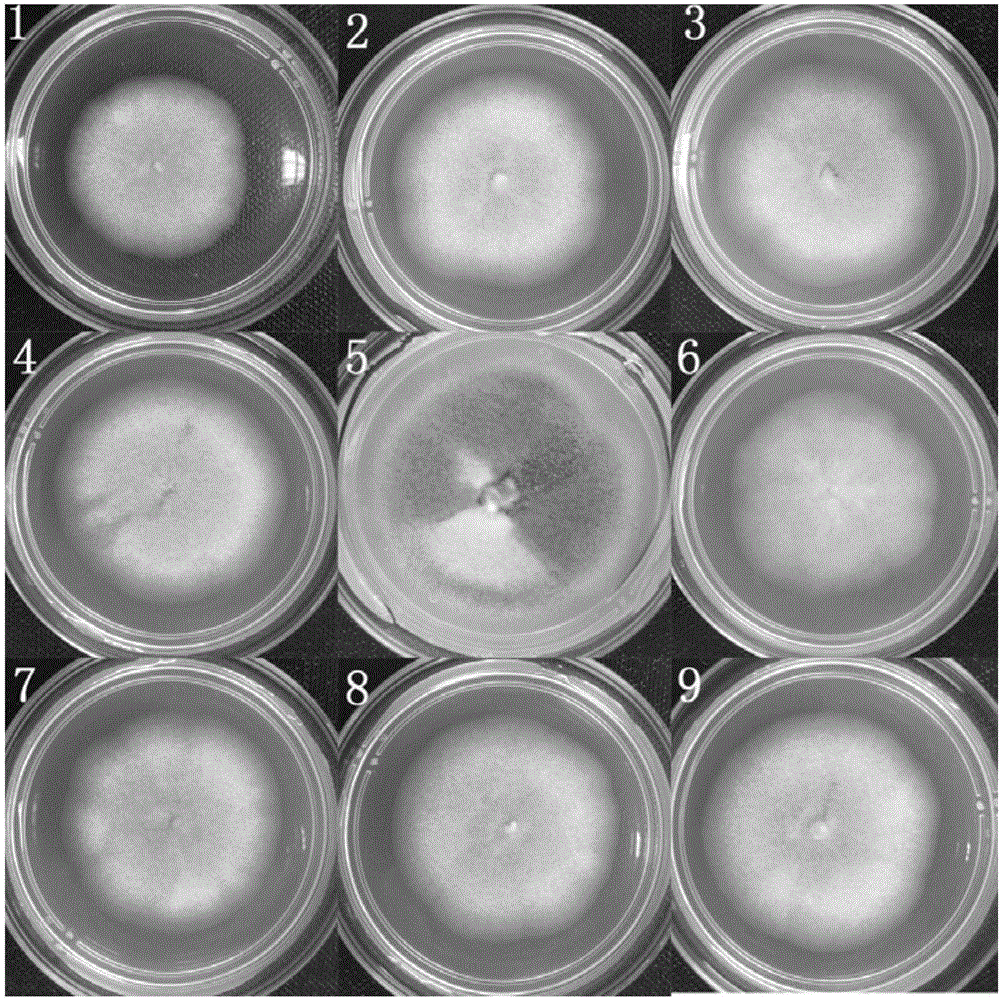
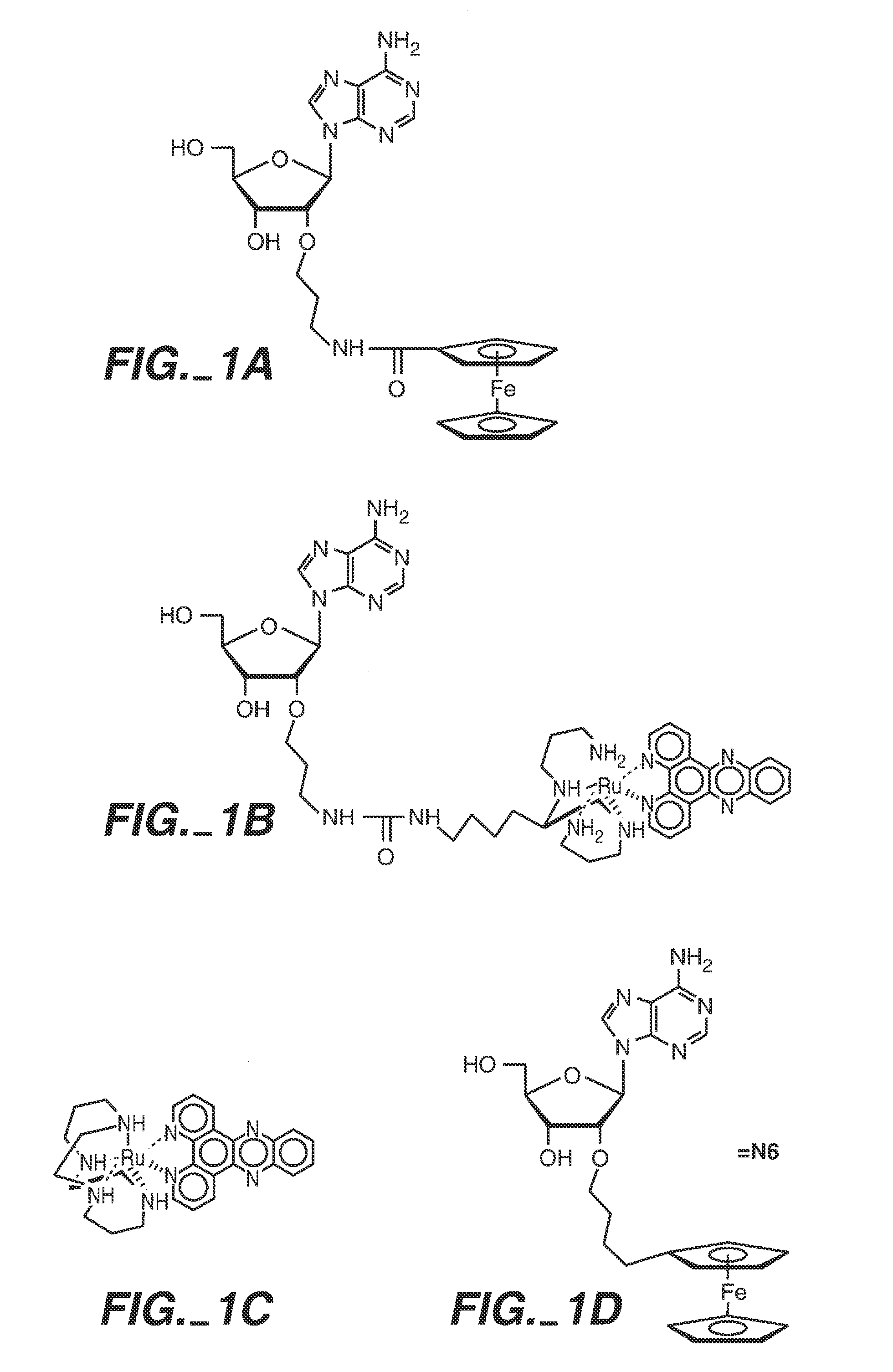
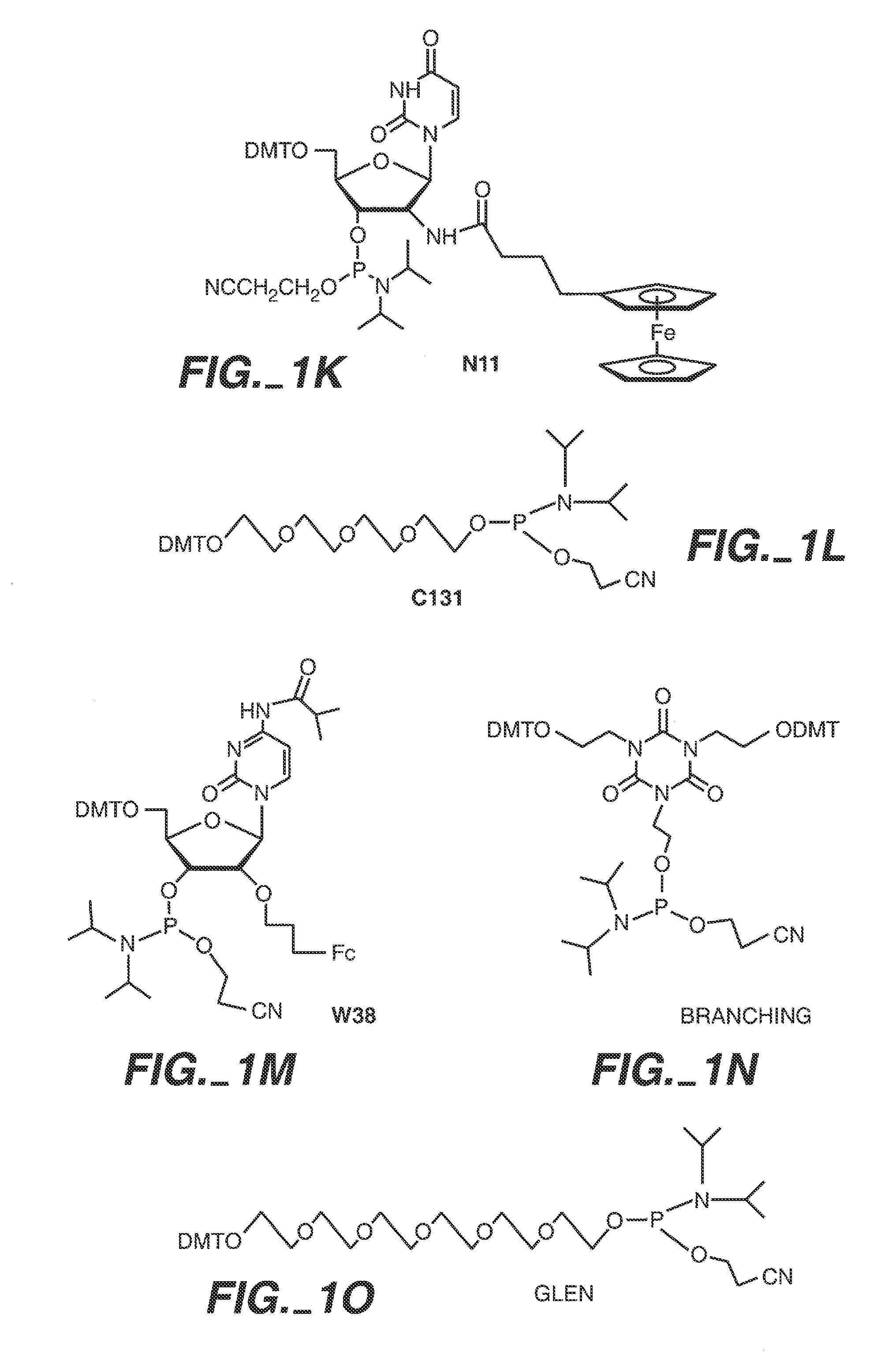
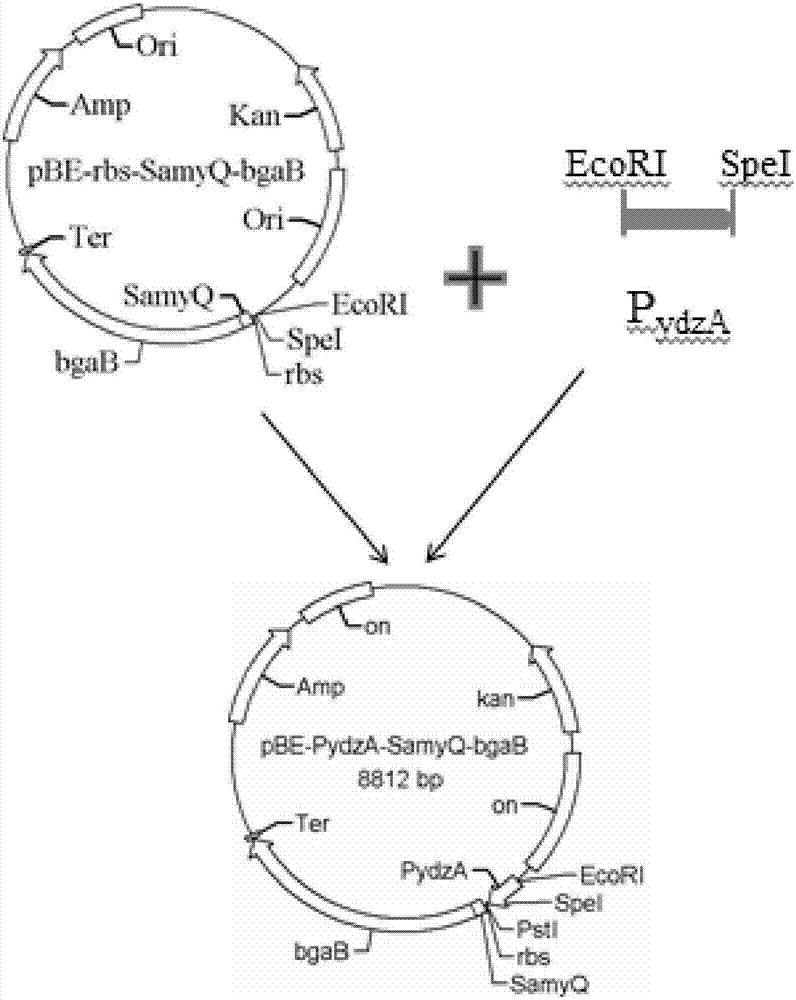
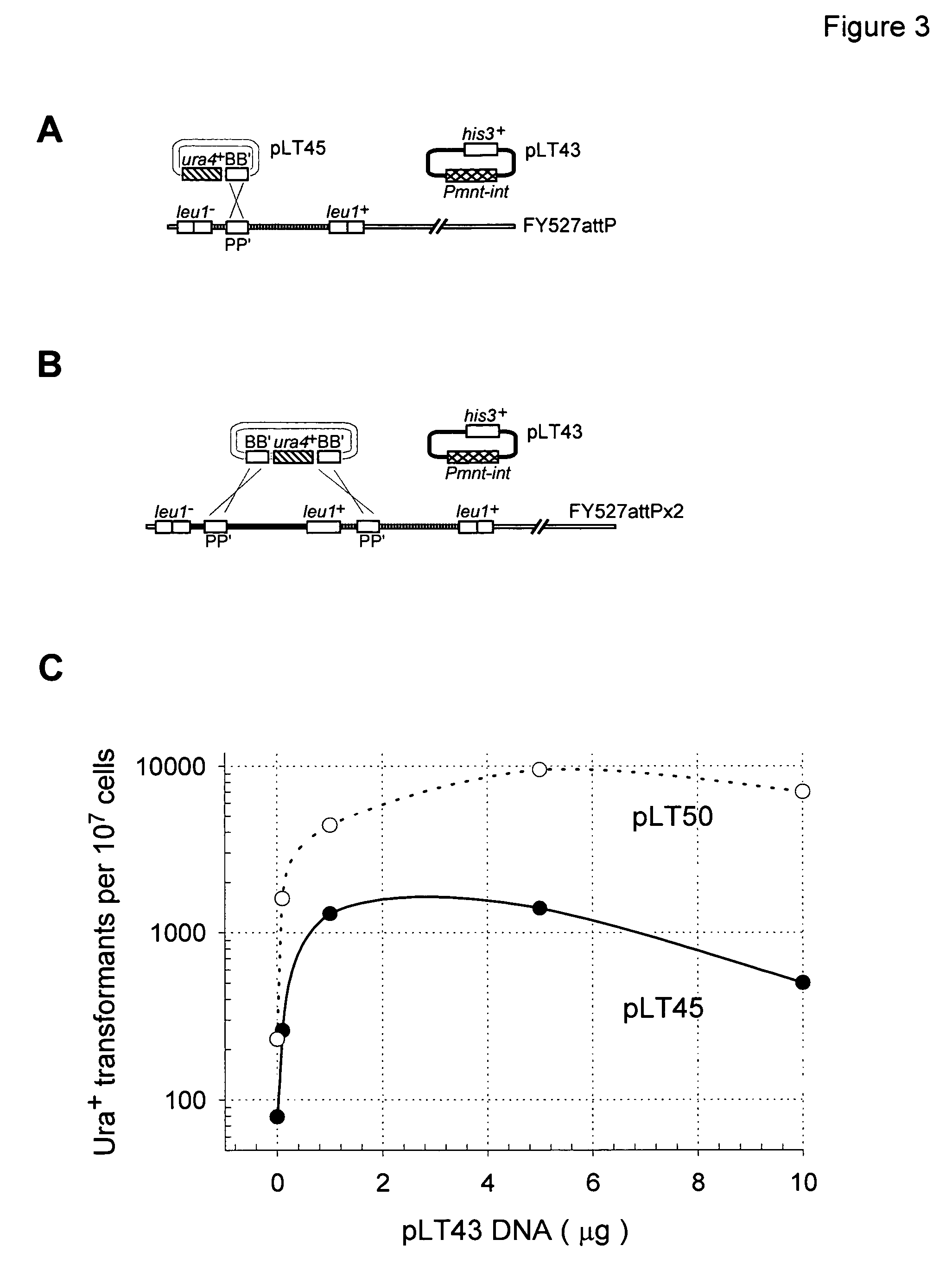
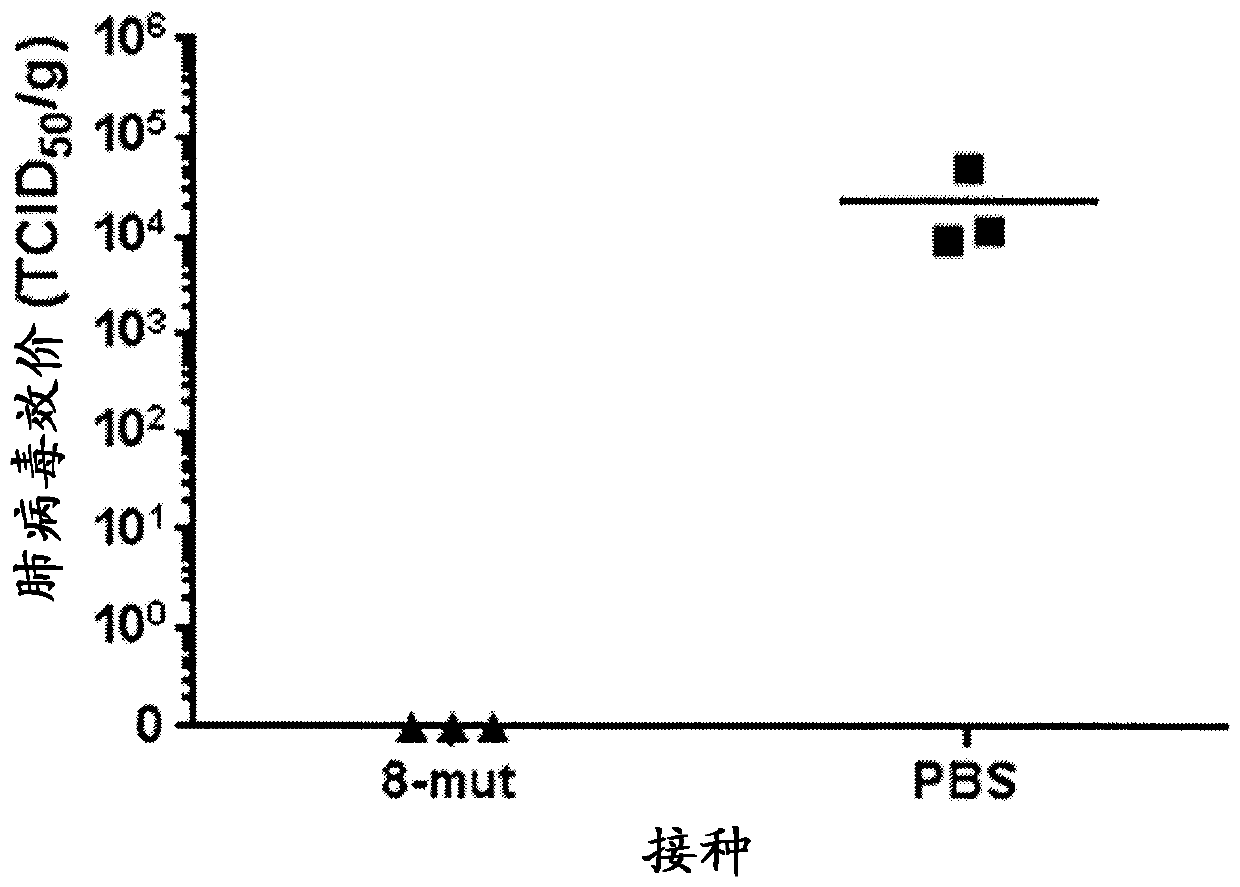
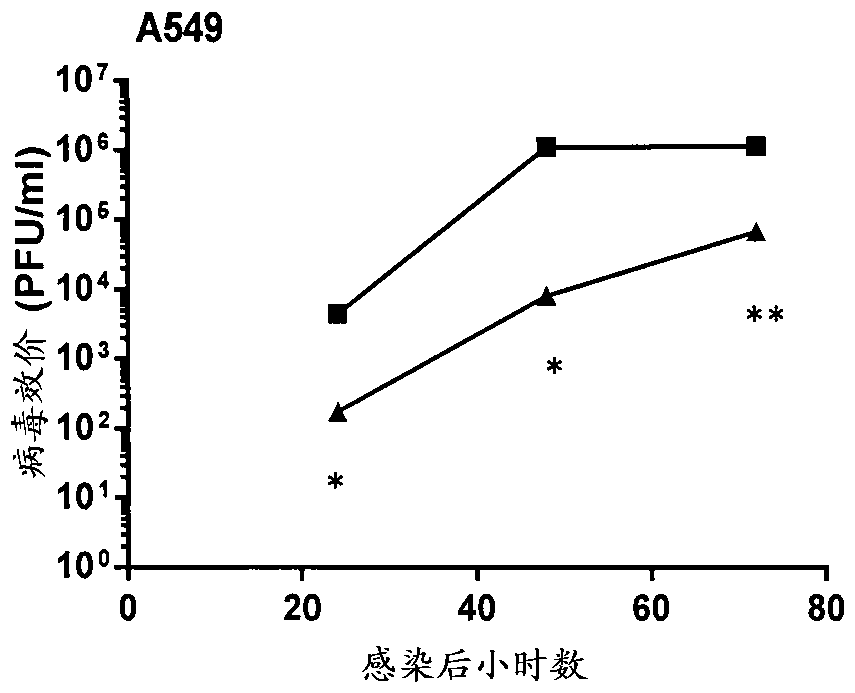
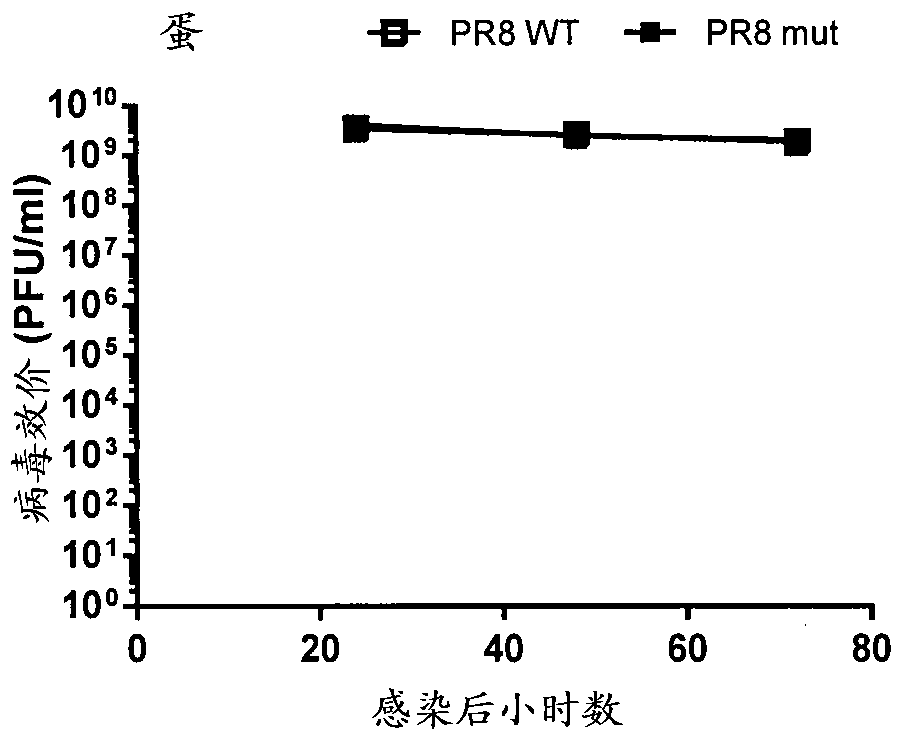
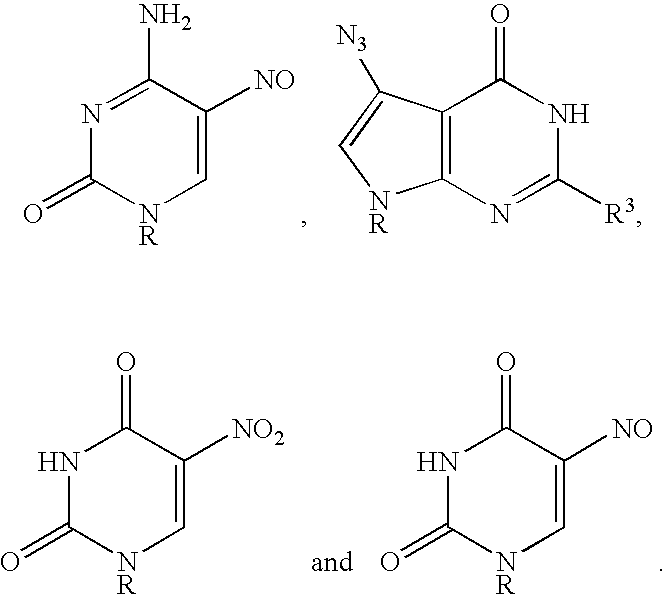
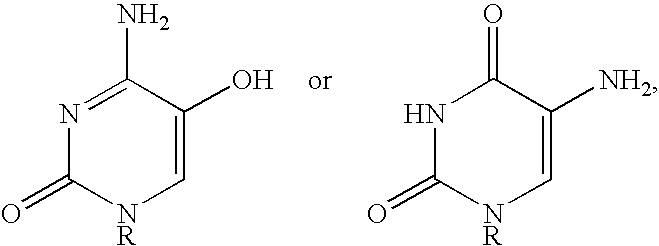
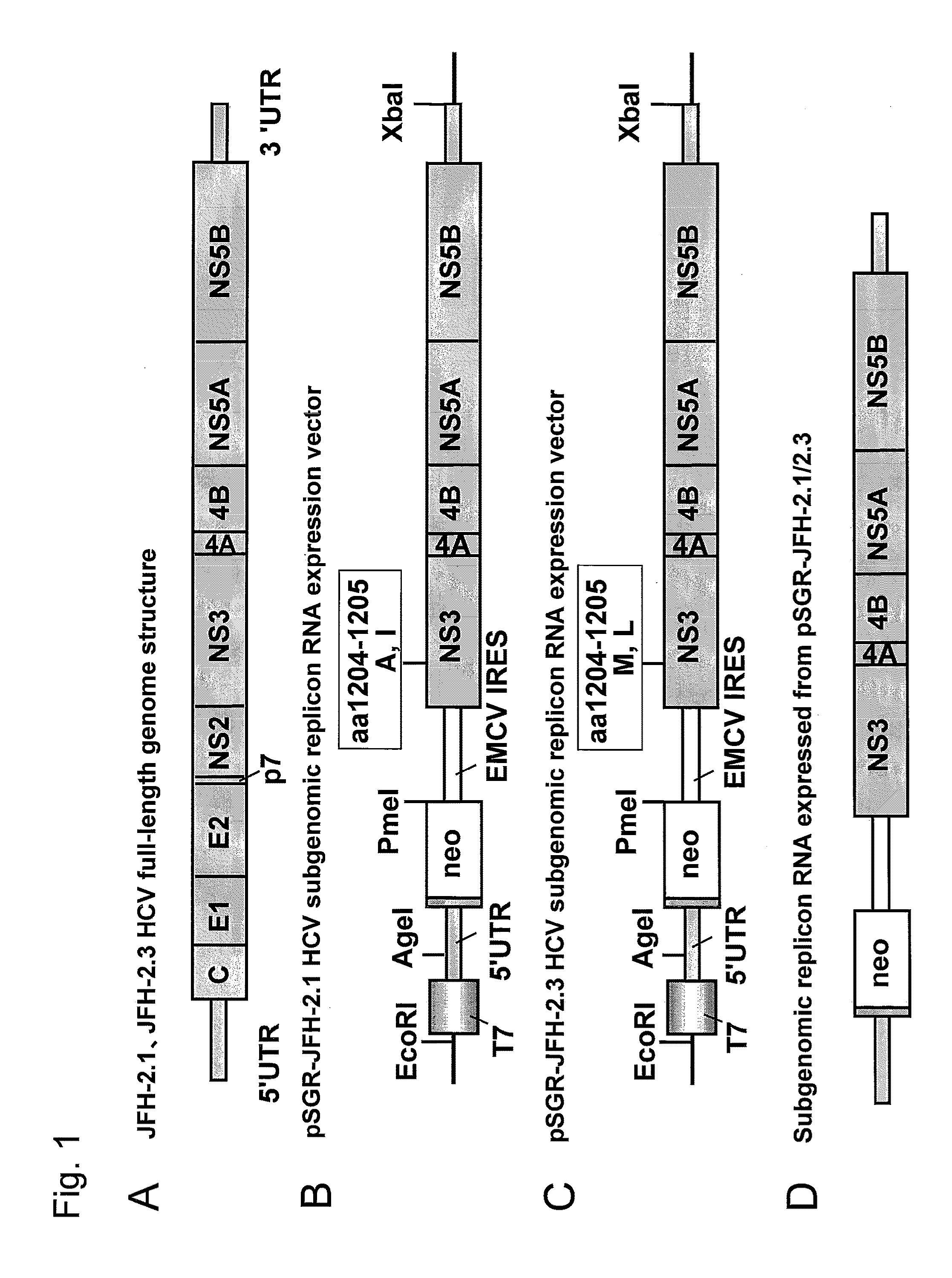
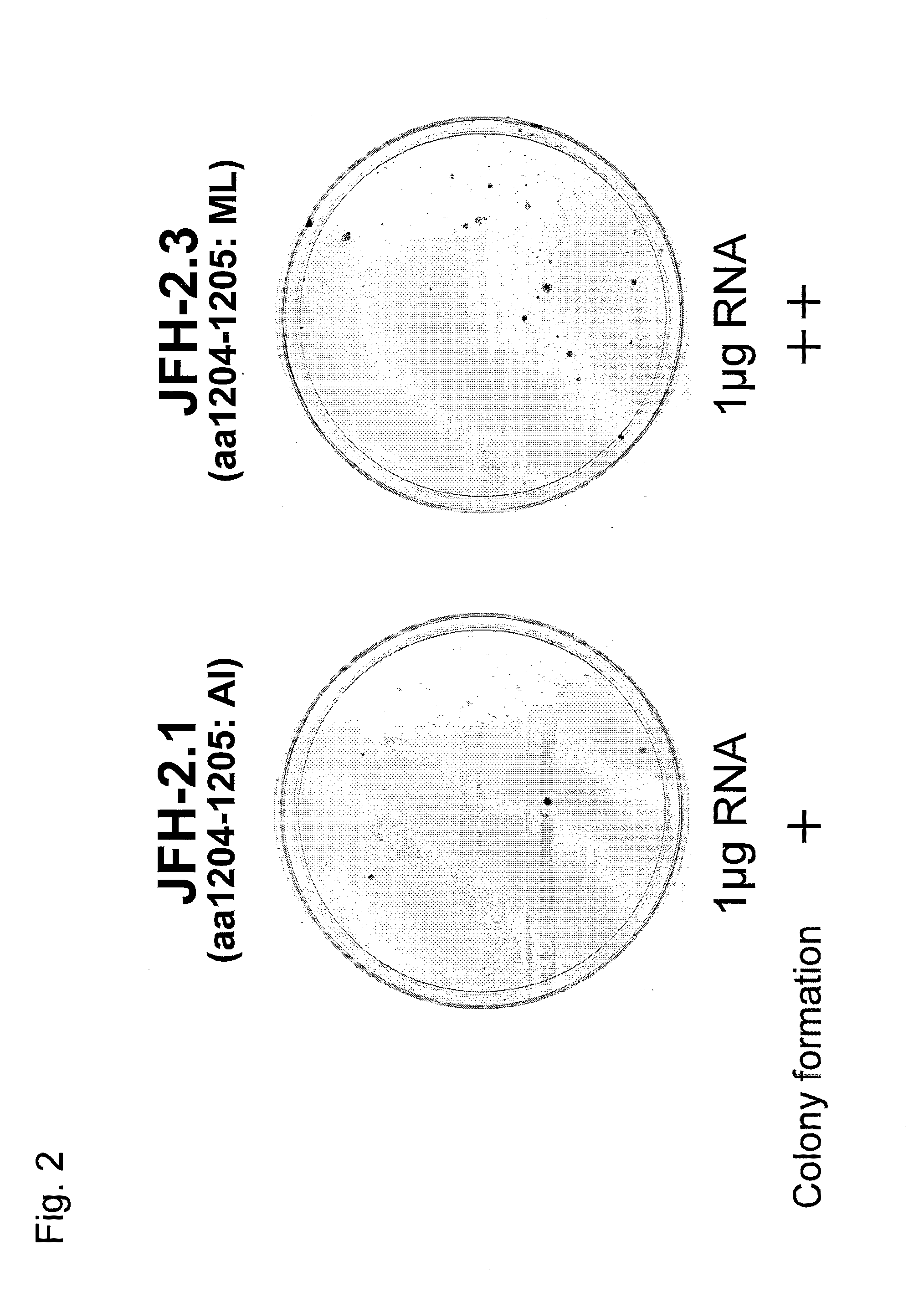
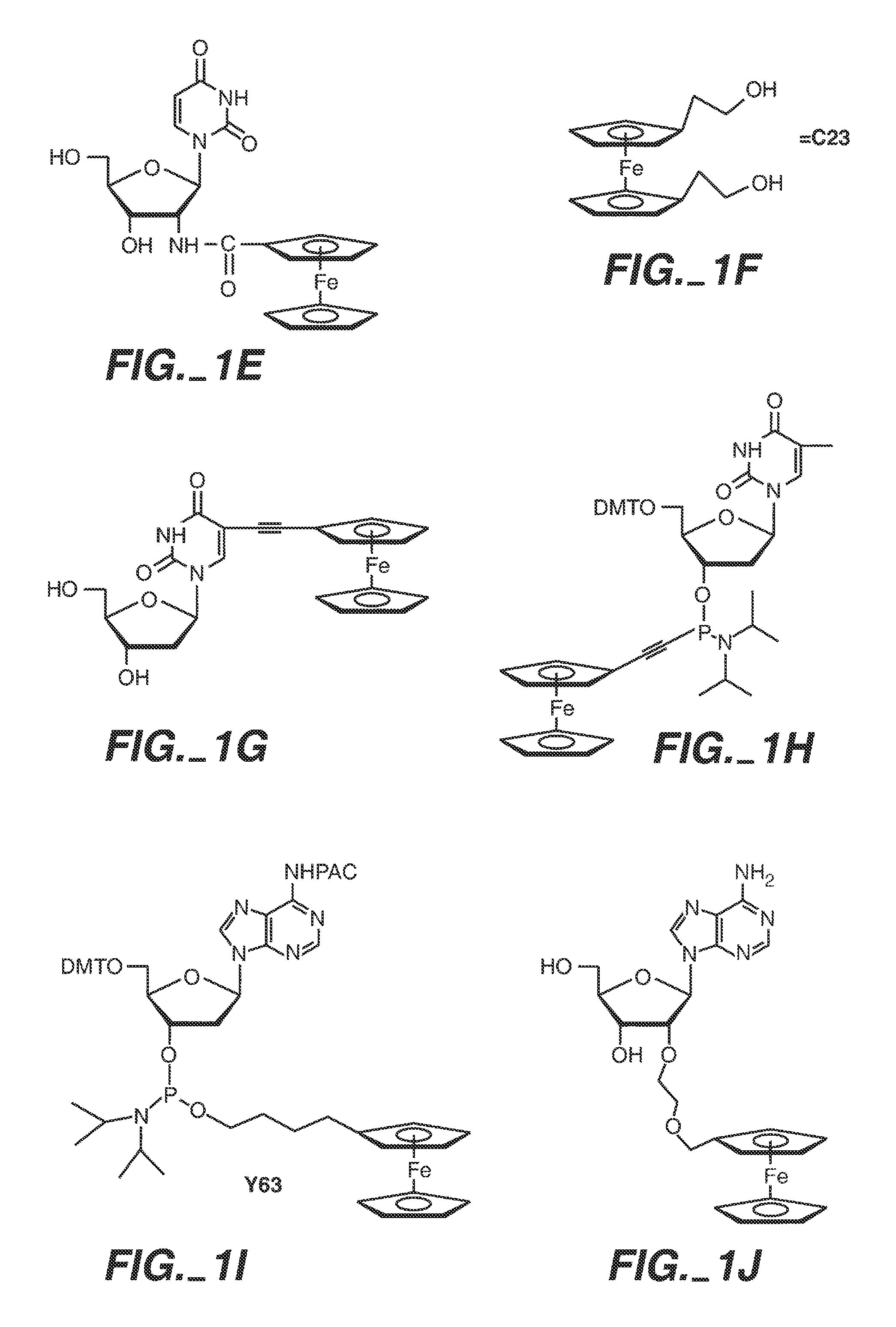Patents
Literature
57 results about "Nucleotide substitution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
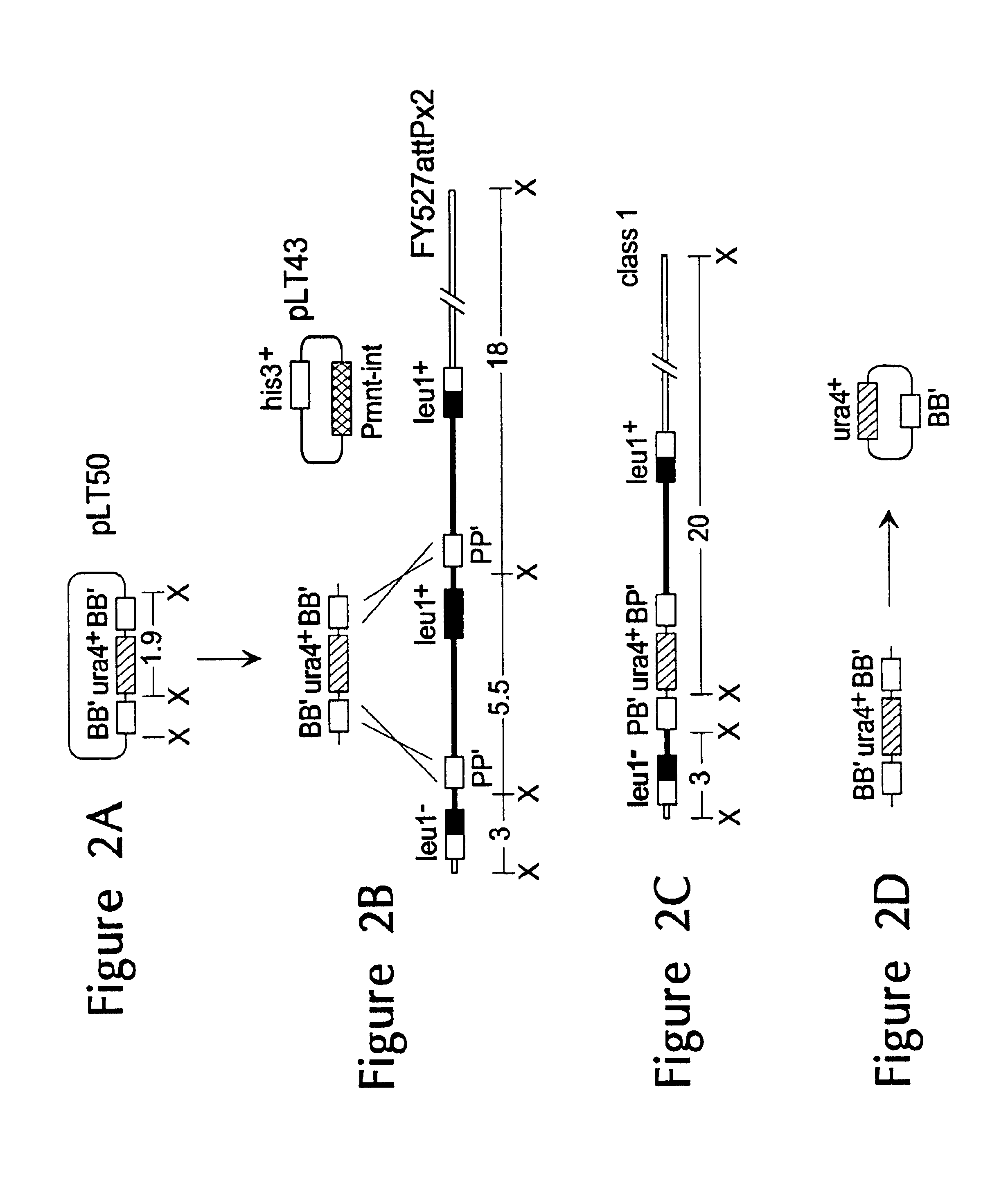
Updated June 20, 2018. A substitution mutation is a type of replication error during DNA replication which places the wrong nucleotide or sequence of nucleotides in the wrong position. A type of substitution mutation, a point mutation, occurs which a single nucleotide is substituted. This can be seen in the image below.
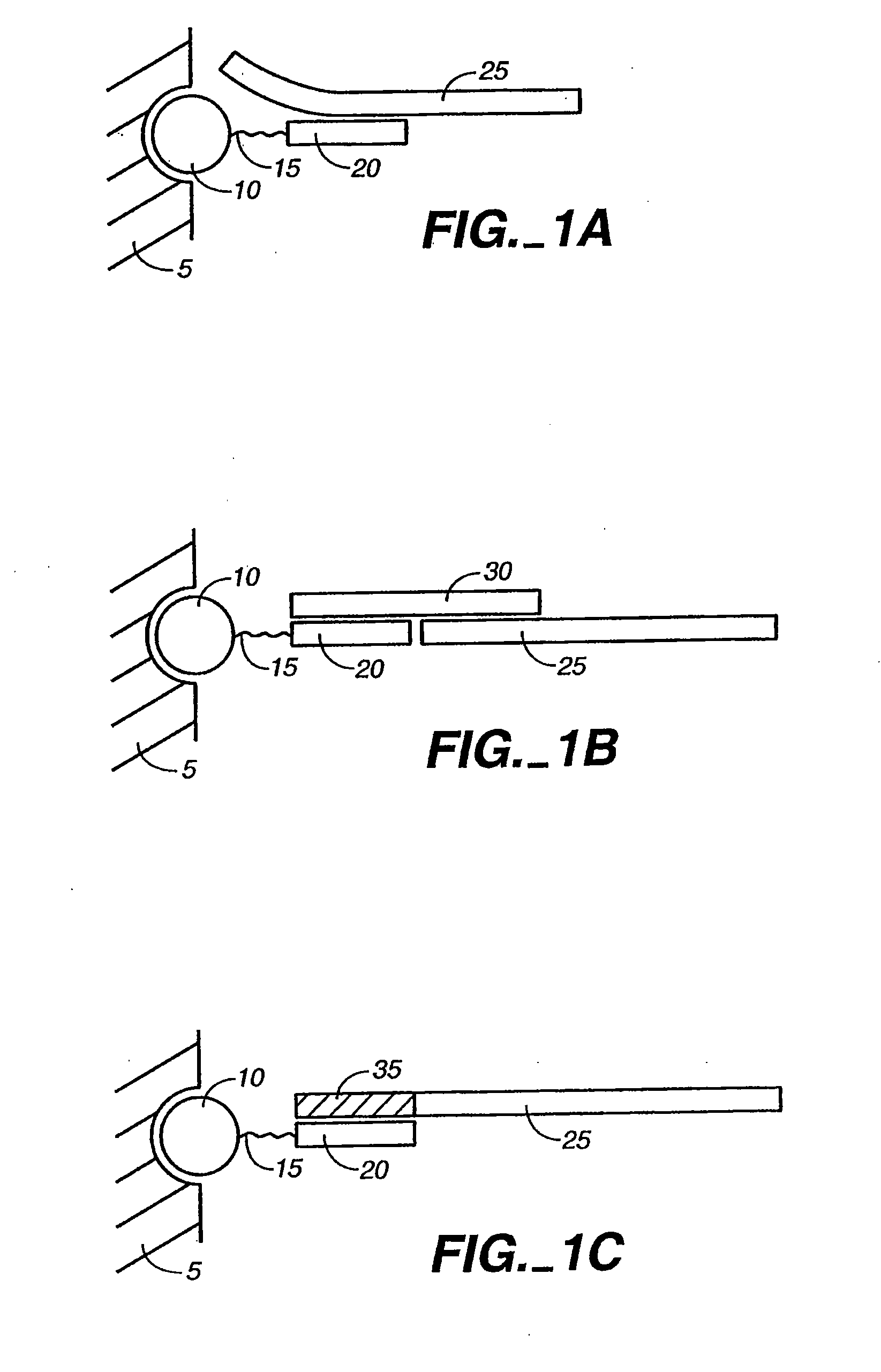
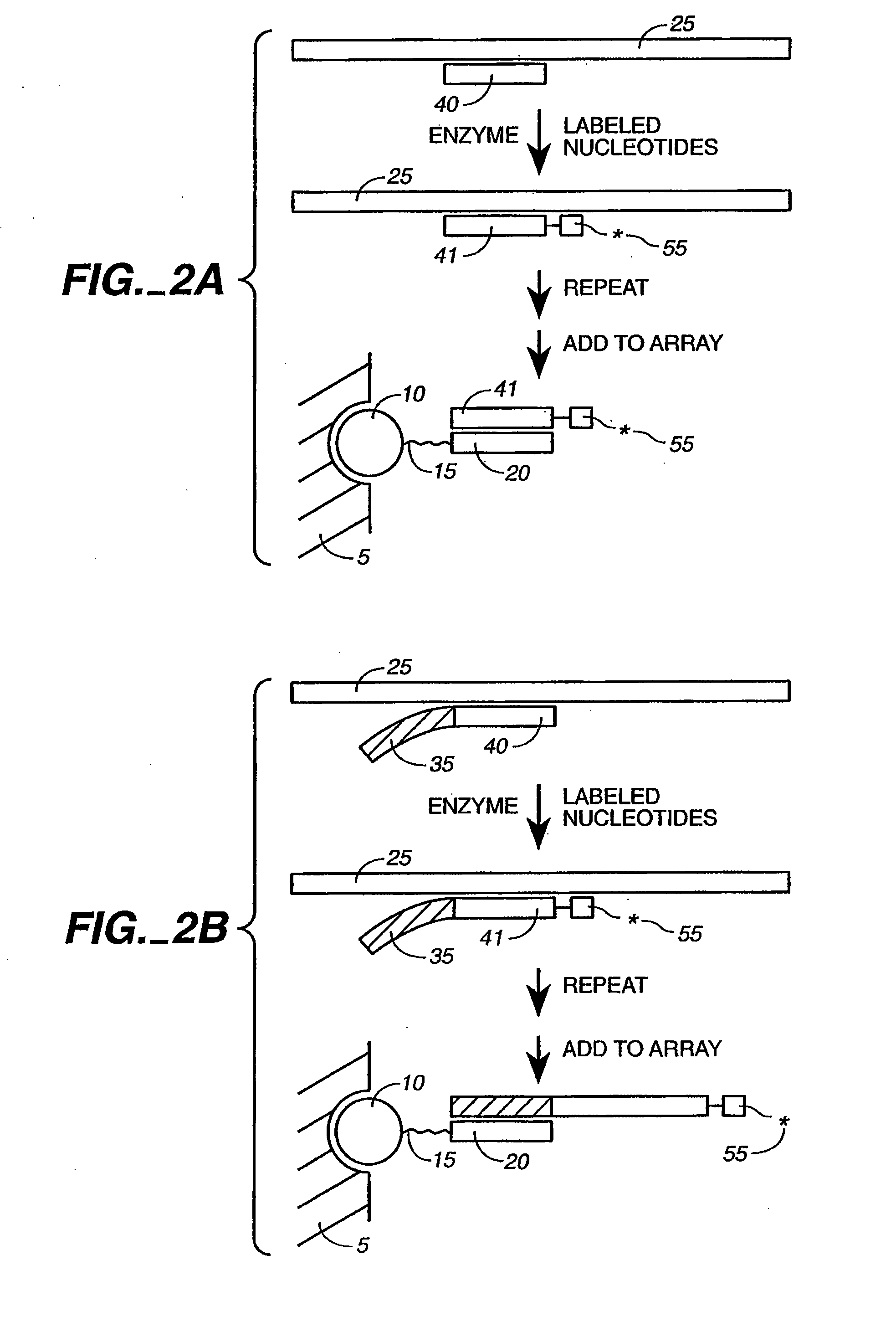
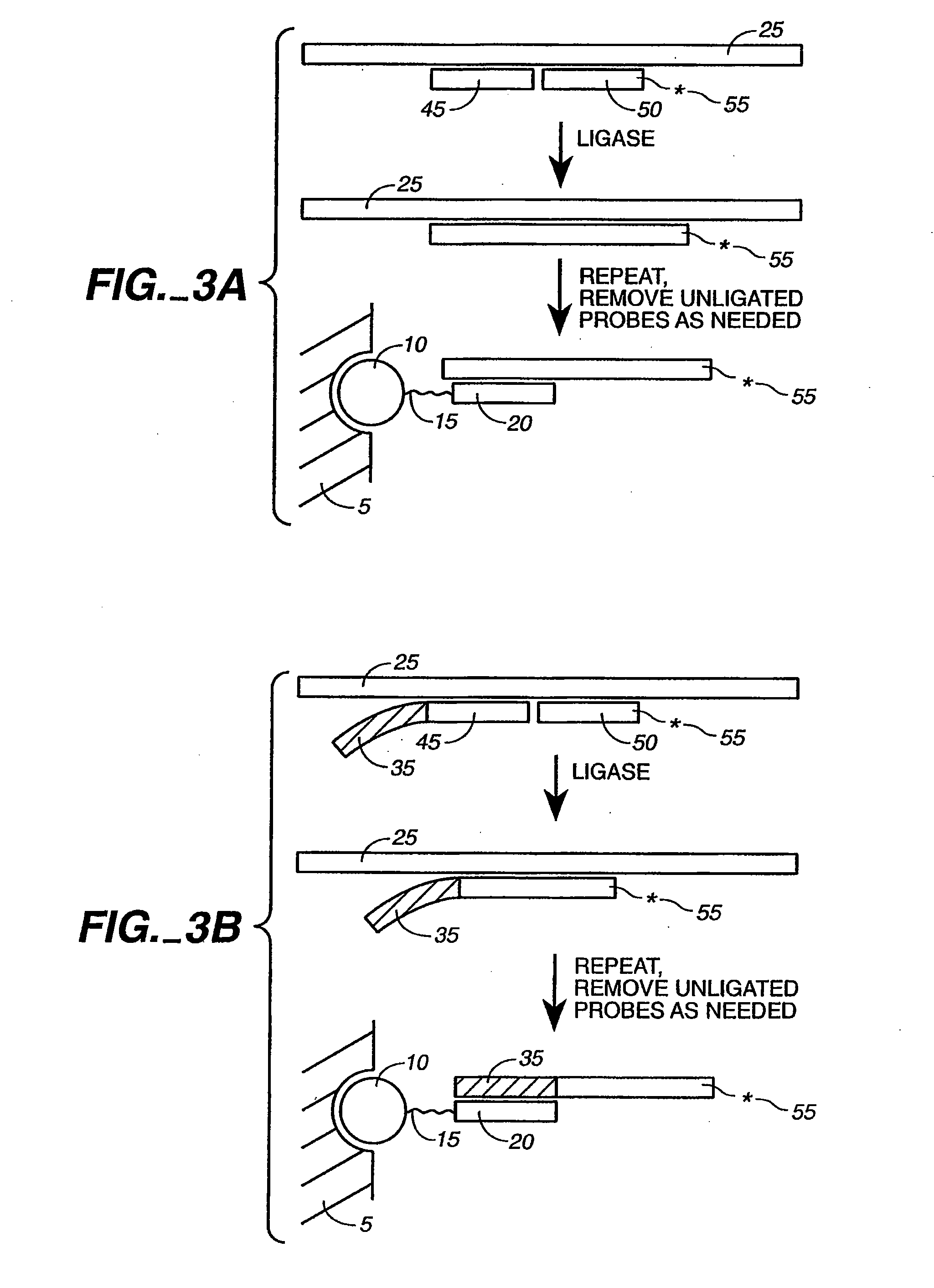
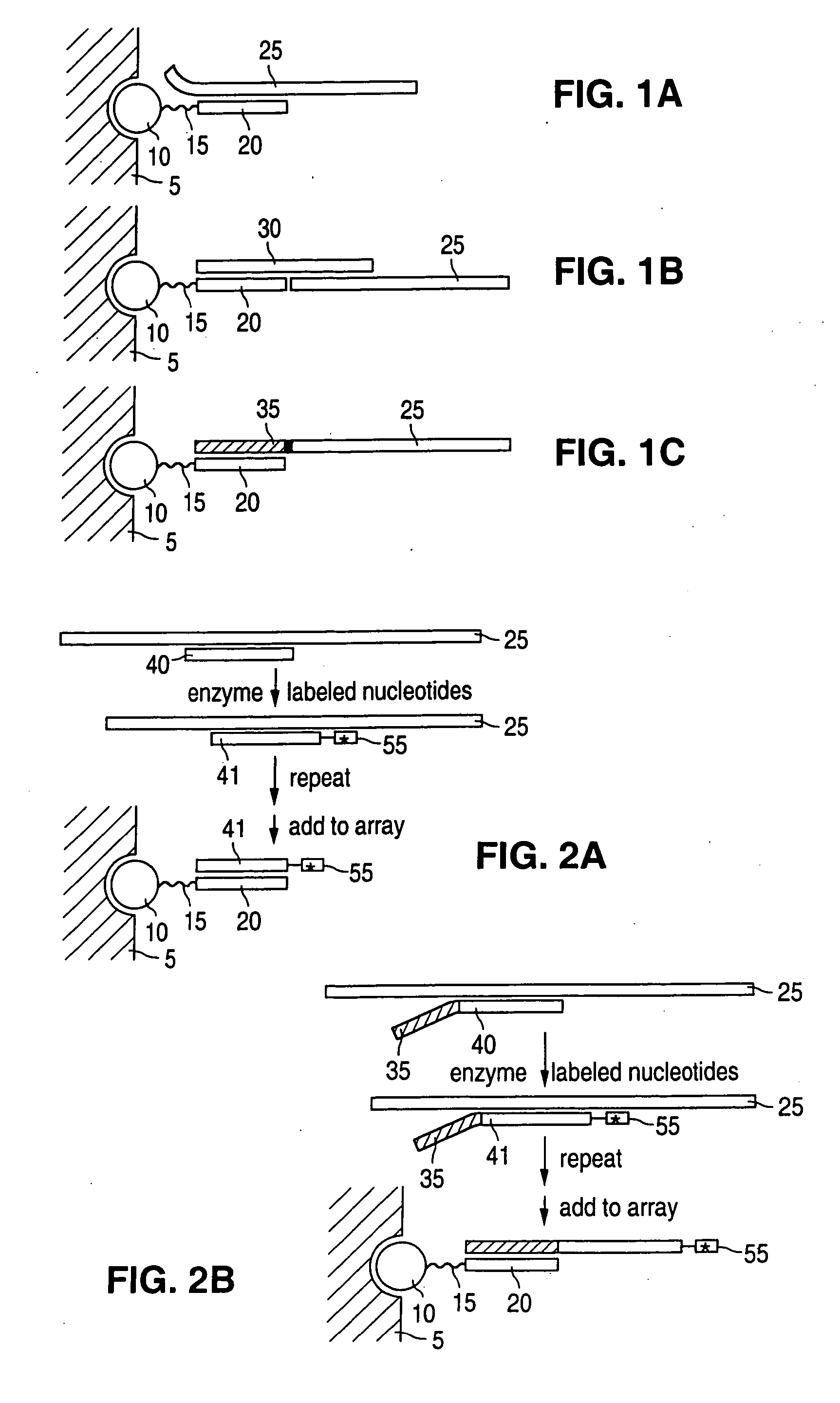
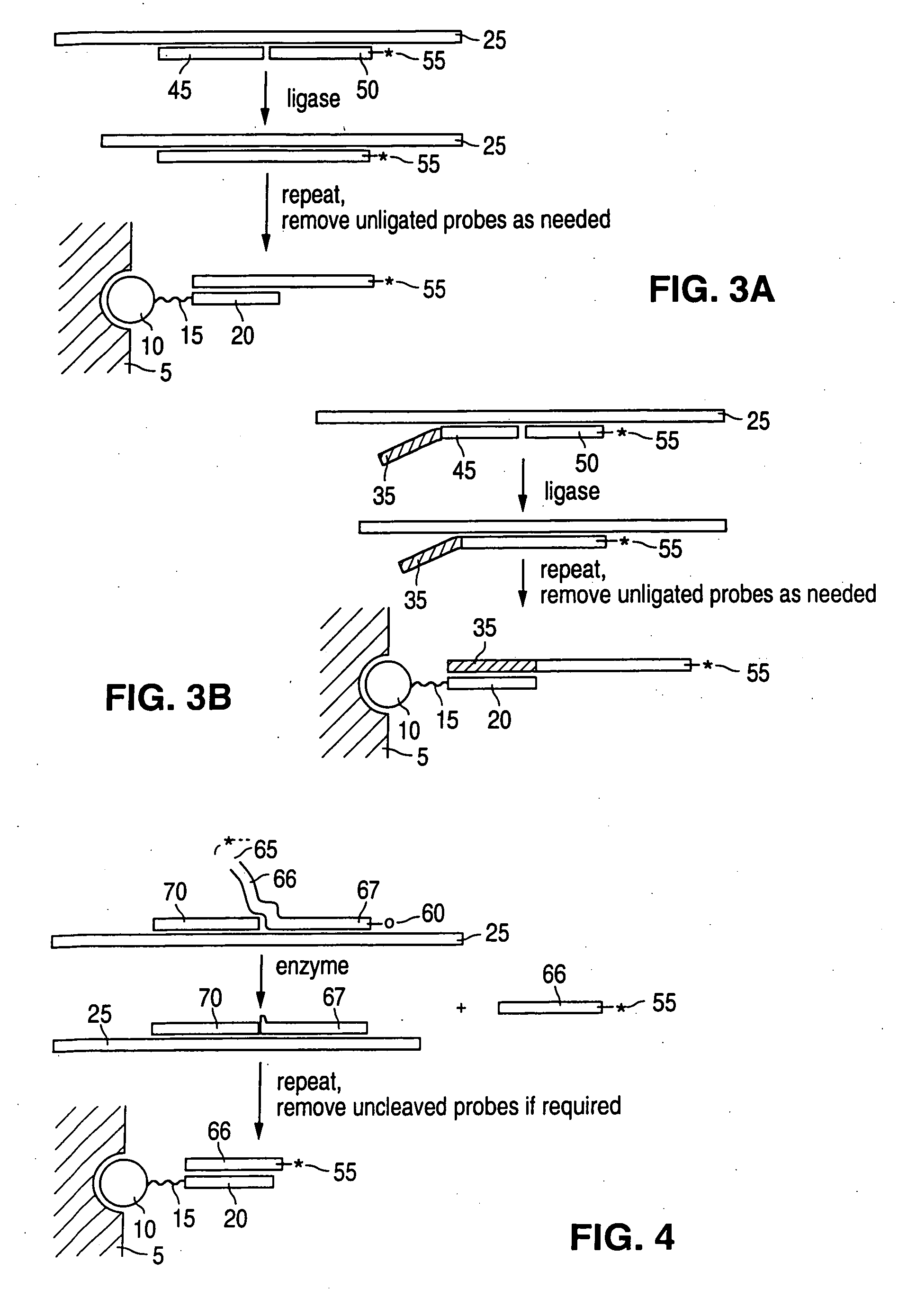
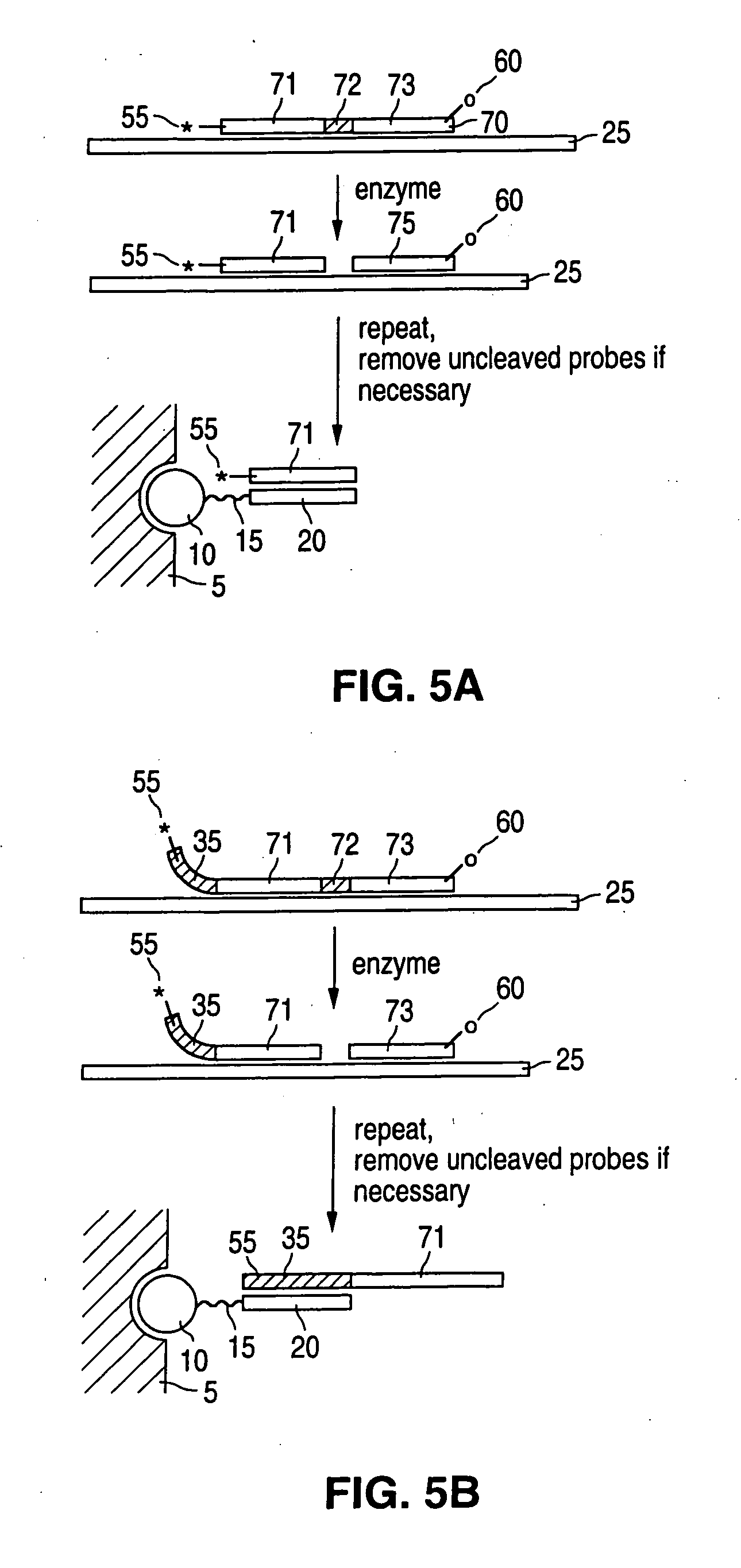
Detection of nucleic acid reactions on bead arrays
InactiveUS20090186349A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotideMicrosphere
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for the use of microsphere arrays to detect and quantify a number of nucleic acid reactions. The invention finds use in genotyping, i.e. the determination of the sequence of nucleic acids, particularly alterations such as nucleotide substitutions (mismatches) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Similarly, the invention finds use in the detection and quantification of a nucleic acid target using a variety of amplification techniques, including both signal amplification and target amplification. The methods and compositions of the invention can be used in nucleic acid sequencing reactions as well. All applications can include the use of adapter sequences to allow for universal arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Method of eliminating inhibitory/instability regions from mRNA
