Patents
Literature
87results about How to "Efficiently sensed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
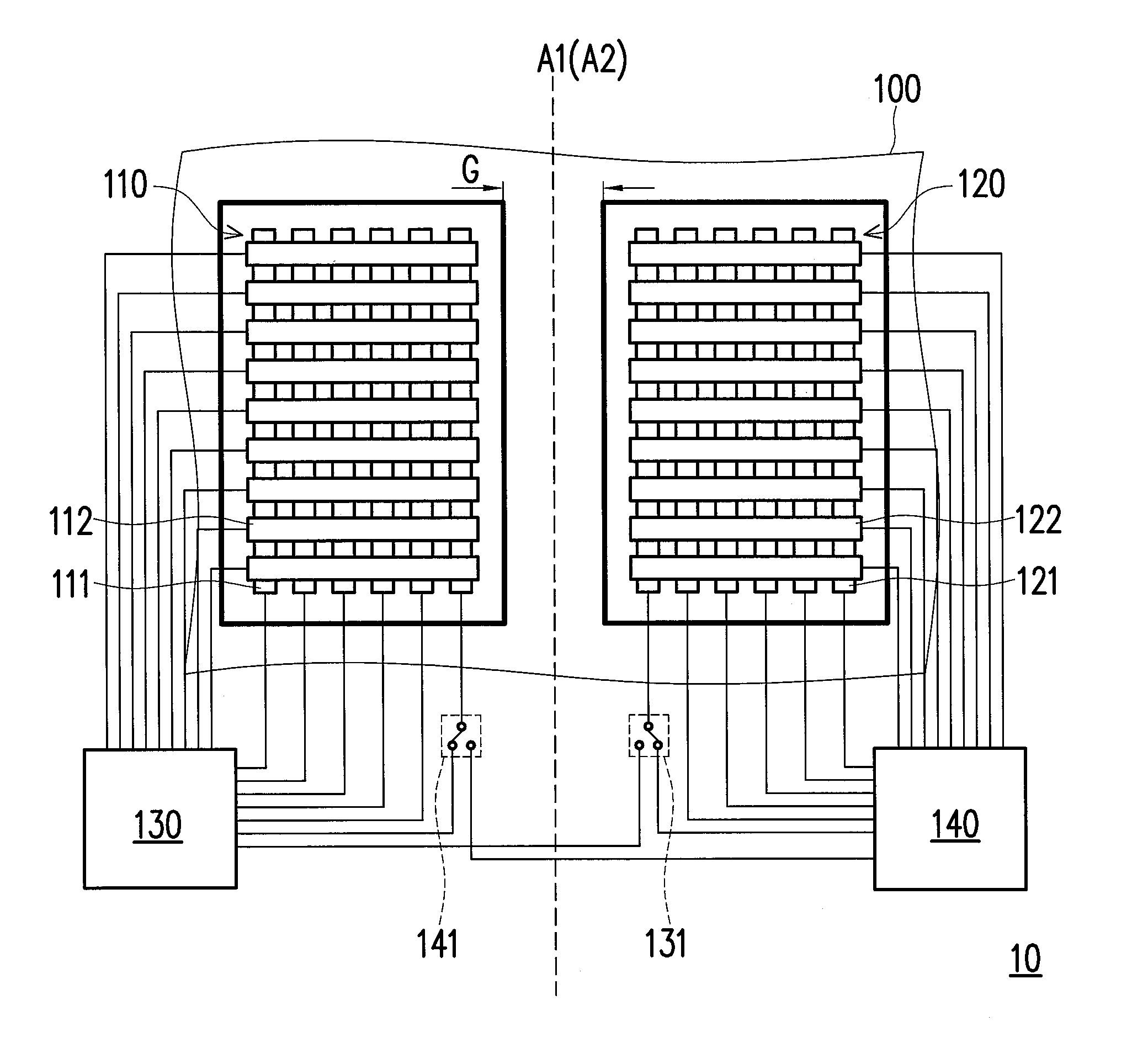
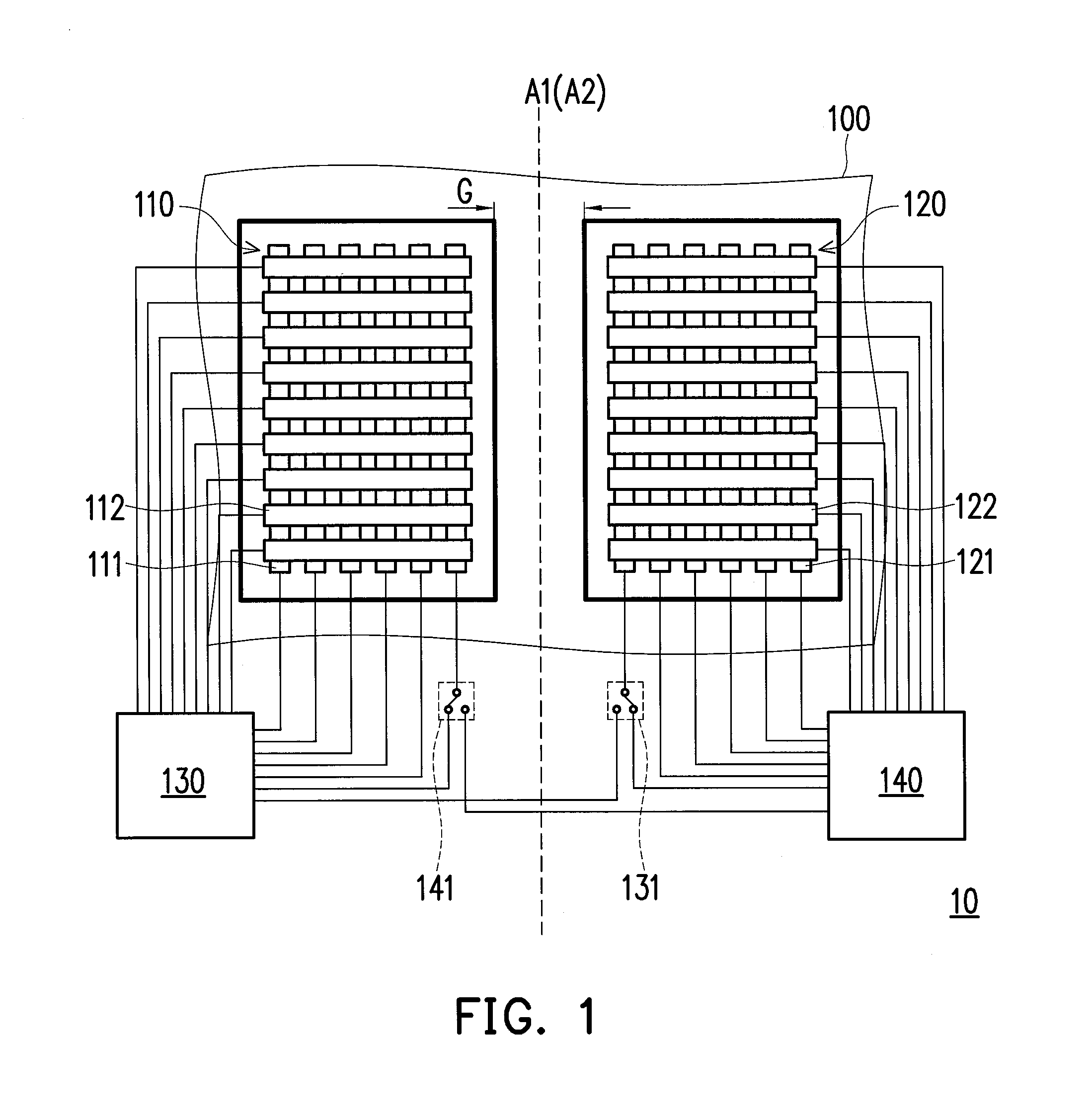
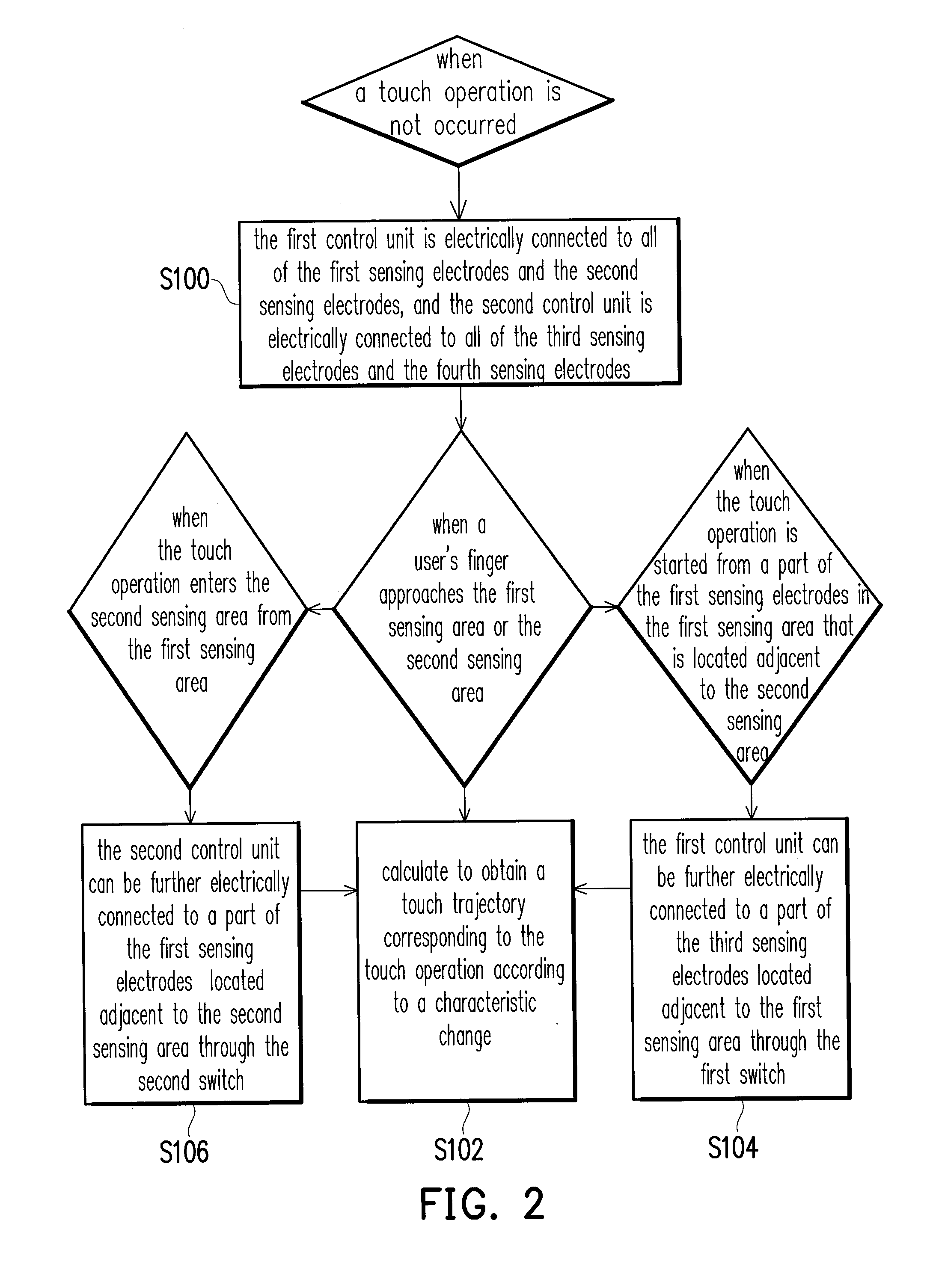
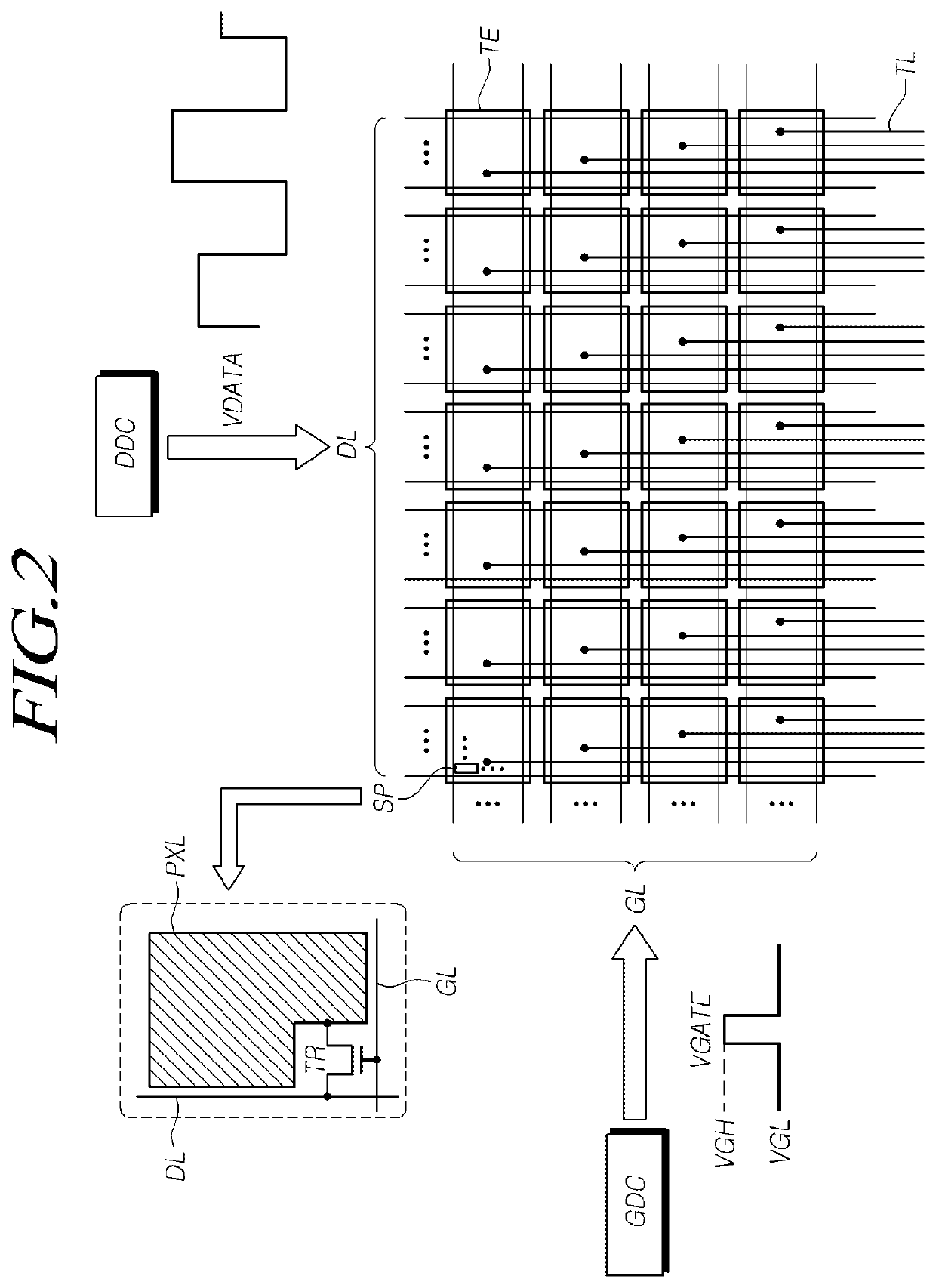
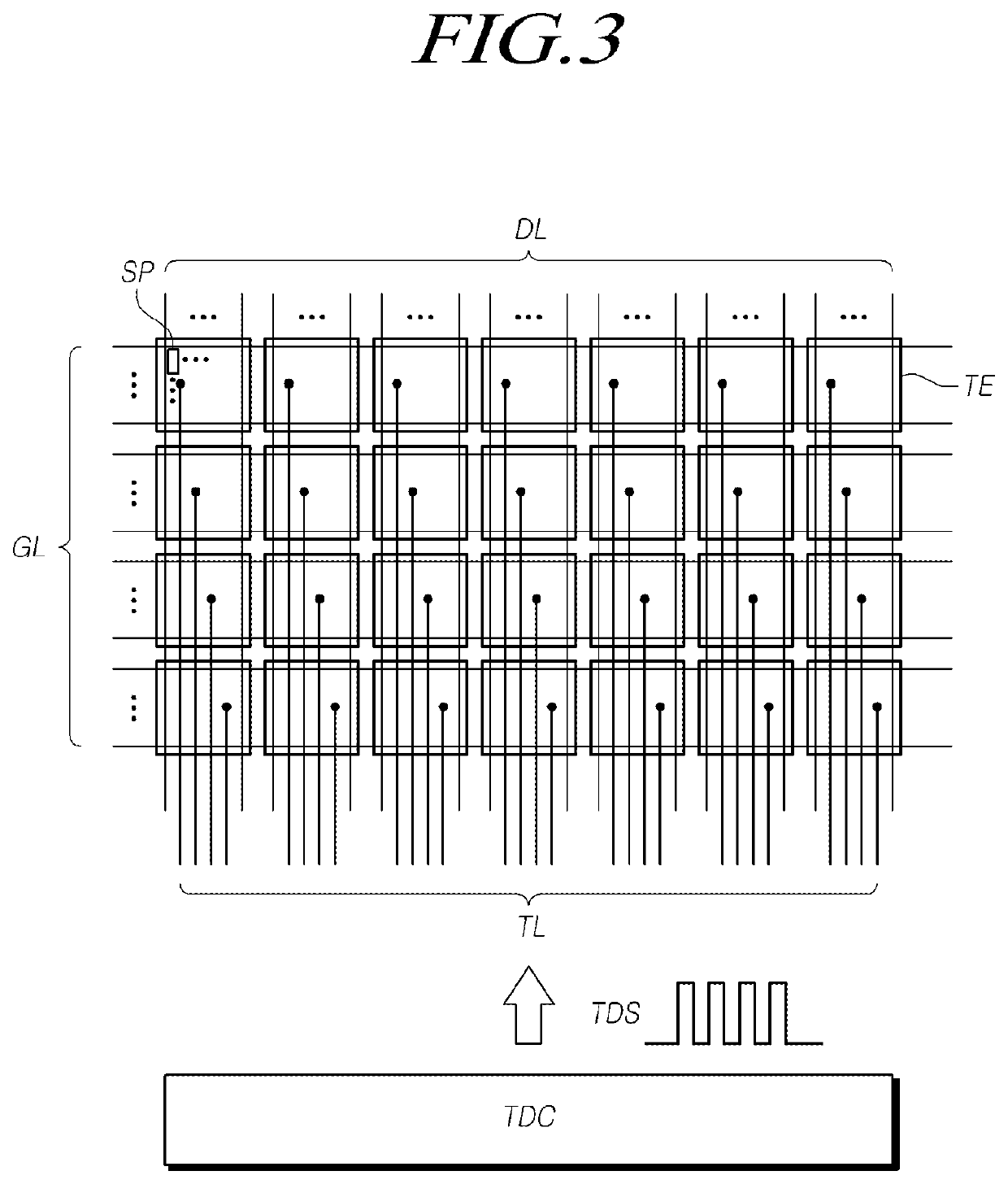
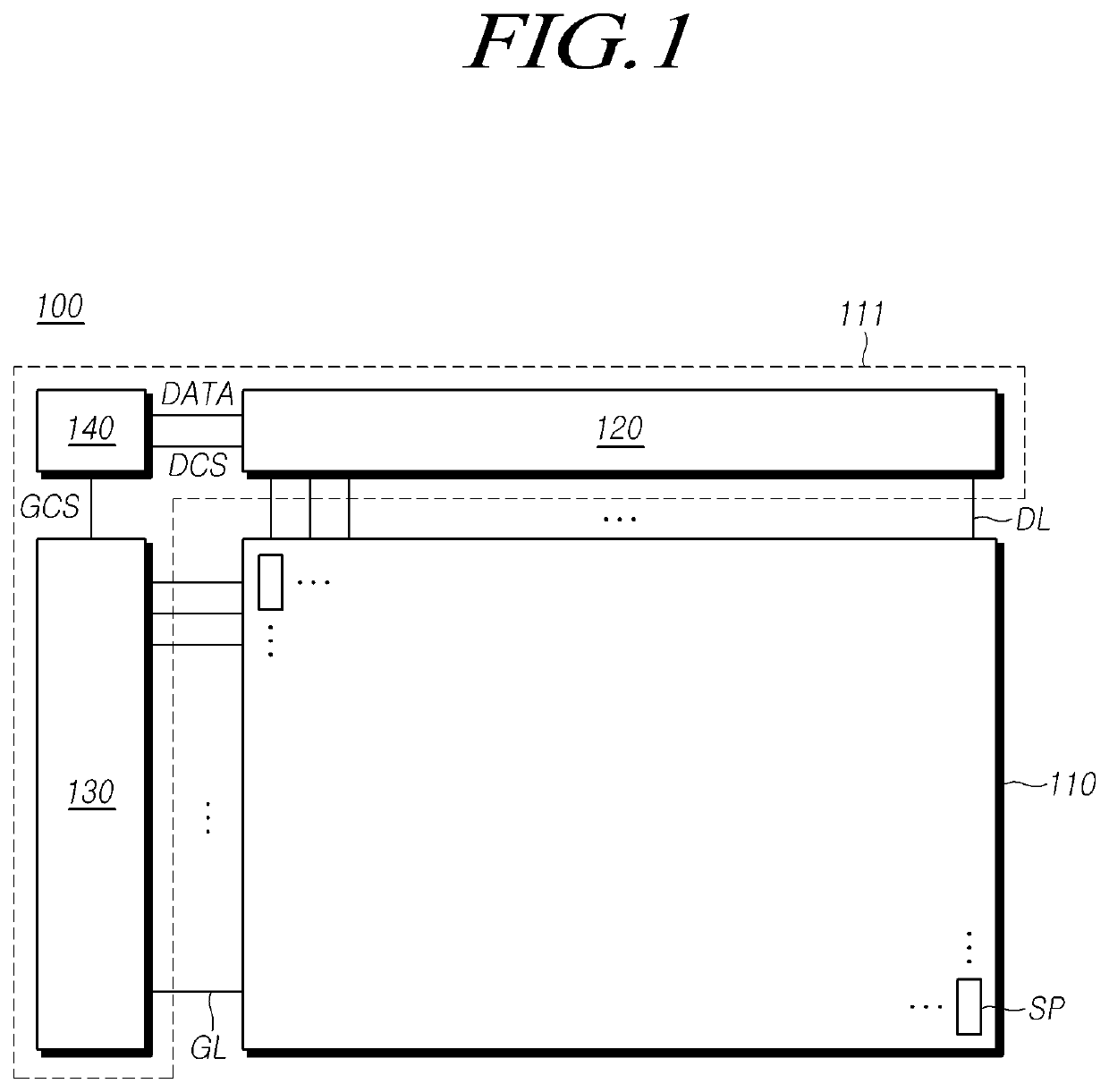
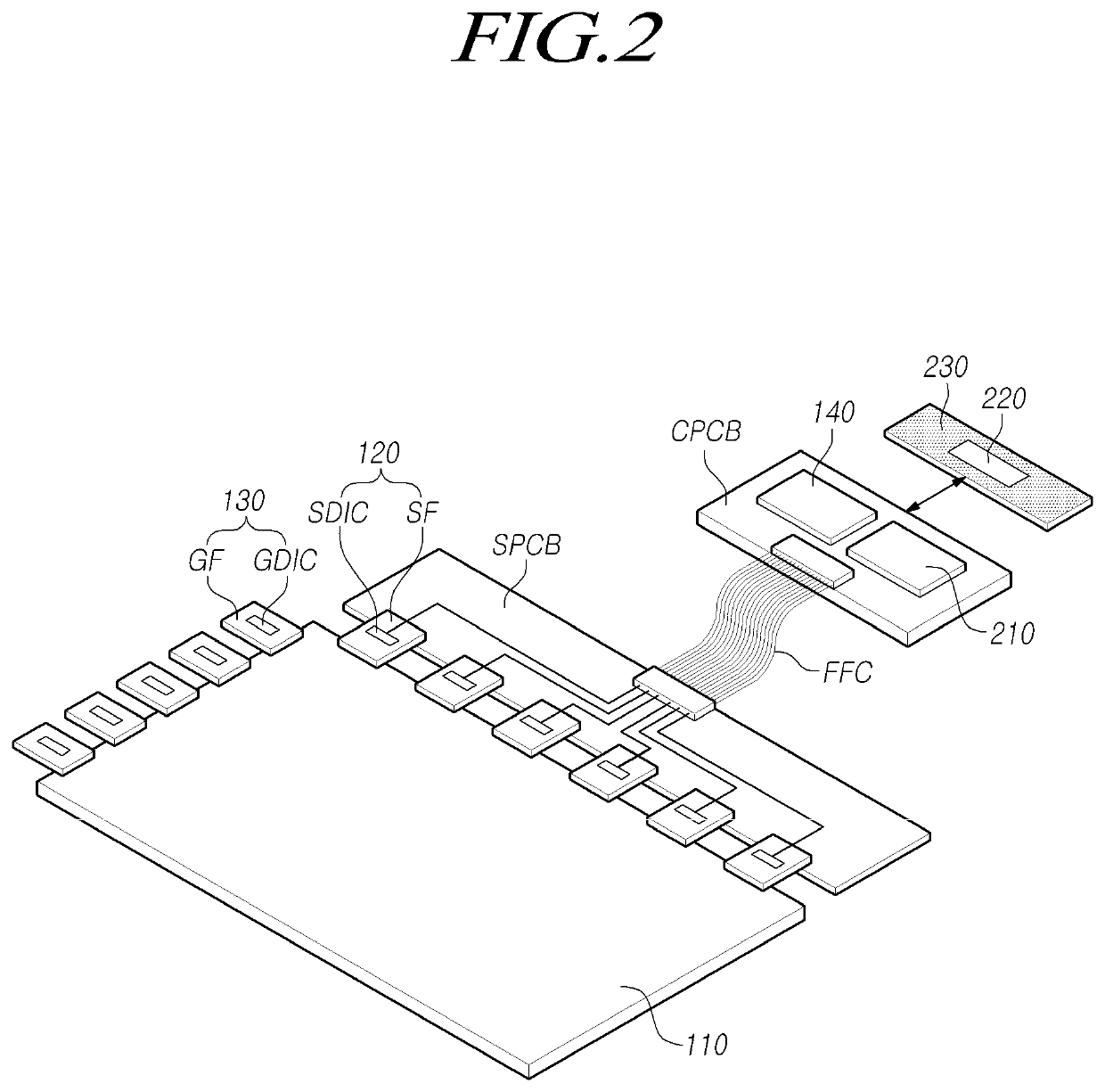
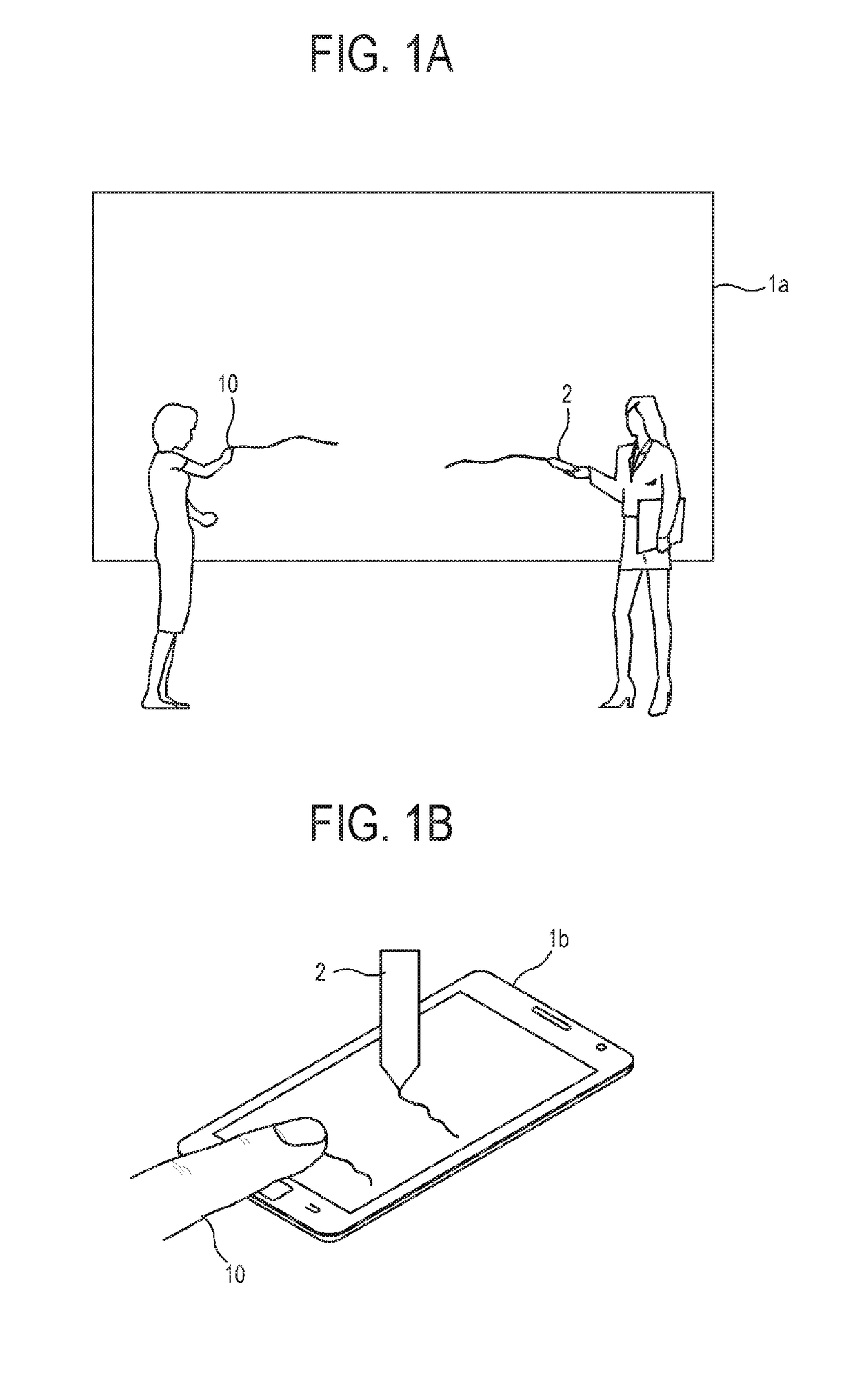
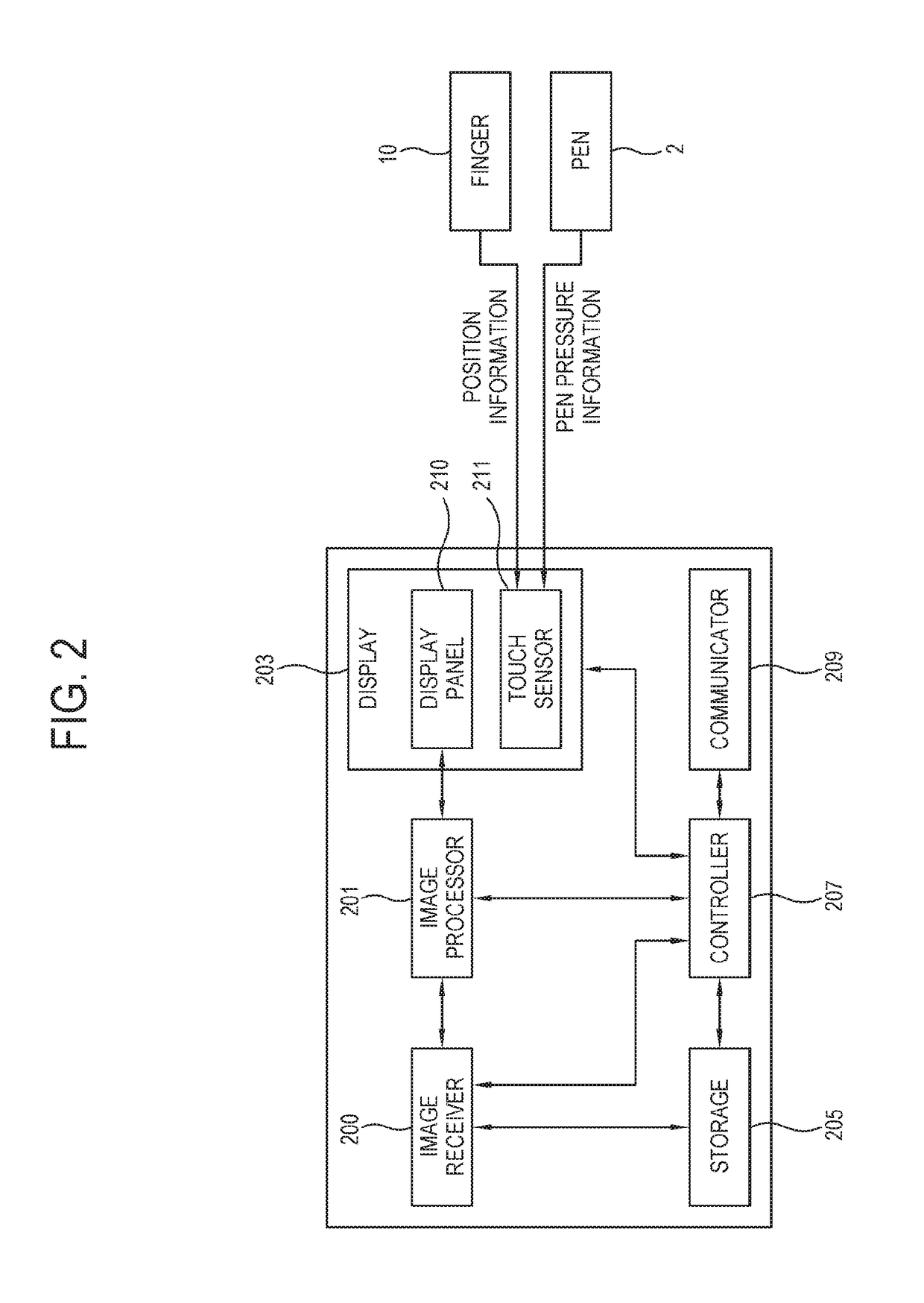
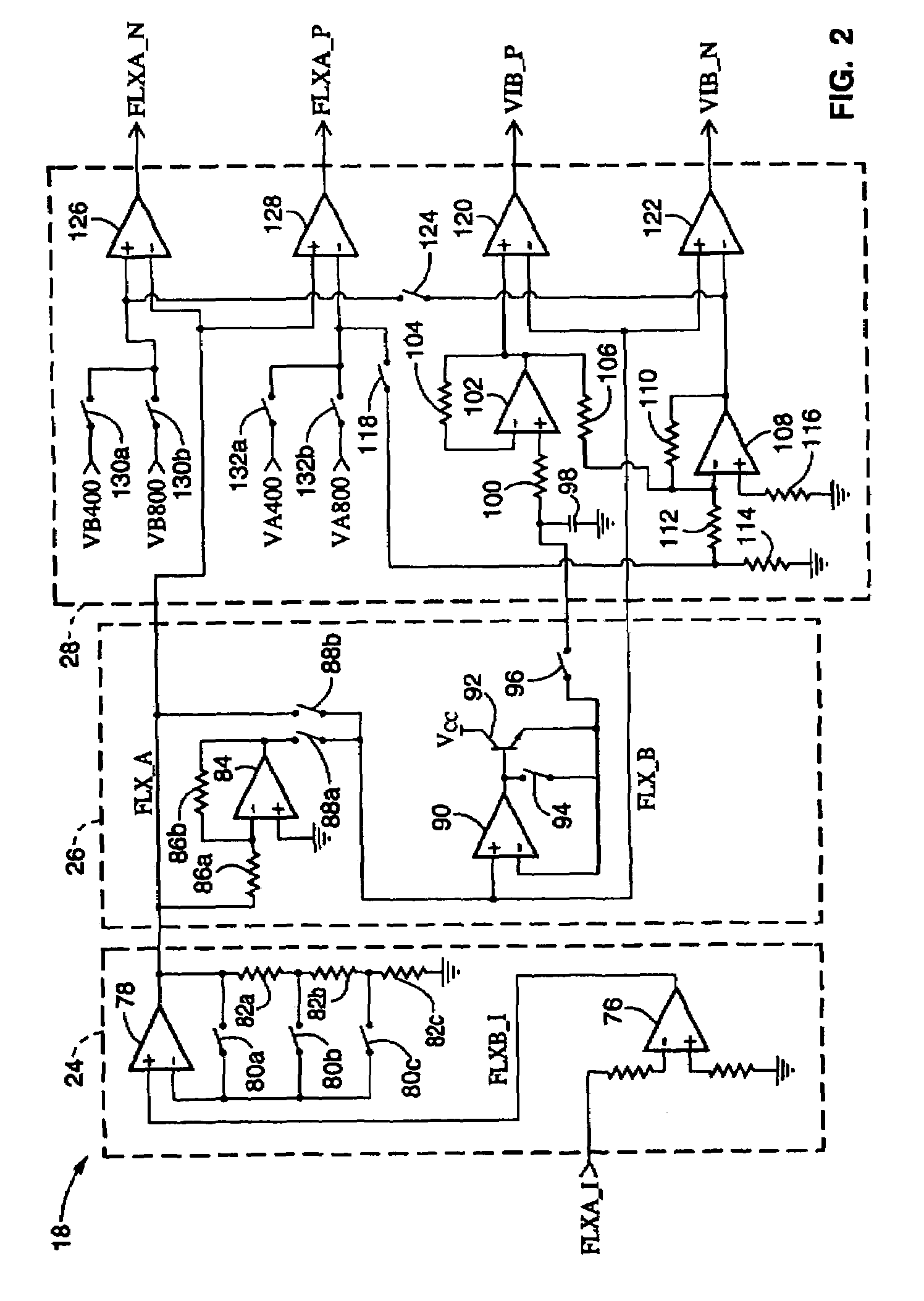
Touch panel and sensing method thereof
ActiveUS20150242022A1Increased durabilityEfficiently sensedDetails for portable computersInput/output processes for data processingComputer scienceTouch panel
A touch panel and a sensing method thereof are provided. The sensing method includes: sensing a touch operation on a touch panel, and getting a touch trajectory of the touch operation. When the touch operation is occurred in a first sensing area, positions of the touch operation are co-located by first sensing electrodes and second sensing electrodes of the first sensing area. When the touch operation is occurred in a second sensing area, positions of the touch operation are co-located by third sensing electrodes and fourth sensing electrodes of the second sensing area. When the touch operation is occurred between the first sensing area and the second sensing area, positions of the touch operation are co-located by the first sensing electrodes and the third sensing electrodes.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
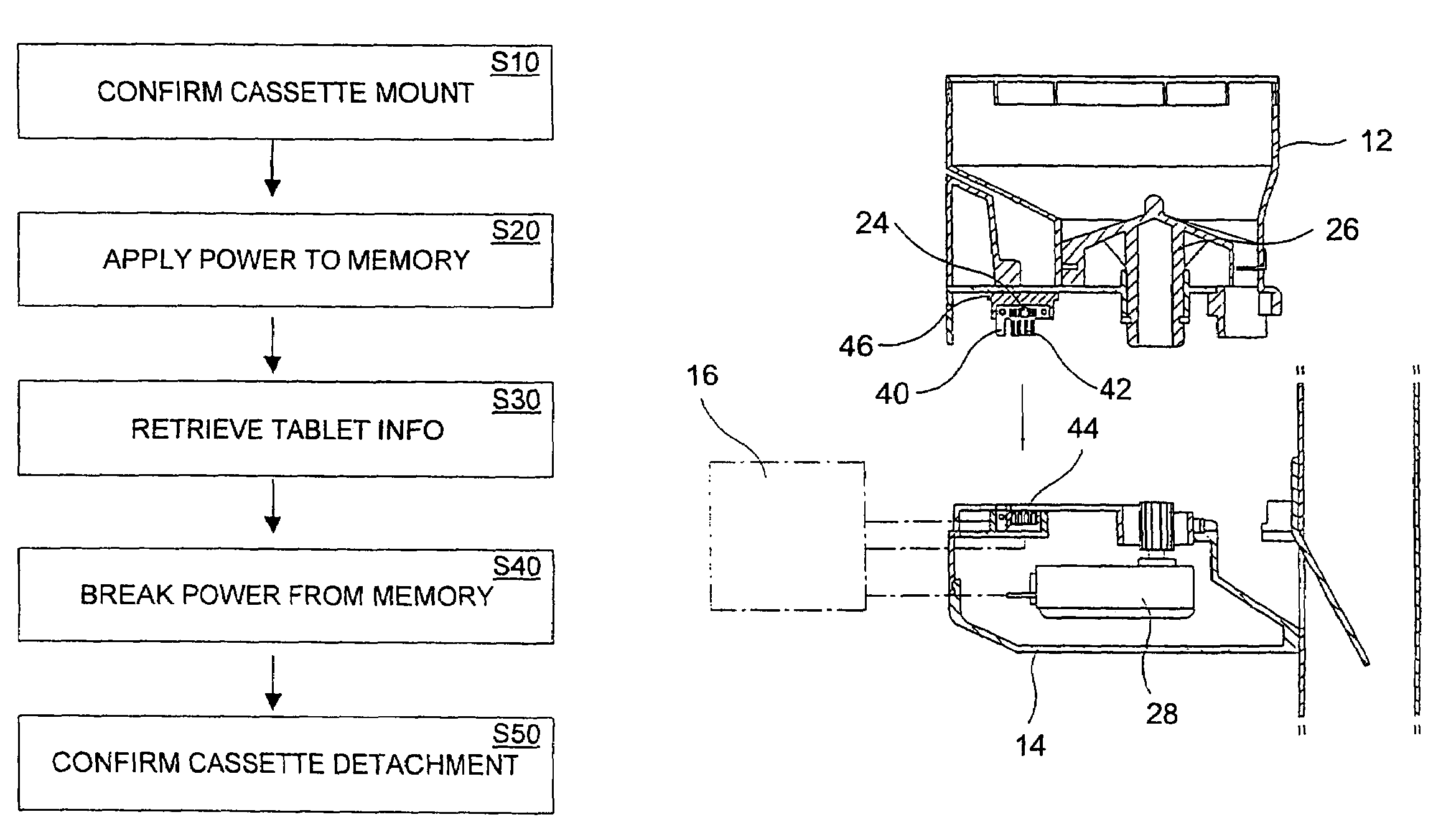
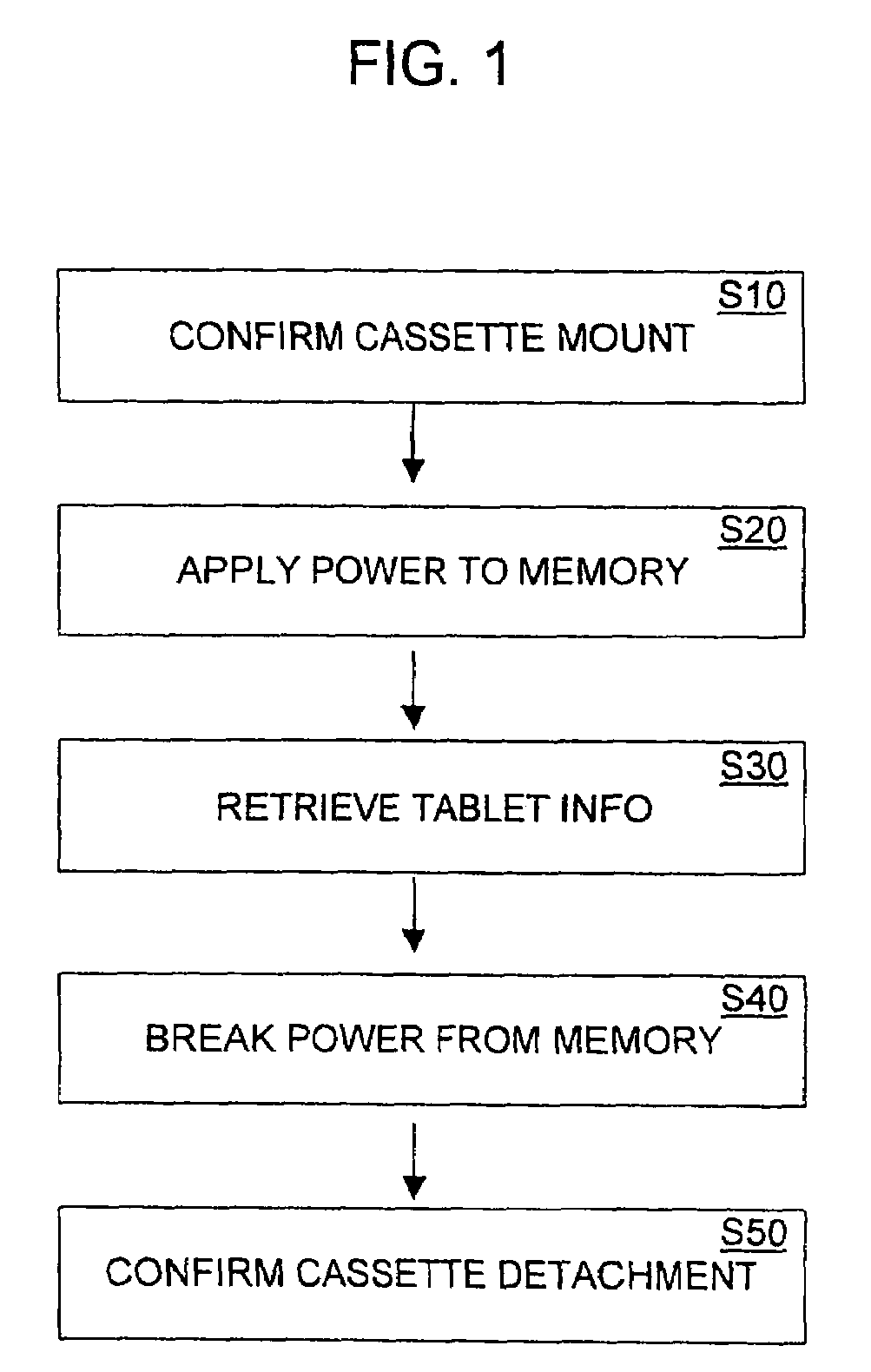
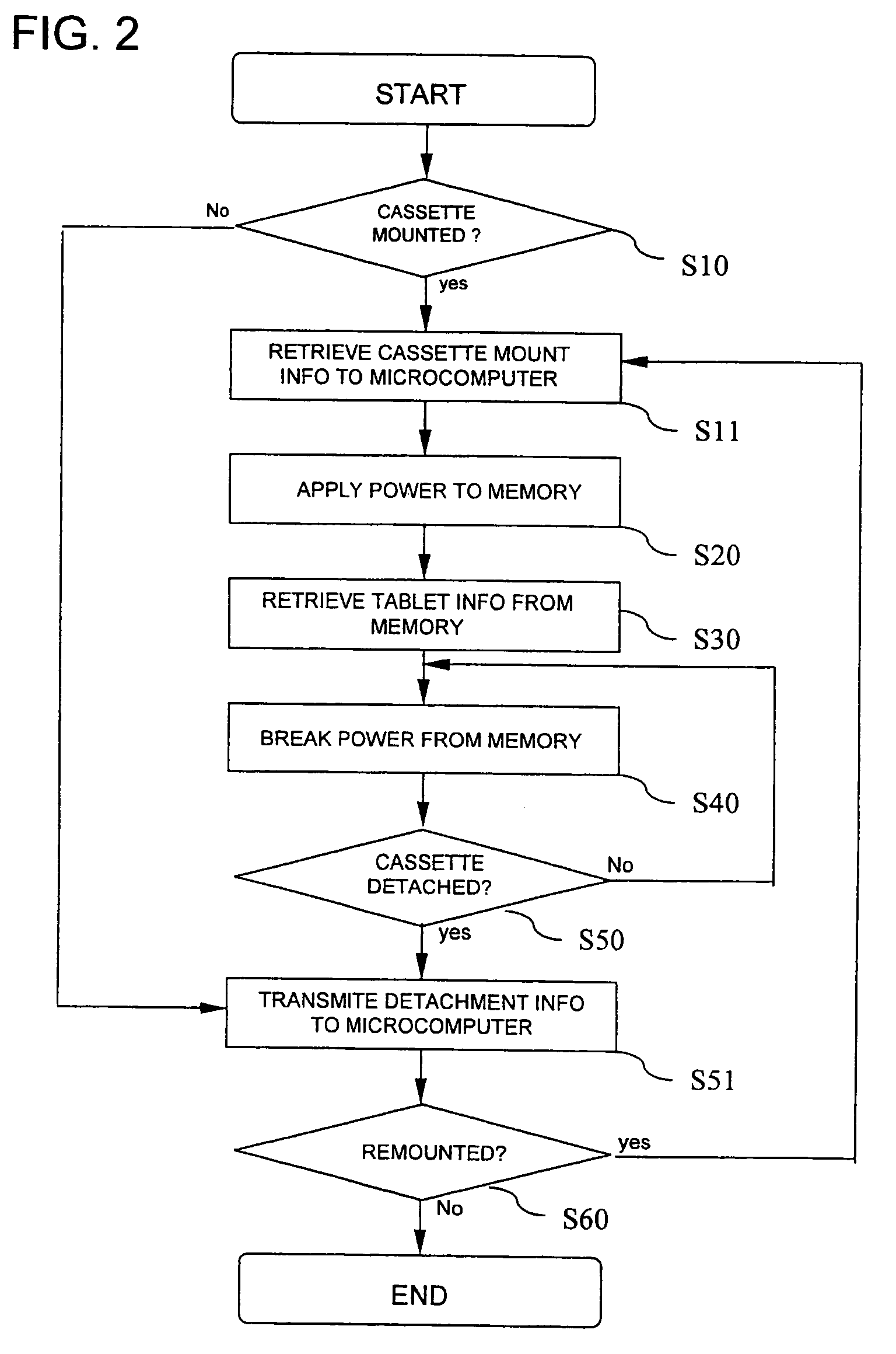
Tablet cassette control method of medication dispensing and packaging system
ActiveUS6957126B2Error minimizationEfficiently sensedDigital data processing detailsCoin-freed apparatus detailsMicrocomputerMagnetic tape
