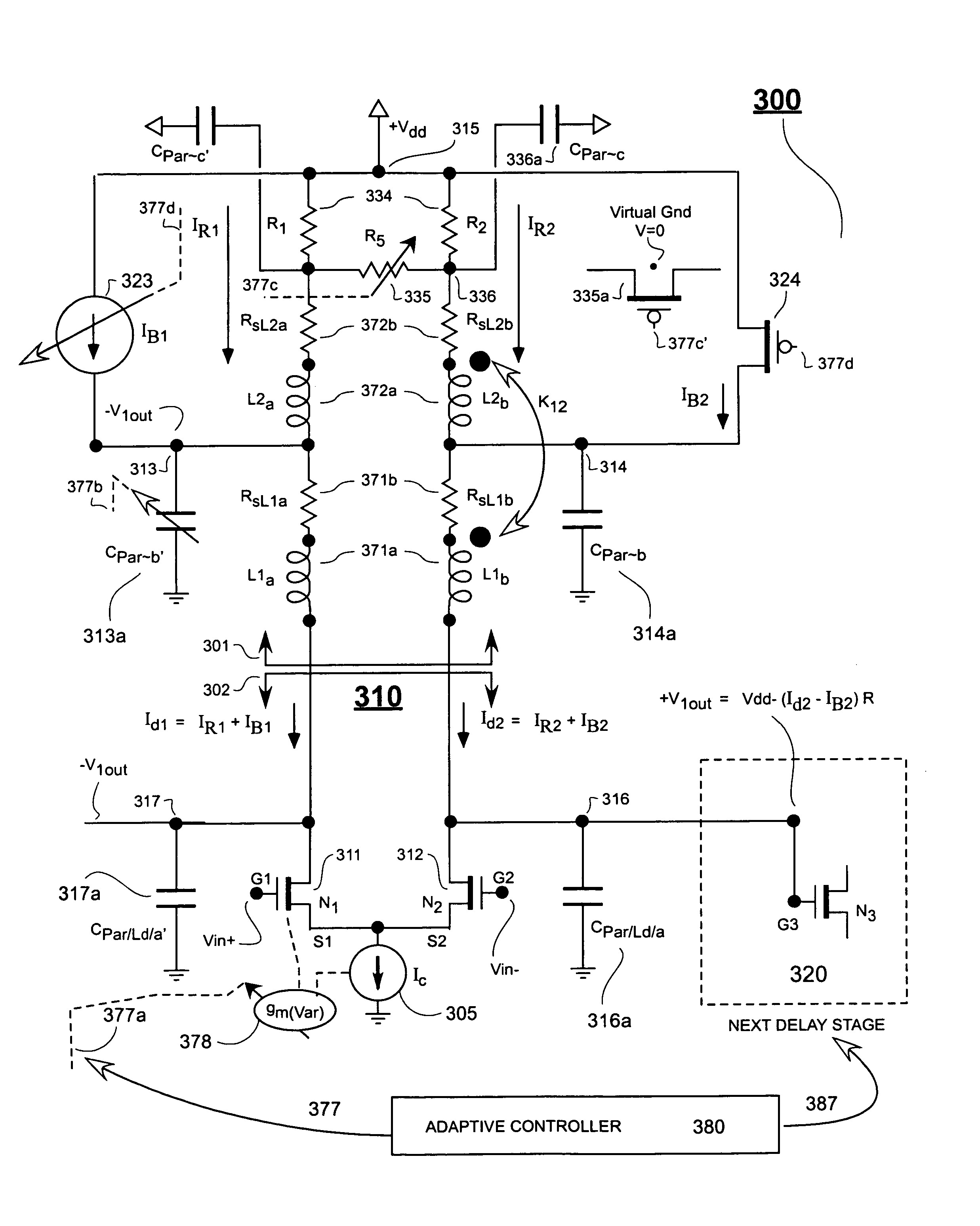
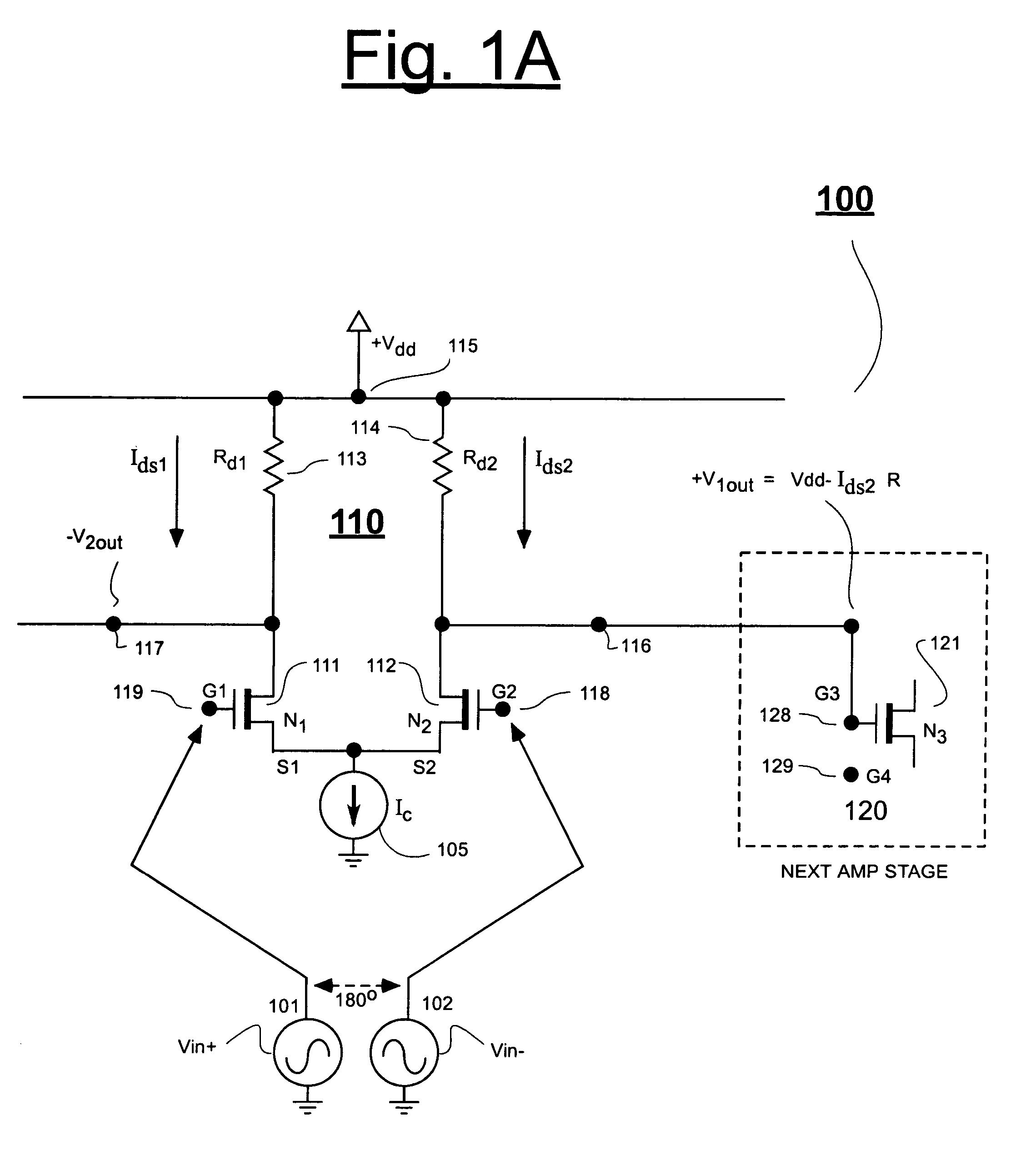
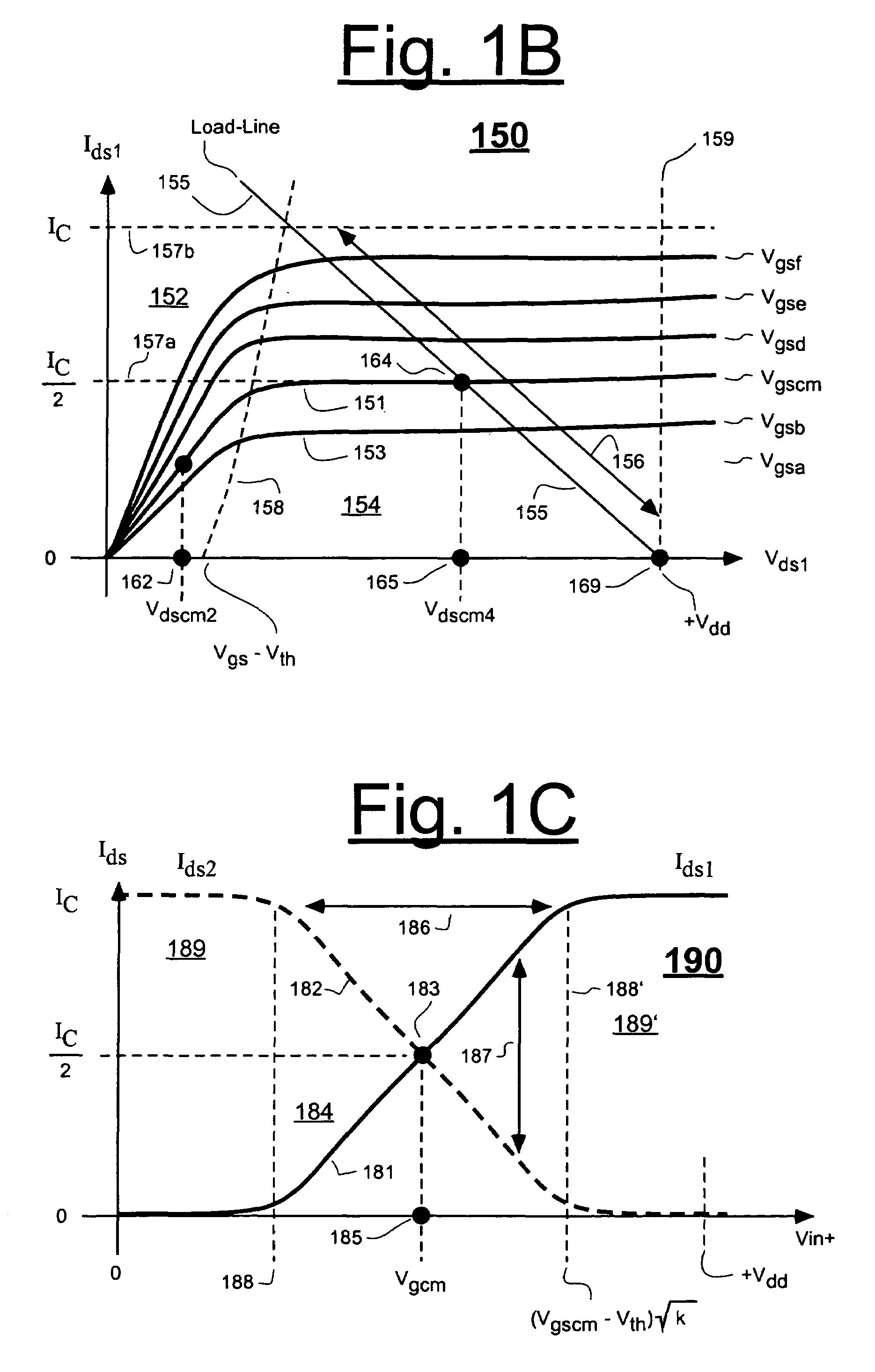
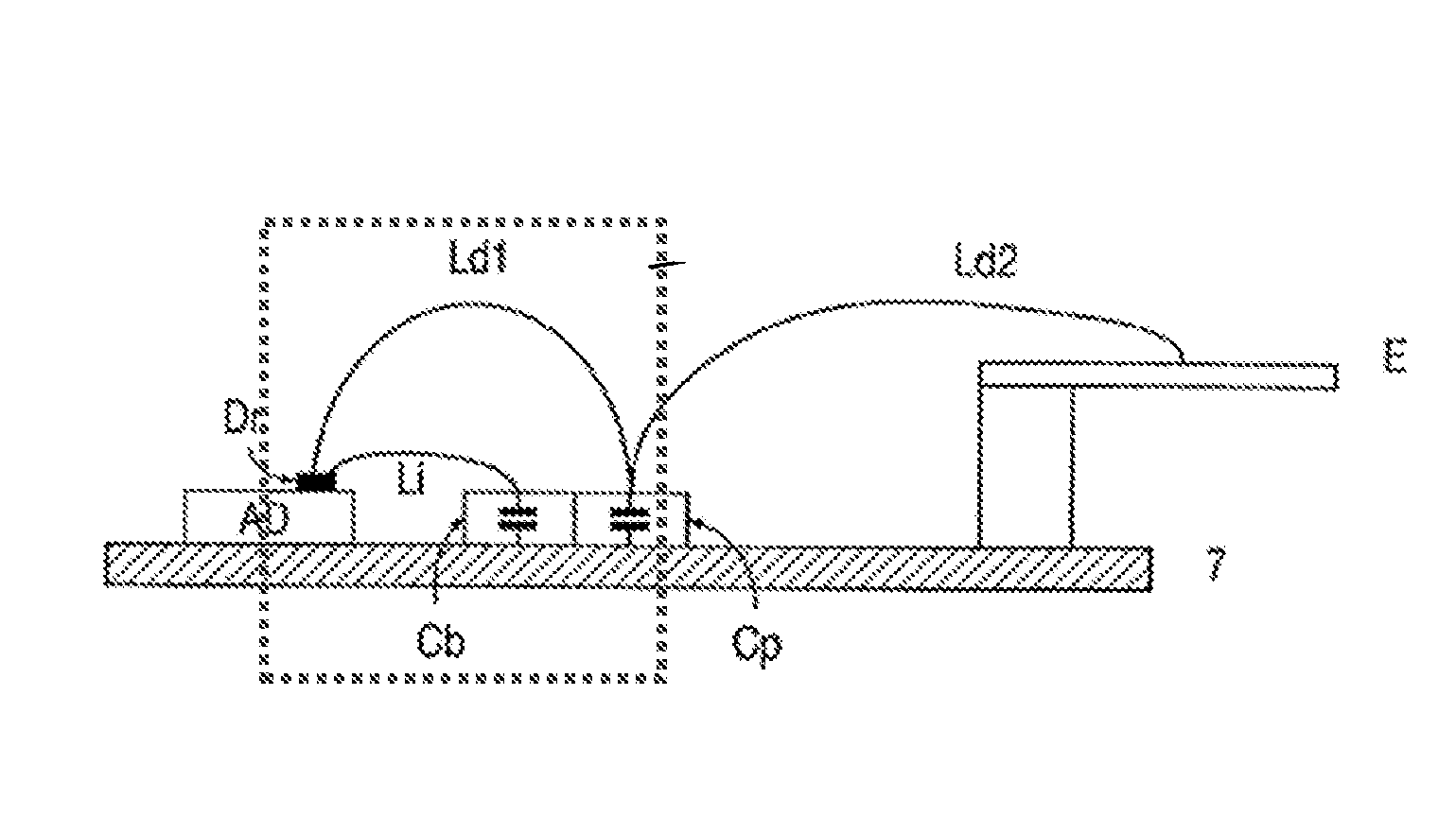
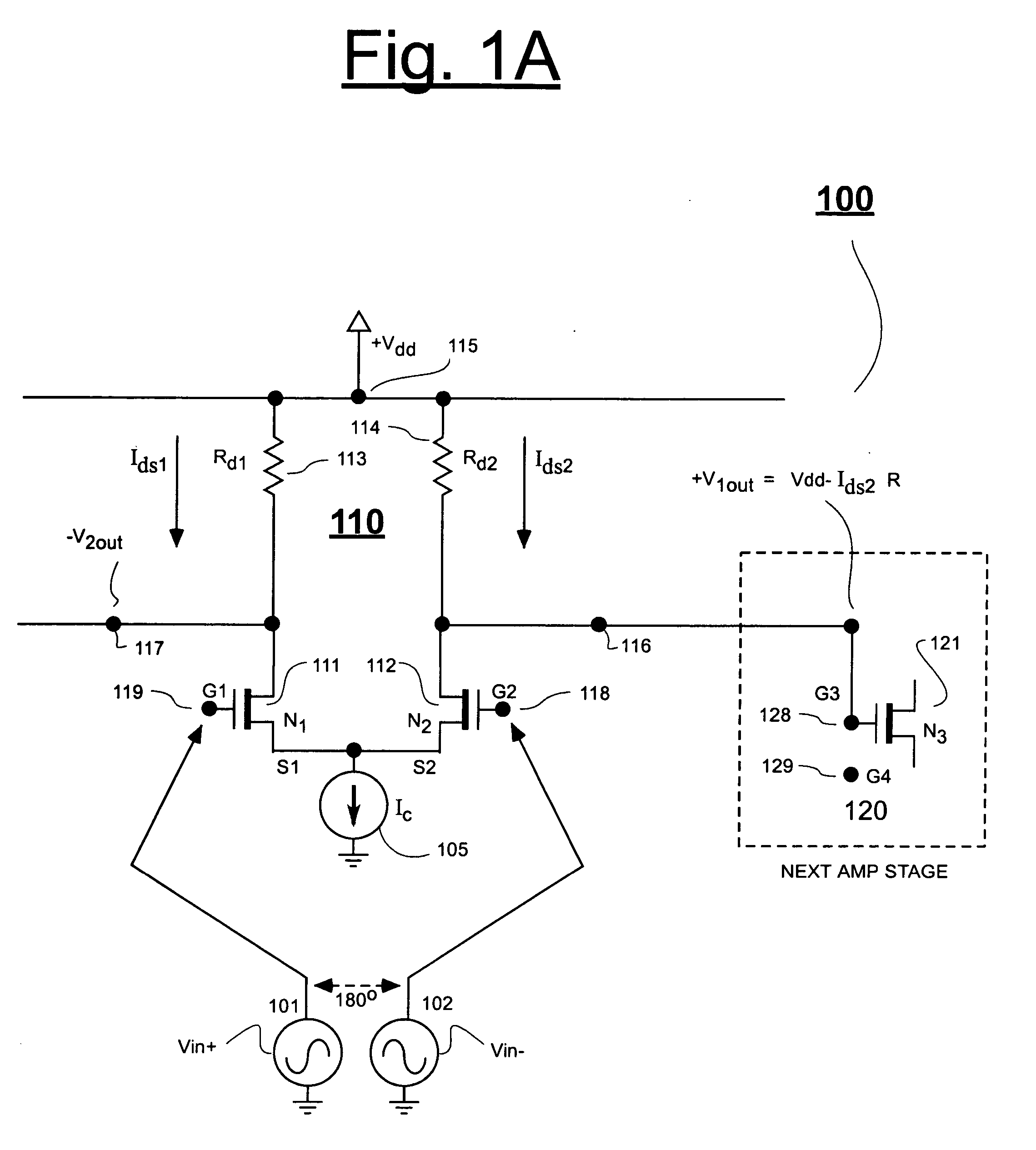
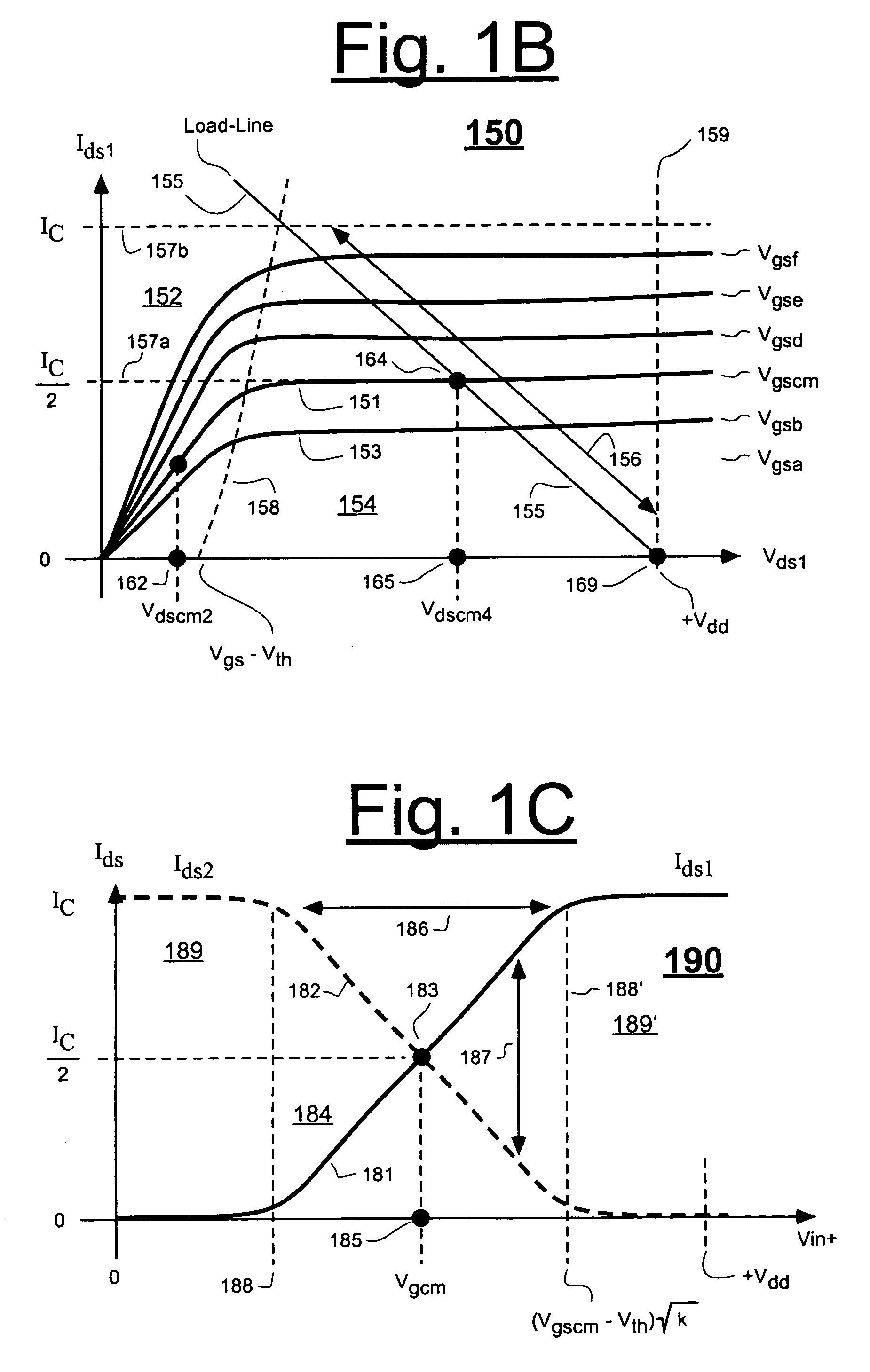
Patents
Literature
1136results about "Amplifier modifications to extend bandwidth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
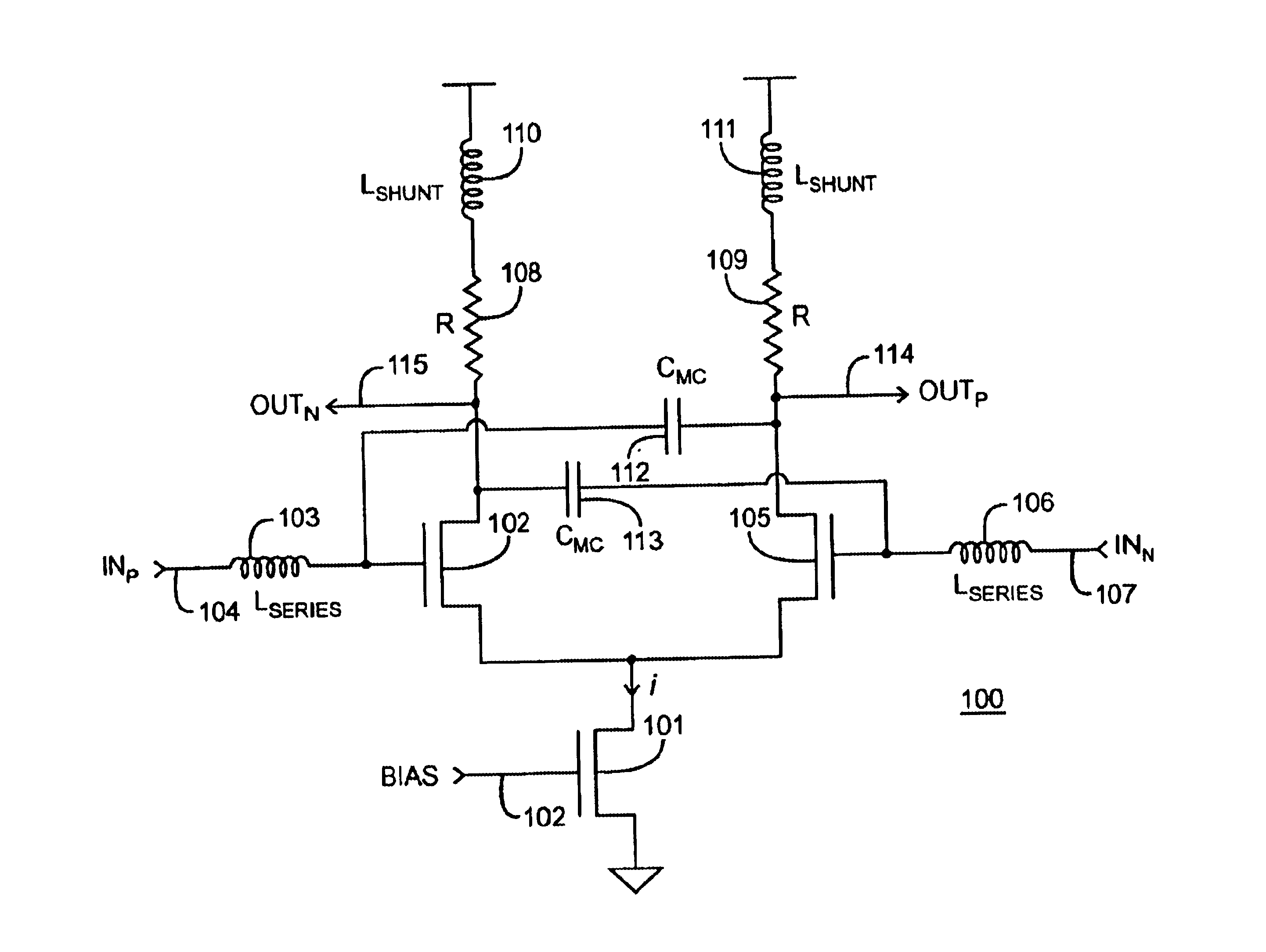
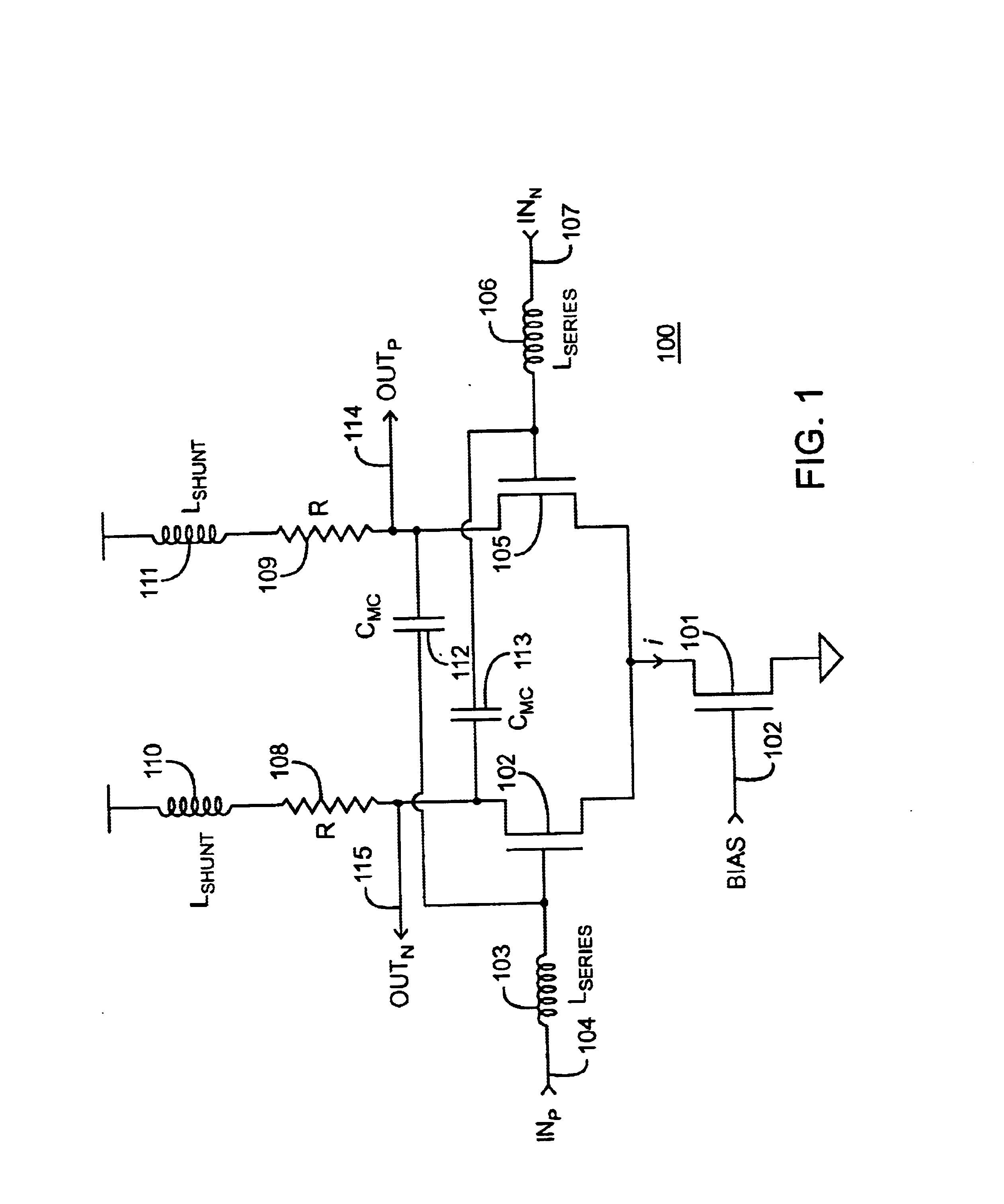
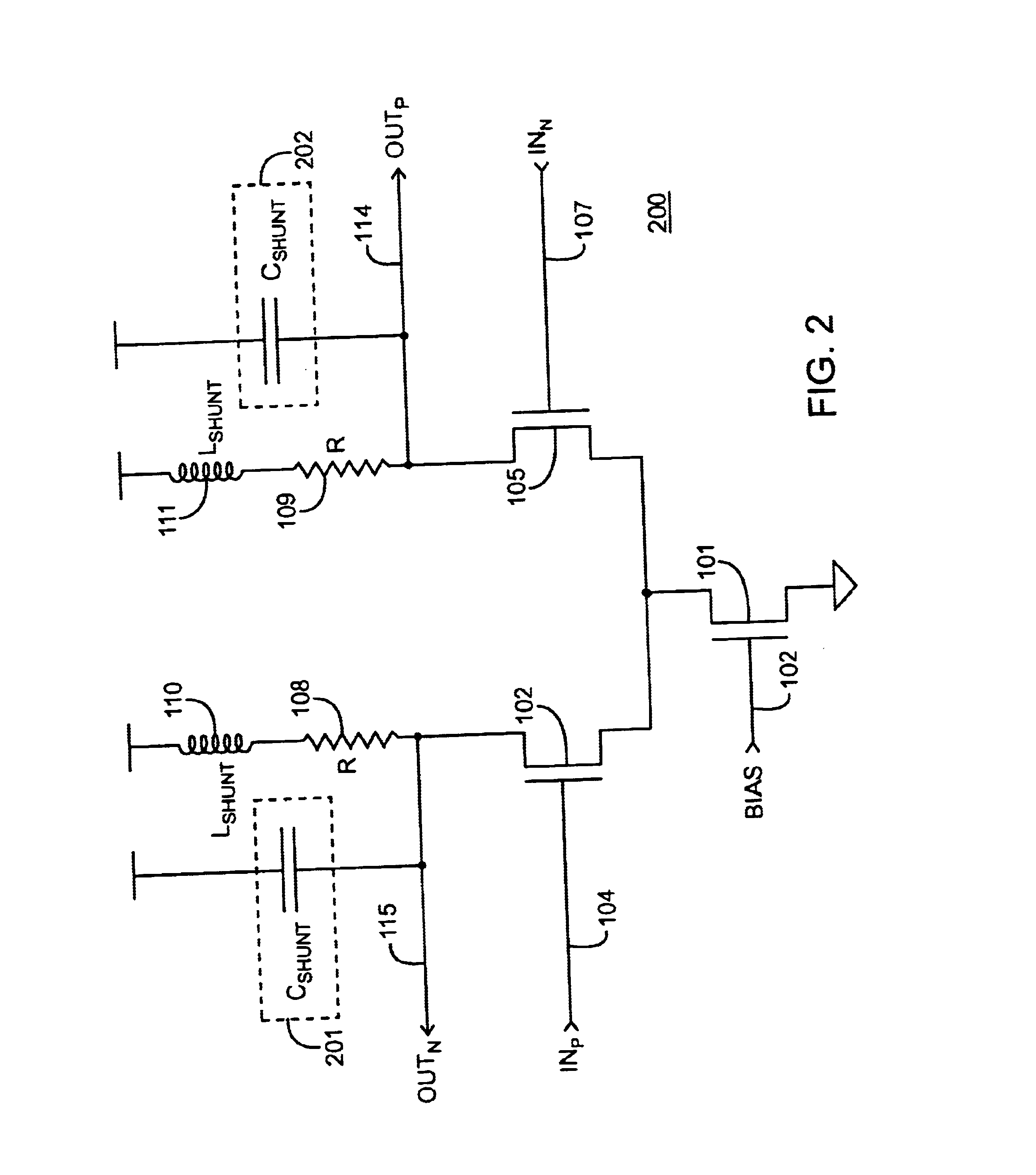
Current-controlled CMOS wideband data amplifier circuits
InactiveUS6624699B2Maximum bandwidth expansionReduced Miller CapacitanceAmplifier combinationsAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceCapacitanceCMOS
Expansion of the bandwidth of a wideband CMOS data amplifier is accomplished using various combinations of shunt peaking, series peaking, and miller capacitance cancellation. These various combinations are employed in any of the amplifier input stage, in intermediate stages, or in the last stage.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
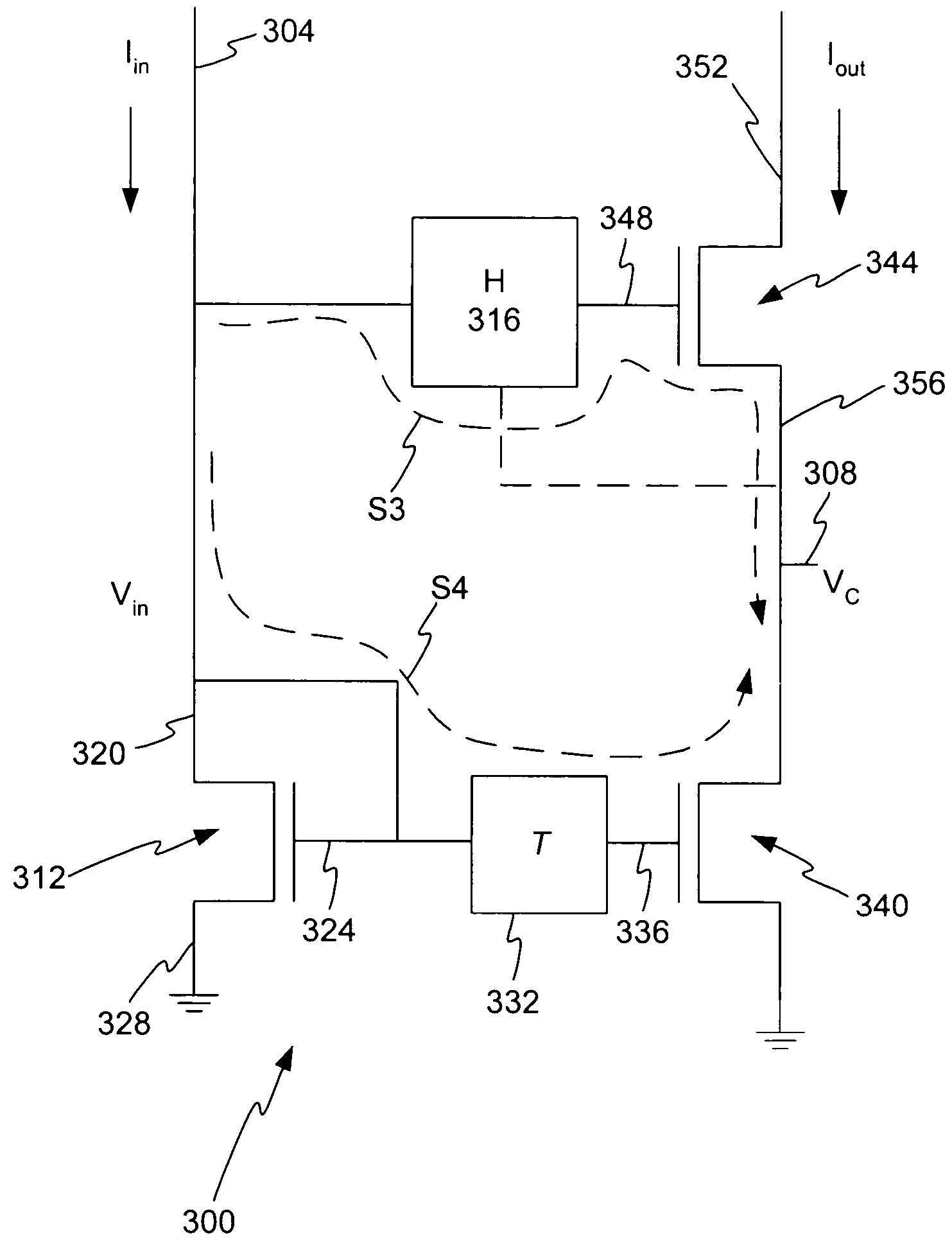
Method and apparatus for increasing the linearity and bandwidth of an amplifier
ActiveUS20050083130A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric variable regulationCascodeEngineering
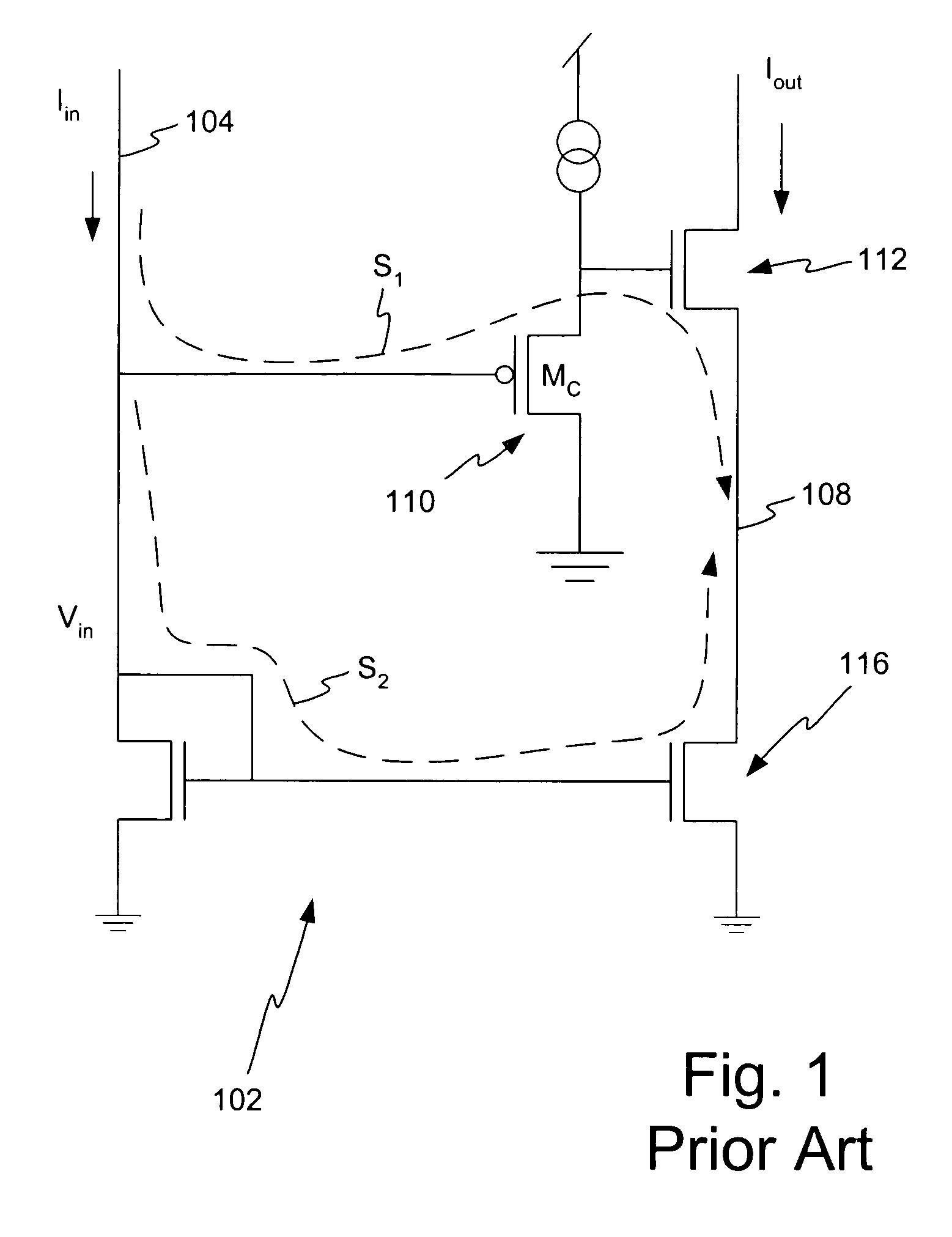
A method and apparatus is disclosed for improving high frequency performance of an amplifier, such as for example, a current mirror. In one embodiment, a delay element is introduced in a current mirror signal path to account for signal propagation delay that may exist in one or more alternative signal paths. The delay element maintains desired phase alignment at a cascade node of the current mirror thereby establishing, in one embodiment, the cascode