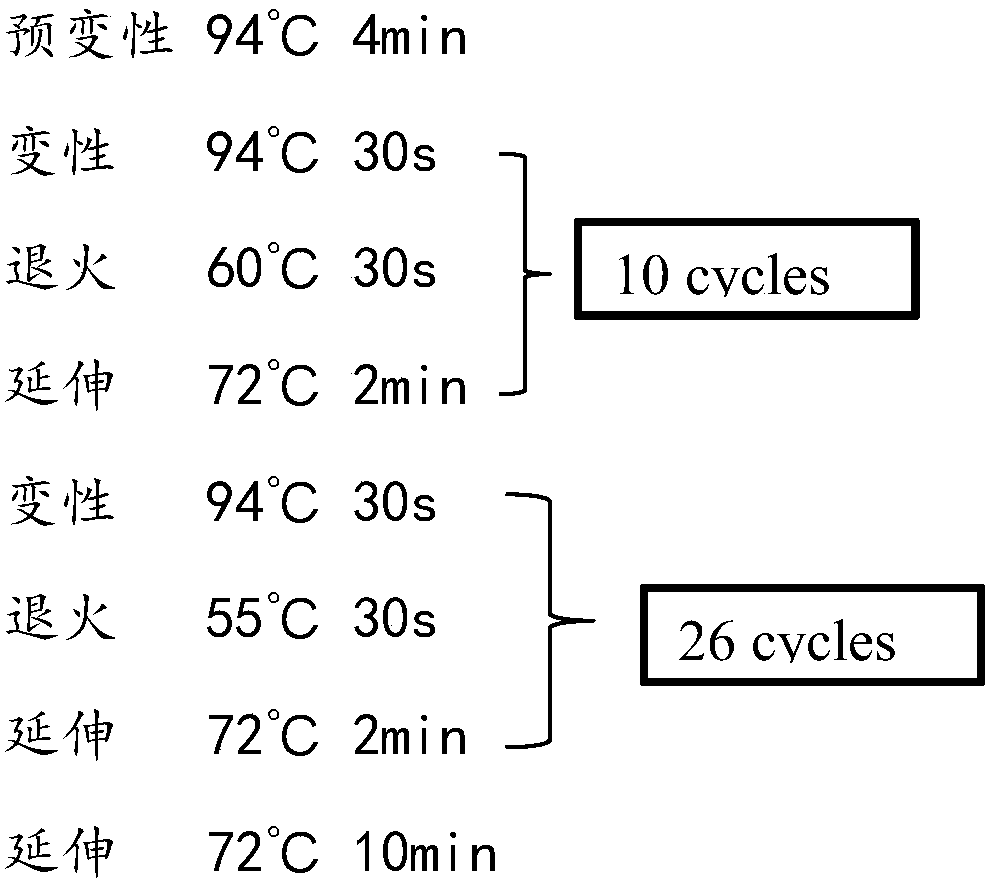
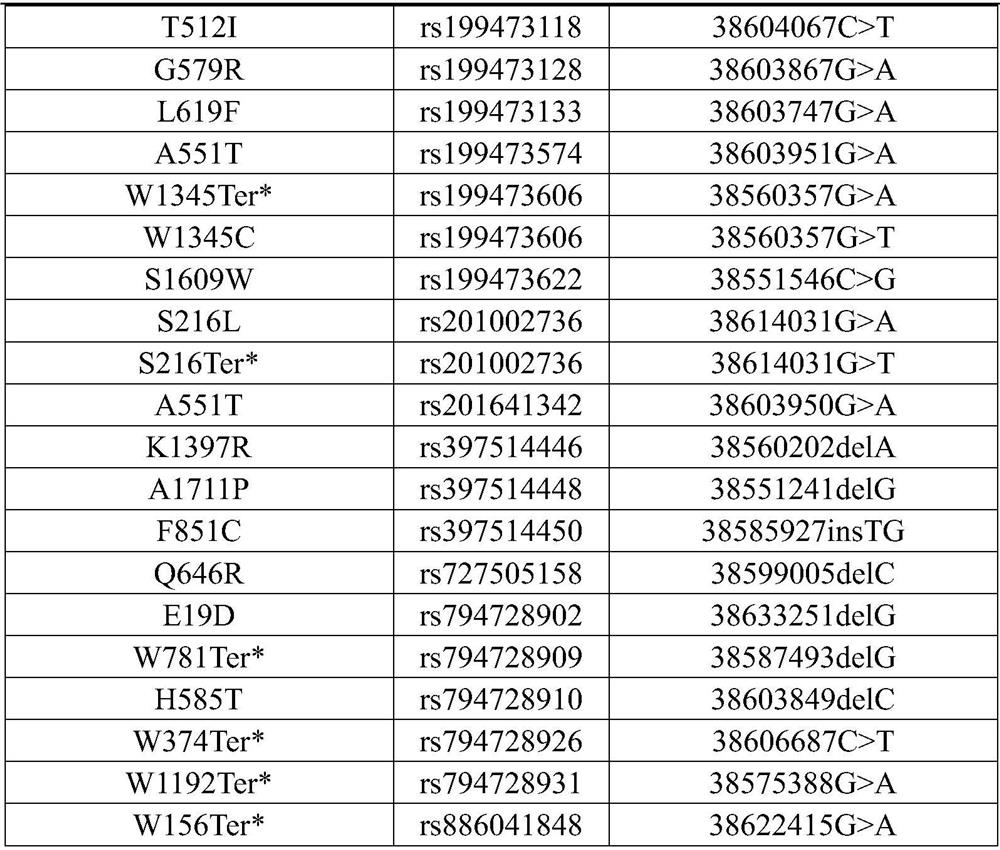
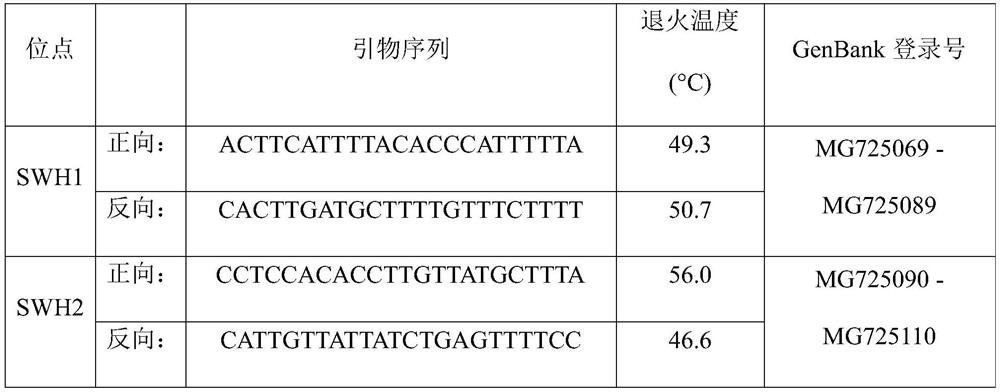
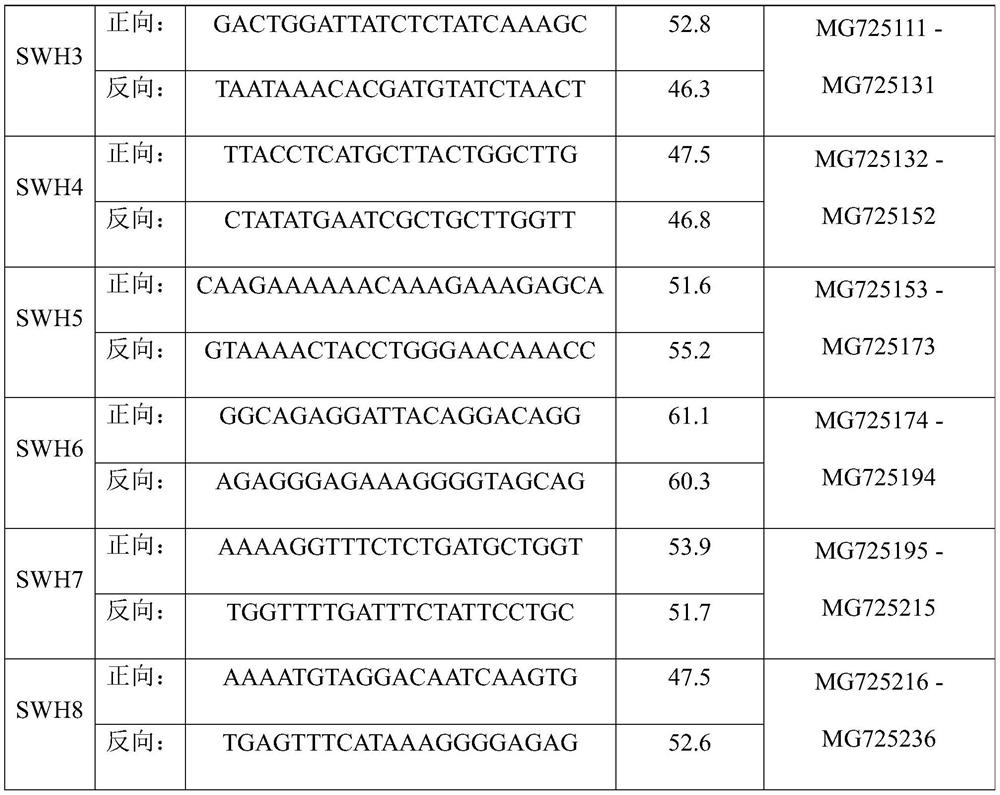
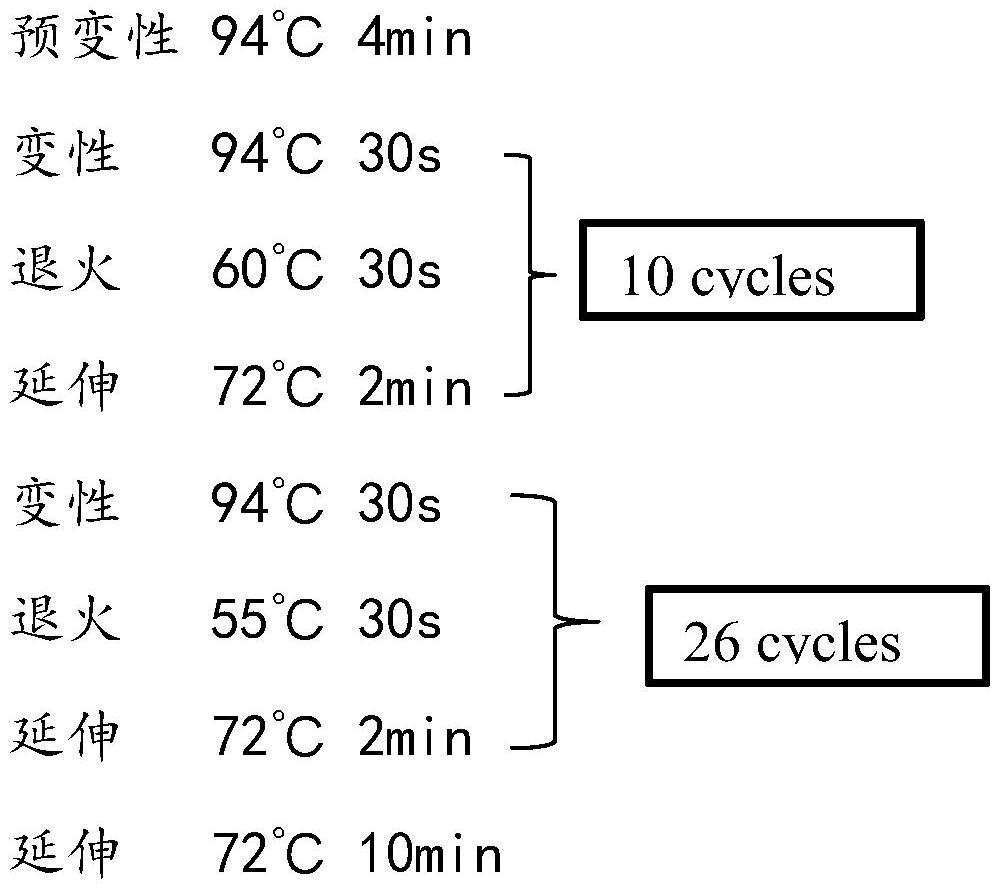
Patents
Literature
37 results about "Genome alignment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Structural alignment (genomics) Structural alignment is a form of sequence alignment based on comparison of shape. These alignments attempt to establish equivalences between two or more polymer structures based on their shape and three-dimensional conformation. This process is usually applied to protein tertiary structures...
Method and computer software product for genomic alignment and assessment of the transcriptome
InactiveUS20050244883A1Reduce quality problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenome alignmentNucleic Acid Probes
In one embodiment of the invention, computerized methods are provided for analyzing transcript sequence clusters by aligning the transcripts with genomic sequences to determine whether a cluster needs to be sub-clustered and whether clusters should be merged. In addition, in some embodiments, transcript sequences are trimmed according to their alignment with their corresponding genomic sequences. The modified clusters and trimmed sequences may be used for nucleic acid probe array design.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Method for detecting DNA variation level by using polymolecular tags
InactiveCN106893774AImprove accuracyLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementGenome alignmentA-DNA
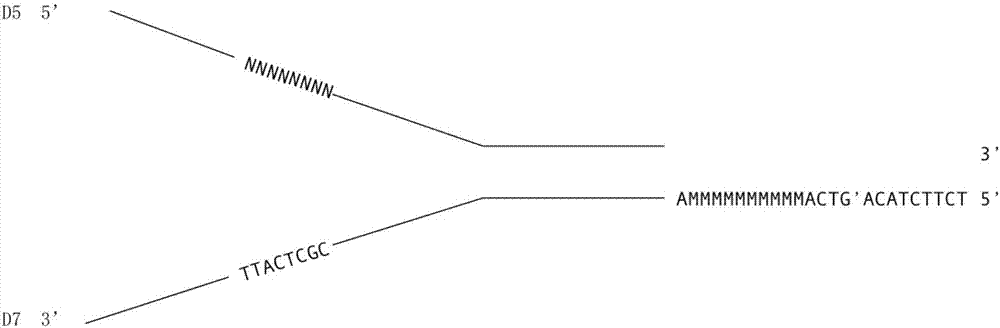
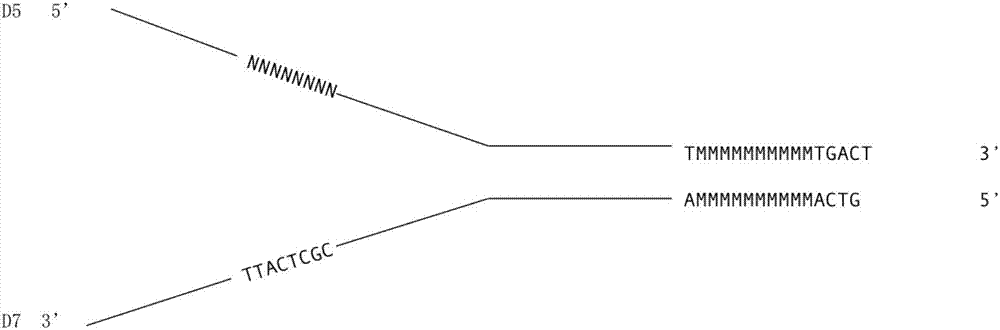
The invention relates to a method for detecting a DNA variation level by using polymolecular tags. The method comprises the following steps: inserting a first DNA tag N1 into D5 so as to obtain a first single stranded DNA molecule, wherein the sequence length of the N1 is 2-12bp; inserting a second DNA tag N2 and a third DNA tag N3 into D7 so as to obtain a second single stranded DNA molecule, wherein sequence lengths of the N2 and N3 are respectively 2-12bp and 2-20bp; mixing the two single stranded DNA molecules, annealing, carrying out a DNA polymerization reaction, and performing digestion by using restriction enzymes so as to obtain a DNA linker sequence containing a first sticky end; breaking to-be-detected DNA into short DNA fragments, and adding a second sticky end in reverse complement with the first sticky end at two ends of the DNA fragments; and connecting the DNA linker sequence and the short DNA fragments, performing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and sequencing, contrasting with human reference genome so as to judge the variation level of the to-be-detected DNA.