InactiveUS6174666B1Microbiological testing/measurementVirus peptidesImmunodeficiency virusInstability
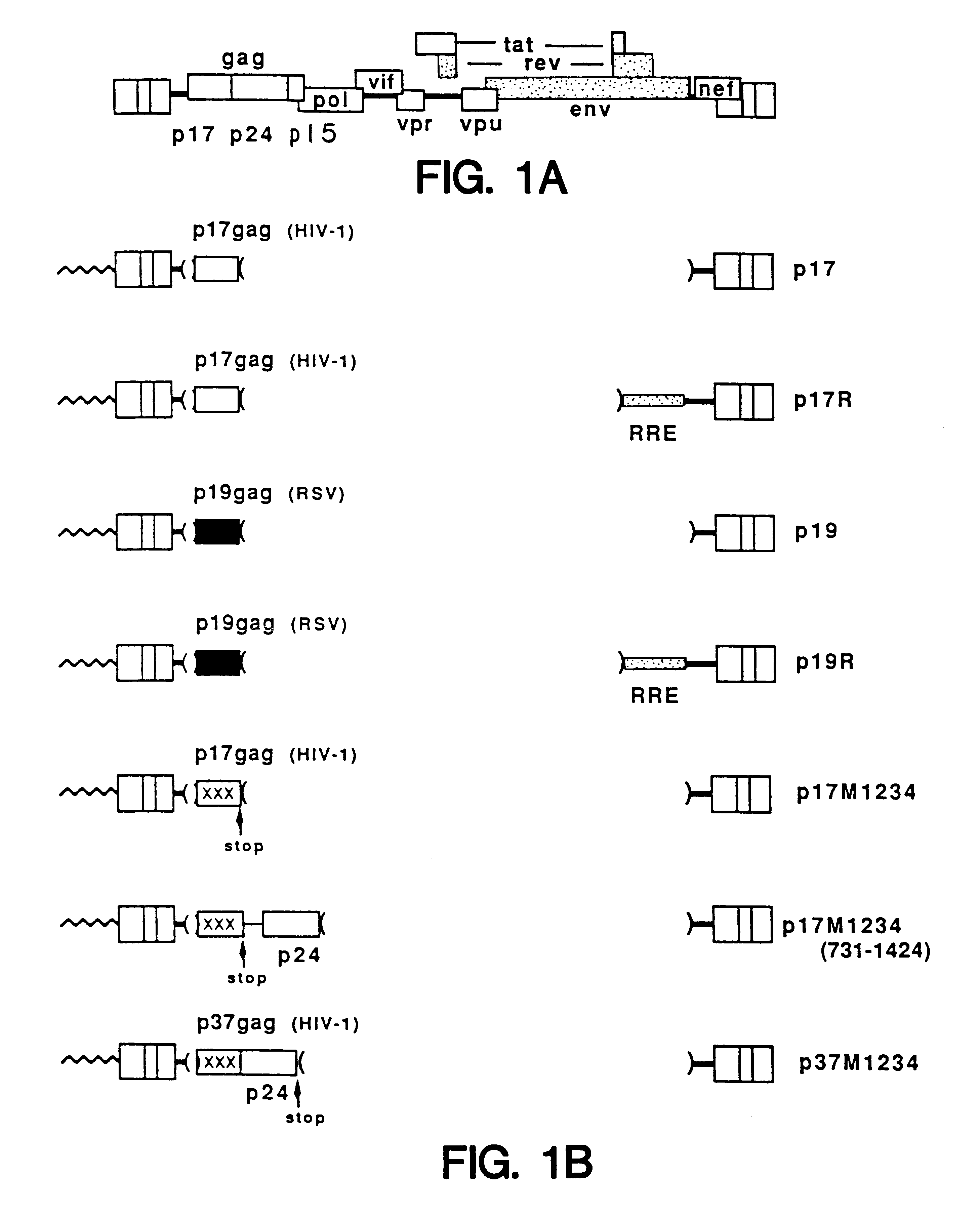
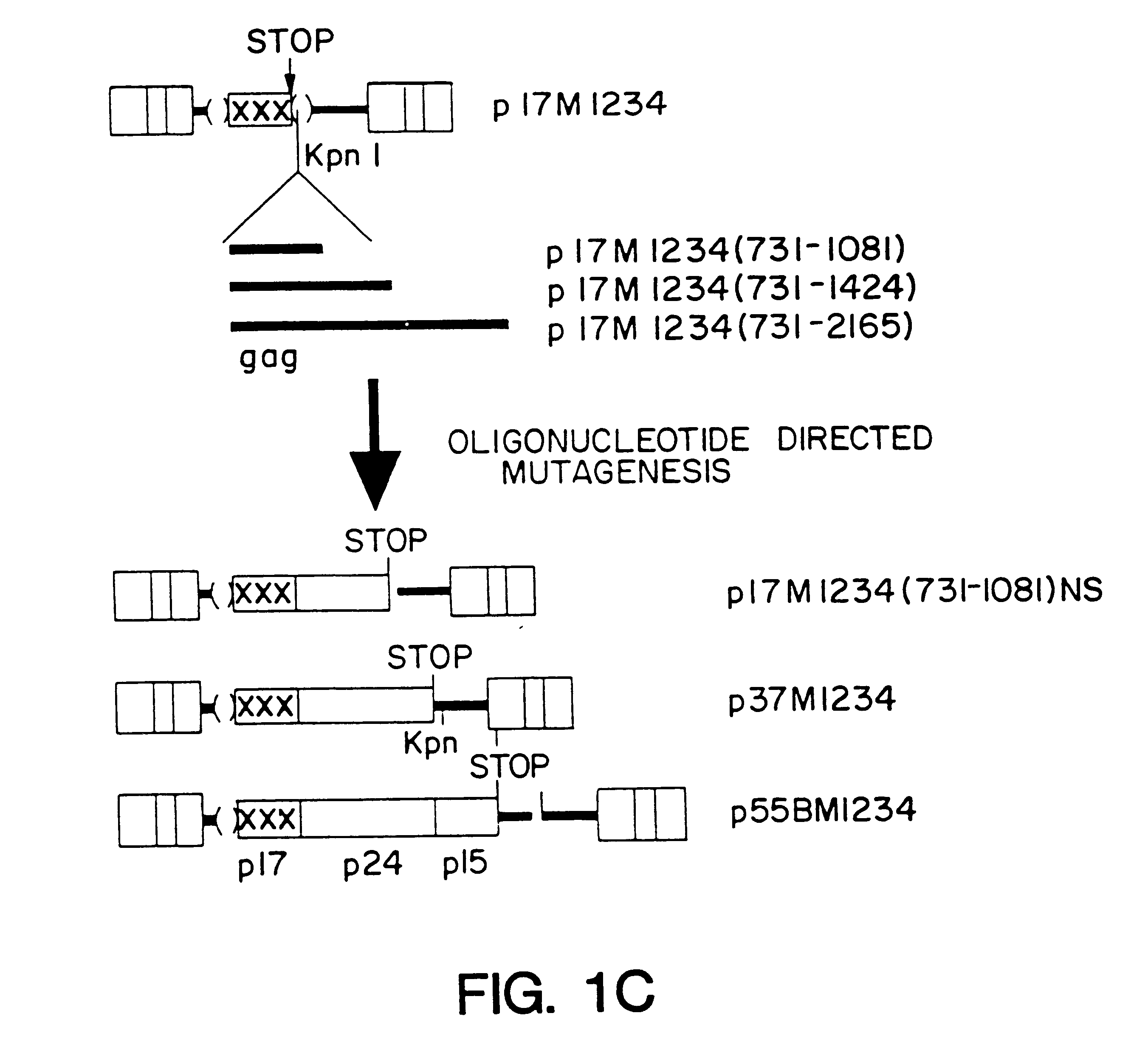
A method of locating an inhibitory / instability sequence or sequences within the coding region of an mRNA and modifying the gene encoding that mRNA to remove these inhibitory / instability sequences by making clustered nucleotide substitutions without altering the coding capacity of the gene is disclosed. Constructs containing these mutated genes and host cells containing these constructs are also disclosed. The method and constructs are exemplified by the mutation of a Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 Rev-dependent gag gene to a Rev-independent gag gene. Constructs useful in locating inhibitory / instability sequences within either the coding region or the 3' untranslated region of an mRNA are also disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Detection of nucleic acid reactions on bead arrays
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for the use of microsphere arrays to detect and quantify a number of nucleic acid reactions. The invention finds use in genotyping, i.e. the determination of the sequence of nucleic acids, particularly alterations such as nucleotide substitutions (mismatches) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Similarly, the invention finds use in the detection and quantification of a nucleic acid target using a variety of amplification techniques, including both signal amplification and target amplification. The methods and compositions of the invention can be used in nucleic acid sequencing reactions as well. All applications can include the use of adapter sequences to allow for universal arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Detection of nucleic acid reactions on bead arrays
