Patents
Literature
153results about How to "Avoid large vibrations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
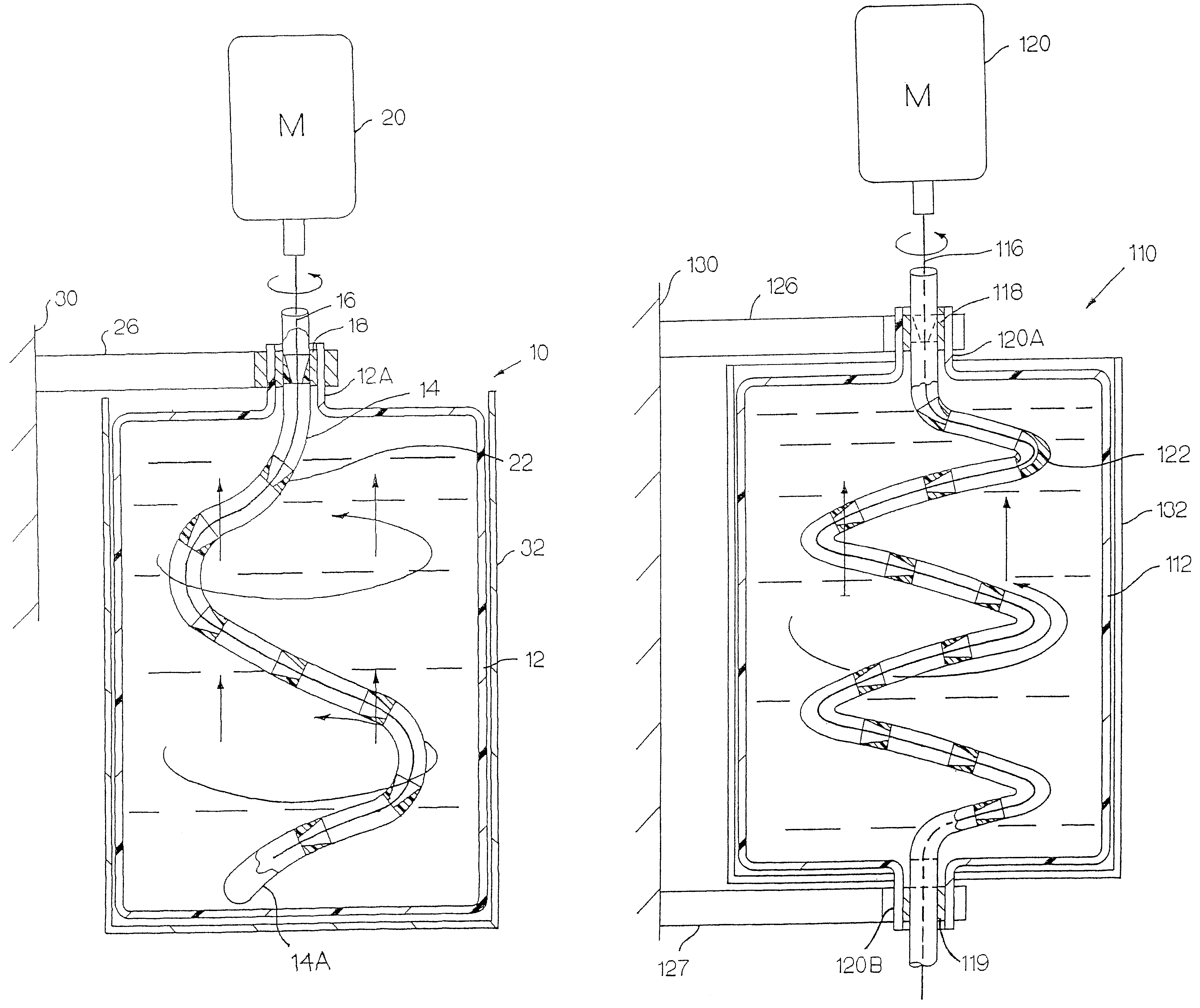
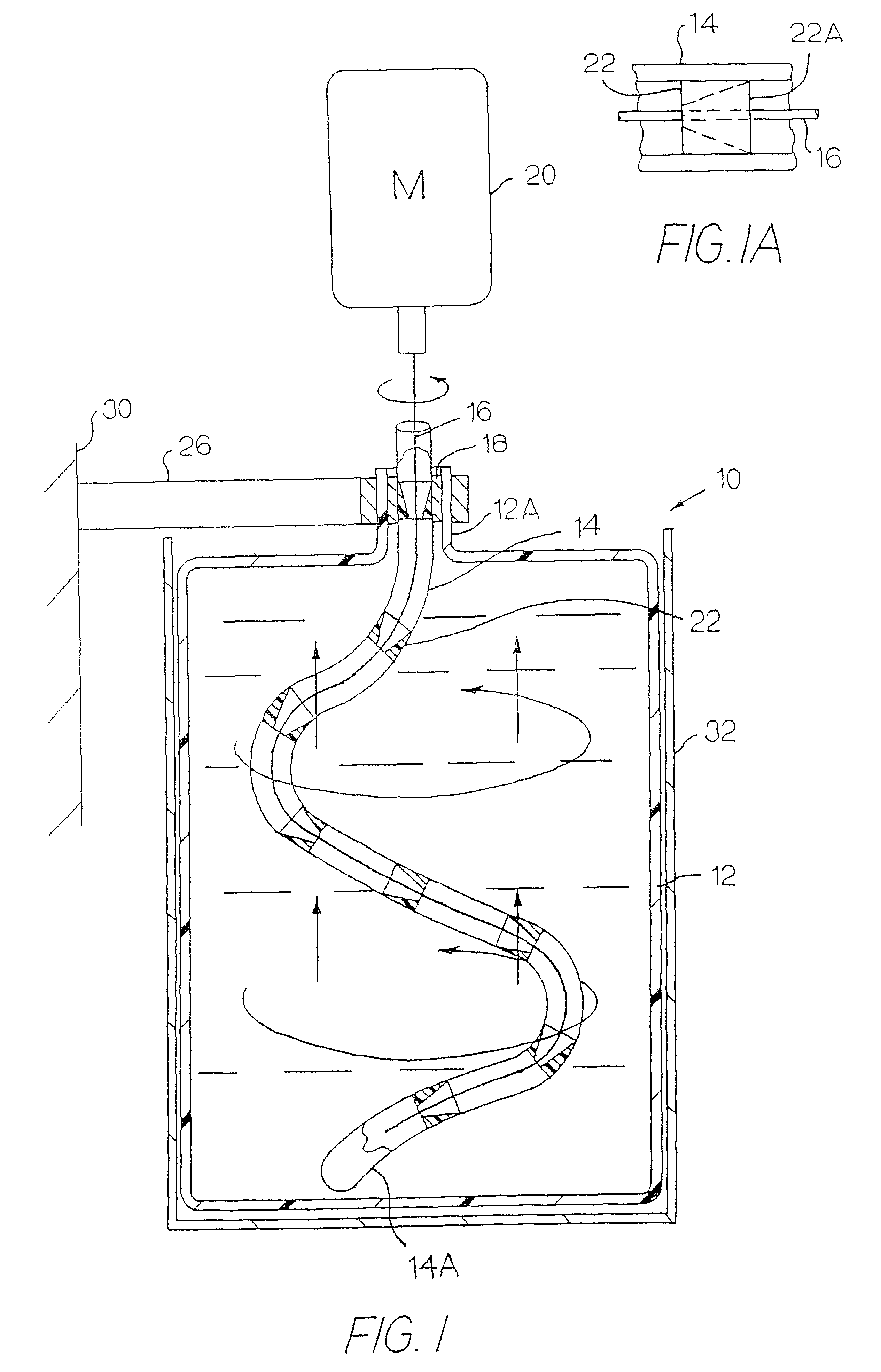
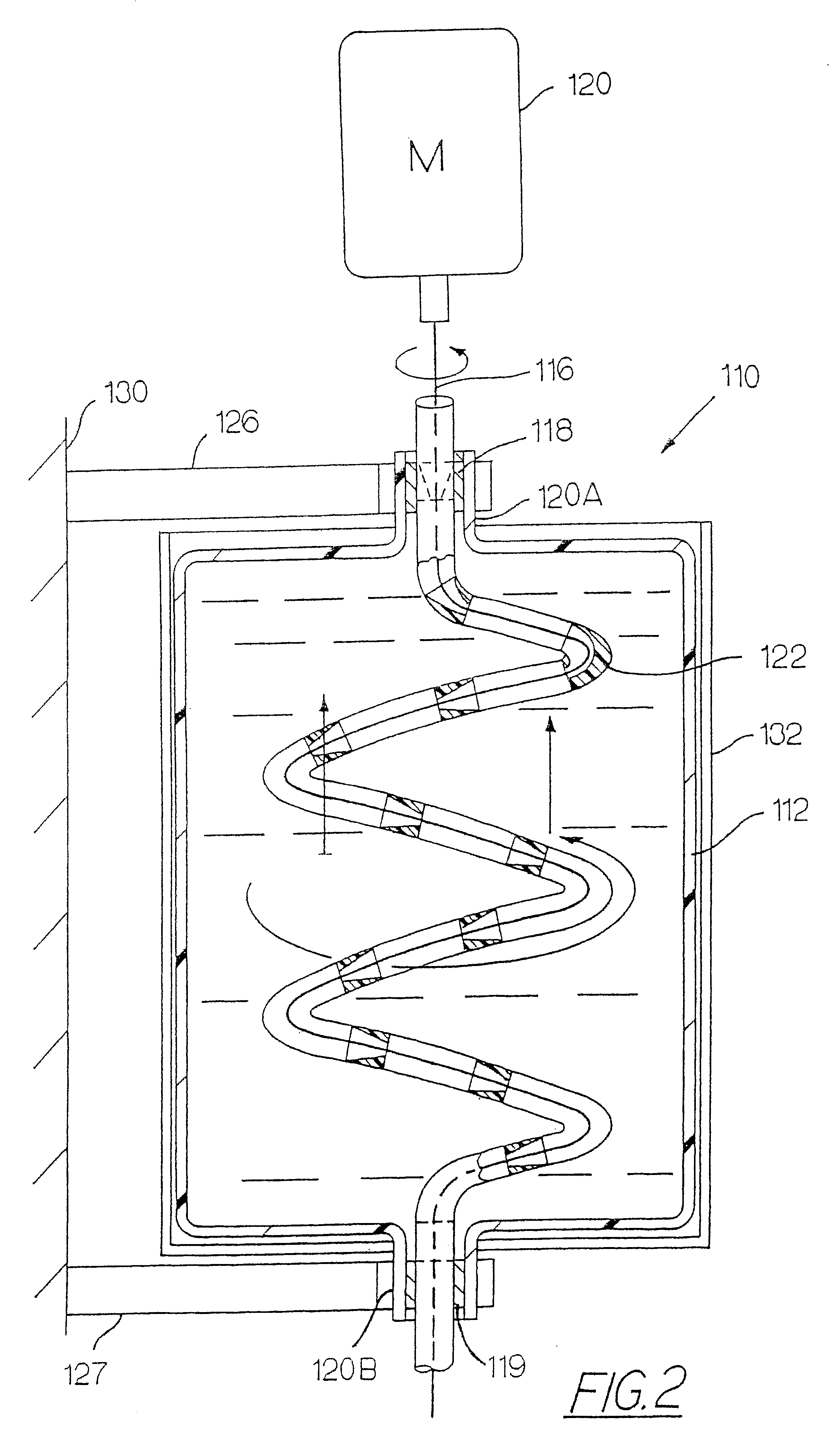
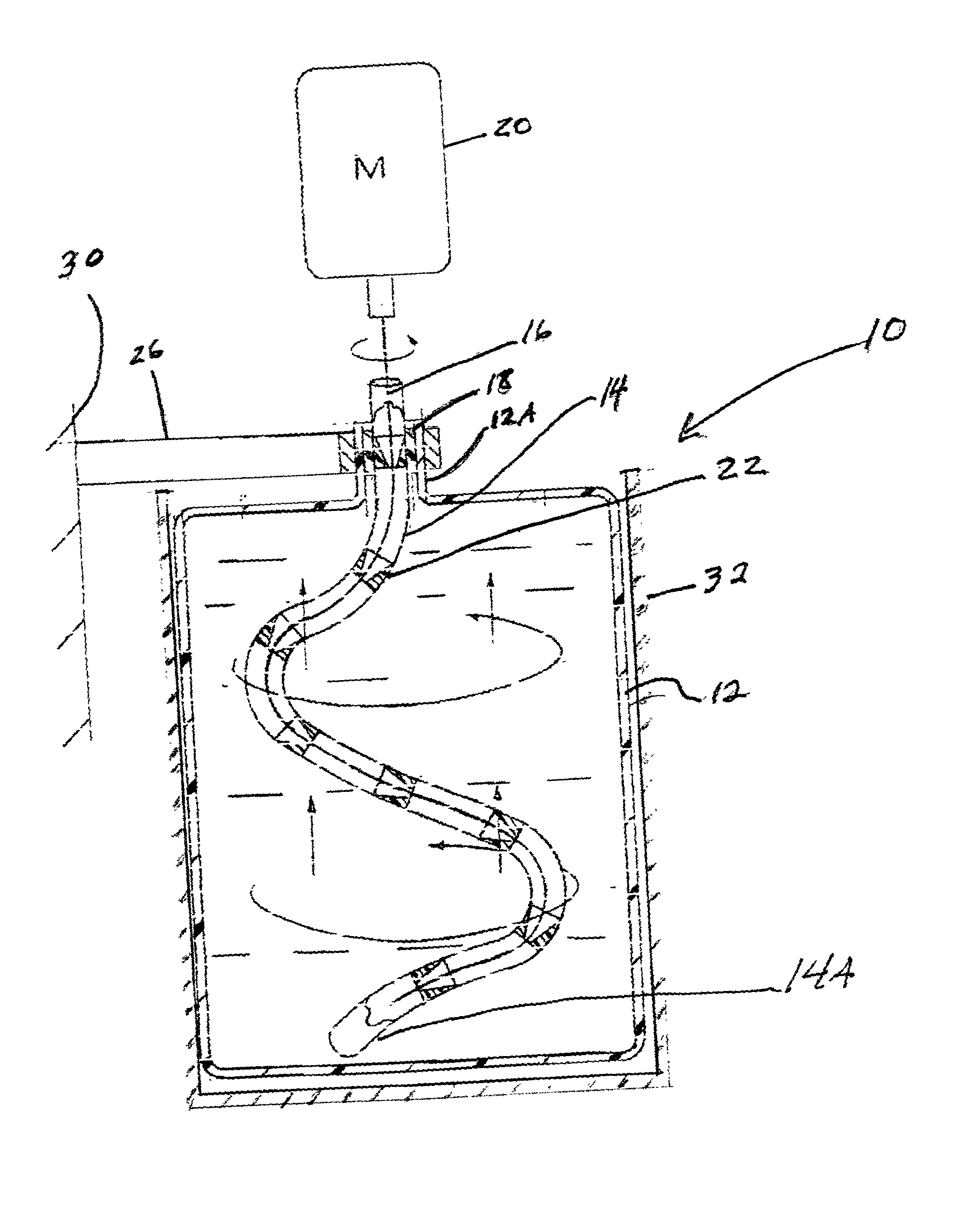
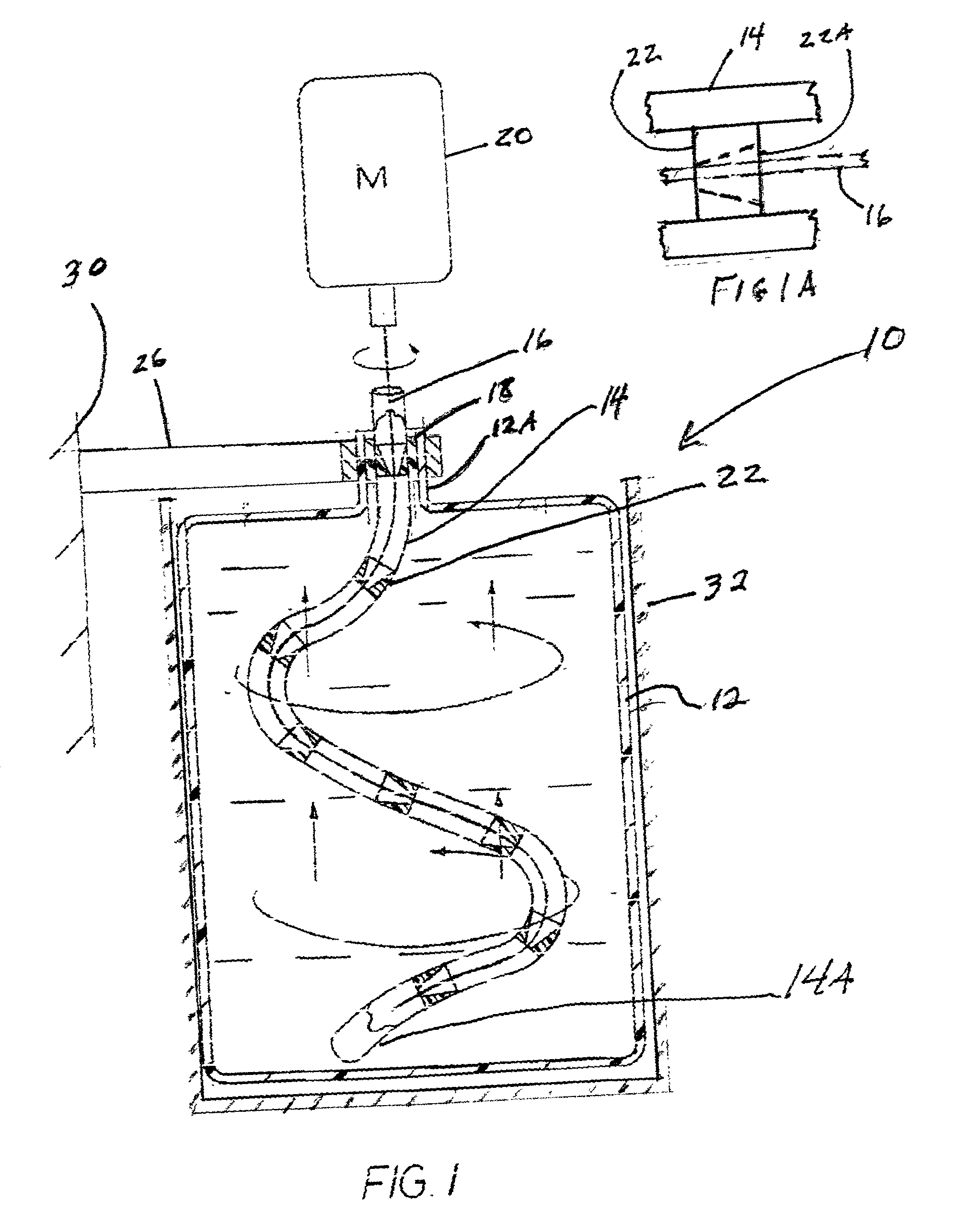
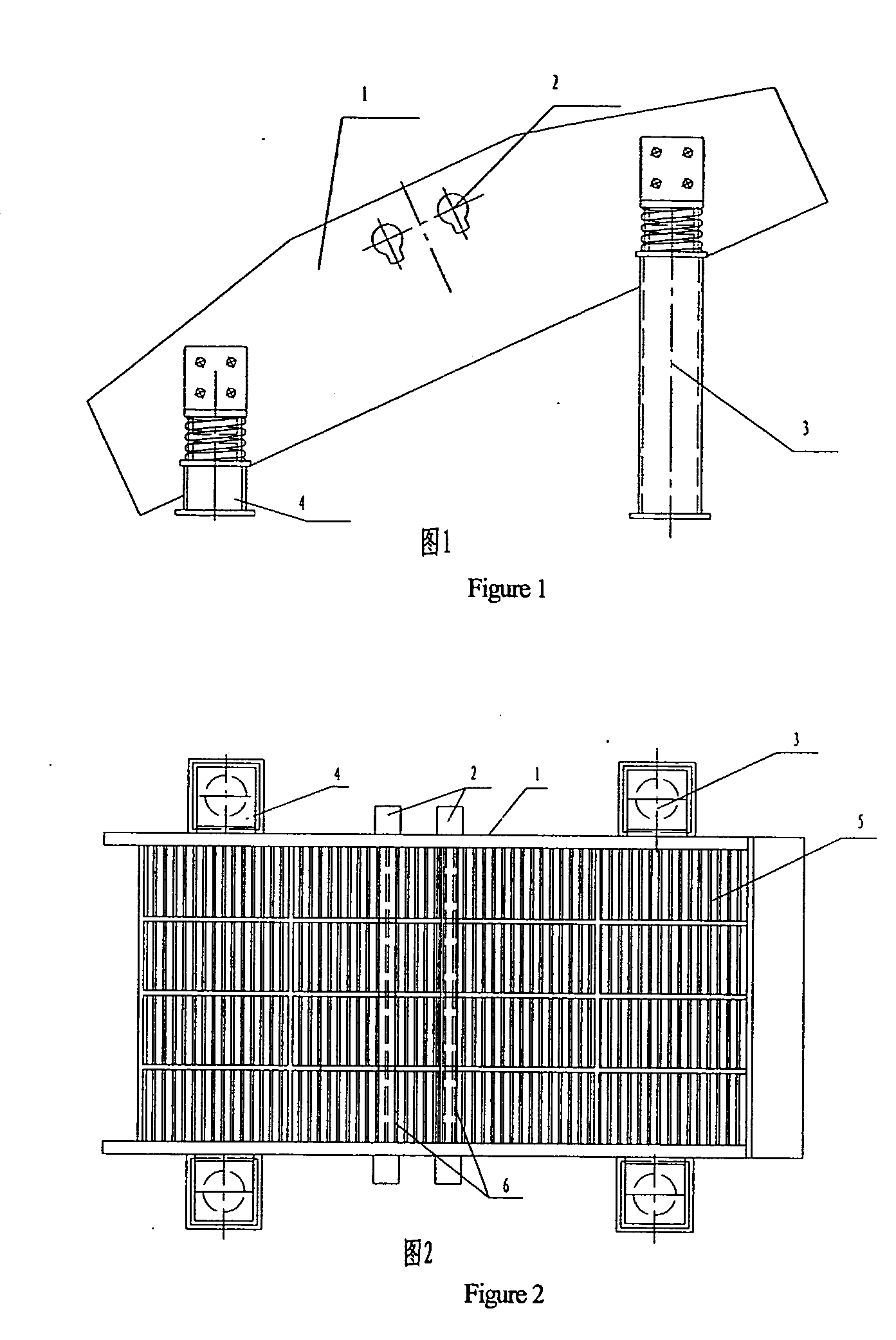
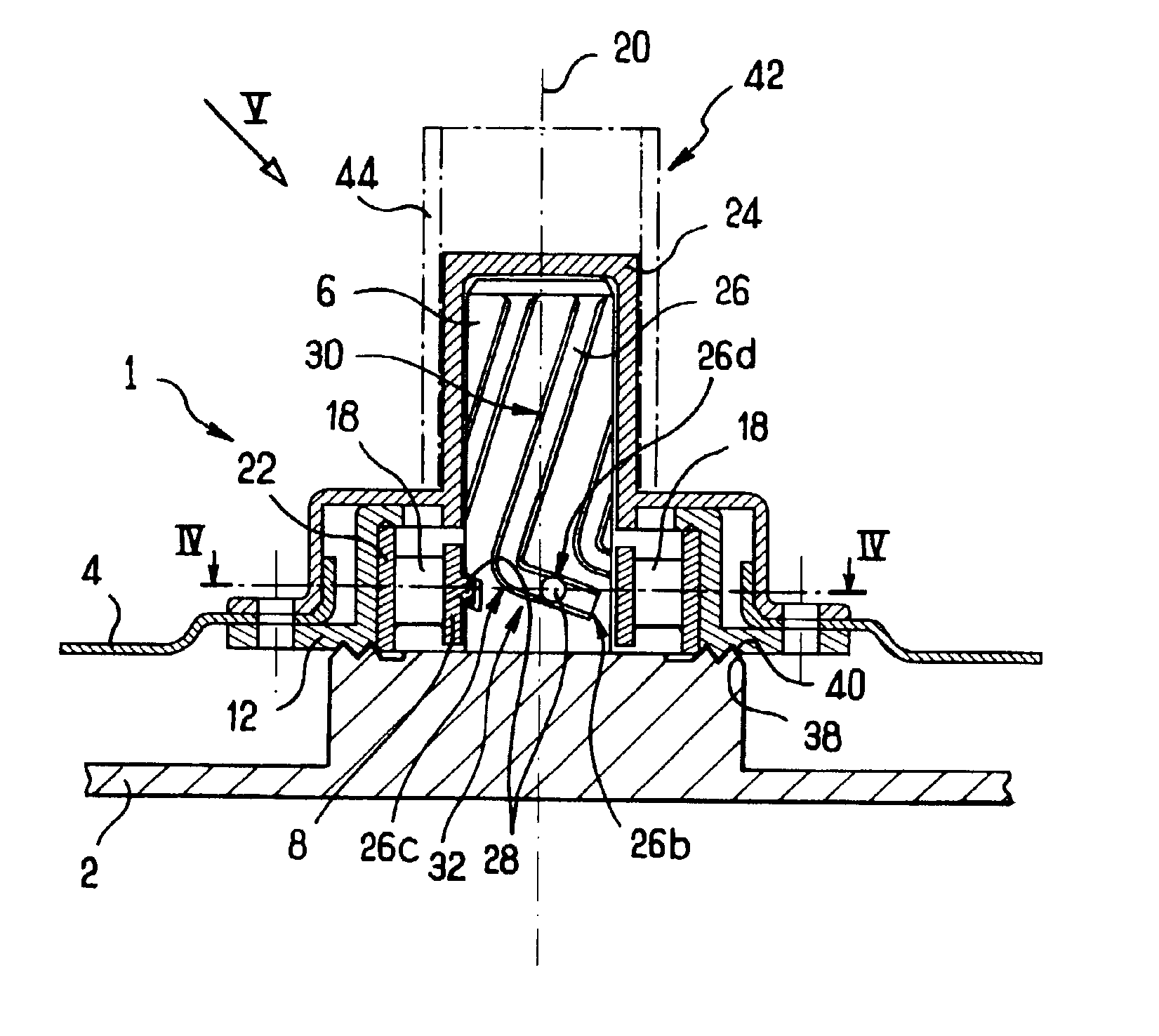
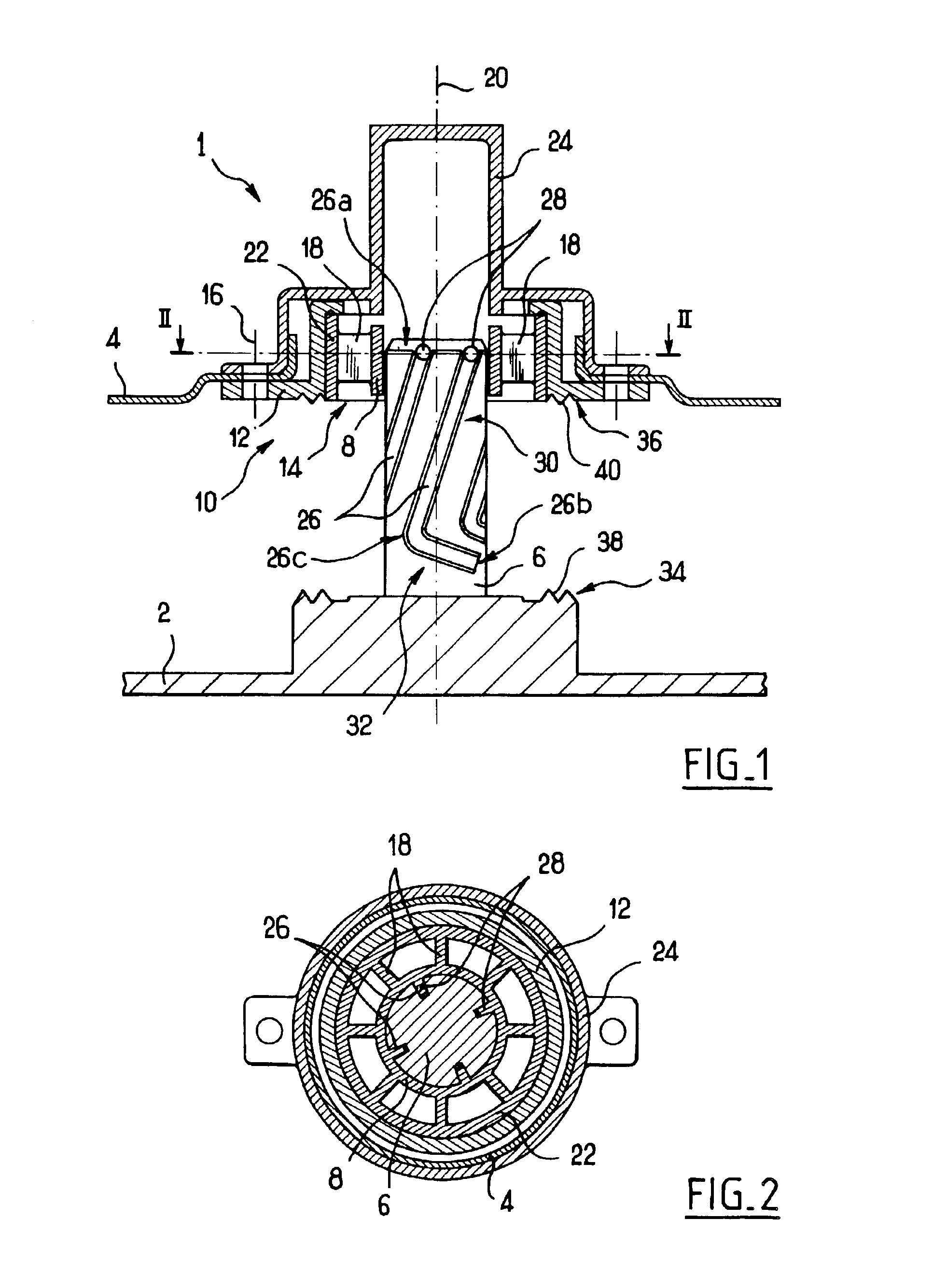
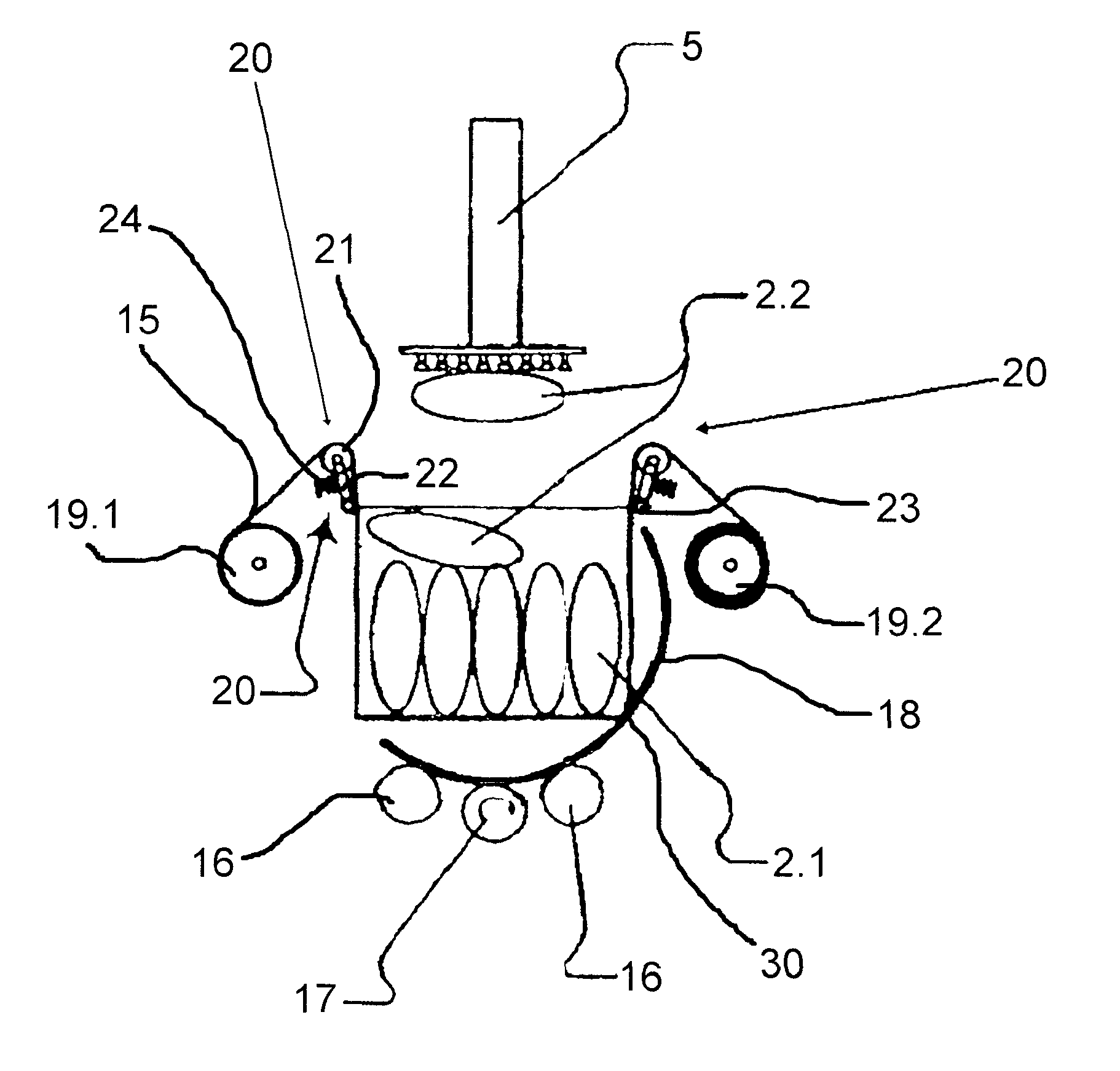
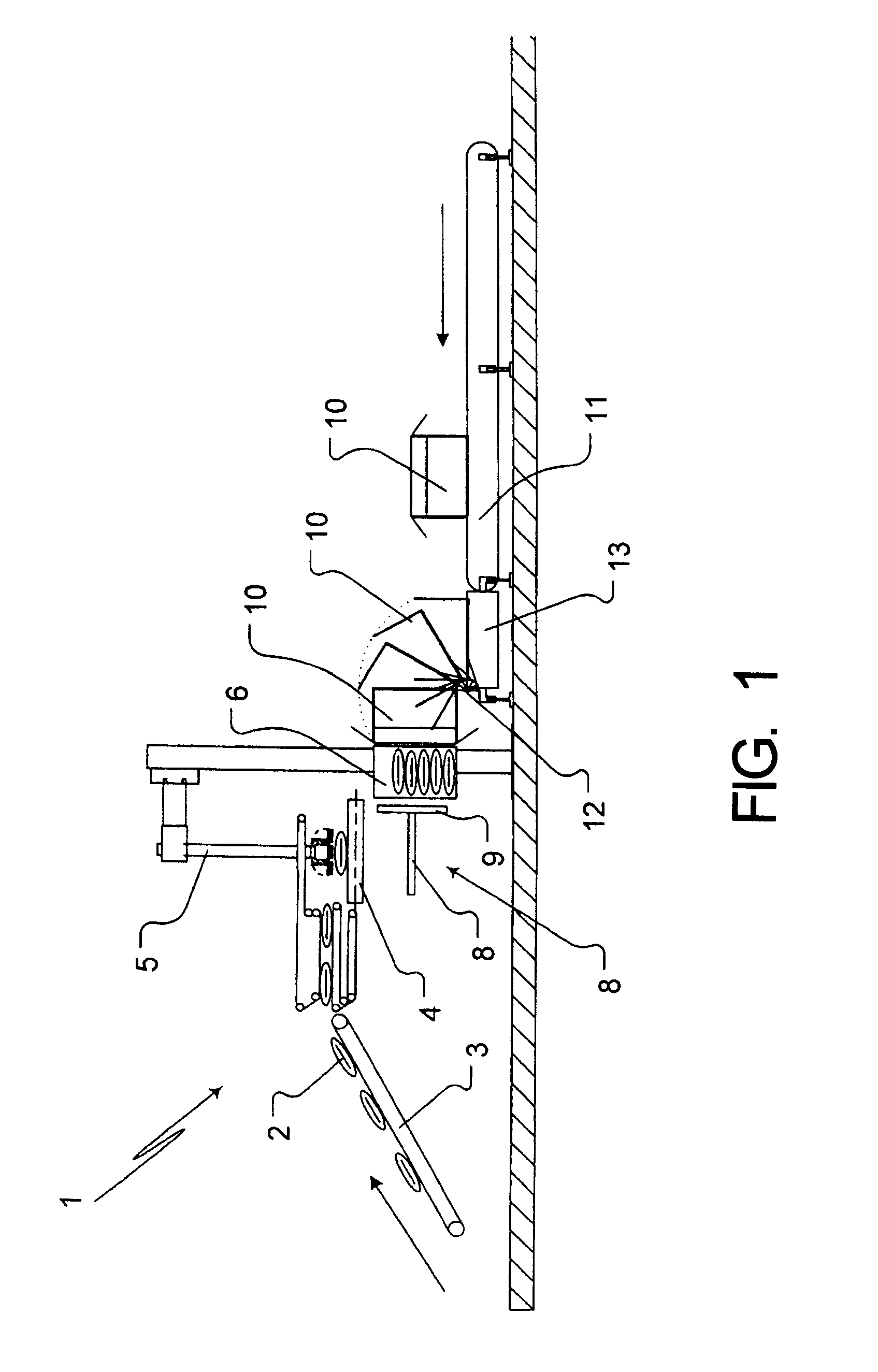
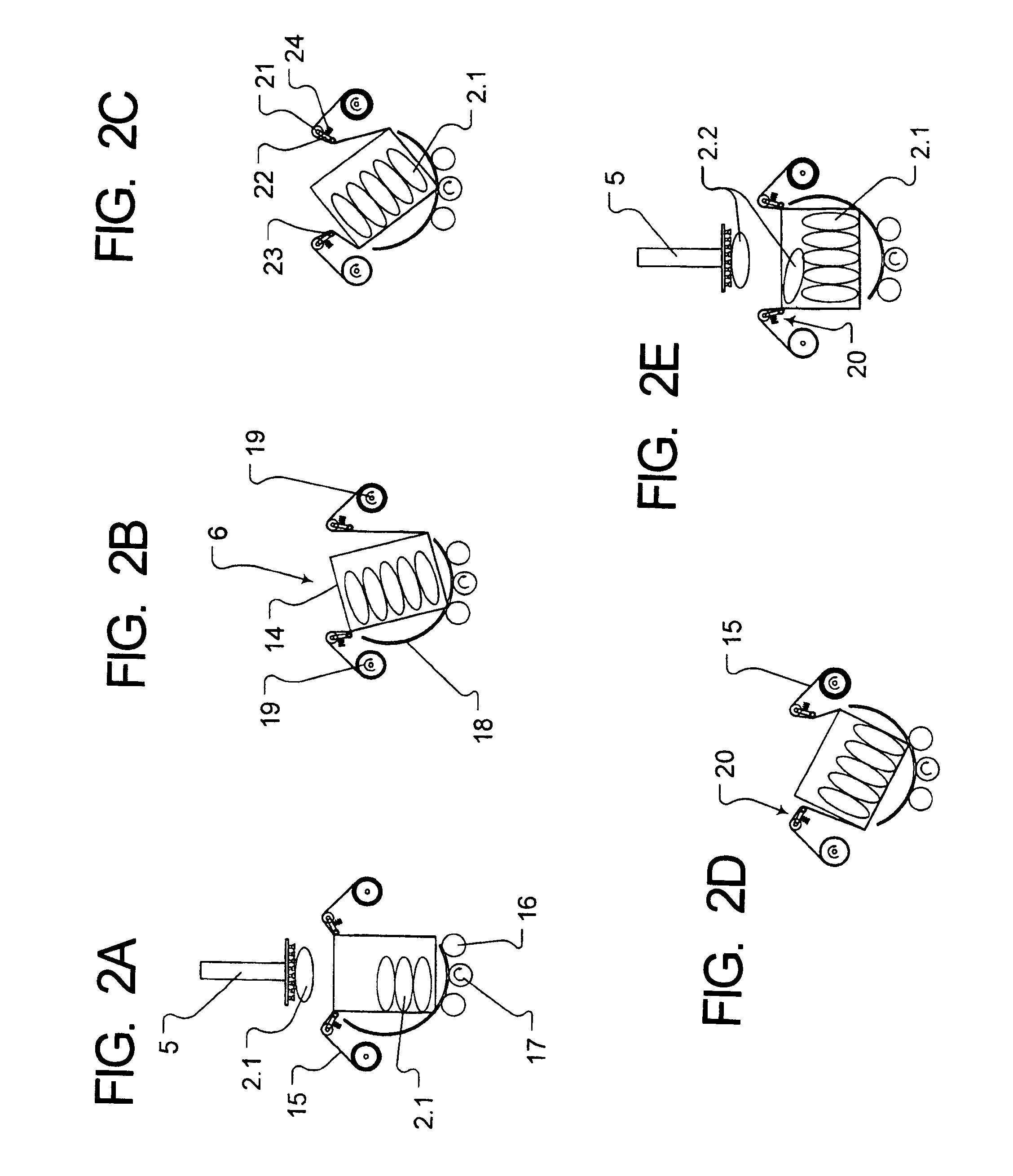
Apparatus and method for mixing materials sealed in a container under sterile conditions
InactiveUS6494613B2Reduce frictionAvoid large vibrationsTransportation and packagingRotary stirring mixersEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:PALL TECH UK
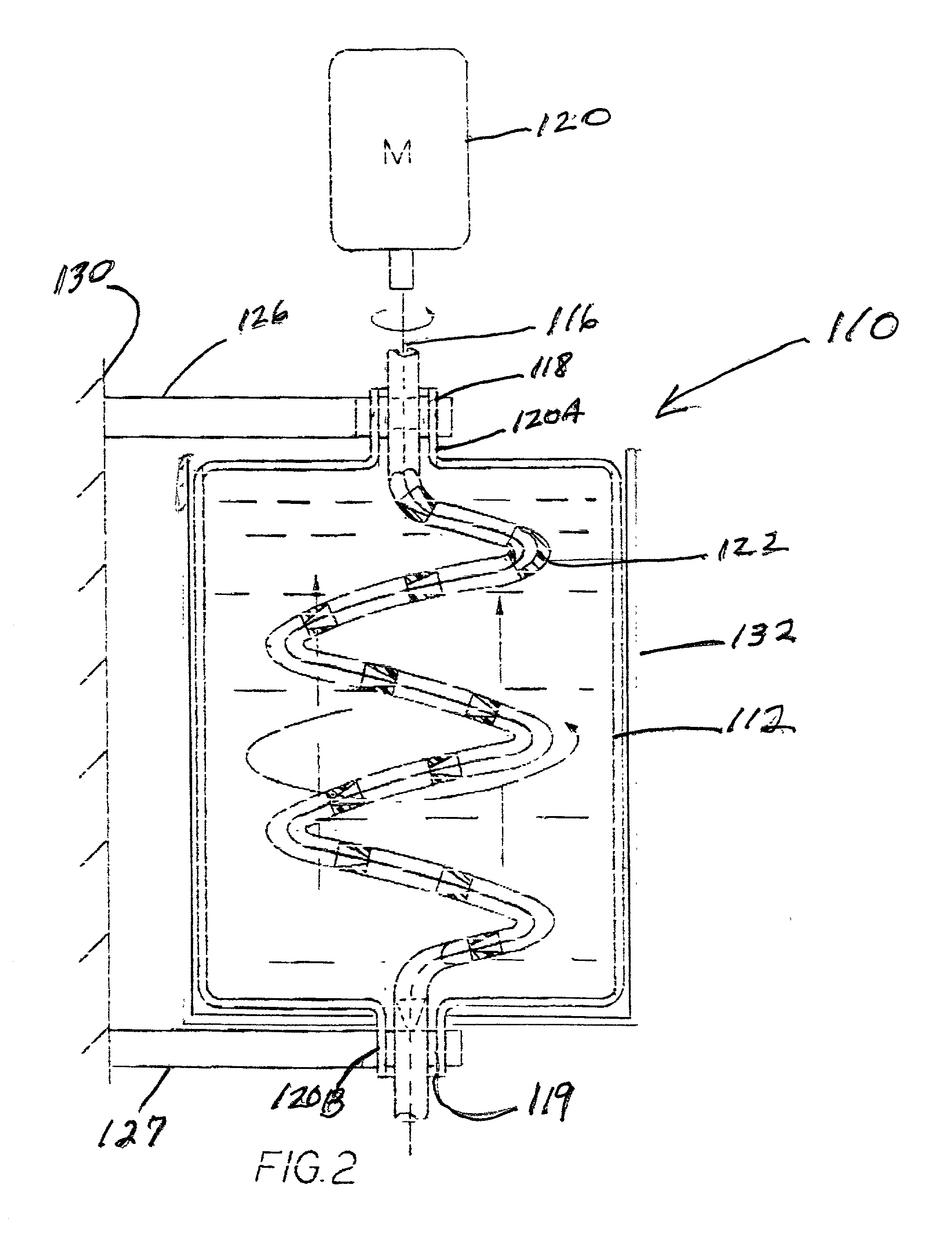
Apparatus and method for mixing materials sealed in a container under sterile conditions
InactiveUS20020105856A1Reduce frictionAvoid large vibrationsFlow mixersRotary stirring mixersEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:PALL TECH UK
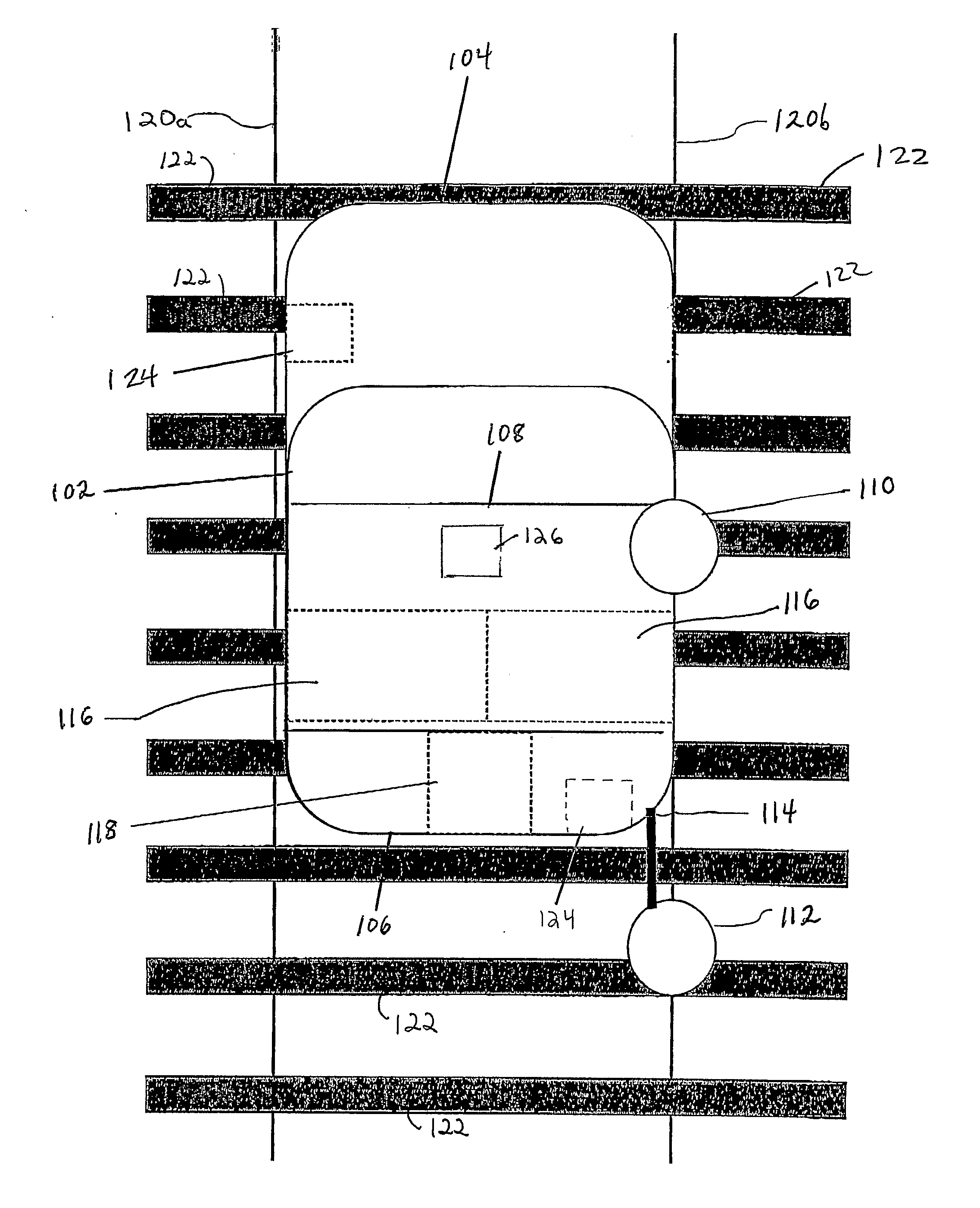