Owner:苏州首度基因科技有限责任公司 +1
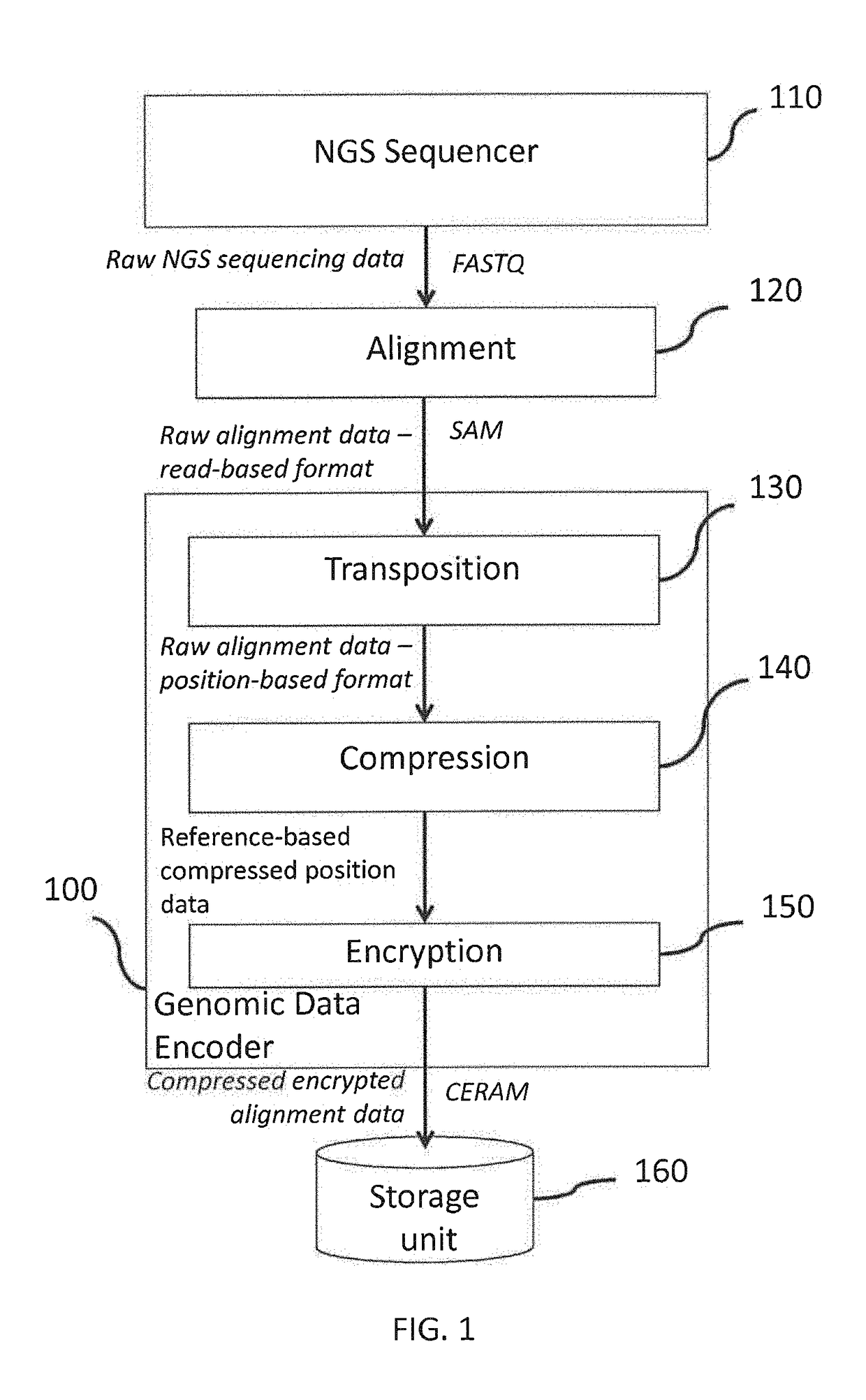
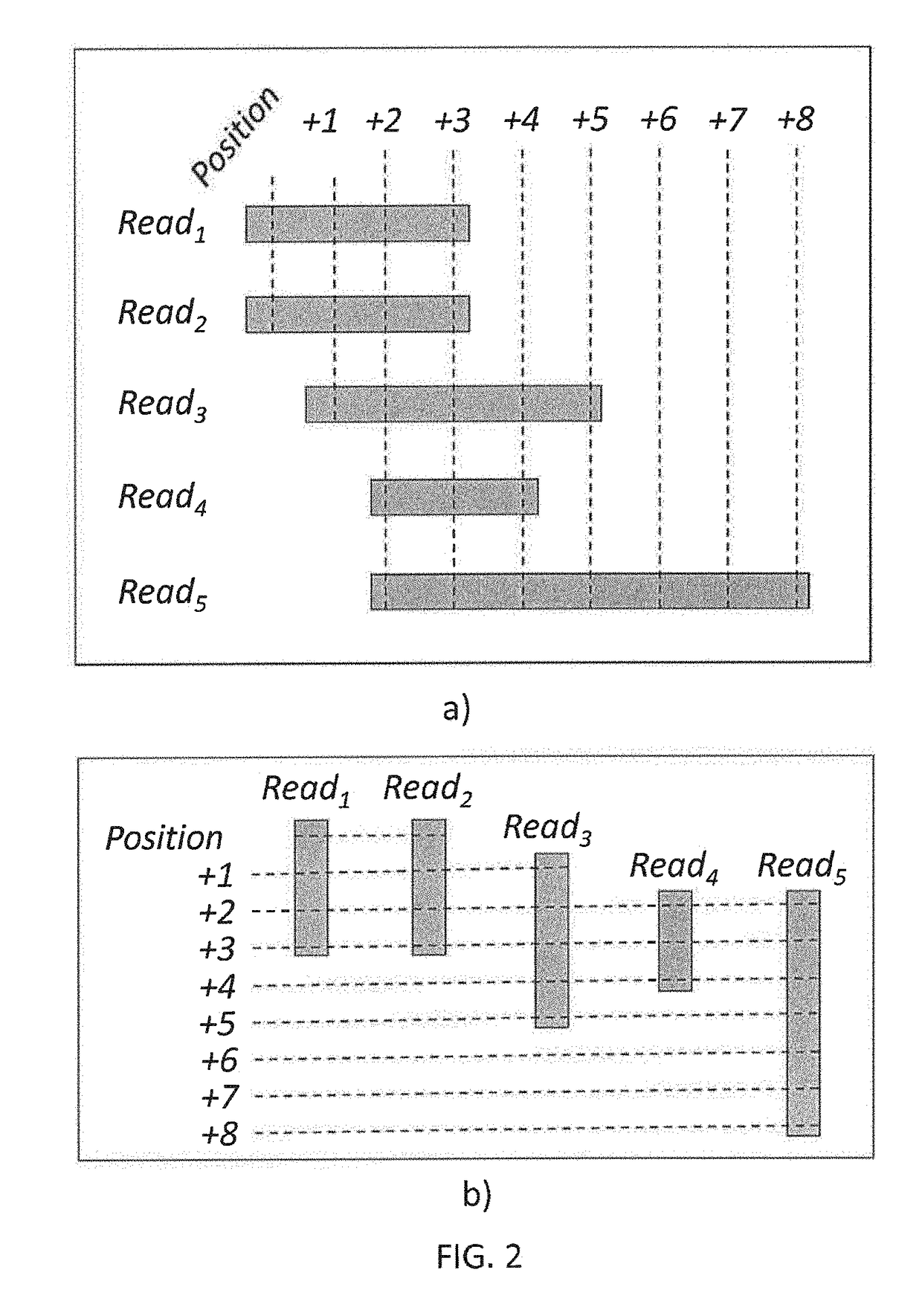
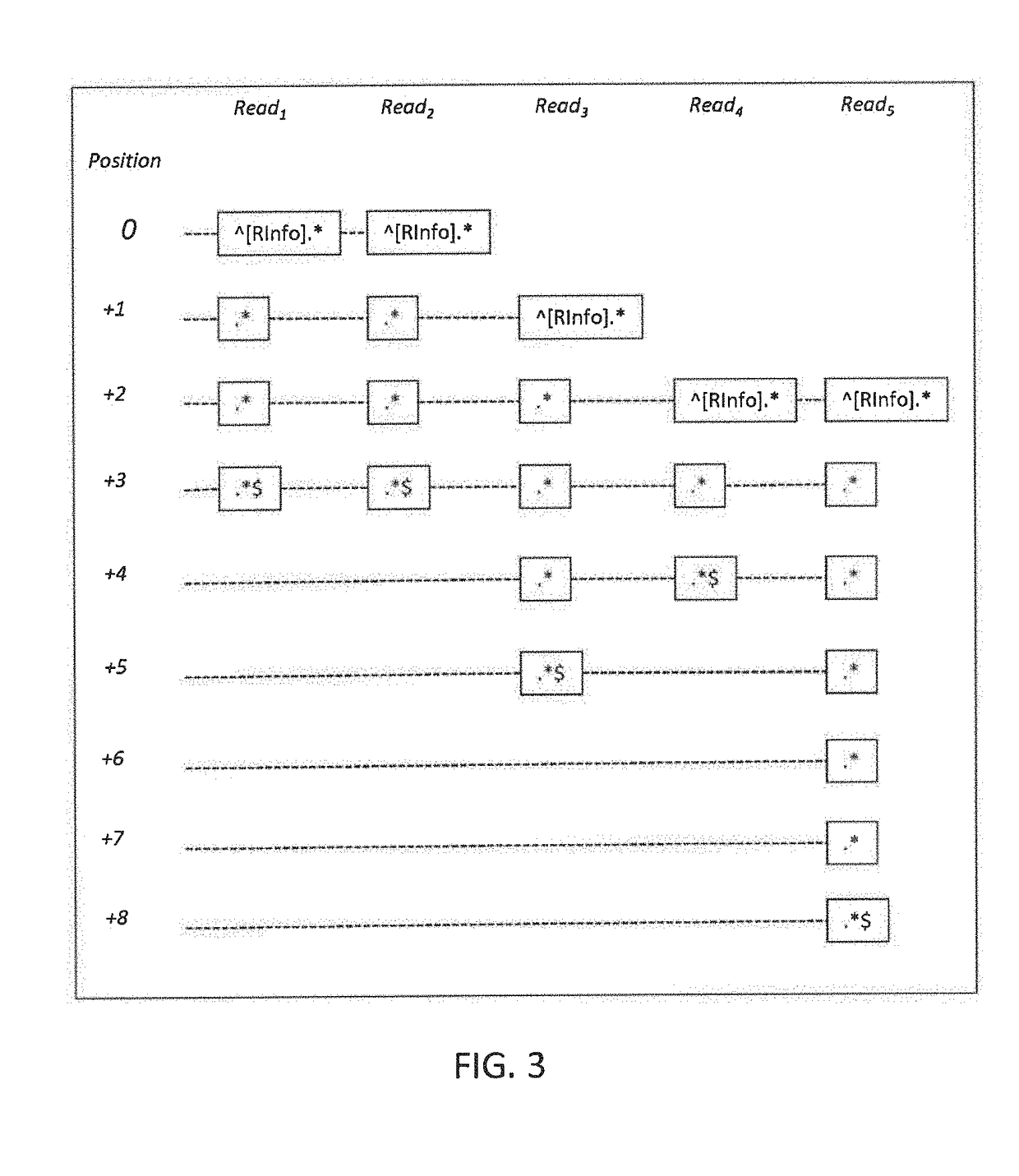
Methods to compress, encrypt and retrieve genomic alignment data
ActiveUS20190087601A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesHandling data according to predetermined rulesGenome alignmentData stream
A genomic data decoder may jointly compress and encrypt genomic data alignment information while preserving the privacy of sensitive genomic data elements at retrieval stage. Genomic data alignment information organized as a read-based alignment data stream may be transposed into a position-based alignment data stream. The position-based alignment information may been coded into a reference-based alignment data stream. The reference-based alignment data stream may be encrypted with a combination of order-preserving encryption of the genomic position information and symmetric encryption of the reference-based alignment differential data. Differential encoding and entropy coding schemes may further compress the reference-based alignment data stream. The resulting compressed and encrypted stream may be indexed and stored in a biobank storage unit. A genomic data decoder may efficiently retrieve, decrypt and decode a specific subset of the resulting compressed and encrypted stream without leaking information on the other genomic data subsets in the resulting stream.
Owner:SOPHIA GENETICS
Genomic-data storage method and electronic device
ActiveCN107480466AImprove efficiencyInput/output to record carriersSpecial data processing applicationsGenome alignmentAccess frequency
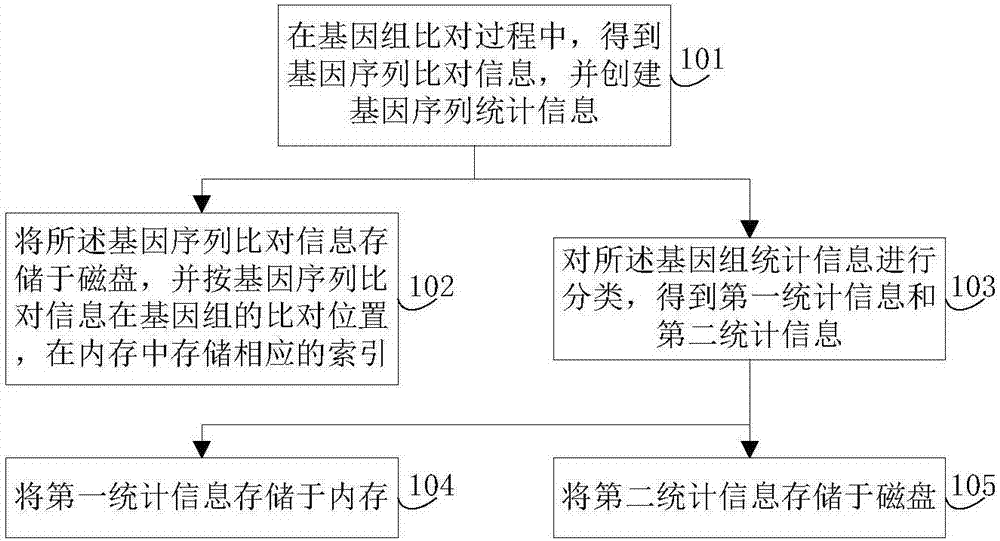
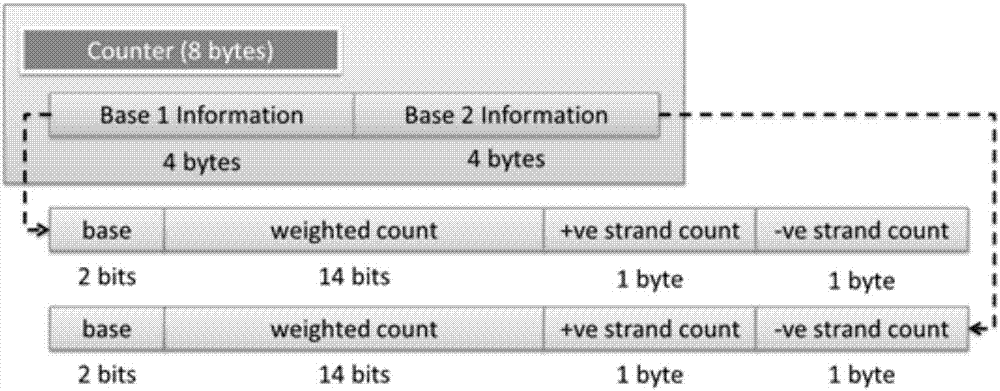
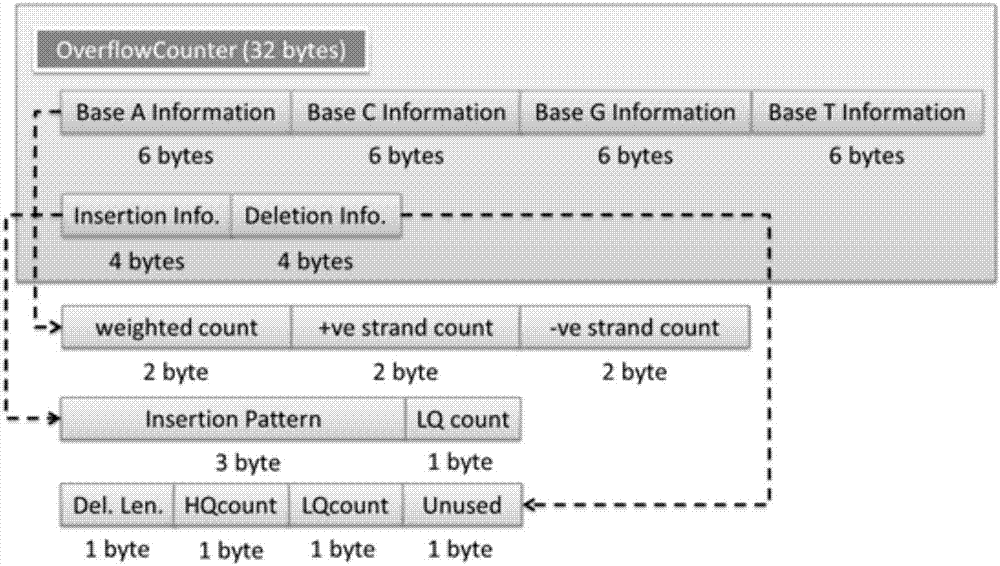
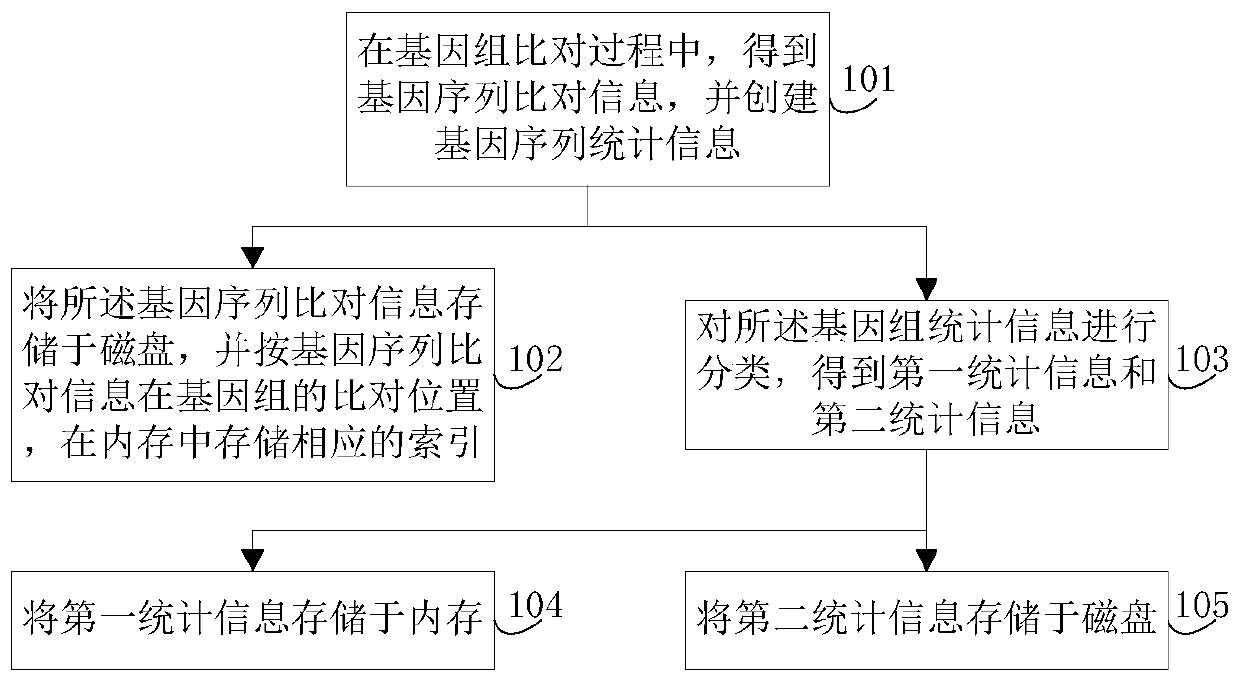
The invention discloses a genomic-data storage method. The genomic-data storage method includes the steps that in the genome comparison process, gene-sequence comparison information is obtained, and gene-sequence statistical information is established; the gene-sequence comparison information is stored in a magnetic disk, and according to comparison positions of the gene-sequence comparison information in a genome, corresponding indexes are stored in a memory, wherein the indexes are storage positions of the gene-sequence comparison information in the magnetic disk; genome statistical information is classified, and first statistical information and second statistical information are obtained; the first statistical information is stored in the memory, wherein the first statistical information is statistical information with the access frequency higher than the preset frequency in the variation detection process; the second statistical information is stored in the magnetic disk, wherein the second statistical information is statistical information which cannot be stored in the memory and / or statistical information with the access frequency lower than the preset frequency in the variation detection process. The invention also discloses an electronic device with the genomic-data storage method.
Owner:UNITED ELECTRONICS
DNA next generation sequencing whole-process quality analysis method
ActiveCN109637581AGuaranteed correctnessMeet the needs of practical applicationsProteomicsGenomicsGenome alignmentProcess quality
The invention relates to a DNA next generation sequencing whole-process quality analysis method. The method comprises the steps 1), genetic sequencing is conducted on a biological sample; 2), biological sequencing data obtained by genetic sequencing is uploaded; 3), quality analysis is conducted on an original sequencing sequence file fastq; 4), quality analysis is conducted on a bam file on whichgenome comparison is completed; 5), quality analysis is conducted on a mutation information vcf file. The method has the advantages that a detailed quality report is given by adopting genetic sequencing whole-process, the accuracy of each step can be ensured, a correct result can be given in the final result, detailed analysis is conducted on the fastq, the bam and the vcf file, the quality analysis report is not only an evaluation operation on the reliability of the result but also a feedback of an original experimental operation, and the practical demands can be well met.
