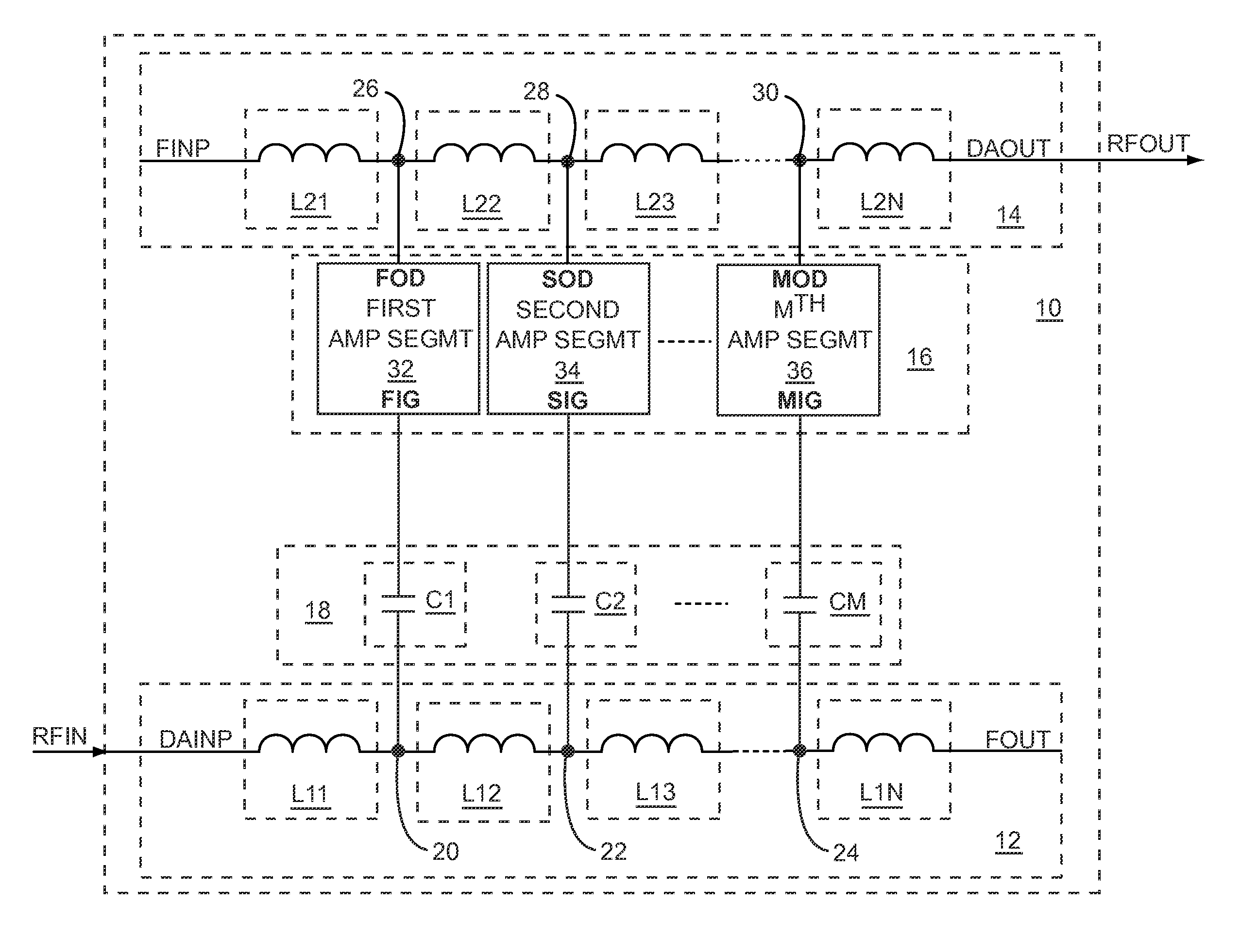
Multi-stage broadband amplifiers
ActiveUS20070096831A1High frequency amplifiersAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierBroadband amplifiers
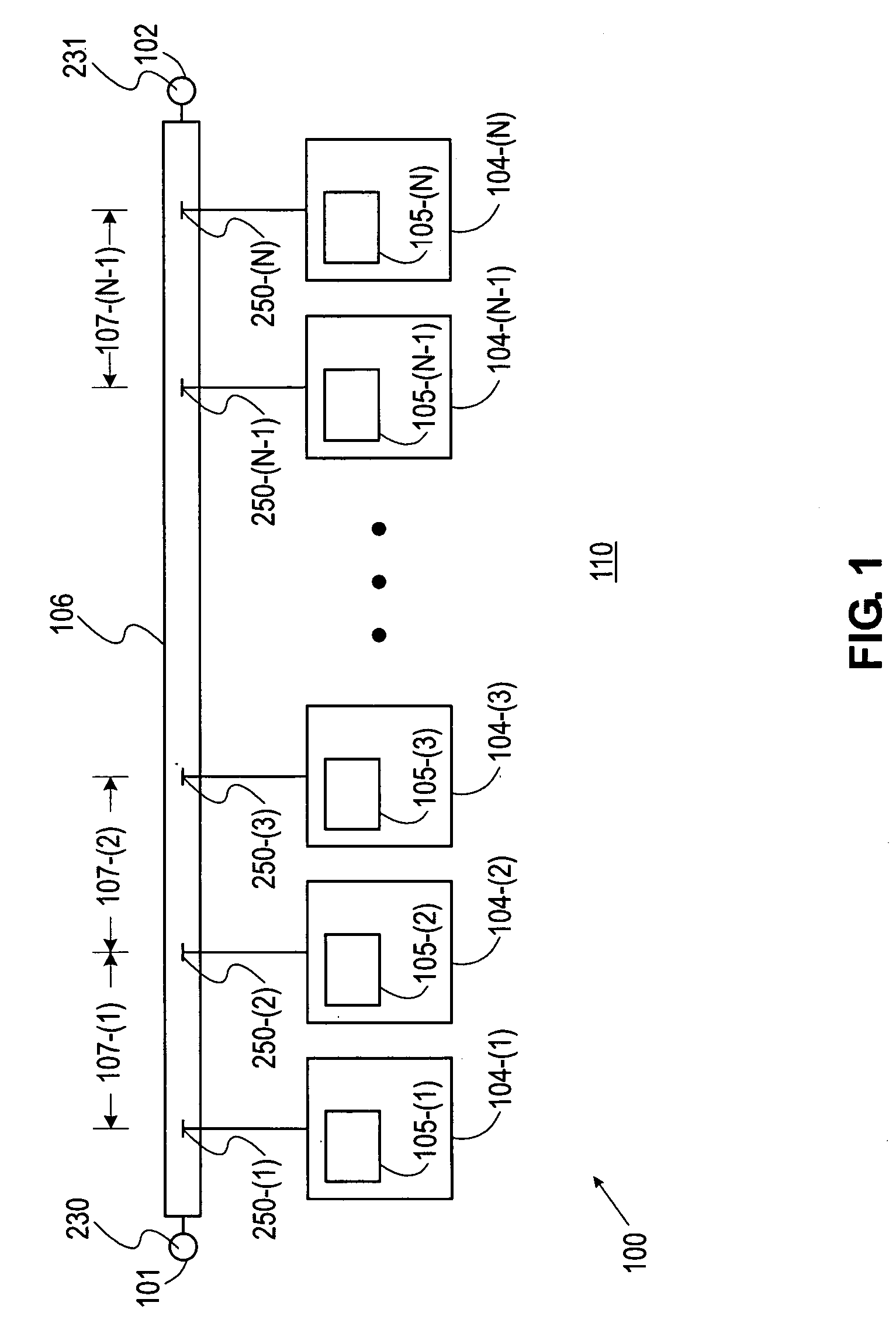
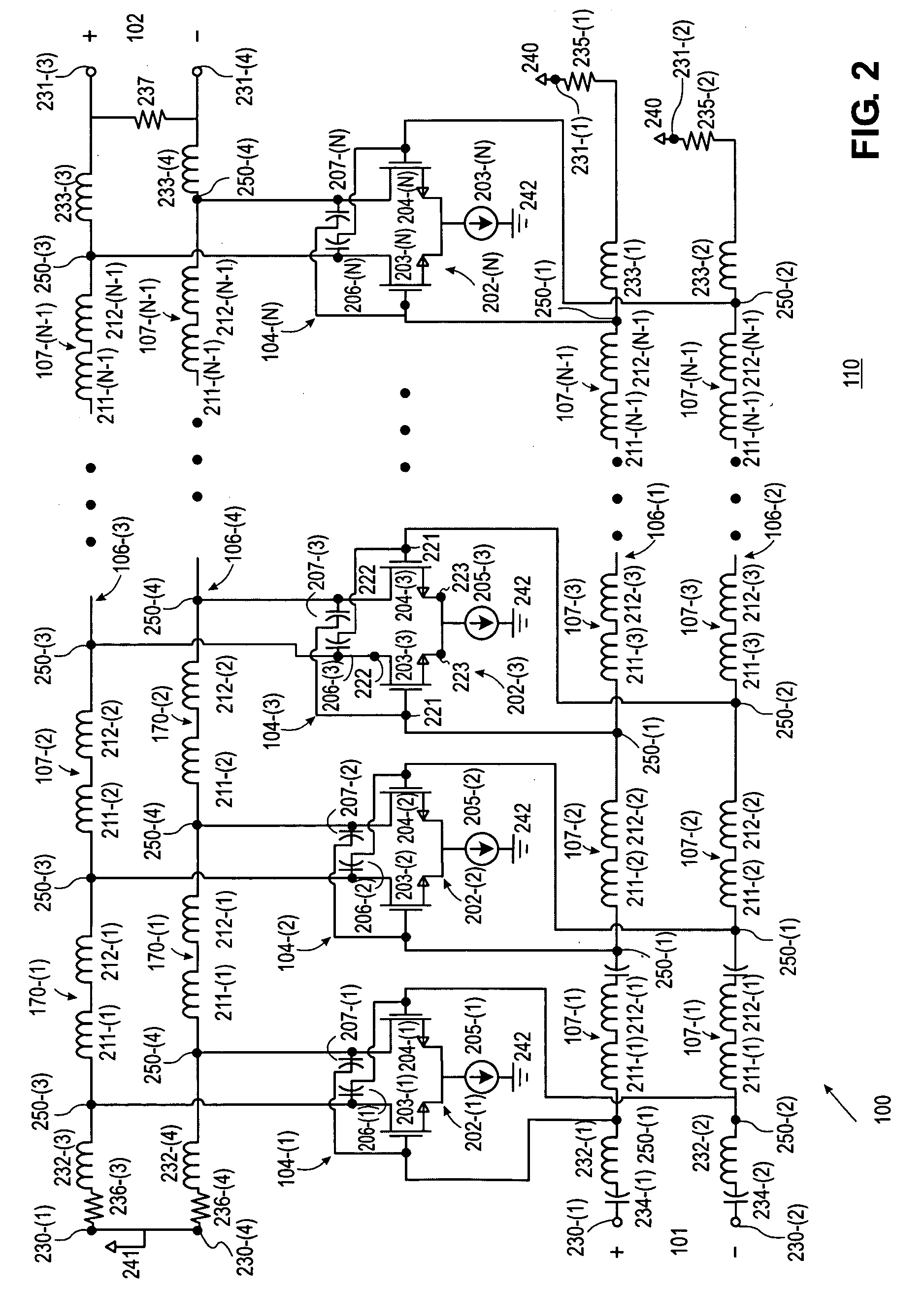
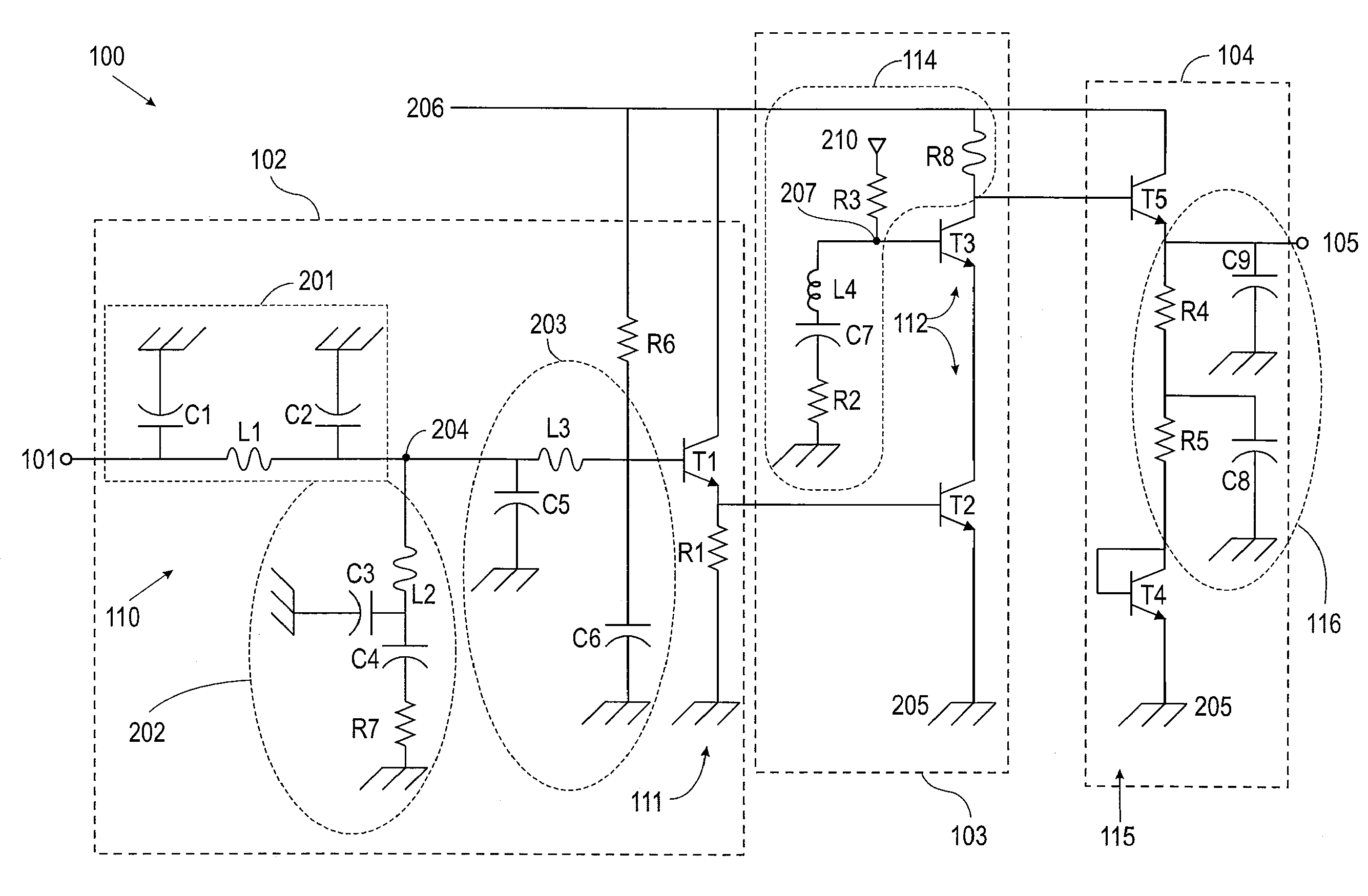
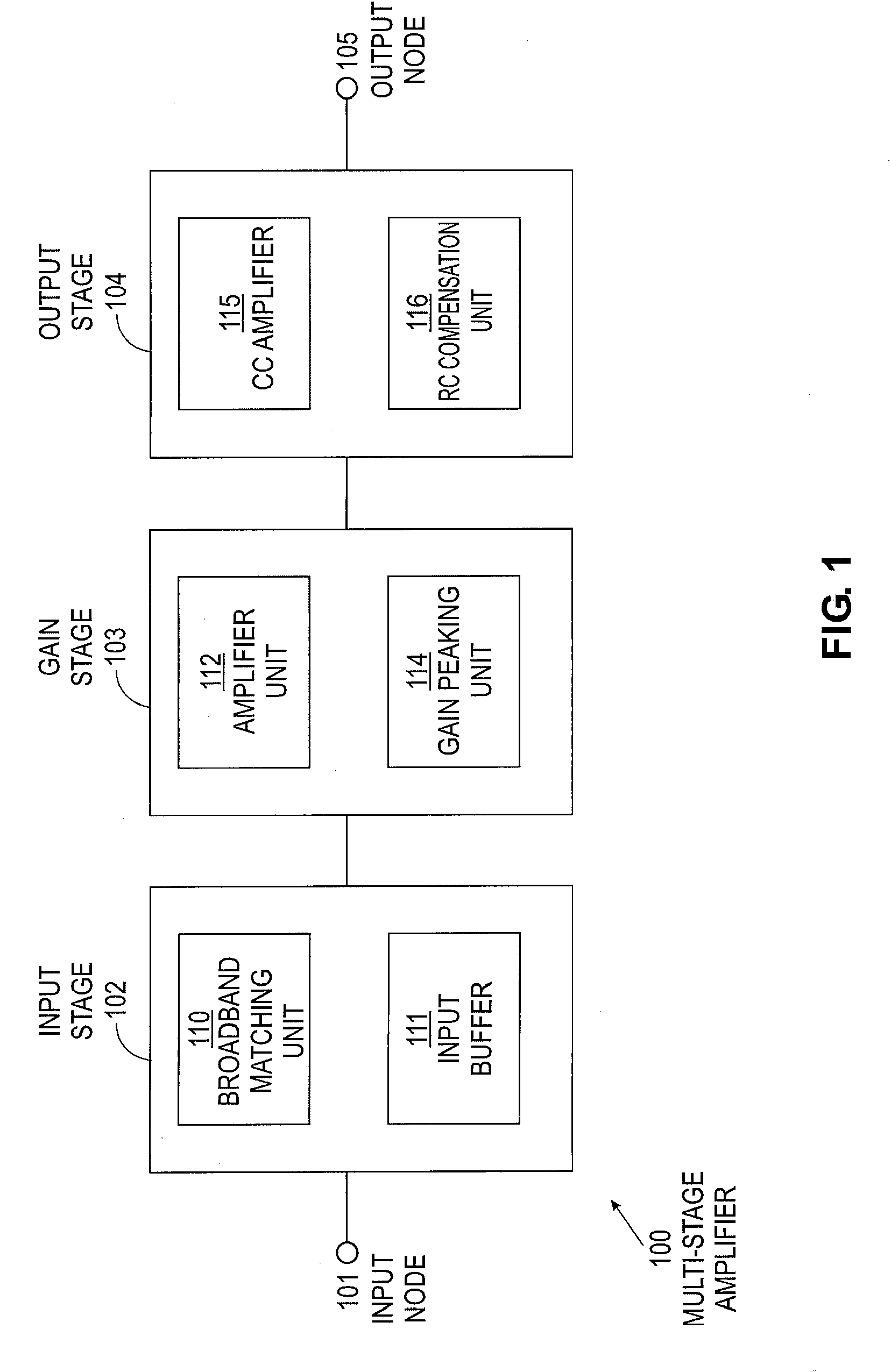
Provided herein are multi-stage broadband amplifier configured to achieve a high gain-bandwidth product in a non-distributed architecture and methods for designing the same. The broadband amplifier can include an input stage having a broadband matching unit and an input buffer unit, a gain stage having an RLC network and a amplifier unit and an output stage having a common collector amplifier and an RC compensation unit.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Broadband programmable gain amplifier based on operational amplifier
InactiveCN101917171ASimple structureHigh bandwidthGain controlDifferential amplifiersNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a broadband programmable gain amplifier based on an operational amplifier. By designing an operational amplifier with two poles and a zero point and using a zero point compensated secondary pole realized by a feedforward structure, the amplifier expands running bandwidth when ensuring 60dB low-frequency gain and obtains 10MHz cut-off bandwidth and the gain bandwidth product of 4.5GHz. The whole programmable gain amplifier realizes the regulation of 10MHz bandwidth and 50dB gain. The invention has negative feedback structure, stable performance and higher linearity, and the gain depends on the ratio of feedback resistance and input resistance; and the end-to-end input and output can be realized, and a signal dynamic range is wide.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Miller-compensated amplifier
ActiveCN1893260AIncrease pole separationImprove stabilityAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceCapacitanceNegative feedback
A Miller-compensated amplifier, having an amplifier input and an amplifier output, comprises a first gain stage, a second gain stage, a third gain stage, and a capacitor. The first gain stage has the amplifier input as a first gain stage input thereto and a first gain stage output. The second gain stage has a second gain stage input, coupled to the first gain stage output, and a second gain stage output. The third gain stage has a third gain stage input, coupled to the second gain stage output, and provides an output voltage at the amplifier output. The capacitor is coupled between the amplifier output and the second gain stage input. The Miller-compensated amplifier provided by the invention separates pole of the amplifier by adding a Miller-compensated capacitor so as to improving the stability of the negative feedback loop, and can keep constant gain-bandwidth product of the amplifier without reducing frequency width.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