A tablet cassette control method of a medication dispensing and packaging system having a microcomputer, a medication dispensing unit with a plurality of tablet cassettes each mounted on a cassette rack, and a medication packaging unit disposed below the dispensing unit to package tablets released from the dispensing unit into a series of tablet containing paper bags, the control method comprises confirming the mounting of the tablet cassette on the cassette rack, applying a power to a memory in the tablet cassette to activate the memory, retrieving tablet information saved in the memory to the microcomputer, and breaking the power from the memory while maintaining operation of the system.
Owner:KIM JUN HO
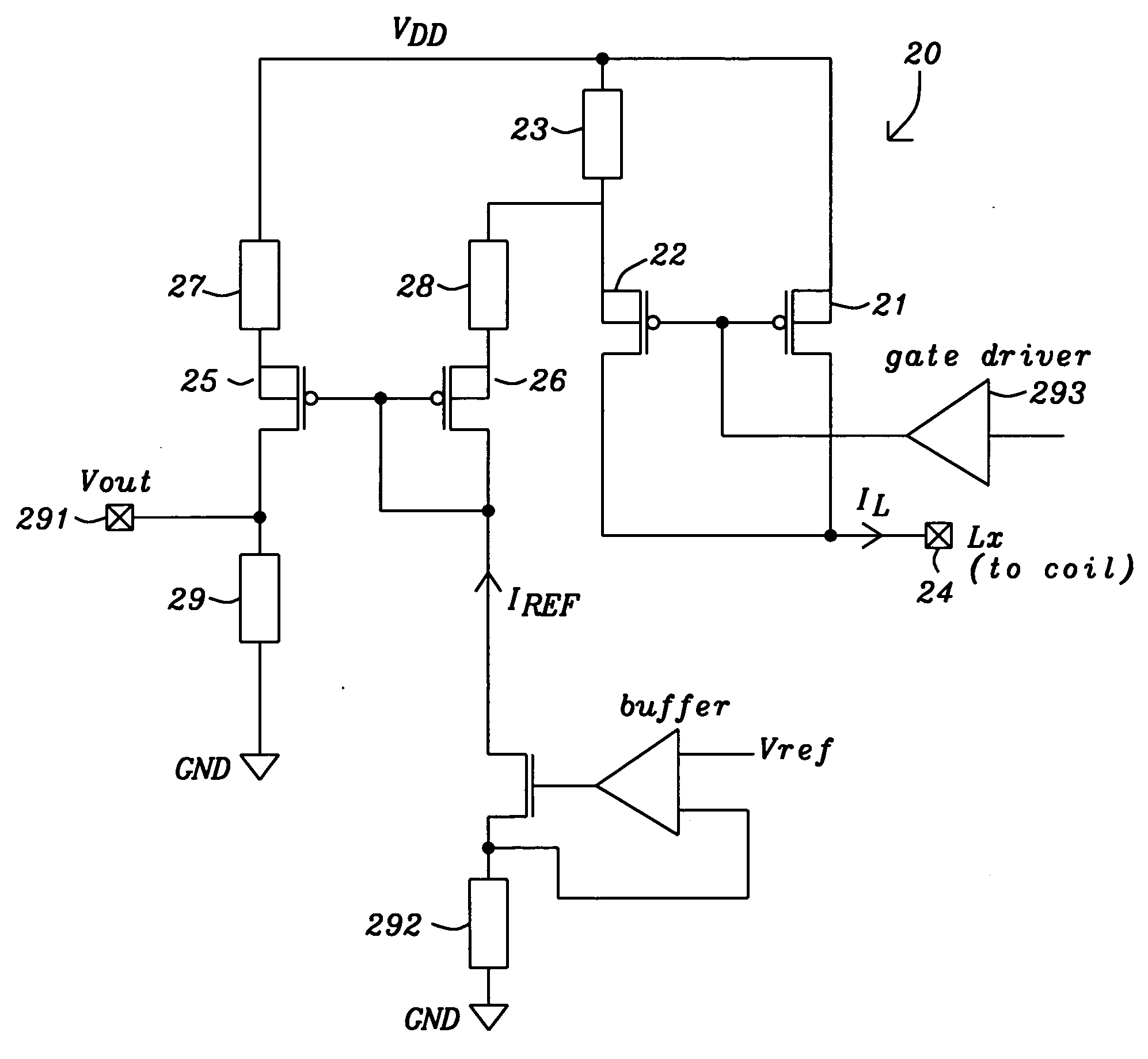
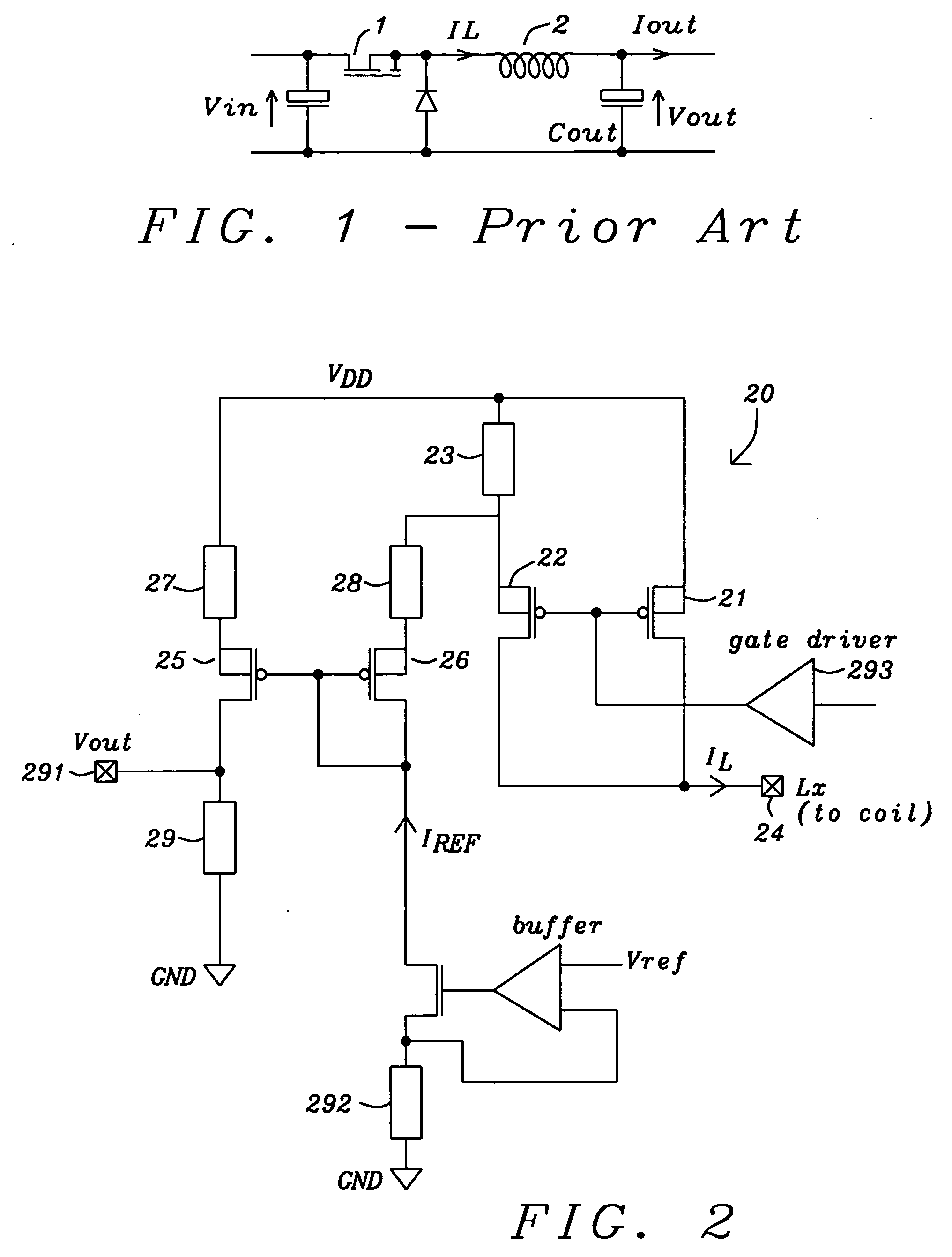
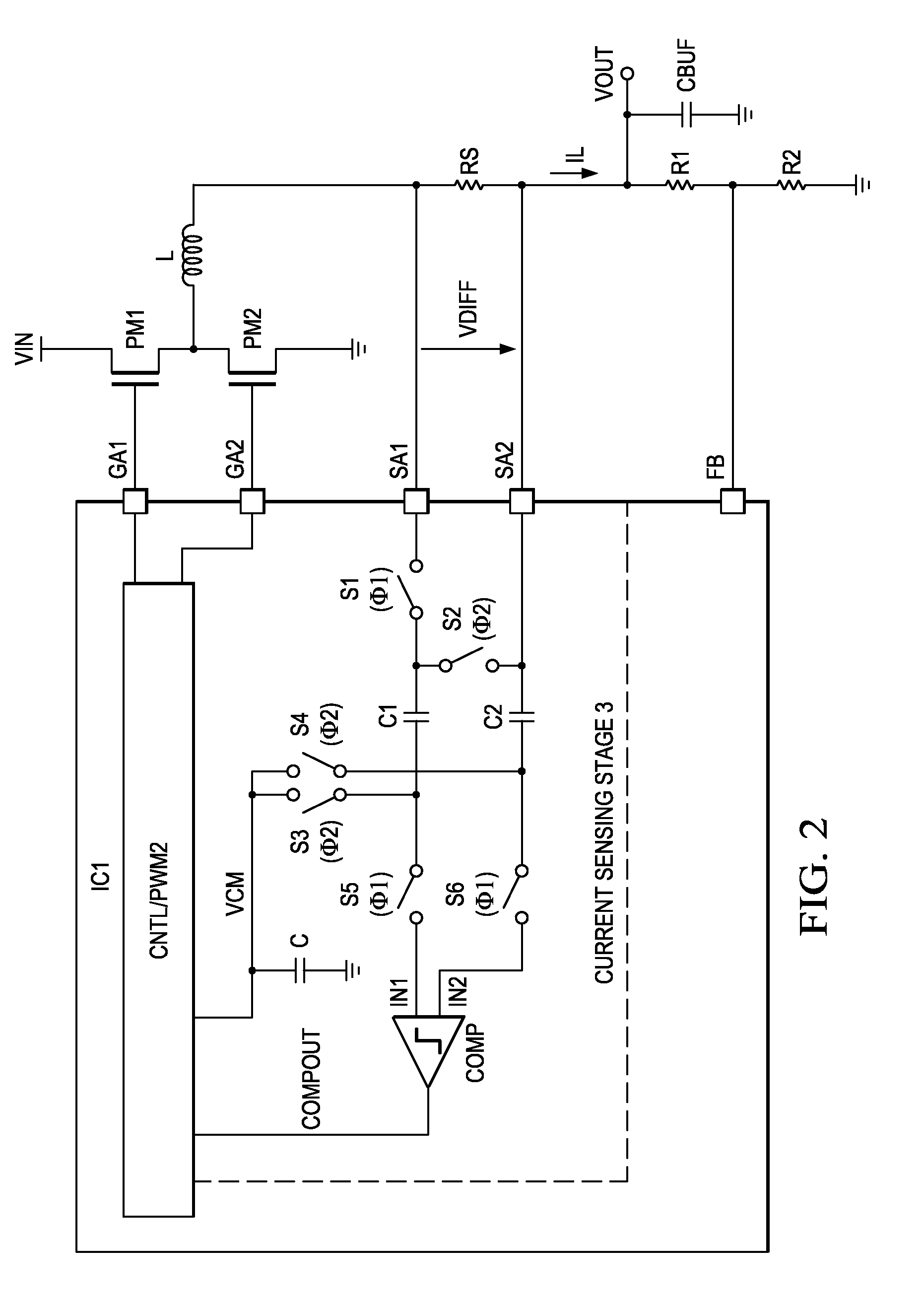
Current sensing circuit for DC/DC buck converters
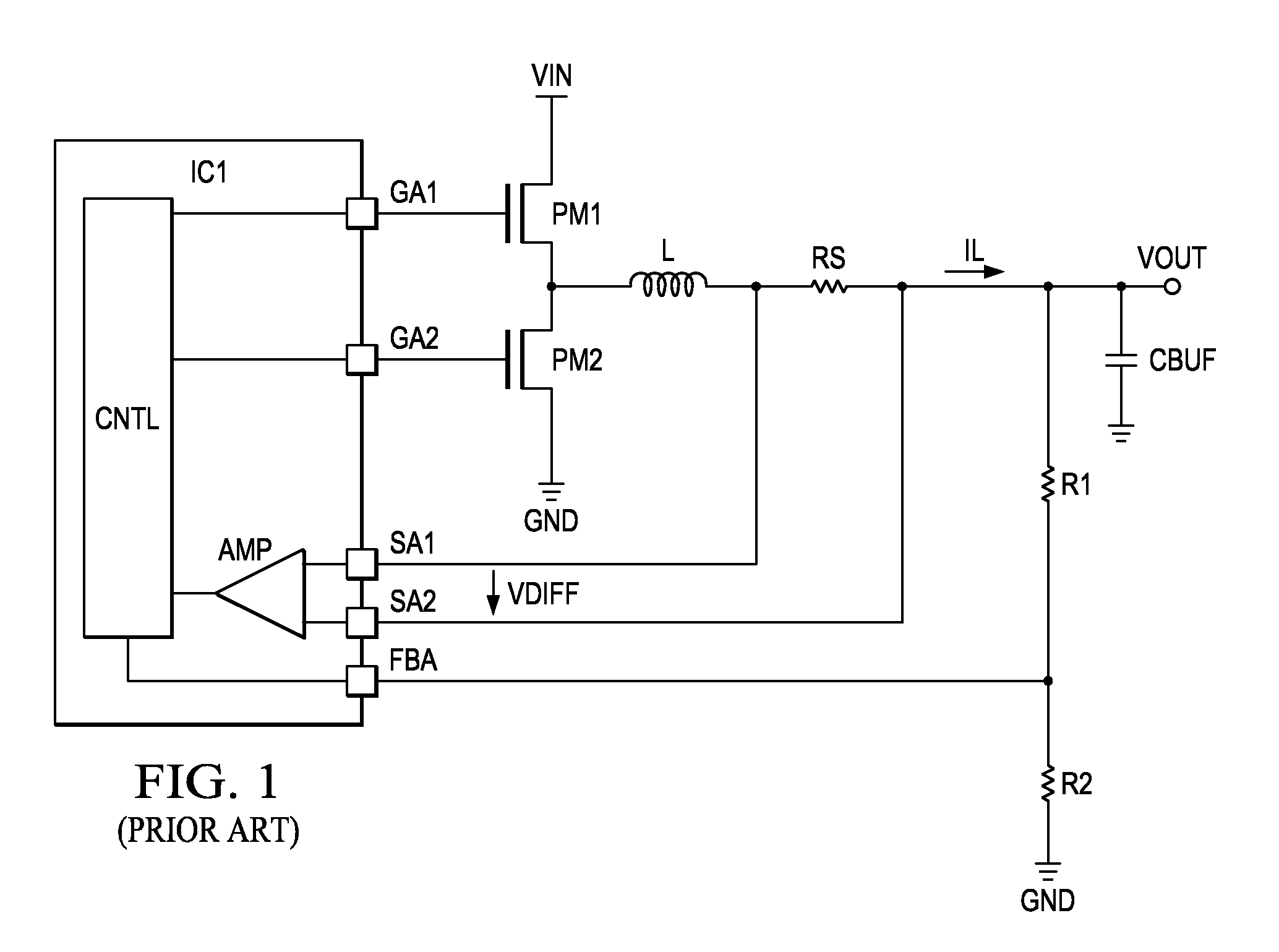
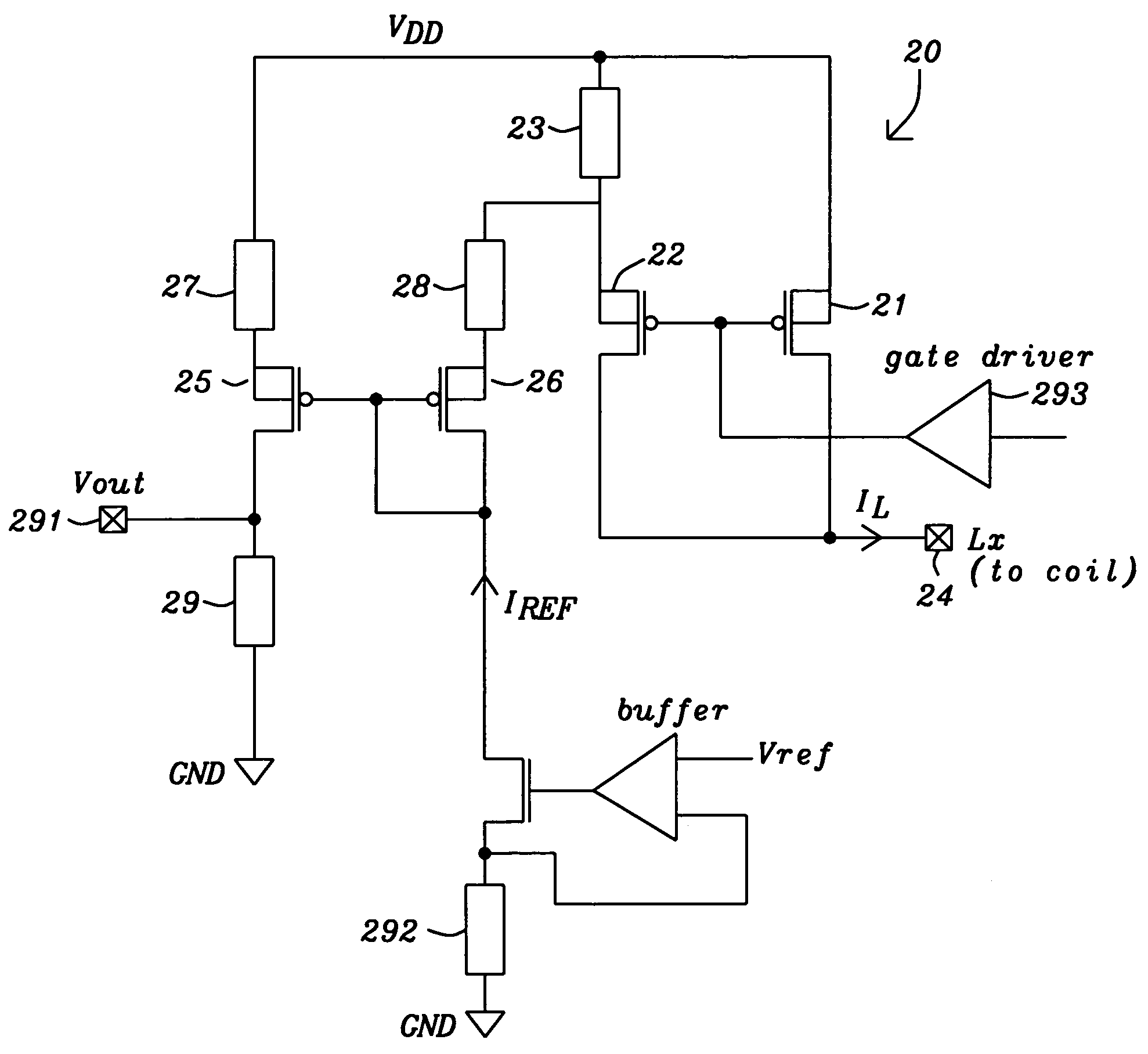
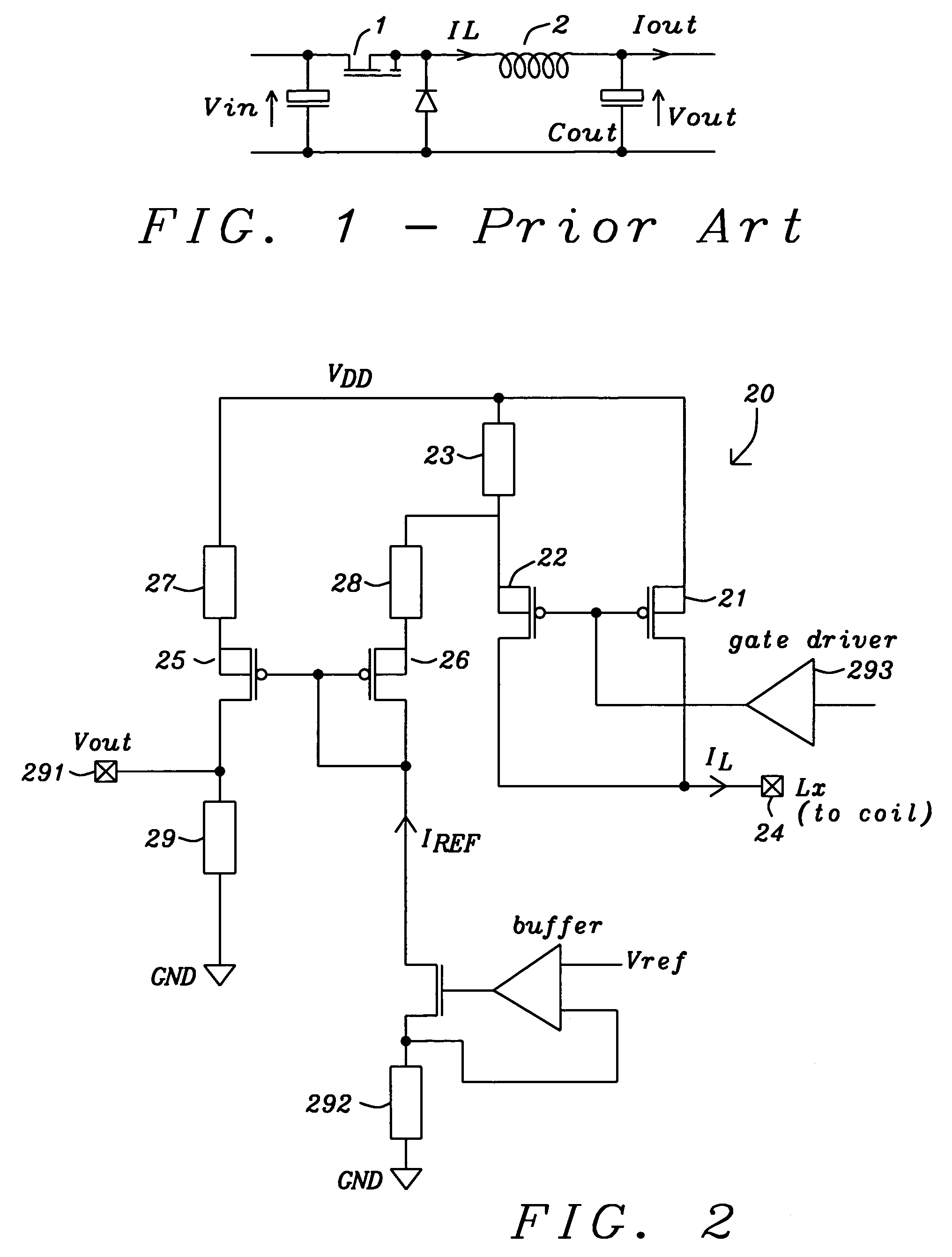
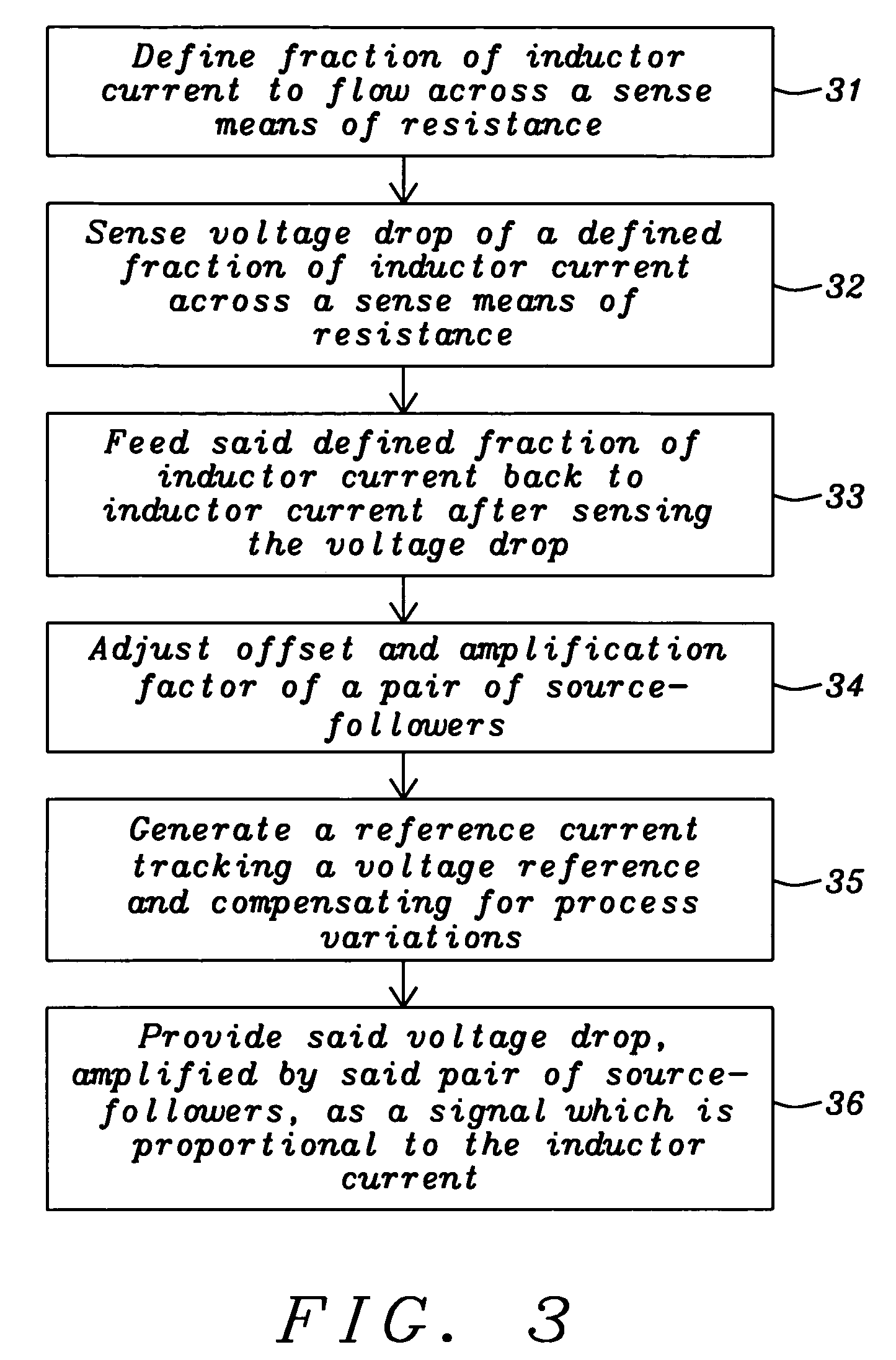
ActiveUS20050127888A1Minimal loss of efficiencyShort stabilization timeDc-dc conversionCurrent measurements onlyElectrical resistance and conductanceBuck converter
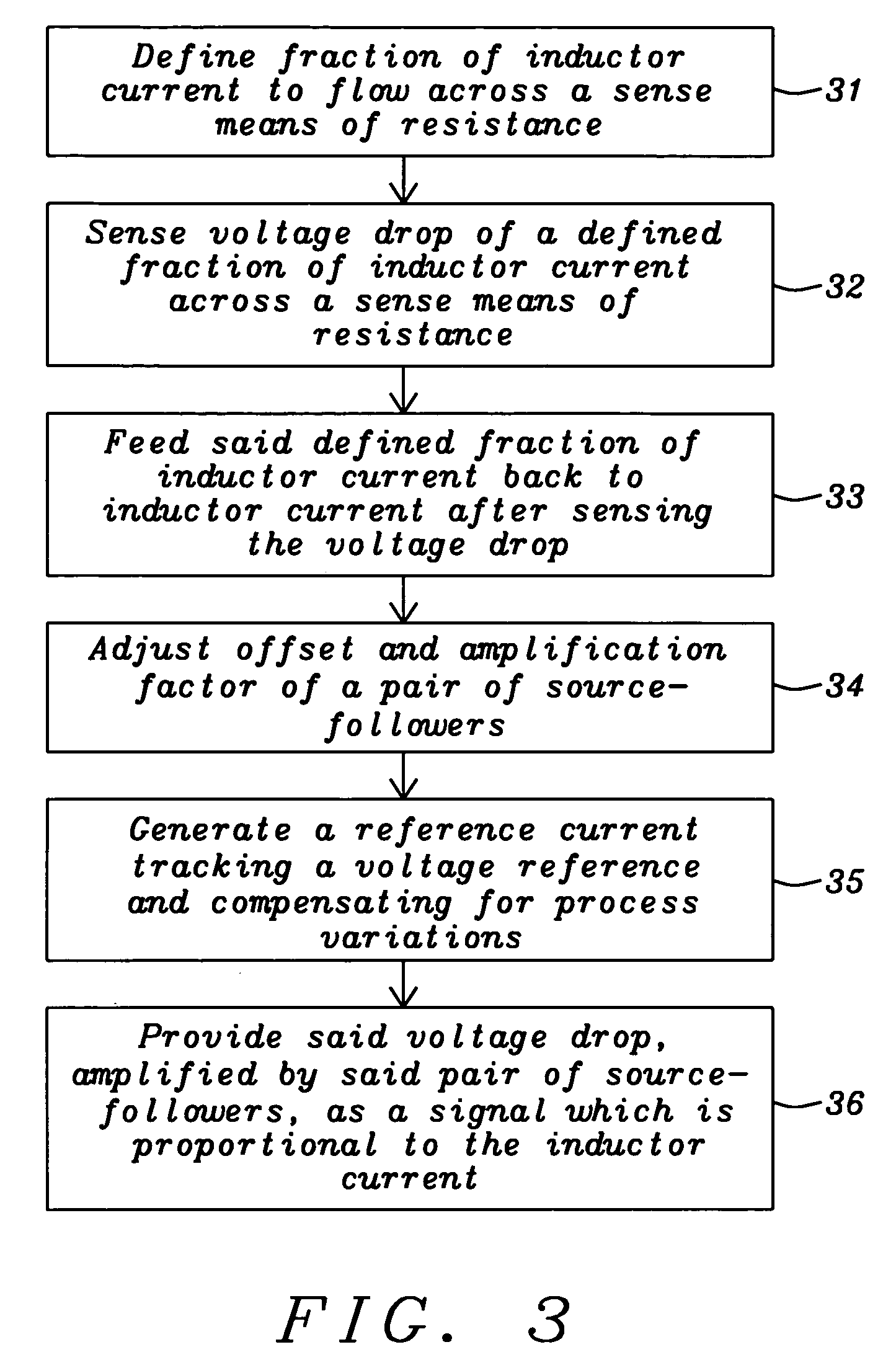
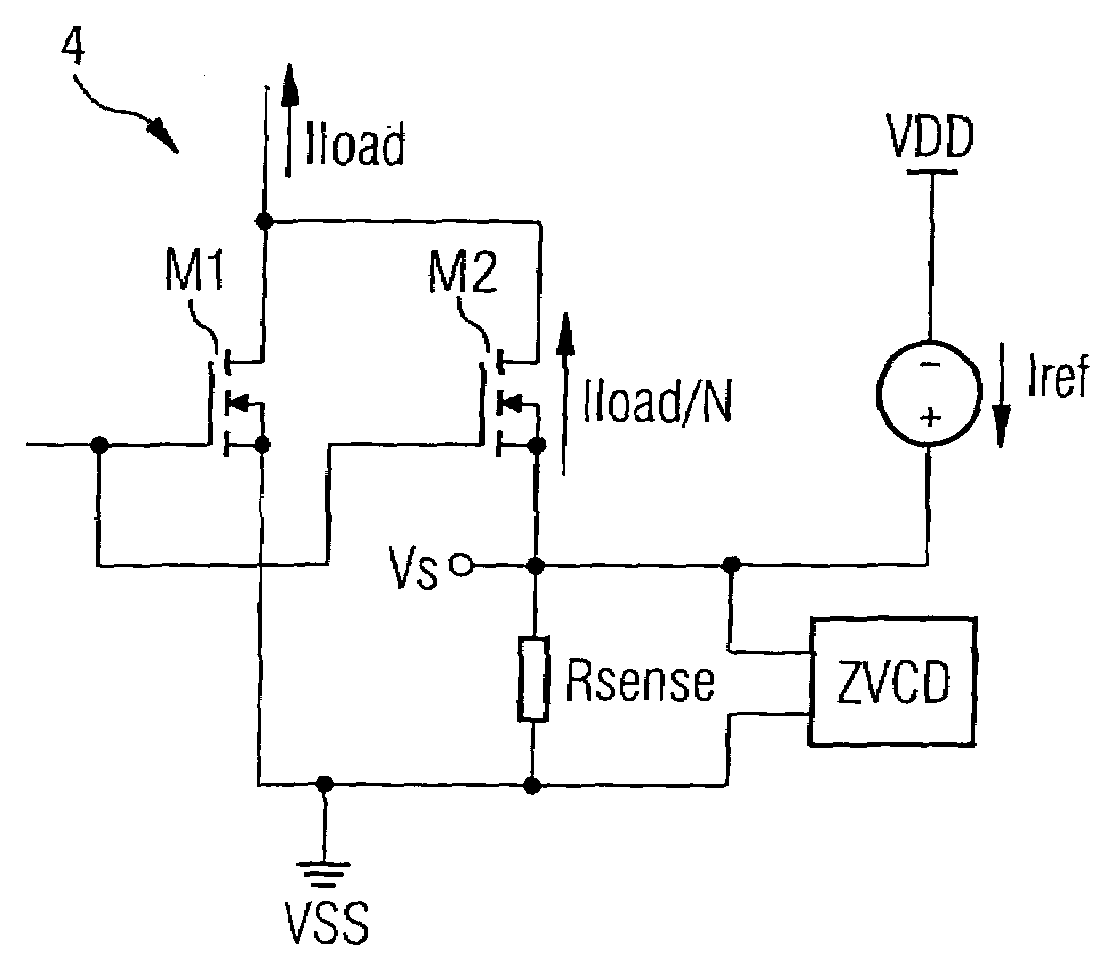
A circuit and a related method to sense the inductor current of CD / DC buck converters have been achieved. The inductor current is sensed by generation of a voltage drop across a fully integrated sense resistor. The voltage drop is proportional to the inductor current in the pass device by supplying a fraction of the inductor current out of a source-follower, which matches to the pass device. The source of said source-follower is connected to a sense-resistor that is connected to the same supply as the pass device. The current, which is needed to generate the voltage drop, is fed back into the inductor current minimizing therefore the efficiency loss. Mirroring, amplification and offset correction of the voltage drop across the sense-resistor is performed by using a single matching pair of source-follower, which is supplied by a current tracking the internal reference voltage and the process variations of the resistors.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Method and apparatus for controlling refrigeration
