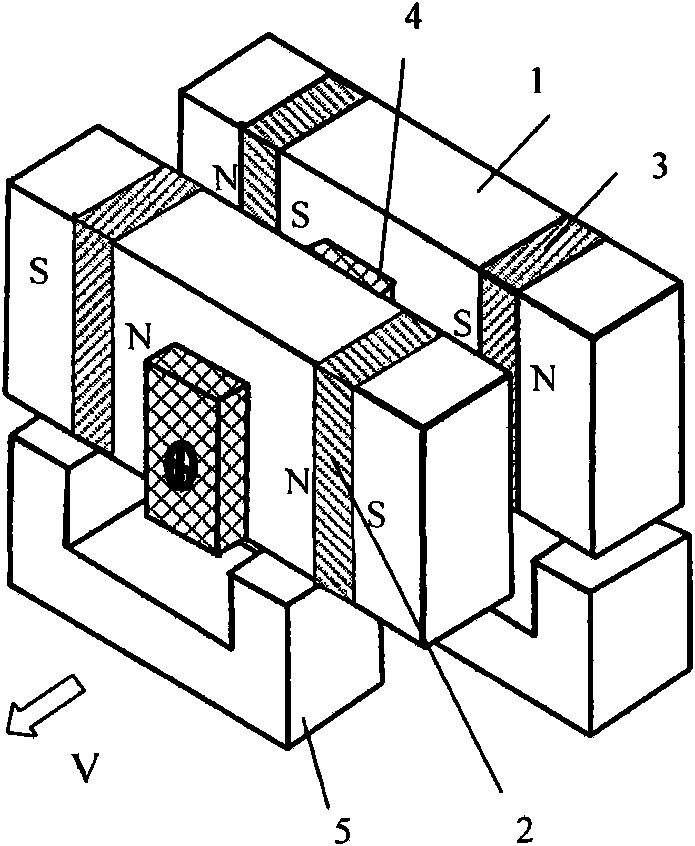
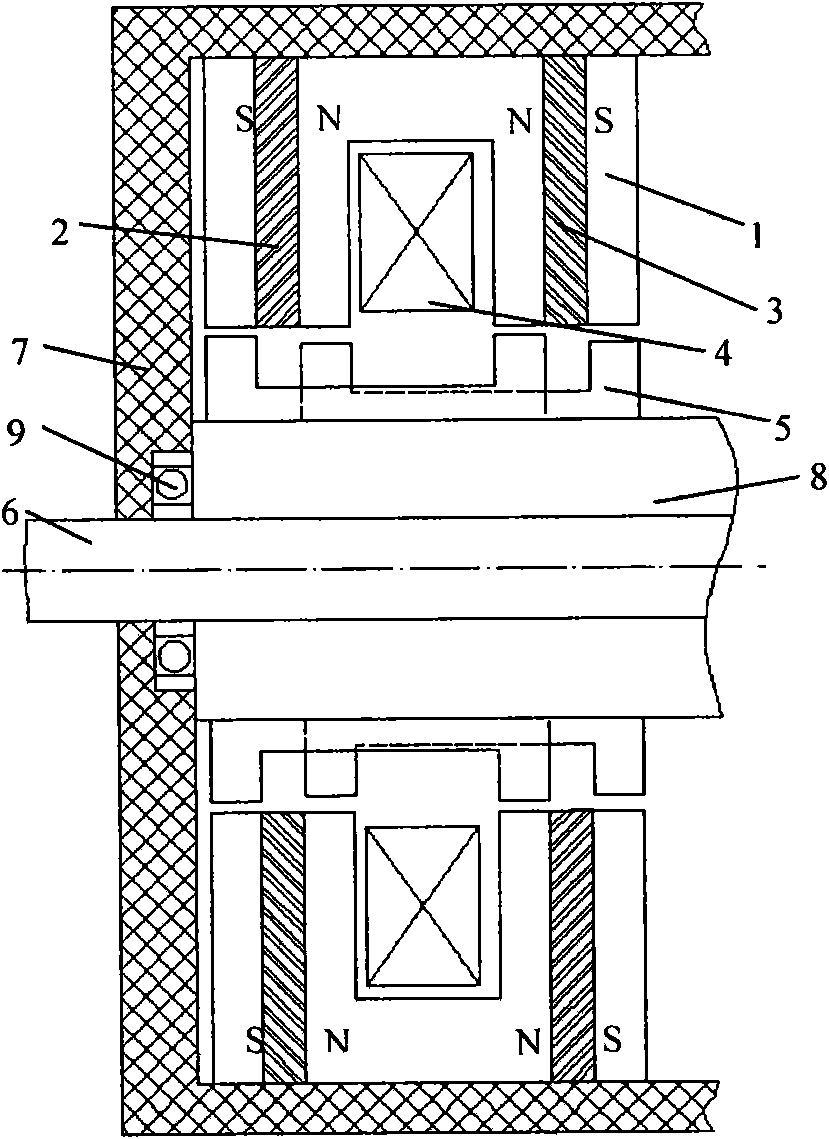
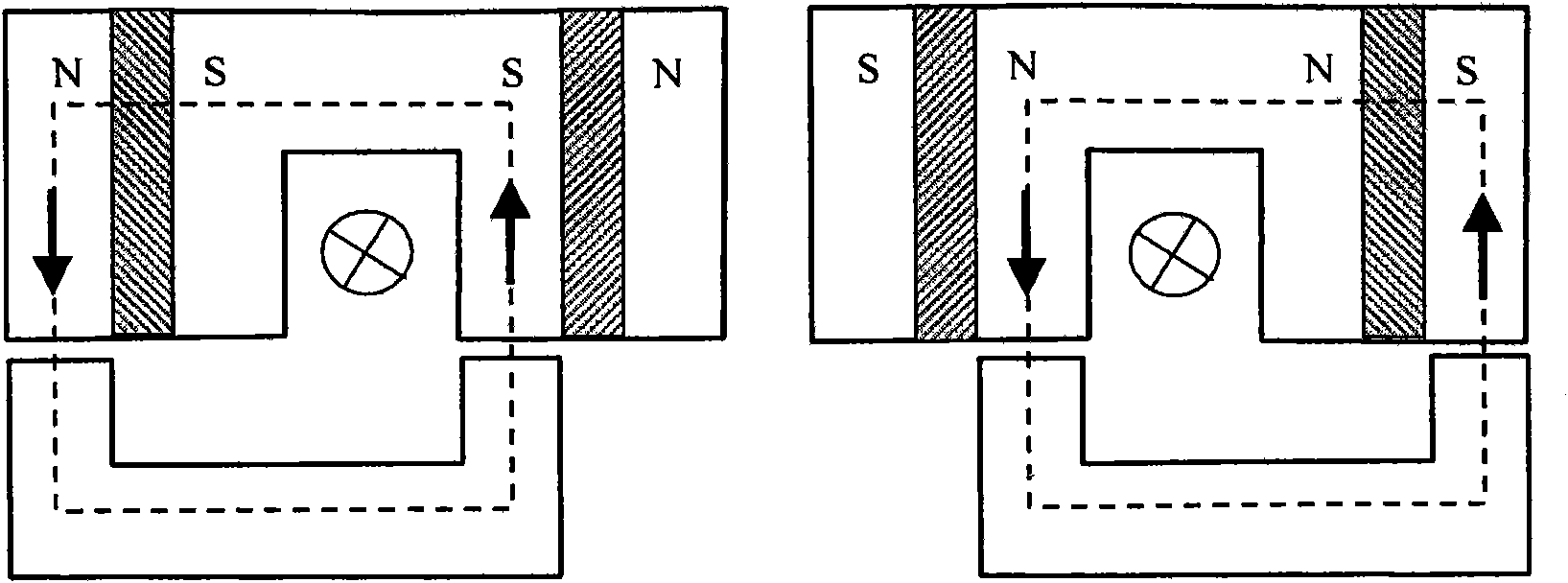
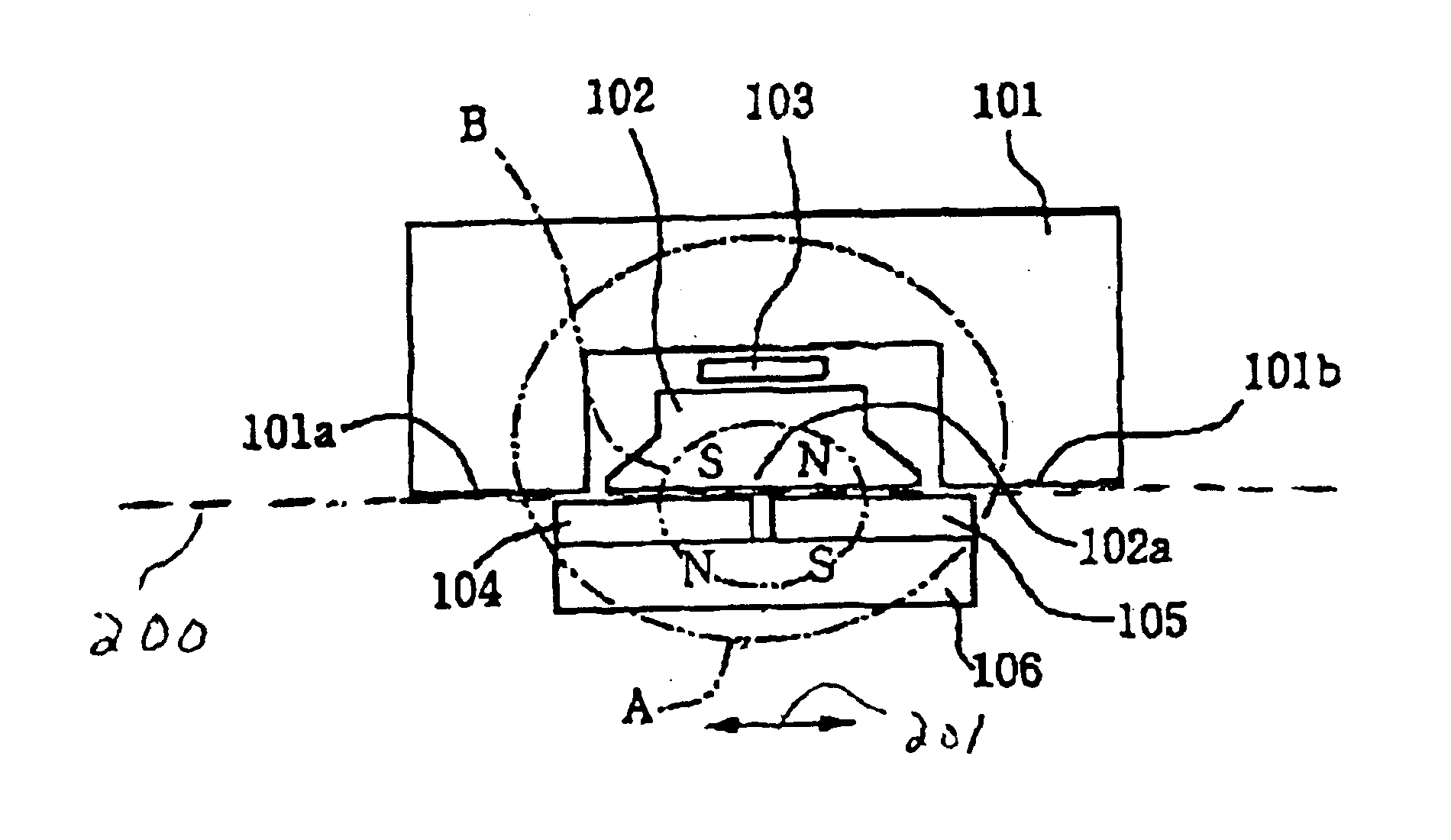
Patents
Literature
285results about How to "Reduce leakage flux" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
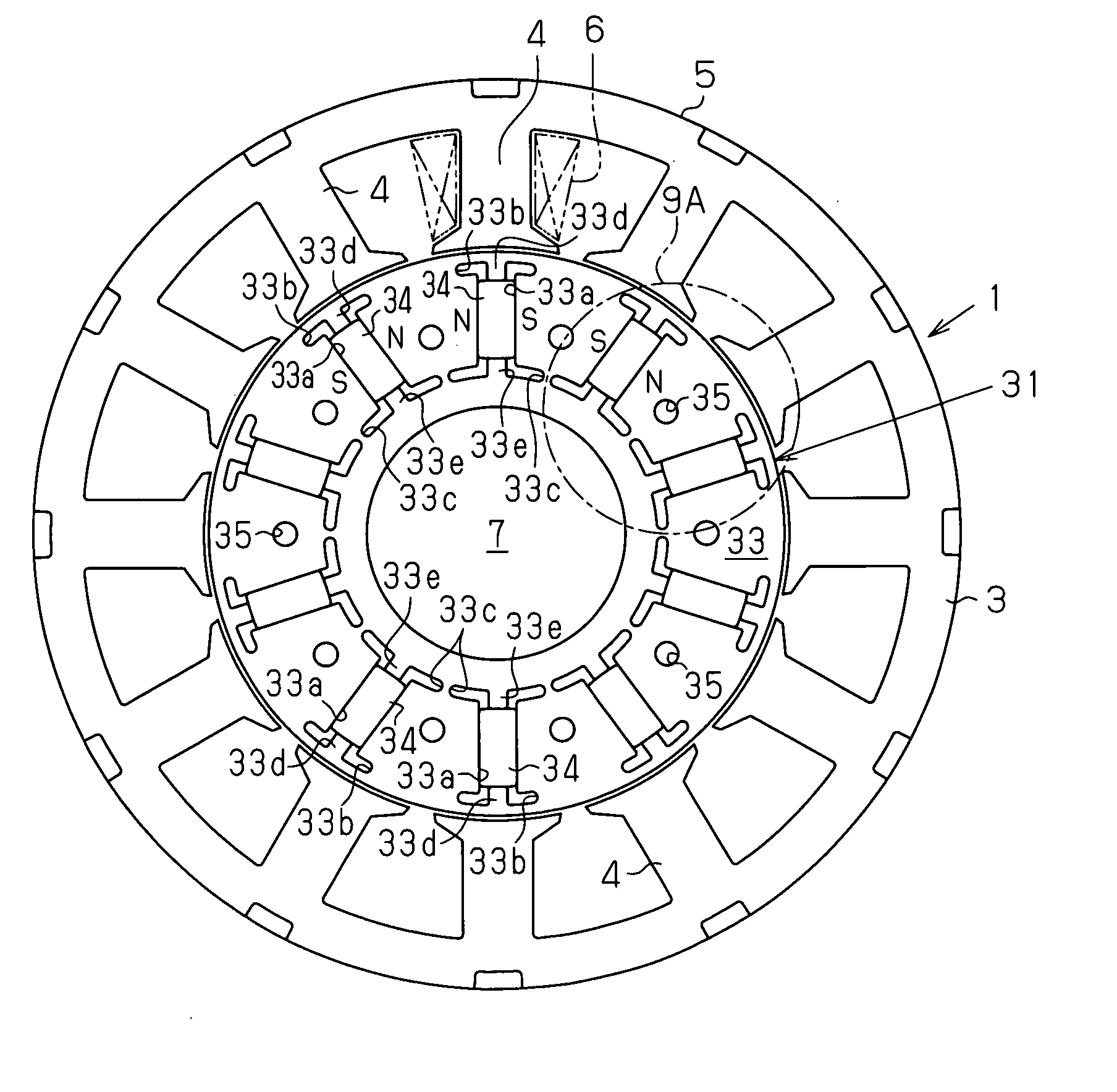
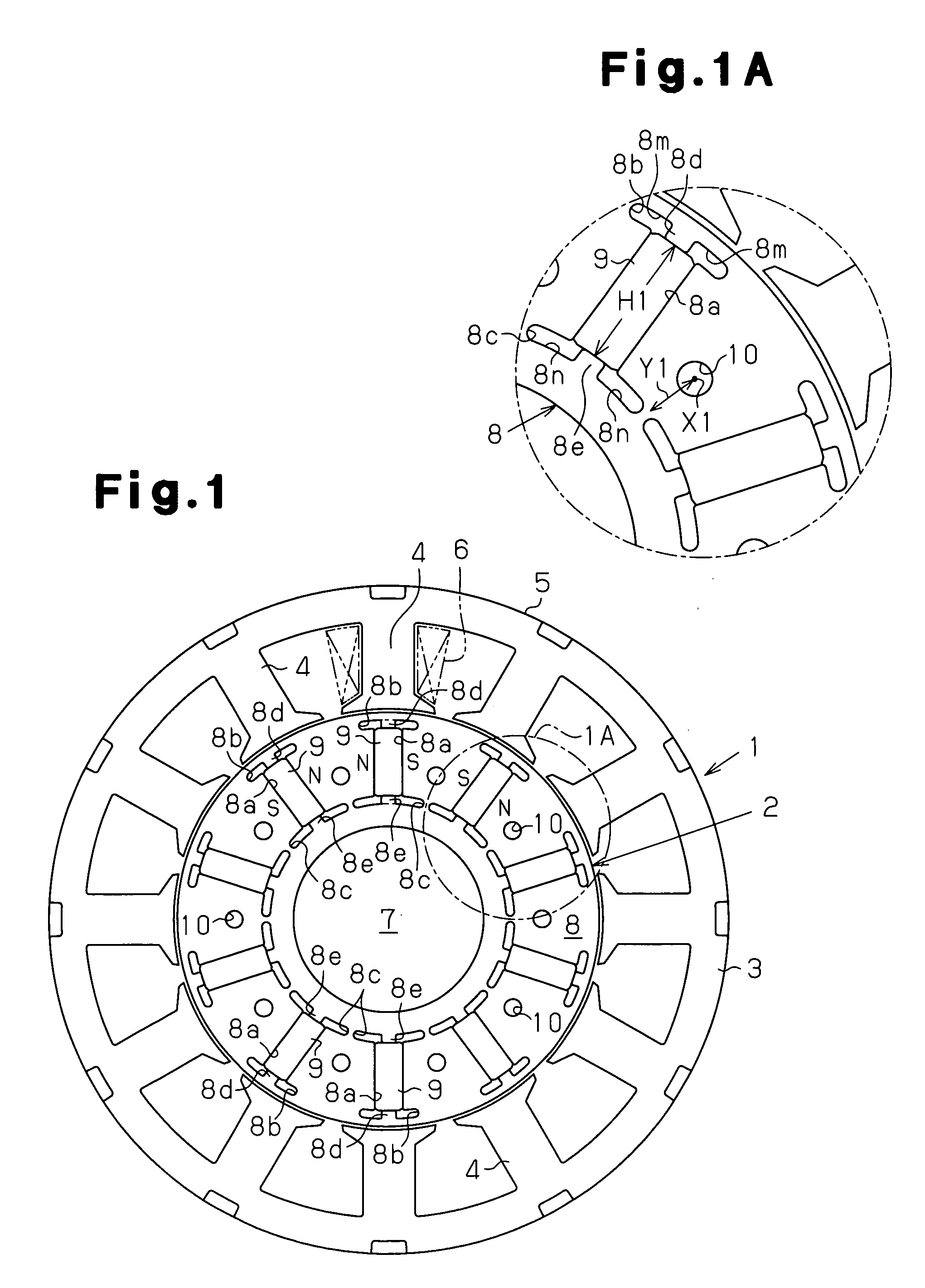
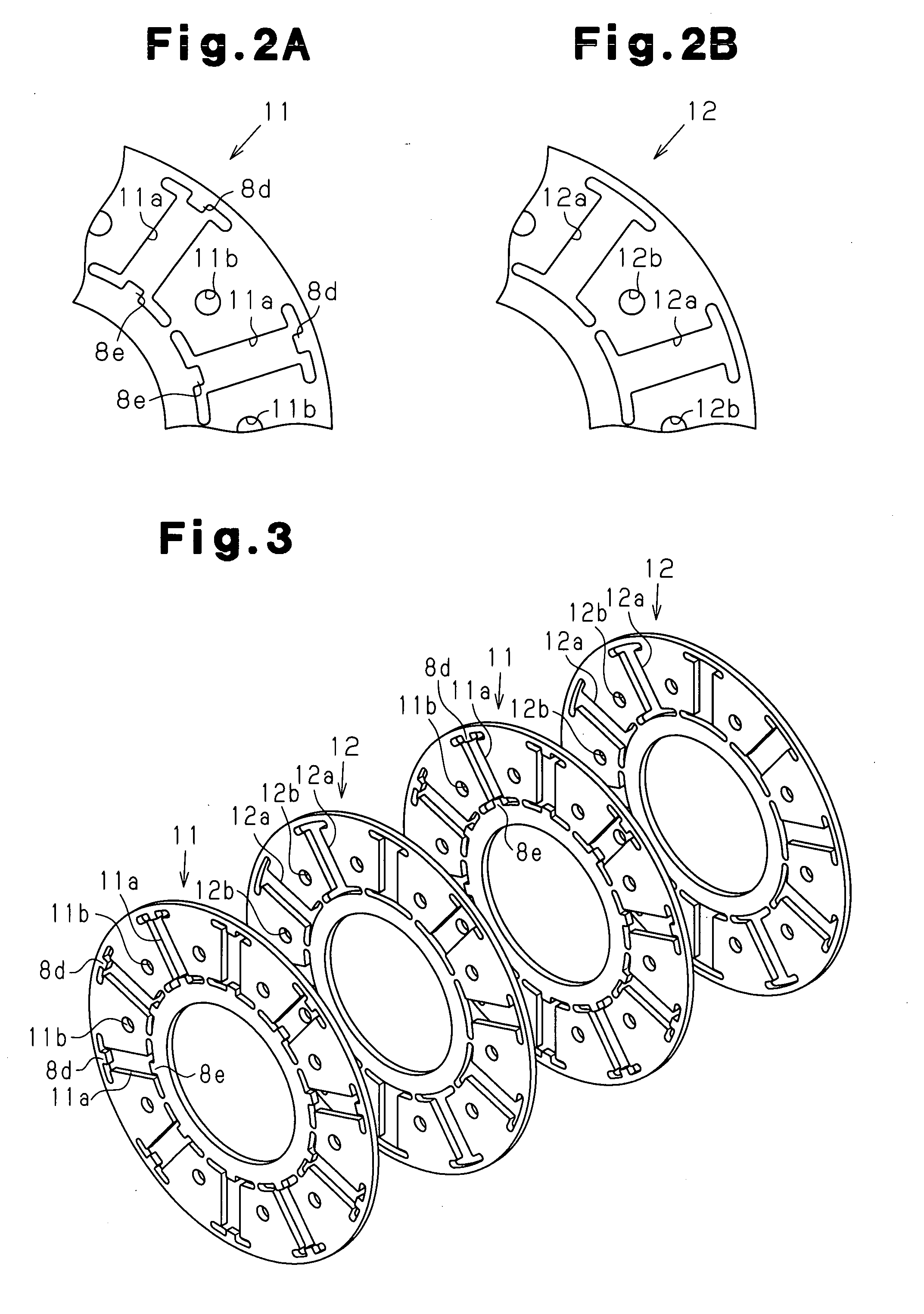
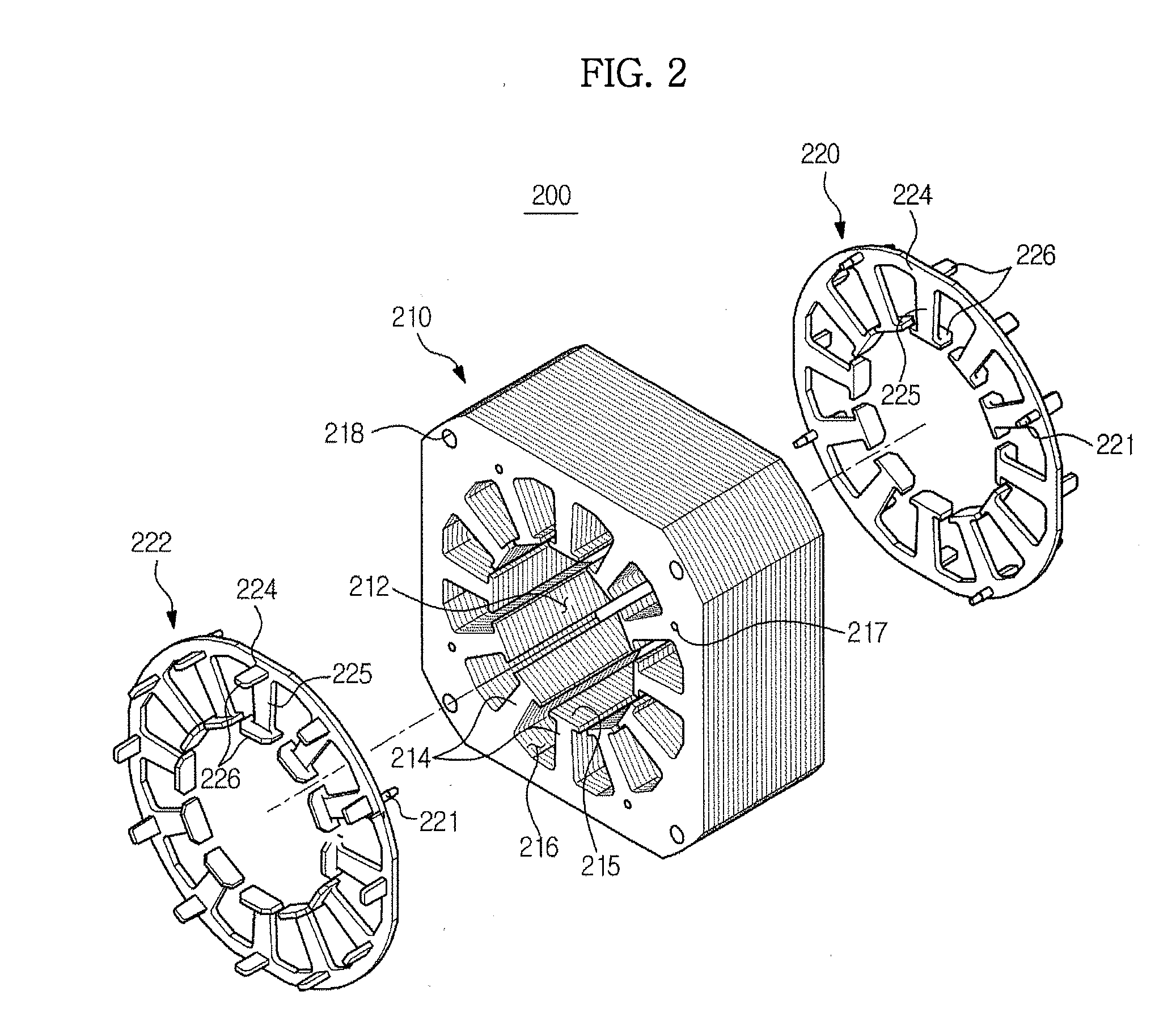
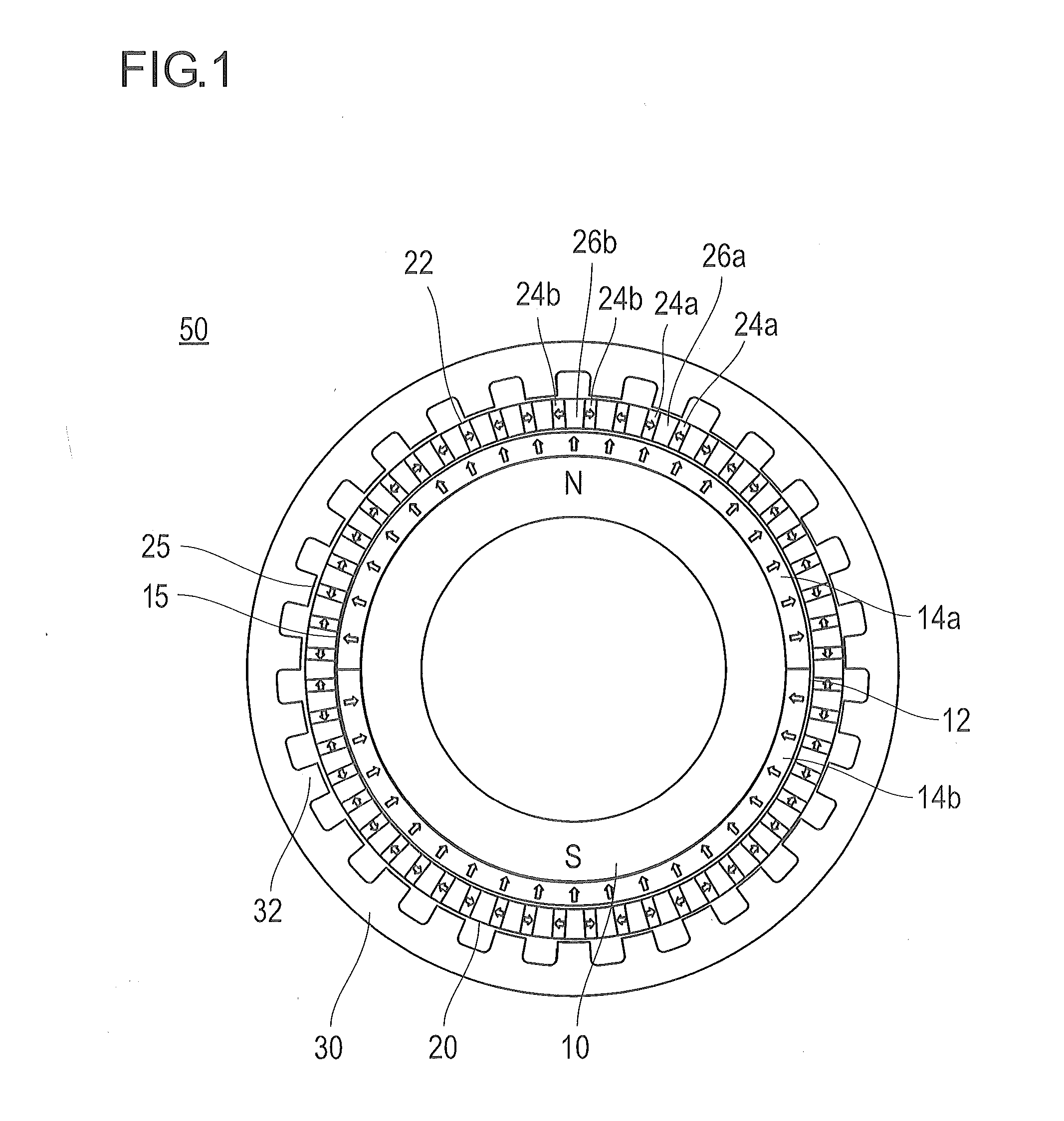
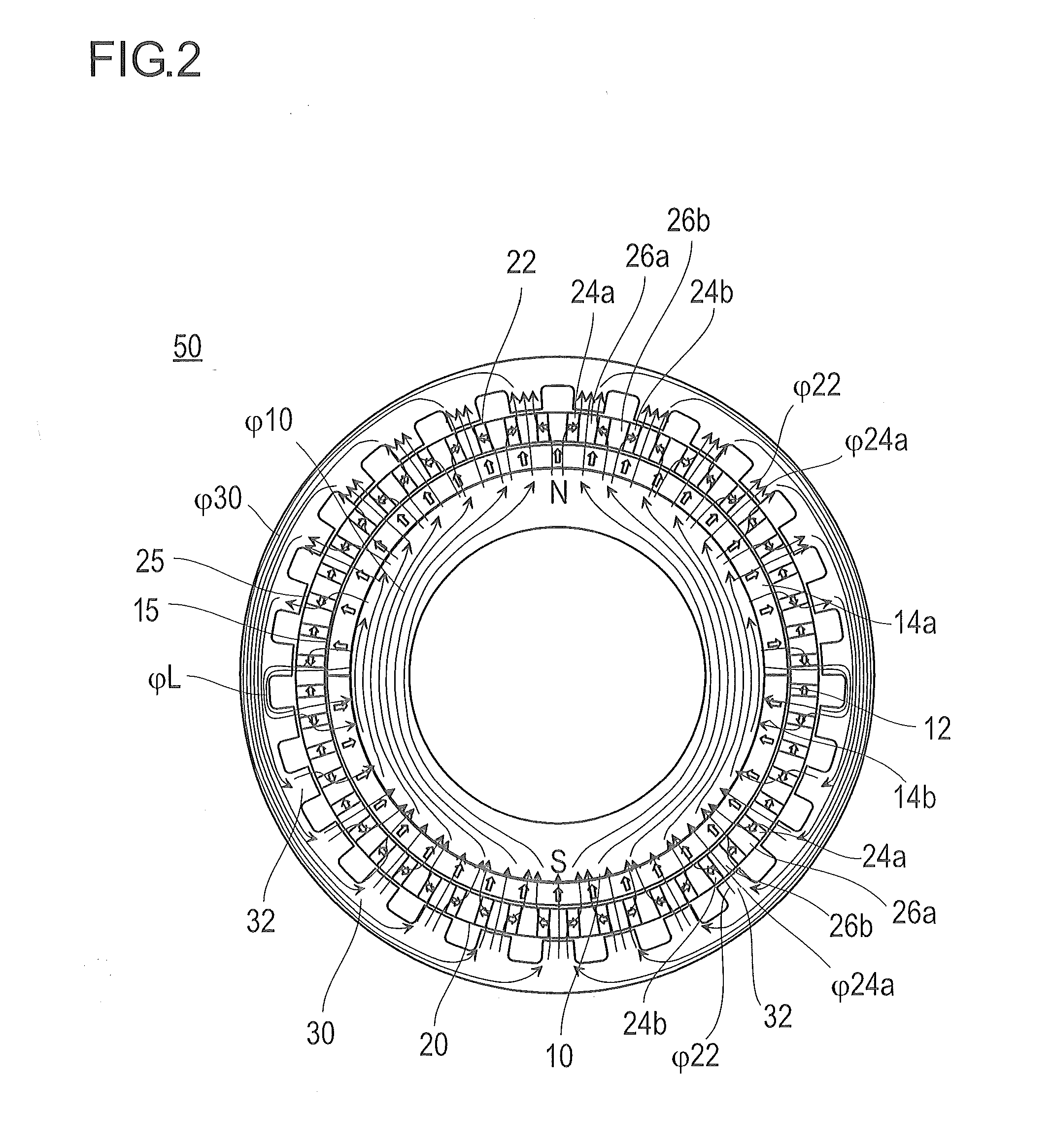
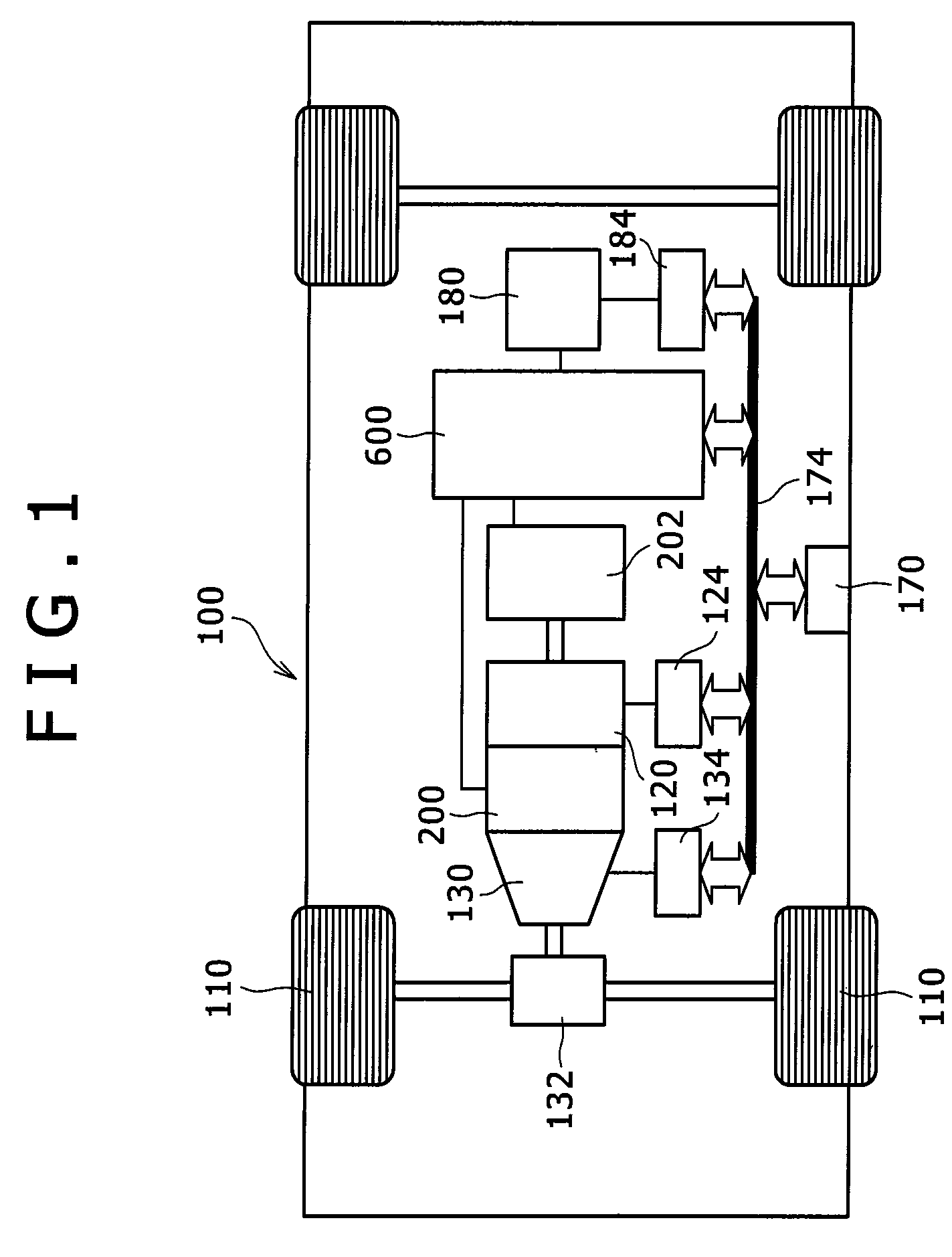
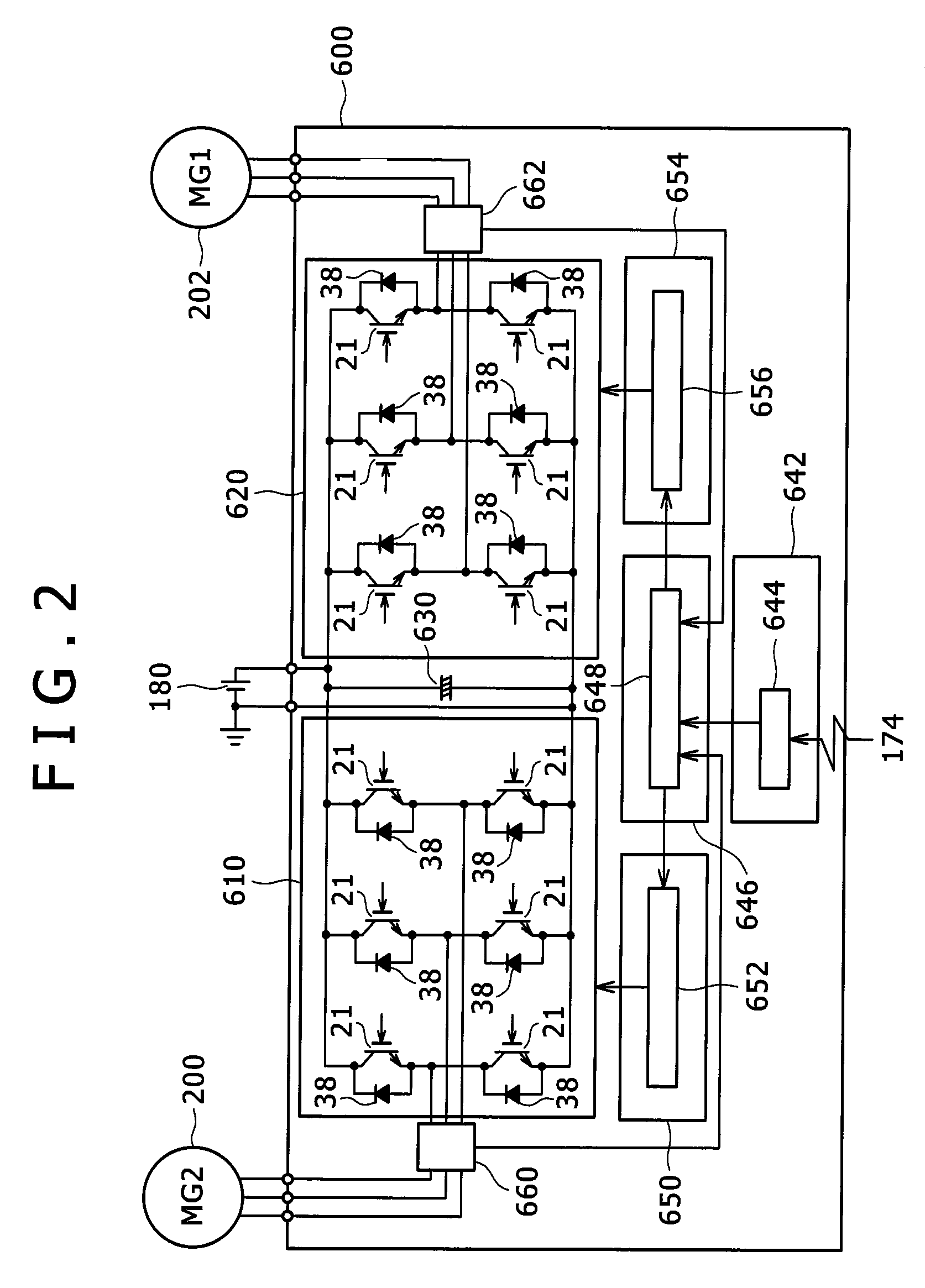
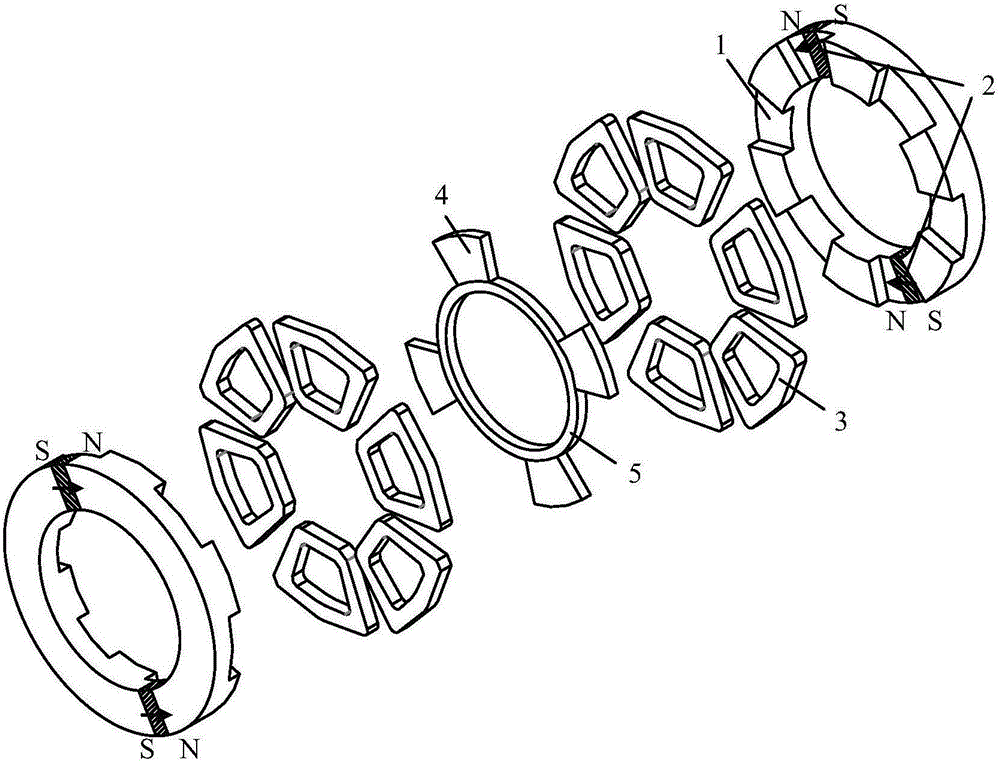
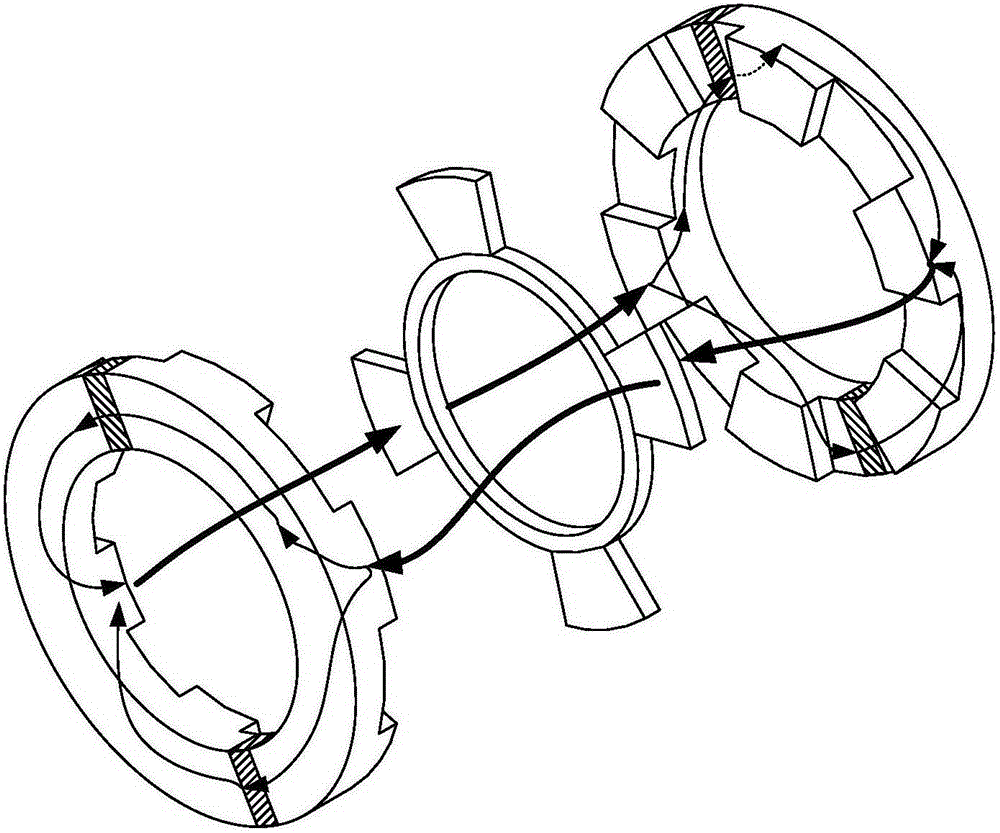
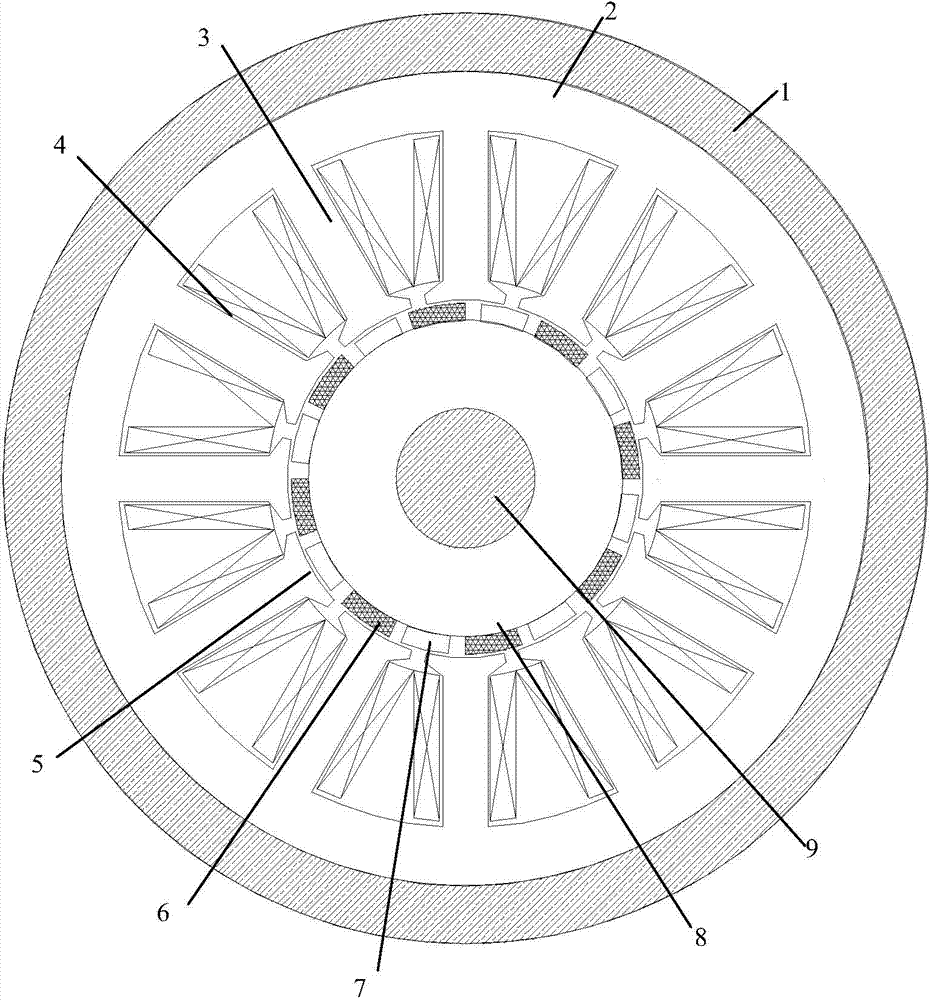
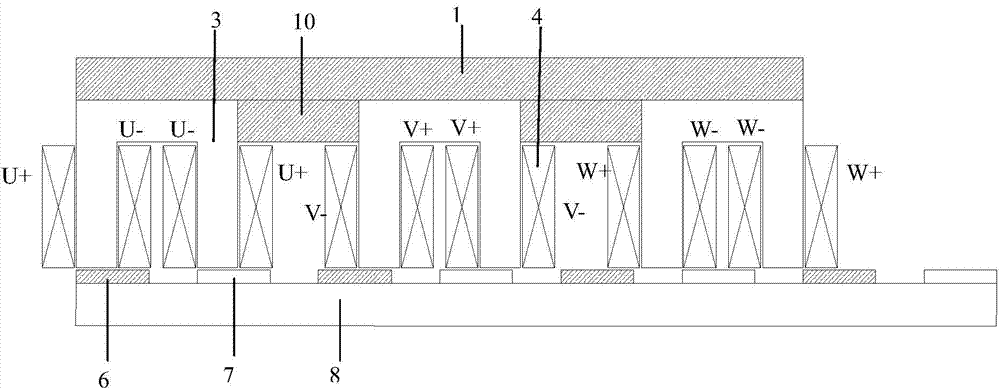
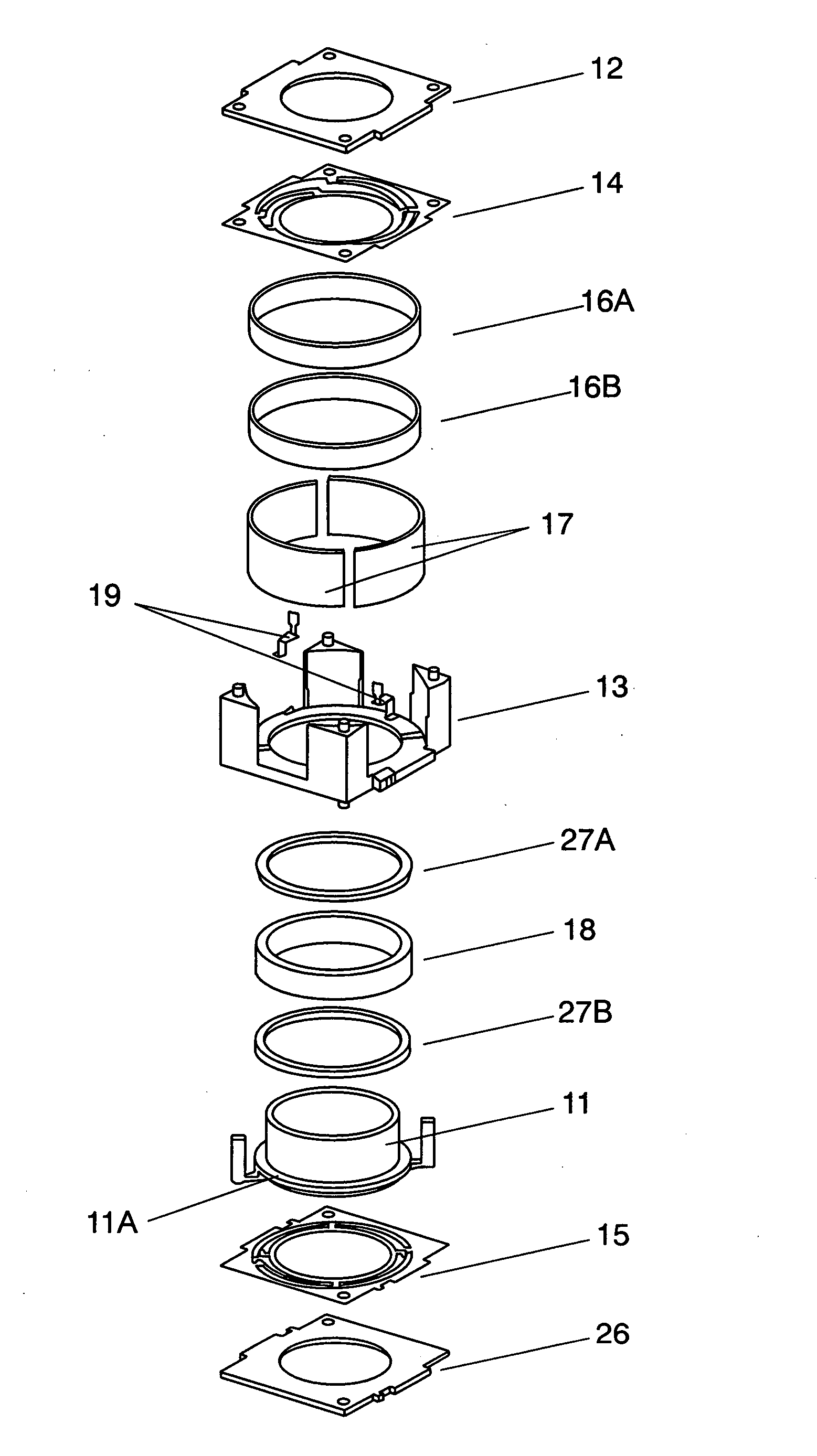
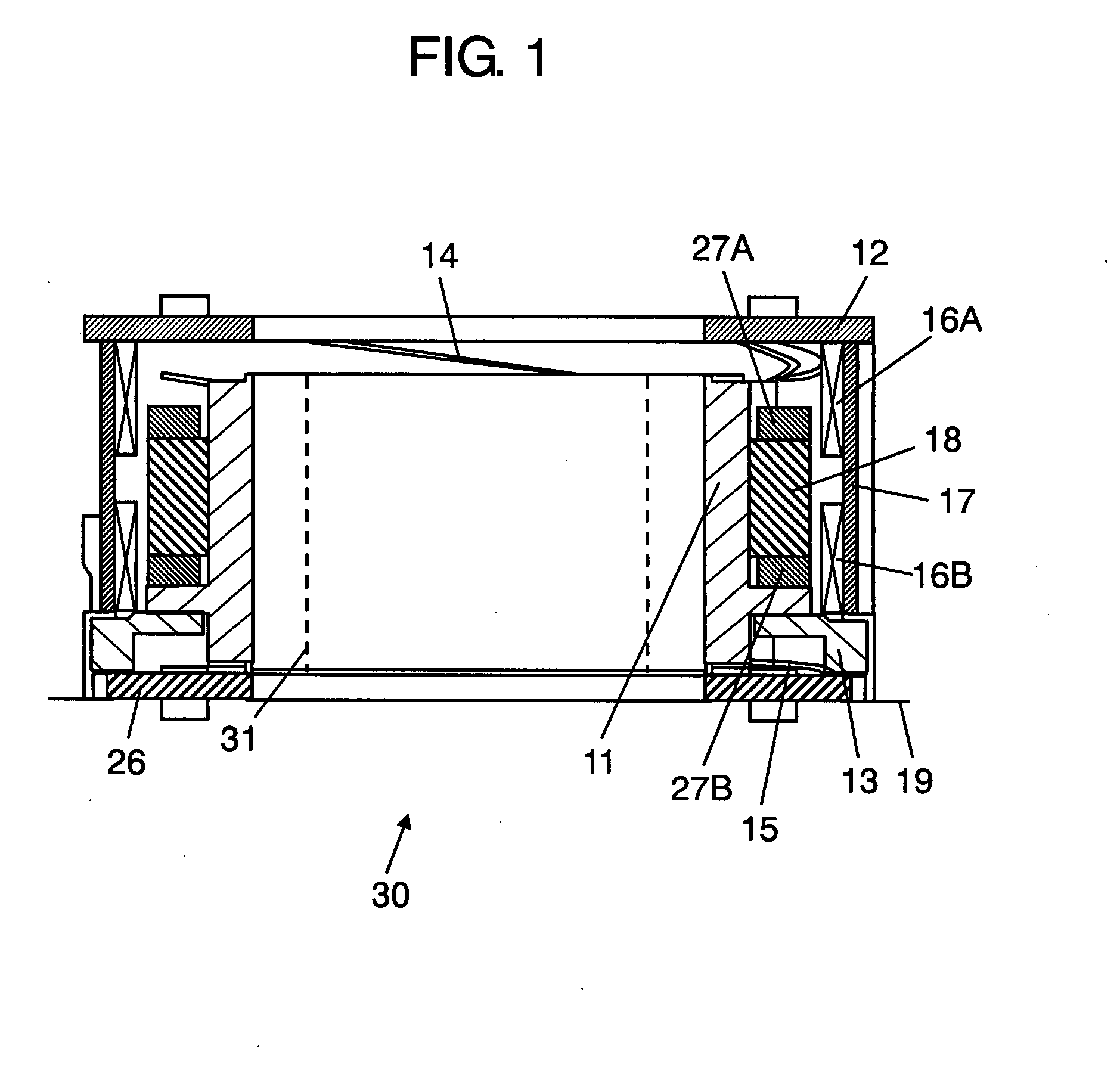
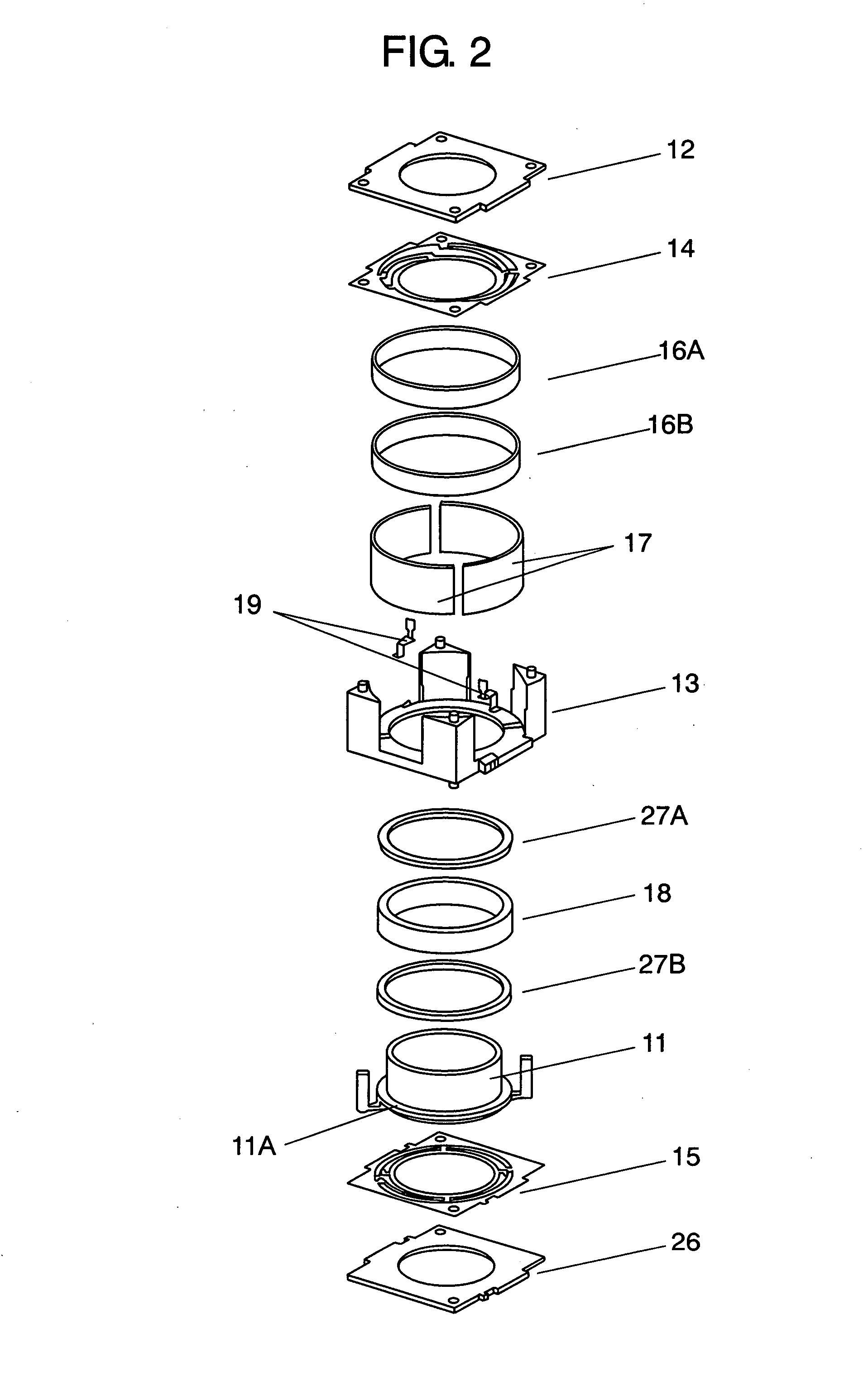
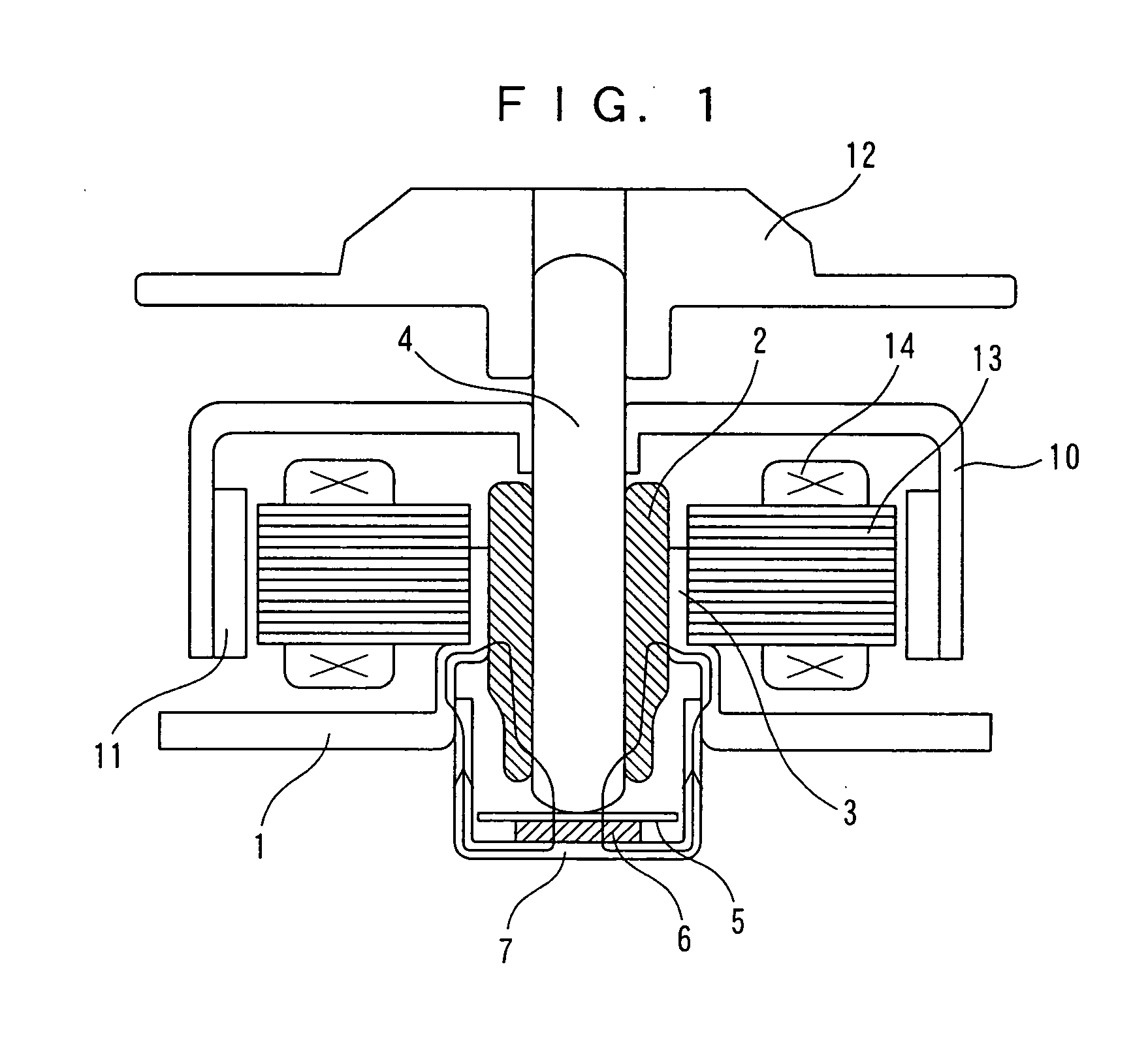
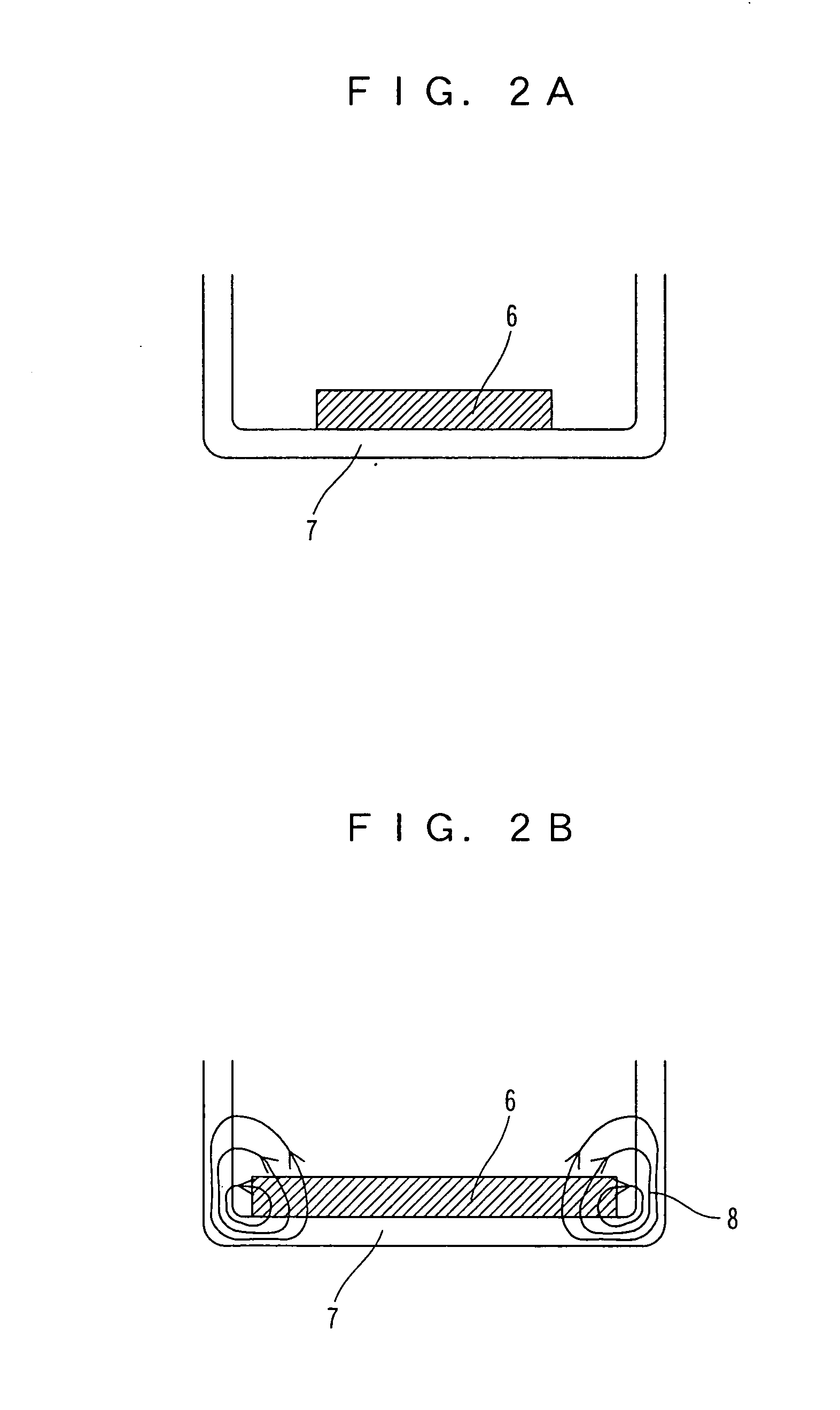
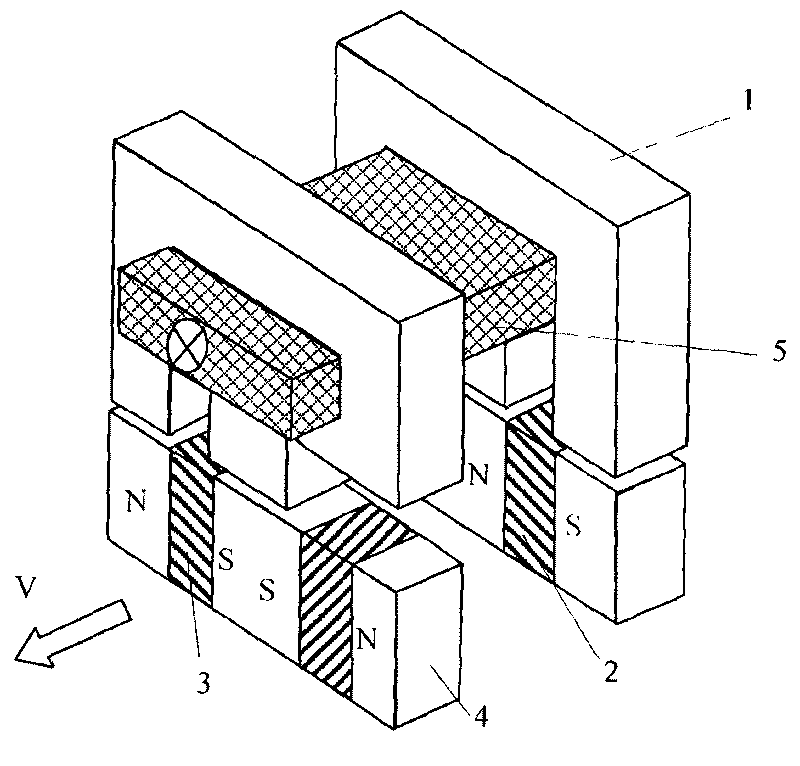
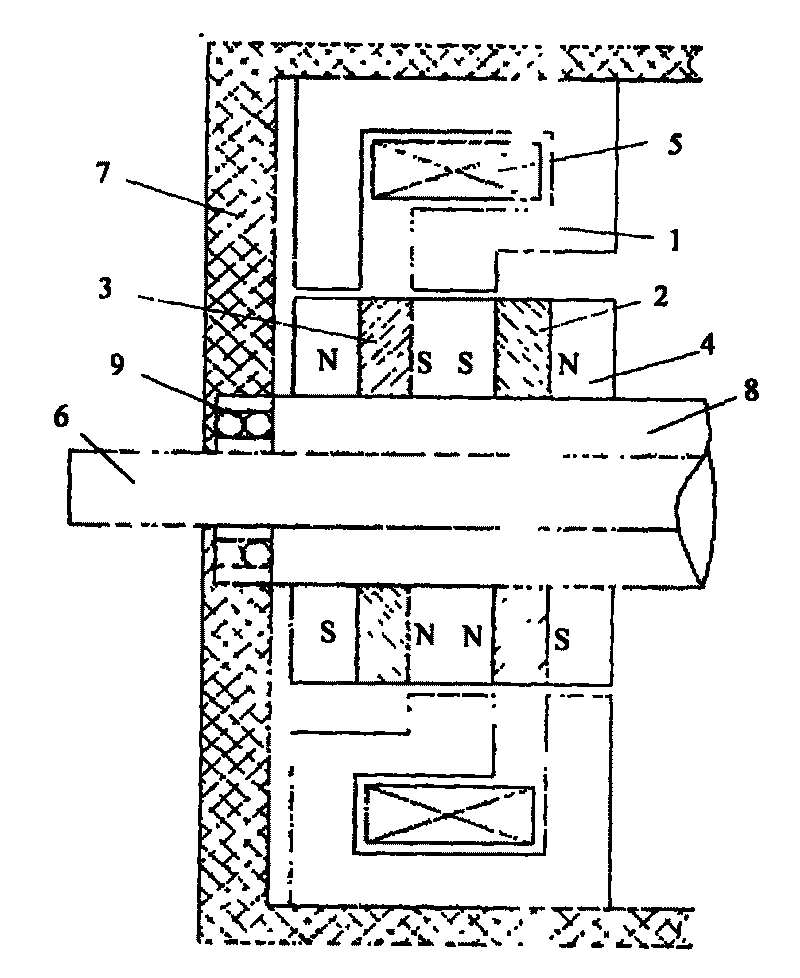
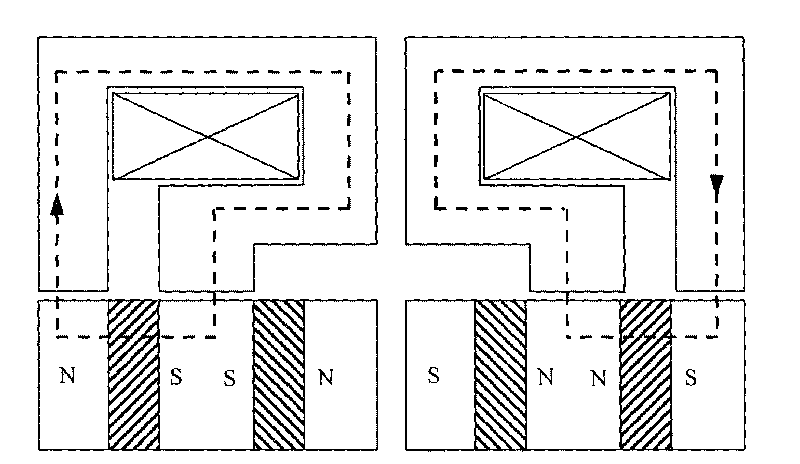
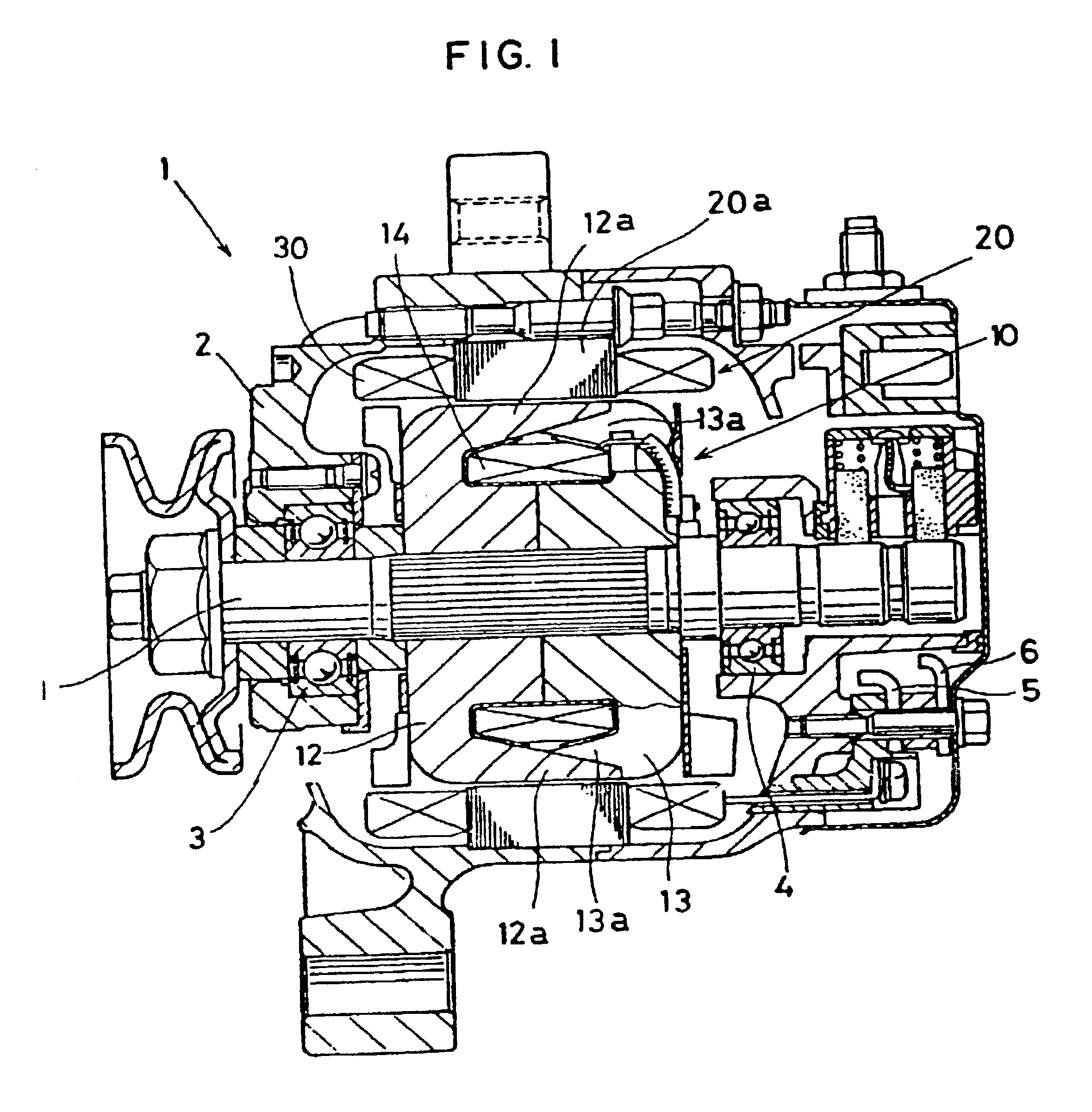
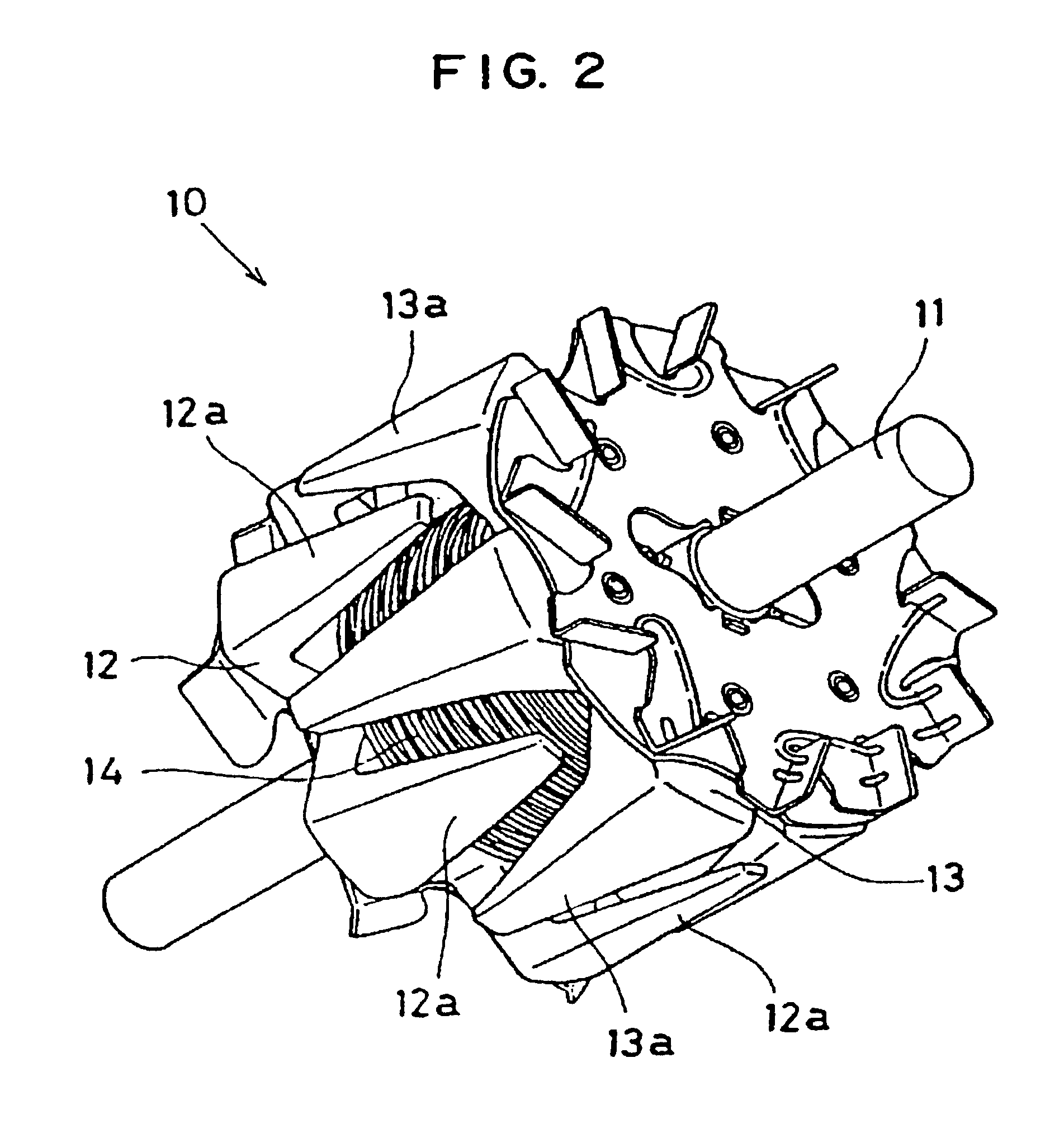
Embedded magnet type rotating electric machine
ActiveUS20070252469A1Reduce leakage fluxMagnetic circuit rotating partsAsynchronous induction motorsElectric machineEngineering
A plurality of magnets are arranged in accommodating holes each extending in a radial direction. A rotor core is provided with an extension portion in a circumferential direction extending further outward in the circumferential direction with respect to the magnet from at least one of a radially outer end and a radially inner end in the accommodating hole, and a radial regulating portion regulating a movement of the magnet in the radial direction. The radial regulating portion extends in the radial direction so as to correspond to a center in the circumferential direction of the accommodating hole. The dimension in the circumferential direction of a portion of the radial regulating portion that is brought into contact with the magnet is smaller than the dimension in the circumferential direction of the magnet. A cross-sectional area of the radial regulating portion as seen from the radial direction is small, in comparison with the case in which the radial regulating portion extends entirely in the axial direction of the rotor core. Accordingly, it is possible to reduce a leakage flux in a rotating electric machine.