Library building method and application
A precipitation method and sequencing library technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve the problems of high nucleic acid read repetition rate, inability to build a library for samples with too high nucleic acid fragments, and low gene alignment rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
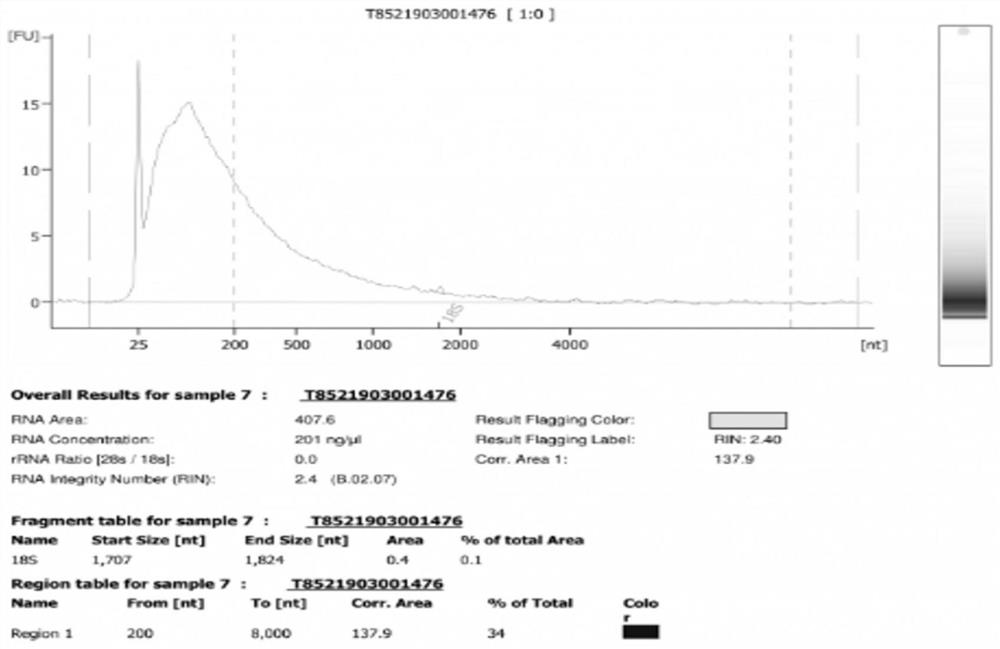
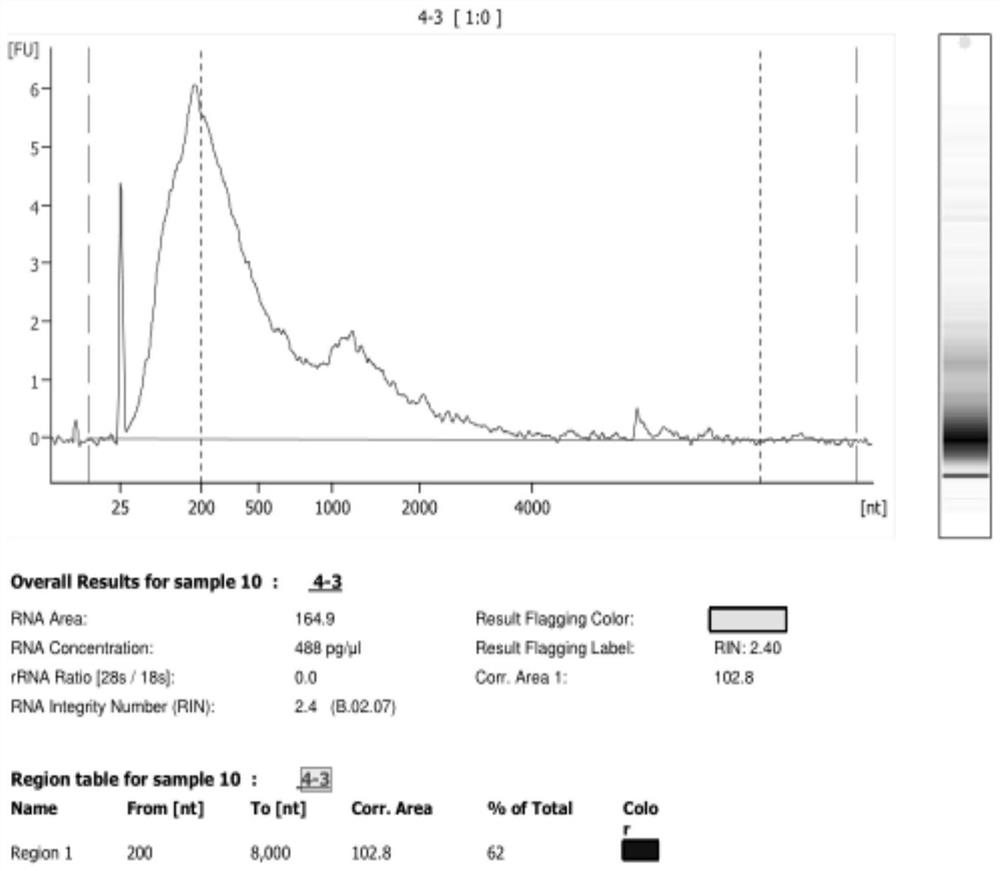
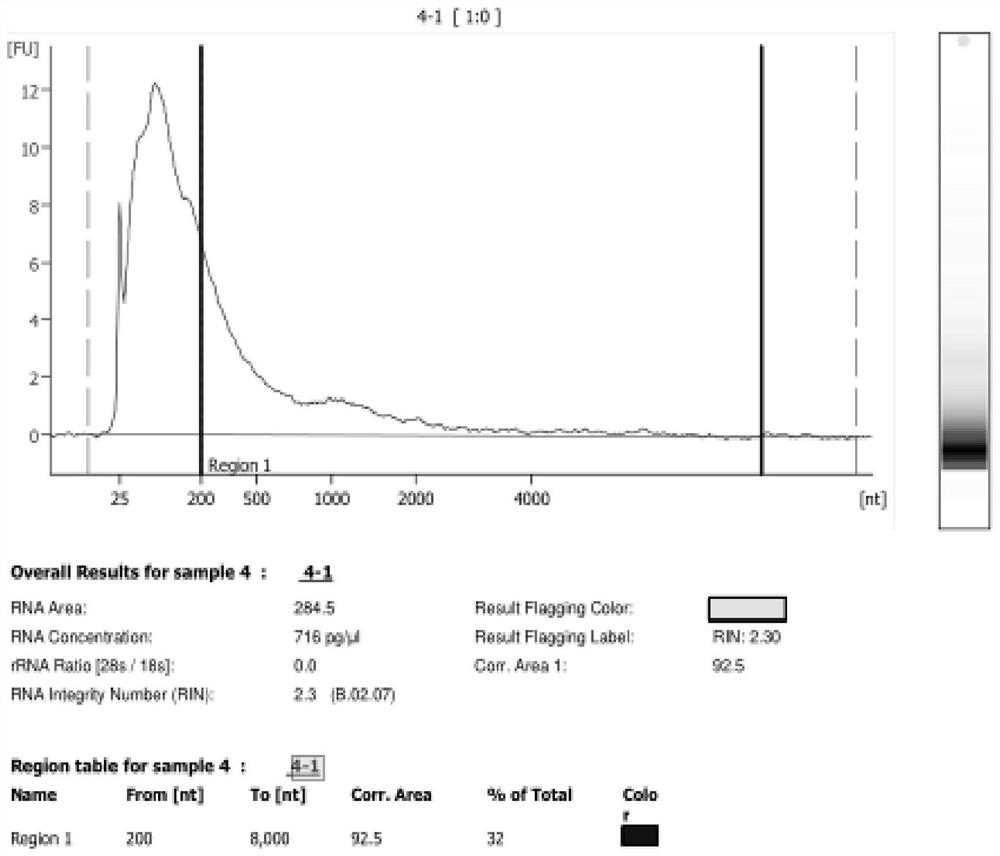
[0029] Take FFPE samples and use PureLink TM The FFPE RNA Isolation Kit extracts RNA from the sample, and detects the DV200 of the sample (DV200=>200bp fragment nucleic acid total / sample nucleic acid total * 100%), DV200 is 34%, take 100ng nucleic acid as experimental group A, take 100ng nucleic acid is the B control group. The nucleic acid in the experimental group was purified by the improved process, and the control group was purified by the traditional method (AMPure XP kit). The results are shown in Table 1.
[0030] Nucleic acid purification steps in experimental group:
[0031] 1. RNA sample purification:
[0032] The RNA samples were purified by low-temperature centrifugation with absolute ethanol, 1 microliter of 20 μg / μL glycogen, and 3M sodium acetate. The volume ratio of 3M sodium acetate solution to the RNA sample was 0.1:1, and the absolute ethanol and RNA The volume ratio of the samples was 2.5:1.
[0033] 2. The solution obtained in step 1 was refrigera...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Use the sequencing libraries of the experimental group and the control group to construct the library: first, the DNA of the treated experimental group and the control group was constructed using the MGIEasy universal DNA library preparation kit made by MGI, and used according to the operation of the library construction kit. Note, add the corresponding reagents for end repair and the 3' end for adding A bases, then add the reaction reagents to connect the adapters with T base sticky ends, use magnetic beads to purify and amplify the library fragments by PCR, and repeat Use magnetic bead purification to remove impurities introduced in the PCR stage, and perform on-machine sequencing after completing the library construction. The sequencing results of the experimental group and the control group were analyzed respectively. For the bioinformatics analysis process of the experimental group and the control group, please refer to the appendix. Figure 4 , the flow before adj...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com