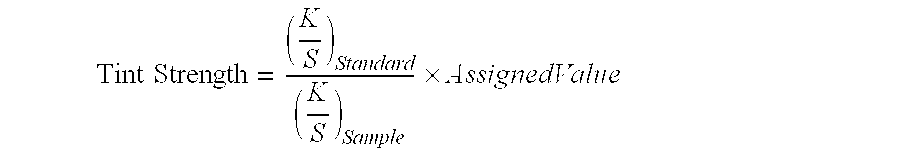Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Improve scattering efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Core-shell particles for electrophoretic display
InactiveUS20060132896A1High refractive indexLow refractive indexPigmenting treatmentOrganic dyesElectrophoresisRefractive index
The invention relates to electrophoretic displays comprising core-shell pigment particles having a core of low specific gravity and low refractive index and a shell of high refractive index.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
Titanium dioxide pigment and manufacturing method
In one aspect, the invention provides a titanium dioxide pigment. The titanium dioxide pigment comprises a plurality of titanium dioxide particles, and a polymer deposited on the titanium dioxide particles for inhibiting agglomeration of the titanium dioxide particles in an aqueous based coating formulation. The titanium dioxide particles have anchoring moieties associated therewith for facilitating anchoring of the polymer to the particles. The polymer is a copolymer having anchoring groups for attaching to the anchoring moieties associated with the titanium dioxide particles and hydrophobic end groups for attaching to the resin of the coating formulation. In another aspect, the invention provides a method of manufacturing a titanium dioxide pigment.
Owner:TRONOX LLC
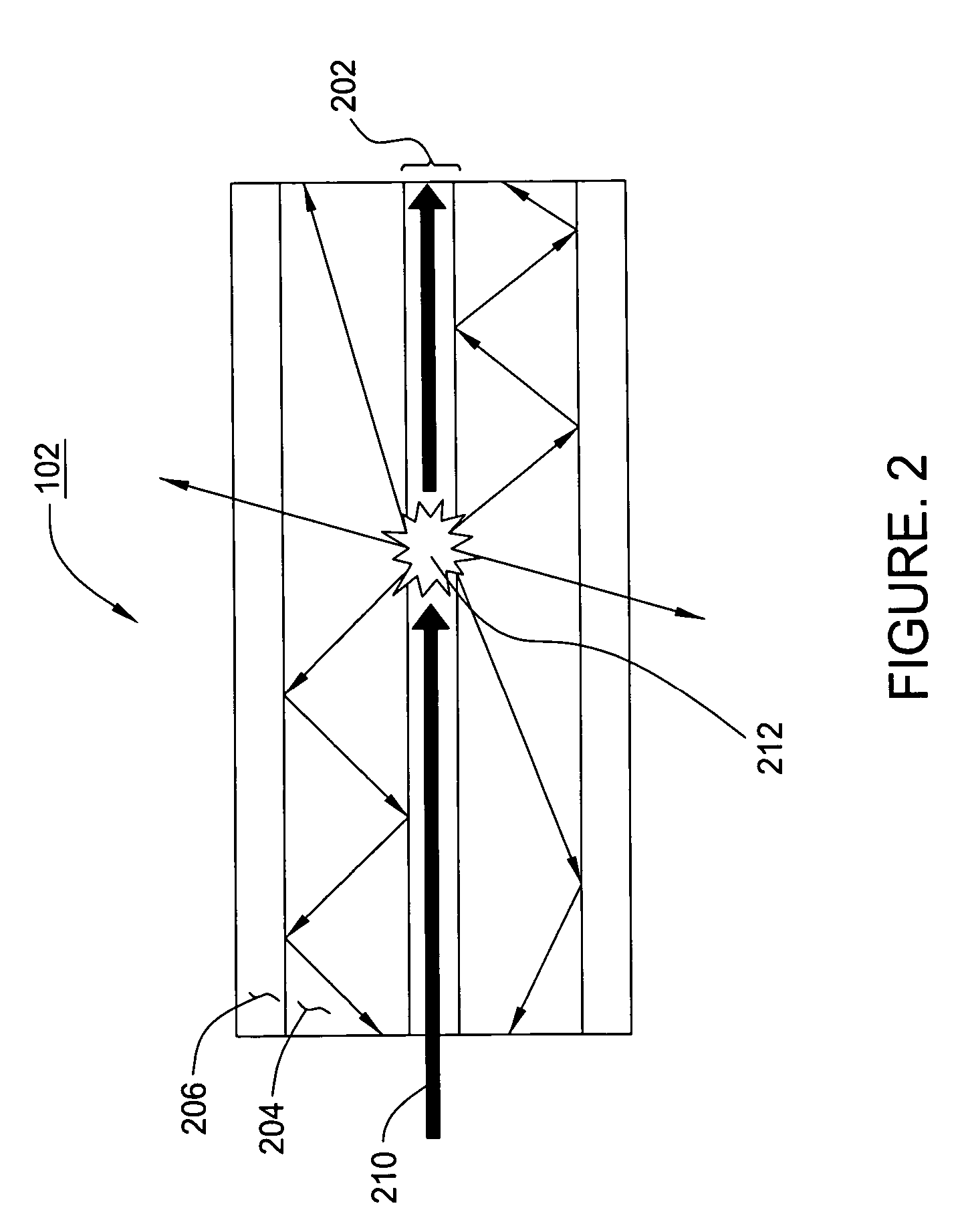
Efficient distributed sensor fiber
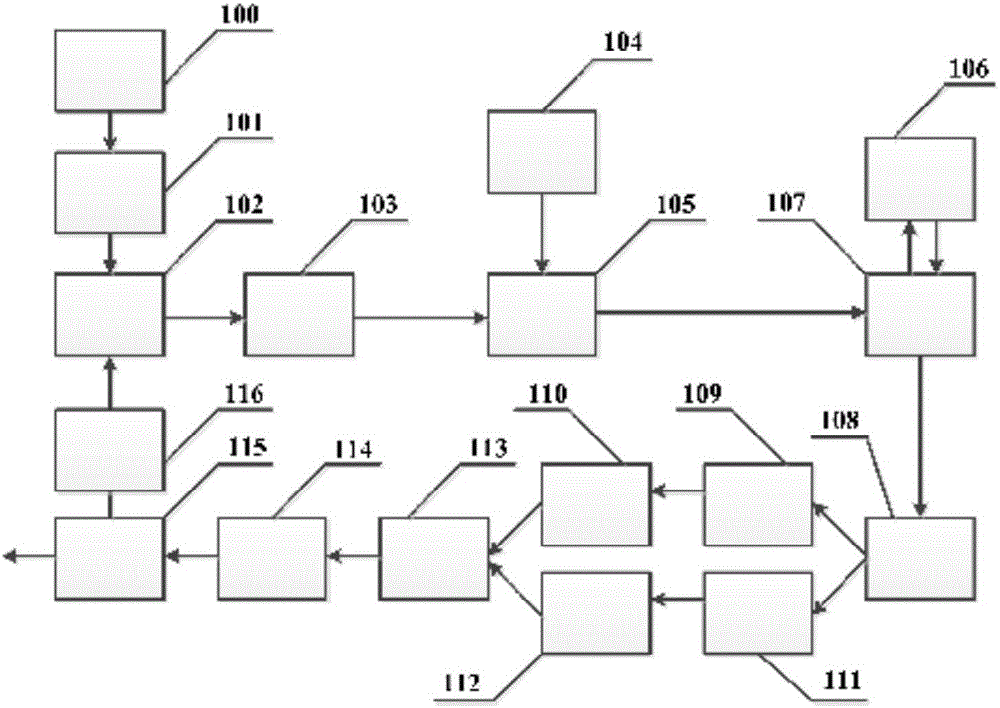
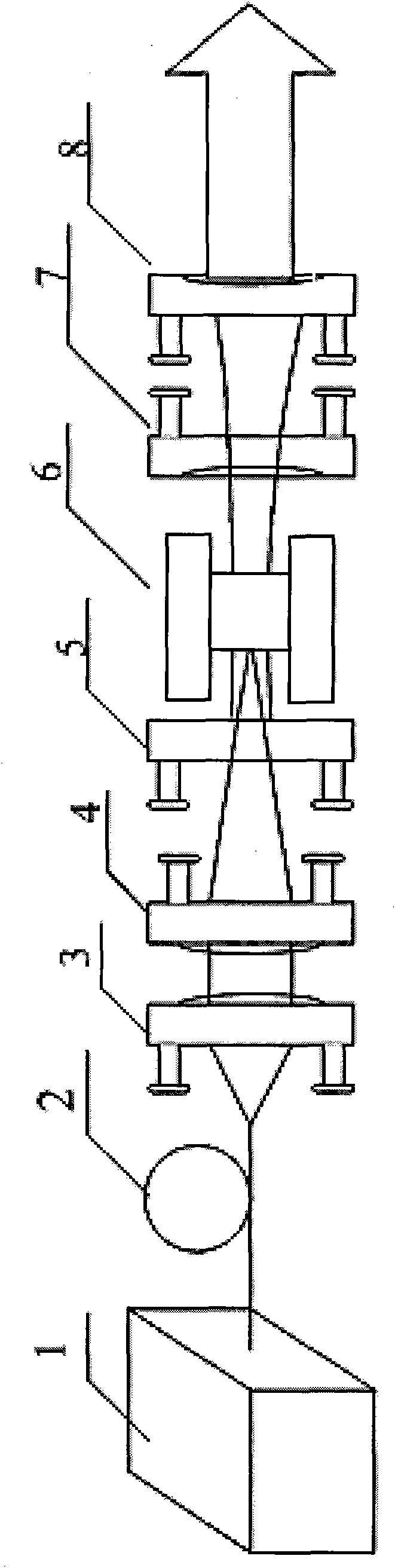
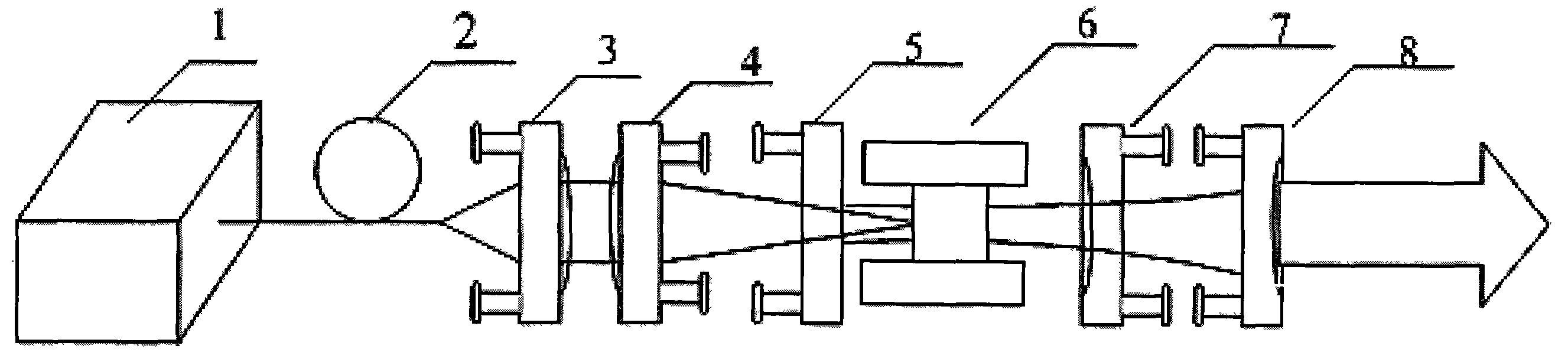
ActiveUS7113659B2Improve scattering efficiencyEasy to captureRadiation pyrometryOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberWaveguide
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
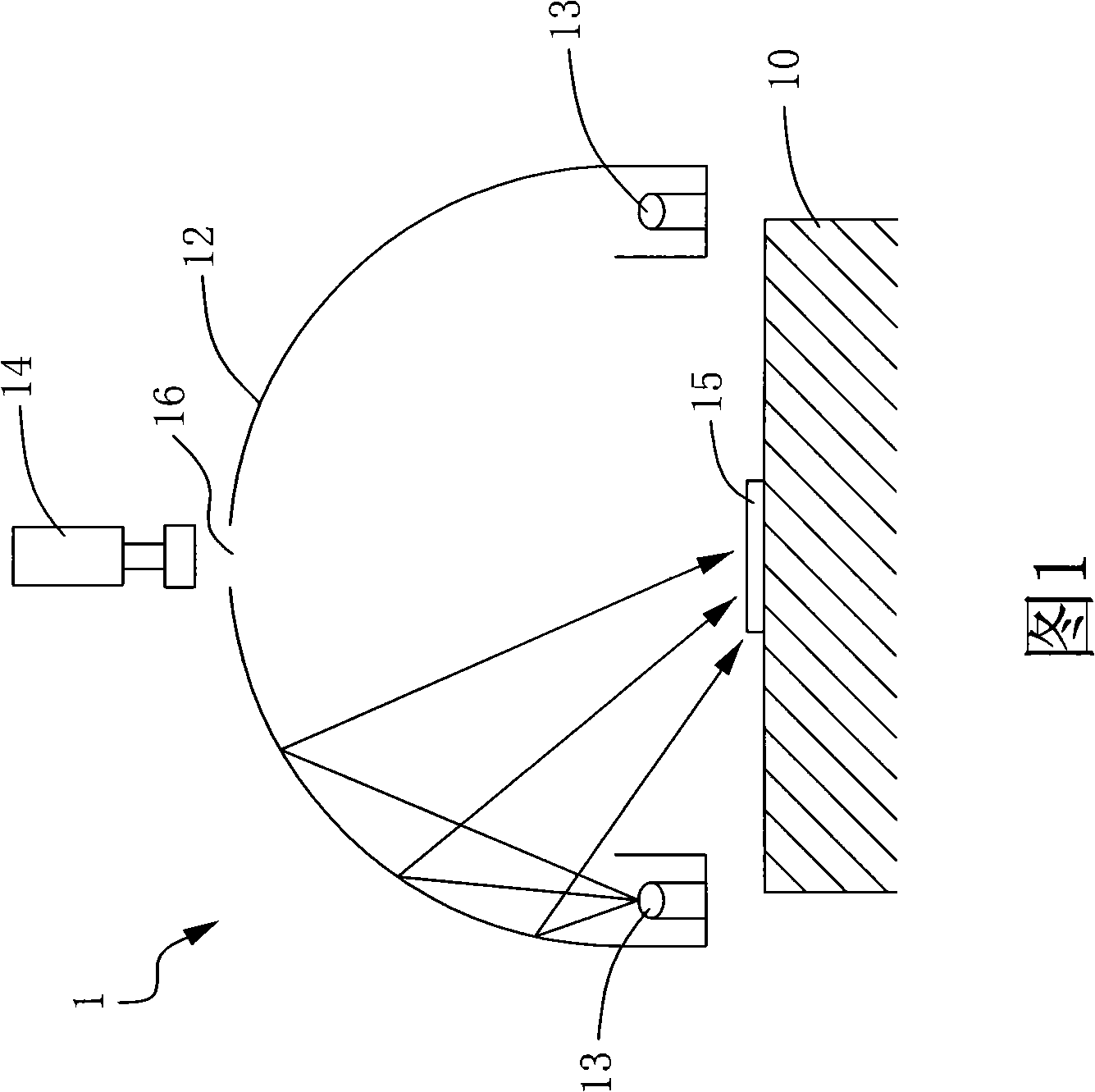
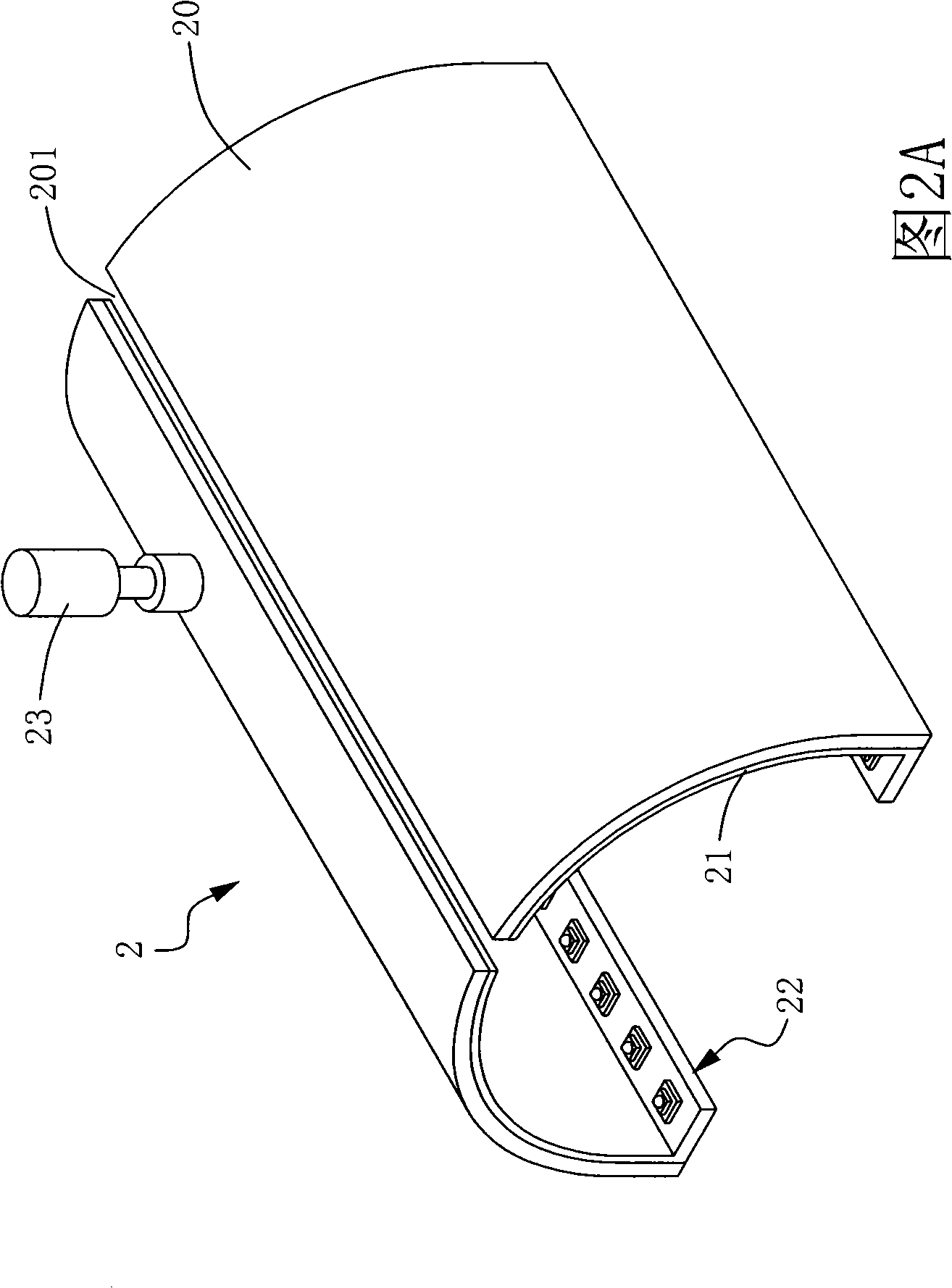
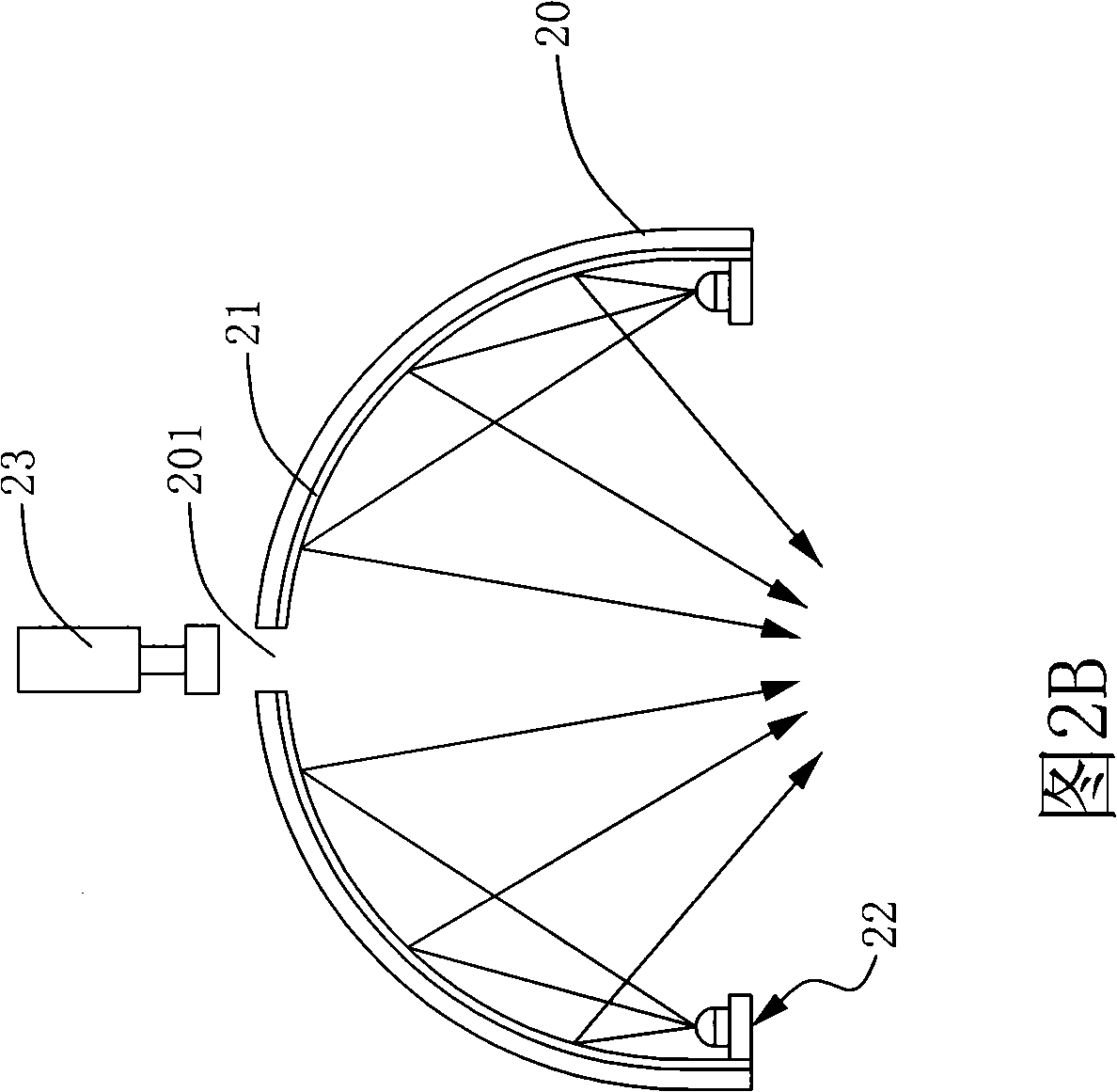
Checking system light source stray illumination device
InactiveCN101290090AImprove scattering efficiencyUniform lightLighting heating/cooling arrangementsElectric lightingScattered lightLight source
