Personalized vaccine
A cancer vaccine, hydrophobic technology, applied in the direction of vaccines, multivalent vaccines, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of lengthy and low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0243] Example 1: Immunization with polypeptide constructs
[0244] Vector construction and production
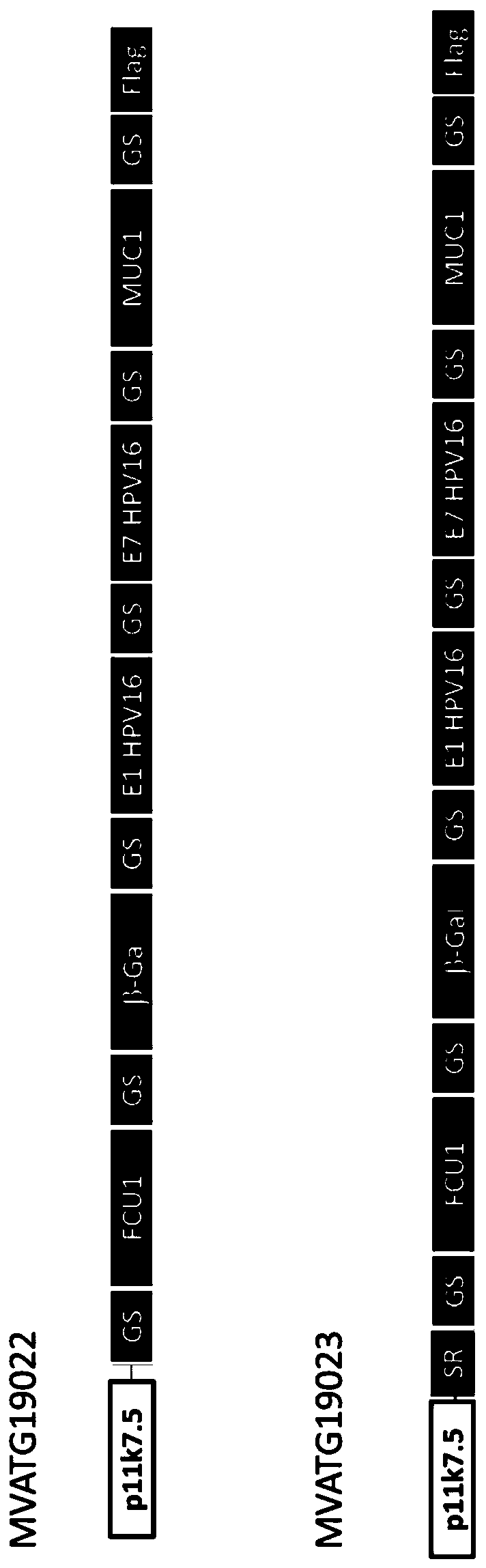
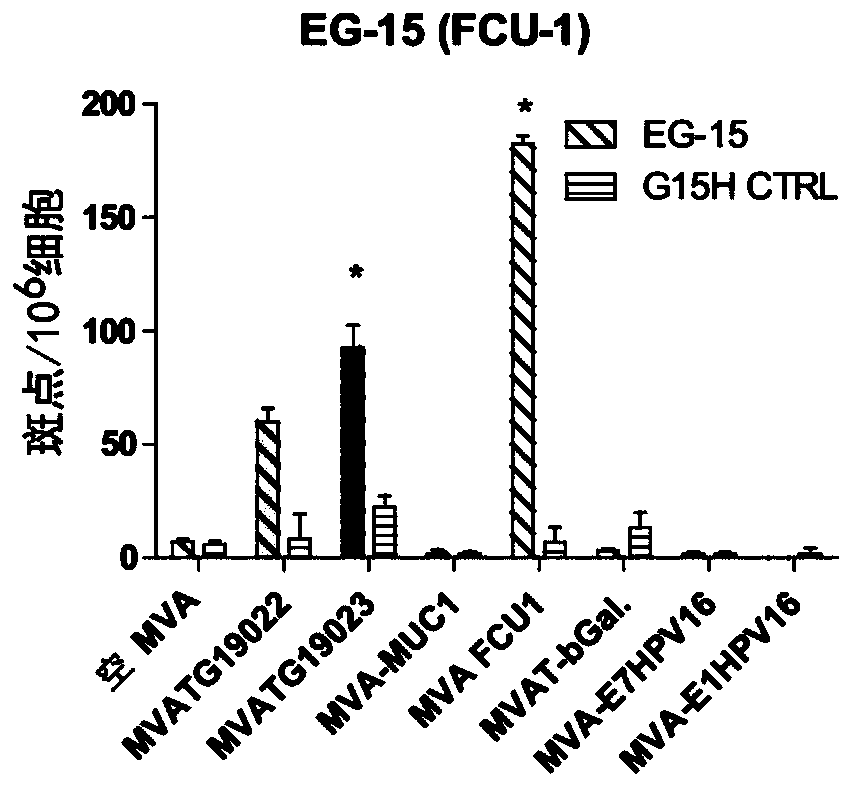
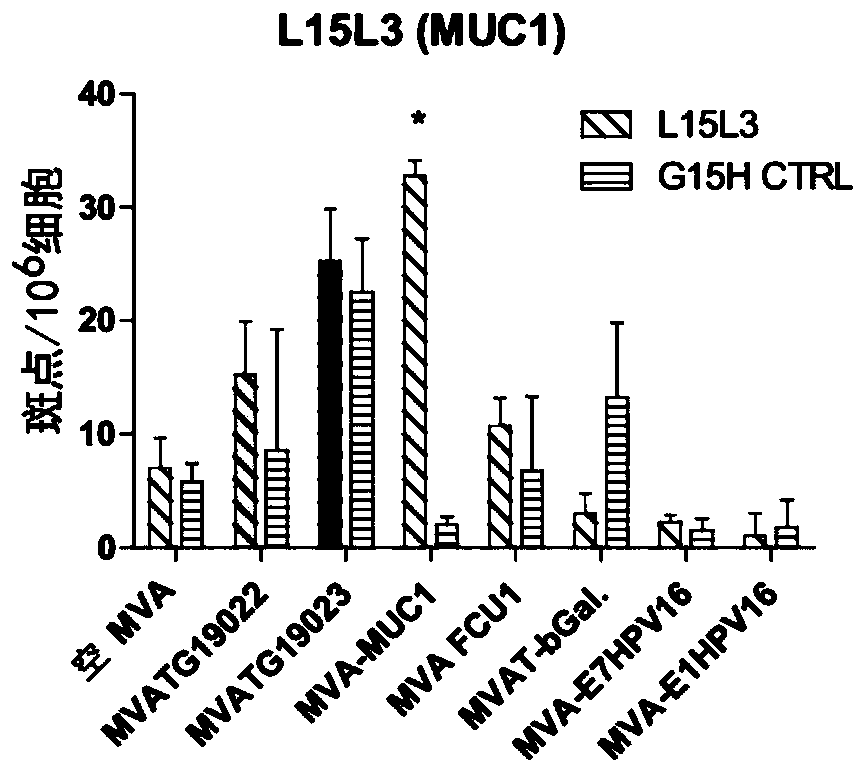
[0245] Such as figure 1 As shown, two MVA constructs MVATG19022 and MVATG19023 were generated to express fusions of 5 peptides derived from multiple antigens separated from each other by a 10 amino acid GS linker for optimal fusion Peptide processing and epitope presentation. Each peptide is a 27mer and contains a validated C57bl / 6 T cell epitope. The pentapeptide coding sequence was placed under the control of the p11k7.5 promoter (SEQ ID NO:8) and this cassette was inserted into deletion III of the MVA genome. More specifically, the pentapeptide fusion comprises FCU1 derived peptide (SEQ ID NO:1), b-Gal derived peptide (SEQ ID NO:2), HPV-16E1 derived peptide (SEQ ID NO: 2) from 5' to 3' 3), HPV-16E7-derived peptide (SEQ ID NO:4) and MUC1-derived peptide (SEQ ID NO:5), wherein there is a 10-mer GS linker before the FCU1 peptide, between the peptides, and after the MUC1...
Embodiment 2
[0264]Example 2: Immunization with CT26 neopeptide constructs
[0265] Selection of new CT26 peptides