InactiveUS6976368B1Efficiently sensedThermometer detailsDomestic stoves or rangesEngineeringIngested food
A thermal sensor (20) located in the centre of a food simulant composition (24) linked to a remote measuring indicating and / or regulating device (28). The temperature of the food simulant changes in the same way as food stored in its vicinity and is unaffected by the movement of the ambient air which varies in temperature dramatically. This allows an actual reading and recording of stored food temperature and the regulation of the temperature within a refrigerated space by a thermostat (16). Its uses are mainly for frozen, chilled and refrigerated food, and the reading of temperature of food cooked for example in micro-wave ovens.
Owner:UNIVERSAL MASTER PRODS
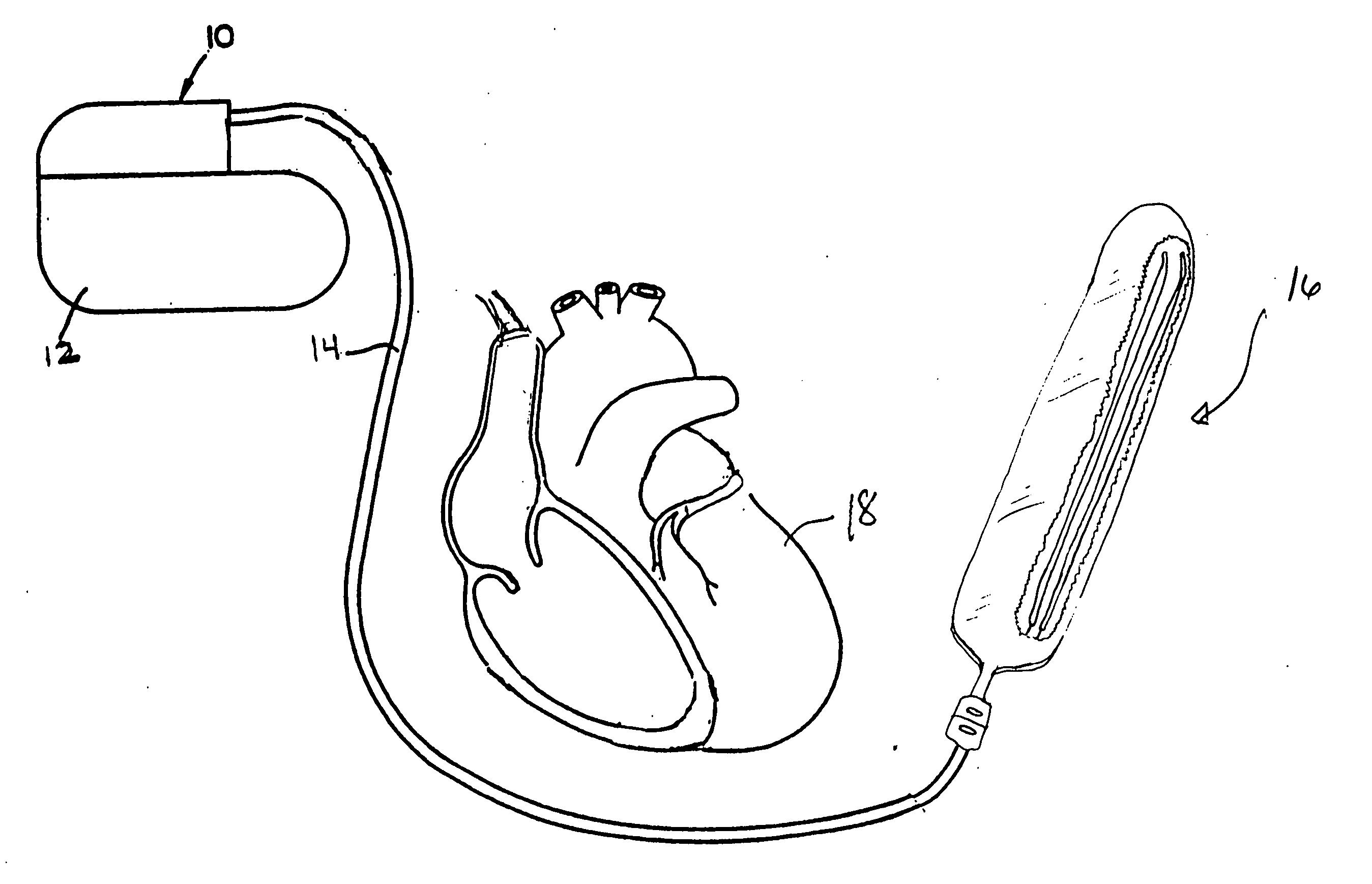
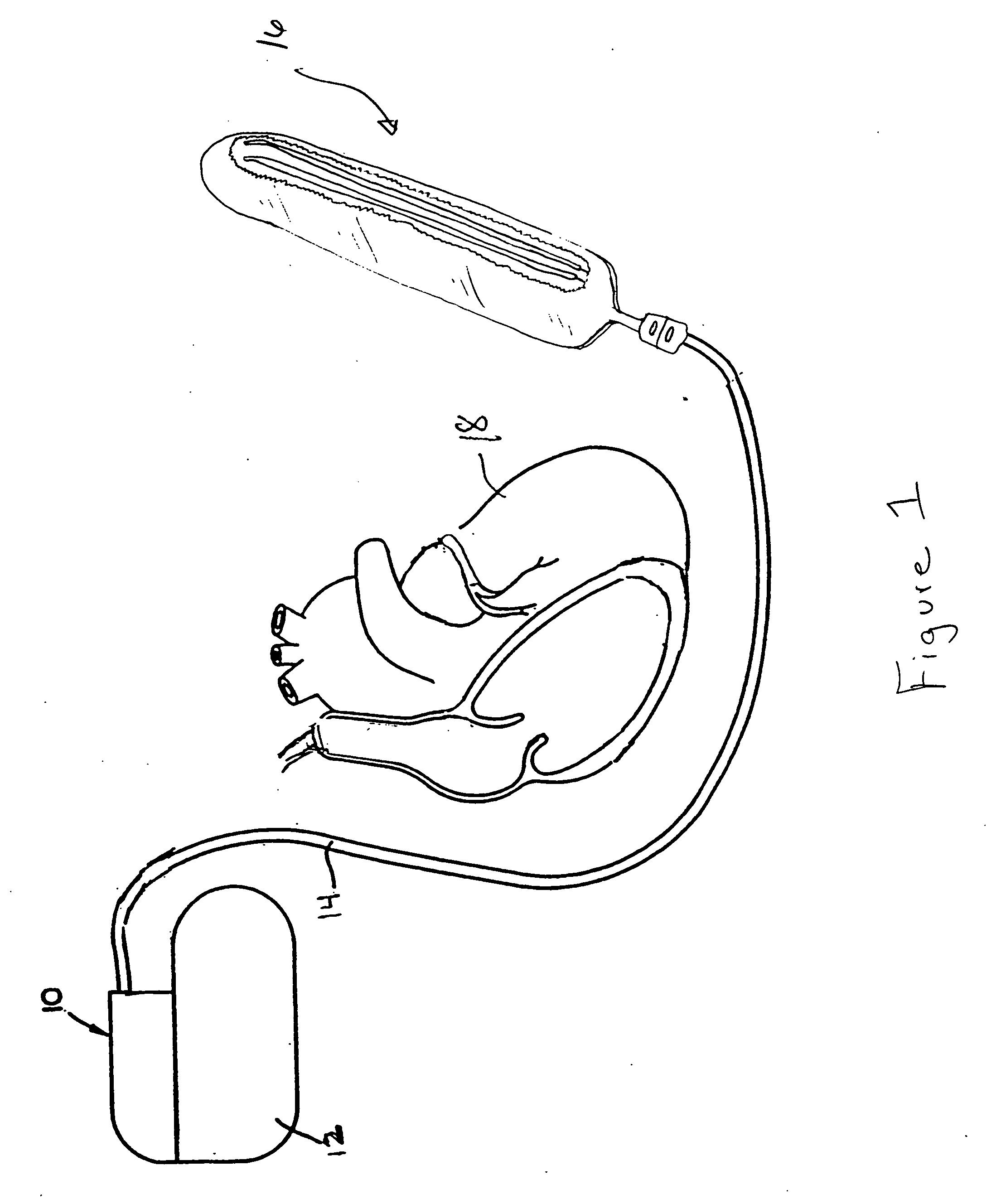
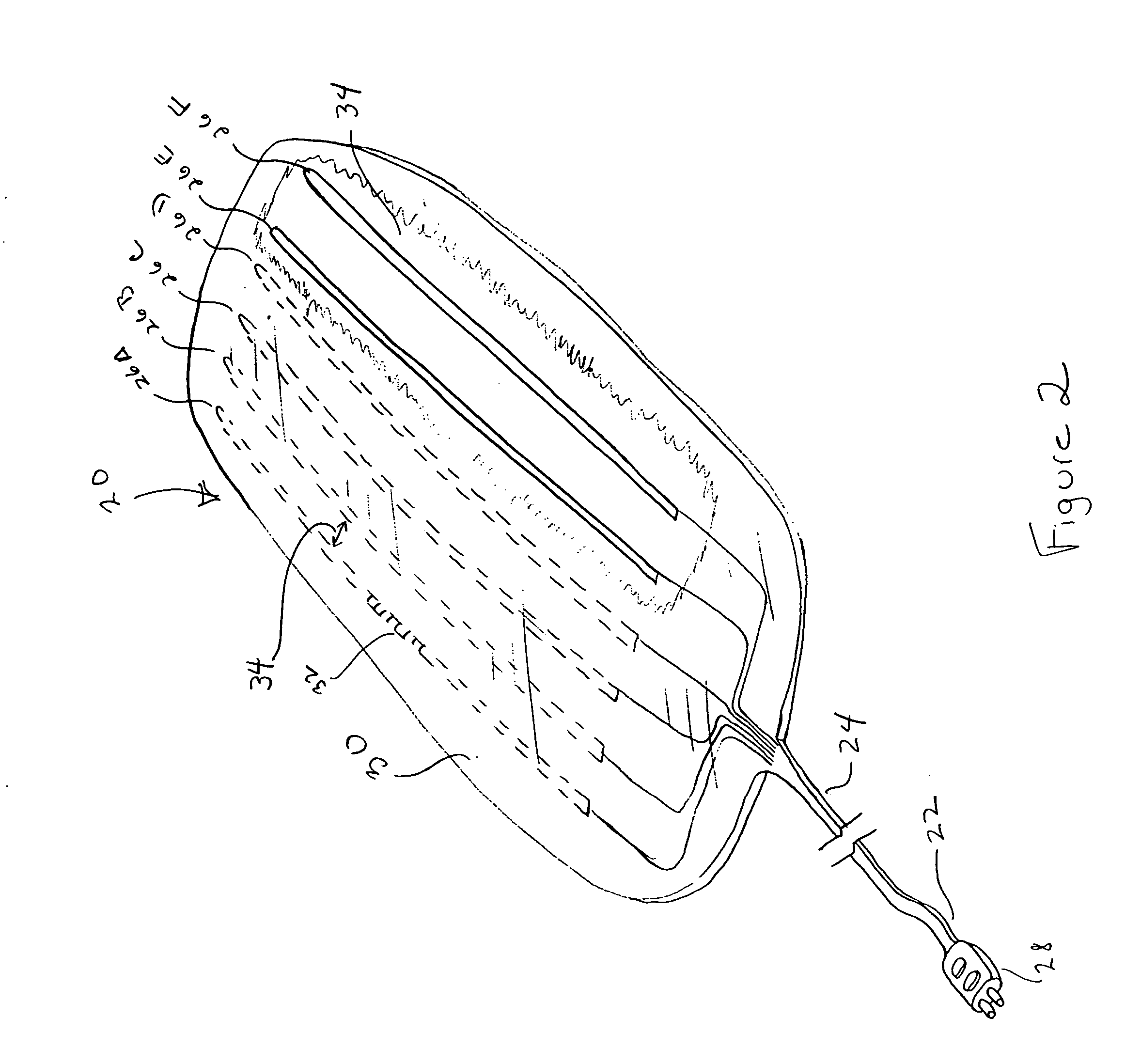
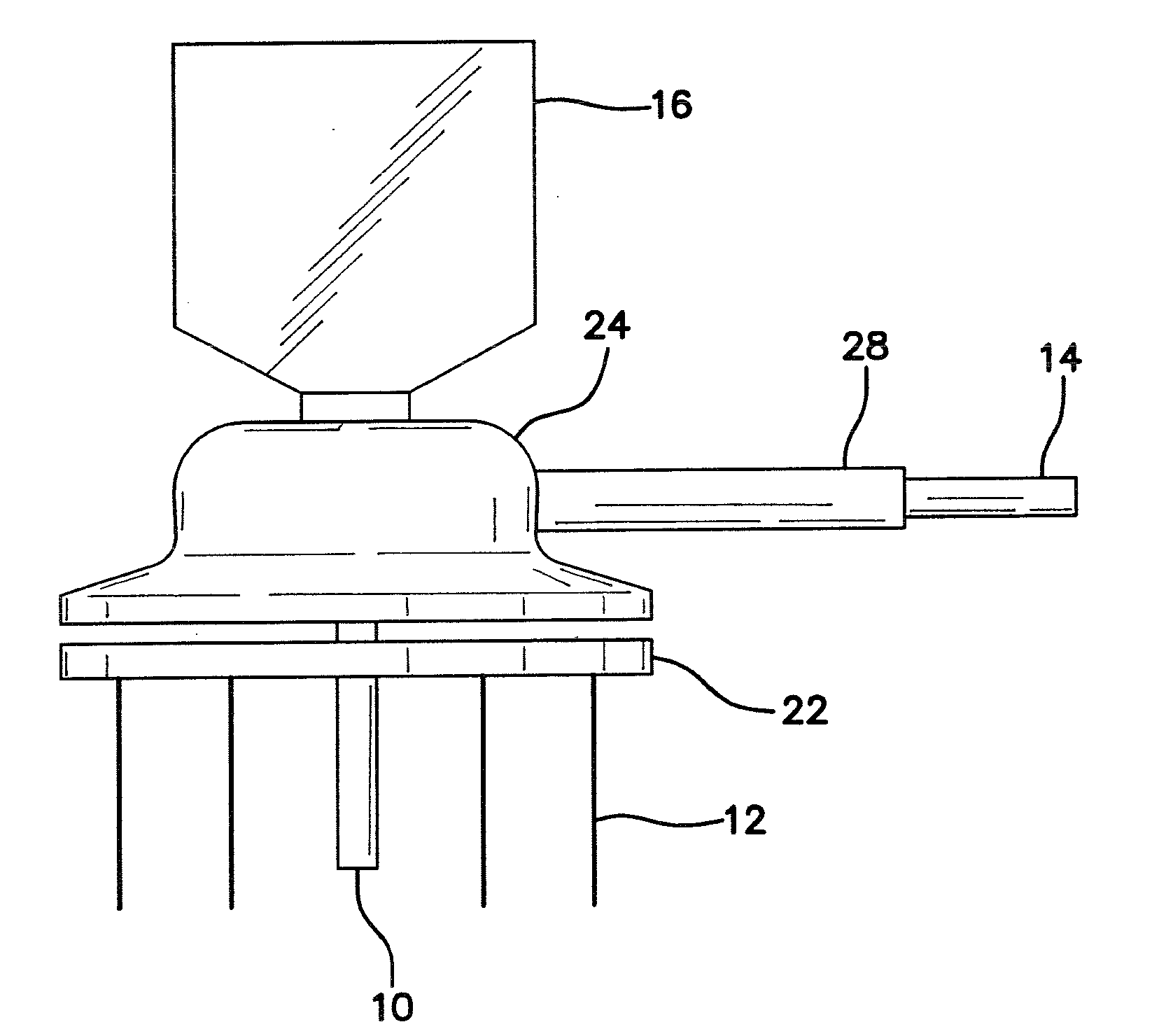
Subcutaneous lead system for detection and treatment of malignant ventricular arrhythmia
InactiveUS20050021093A1Improve protectionSuccessful treatment of arrhythmiasInternal electrodesHeart stimulatorsLead systemHypsarrhythmia
A method and apparatus for treating malignant ventricular arrhythmias is provided. The apparatus includes a lead system that is placed subcutaneously in a patient and a pulse generator connected to lead system by lead. The lead system includes a plurality of energy delivery electrodes for delivering energy stimulation to a patient's heart and a plurality of monitoring electrodes for monitoring the occurrence of or sensing an arrhythmia. The lead system is encapsulated in a sheath of biocompatible material to prevent electrodes from contacting each other and shorting out or shorting together.