Owner:江苏医联生物科技有限公司
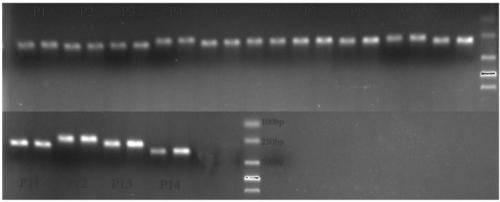
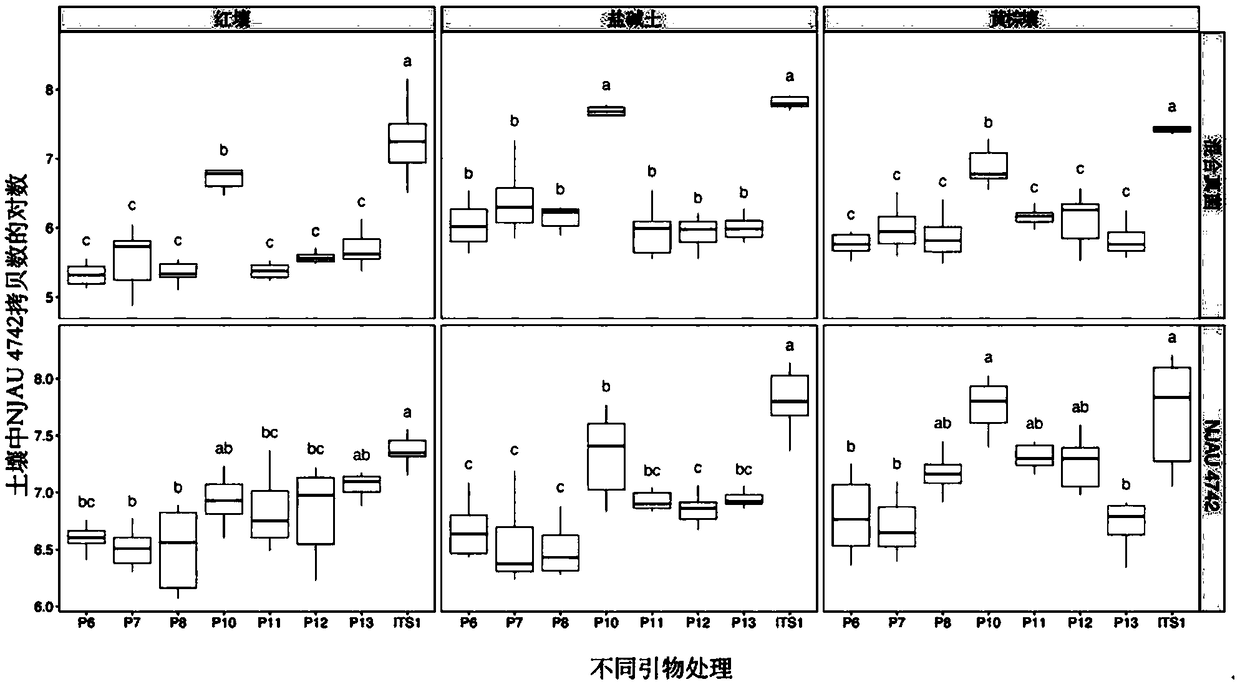
Two step genome comparison method for designing quantitative PCR specific primer of guizhouense NJAU 4742
ActiveCN108949908AImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesGenome alignmentStrain specificity
The invention discloses a two step genome comparison method for designing a quantitative PCR specific primer of guizhouense NJAU 4742. At first, full genome sequence of NJAU 4742 is compared in NCBI database and JGI database; genome segments, which are not matched and greater than 500 bp, are picked out; then the screened segments are compared with the full genome of a guizhouense strain 916; anda primer sequence with unique bases is designed. At the same time, three pairs of primers, which are prepared by inserting labeled segments into a gfp labeled strain (gfp-NJAU 4742), are used to examine the specificity of the primers designed based on the genome. By examining the amplification specificity of strains of same genus and different species, re-detecting the soil addition, and actuallydetecting the potting soil, an optimal quantitative PCR primer is screened out. The provided primer design method and design strain specific primer can be applied to quantitative PCR specific primer design of other strains and quantifying of guizhouense NJAU 4742.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
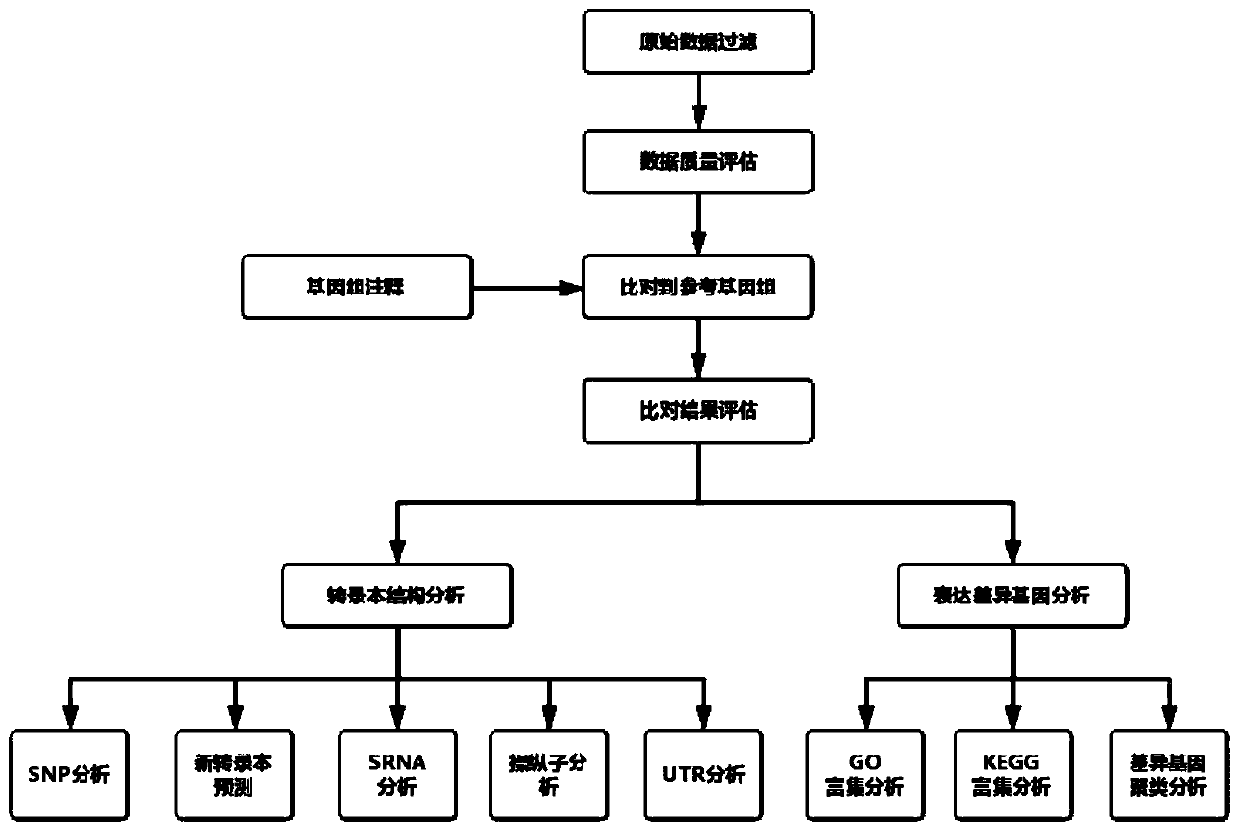
Automated analysis method for prokaryotic transcriptome based on second generation sequencing
PendingCN110047560AConvenient error queryQuick check for errorsProteomicsGenomicsGenome alignmentStructure analysis
The invention discloses an automated analysis method for prokaryotic transcriptome based on second generation sequencing. The automated analysis method includes the steps: an original logout data filtering and quality control step; a genome comparison step; a transcript structure analysis step; a gene expression quantification and differential expression analysis step; and a result sorting step. The automated analysis method for prokaryotic transcriptome based on second generation sequencing has the advantages of: covering most of the analysis content required by the market, automatically sorting out all the analysis results, and after completing the analysis of each part, automatically counting, visualizing, and sorting the results, so that the results are arranged in order and can be directly used for generation of a report; being visible for all the operation steps, thus being convenient for error query; and when performing each step analysis, recording the used command lines and parameters and the log results generated during the operation, and once the program runs incorrectly, being able to quickly check the error.
Owner:南京派森诺基因科技有限公司
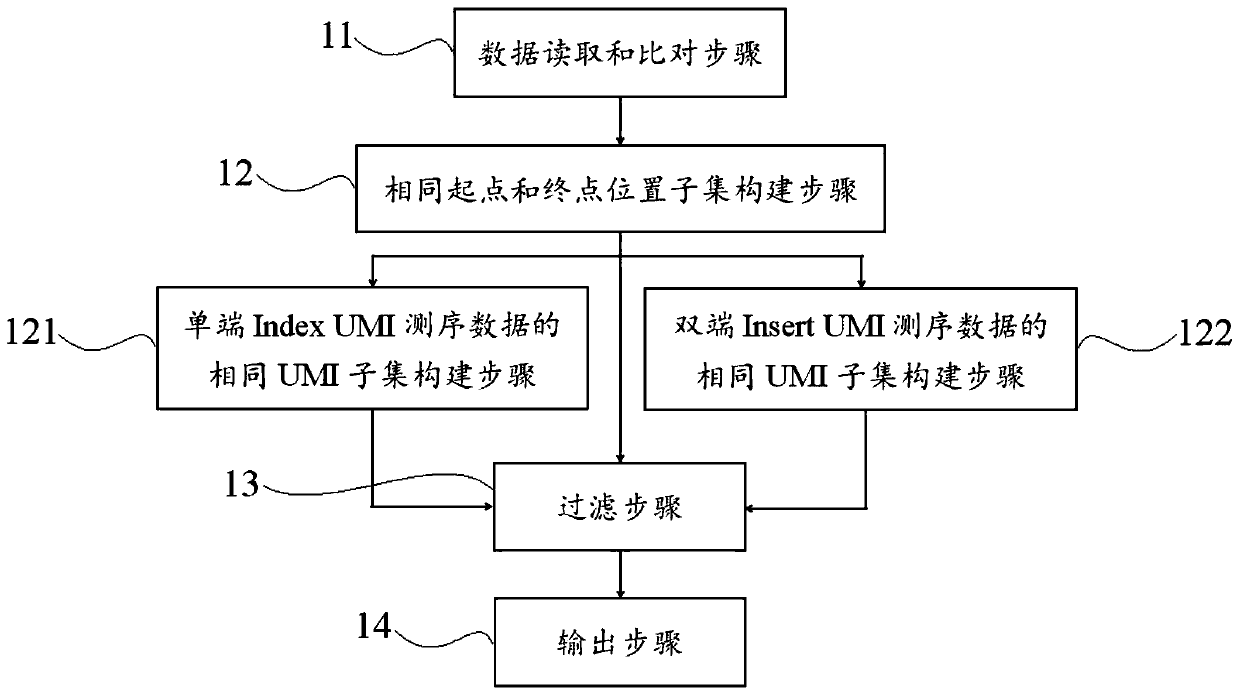
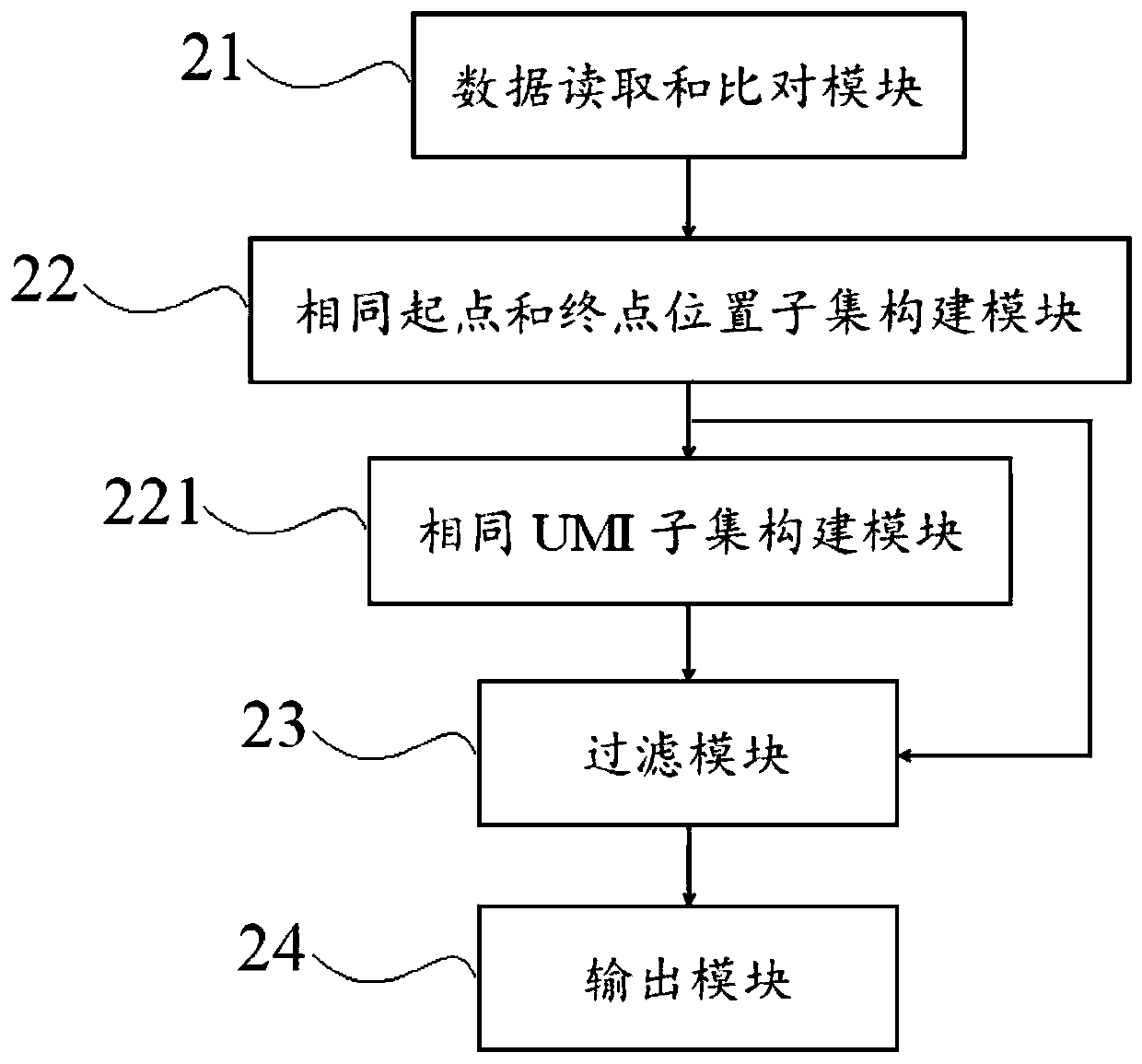
Method and device for correcting high-flux sequencing data
The invention discloses a method and a device for correcting high-flux sequencing data. The method comprises the steps of comparing read pair or read data which are obtained through sequencing with areference genome; classifying the read pair or read with the same starting point and terminal point positions as one Ai subset; comparing each base sequence of the read pair or read in each subset ata genome comparing position, eliminating repetitions and false positive mutation sites according to a preset mutation threshold; and finally outputting consistent data with high coverage range, wherein only the corrected single read pair or read is reserved in each subset. The method according to the invention can eliminate a large number of repetitions and false positive mutations generated in database establishing, hybridization capturing and PCR in high-flux sequencing. The method is suitable for high-depth sequencing with easy false positive mutation generation in eliminated cancer tissuemutation detection, liquid biopsy and the like. The method lays a basis for improving detecting quality and efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN HAPLOX BIOTECH
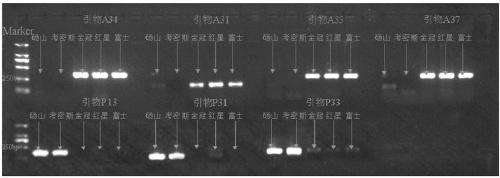
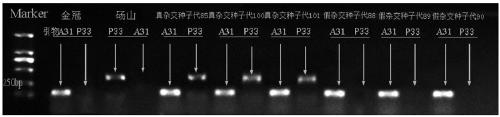
Molecular marker primer composition for identifying inter-hybrid seeds of pears and apples and application thereof
ActiveCN109486991AIncrease credibilityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPEARGenome alignment
The invention discloses a molecular marker primer composition for identifying inter-hybrid seeds of pears and apples and an application thereof. Specific sequences of pear and apple genomes are detected by a method of whole genome comparison, seven pairs of molecular marker specific primers P13, P31, P33, A31, A33, A34 and A37 are developed newly, and positive and negative primer sequences are asshown in a table 1. By identifying the inter-hybrid offsprings of pears and apples by means of the specific primers, specific amplified strips of the pears, apples and hybrid offsprings can be obtained, separately, that is, the inter-hybrid seeds of the pears and the apples are detected truly. The molecular marker based on the specific sequences of the genomes can be used for identifying the inter-hybrid seeds of pears and apples and has important theoretical and practical guiding meaning in improving genetic breeding progress of fruit trees and accelerating molecular assisted selective breeding.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for data analysis of miRNA in animals with reference data based on miRBase database
The invention discloses a method for data analysis of miRNA in animals with reference data based on a miRBase database. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of preparation, filtration of logout data, genome alignment, small RNA annotation, miRNA feature analysis, miRNA expression quantity analysis, miRNA function and pathway analyses, and result sorting. The method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that an analysis result is complete, and comprises involved miRNA analysis content and other detected small RNA information annotation, automated analysis is achieved, and statistics and sorting of all analysis content and results can be automatically and rapidly conducted only by providing related database information. All operation steps are visible, and thus errors can be conveniently checked, applied command lines and parameters and log results generated in operation can all be recorded when analysis is conducted step by step, and once a program fails during running, the errors can be rapidly queried.