The present invention discloses a light source scattering illumination device for a detecting system. The device comprises a reflection cover body, a Teflon scattering layer and at least one luminous device. The reflection cover body is provided with a slotted hole. The Teflon (PTFE) scattering layer is arranged on the inner wall of the reflection cover body. The at least one luminous device is arranged inside the reflection cover body. The luminous device is further provided with a plurality of luminous bodies which are arranged in the form of arrays to provide a light source. With the Teflon scattering layer in the present invention, perfect scattering efficiency can be provided and uniform scattered light can be generated. Through selecting high power light emitting diodes as a luminous source, the luminous device also can provide perfect light strength so that the light source scattering device can generate high brightness and the uniform scattered light to solve the problem that the detecting system is insufficient in illumination strength.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
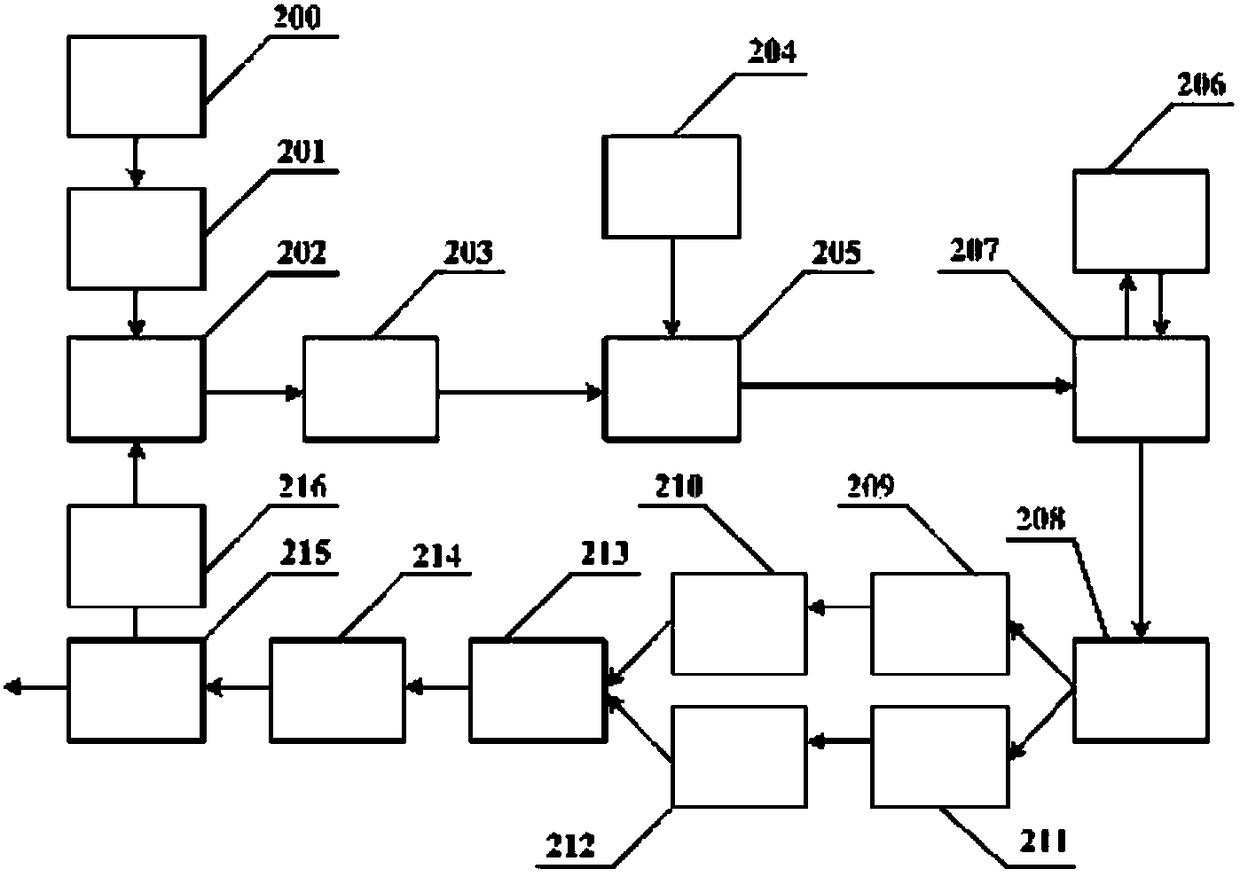
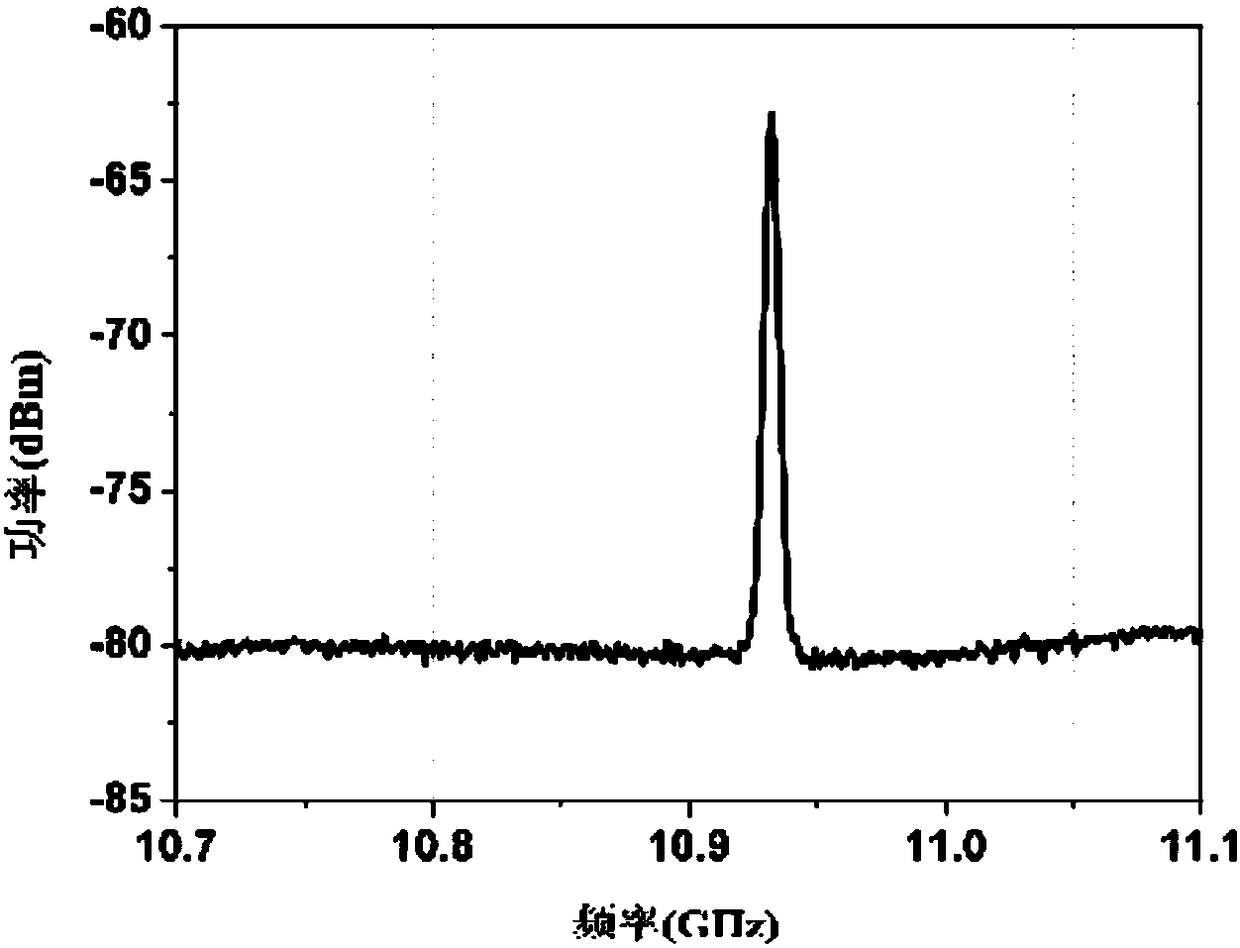
Microwave signal generating device and method of photoelectric oscillator based on liquid-core optical fiber Brillouin scattering effect
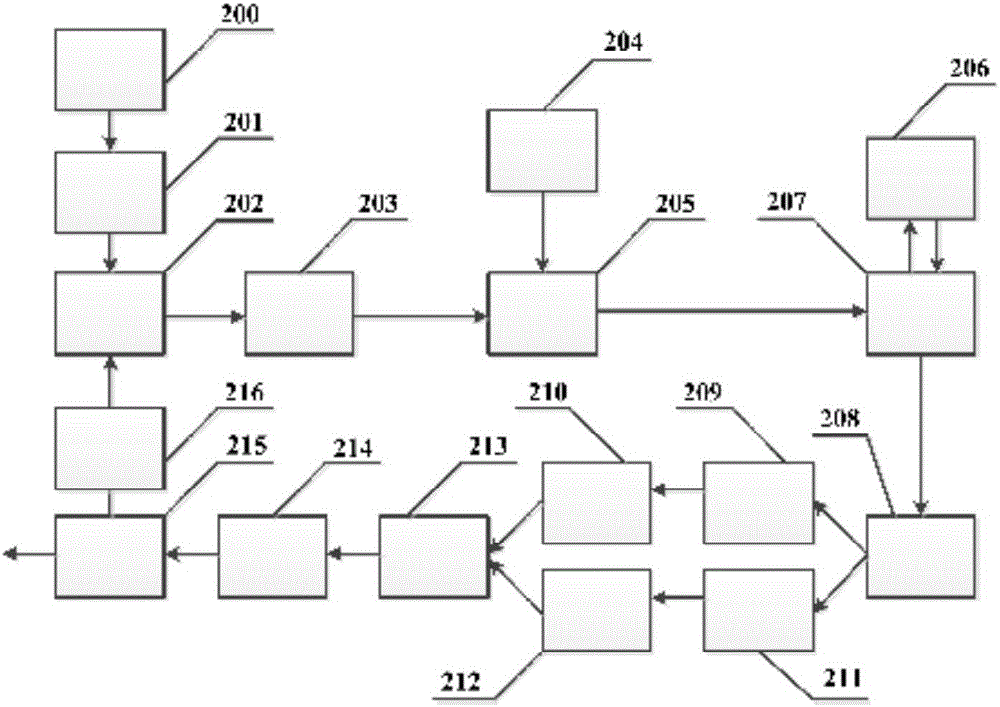
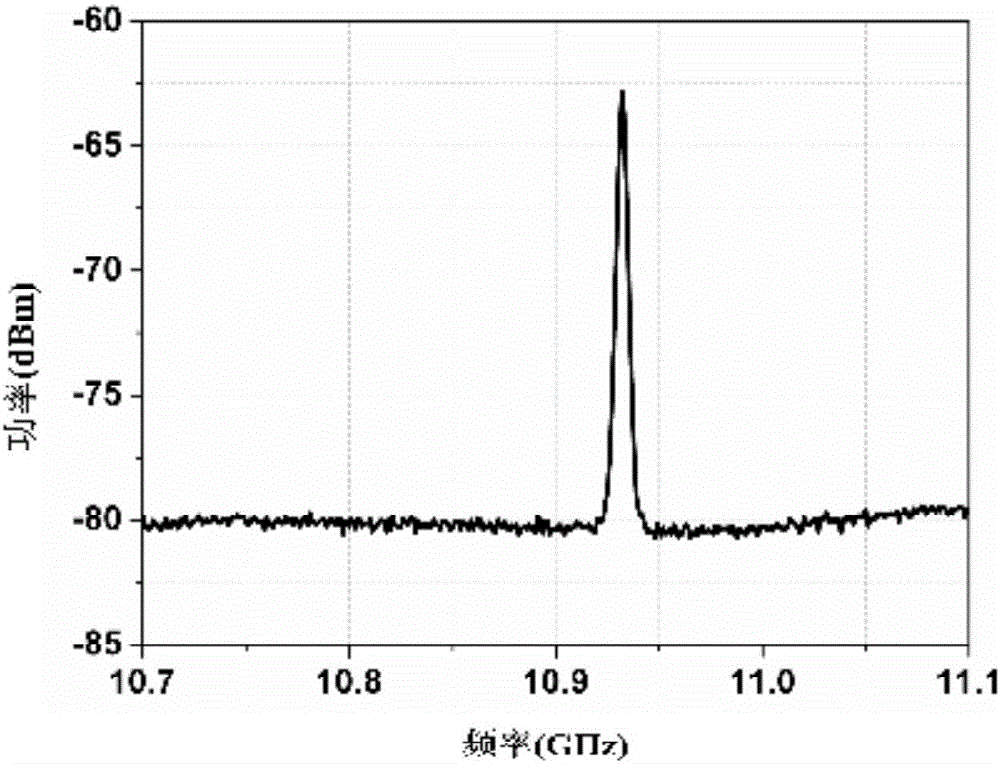
ActiveCN105811225AImprove scattering efficiencyReduce phase noiseSolid masersOptical polarizationBrillouin scattering
The invention discloses a microwave signal generating device and method of a photoelectric oscillator based on a liquid-core optical fiber Brillouin scattering effect.The microwave signal generating device includes a Brillouin scattering pump laser, an isolator, a modulator, a liquid-core optical fiber, a signal laser, a first circulator, a third laser, a second ring, a polarization beam splitter, a first optical fiber, a second optical fiber, a first polarization controller, a second polarization controller, a polarization beam combiner, a photoelectric detector, a coupler and a power amplifier.The device and the method can not only produce high-frequency microwave signals and can also obtain tunable microwave signals wider in tuning range.