High-gain low-noise optimal bias regulating type cascode trans-impedance amplifier
InactiveCN106253856AHigh gainHigh bandwidthAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlLow noiseCascode
The invention discloses a cascode transimpedance amplifier with high gain, low noise and optimal bias adjustment, which includes: a main amplifier and an auxiliary amplifier, and also includes: a connection between the output terminal of the auxiliary amplifier and the gate of the main amplifier In between, a bias circuit with a high-pass filter structure is added to isolate the DC bias of the main amplifier and the auxiliary amplifier, so that both work in the best bias state; a cascode amplifier is used to replace the DC bias in the auxiliary amplifier Common-source stage amplifier, providing higher gain-bandwidth product; series inductor L at the input 1 , the series inductor L between the common-source and common-gate devices of the cascode amplifier 2 , the two inductances, the photodetector capacitance at the input end and the parasitic capacitance of the MOS tube form two π-type matching networks respectively. On the premise of ensuring that the overall bandwidth of the transimpedance amplifier is not reduced, the present invention improves the circuit gain and reduces noise, and finally realizes the RGC transimpedance amplifier with high gain and low noise.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Wideband dual amplifier circuits
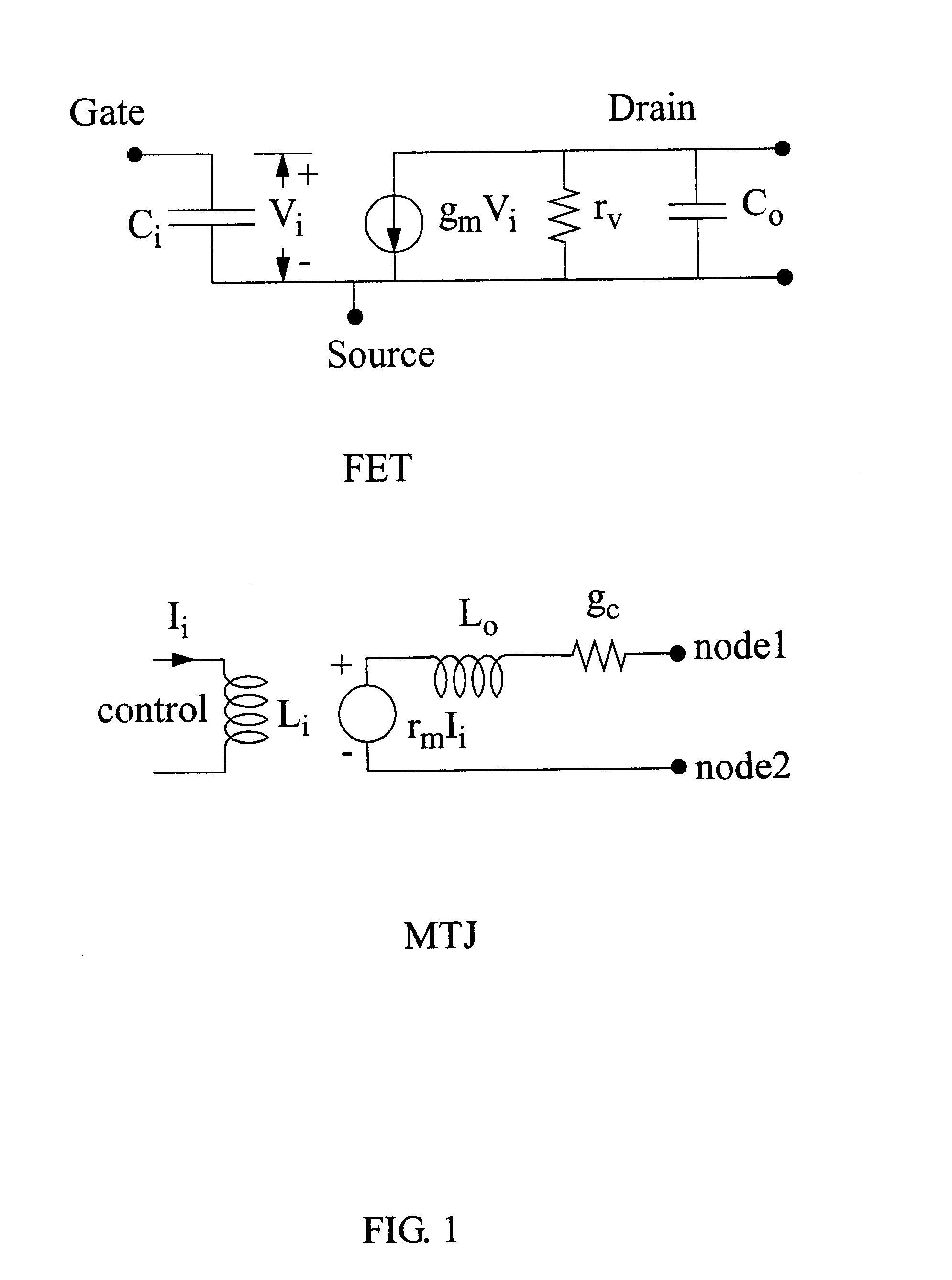
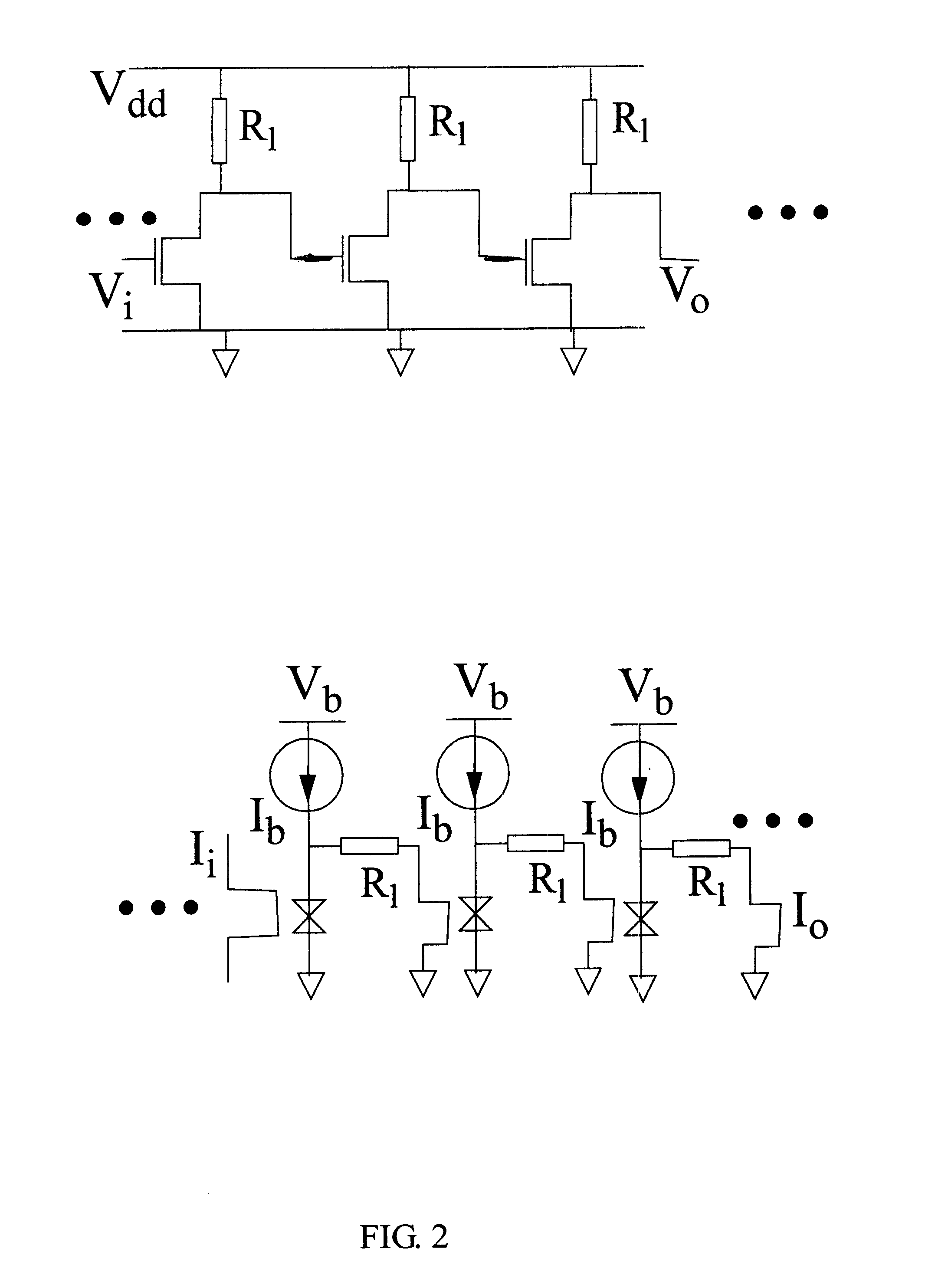
InactiveUS6356147B1Increased Gain BandwidthCancel noiseAmplifier combinationsAmplififers with field-effect devicesAudio power amplifierEngineering
Dual amplifying circuits having a magnetic tunnel junction device and a field effect transistor configured in a complementing set are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, the field effect transistor is operable to control a current level of a current operating signal flowing through the magnetic tunnel junction device. In another embodiment, the magnetic tunnel junction device is operable to control a voltage level of a voltage signal being applied to a gate terminal of the field effect transistor. The gain-bandwidth product of both embodiments is greater than the individual gain-bandwidth products of the individual devices through the elimination of noise contributing resistive type circuit elements.