node (Vc) in an AC ground state. To extend current mirror high frequency capability an embodiment is disclosed having cross-coupled capacitors, active elements, or one or more other devices configured to provide positive feedback to one or more current mirror inputs. The positive feedback may be selectively configured to increase the operational bandwidth of the current mirror.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
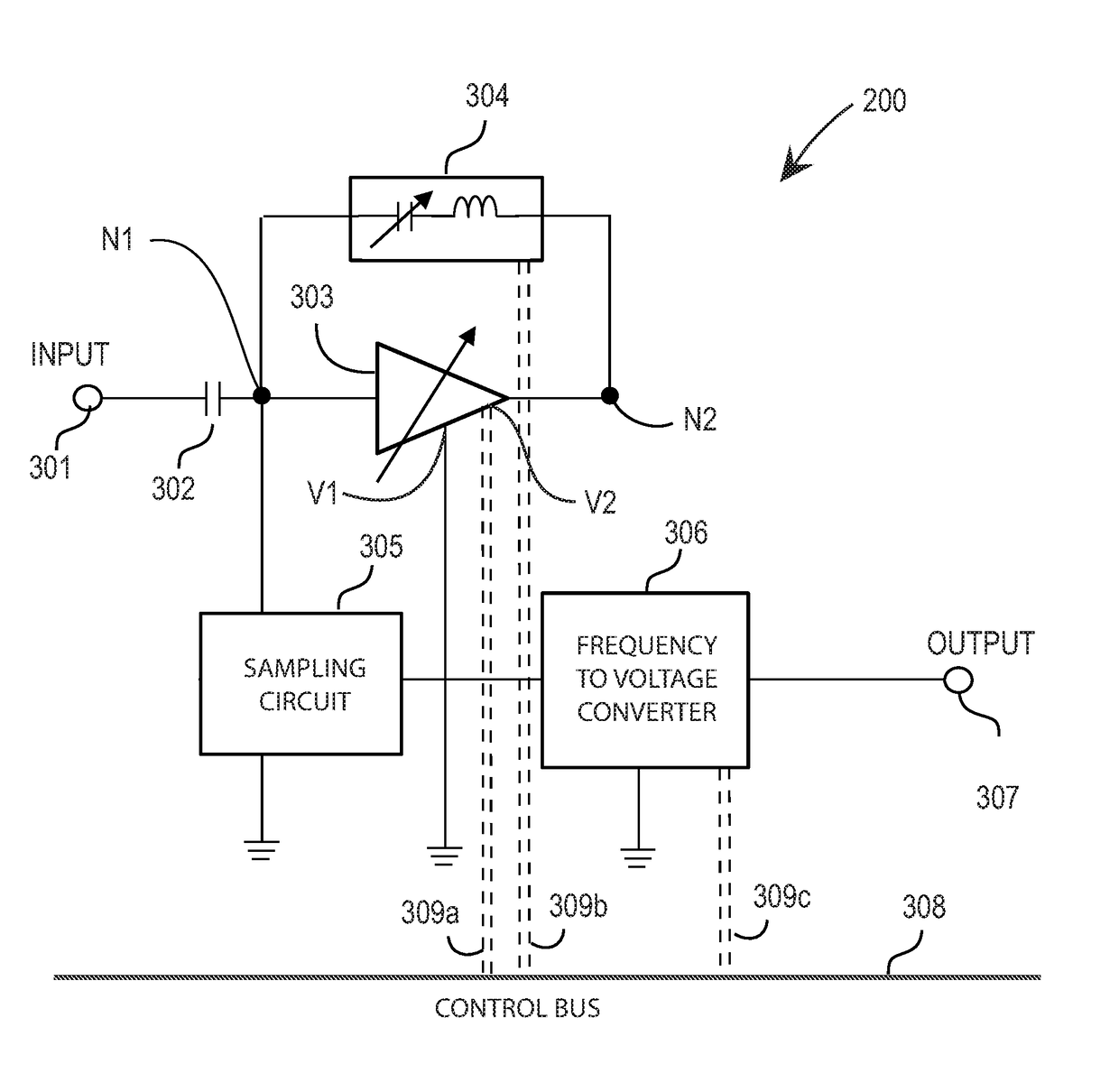
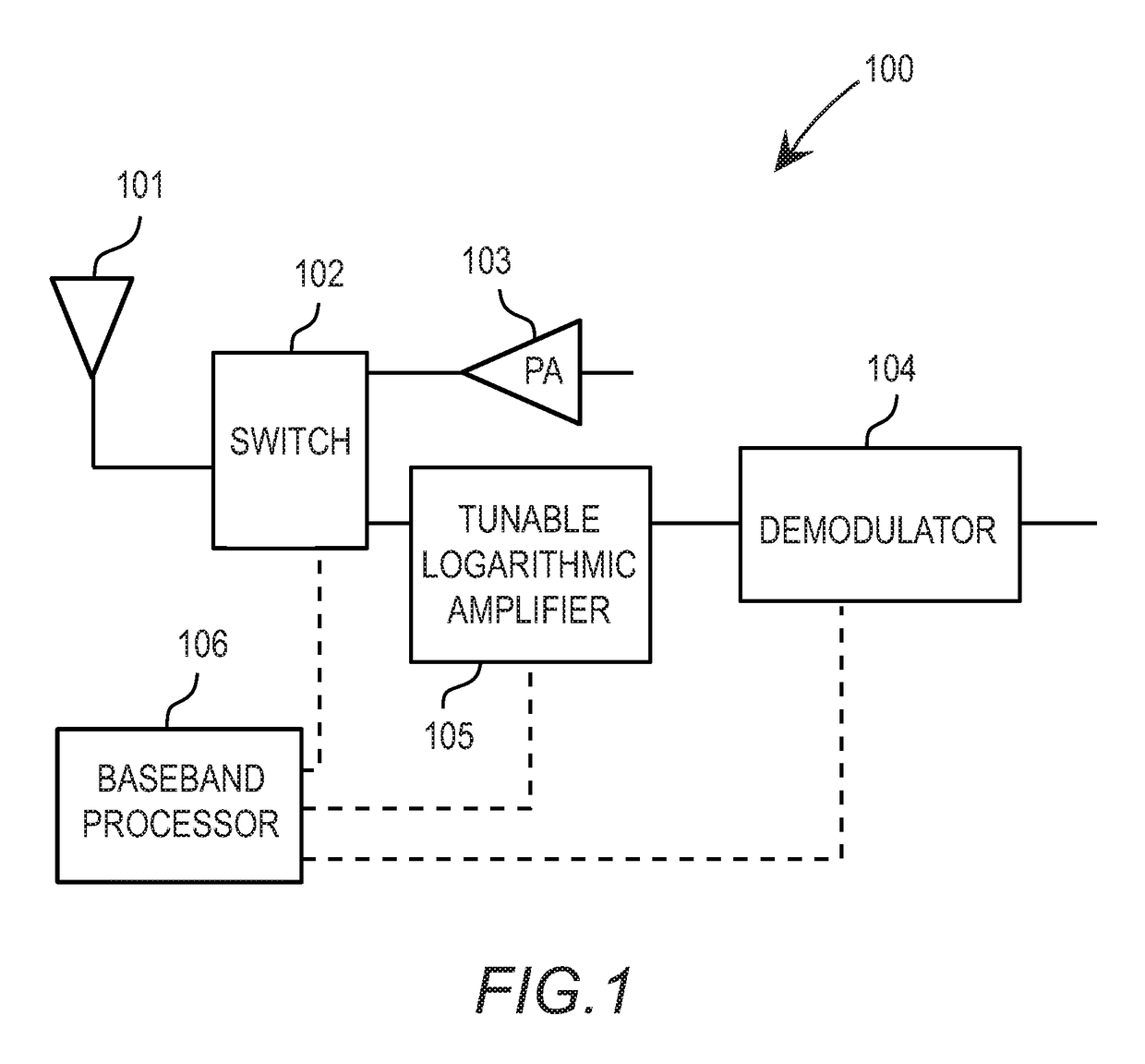
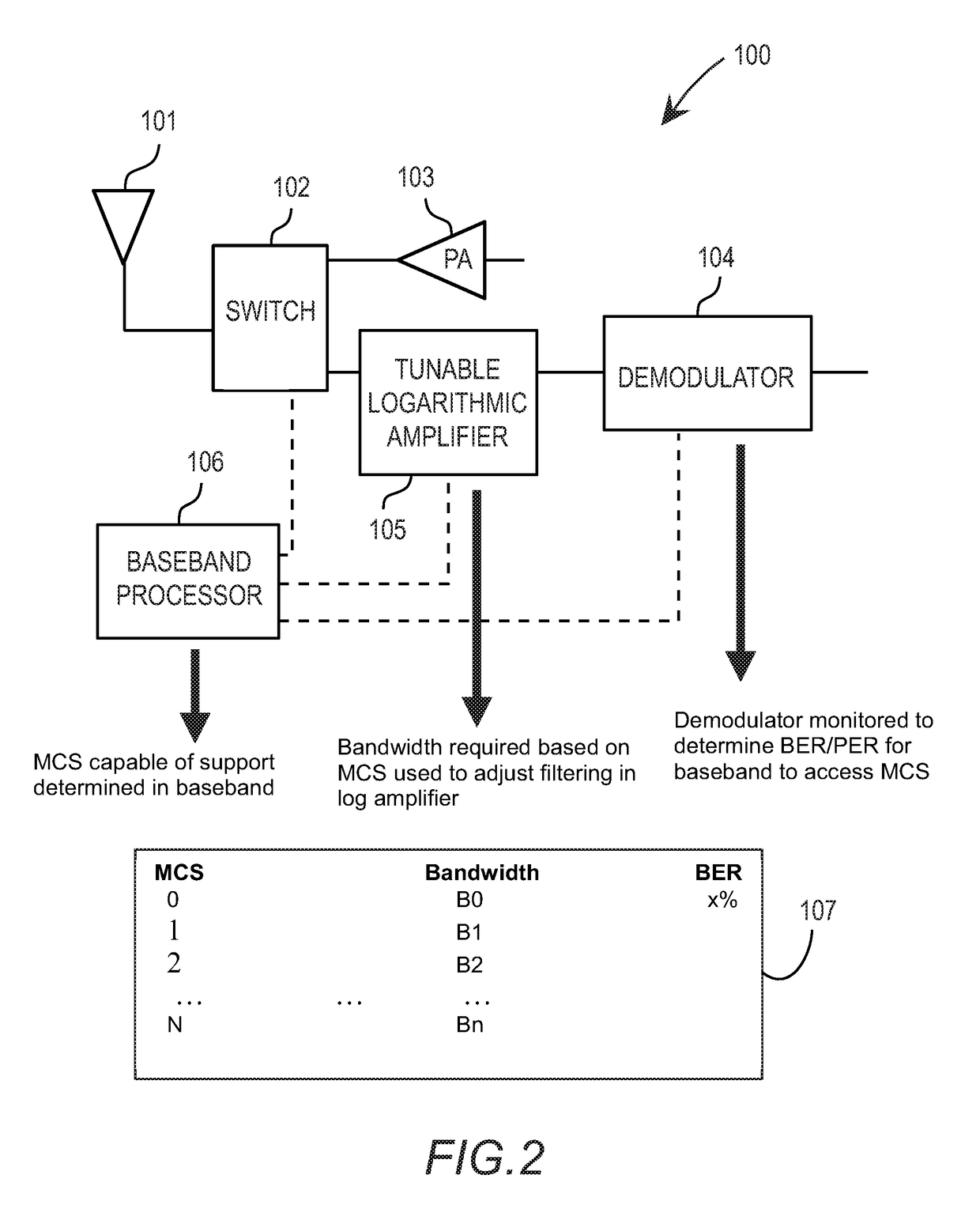
Tunable logarithmic amplifier
ActiveUS9755580B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePower amplifiersAudio power amplifierControl signal
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS (SAN DIEGO) INC
Semiconductor device with feedback control
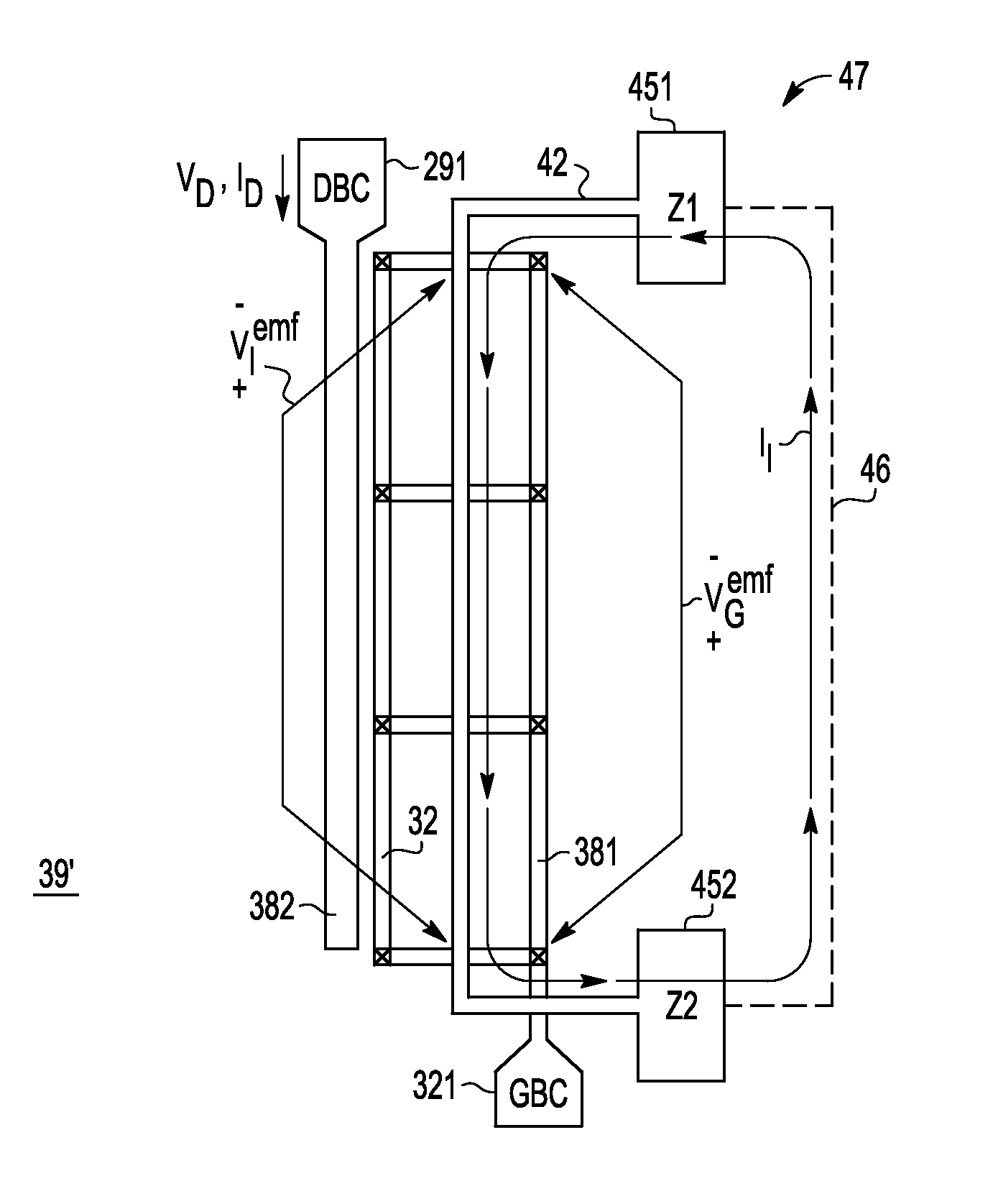
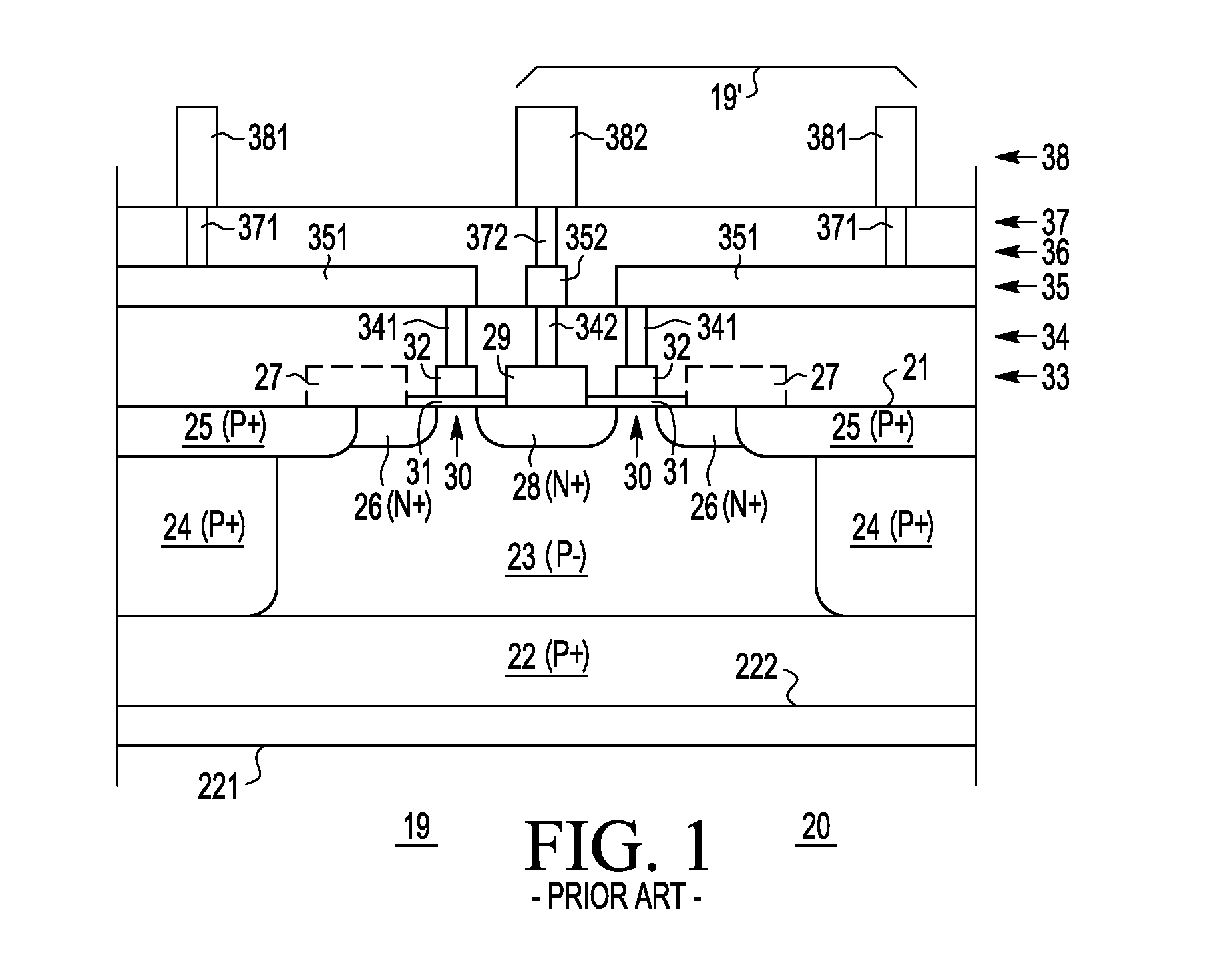
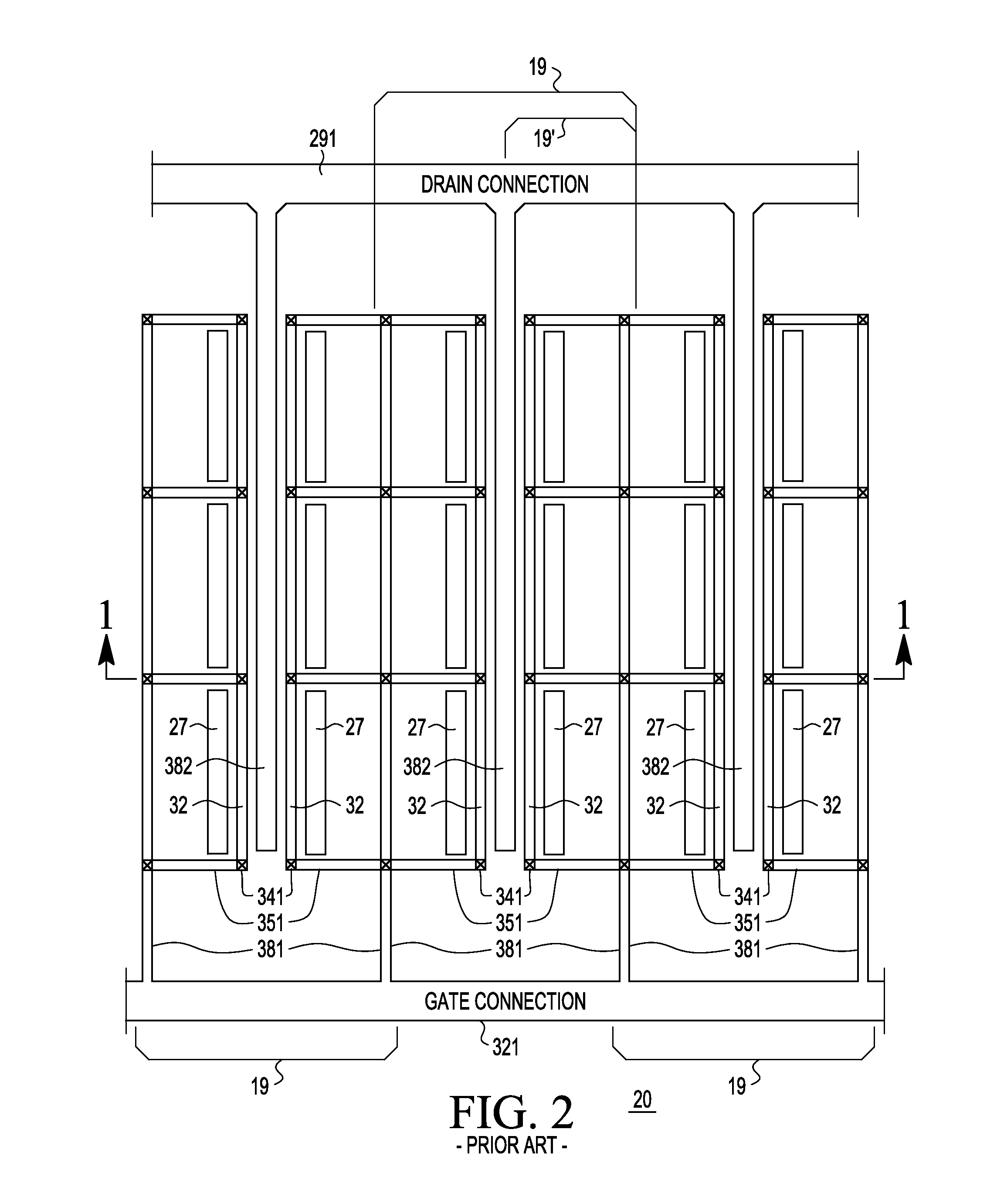
An electronic element (39′, 39, 40) having feedback control is provided by placing an inductive interposer (42) between the output connection or bus (382) and the input connection or bus (381), wherein the inductive interposer (42) forms part of a closed circuit (47) with the inductive interposer (42) substantially parallel with the output connection or bus (382) and input connection or bus (381) for a distance permitting significant inductive coupling therebetween. In a preferred embodiment, the closed circuit (47) containing the inductive interposer (42) comprises impedance ZT. By including various circuit elements (e.g., resistance, capacitance, and / or inductance) in ZT, the output-to-input feedback can be modified to advantage. This greatly increases the available design freedom, especially for power devices, such as for example, field effect, MOSFET, LDMOS. bipolar and other power devices that use substantially parallel input and output bus structures.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Amplifier arrangement for ultra-wideband applications and method
InactiveUS20070085617A1Increase frequencyReduced frequency dependenceAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesOscillations generatorsUltra-widebandAudio power amplifier
An amplifier arrangement for ultra-wideband, UWB, applications and. a method to amplify a UWB signal are presented. A transistor, whose control input forms an input of the arrangement, is connected to a resonant circuit having a controllable resonator frequency. At the resonator circuit, an output of the arrangement is formed. The resonant circuit includes a frequency determining inductance whose value is controllable. By doing this, it is possible to preselect different frequency bands, while achieving the same gain characteristics in each band.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Active balun device
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
RF power transistor circuit
A radio frequency (RF) power transistor circuit includes a power transistor and a decoupling circuit. The power transistor has a control electrode coupled to an input terminal for receiving an RF input signal, a first current electrode for providing an RF output signal at an output terminal, and a second current electrode coupled to a power supply voltage terminal. The decoupling circuit includes a first inductive element, a first resistor, and a first capacitor coupled together in series between the control electrode of the first power transistor and the power supply voltage terminal. The first decoupling circuit is for dampening a resonance at a frequency lower than an RF frequency.