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for the use of microsphere arrays to detect and quantify a number of nucleic acid reactions. The invention finds use in genotyping, i.e. the determination of the sequence of nucleic acids, particularly alterations such as nucleotide substitutions (mismatches) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Similarly, the invention finds use in the detection and quantification of a nucleic acid target using a variety of amplification techniques, including both signal amplification and target amplification. The methods and compositions of the invention can be used in nucleic acid sequencing reactions as well. All applications can include the use of adapter sequences to allow for universal arrays.
Owner:GUNDERSON KEVIN +2
DNA fragment with functions of promoter and application of DNA fragment
ActiveCN106480036ASpecific expression activityEasy constructionFungiMicroorganism based processesNucleotideDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a DNA fragment with functions of a promoter and application of the DNA fragment. The DNA fragment is any one of the following sequences of (a) a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1 or SEQ ID NO.2 or a complementary sequence of the nucleotide sequence; (b) a nucleotide sequence which is obtained by conducting substitution or deletion or addition of one or more nucleotides on the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1 or SEQ ID NO.2 and has the functions same as those of the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1 or SEQ ID NO.2 as the promoter or a complementary sequences of the nucleotide sequence. The DNA fragment has the functions of the promoter and has the very high specific expression activity, expression of gRNA in a CRISPR-Cas9 system can be achieved on the condition that an inducer does not need to be added, and therefore a U6 promoter from aspergillus niger can be applied in a CRISPR-Cas9 system of the aspergillus niger.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Sequence determination of nucleic acids using electronic detection