Owner:IBM CORP
Non-uniform distributed multi-stage circuits
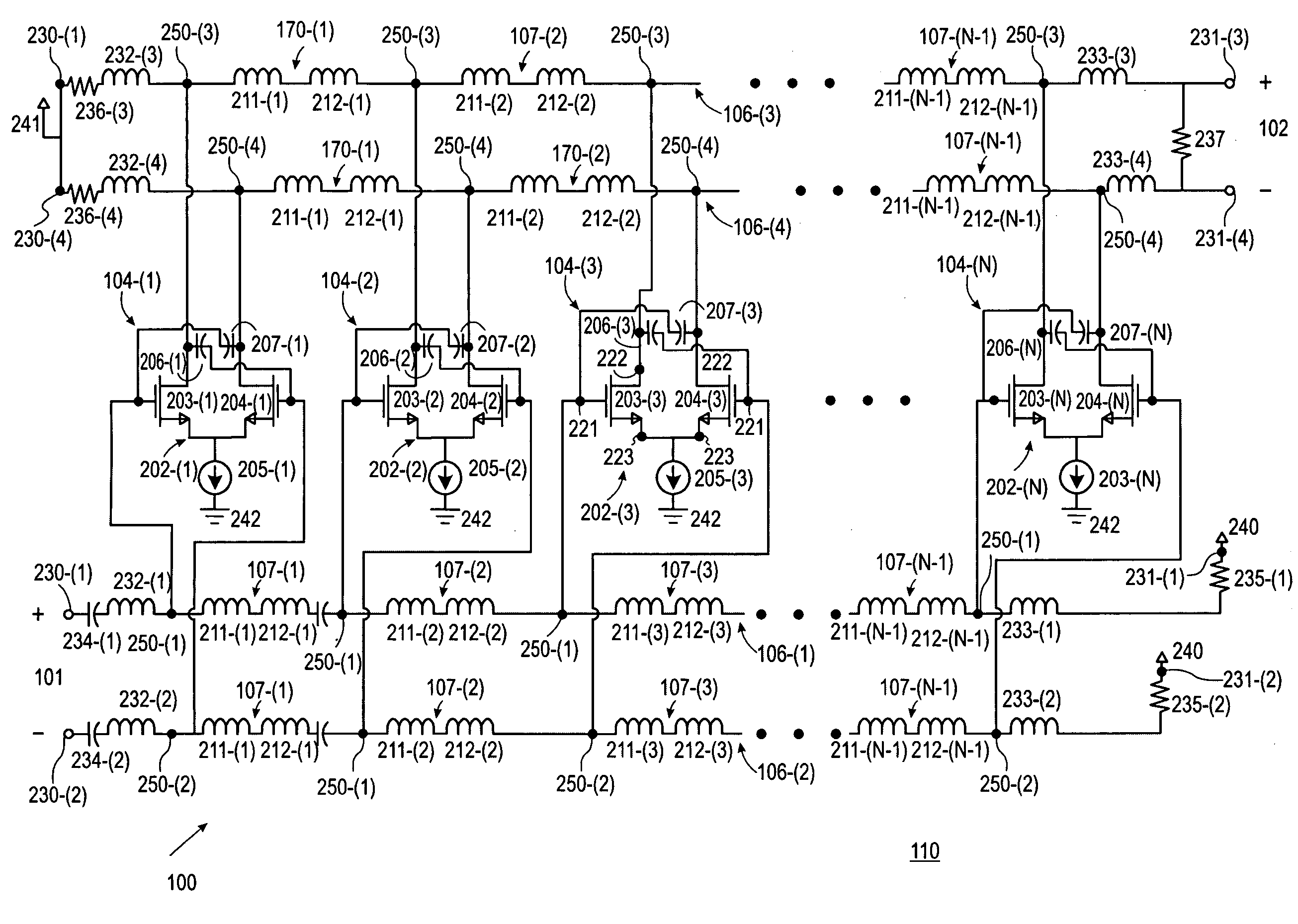
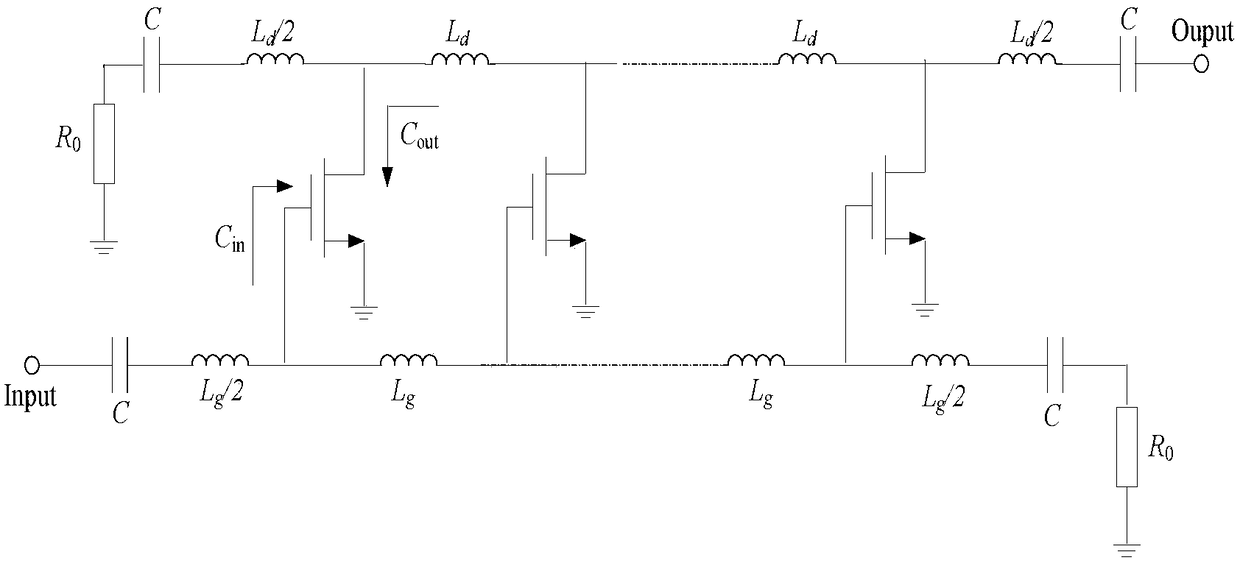
Provided herein is a non-uniform multi-stage distributed circuit capable of operation with an improved gain-bandwidth product. The circuit can include an input port, an output port and a transmission line coupled therebetween. Two or more amplifier stages can be coupled successively to the transmission line. Each amplifier stage can include a transistor having a transistor parameter, which can be scaled to be less than the transistor parameter of any preceding amplifier stage. The inductance of each portion of the transmission line between adjacent stages can also be scaled to be less than the inductance of the portion of the transmission line between any preceding amplifier stages. The inductance can be scaled in addition to or instead of the transistor parameter.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multi-stage broadband amplifiers
ActiveUS7652539B2High frequency amplifiersAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierBroadband amplifiers
Provided herein are multi-stage broadband amplifier configured to achieve a high gain-bandwidth product in a non-distributed architecture and methods for designing the same. The broadband amplifier can include an input stage having a broadband matching unit and an input buffer unit, a gain stage having an RLC network and a amplifier unit and an output stage having a common collector amplifier and an RC compensation unit.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Class AB folded-cascode amplifier having cascode compensation
ActiveUS7414473B1Improved gain-bandwidth productDifferential amplifiersAmplifier detailsEngineeringGain–bandwidth product
A class AB folded-cascode amplifier having improved gain-bandwidth product, comprises a differential input circuit including a differential transistor pair coupled to a source of tail current and responsive to a differential input signal for conducting a first current, a cascode circuit coupled to the differential input circuit for supplying a second current thereto, and a class AB output stage. A compensation circuit is configured for feeding back mutually complementary compensation signals from an output node to the differential input circuit.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Cascaded distributed low-noise amplifier
ActiveCN108336978ALower noise figureExcellent radio frequency indexAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlArtificial transmission lineAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a cascaded distributed low-noise amplifier. The cascaded distributed low-noise amplifier comprises a first stage amplifier, a second stage amplifier, and a third stage amplifier; each of the amplifiers is composed of a gain and an on-chip inductor, and the structures