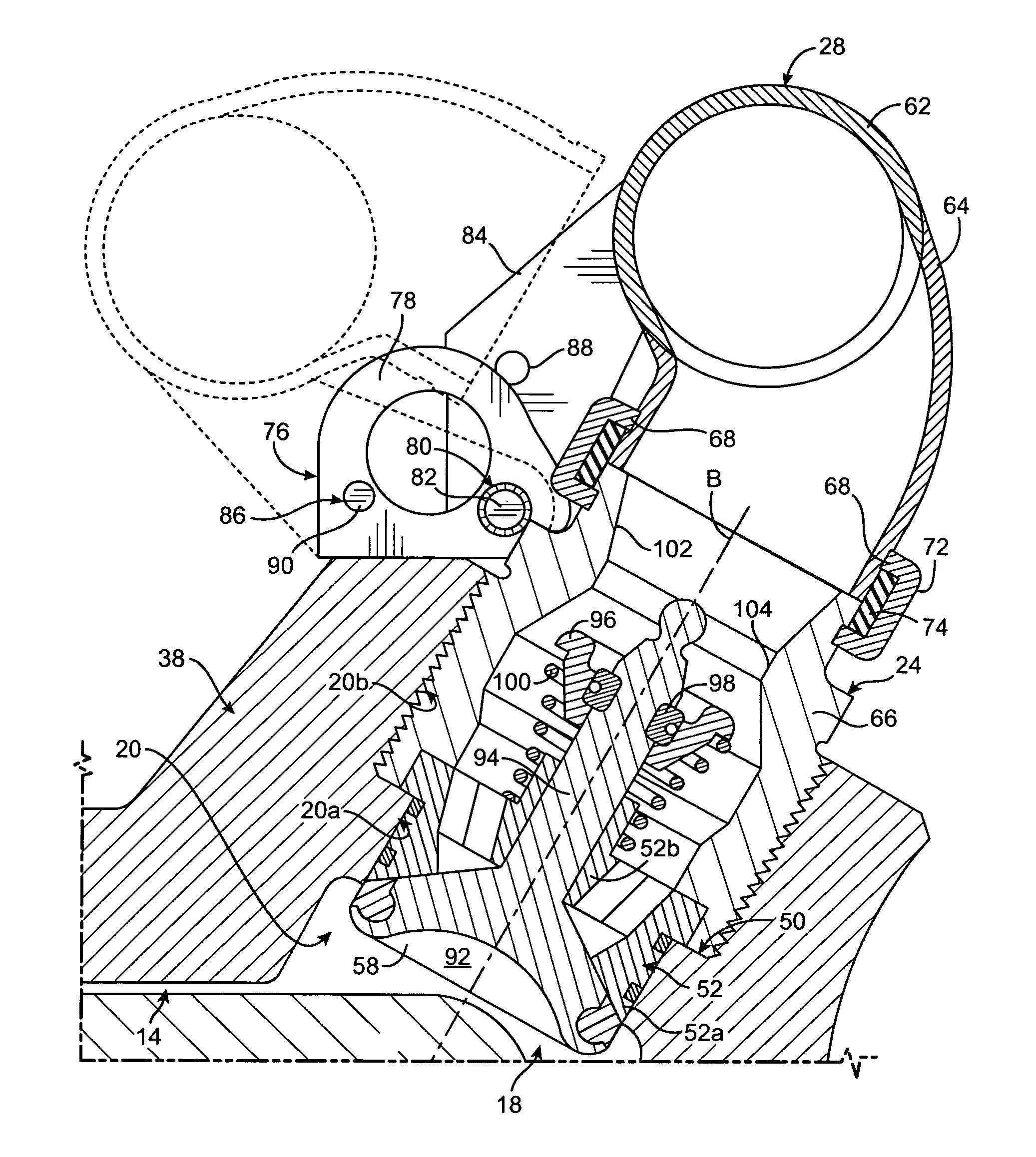
Railroad surveying and monitoring system
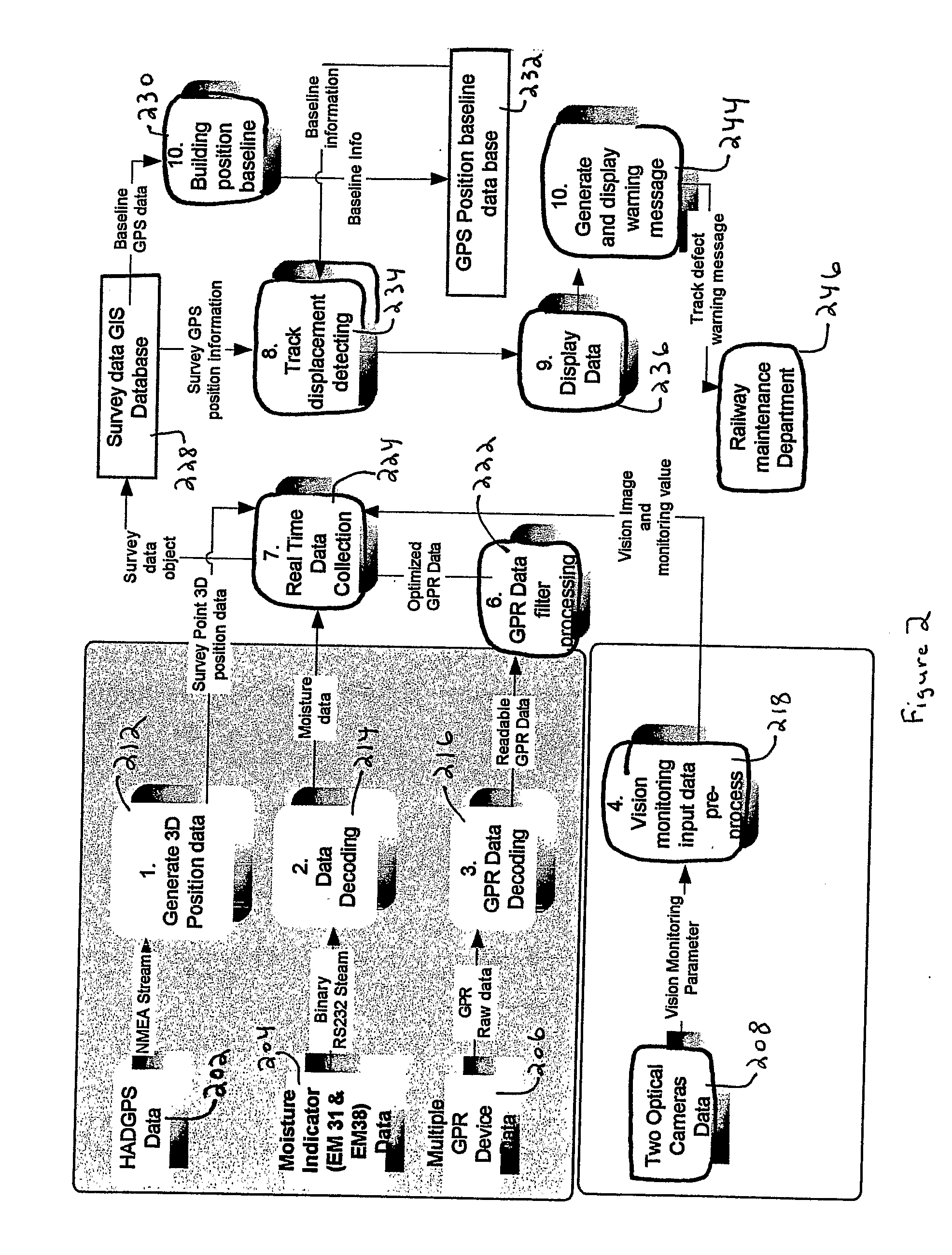
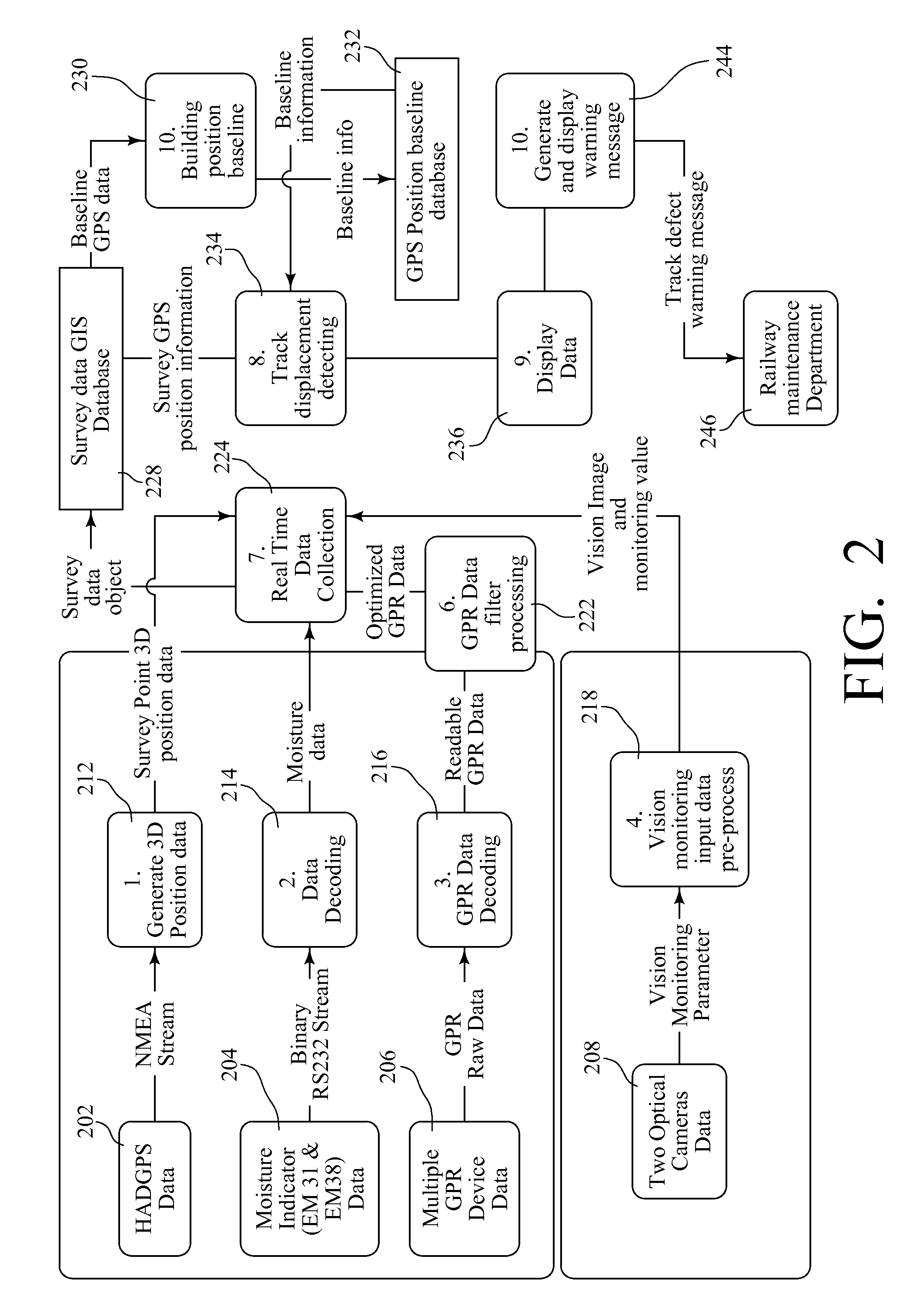
InactiveUS20100026551A1Easy to adaptOptimizationPosition fixationTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesTerrainLandform
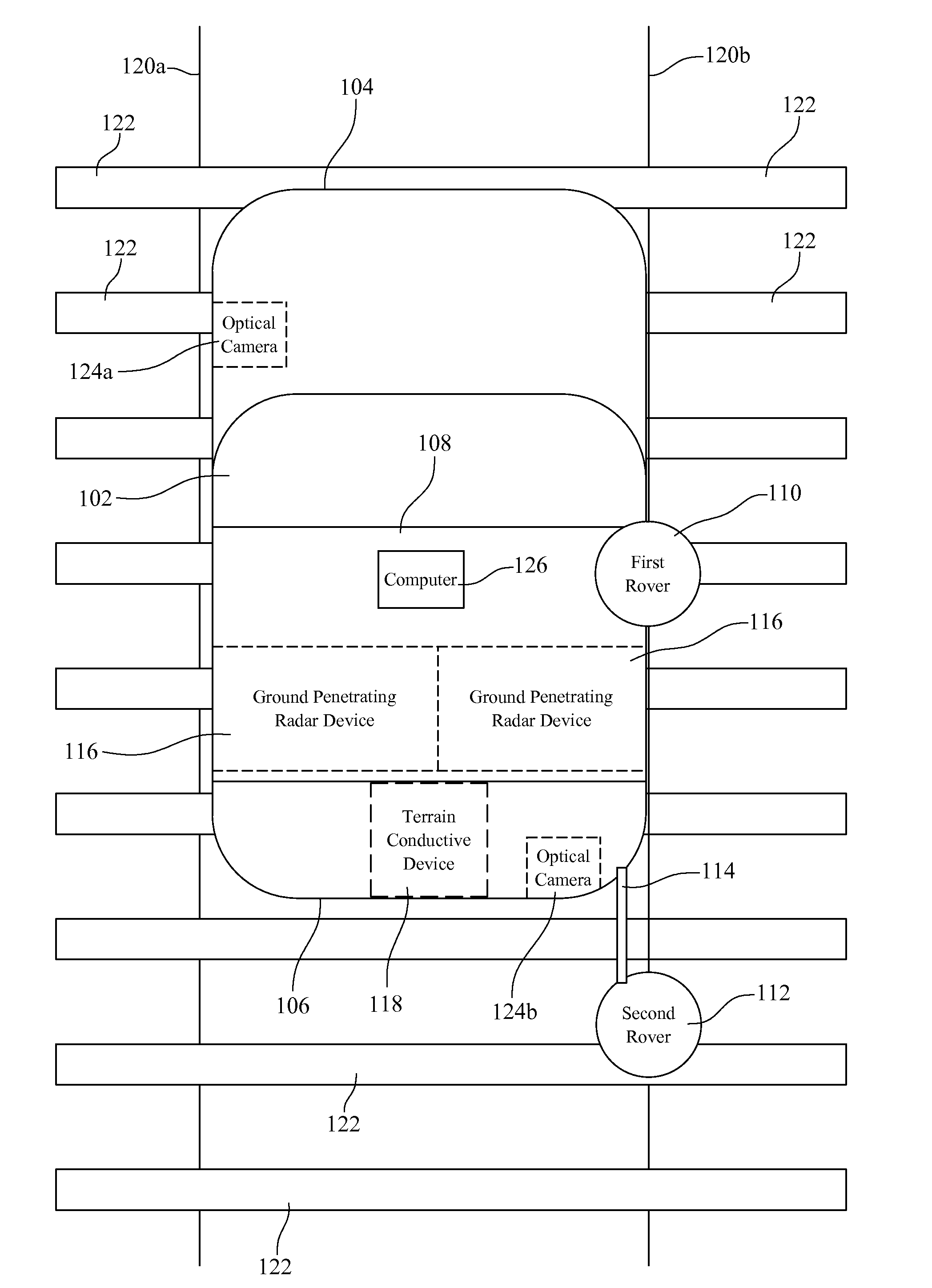
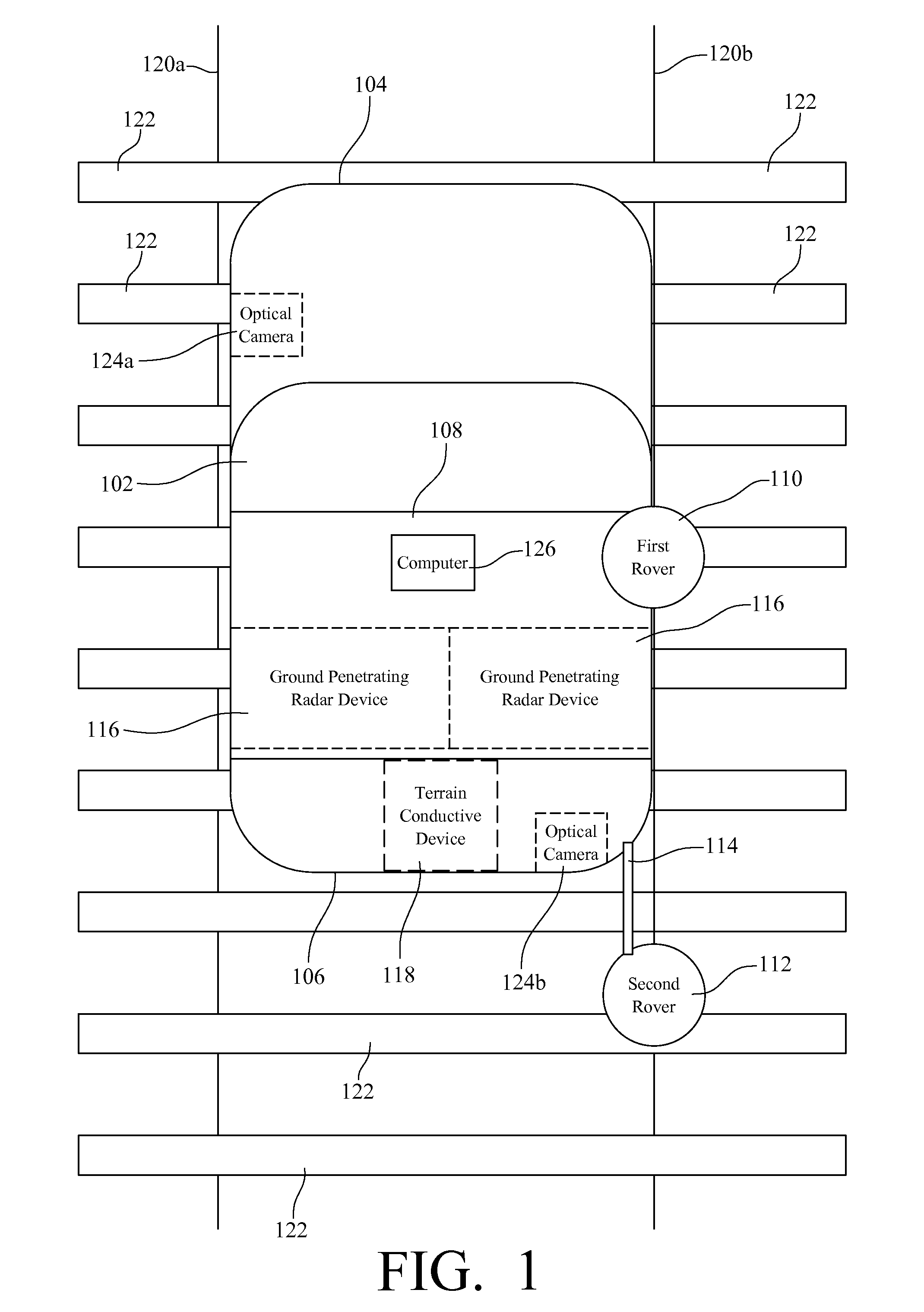
A Railroad Surveying and Monitoring System configured on a mobile platform for surveying, monitoring, and analyzing rail position and superstructure and terrain substructure of railroad tracks (20a,b) or other structures. The system employs two or more High Accuracy Differential Global Positioning System devices (110,112), ground penetrating radar devices (116), terrain conductivity instruments (118), optical cameras (124), and data receivers and processors (126), which in turn process, display, and store the data in a usable database. Precise coordinate data generated from a High Accuracy Global Positioning System provides both location data for subsurface sensors and surface sensors and rail position coordinates to monitor track displacements during track inspection in real time.