Owner:NXP USA INC
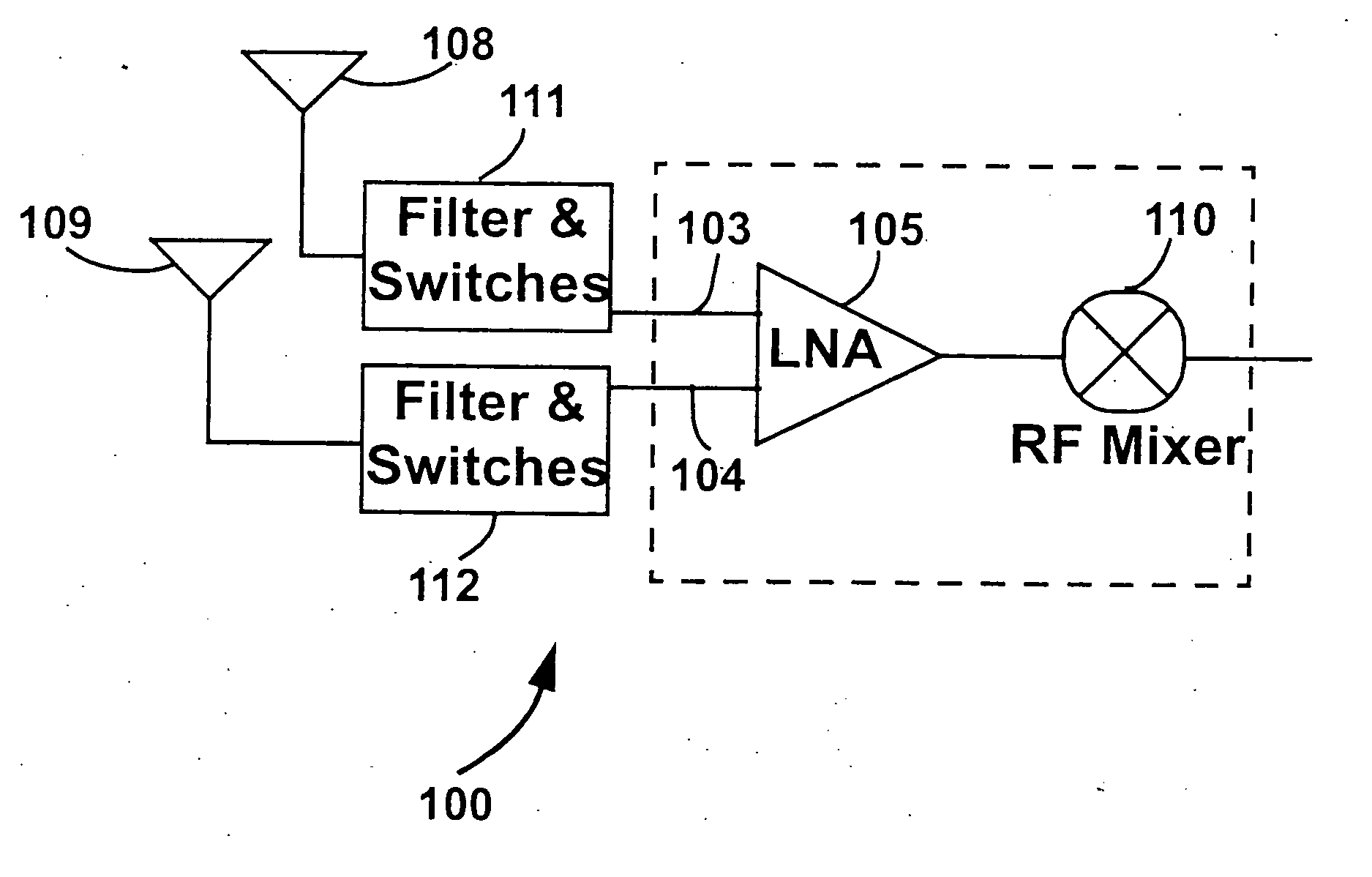
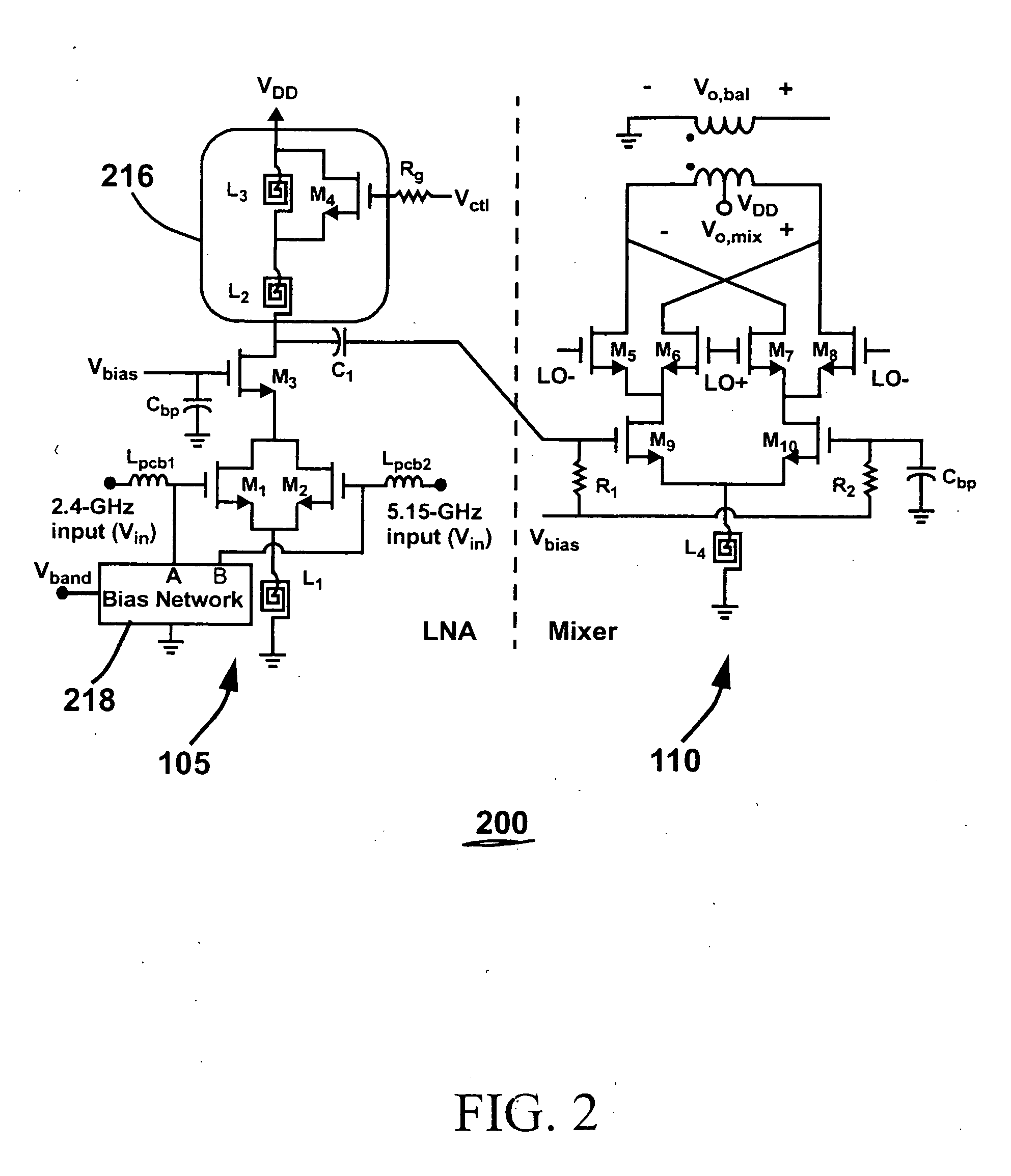
Dual-band CMOS front-end with two gain modes
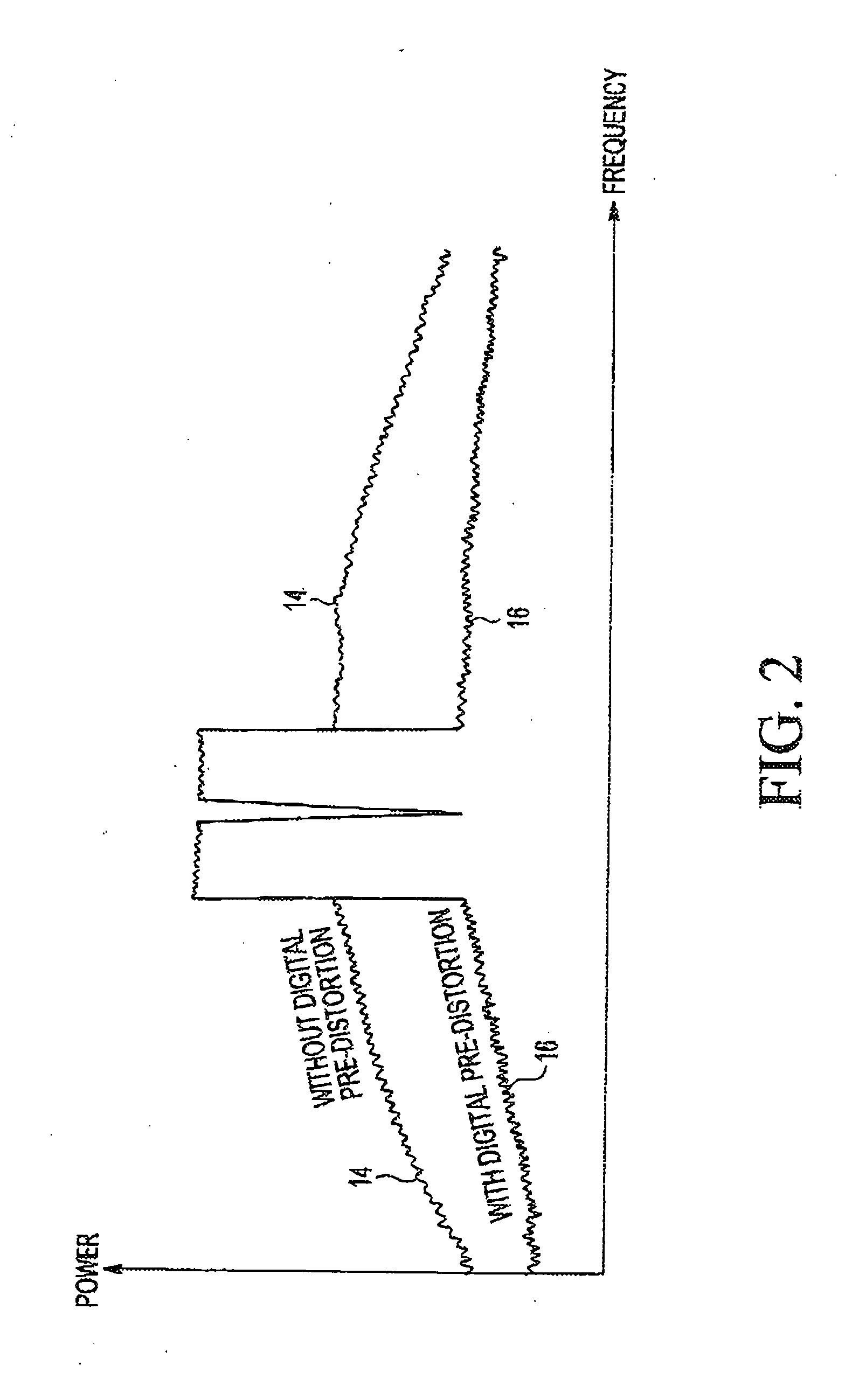
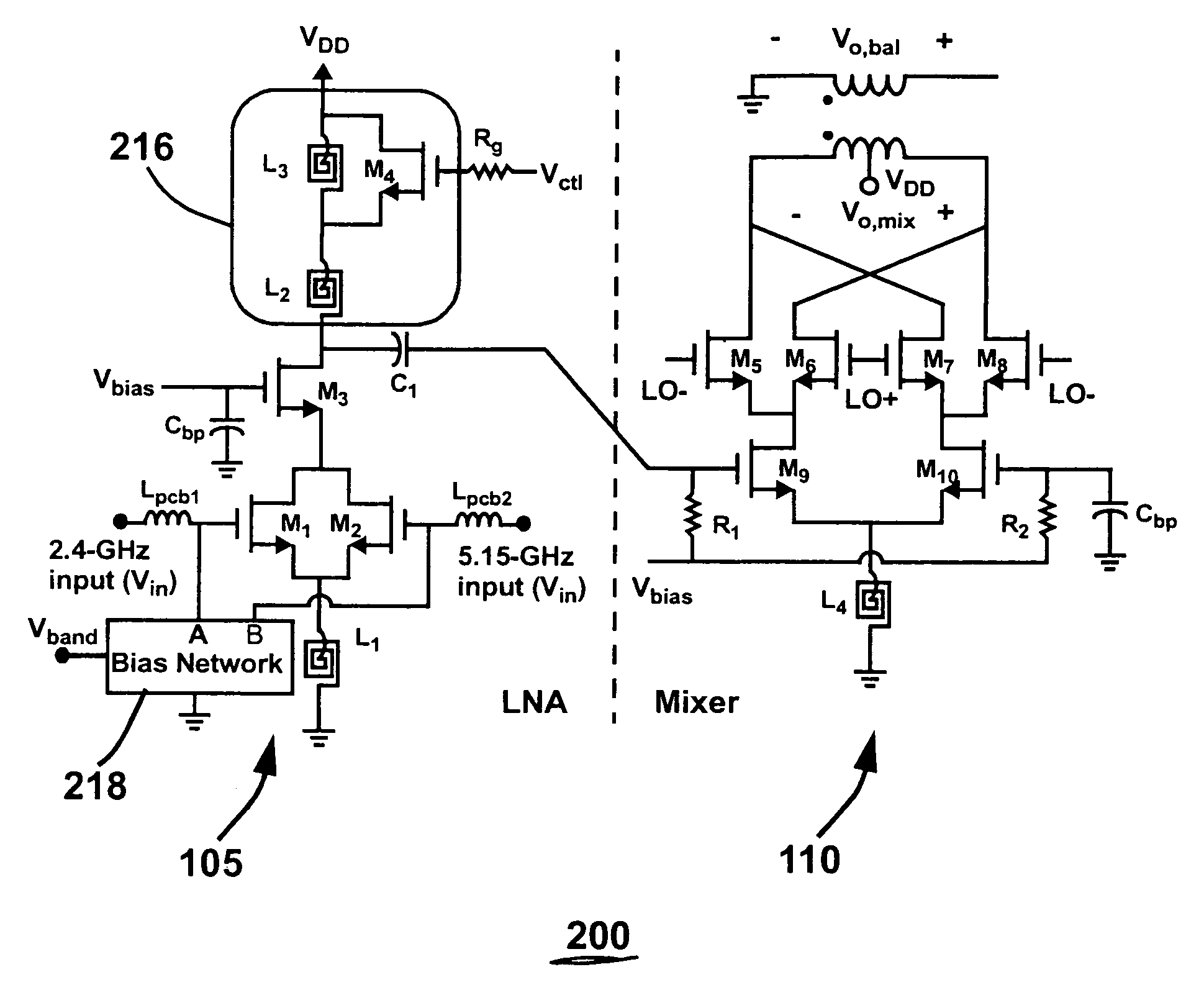
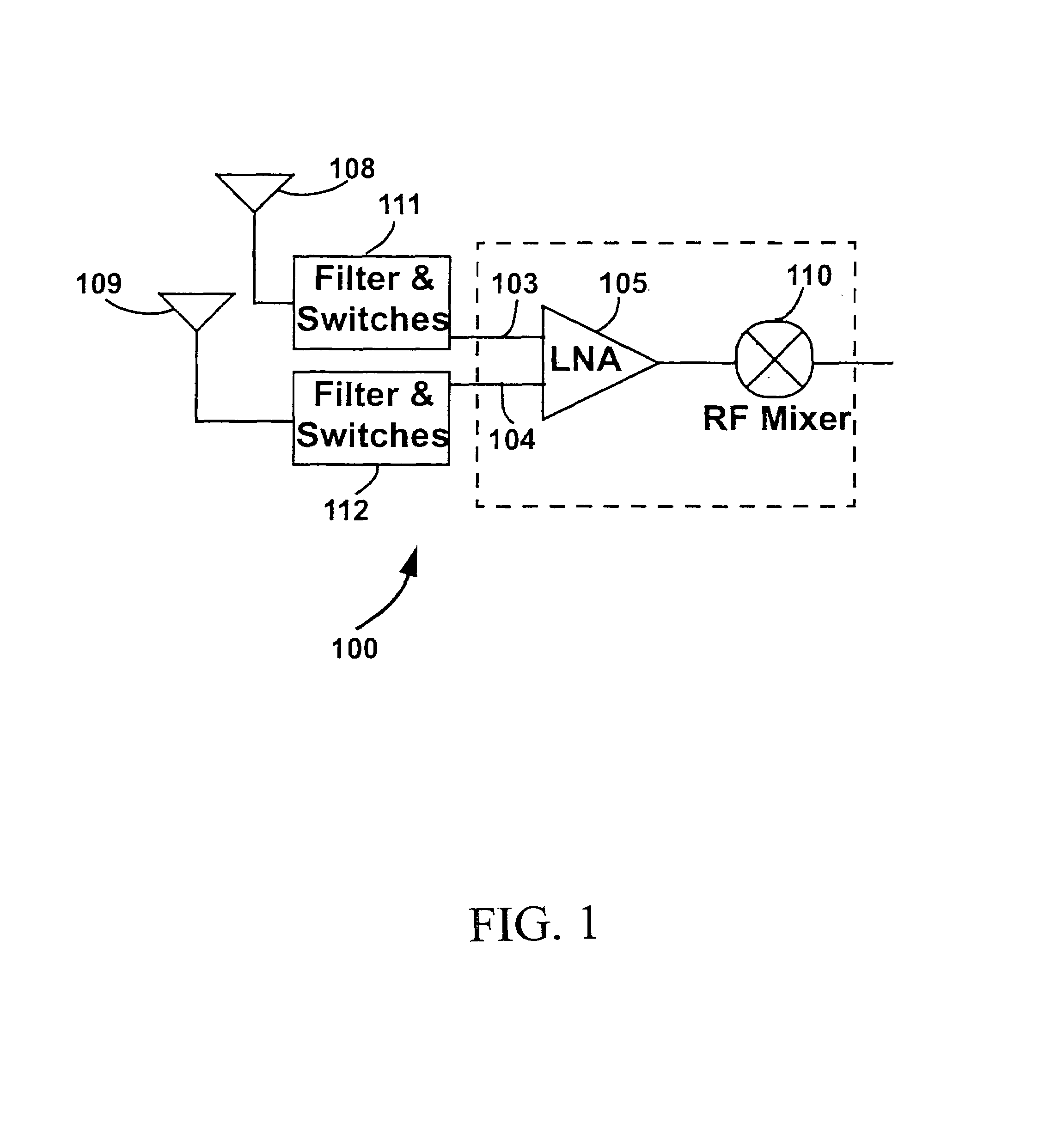
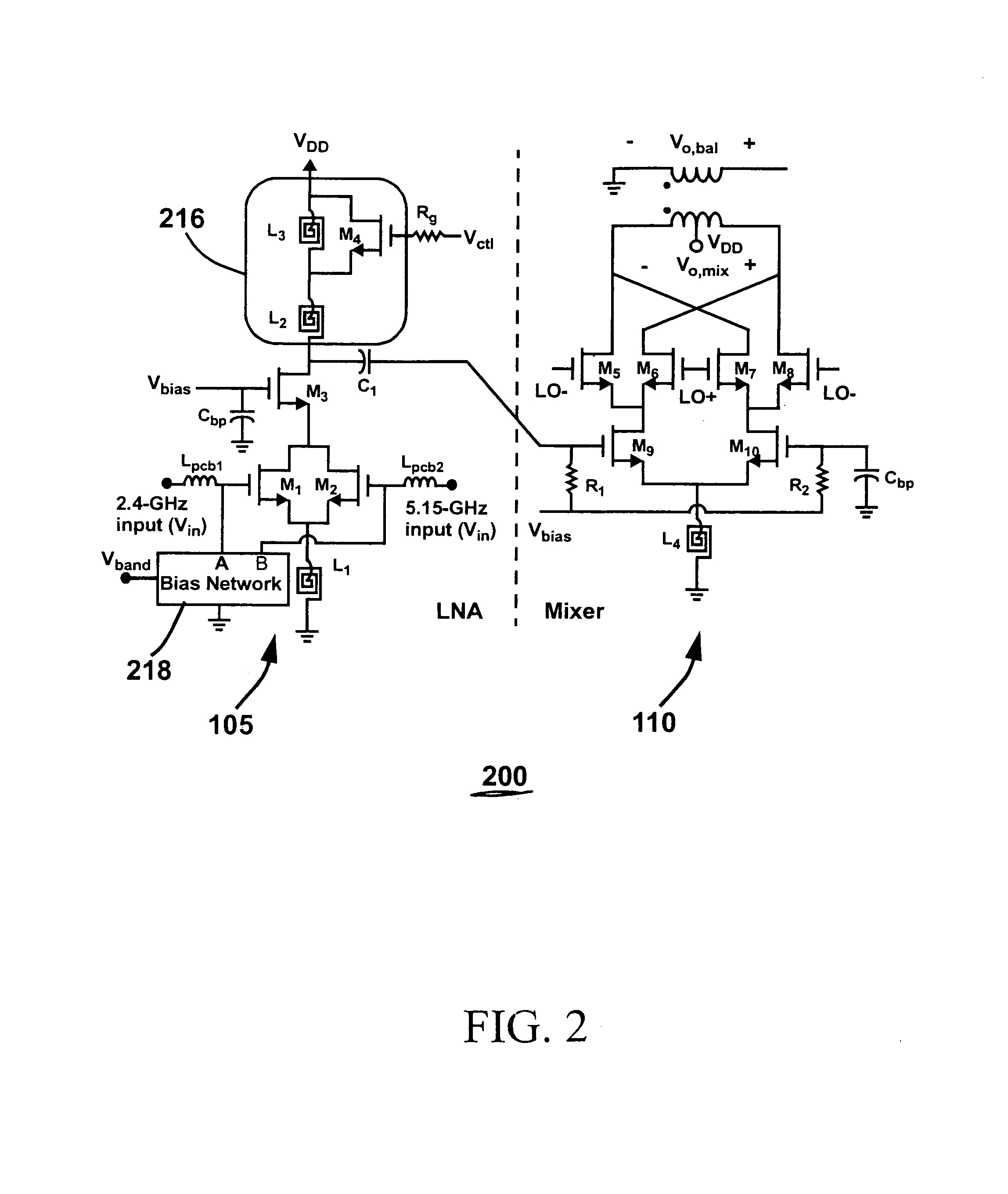
A multi-band low noise amplifier (LNA) 105 includes an input stage having at least two inputs, a first input (103) coupled to a first input transistor for receiving signals in a first frequency band and a second input (104) coupled to a second input transistor for receiving signals in a second frequency band. The second frequency band spaced apart from the first frequency band. A bias network (218) having a band select input is coupled to the first and second input transistor, wherein a signal level applied to the band select input turns on one of the input transistors and turns off the other input transistors. The LNA (105) operates in the first frequency band when the first input transistor is on and the second frequency band when the second input transistor is on. A switched resonator (216) having a control input is provided, wherein application of a control signal to the control input tunes a resonant frequency of the LNA, and provides gain select, for operation in either the first or second frequency band.
Owner:O KENNETH K +1
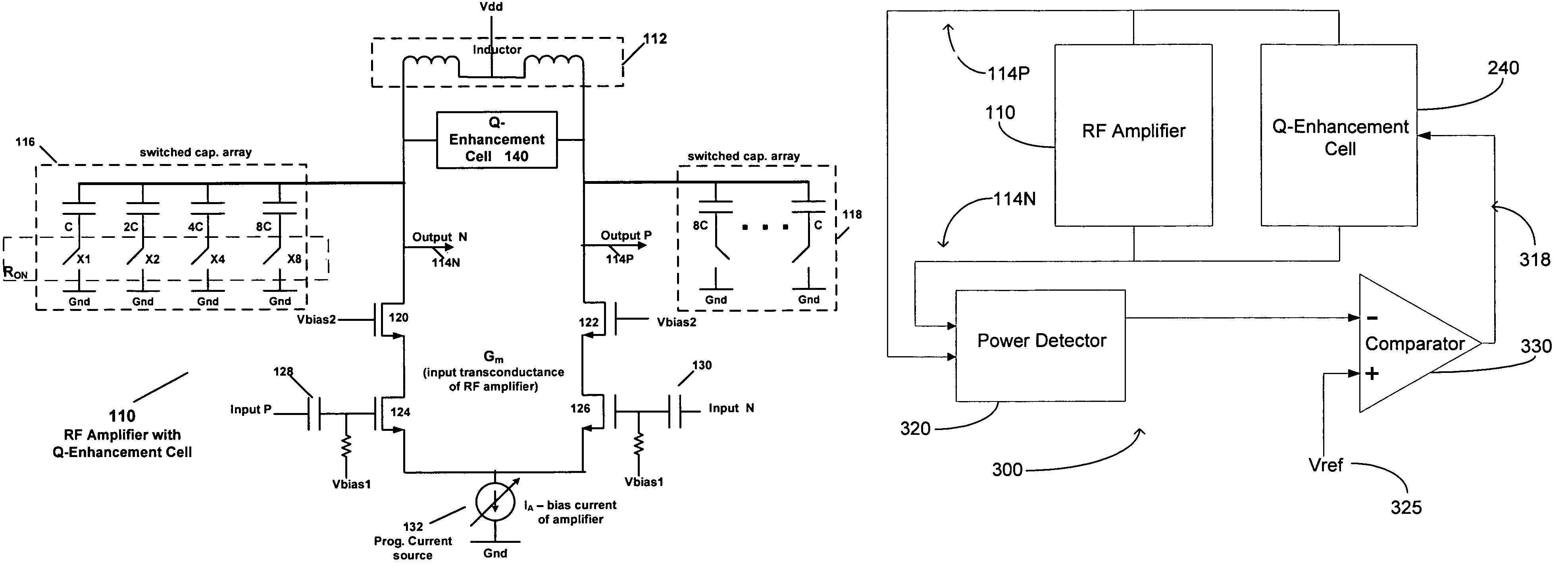
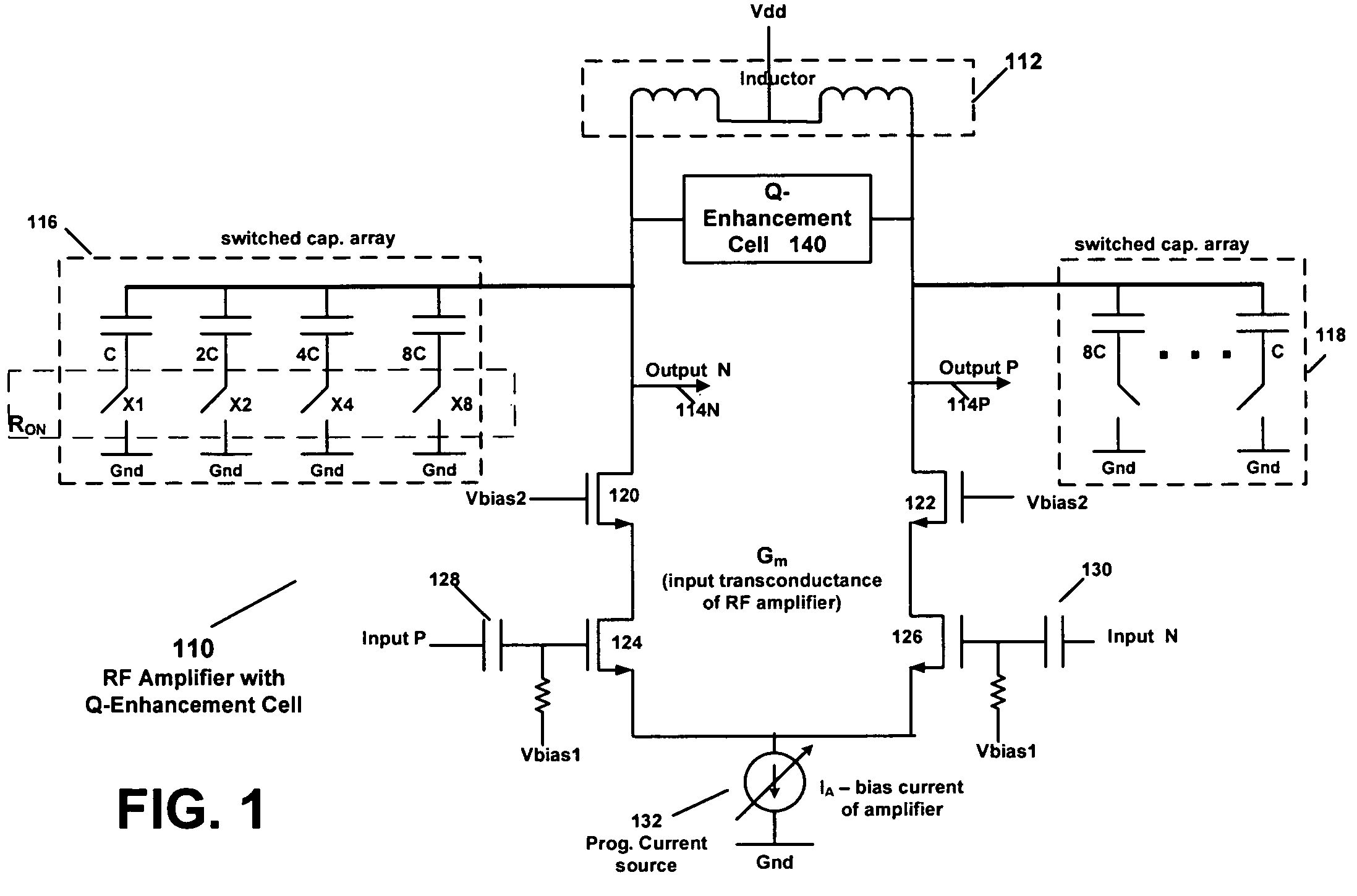
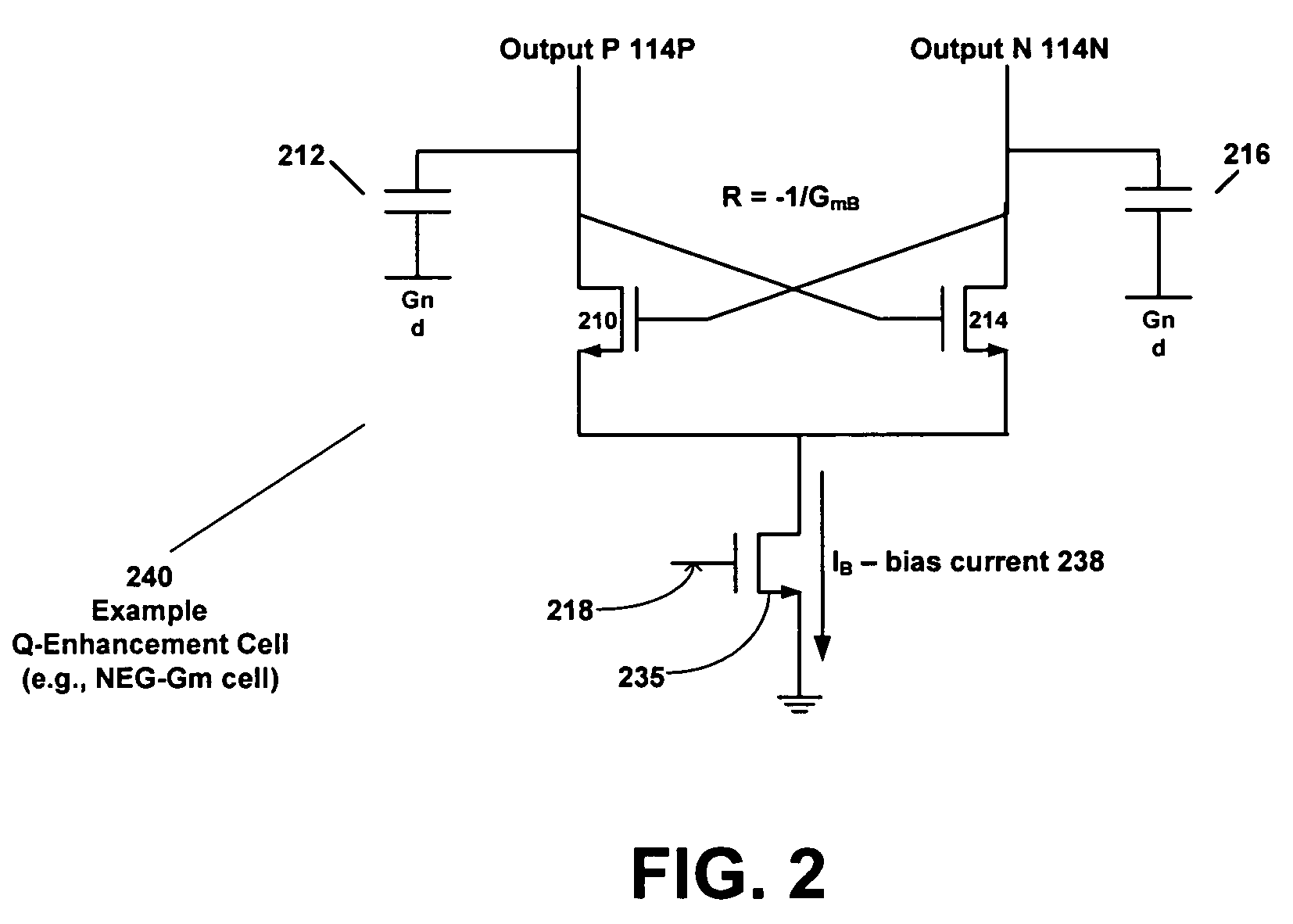
Circuit with Q-enhancement cell having feedback loop
According to an example embodiment, an amplitude feedback loop may include an RF amplifier, a detector, a comparator, and a Q-enhancement cell. In an example embodiment, the RF amplifier has an output signal, and the detector has an input coupled to the output signal of the RF amplifier and is configured to detect a level of the output signal of the RF amplifier. The comparator circuit may receive as inputs a reference voltage and the output of the detector. Also, the comparator circuit is configured to output a control signal based on a difference between the reference voltage and the output signal of the power detector. The Q-enhancement cell may be coupled to the RF amplifier and have an input coupled to an output of the comparator circuit. A bias current of the Q-enhancement cell may be adjusted based on the control signal output by the comparator circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
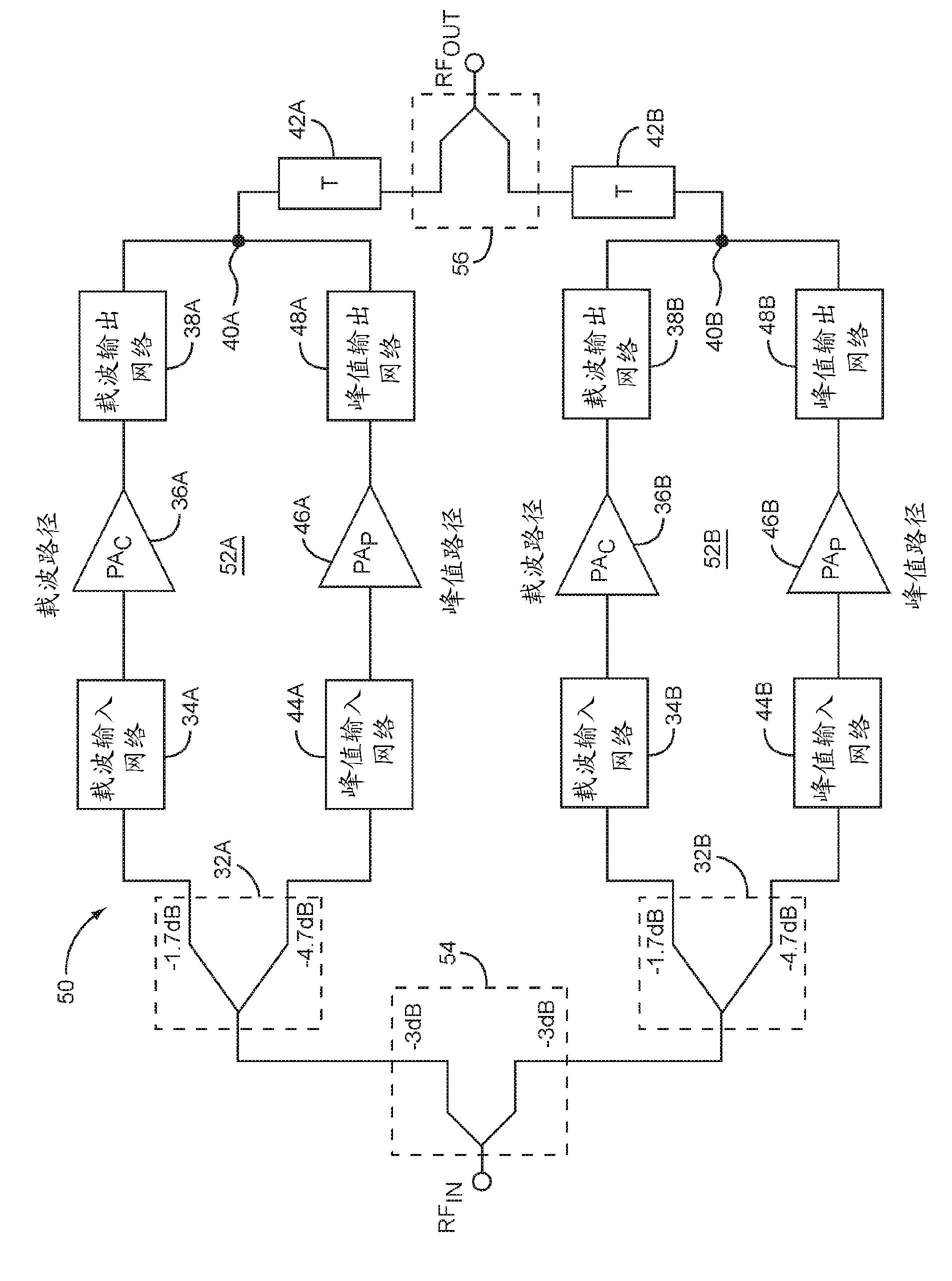
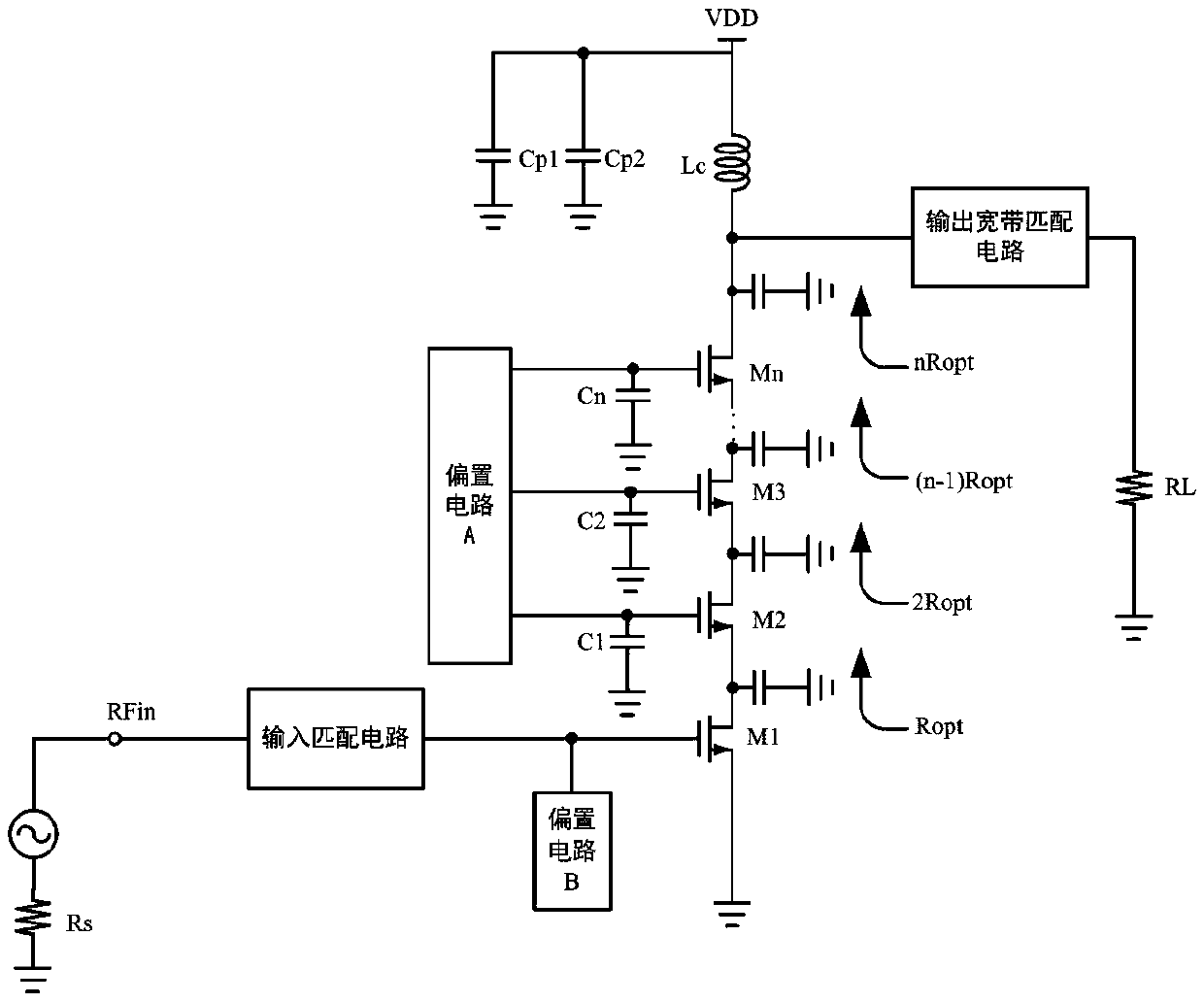
Method for widening bandwidth of Doherty power amplifier and Doherty power amplifier improved with method
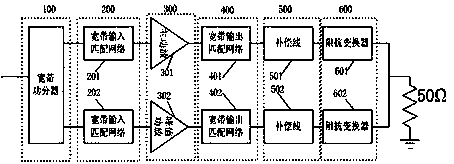
InactiveCN103457541AImprove performanceSolve the problem of not being able to realize broadbandAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthSoftware define radioImpedance Converter
The invention provides a method for widening the bandwidth of a Doherty power amplifier and the Doherty power amplifier improved with the method. The Doherty power amplifier comprises a bandwidth power distributor module, a bandwidth input matching network module, a main power amplifier, a peak value power amplifier, a bandwidth output matching network module, a compensation line module and an impedance converter module, wherein the compensation line module comprises a compensation line of a main power amplifier branch and a compensation line of the peak value power amplifier branch, the compensation line of the main power amplifier branch converts load impedance into an optimal load impedance point in a lower power state; the compensation line of the peak value power amplifier branch enables the output impendence of the peak value power amplifier to present infinity and prevents the power of the main amplifier from being leaked to the peak value power amplification branch in a low power state. According to the invention, the bandwidth of the Doherty power amplifier can be widened and the returning efficiency of the Doherty power amplifier can be improved, load conditioning can be better achieved, the Doherty power amplifier can be applied to a multi-module base station and software radio, and energy conservation and cost reduction are facilitated.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Wideband active balun LNA topology with narrow-band filtering and noise cancelling
ActiveUS9054648B1Balanced differential signal outputSuperior IIP performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceHigh frequency amplifiersLow noiseEngineering