of the gain units of the amplifiers are completely same; the on-chip inductor and the input impedance of each gain unit form an input artificial transmission line, and the on-chip inductor and the output impedance of each gain unit form an output artificial transmission line. And the gain units of the amplifiers adopt the structure in single-end input to differential output. The low-noise amplifier disclosed by the invention is simple in structure, low in input echo loss, small in in-band fluctuation, high in gain, and low in noise coefficient; the limitation on the gain bandwidth product in the traditional amplifier can be overcome, the large flat gain can be obtained in wide frequency band, and the good noise performance is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
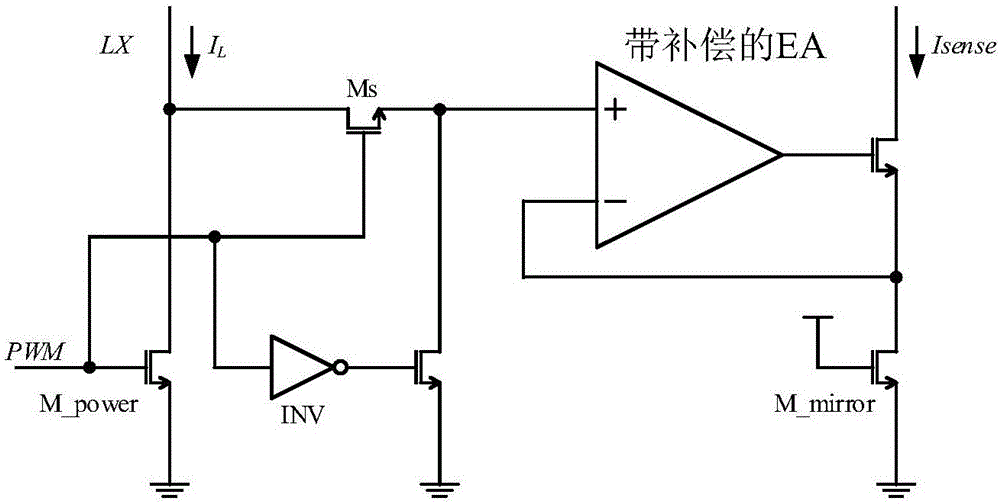
Current sampling circuit
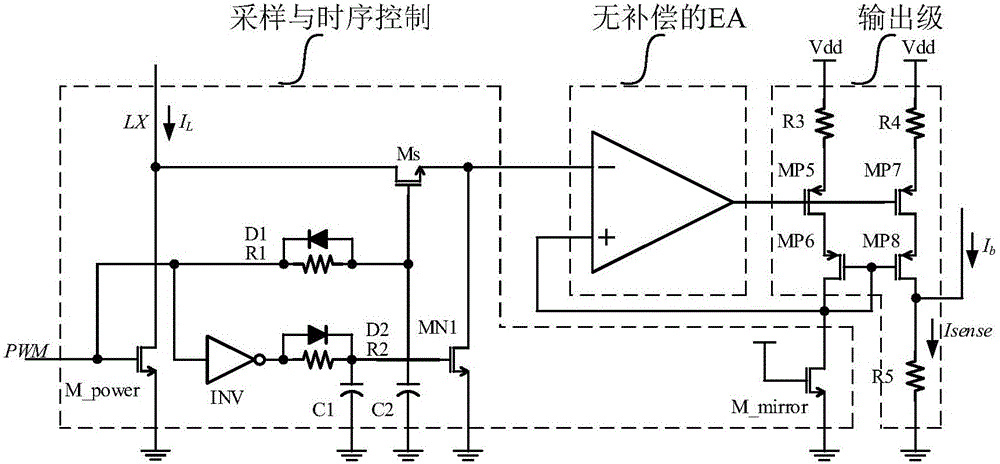
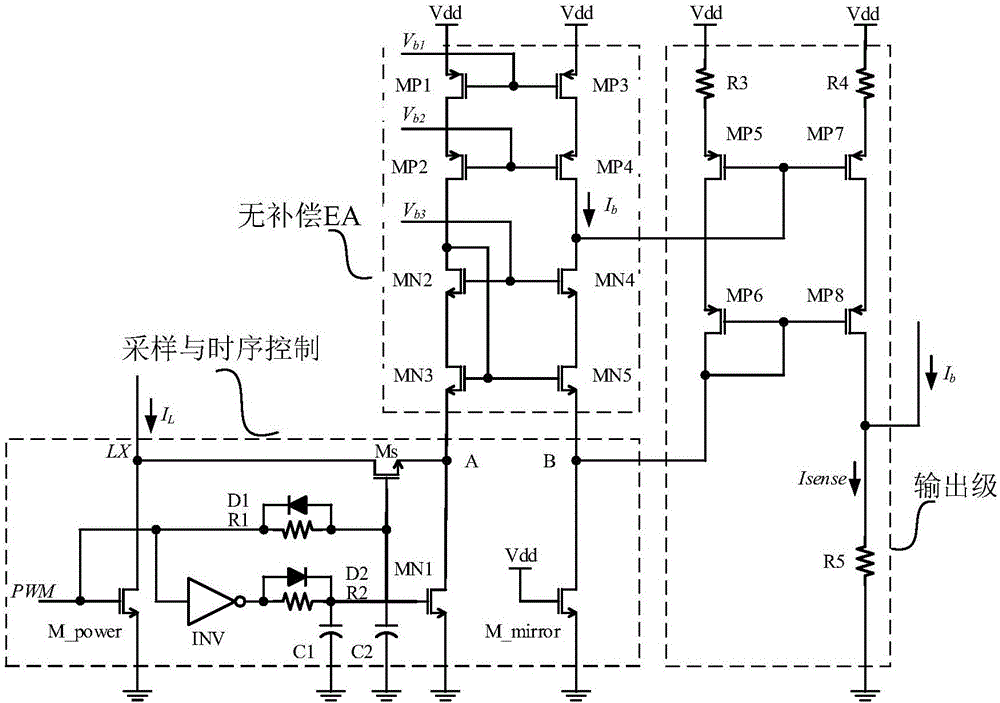
The invention belongs to the technical field of integrated circuits and particularly relates to a current sampling circuit. The current sampling circuit comprises a sampling and time sequence control module, an uncompensated error amplifier EA module and an output stage, wherein the input end of the sampling and time sequence control module is connected with inductive current IL, two output ends of the sampling and time sequence control module are connected with the in-phase input end and the inverted input end of the uncompensated error amplifier EA module respectively, the input end of the output stage is connected with the output end of the uncompensated error amplifier EA module, and the output end of the output stage outputs sampling current Isense. The current sampling circuit has the advantages that the uncompensated error amplifier EA module guarantees sufficient gain and requires no compensating circuit, so that a GBW (gain bandwidth product) of an error amplifier EA is increased to 10 M and above; a time sequence control network of the sampling and time sequence control module restrains burr generated by switching signals, so that influences of PMW signals and LX dot signals on the input end of the uncompensated error amplifier EA and final sampling output current are lowered.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Class AB folded-cascode amplifier having cascode compensation
A class AB folded-cascode amplifier having improved gain-bandwidth product, comprises a differential input circuit including a differential transistor pair coupled to a source of tail current and responsive to a differential input signal for conducting a first current, a cascode circuit coupled to the differential input circuit for supplying a second current thereto, and a class AB output stage. A compensation circuit is configured for feeding back mutually complementary compensation signals from an output node to the differential input circuit. Another compensation circuit is configured for feeding back a signal from the output of the output stage to the input of the output stage.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