ActiveUS7935481B1Material nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementSelf-assembled monolayerNucleophilic substitution
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for the use of self-assembled monolayers to electronically detect nucleic acids, particularly alterations such as nucleotide substitutions (mismatches) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC +1
DNA fragment with promoter function and application
ActiveCN104630229AStrong specific expression activityHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBinding siteNucleotide
The invention discloses a DNA fragment with a promoter function and an application. The DNA fragment is any one of the following sequences: (a) a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 or a complementary sequence of the nucleotide sequence; (b) a nucleotide sequence having a promoter function identical to SEQ ID NO: 1 or a complementary sequence of the nucleotide sequence obtained by substituting, deleting or adding one or more nucleotides on the nucleotide sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO: 1; and (c) sequences of one or more ribosome bind sites added in the nucleotide sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO: 1. The DNA has a promoter function and is high in expression activity, and high expression of exogenous genes can be realized under a condition that inducers are not needed, and the DNA fragment is applied to expression of heatproof beta-galactosidase and transglutaminase. An effective tool is particularly provided for expression of bacillus amyloliquefaciens.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Methods for genetic analysis of SARS virus
The invention provides arrays and probes for resequencing a SARS virus using an array of probes that are complementary to a SARS reference sequence and to each possible single nucleotide substitution of the reference sequence. Methods of identifying mutations in viral sequences and methods of characterizing viral isolates are also provided. The invention also provides high throughput methods to monitor epidemics and pandemics caused by pathogens such as viruses.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
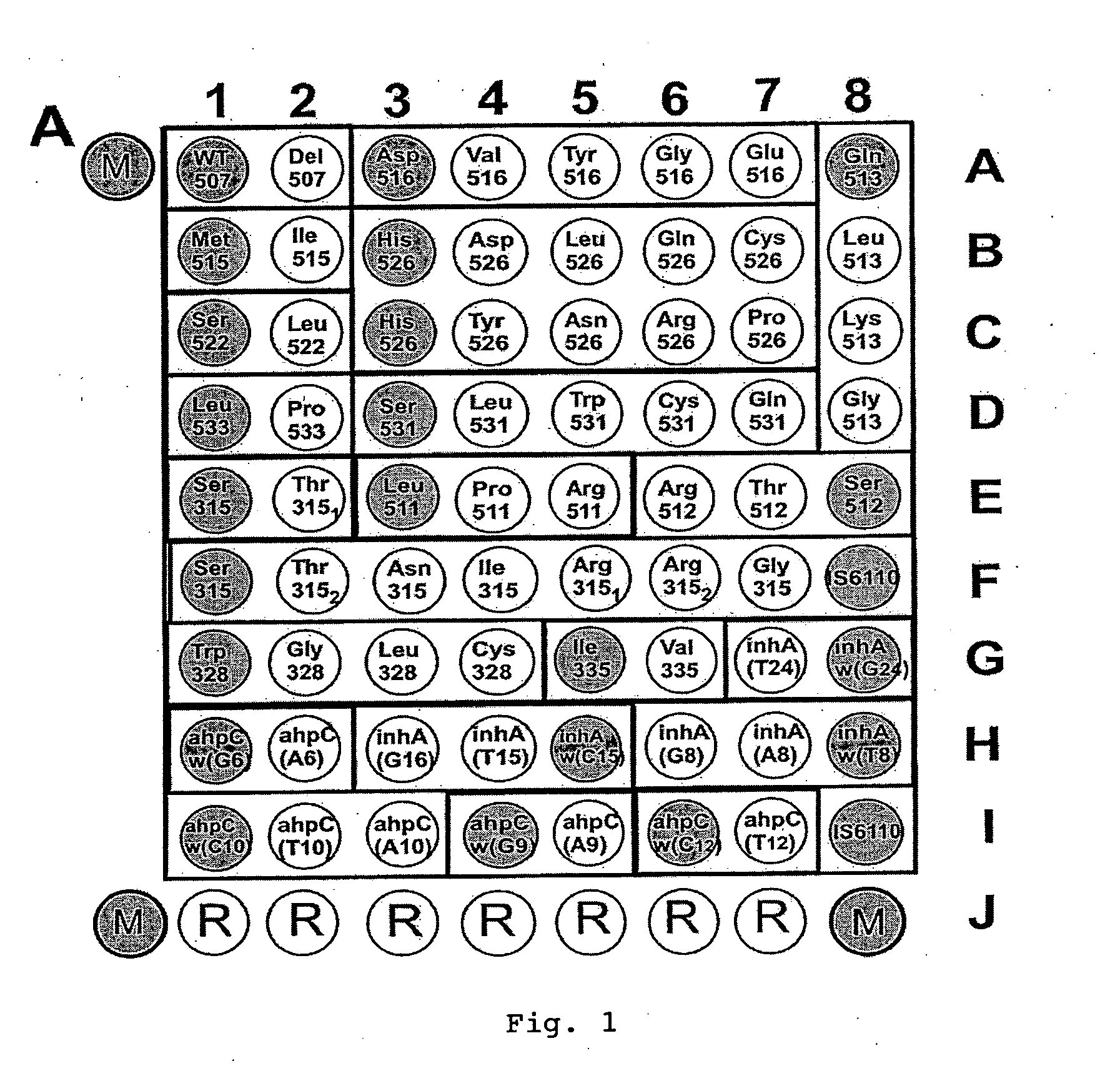
Method for simultaneous detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and identification of mutations in mycobacterial DNA resulting in the resistance of microorganisms to rifampicin and isoniazid on biological microarrays, set of primers, biochip, and set of oligonucleotide probes used in the method
InactiveUS20100261163A1Low costShort timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIsoniazidNucleotide
The present invention relates to molecular biology, microbiology, and medicine and provides the method for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex with simultaneous evaluation of sensitivity of the strains to rifampicin and isoniazid in clinical sample on differentiating biochip. The method is based on two-stage multiplex PCR to obtain fluorescent DNA fragments followed by hybridization of these fragments on microarray containing the set of specific discriminating oligonucleotides. The determination of the resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to rifampicin and isoniazid is carried out by evaluation of point nucleotide substitutions in DNA of microorganism. The present invention allows conduct analysis directly in clinical sample, to evaluate a number of mutations simultaneously, to decrease the cost price of analysis, and to reduce the time of its conducting. The present invention also relates to set of primers, biochip, and set of oligonucleotide probes used in realization of the method.