Owner:东台城东科技创业园管理有限公司
Porous Photonic Crystal with Light Scattering Domains and Methods of Synthesis and Use Thereof
InactiveUS20080212068A1Easy to resolveImprove scattering efficiencySamplingMaterial analysis by optical meansPorous substratePhotonics
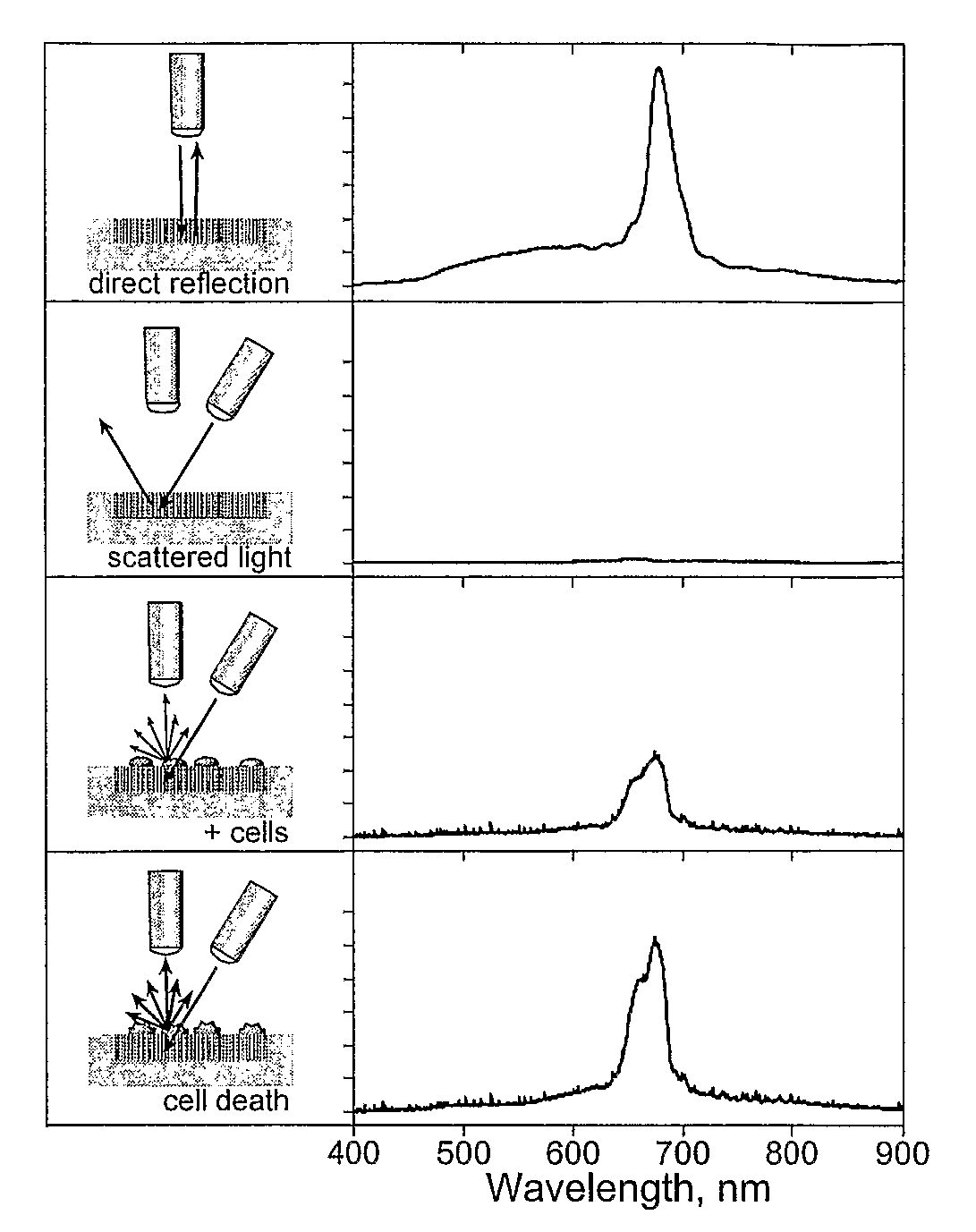
The invention includes sensors and sensing methods for determining cell morphology and / or chemical composition of an analyte. A porous substrate exhibiting a first optical signal is exposed to a target analyte and subsequently monitored for changes in the optical signal. More specifically, a photonic or porous substrate having a well-defined and highly tunable reflectivity or transmission spectrum, such as porous silicon (Si), porous alumina, porous Ge, porous GaAs, porous SiO2 and porous polymer, is used for example. A porous or photonic substrate is exposed to an analyte, such as a cell or other macromolecule, and changes in the scattered light are observed over time to determine cell morphology and / or chemical composition of the analyte using the substrate.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Self-stimulated Raman scattering laser of In-Band pump
InactiveCN101807774AHigh beam qualityReduce thermal effectsLaser using scattering effectsDielectricStimulate raman scattering
The invention discloses a self-stimulated Raman scattering laser of an In-Band pump, which comprises a laser pump source, a laser energy transfer optical fiber, a first planoconvex lens for collimation, a second planoconvex lens for focusing, a reflection mirror of a resonator cavity, a laser gain dielectric crystal, a laser output mirror and a laser collimating mirror which are sequentially arranged, wherein pump light outputted by the laser pump source is transmitted to the first planoconvex lens via the laser energy transfer optical fiber, collimated by the first planoconvex lens, focused by the second planoconvex lens and further focused on the end surface of the laser gain dielectric crystal, the laser gain dielectric crystal produces stimulated radiation after absorbing the pump light, when the radiation of fundamental frequency light in the resonator cavity exceeds the self-stimulated Raman scattering threshold of the laser gain dielectric crystal, the produced Raman laser is collimated and outputted by the laser collimating mirror. The self-stimulated Raman scattering laser can improve the self-stimulated Raman scattering conversion rate, eliminate the thermal relaxation process from the pump energy level to the laser energy level of electrons of the conventional pump way, improve the quantum efficiency, reduce the heat and increase the self-stimulated Raman scattering conversion rate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Directly-pumping self-stimulated Raman scattering human eye safe waveband laser
InactiveCN101814695AImprove scattering efficiencyReduce thermal effectsLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialStimulate raman scatteringElectron
The invention discloses a directly-pumping self-stimulated Raman scattering human eye safe waveband laser. The laser comprises a laser pumping source, a laser energy transmission fiber, a plano-convex lens collimator, a plano-convex focus lens, a cavity reflector, a laser gain medium crystal, a laser output mirror and a laser collimating lens, wherein pumping light output by the laser pumping source is transmitted to the plano-convex lens collimator through the laser energy transmission fiber; after being collimated, the pumping light is focused on the end face of the laser gain medium crystal through the plano-convex focus lens; the laser gain medium crystal absorbs the pumping light and generates stimulated radiation with a waveband of 1.3 microns; and when the radiation with the waveband of 1.3 microns surpasses a self-stimulated Raman scattering threshold value of the laser gain medium crystal, generated human eye safe waveband laser with the waveband of 1.5 microns is collimated and output by the output mirror. The laser has the advantages of enhancing self-stimulated Raman scattering conversion rate in the waveband of Nd3+1.3 microns, eliminating thermal relaxation process of electronics from a pumping energy grade to a laser energy grade in a conventional pumping mode, enhancing quantum efficiency and reducing heat.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing three-dimensional bismuth ferrite visible light catalytic material by using direct-write forming technology
InactiveCN106391039AImprove scattering efficiencyLarge specific surface areaCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPotassium hydroxideSlurry
The invention provides a method for preparing a three-dimensional bismuth ferrite visible light catalytic material by using a direct-write forming technology. The method comprises the following steps: providing and dissolving ferric nitrate, bismuth nitrate, nitric acid and potassium hydroxide into a mixed solution, and preparing bismuth ferrite nano powder through a hydrothermal synthesis method; after mixing the bismuth ferrite nano powder with an additive, adding the mixture into deionized water, and preparing bismuth ferrite mixed slurry of which the solid phase content is 40 to 80 wt percent; pre-designing a three-dimensional structural drawing through CAD (Computer Aided Design) software, converting the three-dimensional drawing into a code language capable of being recognized by a computer, putting the bismuth ferrite mixed slurry in a forming needle cylinder, enabling the forming needle cylinder to move along a path designated by the computer under the driving of a direct-write platform, extruding and forming layer by layer at the same time, periodically overlaying back and forth, and forming a mult-layer ordered three-dimensional porous structure blank; carrying out pre-sintering and sintering thermal treatment on the three-dimensional porous structure blank, thus obtaining a three-dimensional bismuth ferrite body having a visible light photocatalysis characteristic.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Washing machine having a condensing duct
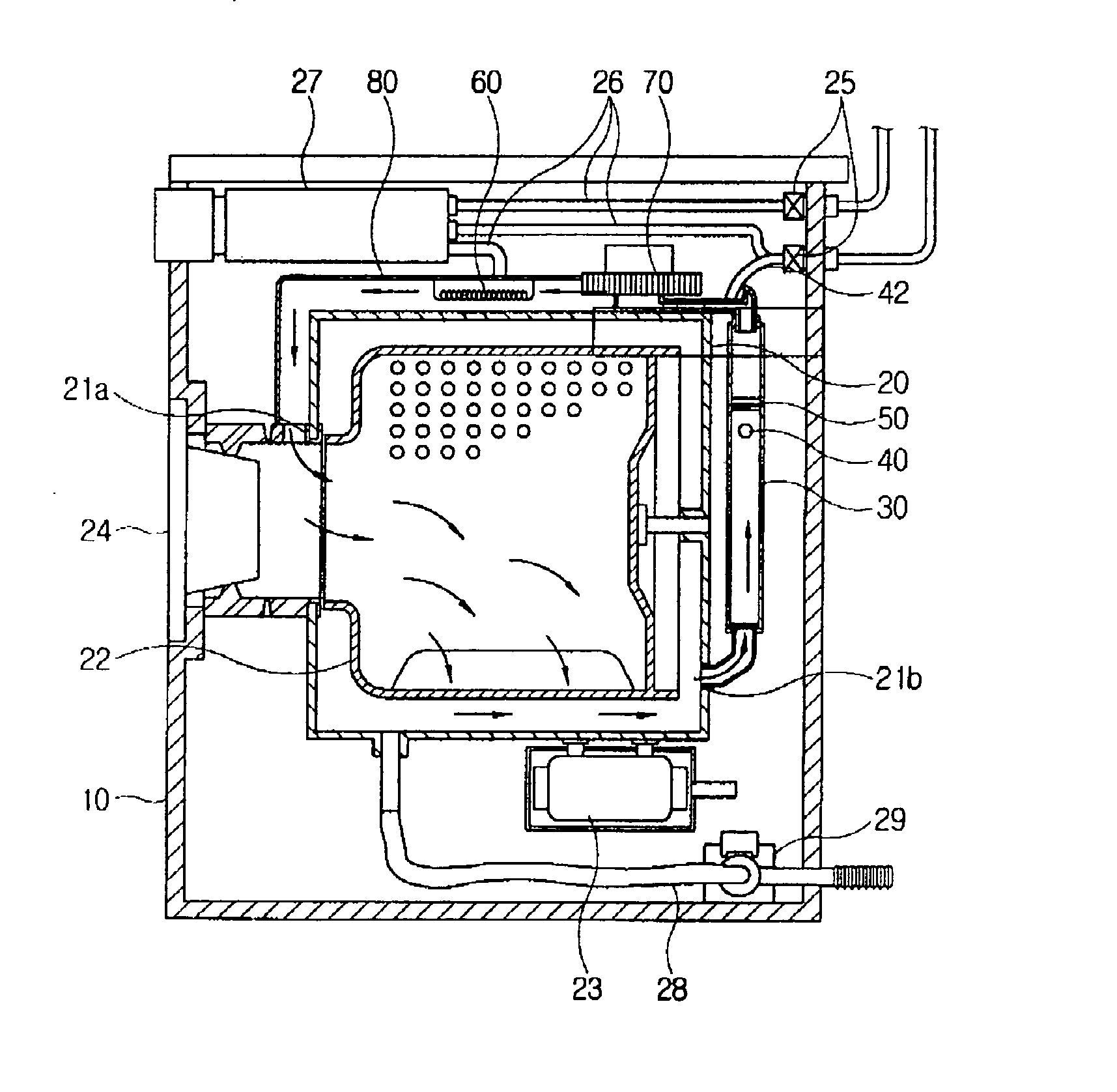
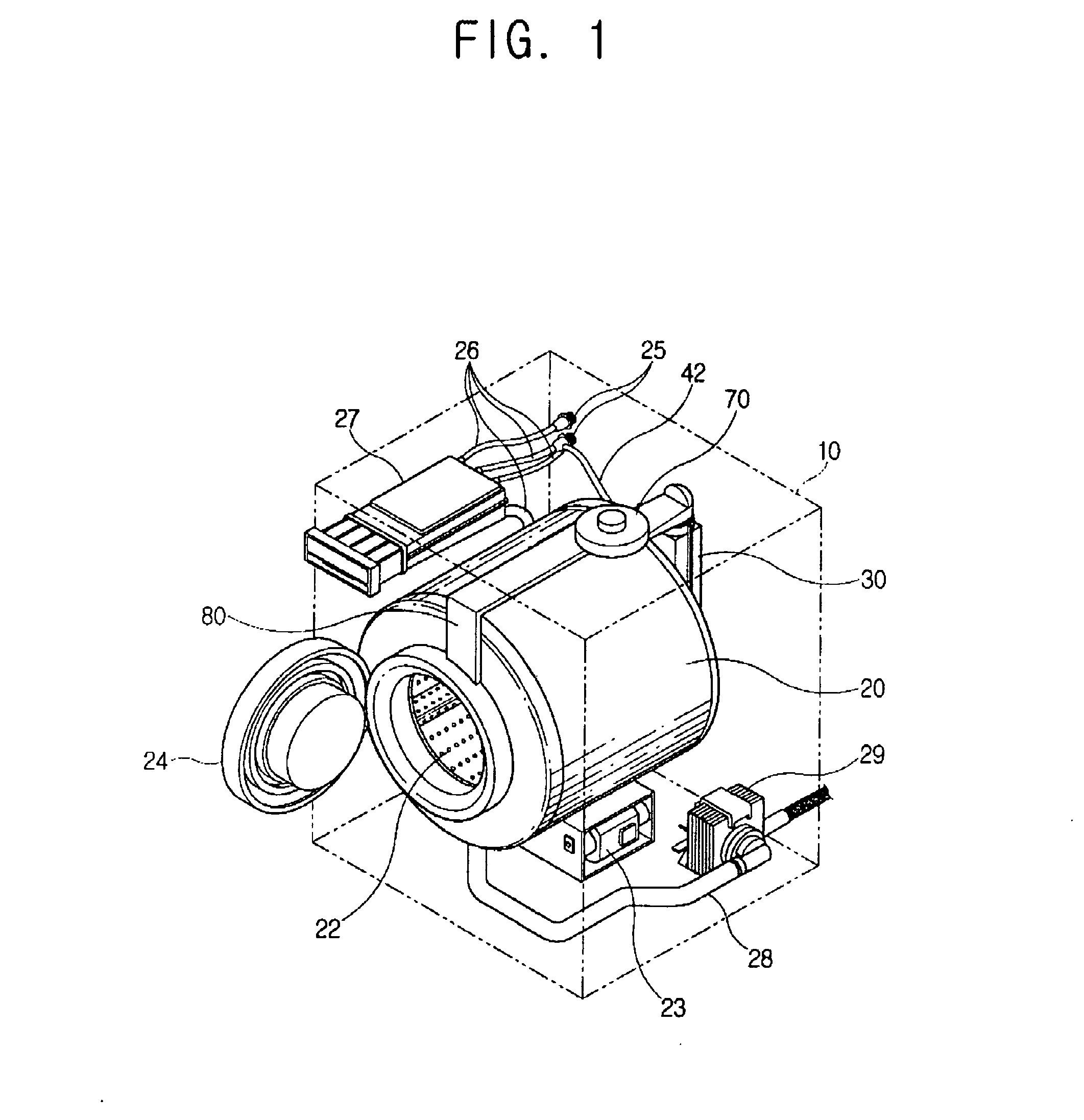
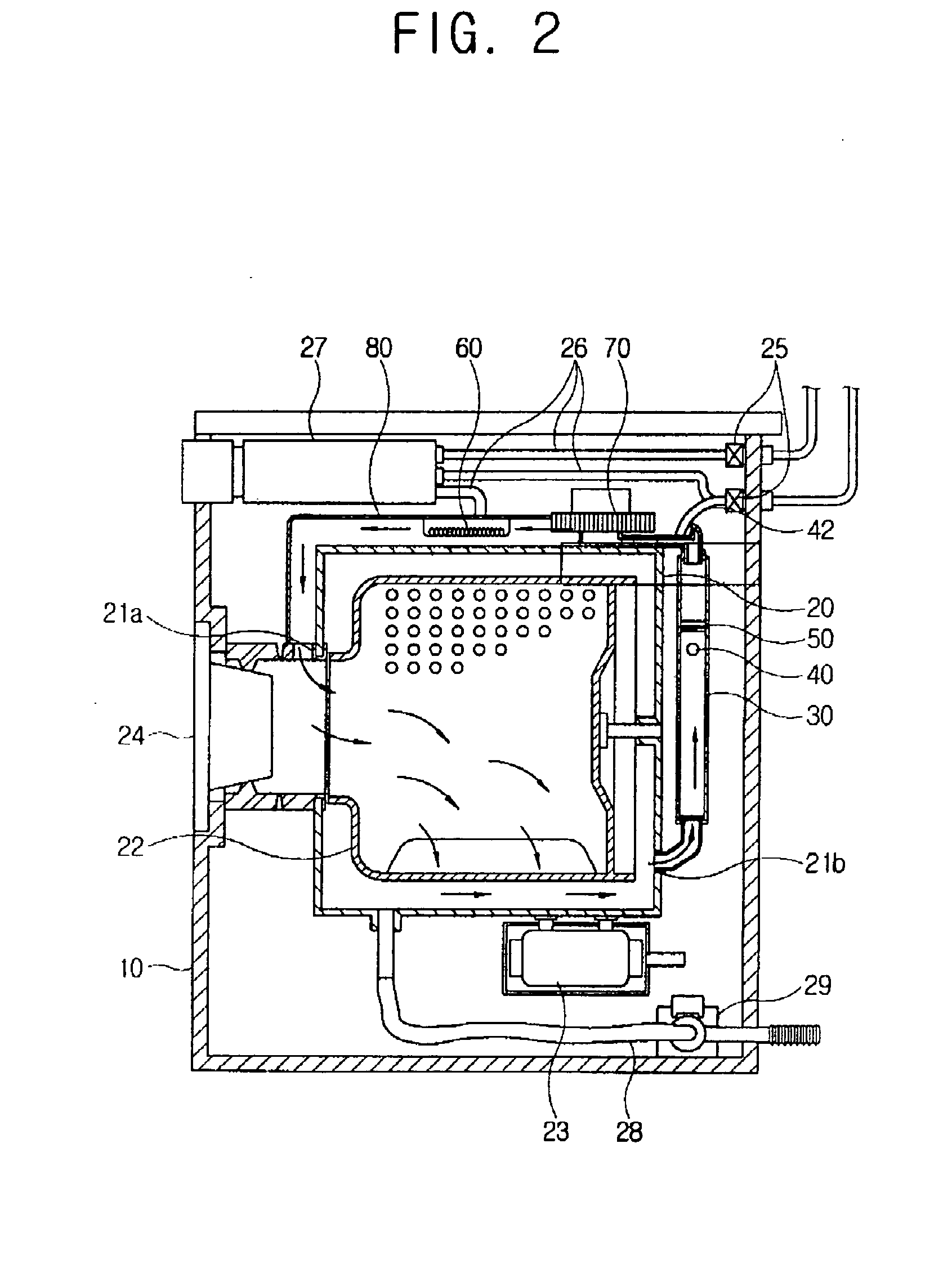
InactiveUS20060101870A1Improve scattering efficiencyOther washing machinesWashing machine with receptaclesEngineeringCondensed water
A washing machine includes a drum and a condensing duct that communicates with the drum. The condensing duct includes an air inlet unit, a condensing unit and an air outlet unit which are connected sequentially. A condensed water jetting member is provided inside the condensing unit and a backward flow blocking guide is provided inside the condensing unit. The condensing unit has a flow width larger than the air inlet unit and the air outlet unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Enhanced cellular assay method for use in flow cytometry or similar instruments using optically resonant particles
InactiveUS7611849B2Simplifying assayInexpensive to automateMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological particle analysisLight scatter measurementOptical instrumentation
This invention relates to the field of biological assays where cells can be classified and enumerated using flow cytometry optical instrumentation. The invention combines information from multi-angle, light scatter from the cell itself and multi-angle light scatter from small, optically resonant particles that are selectively bound to surface molecules on the cell to carry out classification and enumeration. This light scatter method enables an instrumentation system that is simple to use, inexpensive to build, and mechanically robust; making it suitable for use in remote clinical environments.
Owner:POINT CARE TECH
Method for making high tint strength pigment compositions
InactiveUS20070137526A1Effective lightingLight scattering efficiencyPigmenting treatmentTitanium dioxideCelsius DegreeSlurry
The invention concerns a method for making a pigment composition comprising inorganic base particles and one or more inorganic spacer particles precipitated thereon, including the steps of forming an aqueous slurry of the inorganic base particles, if necessary, milling the aqueous slurry so that at least about 50% of the inorganic base particles are less than 0.5 microns in size, heating the slurry as needed to achieve and maintain a temperature of at least about 40 degrees Celsius, adjusting the pH of the slurry as needed to achieve and maintain a pH in the range of from 4 to 9, adding the inorganic spacer particles to the slurry while maintaining such temperature and pH conditions and with intensive mixing, and finally, recovering the pigment composition from the slurry.
