Method for assessing genome alignment basis
A genome and reference genome technology, applied in genomics, proteomics, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as slow calculation, not using known mutations, and expensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
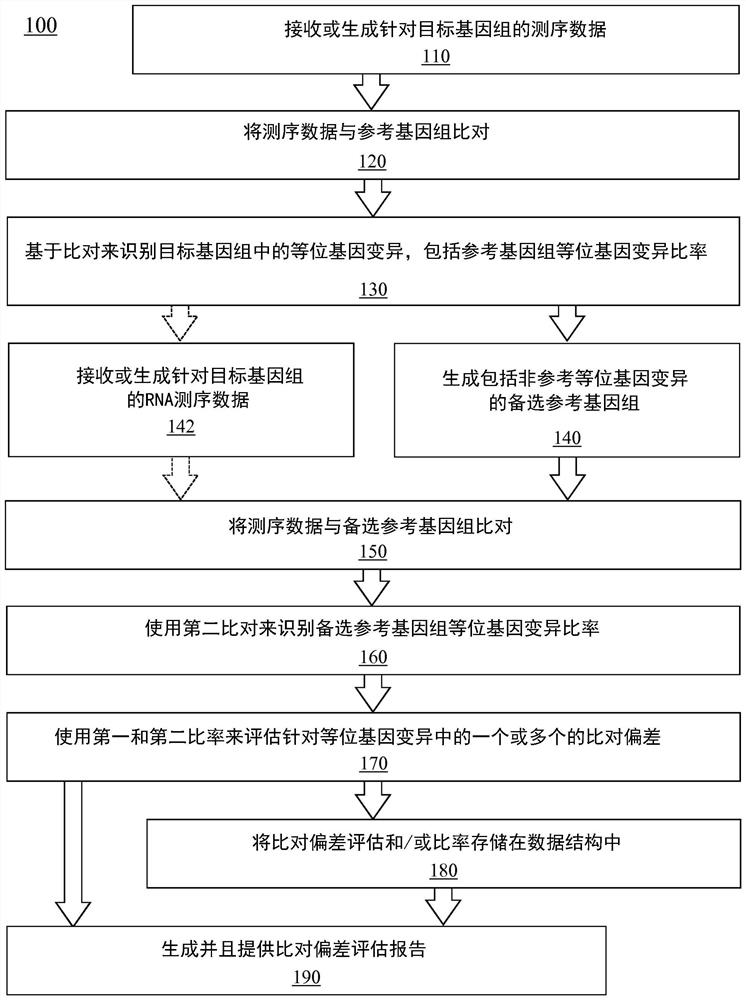
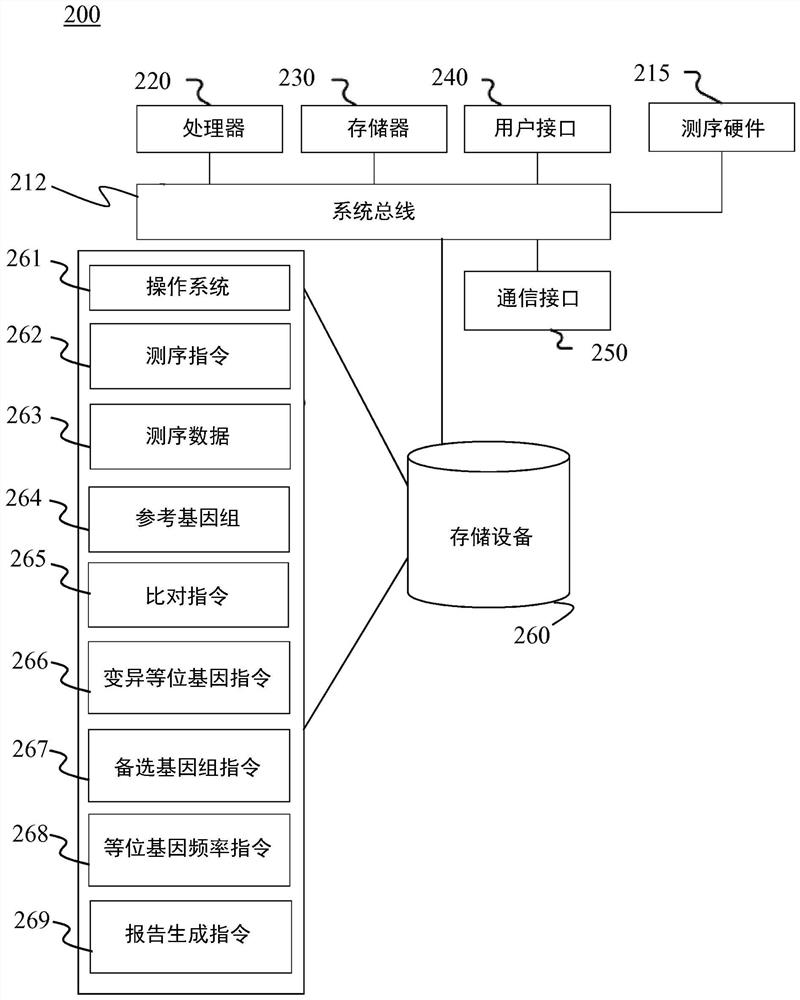
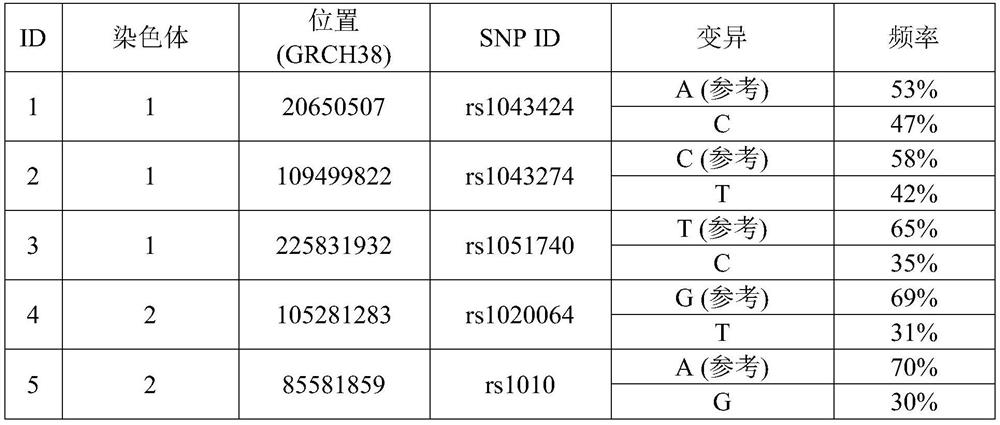
[0024] The present disclosure describes various embodiments of systems and methods for analyzing genome sequencing using an alternative reference genome generated from heterozygous alleles identified in the analyzed genome. More generally, Applicants have recognized and appreciated that it would be beneficial to provide methods for reducing alignment bias during alignment of sequencing reads. The system, which may optionally include a sequencing platform, generates or receives sequencing data, including sequencing reads from a genome of interest. The reads are aligned to the reference genome to identify the heterozygous positions, the variant alleles at each heterozygous position, and the ratio of the variant alleles at each heterozygous position. An alternate reference genome is generated using the identified non-reference allelic variants for each of the identified heterozygous positions. The system then aligns the same set of reads to the generated alternative reference ge...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com