Owner:UCHREZHDENIE ROSSIISKOI AKADI NAUK INST MOLEKULYARNOI BLOLOGII IM V A ENGELGARDTA RAN IMB RAN
Methods for the replacement, translocation and stacking of DNA in eukaryotic genomes
InactiveUS6936747B2Reduce in quantityImprove efficiencySugar derivativesStable introduction of DNAMammalPlant cell
The present invention includes compositions and methods for site-specific polynucleotide replacement in eukaryotic cells. These methods include single polynucleotide replacement as well as gene stacking methods. Preferred eukaryotic cells for use in the present invention are plant cells and mammalian cells.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
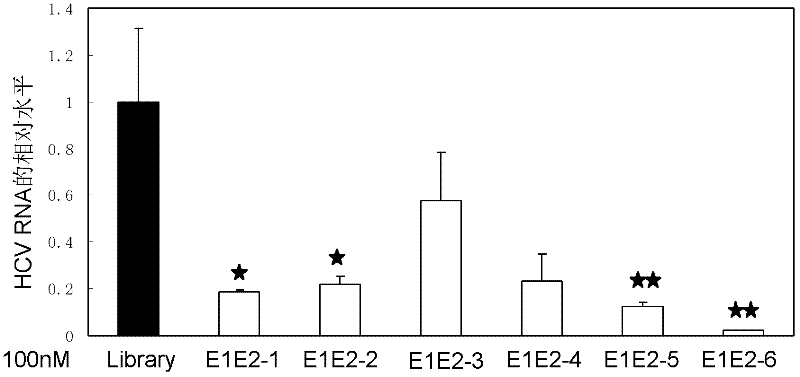
Nucleic acid aptamer capable of identifying HCV E1E2 (hepatitis C virus E1E2), nucleic acid aptamer derivatives and screening method and application thereof
InactiveCN102229932AHigh affinityLow costGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein detectionNucleotide
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer capable of identifying HCV E1E2 (hepatitis C virus E1E2), which is a DNA fragment having a sequence shown in any one of SEQ ID No.1 to SEQ ID No.5. Derivatives of the nucleic acid aptamer include nucleotide-substituted RNA nucleic acid aptamers, skeleton-modified derivatives, peptide nucleic acid derivatives and derivatives of nucleic acid aptamer conjugated with radioactive molecules. A method for screening the nucleic acid aptamer comprises the following steps: firstly preparing HCV E1E2 proteins with histidine tags and then preparing pET200 / D / LacZ proteins with histidine tags, then immobilizing the proteins and designing a random nucleic acid library, and finally screening nucleic acid aptamers. Specifically, the screening step comprises the following steps: pre-treating the DNA library, performing reverse screening, performing forward screening, and repeatedly screening, to obtain the nucleic acid aptamer with strong competitiveness and optimized sequence length. The nucleic acid aptamer and derivatives thereof can be applied to preparing HCV E1E2 protein detection kits or diagnostic kits as well as agents for suppressing HCV infection in liver cells.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Attenuated influenza viruses and vaccines
InactiveUS20120269849A1High genetic stabilityMaximum safetySsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesNucleotideProtection sex
The present provides attenuated influenza viruses comprising a modified viral genome containing a plurality of nucleotide substitutions. The nucleotide substitutions result in the rearrangement of preexisting codons of one or more protein encoding sequences and changes in codon pair bias. Substitutions of non-synonymous and synonymous codons may also be included. The attenuated influenza viruses enable production of improved vaccines and are used to elicit protective immune responses.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Attenuated viruses useful for vaccines
This invention provides an attenuated virus which comprises a modified viral genome containing nucleotide substitutions engineered in multiple locations in the genome, wherein the substitutions introduce synonymous deoptimized codons into the genome. The instant attenuated virus may be used in a vaccine composition for inducing a protective immune response in a subject. The invention also provides a method of synthesizing the instant attenuated virus. Further, this invention further provides a method for preventing a subject from becoming afflicted with a virus-associated disease comprising administering to the subject a prophylactically effective dose of a vaccine composition comprising the instant attenuated virus.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Signal peptide capable of effectively improving protein secretion efficiency and application of signal peptide
InactiveCN107936096APromote secretionAchieve secretory expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesZymogenSequence signal
The invention discloses a signal peptide capable of effectively improving protein secretion efficiency and an application of the signal peptide. The amino acid sequence of the signal peptide is shownin SEQ ID NO.1. The nucleotide sequence for encoding the signal peptide is selected from any of the following sequences: (a) a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2 or a complementary sequence of the nucleotide sequence; and (b) a nucleotide sequence which is obtained through substitution, deletion or addition of one or more nucleotides of the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2, has a same function of being used a signal peptide with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2, or a complementary sequence of the obtained nucleotide sequence. According to the invention, an expressionvector with the combination of the signal peptide and beta-galactosidase encoding gene / transglutaminase zymogen encoding gene is constructed from a vacillus subtilis homologous protein signal peptidelibrary, the signal peptide capable of increasing the secretion of beta-galactosidase can be screened out, and the secretion expression of the transglutaminase zymogen is realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
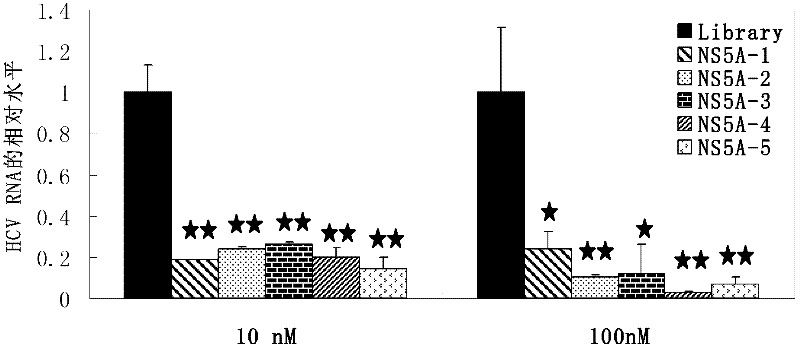
Aptamer capable of identifying hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural 5A (NS5A) protein, derivatives thereof and screening method and use thereof
InactiveCN102229933ALow costEfficient preparationMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideScreening method
The invention discloses an aptamer capable of identifying a hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural 5A (NS5A) protein, which is a DNA fragment represented by any of sequences from SEQ ID No.1 to SEQ ID No.5. The derivatives of the aptamer comprise nucleotide substituted RNA aptamers, skeleton-restructured derivatives, restructured peptide nucleic acid derivatives and radioactive molecule connected derivatives. The screening method of the aptamer comprises: preparing HCV NS5A protein with histidine marker, and preparing protein pET200 / D / LacZ; immobilizing the proteins, and designing a random nucleic acid library; and finally, screening the aptamer by pretreating the DNA library, performing reverse screening, screening and repeated screening and other steps, wherein the obtained aptamer has high competition power and optimized sequence length. The aptamer and the derivatives thereof can be used in the preparation of detection kit or diagnosis reagent for the HCV NS5A protein and can also be used in preparation of reagents for inhibiting replication of hepatitis C virus in liver cells.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Live-attenuated virus and methods of production and use
ActiveUS20160354460A1Slow replicationProvide immunitySsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsFowlAttenuated vaccine