Owner:TEAM BROWN
Chronically implantable hybrid cannula-microelectrode system for continuous monitoring electrophysiological signals during infusion of a chemical or pharmaceutical agent
InactiveUS20090187159A1Increasing its useful lifespanEfficiently sensedMedical devicesSensorsMultivariate statisticalPharmaceutical care
A device for assessing the effects of diffusible molecules on electrophysiological recordings from multiple neurons allows for the infusion of reagents through a cannula located among an array of microelectrodes. The device can easily be customized to target specific neural structures. It is designed to be chronically implanted so that isolated neural units and local field potentials are recorded over the course of several weeks or months. Multivariate statistical and spectral analysis of electrophysiological signals acquired using this system could quantitatively identify electrical “signatures” of therapeutically useful drugs.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Switched mode power supply with current sensing
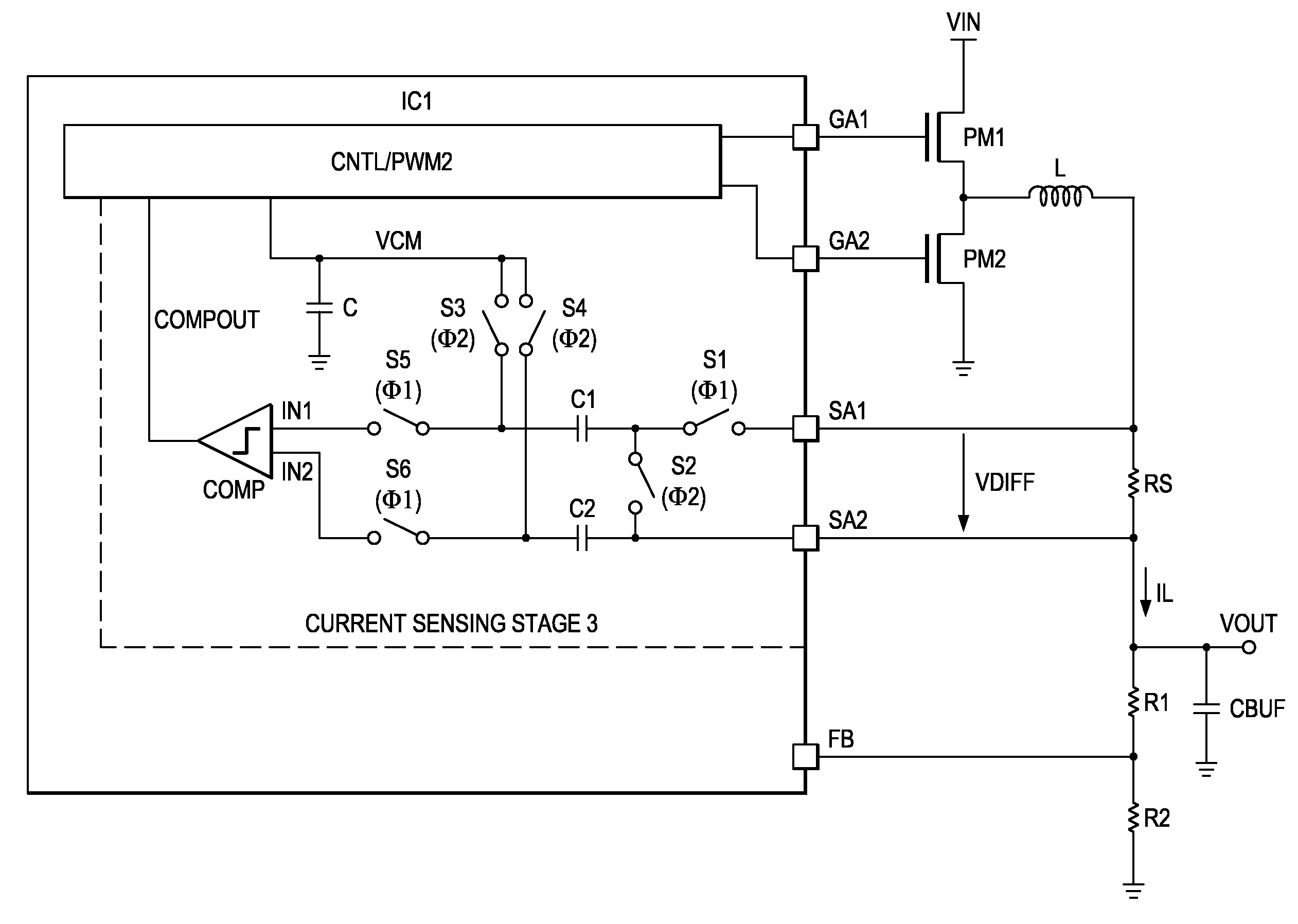
ActiveUS20100231187A1Improve accuracyLess complexDc-dc conversionCurrent measurements onlyCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
An electronic device for switched mode DC-DC conversion is provided that includes a stage for sensing an output current causing a voltage difference between a first and a second node. The current sensing stage includes a comparator being capacitively coupled with a first input to the first node and with a second input to the second node for determining a magnitude of the output current.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
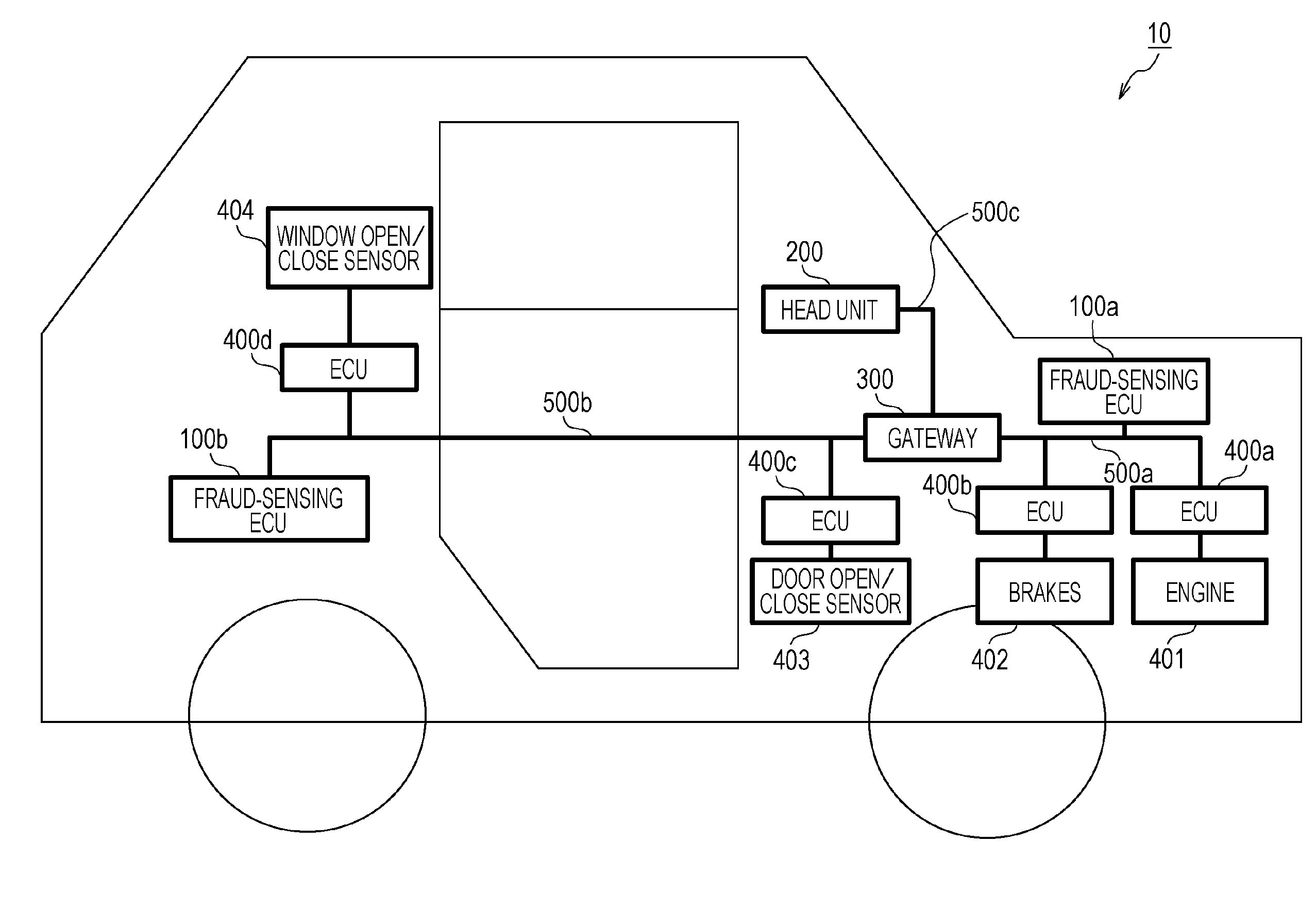
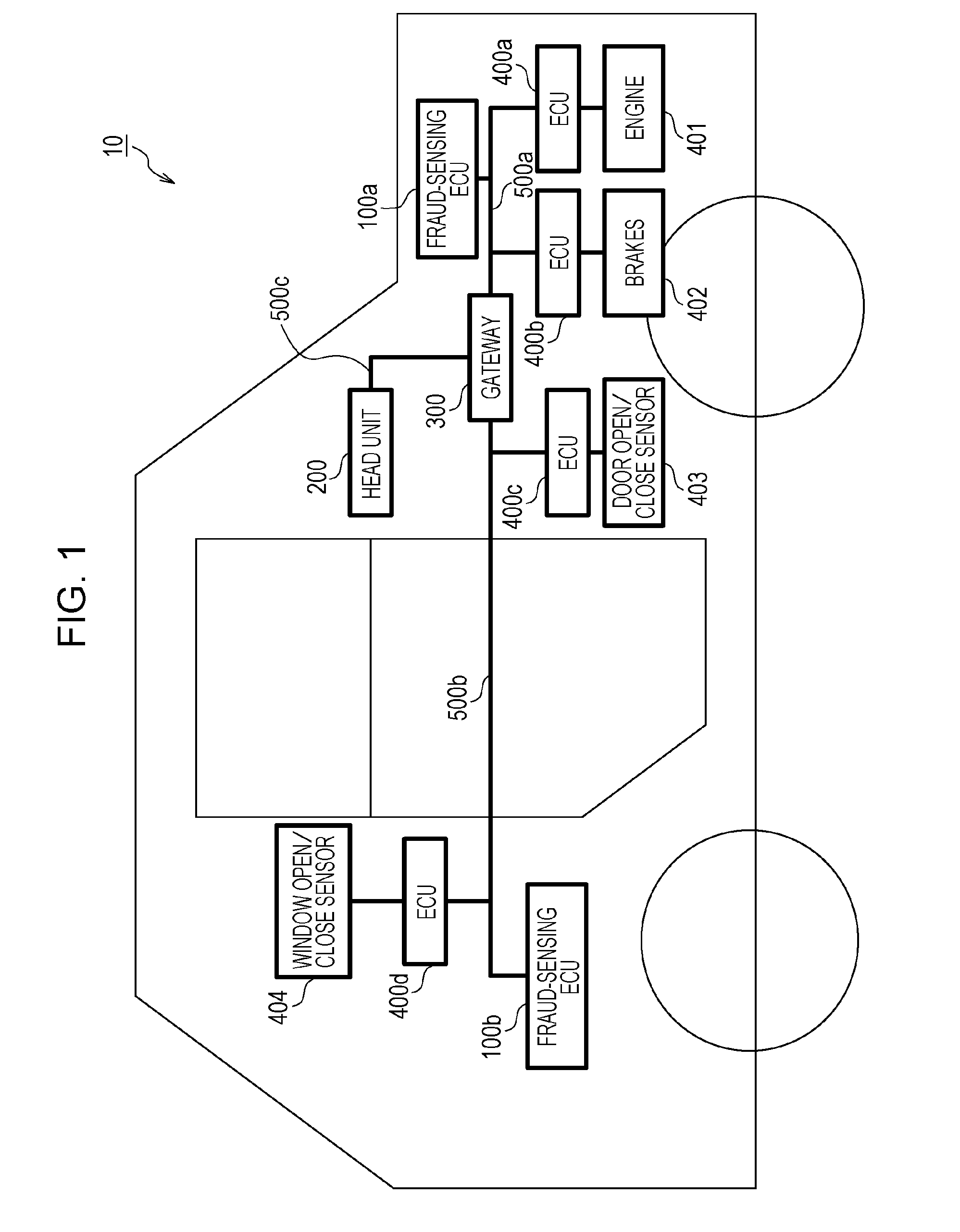
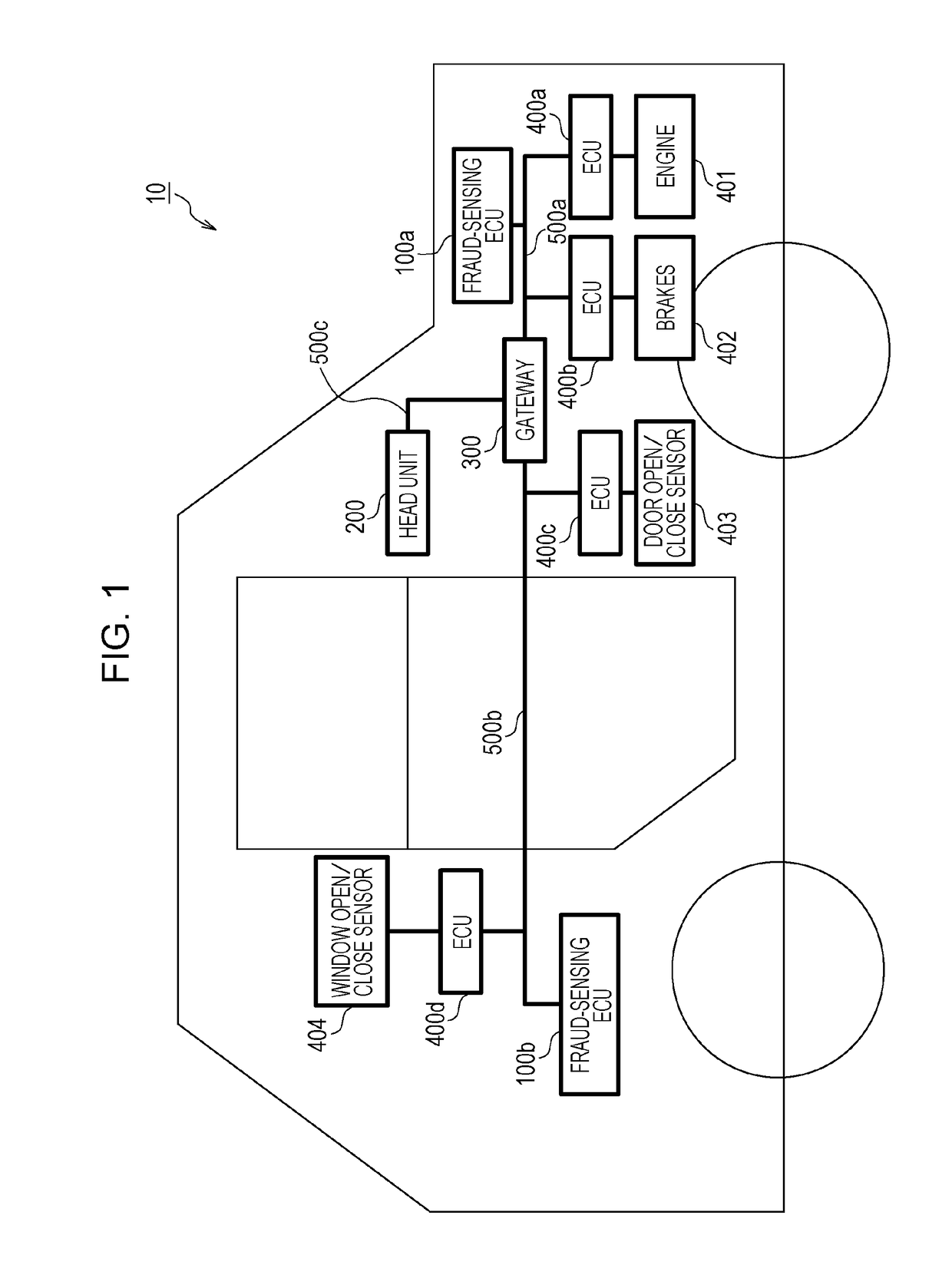
Method for sensing fraudulent frames transmitted to in-vehicle network
ActiveUS20160294855A1Reduce consumptionEfficiently sensedData switching by path configurationElectric/fluid circuitIn vehicleElectronic control unit
A fraud sensing method for use in an in-vehicle network system including a plurality of electronic control units that communicate with each other via a bus includes detecting that a state of a vehicle satisfies a predetermined condition, and switching, upon detecting that the state of the vehicle satisfies the predetermined condition, an operation mode of a fraud-sensing electronic control unit connected to the bus between a first mode in which a first type of sensing process for sensing a fraudulent message in the bus is performed and a second mode in which the first type of sensing process is not performed.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Current sensing circuit
ActiveUS7336085B2Efficient detectionEfficiently sensedResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic switchingElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A circuit arrangement for detecting a load current through a load includes a main transistor, a sensing transistor through which a load current flows that is a measure of the load current flowing through the main transistor. In addition, a resistance is connected in series with the load path of the sensing transistor, and a current source is connected to a node arranged between the sensing transistor and the resistance. A detector detects the load current flowing through the main transistor by measuring the voltage across the resistance.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Device for improving the visibility conditions in a motor vehicle
ActiveUS20050075760A1The device operates reliablyImprove applicabilityDigital data processing detailsInstrument arrangements/adaptationsVisibilityDisplay device
The invention relates to a device for improving the visibility conditions in a motor vehicle, having a radiation source for infrared radiation for irradiating the surroundings of the vehicle, having an infrared-sensitive camera for taking images of at least part of the irradiated surroundings, having a display unit for displaying collected image data, and having a control unit for controlling the device. Furthermore, a sensing unit for a recommended maximum velocity vmax is provided and is connected to the control unit. A velocity sensor which is connected to the control unit is provided in such a way that the control unit causes the display to be switched off when the vehicle velocity v exceeds the maximum velocity vmax. The display is preferably switched on when the vehicle velocity v drops below the maximum velocity vmax. The sensing unit for a recommended maximum velocity vmax is preferably designed in such a way that the recommended maximum velocity vmax is determined from the road profile or from the driving behavior of the vehicle or from received radio signals. This device ensures that the vehicle with the device operates in a safe way for the user.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
Rotary massage device
InactiveUS20100286577A1Promote blood circulationRelieve fatigueRoller massageEngineeringMassage - action
A rotary massage device includes a housing in which an assembly of a worm shaft and a worm gear is operable to drive a gear plate in rotation. The gear plate includes a plurality of mounting seats of different heights for placement of a plurality of massage members thereon, wherein the massage members may have different sizes. Between the housing and the gear plate are mounted a plurality of cushion elements, which include multiple pins passing through the housing and abut against the gear plate, each pin being mounted with a spring. During operation, the actuating mechanism drives the gear plate and the massage members of different heights in rotation. Through the cushion elements, swaying movements of the gear plate can be cushioned in an effective manner, so that a user in contact with the massage members can also feel pressing and kneading massage actions.