Owner:TRONOX LLC
Titanium dioxide pigment and manufacturing method
ActiveUS9315615B2Improve opacity and light stability and durabilityExcellent characteristicsPigmenting treatmentConjugated diene hydrocarbon coatingsEnd-groupPigment
In one aspect, the invention provides a titanium dioxide pigment. The titanium dioxide pigment comprises a plurality of titanium dioxide particles, and a polymer deposited on the titanium dioxide particles for inhibiting agglomeration of the titanium dioxide particles in an aqueous based coating formulation. The titanium dioxide particles have anchoring moieties associated therewith for facilitating anchoring of the polymer to the particles. The polymer is a copolymer having anchoring groups for attaching to the anchoring moieties associated with the titanium dioxide particles and hydrophobic end groups for attaching to the resin of the coating formulation. In another aspect, the invention provides a method of manufacturing a titanium dioxide pigment.
Owner:TRONOX LLC
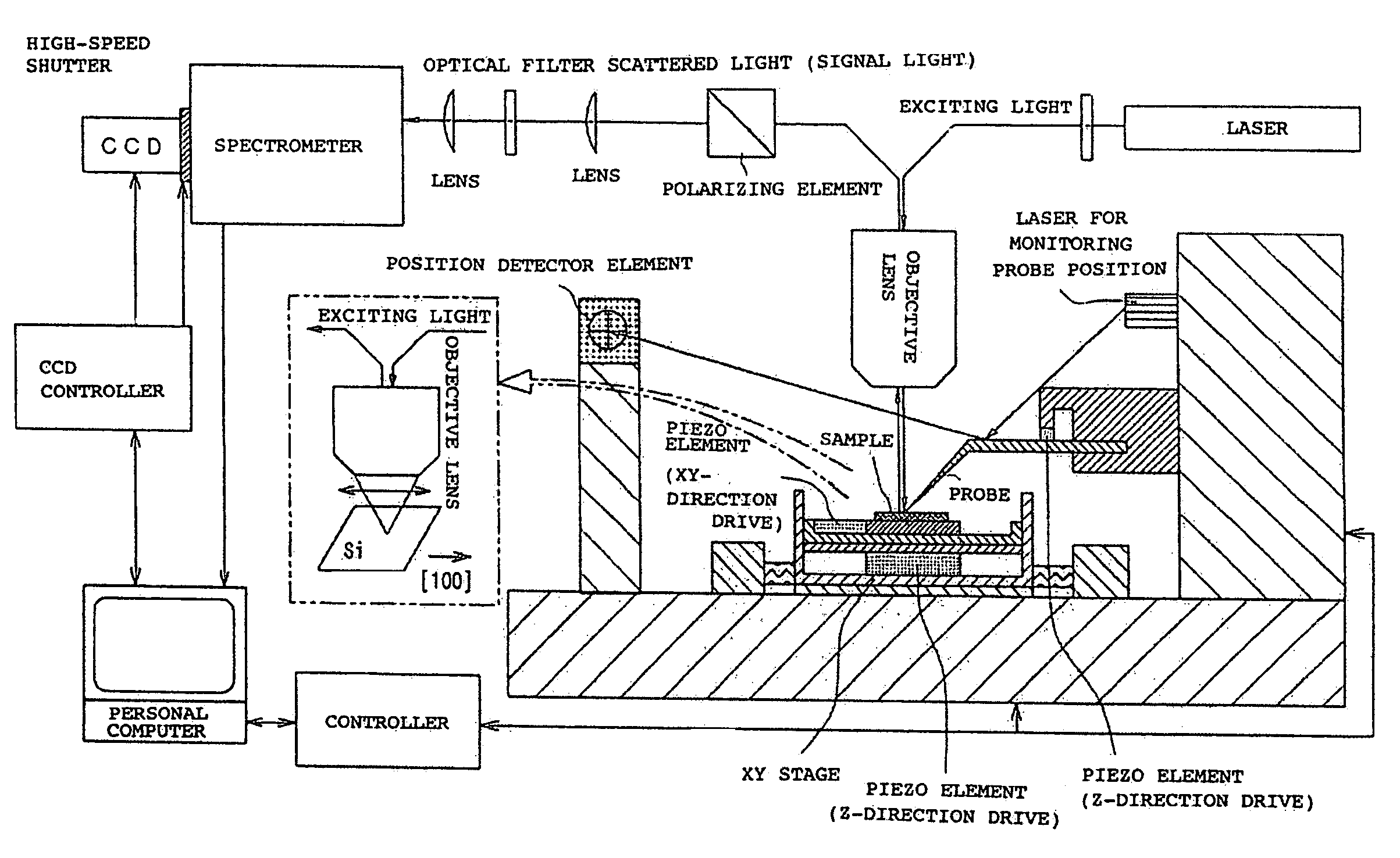
Optical measurement method and device
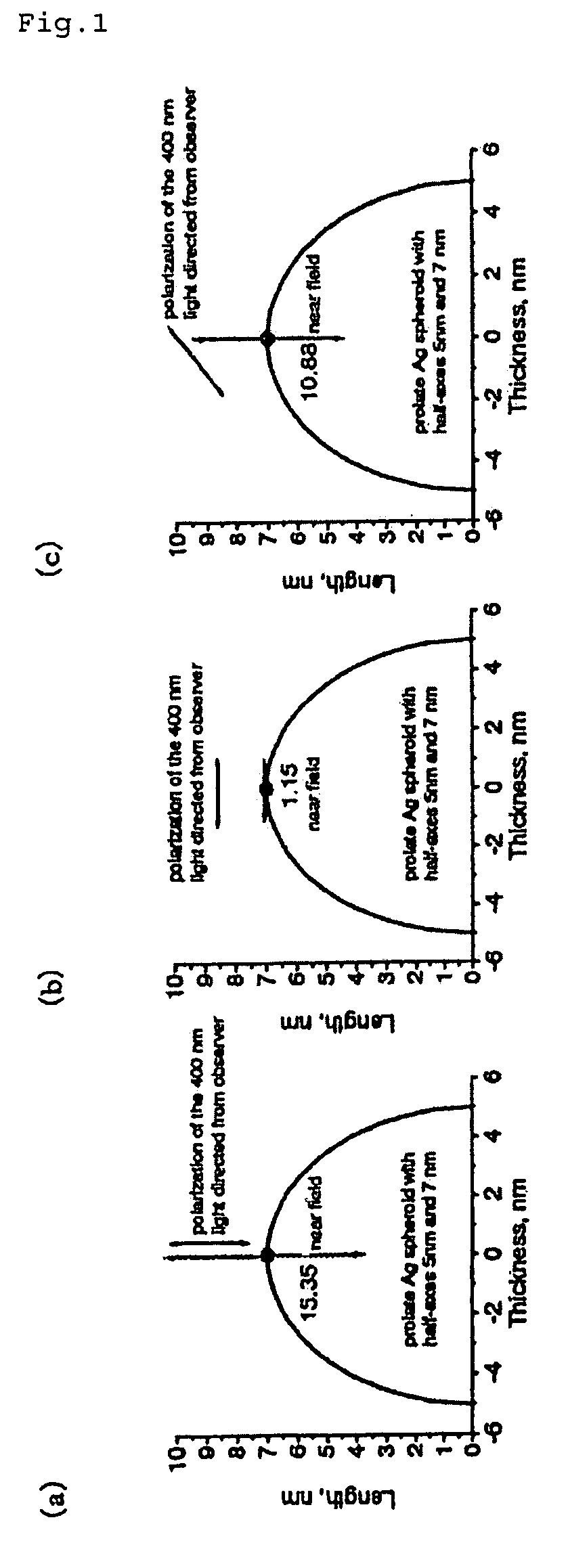
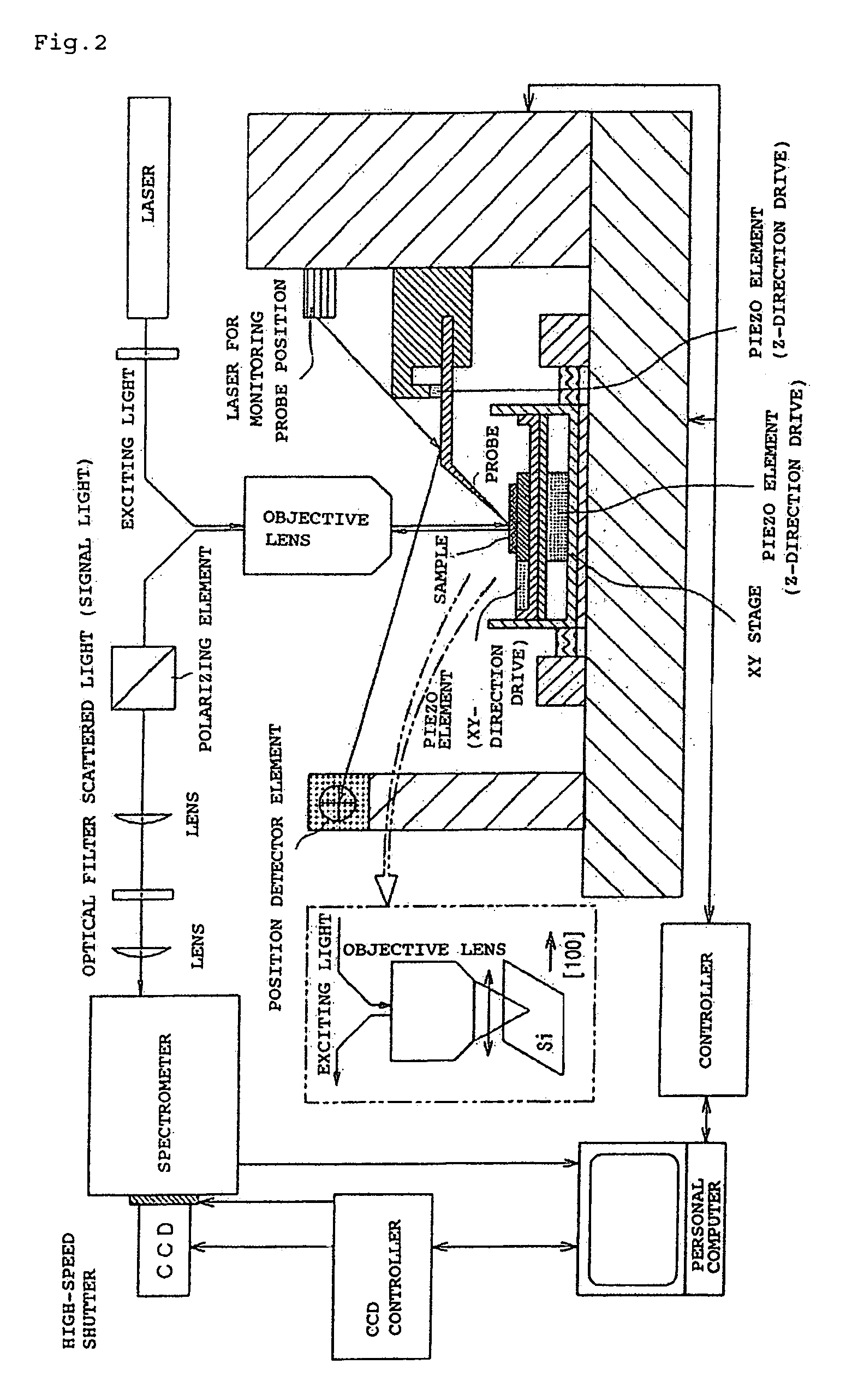
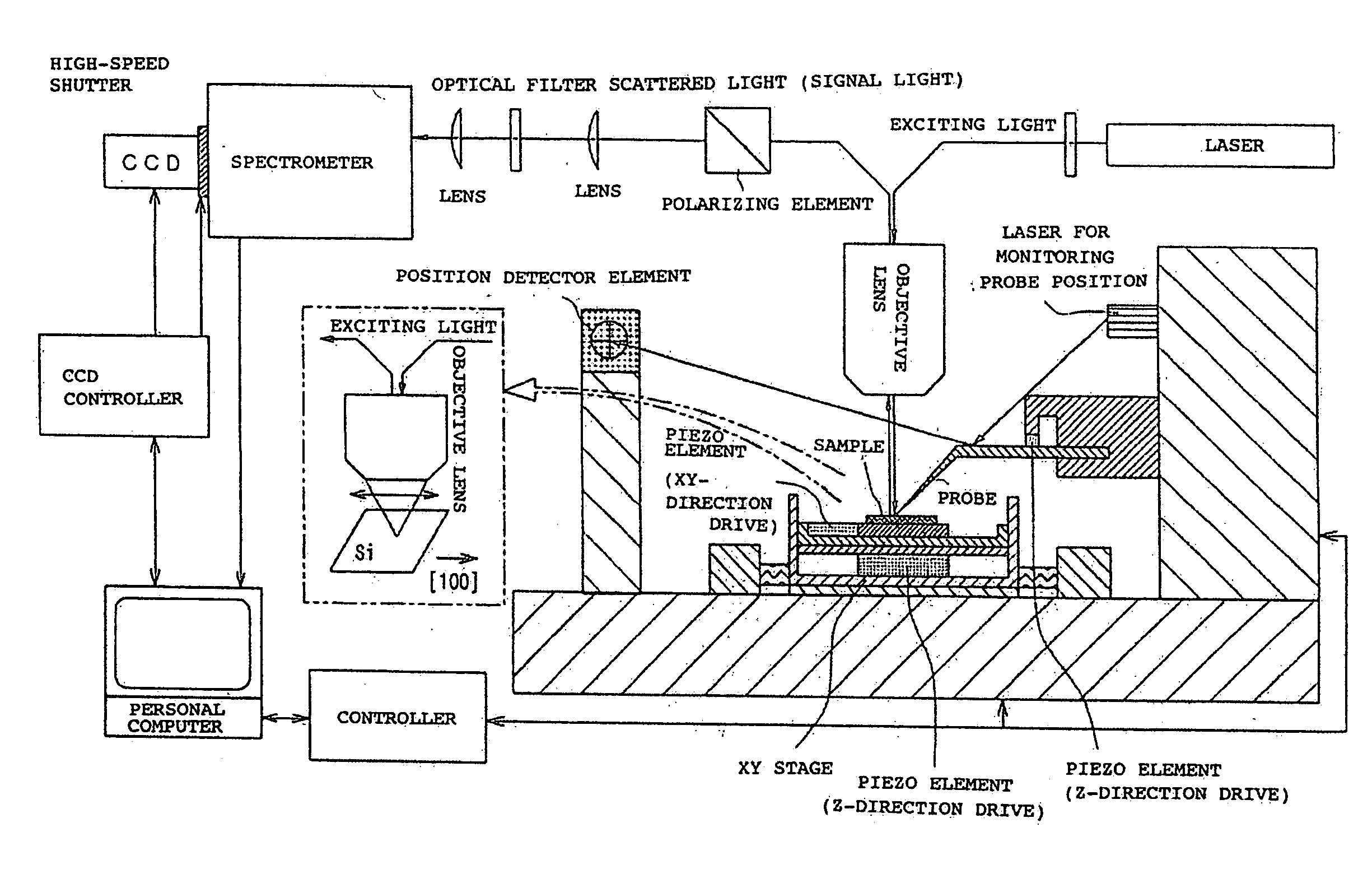
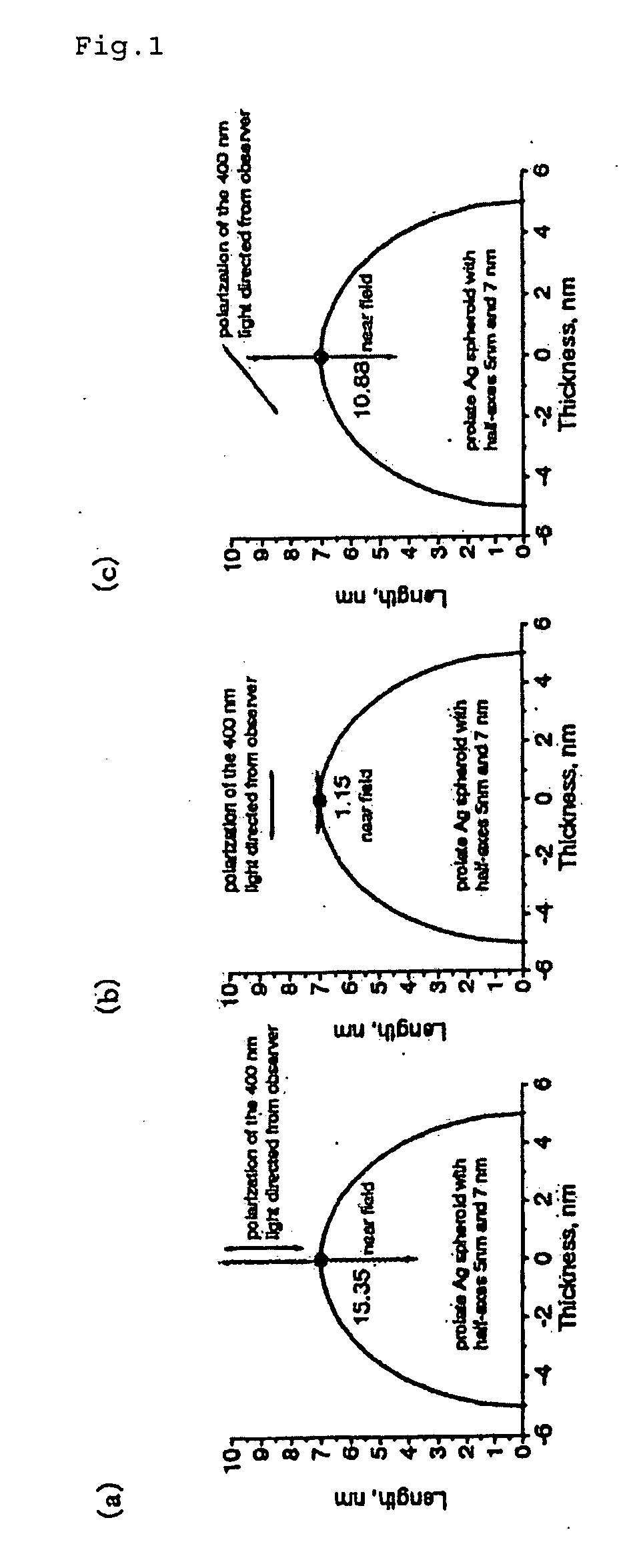
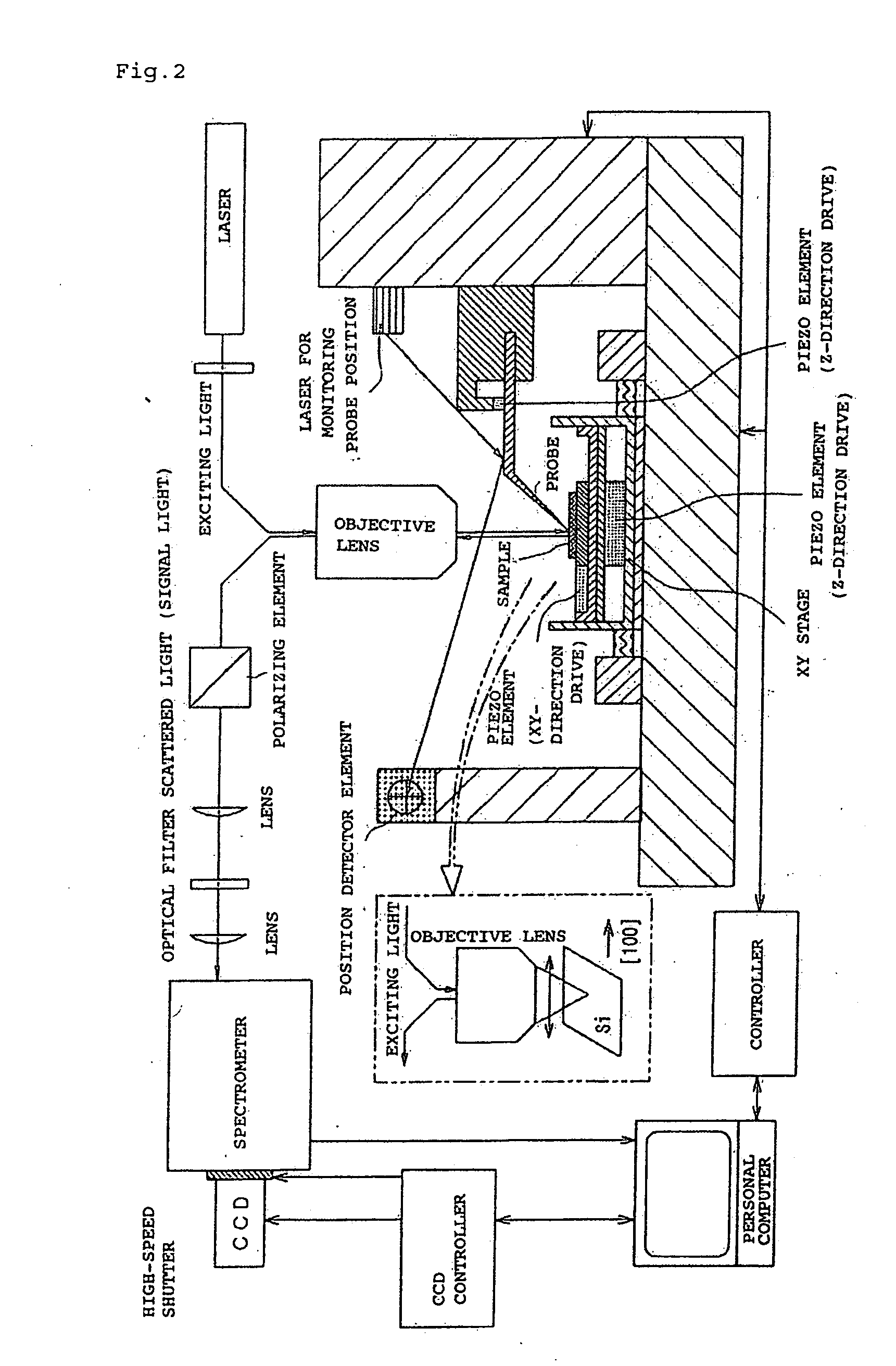
InactiveUS7408635B2Improve scattering efficiencyLow efficiencyRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringLight irradiationImage resolution
An optical measurement of a crystalline sample to be measured. The sample is irradiated with an exciting light from the polarization direction in which the Raman scattering is prohibited by the selection rule. When a metal probe is brought to proximity to the sample to be measured, the selection rule is eased locally only in the proximity portion near the probe end in order that Raman scattering becomes active. Thus, a Raman signal only from the proximity portion near the probe end is detected. An optical measurement apparatus having an optical arrangement for measuring a signal light re-emitted from a sample to be measured when the sample is irradiated with an exciting light is provided. The optical measurement apparatus comprises a means for limiting the polarization state of the exciting light or signal light and a means for bringing a metal probe near the sample to be measured. The optical measurement apparatus is used to measure the signal light obtained by locally easing the limitation on the polarization state by bringing the metal probe near the sample. Therefore, Raman scattering light from silicon or the like can be measured with high space-resolution exceeding the light diffraction limit.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Metamaterial spunbond cloth and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113293519AHigh emissivityImprove scattering efficiencyNon-woven fabricsAdhesivesFiberPolymer substrate
The invention discloses metamaterial spunbond cloth and a preparation method thereof. The metamaterial spunbond cloth comprises at least one single-layer fiber spunbond layer; the single-layer fiber spunbond layer comprises metamaterial fibers; the metamaterial fibers are interwoven and overlapped to form pores; in the pores, the pores with the diameter being 100-3000 nm are reflection pores, and the total volume of the reflection pores accounts for 10%-90% of the volume of the spunbond cloth; the metamaterial fibers are formed by a composite material comprising a polymer substrate material and micro-nano particles; and the average particle size of the micro-nano particles is 100-3000 nm. The metamaterial fibers are arranged in an interwoven mode and the micro-nano particles in the fibers are arranged randomly, the spunbond cloth with the metamaterial characteristics is formed, ultra-wideband optical responses of 0.3-2.5 micrometers and 8-13 micrometers are generated based on the photonic design, then solar radiation and human infrared heat radiation are guided and controlled, and photo-thermal regulation and control are carried out on the microenvironment temperature of the cloth and the human skin to realize efficient thermal management.