Owner:南京派森诺基因科技有限公司
Excavation method for salt-tolerant gene of salix matsudana
InactiveCN110484599AIngenious designExcavate accuratelyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationCandidate Gene Association StudySalix warburgii
The invention provides an excavation method for a salt-tolerant gene of salix matsudana. The method comprises the steps that salt-tolerant salix matsudana and salt-sensitive salix matsudana are crossbred to obtain an F1 population, the F1 population is divided into salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive filial generations, and through salt stress, root systems of the salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive filial generations are subjected to transcriptome sequencing to obtain differential expression gene sequences separately; based on the salt-tolerant filial generation, a high-density genetic map is established, salt tolerance QTLs positioning is conducted, a QTL section is obtained through calculation, the QTL section, the differential expression gene sequences and a salix matsudana whole genome arecompared, and through analysis, the salt-tolerant candidate gene is obtained; through salt stress, the relative expression of the salt-tolerant candidate gene of the salt-tolerant filial generation ismeasured, the salt-tolerant candidate gene is determined as a salt-tolerant re-selection gene, instantaneous conversion is conducted, a salt-tolerant physiological index of a salix matsudana seedlingis detected, and the salt-tolerant re-selection gene is determined as a salt-tolerant gene. According to the excavation method, the problem is solved that during traditional salt-tolerant salix matsudana breeding, the salt-tolerant gene cannot be accurately found out.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Method and device for detecting human genome virus integration site
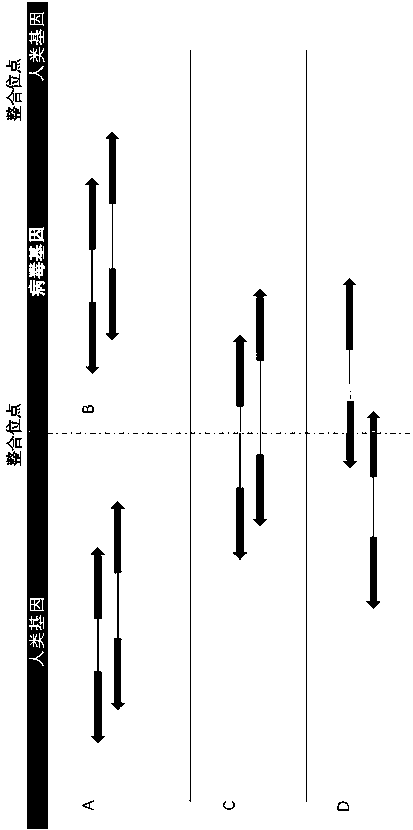
ActiveCN110957008AHigh utility valuePrecise positioningBiostatisticsProteomicsHuman DNA sequencingGenome alignment
The invention relates to a method and a device for detecting a human reference genome virus integration site, and belongs to the technical field of gene detection bioinformatics analysis. The method comprises the steps of genome alignment, sliding cutting, short sequence alignment and integration. According to the method, reads which are not compared with a human reference genome and a virus genome at the same time are subjected to sliding cutting, the cut sub-sequences (or short sequences) are compared again, through clustering, correlation and covariance processing of the comparison positions and the sequence of a certain reads segmentation sequence, all highly possible comparison positions can be listed in the analysis process, reads for simultaneously comparing human reference genomesand virus genomes can be accurately found out and accurately positioned, and the error range is within 3bp. The method is low in calculation resource requirement and high in operation speed, and has relatively high practical value.
Owner:GUANGZHOU JINYUDA LOGISTICS CO LTD
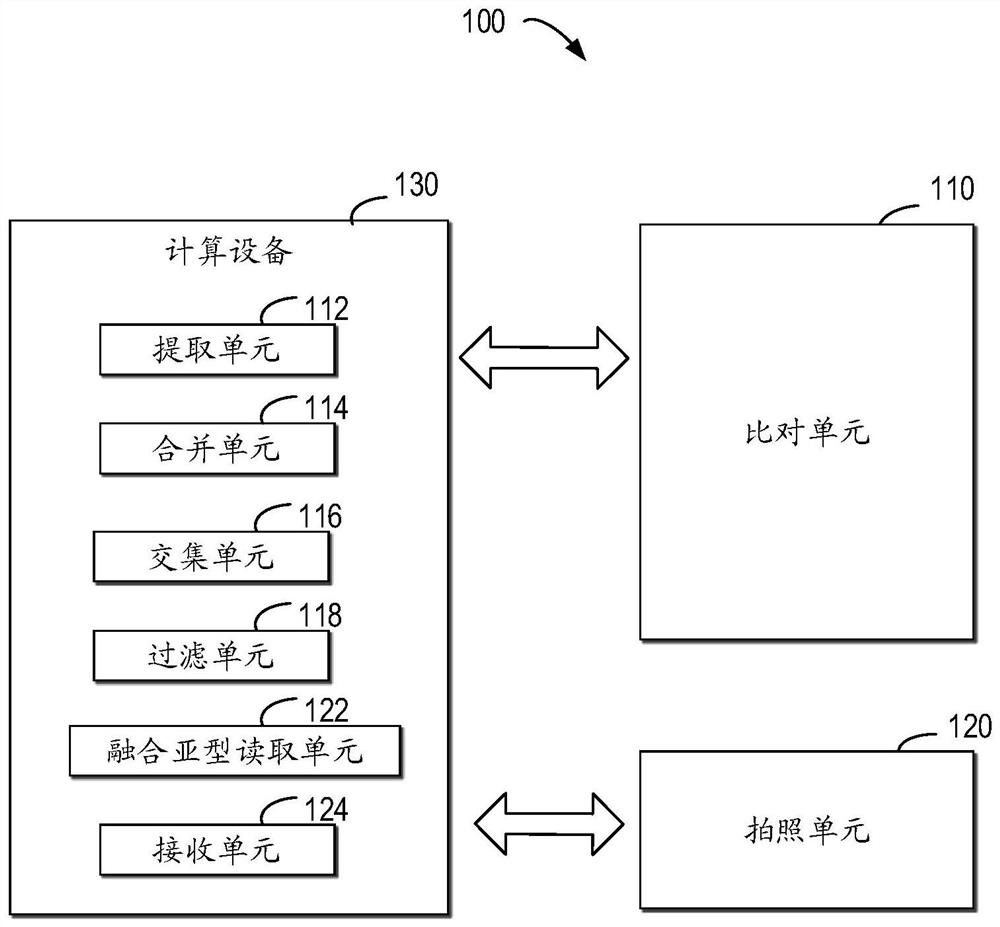
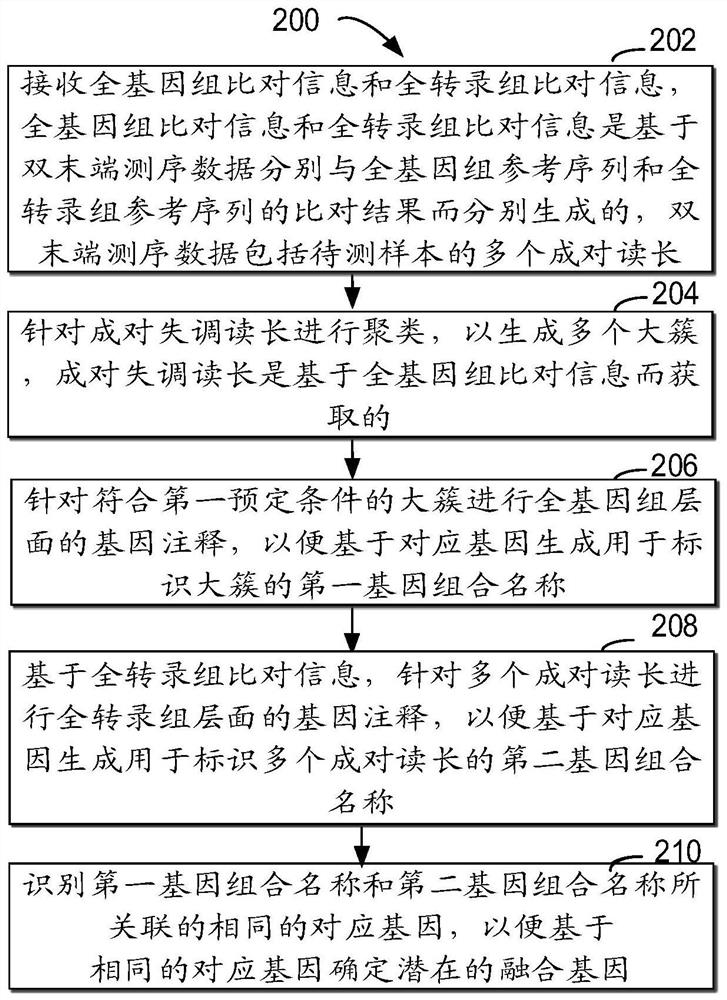
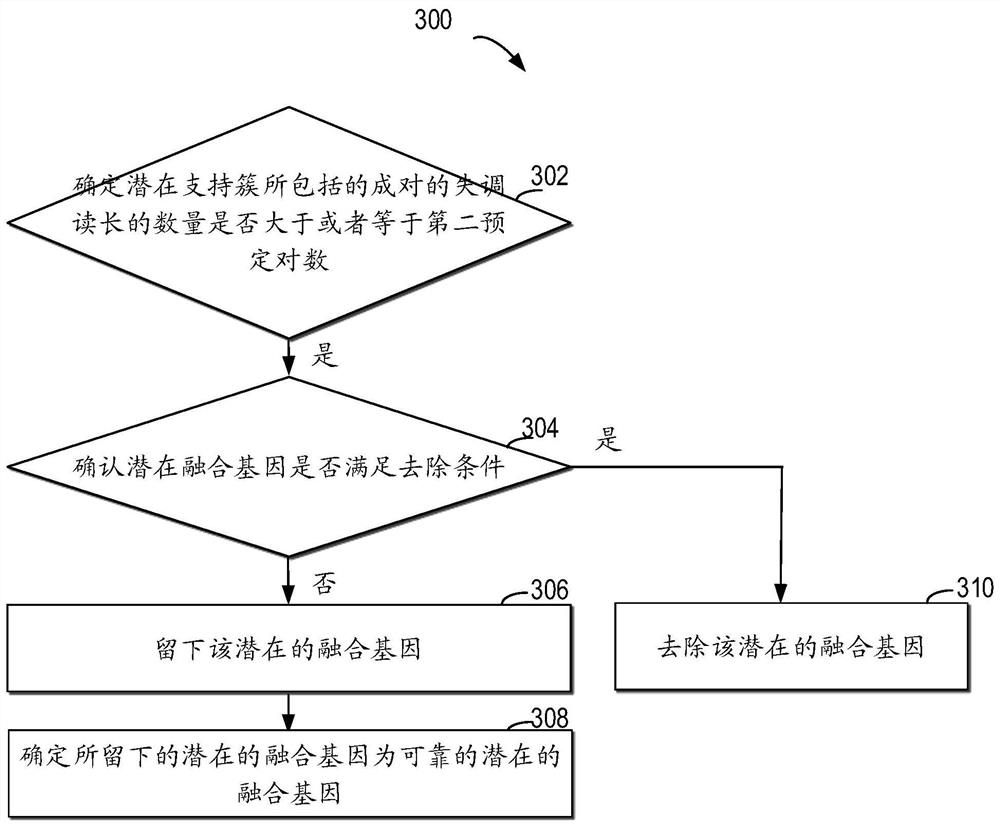
Method for detecting RNA level gene fusion, electronic device, and computer storage medium
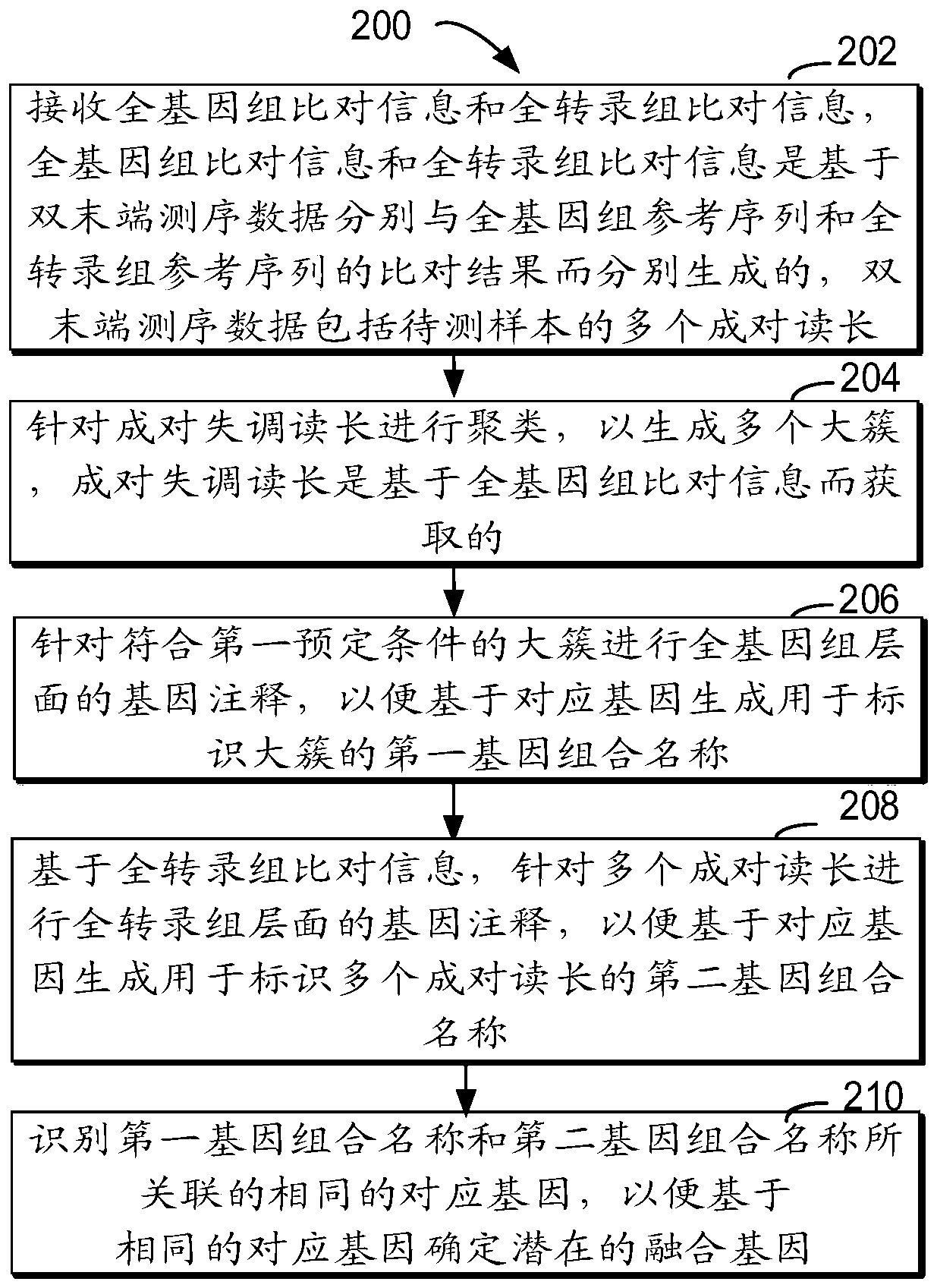
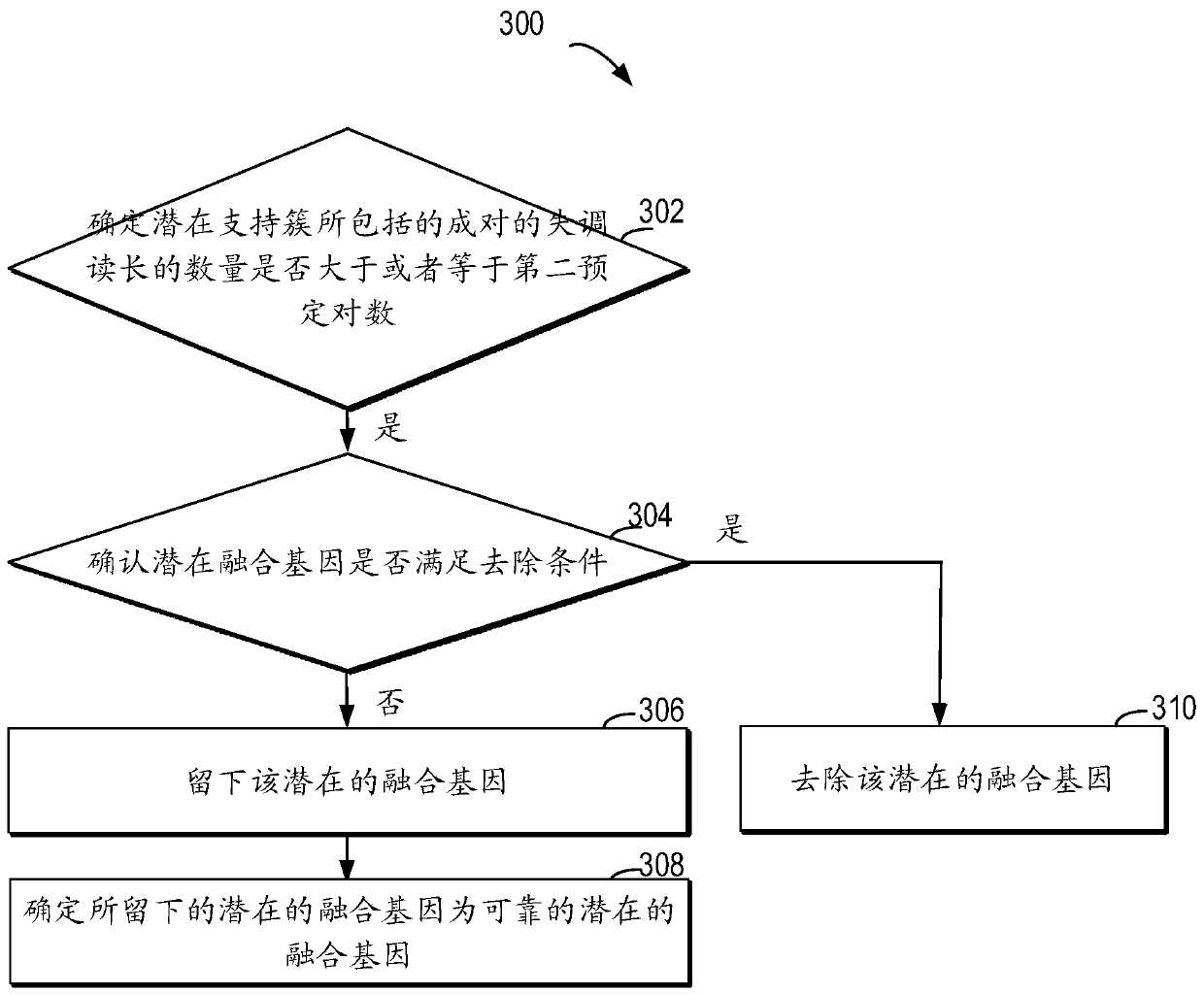
ActiveCN111292809AQuick and correct identificationBiostatisticsProteomicsGenome alignmentGene Annotation
The invention relates to a method for detecting RNA level gene fusion, electronic equipment and a computer storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: receiving whole genome comparison information and whole transcriptome comparison information; clustering the paired maladjusted read lengths to generate a plurality of large clusters; carrying out whole-genome-level gene annotation onthe large clusters meeting a first preset condition so as to generate first gene combination names for identifying the large clusters based on the corresponding genes; based on the whole transcriptomecomparison information, performing whole transcriptome-level gene annotation on the plurality of paired read lengths so as to generate a second gene combination name for identifying the plurality ofpaired read lengths based on the corresponding gene; and identifying the same corresponding genes associated with the first gene combination name and the second gene combination name so as to determine the same corresponding genes as potential fusion genes. The method is beneficial to rapid and correct recognition of false positive results, and the false positive results of a gene fusion detectionresult can be obviously reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI ORIGIMED CO LTD +1
Construction method of whole-genome exon sequence capture probe
The invention relates to a kit for capturing a whole-genome exon sequence. The kit is a target sequence capture system based on the hybridization principle. An exon capture probe is designed, and a large quantity of exomes are obtained by hybridization to perform high-throughput sequencing and human whole genome comparison; and then, data analysis is performed, and the capture efficiency is calculated. The kit provided by the invention can provide high-quality target sequence enrichment, and has high specificity, high accuracy and excellent reproducibility in whole genome exon sequencing; the whole genome exon sequencing becomes the most effective policy for identifying the disease-causing gene of the Mendel disease; and the kit is also applied to the study and clinical diagnosis of the gene susceptible to complex diseases, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING CENT FOR PHYSICAL & CHEM ANALYSIS
Amplification primers for identification of olea europaea l. varieties based on SNP loci, screening method and identification method
ActiveCN109554501AClear peak shapeInexpensive testingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenome alignmentScreening method
The invention discloses amplification primers for identification of olea europaea l. varieties based on SNP loci, a screening method, an identification method and 8 pairs of olea europaea l. amplifiedprimers. By restriction endonuclease digestion, clone sequencing and genome comparison analysis of olea europaea l. varieties leaf DNA, high reliability and repeatability single-copy fragments are selected, and the single-copy fragments are selected to design amplification primers; then the amplification primers designed by the selected single-copy fragments are used for amplifying olea europaeal. varieties leaf DNA by PCR, and 8 pairs of single-copy nuclear gene markers with high amplification efficiency and rich variation are screened out. The 8 pairs of olea europaea l. amplified productsare relatively pure and have clear peak shapes and no need of fluorescent primers, and the detection cost is low. The 8 pairs of olea europaea l. Single-copy nuclear gene markers can be used for identifying the olea europaea l. varieties.