Owner:MARSHALL UNIV RES
Hydrodynamic torque converter
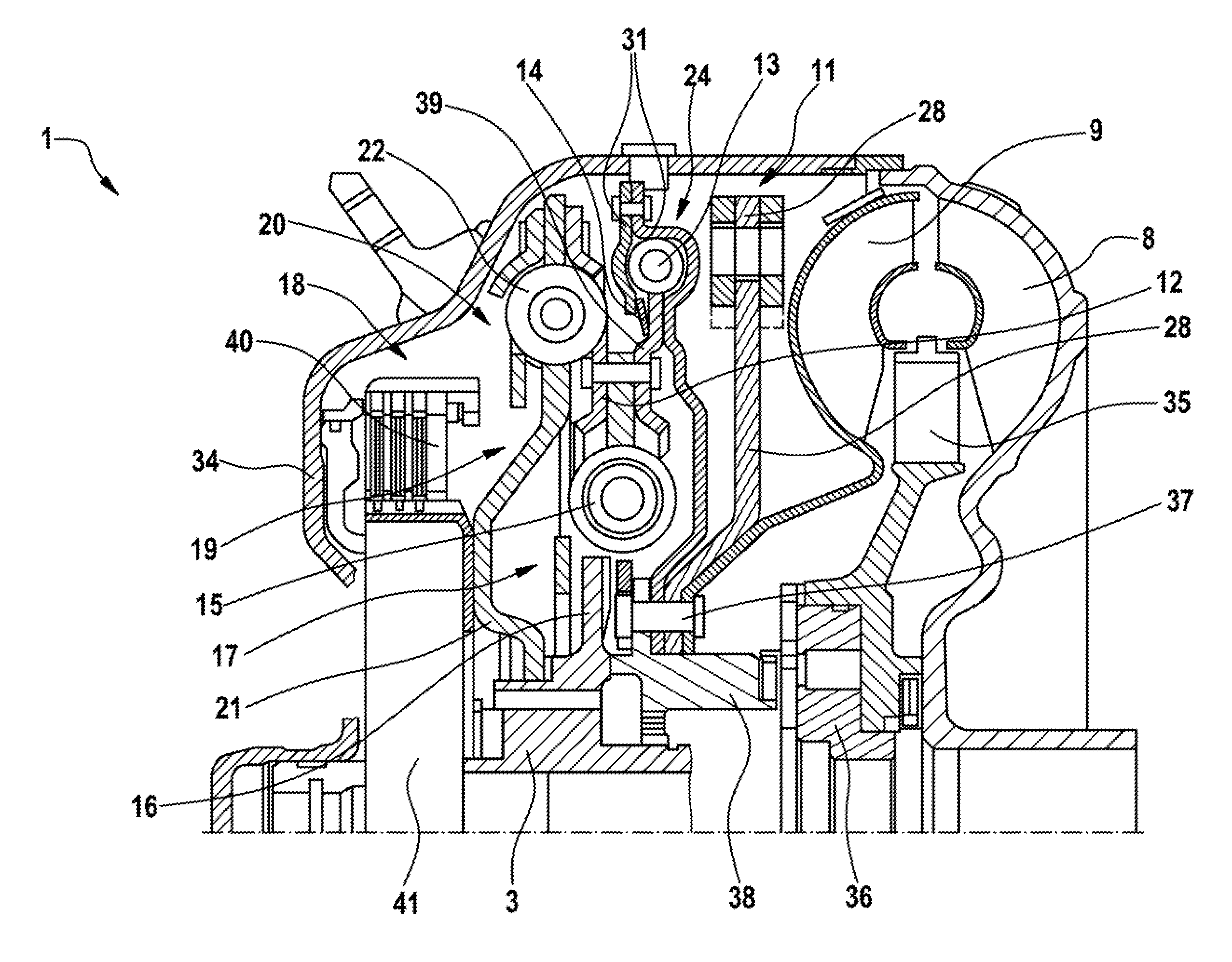
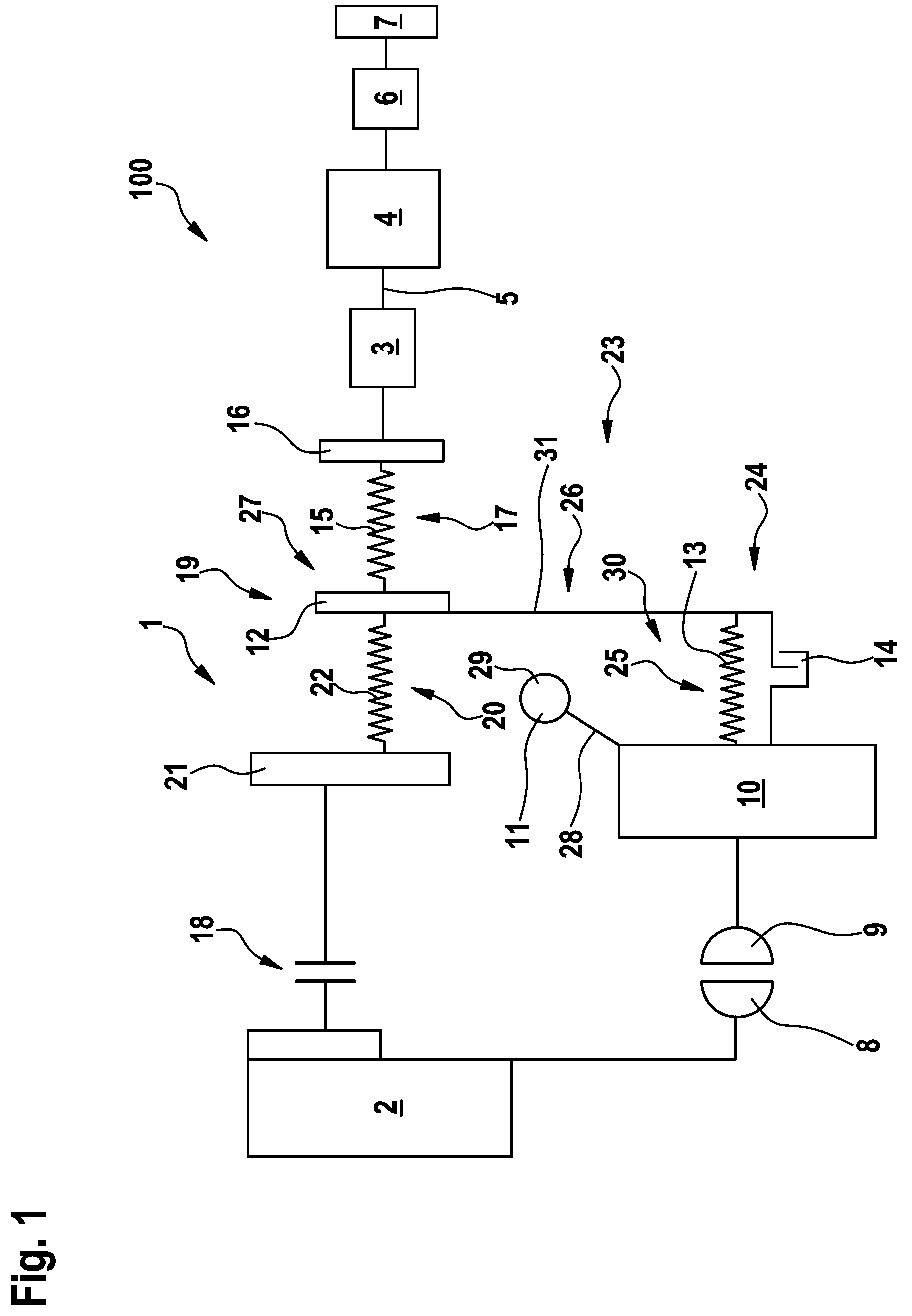
ActiveUS20110192692A1Simplify designVibration angle be reduceYielding couplingRotary clutchesImpellerPower flow
A hydrodynamic torque converter (1), comprising a turbine wheel (9) driven by an impeller (8) and connected to an output part, and comprising a housing (34), in which a torsional vibration damper (19) having several damper stages (17, 20) and a centrifugal force pendulum (11), and also a converter lockup clutch (18) connecting a housing and an output part (3), are accommodated. In order to avoid any striking of the pendulum masses of the centrifugal force pendulum in internal combustion engines having large oscillating angles driving the torque converter, a turbine damper is connected in the power flow upstream of the centrifugal force pendulum.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
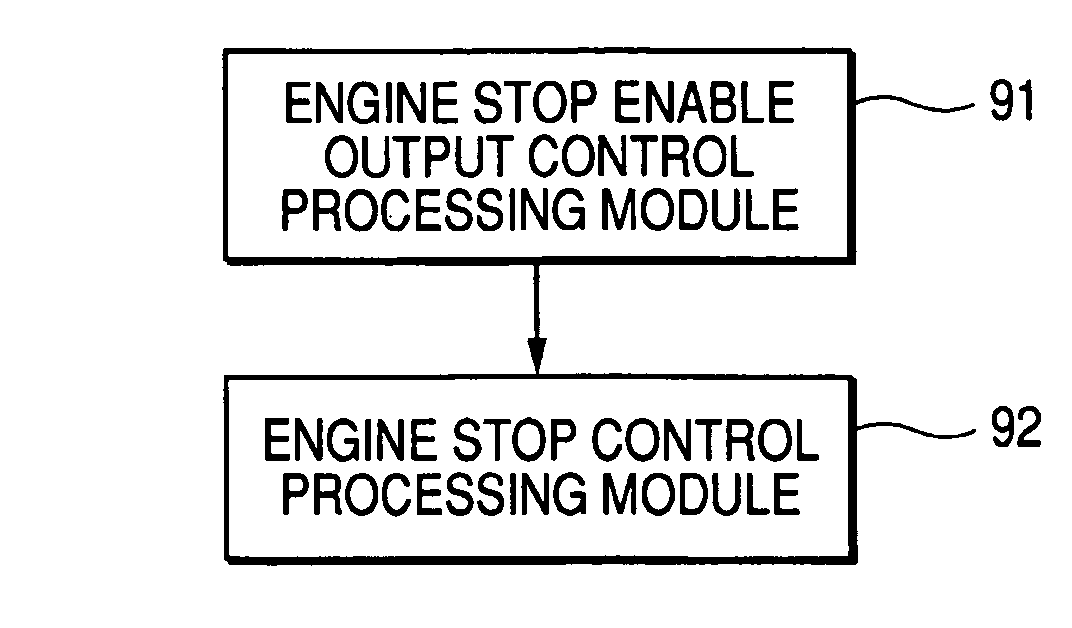
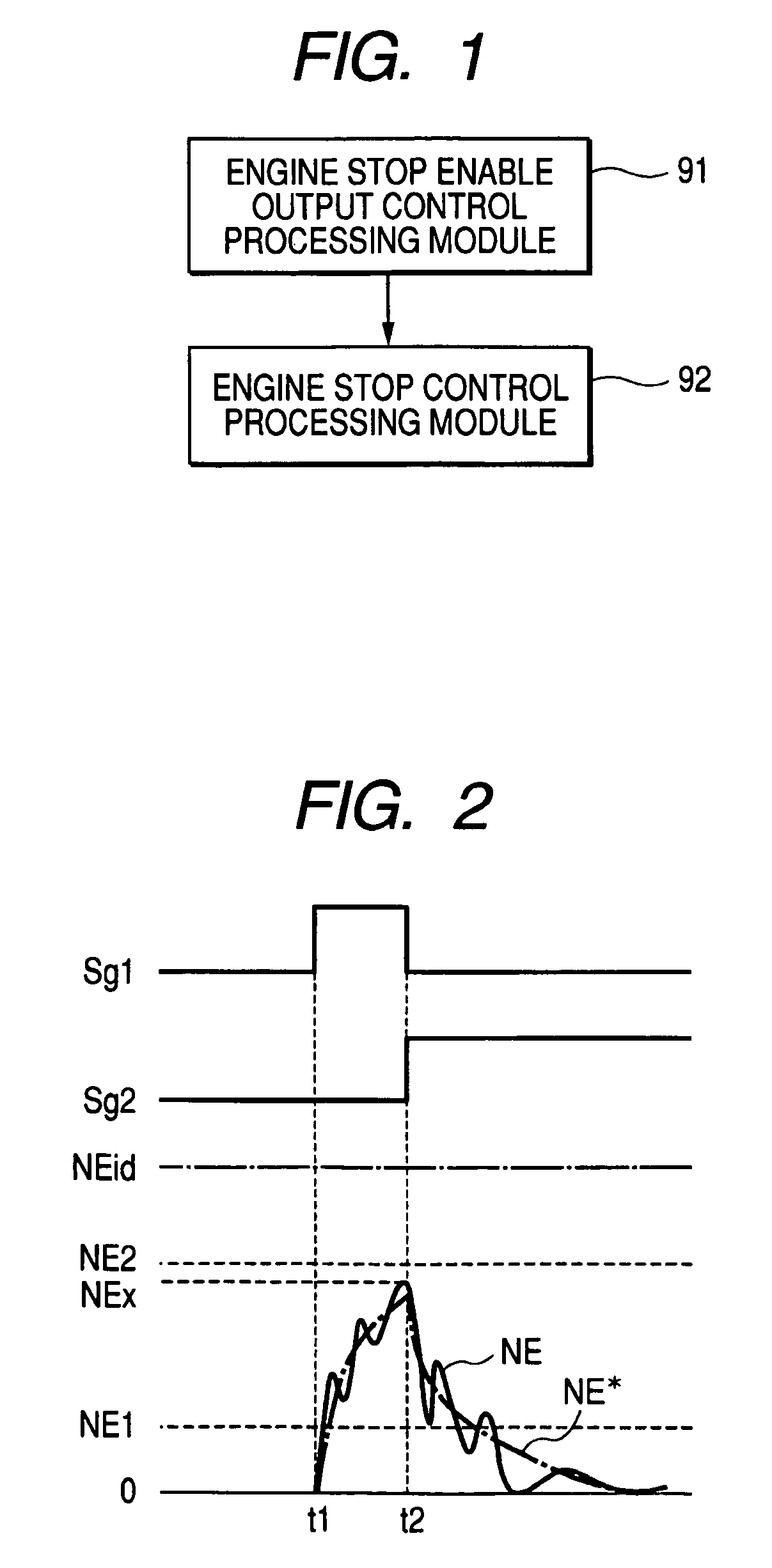
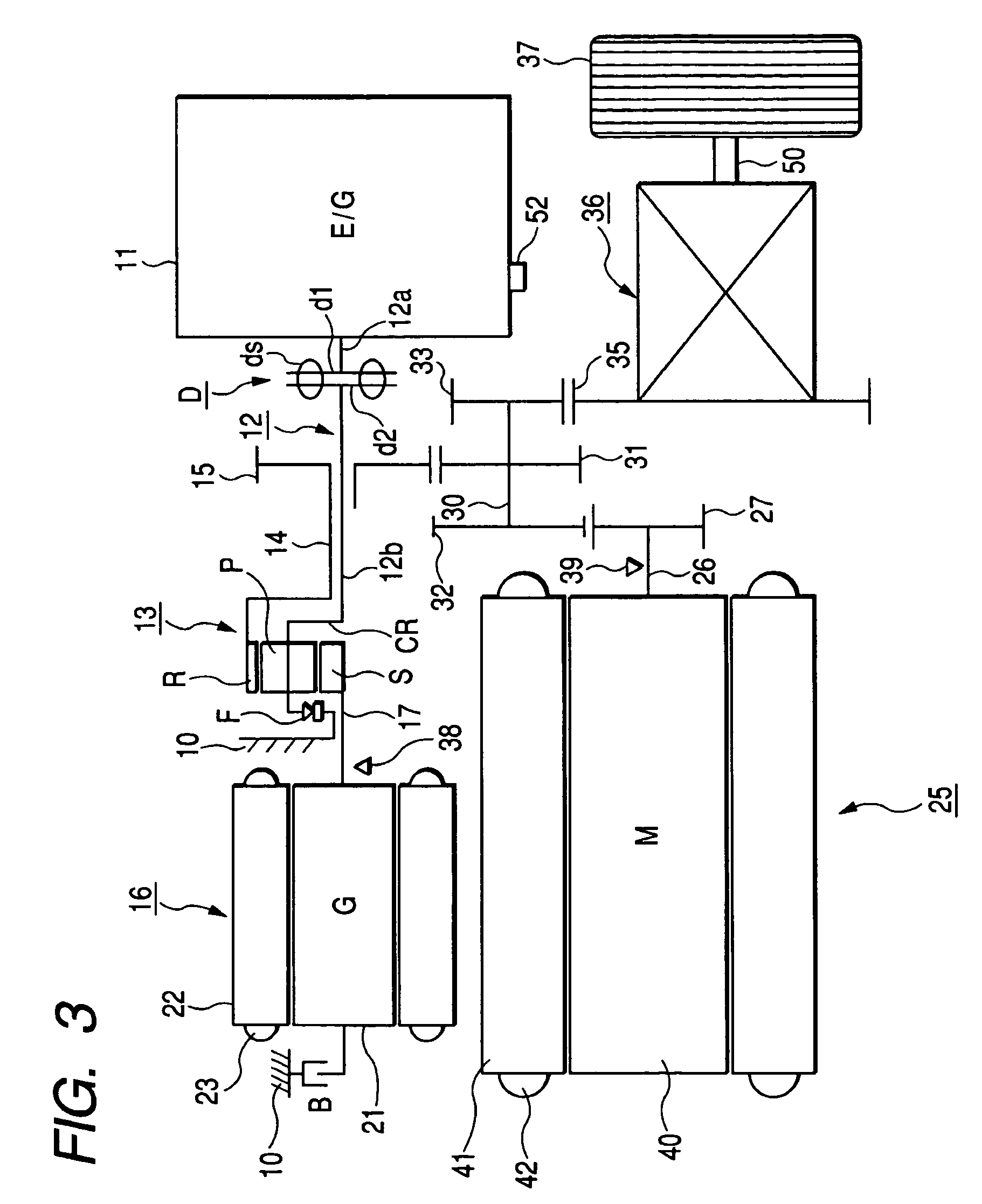
Control apparatus for driving vehicle and control method for driving vehicle
InactiveUS7207304B2Prevent large vibrationReduced durabilityHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlEngineeringAutomotive engineering
Large vibrations can be prevented from being generated during engine rotation. A control apparatus for driving a vehicle has an engine stop permission output control processing module which: reads engine rotational speed; determines whether the engine rotational speed takes a value within a predetermined stop disable range; does not output an engine stop permission when the engine rotational speed takes a value within the stop disable range; and outputs an engine stop permission when the engine rotational speed takes a value except the value within the stop disable range, and an engine stop control processing module which stops an engine when the engine stop permission is outputted. In this case, when the engine rotational speed takes the value except the value within the stop disable range, the engine stop permission is outputted to stop the engine.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
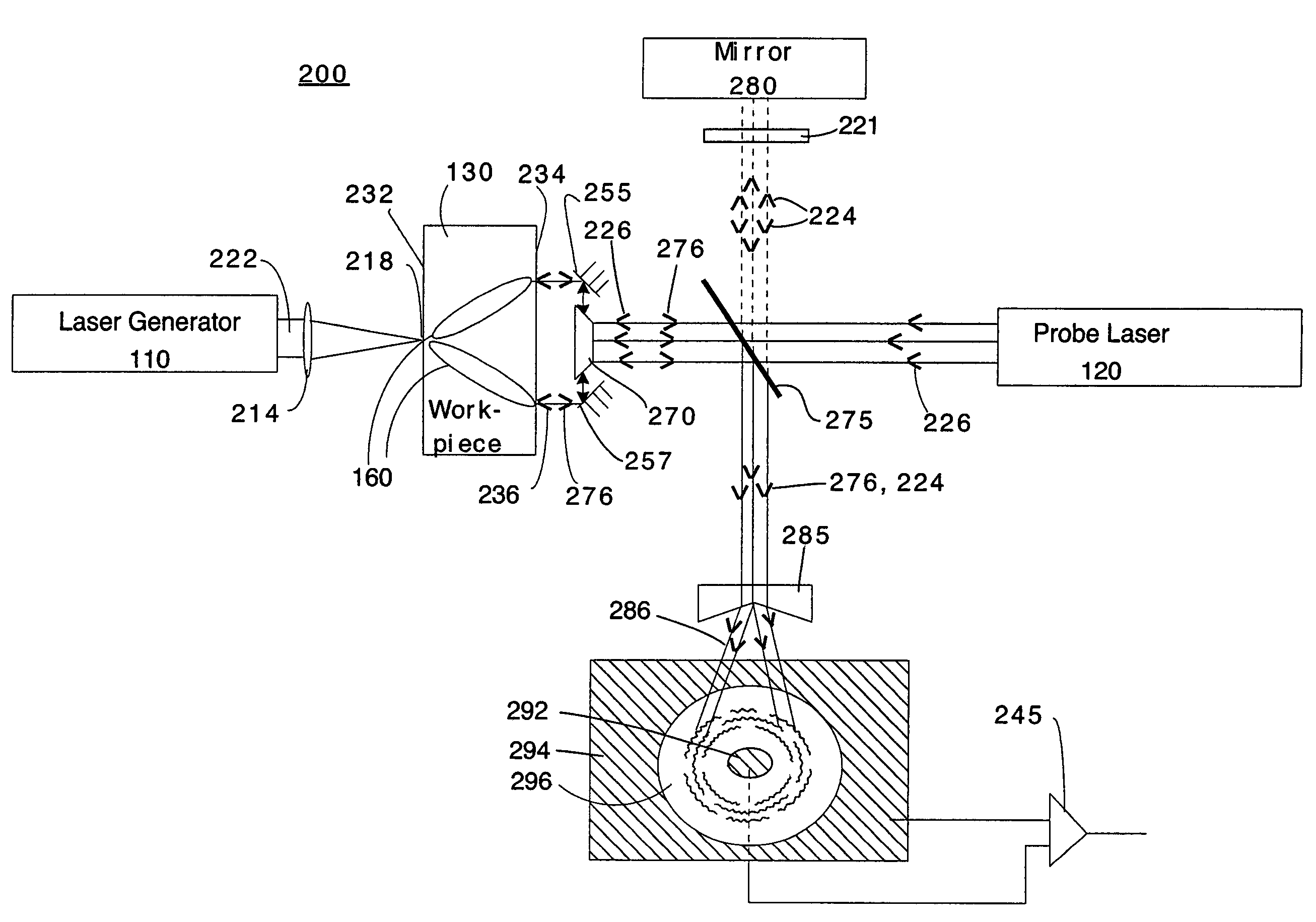
Ultrasound single-element non-contacting inspection system
InactiveUS7262861B1Low costReduce complexityVibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
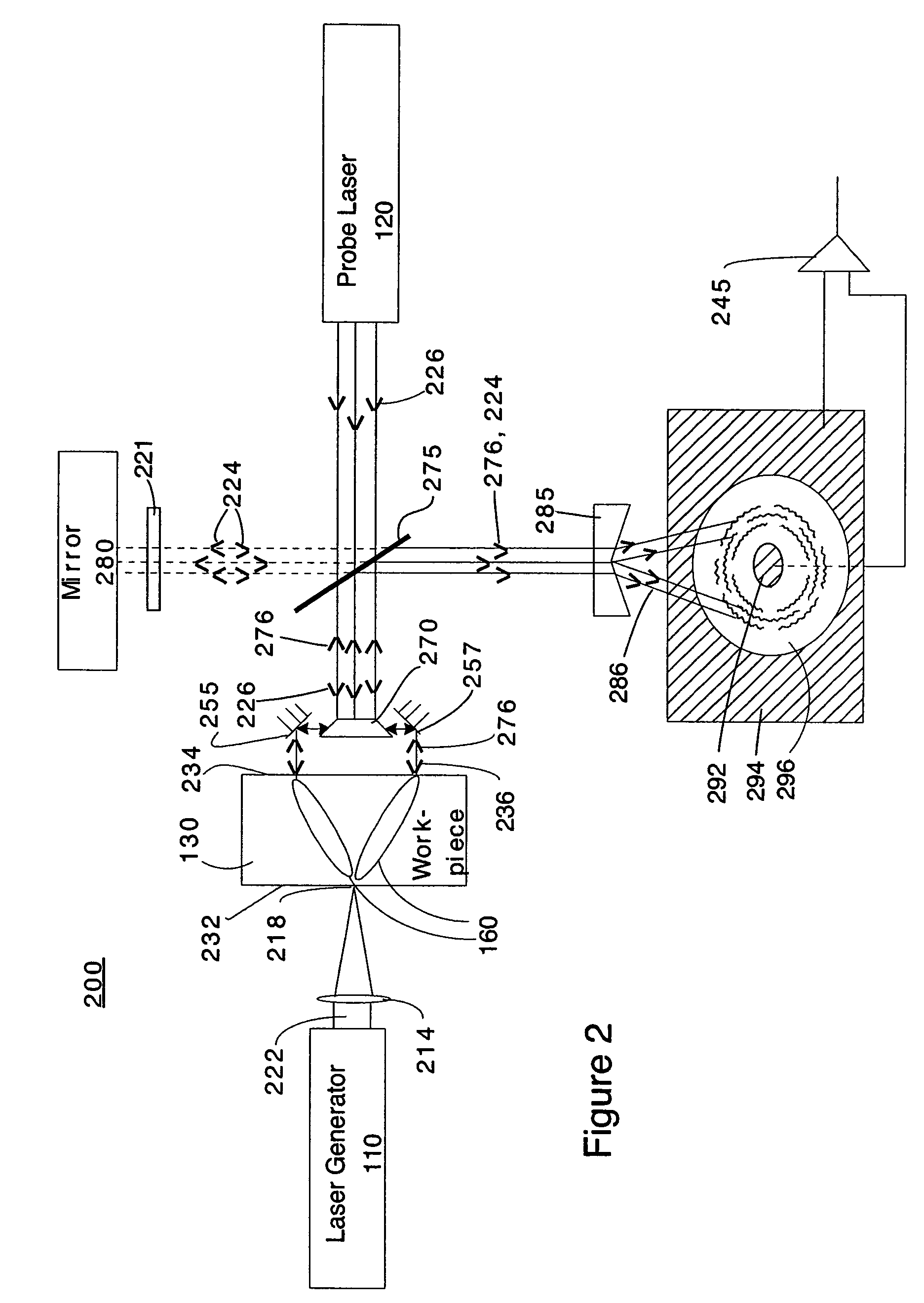
A laser ultrasonic inspection apparatus and method which enables remote sensing of thickness, hardness, temperature and / or internal defect detection is disclosed. A laser generator impinges a workpiece with light for generating a thermo-elastic acoustic reaction in a workpiece. A probe laser impinges the workpiece with an annularly-shaped probe light for interaction with the acoustic signal in the workpiece resulting in a modulated return beam. A photodetector having a sensitive region for detecting an annularly-shaped fringe pattern generated by an interaction of a reference signal and with the modulated return beam at said sensitive region.