Presented herein are live-attenuated viruses and methods of generating thereof from a parental virus through a plurality of nucleotide substitutions in the viral genome. The nucleotide substitutions result in a change in codon usage bias within codons of one or more protein encoding sequences and no change in amino acid sequences of the proteins. The live-attenuated viruses display unaltered replication in avian hosts for propagation, but attenuated replication in mammalian hosts, when compared to the replication of the parental virus. The live-attenuated viruses in a form of improved vaccines can be used to elicit protective immune responses.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
DNA fragment of bacillus subtilis with promoter function and application thereof
ActiveCN106947766AHigh activityIncrease transcriptional activityVectorsBacteriaNucleotideBinding site
The invention discloses a DNA fragment of bacillus subtilis with a promoter function and application thereof. The DNA fragment is any one of a, the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 or a complementary sequence thereof; b, a nucleotide sequence obtained by substituting, deleting or adding one or more nucleotides of the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and having the promoter function the same as that of the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, or a complementary sequence thereof; and c, a sequence obtained by adding one or more ribosome bind sites to the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The DNA fragment has the promoter function, and also has high expression activity. High expression of exogenous genes can be achieved without adding an inductor. The DNA fragment can be applied to expression of thermostable beta-galactosidase and transglutaminase, and particularly, an effective element is provided for a bacillus subtilis expression-secretion system.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Nucleotide-containing fertilizer
InactiveCN102731211APromote physiological metabolismPromote growthFertilizer mixturesPlant hormoneNucleotide
The invention discloses a nucleotide-containing fertilizer. The nucleotide-containing fertilizer replaces the traditional plant hormones with the nucleotide so as to avoid that the excessive hormones deposited in fruits and vegetables accumulated in human bodies to harm the health of people. The nucleotide in the fertilizer is absorbed by roots, stems and leaves of plants to improve absorbing ability of the root systems of the plants, promote the physiological metabolism of the plants, activate the diphosphoribulose carboxylase, enhance the fixing ability of carbon dioxide, increase the content of the chlorophyll of leaves of the plants and promote the photosynthesis. The detailed functions of the fertilizer are to promote the reproduction of root system, green leaves, accelerate the growth of the plants, significantly enhance the output and quality of crops, and also remarkably improve the stress resistance of the crops. Therefore, the fertilizer has multiple advantages, and is particularly suitable for popularization and application in the agricultural field. The market prospect of the fertilizer is very wide.
Owner:DALIAN ZHEN AO BIOLOGY AGRI TECH
DNA fragment with promoter function and use thereof
ActiveCN106086025AHigh activityIncrease transcriptional activityVectorsBacteriaBinding siteNucleotide
The invention discloses a DNA fragment with a promoter function and a use thereof. The DNA fragment has a sequence selected from (a), a nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO. 1 or its complementary sequence, (b), a nucleotide sequence which is derived from the nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO. 1 through replacement, deletion or addition of one or multiple nucleotides and has a promoter function the same to that of the nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO. 1, or its complementary sequence, and (c), a sequence derived from the nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO. 1 through addition of one or more ribosome binding sites. The DNA fragment has a promoter function and strong specific expression activity, realizes high exogenous gene expression without an inducer and provides an effective element for bacillus subtilis expression of an exogenous gene.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
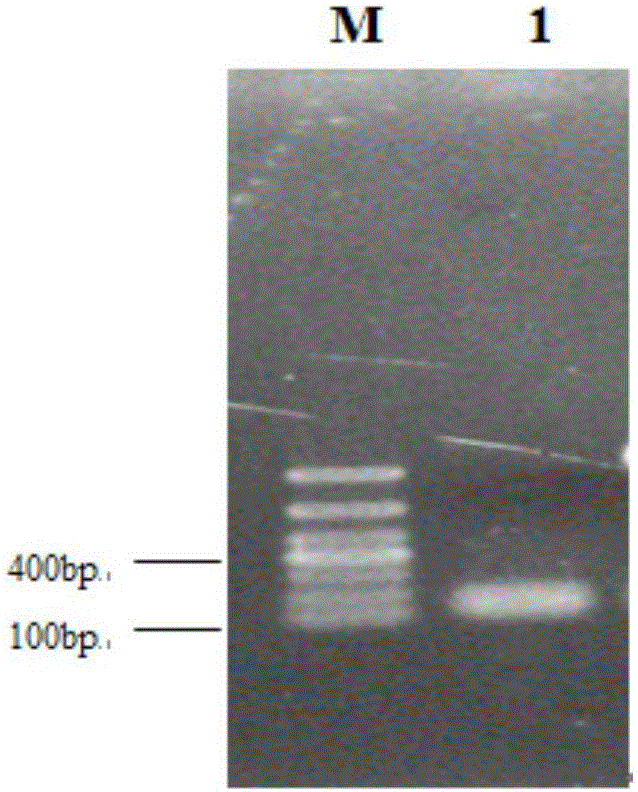
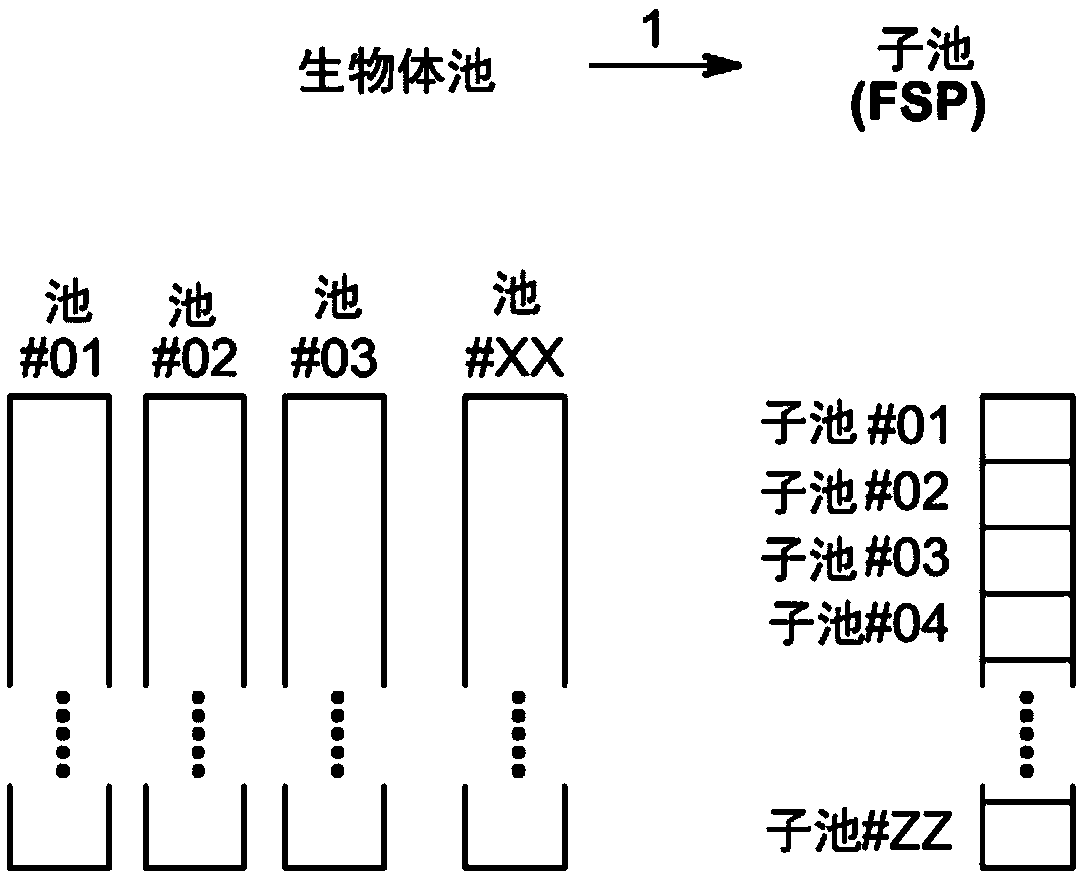
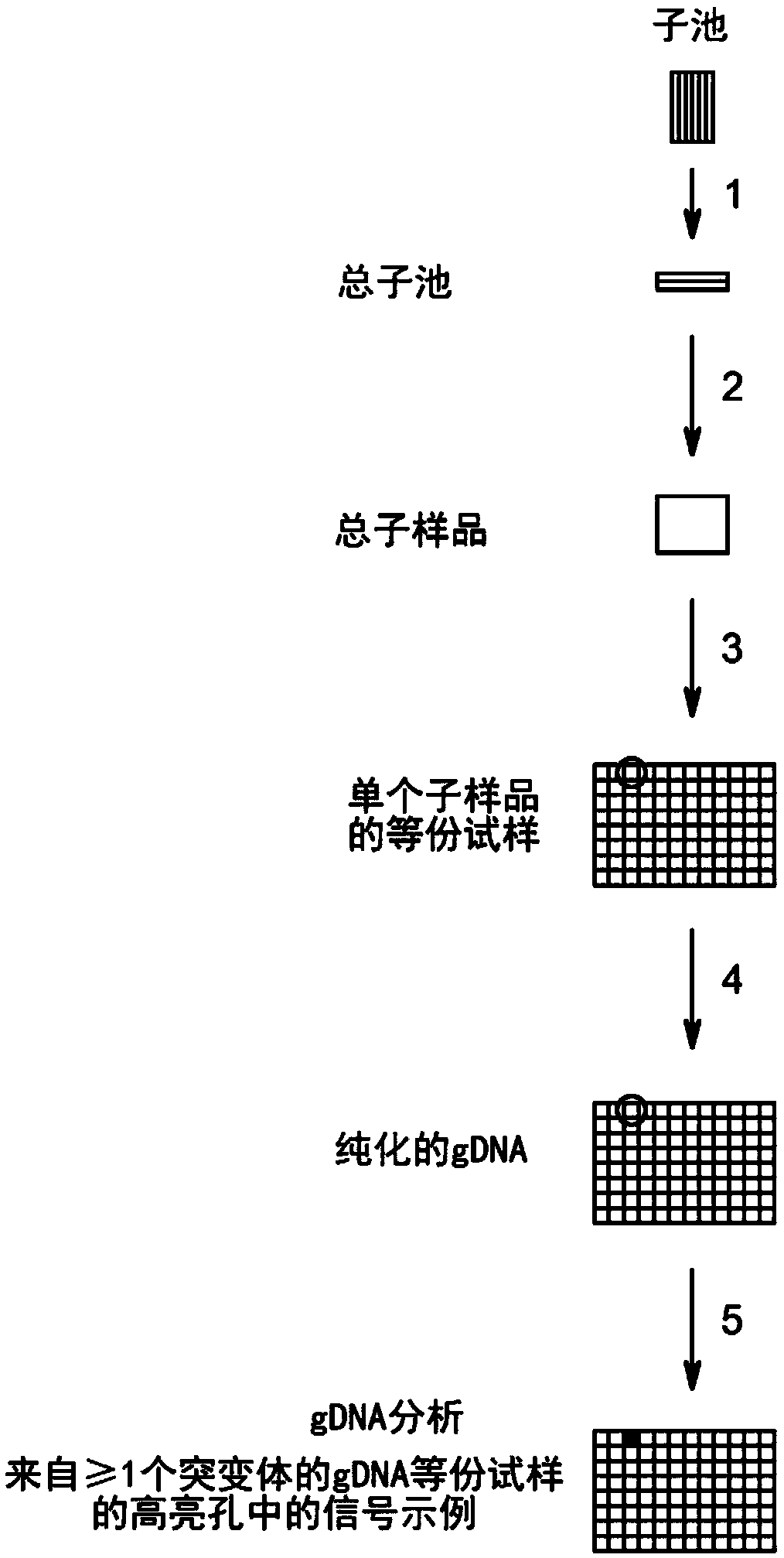
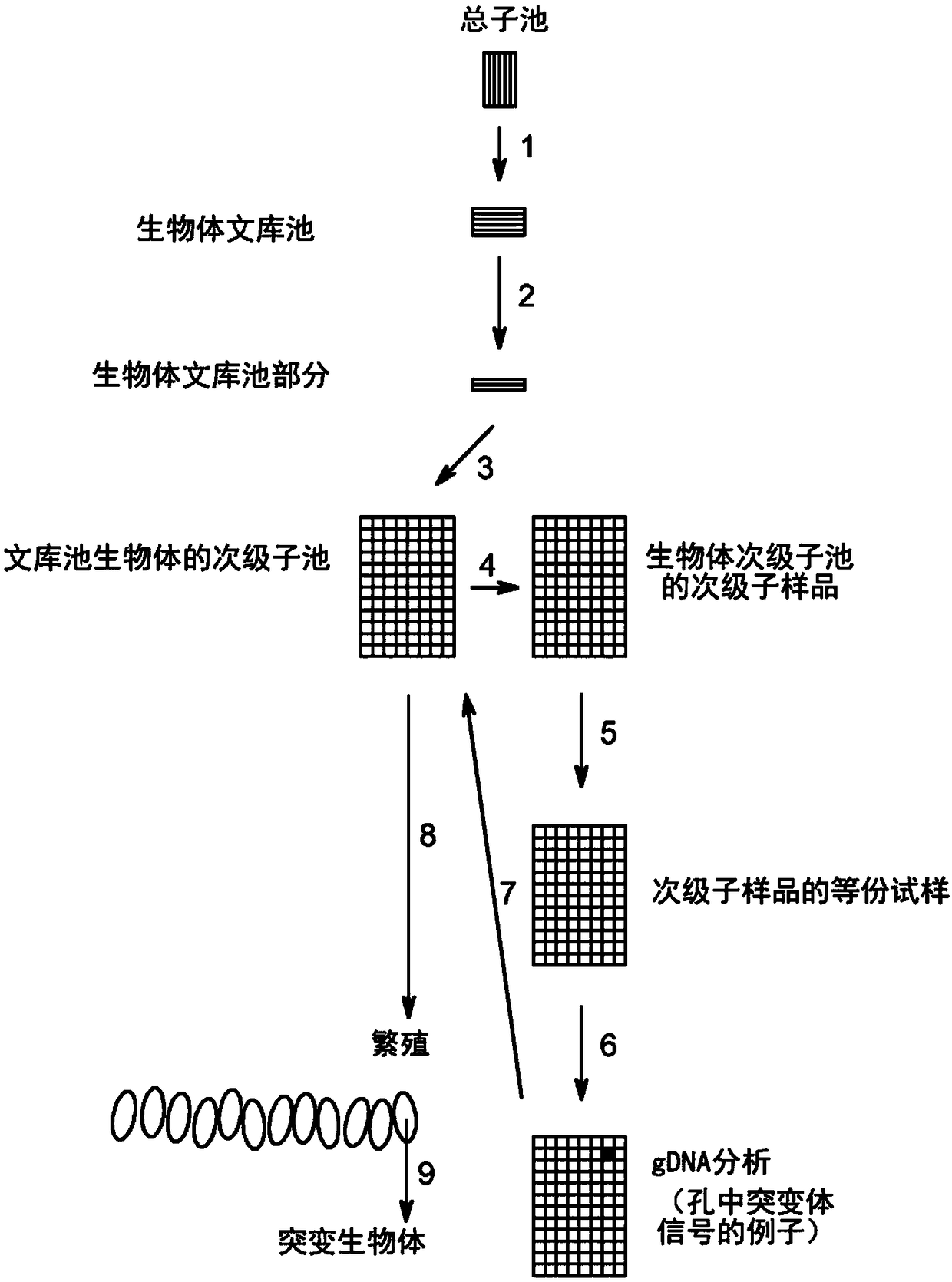
Method to screen for a mutant within a population of organisms by applying a pooling and splitting approach
In traditional plant breeding approaches, chemical mutagenesis may be utilized to introduce nucleotide substitutions at random in the genome of a plant, i.e. without possibilities to control the sitesof nucleotide changes. Because of genome complexities, the statistical probability is extremely little when it comes to finding a predetermined nucleotide substitution. The present invention, however, demonstrates how a novel, alternative use of digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR), preferably droplet dPCR (ddPCR), is developed to exploit finding of specific nucleotide substitutions in mutated genes. The entire platform comprises a screening method with a library of mutagenized organisms, digital PCR -based systems and a set-up to propagate and analyze identified, mutated organisms.
Owner:CARLSBERG BREWERIES AS
HIV and Hepatitis C Microarray to Detect Drug Resistance
The invention provides arrays and probes for resequencing gene sequences of HIV and HCV using an array of probes complementary to a set of reference sequences, and to each possible single nucleotide substitution of the reference sequences, and for identifying known mutations in HIV and HCV gene sequences associated with resistance to antiviral therapy. Methods of identifying mutations in HIV and HCV sequences, methods of characterizing HIV and HCV isolates, and methods of evaluating and optimizing a patient's antiviral therapy regimen are also provided.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Method of improving the activity of cellulase enzyme mixtures in the saccharification (LIGNO)cellulosic material
InactiveUS20130280764A1Reduced activityLower Level RequirementsHydrolasesMicroorganismsMucor speciesNeurospora
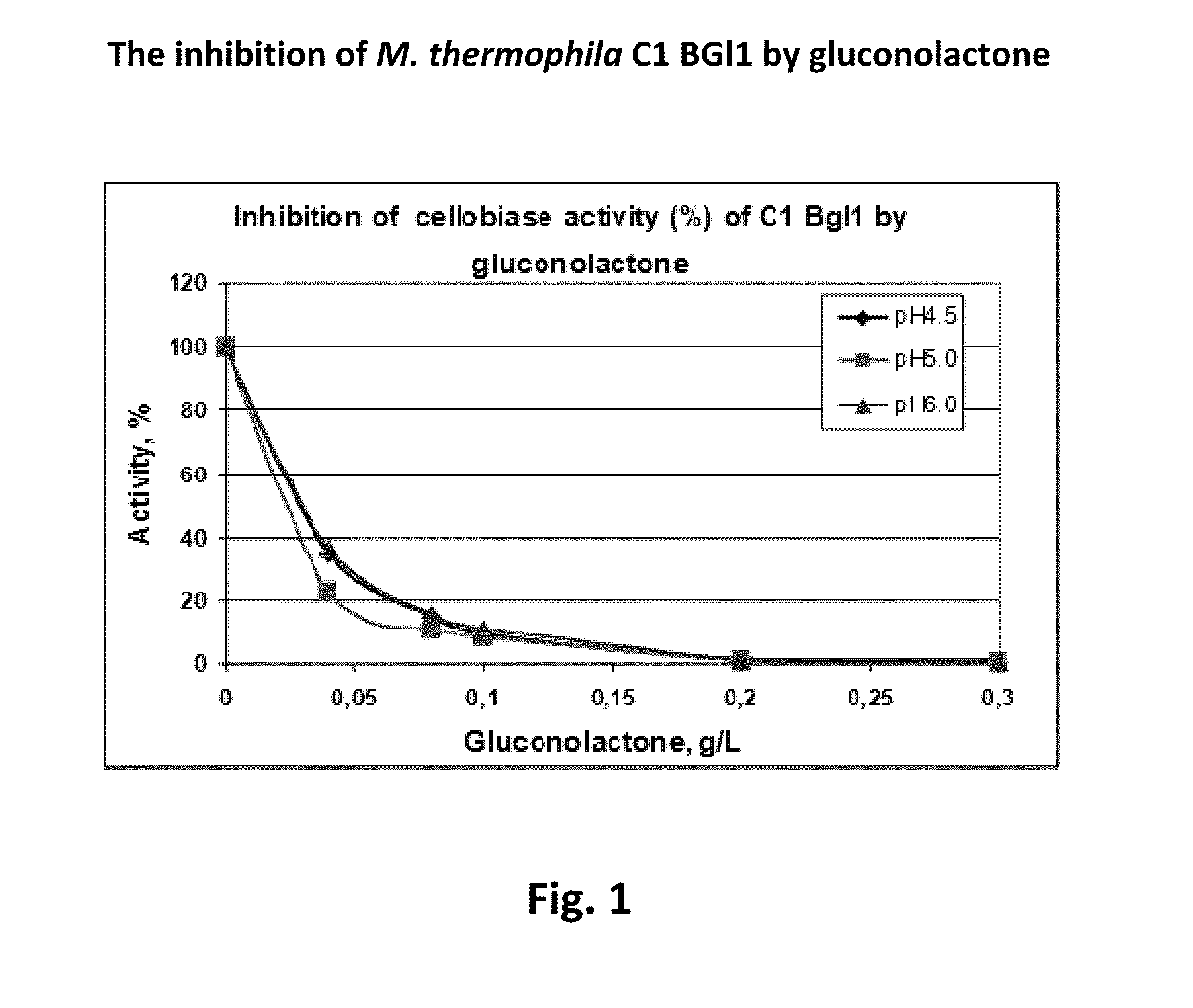
The present invention relates to modified filamentous fungal organisms having improved activity profiles with respect to the conversion of complex carbohydrates into simple sugars from cellulosic materials, including fungal organisms belonging to a genus selected from the group consisting of: Chrysosporium, Thielavia, Talaromyces, Thermomyces, Thermoascus, Neurospora, Aureobasidium, Filibasidium, Piromyces, Corynascus, Cryplococcus, Acremonium, Tolypocladium, Scytalidium, Schizophyllum, Sporotrichum, Penicillium, Gibberella, Myceliophthora, Mucor, Aspergillus, Fusarium, Humicola, Trichoderma, and Talaromyces, plus anamorphs and teleomorphs thereof. Filamentous fungal organisms having improved activity profiles are obtained by modifying genes encoding enzymes involved in the production of cellobionolactone, cellobionic acid, gluconolactone, gluconic acid, and related products, by a variety of mutagenic methods, resulting in nucleotide substitutions, insertions, and deletions, increasing the level of saccharification in enzyme mixtures obtained from the modified organisms.