Owner:INST OF FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY +1
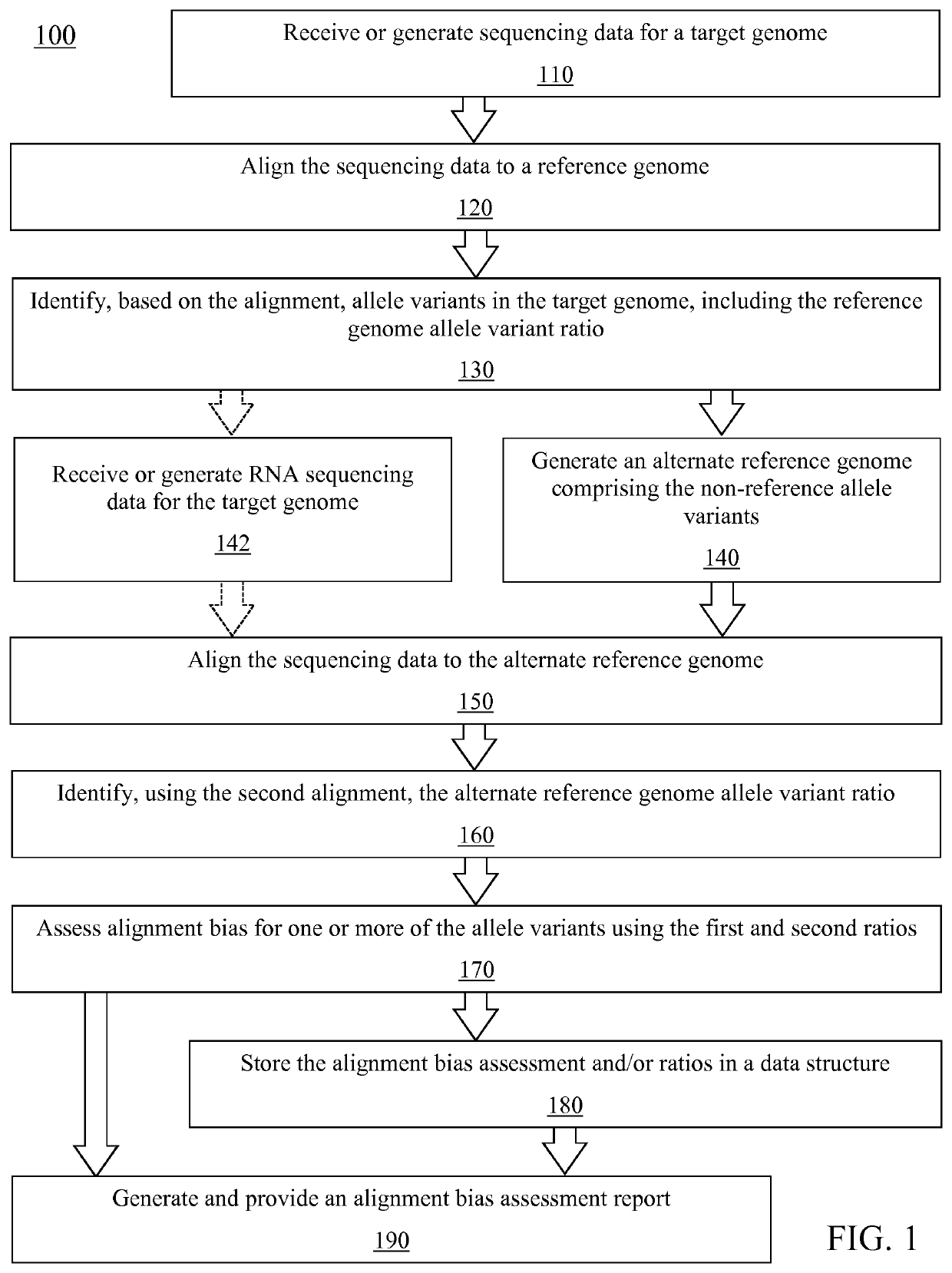
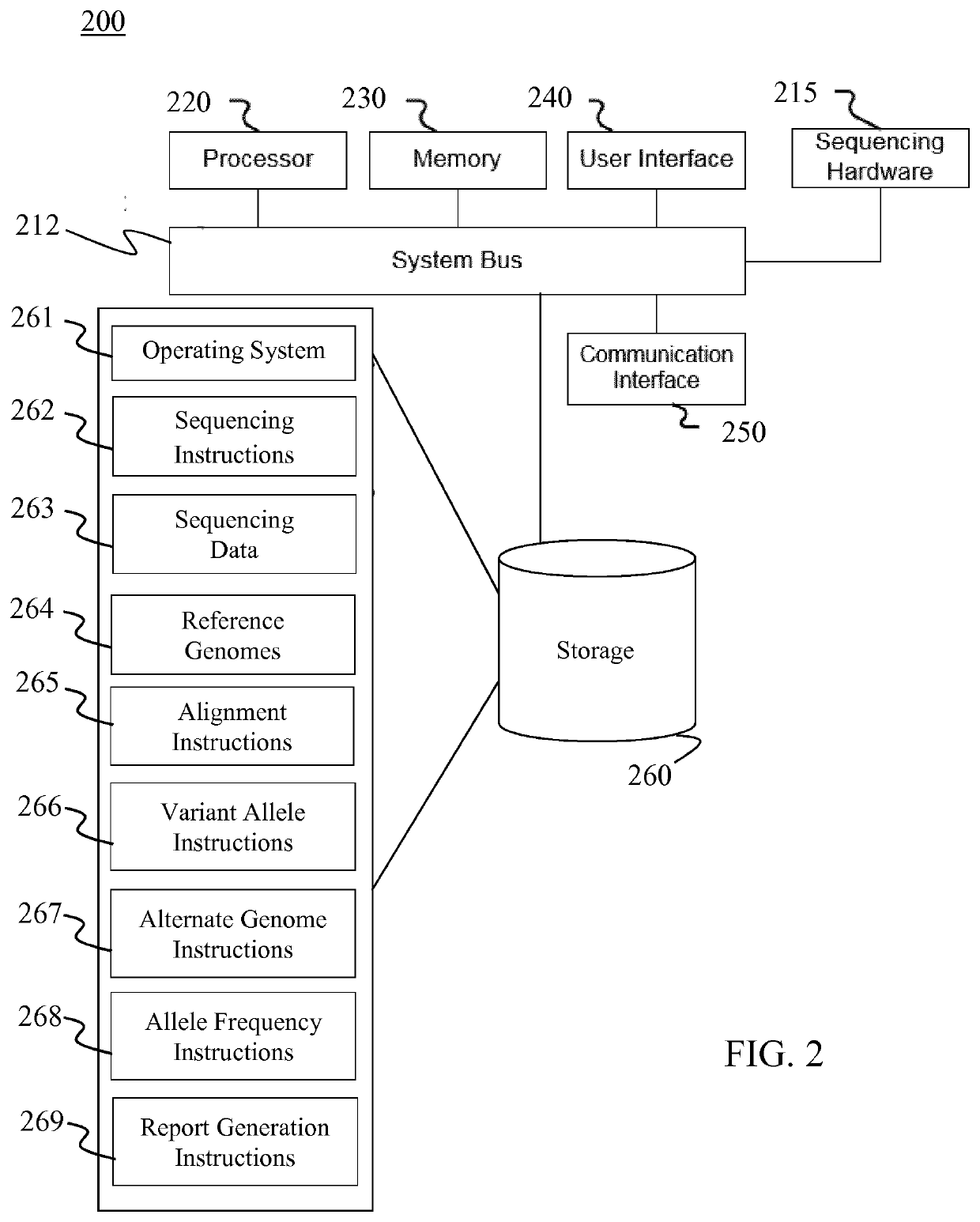
Method for assessing genome alignment basis
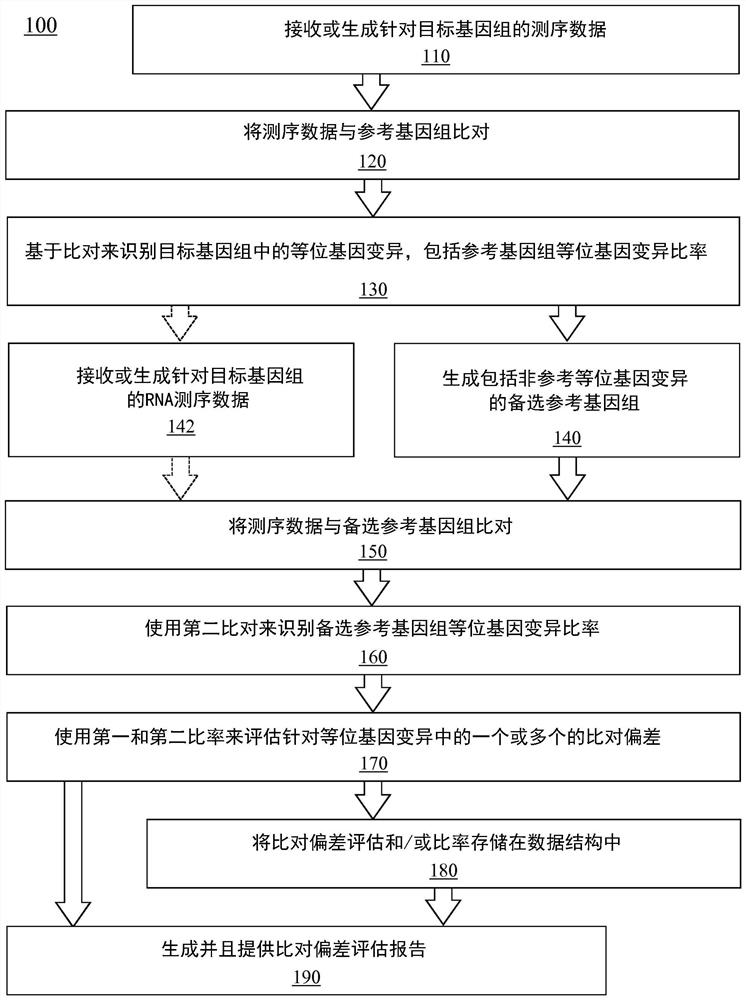
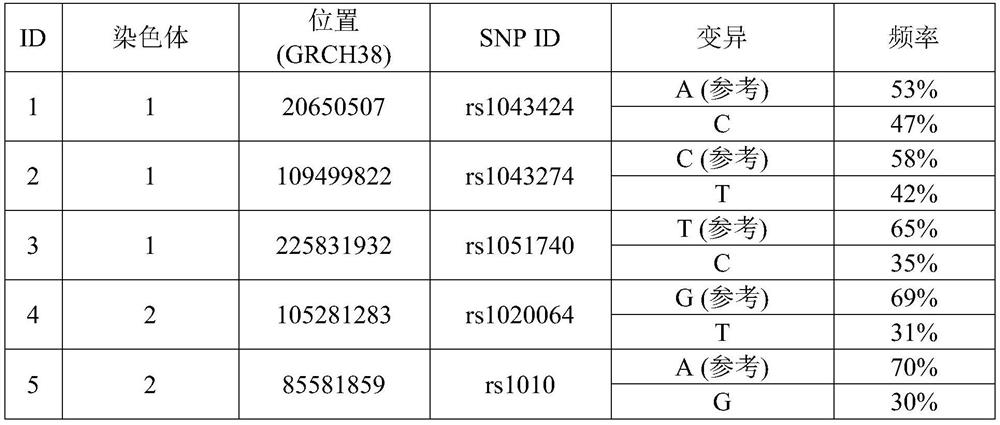
A method (100) for analyzing a target genome, comprising: (i) aligning (120) sequencing data from the target genome to a reference genome; (ii) identifying (130) heterozygous locations, comprising an identification of allele variants and a frequency of each allele, the allele variants comprising both a reference allele variant and a non-reference allele variant; (iii) generating (140) an alternate reference genome, wherein the identified non-reference allele variant for the identified heterozygous locations replaces the reference allele variant in the reference genome; (iv) aligning (150) sequencing data to the alternate reference genome; (v) identifying (160) a frequency of the allele variants at each of the heterozygous locations; (vi) assessing (170) alignment bias at the identified heterozygous locations, comprising comparing the frequency of allele variants from the reference genome alignment to the frequency of allele variants from the alternate genome alignment; and (vii) generating (190) a report comprising the assessment of alignment bias.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Assembly method and assembly device for chromosome level genome
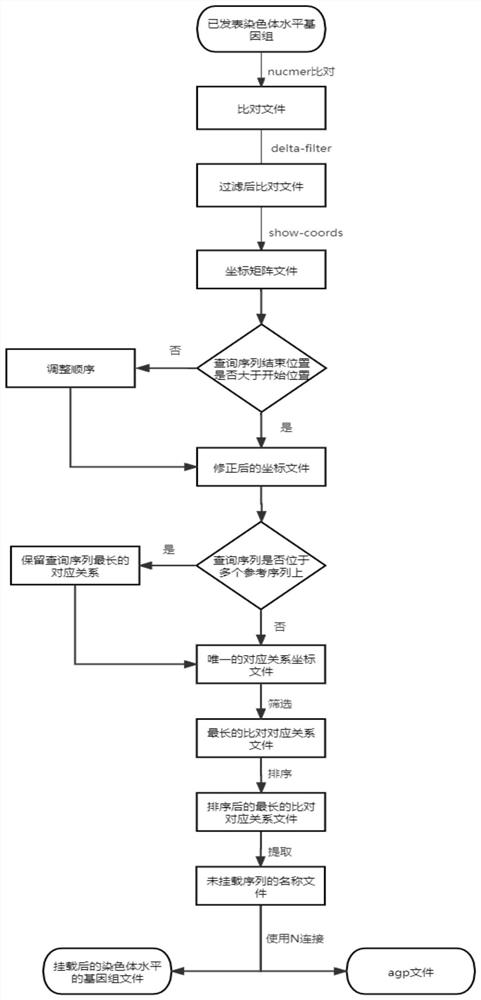
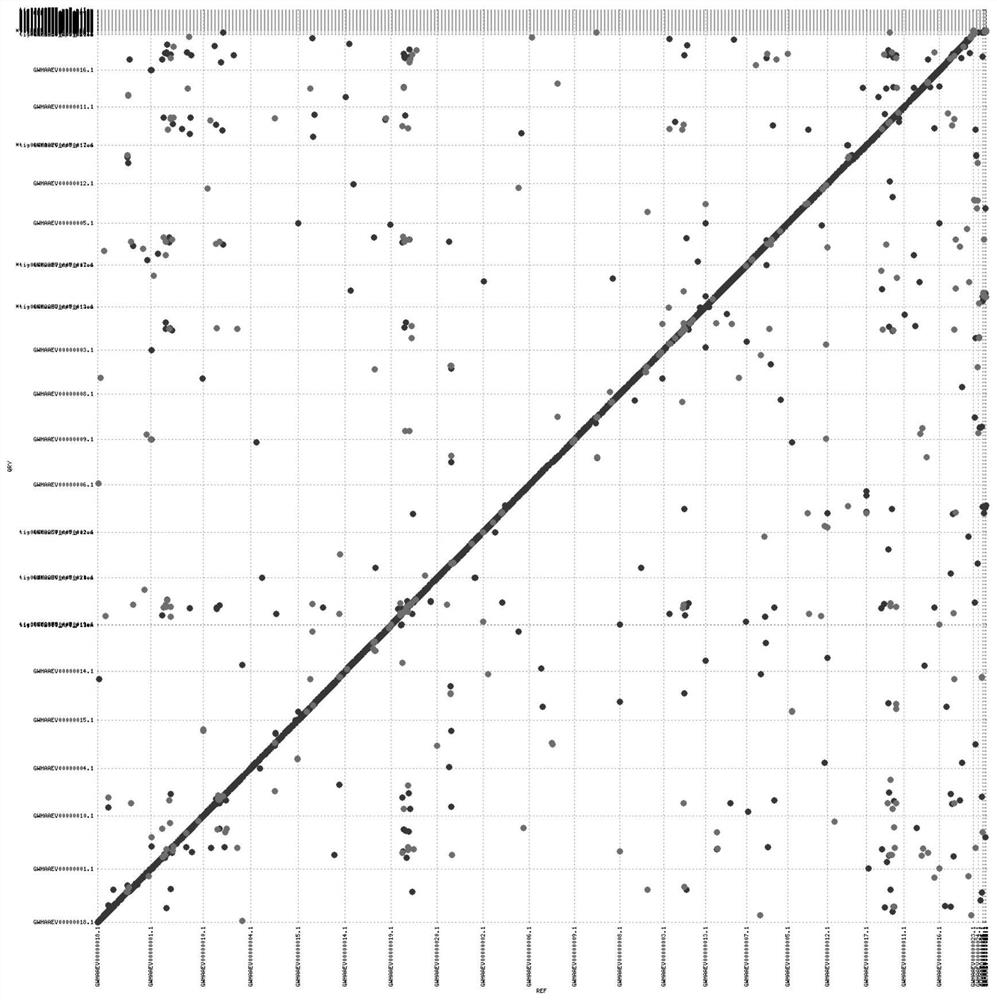
The invention provides an assembling method and an assembling device for a chromosome level genome. The assembling method comprises the following steps: acquiring a known chromosome level genome of the same species as a reference genome; comparing the contigs or scaffolds of the individuals to be assembled with the reference genome to obtain corresponding coordinate information; and according to the coordinate information, mounting the contigs or scaffolds of the to-be-assembled individuals to chromosome levels to obtain chromosome level genomes of the to-be-assembled individuals. For a species which is difficult to provide Hi-C data, the published chromosome level genome of the same species is used as a reference genome, and a contig or a scaffold level genome of a newly detected individual is compared to the reference genome, so that the aim of mounting the newly detected individual to a chromosome level with parameters is fulfilled.