Owner:WUHAN GEWUGANZHI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Optical measurement method and device
InactiveUS20070013907A1Reduce dispersionImprove scattering efficiencyRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringLight irradiationImage resolution
An optical measurement of a crystalline sample to be measured. The sample is irradiated with an exciting light from the polarization direction in which the Raman scattering is prohibited by the selection rule. When a metal probe is brought to proximity to the sample to be measured, the selection rule is eased locally only in the proximity portion near the probe end in order that Raman scattering becomes active. Thus, a Raman signal only from the proximity portion near the probe end is detected. An optical measurement apparatus having an optical arrangement for measuring a signal light re-emitted from a sample to be measured when the sample is irradiated with an exciting light is provided. The optical measurement apparatus comprises a means for limiting the polarization state of the exciting light or signal light and a means for bringing a metal probe near the sample to be measured. The optical measurement apparatus is used to measure the signal light obtained by locally easing the limitation on the polarization state by bringing the metal probe near the sample. Therefore, Raman scattering light from silicon or the like can be measured with high space-resolution exceeding the light diffraction limit.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
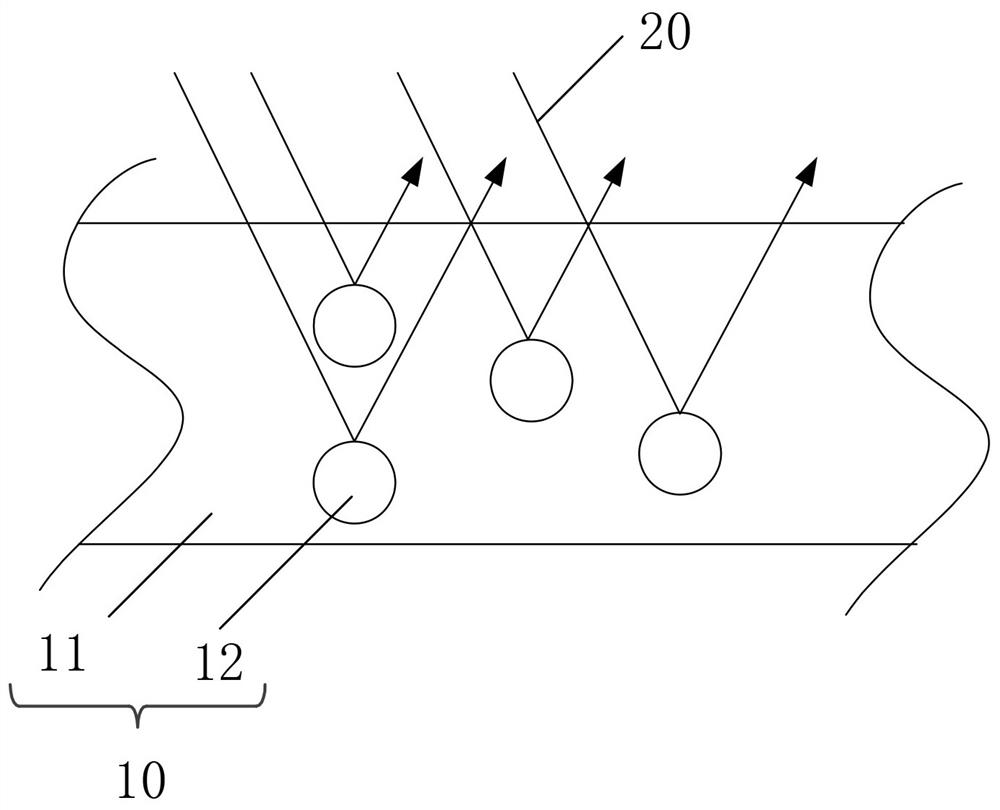
Reflection type liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20110157529A1Increasing azimuth dependenceIncrease brightnessNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayLiquid crystal
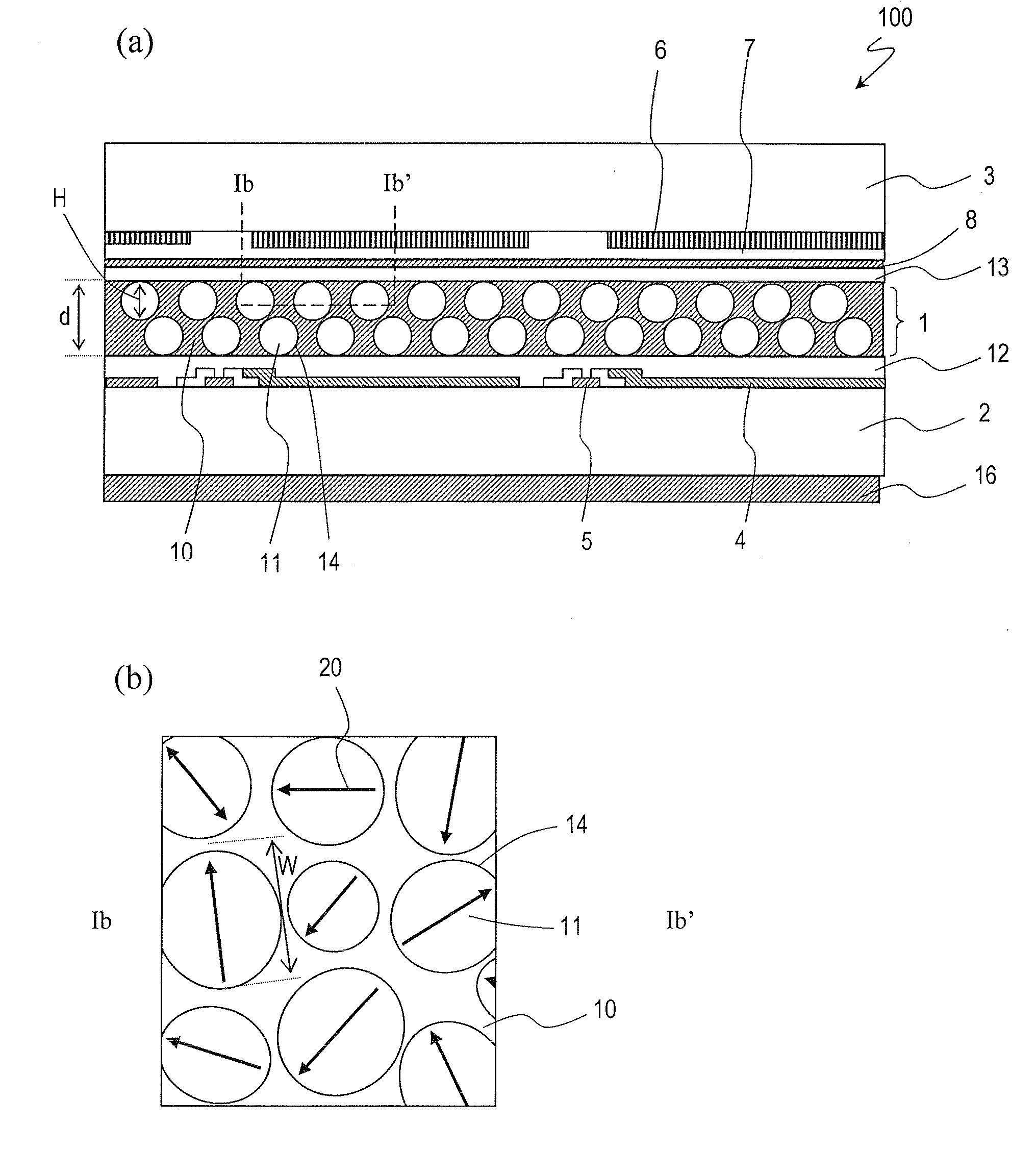
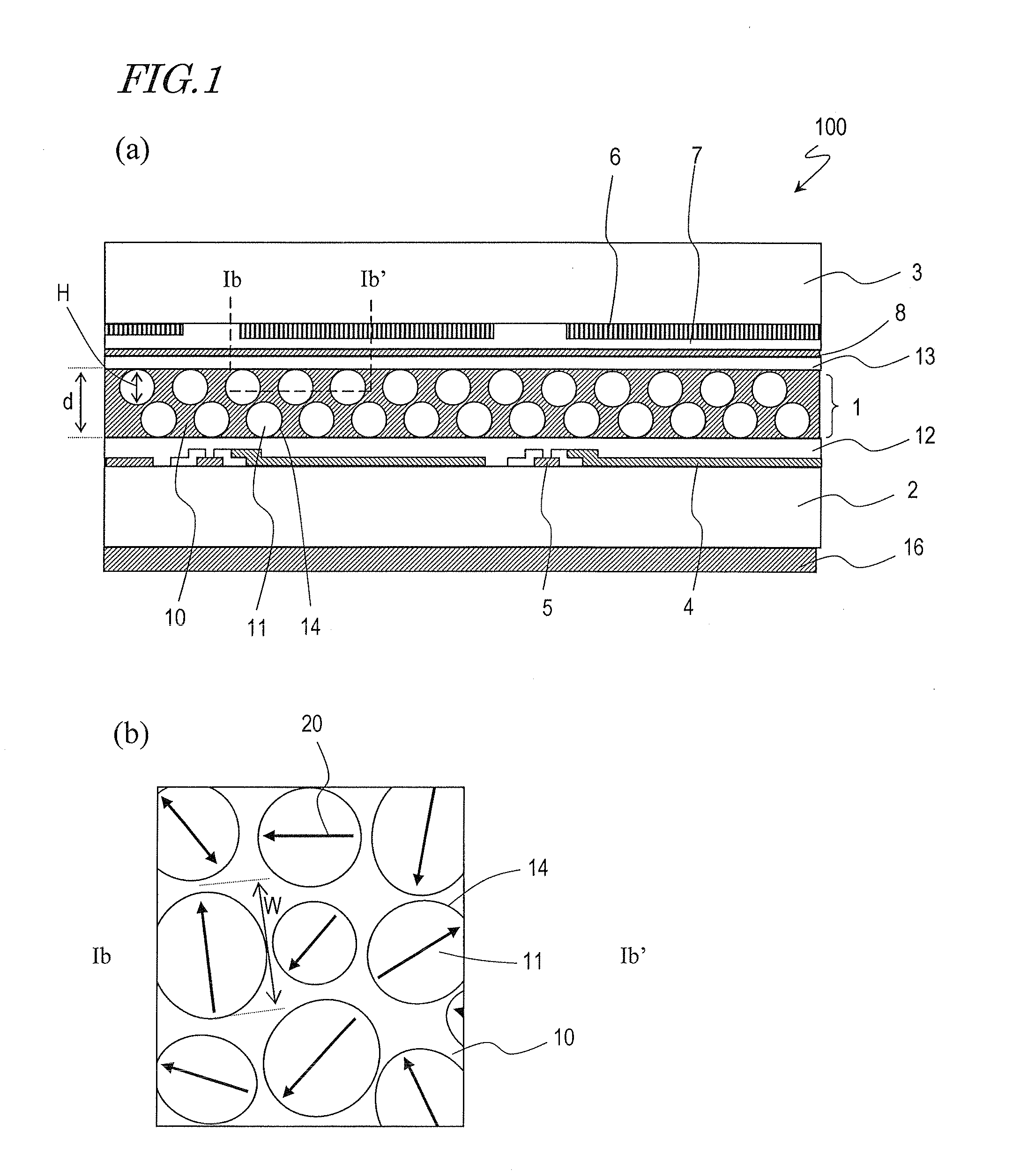
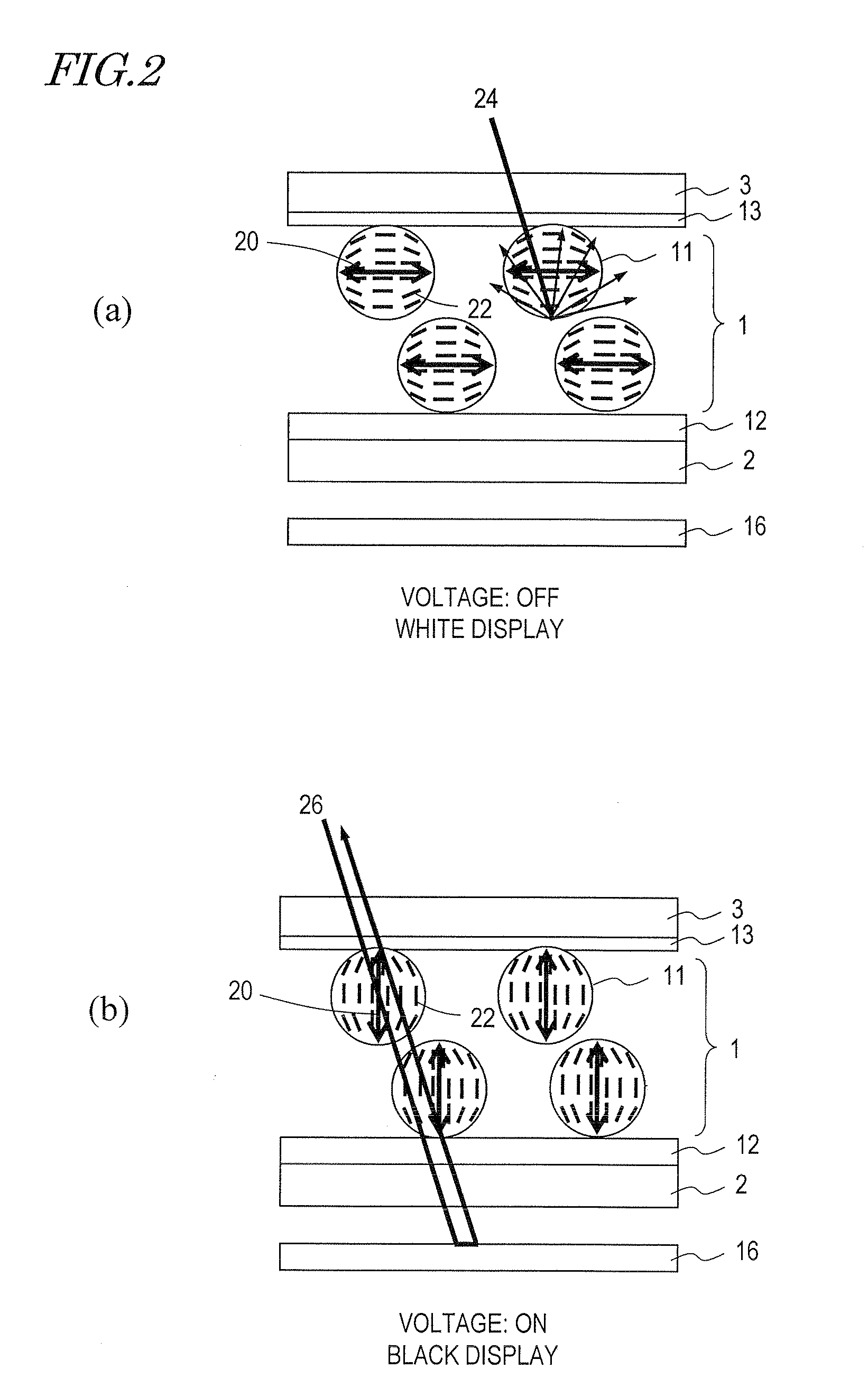
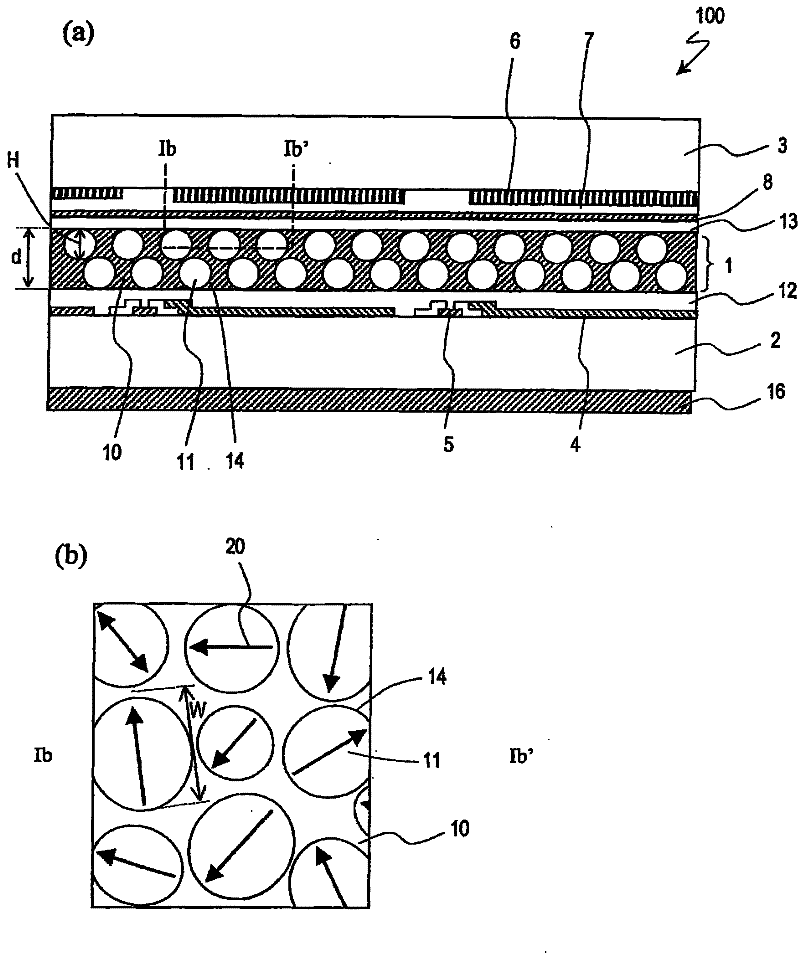
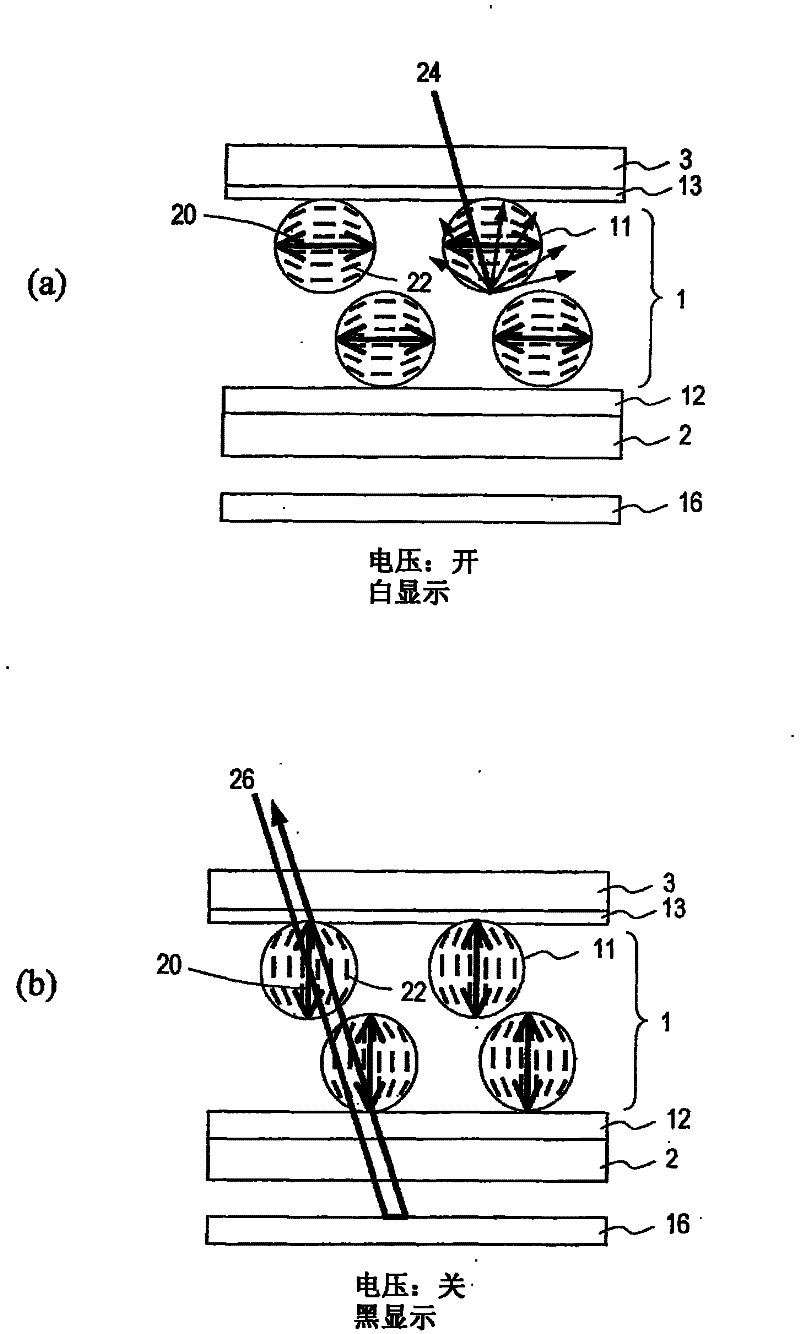
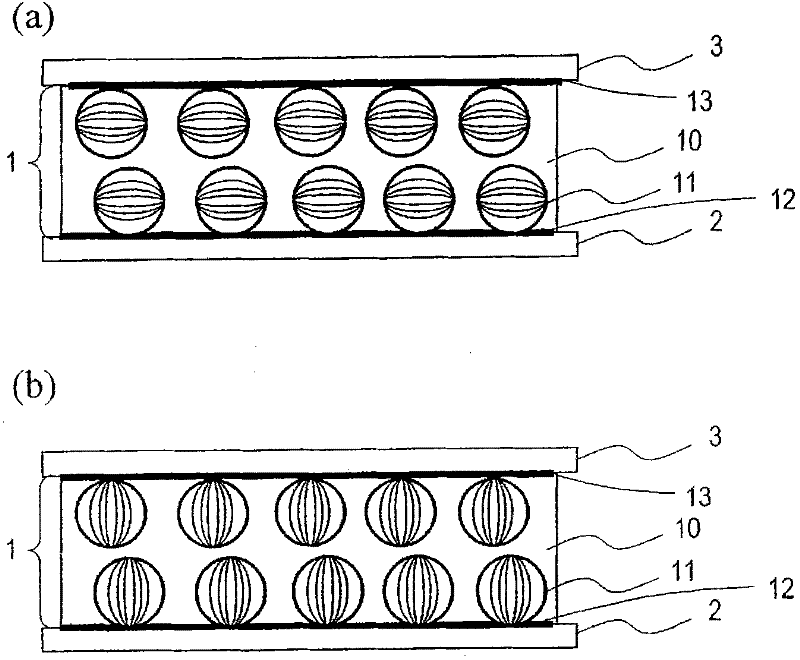
A liquid crystal display device includes a liquid crystal layer 1 whose state is switchable between a light-transmitting state and a light-scattering state, a front substrate 3 and a rear substrate 2 between which the liquid crystal layer 1 is held, a pair of electrodes 4, 8 between which the liquid crystal layer 1 is interposed and which are configured to apply a voltage across the liquid crystal layer 1, and first and second alignment films 13, 12 respectively provided between the liquid crystal layer 1 and the front substrate 3 and between the liquid crystal layer 1 and the rear substrate 2. The liquid crystal layer 1 includes, in each of the pixels, a continuous wall 10, a plurality of small sections 14 separated by the wall 10, and a plurality of liquid crystal regions 11, each of which is formed in any one of the plurality of small sections 14. The plurality of liquid crystal regions 11 include first and second liquid crystal regions 11 which have directors 20 in a plane parallel to the liquid crystal layer 1. The directors 20 of the first and second liquid crystal regions 11 are oriented in different directions.
Owner:SHARP KK
Self-stimulated Raman scattering laser of In-Band pump
InactiveCN101807774BHigh beam qualityReduce thermal effectsLaser using scattering effectsDielectricStimulate raman scattering