The present invention provides a wideband active balun LNA topology with narrow-band filtering and noise cancelling. The amplifier includes three transconductance stages, a feedback network, and a load. The first and second transconductance stages are connected in parallel to receive the input signal. The differential output of the first transconductance stage is fed back to voltage input through a differential-to-single-end-end feedback network, while the output of the first transconductance, passing through the third transconductance, is added to the output of the second transconductance stage in proper phase. The present invention accomplish both wideband low-noise amplification and narrow-band filtering without inserting interface stages, thereby improving the linearity and noise performance of the whole circuit. Noise cancellation technique is implemented in differential way to ensure the low noise figure. The present invention also achieves single-end to differential conversion with balanced output and superior second order linearity performance.
Owner:MONTAGE TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
High-bandwidth low-power consumption frequency-compensation three-stage operational amplifier
InactiveCN101917169AGood compensationIncrease separation resistanceEnergy efficient ICTAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyLoad circuitWireless communication protocol
The invention belongs to the technical field of analog IC (Integrated Circuit) design, in particular to a high-bandwidth low-power consumption frequency-compensation three-stage operational amplifier. The amplifier comprises an input stage, a second stage, an output stage, a common mode feedback stage, a comprehension circuit, an internal feedforward circuit, wherein the second stage is connectedwith the input stage, the output stage is connected with the second stage and used for amplifying a signal output by the second stage and driving an external load circuit, the common mode feedback stage extracts the common mode level of the differential output stage and stabilizes the common mode level, the comprehension circuit comprises a traditional trsanscondutance comprehension circuit, a miller comprehension circuit and a resistor for separating a high-frequency zero pole, and the internal feedforward circuit is used for comprehending an internal additional pole and forming a push-pull circuit together with the output stage to reduce static power consumption. The three-stage operational amplifier realizes high gain, high bandwidth and high stability under the condition of little DC power consumption and can be used in a high-speed analog-digital conversion circuit, such as a sigma-delta modulator suitable for the bandwidth of an LTE (Line Terminator Equipment) wireless communication protocol.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Low noise amplifier for wideband tunable matching
ActiveUS7323939B2Improve performanceNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierEngineering
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Enhanced doherty amplifier
The disclosure relates to an enhanced Doherty amplifier that provides significant performance improvements over conventional Doherty amplifiers. The enhanced Doherty amplifier includes a power splitter, combining node, a carrier path, and a peaking path. The power splitter is configured to receive an input signal and split the input signal into a carrier signal provided at a carrier splitter output and a peaking signal provided at a peaking splitter output. The carrier path includes carrier power amplifier circuitry, a carrier input network coupled between the carrier splitter output and the carrier power amplifier circuitry, and a carrier output network coupled between the carrier power amplifier circuitry and the Doherty combining node.; The peaking path includes peaking power amplifier circuitry, a peaking input network coupled between the peaking splitter output and the peaking power amplifier circuitry, and a carrier output network coupled between the power amplifier circuitry and the Doherty combining node.
Owner:CREE INC
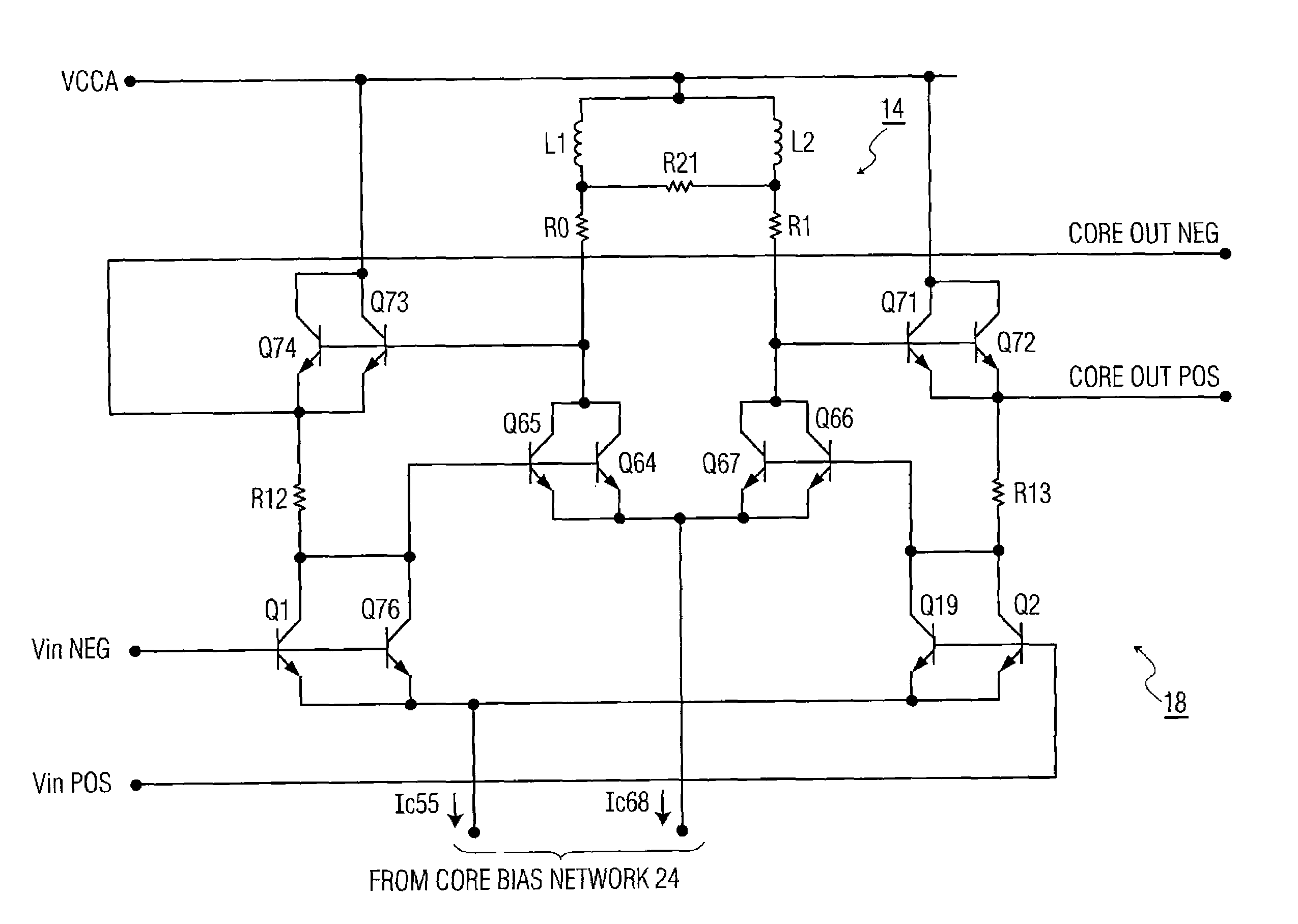
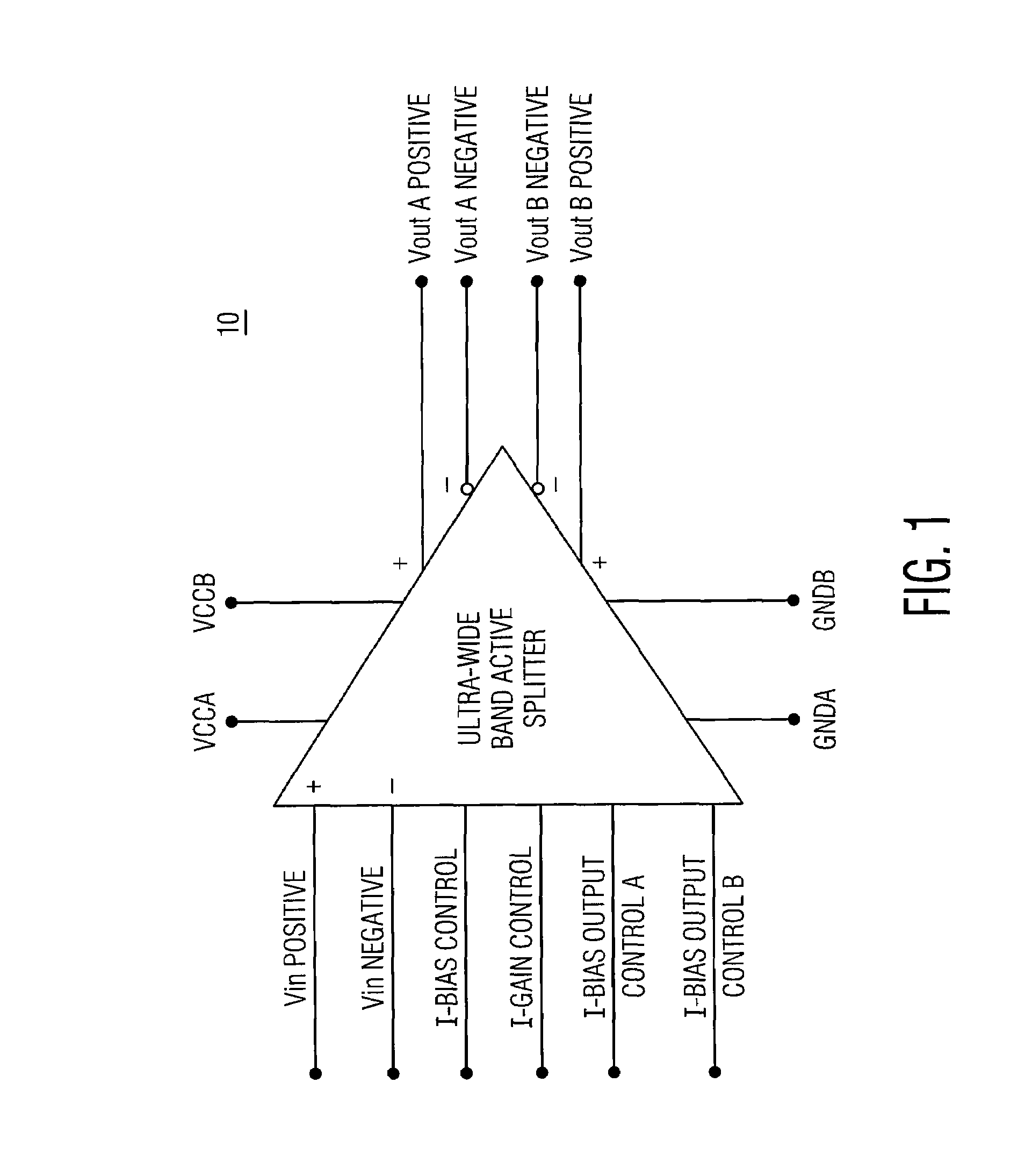
Ultra wide band, differential input/output, high frequency active splitter in an integrated circuit
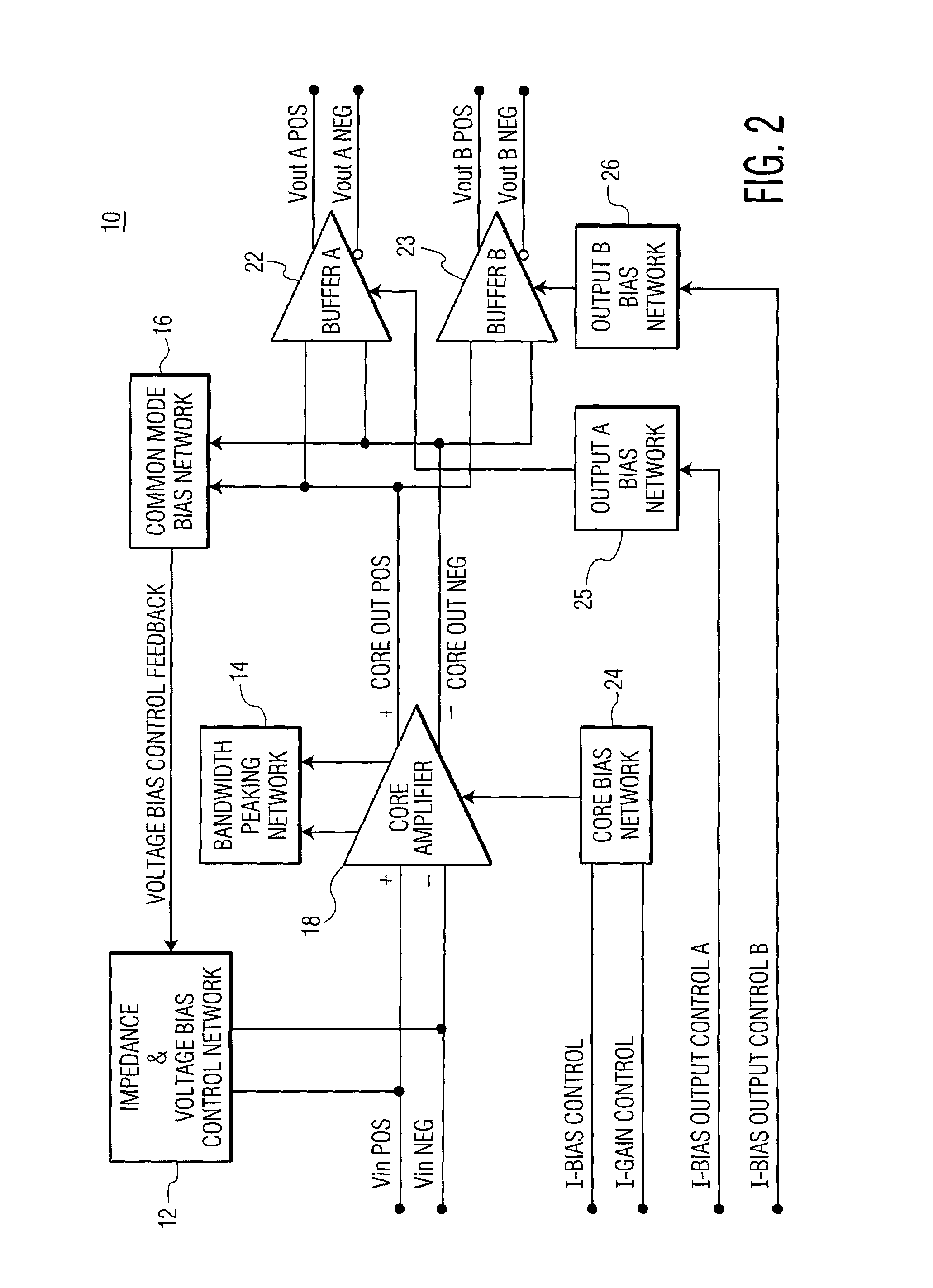
ActiveUS7400193B2Increase frequency bandwidthAmplifier combinationsDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