[0266] Based on various criteria described in the art, such as low MHC class I binding score, presence of CD8+ T-cell epitopes (Kreiter et al., 2015, Nature 520(7549):692-6) and in the genome of the corresponding CT26 tumor cell line In the presence of single residue mutations, 10 CT26 mutated novel peptides were selected for expression in MVA constructs (amino acid sequences are given in SEQ ID NO: 22-31). Each new peptide is a 27mer containing a mutation at a central position (position 14) and separated from the subsequent new peptide by a 10 amino acid GS linker for optimal processing and epitope presentation.
[0267] Vector construction and generation
[0268] Two MVA constructs were generated, MVTAG19030 and MVTAG19038, respectively, for the expression of the above CT26 neopeptide arranged in two fusions (pentapeptides). The first pentapeptide fusion was placed unde...
Embodiment 3
[0278] Example 3: Human Neopeptide Constructs
[0279] Identification and selection of new peptides
[0280] Whole-exome sequencing (WES) was performed on tumor and germline samples from patients with NSCLC in paired-end format (2x150bp) to identify tumor-specific somatic mutations. Regarding information, raw data is provided by sequencing tools in a standard file format called FASTQ. Each sequencing run generates a FASTQ file that provides short-read sequences and a per base quality score, or Phred score. It is based on the estimated error probability during the base calling step (Cock et al., 2010, Nucl. Acid Res. 38(6):1767-71). In paired-end sequencing, two FASTQ files are generated, one for each end of a library fragment. Therefore, the resulting files must remain paired during the quality filtering step, i.e., the two reads of a pair must have passed the filter. The criteria evaluated in this filtering step are mainly based on Phred scores, especially at the 3' end o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com