Owner:TSAI MING WEI
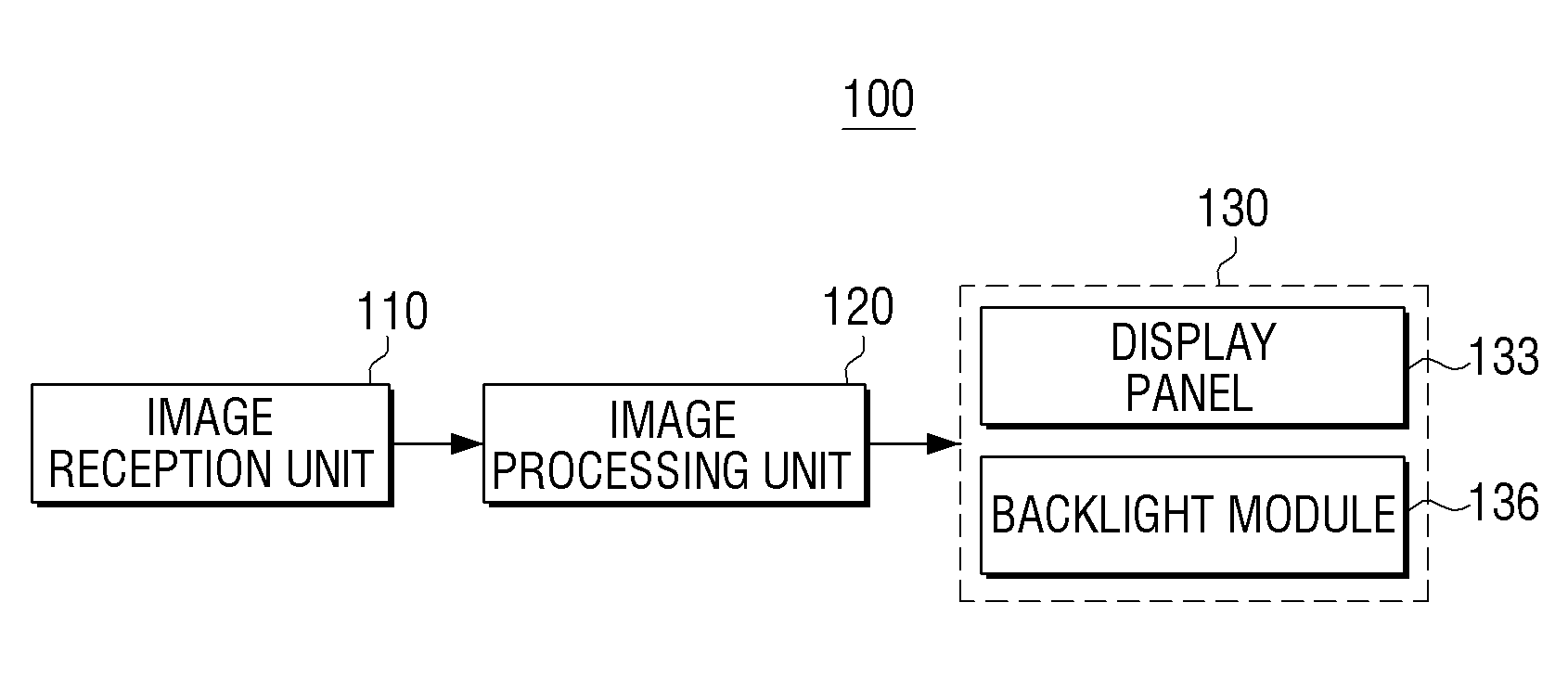
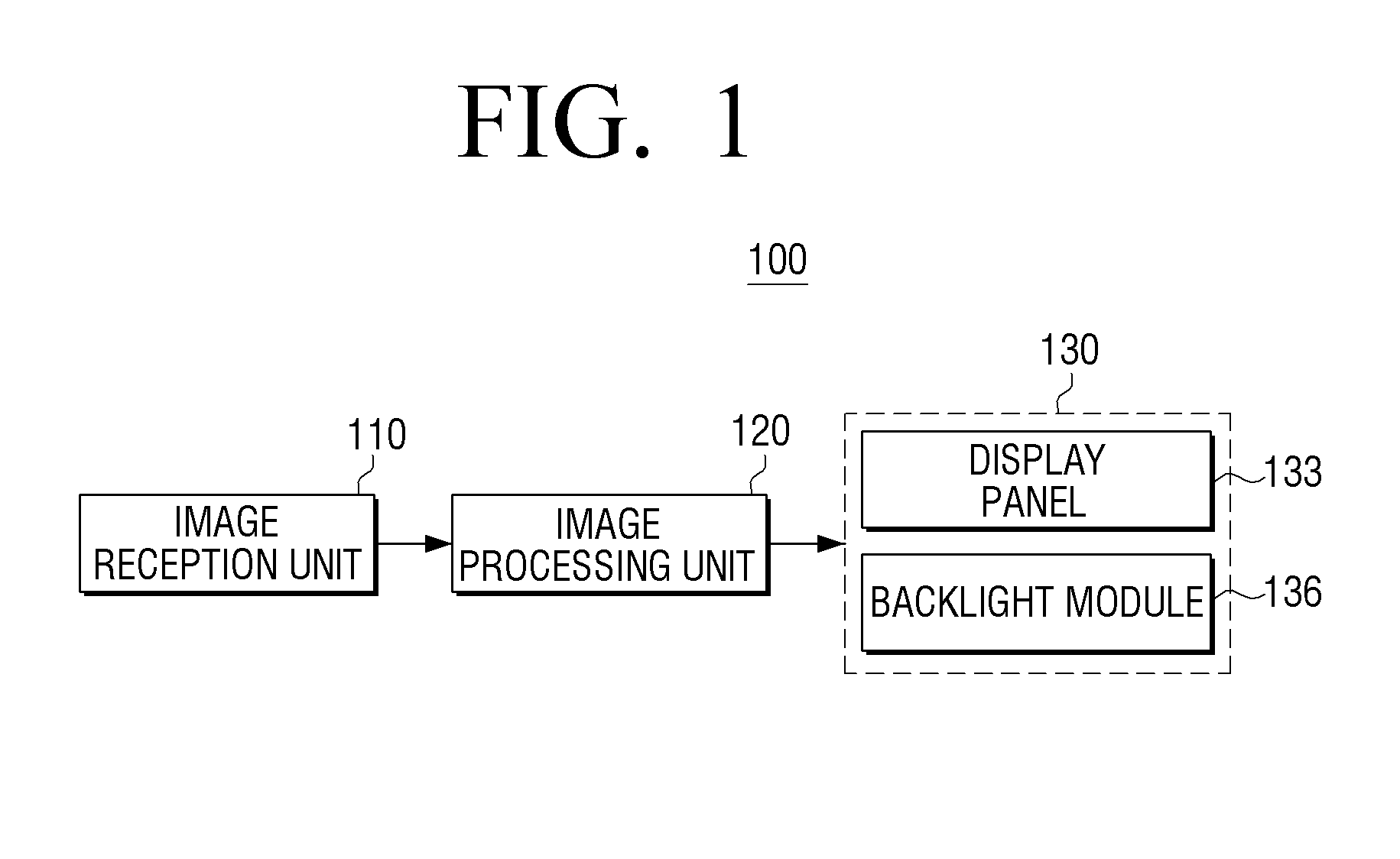
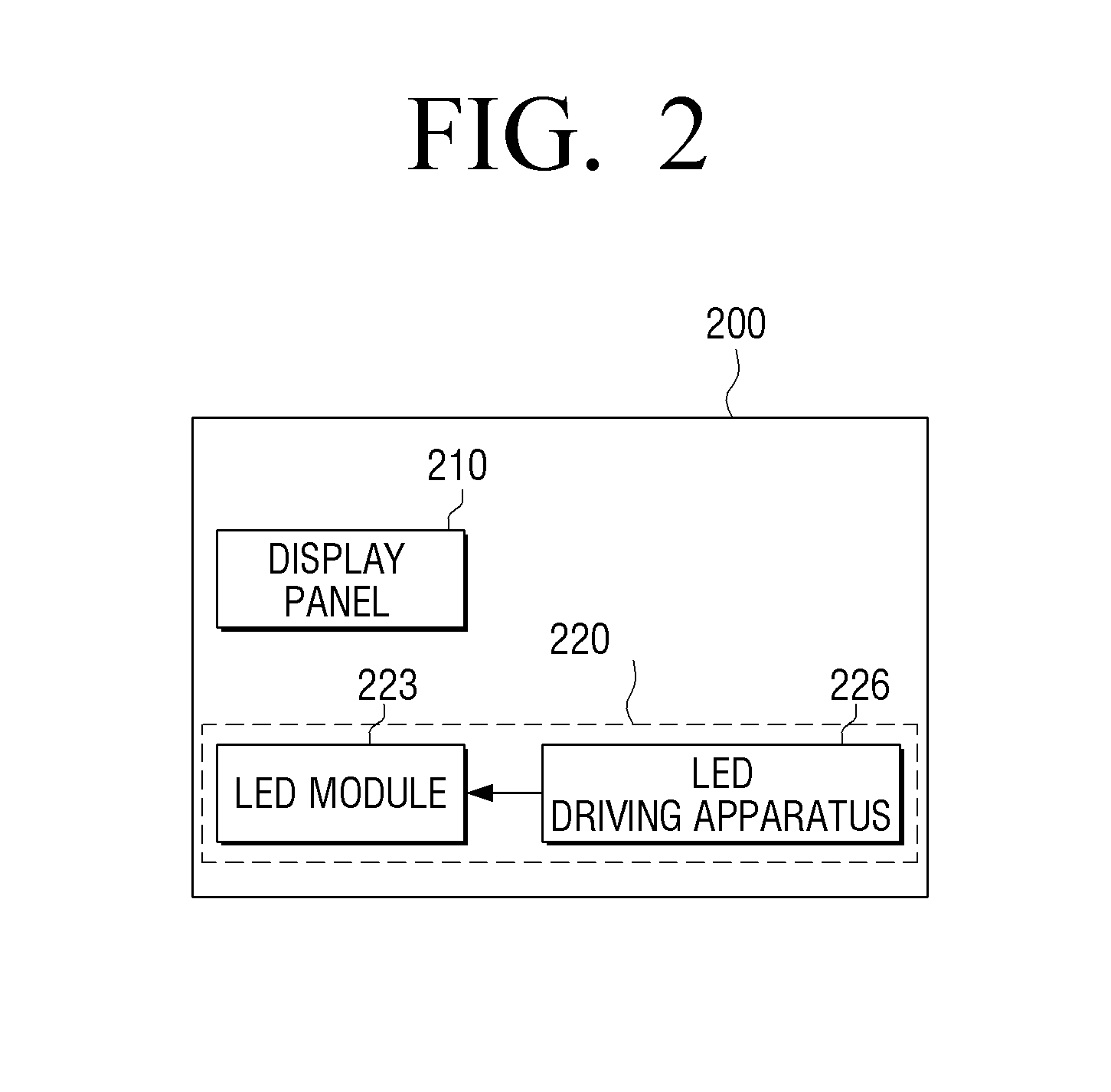
LED driving apparatus and method and display apparatus using the LED driving apparatus and method
InactiveUS20130113844A1Efficiently sensedReduce output voltageElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringVoltage reference
A display apparatus is provided. The display apparatus includes a display panel which displays an image; a light-emitting diode (LED) module which provides backlight to the display panel; an LED driving unit which applies a driving voltage to the LED module; and an LED driving control unit which senses the driving voltage from the LED module and stops an operation of the LED driving unit if the sensed driving voltage is lower than a first reference voltage or higher than a second reference voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
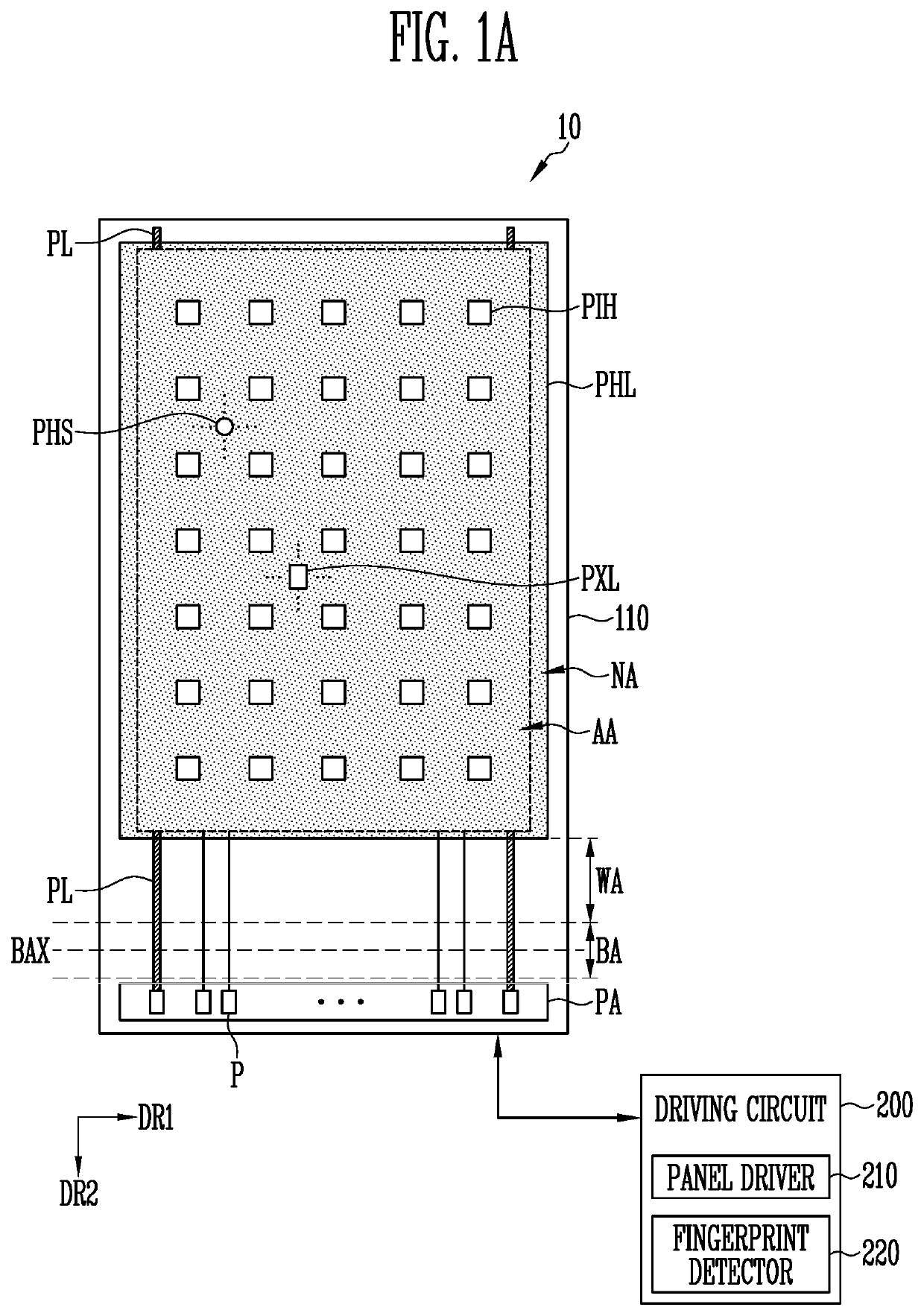
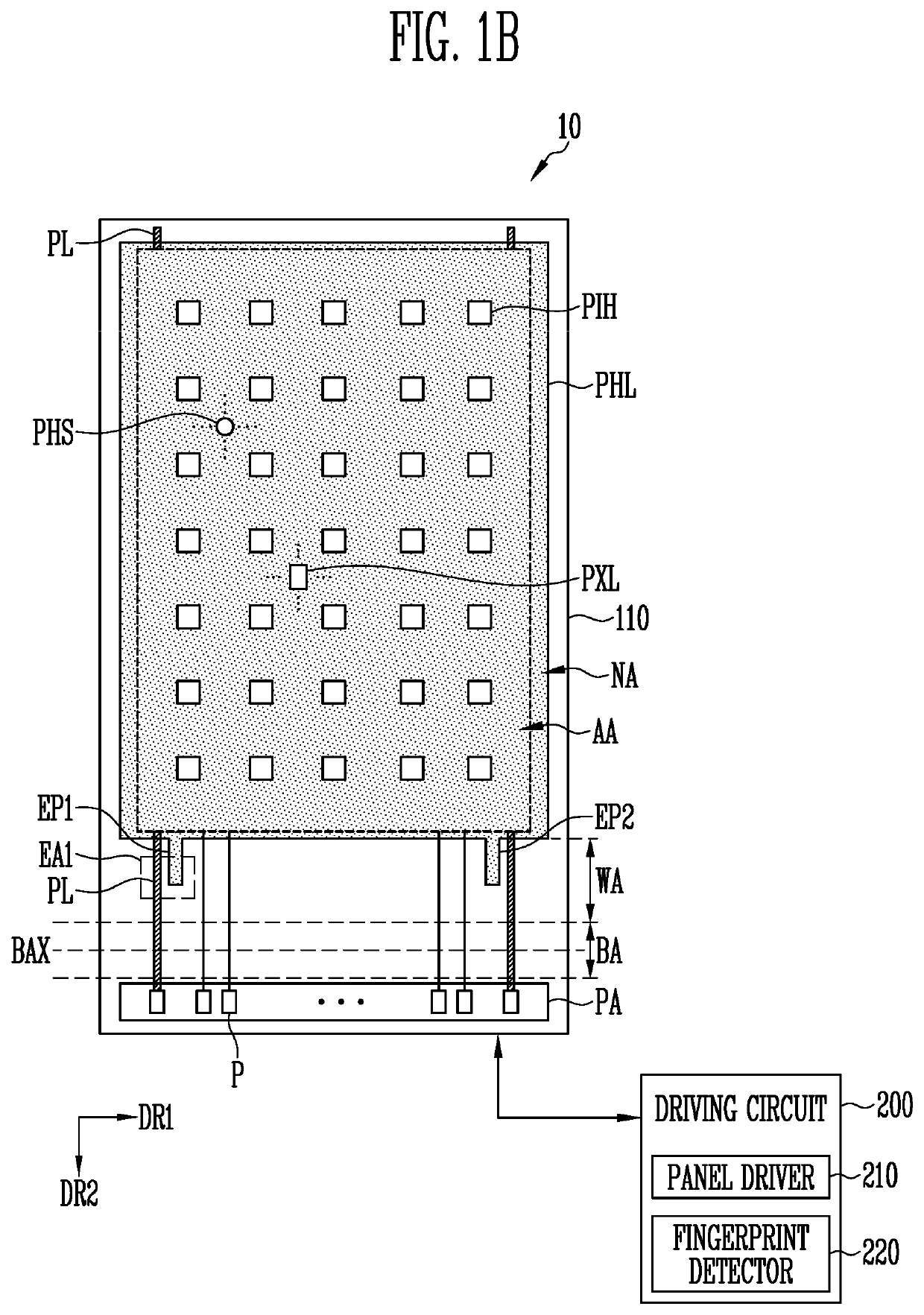
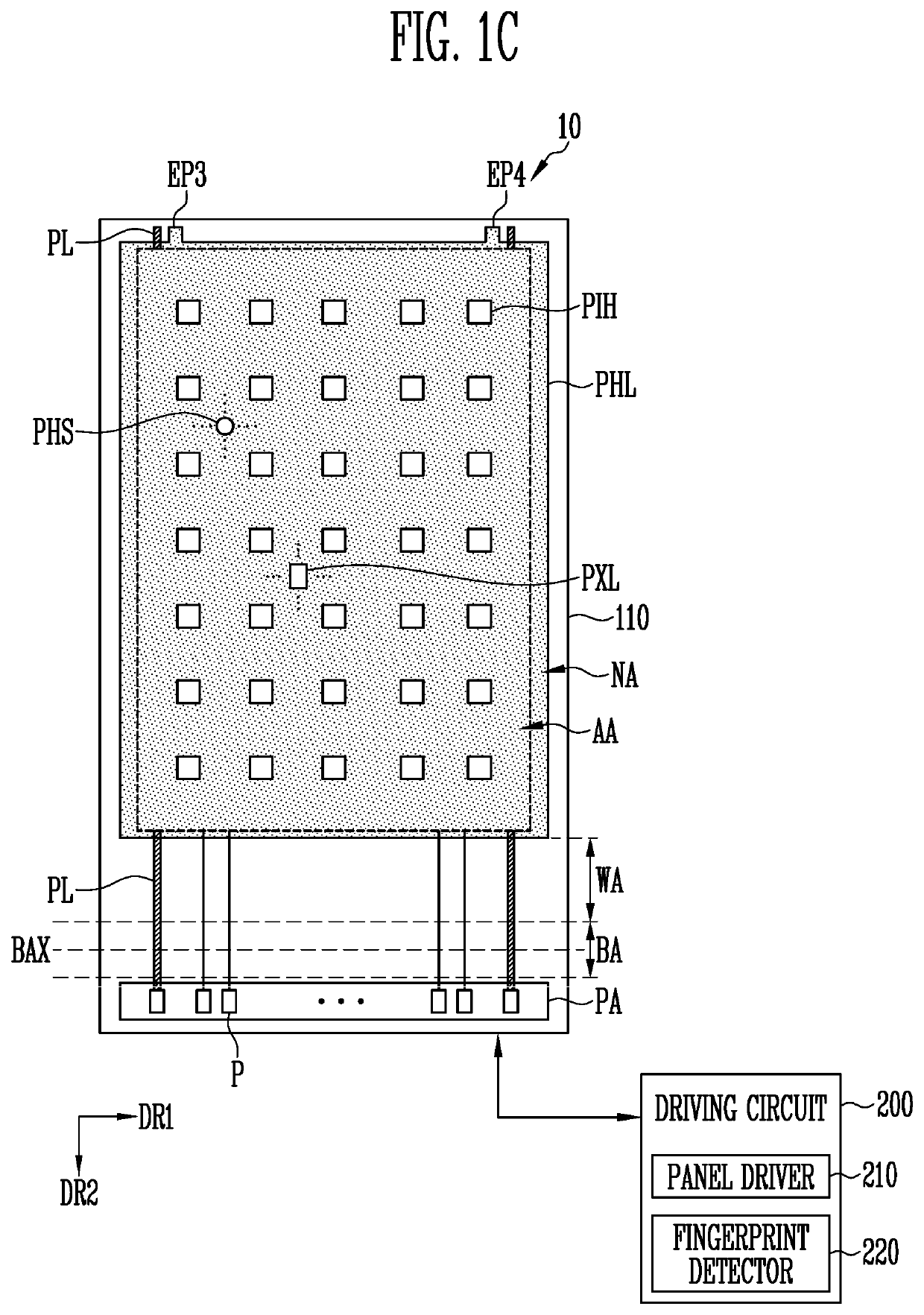
Display device
PendingUS20200395433A1Easy loadingDeteriorating qualitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceHemt circuits
A display device includes: a substrate including a display area having a plurality of pixel areas and a non-display area surrounding at least one side of the display area; a light-blocking layer disposed on a first surface of the substrate and including light transmissive areas to allow incident light to pass therethrough; a circuit-element layer disposed on the light-blocking layer and including a plurality of conductive layers; a light-emitting element layer disposed on the circuit-element layer and including light-emitting elements; and a sensor layer disposed on a second surface of the substrate opposing the first surface to sense the light passing through the light transmissive areas. The light-blocking layer is electrically coupled to at least one of the plurality of conductive layers.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
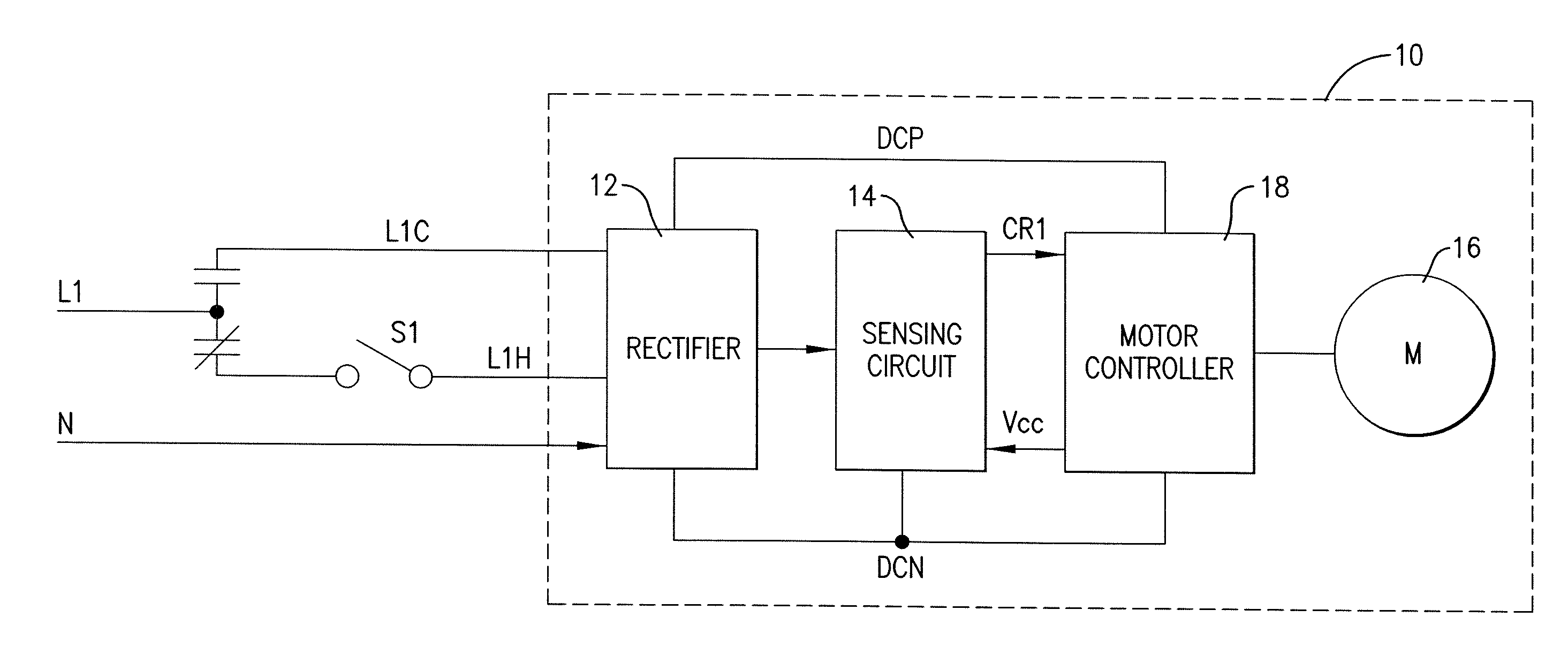
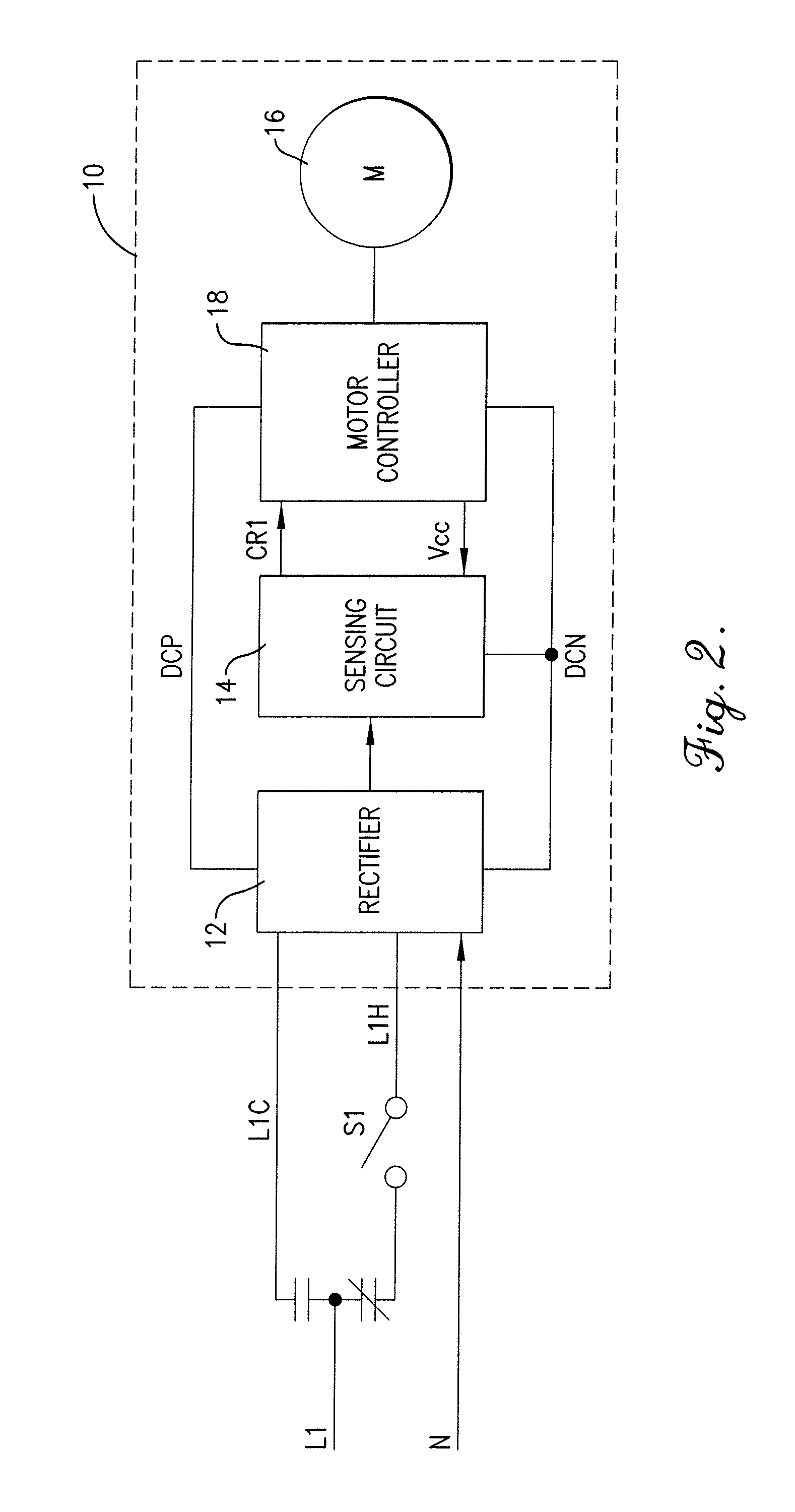
Blower motor for HVAC systems
ActiveUS20110260666A1Easily customizedCostly and time-consumeMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlHVACCooling power
A blower motor assembly having a variable speed motor that is suitable for direct, drop-in replacement in a residential HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) system that employs a PSC motor. The blower motor assembly includes at least a neutral input and two hot AC line connections, one for connection to the heating power source and the other to the cooling power source. A sensing circuit senses which of the inputs is energized by sensing either voltage or current on the inputs. The sensing circuit delivers a corresponding signal to a motor controller to control the speed of the variable speed motor. The blower motor assembly may also be equipped with additional hot AC inputs, more than one neutral line, and several sensing circuits for sensing current or voltage in the hot inputs and / or the neutral lines for controlling various aspects of the variable speed motor.