A wideband splitter includes a core amplifier for receiving a single pair of differential input signals and providing first and second pairs of differential output signals. The first pair of differential output signals and the second pair of differential outputs have substantially identical characteristics. A signal gain is implemented between the received single pair of differential input signals and the first and second pair of differential output signals. The signal gain is substantially constant across the frequency bandwidth of the core amplifier. A bandwidth peaking network is coupled to the core amplifier and includes (a) a first coil and a first resistor connected in series and (b) a second coil and a second resistor connected in series. The bandwidth peaking network is configured to increase the frequency bandwidth of the core amplifier.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit having latch circuit applied changeable capacitance and method thereof
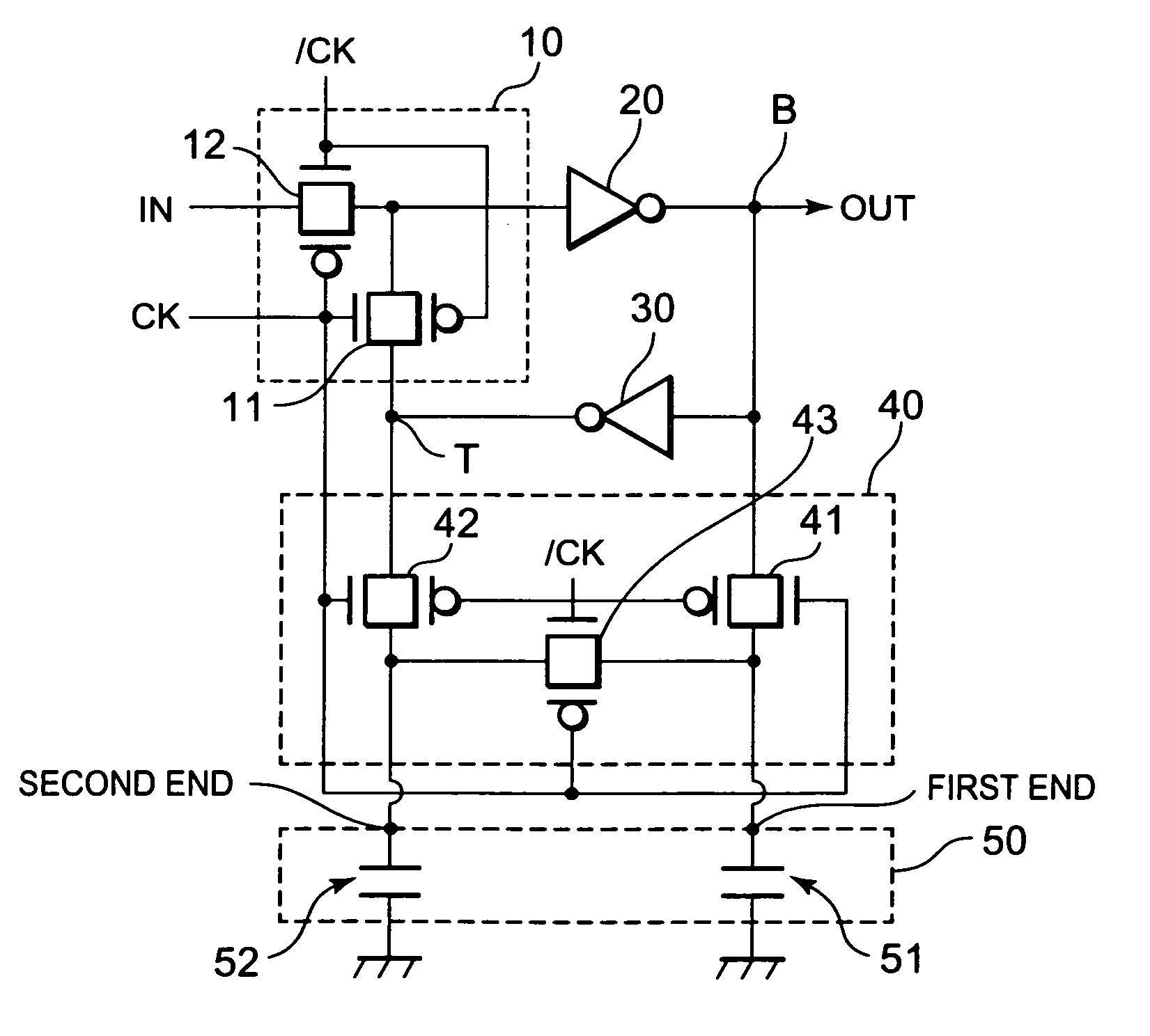
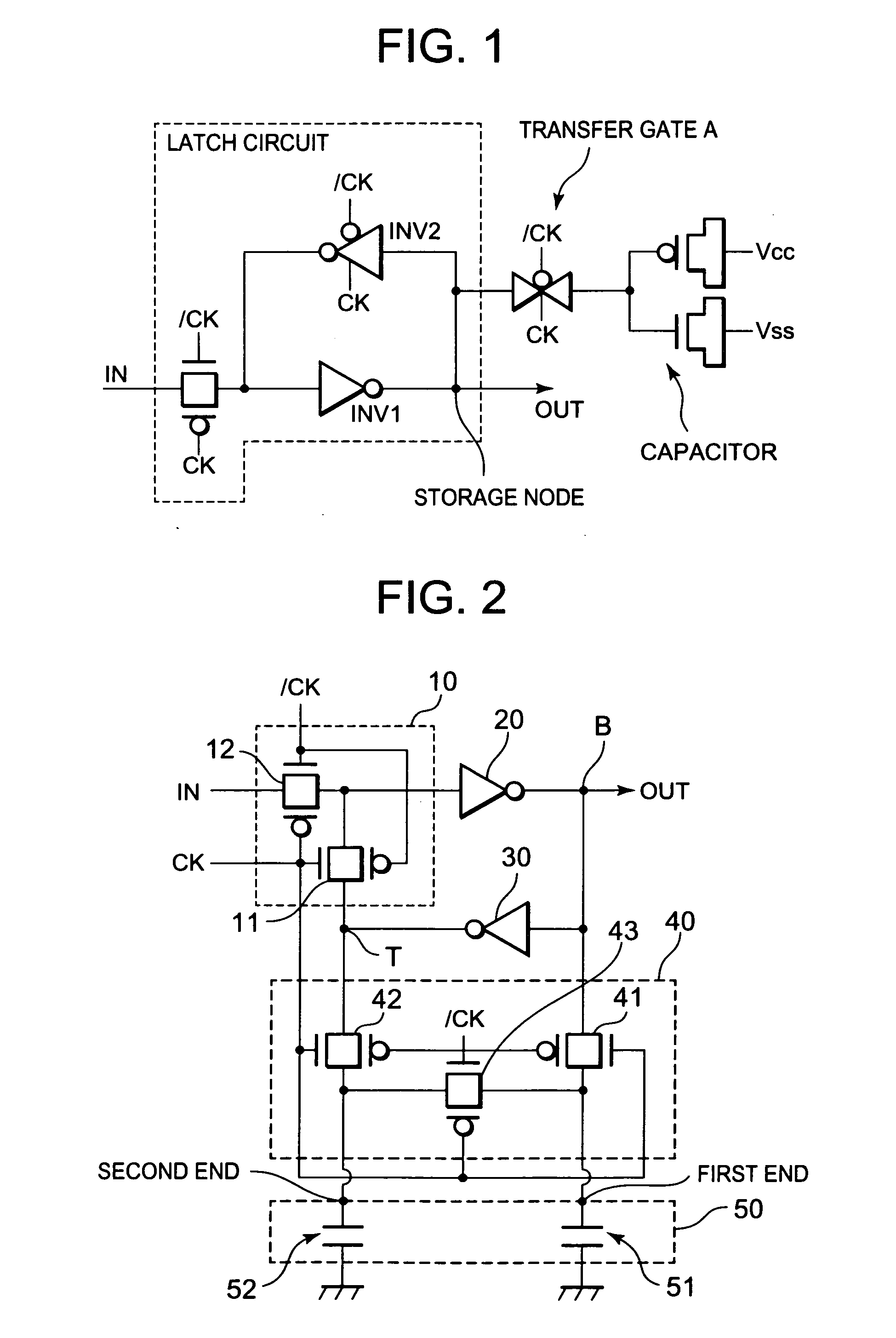
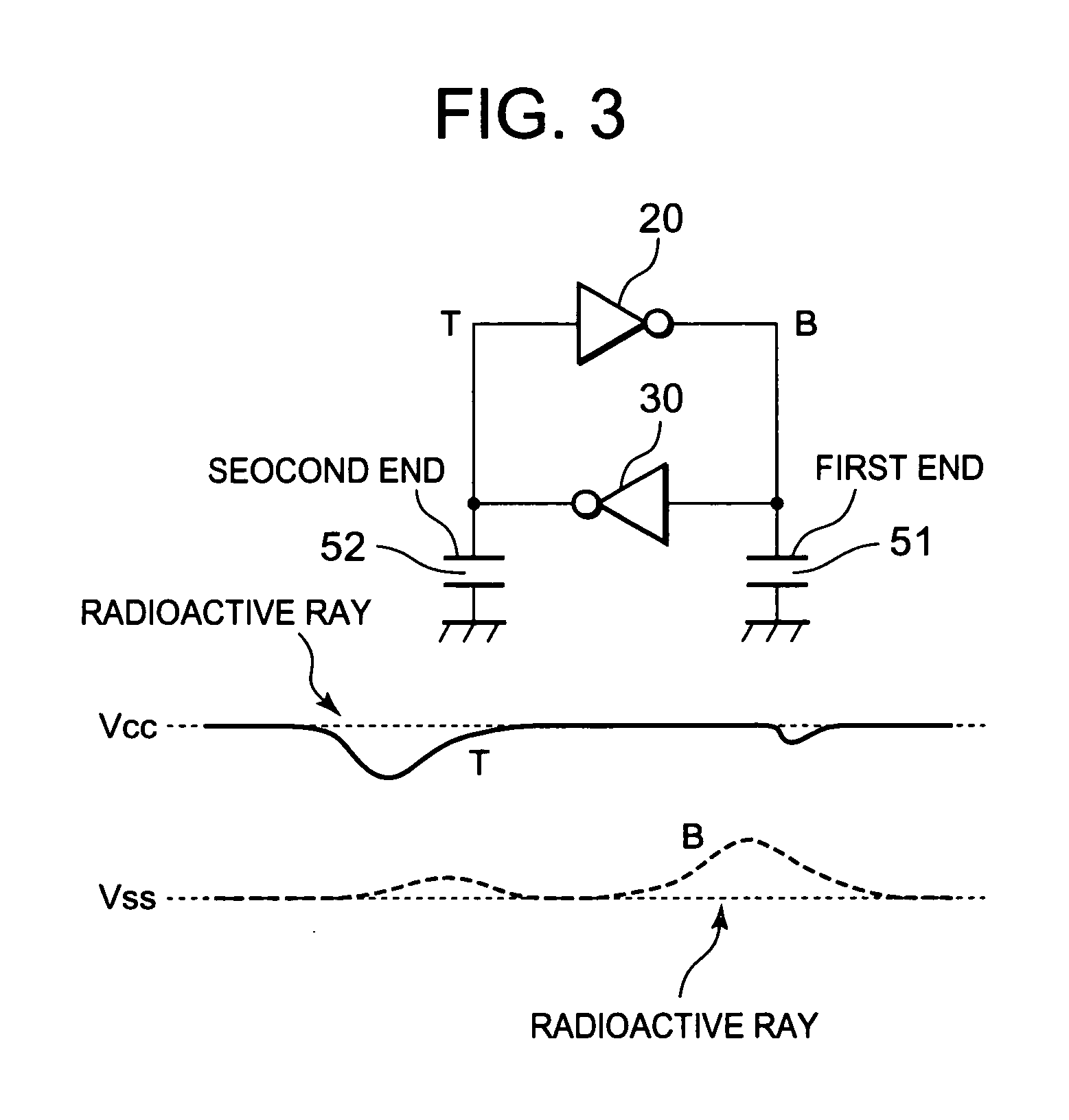
InactiveUS20100019839A1Increase capacityReduce amountElectronic switchingDigital storageCapacitanceEngineering
A semiconductor integrated circuit includes a flip-flop circuit, a capacitive element, and a switch circuit. The switch circuit includes a first switch circuit which couples the capacitive element to two nodes of the flip-flop circuit at a first timing, and a second switch circuit which short-circuits ends of the capacitive element connected to the two nodes at a second timing different from the first timing.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Full-difference CMOS ultra wide band low-noise amplifier
InactiveCN101656516ASimple structureReduce usageEnergy efficient ICTAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTransconductanceLow-noise amplifier
The invention relates to a full-difference CMOS ultra wide band low-noise amplifier which can be applied in the ultra wide band of 3.1-4.8GHz and 3.1-10.6GHz or can be applied in cognitive radio frequency front end of 900MHz-6GHz. The amplifier is based on common-source transconductance input and resistance negative feedback structure and is composed of a matching stage, an amplifying stage, a feedback stage and a load stage, wherein, the matching stage uses grid electrode inductance to tune wideband input impedance; the amplifying stage uses a current multiplexing common-source stage NMOS tube and a PMOS tube to serve as the input end, a common-grid electrode NMOS tube which is connected with the drain terminal output thereof is used as a current follower; an NMOS tube between an input NMOS tube grid electrode and a current follower NMOS tube drain electrode and resistance form a voltage-current type negative feedback circuit; the load stage uses resistance to load. The invention hassimple structure, occupies small chip area, has high gain and low power consumption and can satisfy the requirement of radio frequency front end of a wideband communication system.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
RF power transistor circuit
A radio frequency (RF) power transistor circuit includes a power transistor and a decoupling circuit. The power transistor has a control electrode coupled to an input terminal for receiving an RF input signal, a first current electrode for providing an RF output signal at an output terminal, and a second current electrode coupled to a power supply voltage terminal. The decoupling circuit includes a first inductive element, a first resistor, and a first capacitor coupled together in series between the control electrode of the first power transistor and the power supply voltage terminal. The first decoupling circuit is for dampening a resonance at a frequency lower than an RF frequency.
Owner:NXP USA INC
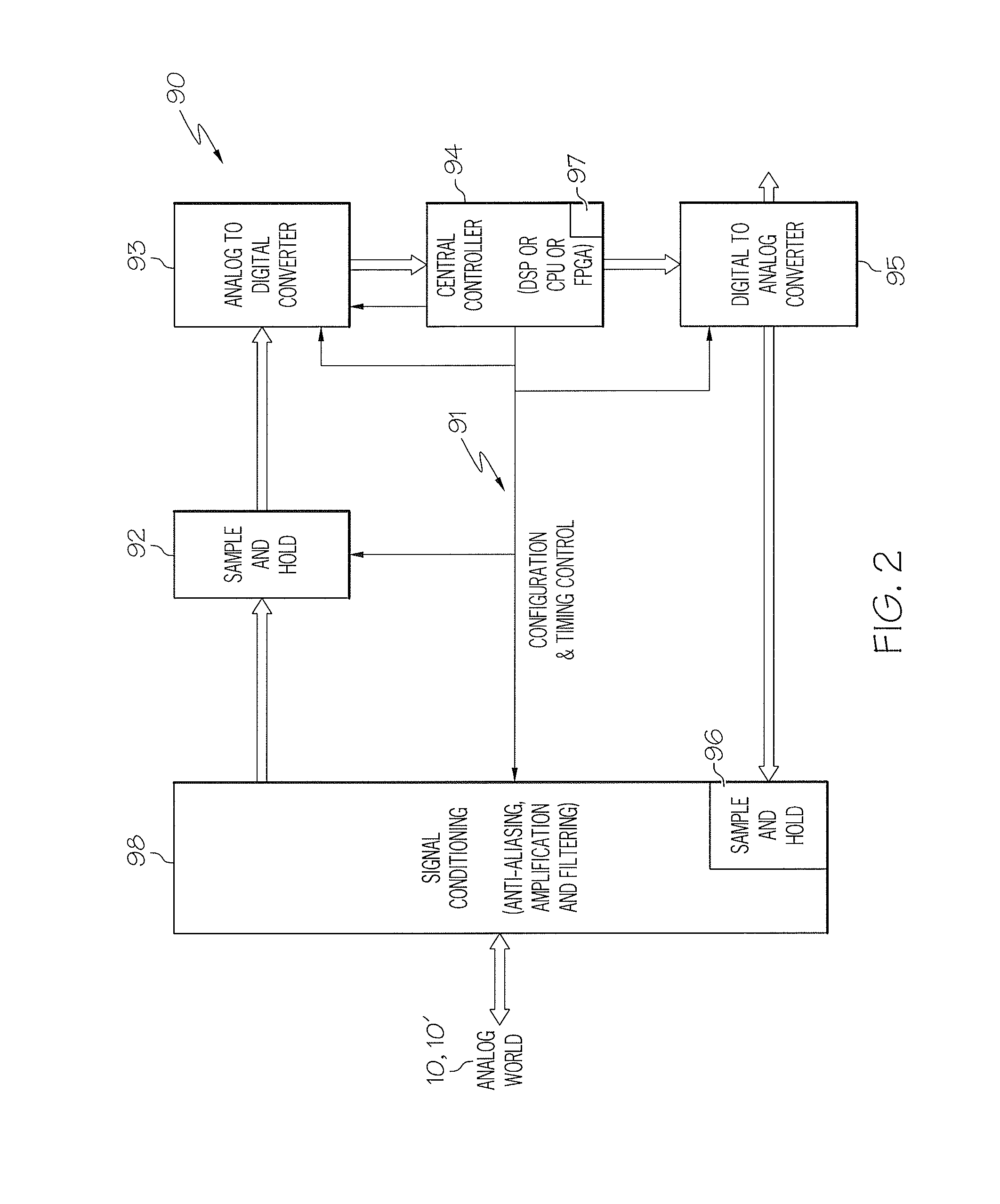
Re-configurable multipurpose analog interface
InactiveUS20110241916A1Electric signal transmission systemsAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierA d converter
Systems and apparatus are provided for interfacing a digital controller with an analog input means. The system comprises a digital controller with the input of the digital controller coupled to the output of the analog-to-digital converter. The system further comprises a digital-to-analog converter coupled to an analog interface circuit. The analog interface circuit comprises a reconfigurable RC network switchably coupled to a first amplifier or to a second amplifier. The analog interface circuit further comprises a third amplifier having an input being coupled to an output of the second amplifier and the output of the third amplifier being coupled to the one or more input signal paths to the first amplifier.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Low noise amplifier for wideband tunable matching
ActiveUS20060132242A1Improve performanceNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierInductor