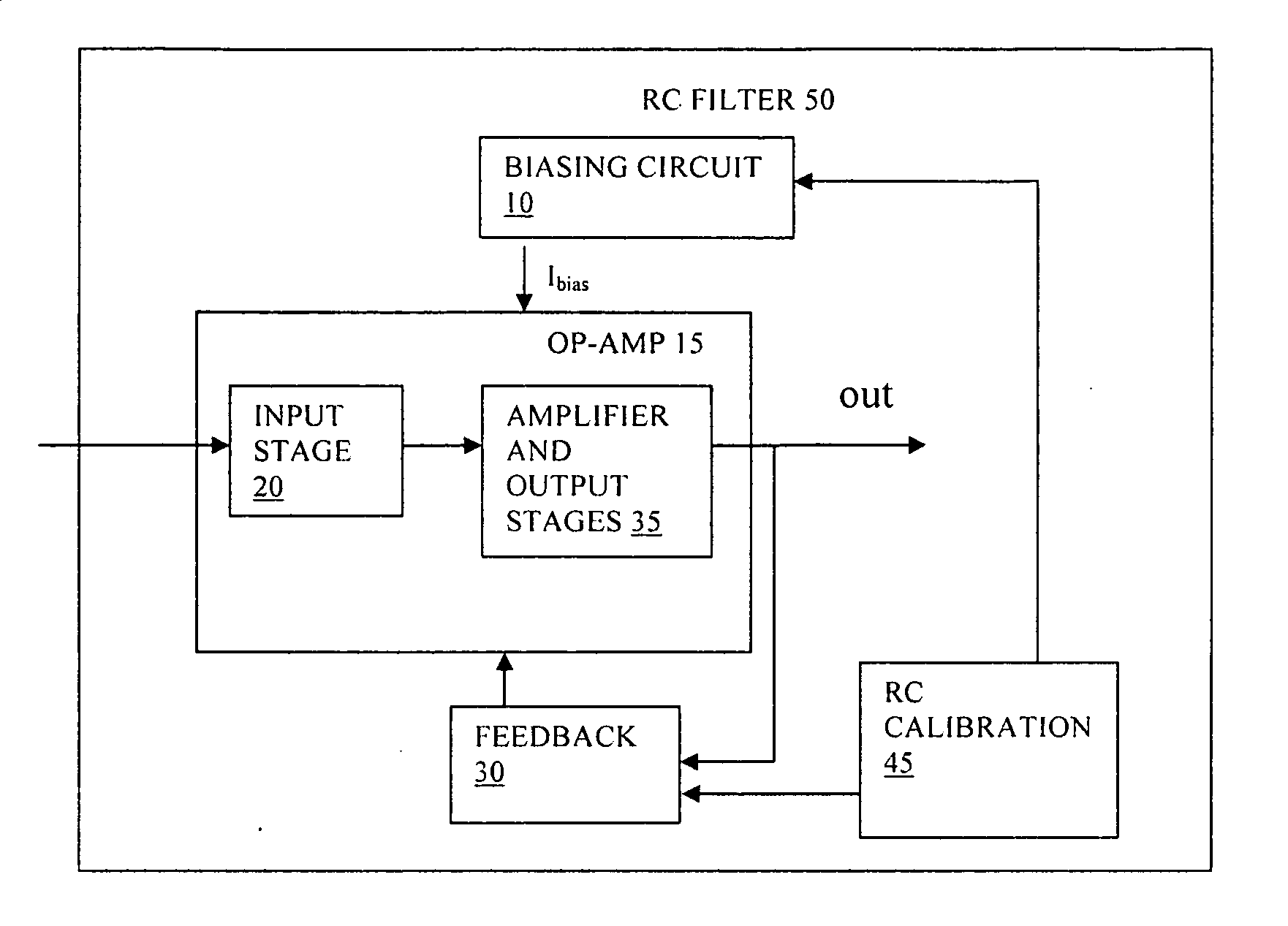
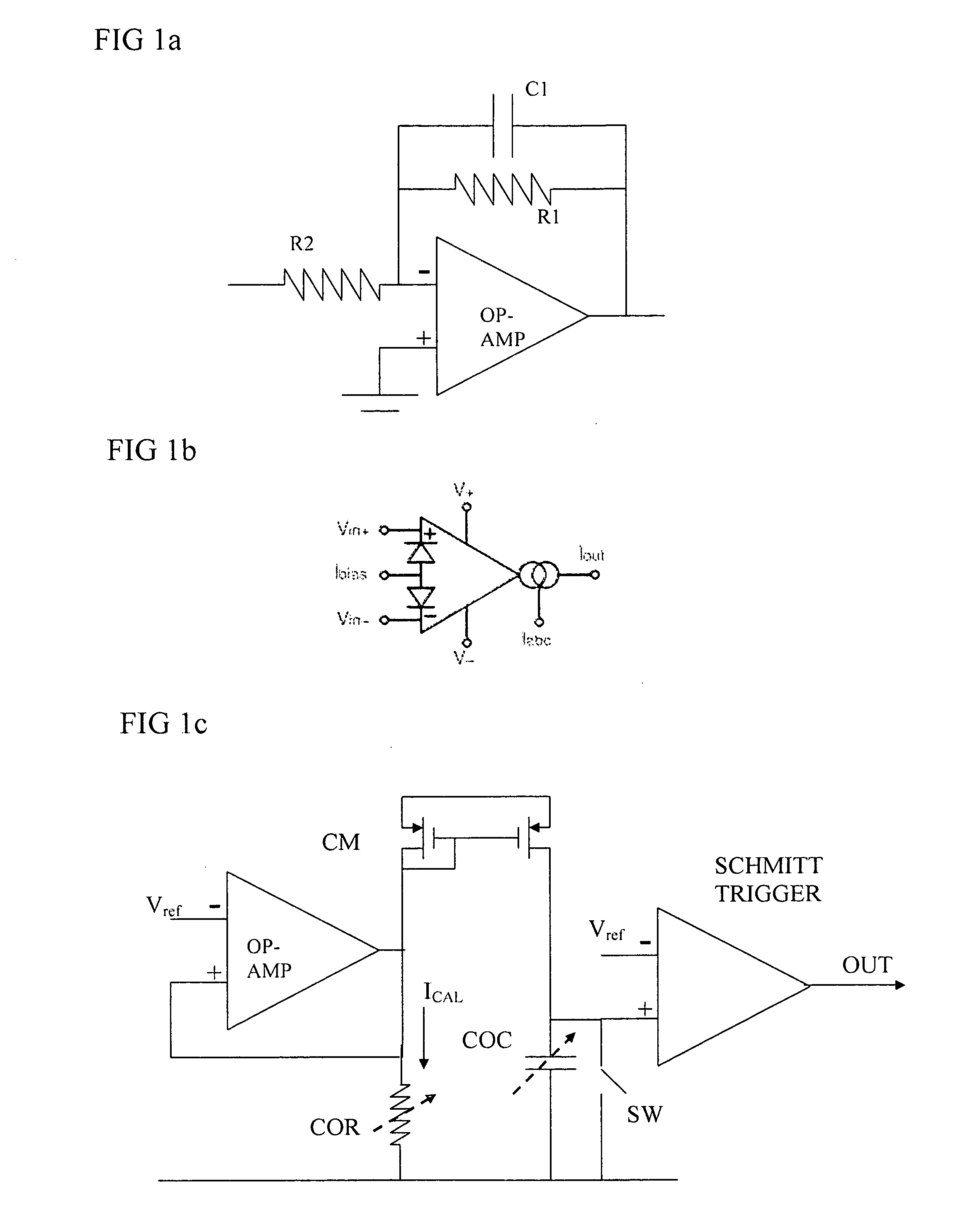
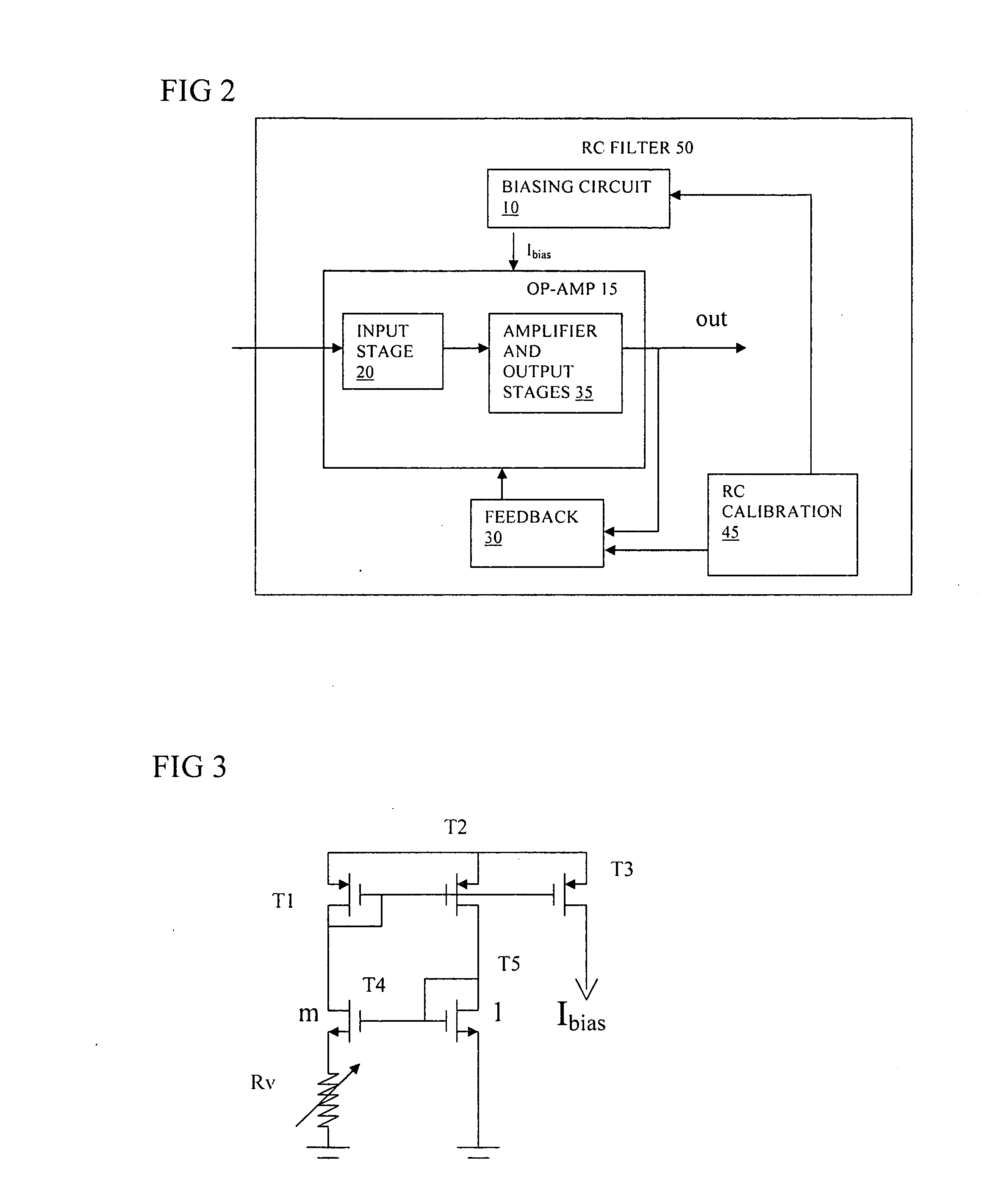
Bandwidth calibration of active filter
InactiveUS20080100373A1Decrease gain bandwidthReduce the required powerActive element networkAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierOperational transconductance amplifier
An active RC filter has an op-amp and a biasing circuit arranged to bias the op-amp to set a gain bandwidth product of the op-amp according to a desired pole frequency of the filter. The biasing circuit is operable according to an output of an RC calibration circuit. The op-amp can be an OTA transconductance amplifier, and the biasing circuit can be arranged to maintain a constant product of R and transconductance at an input of the transconductance amplifier. This biasing can help to set the pole frequency more accurately and can thus reduce the need for bandwidth margin to be provided to allow for manufacturing process variations.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Capacitively-coupled distributed amplifier with baseband performance
ActiveUS8035449B1Broaden output power bandwidthIncrease output impedanceAmplifiers wit coupling networksCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
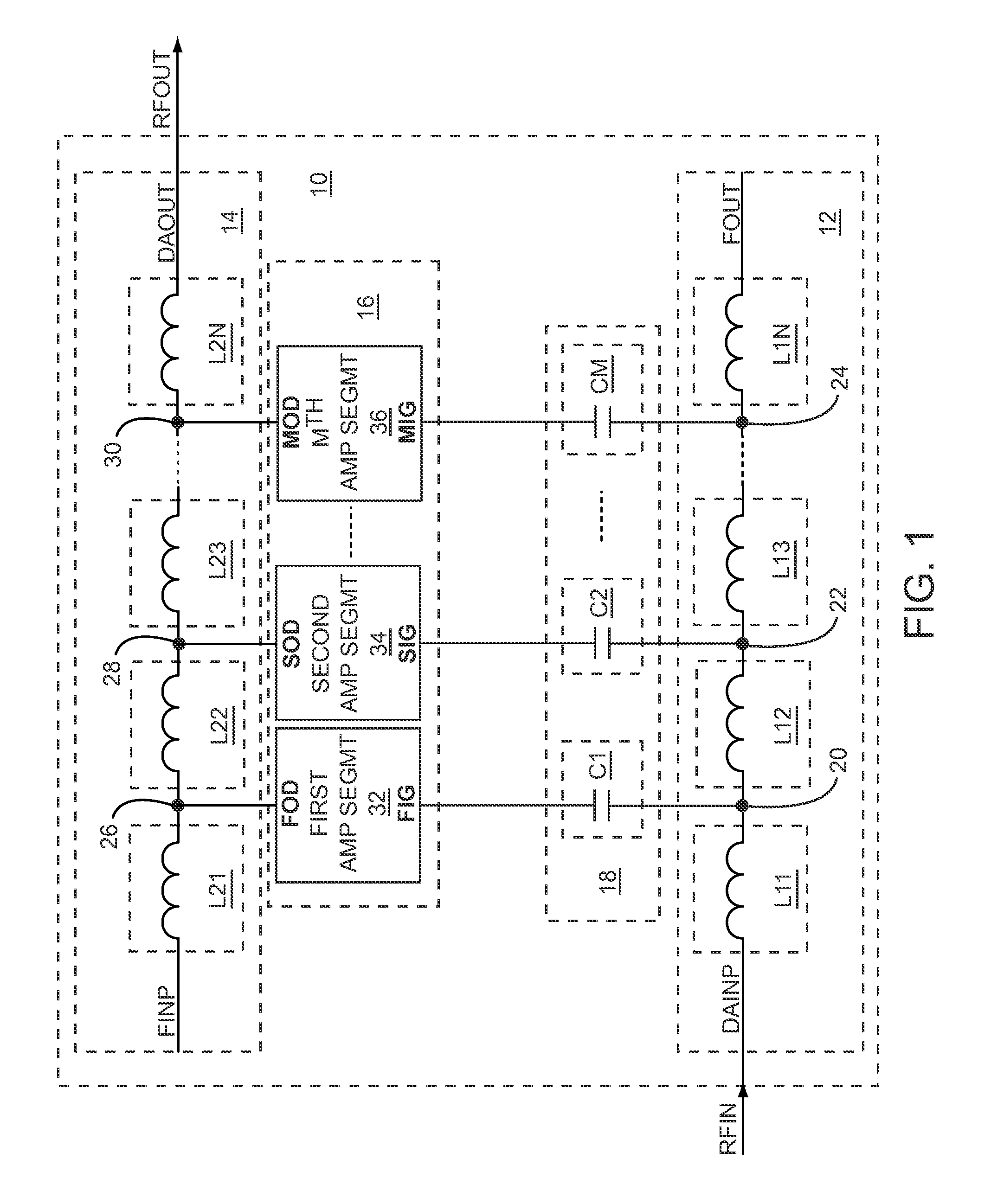
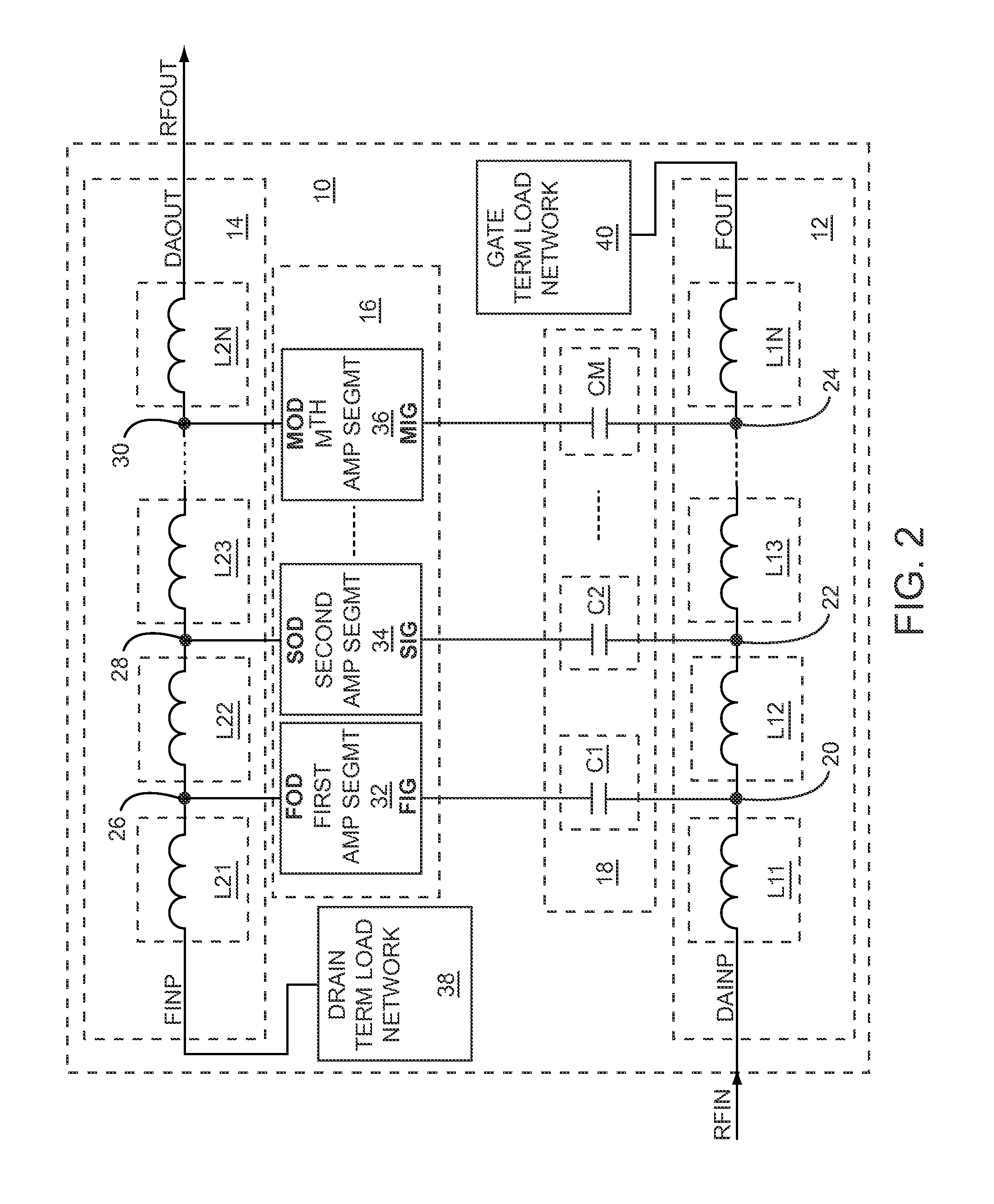
The present disclosure relates to a capacitively-coupled distributed amplifier (DA) having an input line and an output line that are coupled to one another through a broadband interface network and DA segments. The input line receives an input signal and the output line provides an output signal based on amplifying the input signal. The broadband interface network includes a group of capacitive elements coupled between the input line and the DA segments to extend a gain-bandwidth product of the DA. The broadband interface network further includes a resistor divider network coupled between the input line and the DA segments to extend a lower end of an operating bandwidth of the DA. As such, the operating bandwidth of the DA may extend from baseband frequencies to microwave frequencies.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Compensation methods for digital source-measure-units (SMUs)
ActiveUS8797025B2Increase flexibilityConvenient and accurateElectronic circuit testingResistance/reactance/impedenceZero frequencyDigital control