Owner:NIDEC MOTOR CORP
Method for sensing fraudulent frames transmitted to in-vehicle network
ActiveUS10187406B2Reduce consumptionEfficiently sensedNetworks interconnectionElectric/fluid circuitIn vehicleOperation mode
A fraud sensing method for use in an in-vehicle network system including a plurality of electronic control units that communicate with each other via a bus includes detecting that a state of a vehicle satisfies a predetermined condition, and switching, upon detecting that the state of the vehicle satisfies the predetermined condition, an operation mode of a fraud-sensing electronic control unit connected to the bus between a first mode in which a first type of sensing process for sensing a fraudulent message in the bus is performed and a second mode in which the first type of sensing process is not performed.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Current sensing circuit for DC/DC buck converters
ActiveUS6992473B2Minimal loss of efficiencyShort stabilization timeDc-dc conversionCurrent measurements onlyBuck converterVoltage drop
A circuit and a related method to sense the inductor current of CD / DC buck converters have been achieved. The inductor current is sensed by generation of a voltage drop across a fully integrated sense resistor. The voltage drop is proportional to the inductor current in the pass device by supplying a fraction of the inductor current out of a source-follower, which matches to the pass device. The source of said source-follower is connected to a sense-resistor that is connected to the same supply as the pass device. The current, which is needed to generate the voltage drop, is fed back into the inductor current minimizing therefore the efficiency loss. Mirroring, amplification and offset correction of the voltage drop across the sense-resistor is performed by using a single matching pair of source-follower, which is supplied by a current tracking the internal reference voltage and the process variations of the resistors.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Touch display device and touch sensing circuit
ActiveUS20200210021A1Improve the sense of speedIncrease pen search speedInput/output processes for data processingComputer hardwareDisplay device
A touch display device comprises a touch panel including a plurality of touch electrodes; and a touch driving circuit configured to sense one or more of the plurality of touch electrodes, wherein the touch driving circuit has an operation period including a plurality of touch intervals that includes a first sensing interval and a second sensing interval, and the first sensing interval includes at least a first time division sensing interval and the second sensing interval includes at least a second time division sensing interval, and wherein the touch driving circuit is configured to detect a pen signal output from a first pen through one or more touch electrodes of the plurality of touch electrodes during the first time division sensing interval, and detect a pen signal output from a second pen through one or more touch electrodes of the plurality of touch electrodes during the second time division sensing interval.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Driver circuit, light-emitting display device, and driving method
ActiveUS20200043421A1Accurately luminance deviationAccurately for luminance deviationStatic indicating devicesCell component detailsComputer hardwareDriver circuit
The present disclosure describes a driver circuit, a light-emitting display device, and a driving method. Even in the case that other video control driving, e.g., fake data insertion driving, is performed during sensing driving, the sensing is not influenced by the other video control driving, e.g., fake data insertion driving. Sensing errors are prevented, and image quality is improved.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
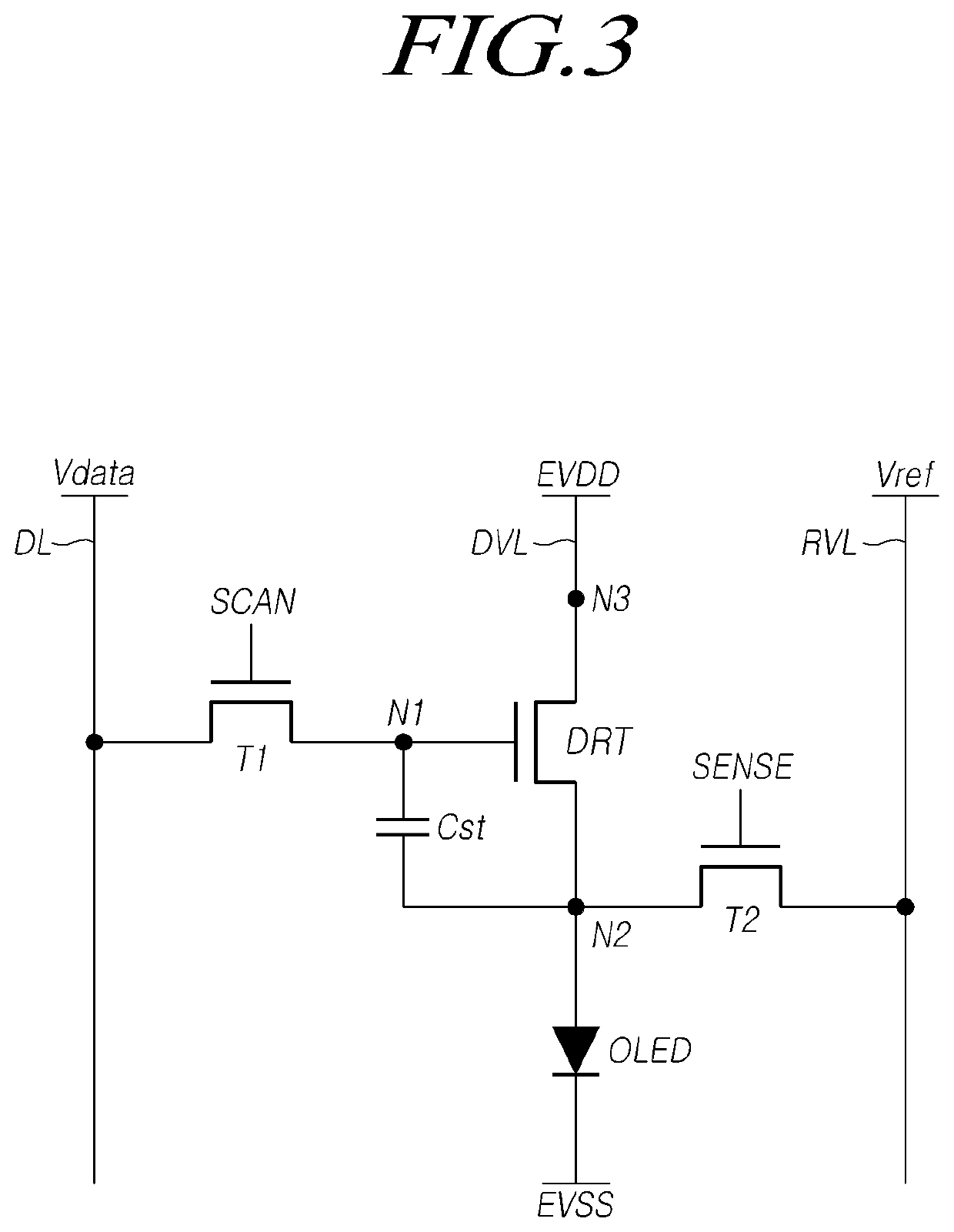
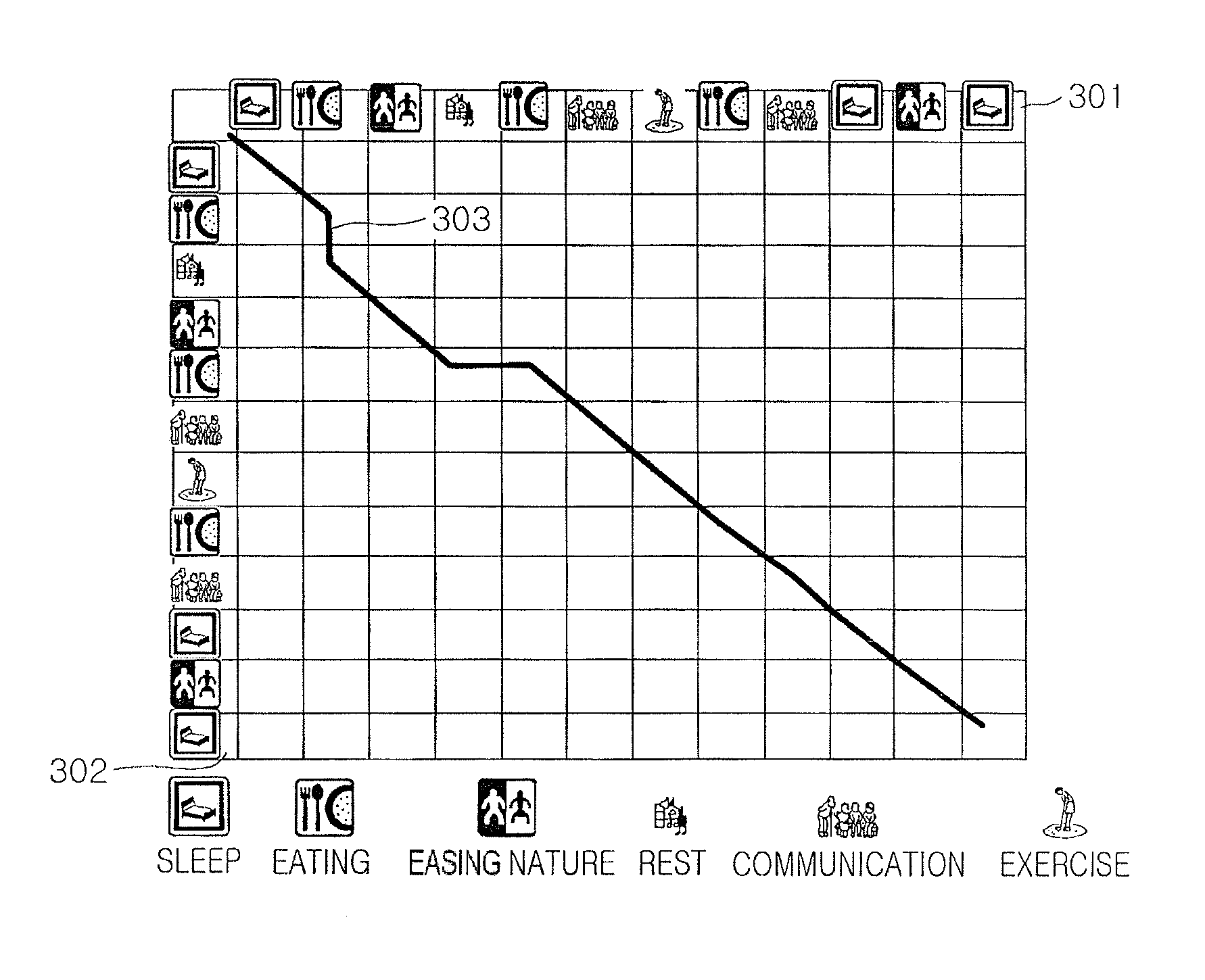
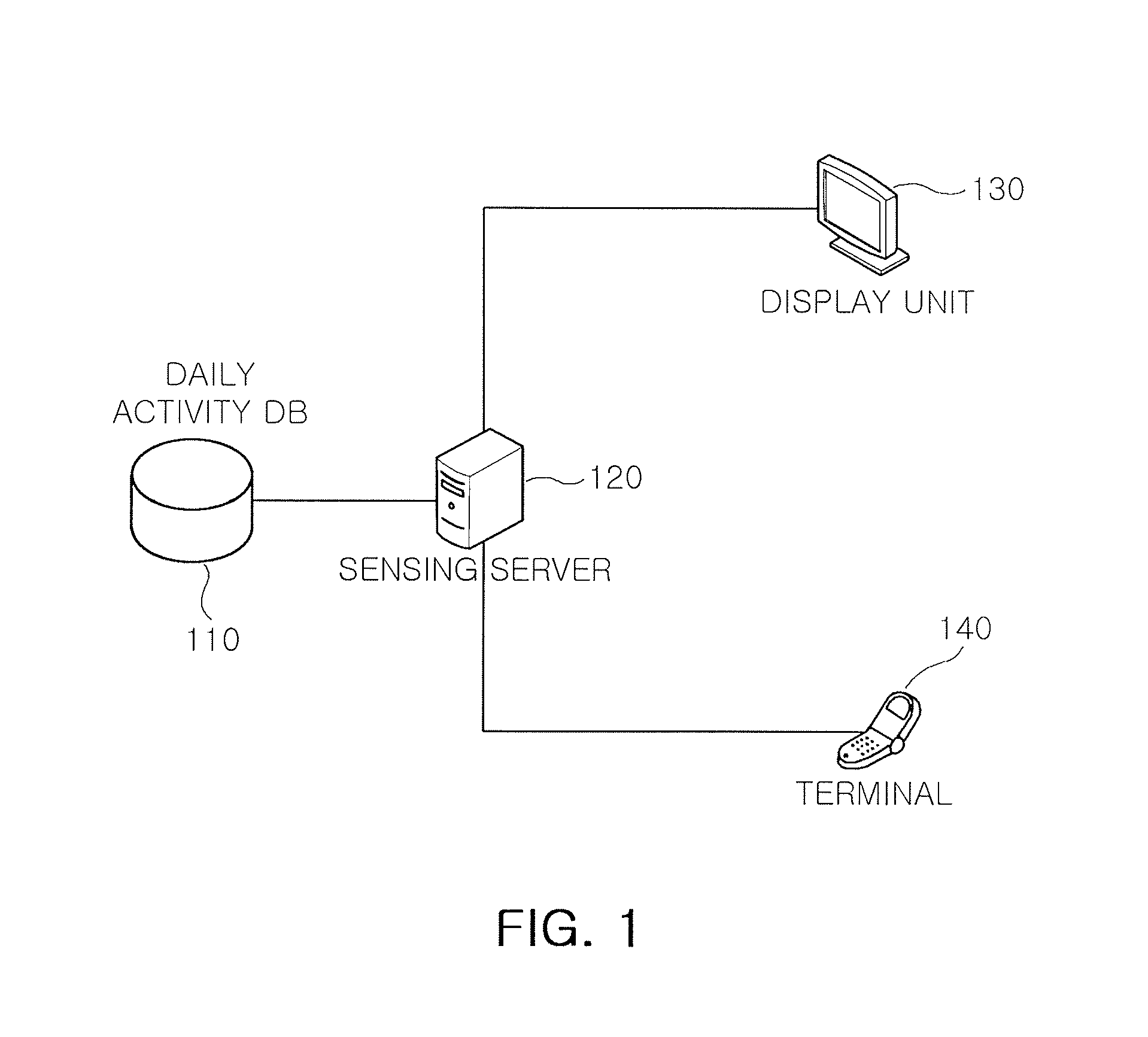
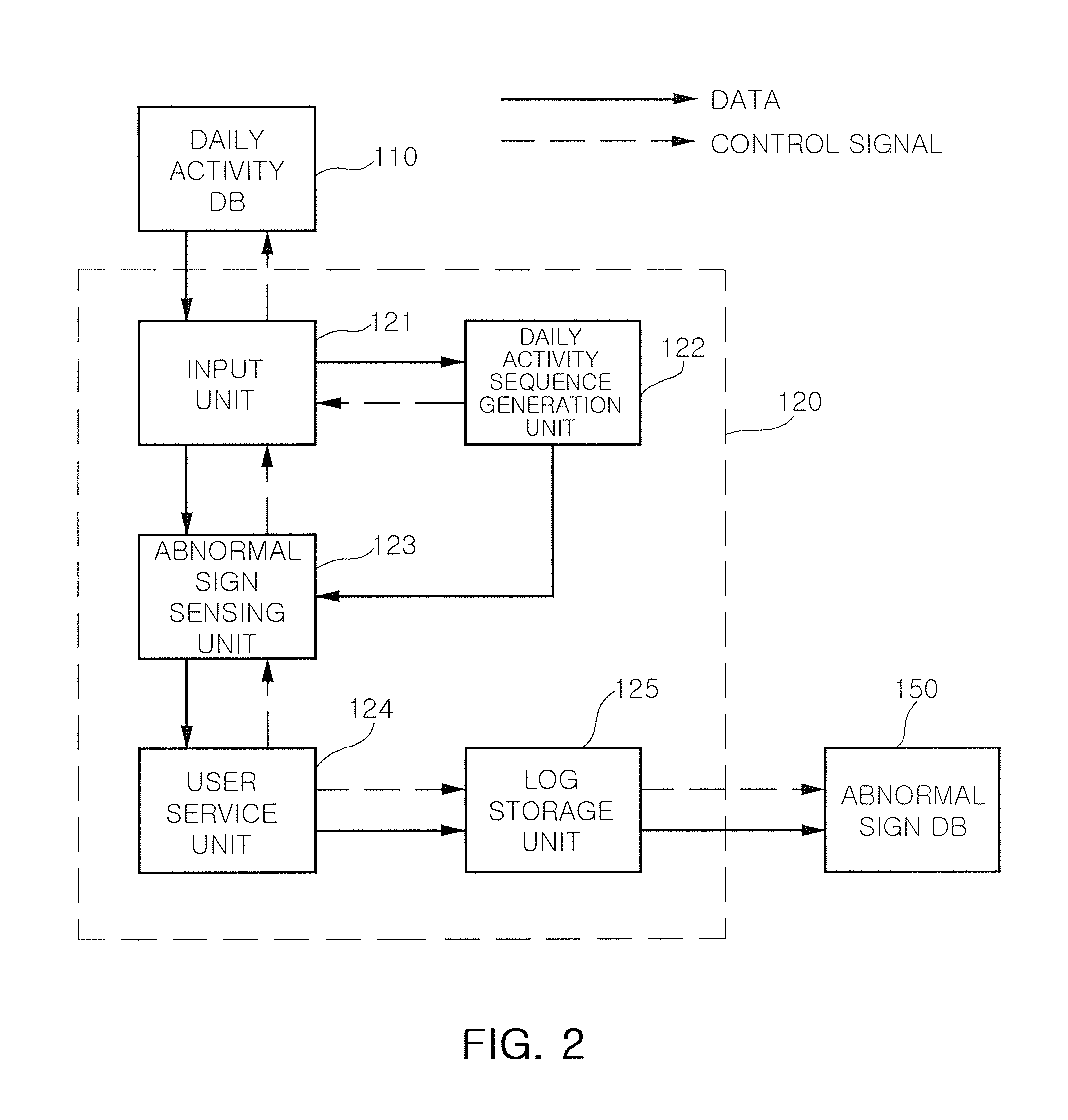
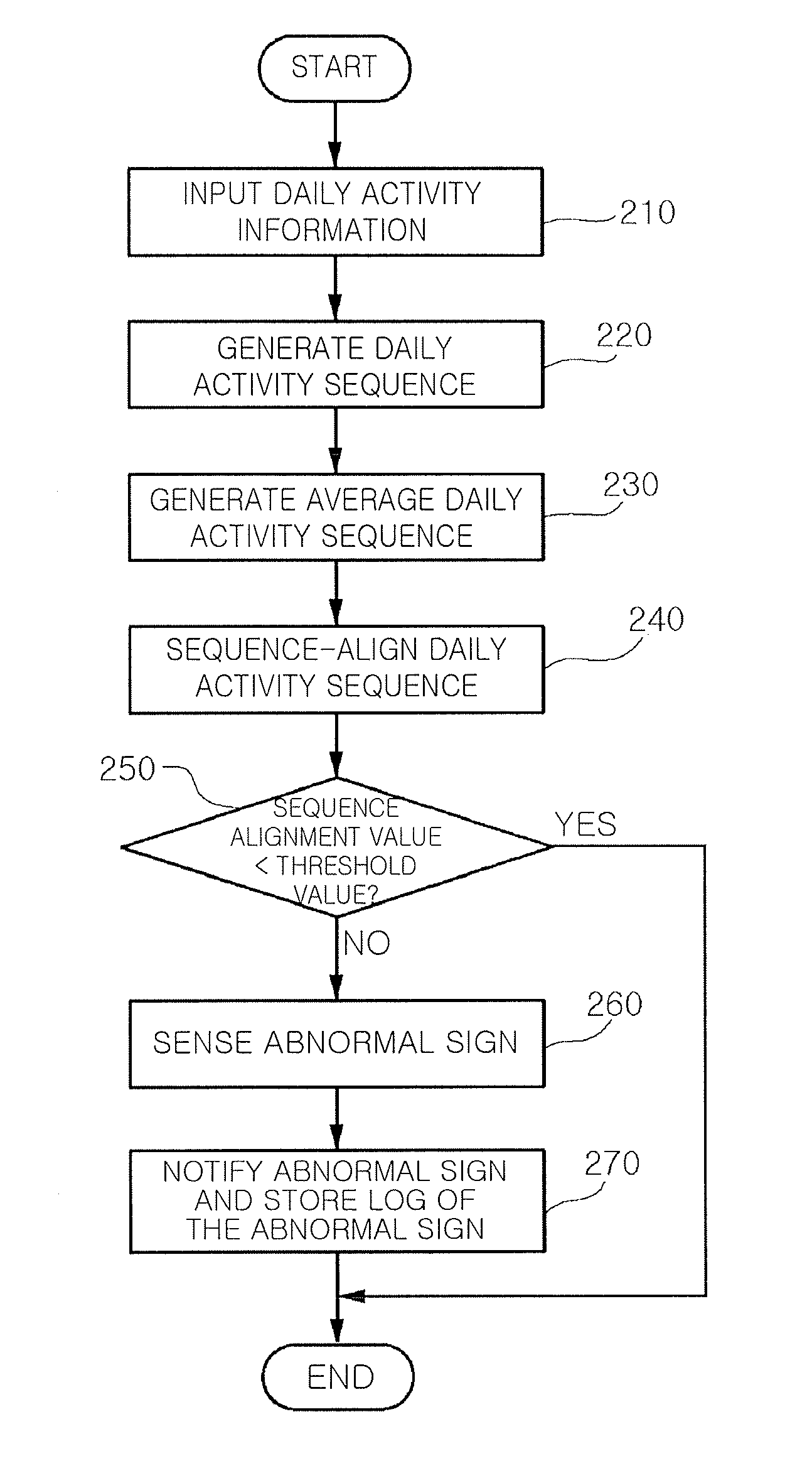
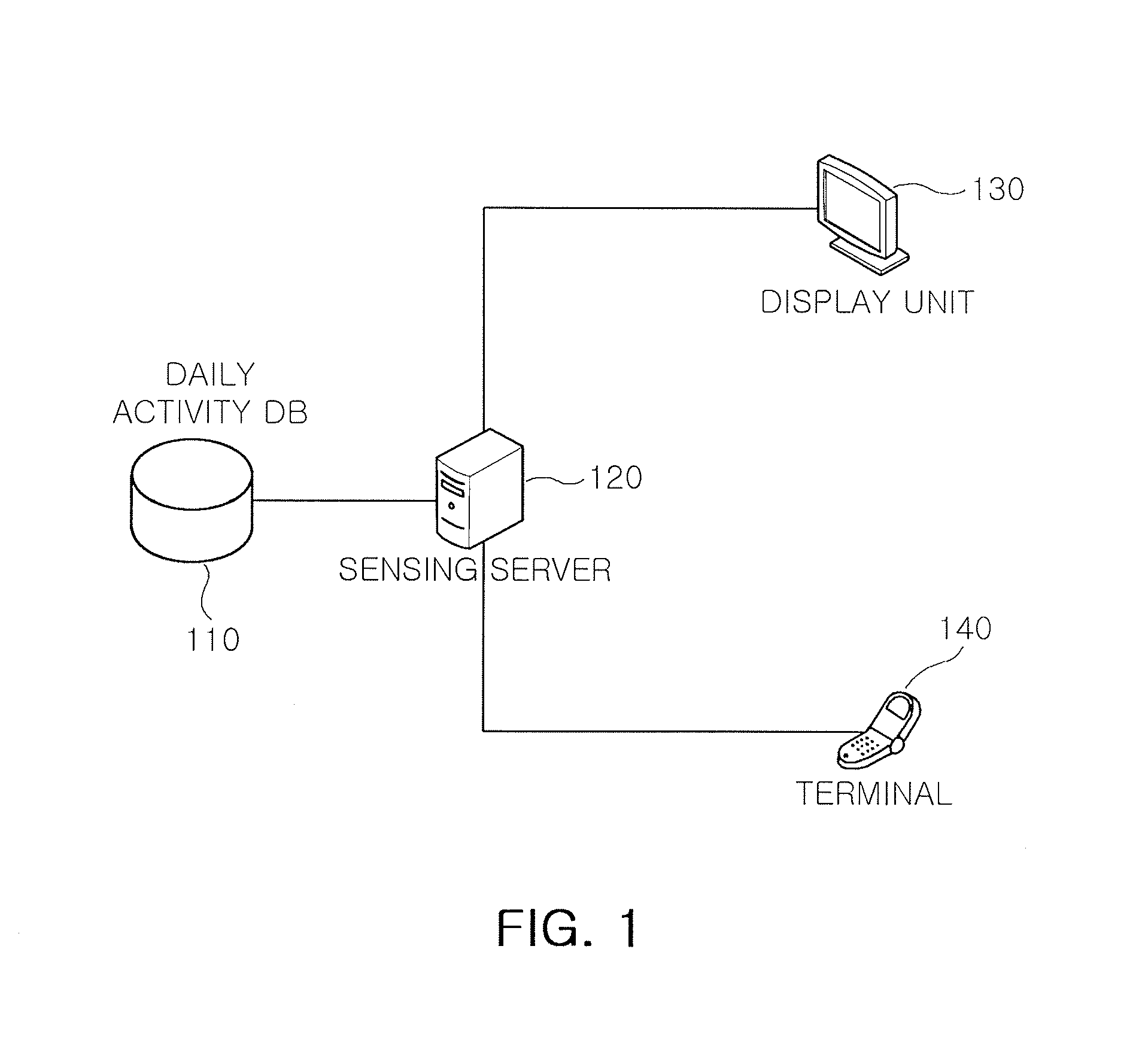
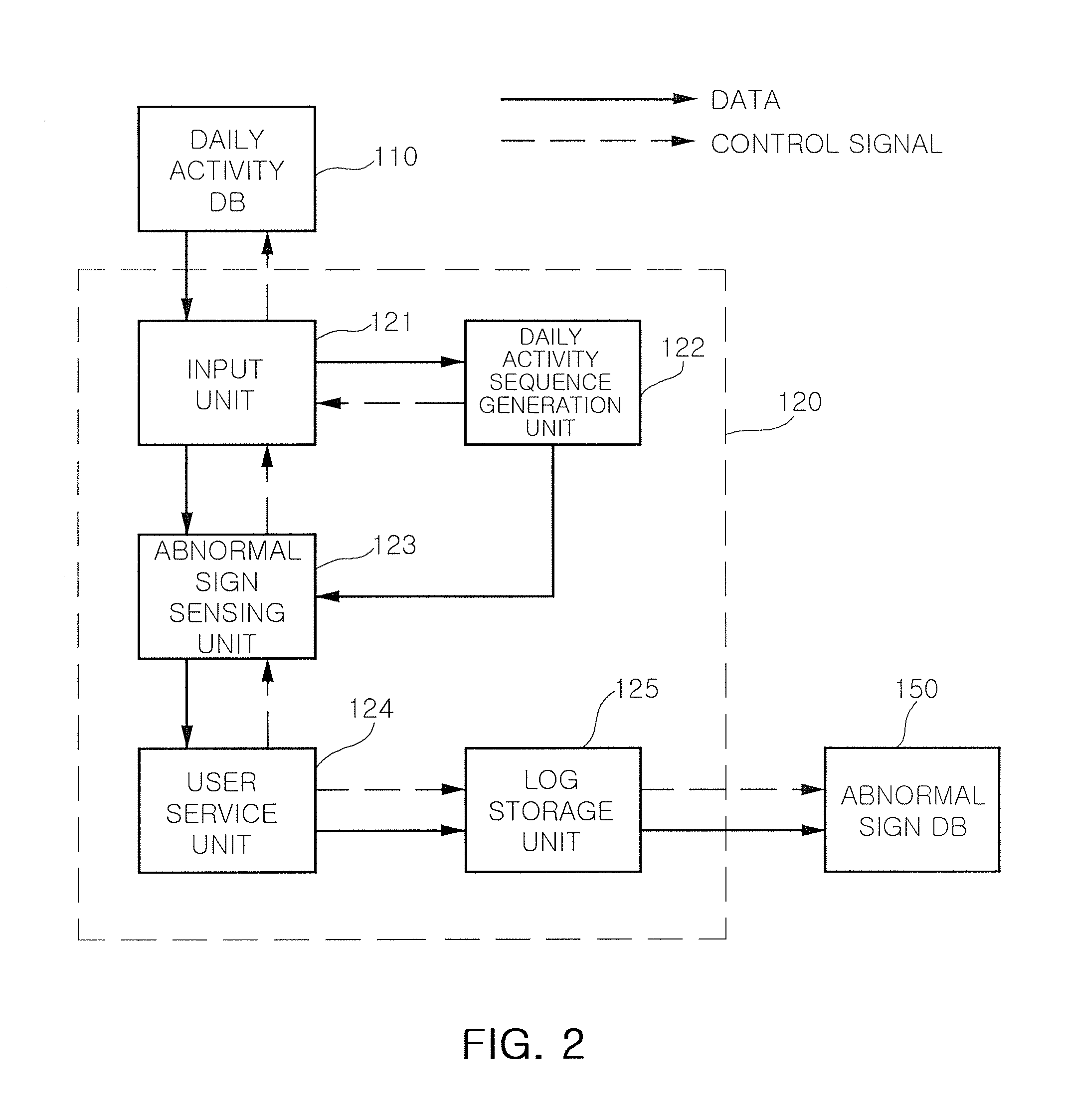
Method and system for sensing abnormal signs in daily activities
InactiveUS7847682B2Efficiently sensedData processing applicationsMedical automated diagnosisSequence alignment algorithmOlder people
There are provided a method and system for sensing abnormal signs in daily activities, the method comprising, at the system, sensing the daily activities, reading previously stored daily activity information, generating a daily activity sequence based thereon, sensing the abnormal signs from the daily activity sequence by using a preset sequence alignment algorithm, and providing the sensed abnormal signs to a user. As described above, the abnormal signs, which should be checked to provide care services, are sensed via changes in a daily activity pattern and added to a care service system that will be installed in welfare facilities for the aged or a home of a solitary old person, thereby effectively sensing the abnormal signs in daily activities of the aged.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Fluorescent organic nanofibrils as sensory materials for explosives detection
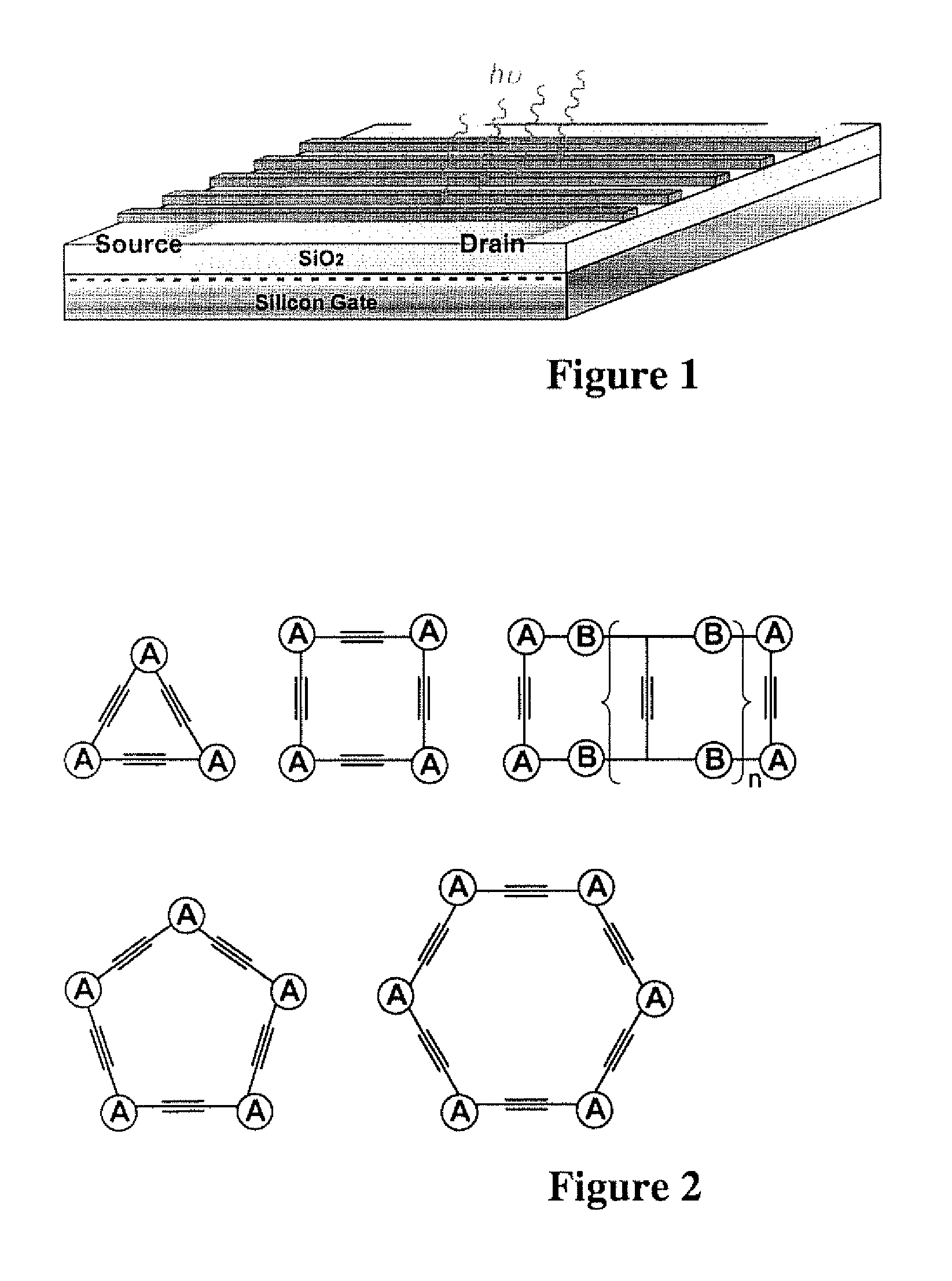
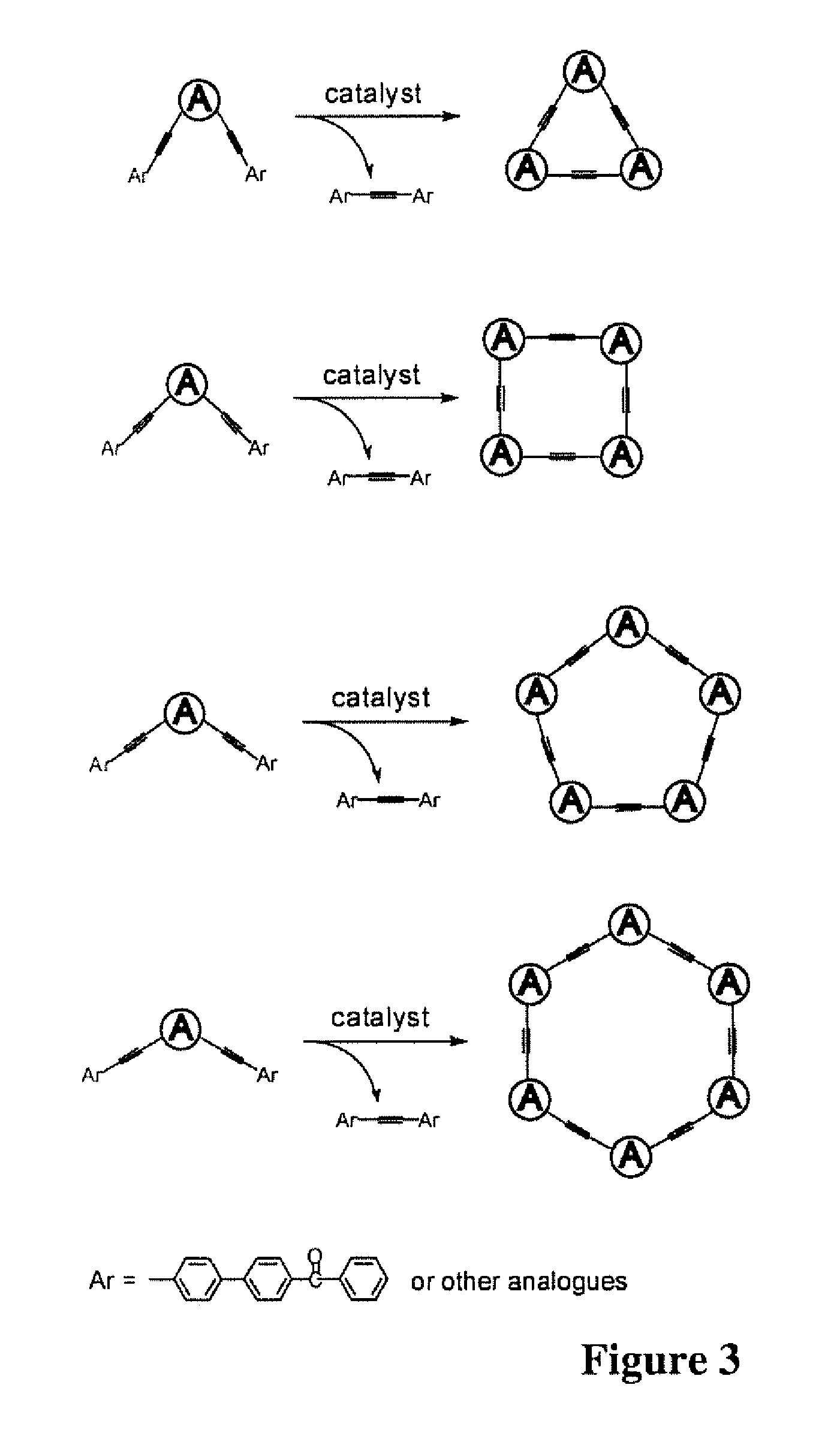
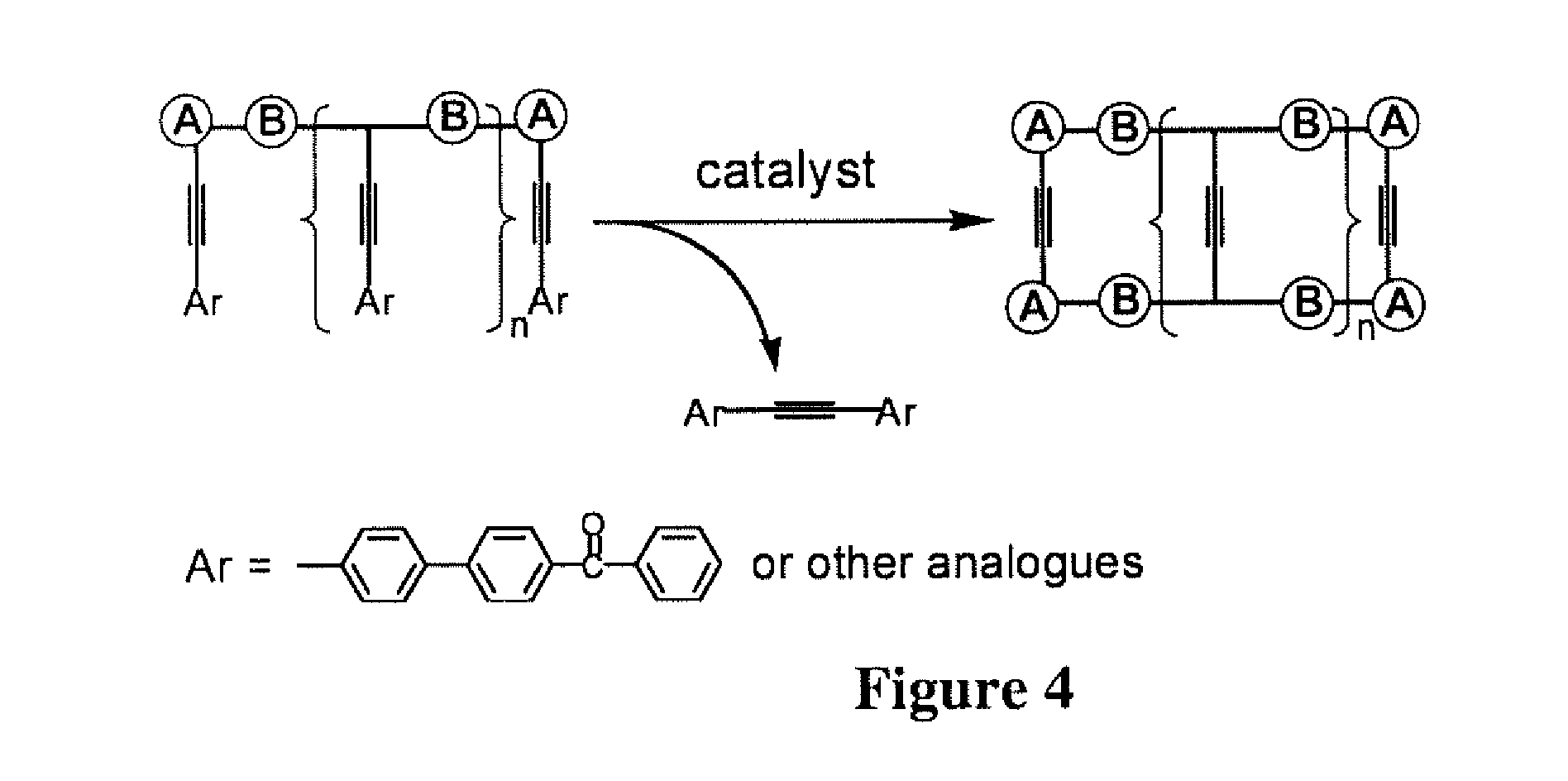
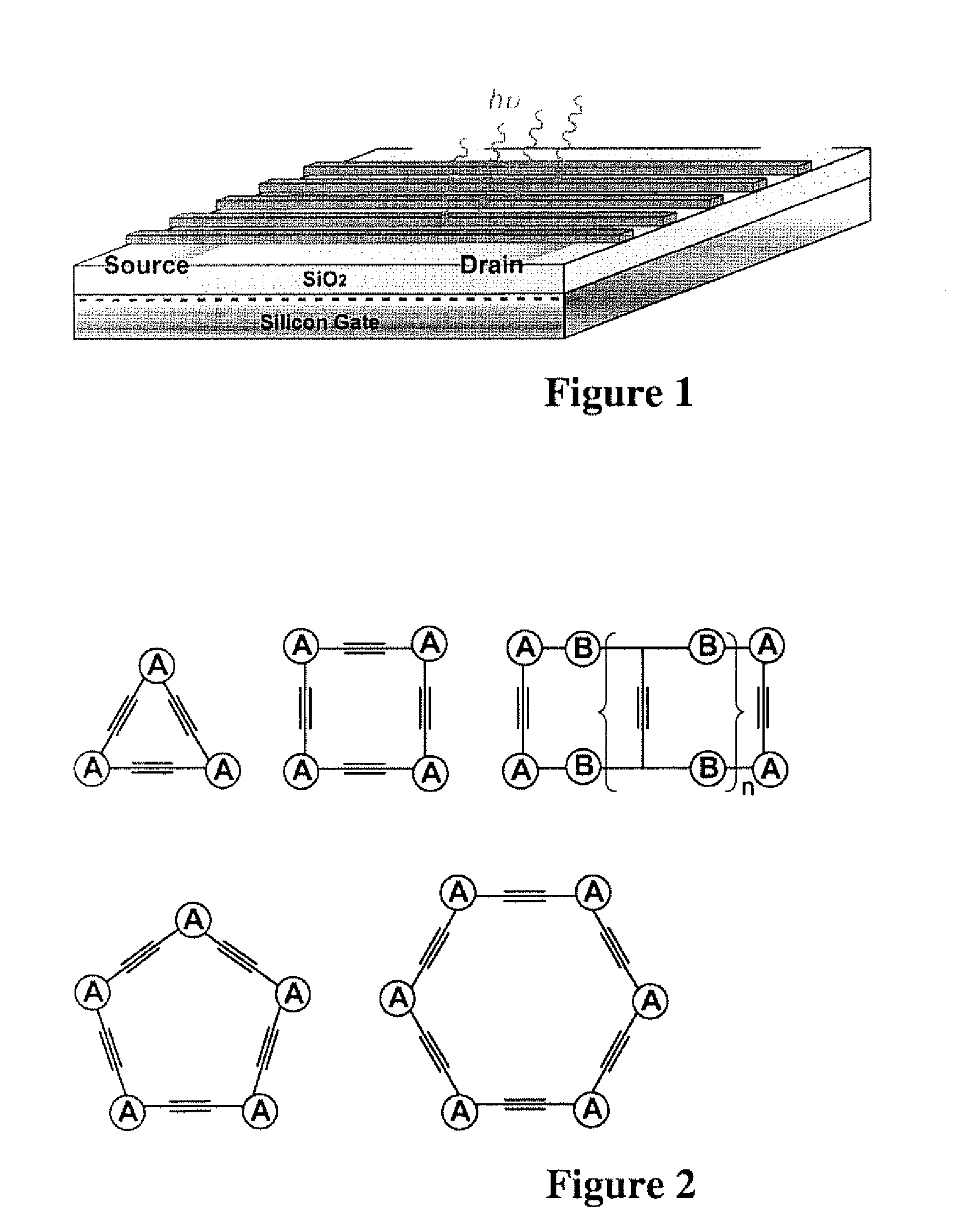
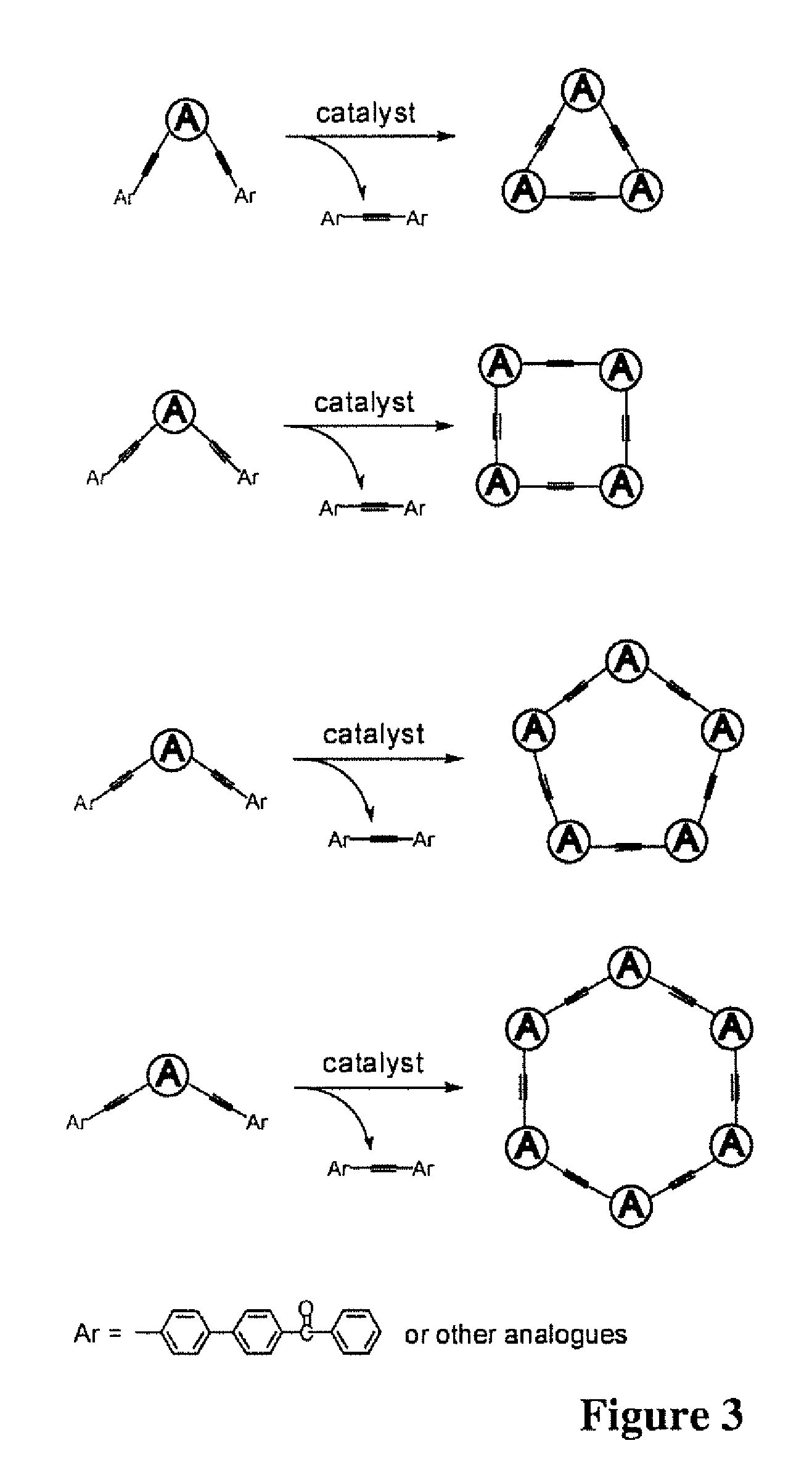