Owner:HRL LAB
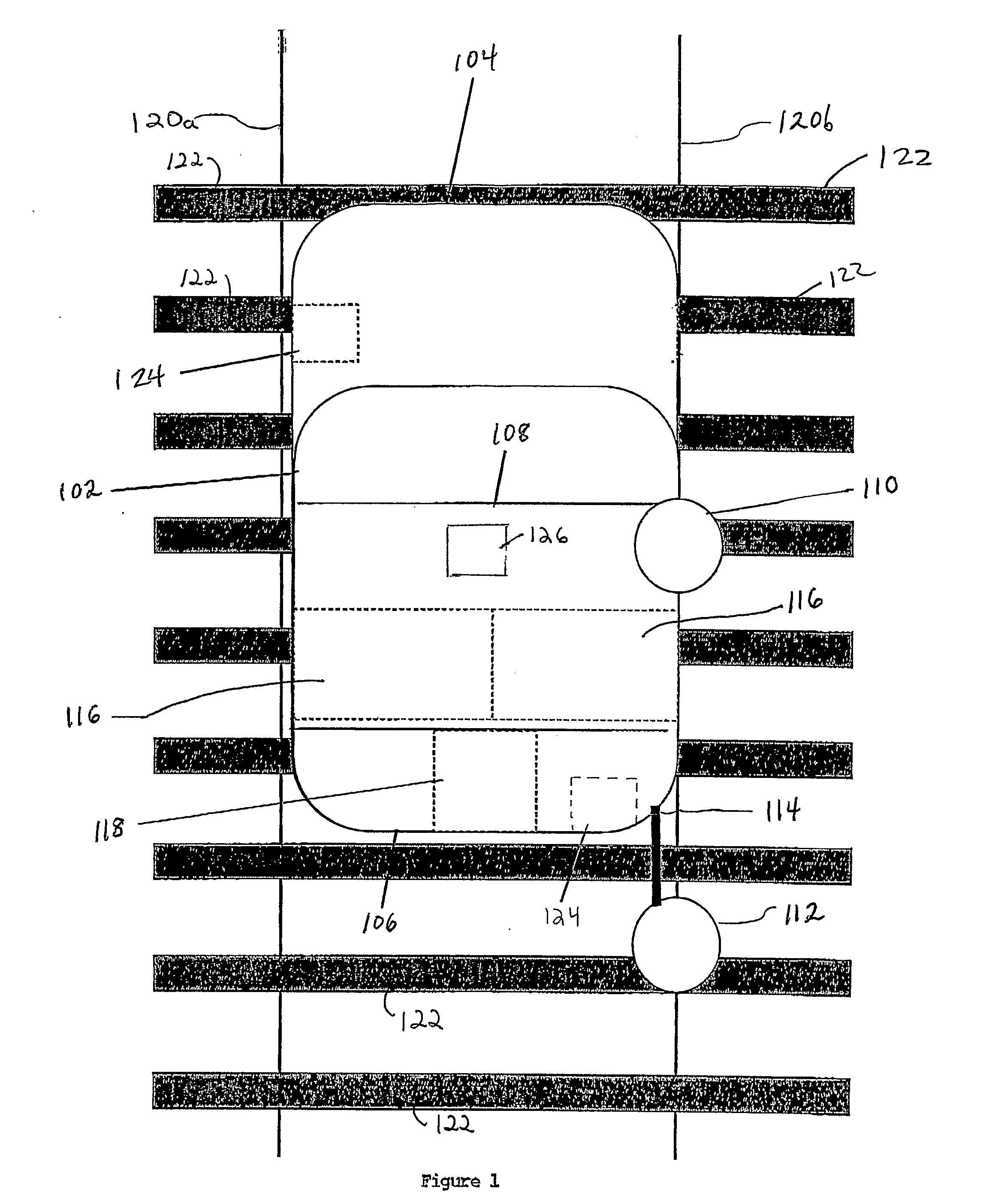
Railroad surveying and monitoring system
InactiveUS8180590B2Avoid large vibrationsPosition fixationTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesTrackwayMonitoring system
A Railroad Surveying and Monitoring System configured on a mobile platform for surveying, monitoring, and analyzing rail position and superstructure and terrain substructure of railroad tracks (20a,b) or other structures. The system employs two or more High Accuracy Differential Global Positioning System devices (110,112), ground penetrating radar devices (116), terrain conductivity instruments (118), optical cameras (124), and data receivers and processors (126), which in turn process, display, and store the data in a usable database. Precise coordinate data generated from a High Accuracy Global Positioning System provides both location data for subsurface sensors and surface sensors and rail position coordinates to monitor track displacements during track inspection in real time.
Owner:MARSHALL UNIV RES
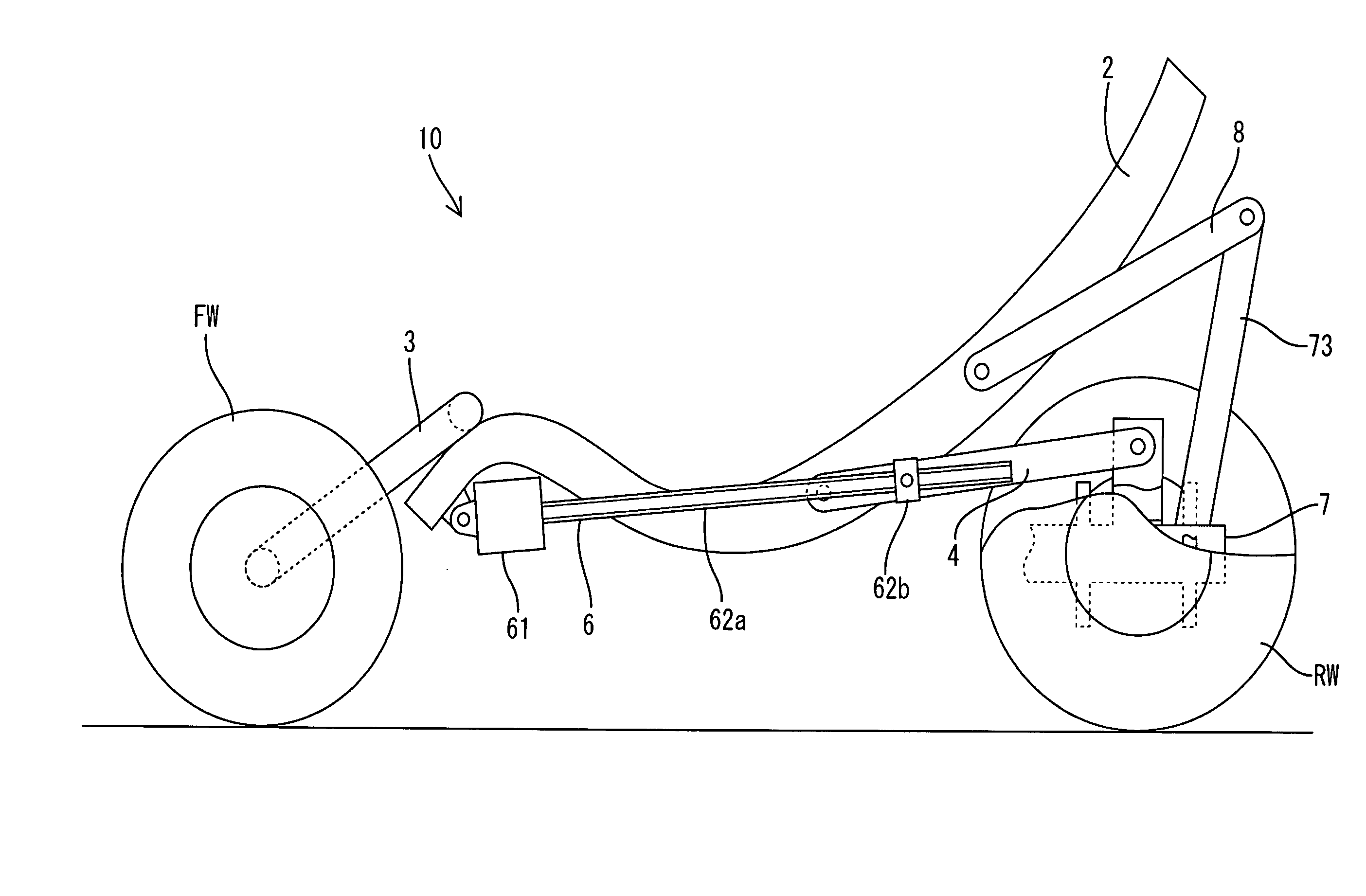
Vehicle Having An Adjustable Wheel Base
InactiveUS20080116665A1Simple structureEasy to adjustCarriage/perambulator accessoriesUnderstructuresEngineeringMechanical engineering
The front wheels of the vehicle having an adjustable wheel base are joined to the front portion of a main frame, on which a vehicle seat is mounted. The upper ends of a pair of rotating arms are rotatably joined to the main frame. The lower ends of the rotating arms are rotatably joined to the rear wheels. The upper arms and the lower arm are provided rotatably connected together such that the main frame and the rear wheels are joined at the back of the rotating arms. The operating portion of the operating apparatus, on which the main frame is installed, is joined via the operating links to the rotating arms. By operating the operating apparatus, the rotating arms are rotated by the operating links and the rear wheels are moved with respect to the front wheels. Simultaneously, the inclination of the main frame is changed.
Owner:TOYOTA SHATAI KK +1
Link actuation device
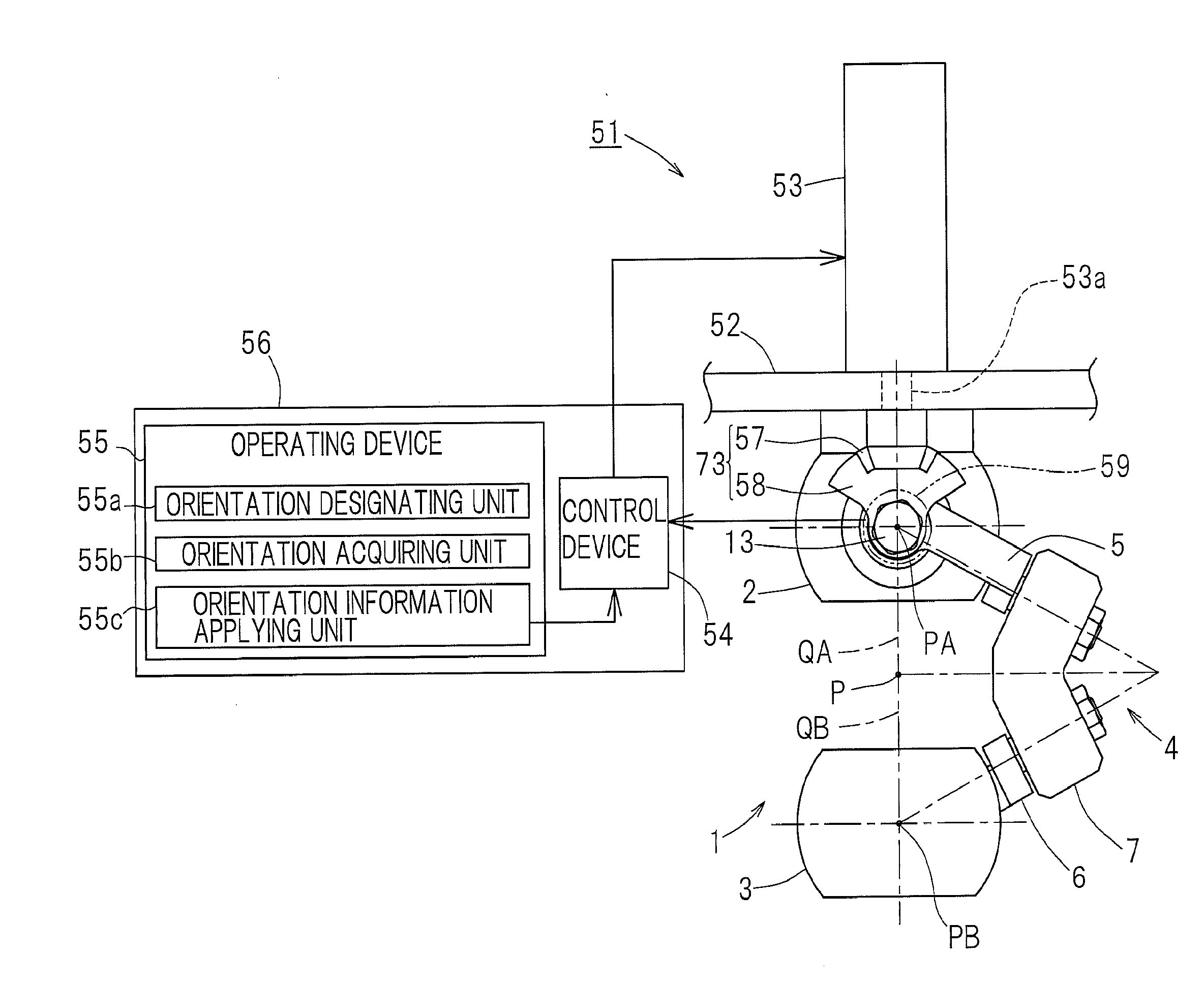
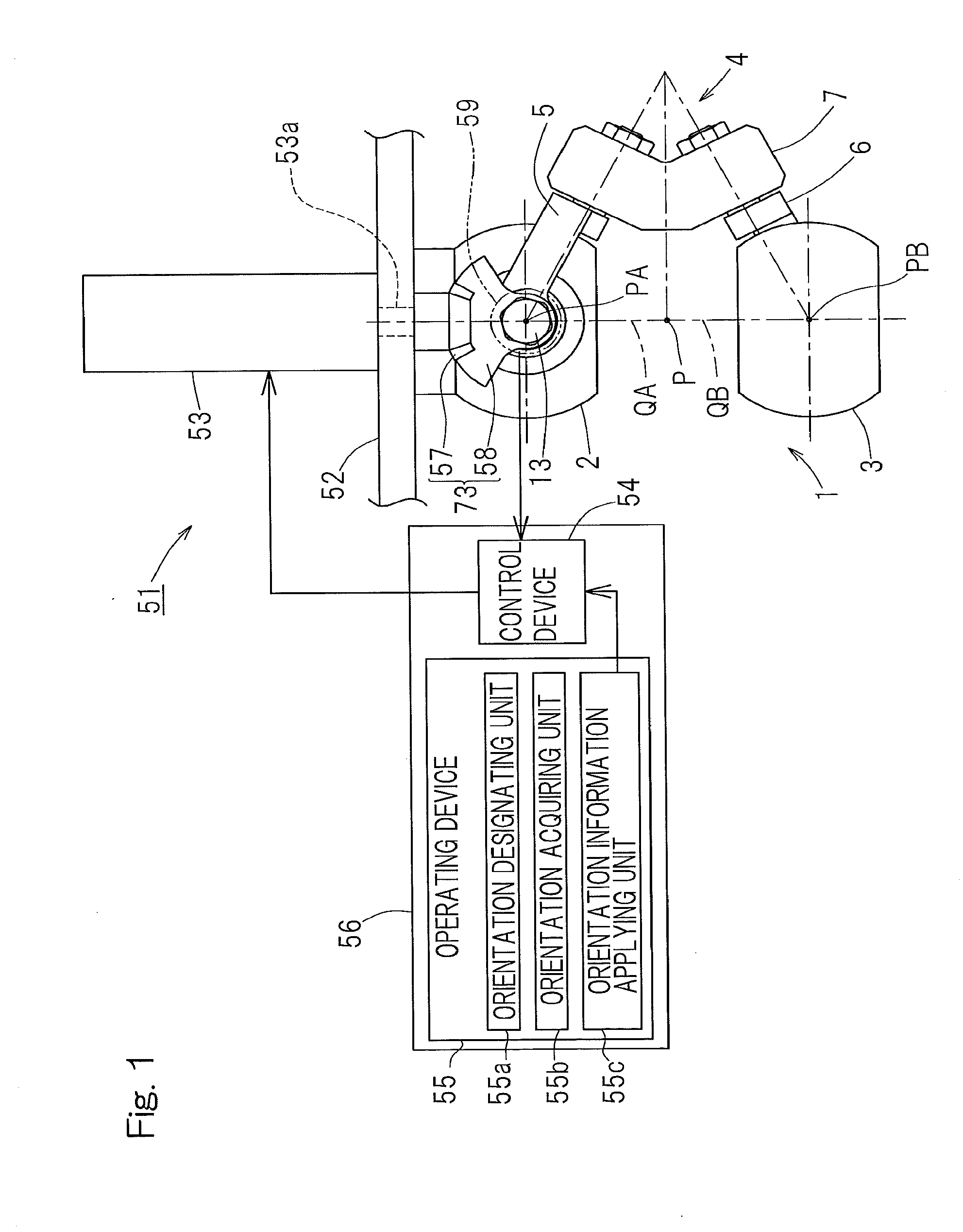
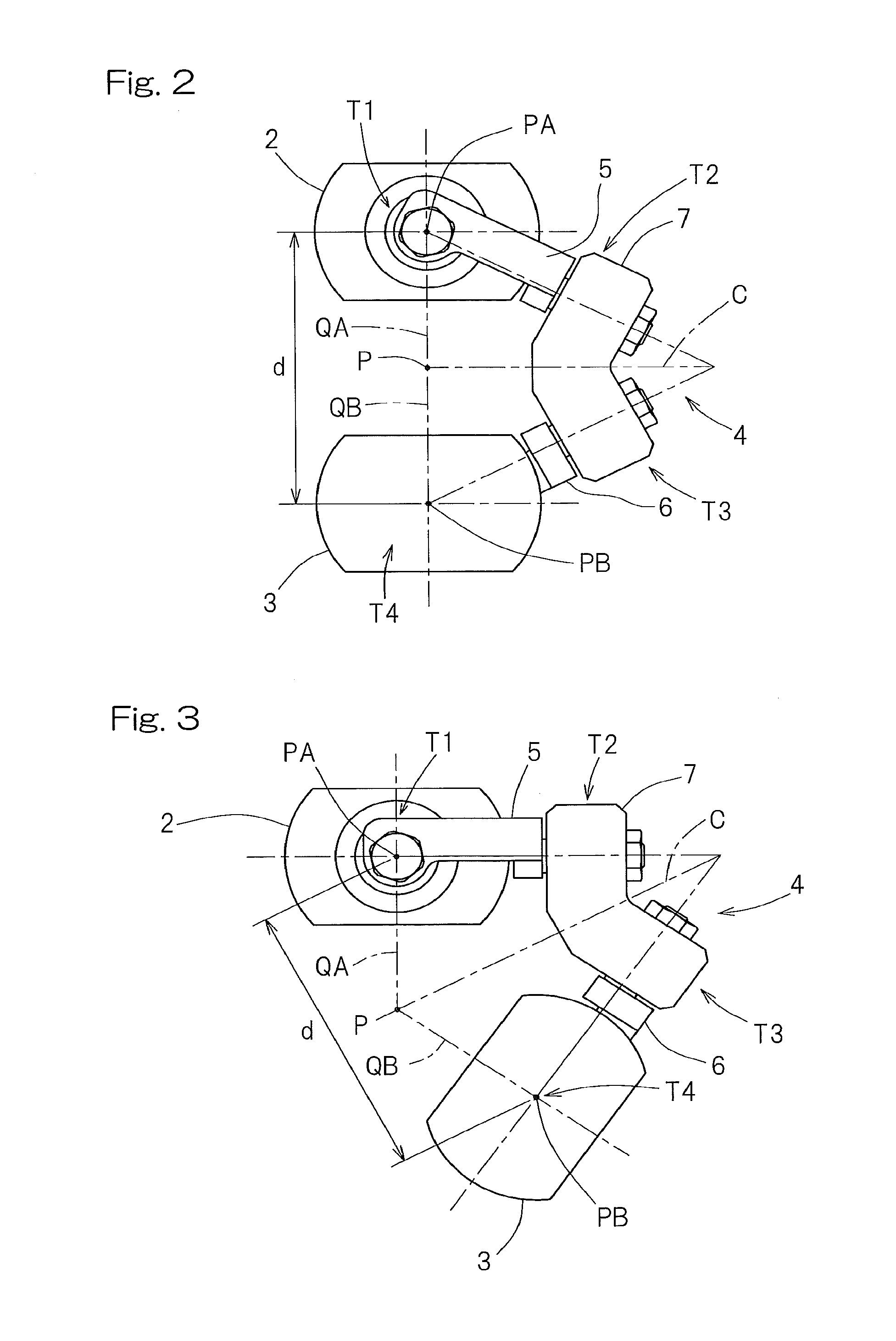
ActiveUS20150088308A1Large working rangeAccurate operationProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorOrthogonal coordinatesProximal point
A link actuation device includes a distal end side link hub connected with a proximal end side link hub through three or more sets of link mechanisms for alteration in orientation. By means of an actuator provided in the two or more set of the link mechanism, the distal end orientation, which is the orientation of the distal end side link hub relative to the proximal end link hub, is changed arbitrarily. The operating device includes an orientation designating unit for designating the distal end orientation aimed at by means of a coordinate position on the orthogonal coordinate system by an artificial manipulation, an orientation acquiring unit for acquiring the distal end orientation that is expressed by an angular coordinate system through calculation, and an orientation information applying unit for applying information on the distal end orientation so acquired to a control device for controlling the actuator.
Owner:NTN CORP
Mounting structure of a power unit for a utility vehicle
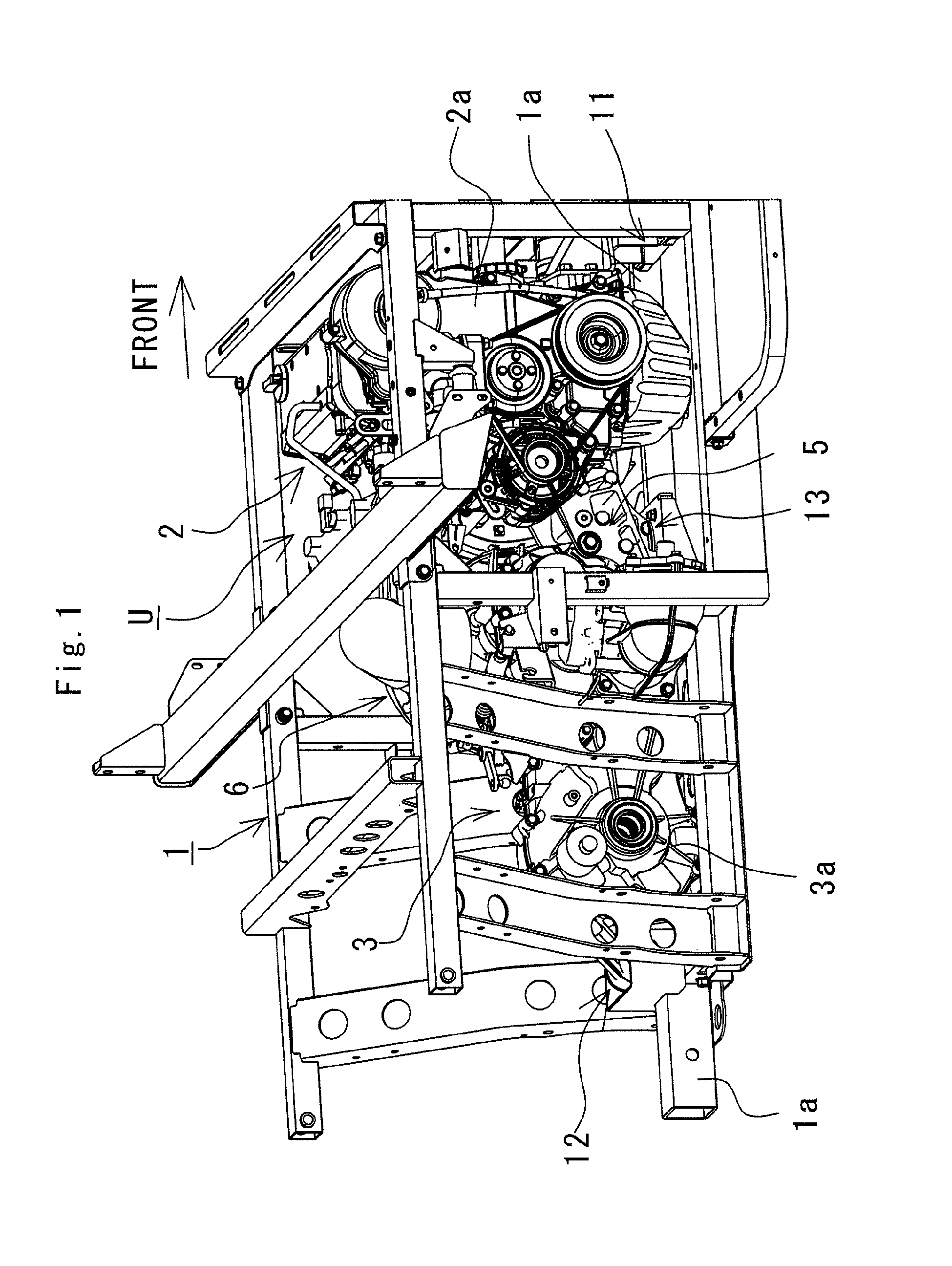
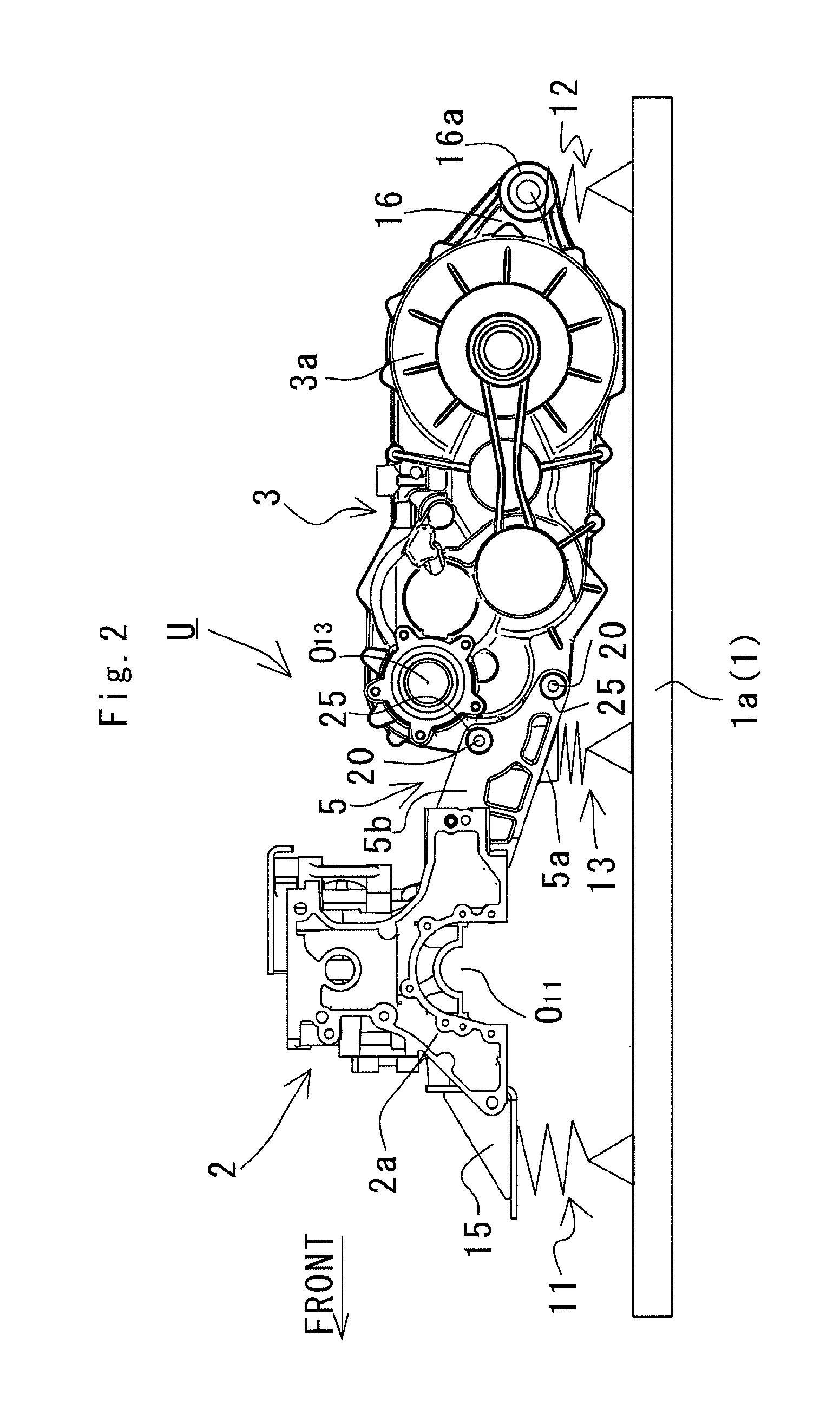
ActiveUS8727063B1Improve installation strengthImprove ride qualityAgricultural vehiclesElectric propulsion mountingVehicle framePower unit
In a mounting structure of a power unit for a utility vehicle, the power unit includes an engine and a transmission coupled onto one side of the engine in a vehicular lengthwise direction. A lower end substantially at the center of the engine in a vehicular widthwise direction and a lower end substantially at the center of the transmission in the vehicular widthwise direction are mounted to an upper surface of a chassis frame by a front mounting mechanism with a damper and a rear mounting mechanism with a damper.