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Rotary electric machine and electric vehicle
ActiveUS20090224627A1Reduce pulsationSlow down drastic changesHybrid vehiclesPropulsion by batteries/cellsElectric machineEngineering
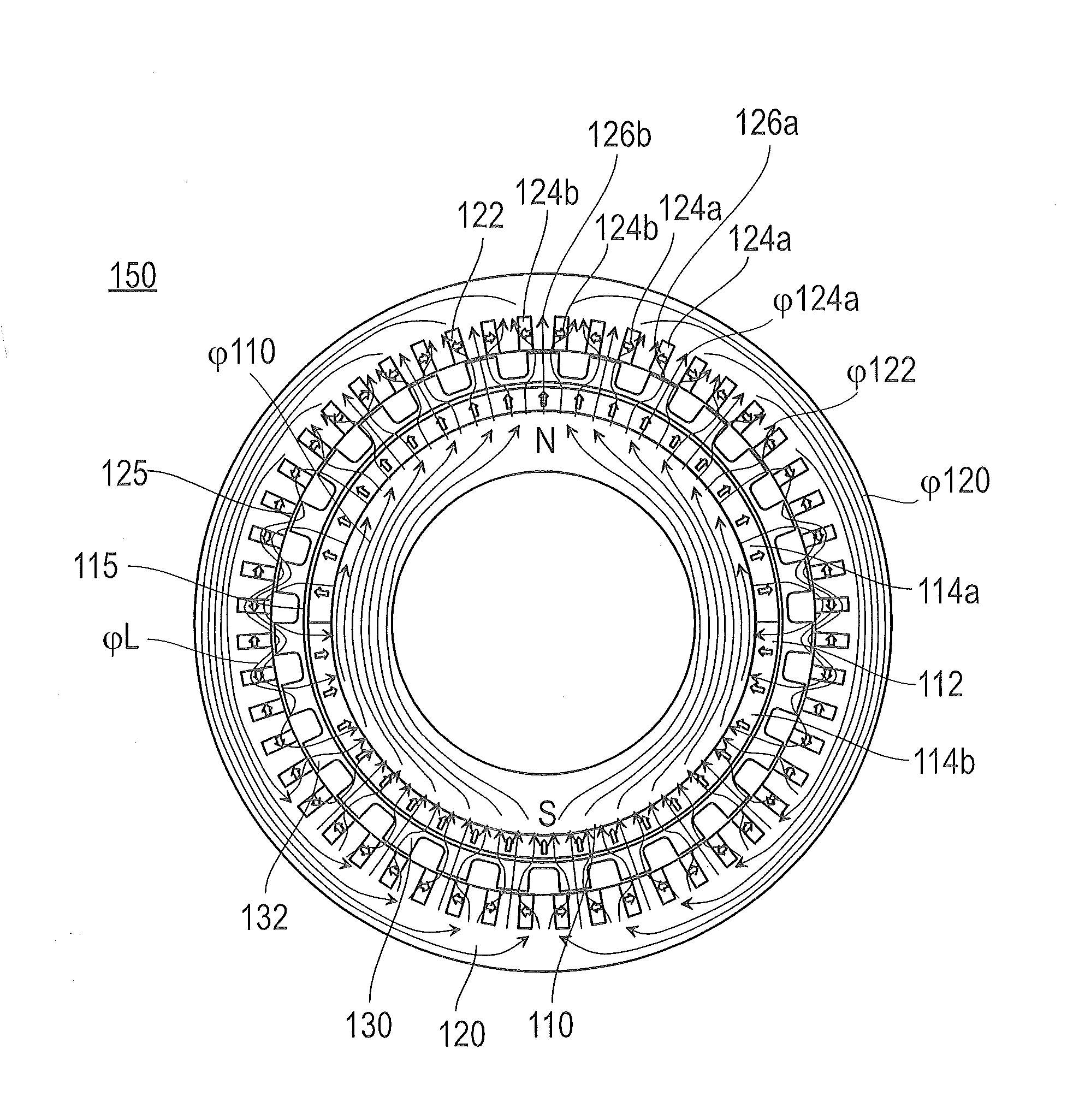
A rotary electric machine includes a stator having stator windings; and a rotor rotatably disposed in the stator, said rotor having a rotor core provided with a plurality of magnets and a plurality of magnetic auxiliary salient poles formed between poles of the magnets. In this rotary electric machine: a magnetic air gap is provided in an axial direction of the rotor in a position shifted in a circumferential direction from a q axis passing through a center of the magnetic auxiliary salient pole within the magnetic auxiliary salient pole; and an amount of shifting the magnetic air gap from the q axis in the circumferential direction differs according to a position of the magnetic air gap in the axial direction so as to cancel torque pulsation in energization caused due to the magnetic air gap.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Motor and washing machine having the same
InactiveUS20130057103A1Reduce leakage fluxIncreased durabilityMagnetic circuit rotating partsOther washing machinesInterior spaceEngineering
A motor includes a stator having stator cores, a coil wound around the stator cores, and a rotor disposed at an inner side of the plurality of stator cores. The rotor includes a sleeve, a plurality of rotor cores arranged in a circumferential direction of the rotor, a plurality of bridges arranged to connect the sleeve to each of the plurality of rotor cores, a plurality of permanent magnets provided between the rotor cores to form an interior space with respect to the sleeve while being spaced apart from the sleeve, and a plurality of support protrusions protruding from the sleeve in an outward radial direction of the sleeve to support the plurality of