A source-measure unit (SMU) may be implemented with respective digital control loops for output voltage and output current. The output voltage and output current may be measured with dedicated ADCs (analog-to-digital converters). The readings obtained by the ADCs may be compared to a setpoint, which may be set in a digital loop controller. The digital loop controller may be used to produce an output to drive a DAC (digital-to-analog converter) until the output voltage and / or output current and / or a function thereof reach the respective desired levels. The digital loop controller may implement respective integrating functions for the respective digital control loops, and may also implement a compensation function featuring pole-zero pairs to stabilize the respective current / voltage outputs. Coefficients of the compensation function may be calculated based on user programmable parameters corresponding to the gain bandwidth product, compensation frequency, and ratio of the added pole-zero frequencies.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
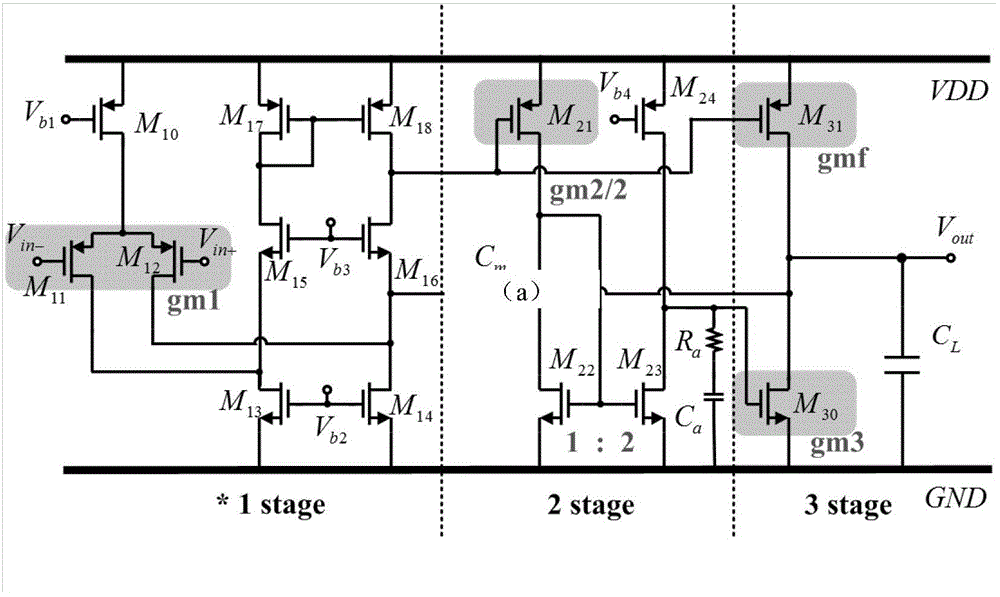
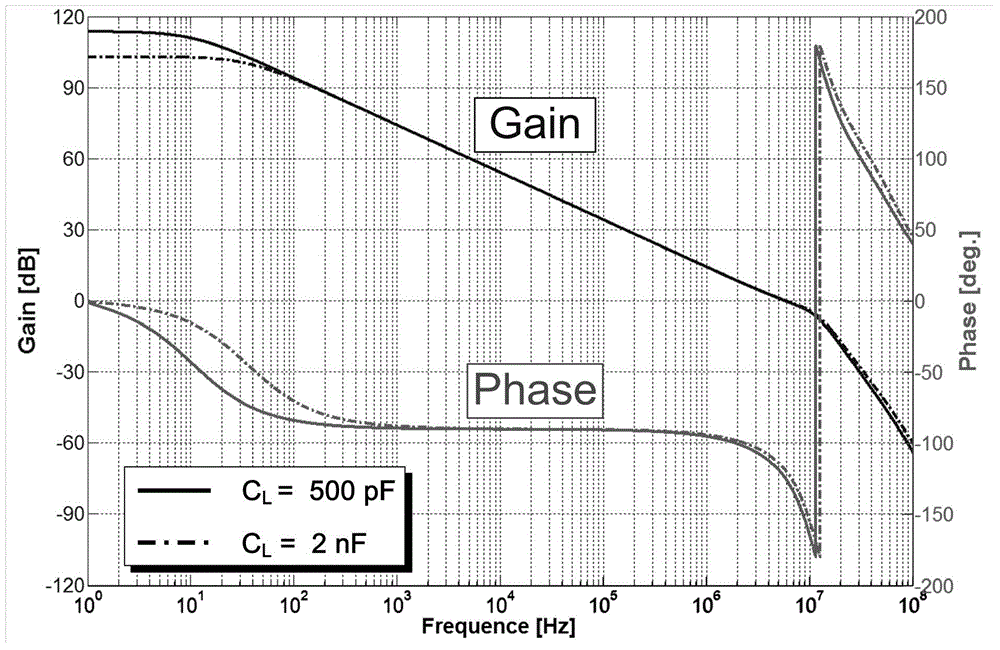
Low-power consumption three-level operational amplifier for driving large-load capacitor
InactiveCN104601123AGood slew rateDifferential amplifiersAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthCapacitanceThree level
The invention discloses a low-power consumption three-level operational amplifier for driving a large-load capacitor. The amplifier is composed of fifteen MOS transistors, two capacitors and a resistor Ra, wherein the fifteen MOS transistors comprise the first PMOS transistor M10, the second PMOS transistor M11, the third PMOS transistor M13, the fourth PMOS transistor M17, the fifth PMOS transistor M18, the sixth PMOS transistor M21, the seventh PMOS transistor M24, the eighth PMOS transistor M31, the first NMOS transistor M13, the second NMOS transistor M14, the third NMOS transistor M15, the fourth NMOS transistor M16, the fifth NMOS transistor M22, the sixth NMOS transistor M23 and the seventh NMOS transistor M30; the two capacitors comprise the first compensation capacitor Cm and the second compensation capacitor Ca. Compared with the prior art, the three-level operational amplifier can drive the large-load capacitor (hundreds of pF) under the low-voltage low-power consumption (microW) condition, and has a large gain bandwidth product and a better swing rate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Adaptive bandwidth control in a kinescope amplifier
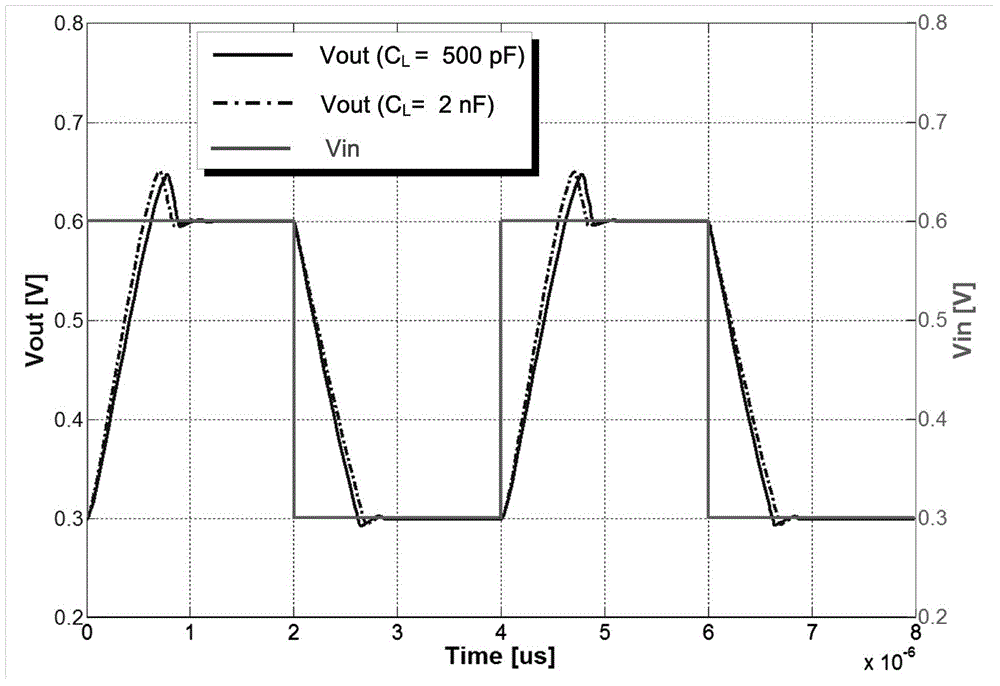
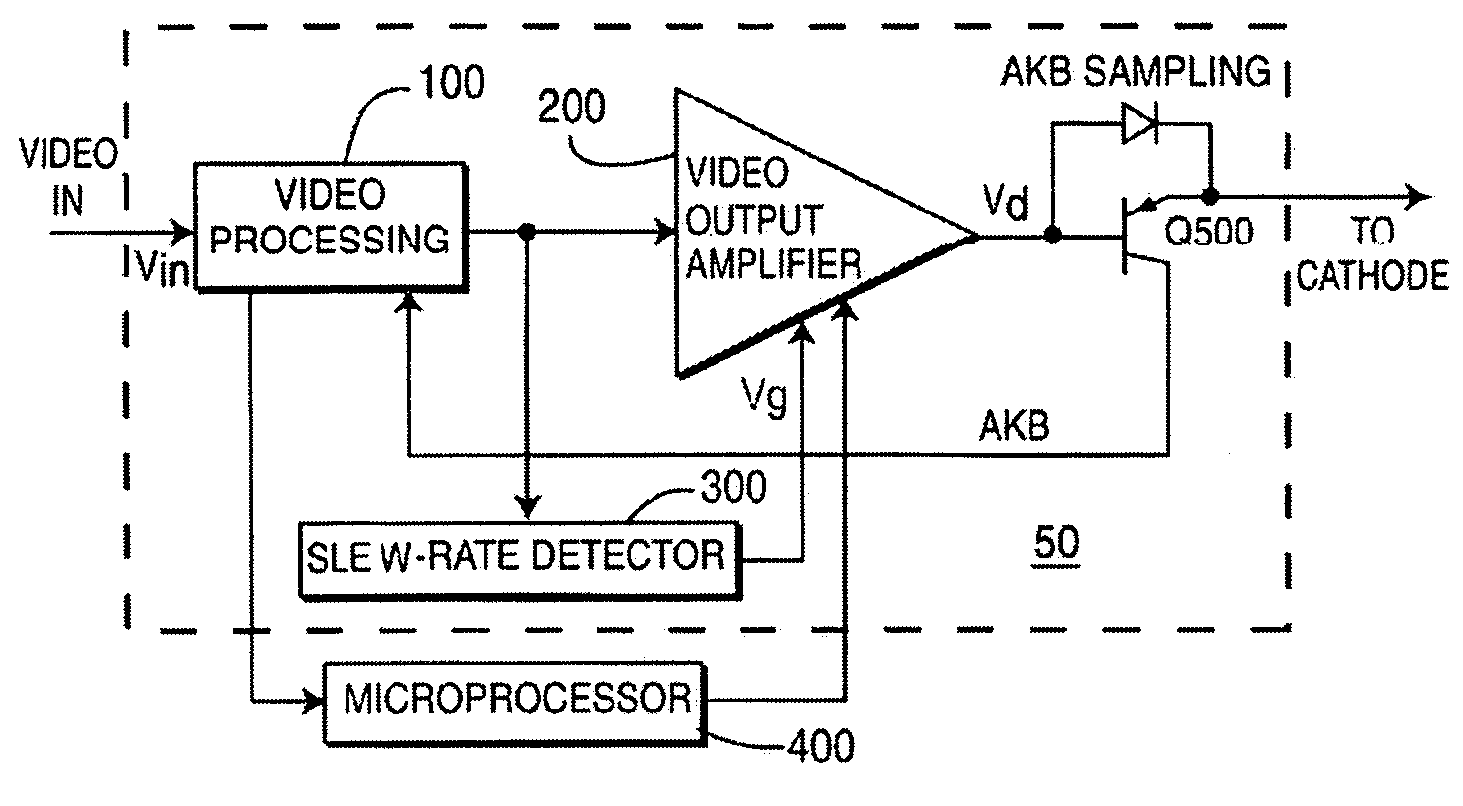
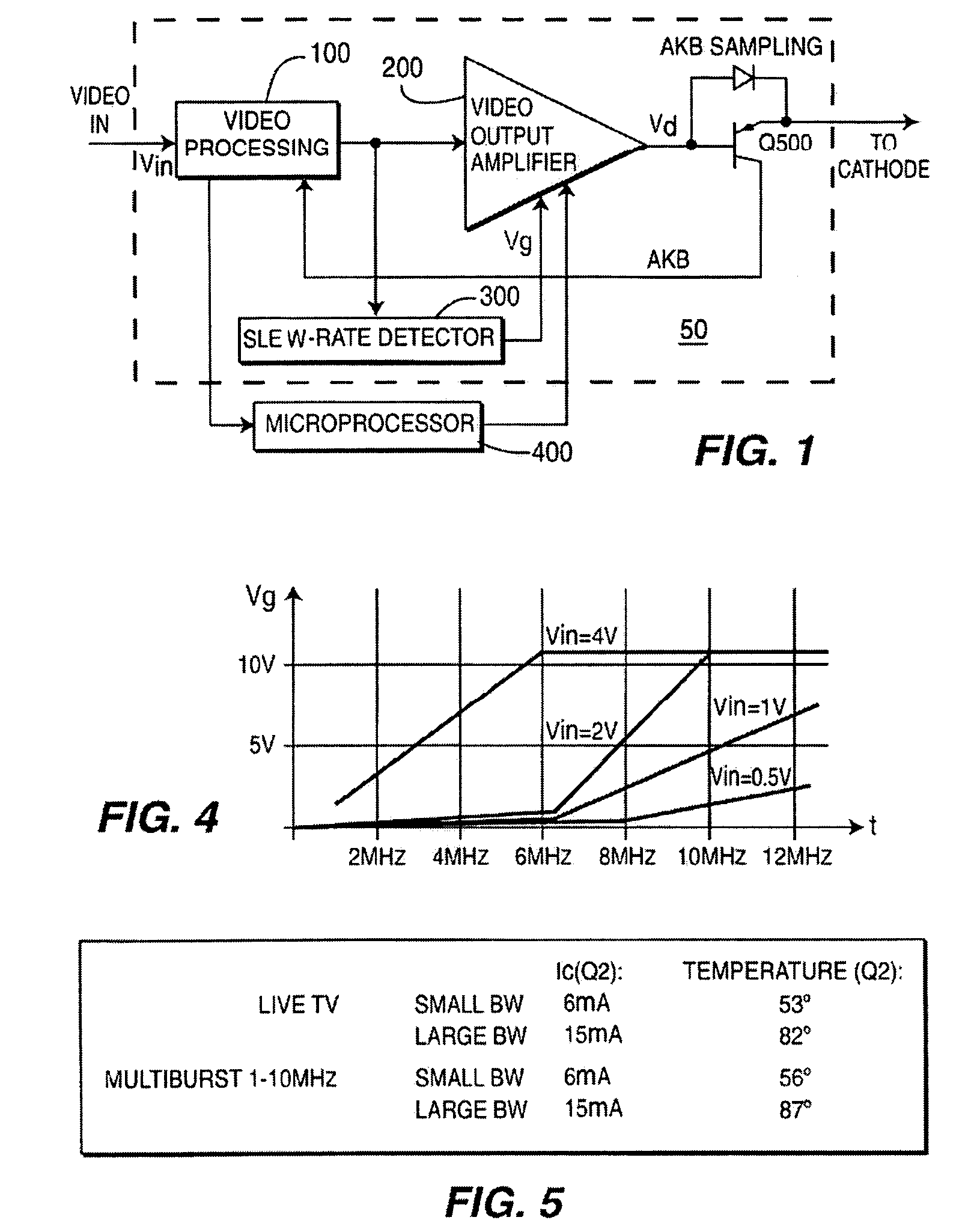
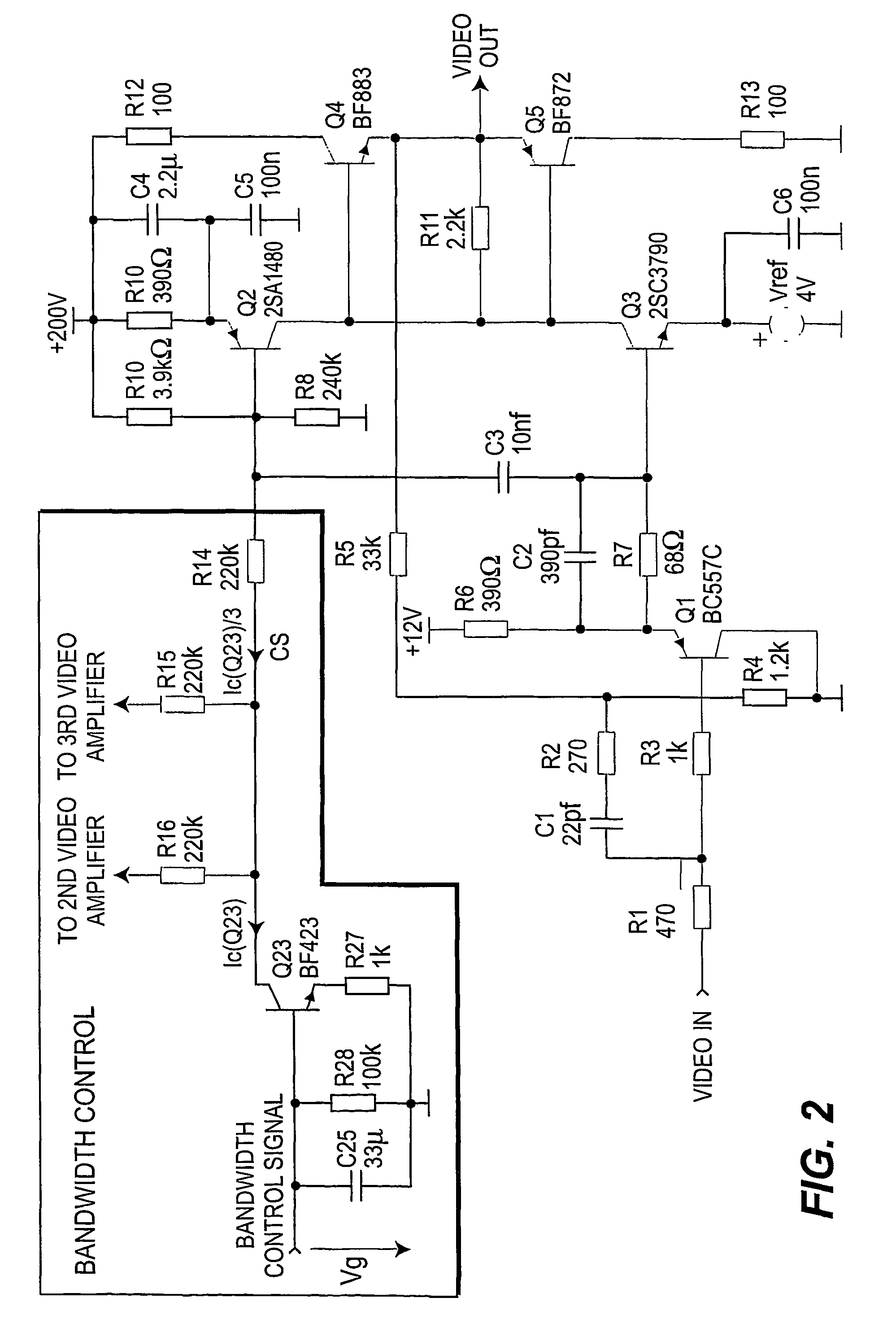
InactiveUS7277136B2Reduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsAudio power amplifierControl signal
A method for controlling dissipation in a video amplifier for a display signal. The method comprises the steps of setting a first current for establishing a first gain bandwidth product in the video amplifier. Generating a control signal in accordance with a slew rate of the display signal. Modifying the first current responsive to the control signal such that the video amplifier gain bandwidth product is controlled in accordance with the slew rate of said display signal.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