Owner:KAWASAKI MOTORS LTD
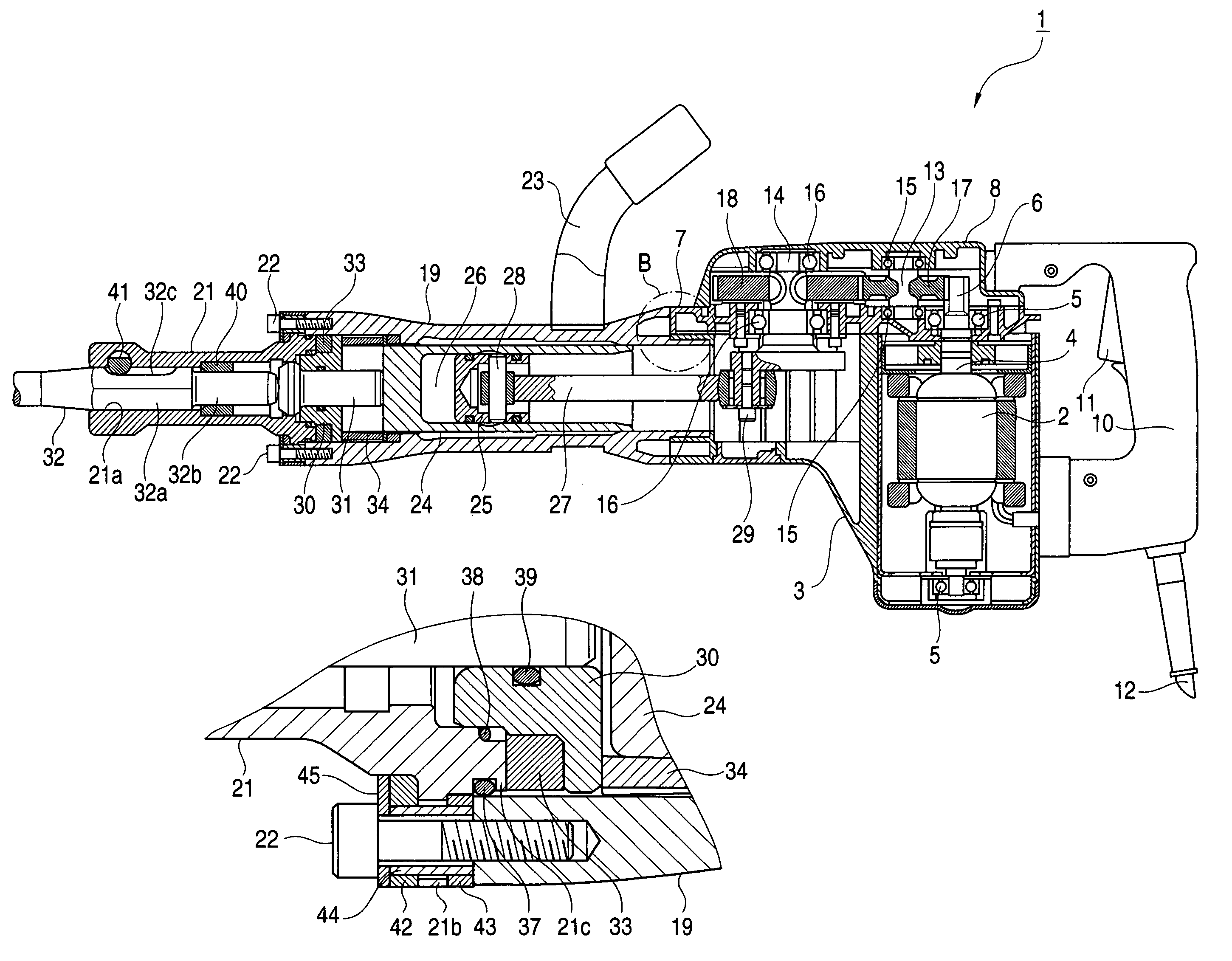
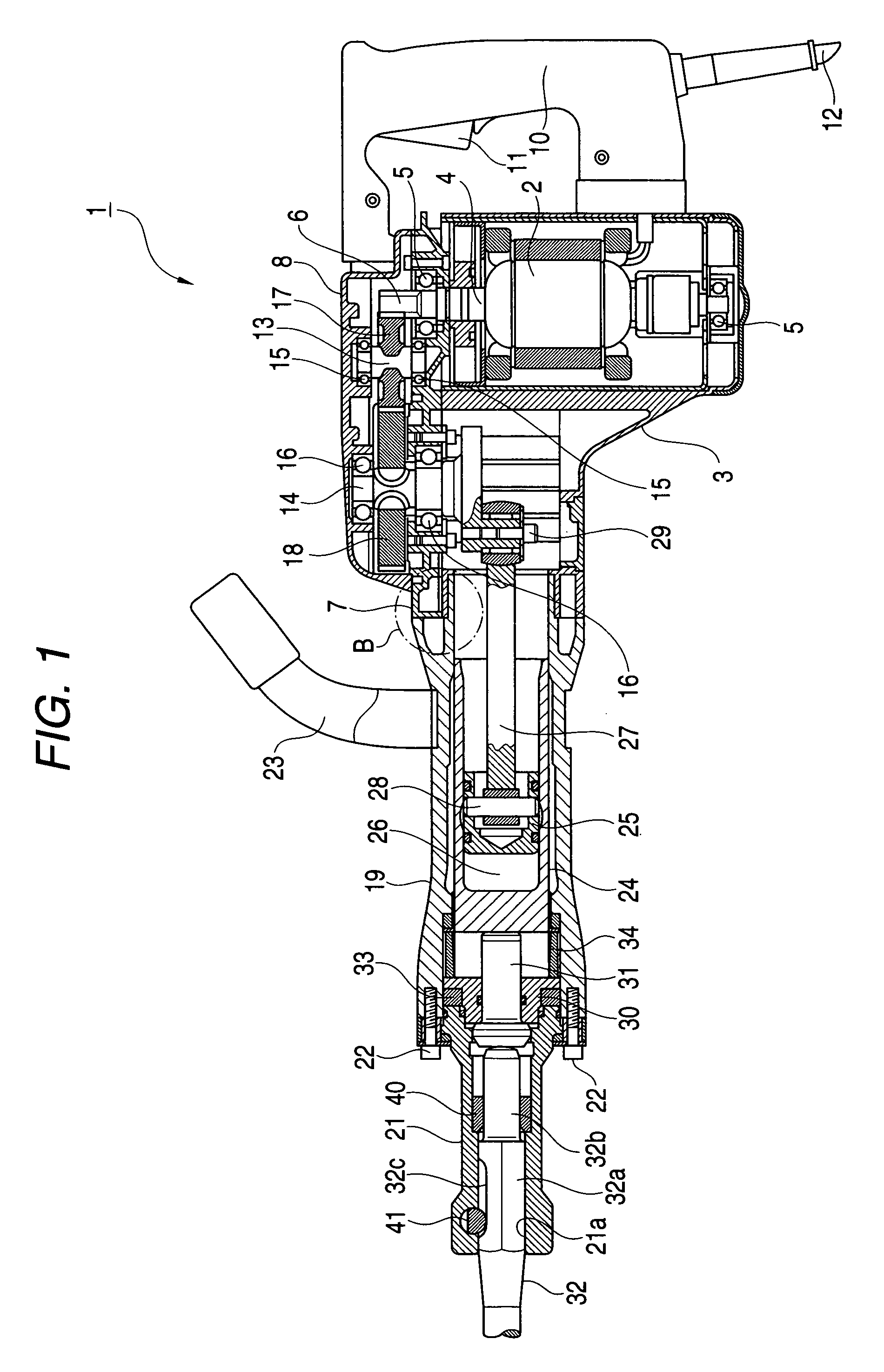
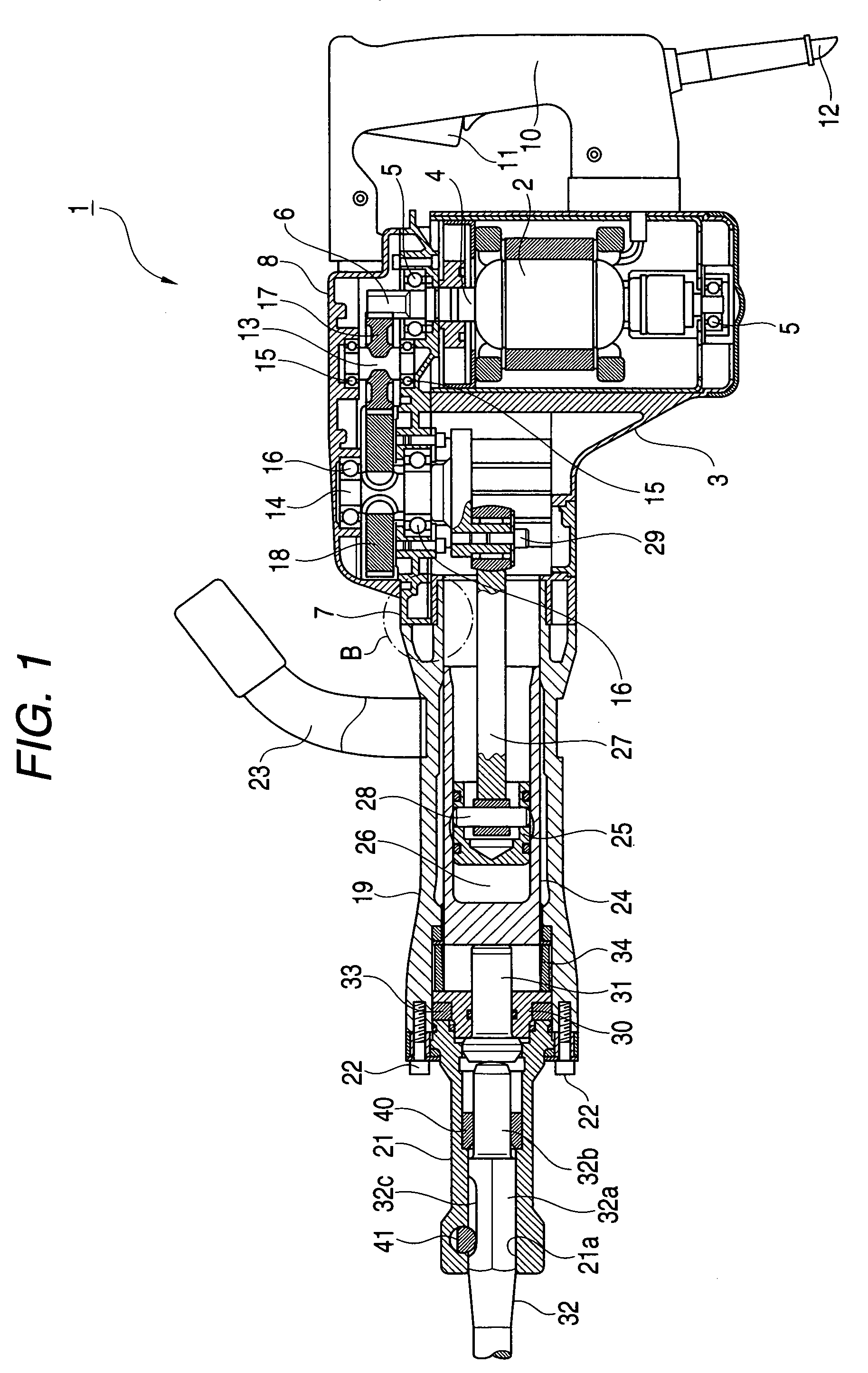
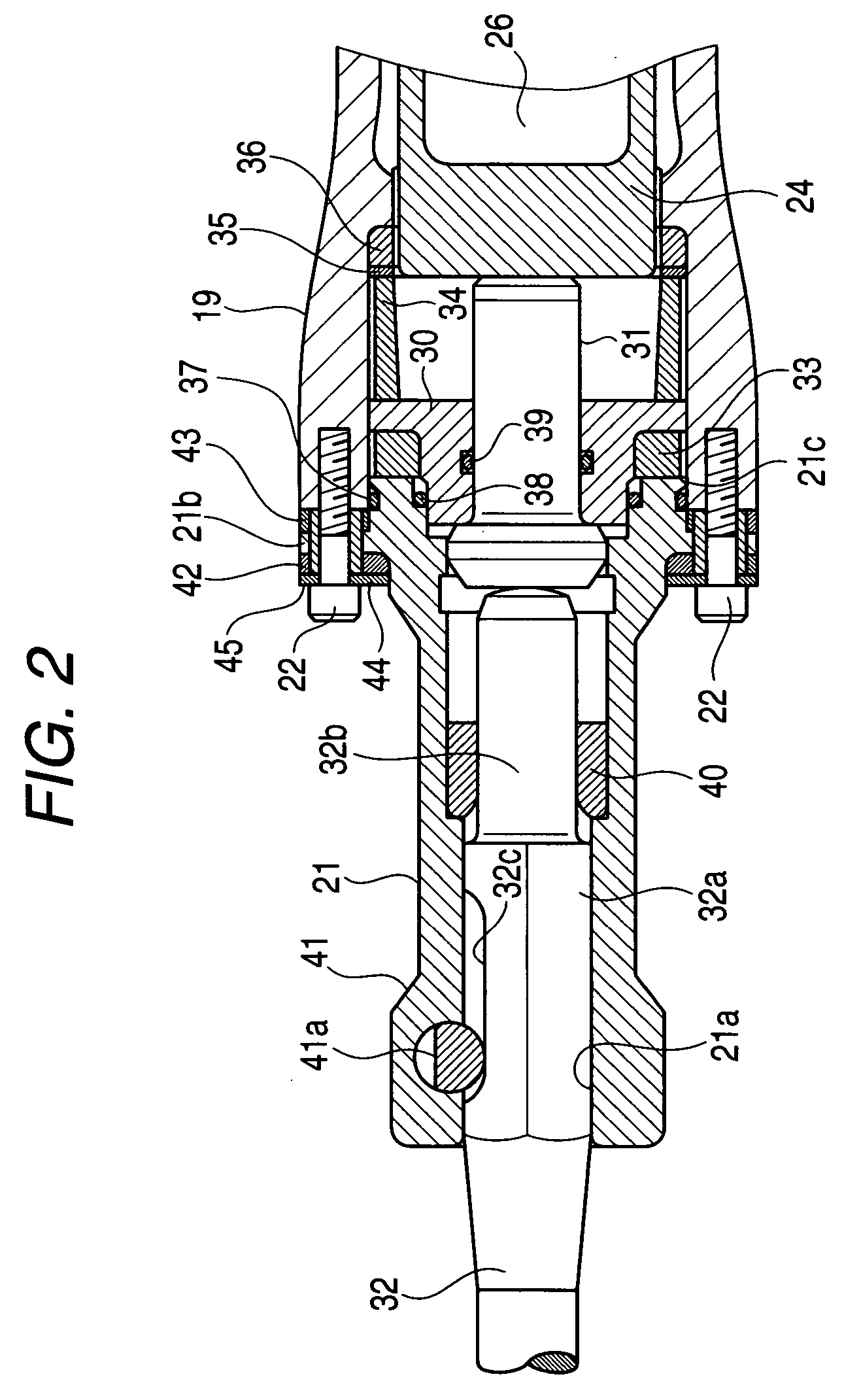
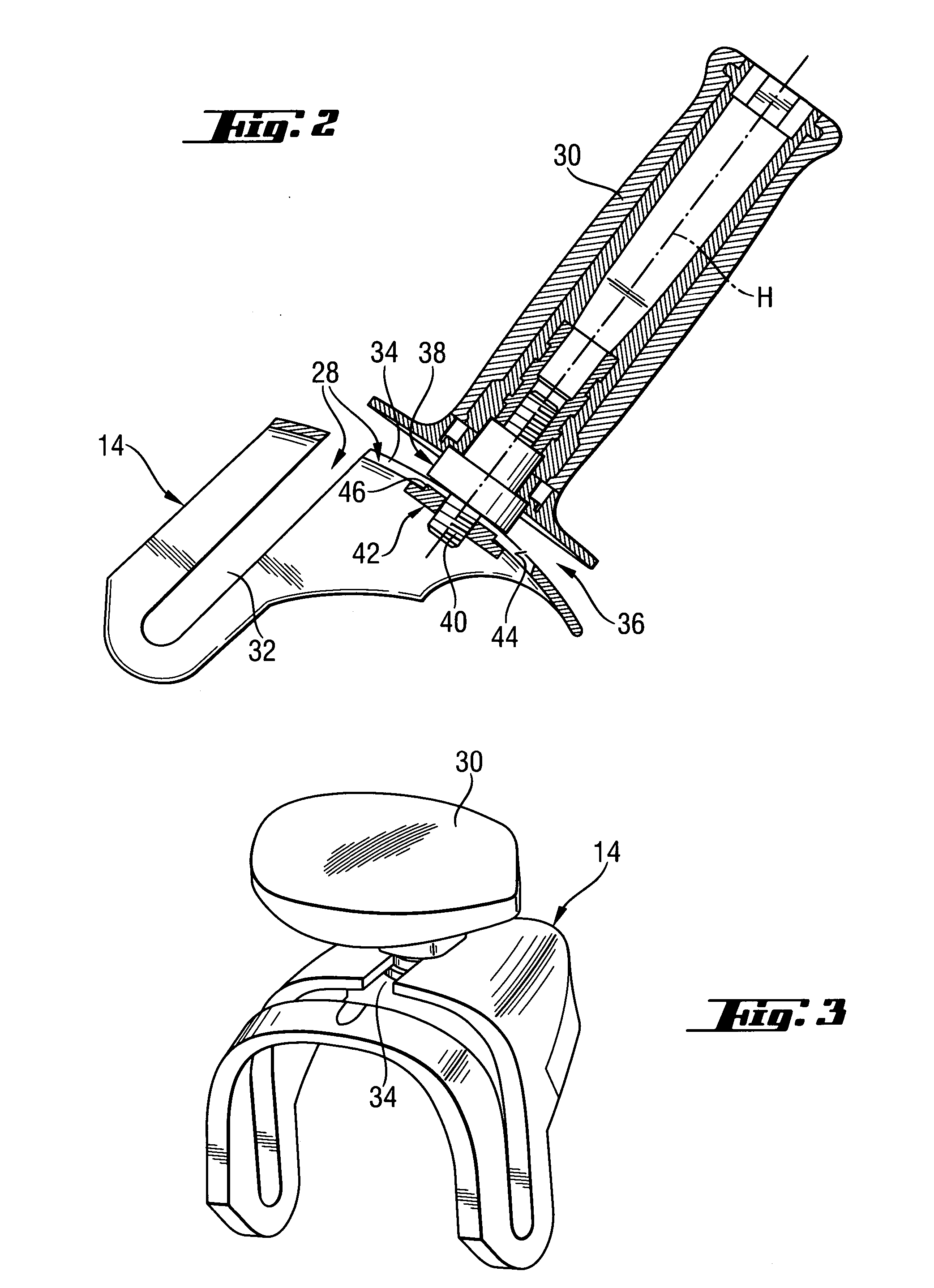
Striking tool
ActiveUS7819203B2Avoid large vibrationsReduce noiseSleeve/socket jointsTurning machine accessoriesEngineeringPiston
An impact force is transmitted to a tip end tool due to the changes of the air pressure within an air chamber generated by the reciprocal operation of the piston within a striker. The attachment portion of a tip end tool holding member for holding the tip end tool to a cylinder casing is sandwiched between buffers disposed in the two directions of the axial direction of the tool thereby to elastically support the tip end tool holding member to be movable in the two directions of the axial direction of the tool.
Owner:KOKI HLDG CO LTD
Fluid end assembly
InactiveUS20110206546A1Extend working lifeEasy to replacePositive displacement pump componentsPositive-displacement liquid enginesEngineeringFluid supply
A fluid end assembly including a pump housing with a number of interior passages for the flow of fluids. The housing has a plunger bore with a closed inner end and an open outer end. A suction passage intersects the plunger bore. A discharge passage intersects both the plunger bore and the suction passage such that the discharge passage, the suction passage, and the plunger bore radiate outwardly from their point of intersection to define a shape resembling a “Y”. A connector passage branches from the discharge passage. An outlet passage intersects the connector passage and passes through the pump housing at right angles to the plunger bore. A reciprocating plunger is located in the plunger bore. A suction valve is located in the suction passage. A discharge valve is located in the discharge passage. A fluid supply manifold is pivotally secured to the housing and is in fluid communication with the suction passage.
Owner:FORUM US
Device for directional drilling
ActiveUS20120285746A1Continuous regulationControl deflectionDirectional drillingDrive shaftDirectional drilling
A drill string section for directional drilling includes an outer casing which encases an adjustment mechanism for adjusting drilling direction and angular deflection during drilling. The adjustment mechanism has an outer shaft that is rotatably arranged relative to the outer casing and is configured with an axial eccentric first bore having a first bore axis that is parallel to the centre axis. The adjustment mechanism further includes an inner shaft that is rotatably arranged in the first bore and is configured with an axial, eccentric second bore for passage of a drive shaft for a drill bit
Owner:NABORS LUX 2 SARL
Striking tool
ActiveUS20050269117A1Suppress generationReduce noiseSleeve/socket jointsTurning machine accessoriesEngineeringPiston
An impact force is transmitted to a tip end tool due to the changes of the air pressure within an air chamber generated by the reciprocal operation of the piston within a striker. The attachment portion of a tip end tool holding member for holding the tip end tool to a cylinder casing is sandwiched between buffers disposed in the two directions of the axial direction of the tool thereby to elastically support the tip end tool holding member to be movable in the two directions of the axial direction of the tool.
Owner:HITACHI KOKI CO LTD
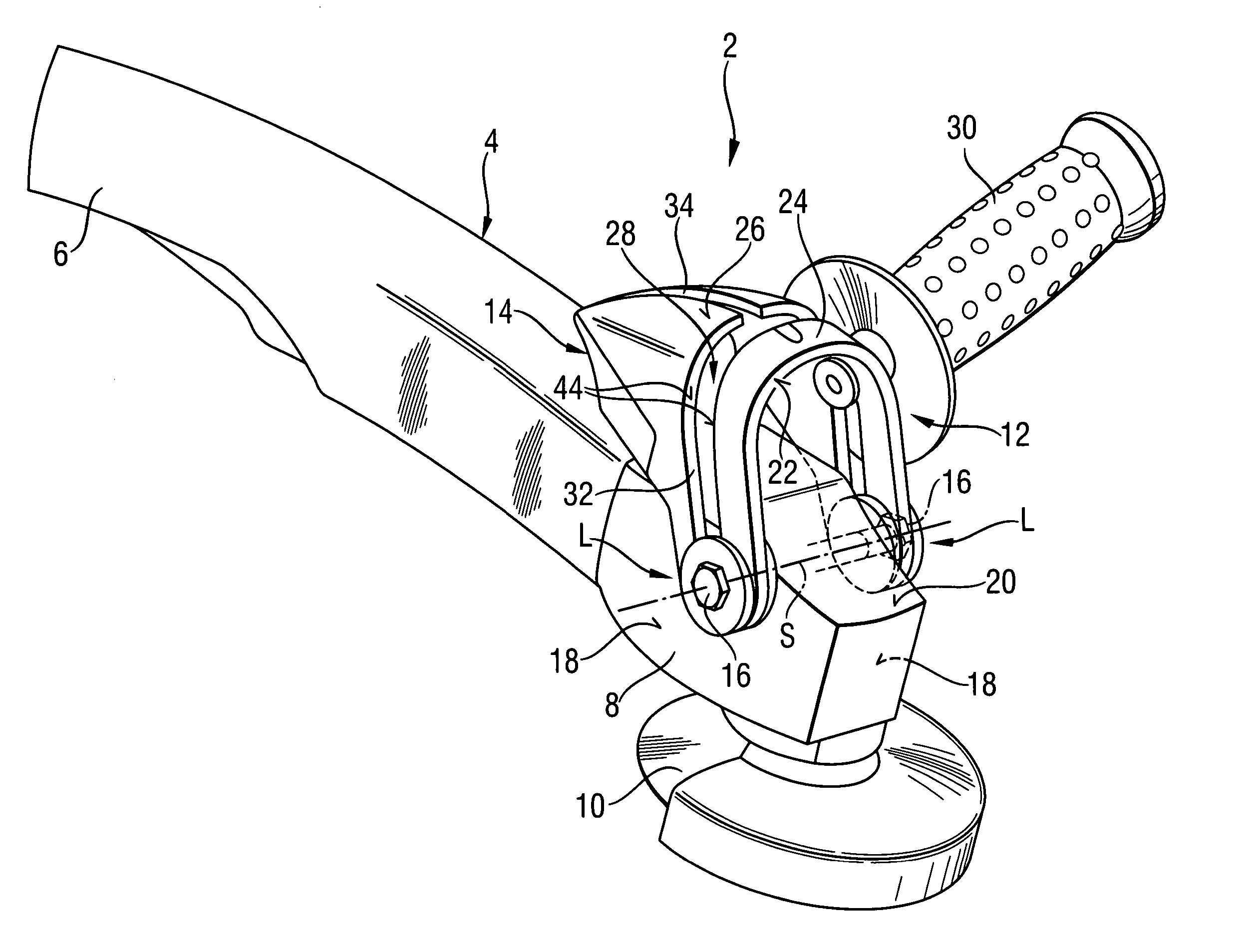
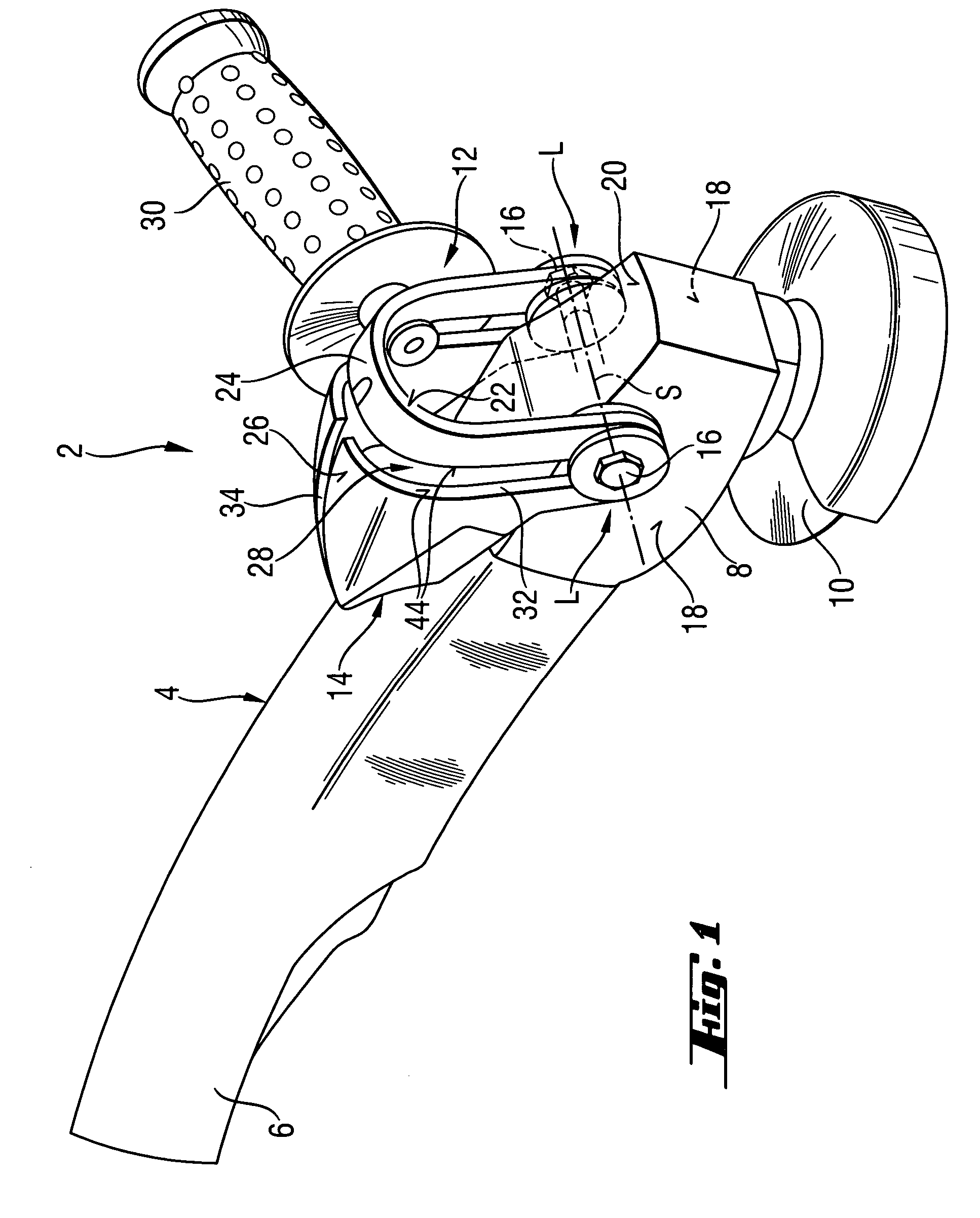
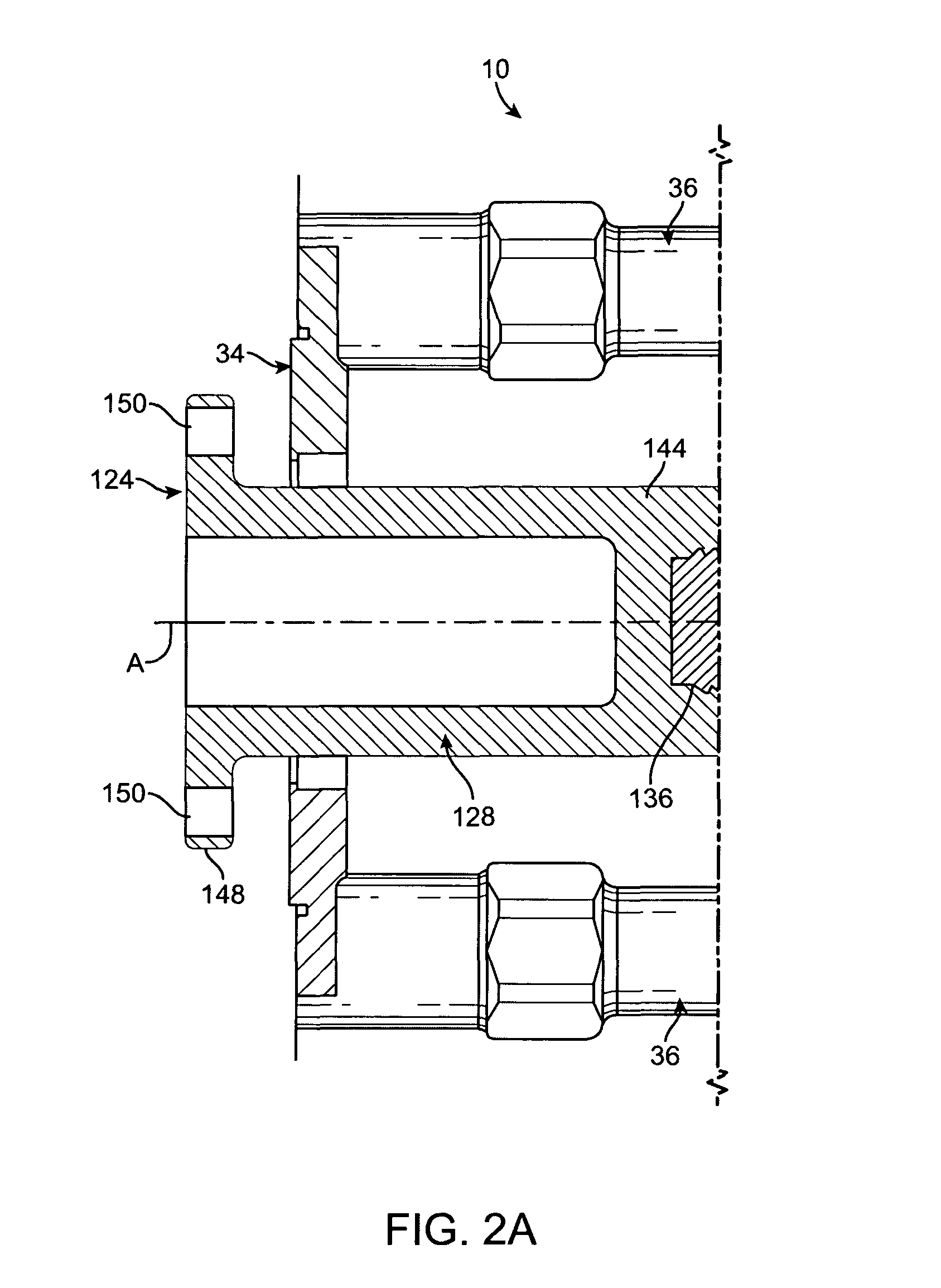
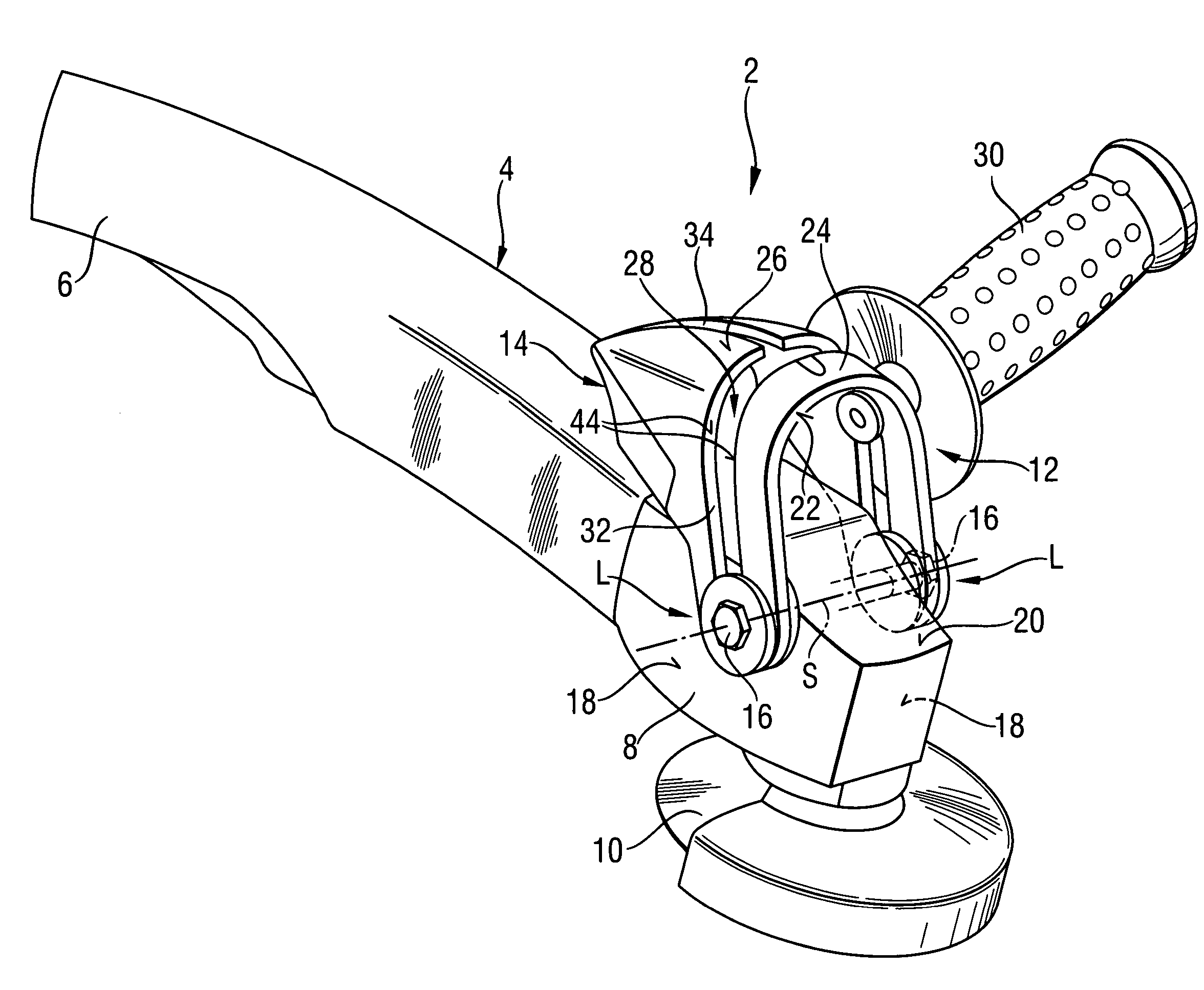
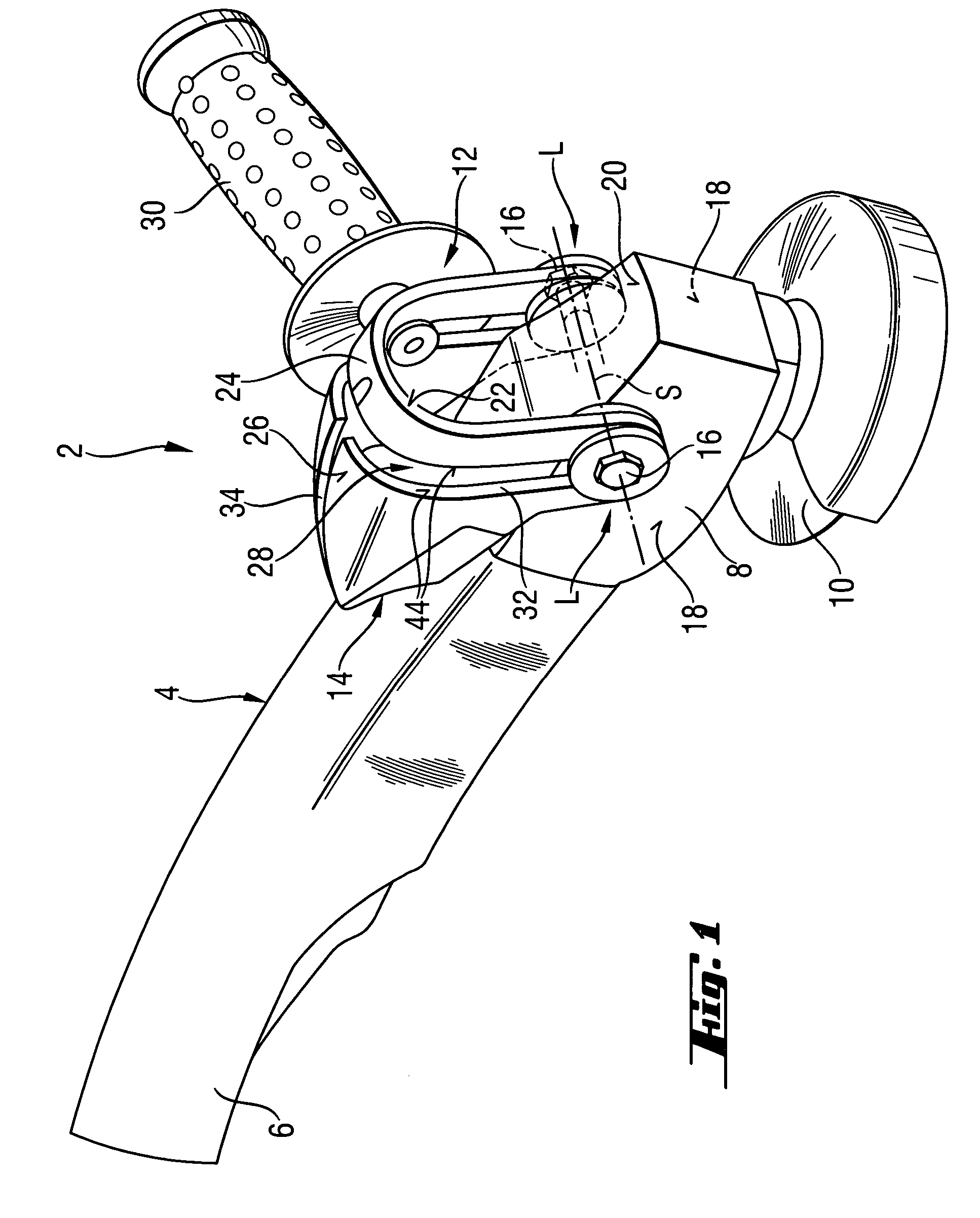
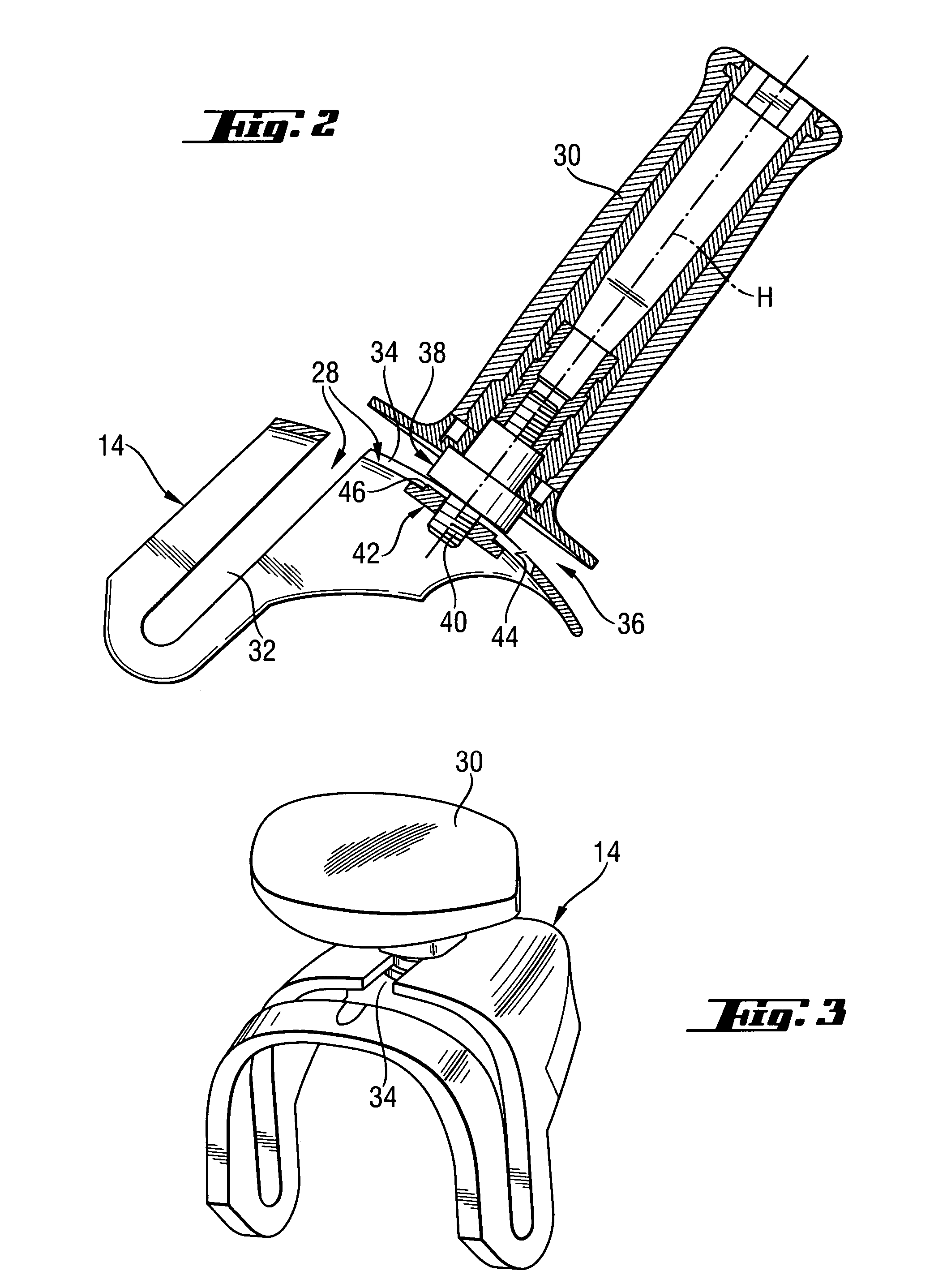
Hand-held power tool with an auxiliary handle
InactiveUS20050217440A1Easily positionEasily repositionTravelling carriersHoldersPower toolEngineering
A hand-held power tool, such as an angular grinder, includes a housing (4) having a main handle (6), and a support member (14) for supporting a side handle (30) in different positions relative thereto and pivotable relative to the housing (4) about two support points (L).