The invention discloses a self-stimulated Raman scattering laser of an In-Band pump, which comprises a laser pump source, a laser energy transfer optical fiber, a first planoconvex lens for collimation, a second planoconvex lens for focusing, a reflection mirror of a resonator cavity, a laser gain dielectric crystal, a laser output mirror and a laser collimating mirror which are sequentially arranged, wherein pump light outputted by the laser pump source is transmitted to the first planoconvex lens via the laser energy transfer optical fiber, collimated by the first planoconvex lens, focused by the second planoconvex lens and further focused on the end surface of the laser gain dielectric crystal, the laser gain dielectric crystal produces stimulated radiation after absorbing the pump light, when the radiation of fundamental frequency light in the resonator cavity exceeds the self-stimulated Raman scattering threshold of the laser gain dielectric crystal, the produced Raman laser is collimated and outputted by the laser collimating mirror. The self-stimulated Raman scattering laser can improve the self-stimulated Raman scattering conversion rate, eliminate the thermal relaxation process from the pump energy level to the laser energy level of electrons of the conventional pump way, improve the quantum efficiency, reduce the heat and increase the self-stimulated Raman scatteringconversion rate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Reflection type liquid crystal display device
ActiveCN102132198AImprove scattering efficiencyIncreasing the thicknessNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayLiquid crystal
Provided is a reflection type liquid crystal display device comprising a liquid crystal layer (1), which can be switched between a transmission state and a scattering state, a front substrate (3) and a back substrate (2) for holding the liquid crystal layer (1) inbetween, a pair of electrodes (4 and 8) arranged across the liquid crystal layer (1) for applying a voltage to the liquid crystal layer(1), and first and second orientation films (13 and 12) formed between the liquid crystal layer (1), and the front substrate (3) and the back substrate (2), respectively. The liquid crystal layer (1)includes, for each pixel, a continuous wall (10), a plurality of small chambers (14) separated by the wall (10), and a plurality of liquid crystal regions (11) individually formed in any of the smallchambers (14). The liquid crystal regions (11) have first and second liquid crystal regions (11) having directors (20) in a plane parallel to the liquid crystal layer (1). The directors (20) of the first and second liquid crystal regions (11) are oriented in directions different from one another.
Owner:SHARP KK
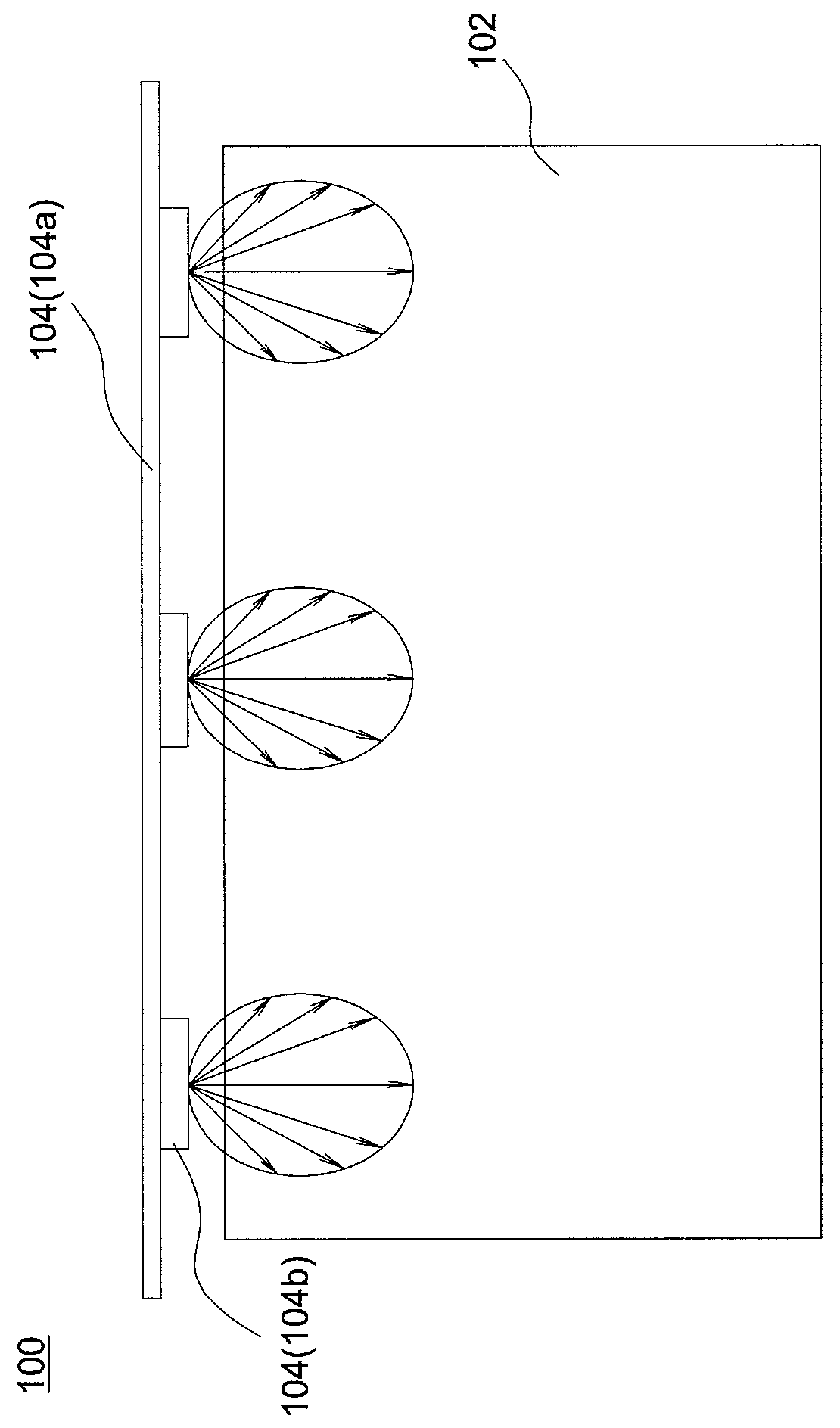
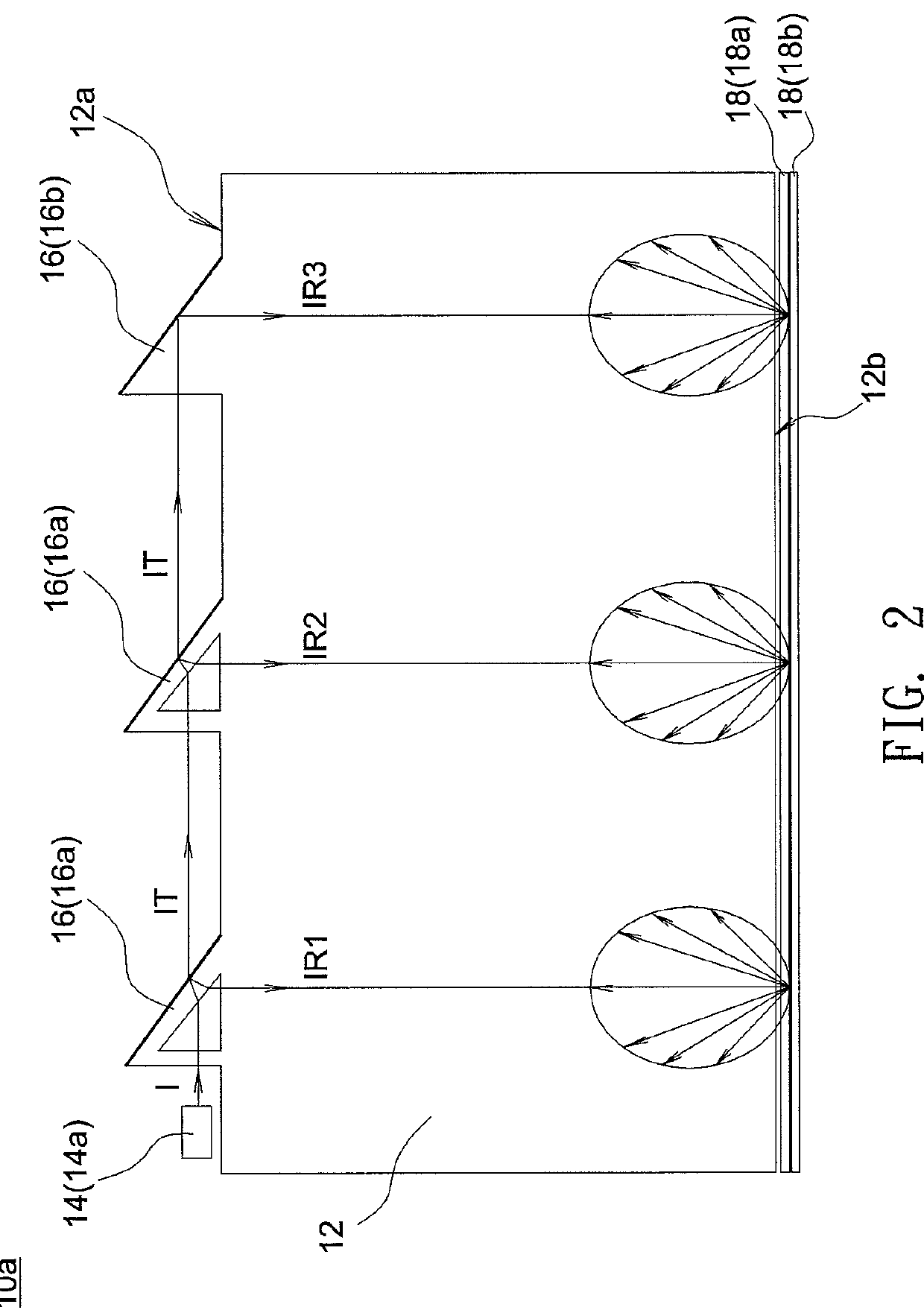
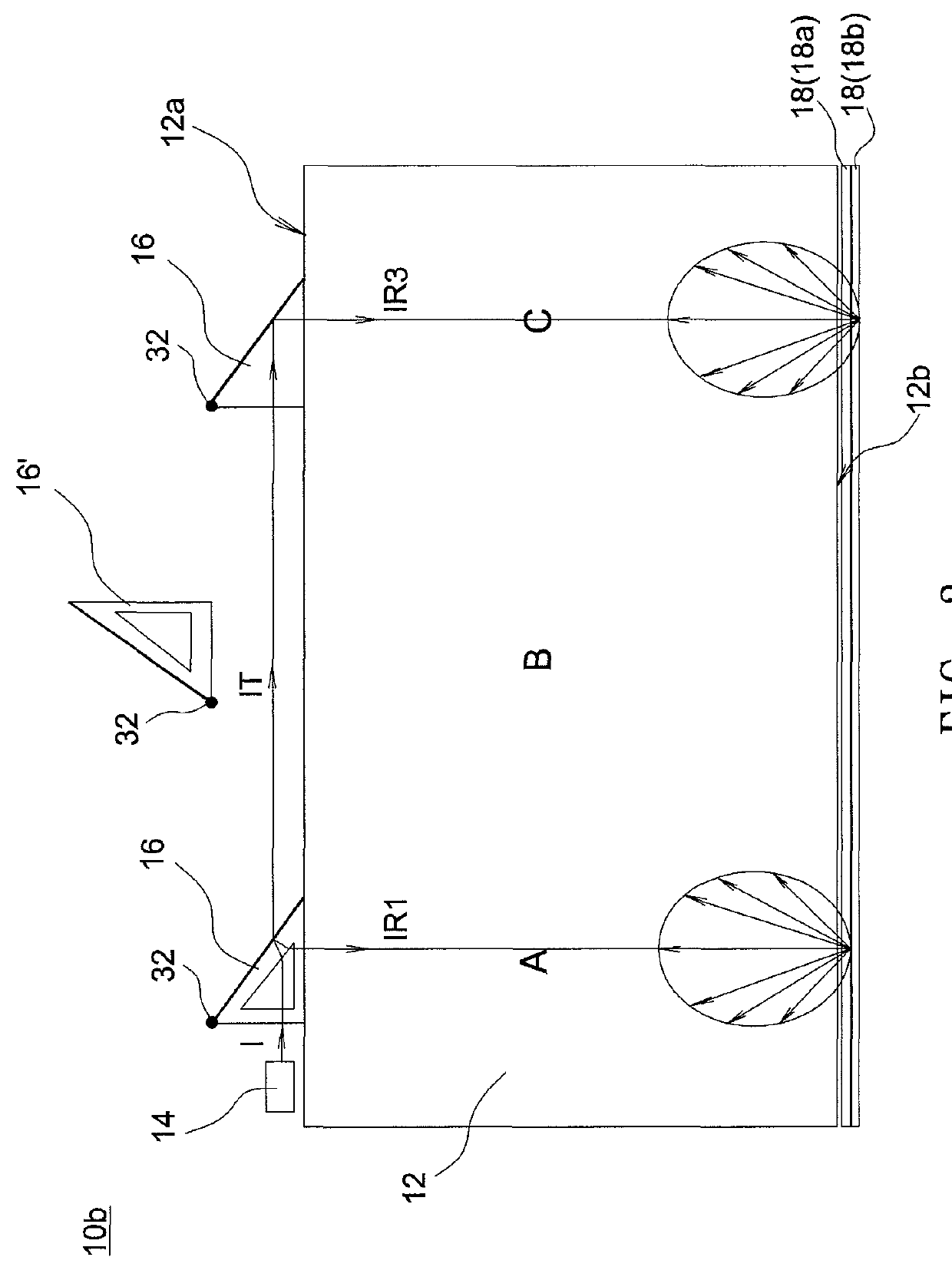
Backlight module
ActiveUS20180067362A1Reduce manufacturing costReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight guideLight beam
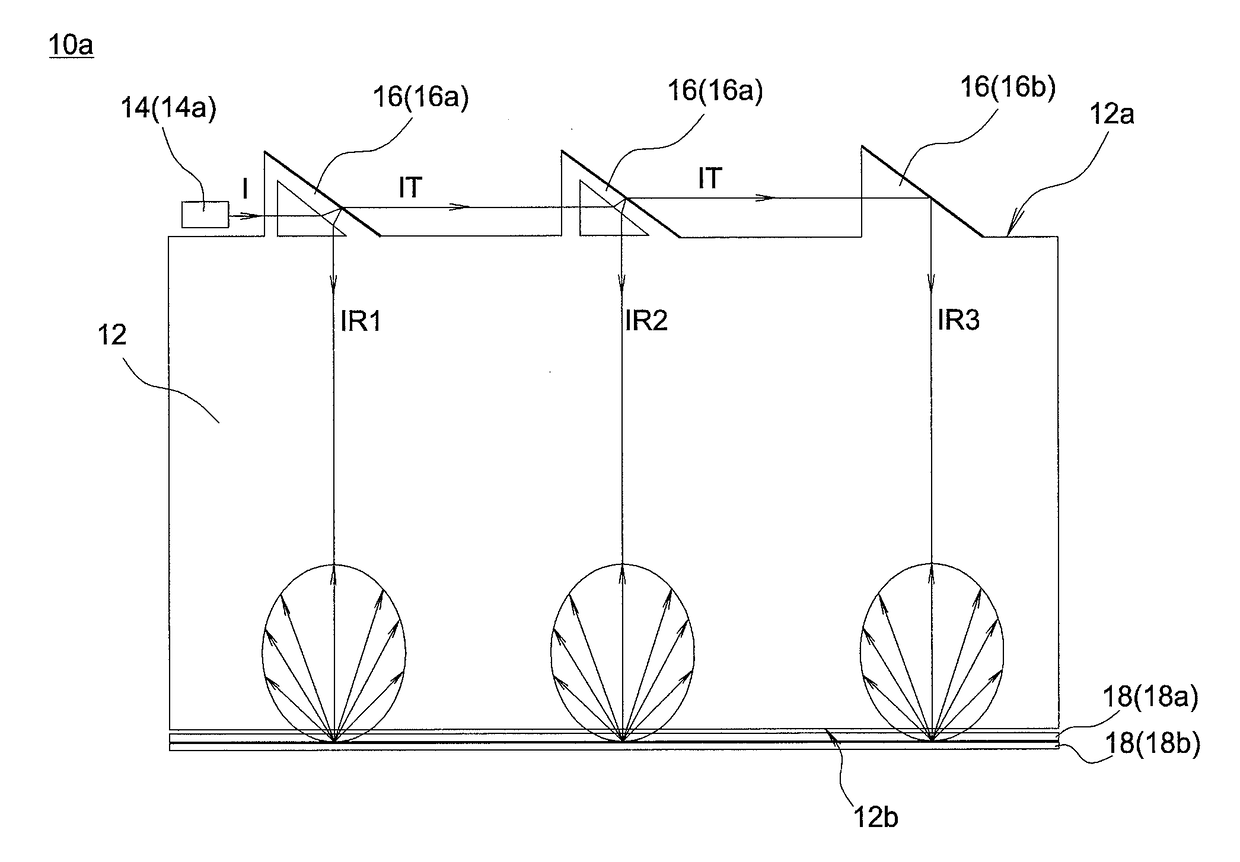
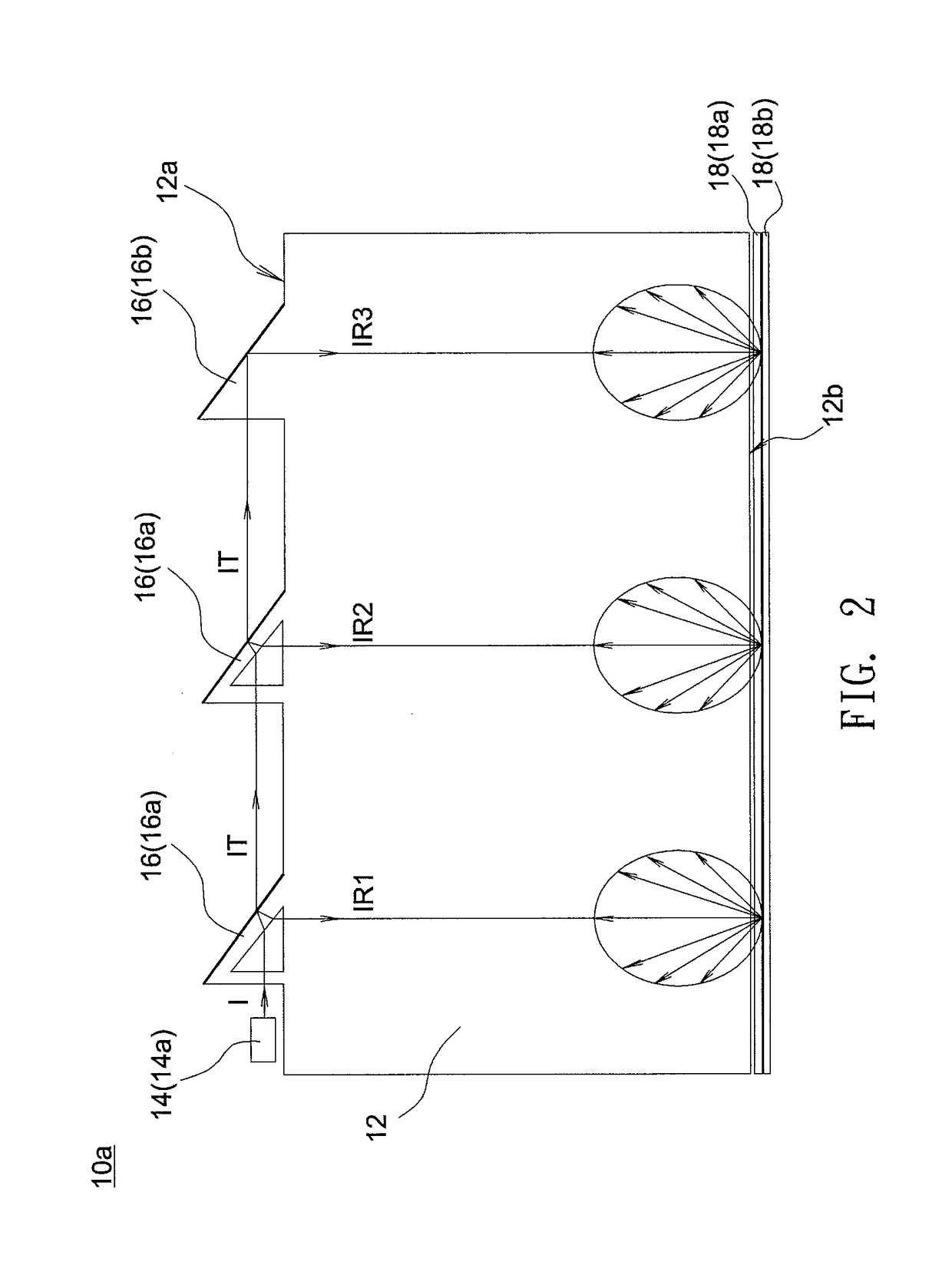
A backlight module includes a light guide plate, a plurality of light transmission elements and a light source. The light guide plate has at least one light incident surface, and the light transmission elements are disposed near the light incident surface and aligned to from at least one light transmission element row. The light source is disposed near one end of the light transmission element row and capable of emitting a light beam to the light transmission element row. Each of the light transmission elements reflects a part of the light beam to the light guide plate to form multiple independent light reflection paths, and the light transmission elements successively transmits a part of the light beam to form a light transmission path in the light transmission element row.
Owner:CORETRONIC
Deep ultraviolet semiconductor light emitting diode epitaxial structure
ActiveCN112635628AImprove lattice qualityQuality improvementSemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencySemiconductor materials