permanent magnets while corresponding to the plurality of permanent magnets, respectively, the plurality of support protrusions being arranged between the bridges while being spaced apart from the bridges in the circumferential direction of the rotor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electrical machine stator and rotor
InactiveUS6849985B2Improve efficiencyReduce leakage fluxMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsEngineeringConductor Coil
A stator or a rotor for an electrical machine comprises a plurality of circumferentially separated, radially extending teeth, wherein each tooth having a single winding and is provided with an axially and radially extending reluctance barrier to increase the reluctance of each tooth regarding propagation of a magnetic field not interacting with the winding of said tooth.
Owner:HOGANAS AB
Composite magnetic core structure and magnetic element
ActiveCN102956344AHigh application frequencyImprove consistencyTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsInorganic material magnetismMagnetic fluxMagnetic core
The embodiment of the invention discloses a composite magnetic core structure and a magnetic element, which are used for reducing magnetic core loss and increasing the frequency of application. In the embodiment of the invention, the composite magnetic core structure consists of a first magnetic core part and a second magnetic core part, the first magnetic core part is made of low-magnetic permeability soft magnetic material, the second magnetic core part is made of high-magnetic permeability soft magnetic material, and the first magnetic core part and the second magnetic core part are combined and formed into a magnetic flux loop.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
Power transmission device
InactiveUS20140217743A1Great allowable torqueWide rangeDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesPropellersLow speedInductor