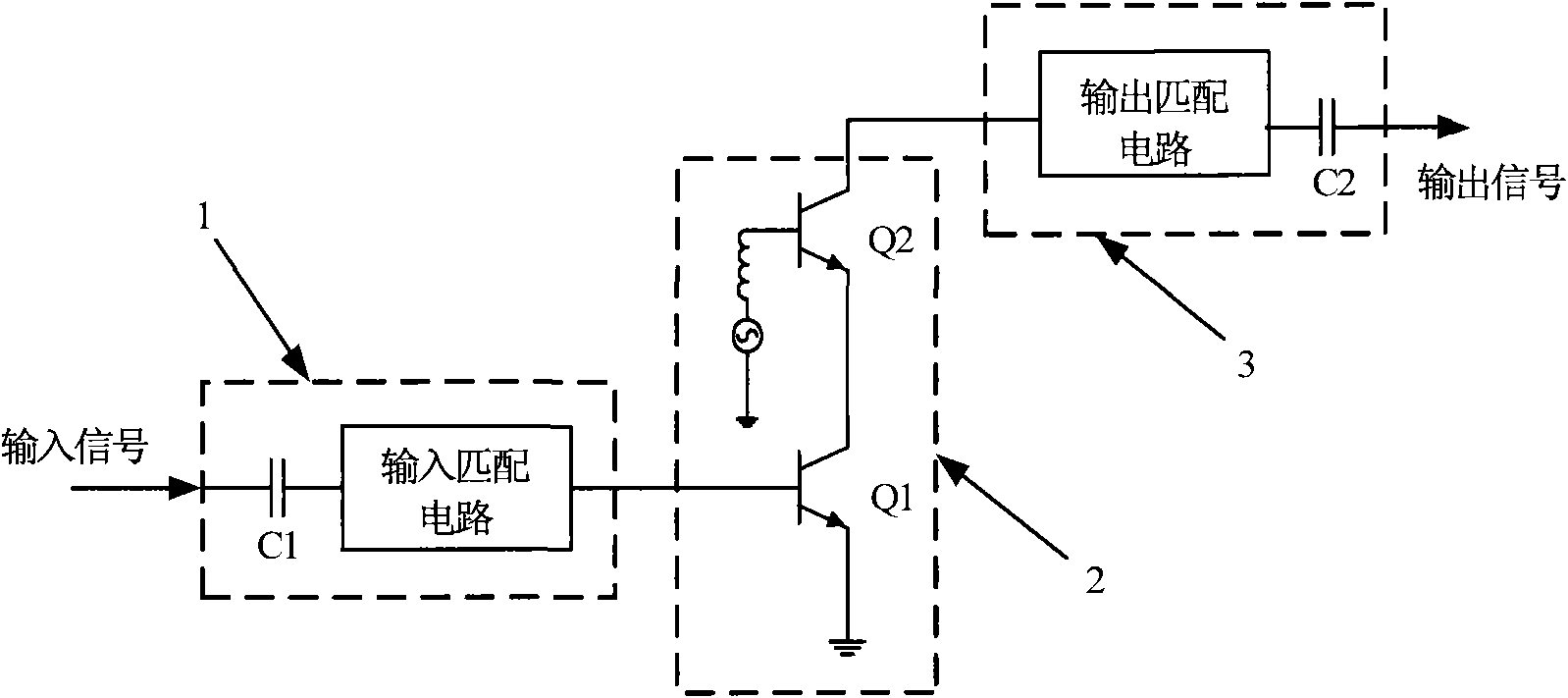
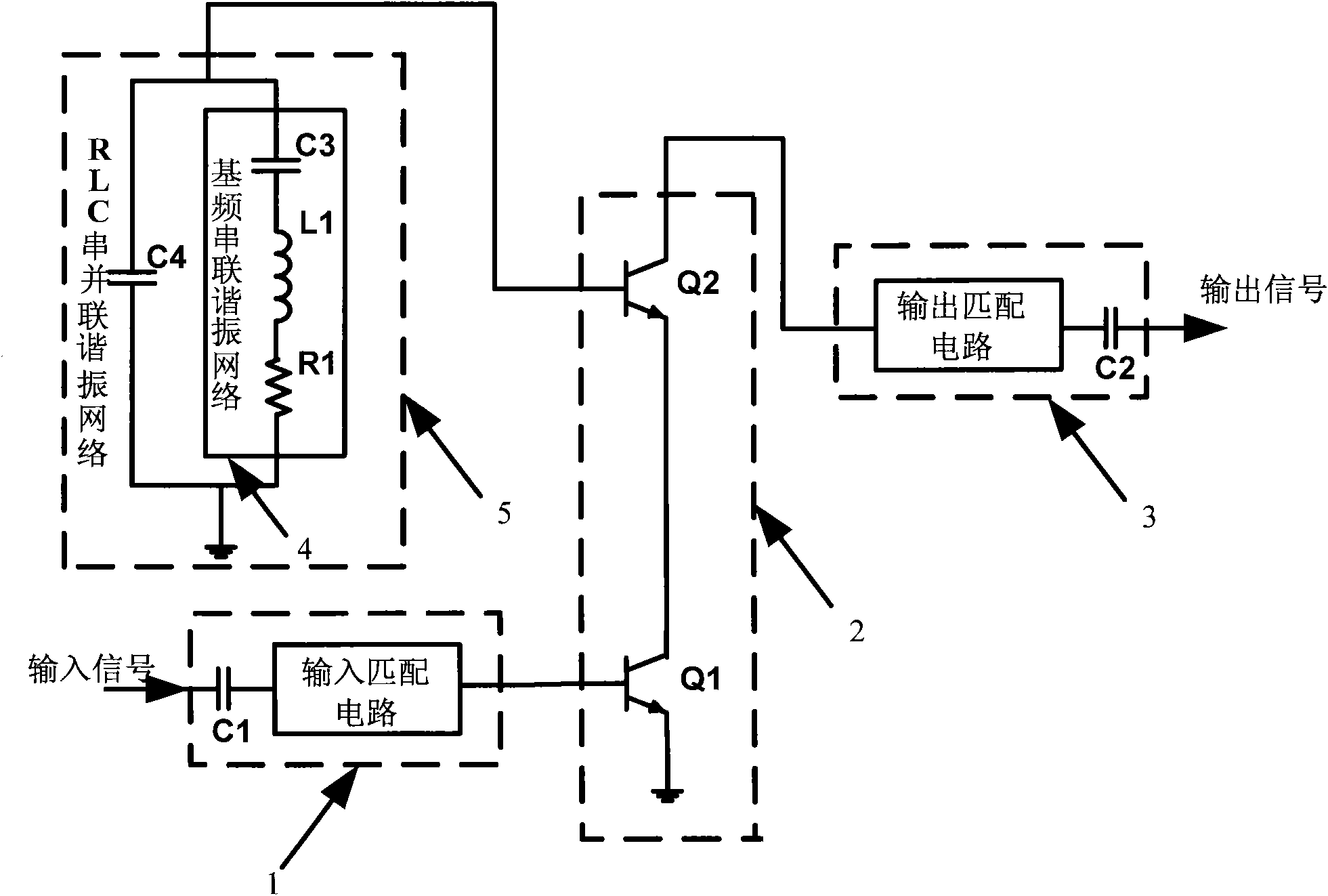
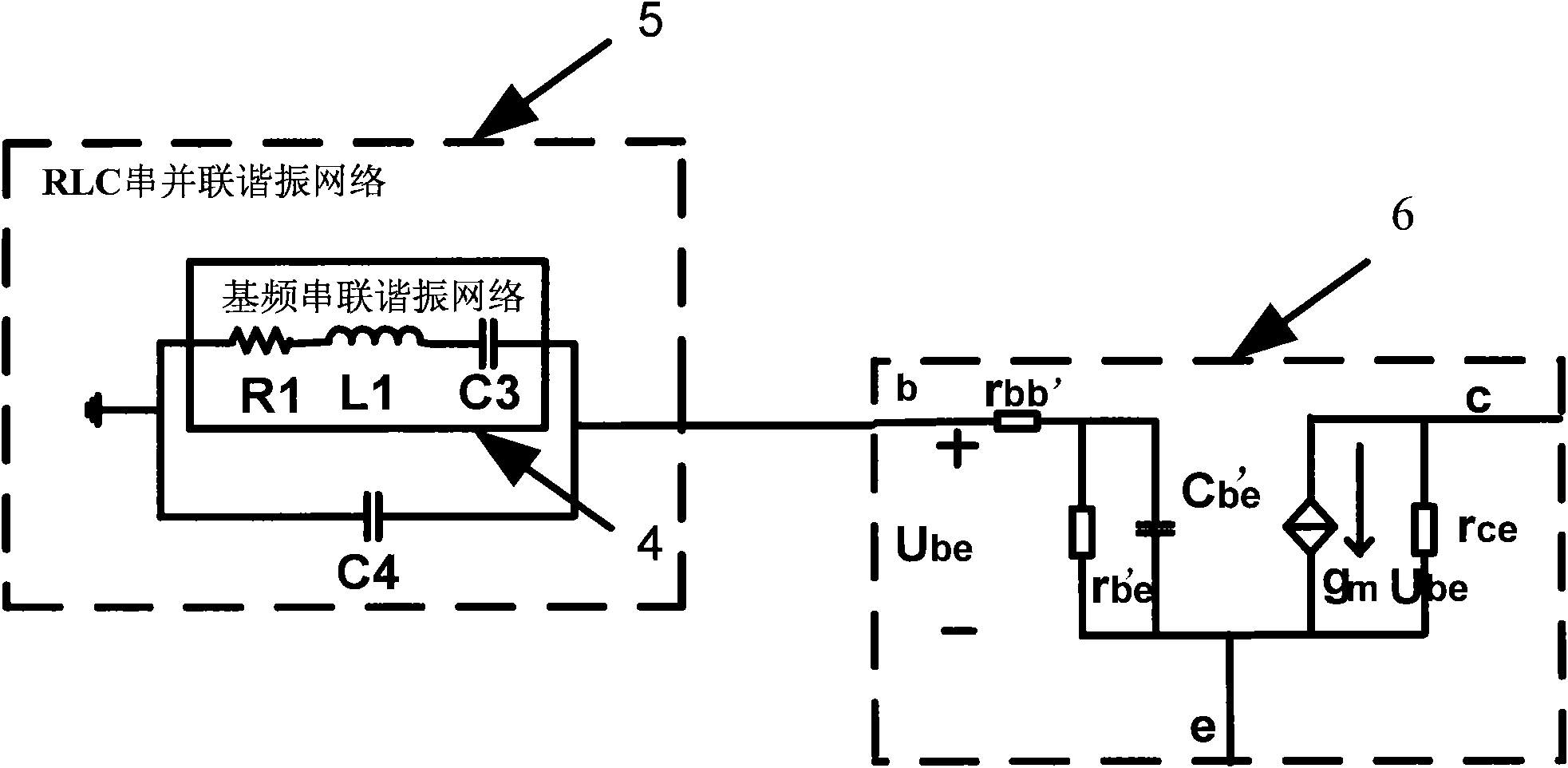
Radio-frequency CASCODE structure power amplifier with improved linearity and power added efficiency
InactiveCN101882912AEnhanced inhibitory effectImproved Power Added EfficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionEnergy efficient ICTBroadband power amplifierCascode
The invention disclose a radio-frequency Cascode structure power amplifier with improved linearity and power added efficiency, comprising a Cascode structure comprising a common-emitter input transistor and a common-base output transistor, an input matching network connected from a signal input port of the power amplifier and a base of the input transistor, and an output matching network connected from a collector of the output transistor to the signal output port of the power amplifier. The base of the output transistor is connected with an RLC series-parallel resonant network capable of improving the gain of a baseband signal and restraining input of a secondary harmonic signal. The radio-frequency Cascode structure power amplifier obviously improves the linearity and power added efficiency of the CASCODE structure power amplifier without increasing the static power consumption of the power amplifier by means of increasing the baseband gain and restraining the harmonic signal by the RLC series-parallel resonant network; and the radio-frequency Cascode structure power amplifier effectively increases the gain bandwidth product of the Cascode structure wideband power amplifier.
Owner:SUZHOU INNOTION TECH
Capacitively-coupled non-uniformly distributed amplifier
ActiveUS8058930B1High bandwidthIncrease output impedanceBreathing filtersAmplifier combinationsCapacitanceDistributed amplifier
The present disclosure relates to a capacitively-coupled non-uniformly distributed amplifier (NDA) having an input line and an output line that are coupled to one another through an input network and DA segments. The input network includes a group of capacitive elements coupled between the input line and the DA segments to extend a gain-bandwidth product of the NDA. The output line includes inductive elements, and since the NDA is non-uniformly distributed, an inductance of each inductive element decreases moving from an input end of the output line to an output end of the output line to compensate for decreasing impedance along the output line. To compensate for phase velocity variations along the output line, a capacitance of each capacitive element that is coupled to the input line decreases moving from an input end of the input line to an output end of the input line.