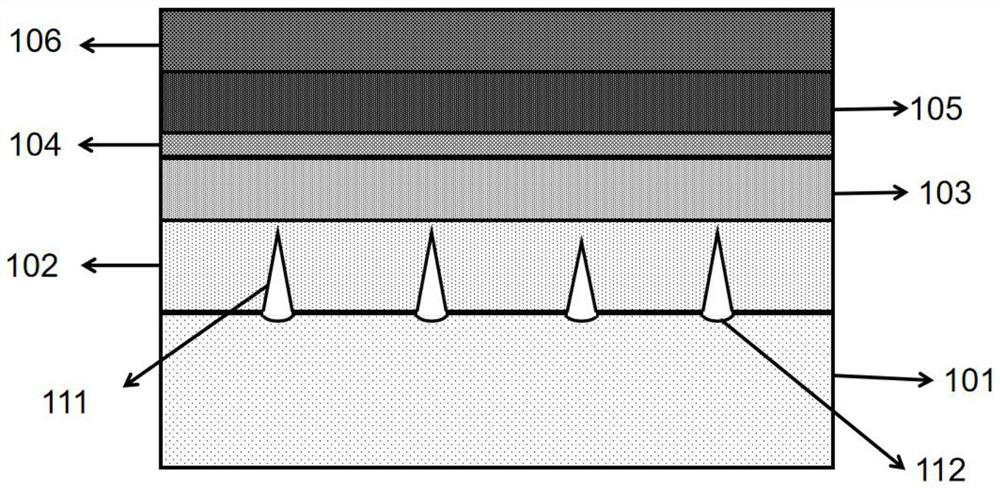
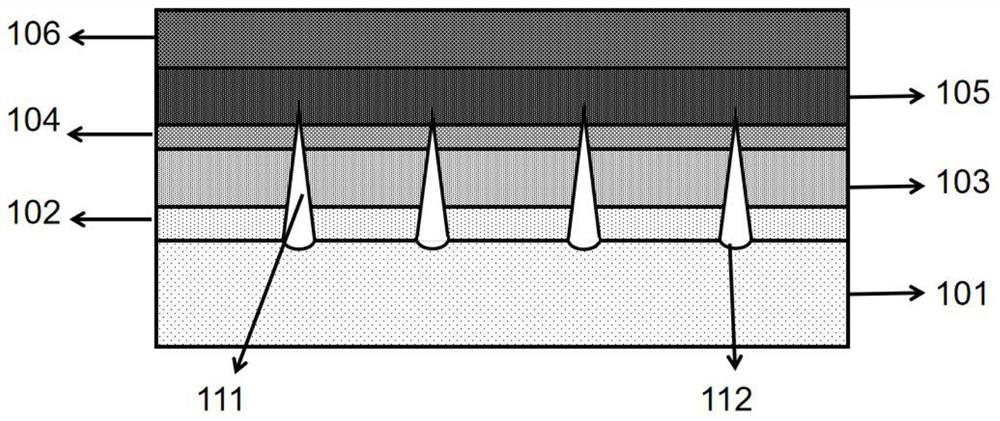
The invention relates to a deep ultraviolet semiconductor light emitting diode epitaxial structure. The epitaxial structure sequentially comprises a patterned substrate, a semiconductor buffer layer, an n-type semiconductor material layer, a multi-quantum well layer, a p-type electron blocking layer and a p-type semiconductor material transmission layer in an epitaxial direction, wherein grooves are etched in the patterned substrate, a cavity structure vertically grows upwards on each groove, and the cavity structures penetrate through the semiconductor buffer layer, the n-type semiconductor material layer and the multi-quantum well layer. The top part positions of the cavity structures are divided into the following three types: the first type is that the cavity structures are polymerized on the p-type electron barrier layer, and the polymerization depth of the cavities in the p-type electron barrier layer is 10-100 nm; or the second type is that the cavity structures continuously penetrate through the p-type electron barrier layer and are polymerized on the p-type semiconductor material transmission layer, and the polymerization depth of the cavities in the p-type semiconductor material transmission layer is 10-500 nm; or the third type is that cavity structures continuously penetrate through the p-type electron barrier layer and the p-type semiconductor material transmission layer, cavities are not polymerized, and round holes appear in the surface of the p-type semiconductor material transmission layer. According to the deep ultraviolet semiconductor light emitting diode epitaxial structure, the internal quantum efficiency of the deep ultraviolet LED can be improved; and the cavity structures are incorporated into quantum wells, so that the scattering feature of light can be effectively improved, and the light extraction efficiency of the deep ultraviolet light-emitting diode is improved.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Patterned substrate, preparation method thereof, light emitting diode and preparation method of light emitting diode
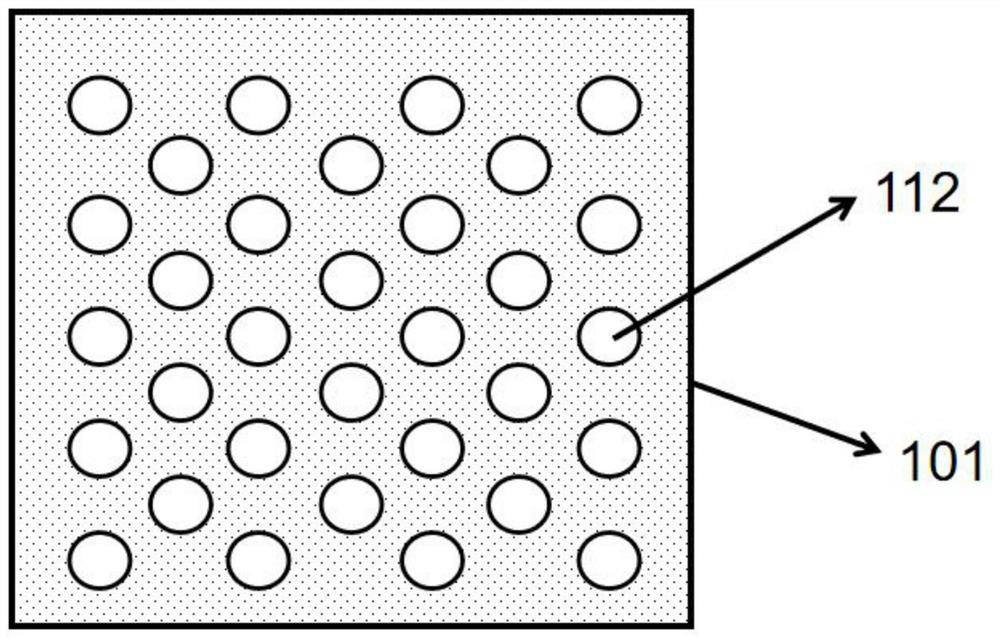
InactiveCN112701198AHigh scattering rateImprove reflection efficiencySemiconductor devicesPatterned substrateLight-emitting diode
The invention discloses a patterned substrate, a preparation method thereof, a light emitting diode and a preparation method of the light emitting diode. In one embodiment, the patterned substrate comprises a substrate and a plurality of patterned structures which are formed on the surface of the substrate and are periodically and tightly arranged, and the minimum distance between the adjacent patterned structures is smaller than or equal to 0.1 [mu]m; the pattern structure comprises a first part formed on the surface of the substrate and a second part formed above the first part, and the first part comprises a cylindrical part, and a first protruding part and a second protruding part which are uniformly distributed around the cylindrical part; and the first protruding parts and the second protruding parts are arranged at intervals, and the cross section area of the first protruding parts is larger than or equal to that of the second protruding parts. Therefore, the patterned substrate and the light emitting diode provided by the invention can effectively reduce the area and dislocation density of the epitaxial crystal surface and improve the light emitting efficiency; and the scattering efficiency of the light can be further improved, and the brightness of the LED is improved.