Owner:上海诺禾致源医学检验实验室有限公司
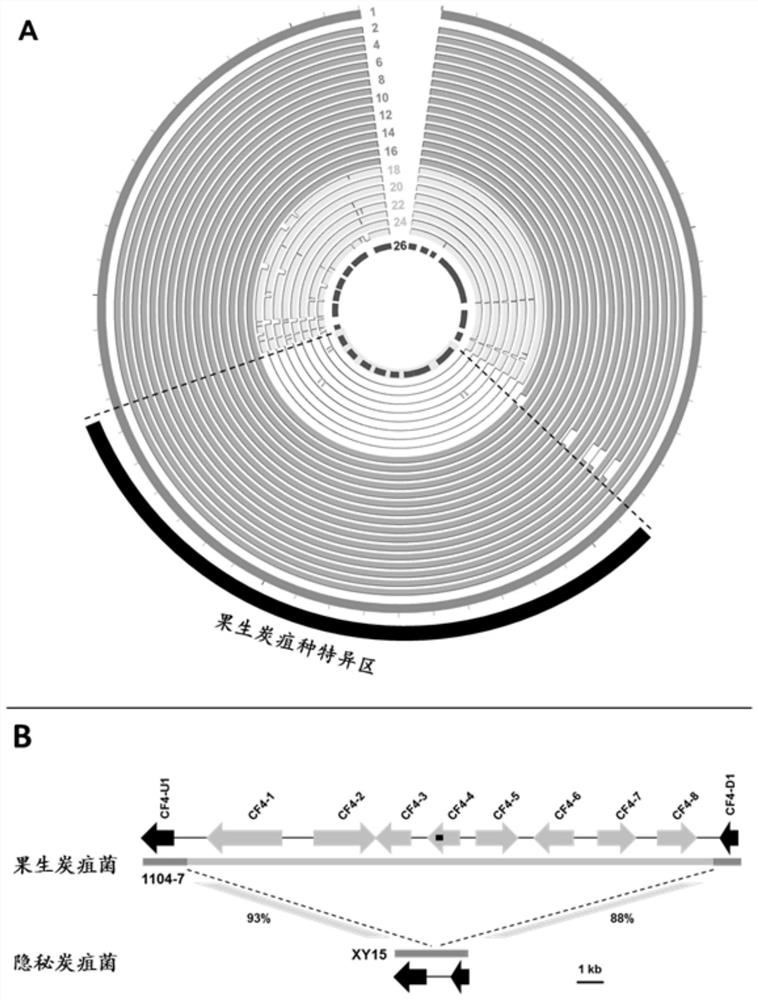
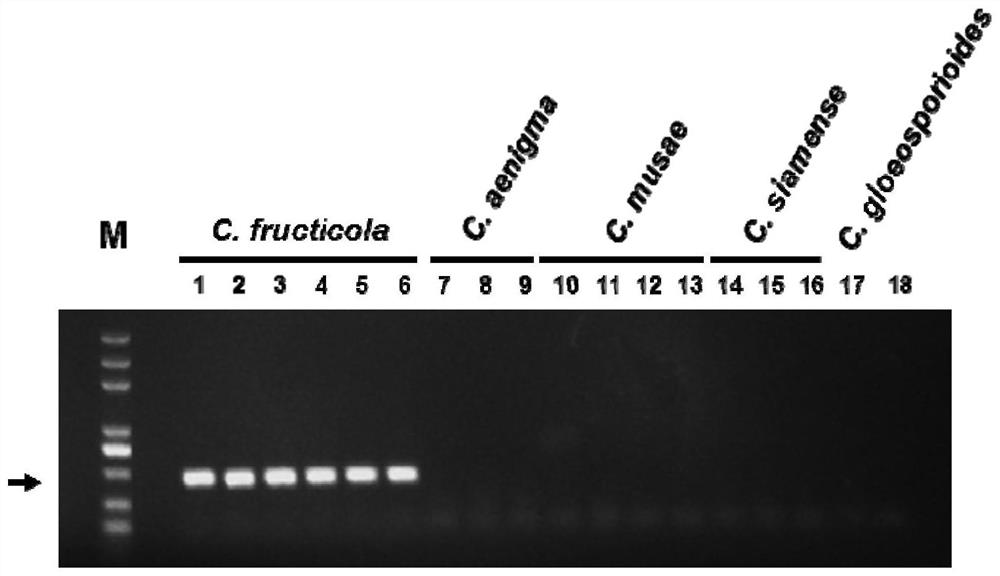
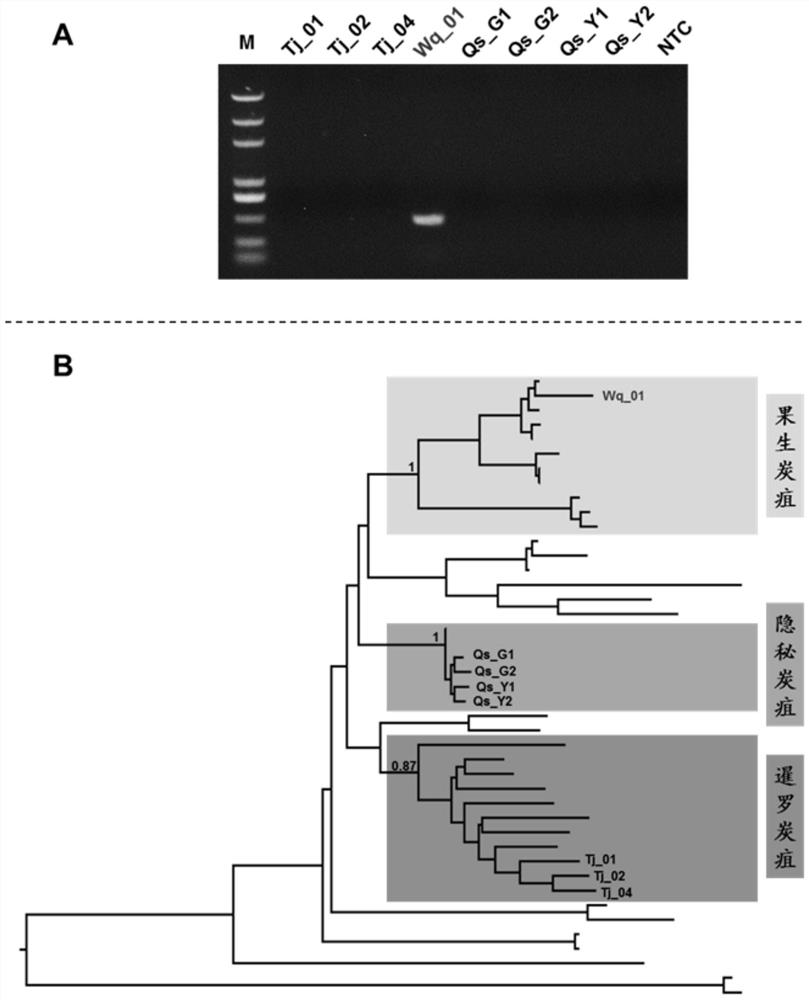
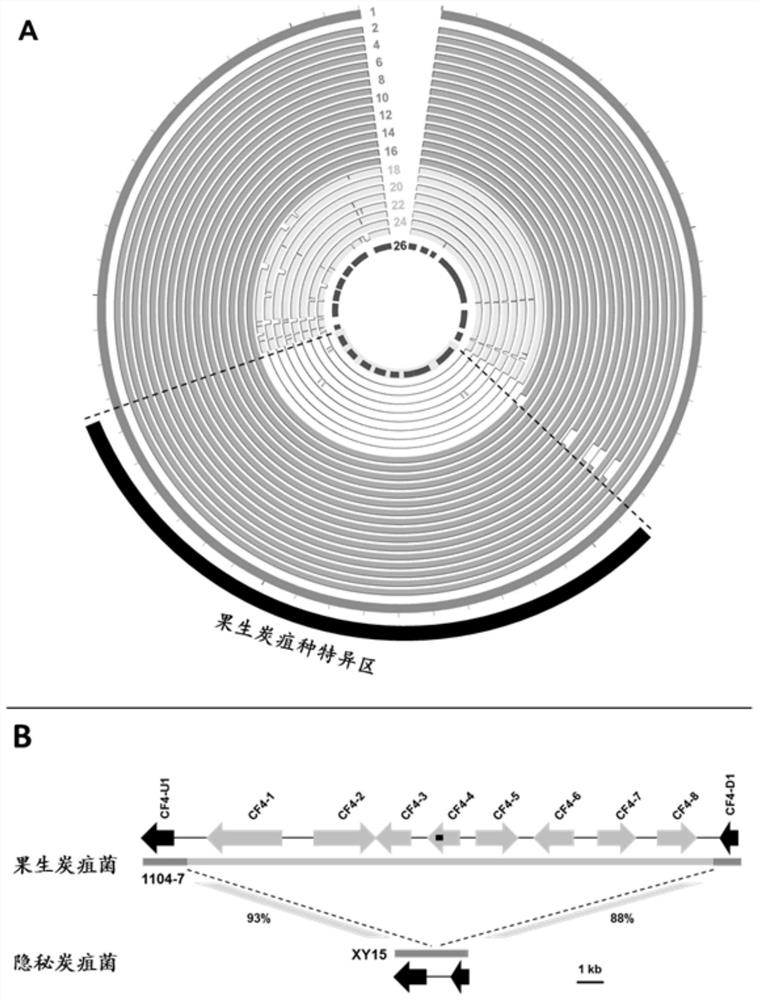
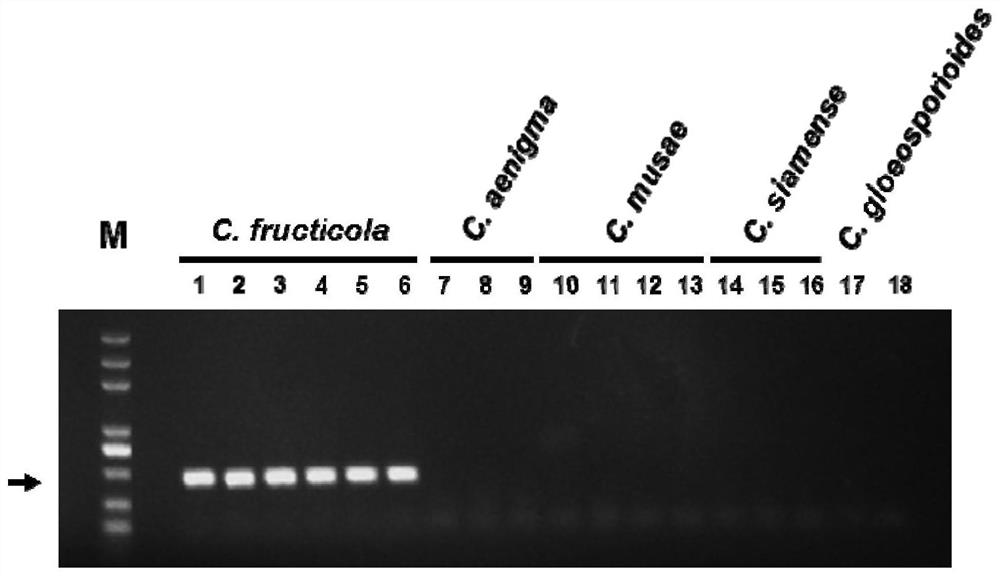
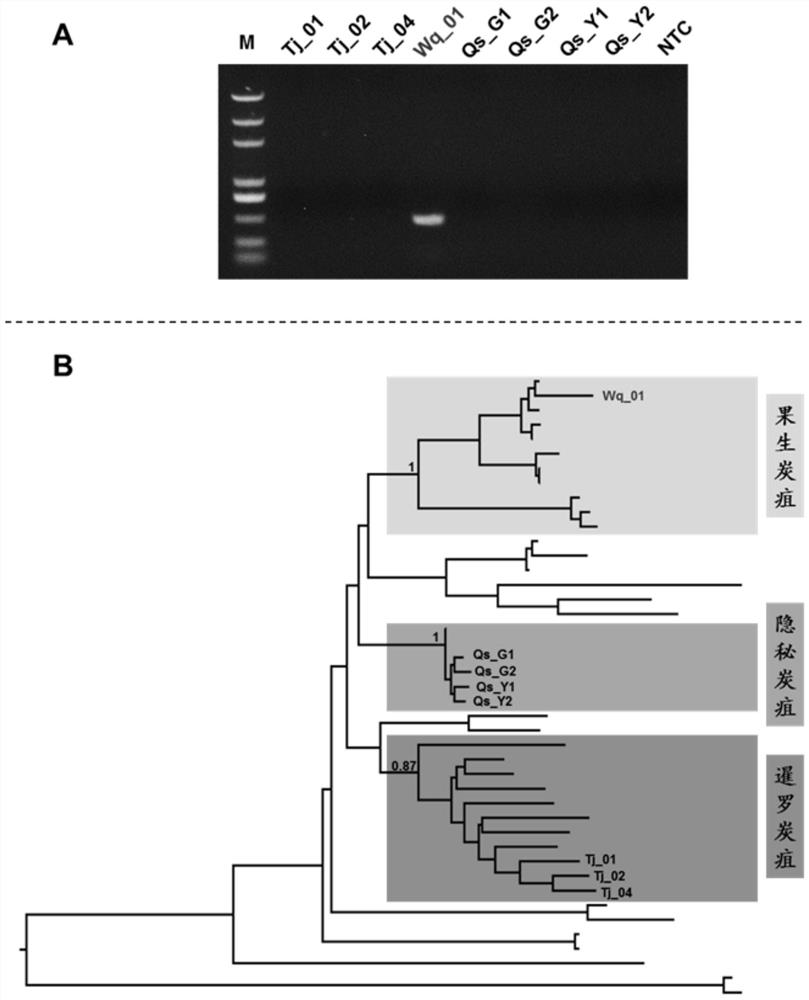
Specific gene sequence of colletotrichum fructicola and application of specific gene sequence
ActiveCN111826459AStrong specificityGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenome alignmentGenetics
The invention discloses a specific gene sequence of colletotrichum fructicola and application of the specific gene sequence. According to the invention, the specific gene sequence of the colletotrichum fructicola is obtained based on whole genome comparison of the colletotrichum fructicola and closely related species thereof, and the specific gene sequence is further utilized to design a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification primer to detect the colletotrichum fructicola, and a related kit is developed. The invention can specifically detect the colletotrichum fructicola (C. fructicola)and distinguishes the colletotrichum fructicola from the closely related species including colletotrichum aenigma (C. aenigma), colletotrichum siamense (C. siamense), colletotrichum musae (C. musae)and the like; and the invention has the advantages of being fast, simple, convenient and accurate.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Detection method of whole genome copy number variation and application of the method
PendingCN111028888AReflect disorderHigh sensitivityMedical automated diagnosisSequence analysisGenome alignmentCancers diagnosis
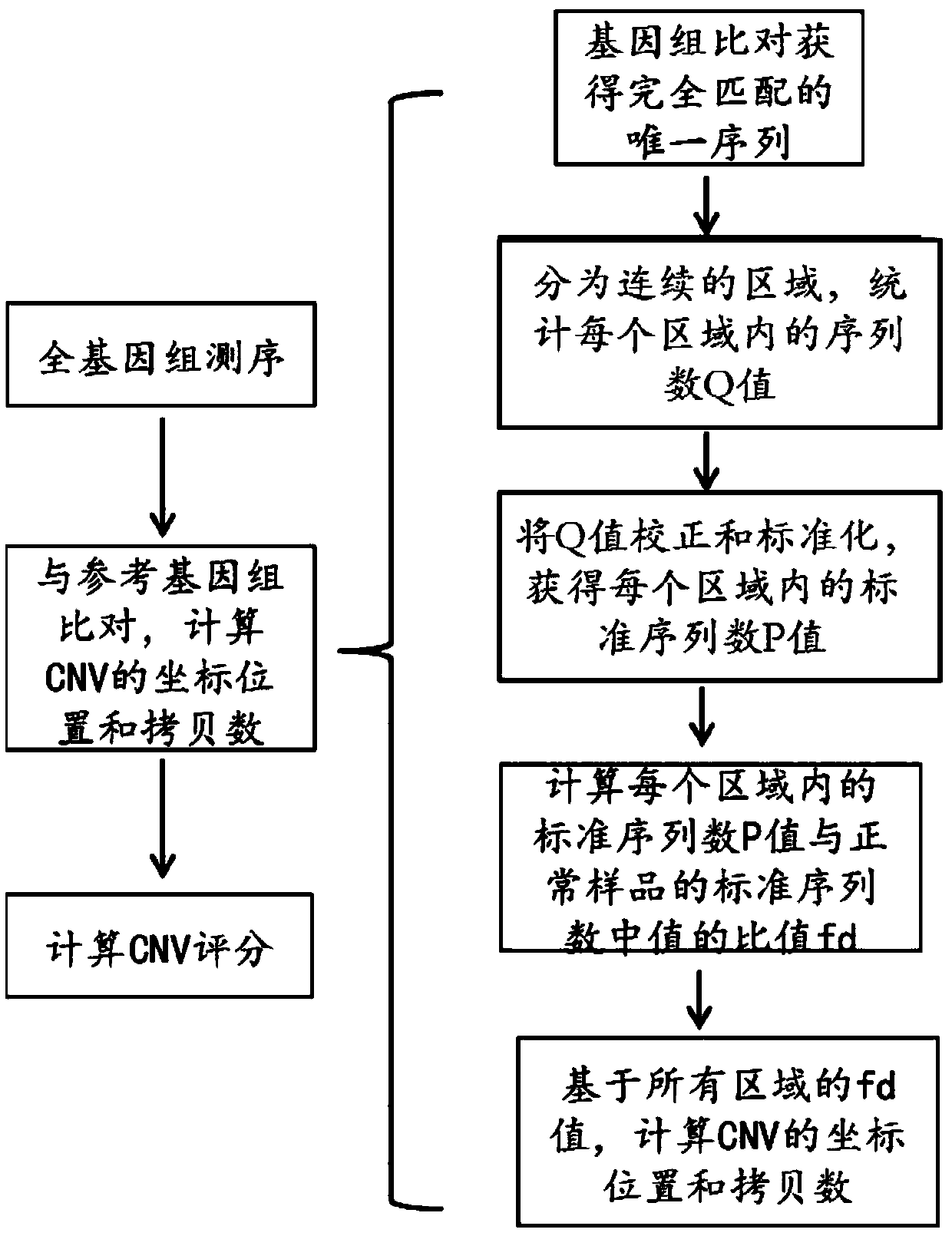
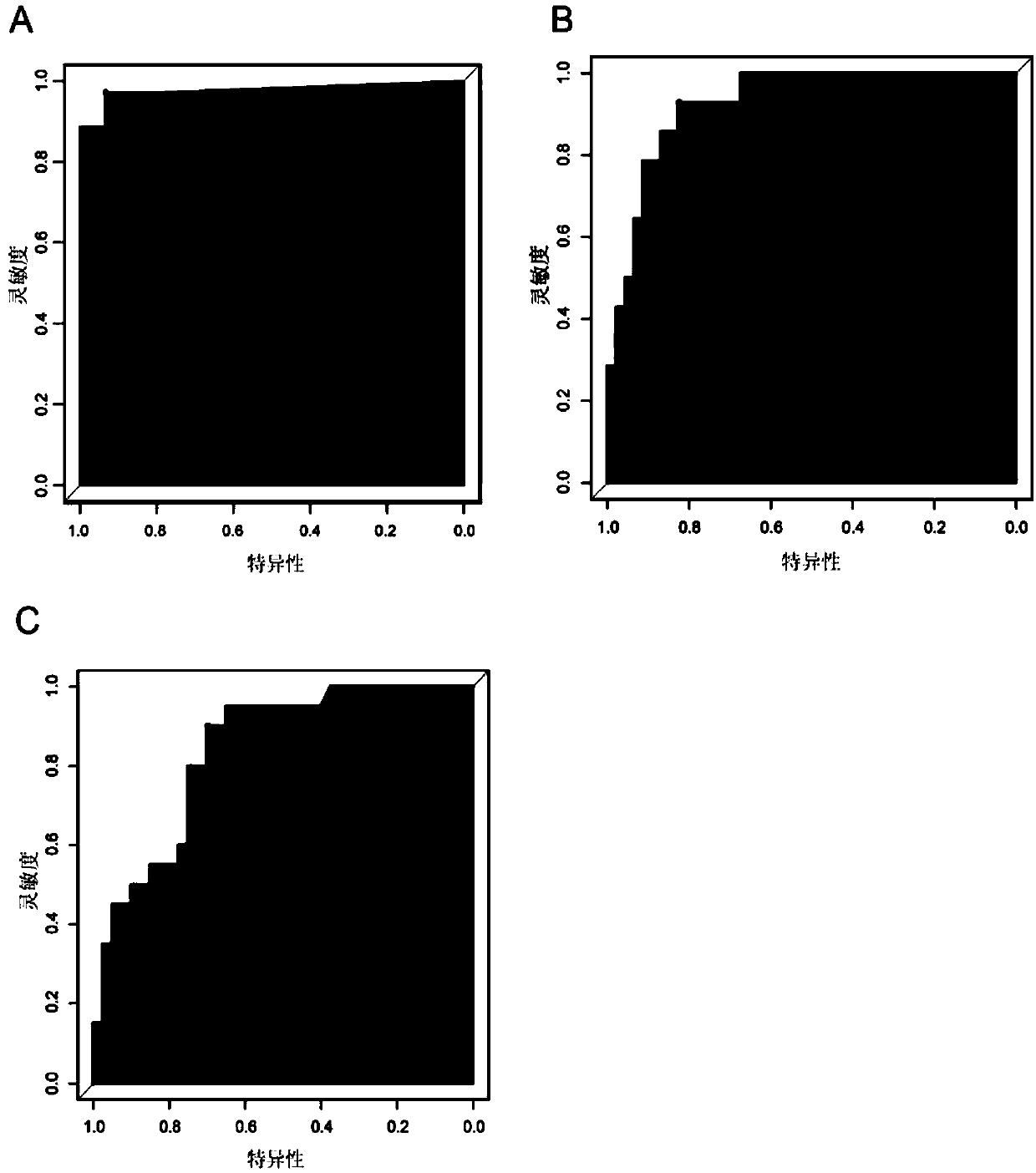
The invention relates to a detection method for whole genome copy number variation (CNV). The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a sequencing result sequence of whole genome sequencing of a DNA sample; (2) comparing the sequencing result sequence with a human reference genome, and calculating the coordinate position of the CNV in a chromosome section and the copy number CN<detection> of the CNV in the section; and (3) calculating the comprehensive CNV<score> of the DNA sample through corresponding formula in which the CNV<length> represents the length of the CNV calculated according to the coordinate position of the CNV in the chromosome segment, the CN<reference> represents the chromosome copy number in a normal sample, and the CNV<score> represents the whole genome copynumber variation of the DNA sample. The invention also relates to the use of said detection method in the diagnosis of cancer as well as a device for diagnosing cancer conditions.