Owner:HILTI AG
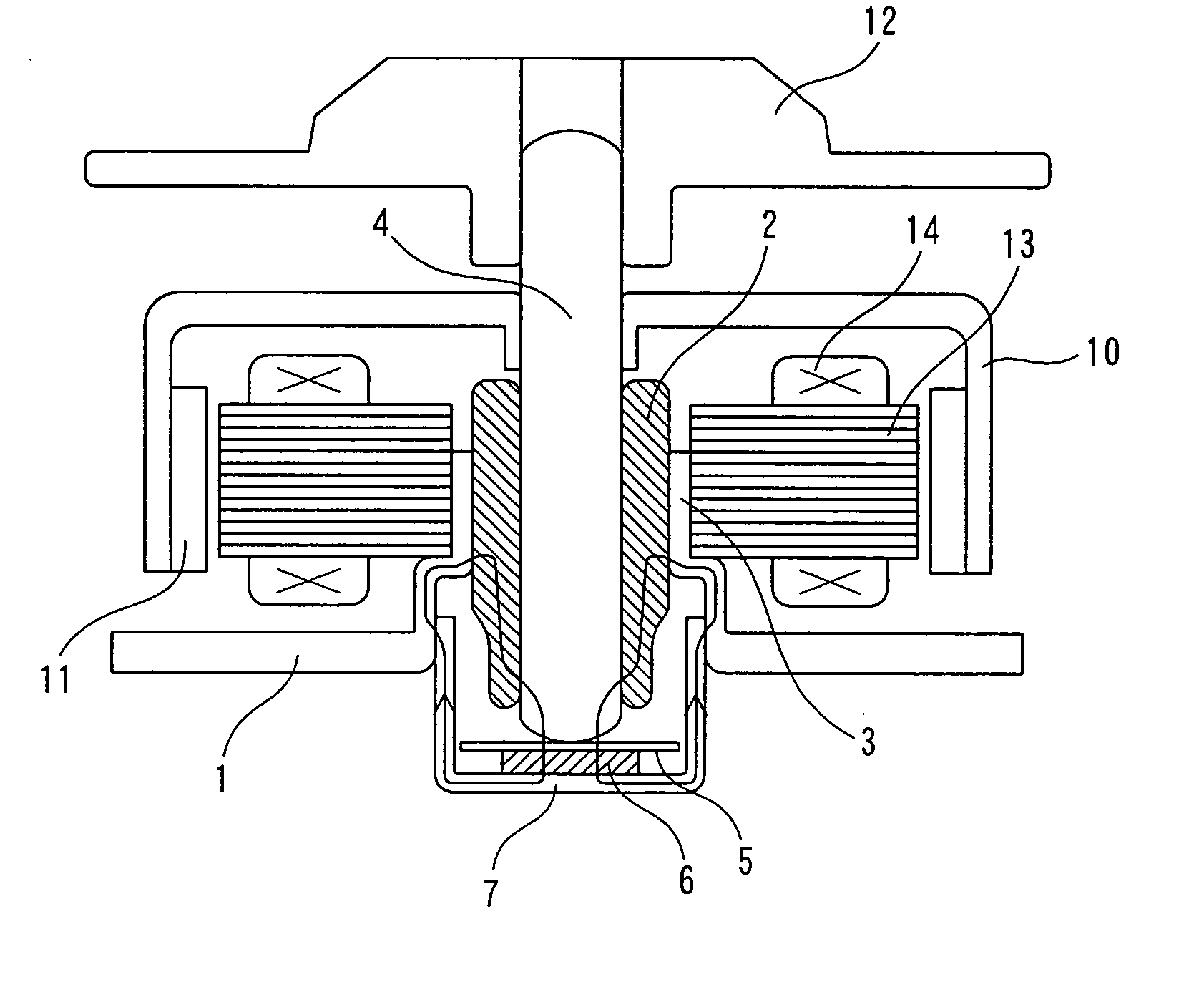
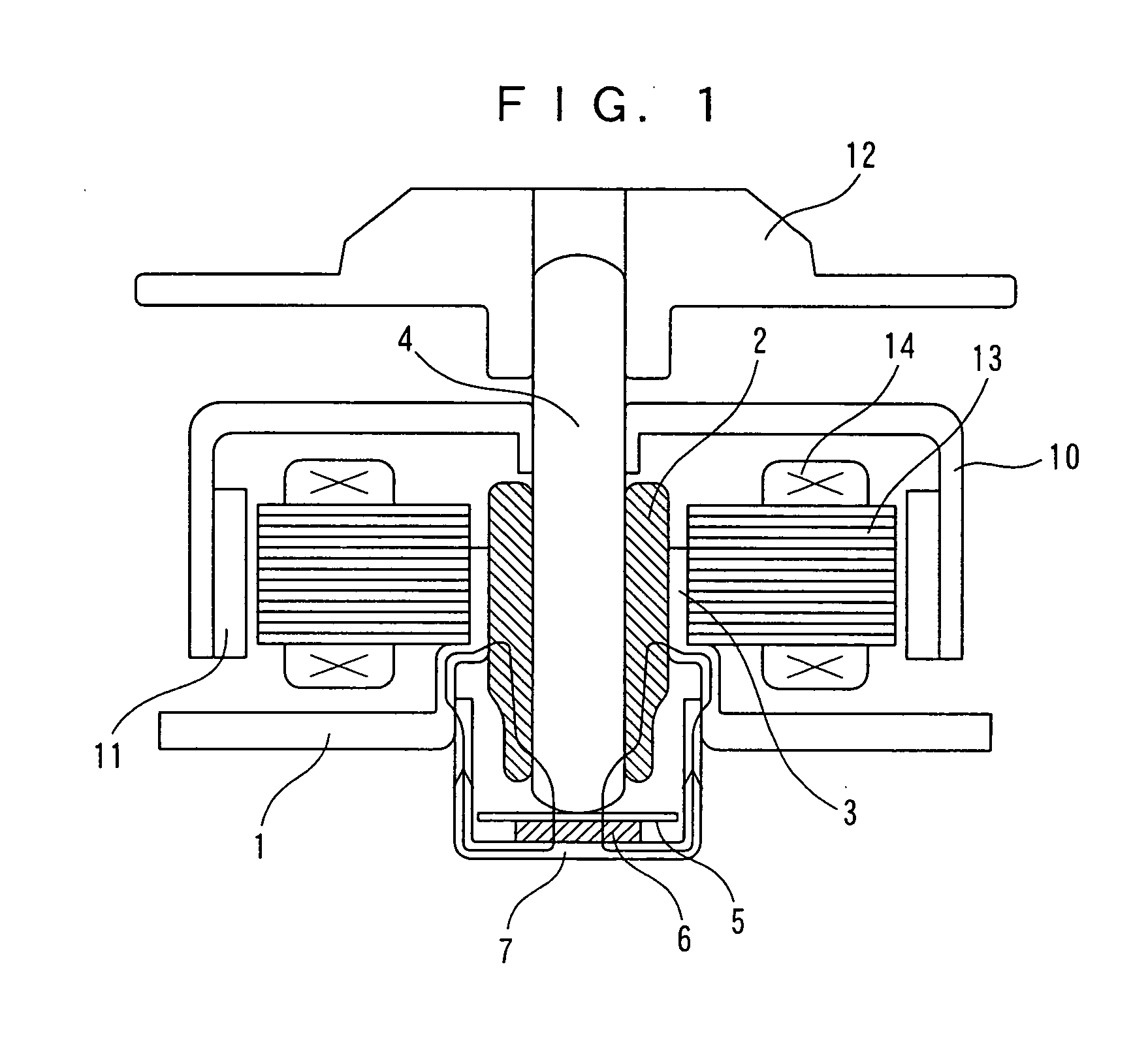
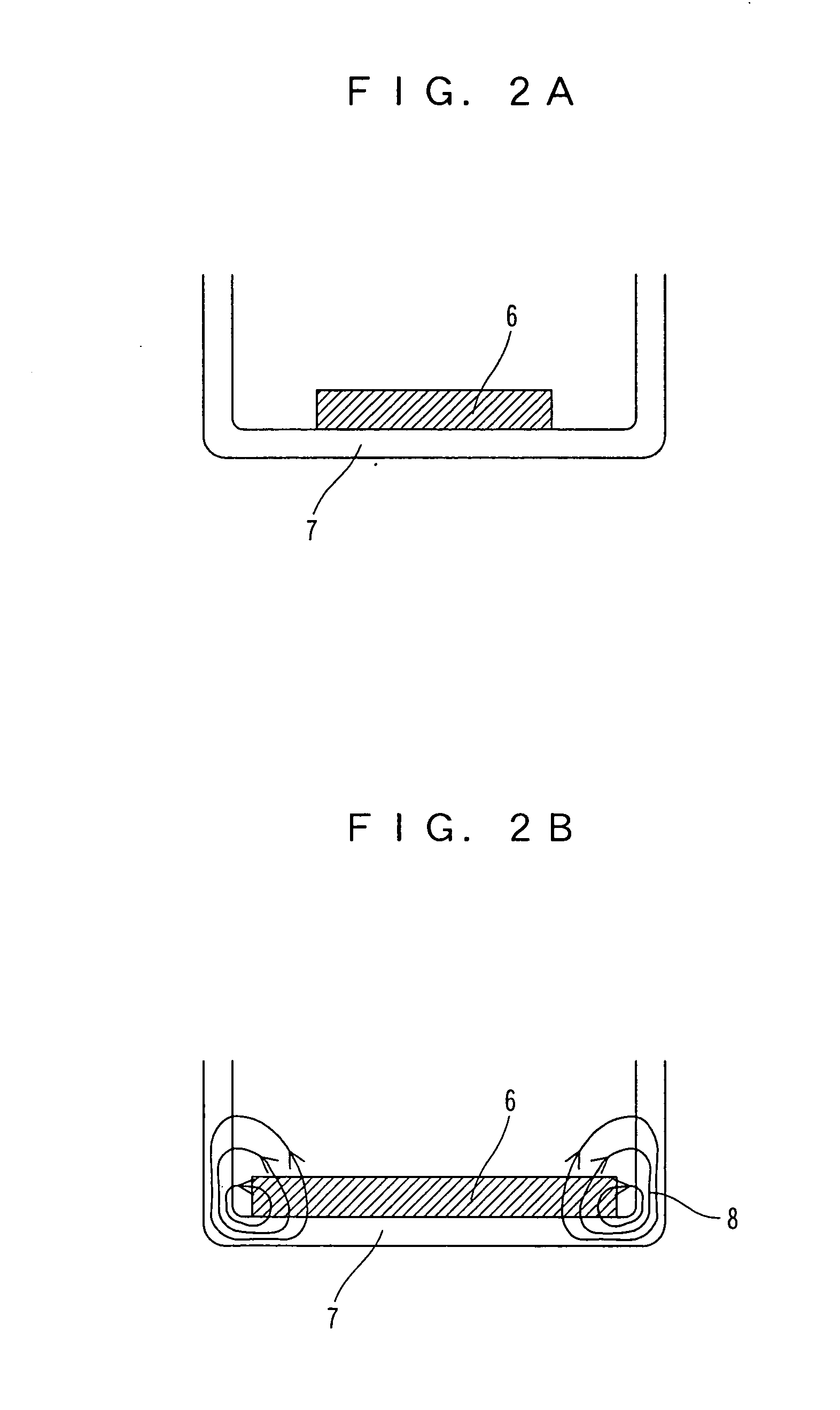
Brushless motor
ActiveUS20050140225A1Avoid large vibrationsSufficient forceShaftsRecord information storageBrushless motorsMagnetic flux
The present invention provides a low vibration brushless motor for reducing the vibration of the motor in an axial direction. In the brushless motor, a bearing is provided in a bearing boss, a shaft is held by the bearing, an end face of the shaft is contacting a thrust receiving member, and the shaft is rotatably axially supported by the bearing. The brushless motor includes a permanent magnet for attracting the end face of the shaft in the thrust direction with the thrust receiving member therebetween, and a bottom receiving part for supporting the permanent magnet, wherein the bearing boss, bearing, shaft, and bottom receiving part are made of a magnetic material, and a closed magnetic path is formed so that a magnetic flux passes through the permanent magnet, bottom receiving part, bearing boss, bearing, and shaft.
Owner:MINEBEA MOTOR MFG
Devices, installations and methods for improved fluid flow measurement in a conduit
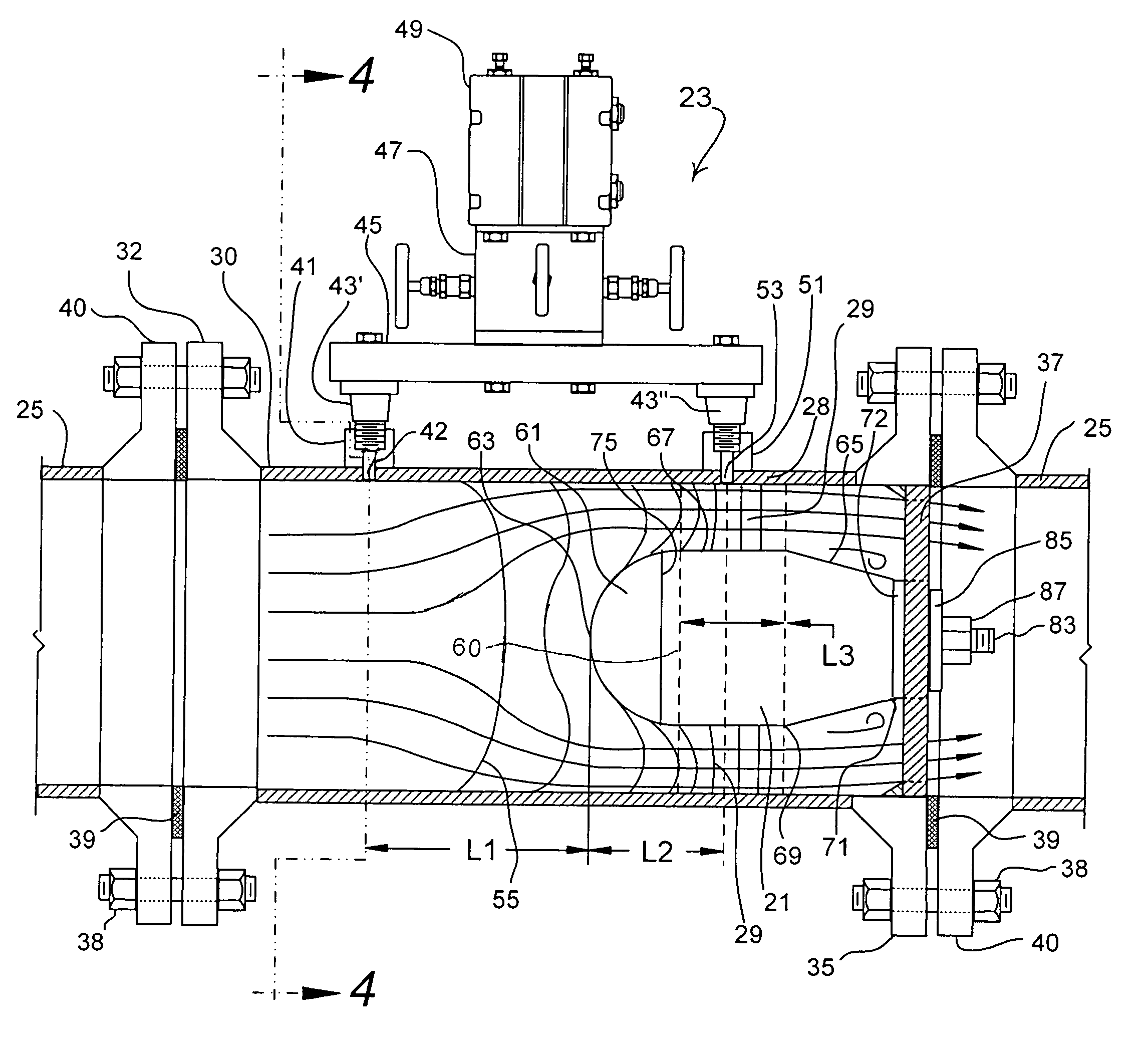
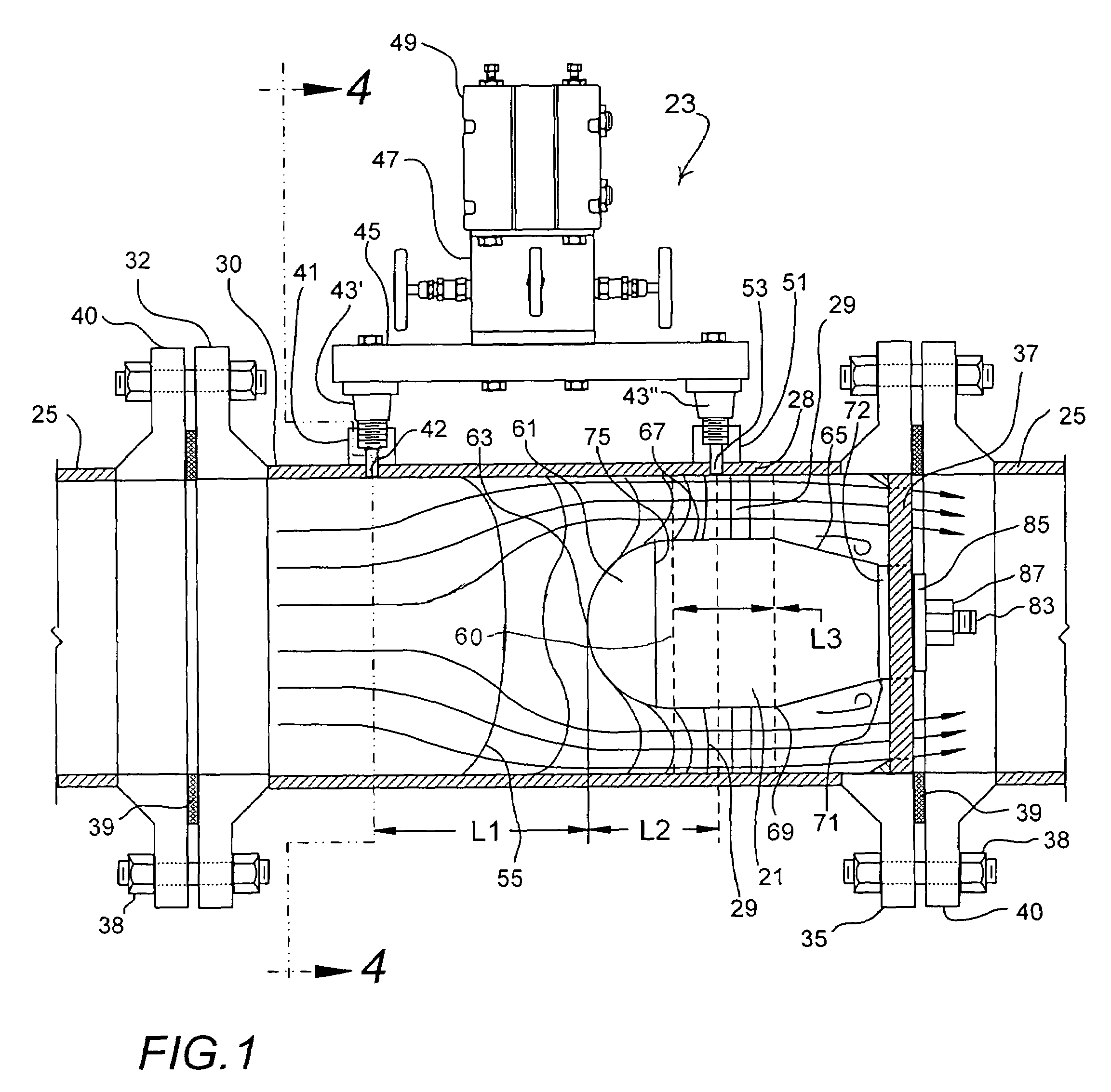
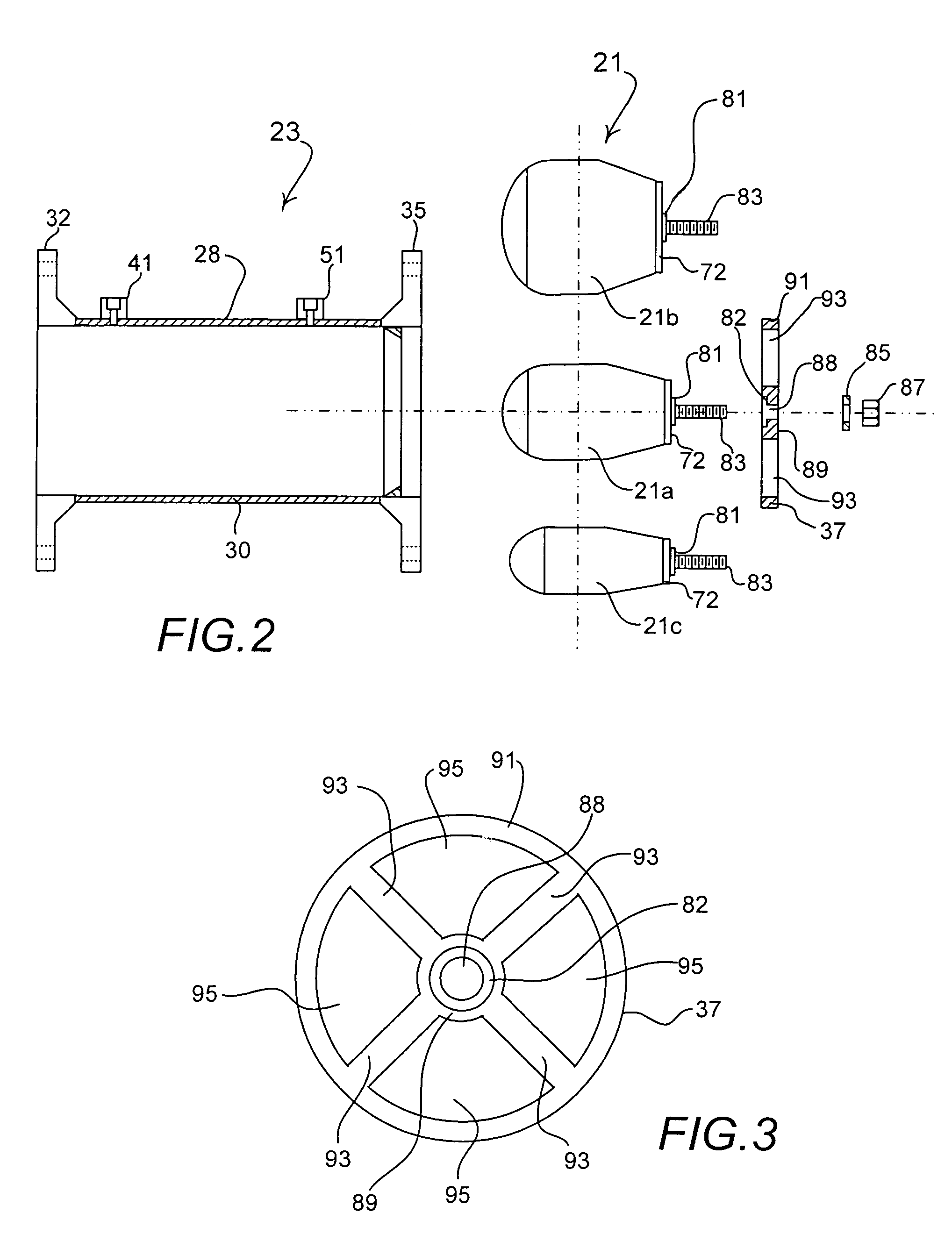
ActiveUS7047822B2Easy to measureEasy to installVolume/mass flow by differential pressureMeasurement deviceDifferential pressure
Differential pressure measurement devices, installations and methods are disclosed, the devices including a main body and retainer. The main body is characterized by a front portion having a substantially constant curvilinear flow facing front surface, a rear portion, and a substantially constant diameter portion between the front portion and the rear portion. The rear portion includes relatively larger and smaller diameter termini. The installation of this invention is maintained in a fluid flow containing conduit and includes a pipe section affixed between sections of the conduit. The device is concentrically located in the otherwise unobstructed flow path defined by the pipe section, with the device retainer downstream of all measurement ports, and obstructs fluid flow thereat to establish annular flow therearound having predictable characteristics.