A power transmission device includes: a high speed magnet rotor which includes a magnet array which is magnetized in a radial direction; a low speed magnet rotor which includes a magnet array which is magnetized in a circumferential direction; and an inductor rotor which allows magnetic fluxes from the magnet array of the high speed magnet rotor to pass, and the high speed magnet rotor, the low speed magnet rotor and the inductor rotor are concentrically arranged and the magnet array of the low speed magnet rotor is formed such that homopolar surfaces of neighboring magnets face each other in the circumferential direction.
Owner:SANYO DENKI CO LTD
Current transformer iron core of amorphous and nano-crystalline magnetically soft alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105047348AReduce magnetic lossReduce lossTransformers/inductances magnetic coresInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureChemical compositionAlloy
The invention discloses a current transformer iron core of amorphous and nano-crystalline magnetically soft alloy and a preparation method of the current transformer iron core. The chemical component atomic percent of the iron core is FeaSibBcMdCueM'f, wherein a is not more than 85 and is not less than 65; b is not more than 25 and is not less than 5; c is not more than 15 and is not less than 0; d is not more than 15 and is not less than 0; e is not more than 5 and is not less than 0, and f is not more than 1 and is not less than 0, and a plus b plus c plus d plus e plus f equals to 100, and M is at least one of Nb, Mo or V, and M' is at least one of Sn, Al, Y and Sb. The preparation method comprises the steps as follows: preparing materials according to atomic percent and smelting to prepare a mother alloy; then crushing the prepared mother alloy to re-melt and covering steel-making slagging constituent to prevent oxidation and deslagging; preparing amorphous alloy ribbons with the re-melted mother alloy by using a single roll rapid solidification ribbon preparation method under ordinary pressure, and finally winding the amorphous alloy ribbons as the amorphous iron core, and performing isothermal annealing crystallization in a vacuum annealing furnace to obtain the amorphous and nano-crystalline magnetically soft alloy of a mutual inductor iron core. The iron core of the invention has high saturation flux density, high permeability, and low magnetic loss so that the mutual inductor has ultrahigh precision and accuracy class.