Owner:BERRYGENOMICS CO LTD +1
Genome data storage method and electronic device
ActiveCN107480466BImprove efficiencyInput/output to record carriersBiostatisticsTerm memoryGenomic data
The invention discloses a genomic-data storage method. The genomic-data storage method includes the steps that in the genome comparison process, gene-sequence comparison information is obtained, and gene-sequence statistical information is established; the gene-sequence comparison information is stored in a magnetic disk, and according to comparison positions of the gene-sequence comparison information in a genome, corresponding indexes are stored in a memory, wherein the indexes are storage positions of the gene-sequence comparison information in the magnetic disk; genome statistical information is classified, and first statistical information and second statistical information are obtained; the first statistical information is stored in the memory, wherein the first statistical information is statistical information with the access frequency higher than the preset frequency in the variation detection process; the second statistical information is stored in the magnetic disk, wherein the second statistical information is statistical information which cannot be stored in the memory and / or statistical information with the access frequency lower than the preset frequency in the variation detection process. The invention also discloses an electronic device with the genomic-data storage method.
Owner:UNITED ELECTRONICS
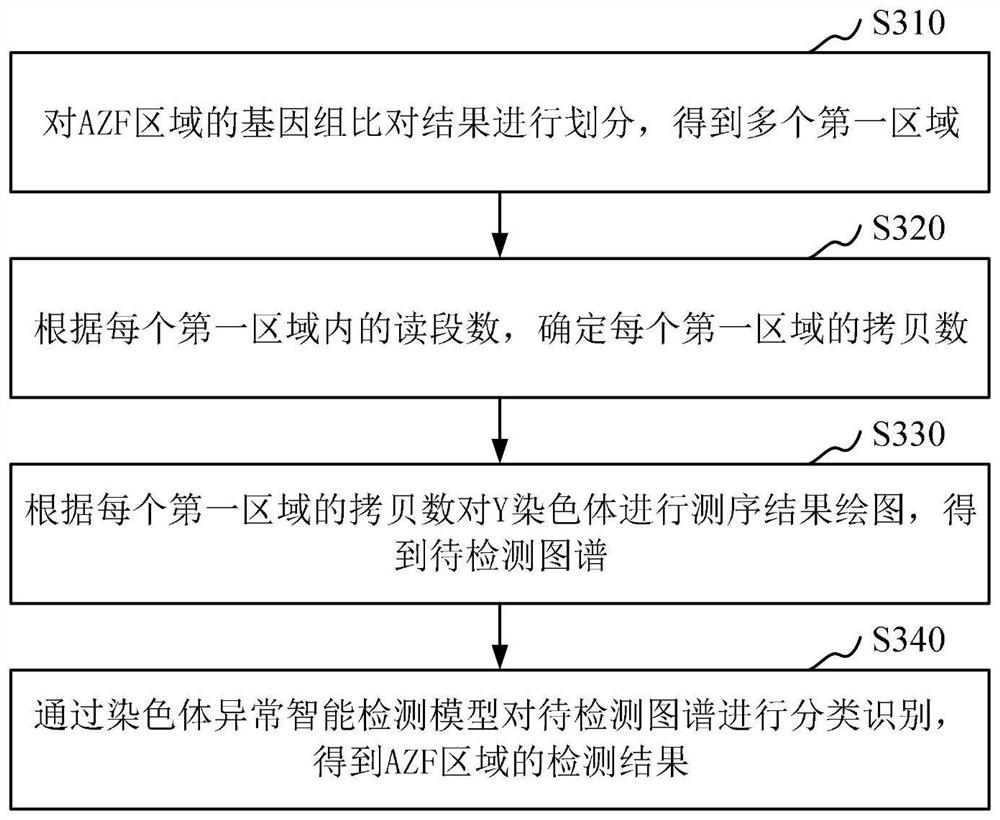
Chromosome abnormality detection method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
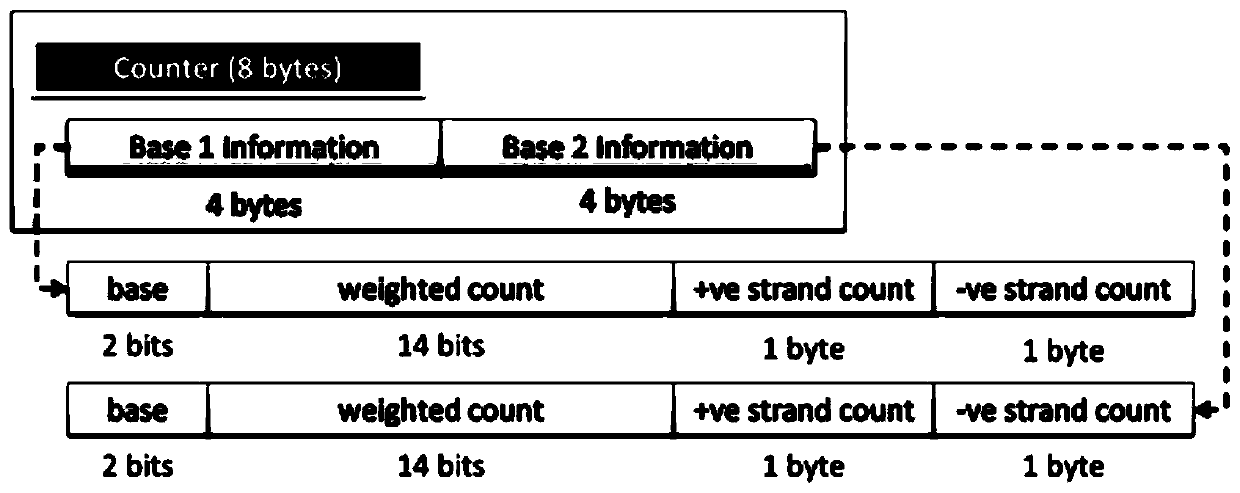
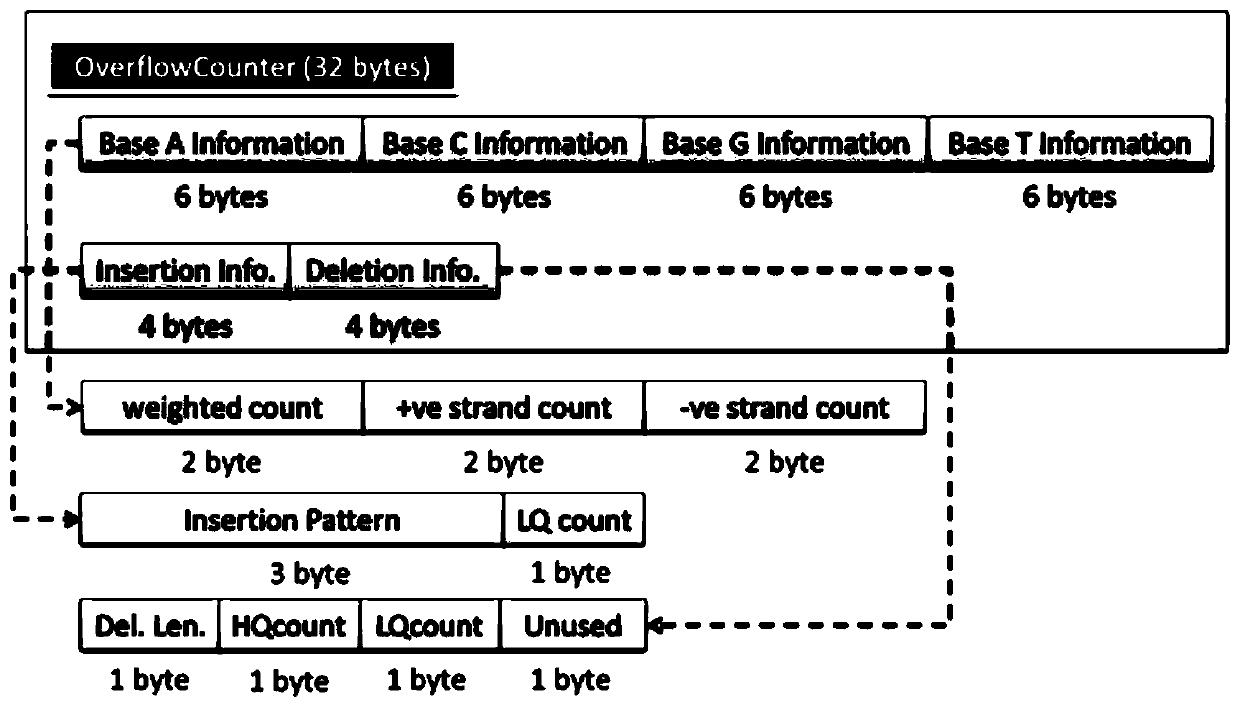
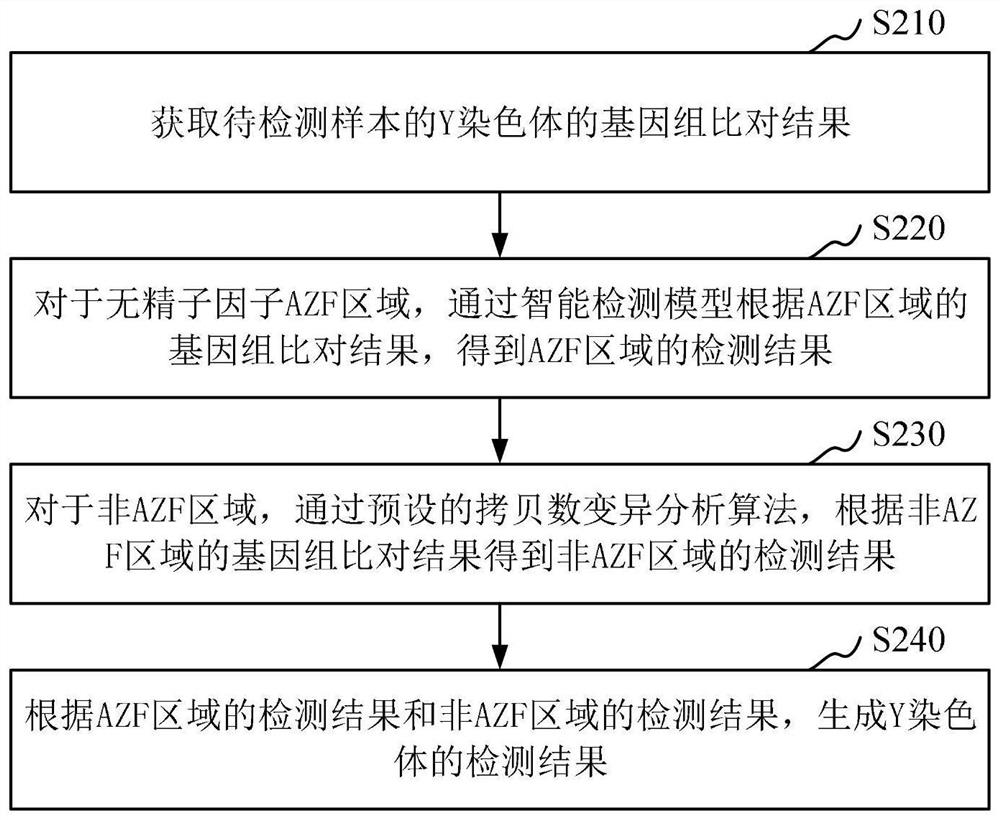
ActiveCN112863602AImprove detection efficiencyIncrease coverageData visualisationBiostatisticsGenome alignmentAlgorithm
The invention relates to a chromosome abnormality detection method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a genome comparison result of a Y chromosome of a to-be-detected sample; for the AZF region, obtaining a detection result of the AZF region through a chromosome abnormality intelligent detection model according to a genome comparison result of the AZF region; for the non-AZF region, obtaining a detection result of the non-AZF region according to a genome comparison result of the non-AZF region through a preset copy number variation analysis algorithm; and generating a detection result of the Y chromosome according to the detection result of the AZF region and the detection result of the non-AZF region. According to the method, the chromosomes are detected and analyzed according to the whole genome comparison result, no additional experiment means is used, the detection efficiency of the chromosomes can be improved, and the detection cost is reduced; different regions of chromosomes are detected based on a machine learning model and a copy number variation analysis algorithm, so the coverage rate of detection and the accuracy of anomaly detection can be improved.
Owner:SUZHOU BASECARE MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD
The Specific Gene Sequence of Fruit Anthracnose Bacteria and Its Application
ActiveCN111826459BStrong specificityGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiotechnologyGenome alignment
The invention discloses the specific gene sequence of fruit anthracnose bacteria and its application. The present invention obtains the specific gene sequence of the fruit anthracnose bacteria based on the whole genome comparison of the fruit anthracnose bacteria and its close relatives, further uses the specific gene sequence to design PCR amplification primers to detect the fruit anthracnose bacteria, and develops related reagents box. The invention can specifically detect C. fructicola, and distinguish it from closely related species such as C. aenigma, C. siamense, and C. musae ; Has the advantages of fast, simple and accurate.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Molecular markers, detection primers and detection methods for identifying Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus pentosus
ActiveCN112143820BStrong specificityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses molecular markers, detection primers and detection methods for identifying plantar lactobacillus and pentosus lactobacillus. Specific molecular markers for identifying Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus pentosus, the nucleotide sequences of which are shown in SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2, SEQ ID NO.3 or 4. The present invention screens new targets for specific molecular detection of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus pentosus by using the whole genome comparison analysis technology, and designs primers for the new molecular targets for PCR amplification, which can specifically identify the two target bacteria. Currently, these molecular markers are not available. See report. Compared with 16S rDNA PCR method and physiological and biochemical method, the method established by the present invention has higher specificity, simple operation, short detection cycle, no need for further sequencing, and low detection cost, especially suitable for rapid initial detection of L.plantarum and L.pentosus Sieve provides an important auxiliary identification method for food production enterprises and testing institutions.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
A kit for detecting sudden cardiac death-related SNPs on scn5a gene related to sudden cardiac death and its detection method
The invention discloses a kit for detecting a sudden cardiac death-related SNP on the SCN5A gene related to sudden cardiac death and a detection method thereof, specifically comprising the following steps: 1. Using DNA extracted from a sample as a template to prepare Multiplex PCR and its detection method Purification treatment; 2. SNaPshot single base extension reaction (SBE) and its purification treatment; 3. Capillary electrophoresis of SNaPshot single base extension product and its result analysis; 4. Sensitivity detection. The invention can detect 45 sudden cardiac death (SCD) related SNPs on the SCN5A gene at one time, and obtain clear conclusions. This method no longer utilizes first-generation sequencing and next-generation sequencing technologies for comparison of the whole genome. There is no need for special instruments and methods to screen for genetic background related to sudden cardiac death.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Amplification primers, screening methods and identification methods for identification of olive varieties based on SNP sites
ActiveCN109554501BClear peak shapeInexpensive testingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenome alignment
The invention discloses an amplification primer, a screening method and an identification method for identifying olive varieties based on SNP sites, and eight pairs of olive amplification primers. The present invention selects highly reliable and reproducible single-copy fragments through restriction endonuclease digestion, cloning and sequencing, and genome comparison analysis of the leaf DNA of olive varieties, and designs amplification primers for single-copy fragments; and then selects single-copy Fragment-designed amplification primers were used to amplify the leaf DNA of olive varieties by PCR, and 8 pairs of single-copy nuclear gene markers with high amplification efficiency and rich variation were screened out. The amplification products of 8 pairs of olives were relatively pure, with clear peak shapes and no Fluorescent primers are needed, and the detection price is low; 8 pairs of single-copy nuclear gene markers in olive can be used for identification of olive varieties.