Owner:VERIS
Hydrodynamic torque converter
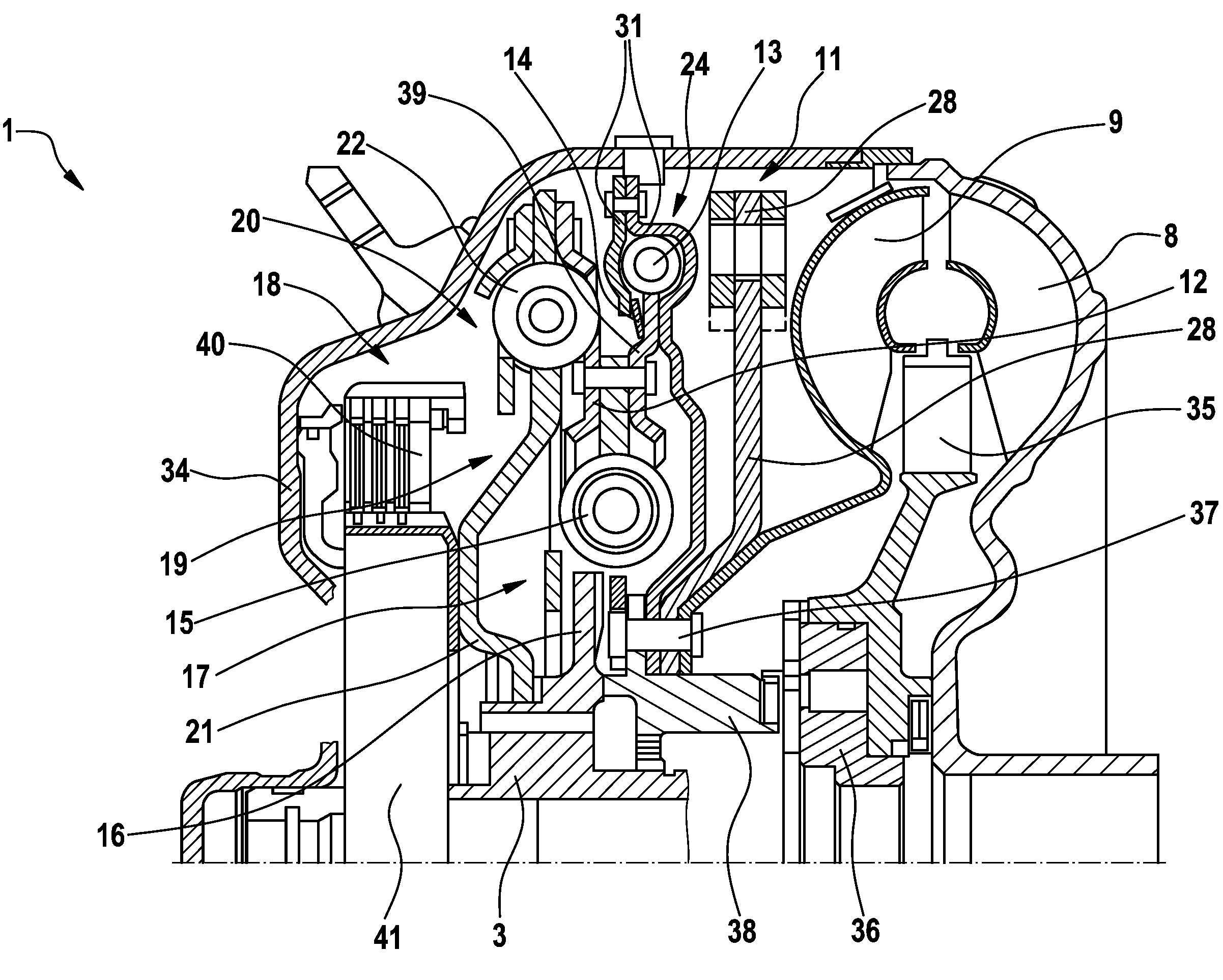
ActiveUS8342306B2Simple designReduce centrifugal forceRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingTurbine wheelExternal combustion engine
A hydrodynamic torque converter (1), comprising a turbine wheel (9) driven by an impeller (8) and connected to an output part, and comprising a housing (34), in which a torsional vibration damper (19) having several damper stages (17, 20) and a centrifugal force pendulum (11), and also a converter lockup clutch (18) connecting a housing and an output part (3), are accommodated. In order to avoid any striking of the pendulum masses of the centrifugal force pendulum in internal combustion engines having large oscillating angles driving the torque converter, a turbine damper is connected in the power flow upstream of the centrifugal force pendulum.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Jigsaw
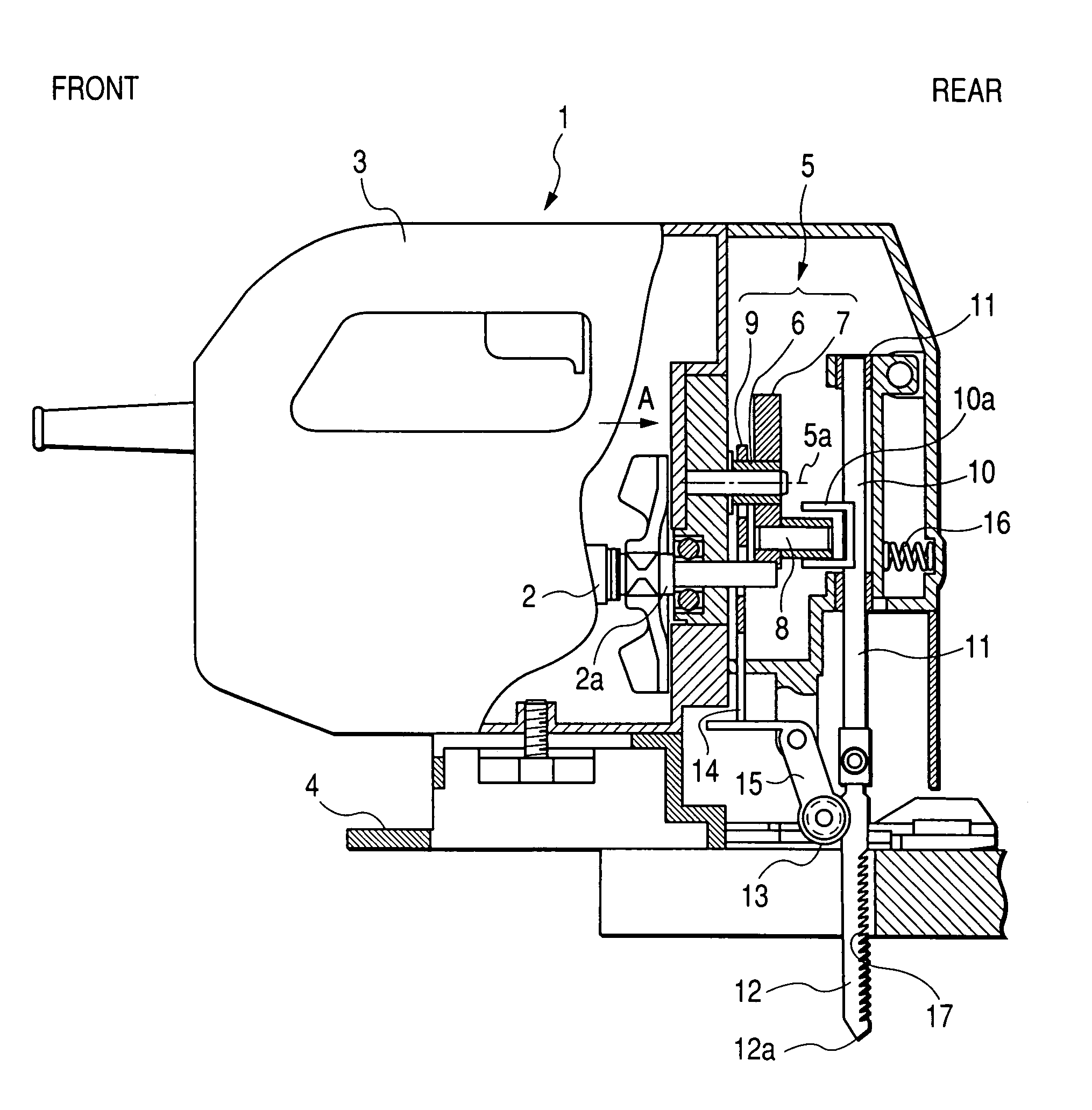
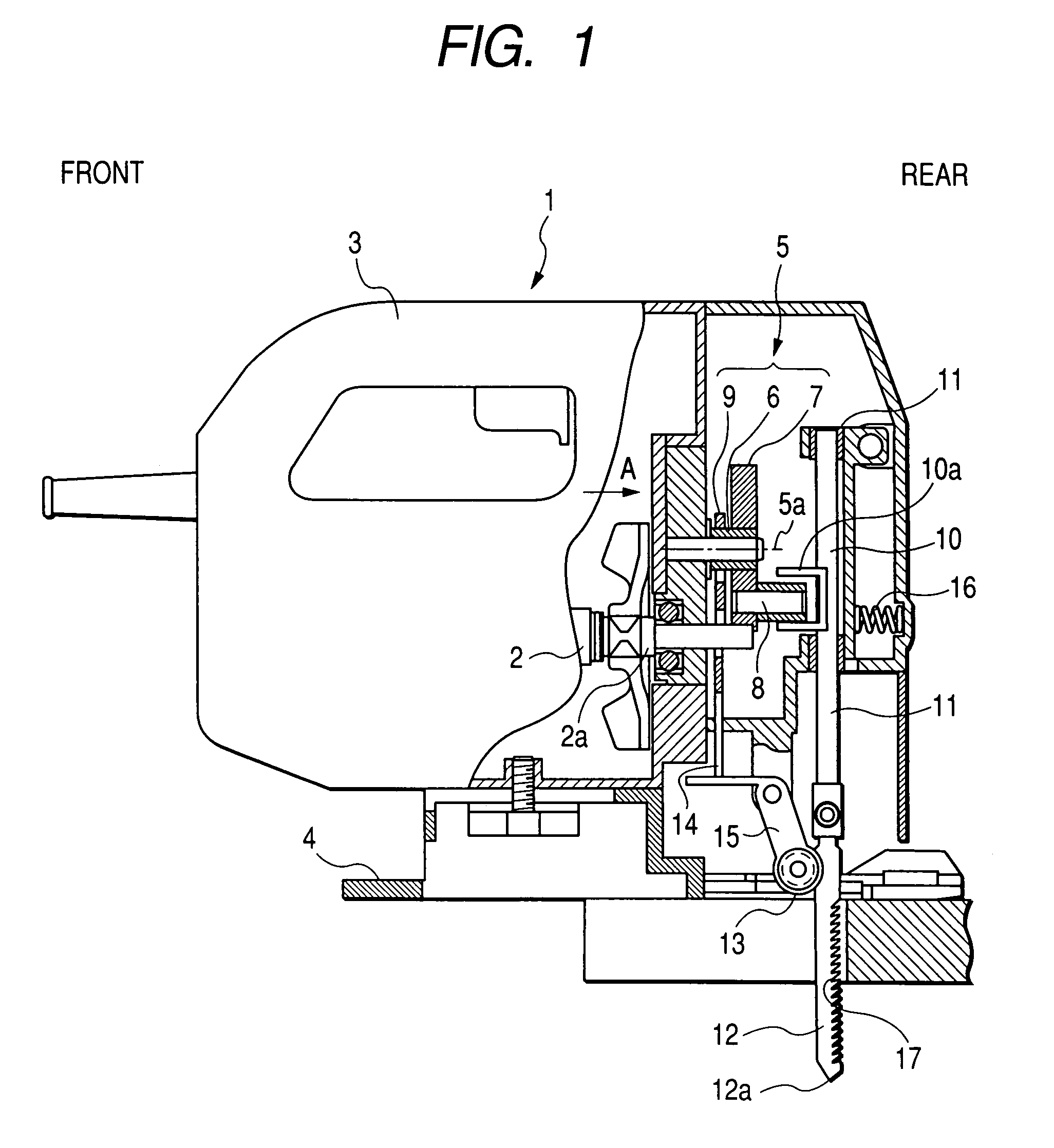
ActiveUS7350302B2Little vibrationImprove cutting performanceMetal sawing devicesGearingRotational axisClassical mechanics
An outer peripheral surface of a cam has an apex disposed of distance from a rotational axis, a first region adjacent the apex opposite to the direction of rotation that increases in distance from the rotational axis during rotation, and a second region adjacent the apex in the rotational direction that decreases in distance from the rotational axis of the cam with the rotation thereof. The apex is disposed where the phase θ thereof advances by 15 degrees and 55 degrees or less in the rotational direction from a position symmetrical to the rotational axis. The rate of change between the second region and the rotational axis is greater than the rate of change between the first region and the rotational axis. A retreat amount X when a saw blade reaches an uppermost point c from a foremost point is set to 0.8 mm.
Owner:KOKI HLDG CO LTD
Piezoelectric resonating device, manufacturing method thereof, piezoelectric resonator, and piezoelectric oscillator
InactiveUS20120137775A1Reduce biasLittle unnecessary vibrationPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyAcceleration measurement using interia forcesPiezoelectric actuatorsEngineering
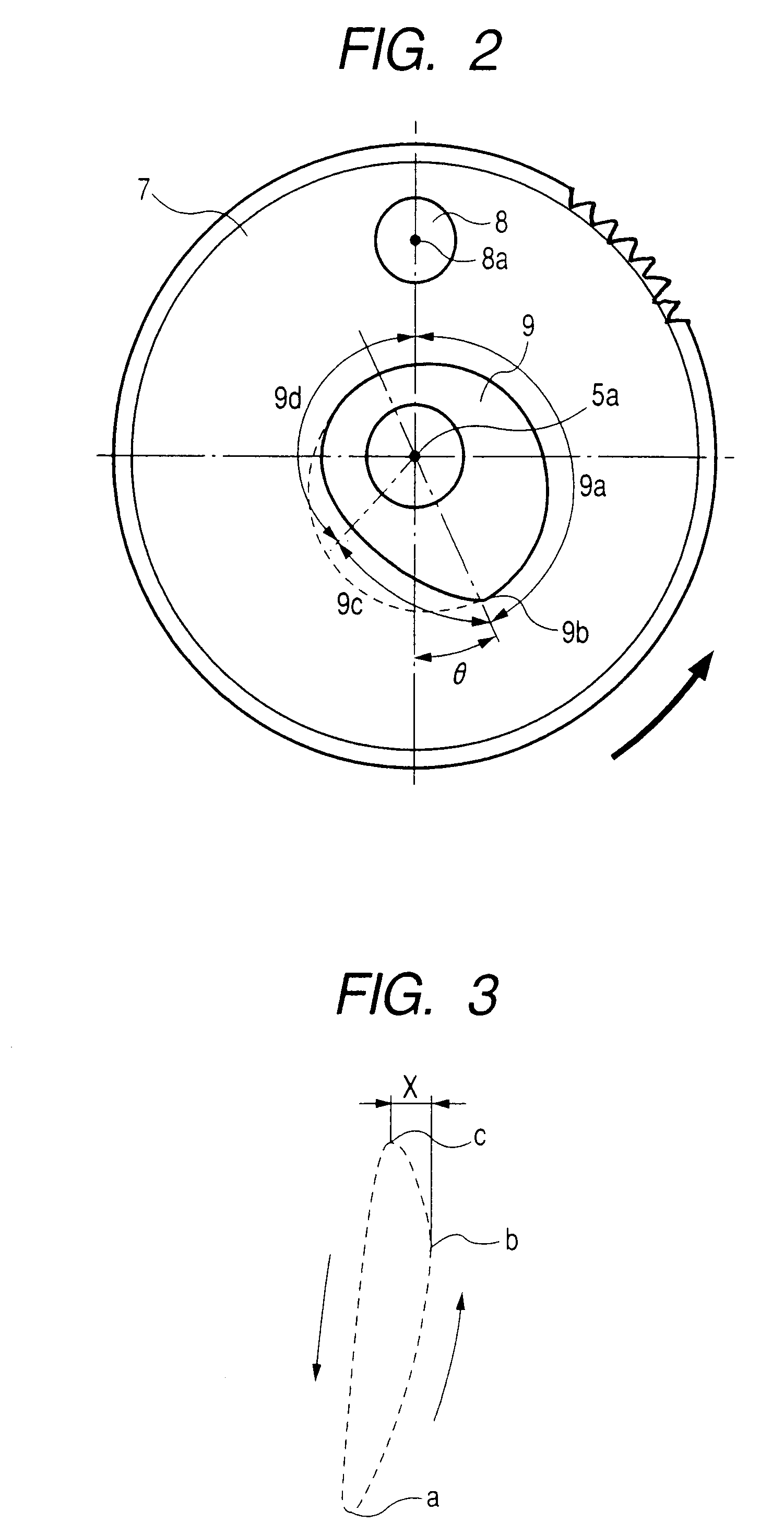
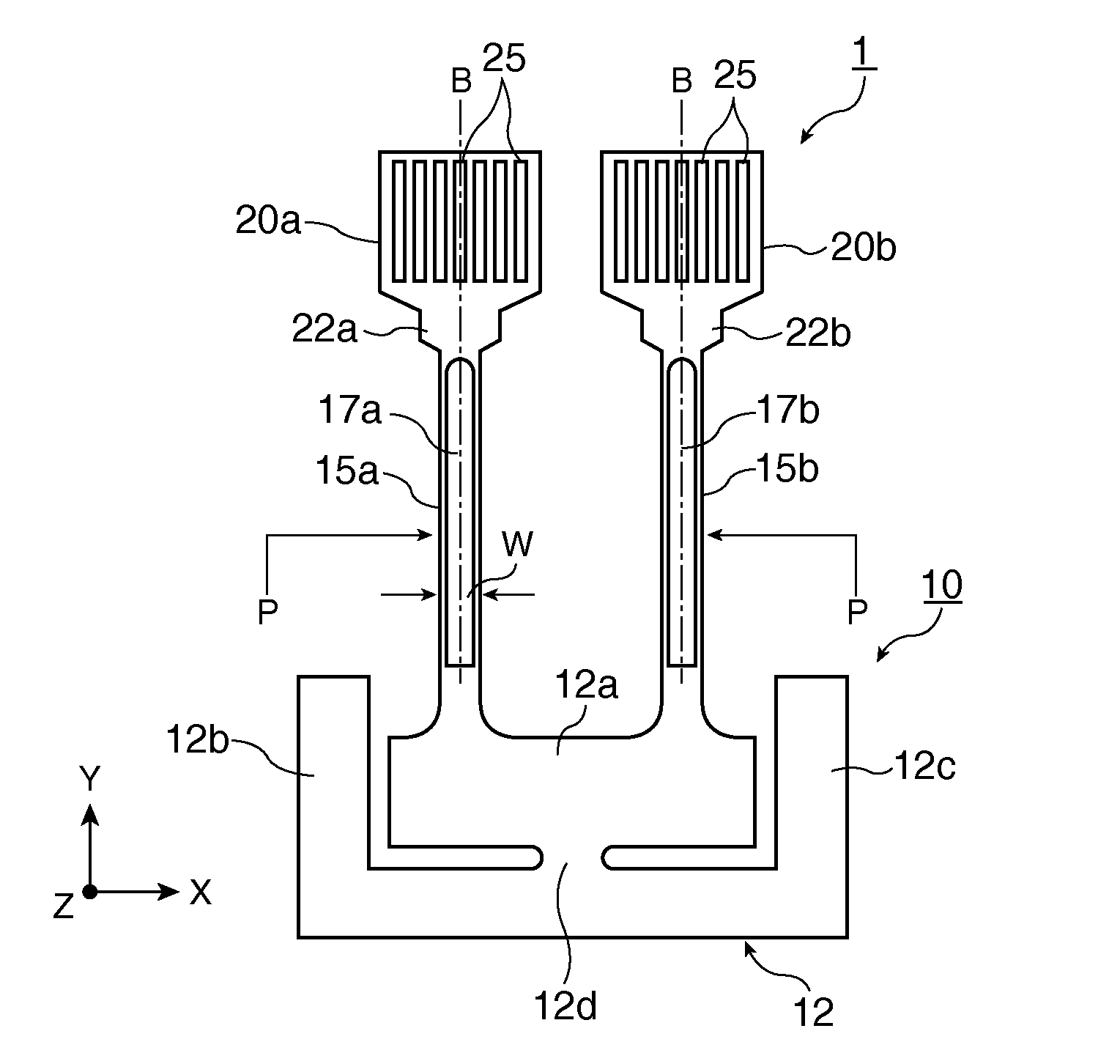
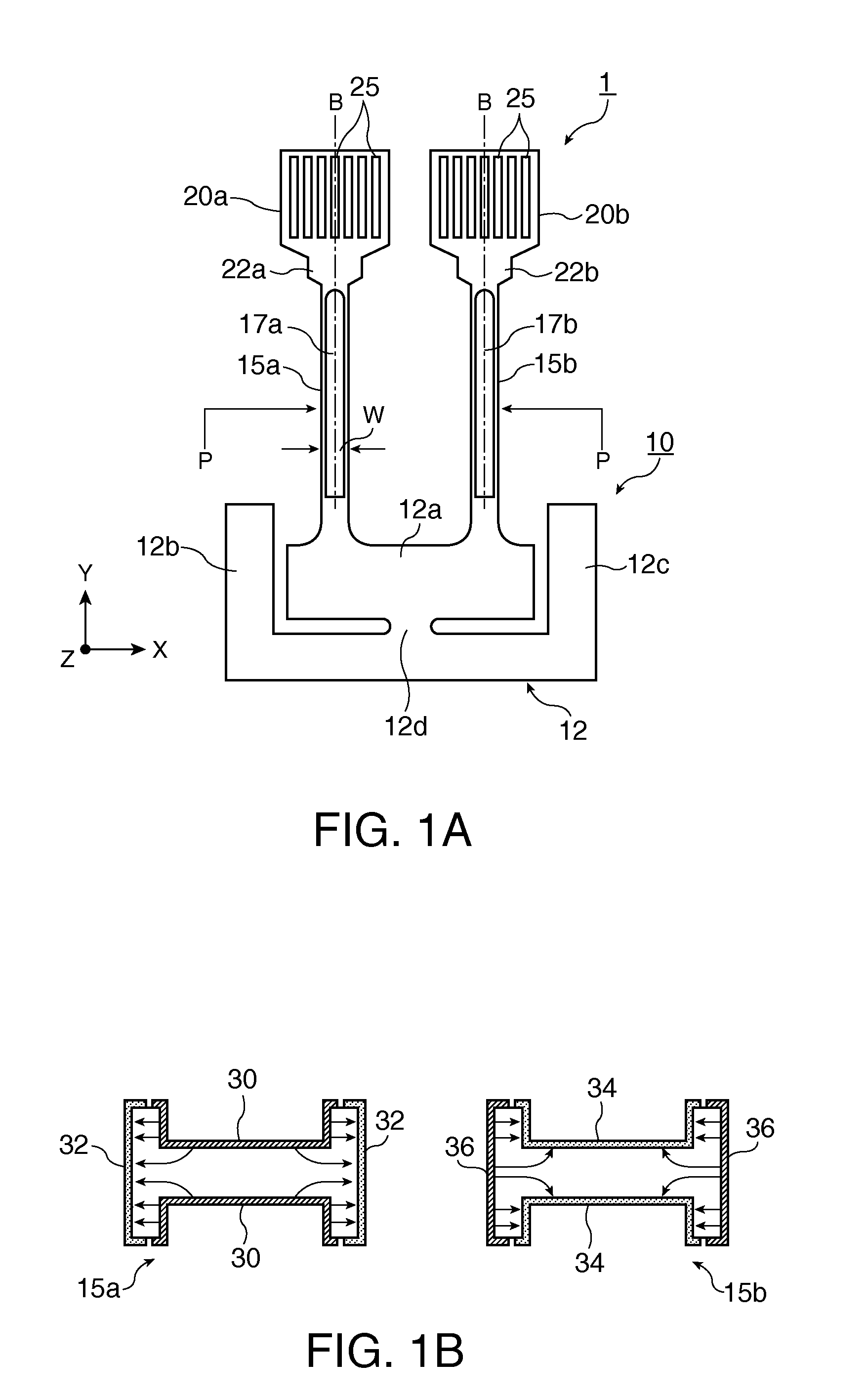
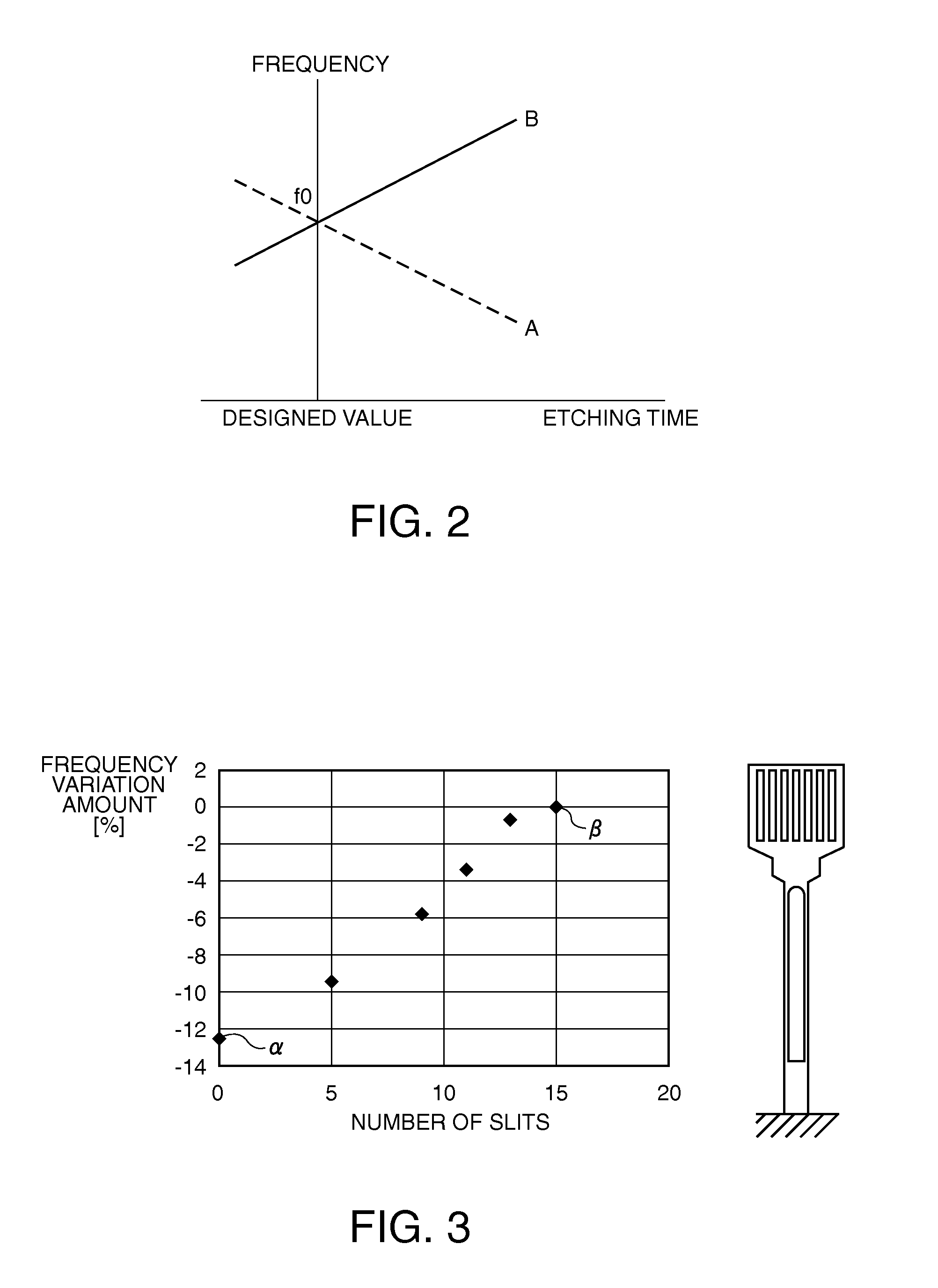
A piezoelectric substrate includes rod-shaped resonating arms; a base portion that connects one set of end portions of the respective resonating arms; weight portions which are formed on the other end portions of the respective resonating arms and which have a width larger than that of the respective resonating arms; and groove portions which are formed on each of the front and rear surfaces along the center line of vibration of the respective resonating arms. The piezoelectric substrate also includes excitation electrodes which are formed on each of the front and rear surfaces of the respective resonating arms including the inner side of the respective groove portions. A plurality of frequency adjustment slits extending in a straight line form along the longitudinal direction of the respective resonating arms are formed on the respective weight portions so as to penetrate through the front and rear surfaces of the weight portions.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
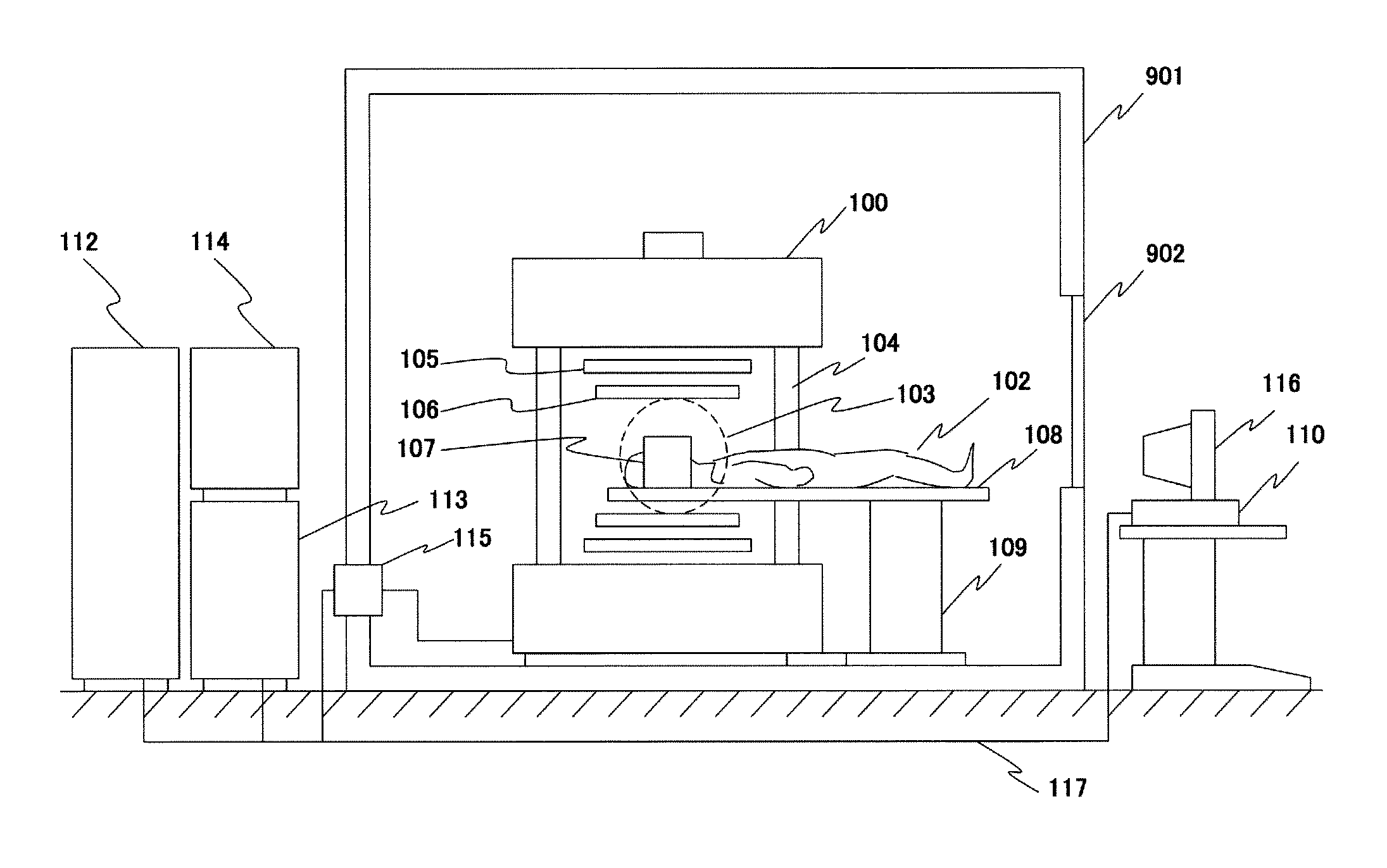
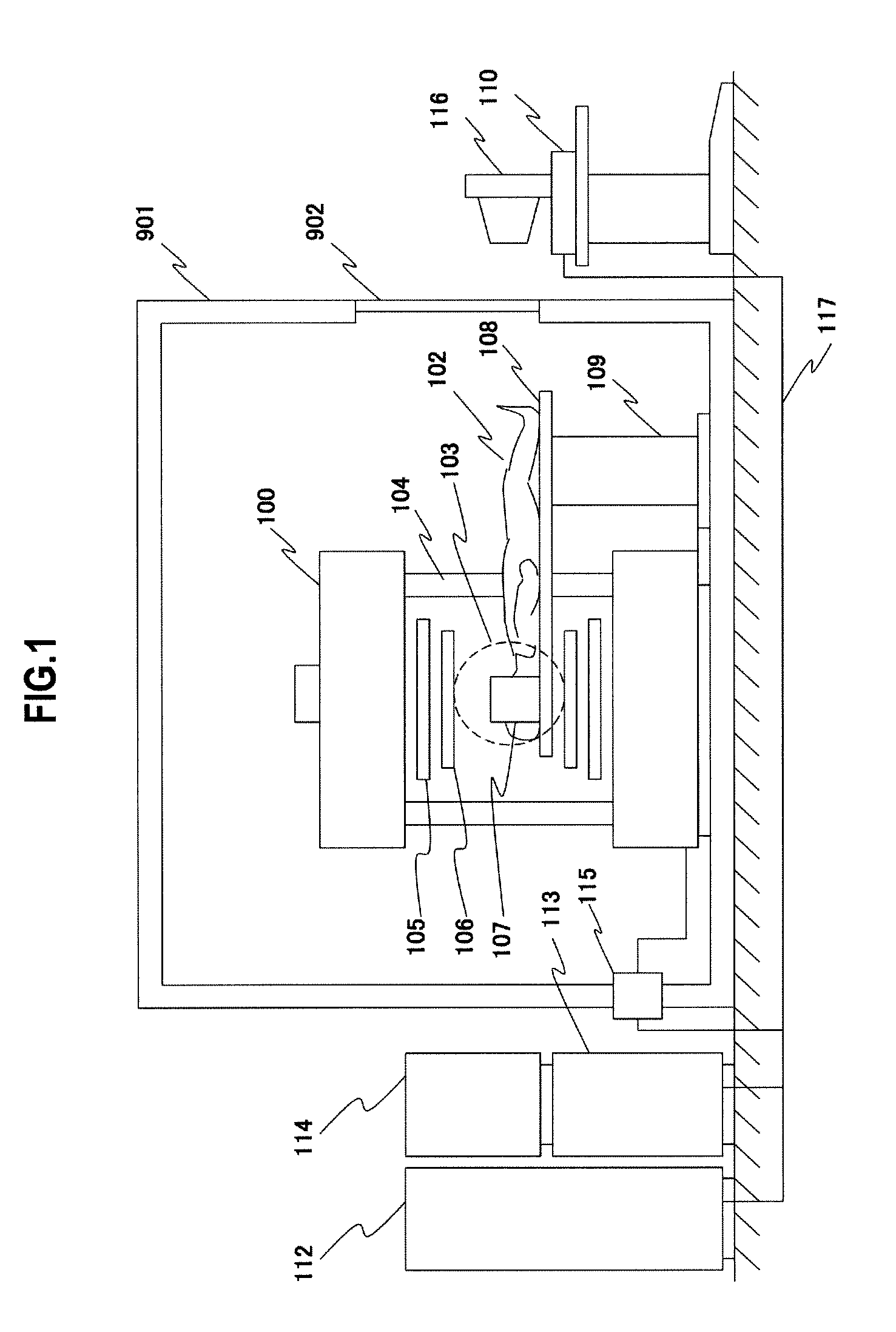
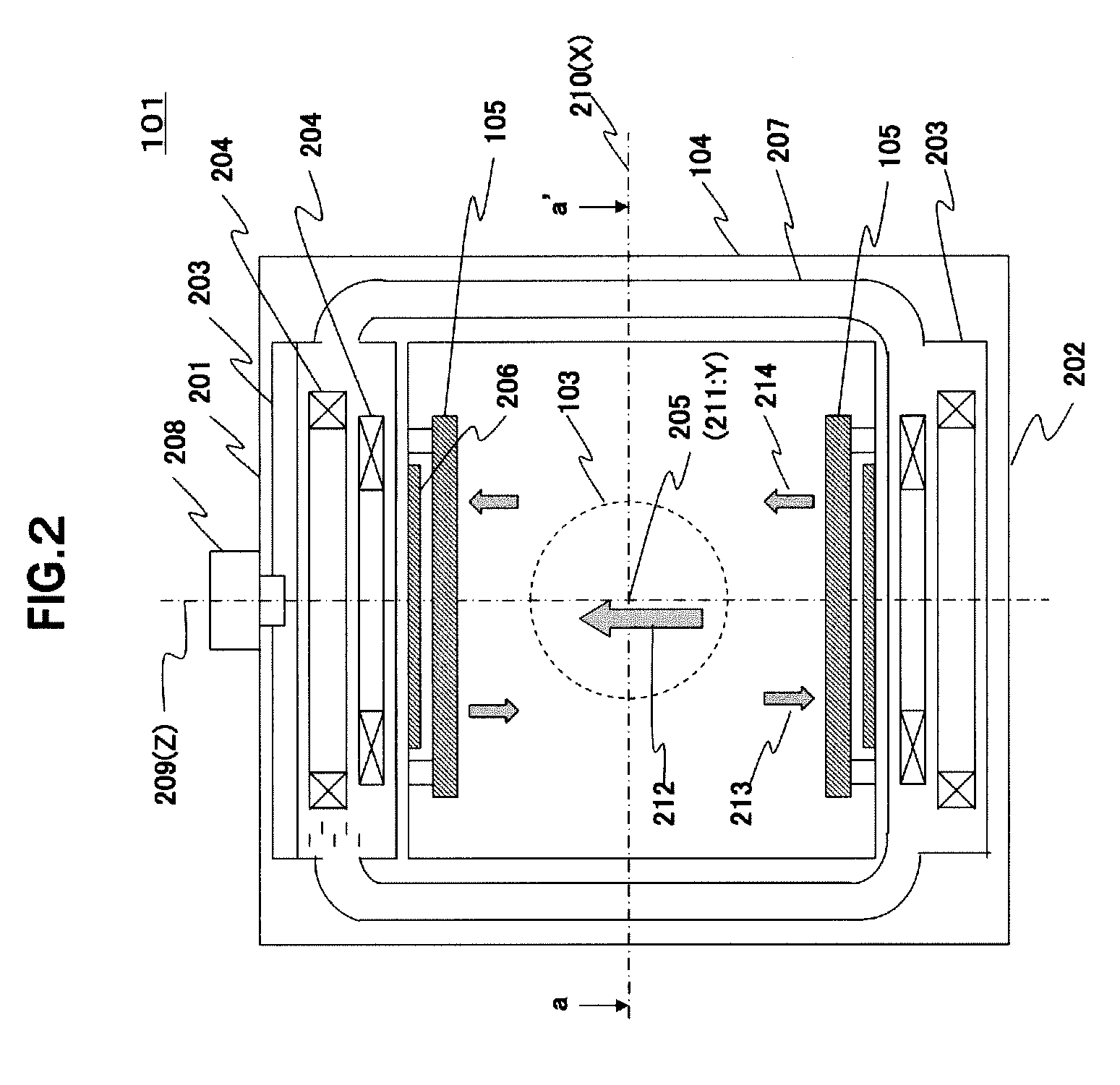
Open-type MRI apparatus, and open-type superconducting MRI apparatus
ActiveUS20110199086A1Small amountAvoid large vibrationsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectrical conductorLorentz force
Provided is an open-type MRI apparatus comprising a pair of magnetic field generating means arranged to face each other across a space for imaging an object, static magnetic field generating means holding means for holding the pair of static magnetic field generating means at a predetermined interval, and a pair of tabular gradient magnetic coil structures arranged on the imaging space side of the static magnetic field generating means.The open-type MRI apparatus is characterized in that the individual tabular gradient magnetic coil structures are fixed on their individually facing static magnetic field generating means at a plurality of positions for suppressing the deformations, which occur in the gradient magnetic coil structures, by the Lorentz forces which act, when driving electric currents are fed to gradient magnetic coils, on the coil conductors.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
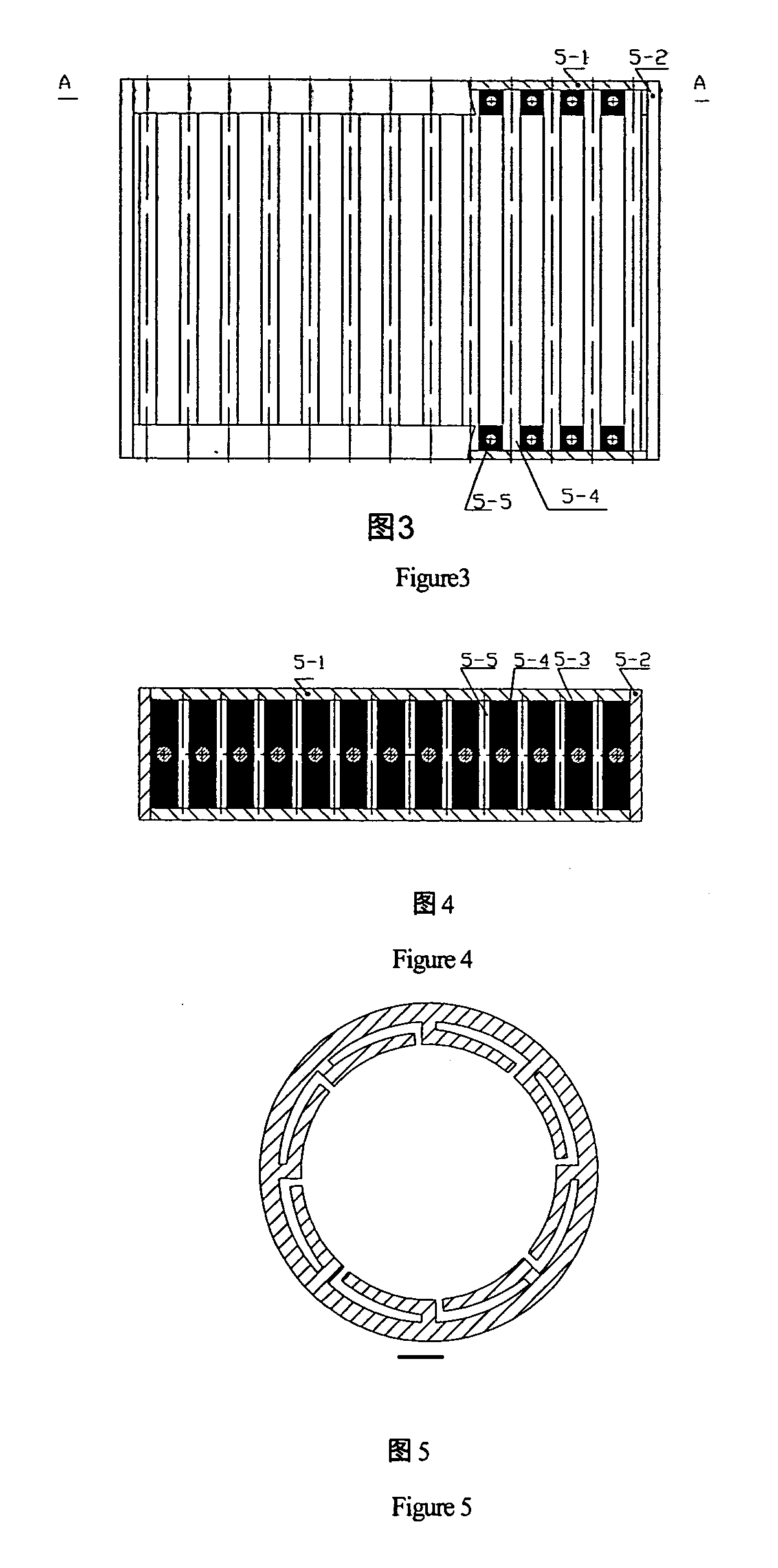
Elastic sieving technique and corresponding large-sized elastic vibration screen
InactiveUS20070261999A1Reduce power consumptionSimple and easy to and maintainSievingScreeningResonanceElastic vibration
An elastic sieving method and corresponding large-sized elastic vibration screen The present invention utilizes a screening surface and a separate sieving machine. A screen mat located on the sieve box is connected to multiple small rectangular screens. While the machine is vibrating, the resonation of screen rods located on the screen mat connected by small rectangular screens are initiated to screen the material and to cause the vibration of the whole vibration screen and realize the conveyance and lamination of materials. Because the screening surface is in a state of resonance, the vibration strength is strong enough to prevent the screen meshes from becoming plugged, allowing for high sieving efficiency. A bearing in the sieving mechanism is installed with a vibration damping ring, placing the bearing in a resonant state, allowing for a low dynamic stress level, which satisfies the process requirement for large-sized vibration screen excitation units with a screening surface as wide as 4800 mm. Thus, the production efficiency of vibration screen is high, the structure of the machine is simple and easy to repair and maintain, and energy consumption is reduced. Furthermore, the dynamic stress level of the sieving machine is low, the reliability is high, and the vibrations are stable. These properties allow the present invention to have a wide range of practical applications, including uses in the coal, metallurgic, chemical and environmental protection fields.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Fluid end assembly