Owner:NEW MATERIALS TECH JIANGSU AMORPHD +1
Rotor of permanent magnet rotating electric machine
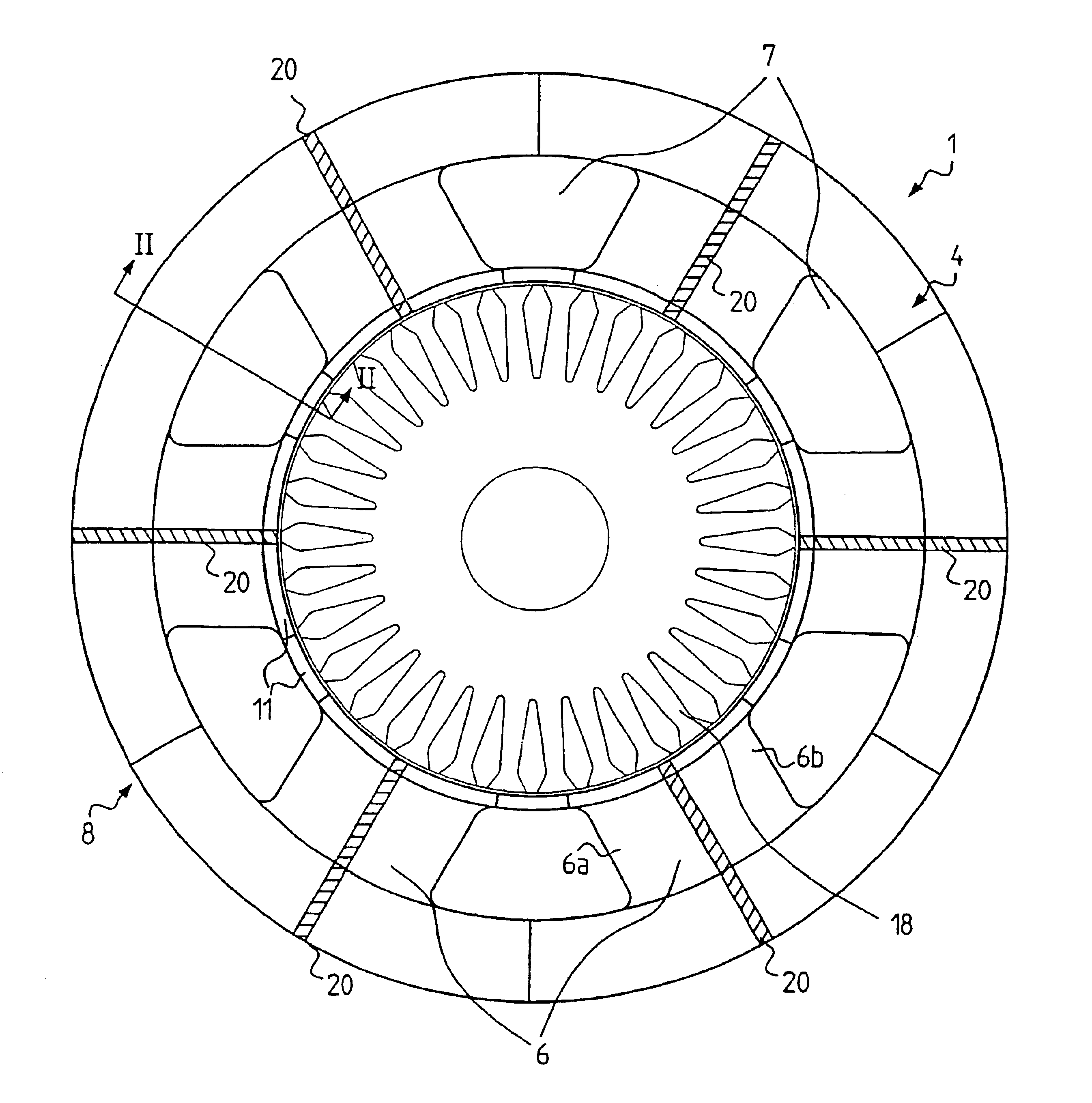
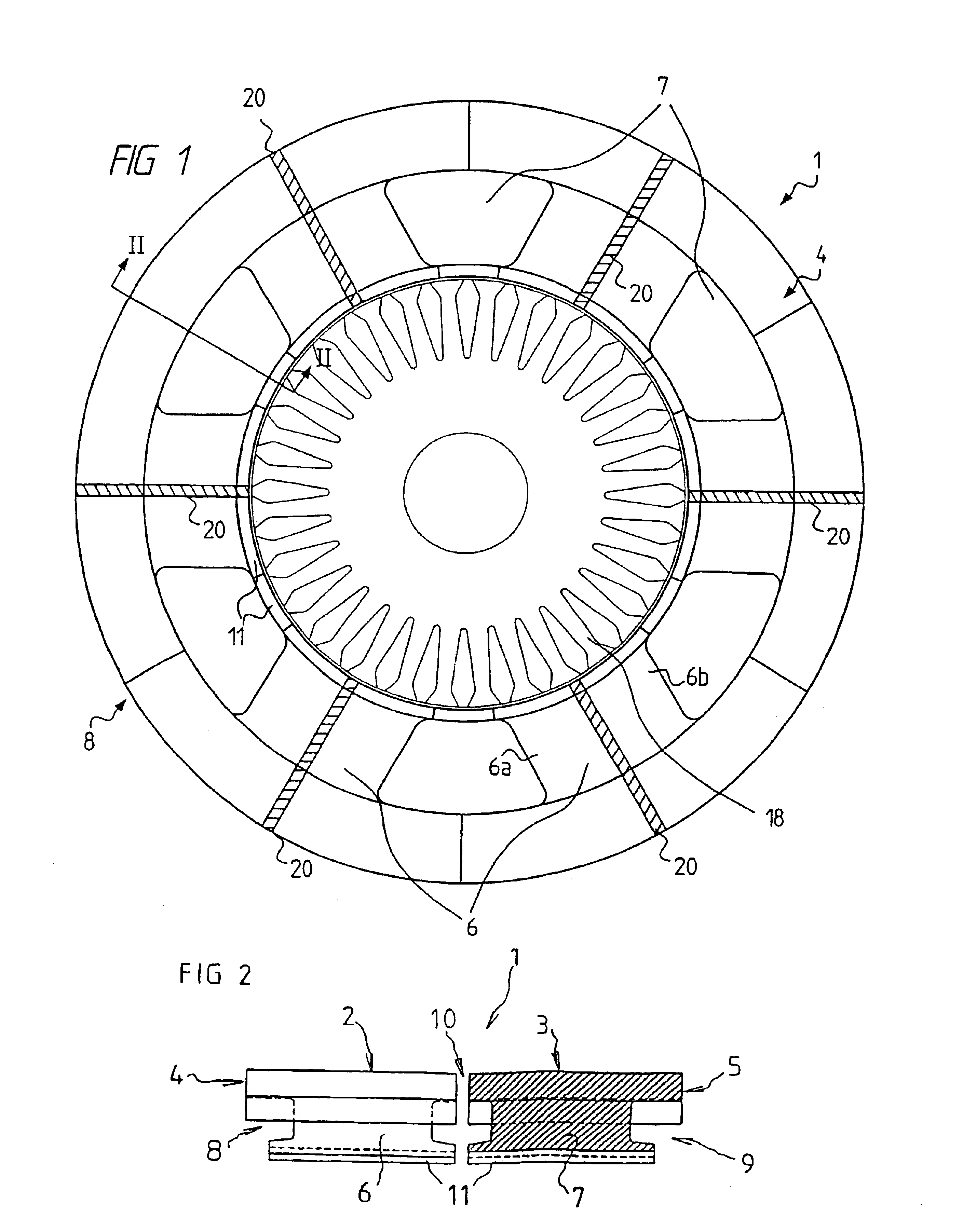
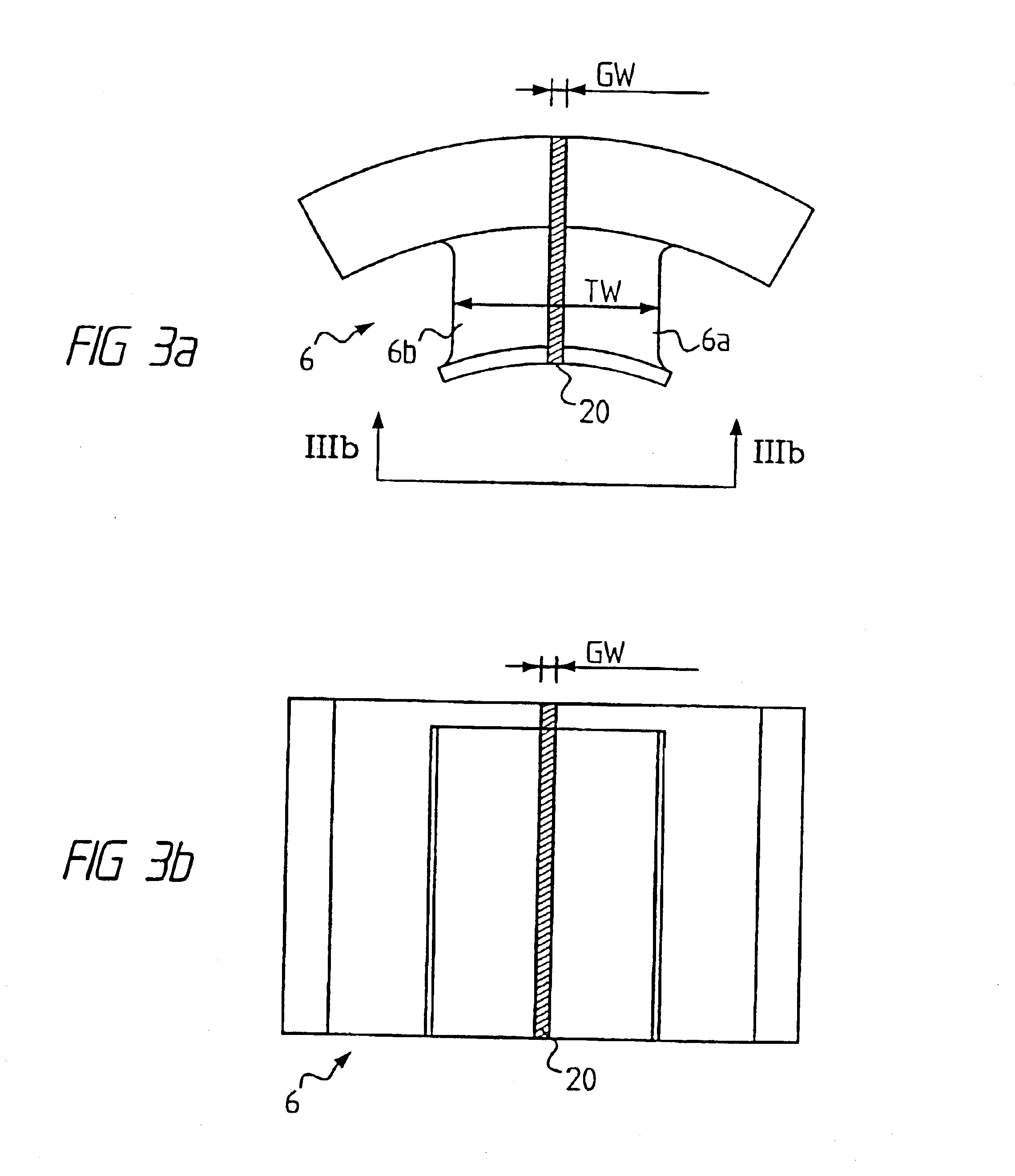
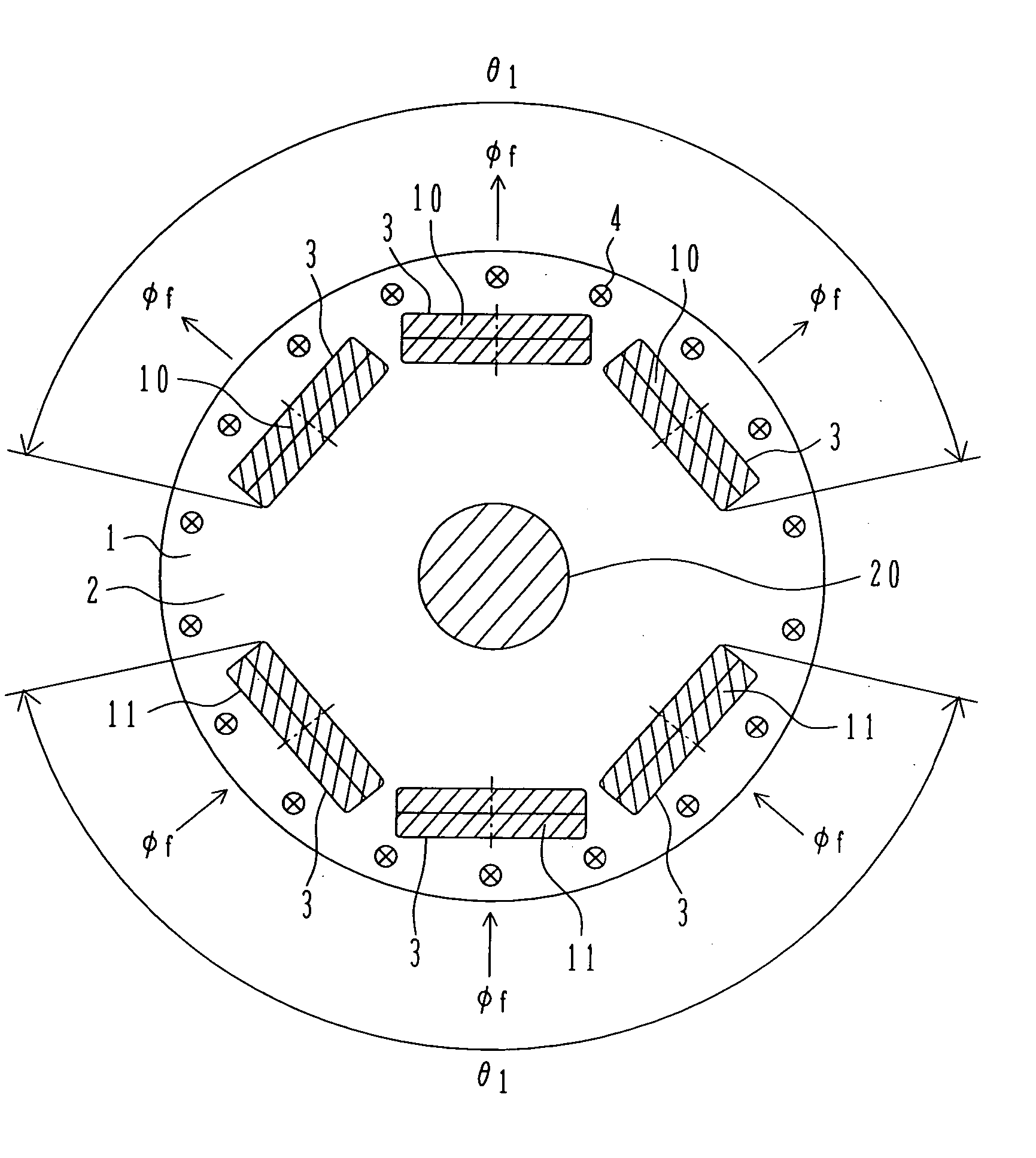
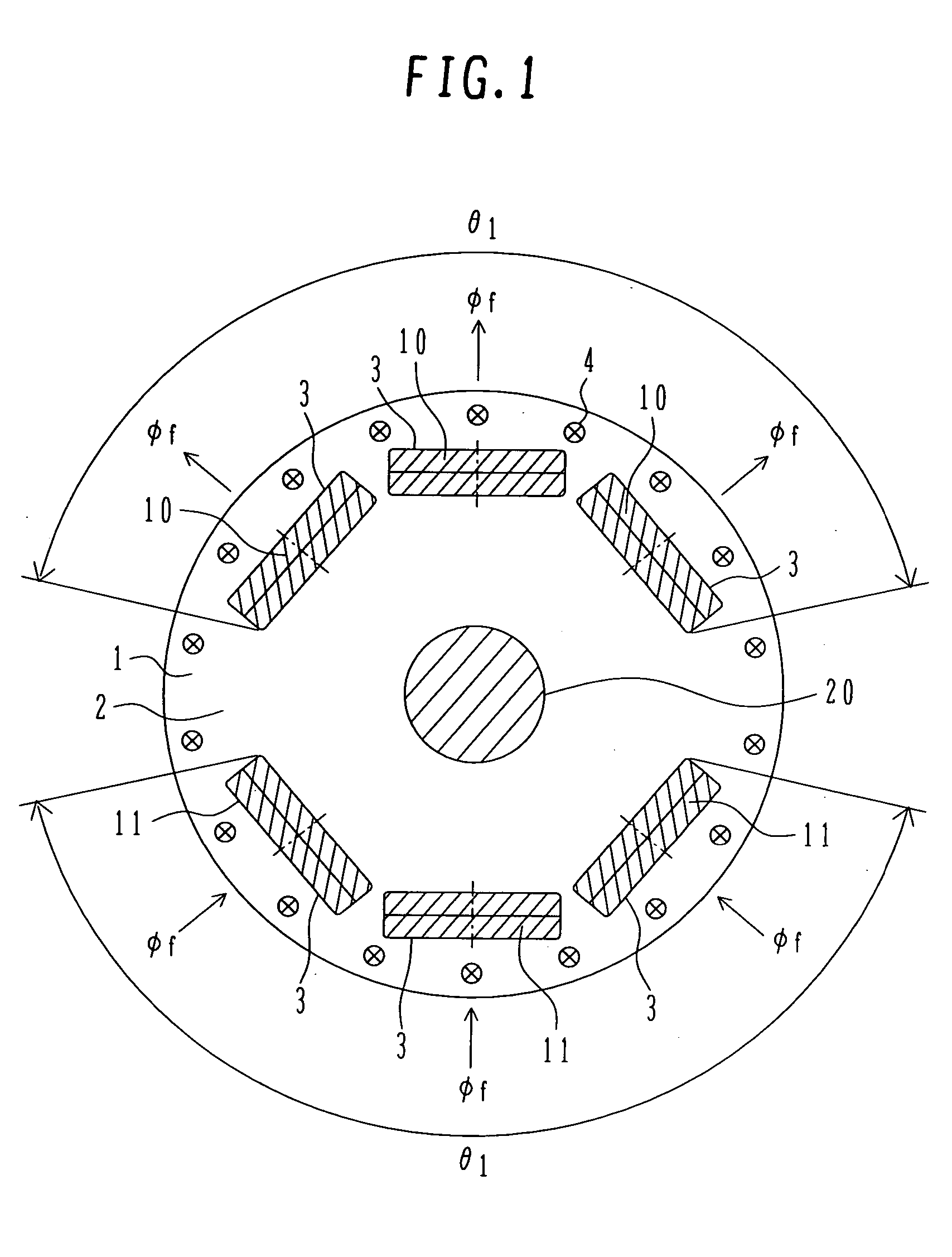
InactiveUS20060103251A1Satisfactory magnetic flux distributionIncreasing fundamental wave effective valueMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machineMagnetic poles
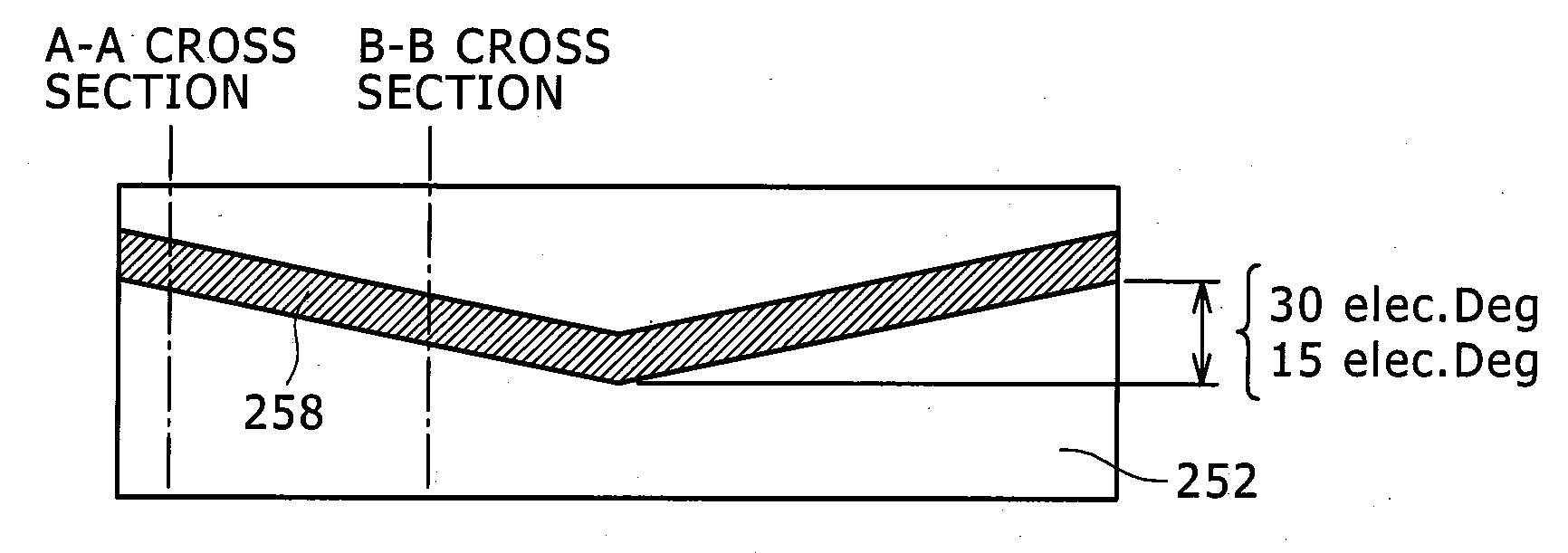
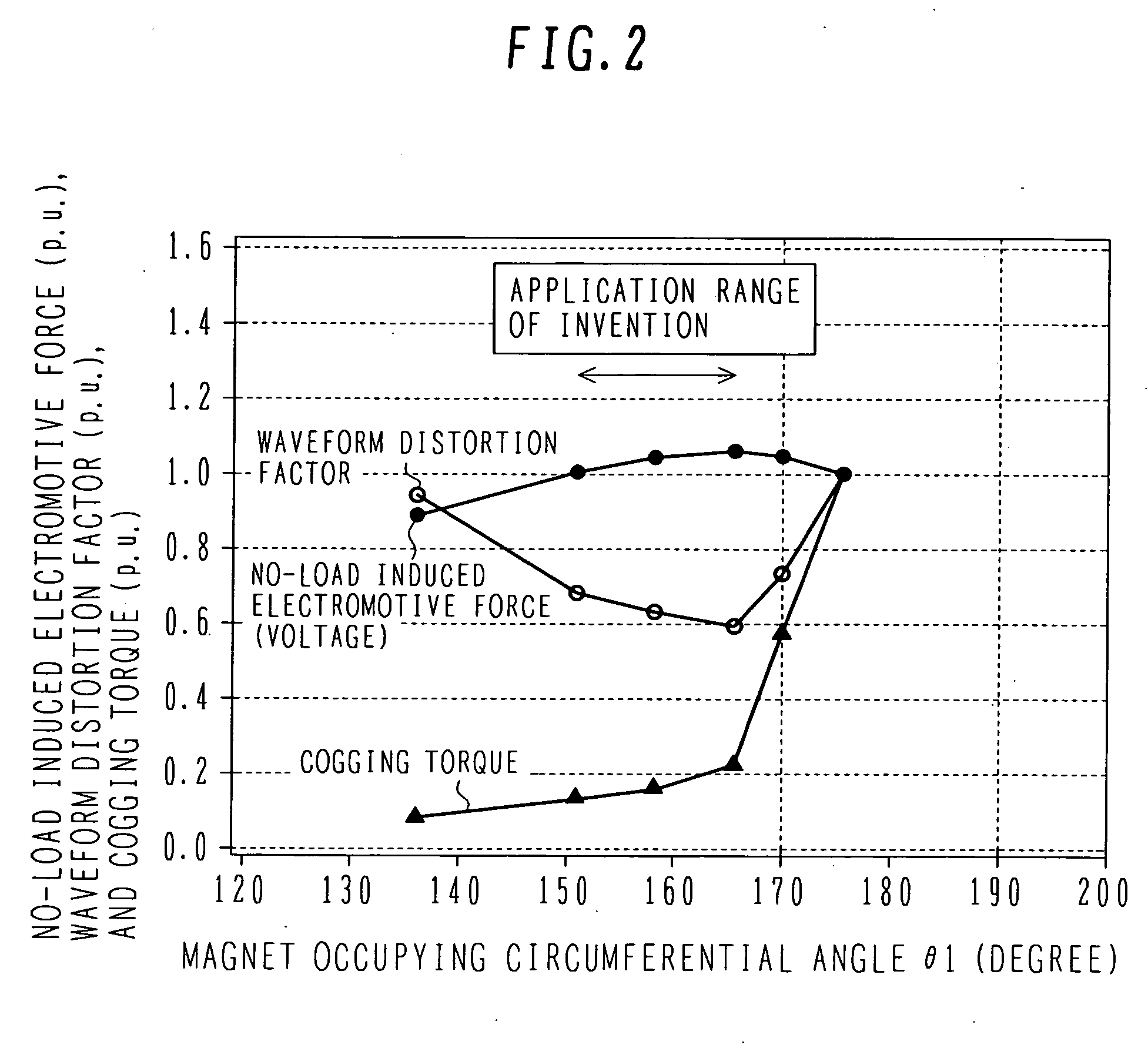
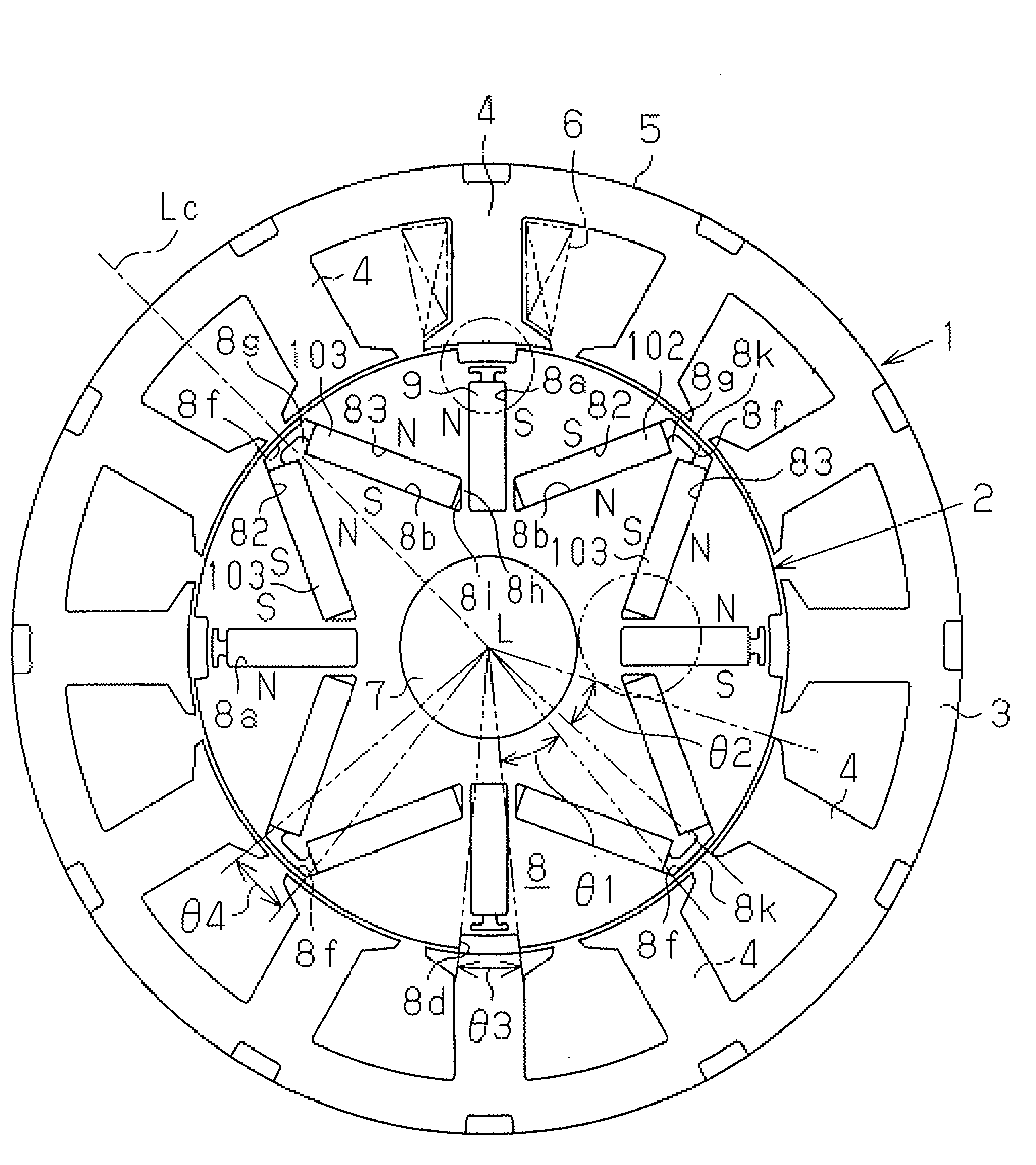
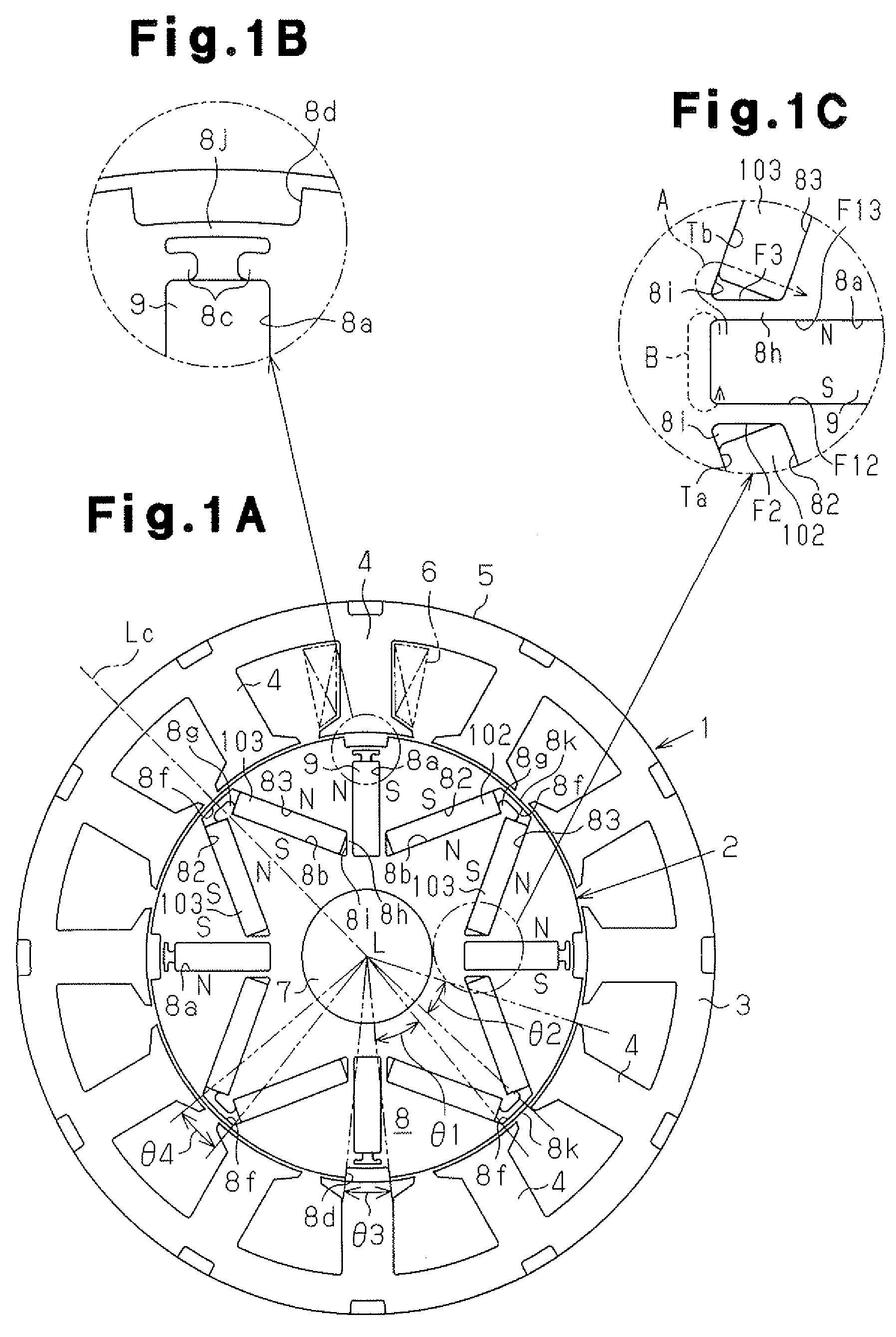
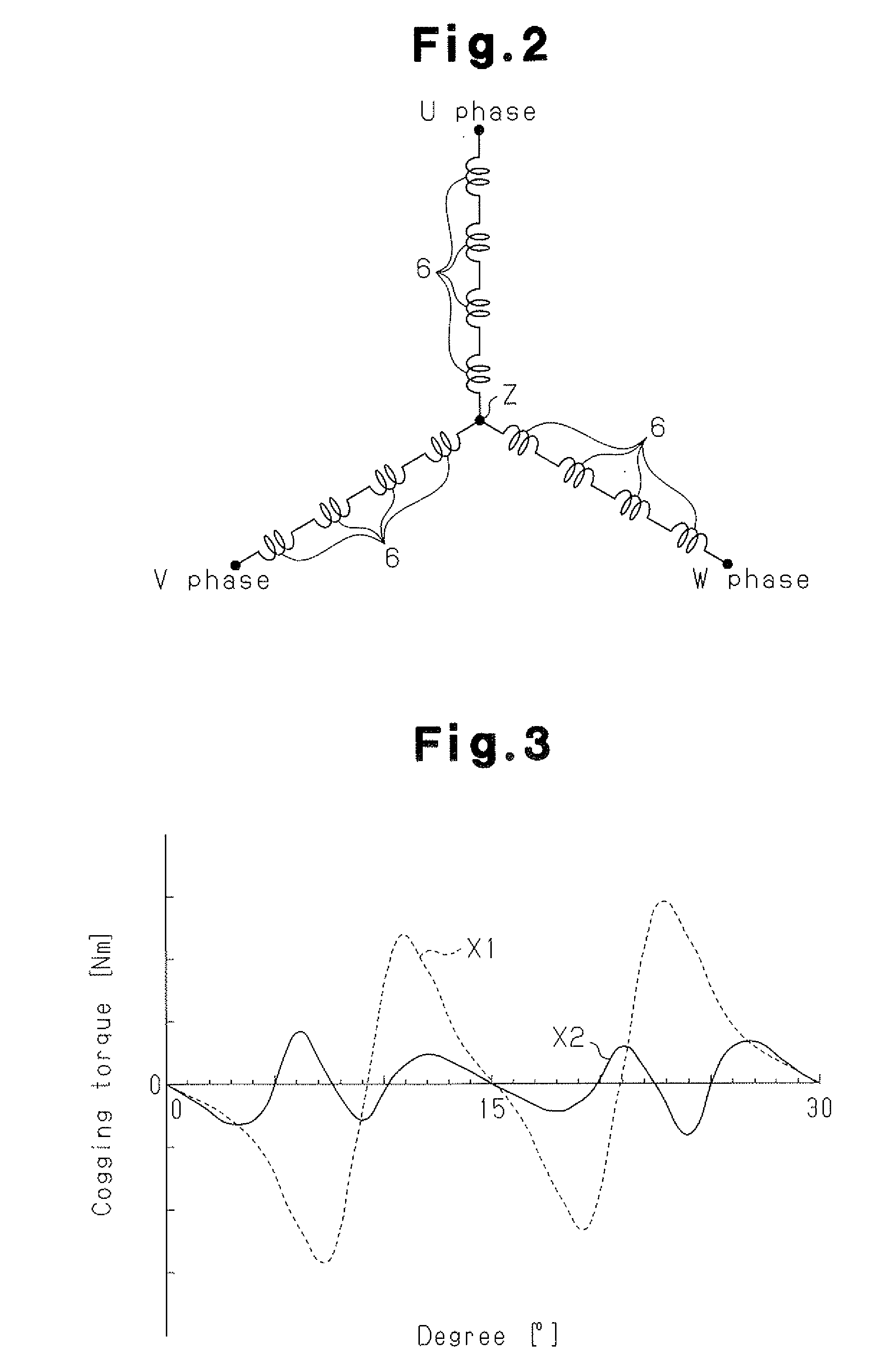
In the prior art in which permanent magnets are regularly arranged over the whole circumference of a rotor core, a satisfactory magnetic flux distribution is hard to obtain, and the cogging torque and the distortion factor of the induced electromotive force waveform are large, whereby characteristics of a rotating electric machine are poor. Also, because the permanent magnets are arranged over the whole circumference, a large number of permanent magnets are required and cost reduction is difficult. A permanent magnet rotating electric-machine of the invention comprises a stator provided with a plurality of windings, and a rotor in which magnets are disposed in slots formed in a rotor core along an outer circumference thereof, the rotor core being fixed on a rotary shaft rotating inside the stator, and in which one magnetic pole is constituted by each group of three or more of the magnets. A total angle occupied by the group of magnets constituting one magnetic pole is in the range of 150 to 165 degrees in terms of an electrical angle.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Rotor of rotary electric machine
InactiveUS20070046137A1Increase magnetic flux of magneticReduce leakage fluxMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machineMagnetic poles
A Lundell type rotor core with a pair of side cores and a magnetic-pole cylindrical portion has a structure in which the magnetic-pole cylindrical portion is mated between both the side cores (also referred to as “pole cores”) in a radial direction at an outside of a field coil wound on a boss portion in the side cores. The magnetic-pole cylindrical portion is made of plural magnetic steel sheets laminated in the axis direction, and is easily deformed rather than both the side cores. The easy deformation characteristic of the magnetic-pole cylindrical portion prevents generation of a gap during the assembling process of the magnetic-pole cylindrical portion and the side cores. Without paying strict dimension control of the components for the rotor core, it is easily possible to prevent any generation of a gap between the side cores and the magnetic-pole cylindrical portion while assembling. It is thereby possible to prevent a deterioration of a magnetic flux flowing in the rotor core.
Owner:DENSO CORP
High performance motor and magnet assembly therefor
InactiveUS7586217B1Improve performanceIncrease forceMagnetic circuit rotating partsPropulsion systemsVariable thicknessHigh flux
Owner:ANORAD
Rotary electric machine with air gaps configured to cancel torque pulsations
ActiveUS8247940B2Reduce pulsationSlow down drastic changesHybrid vehiclesPropulsion by batteries/cellsElectric machineEngineering
A rotary electric machine includes a stator having stator windings; and a rotor rotatably disposed in the stator, said rotor having a rotor core provided with a plurality of magnets and a plurality of magnetic auxiliary salient poles formed between poles of the magnets. In this rotary electric machine: a magnetic air gap is provided in an axial direction of the rotor in a position shifted in a circumferential direction from a q axis passing through a center of the magnetic auxiliary salient pole within the magnetic auxiliary salient pole; and an amount of shifting the magnetic air gap from the q axis in the circumferential direction differs according to a position of the magnetic air gap in the axial direction so as to cancel torque pulsation in energization caused due to the magnetic air gap.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Embedded magnet type motor
InactiveUS20090115280A1Increase torqueIncrease the number ofMagnetic circuitSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsEngineeringMagnet
A rotor of an embedded magnet type motor is disclosed. A rotor core of the motor includes first accommodation holes and V-shaped accommodation holes The first accommodation holes extend in radial directions, and the V-shaped accommodation holes protrude radially outward. The rotor core has grooves at positions corresponding to the first accommodation holes on the outer periphery of the rotor core. Each groove has a width as a dimension in the circumferential direction when viewed from the axial direction. Each first magnet has a width as a dimension in the circumferential direction when viewed from the axial direction. The width of the grooves is larger than the width of the first magnets.
Owner:ASMO CO LTD
Stator for rotary electrical machine
ActiveUS20120146447A1Reducing AC copper lossSimple connection structureMagnetic circuitSynchronous machinesElectrical conductorElectric machine
A stator includes a ring-shaped stator core and a stator winding. The stator core has a plurality of slots arranged in a circumferential direction. The stator winding has a plurality of phase windings. Each phase winding is composed of a plurality of segment conductors 41 disposed such as to be inserted into the slots and connected in series. The segment conductor is divided into two. The phase winding is configured by two divided phase windings connected to each other in parallel. The divided phase windings are respectively configured by a plurality of segment conductors respectively connected in series such that the two divided segment conductors are in parallel with each other.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Short-circuit fault-tolerant vector control method for embedded hybrid magnetic material fault-tolerant cylindrical linear motor