Owner:DYADIC INT USA
Methods for the replacement, translocation and stacking of DNA in eukaryotic genomes
InactiveUS7972857B2Reduce in quantityImprove efficiencyStable introduction of DNAFermentationPlant cellPolynucleotide
The present invention includes compositions and methods for site-specific polynucleotide replacement in eukaryotic cells. These methods include single polynucleotide replacement as well as gene stacking methods. Preferred eukaryotic cells for use in the present invention are plant cells and mammalian cells.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Live-attenuated virus and methods of production and use
The invention discloses a live-attenuated virus and methods of production and use. Presented herein are live-attenuated viruses and methods of generating thereof from a parental virus through a plurality of nucleotide substitutions in the viral genome. The nucleotide substitutions result in a change in codon usage bias within codons of one or more protein encoding sequences and no change in aminoacid sequences of the proteins. The live-attenuated viruses display unaltered replication in avian hosts for propagation, but attenuated replication in mammalian hosts, when compared to the replication of the parental virus. The live-attenuated viruses in a form of improved vaccines can be used to elicit protective immune responses.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
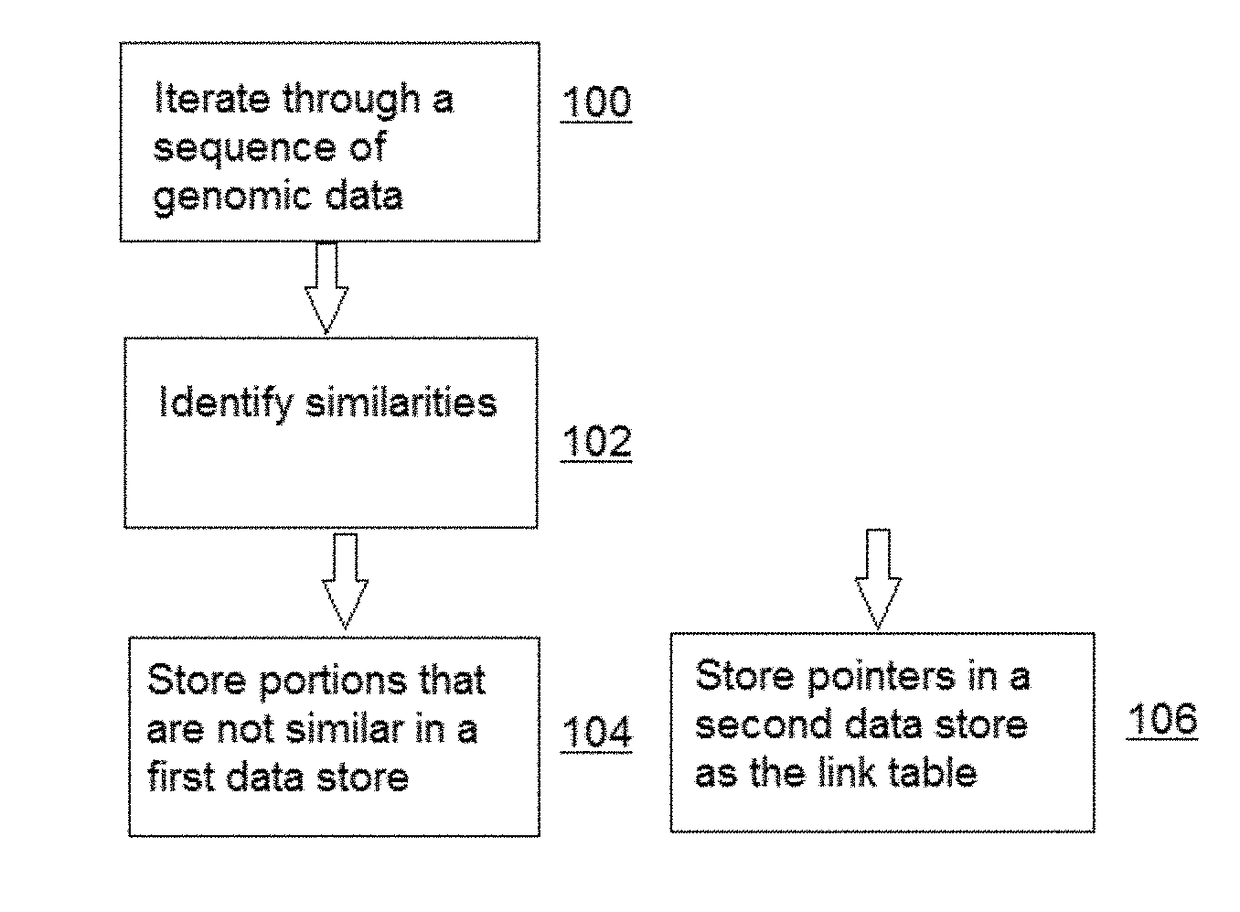
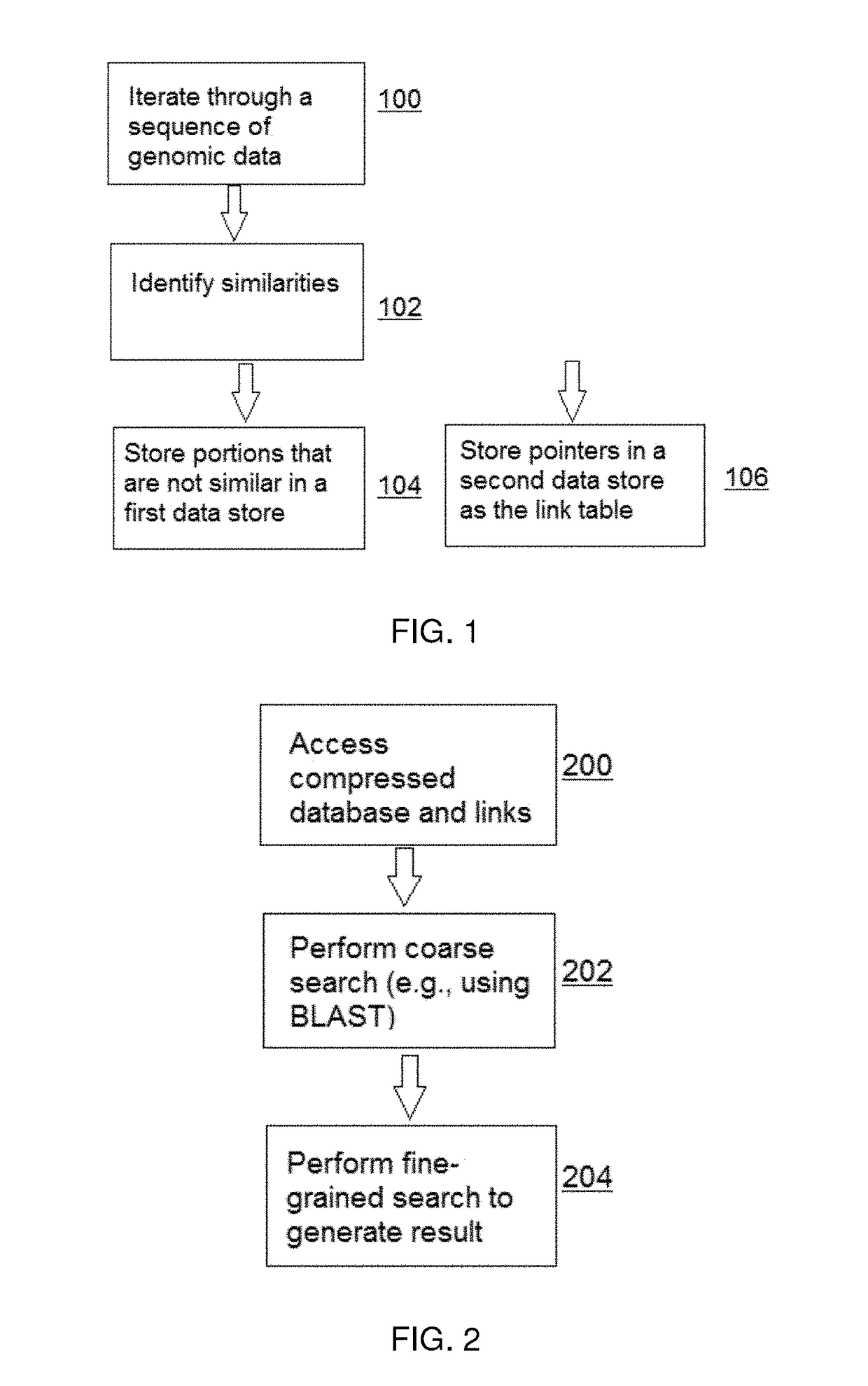
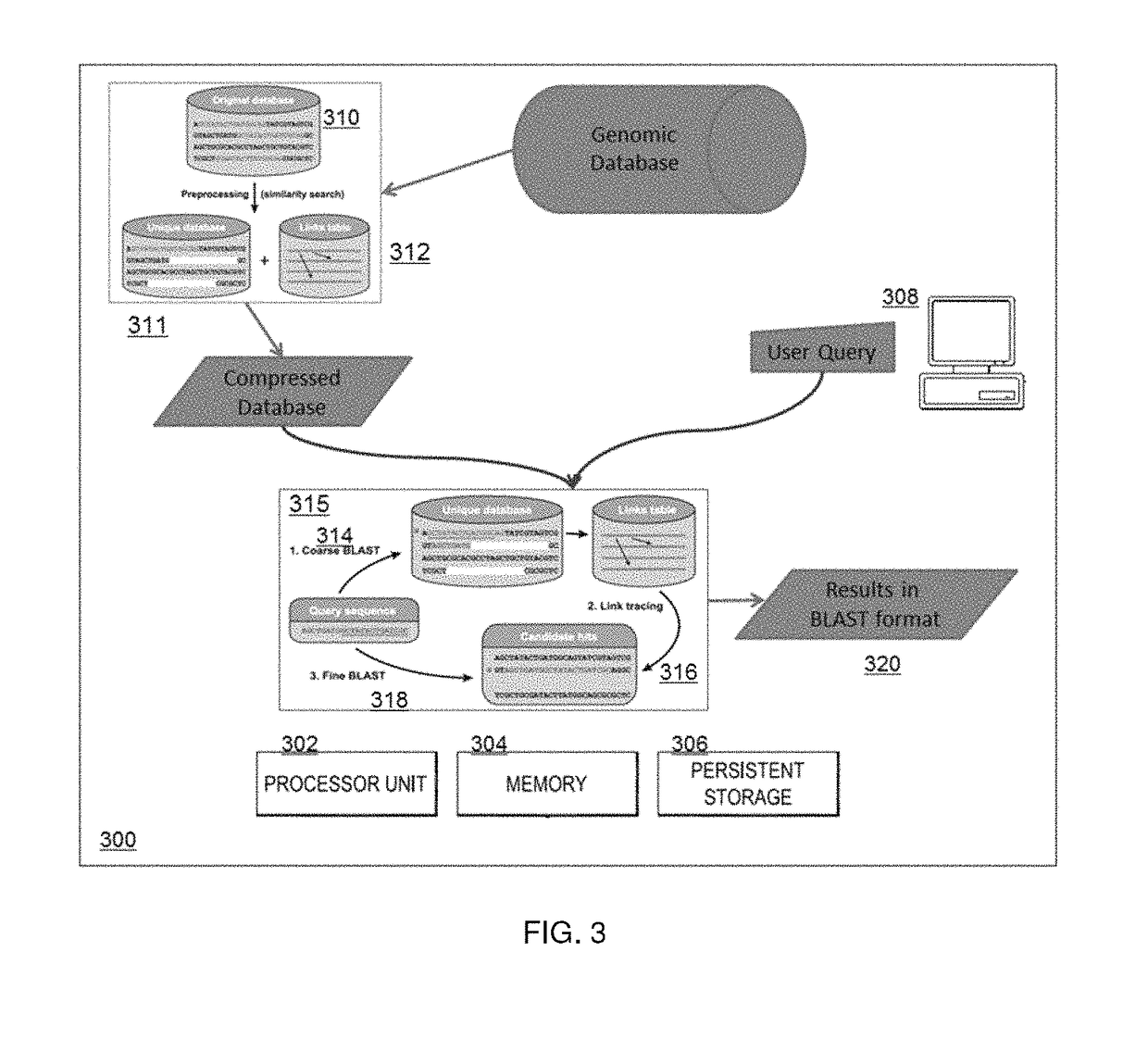
Compressing, storing and searching sequence data
ActiveUS9715574B2Lighten the taskImprove efficiencyCode conversionBioinformaticsDirect computationComplete data
The redundancy in genomic sequence data is exploited by compressing sequence data in such a way as to allow direct computation on the compressed data using methods that are referred to herein as “compressive” algorithms. This approach reduces the task of computing on many similar genomes to only slightly more than that of operating on just one. In this approach, the redundancy among genomes is translated into computational acceleration by storing genomes in a compressed format that respects the structure of similarities and differences important to analysis. Specifically, these differences are the nucleotide substitutions, insertions, deletions, and rearrangements introduced by evolution. Once such a compressed library has been created, analysis is performed on it in time proportional to its compressed size, rather than having to reconstruct the full data set every time one wishes to query it.
Owner:BAYM MICHAEL H +2
Base-modified nucleotides and their use for polymorphism detection
InactiveUS6994998B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolymorphism Detection
The present invention relates to methods for the detection of polymorphisms by substituting a base-modified nucleotide for a natural nucleotide in a polynucleotide. The base-modified nucleotide renders the polynucleotide more susceptible to cleavage at the sites of its incorporation than site consisting of natural nucleotides. The fragments obtained are then analyzed to determine the presence or absence of a polymorphism.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Nucleic acid derived from hepatitis c virus and expression vector, transformed cell, and hepatitis c virus particles each prepared by using the same
InactiveUS20120003720A1Large capacityIncrease capacitySsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesNucleotideHepacivirus
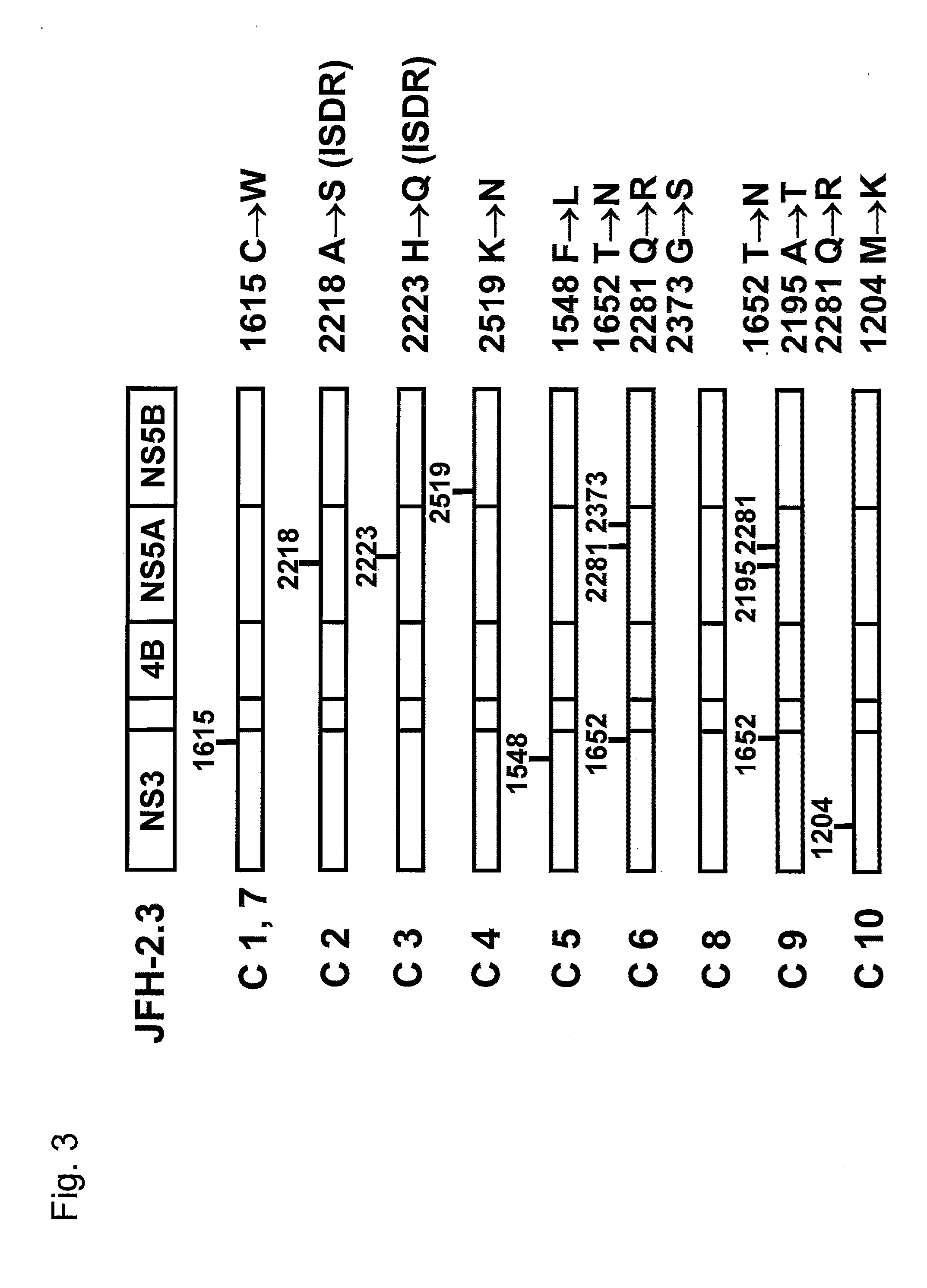
The present invention provides a nucleic acid comprises a 5′ untranslated region, an NS3 protein coding region, an NS4A protein coding region, an NS4B protein coding region, an NS5A protein coding region, an NS5B protein coding region, and a 3′ untranslated region of a hepatitis C virus genome, wherein the nucleic acid has nucleotide substitutions causing one or more amino acid substitutions selected from the group consisting of M(1205)K, F(1548)L, C(1615)W, T(1652)N, A(2196)T, A(2218)S, H(2223)Q, Q(2281)R, K(2520)N, and G(2374)S, as defined using the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 6 in the Sequence Listing as a reference sequence, in the NS3 protein coding region, the NS5A protein coding region, or the NS5B protein coding region.
Owner:TORAY IND INC +2
A computer-implemented and reference-free method for identifying variants in nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS20200005898A1Type accurateUnprecedented performanceData visualisationProteomicsNucleotideVariome
There is provided a computer-implemented method for identifying of nucleic acid variants between two cells, such as a normal cell vs. a pathological cell of a patient, or a cell at two different stages of development. The method is alignment-free, as it does not depend on the use of a reference genome, and is based on the generation and comparison of polymorphic k-mers derived from the nucleotide sequence reads of both biological states. The invention accurately identifies all sorts of genetic variants, ranging from single nucleotide substitutions (SNVs) to large structural variants with great sensitivity and specificity. As a major novelty, it also identifies non-human insertions, such as those derived from retroviruses. Altogether, this invention allows the integration with specific hardware architectures in order to speed up the executions to an unprecedented level.
Owner:BARCELONA SUPERCOMPUTING CENT CENT NAT DE SUPERCOMPUTACION +2
Bacteriophage with Enhanced Lytic Activity
InactiveUS20100240025A1Increase lytic activityImprove satisfactionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideBacteriophage
This invention encompasses an isolated Bacillus phage AP50 that has one or more nucleotide substitutions in the phage genome, whereby the one or more nucleotide substitutions increase lytic activity of the phage. In addition, the invention encompasses proteins expressed by the phages, compositions containing the proteins and / or the phage as well as methods of using the Bacillus phage AP50 to test for the presence of B. anthracis.
Owner:THE HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF MILITARY MEDICINE INC +1
Alignment method for nucleic acid sequences
ActiveUS20190108310A1Alignment deterioratesReduce decreaseSequence analysisComplex mathematical operationsAmino acid substitutionPartial alignment
The current invention concerns a computer-implemented method, a computer system and a tangible non-transitory computer-readable data carrier comprising a computer program product for aligning a query nucleic acid sequence against a reference nucleic acid sequence. An optimal alignment score of the query sequence against the reference sequence is determined by a dynamic programming algorithm. The algorithm is configured for locally optimizing a partial alignment score based on a nucleotide substitution cost, a gap insertion cost, an amino acid substitution cost, as well as a frameshift penalty.
Owner:EMWEB BVBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com