Provided is a low noise amplifier with a common source and a source degeneration, which has linearity, power gain, noise factor, and lossless input matching. The low noise amplifier includes: a first inductor having one terminal connected to an input terminal receiving a signal; a second inductor having one terminal connected to a ground; a MOS transistor having a gate connected to the first inductor, a source connected to the other terminal of the second inductor, and a drain transmitting a signal; and a variable capacitor connected between the source and gate of the MOS transistor and varying an input matching frequency at the input terminal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Radio-frequency ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier based on inductance compensation
InactiveCN102497167AImprove transconductanceHigh gainAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceHigh frequency amplifiersUltra-widebandTuned amplifier
The invention discloses a radio-frequency ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier based on inductance compensation, relating to a radio-frequency integrated circuit technology. The radio-frequency ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier mainly consists of an input amplification-stage circuit, a feedback-stage circuit, a matching-stage circuit, a load-stage circuit, a bias-stage circuit and an output buffering-stage circuit jointly. According to the radio-frequency ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier, both the input matching stage and the load stage are subjected to inductance compensation, and the sensitivity of the low-noise amplifier on the technology is reduced by adopting a current multiplexing technology with independent bias, so that the performance is more stable, the ultra-wideband is also realized, and the working frequency range is 0.1-12GHz; meanwhile, the radio-frequency ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier gets favorable indexes, such as noise, linearity, gain, power consumption and the like and is suitable for an ultra-wideband multi-standard wireless communication receiving system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Amplification circuit
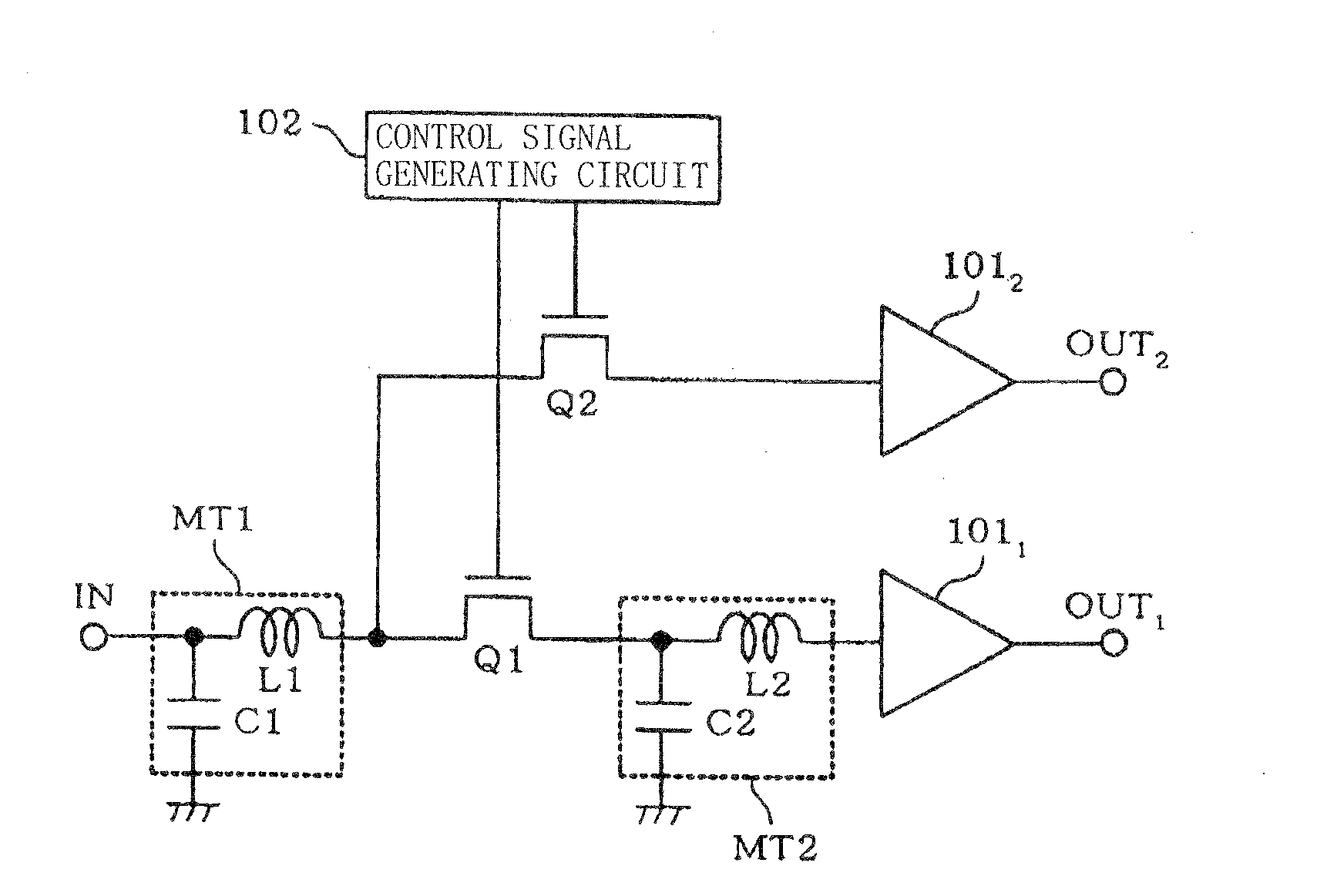
ActiveUS20100060354A1Wide dynamic rangeImprove signal qualityAmplifier combinationsAmplifiers using switched capacitorsAudio power amplifierControl signal
The present invention is aimed at realizing an amplifying circuit whose chip size is prevented from being significantly increased even if the number of compatible frequencies increases, and which has a wide dynamic range when it operates under a low voltage. The amplifying circuit includes a plurality of impedance converting circuits connected to each other by a switching circuit of a first type having a signal cutting-off function, a switching circuit of a second type connected to a path branched from an input side of the switching circuit of the first type, the switching circuit of the second type having a signal cutting-off function, amplifiers connected respectively to an output side of one of the impedance converting circuits in a final stage and to an output side of the switching circuit of the second type, and a control signal generating circuit for controlling connection / disconnection between said switching circuit of the first type and said switching circuit of the second type; wherein either one of the paths is selected to input a signal to one of the amplifiers.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Radio-frequency power amplifier with stack structure
InactiveCN105515542AImprove pressure resistanceIncreased power output capabilityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a radio-frequency power amplifier with a stack structure. The radio-frequency power amplifier comprises an input matching circuit, an output broadband matching circuit, a biasing circuit A, a biasing circuit B and a power amplification circuit, and the power amplification circuit is formed by stacking of at least two transistors with drains and sources connected. A radio-frequency signal source is connected with a grid electrode of the bottom transistor of the power amplification circuit through the input matching circuit, the biasing circuit B is connected with the grid electrode of the bottom transistor, and the source of the bottom transistor is grounded. The drain of the top transistor of the power amplification circuit is connected with a load through the output broadband matching circuit. Integral linearity, output voltage swing, operation bandwidth, power efficiency, power gain and maximum output power of the radio-frequency power amplifier are increased, and excellent second harmonic inhibition effects are achieved.