InactiveUS20120288950A1Efficiently quenchedMinimal ring strainMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNanosensorsFiberSynthesis methods
A class of fluorescent, organic nanofibrils, and particularly the films comprising entangled piling of these nanofibrils exhibiting effective quenching of their fluorescence upon exposure the vapor of explosives is disclosed. A sensor and a method for sensing the explosives vapor and other volatile organic compounds is disclosed, including the explosives taggants through the modulation of the fluorescence of the nanofibril film and the electrical conductivity of the nanofibrils. A development of synthetic methods is disclosed, such as protocols and techniques that lead to the production of various arylene-ethynylene macrocycle (AEM) molecules, which consist of a shape-persistent, toroidal scaffold in planar conformation, with minimal ring strain and highly tunable ring sizes (from 0.5 nm to above 10 nm). An approach to optimization of the one-dimensional molecular arrangement along the long axis of the nanofibril is also disclosed, which provides increased exciton migration and charge transport (via pi-electronic delocalization).
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
Flourescent organic nanofibrils based on arylene-ethylene macrocycles as sensory materials for explosives detection
ActiveUS8153065B2Efficiently quenchedMinimal ring strainAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by electrical excitationFiberFluorescence
The present invention relates to a class of fluorescent, organic nanofibrils, and particularly the films comprising entangled piling of these nanofibrils exhibiting effective quenching of their fluorescence upon exposure the vapor of explosives. The invention also relates to a sensor and a method for sensing the explosives vapor and other volatile organic compounds, including the explosives taggants through the modulation of the fluorescence of the nanofibril film and the electrical conductivity of the nanofibrils. The invention also relates to a development of synthetic methods, protocols and techniques that leads to production of various arylene-ethynylene macrocycle (AEM) molecules, which consist of a shape-persistent, toroidal scaffold in planar conformation, with minimal ring strain and highly tunable ring sizes (from 0.5 nm to above 10 nm). The invention also relates to an approach to optimization of the one-dimensional molecular arrangement along the long axis of the nanofibril, which provides increased exciton (excited state) migration (via cofacial intermolecular electronic coupling) and charge transport (via pi-electronic delocalization). A combination of long-range exciton migration and efficient charge transport makes the nanofibrils ideal as sensory materials for detecting explosives and other volatile organic compounds through both optical and electrical sensing mechanisms.
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
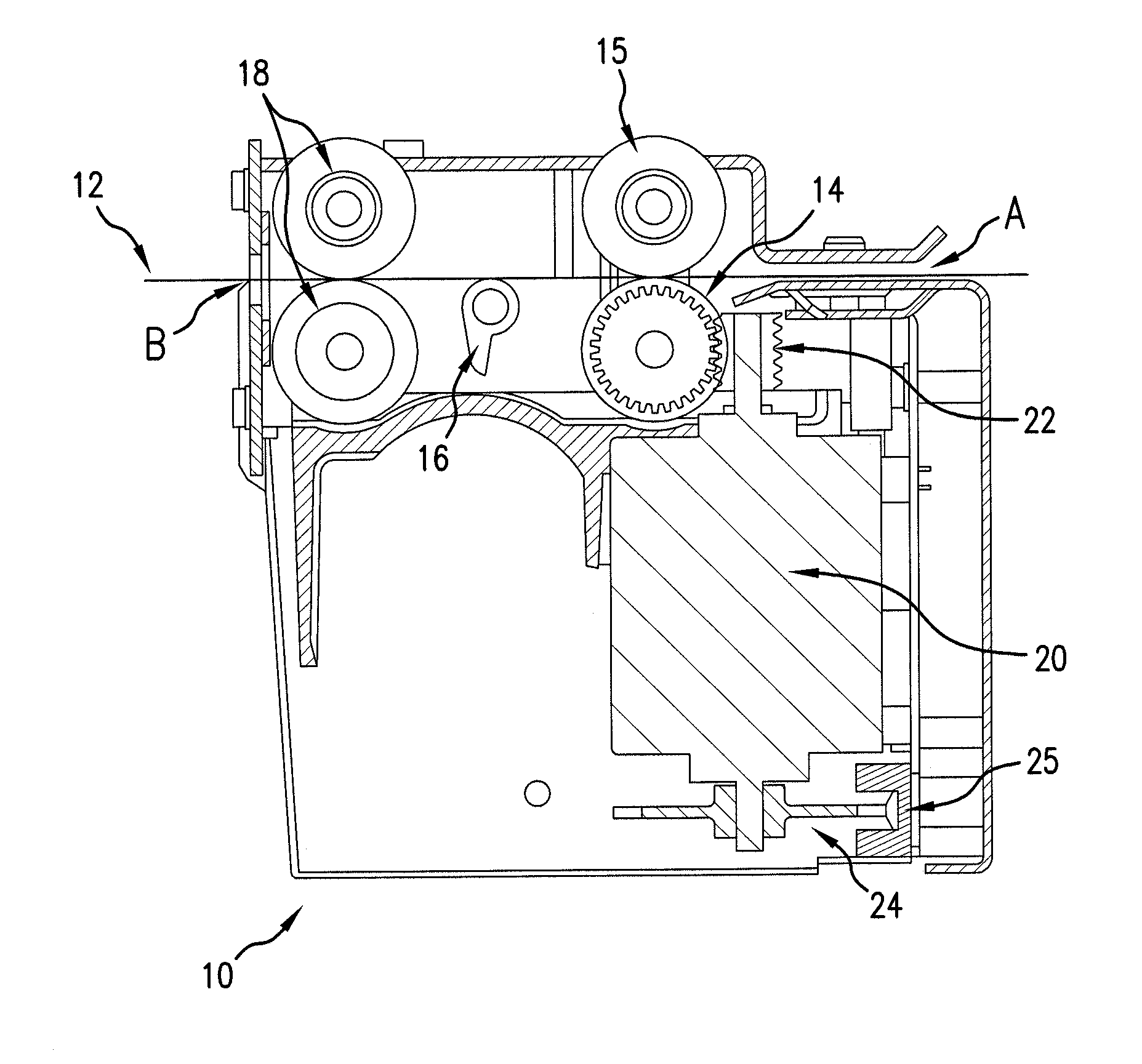
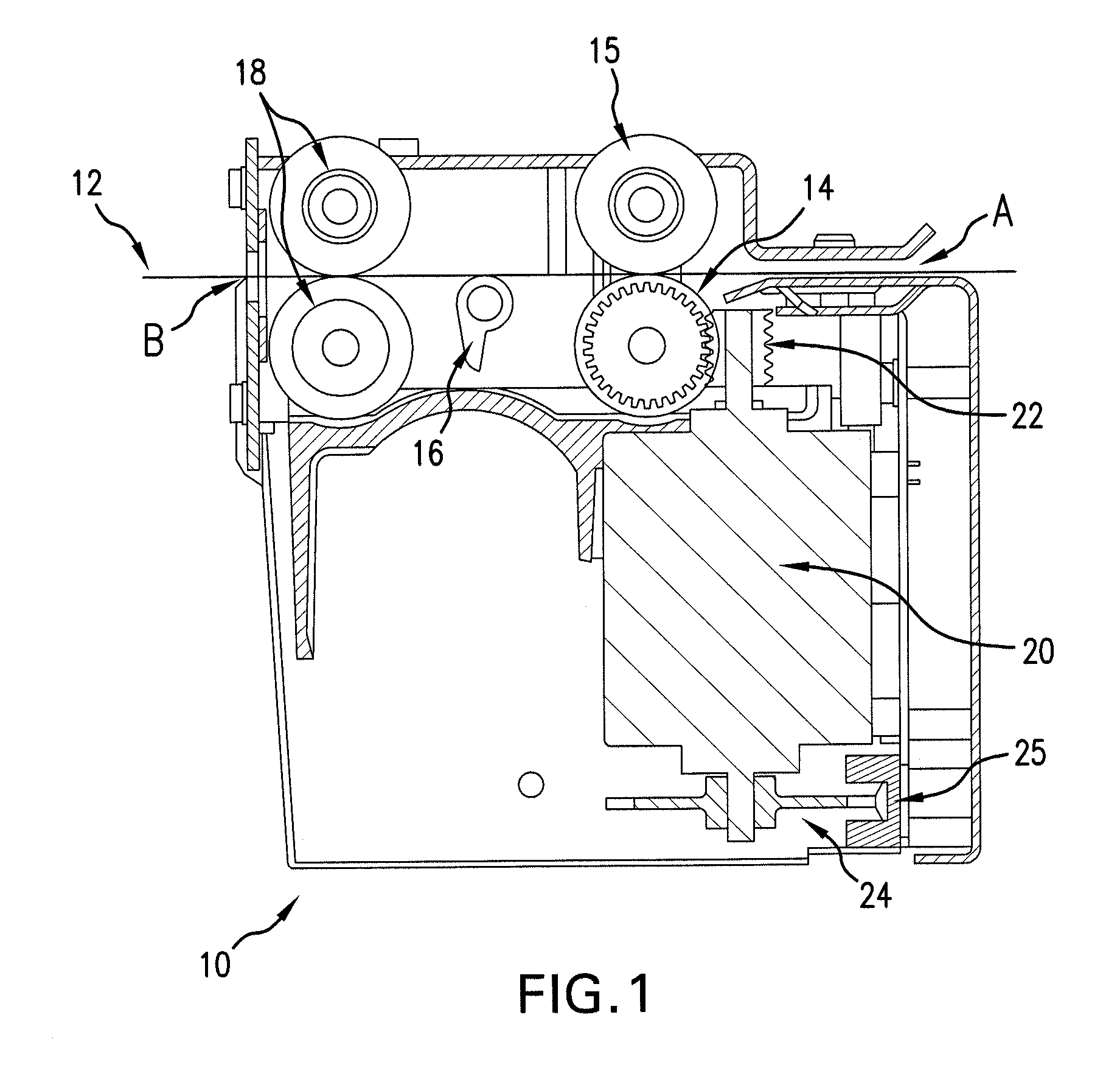
Perforated Ticket Dispensing Machine
ActiveUS20120085777A1Improve complianceEasy to disassembleAutomatic control devicesPrecision positioning equipmentLeaf spring
The present invention provides an independently operable and serviceable ticket burster machine that properly handles perforated tickets of all shapes, sizes and thicknesses. The present invention includes a ticket burster element, an exit sensor with a mechanical flag switch, an inventory flag spanning the entire width of the ticket input slot and having an optical slot switch, a slidable ticket guide, one or more leaf spring arrangements and versatile and durable rollers.
Owner:IGT GLOBAL SOLUTIONS CORP
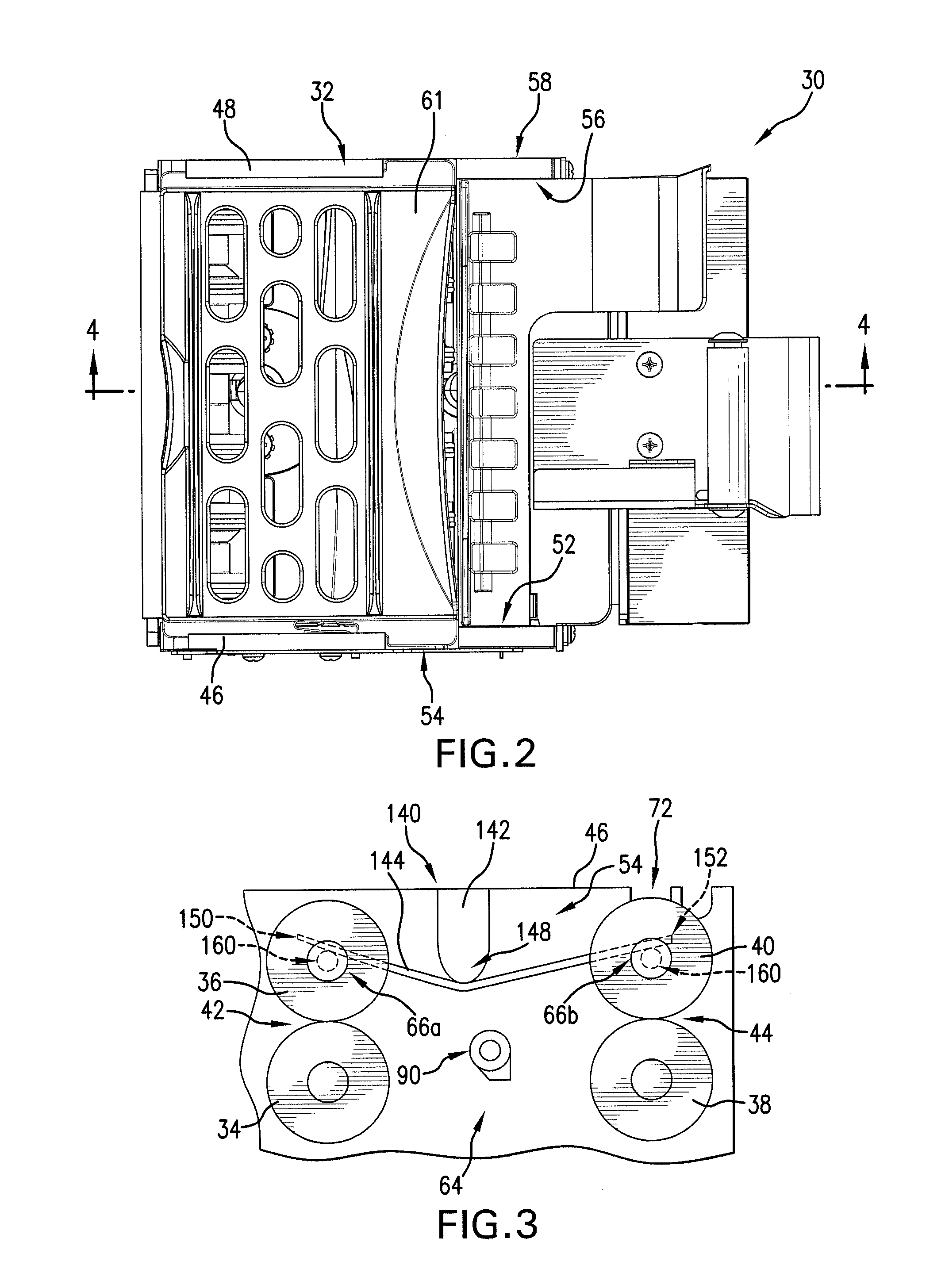
Device for tracing movement of mobile robot and method thereof
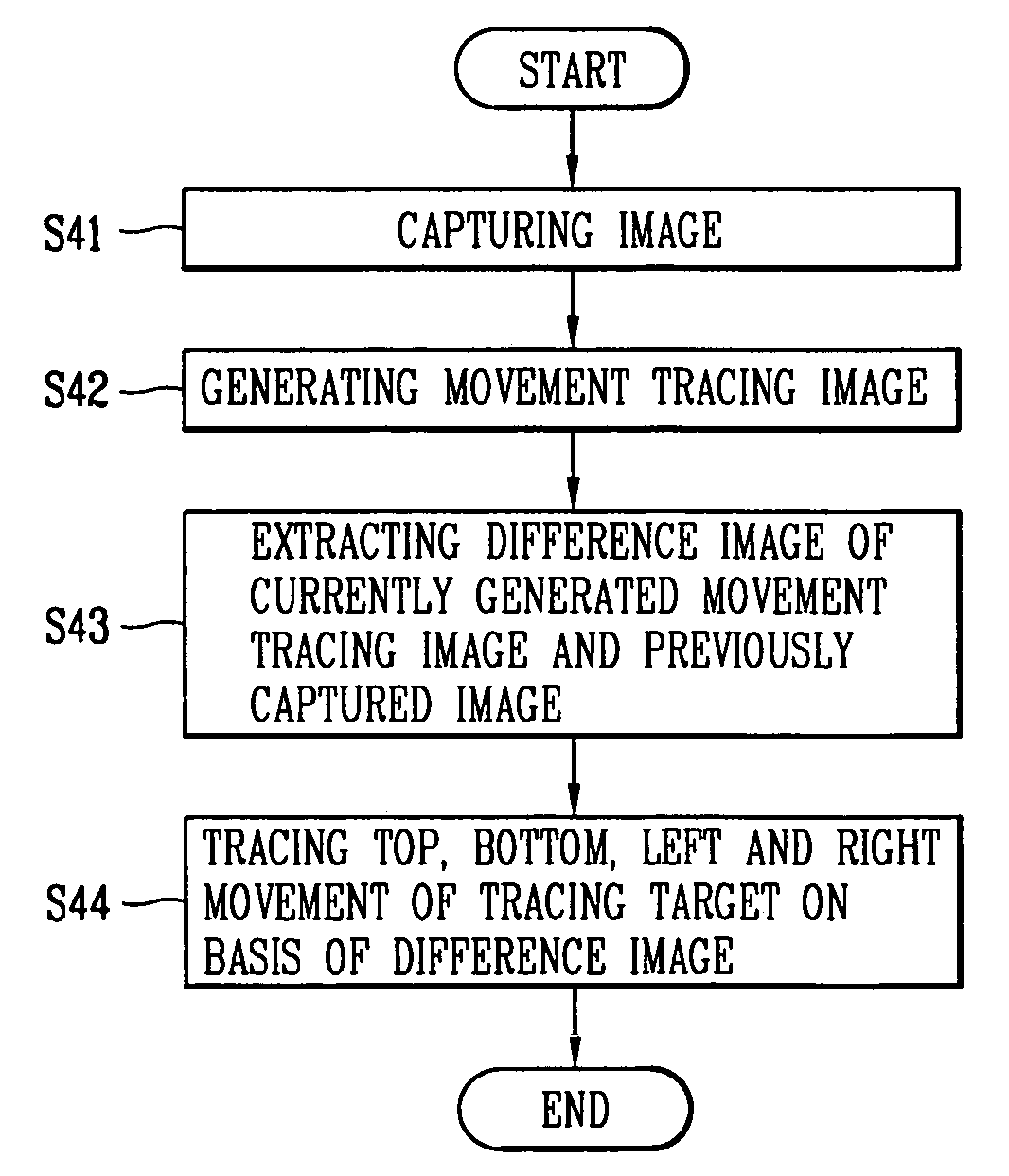
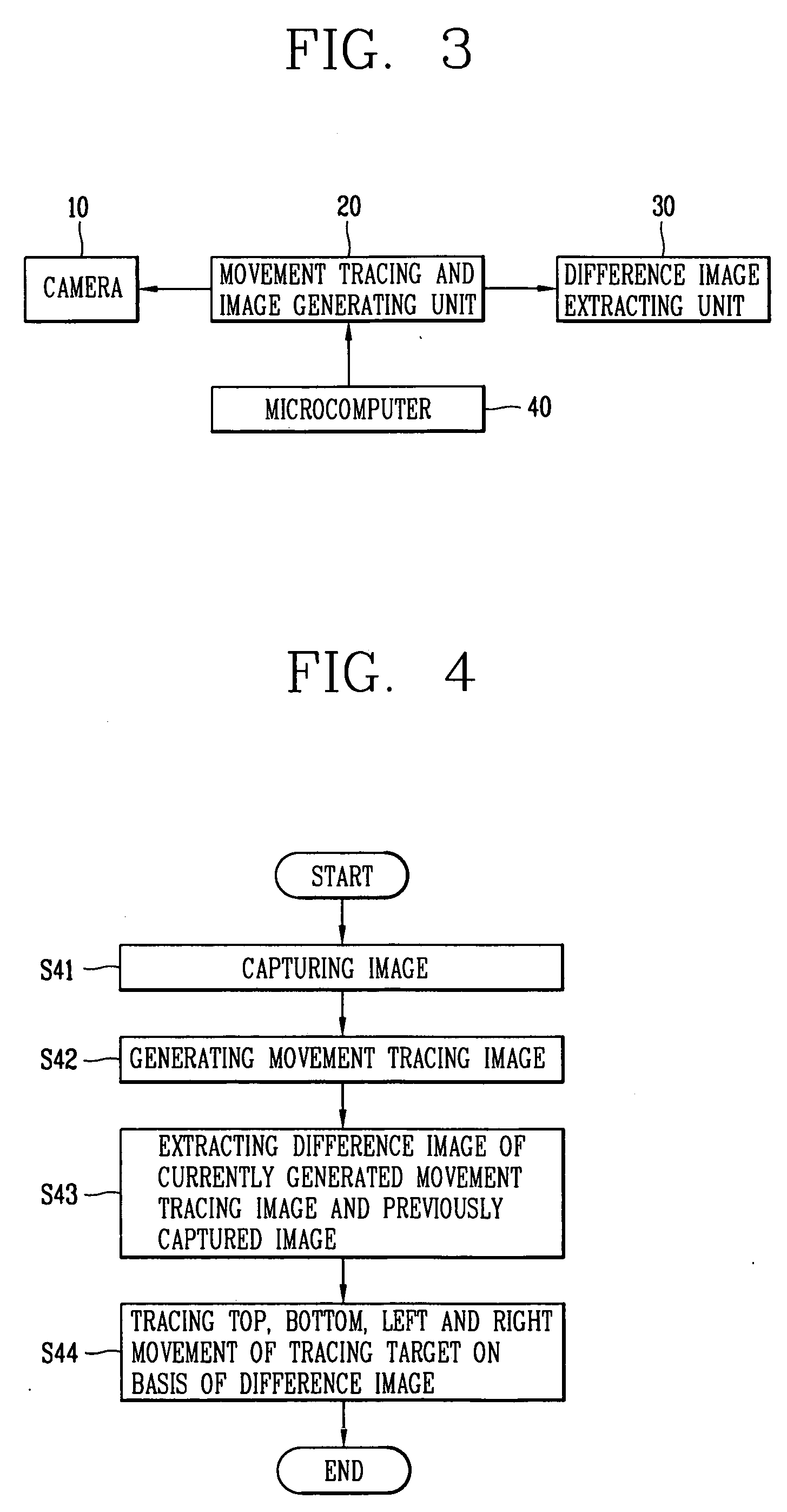
InactiveUS20060100742A1Reduce computationEfficiently sensedProgramme controlCarpet cleanersMicrocomputerImage extraction
Disclosed are a device for tracing a movement of a mobile robot and a method thereof. The device for tracing a movement of a mobile robot includes: a camera for capturing a specific object; a movement tracing and image generating unit for setting a reference area in the present image produced by capturing the specific object by the camera and generating the present image in which the reference area is set; a difference image extracting unit for extracting a difference image of pixels of the edge of the reference area of the present image and pixels of the reference area of a previous image; and a microcomputer for tracing a movement of the specific object based on the extracted difference image.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
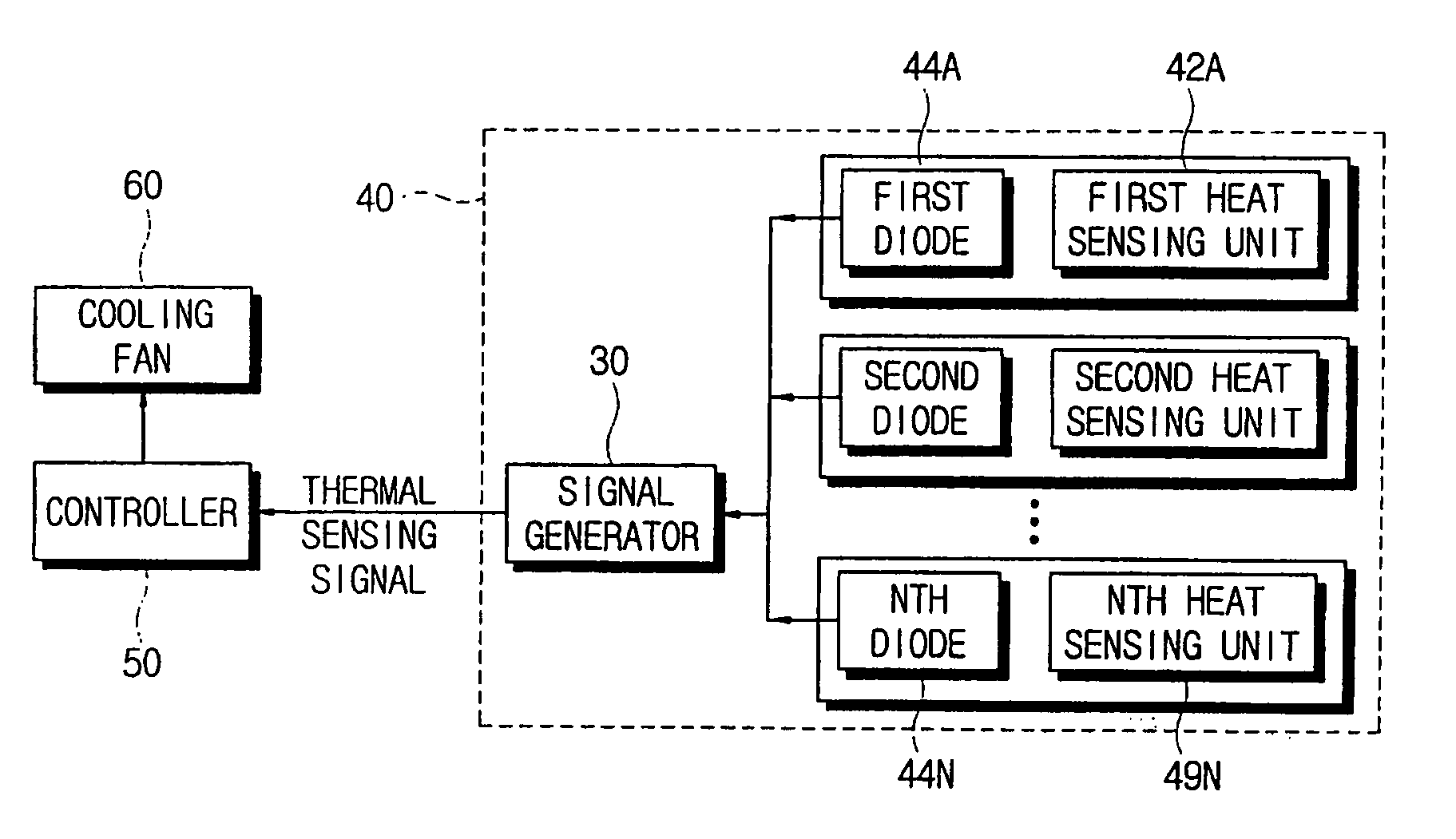
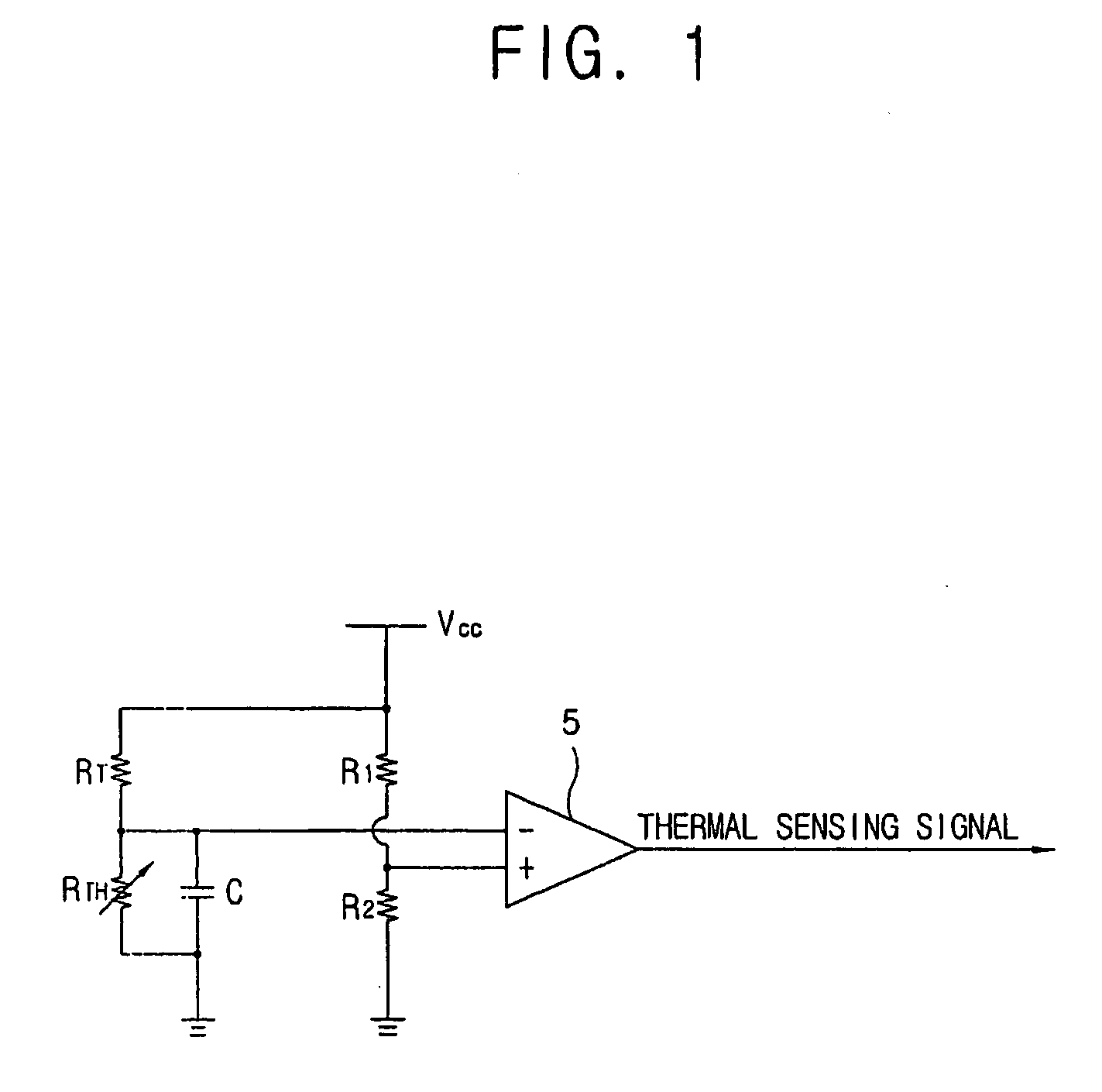
Thermal sensing apparatus and computer system incorporating the same
InactiveUS20060285575A1Efficiently sensedThermometer detailsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringSignal generator
A thermal sensing apparatus is provided with a simple diode module for sensing a temperature of a plurality of points or positions within a computer system. Such a thermal sensing apparatus comprises: a plurality of heat sensing units provided at different points or positions for sensing heat generated from one or more sensing subjects; a plurality of switching units connected to the plurality of heat sensing units; and a signal generator which compares a predetermined standard voltage and an input signal, which is changed when at least one of the plurality of switching units turns on, based on a sensing result from the plurality of heat sensing units, and generates a predetermined thermal sensing signal according to a comparision result.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Display apparatus and control method thereof