Owner:FUJIAN JING AN OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
LED fluorescent lamp with large light emitting angle
InactiveCN104141887AImprove the efficiency of scatteringIncrease the light output anglePoint-like light sourceElectric lightingEngineeringRadian
The invention discloses an LED fluorescent lamp with a large light emitting angle, and belongs to the technical field of LED illumination lamps. The LED fluorescent lamp comprises an optically designed lamp cover, and a lamp holder with a circularly arched cross section, wherein the lamp cover and the lamp holder are buckled to take a cylindrical shape; a lamp tube inner hole forms an accommodating space; an aluminum baseplate clamping groove, a bar-shaped aluminum baseplate, a light emitting module, a barb, a lamp cover clamping groove and a heat dissipating aluminum piece are arranged in the accommodating space; the splayed heat dissipating aluminum piece is connected to the two ends of the aluminum baseplate clamping groove; the aluminum baseplate clamping groove and the heat dissipating aluminum piece are connected as an integrated structure; the inclination of the heat dissipating aluminum piece is within 180-240 degrees; and the radian of the lamp cover is larger than the radian of the lamp holder. Light rays are fully reflected and diffused through the specially designed lamp cover, so that the light emitting rate reaches 94%; the light emitting angle reaches 180-240 degrees through the heat dissipating aluminum piece with adjustable inclination angle; and the LED fluorescent lamp with the large light emitting angle improves the scattering efficiency, increases the light emitting angle of the light rays, reduces the irradiation dead angle, and enhances the light emitting strength and uniformity of the lamp cover.
Owner:江苏盛弘光电科技有限公司
Passive tag for electronic tag field
InactiveCN102903004ANo working thresholdLong communication distanceRecord carriers used with machinesEngineeringCopper
The application discloses a passive tag which comprises a copper-clad substrate, an antenna and a dielectric slab, wherein the antenna and the dielectric slab are all positioned on the copper-clad substrate; the antenna comprises an antenna upper arm and an antenna lower arm; the antenna upper arm and the antenna lower arm are positioned on the same straight line; a gap is formed between the antenna upper arm and the antenna lower arm; a plurality of metal wires which are parallel to each other and between two of which a gap is formed are arranged on the dielectric slab; the extending direction of the metal wire is parallel to the antenna upper arm and the antenna lower arm; and the separated end parts of the antenna upper arm and the antenna lower arm are respectively connected with two ends of a metal wire in the plurality of metal wires. The passive tag does not have a working threshold, is long in communication distance, safe, reliable, small in size, convenient to process, low in cost and convenient to popularize and use, wherein the cost of a reader-writer can be reduced obviously.
Owner:盛世铸成科技(北京)有限公司
OLED display panel and manufacturing method of OLED display panel
InactiveCN106299151AImprove consistencyImprove scattering efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLuminous efficacyElectrode
The invention provides an OLED display panel. The OLED display panel comprises a substrate, a first electrode, a partition wall and a scattering layer, wherein the partition wall is positioned between the substrate and the first electrode; and the scattering layer is formed on the substrate and is positioned in an area surrounded by the partition wall. According to the OLED display panel provided by the invention, the scattering efficiency of the scattering layer can be improved, so that the luminous efficiency can be strengthened, and the luminous performance is improved. The invention also provides a manufacturing method of the OLED display panel.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Diffuse reflective film and method of making the same
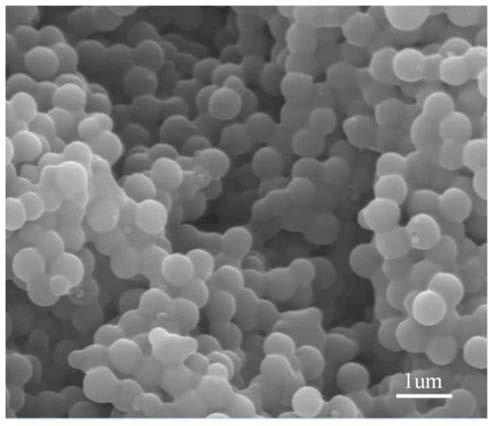
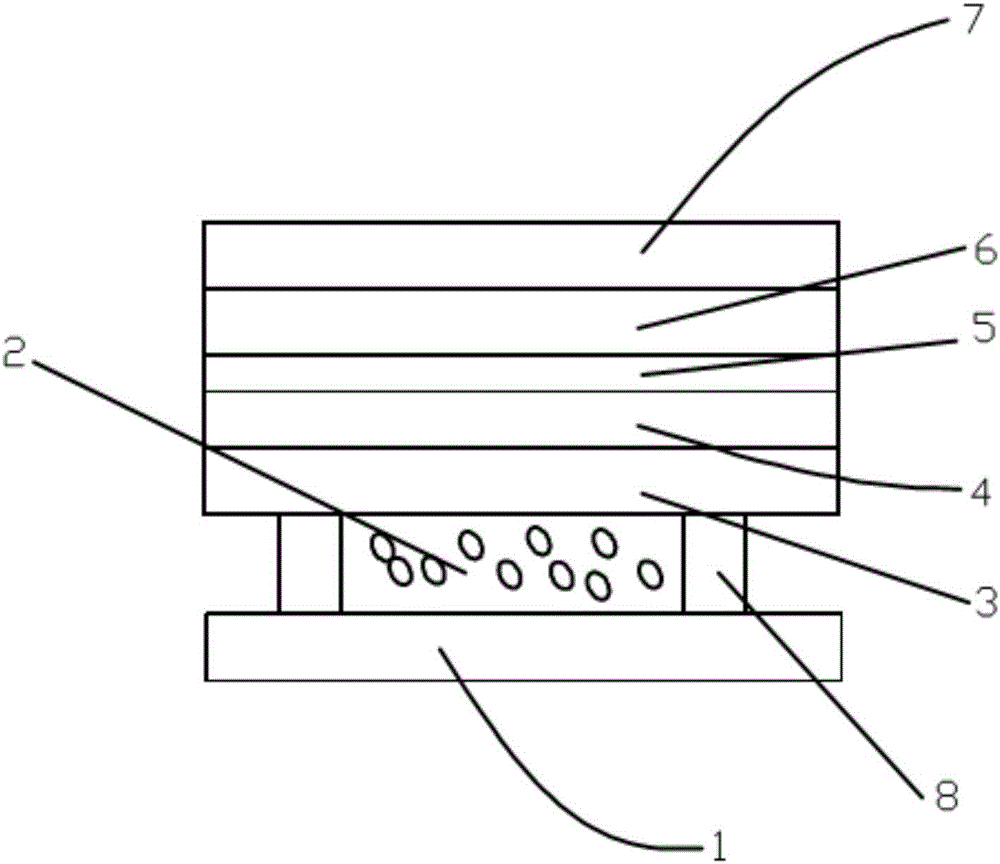
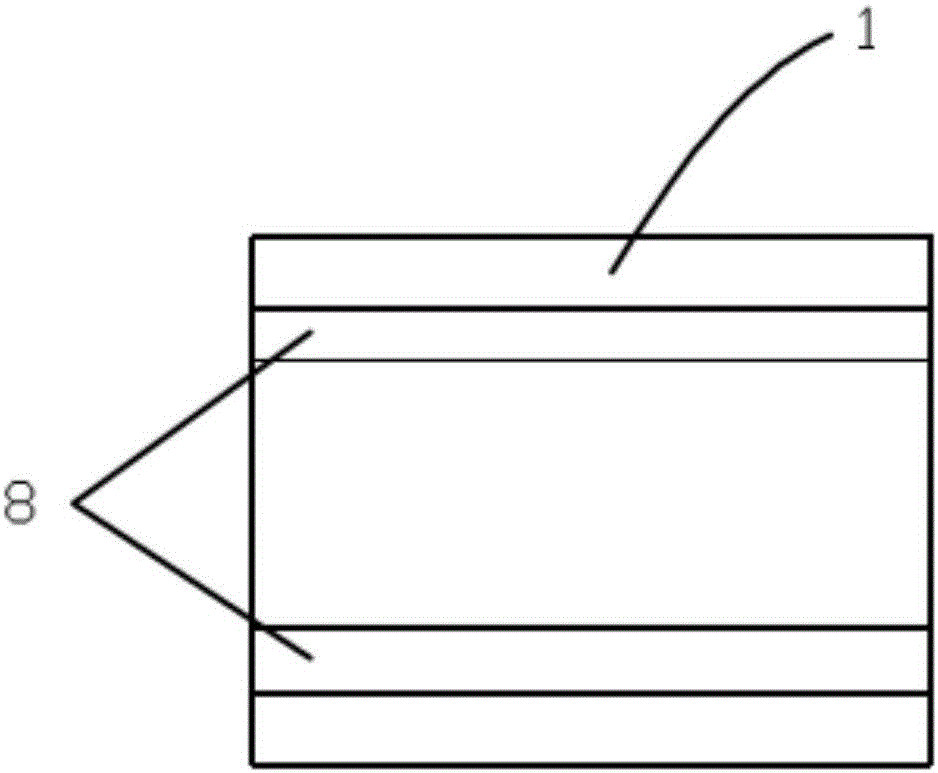
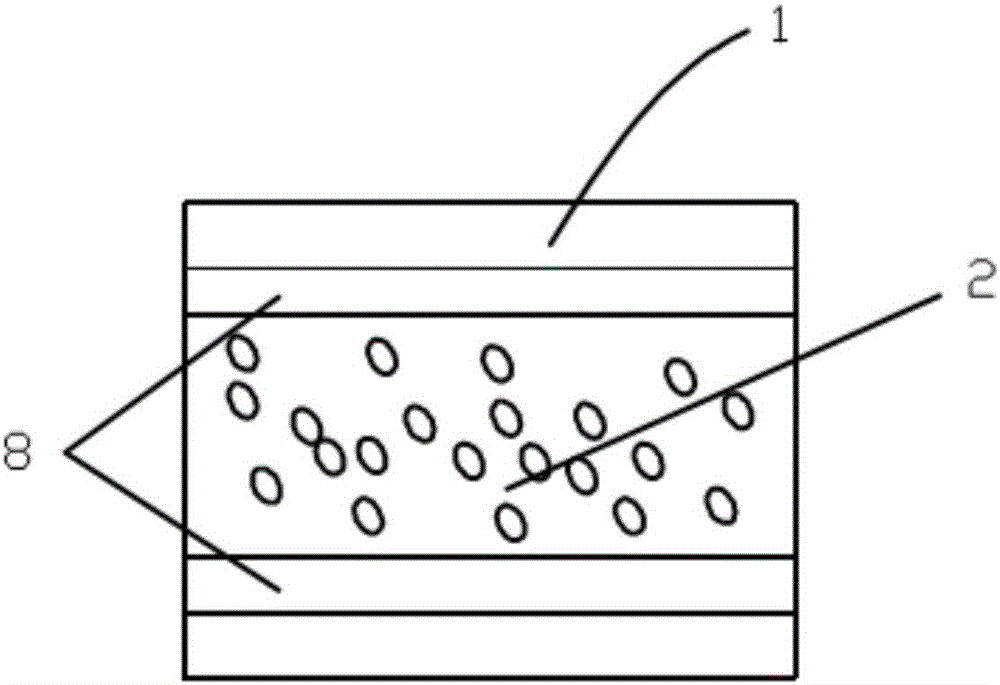
InactiveCN105785488BImprove scattering efficiencyImprove reflectivityDiffusing elementsMicrosphereDiffuse reflection
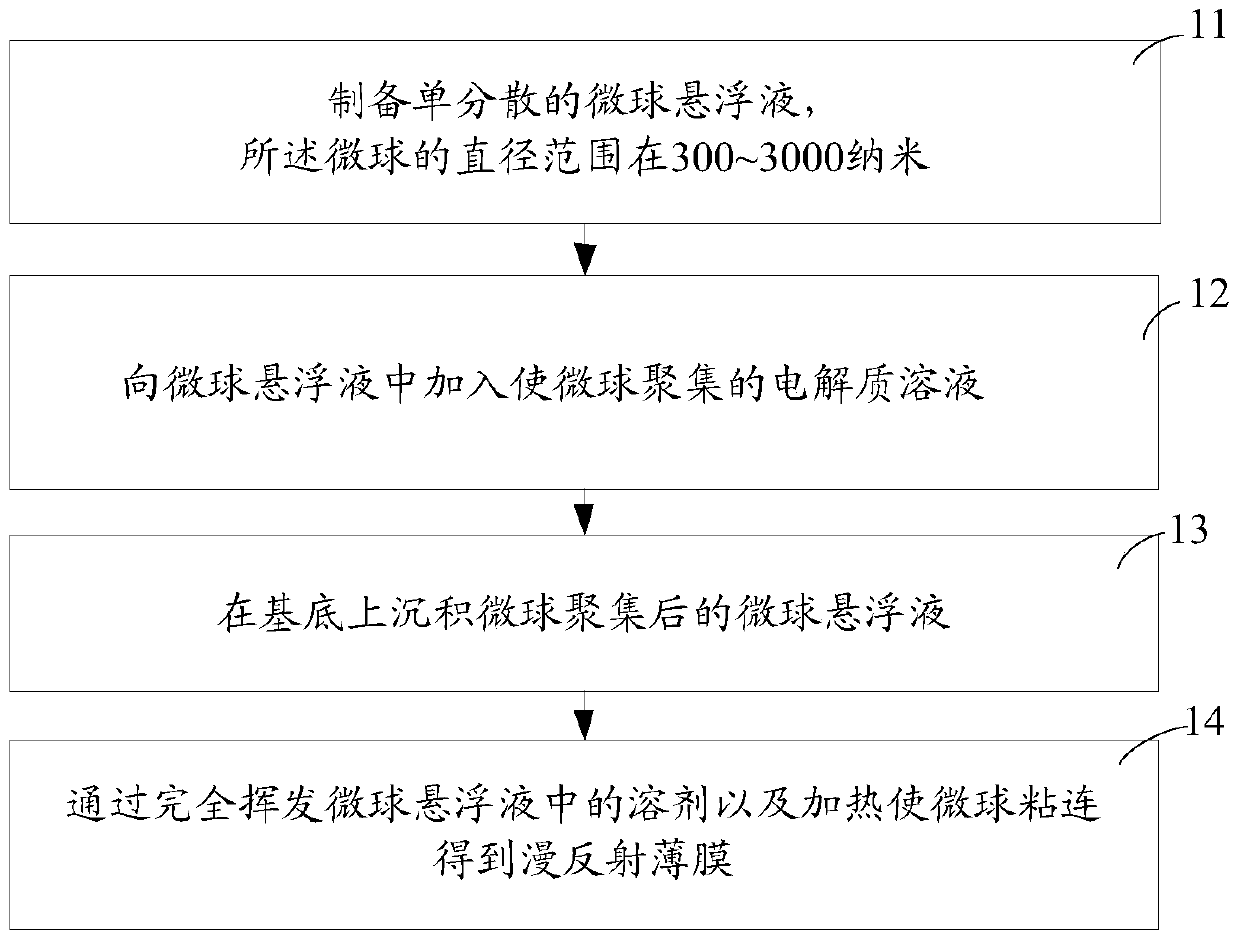
The invention discloses a diffuse reflection film. The diffuse reflection film is composed of randomly-stacked monodisperse microspheres which have no light absorption ability or have a low light absorption rate; the diameter of the microspheres ranges from 300 to 3000 nm. The invention also discloses a manufacturing method of the diffuse reflection film. The method includes the following steps that: a microsphere suspension is prepared, the diameter of microspheres ranging from 300 to 3000 nm; an electrolyte solution making the microspheres aggregated is added into the suspension; the microsphere-aggregated microsphere suspension is deposited on a substrate; and a solvent in the microsphere suspension is completely volatilized, heating is carried out so as to make the microspheres adhered, and therefore, the diffuse reflection film can be obtained. With the diffuse reflection film and the manufacturing method thereof provided by the invention adopted, high-reflectivity diffuse reflection can be realized with a very thin film material.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Backlight module
ActiveUS10042205B2Reduce manufacturing costReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight guideLight reflection
A backlight module includes a light guide plate, a plurality of light transmission elements and a light source. The light guide plate has at least one light incident surface, and the light transmission elements are disposed near the light incident surface and aligned to from at least one light transmission element row. The light source is disposed near one end of the light transmission element row and capable of emitting a light beam to the light transmission element row. Each of the light transmission elements reflects a part of the light beam to the light guide plate to form multiple independent light reflection paths, and the light transmission elements successively transmits a part of the light beam to form a light transmission path in the light transmission element row.
Owner:CORETRONIC
Microwave signal generation device and method of photoelectric oscillator based on liquid core optical fiber Brillouin scattering effect
ActiveCN105811225BImprove scattering efficiencyReduce phase noiseSolid masersEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a microwave signal generating device and method of a photoelectric oscillator based on a liquid-core optical fiber Brillouin scattering effect.The microwave signal generating device includes a Brillouin scattering pump laser, an isolator, a modulator, a liquid-core optical fiber, a signal laser, a first circulator, a third laser, a second ring, a polarization beam splitter, a first optical fiber, a second optical fiber, a first polarization controller, a second polarization controller, a polarization beam combiner, a photoelectric detector, a coupler and a power amplifier.The device and the method can not only produce high-frequency microwave signals and can also obtain tunable microwave signals wider in tuning range.
Owner:东台城东科技创业园管理有限公司
Lawn lamp for expelling insects by using light scattering
PendingCN113566149ARealize the scattering effectTo achieve the dispel effectElectric circuit arrangementsLighting elementsLiquid waterMetal sheet
The invention relates to the related technical field of lawn lamps, and discloses a lawn lamp for expelling insects by using light scattering. The lawn lamp comprises a mounting base, a liquid injection lamp shell capable of being filled with liquid is fixedly mounted on the mounting base, the liquid injection lamp shell is filled with water to improve the lighting effect and cooperatively realize the light scattering insect expelling effect, a light sensation lifting device is fixedly installed in the liquid injection lamp shell, and the light sensation lifting device comprises a function carrying body. According to the lawn lamp capable of expelling insects through light scattering, the light scattering principle is applied, common pests such as mosquitoes and flies in gardens have the unified characteristic of compound eye insects, and when the scattering illumination cavity filled with waterworks without illumination in the daytime, the light scattering effect can be achieved through cooperation of metal sheets in the cavity and liquid water, so that the effect of dispersing the compound eye insects can be achieved.
Owner:王焕荣
A deep ultraviolet semiconductor light-emitting diode epitaxial structure
ActiveCN112635628BImprove lattice qualityQuality improvementSemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencySemiconductor materials
The invention relates to an epitaxial structure of a deep ultraviolet semiconductor light emitting diode. The epitaxial structure sequentially includes a pattern substrate, a semiconductor buffer layer, an n-type semiconductor material layer, a multi-quantum well layer, a p-type electron blocking layer, and a p-type semiconductor material transport layer along the epitaxial direction; etching on the pattern substrate There are grooves. On each groove, a cavity structure is grown vertically upward. The cavity structure passes through the semiconductor buffer layer, n-type semiconductor material layer, and multiple quantum well layers. The top positions are the following three types: the first , aggregated in the p-type electron blocking layer, the aggregation depth of the cavity in the p-type electron blocking layer is 10-100nm, or, the second type, continue to pass through the p-type electron blocking layer, and aggregate in the p-type semiconductor material transport layer, The aggregation depth of the cavity in the p-type semiconductor material transport layer is 10-500nm, or, the third type, continue to pass through the p-type electron blocking layer and the p-type semiconductor material transport layer, the cavity is not aggregated, and the p-type semiconductor material The surface of the transmission layer appears as circular holes. The invention can improve the internal quantum efficiency of the deep-ultraviolet LED; and the cavity structure is incorporated into the quantum well, which can effectively improve the light scattering characteristics and improve the light extraction efficiency of the deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diode.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com