InactiveCN105245156ASimple structureImprove reliabilityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlVoltage source inverterCompensation strategy
The invention discloses a short-circuit fault-tolerant vector control method for an embedded hybrid magnetic material fault-tolerant cylindrical linear motor. The short-circuit fault-tolerant vector control method comprises the following steps: building a five-phase embedded hybrid magnetic material fault-tolerant cylindrical linear motor model; compensating normal thrust missing caused by a short-circuit fault phase and suppressing a thrust ripple caused by phase short-circuit current with non-fault phase current of the motor; and obtaining expected phase voltage by adopting a series of coordinate conversion and voltage feed-forward compensation strategies, and achieving a fault-tolerant vector control after the phase short-circuit fault of the motor by a zero-sequence voltage harmonic injection-based CPWM modulation mode. According to the short-circuit fault-tolerant vector control method, the motor can suppress the thrust ripple of the motor under the condition of a phase short-circuit fault-tolerant operation; more importantly, the dynamic property, the steady-state performance and the properties in a normal state are consistent; the switching frequency of a voltage source inverter is constant; a CPU is low in overhead; and a natural coordinate system only needs to counterclockwise rotate a certain angle in any phase short-circuit fault, so that the motor fault-tolerant operation can be achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Stator permanent-magnetic doubly salient disc-type motor
ActiveCN105245073AAvoid damageEasy to installMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machinesTorque densityNon magnetic
The present invention discloses a stator permanent-magnetic doubly salient disc-type motor, which comprises stator mechanisms, a rotor mechanism and a motor shaft, wherein the rotor mechanism is arranged between the two stator mechanisms, the rotor mechanism and the stator mechanisms are arranged on the motor shaft, each stator mechanism comprises a stator core, two permanent magnets and 2N annular armature windings, 2N stator teeth are evenly distributed on the inner wall of each stator core, a groove between every two adjacent stator teeth is a stator groove, the permanent magnets magnetized in the peripheral direction are arranged in centers of any pair of stator grooves on the same diameter, and the 2N annular armature windings respectively sleeve the 2N stator teeth; and the rotor mechanism comprises a plurality of rotor cores and a non-magnetic-conductive rotor bracket, the plurality of rotor cores are evenly distributed on the outer circumference of the non-magnetic-conductive rotor bracket, and the rotor cores form rotor salient poles. The stator permanent-magnetic doubly salient disc-type motor can effectively improve the reliability of the motor, reduces size and weight of the motor, improves power density and torque density of the motor, and is suitable to be used in occasions with strict requirements on size of generators or motors.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Linear rotation permanent magnet actuator adopting staggered pole structure
The invention discloses a linear rotation permanent magnet actuator adopting a staggered pole structure. the linear rotation permanent magnet actuator comprises a housing (1), a stator, a rotor and a rotating shaft (9), wherein the stator is provided with three groups of stator units in the axial direction, the three groups of stator units are connected by virtue of non-magnetic-conducting connectors (10); the stator is provided with first magnetic poles (6) and second magnetic poles (7) which are alternatively arranged in the axial direction, the first magnetic poles (6) comprise first permanent magnetic poles (61) and first iron poles (62) which are alternatively arranged in the circumferential direction, the second magnetic poles (7) comprise second permanent magnetic poles (71) and second iron poles (72) which are alternatively arranged in the circumferential direction, and the first permanent magnetic poles (61) and the second permanent magnetic poles (71) are opposite in magnetism. According to the linear rotation permanent magnet actuator, the consumption of a permanent magnet is greatly reduced, the size of the actuator is reduced, and the power density is increased.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
High performance motor and magnet assembly therefor
InactiveUS7291953B1High performanceReduce leakage fluxSynchronous generatorsWindingsMagnetVariable length
A magnet assembly includes a back iron and an array of magnets. The back iron is in the form of a plate having opposed surfaces. The magnets are arranged along one of the surfaces, with the other surface being dimensioned and configured according to the magnetic field distribution associated with the magnets. The back iron geometry provides for reduced mass, reduced leakage flux, and high flux densities to improve performance of a linear motor that employs such a magnet assembly. Additionally, the back iron can be a magnetically conductive annular ring, such as is employed in a rotary motor. Moreover, the magnets can be arranged in a manner that generates a Halbach array to increase force output in a desired direction while canceling stray magnetic fields in other directions. Similar reduced-mass designs can be employed in conjunction with a back iron of a fixed cross-section and magnets of variable thicknesses, variable lengths, and / or variable widths. In a case where the arrangement is employed in a platen and forcer system, plates on both the platen and forcer may be scalloped to reduce mass.
