Method for identifying cytoplasm type of three-line sterile rice by detecting chloroplast DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid)
A chloroplast, cytoplasmic technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as inability to distinguish cytoplasmic, no cytoplasmic marker traits, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
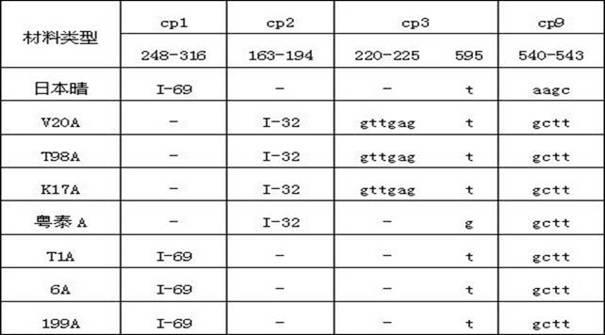
[0010] In the present invention, 32 typical indica rice and typical japonica rice cytoplasms were used as controls, and the chloroplast DNA sequences of 17 three-line sterile lines from different sources were analyzed, and it was found that different types of sterile cytoplasms had characteristic bases or base sequences, and the chloroplast primers The amplified sequence difference of cp1, cp2, cp3 and cp9 established three chloroplast DNA molecular fingerprints of wild type, red lotus type and BT type.
[0011] Using conventional rice Nipponbare as a control, PCR amplification products of chloroplast DNA of three-line male sterile lines such as V20A were cloned and sequenced, and the sequence results are shown in Table 1.
[0012] Table 1
[0013]
[0014] Note: "-" means missing the sequence.
[0015] Chloroplast primers described in Table 1
[0016] cp1: forward sequence 5-gtggacctgactccttgaa-3, reverse sequence 5-agccgaggtcgtggtaa-3;
[0017] cp2: forward sequence 5-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com