Owner:臻智微芯(广州)技术有限公司
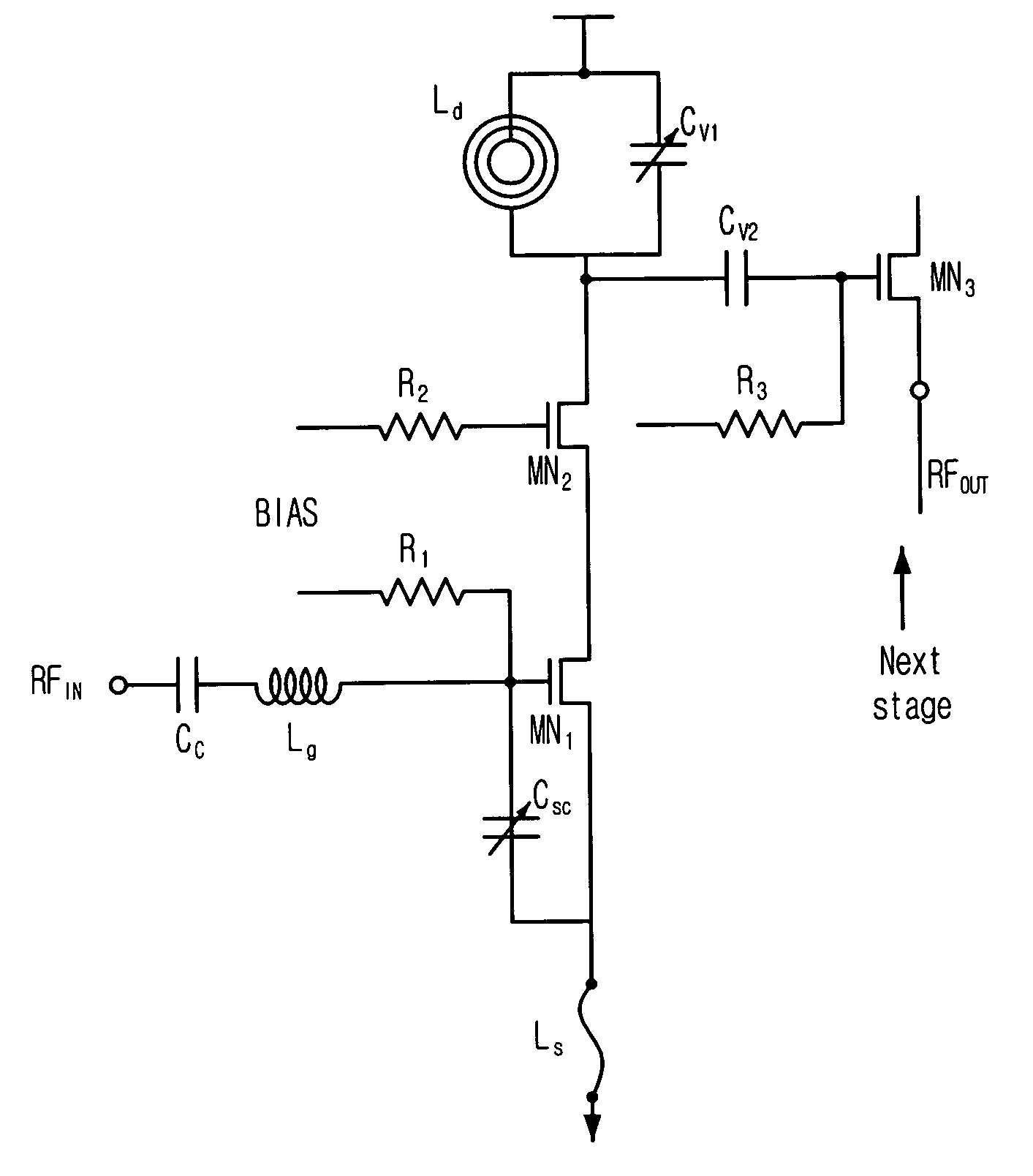
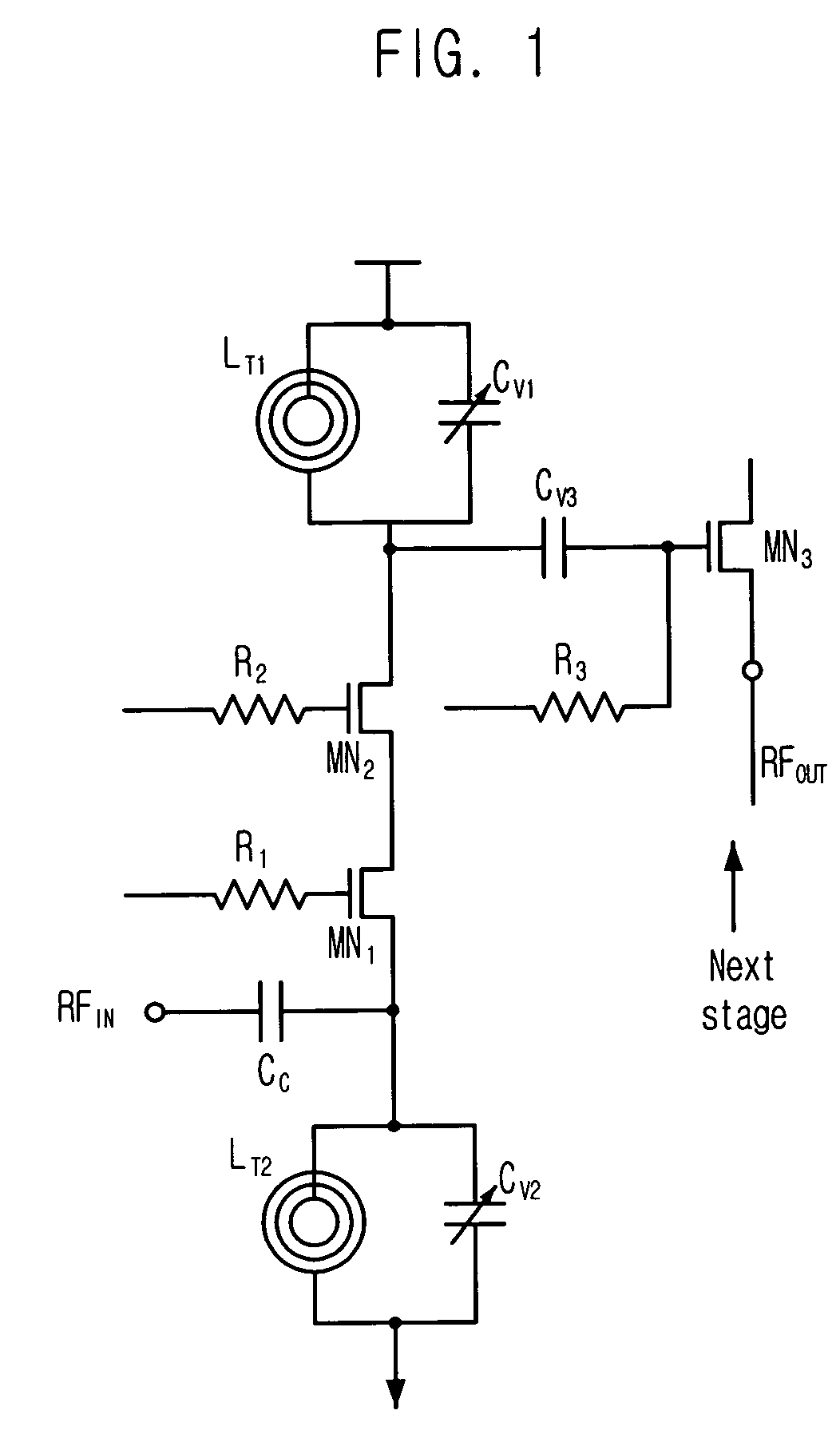
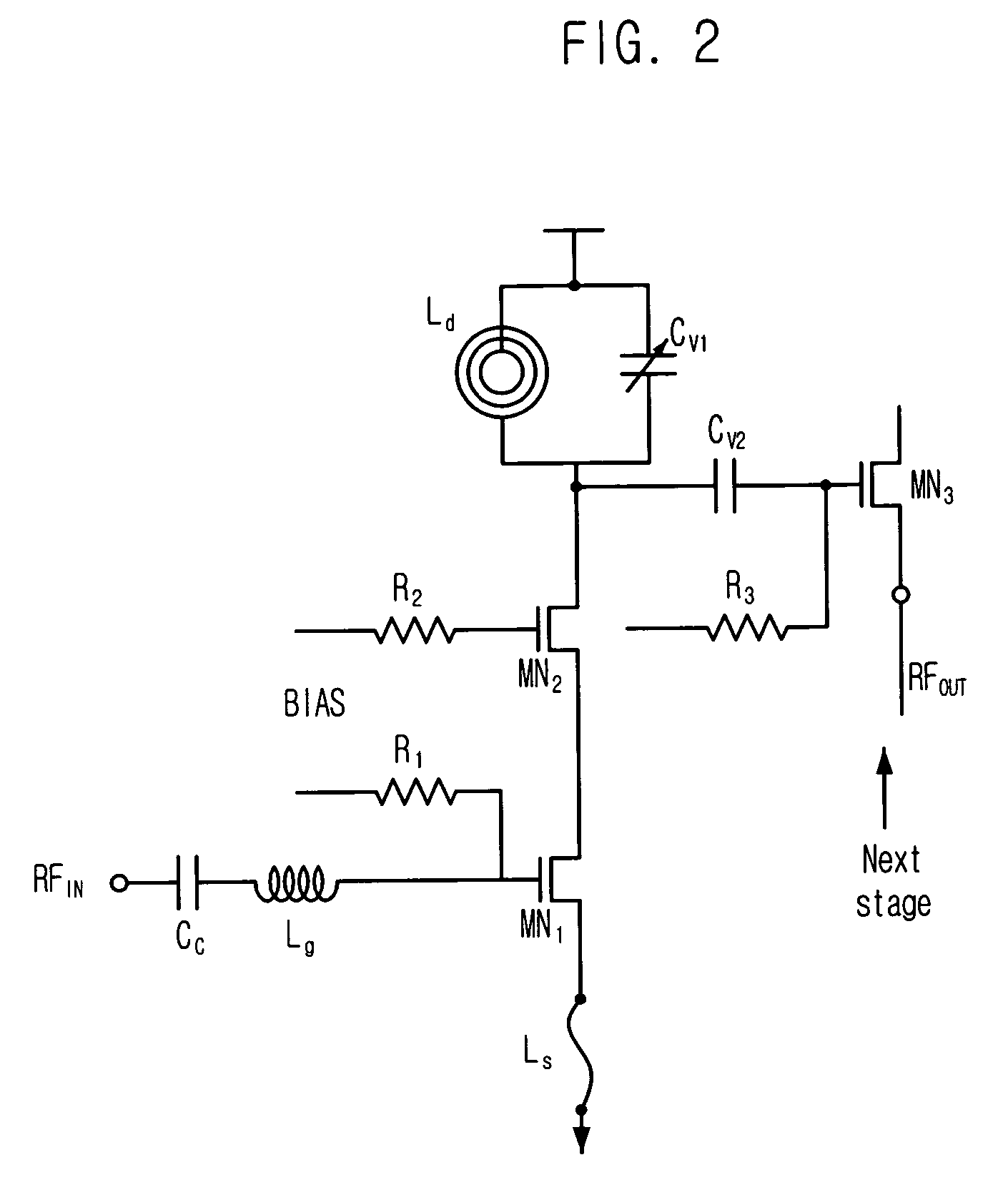
Dual-band CMOS front-end with two gain modes
InactiveUS20050248402A1Operation is disabledImproved and small footprintClosuresGain controlCMOSMulti band
A multi-band low noise amplifier (LNA) 105 includes an input stage having at least two inputs, a first input (103) coupled to a first input transistor for receiving signals in a first frequency band and a second input (104) coupled to a second input transistor for receiving signals in a second frequency band. The second frequency band spaced apart from the first frequency band. A bias network (218) having a band select input is coupled to the first and second input transistor, wherein a signal level applied to the band select input turns on one of the input transistors and turns off the other input transistors. The LNA (105) operates in the first frequency band when the first input transistor is on and the second frequency band when the second input transistor is on. A switched resonator (216) having a control input is provided, wherein application of a control signal to the control input tunes a resonant frequency of the LNA, and provides gain select, for operation in either the first or second frequency bands.
Owner:O KENNETH K +1
Low voltage broadband gain cell
InactiveUS7170349B2Wide bandwidthReduce capacitive lumping effectAmplifier combinationsDifferential amplifiersLow voltageEngineering
T-coil structures are used in one embodiment to inject programmably-variable amounts of transistor biasing currents into the respective drains of current sinking transistor means of a broadband differential amplifier such that, when the differential amplifier is in common mode, total transistor drain current will exceed total voltage-dropping current passing through corresponding voltage-dropping resistances of the amplifier's transistor means. The T-coil structures keep the parasitic capacitances of the programmable current sources that provide the bias currents de-lumped from capacitances of the amplifier's output nodes and / or capacitances of the amplifier's voltage-dropping resistances (variable resistances) to thereby maintain a wide bandwidth.
Owner:SCINTERA NETWORKS
Radiofrequency amplifier
ActiveUS20120146723A1Losses within the package can be reducedMinimizing overall package sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierOutput impedance
The invention relates to high power radiofrequency amplifiers, in particular to amplifiers having output impedance matching networks, exemplary embodiments of which include a radiofrequency amplifier having an active device mounted on a substrate within a device package, the amplifier having an output impedance matching network comprising a high pass network provided at least partly on the active device and a low pass network having a first inductive shunt connection between an output of the active device and a first output lead and a second inductive shunt connection between the output of the active device and a second output lead, wherein part of the second output lead forms an inductance contributing to the inductance of the low pass network.
Owner:AMPLEON NETHERLANDS
Switchable Multiband LNA Design
ActiveUS20100301946A1Consumes less design areaReduce noiseNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGated amplifiersLow noiseResonance
A low noise amplifying (LNA) circuit comprising an amplifying section (11, 12) and a feedback means (14) arranged for providing input matching from the output to the input. The LNA circuit further comprises at least one frequency band determining inductor (15) having a predetermined resonance frequency for influencing at least one frequency band in which the amplifying section operates. The at least one inductor is directly connected to the output of the circuit and the feedback means (14) provides a feedback connection for the section (s) to the input. In this way, the at least one frequency band in which the amplifying section operates is substantially completely determined by the at least one frequency band determining inductor (15).
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
Re-configurable multipurpose analog interface
InactiveUS8054208B2Electric signal transmission systemsAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesDigital analog converterAudio power amplifier
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
High-efficiency wideband power amplifier with band-pass filter response function
ActiveCN103825564AReduce volumeSimple structureMultiple-port networksPower amplifiersBandpass filteringAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a high-efficiency wideband power amplifier with a band-pass filter response function. The high-efficiency wideband power amplifier comprises a DC biasing circuit, a power amplification transistor, an input match circuit and an output match circuit. A microstrip line band-pass filter with different port impedances and a section of tuning microstrip line are designed to be used as the output match circuit of the power amplifier, the function of the filtering is achieved, meanwhile, the circuits are made to have the band-pass filter response characteristic, and two transmission zeros are generated on the edge of a passband. Compared with a traditional cascade circuit of a power amplifier and a filter, due to the fact that the microstrip line band-pass filter is used as the output match circuit, the entire circuit is small in size, small in loss and wide in working band, and high edge selectivity is achieved due to the two transmission zeros. The high-efficiency wideband power amplifier with the high-pass filter response function is achieved, and testing result validation is provided.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Low voltage broadband gain cell
InactiveUS20060061415A1Wide bandwidthReduce capacitive lumping effectAmplifier combinationsDifferential amplifiersLow voltageEngineering
T-coil structures are used in one embodiment to inject programmably-variable amounts of transistor biasing currents into the respective drains of current sinking transistor means of a broadband differential amplifier such that, when the differential amplifier is in common mode, total transistor drain current will exceed total voltage-dropping current passing through corresponding voltage-dropping resistances of the amplifier's transistor means. The T-coil structures keep the parasitic capacitances of the programmable current sources that provide the bias currents de-lumped from capacitances of the amplifier's output nodes and / or capacitances of the amplifier's voltage-dropping resistances (variable resistances) to thereby maintain a wide bandwidth.
Owner:SCINTERA NETWORKS
Popular searches
Amplifiers with semiconductor devices only Dc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stages Network topologies Wireless commuication services Transmission Low noise amplifier Machine-to-machine/machine-type communication service Semiconductor devices Single resonant circuit with varying inductance and capacitance simultaneously Amplififers with field-effect devices
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com