Owner:INST OF FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY +1
Method, electronic device and computer storage medium for detecting gene fusion at rna level
The invention relates to a method for detecting RNA level gene fusion, electronic equipment and a computer storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: receiving whole genome comparison information and whole transcriptome comparison information; clustering the paired maladjusted read lengths to generate a plurality of large clusters; carrying out whole-genome-level gene annotation onthe large clusters meeting a first preset condition so as to generate first gene combination names for identifying the large clusters based on the corresponding genes; based on the whole transcriptomecomparison information, performing whole transcriptome-level gene annotation on the plurality of paired read lengths so as to generate a second gene combination name for identifying the plurality ofpaired read lengths based on the corresponding gene; and identifying the same corresponding genes associated with the first gene combination name and the second gene combination name so as to determine the same corresponding genes as potential fusion genes. The method is beneficial to rapid and correct recognition of false positive results, and the false positive results of a gene fusion detectionresult can be obviously reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI ORIGIMED CO LTD +1
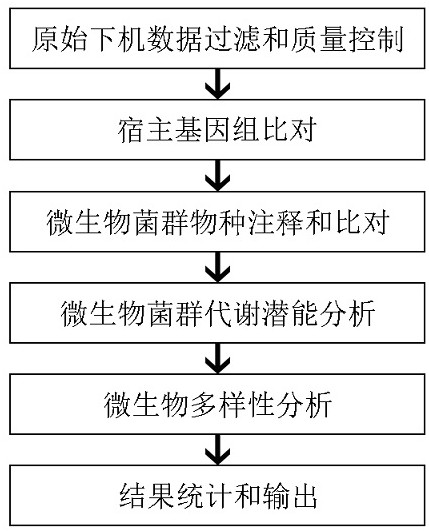
Automatic analysis method for fecal microorganism diversity
InactiveCN112614540ADiversity understandingAvoid mistakesData visualisationProteomicsMicroorganismDiversity index
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and discloses an automatic analysis method for fecal microorganism diversity, which comprises the steps of original offline data filtration and quality control, host genome comparison, microorganism flora species annotation and comparison, microorganism flora metabolic potential analysis, microorganism diversity analysis, result statistics and output and the like. In the method, Python script connection is used in all the steps to achieve automatic analysis, so that tedious manual operation is reduced, various errors caused by the manual operation are reduced, and the abundance, metabolic pathways and other information of different microbial florae in a sample are analyzed while the Shannon diversity index and the Simpson diversity index are calculated, and the method is suitable for large-scale popularization and application. Therefore, diversity of fecal microorganisms can be understood more comprehensively, intermediate results generated in all steps can be output in the running process of the process, corresponding data can be subjected to statistical analysis and arrangement, and a corresponding chart is output to facilitate the browsing of a user; meanwhile, all process related information is recorded in a process running log, so that screening can be carried out conveniently when the process is in error.
Owner:天津奇云诺德生物医学有限公司
Library building method and application
PendingCN114854824ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenome alignmentInformatics
The invention provides a library building method which comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out splitting decomposition treatment on a paraffin-embedded biological sample, and collecting a nucleic acid sample from a splitting decomposition solution obtained by the splitting decomposition treatment by utilizing a precipitation method, the nucleic acid sample containing a nucleic acid fragment with the length of less than 200bp; (2) carrying out terminal repair on the concentrated nucleic acid and adding a joint so as to obtain a nucleic acid sample connected with the joint; and (3) carrying out amplification treatment on the nucleic acid sample connected with the joint so as to obtain amplification products, and forming the sequencing library by the amplification products. The method is suitable for library building of trace and fragmented nucleic acid samples, the library building success rate can be effectively increased, the read repetition rate of subsequent informatics analysis is effectively reduced, and the genome comparison rate is increased.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
Sequencing data processing method and device
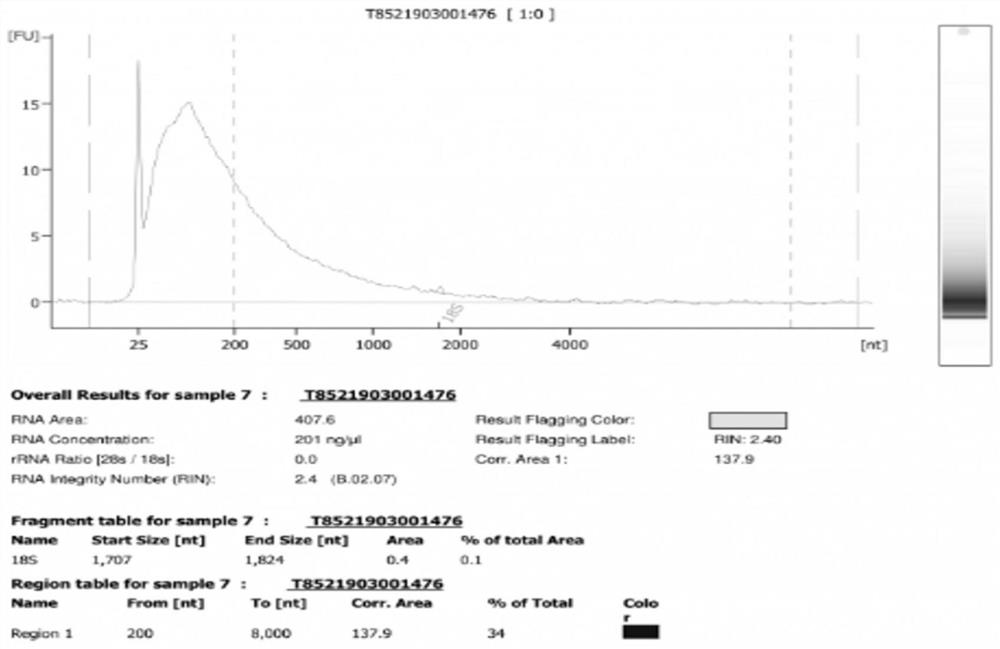
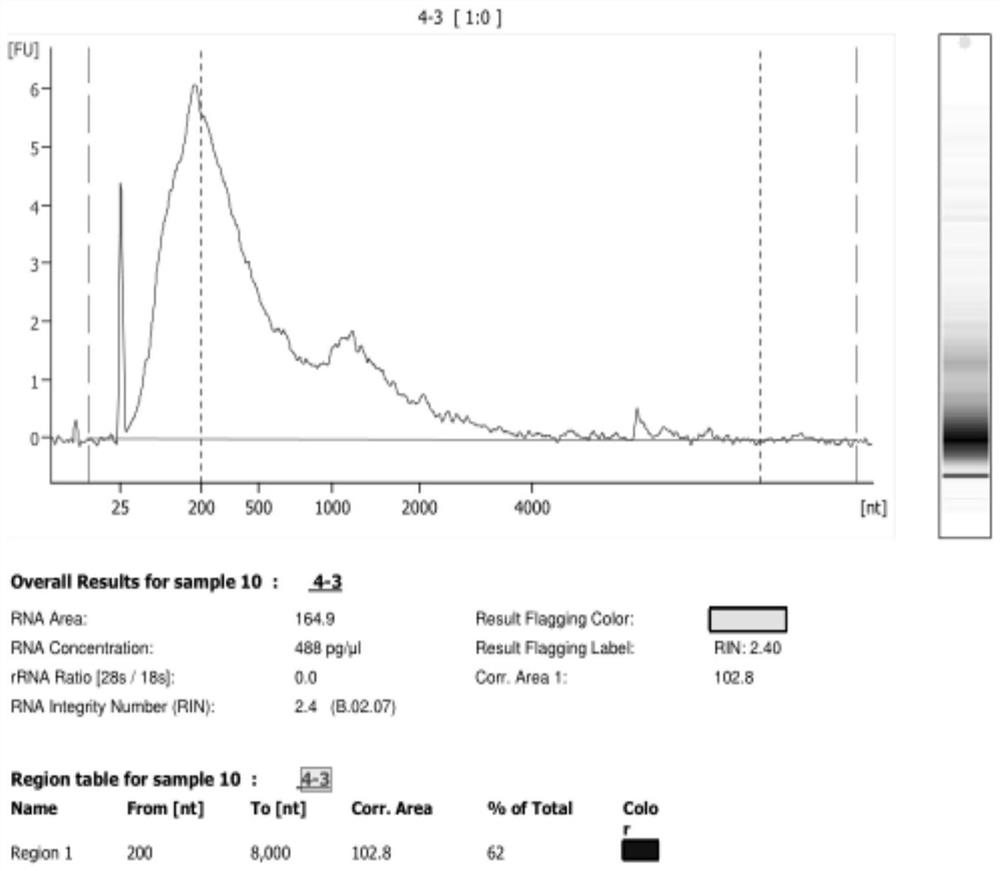
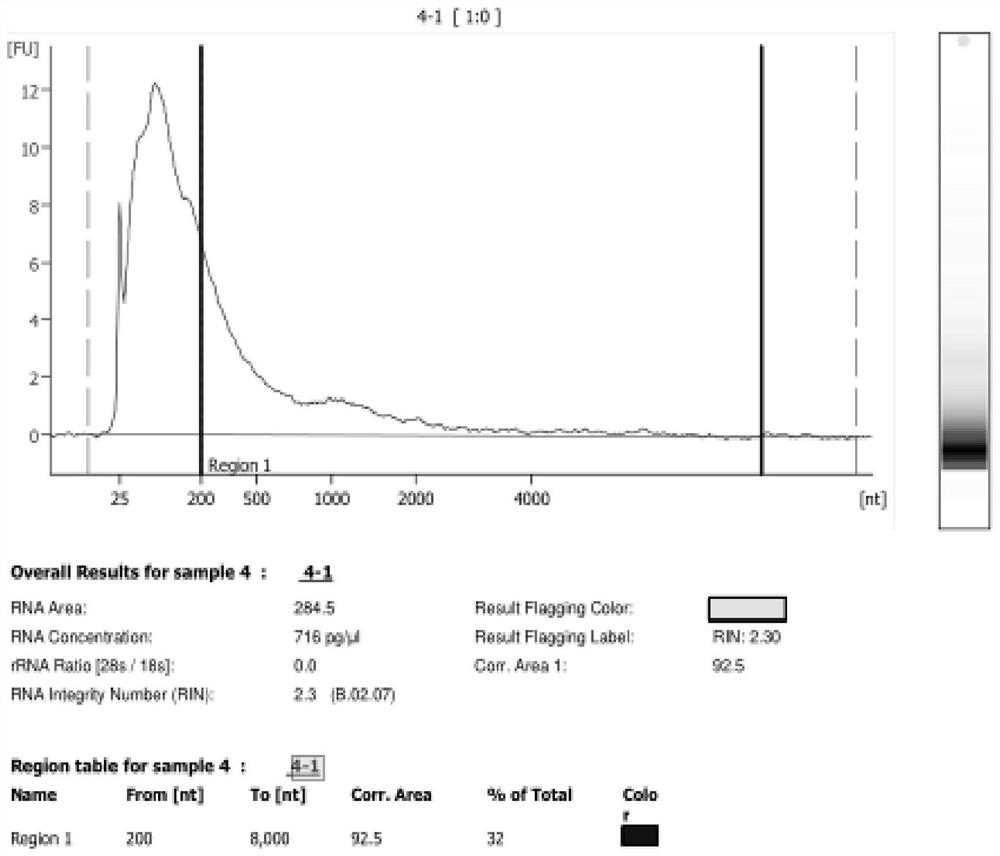
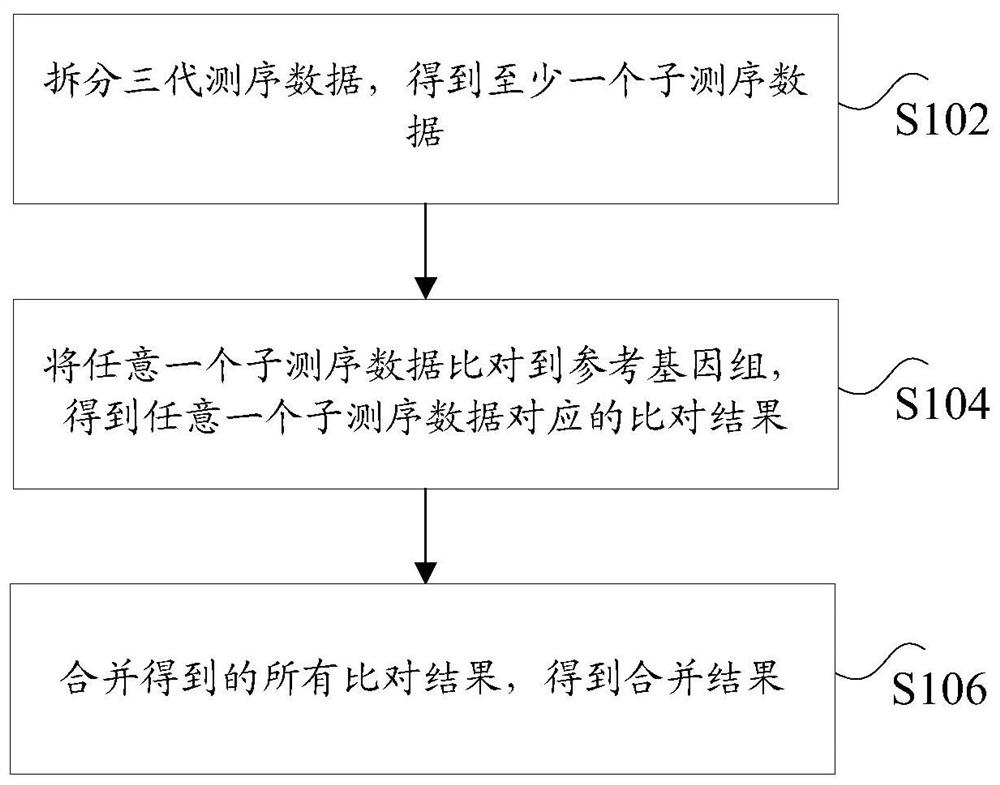
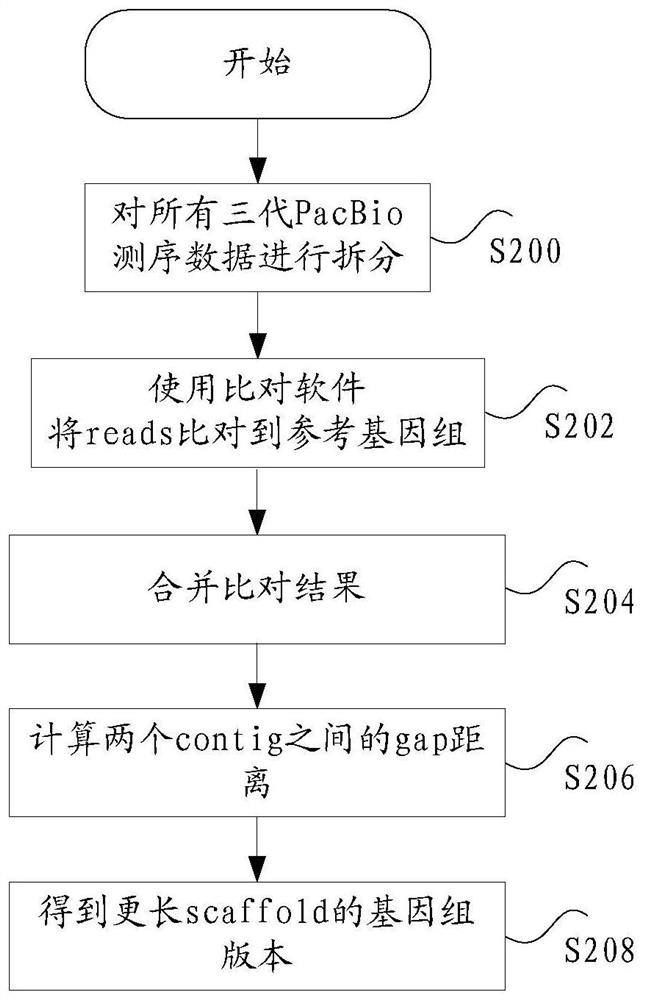
ActiveCN108776749BReduce alignmentShorten the time required for assemblyHybridisationInstrumentsGenome alignmentData mining
The invention discloses a sequencing data processing method and device. Among them, the method includes: splitting the three-generation sequencing data to obtain at least one sub-sequencing data; comparing any sub-sequencing data to the corresponding reference genome to obtain the comparison result corresponding to any sub-sequencing data; For the result, get the merged result. The invention solves the technical problem that a large amount of resources and time are needed to complete the comparison of the genome in the process of genome assembly in the prior art, resulting in slow comparison speed and low efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING NOVOGENE TECH CO LTD
Method for assessing genome alignment basis
PendingUS20210319849A1Reduce alignment biasReduce alignmentData visualisationProteomicsGenome alignmentGenetics
A method (100) for analyzing a target genome, comprising: (i) aligning (120) sequencing data from the target genome to a reference genome; (ii) identifying (130) heterozygous locations, comprising an identification of allele variants and a frequency of each allele, the allele variants comprising both a reference allele variant and a non-reference allele variant; (iii) generating (140) an alternate reference genome, wherein the identified non-reference allele variant for the identified heterozygous locations replaces the reference allele variant in the reference genome; (iv) aligning (150) sequencing data to the alternate reference genome; (v) identifying (160) a frequency of the allele variants at each of the heterozygous locations; (vi) assessing (170) alignment bias at the identified heterozygous locations, comprising comparing the frequency of allele variants from the reference genome alignment to the frequency of allele variants from the alternate genome alignment; and (vii) generating (190) a report comprising the assessment of alignment bias.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com