Owner:ANORAD
Lens actuator, and electronic device using the same
A lens actuator is provided for moving a movable part including a lens, with respect to a fixed part in the optical axis direction of the lens. The lens actuator includes (a) a magnet disposed on the surface of the movable part facing the fixed part and magnetized in the optical axis direction, (b) a coil disposed on the surface of the fixed part facing the magnet, and (c) a pair of magnetic materials disposed on both sides of the magnet in the optical axis direction, to direct magnetic flux from the magnet toward the coil.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Brushless motor
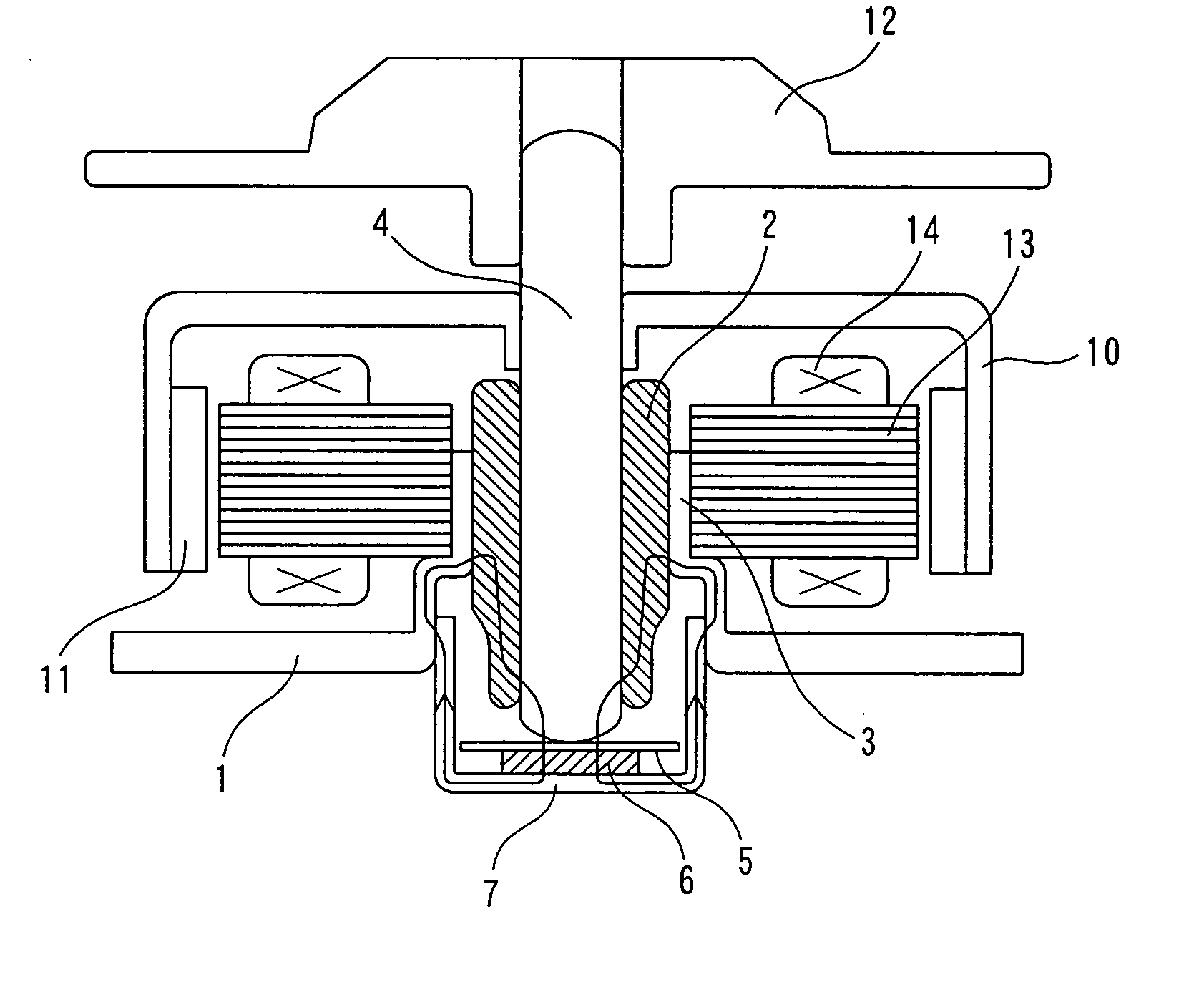
ActiveUS20050140225A1Avoid large vibrationsSufficient forceShaftsRecord information storageBrushless motorsMagnetic flux
The present invention provides a low vibration brushless motor for reducing the vibration of the motor in an axial direction. In the brushless motor, a bearing is provided in a bearing boss, a shaft is held by the bearing, an end face of the shaft is contacting a thrust receiving member, and the shaft is rotatably axially supported by the bearing. The brushless motor includes a permanent magnet for attracting the end face of the shaft in the thrust direction with the thrust receiving member therebetween, and a bottom receiving part for supporting the permanent magnet, wherein the bearing boss, bearing, shaft, and bottom receiving part are made of a magnetic material, and a closed magnetic path is formed so that a magnetic flux passes through the permanent magnet, bottom receiving part, bearing boss, bearing, and shaft.
Owner:MINEBEA MOTOR MFG
Monolithic ceramic electronic component and method for manufacturing monolithic ceramic electronic component
ActiveUS20050018382A1Leakage flux is lowReliability of deteriorateFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsPorosityMetallurgy
A monolithic ceramic component includes a coil-including region formed by stacking ceramic green sheets for defining inner layers having a porosity of about 30% to about 80%, and outer layer regions formed by stacking ceramic green sheets for defining outer layers have a porosity of about 10% or less. Outer electrodes are provided on the right end surface and the left end surface of a sintered ceramic laminate. That is, the outer electrodes are provided on the main surfaces of outermost ceramic sheets for outer layers.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Flux switching type magnetic-concentration transverse flux permanent magnetic wind generator
InactiveCN101741197AAvoid the situation that only corresponds to one stator coreIncreased torque densityMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsTransverse fluxElectric machine
The invention relates to a flux switching type magnetic-concentration transverse flux permanent magnetic wind generator, in particular to a novel high-performance and direct-driving type transverse flux permanent magnetic wind generator. The generator comprises a stator, a rotor, permanent magnets and a winding. The stator consists of a plurality of stator cores (1) and an armature winding (5), wherein the stator cores (2) are distributed around the rotor. Two adjacent stator cores (1) in the circumferential direction are arranged in bilateral symmetry, and the stator cores are arranged on a casing (7) made from non-magnetic conductive material. Rotor cores (4) are arranged on a barrel (8) made from the non-magnetic conductive material. The barrel is connected with a motor rotary shaft (6), and is connected with a motor casing (7) through a bearing (9). Both sides of the rotor cores (4) are respectively embedded into permanent magnets (2) and (3), and the pole directions are opposite. The pole directions of the permanent magnets (2) and (3) of two adjacent rotor cores (4) in the peripheral direction are opposite. According to the motor structure, the single-phase generator can be manufactured, and the multiple-phase generator also can be manufactured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Magnetic flux switching type transverse magnetic flux permanent magnetism wind mill generator
InactiveCN101577449AAvoid the situation that only corresponds to one stator coreIncreased torque densityMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic polesNon magnetic
The invention provides a magnetic flux switching type transverse magnetic flux permanent magnetism wind mill generator, which is a novel transverse magnetic flux permanent magnetism wind mill generator which is high in power density and torque density and is directly driven. A stator consists of a plurality of stator cores(1) distributed around a rotor and an armature winding(4); each stator core(1) is U-shaped, both sides of the stator core(1) are embedded with a first permanent magnet(2) and a second permanent magnet(3), and magnetic pole directions of the two permanent magnets are opposite; the ring-shaped winding(4) is arranged in the stator; the magnetic poles of the first permanent magnets(2) of the two adjacent stator cores(1) are opposite, and the magnetic poles of the second permanent magnets(3) of the two adjacent stator cores(1) are also opposite; all rotor cores(5) are the same in size; the two adjacent rotor cores(5) are aligned left and right respectively and arranged at intervals; the rotor cores(5) are made by overlapping silicon steel sheets and arranged on a cylinder(8) made of non-magnetic conduction materials to form the whole rotor; and the rotor is connected with a rotating shaft of a motor (6) and then connected with a shell(7) through a bearing(9).
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Non-contact position sensor having specific configuration of stators and magnets
InactiveUS6867582B2Reduce leakage fluxFreedom of movementSolid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesHall elementContact position
A non-contact position sensor including a first stator having two magnet facing sides, a second stator having one magnet facing side aligned with the two magnet facing sides along a locus, a hall element between the first and second stators, and two magnets located next to each other along the locus opposite the three magnet facing sides so as to move freely along the locus. When configured as a rotary sensor, an arbitrary angle of usage can be set. When configured as a linear sensor, a magnet can be made thick without increasing leakage of magnetic flux.
Owner:MIKUNI CORP
Embedded magnet type motor
InactiveUS20080265706A1Increase torqueIncrease the number ofMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsControl theoryMagnet
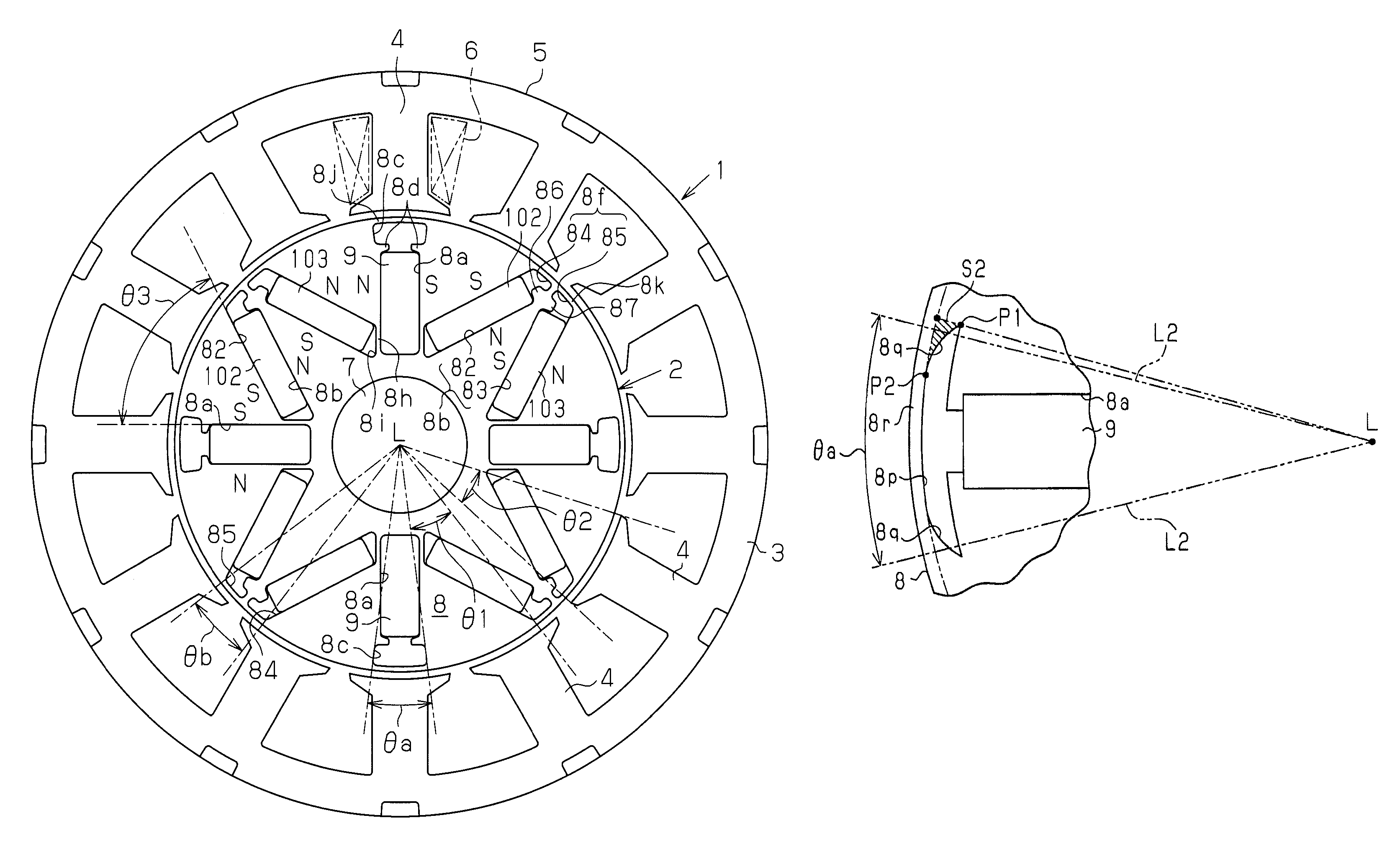
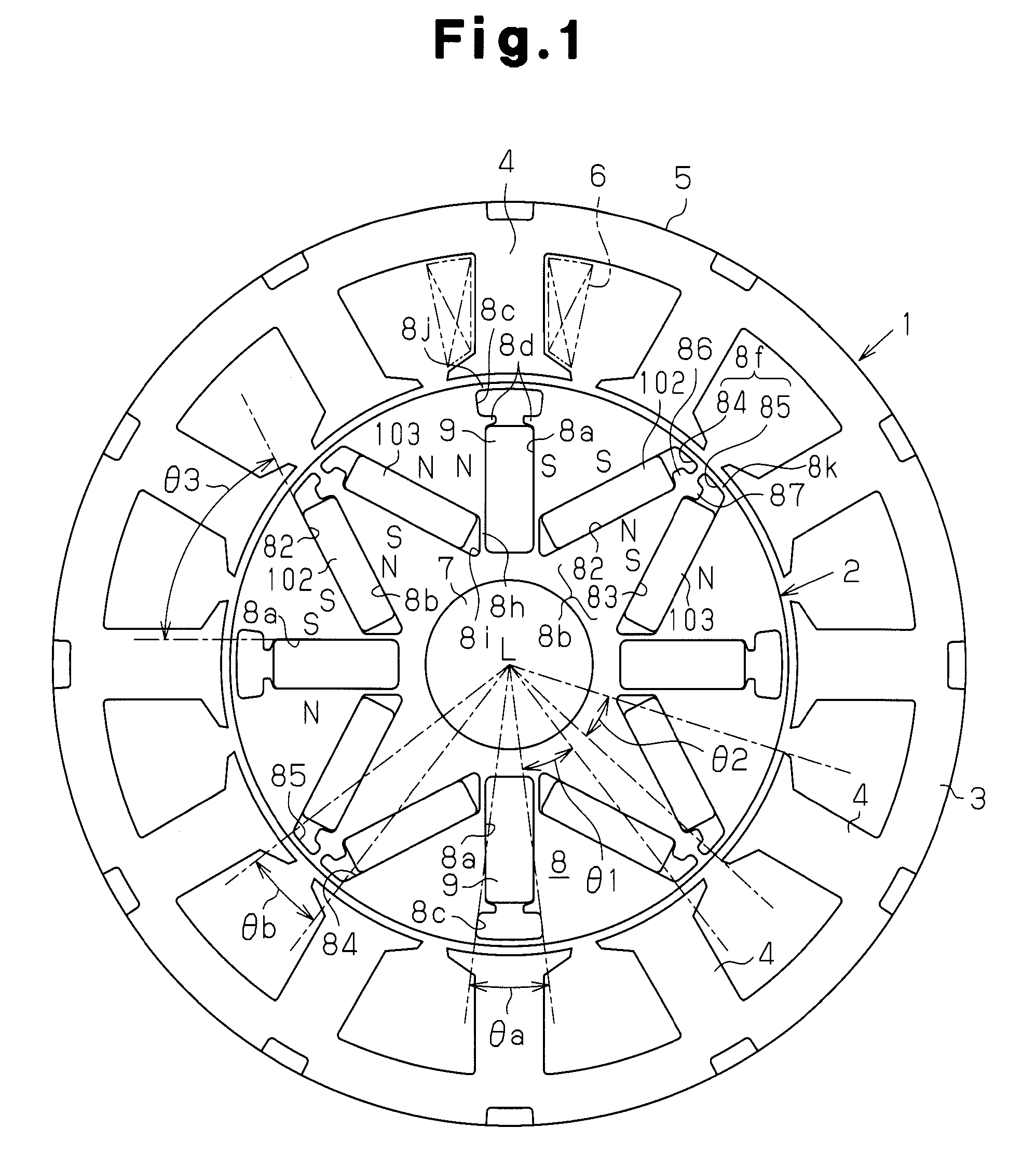