Owner:QORVO US INC
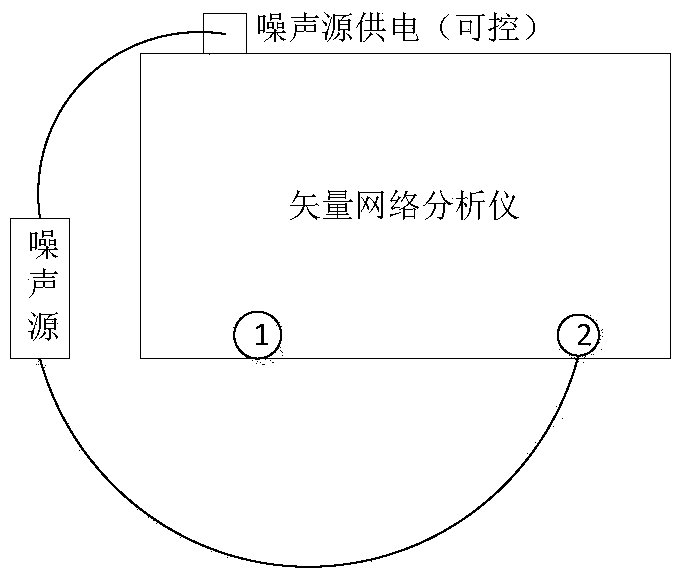
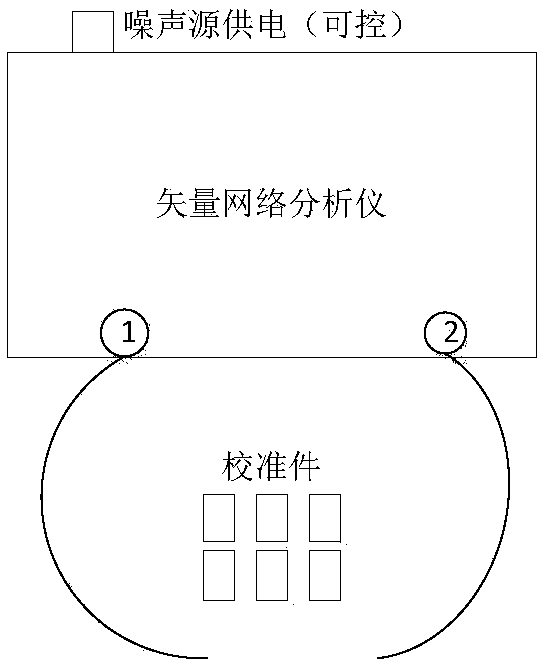
Noise coefficient test method based on vector network analyzer and noise source
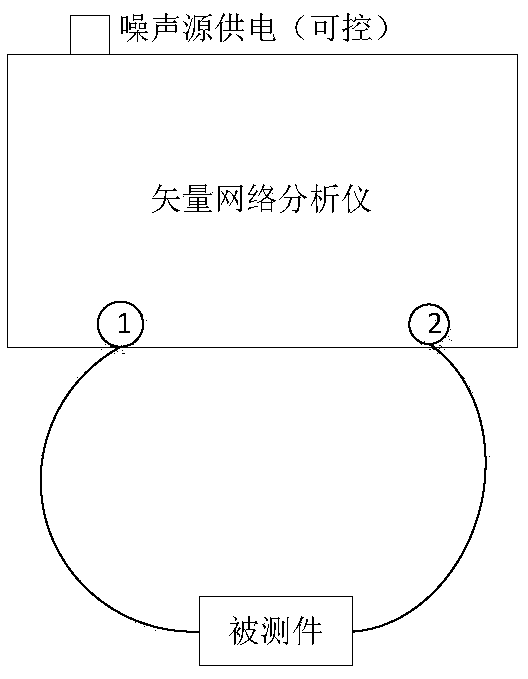
ActiveCN108828336ATroubleshoot match errorsImprove accuracyNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementGain–bandwidth productComputer science
The invention discloses a noise coefficient test method based on a vector network analyzer and a noise source, and belongs to the technical field of test. The method can be used to overcome the problem of a matching error between a tested piece and an instrument, is especially suitable for the condition that the tested piece is not matched well, and can be used to improve the test accuracy. The method is used in combination with a noise receiver of the vector network analyzer, the dynamic test range is widened, and both low and high noise coefficients can be measured accurately via the method;the vector network analyzer is used to measure the gain of the test piece; the vector network analyzer calibrates an error item via a port to obtain the most accurate gain of the test piece; the noise source is used to represent the receiver; and the noise source represents a gain bandwidth product of the receiver, the gain bandwidth product is measured accurately via formulas in cold and hot states, and the noise source can be traced back.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIS TECH INSTR CO LTD
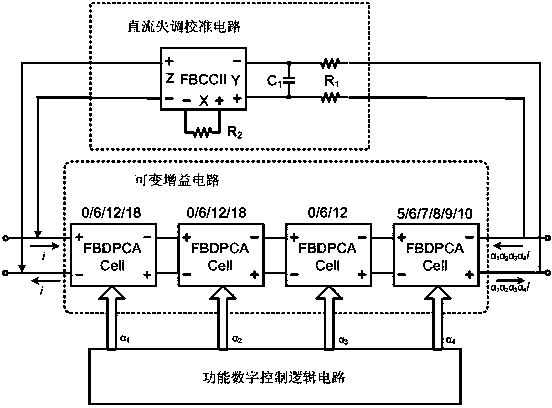
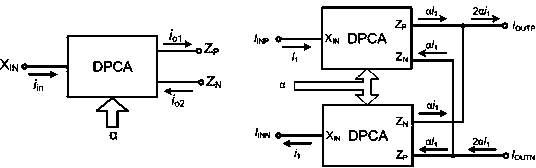
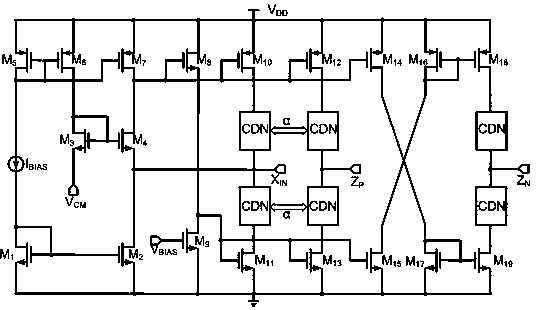
Variable gain amplifier in current mode
ActiveCN104393845AReduce power consumptionImprove input and output dynamic rangeNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceHigh resistanceControl signal
The invention discloses a novel variable gain amplifier circuit in a current mode. The variable gain amplifier circuit comprises a variable gain circuit, a functional digital control logic circuit and a direct current offset calibration circuit, wherein the variable gain circuit comprises four full balanced digital programmable current amplifiers; the functional digital control logic circuit is used for coding a control signal into a binary signal and then controlling gain decibels of the variable gain circuit; and the direct current offset calibration circuit feeds a low-frequency signal output by the variable gain circuit back to an input end of the variable gain circuit to form a negative feedback loop. In the amplifier circuit in the current mode, signal input is low resistance, signal output is high resistance, and a circulating signal is a current signal and is not influenced by the magnitude of voltage. A variable gain amplifier in the current mode is in a Class-AB output structure, so that the power consumption of the circuit is greatly reduced. The current amplifier is free from limitation of a gain bandwidth product, so that the bandwidth is not limited on any gain almost.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Gain-boosted operational amplifier applicable to TFT-LCD drive circuit
InactiveCN105322897AIncrease the output resistanceIncrease DC GainDifferential amplifiersPositive-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention relates to large-scale integrated circuits, and aims to boost input transconductance and output resistance of an amplifier, further improve direct current gain of the amplifier and finally realize boost of direct current gain and gain bandwidth product of the amplifier under the condition of same chip area. Therefore, the technical scheme of the invention is a gain-boosted operational amplifier applicable to a TFT-LCD drive circuit. The gain-boosted operational amplifier applicable to the TFT-LCD drive circuit is composed of a Recycling folded cascade amplification stage, an output resistance boosting loop, a transconductance boosting loop and a high swing output stage; differential mode signals Vin- and Vin+ are input through the Recycling folded cascade amplification stage, then, the signals are subjected to the cross positive feedback effect of the output resistance boosting loop stage and the transconductance boosting loop stage and further subjected to current multiplication of a cascade current mirror, and finally, the signals are output to an output end through the high swing output stage. The gain-boosted operational amplifier applicable to the TFT-LCD drive circuit is mainly applied to the large-scale integrated circuits.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Double-second-order active RC filter circuit and compensation method thereof
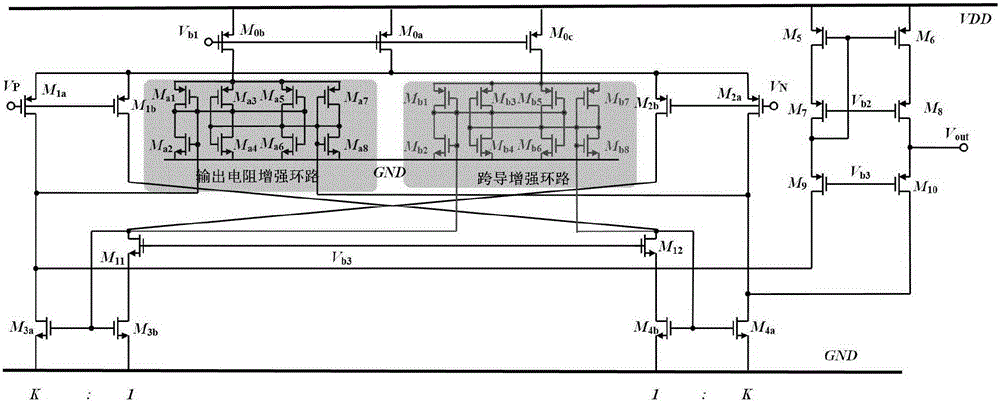
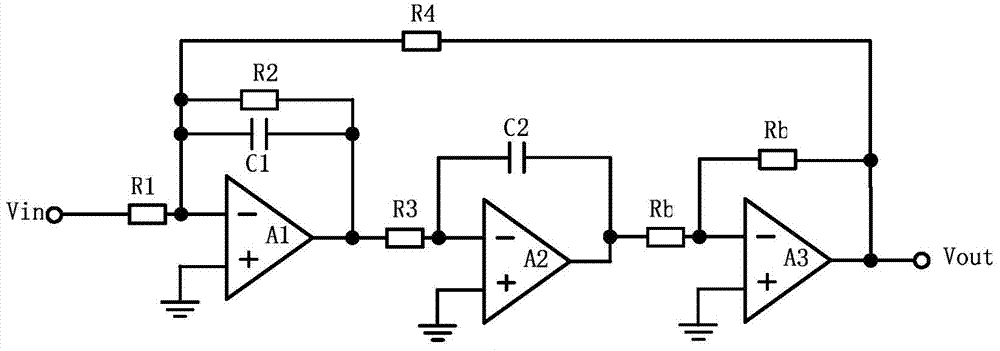
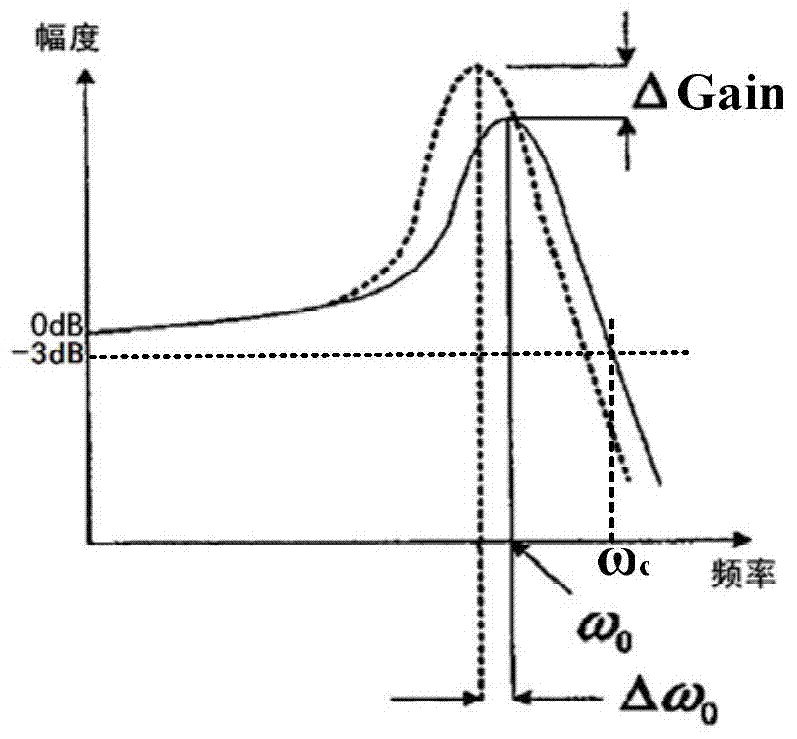
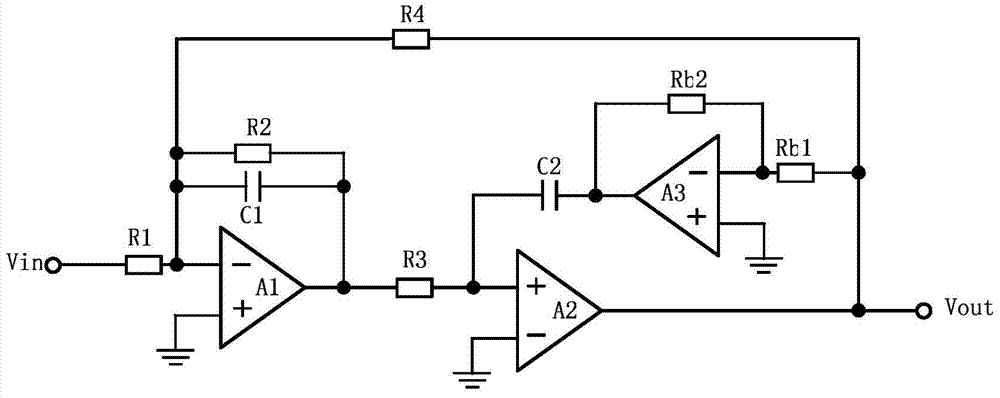
ActiveCN103795372AMinimize sensitivityReduce power consumptionFrequency selective two-port networksIntegratorFeed forward network
The invention relates to a double-second-order active RC filter circuit and a compensation method thereof. The circuit comprises an Akerberg-Mossberg double-second-order unit and a resistor R5, wherein one end of the resistor R5 is connected with the inverted input end of an operational amplifier A1 of the Akerberg-Mossberg double-second-order unit, and the other end of the resistor R5 is connected with the output end of an operational amplifier A3 of the Akerberg-Mossberg double-second-order unit. According to the double-second-order active RC filter circuit and the compensation method thereof, the double-second-order active filter circuit with a high Q value is built by using the operational amplifiers with low gain bandwidth products, sensitiveness to the gain bandwidth products of the operational amplifiers of the Q value is minimized, and power consumption of a filter is reduced. An active feedback network is built by means of an existing reverse buffer, leading phase quantity matched with the gain bandwidth products of the operational amplifiers is provided, and the best phase compensation is conducted on consumption of two integrators of a feed-forward network in a frequency range of a filter transmission band.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RUNXIN INFORMATION TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com