InactiveUS8998593B2Extend working lifeEasy to replaceOrganic compound preparationPositive displacement pump componentsEngineeringFluid supply
Owner:FORUM US
Hand-held power tool with an auxiliary handle
InactiveUS7392568B2Expand positioning possibilityComfortable to holdTravelling carriersHoldersHand heldEngineering
Owner:HILTI AG
Accumulator for elongated products, such as tubes and the like
InactiveUS6840368B2Modest flexural resistanceOvercomes shortcomingStorage devicesConveyor partsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:FABIO PERINI SPA
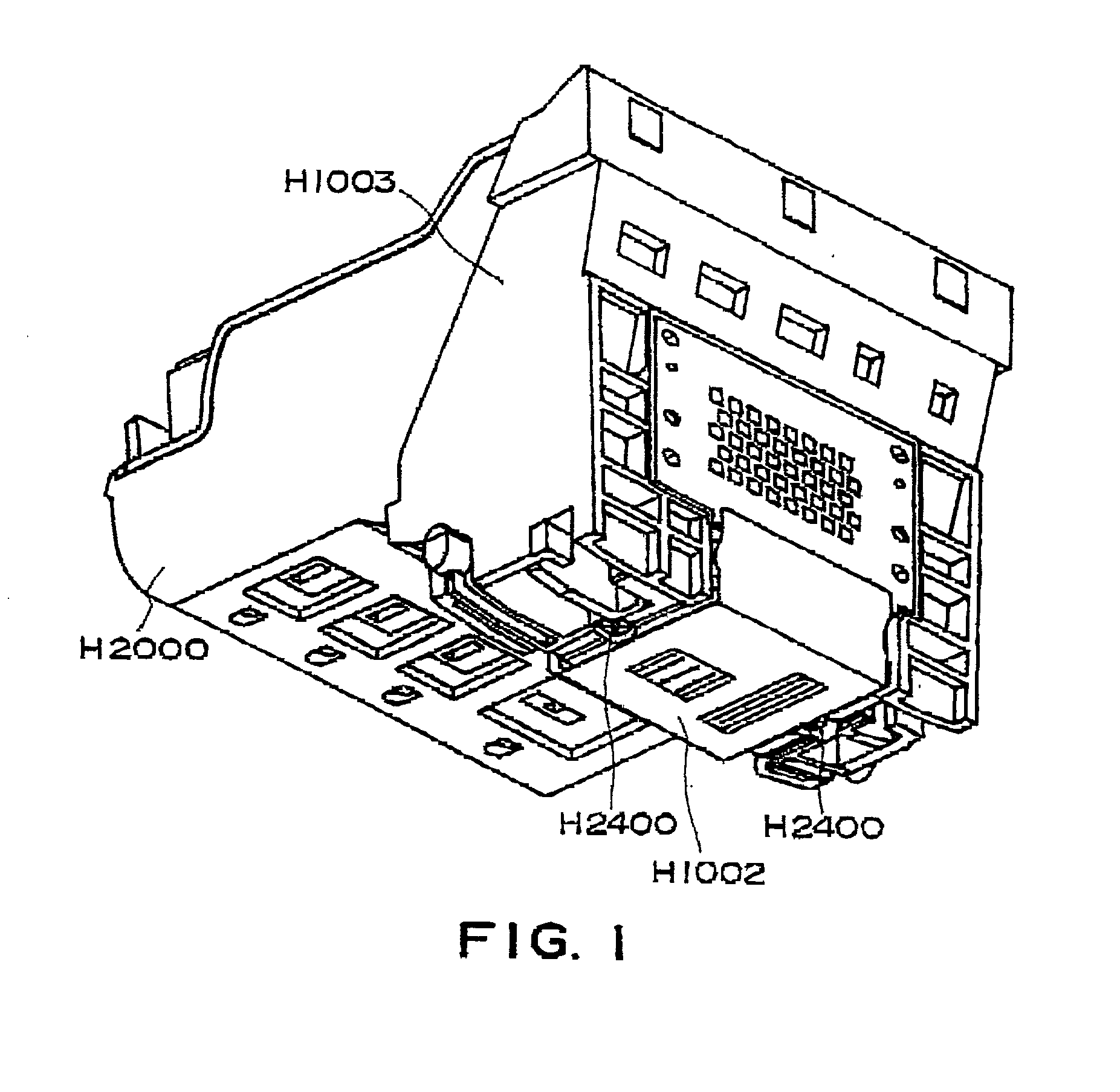
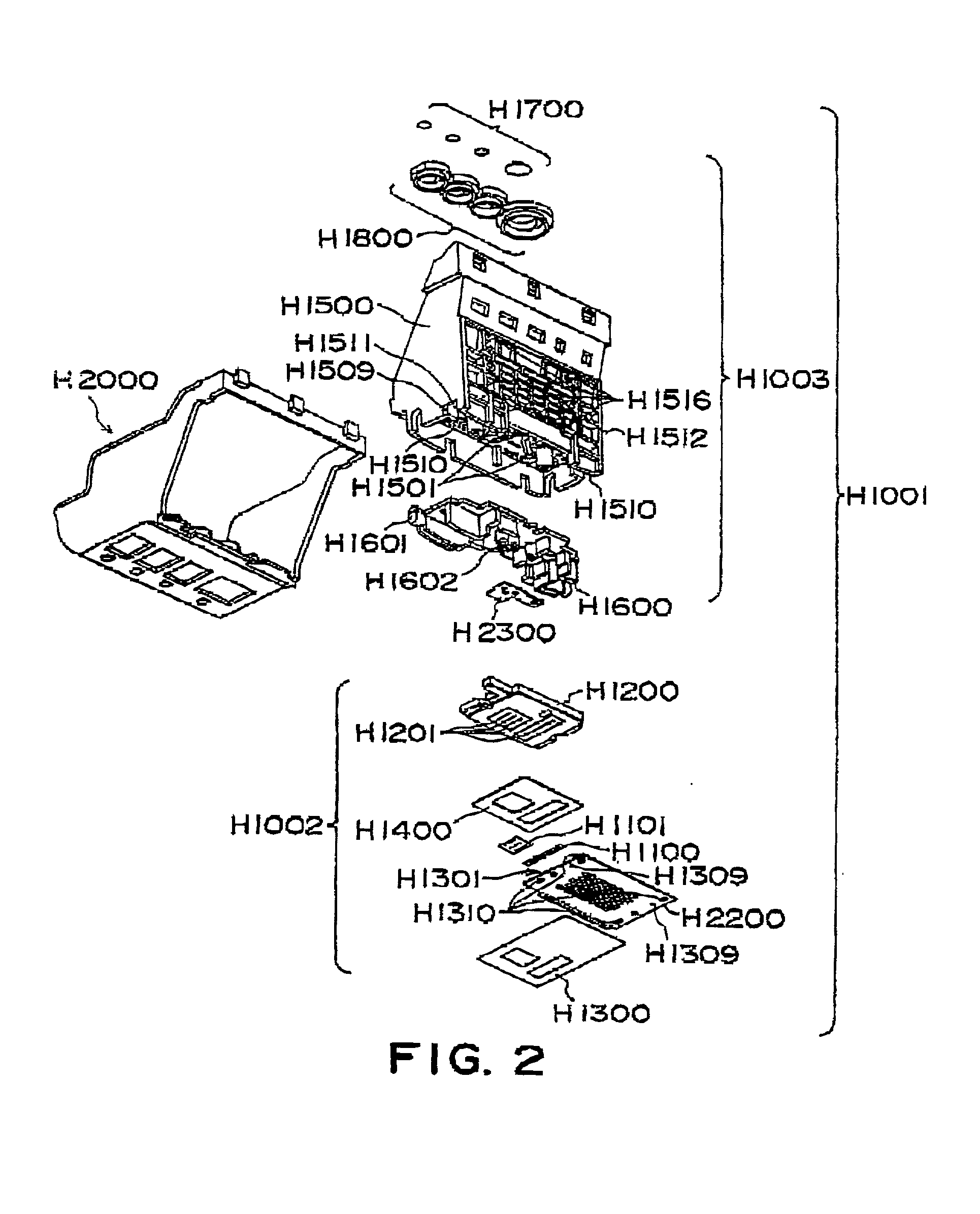
Ink jet recording head and recording apparatus
An ink jet recording head includes a plurality of recording element substrates each having a plurality of recording elements for applying ejection energy to recording liquid; a plurality of flow paths for the recording liquid which is to receive ejection energy; a supply port for supplying the recording liquid to the plurality of flow paths; a plurality of ejection outlets for ejecting the recording liquid, the ejection outlets being disposed face to the recording elements, respectively; wherein distances between the recording elements and the ejection outlets in at least one of the recording element substrates are different from distances between the recording elements and ejection outlets of another one of the recording element substrates, and wherein liquid ejection systems of the recording elements of the at least one of the recording element substrates and the recording elements of tho another one of the recording element substrates, are different.
Owner:CANON KK
Fixing assembly with helical ramp
InactiveUS6863465B2Low costLess tendency to moveInstrument arrangements/adaptationsSuperstructure subunitsBiomedical engineeringHelix
An assembly comprising two parts to be assembled, a substantially cylindrical peg, a ring, a support comprising pins, means for guiding in rotation the ring relative to the support, and resilient means linked on the one hand to the ring and on the other hand to the support. The assembly further comprises a helical ramp provided on the peripheral surface of the peg and intended to receive the pin, said helical ramp comprising a first portion and a second portion in opposed helical directions.
Owner:FAURECIA INTERIEUR IND
Watercraft Propelled By a Water Jet
InactiveUS20090093174A1Easy to restartAvoid surface defectsWater sport boardsPropulsive elementsThrottle controlImpeller
A watercraft propelled by a water jet includes an sealed hull portion including an upper deck and a bottom surface, an engine compartment located behind the sealed hull portion and containing a propulsion and steering system including an engine, a bladed impeller driven by the engine for inducting water and forcing the inducted water away from the craft through a directionally displaceable nozzle, and a control lever located on the upper deck including an engine throttle control and a steering control for adjusting the directionally displacement of the nozzle.
Owner:SURFANGO
Package filling plant, a packing device and method for grouping a packing formation of packages and containers, and a packing device and method for grouping a packing formation of packages and containers
ActiveUS20110167771A1Broad possible spectrumMinimize the possibilitySolid materialLiquid materialTrademarkEngineering
A package filling plant, a packing device and method for grouping a packing formation of packages and containers, and a packing device and method for grouping a packing formation of packages and containers. The abstract of the disclosure is submitted herewith as required by 37 C.F.R. §1.72(b). As stated in 37 C.F.R. §1.72(b): A brief abstract of the technical disclosure in the specification must commence on a separate sheet, preferably following the claims, under the heading “Abstract of the Disclosure.” The purpose of the abstract is to enable the Patent and Trademark Office and the public generally to determine quickly from a cursory inspection the nature and gist of the technical disclosure. The abstract shall not be used for interpreting the scope of the claims. Therefore, any statements made relating to the abstract are not intended to limit the claims in any manner and should not be interpreted as limiting the claims in any manner.
Owner:KHS GMBH
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape cartridge
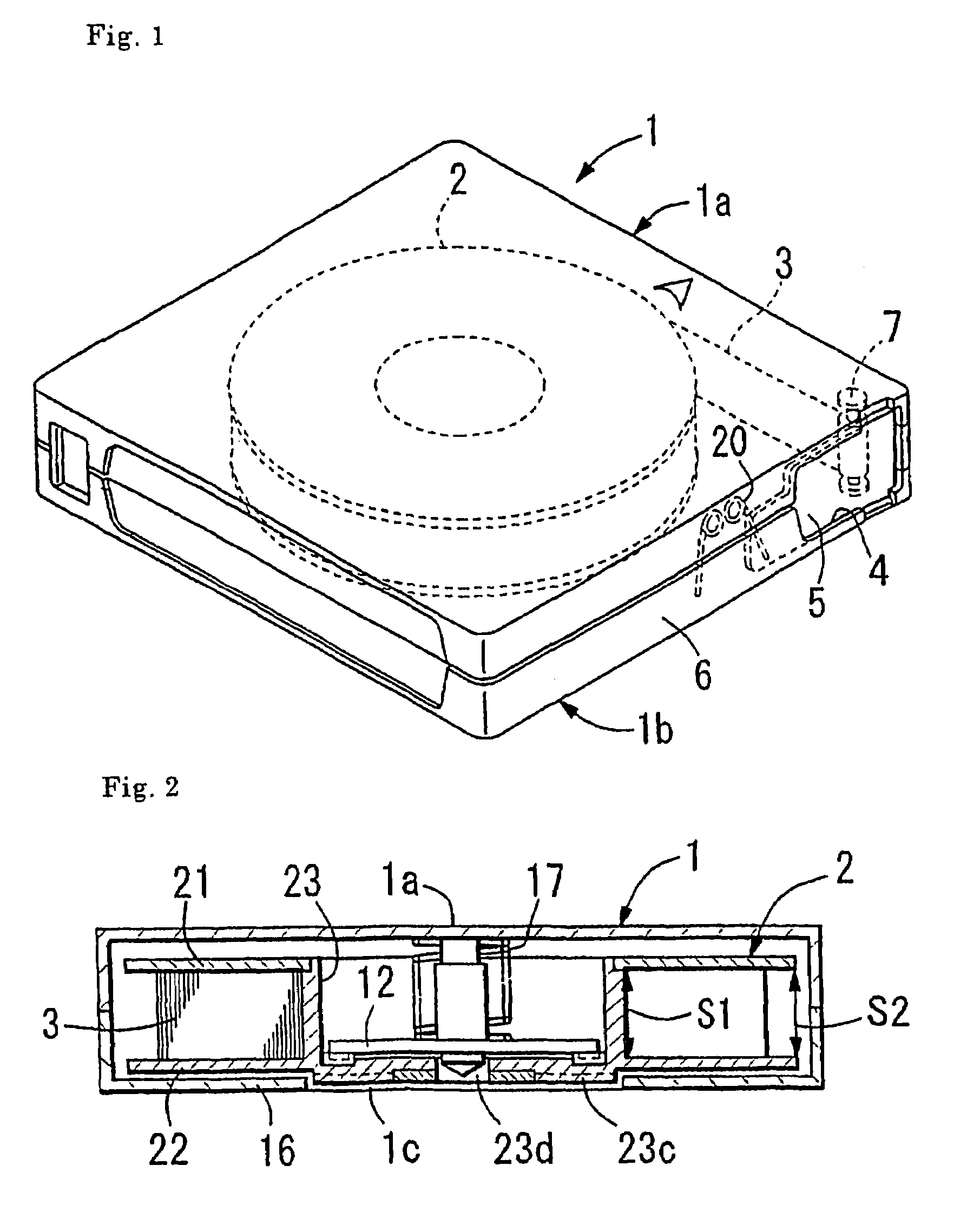
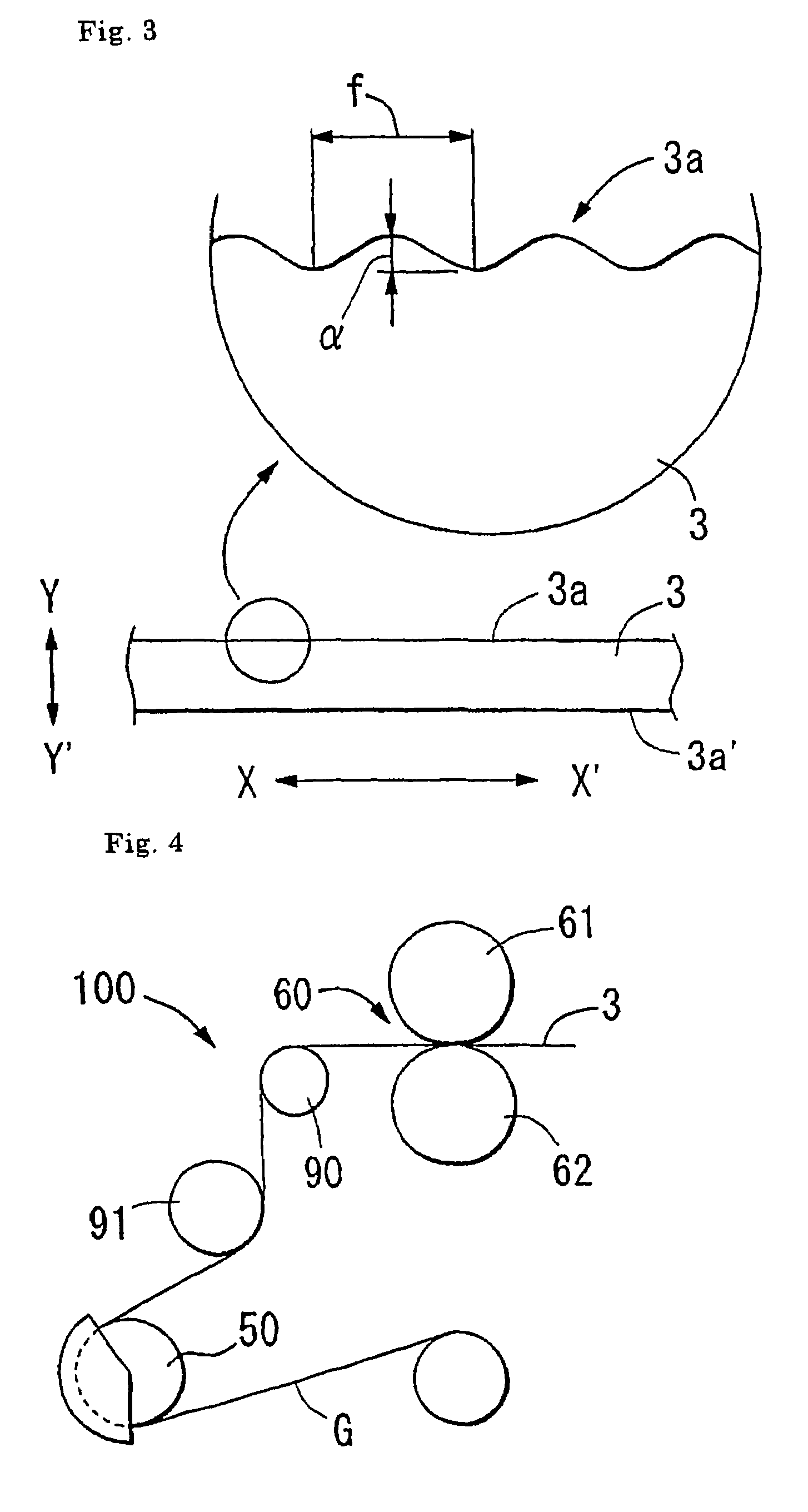
InactiveUS7092199B2Excellent off-track preventive performanceAvoid edge damageMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersMetre/secondMagnetic tape
A magnetic tape which is run at a speed of 4 m / sec. or higher and has recording tracks with a width of 21 μm or less, and which includes a non-magnetic support, at least one magnetic layer formed on one surface of the non-magnetic support, and a backcoat layer formed on the other surface of the non-magnetic support, wherein servo signals for controlling tracking are recorded on the magnetic layer or the backcoat layer, the value of (α / W) X (V / f) is 10 [s−1] or less, and / or the value of (α / W) is 0.1 or less, wherein V [mm / sec.] is the tape-running speed; α [μm] is an amount of a weave with a cycle of f [mm] on one edge of the tape or the other edge thereof, as the reference side, for the running of the tape; and W [μm] is a width of the recording track. The magnetic tape can decrease PES and off-track and thus is excellent in servo tracking performance.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com