An embedded magnet type motor is disclosed. The rotor core of the motor has radially extending first accommodation holes and V-shaped accommodation holes. Each V-shaped accommodation hole includes a second accommodation hole and a third accommodation hole. A first gap is formed in each first accommodation hole. The first gap is not occupied by the corresponding first magnet. A second gap is formed in each second accommodation hole. The second gap is not occupied by the corresponding second magnet. A third gap is formed in each third accommodation hole at a radially outer portion. The third gap is not occupied by the corresponding third magnet. Each second gap and the adjacent third gap form one V-shaped gap. The angular width θa of each first gap and the angular width θb of each V-shaped gap are determined to satisfy the expression: 0.60<θa / θb<1.60.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Magnetic Element
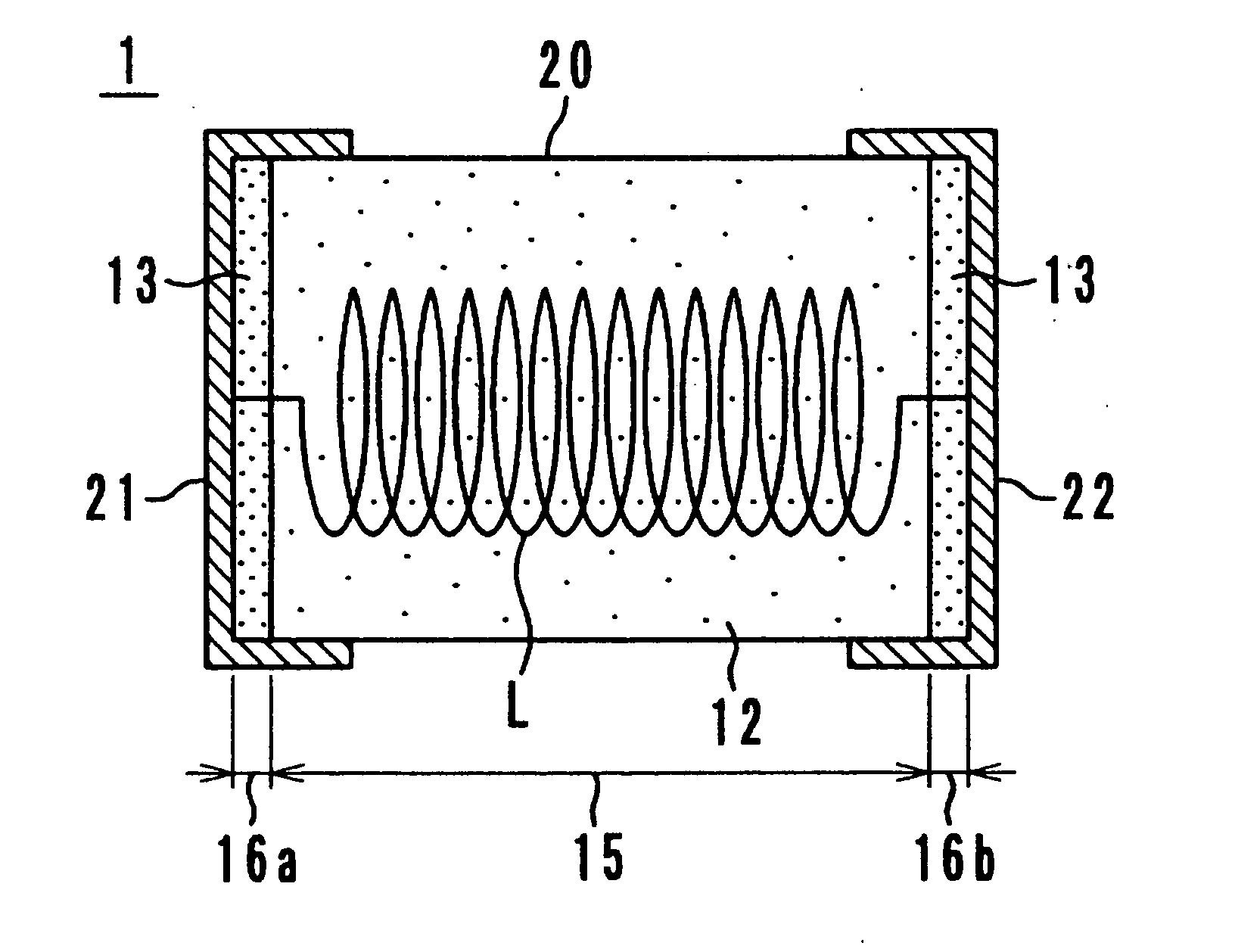
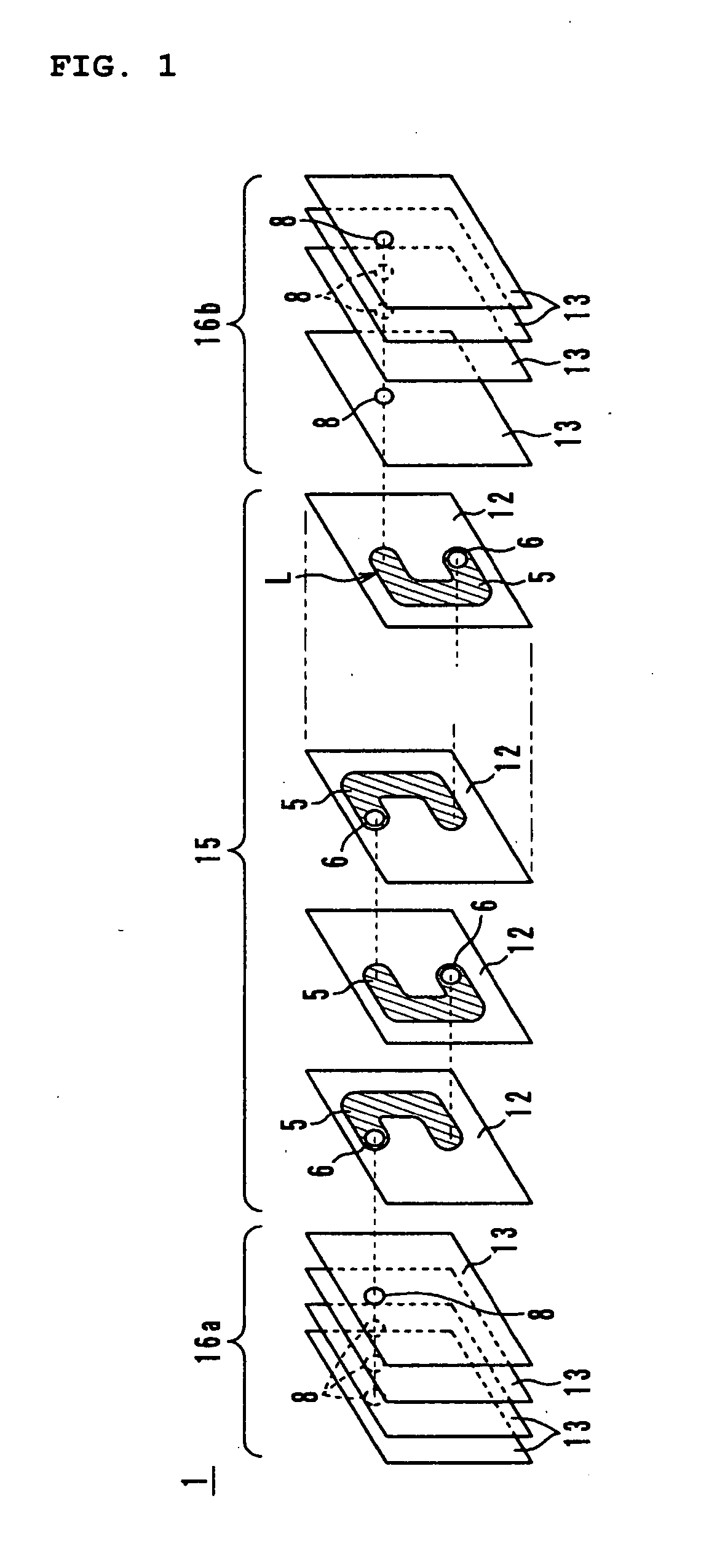
ActiveUS20080024255A1Reduce leakage fluxSaturation magnetic flux density can be increasedTransformers/inductances casingsCores/yokesElectrical and Electronics engineeringMagnetic core
Owner:SUMIDA CORP
Linear motor
ActiveUS20110248579A1Reduce Flux LeakageIncrease thrustMagnetic circuitPropulsion systemsElectrical polarityMagnetic poles
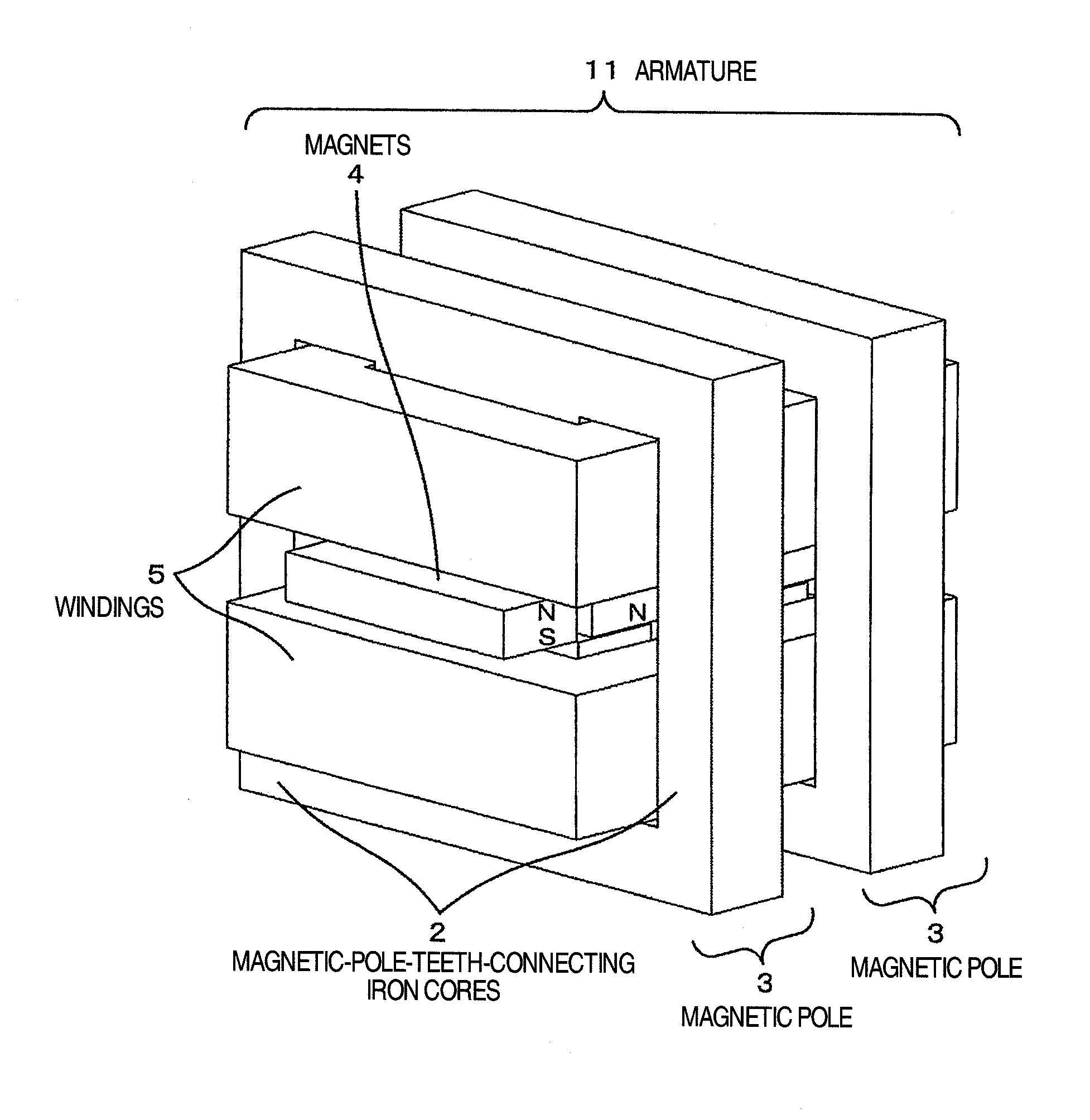
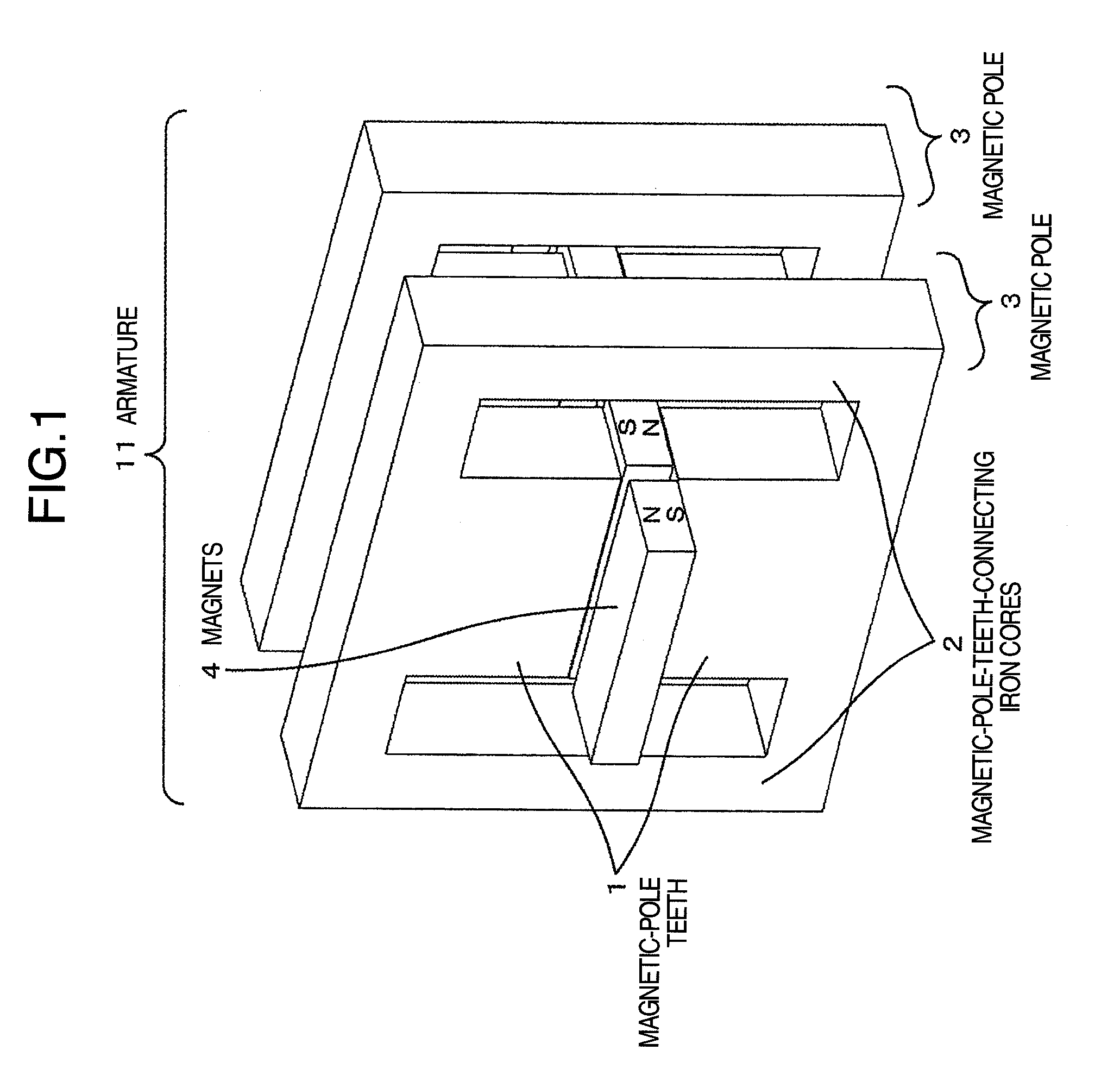
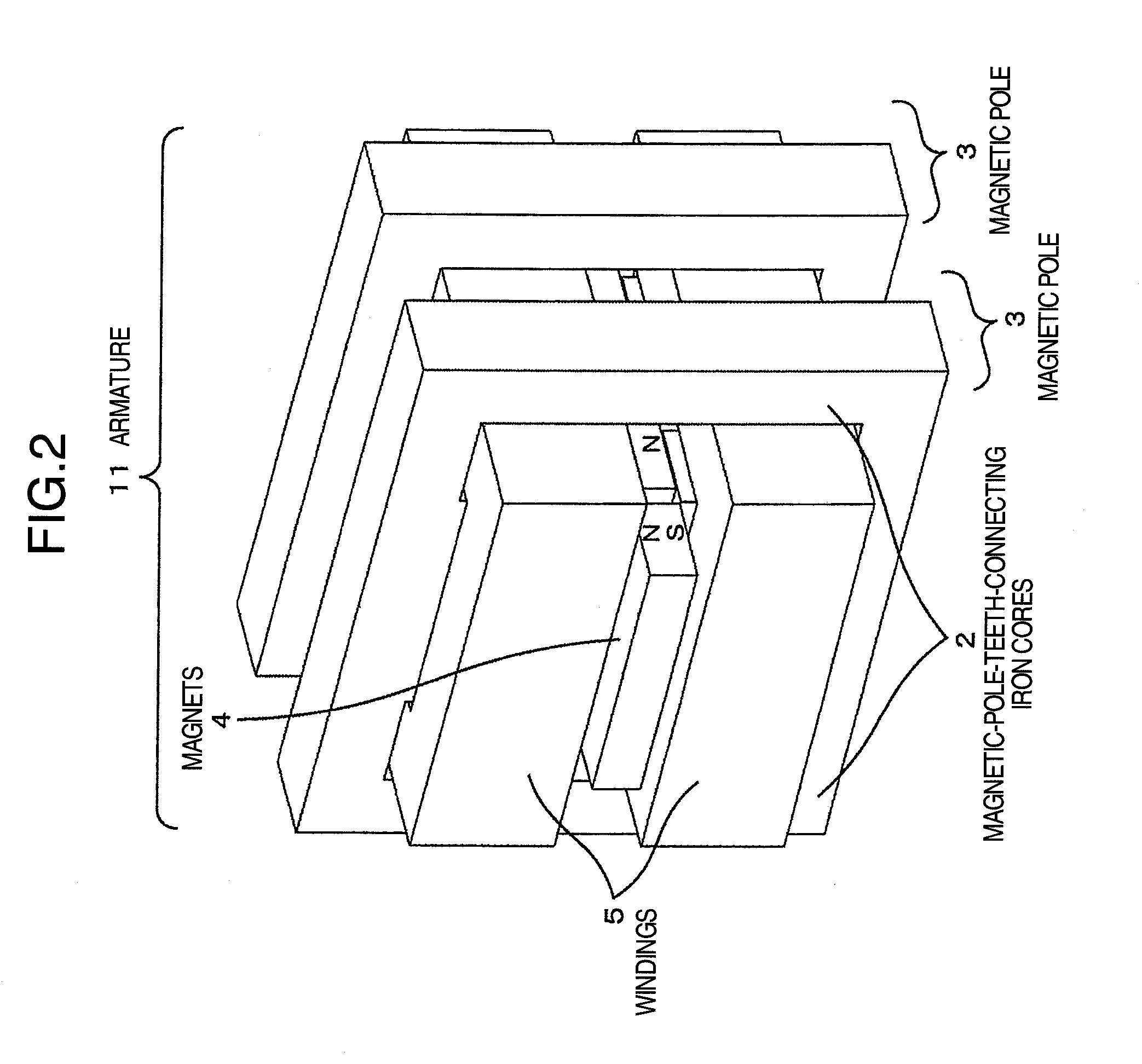
A linear motor including magnetic-pole teeth which pinch and hold permanent magnets deployed in a displacer, a plurality of iron cores used for continuously connecting the magnetic-pole teeth, windings wound around the plurality of iron cores in batch, and the displacer in which positive and negative magnetic poles of the permanent magnets are arranged alternately. A plurality of magnetic poles including the magnetic-pole teeth and the iron cores are deployed along a longitudinal direction of the displacer. The windings which are common to the plurality of magnetic poles are deployed on the iron cores. The leakage magnetic flux between the adjacent magnetic poles is reduced by making polarities of the plurality of deployed magnetic poles one and the same polarity.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Alternating current generator having a plurality of independent three-phase windings
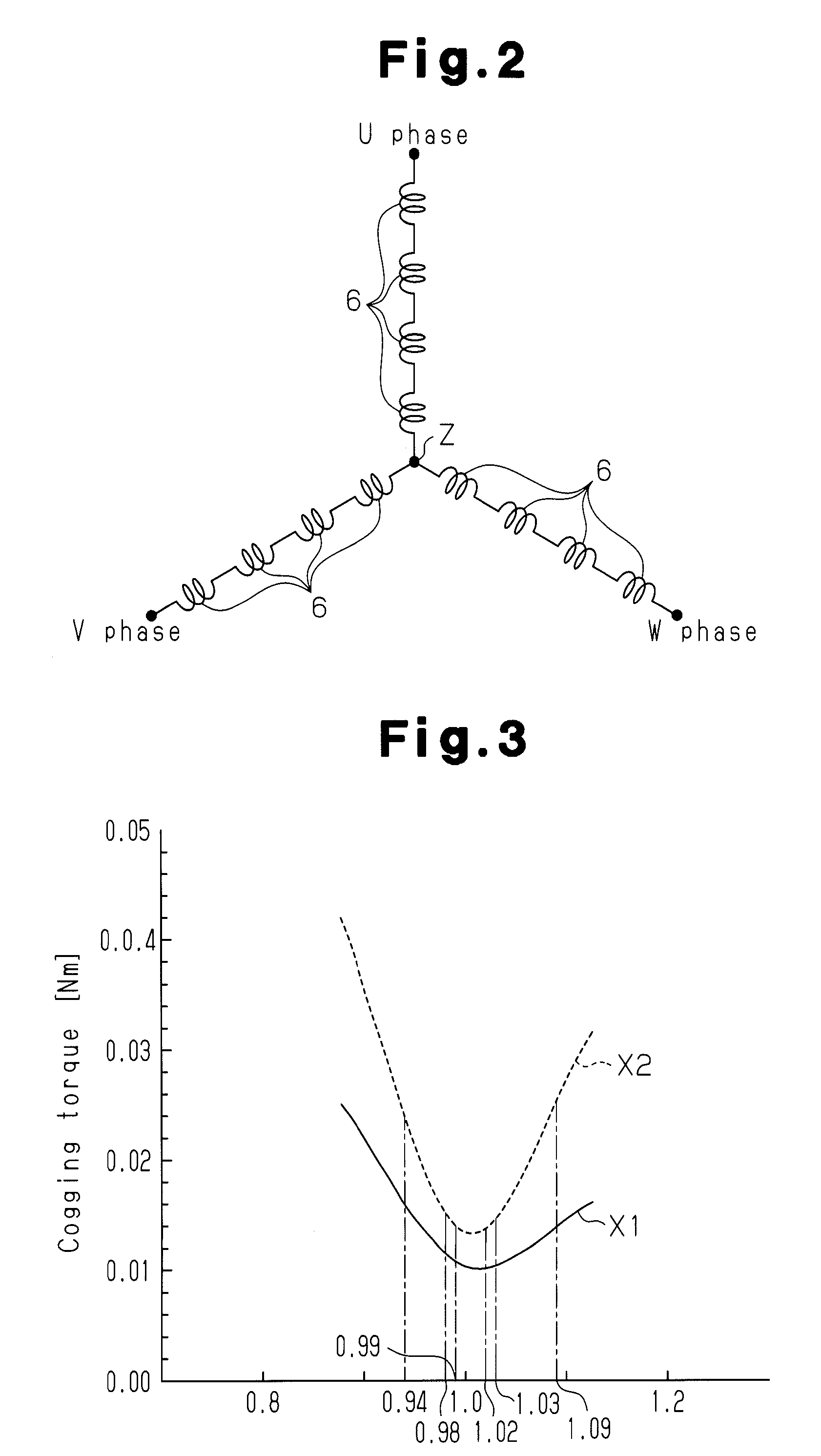
InactiveUSRE38464E1Reduce magnetic noiseReduce leakage fluxSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsAlternating currentConductor Coil
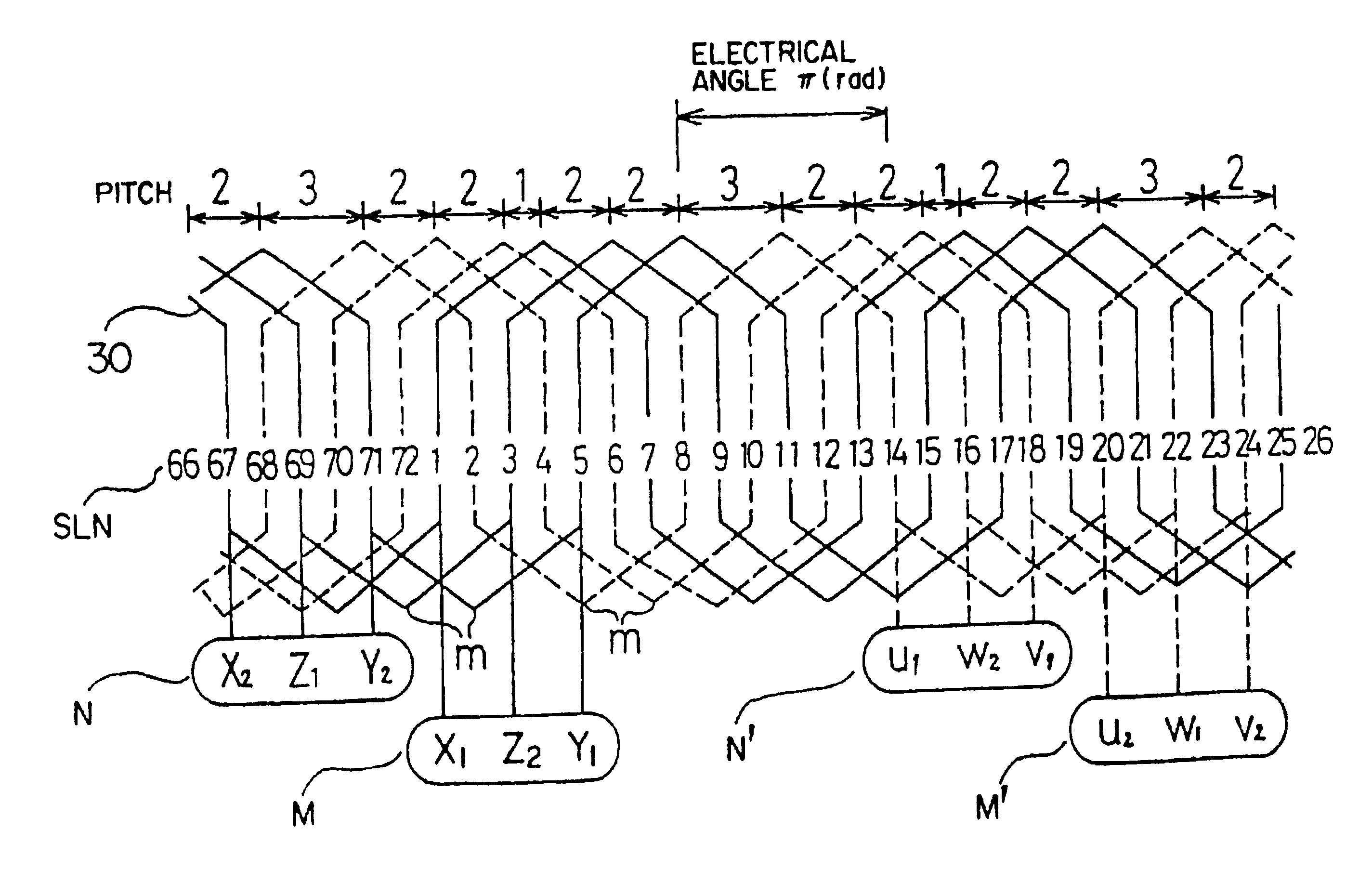
There is provided an alternating current generator comprising: a rotatably supported field rotor having a pair of opposed rotor pole cores, each being provided with P / 2 claw poles wherein P is an even number, and a field winding wound on the rotor pole cores; an armature core located around the outer periphery of the field rotor and having axially extending 3nP slots wherein n is an integer more than one; n independent sets of three-phase windings, each being wound on the armature core by being inserted in the slots so that the n sets of three-phase windings are shifted from each other by electrical angle of .pi. / (3n) radians; and three-phase rectifiers connected with the n sets of three-phase windings to rectify output voltages generated by the three-phase windings.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Embedded type mixing magnetic material fault-tolerant cylindrical linear motor
The invention discloses an embedded type mixing magnetic material fault-tolerant cylindrical linear motor which comprises primary bodies and secondary bodies. The length of each primary body is smaller than that of each secondary body. An air gap is reserved between each primary body and the corresponding secondary body. Each primary body comprises armature teeth, fault-tolerant teeth and a coil winding. The 2*m armature teeth and the 2*m fault-tolerant teeth are uniformly distributed on each primary body, wherein m is the phase number of the motor and is larger than or equal to three; the armature teeth and the fault-tolerant teeth are arranged at intervals in a staggered mode. Only one set of disc-shaped coil windings are placed into an armature tooth groove of each primary body. No windings are arranged on the fault-tolerant teeth. The secondary bodies of the motor are made of mixing magnetic materials, a part of ferrite is used for replacing a part of rare earth permanent magnets to form four different mixing magnetic material structures, on one hand, the quantity of the adopted rare earth permanent magnets is greatly reduced, and the cost of the motor is reduced; on the other hand, as the magnetic energy product of the permanent magnets is reduced, the eddy-current loss of the motor is reduced greatly, and efficiency of the motor is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Heat-treating furnace with magnetic field and heat treatment method using same
InactiveUS6833107B2Reduce magnetic field leakageUniform magnetic fieldFurnaces without endless coreBaking ovenMagnetizationMagnetic flux
A heat-treating furnace with a magnetic field comprising (a) a magnetic field-generating means constituted by an outer, ring-shaped, permanent magnet assembly comprising a plurality of permanent magnet segments combined with their magnetization directions oriented such that a magnetic flux flows in a diameter direction, and an inner, ring-shaped, permanent magnet assembly disposed inside the outer, ring-shaped, permanent magnet assembly and comprising a plurality of permanent magnet segments combined with their magnetization directions oriented such that a magnetic flux flows in a diameter direction; and (b) a heat treatment means disposed in a center hole of the inner, ring-shaped, permanent magnet assembly and comprising a cooling means, a heating means, and a heat-treating container containing heat-treating holder for holding a plurality of articles to be heat-treated in this order from outside, wherein an axial center of a magnetic field generated by the inner and outer ring-shaped, permanent magnet assemblies is substantially identical with an axial center of an article assembly in the heat-treating container.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Embedded magnet type motor
InactiveUS7732965B2Increase torqueIncrease the number ofMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsControl theoryMagnet
An embedded magnet type motor is disclosed. The rotor core of the motor has radially extending first accommodation holes and V-shaped accommodation holes. Each V-shaped accommodation hole includes a second accommodation hole and a third accommodation hole. A first gap is formed in each first accommodation hole. The first gap is not occupied by the corresponding first magnet. A second gap is formed in each second accommodation hole. The second gap is not occupied by the corresponding second magnet. A third gap is formed in each third accommodation hole at a radially outer portion. The third gap is not occupied by the corresponding third magnet. Each second gap and the adjacent third gap form one V-shaped gap. The angular width θa of each first gap and the angular width θb of each V-shaped gap are determined to satisfy the expression: 0.60<θa / θb<1.60.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com