ActiveUS20180081492A1Efficiently sensedShorten speedInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceHuman–computer interaction
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of eliminating impact/shock related false alarms in an acoustical glassbreak detector
ActiveUS7388487B2Efficiently sensedBurglar alarm by glass breakingAnti-theft devicesShock waveDetector circuits
Owner:ADEMCO INC
Method of using dopamine reuptake inhibitors and their analogs for treating diabetes symptoms and delaying or preventing diabetes-associated pathologic conditions
ActiveUS9119843B2Attenuate diabetic neurologicalLow extremityBiocideMetabolism disorderAcute hyperglycaemiaNorepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
Method of using dopamine reuptake inhibitors, e.g., sydnonimine derivatives, for the management of diabetic symptoms and associated complications or conditions, such as hyperglycemia and diabetic neuropathy.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
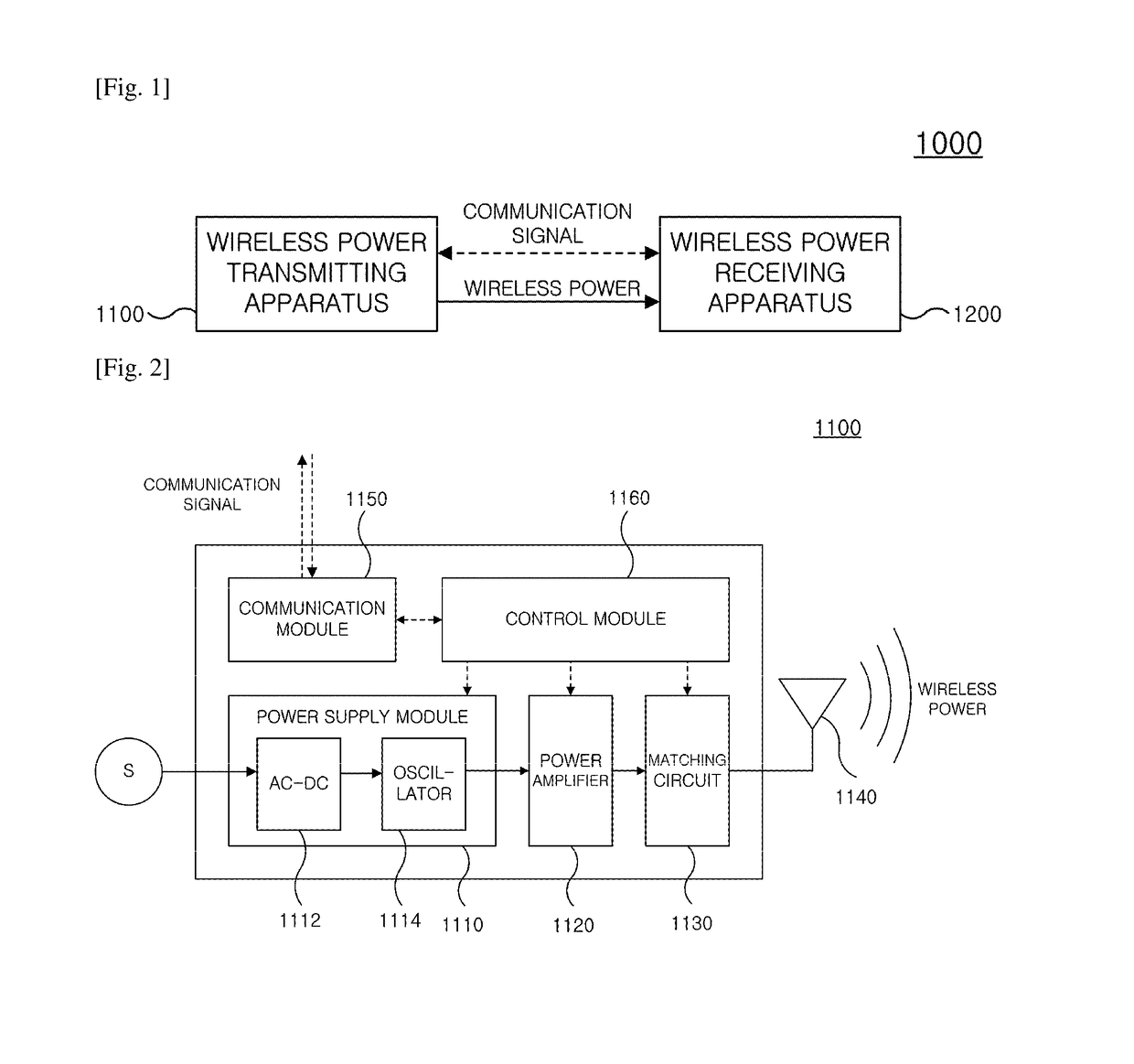
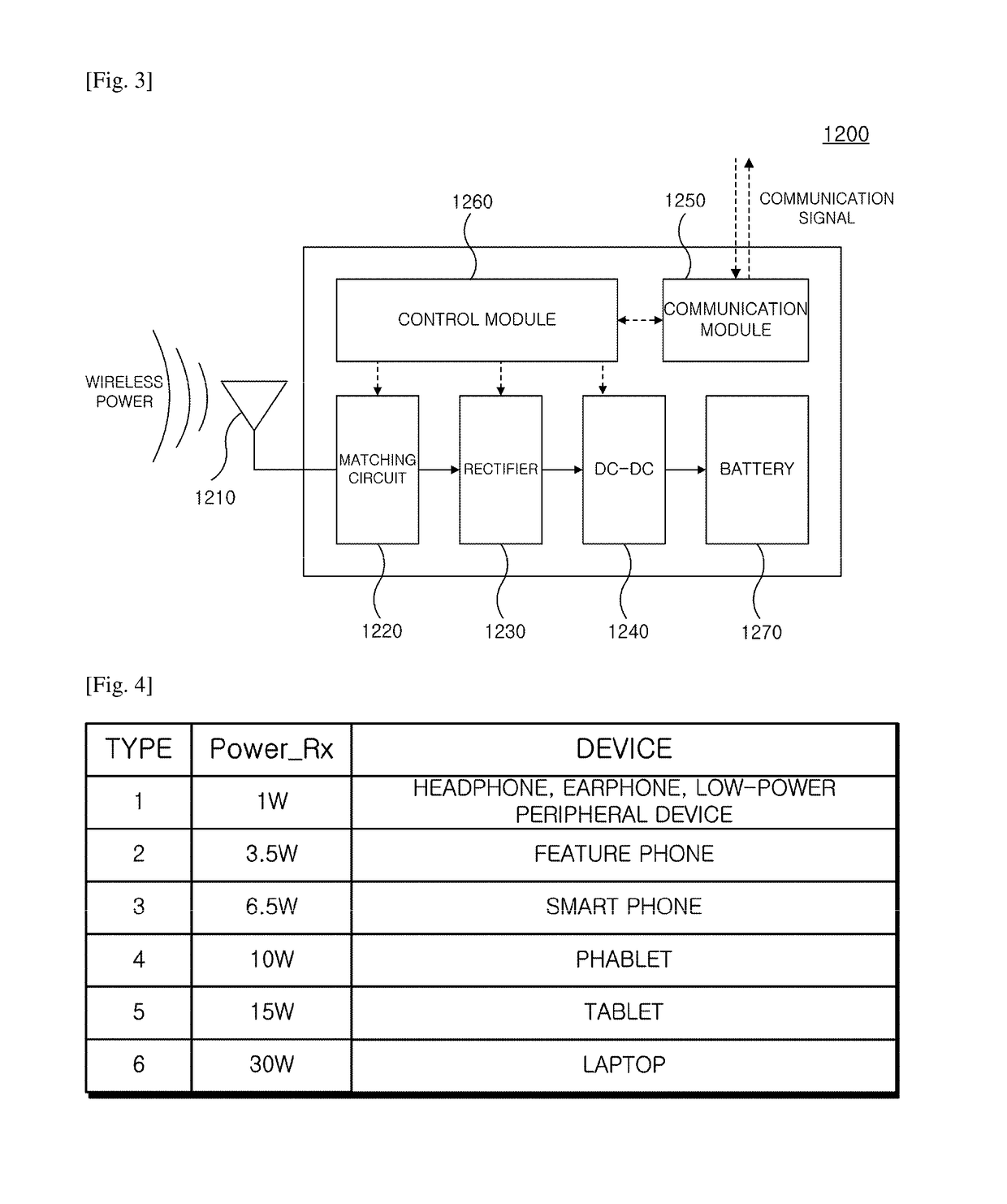
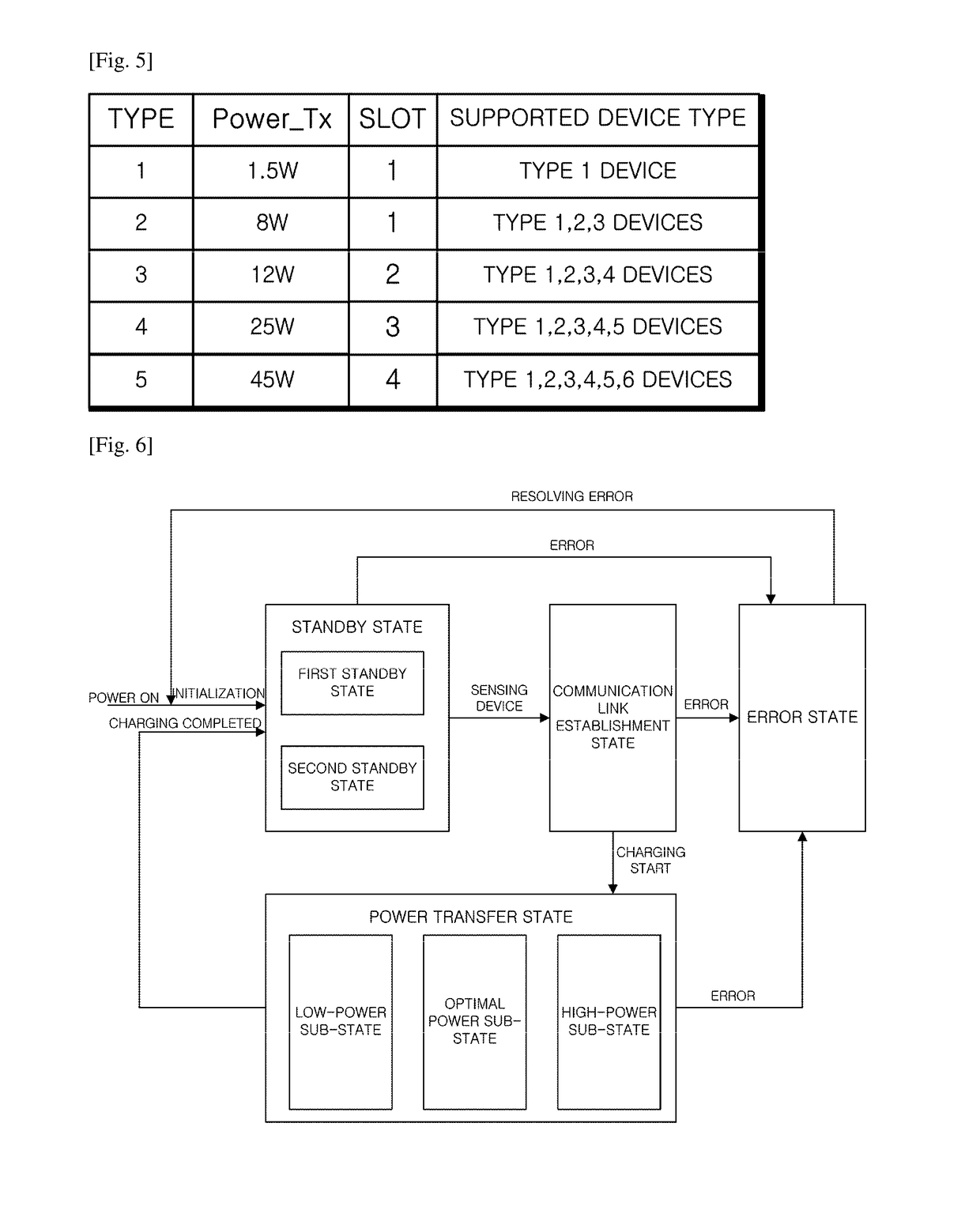
Wireless power transmission apparatus and wireless power transmission method
ActiveUS10141785B2Minimize power consumptionEfficiently sensedNear-field transmissionTransformersElectric power transmissionTransmitted power
The present invention relates to a method for verifying a charging state of a wireless power receiving apparatus in the wireless power transmitting apparatus, and more particularly, to an apparatus and a method for efficiently performing and controlling wireless power transmission.To this end, the present invention provides a wireless power transmitting method, wherein a standby state of determining whether at least one wireless power receiving apparatus is positioned within a wireless charge range of the wireless power transmitting apparatus and a power transfer state of transmitting power to the corresponding wireless power receiving apparatus when at least one wireless power receiving apparatus is detected in the standby state are provided, and the standby state includes a first standby state of periodically transmitting a weak detector signal and a strong detector signal and a second standby state in which at least one of a transmission period of the weak detector signal and a transmission period of the strong detector signal is different from that of the first standby state, the method including: determining any one state of the first standby state and the second standby state of the wireless power transmitting apparatus; and transmitting the weak detector signal and the strong detector signal based on the determined standby state, wherein the transmission period of the weak detector signal in the second standby state is longer than the transmission period of the weak detector signal in the first standby state.
Owner:WILUS INST OF STANDARDS & TECH
Method and system for sensing abnormal signs in daily activities
InactiveUS20090066501A1Efficiently sensedData processing applicationsMedical automated diagnosisSequence alignment algorithmOlder people
There are provided a method and system for sensing abnormal signs in daily activities, the method comprising, at the system, sensing the daily activities, reading previously stored daily activity information, generating a daily activity sequence based thereon, sensing the abnormal signs from the daily activity sequence by using a preset sequence alignment algorithm, and providing the sensed abnormal signs to a user. As described above, the abnormal signs, which should be checked to provide care services, are sensed via changes in a daily activity pattern and added to a care service system that will be installed in welfare facilities for the aged or a home of a solitary old person, thereby effectively sensing the abnormal signs in daily activities of the aged.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
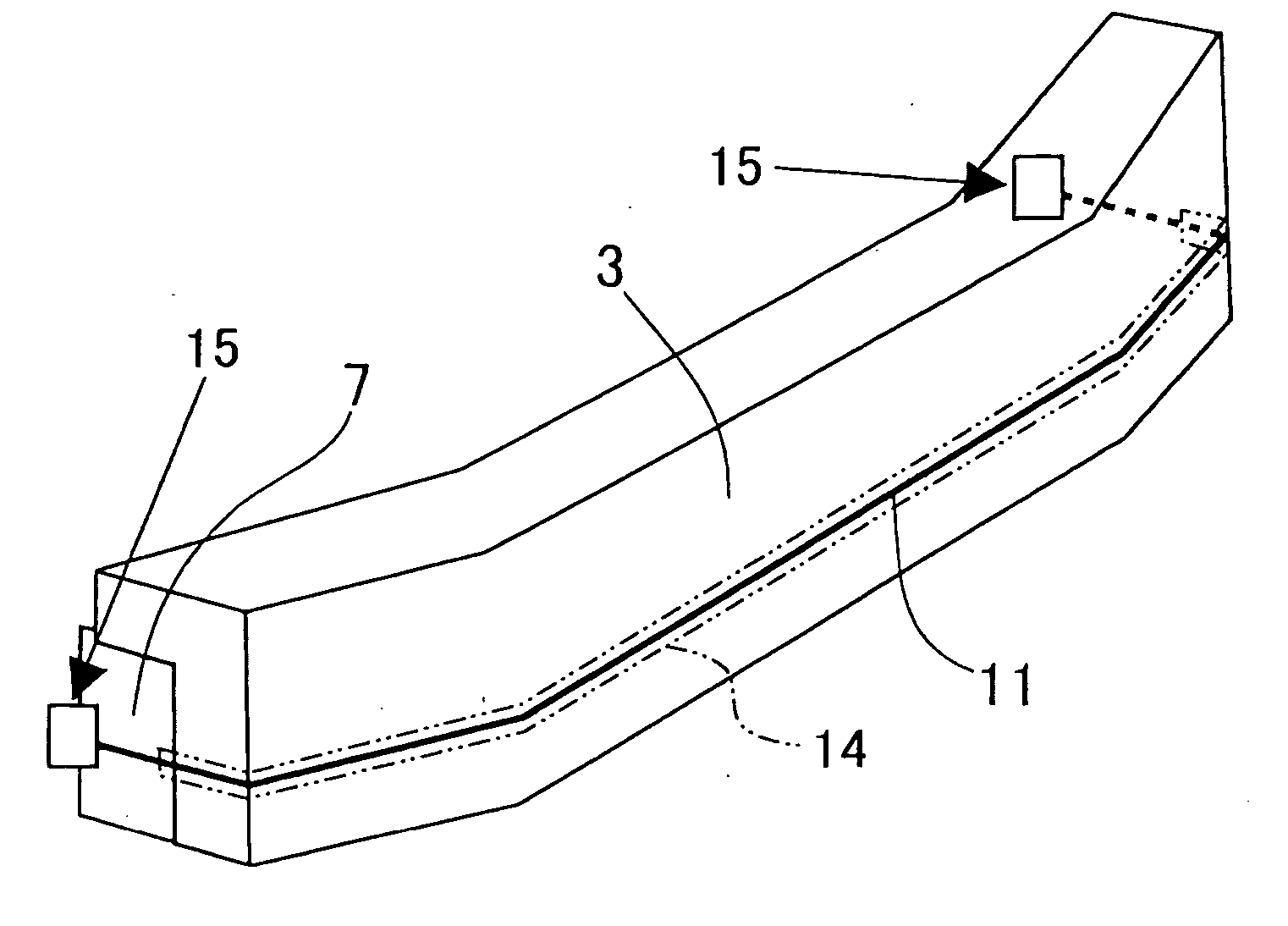
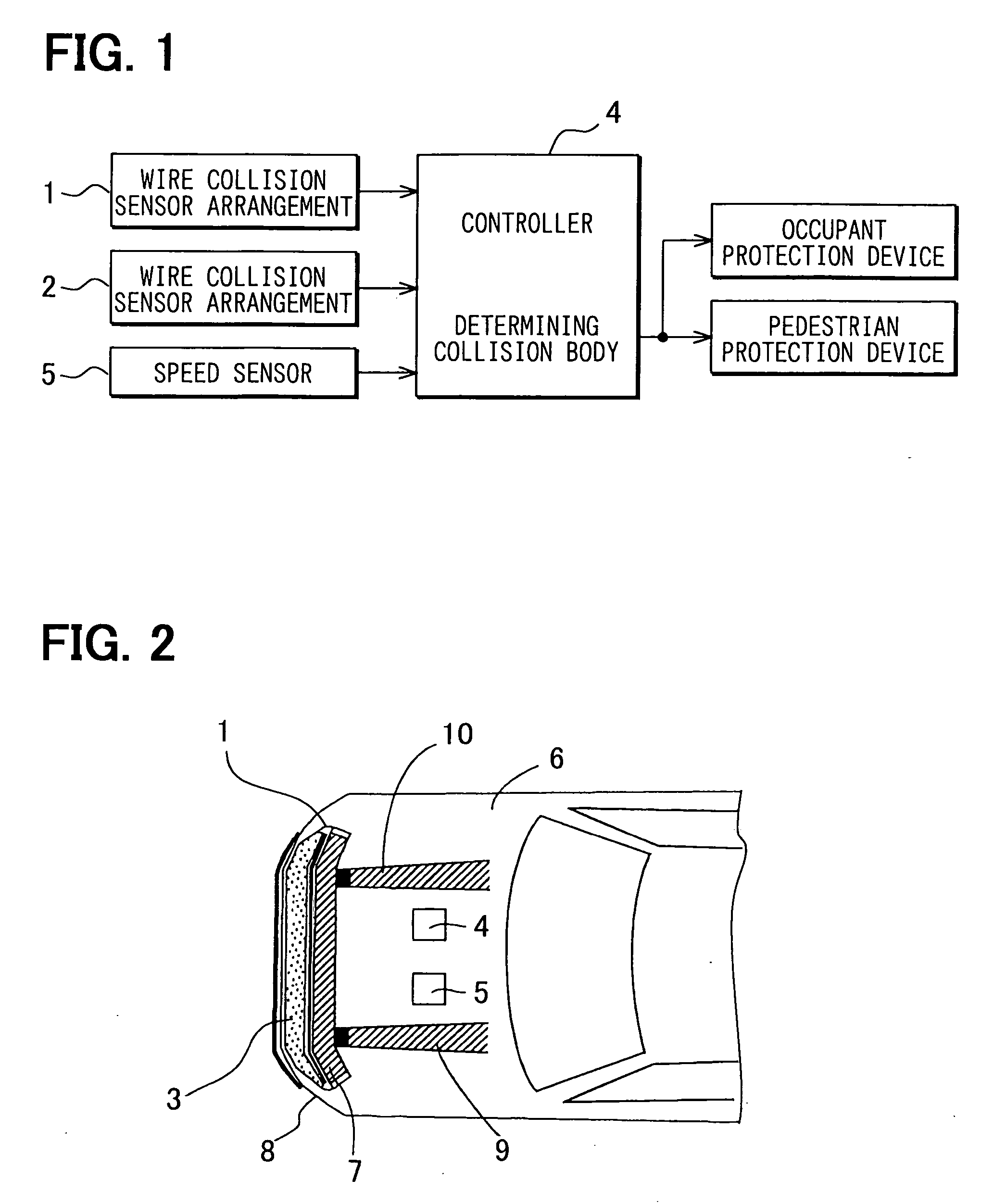
Wire collision sensor system
InactiveUS20060076799A1Efficiently sensedVehicle seatsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementMechanical engineeringInductance
A wire collision sensor system for a vehicle, which includes a vehicle body, includes a bumper, a wire, a wire deformation sensor and a determination circuit. The bumper is mounted on a longitudinal end portion of the vehicle body. The wire, which senses a collision of the vehicle, is received in the bumper and extends along the bumper in a transverse direction of the vehicle. The wire is connected to at least one of the vehicle body and the bumper at both ends in such a manner that the wire is displaceable in a longitudinal direction of the wire. The wire deformation sensor electrically senses a physical quantity, which is associated with a deformation of the wire at a time of the collision. The wire deformation sensor transmits an output, which indicates the sensed physical quantity. The determination circuit determines a state of the collision based on the output.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com